Text
Introduction to Roles Under Cybersecurity

Cybersecurity is always important and never goes out of style. But many people trying to get into it spend a lot of money on courses without knowing what’s really useful. I prefer learning for free because you don’t always need a certificate if you’re good at researching on your own. Recently, I got interested in SIEM tools and wanted to know more about other jobs in cybersecurity. That’s when I found TryHackMe.com. It’s not completely free, but they offer some helpful basics for free, which is a great way to start learning without spending too much.
Below content is taken down from tryhackme.com just to bring it to attention for all individual about the roles and responsibilities, so that you my friend can just login to it and try exploring free courses or just research the specific area of interest from below list on Youtube.
Cybersecurity roles generally fall into two main categories: Offensive and Defensive. Here's a quick overview of each:
Introduction to Offensive Security:
Offensive security is the process of breaking into computer systems, exploiting software bugs, and finding loopholes in applications to gain unauthorized access to them.
What careers are there?
The cyber careers room goes into more depth about the different careers in cyber. However, here is a short description of a few offensive security roles:
Penetration Tester - Responsible for testing technology products for finding exploitable security vulnerabilities.
Red Teamer - Plays the role of an adversary, attacking an organization and providing feedback from an enemy's perspective.
Security Engineer - Design, monitor, and maintain security controls, networks, and systems to help prevent cyberattacks.
Offensive security focuses on one thing: breaking into systems. Breaking into systems might be achieved through exploiting bugs, abusing insecure setups, and taking advantage of unenforced access control policies, among other things. Red teams and penetration testers specialize in offensive security
Introduction to Defensive Security:
Defensive security is somewhat the opposite of offensive security, as it is concerned with two main tasks:
Preventing intrusions from occurring
Detecting intrusions when they occur and responding properly
Blue teams are part of the defensive security landscape.
Some of the tasks that are related to defensive security include:
User cyber security awareness: Training users about cyber security helps protect against various attacks that target their systems.
Documenting and managing assets: We need to know the types of systems and devices that we have to manage and protect properly.
Updating and patching systems: Ensuring that computers, servers, and network devices are correctly updated and patched against any known vulnerability (weakness).
Setting up preventative security devices: firewall and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) are critical components of preventative security. Firewalls control what network traffic can go inside and what can leave the system or network. IPS blocks any network traffic that matches present rules and attack signatures.
Setting up logging and monitoring devices: Without proper logging and monitoring of the network, it won’t be possible to detect malicious activities and intrusions. If a new unauthorized device appears on our network, we should be able to know.
There is much more to defensive security, and the list above only covers a few common topics.
we will cover two main topics related to defensive security:
Security Operations Center (SOC), where we cover Threat Intelligence
Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR), where we also cover Malware Analysis
Security Operations Center (SOC)
A Security Operations Center (SOC) is a team of cyber security professionals that monitors the network and its systems to detect malicious cyber security events. Some of the main areas of interest for a SOC are:
Vulnerabilities: Whenever a system vulnerability (weakness) is discovered, it is essential to fix it by installing a proper update or patch. When a fix is not available, the necessary measures should be taken to prevent an attacker from exploiting it. Although remediating vulnerabilities is of vital interest to a SOC, it is not necessarily assigned to them.
Policy violations: We can think of a security policy as a set of rules required for the protection of the network and systems. For example, it might be a policy violation if users start uploading confidential company data to an online storage service.
Unauthorized activity: Consider the case where a user’s login name and password are stolen, and the attacker uses them to log into the network. A SOC needs to detect such an event and block it as soon as possible before further damage is done.
Network intrusions: No matter how good your security is, there is always a chance for an intrusion. An intrusion can occur when a user clicks on a malicious link or when an attacker exploits a public server. Either way, when an intrusion occurs, we must detect it as soon as possible to prevent further damage.
Security operations cover various tasks to ensure protection; one such task is threat intelligence.
Threat Intelligence
In this context, intelligence refers to information you gather about actual and potential enemies. A threat is any action that can disrupt or adversely affect a system. Threat intelligence aims to gather information to help the company better prepare against potential adversaries. The purpose would be to achieve a threat-informed defense. Different companies have different adversaries. Some adversaries might seek to steal customer data from a mobile operator; however, other adversaries are interested in halting the production in a petroleum refinery. Example adversaries include a nation-state cyber army working for political reasons and a ransomware group acting for financial purposes. Based on the company (target), we can expect adversaries.
Intelligence needs data. Data has to be collected, processed, and analyzed. Data collection is done from local sources such as network logs and public sources such as forums. Processing of data aims to arrange them into a format suitable for analysis. The analysis phase seeks to find more information about the attackers and their motives; moreover, it aims to create a list of recommendations and actionable steps.
Learning about your adversaries allows you to know their tactics, techniques, and procedures. As a result of threat intelligence, we identify the threat actor (adversary), predict their activity, and consequently, we will be able to mitigate their attacks and prepare a response strategy.
Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR)
This section is about Digital Forensics and Incident Response (DFIR), and we will cover:
Digital Forensics
Incident Response
Malware Analysis
Digital Forensics
Forensics is the application of science to investigate crimes and establish facts. With the use and spread of digital systems, such as computers and smartphones, a new branch of forensics was born to investigate related crimes: computer forensics, which later evolved into, digital forensics.
In defensive security, the focus of digital forensics shifts to analyzing evidence of an attack and its perpetrators and other areas such as intellectual property theft, cyber espionage, and possession of unauthorized content. Consequently, digital forensics will focus on different areas such as:
File System: Analyzing a digital forensics image (low-level copy) of a system’s storage reveals much information, such as installed programs, created files, partially overwritten files, and deleted files.
System memory: If the attacker is running their malicious program in memory without saving it to the disk, taking a forensic image (low-level copy) of the system memory is the best way to analyze its contents and learn about the attack.
System logs: Each client and server computer maintain different log files about what is happening. Log files provide plenty of information about what happened on a system. Some traces will be left even if the attacker tries to clear their traces.
Network logs: Logs of the network packets that have traversed a network would help answer more questions about whether an attack is occurring and what it entails.
Incident Response
An incident usually refers to a data breach or cyber attack; however, in some cases, it can be something less critical, such as a misconfiguration, an intrusion attempt, or a policy violation. Examples of a cyber attack include an attacker making our network or systems inaccessible, defacing (changing) the public website, and data breach (stealing company data). How would you respond to a cyber attack? Incident response specifies the methodology that should be followed to handle such a case. The aim is to reduce damage and recover in the shortest time possible. Ideally, you would develop a plan ready for incident response.
The four major phases of the incident response process are:
Preparation: This requires a team trained and ready to handle incidents. Ideally, various measures are put in place to prevent incidents from happening in the first place.
Detection and Analysis: The team has the necessary resources to detect any incident; moreover, it is essential to further analyze any detected incident to learn about its severity.
Containment, Eradication, and Recovery: Once an incident is detected, it is crucial to stop it from affecting other systems, eliminate it, and recover the affected systems. For instance, when we notice that a system is infected with a computer virus, we would like to stop (contain) the virus from spreading to other systems, clean (eradicate) the virus, and ensure proper system recovery.
Post-Incident Activity: After successful recovery, a report is produced, and the learned lesson is shared to prevent similar future incidents.
Malware Analysis
Malware stands for malicious software. Software refers to programs, documents, and files that you can save on a disk or send over the network. Malware includes many types, such as:
Virus is a piece of code (part of a program) that attaches itself to a program. It is designed to spread from one computer to another; moreover, it works by altering, overwriting, and deleting files once it infects a computer. The result ranges from the computer becoming slow to unusable.
Trojan Horse is a program that shows one desirable function but hides a malicious function underneath. For example, a victim might download a video player from a shady website that gives the attacker complete control over their system.
Ransomware is a malicious program that encrypts the user’s files. Encryption makes the files unreadable without knowing the encryption password. The attacker offers the user the encryption password if the user is willing to pay a “ransom.”
Malware analysis aims to learn about such malicious programs using various means:
Static analysis works by inspecting the malicious program without running it. Usually, this requires solid knowledge of assembly language (processor’s instruction set, i.e., computer’s fundamental instructions).
Dynamic analysis works by running the malware in a controlled environment and monitoring its activities. It lets you observe how the malware behaves when running.
Careers in Cyber
1. Security Analyst :
Security analysts are integral to constructing security measures across organizations to protect the company from attacks. Analysts explore and evaluate company networks to uncover actionable data and recommendations for engineers to develop preventative measures. This job role requires working with various stakeholders to gain an understanding of security requirements and the security landscape.

