#elasticsearch
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Interactive and Conversational Search with Google Cloud and Elasticsearch

These days, where we have such a lot of online information, it’s truly essential to find what you really want rapidly and precisely. That is the very thing that this blog post is about. We will discuss a better approach for looking and searching online, utilizing something many refer to as interactive and conversational search.
This method makes searching more like having a chat, and it uses some cool tools from Google Cloud and Elasticsearch. We’ll take a gander at how these better approaches for looking are unique in relation to the old ones, and how Google Cloud’s most recent tech improves looking through even. We’re likewise going to look at Elasticsearch, which is a search engine web index, and perceive how it cooperates with Google Cloud to make your searches fast and simple.
What is Interactive and Conversational Search?
A flow method for looking for information that goes beyond the usual practice of inputting keywords into a search engine is interactive and conversational search. All things being equal, it empowers clients to communicate with the search system in a more normal and conversational manner, using text or voice.
This technology utilizes progress in artificial intelligence, especially in natural language processing and machine learning, to comprehend, interpret, and answer client inquiries in a way like that of a human. The objective is to further develop the search experience by making it more automatic, productive, and easy to understand.
Users can get clarification on pressing issues or make demands in natural language, and the system is intended to comprehend the context and intent behind these searches, resulting in more accurate and relevant replies.
This technology is particularly helpful in applications requiring fast and exact information retrieval, such as customer service bots, personal digital assistants, and sophisticated data analysis tools.
Google Cloud – Powering Advanced Search Capabilities
What is Google Cloud?
Google Cloud is a Google cloud computing service that provides a variety of server and computation choices for web applications. It offers computing, storage, and Application Development Services that are provided on Google hardware, allowing developers and organizations to develop, test, and roll out applications on Google’s highly scalable and dependable infrastructure.
Let’s discuss various aspects of Google Cloud
The AI and Machine Learning Edge of Google Cloud
At its core, Google Cloud uses the force of power of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to offer extraordinary abilities in information handling and analytics. These technologies are significant in understanding and interpreting the vast amount of data generated day to day. Google Cloud’s sAI and ML services are intended to be available and adaptable, making them reasonable for organizations, all things considered.
The strength of Google Cloud lies in its complex calculations and neural networks, which are continually learning and evolving. This consistent improvement considers more precise expectations and insights, essential for making a proficient and intelligent search experience.
Enhancing Search Functionalities with Google Cloud
Google Cloud significantly enhances search functionalities in several ways, most notably through natural language processing (NLP). NLP is a branch of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and human language. It enables machines to understand, interpret, and respond to human language in a useful and meaningful way.
One of the key applications of NLP in search is understanding the context and intent behind user queries. Traditional search engines might struggle with complex or conversational queries, but with Google Cloud’s NLP capabilities, search engines can interpret these queries more effectively. This means users can ask questions in natural, conversational language and receive more accurate and relevant results.
For example, if a user searches for “best strategies for online marketing in 2023,” Google Cloud’s NLP tools can analyze the query to understand the specific intent – in this case, looking for recent and effective online marketing strategies. The search engine can then prioritize content that is not only relevant to online marketing but also current and strategy-focused.
Real-World Applications and Future Potential
The applications of Google Cloud’s search capabilities are vast and varied. From powering sophisticated recommendation engines in e-commerce platforms to enabling efficient document search in large corporate databases, the potential is limitless. The real power lies in its adaptability and how businesses can leverage these tools to meet their specific needs.
As we look to the future, the integration of AI and ML in search is only set to deepen. With advancements in AI and machine learning, particularly in areas like deep learning and predictive analytics, Google Cloud is well-positioned to lead this charge. The potential for creating even more personalized, intuitive, and intelligent search experiences is immense, paving the way for a new era in digital information access and management.
Elasticsearch – The Backbone of Search Engines
Elasticsearch stands out as a pivotal technology. Originally released in 2010, it has rapidly grown to become a key player in the search engine landscape, renowned for its speed, scalability, and robust set of features.
What is Elasticsearch?
Elasticsearch is an open-source, distributed search and analytics engine, designed for horizontal scalability, reliability, and easy management. It is built on top of Apache Lucene, a high-performance, full-text search engine library. This foundation enables Elasticsearch to not only perform complex searches but also to handle large volumes of data in real time.
Also Read: Explore Elasticsearch and Why It’s Worth Using?
Core Features of Elasticsearch
Full-Text Search: At its core, Elasticsearch excels in full-text search. It breaks down texts into individual terms or phrases and allows for complex query types including fuzzy matching, wildcard searches, and synonym handling. This makes it extremely powerful for searching through large volumes of text-heavy data.
Scalability: One of the most amazing elements of Elasticsearch is its capacity to scale. It can deal with petabytes of structured and unstructured information, and its appropriate nature implies that it can develop with your necessities. Whether you’re a little startup or a huge endeavor, Elasticsearch adjusts to your data requirements without compromising on performance.
Real-Time Data and Analytics: Elasticsearch works progressively. As soon as a document is indexed, it’s searchable. This feature is critical for applications that require immediate insights from their data, like monitoring tools, financial analysis, and e-commerce platforms.