Responsibilities:
· Working with various stakeholders to analyze the cyber security throughout the company
· Compile ongoing reports about the safety of networks, documenting security issues and measures taken in response
· Develop security plans, incorporating research on new attack tools and trends, and measures needed across teams to maintain data security.
Learning Paths:
TryHackMe's learning paths will give you both the fundamental technical knowledge and hands-on experience, which is crucial to becoming a successful Security Analyst.
· Introduction to Cyber Security
· Pre-Security
· SOC Level 1
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
2. Security Engineer:
Security engineers develop and implement security solutions using threats and vulnerability data - often sourced from members of the security workforce. Security engineers work across circumventing a breadth of attacks, including web application attacks, network threats, and evolving trends and tactics. The ultimate goal is to retain and adopt security measures to mitigate the risk of attack and data loss.

Responsibilities:
· Testing and screening security measures across software
· Monitor networks and reports to update systems and mitigate vulnerabilities
· Identify and implement systems needed for optimal security
Learning Paths:
TryHackMe's learning paths will give you both the fundamental technical knowledge and hands-on experience, which is crucial to becoming a successful Security Engineer.
· SOC Level 1
· JR Penetration Tester
· Offensive Pentesting
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
3. Incident Responder:
Incident responders respond productively and efficiently to security breaches. Responsibilities include creating plans, policies, and protocols for organisations to enact during and following incidents. This is often a highly pressurised position with assessments and responses required in real-time, as attacks are unfolding. Incident response metrics include MTTD, MTTA, and MTTR - the meantime to detect, acknowledge, and recover (from attacks.) The aim is to achieve a swift and effective response, retain financial standing and avoid negative breach implications. Ultimately, incident responders protect the company's data, reputation, and financial standing from cyber attacks.

Responsibilities:
· Developing and adopting a thorough, actionable incident response plan
· Maintaining strong security best practices and supporting incident response measures
· Post-incident reporting and preparation for future attacks, considering learnings and adaptations to take from incidents
Learning Paths:
TryHackMe's learning paths will give you both the fundamental technical knowledge and hands-on experience, which is crucial to becoming a successful Incident Responder.
· SOC Level 1
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
4. Digital Forensics Examiner:
If you like to play detective, this might be the perfect job. If you are working as part of a law-enforcement department, you would be focused on collecting and analyzing evidence to help solve crimes: charging the guilty and exonerating the innocent. On the other hand, if your work falls under defending a company's network, you will be using your forensic skills to analyze incidents, such as policy violations.

Responsibilities
· Collect digital evidence while observing legal procedures
· Analyze digital evidence to find answers related to the case
· Document your findings and report on the case
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
5. Malware Analyst:
A malware analyst's work involves analyzing suspicious programs, discovering what they do and writing reports about their findings. A malware analyst is sometimes called a reverse-engineer as their core task revolves around converting compiled programs from machine language to readable code, usually in a low-level language. This work requires the malware analyst to have a strong programming background, especially in low-level languages such as assembly language and C language. The ultimate goal is to learn about all the activities that a malicious program carries out, find out how to detect it and report it.

Responsibilities
· Carry out static analysis of malicious programs, which entails reverse-engineering
· Conduct dynamic analysis of malware samples by observing their activities in a controlled environment
· Document and report all the findings
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
6. Penetration Tester:
You may see penetration testing referred to as pentesting and ethical hacking. A penetration tester's job role is to test the security of the systems and software within a company - this is achieved through attempts to uncover flaws and vulnerabilities through systemized hacking. Penetration testers exploit these vulnerabilities to evaluate the risk in each instance. The company can then take these insights to rectify issues to prevent a real-world cyberattack.

Responsibilities:
· Conduct tests on computer systems, networks, and web-based applications
· Perform security assessments, audits, and analyse policies
· Evaluate and report on insights, recommending actions for attack prevention
Learning Paths:
TryHackMe's learning paths will give you both the fundamental technical knowledge and hands-on experience, which is crucial to becoming a successful Penetration Tester.
· JR Penetration Tester
· Offensive Pentesting
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
7. Red Teamer:
Red teamers share similarities to penetration testers, with a more targeted job role. Penetration testers look to uncover many vulnerabilities across systems to keep cyber-defence in good standing, whilst red teamers are enacted to test the company's detection and response capabilities. This job role requires imitating cyber criminals' actions, emulating malicious attacks, retaining access, and avoiding detection. Red team assessments can run for up to a month, typically by a team external to the company. They are often best suited to organisations with mature security programs in place.

Responsibilities:
· Emulate the role of a threat actor to uncover exploitable vulnerabilities, maintain access and avoid detection
· Assess organisations' security controls, threat intelligence, and incident response procedures
· Evaluate and report on insights, with actionable data for companies to avoid real-world instances
Learning Paths:
TryHackMe's learning paths will give you both the fundamental technical knowledge and hands-on experience, which is crucial to becoming a successful Red Teamer.
· JR Penetration Tester
· Offensive Pentesting
· Red Teamer
0 notes
Text
Traditional Web Scraping VS Web Scraping AI
Web scraping has become a key component in a world where data is worth as much as gold. The internet is the largest collection of knowledge, but a big portion of it is unorganized and scattered over several websites in different formats. This data is collected more easily for analysis, storing, and used when it is collected in an organized way thanks to web scraping.
Whether you’re a business trying to understand market trends, a researcher gathering data, or just someone curious about what’s out there on the web, web scraping helps you get the information you need. But with the rise of AI, the way we scrape data from the web is changing. In this blog, we’re going to explore the differences between traditional web scraping and AI-driven web scraping, helping you decide which approach might be best for your needs.

Understanding Traditional Web Scraping –
Traditional web scraping might be compared to the profession of detective. To uncover hints, like class names and tags, that will lead you to your data, you develop code that crawls through a website's HTML structure. You have complete control over all elements with this hands-on approach.
As traditional web scraping has a simple set up for straightforward websites, it is fast and effective when dealing with static and structured web sites. It does not take much time to setup or scrub the data assuming there are no structural changes which requires more maintenance, and it has very little ability to understand the relevance or meaning of the information.
Tools & Technologies You should be familiar with:
For a beginner the basic techstack requirement are understanding of Python, pandas (Python), Requests (Python), BeautifulSoup, HTML/CSS, Web Architectures, Browser Developer Tools and any IDE. In selecting an Integrated Development Environment (IDE), I would suggest using what is known as a Jupyter Notebook in Anaconda as it is user friendly. Other languages and associated libraries can also be used, however the programming and library I have mentioned are easy tools to get started with.
To get started with scraping project or example you can check our recent blog on Scrape Amazon Product Reviews With Python that consist of steps and script along with proper step by step guide to follow.
Why People Love It:
1.Preciseness: When you write the code yourself, you can get exactly the data you want, no more, no less.
2.Control: You’re the one calling the shots, so you can make the scraping process as simple or as complex as you need.
Downsides:
1. Limited scalability- with growing data needs and use, it usually becomes unhandy and perhaps impossible to scrape in traditional ways
2. Understanding Code - you must comprehend the site architecture and tell yourself to utilize code; it takes most beginners a good amount of time to code.
For better practical understanding with an example you should check out this article : Scraping Website OR If you are someone who just wants to scrape a website be it on large scale or small scale using scraping services you can reach out to Data Scraping Service Provider.
Understanding web scraping AI
Let's now take a look and discuss the newest member of the scene: AI web scraping.
AI web scraping is like employing a very smart assistant, if traditional web scraping is like working as a detective. The process of extracting data will get smoother and more effective with this assistant's ability to learn and adapt on the fly.
On the other hand, AI-based web scraping is more adaptable to changes in website structure, minimizes manual interference and maintenance with self-learning capabilities, and can understand information depending on the situation. Yet, you may need specialists with advanced knowledge of machine learning and NLP to retrieve data efficiently and without possible errors.
Tools & Technologies You should be familiar with:
Some popular AI web scraping tools: Diffbot, Bardeen.ai, ScrapeStorm, these are few top performing AI tools used to do web scraping with just understanding the functionality of the tool itself, No Code = No Headache.
To demonstrate an example and steps to follow along for extracting data using AI you could checkout our recent blog post Web Scraping with AI.
Why People Love It:
Flexibility: The main benefit of AI web scraping is flexibility. In the past, traditional web-scrapers would fail to correctly scrape data when a website changes its architecture. AI was built to be able to handle these changes automatically, reducing maintenance, improving data extraction reliability, and significantly lowering errors.
Efficiency: You must consider AI web scraping if you need to scrape a lot of web data at once. These tools work best at scale. Whether you're scraping thousands of product listings or millions of social media posts, AI web scraping does excellently well with processing of the data.
User-Friendly: Fortunately, you do need to be an expert coder to utilize these AI web scraping tools. The majority have intuitive, no-code interfaces, so they are accessible to everyone, marketers, researchers, etc. Everyone can take advantage of the data.
Downsides:
1.Initial Configuration: While AI-based scraping tools, like any software, will take a little time to set up initially, they are generally very usable and intuitive platform. You will likely have to give some time to training the AI to recognize the data you want. This may carry some learning curve for you, especially if you do not have prior experience of AI and its use to scrape images, text, or Libraries.
2.Expense: AI scraping tools typically require you to subscribe to use them, and over time these costs can become substantive. AI solutions provide real value, but their cost may be excessive for very small projects or individual researchers on a very limited budget.
3.Less Transparency: AI is, by definition, a black box. While JavaScript, etc. expose user data extraction methods entirely, these AI tools operate more like a black box, making it very difficult to troubleshoot if some aspect of the extraction goes wrong. This is because, due to custom enhancements, it can be difficult to point to the issue.
When do I use it?
Traditional 'Web Scraping'
Use this for static websites that have a consistent website structure and fixed templates.
Well-suited for static pages where Fixed Content, such as articles, rarely change.
Suited for simplistic extraction of clearly defined data such as prices of products from e-commerce sites, etc.
No rewards - Its fragile because changes to the page structure or to the content could abruptly break it!
AI-Based 'Web Scraping'
Use this for dynamic websites (those that change frequently)
Great for an adaptive scrapping process, in which it continues to learn and adjusts while extracting data as the layout changes over time.
Great for extracting content from JavaScript elements.
AI-based scrapers also can imitate human browsing by clicking through web pages and bypassing common anti-bot measures.
Key difference between traditional and AI-based web scraping:
1. Approach
Traditional web scraping: this requires user dependent guidelines and scripts. This also requires you to manually create coding parameters in order to identify specific data points from webpages and work with dynamic content. You normally use libraries such as BeautifulSoup or Scrapy or use Selenium.
AI-enabled web scraping: Uses machine learning and NLP to automatically comprehend and build upon the models of web page structure. AI-enabled programs build on parameters from learning examples making them much more flexible: they are highly capable of being able to deal with structure on different websites.
2. Complexities
Traditional web scraping: Performs poorly with complex and/or dynamic data such as JavaScript-rendered content, CAPTCHA, infinite scrolling, etc. Typically, if it is complicated, additional code and tools are necessary.
AI-powered web scraping: Performs well with complex scenarios including dynamic content. AI models autonomously and naturally operate with web pages as if they were a human user navigating a web content page. Thus, AI models will be able to scrap for data within more complex sites.
3. Speed and Efficiency
Traditional web scraping: Addressing the speed, and efficiency of extracting data from a website tends to be slower notably during a large-scale extraction and/or if you are extracting from a more complicatedly built site. Generally, each website that is too complex will require more custom code defined by the user to get the results necessary.
AI-powered web scraping: Is even more efficient than traditional but is also somewhat faster when extracting data from a site. AI tools can learn quickly as well as adapt to a wide variety of sites in a relatively few steps. AI tool for web scraping can even eliminate the data extraction to a pre-processing stage.
4. Scalability
Traditional web scraping: scalability is not easily achievable because the site scraping, and code written for each site receives a time investment. Constant maintenance and periodic updates to the code become necessary over time.
AI-Enabled web scraping: More scalable as the trained AI models can address multiple web webpages structure at once and adapt to actually using only minor human coding.
5. Accuracy and Quality of Data
Traditional web scraping: May result in lower data accuracy if the website structure changes, or more commonly, if the scraper just simply misses any representation.
AI-enabled web scraping: Can result in much more data accuracy, as AI-understanding of the content relies on capturing and understanding context and semantics in their learning and corresponding in extracting pages.
6. Learning Curve
Traditional web scraping: Requires a user who has knowledge of coding and/or their understanding of web technologies such as Html, Css, Javascript. The learning curve can be steep for beginners.
AI-dependent web scraping: Increases potential access for program participants to scrape webpages. For digital users, traditional web scraping rarely qualifies for access without specialist coding skills like Html ,Css, Javascript, etc. AI enabled apps often include user interfaces that can still engage non-technical users with less maybe none coding prowess so they are much more likely to be able to code without the limitations of web technologies would limit or confound in coding.
7. Use Cases
Traditional web scraping: Works best for simple projects where scraping has a limited scope, and the website is stable and predictable.
AI-enabled web scraping: Works best projects include variable structures, but also encompass high-level flexibly in websites where the content is being updated frequently, or the target structure can get complex with variable complexity.
Conclusion
In summary, web scraping with traditional method and an AI method are relevant techniques that demonstrate strengths and weaknesses. Traditional web scraping lends itself to carefulness and management in smaller projects or very targeted data extraction; however, it demands coding knowledge and can be laborious and time-consuming overhead. In contrast, using AI for web scraping demonstrates adaptability, scalability, and ease of use applicable to large projects or for anyone seeking a quick turnaround on large projects. AI has a cost that may be higher; however, it is proven by businesses and/or researchers to be justifiable in establishing various institutions established big data practices. Choosing between the two depends on your need and resources: traditional would be preferable on a small scale if you are coding-savvy; otherwise, you would want to consider using AI.
The internet never really stops changing, and neither will the platforms we use to scrape some of the data that can be pulled from it. Web scraping will be a powerful tool whether leveraging traditional methods or AI to scrape data. The future is indeed bright for the extraction of data from the vastness of digital information.
#webscrapingapi#webscrapingservices#web scrapping#web data scraping services#datascience#software engineering
0 notes
Text
Data Lake VS Data Warehouse - Understanding the difference
Data Warehouse & Data Lake

Before we jump into discussing Data Warehouse & Data Lakes let us understand a little about Data. The term Data is all about information or we could say data & information are words that are used interchangeably, but there is still a difference between both of them. So what exactly does it mean ??
Data are "small chunks" of information that do not have value until and unless it is structured, but information is a set of Data that is addressing a value from the words itself.
Now that we understand the concept of Data, let's look forward to learning about Data Warehouse & Data Lake. From the name itself we could get the idea that there is data that is maintained like how people keep things in a warehouse, and how the rivers join together to meet and build a lake.
So to understand technically Data Warehouses & Data Lakes both of the terms are used to introduce the process of storing Data.
Data Warehouse
A Data Warehouse is a storage place where different sets of databases are stored. Before the process of transferring data into a warehouse from any source or medium it is processed and cleaned and containerized into a database. It basically has summarized data which is later used for reporting and analytical purposes.
For an example, let us consider an e-commerce platform. They maintain a structured database containing customer details, product details, purchase history. This data is then cleaned, aggregated and organized in a data warehouse using ETL or ELT process.
Later this Data Warehouse is used to generate reports by analysts to make an informed data driven decision for a business.
Data Lake
A data lake is like a huge storage pool where you can dump all kinds of data—structured (like tables in a database), semi-structured (like JSON files), and unstructured (like images, videos, and text documents)—in their raw form, without worrying about organizing it first.
Imagine a Data Lake as a big, natural lake where you can pour in water from different sources— rivers, rain, streams, etc. Just like the water in a lake comes from different places and mixes together, a data lake stores all kinds of data from various sources.
Store Everything as It Is. In a data lake, you don’t need to clean, organize, or structure the data before storing it. You can just dump it in as it comes. This is useful because you might not know right away how you want to use the data, so you keep it all and figure that out later.
Since the data is stored in its raw form, you can later decide how to process or analyze it. Data scientists and analysts can use the data in whatever way they need, depending on the problem they’re trying to solve.
What is the connection between Data-warehouse and Data-lakes?
Data Lake: Think of it as the first stop for all your raw data. A data lake stores everything as it comes in—whether it’s structured, semi-structured, or unstructured—without much processing. It’s like a big, unfiltered collection of data from various sources.
Data Warehouse: After the data is in the lake, some of it is cleaned, organized, and transformed to make it more useful for analysis. This processed and structured data is then moved to a data warehouse, where it’s ready for specific business reports and queries
Together, they form a data ecosystem where the lake feeds into the warehouse, ensuring that raw data is preserved while also providing clean, actionable insights for the business.
1 note
·
View note
Text
A complete guide on : Web Scraping using AI
Data is readily available online in large amounts, it is an important resource in today's digital world. On the other hand, collecting information from websites might be inefficient, time-consuming, and prone to errors. This is where the powerful method comes into action known as AI Web Scraping, which extracts valuable information from webpages. This tutorial will guide you through the process of using Bardeen.ai to scrape webpages, explain popular AI tools, and talk about how AI enhances web scraping.

AI Web scraping is the term used to describe the act of manually gathering information from websites through artificial intelligence. Traditional web scraping involves creating programs that meet certain criteria so as to fetch data from websites. This technique can work well but proves inefficient on interactive web pages that contain JavaScript and change their contents frequently.
AI Website Scraper makes the scraping process smarter and more adaptable. With improved AI systems, information is better extracted, while data context gets understood properly and trends can be spotted. They are more robust and efficient when it comes to adapting to changes in website structure as compared to traditional scraping techniques.
Why to use AI for Web Scraping?
The usage of artificial intelligence in web scraping has several benefits which make it an attractive choice for different businesses, researchers and developers:
1. Adaptability: In case of any alterations made on the website structure, this kind of web scraper is able to adjust accordingly, ensuring that extraction of data does not end up being interrupted from manual updates always.
2. Efficiency: With automated extraction tools, large volumes of information can be collected within a short time compared with manually doing it.
3. Accuracy: Artificial intelligence will do better in understanding what data means by using machine learning and natural language processing; hence aids in accurately extracting especially unstructured or dynamic ones.
4. Expandability: Projects vary in scope making the ability to easily scale up when handling larger datasets important for AI driven web scraping.
How does AI Web Scraping Work?
AI Web Scraper works by imitating the human way of surfing the internet. When crawling, the AI web scraper makes use of algorithms to scroll the websites on the web and collects the data that might be useful for several purposes. Below is the basic process laid out.
1. Scrolling through the site - The AI web scraper will start the process by browsing the website being to access. Therefore, it's going to crawl everywhere and will track any links to other pages on the site to understand the architecture and find pages in the site that could be of interest.
2. Data extraction – During this step the scraper will extract, find, and distinguish data in which it was designed to, like , text, images, videos, etc. on the website.
3. Processing and structuring the data - The data that was taken is then processed and structured into a format that can be easily analyzed, such as a JSON or CSV file.
4. Resiliency - Websites could change their content or design at any time, so it’s very important that the AI is able to adjust to these changes and continue to scrape without having any issues.
Popular AI Tools for Web Scraping
Several based on AI web scraping technologies have more recently emerged, each with unique functionality to meet a variety of applications. Here are some of the AI web scraping technologies that are regularly mentioned in discussions.
- DiffBot: DiffBot automatically analyzes and extracts data from web pages using machine learning. It can handle complicated websites with dynamic content and returns data in structured fashion.
- Scrapy with AI Integration: Scrapy is a popular Python framework for web scraping. When integrated with AI models, it can do more complicated data extraction tasks, such as reading JavaScript-rendered text.
- Octoparse: This no-code solution employs artificial intelligence to automate the data extraction procedure. It is user-friendly, allowing non-developers to simply design web scraping processes.
- Bardeen.ai: Bardeen.ai is an artificial intelligence platform that automates repetitive operations such as web scraping. It works with major web browsers and provides an easy interface for pulling data from webpages without the need to write code.
What Data Can Be Extracted Using AI Web Scrapers?
Depending on what you want to collect, AI web scraping allows you to collect a wide range of data.
The most popular types are:
- Text data includes articles, blog entries, product descriptions, and customer reviews.
- Multimedia content includes photographs, videos, and infographics.
- Meta-data which include records of the prices, details of the products, the available stock and the rest are part of the organized data.
- Examples of user’s content are comments, ratings, social media posts, and forums.
These data sources may be of many different qualitatively different forms, for example, multimedia or dynamic data. This means that you have an additional chance to get more information, and therefore, to come up with proper staking and planning.
How to Use Bardeen for Web Scraping ai
Barden. AI, on the other hand, is a versatile tool that makes it simple to scrape site data without requiring you to know any coding. Instructions: Applying Bardeen AI to web scraping:
1. Create a field and install Bardeen. ai Extension:
- Visit the bardeen.ai website and create an account.
- Install the Bardeen. The ai browser extension is available for Google Chrome alongside other Chromium-based browsers.
2. Create a New Playbook:
– Once installed, click on Bardeen in the extension. Click on the ai icon in your browser to open dashboard, Click on Create New Playbook to initiate a new automated workflow.
3. Set Up the Scraping Task:
Select “Scrape a website” from the list of templates.
– Input the web URL of your desired scraping website. bardeen.ai will load page automatically and give us an option to choose elements that needed to be extracted.
4. Select Elements:
Utilize the point-and-click interface to choose exact data elements you would like extracted such as text, images or links
- bardeen.ai selects the elements for you and will define extraction rules as per your selection.
5. Run the Scraping Playbook:
- After choosing the data elements, execute the scraping playbook by hitting “Run”.
- Bardeen. ai will automatically use these to scrape the data, and save it in csv or json.
6. Export and Use the Data:
Bardeen (coming soon!) lets you either download the extracted data or integrate it directly into your workflows once scraping is complete. Integration options with tools like Google Sheets, Airtable or Notion.
Bardeen.ai simplifies the web scraping process, making it accessible even to those without technical expertise. Its integration with popular productivity tools also allows for seamless data management and analysis.
Challenges of AI Data Scraping
While AI data scraping has many advantages, there are pitfalls too, which users must be conscious of:
Websites Changes: Occasionally websites may shift their structures or content thereby making it difficult to scrape. Nonetheless, compared to traditional methods, most AI-driven scrapers are more adaptable to these changes.
Legal and Ethical Considerations: When doing website scraping, the legal clauses as contained in terms of service should be adhered to. It is important to know them and operate under them since violation can result into lawsuits.
Resource Intensity: There may be times when using AI models for web scraping requires massive computational resources that can discourage small businesses or individual users.
Benefits Of Artificial Intelligence-Powered Automated Web Scraping:
Despite the problems, the advantages of Automated Web Scraping with AI are impressive. These include:
Fast and Efficient – AI supported tools can scrape large volumes of data at a good speed hence saving time and resources.
Accuracy – When it comes to unstructured or complex datasets, AI improves the reliability of data extraction.
Scalable – The effectiveness of a web scraping tool depends on its ability to handle more data as well as bigger scraping challenges using artificial intelligence therefore applicable for any size project.
The following is a guide if you want your AI Web Scraping to be successful:
To make the most out of AI Web Scraping, consider these tips: To make the most out of AI Web Scraping, consider these tips:
1. Choose the Right Tool: These Web Scrapers are not all the same and are categorized into two main types: facile AI Web Scrapers and complex AI Web Scrapers. Select some tool depending on your requirements – to scrape multimedia or to deal with dynamic pages.
2. Regularly Update Your Scrapers: Web site designs may vary from one layout or structure to the other. These scraping models needs to be updated from time to time so as to ensure it provides the latest data.
3. Respect The Bounds Of The Law: You should always scrape data within the confines of the law. This means adhering to website terms of service as well as any other relevant data protection regulations.
4. Optimize For Performance: Make sure that your AI models and scraping processes are optimized so as to reduce computational costs while improving efficiency at the same time.
Conclusion
AI Web Scraping is one of the most significant ways we are obtaining information from the web. These tools are a more efficient and accurate way of gaining such information as the process has been automated and includes artificial intelligence to make it more scalable. It is very suitable for a business who wish to explore the market, for a researcher who is gathering data to analyze or even a developer who wants to incorporate such data into their application.
This is evident if for example one used tools like Bardeen. ai’s web scraper is designed to be used by anyone, even if they do not know how to code, thus allowing anyone to make use of web data. And as more organizations rely on facts and data more and more, integrating AI usage in web scraping will become a must-have strategy for your business in the contemporary world.
To obtain such services of visit – Enterprise Web Scraping
0 notes
Text
SIEM & ELK Stack: Cyber Security Concept
Security is the most important part for any organization, an organization with no security measures, is definitely a noob at its services. Now that we are learning about security there are a lot of different fields into cyber security one of which is SOC Analyst that I have been keen to learn about. So, I was introduced to SIEM to understand how, what, and why it is used in cybersecurity. Let's take a closer look at what SIEM is and how it functions.
In cybersecurity, a SIEM tool provides companies with advanced monitoring and analysis capabilities, allowing them to track infrastructure activities, identify events, and detect threats before they can impact services or products. To better understand, it tracks everything that has been taken place on a certain device where this tool has been installed.

How SIEM Tools Work:
Data Collection: SIEM tools collect log data and security events from various sources across the IT infrastructure. What exactly it collects as logs ? The data collected can be anything from login attempts, file access, network traffic, configuration changes, to application-specific events.
Data Normalization and Correlation: Once the data is collected, the SIEM tool normalizes it, converting different types of logs into a common format. This makes it easier to analyze and correlate data from different sources. The tool then correlates these events to identify patterns that might indicate a security threat. For example, multiple failed login attempts from a single IP address followed by a successful login might trigger an alert for a potential brute-force attack.
Monitoring and Real-Time Analysis: SIEM tools provide real-time monitoring and analysis of the collected data. They continuously track activities on all monitored devices, generating alerts for suspicious or unusual behavior. This real-time capability allows security teams to respond quickly to potential threats, often before they can cause significant damage.
Threat Detection and Response: By analyzing the correlated data, SIEM tools can detect various types of threats, such as malware, insider threats, data exfiltration, and more. When a potential threat is detected, the SIEM tool can generate alerts, trigger automated responses, or initiate workflows for incident response.
Compliance Reporting: SIEM tools often include reporting capabilities that help organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements. They can generate reports on security events, user activities, and other metrics that are required.
There are some rules that are set into SIEM tools for threat detection, few of them are predefined from MITRE & some are set as custom according to user requirements. This tool not just tracks devices logs and events but can also track a user behavior of an employee working on device provided by firm. Which can be later used to analyze any misuse or illegal activities performed via company asset by a user. .
This is the the best article that I found to understand ELK & more about SIEM : ELK-SIEM Blog
To Understand an installation of ELK I would recommend this resource : Install ElasticSearch Logstash and Kibana on Windows 10 (ELK Stack) (Elastic Stack)
There is a lot to talk about this tool and techstack, Later will definitely share insight on SIEM & ELK with detailed understanding of SOC Analyst role that i have been very much interested to learn about.
For now ciao..
0 notes
Text
Data modeling levels and techniques
Important note: As a junior data analyst, you won't be asked to design a data model. But you might come across existing data models your organization already has in place.

What is data modeling?
Data modeling is the process of creating diagrams that visually represent how data is organized and structured. These visual representations are called data models. You can think of data modeling as a blueprint of a house. At any point, there might be electricians, carpenters, and plumbers using that blueprint. Each one of these builders has a different relationship to the blueprint, but they all need it to understand the overall structure of the house. Data models are similar; different users might have different data needs, but the data model gives them an understanding of the structure as a whole.
Conceptual data modeling gives a high-level view of the data structure, such as how data interacts across an organization. For example, a conceptual data model may be used to define the business requirements for a new database. A conceptual data model doesn't contain technical details.
Logical data modeling focuses on the technical details of a database such as relationships, attributes, and entities. For example, a logical data model defines how individual records are uniquely identified in a database. But it doesn't spell out actual names of database tables. That's the job of a physical data model.
Physical data modeling depicts how a database operates. A physical data model defines all entities and attributes used; for example, it includes table names, column names, and data types for the database.

Data-modeling techniques
There are a lot of approaches when it comes to developing data models, but three common methods are the Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD), Unified Modeling Language (UML) and Data Dictionary diagram. ERDs are a visual way to understand the relationship between entities in the data model. UML diagrams are very detailed diagrams that describe the structure of a system by showing the system's entities, attributes, operations, and their relationships. As a junior data analyst, you will need to understand that there are different data modeling techniques, but in practice, you will probably be using your organization’s existing technique.
You can read more about ERD, UML, and data dictionaries in this data modeling techniques article
0 notes
Text
Web Scraping 103 : Scrape Amazon Product Reviews With Python –

Amazon is a well-known e-commerce platform with a large amount of data available in various formats on the web. This data can be invaluable for gaining business insights, particularly by analyzing product reviews to understand the quality of products provided by different vendors.
In this guide we will look into web scraping steps to extract amazon reviews of a particular product and save it in excel or csv format. Since manually copying information online can be tedious, in this guide we’ll focus on scraping reviews from Amazon. This hands-on experience will enhance our practical understanding of web scraping techniques.
Before we start, make sure you have Python installed in your system, you can do that from this link: python.org. The process is very simple, just install it like you would install any other application.
Now that everything is set let’s proceed:
How to Scrape Amazon Reviews Using Python
Install Anaconda using this link: https://www.anaconda.com/download . Be sure to follow the default settings during installation. For more guidance, please click here.
We can use various IDEs, but to keep it beginner-friendly, let’s start with Jupyter Notebook in Anaconda. You can watch the video linked above to understand and get familiar with the software.
Steps for Web Scraping Amazon Reviews:
Create New Notebook and Save it. Step 1: Let’s start importing all the necessary modules using the following code:
import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import pandas as pd
Step 2: Define Headers to avoid getting your IP blocked. Note that you can search my user agent on google to get your user agent details and replace it below “User-agent”: “here goes your useragent below”.
custom_headers = { "Accept-language": "en-GB,en;q=0.9", "User-agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/605.1.15 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/17.1 Safari/605.1.15", }
Step 3: Create a python function, to fetch the webpage, check for errors and return a BeautifulSoup object for further processing.
# Function to fetch the webpage and return a BeautifulSoup object def fetch_webpage(url): response = requests.get(url, headers=headers) if response.status_code != 200: print("Error in fetching webpage") exit(-1) page_soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "lxml") return page_soup
Step 4: Inspect Element to find the element and attribute from which we want to extract data, Lets Create another function to select the div and attribute and set it to variable , extract_reviews identifies review-related elements on a webpage, but it doesn’t yet extract the actual review content. You would need to add code to extract the relevant information from these elements (e.g., review text, ratings, etc.).
Function to extract reviews from the webpage def extract_reviews(page_soup): review_blocks = page_soup.select('div[data-hook="review"]') reviews_list = []
Step 5: Below code processes each review element and extracts the customer’s name (if available), and stores it in the customer variable. If no customer information is found, customer remains none.
#for review in review_blocks: author_element = review.select_one('span.a-profile-name') customer = author_element.text if author_element else None rating_element = review.select_one('i.review-rating') customer_rating = rating_element.text.replace("out of 5 stars", "") if rating_element else None title_element = review.select_one('a[data-hook="review-title"]') review_title = title_element.text.split('stars\n', 1)[-1].strip() if title_element else None content_element = review.select_one('span[data-hook="review-body"]') review_content = content_element.text.strip() if content_element else None date_element = review.select_one('span[data-hook="review-date"]') review_date = date_element.text.replace("Reviewed in the United States on ", "").strip() if date_element else None image_element = review.select_one('img.review-image-tile') image_url = image_element.attrs["src"] if image_element else None
Step 6: The purpose of this function is to process scraped reviews. It takes various parameters related to a review (such as customer, customer_rating, review_title, review_content, review_date, and image URL), and the function returns the list of processed reviews.
review_data = { "customer": customer, "customer_rating": customer_rating, "review_title": review_title, "review_content": review_content, "review_date": review_date, "image_url": image_url } reviews_list.append(review_data) return reviews_list
Step 7: Now, Let’s initialize a search_url variable with an Amazon product review page URL
def main(): review_page_url = "https://www.amazon.com/BERIBES-Cancelling-Transparent-Soft-Earpads-Charging-Black/product- reviews/B0CDC4X65Q/ref=cm_cr_dp_d_show_all_btm?ie=UTF8&reviewerType=all_reviews" page_soup = fetch_webpage(review_page_url) scraped_reviews = extract_reviews(page_soup)
Step 8: Now let’s print(“Scraped Data:”, data) scraped review data (stored in the data variable) to the console for verification purposes.
# Print the scraped data to verify print("Scraped Data:", scraped_reviews)
Step 9: Next, Create a dataframe from the data which will help organize data into tabular form.
# create a DataFrame and export it to a CSV file reviews_df = pd.DataFrame(data=scraped_reviews)
Step 10: Now exports the DataFrame to a CSV file in current working directory
reviews_df.to_csv("reviews.csv", index=False) print("CSV file has been created.")
Step 11: below code construct acts as a protective measure. It ensures that certain code runs only when the script is directly executed as a standalone program, rather than being imported as a module by another script.
# Ensuring the script runs only when executed directly if __name__ == '__main__': main()
Result:

Why Scrape Amazon Product Reviews?
Scraping Amazon product reviews can provide valuable insights for businesses. Here’s why you should consider it:
● Feedback Collection: Every business needs feedback to understand customer requirements and implement changes to improve product quality. Scraping reviews allows businesses to gather large volumes of customer feedback quickly and efficiently.
● Sentiment Analysis: Analyzing the sentiments expressed in reviews can help identify positive and negative aspects of products, leading to informed business decisions.
● Competitor Analysis: Scraping allows businesses to monitor competitors’ pricing and product features, helping to stay competitive in the market.
● Business Expansion Opportunities: By understanding customer needs and preferences, businesses can identify opportunities for expanding their product lines or entering new markets.
Manually copying and pasting content is time-consuming and error-prone. This is where web scraping comes in. Using Python to scrape Amazon reviews can automate the process, reduce manual errors, and provide accurate data.
Benefits of Scraping Amazon Reviews
● Efficiency: Automate data extraction to save time and resources.
● Accuracy: Reduce human errors with automated scripts.
● Large Data Volume: Collect extensive data for comprehensive analysis.
● Informed Decision Making: Use customer feedback to make data-driven business decisions.
I found an amazing, cost-effective service provider that makes scraping easy. Follow this link to learn more.
Conclusion
Now that we’ve covered how to scrape Amazon reviews using Python, you can apply the same techniques to other websites by inspecting their elements. Here are some key points to remember:
● Understanding HTML: Familiarize yourself with HTML structure. Knowing how elements are nested and how to navigate the Document Object Model (DOM) is crucial for finding the data you want to scrape.
● CSS Selectors: Learn how to use CSS selectors to accurately target and extract specific elements from a webpage.
● Python Basics: Understand Python programming, especially how to use libraries like requests for making HTTP requests and BeautifulSoup for parsing HTML content.
● Inspecting Elements: Practice using browser developer tools (right-click on a webpage and select “Inspect” or press Ctrl+Shift+I) to examine the HTML structure. This helps you find the tags and attributes that hold the data you want to scrape.
● Error Handling: Add error handling to your code to deal with possible issues, like network errors or changes in the webpage structure.
● Legal and Ethical Considerations: Always check a website’s robots.txt file and terms of service to ensure compliance with legal and ethical rules of web scraping.
By mastering these areas, you’ll be able to confidently scrape data from various websites, allowing you to gather valuable insights and perform detailed analyses.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Web Scraping 102: Scraping Product Details from Amazon

Now that we understand the basics of web scraping, let's proceed with a practical guide. We'll walk through each step to extract data from an online ecommerce platform and save it in either Excel or CSV format. Since manually copying information online can be tedious, in this guide we'll focus on scraping product details from Amazon. This hands-on experience will deepen our understanding of web scraping in practical terms.
Before we start, make sure you have Python installed in your system, you can do that from this link: python.org. The process is very simple just install it like you would install any other application.
Install Anaconda using this link: https://www.anaconda.com/download . Be sure to follow the default settings during installation. For more guidance, please click here.
We can use various IDEs, but to keep it beginner-friendly, let's start with Jupyter Notebook in Anaconda. You can watch the video linked above to understand and get familiar with the software.
Now that everything is set let’s proceed:
Open up the Anaconda software and you will find `jupyter notebook` option over there, just click and launch it or search on windows > jupyter and open it.
Steps for Scraping Amazon Product Detail's:
At first we will create and save our 'Notebook' by selecting kernel as 'python 3' if prompted, then we'll rename it to 'AmazonProductDetails' following below steps:

So, the first thing we will do is to import required python libraries using below commands and then press Shift + Enter to run the code every time:

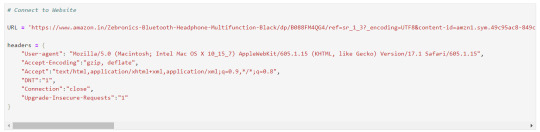
Let's connect to URL from which we want to extract the data and then define Headers to avoid getting our IP blocked.
Note : You can search `my user agent` on google to get your user agent details and replace it in below “User-agent”: “here goes your useragent line” below in headers.
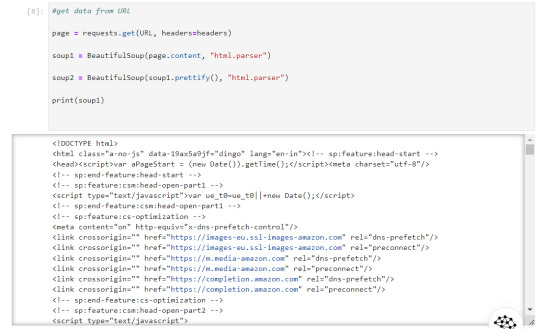
Now that our URL is defined let's use the imported libraries and pull some data.
Now, let's start with scraping product title and price for that we need to use `inspect element` on the product URL page to find the ID associated to the element:
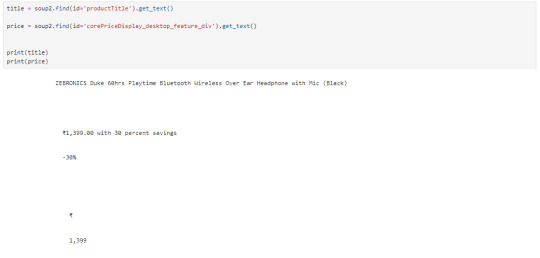
The data that we got is quite ugly as it has whitespaces and price are repeated let's trim the white space and just slice prices:
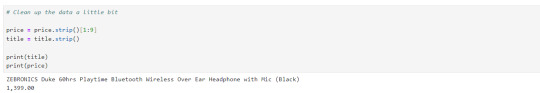
Let's create a timespan to keep note on when the data was extracted.
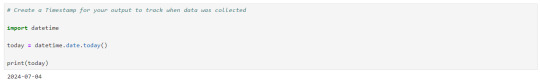
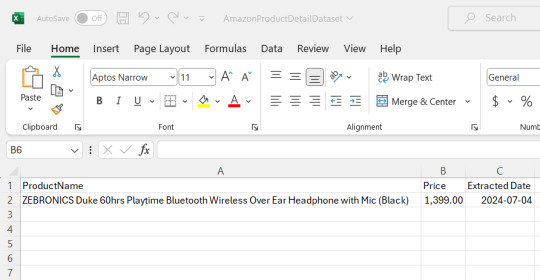
We need to save this data that we extracted, to a .csv or excel file. the 'w' below is use to write the data

Now you could see the file has been created at the location where the Anaconda app has been installed, in my case I had installed at path :"C:\Users\juver" and so the file is saved at path: "C:\Users\juver\AmazonProductDetailDataset"
Instead of opening it by each time looking for path, let's read it in our notebook itself.
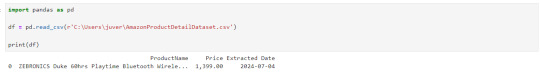
This way we could extract the data we need and save it for ourselves, by the time I was learning this basics, I came across this amazing post by Tejashwi Prasad on the same topic which I would highly recommend to go through.
Next, we’ll elevate our skills and dive into more challenging scraping projects soon.
0 notes
Text
Web Scraping 101: Understanding the Basics
Data Analytics, also known as the Science of Data, has various types of analytical methodologies, But the very interesting part of all the analytical process is collecting data from different sources. It is challenging to collect data while keeping the ACID terms in mind. I'll be sharing a few points in this article which I think is useful while learning the concept of Web Scrapping.
The very first thing to note is not every website allows you to scrape their data.
Before we get into the details, though, let’s start with the simple stuff…

What is web scraping?
Web scraping (or data scraping) is a technique used to collect content and data from the internet. This data is usually saved in a local file so that it can be manipulated and analyzed as needed. If you’ve ever copied and pasted content from a website into an Excel spreadsheet, this is essentially what web scraping is, but on a very small scale.
However, when people refer to ‘web scrapers,’ they’re usually talking about software applications. Web scraping applications (or ‘bots’) are programmed to visit websites, grab the relevant pages and extract useful information.
Suppose you want some information from a website. Let’s say a paragraph on Weather Forecasting! What do you do? Well, you can copy and paste the information from Wikipedia into your file. But what if you want to get large amounts of information from a website as quickly as possible? Such as large amounts of data from a website to train a Machine Learning algorithm? In such a situation, copying and pasting will not work! And that’s when you’ll need to use Web Scraping. Unlike the long and mind-numbing process of manually getting data, Web scraping uses intelligence automation methods to get thousands or even millions of data sets in a smaller amount of time.
As an entry-level web scraper, getting familiar with the following tools will be valuable:
1. Web Scraping Libraries/Frameworks:
Familiarize yourself with beginner-friendly libraries or frameworks designed for web scraping. Some popular ones include: BeautifulSoup (Python): A Python library for parsing HTML and XML documents. Requests (Python): A simple HTTP library for making requests and retrieving web pages. Cheerio (JavaScript): A fast, flexible, and lightweight jQuery-like library for Node.js for parsing HTML. Scrapy (Python): A powerful and popular web crawling and scraping framework for Python.
2. IDEs or Text Editors:
Use Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) or text editors to write and execute your scraping scripts efficiently. Some commonly used ones are: PyCharm, Visual Studio Code, or Sublime Text for Python. Visual Studio Code, Atom, or Sublime Text for JavaScript.
3. Browser Developer Tools:
Familiarize yourself with browser developer tools (e.g., Chrome DevTools, Firefox Developer Tools) for inspecting HTML elements, testing CSS selectors, and understanding network requests. These tools are invaluable for understanding website structure and debugging scraping scripts.
4. Version Control Systems:
Learn the basics of version control systems like Git, which help manage your codebase, track changes, and collaborate with others. Platforms like GitHub and GitLab provide repositories for hosting your projects and sharing code with the community.
5. Command-Line Interface (CLI):
Develop proficiency in using the command-line interface for navigating file systems, running scripts, and managing dependencies. This skill is crucial for executing scraping scripts and managing project environments.
6. Web Browsers:
Understand how to use web browsers effectively for browsing, testing, and validating your scraping targets. Familiarity with different browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Safari can be advantageous, as they may behave differently when interacting with websites.
7.Documentation and Online Resources:
Make use of official documentation, tutorials, and online resources to learn and troubleshoot web scraping techniques. Websites like Stack Overflow, GitHub, and official documentation for libraries/frameworks provide valuable insights and solutions to common scraping challenges.
By becoming familiar with these tools, you'll be equipped to start your journey into web scraping and gradually build upon your skills as you gain experience.
learn more
Some good Python web scraping tutorials are:
"Web Scraping with Python" by Alex The Analyst - This comprehensive tutorial covers the basics of web scraping using Python libraries like BeautifulSoup and Requests.
These tutorials cover a range of web scraping techniques, libraries, and use cases, allowing you to choose the one that best fits your specific project requirements. They provide step-by-step guidance and practical examples to help you get started with web scraping using Python
1 note
·
View note