Distributed Architecture: Its distributed architecture ensures that your data is always available and accessible. Elasticsearch automatically replicates data to ensure resilience and high availability, meaning that even in the case of hardware failure, your search system remains operational.
Powerful API and Ecosystem: Elasticsearch comes with a rich set of APIs that allow for seamless integration with numerous languages such as Java, Python, PHP, JavaScript, and more. The Elastic Stack, which includes Kibana for data visualization and Logstash for data processing, complements Elasticsearch to provide a comprehensive search and data analysis solution.
Applications of Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is used across various industries for different purposes:
E-commerce: For product searches and personalized recommendations.
Logging and Monitoring: For analyzing and visualizing logs in real-time.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): For threat hunting and security analytics.
Search Applications: As the underlying engine for custom search applications across websites and enterprise systems.
Integrating Google Cloud with Elasticsearch
Integrating Google Cloud with Elasticsearch represents a significant advancement in search and data analysis. This integration combines Google Cloud’s cutting-edge artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities with Elasticsearch’s robust, scalable search engine framework.
The result is a powerful synergy that enhances search functionalities, enabling more intuitive, accurate, and real-time responses to complex queries. Businesses can leverage this integration to analyze large datasets, gain actionable insights, and provide users with an unmatched search experience.
Whether it’s processing natural language queries, delivering personalized search results, or offering predictive analytics, the combination of Google Cloud and Elasticsearch paves the way for innovative and efficient data-driven solutions.
Use Cases and Applications
The integration of Google Cloud and Elasticsearch significantly enhances search capabilities across various sectors. In e-commerce, it improves product discovery through natural language queries, enhancing both user experience and sales.
Customer service benefits from AI-powered conversational bots that can handle complex inquiries efficiently. In healthcare, it streamlines access to patient records and medical information, aiding in faster decision-making.
Additionally, for data analytics, this combination simplifies extracting insights from large datasets, making the process more intuitive and efficient. This synergy of Google Cloud’s AI and Elasticsearch’s search functionality marks a leap in creating more user-friendly, intelligent search experiences across diverse industries.
Conclusion
The integration of Google Cloud and Elasticsearch marks a transformative step in search technology. More than a technical feat, it’s a portal to a future where search engines evolve into intelligent partners, adept in processing natural language and delivering precise, efficient results.
This synergy heralds a new wave of innovation across sectors, making our interactions with the digital world more intuitive, responsive, and centered around user needs. As we advance, this blend of Google Cloud’s AI and Elasticsearch’s search prowess promises to redefine not just how we search, but also how we experience the digital landscape. The future of search is conversational, intelligent, and here to revolutionize our digital interactions.
Originally published by: Interactive and Conversational Search with Google Cloud and Elasticsearch
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How To Setup Elasticsearch 6.4 On RHEL/CentOS 6/7?

What is Elasticsearch? Elasticsearch is a search engine based on Lucene. It is useful in a distributed environment and helps in a multitenant-capable full-text search engine. While you query something from Elasticsearch it will provide you with an HTTP web interface and schema-free JSON documents. it provides the ability for full-text search. Elasticsearch is developed in Java and is released as open-source under the terms of the Apache 2 license. Scenario: 1. Server IP: 192.168.56.101 2. Elasticsearch: Version 6.4 3. OS: CentOS 7.5 4. RAM: 4 GB Note: If you are a SUDO user then prefix every command with sudo, like #sudo ifconfig With the help of this guide, you will be able to set up Elasticsearch single-node clusters on CentOS, Red Hat, and Fedora systems. Step 1: Install and Verify Java Java is the primary requirement for installing Elasticsearch. So, make sure you have Java installed on your system. # java -version openjdk version "1.8.0_181" OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_181-b13) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.181-b13, mixed mode) If you don’t have Java installed on your system, then run the below command # yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk Step 2: Setup Elasticsearch For this guide, I am downloading the latest Elasticsearch tar from its official website so follow the below step # wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-6.4.2.tar.gz # tar -xzf elasticsearch-6.4.2.tar.gz # tar -xzf elasticsearch-6.4.2.tar.gz # mv elasticsearch-6.4.2 /usr/local/elasticsearch Step 5: Permission and User We need a user for running elasticsearch (root is not recommended). # useradd elasticsearch # chown -R elasticsearch.elasticsearch /usr/local/elasticsearch/ Step 6: Setup Ulimits Now to get a Running system we need to make some changes of ulimits else we will get an error like “max number of threads for user is too low, increase to at least ” so to overcome this issue make below changes you should run. # ulimit -n 65536 # ulimit -u 2048 Or you may edit the file to make changes permanent # vim /etc/security/limits.conf elasticsearch - nofile 65536 elasticsearch soft nofile 64000 elasticsearch hard nofile 64000 elasticsearch hard nproc 4096 elasticsearch soft nproc 4096 Save files using :wq Step 7: Configure Elasticsearch Now make some configuration changes like cluster name or node name to make our single node cluster live. # cd /usr/local/elasticsearch/ Now, look for the below keywords in the file and change according to you need # vim conf/elasticsearch.yml cluster.name: kapendra-cluster-1 node.name: kapendra-node-1 http.port: 9200 to set this value to your IP or make it 0.0.0.0 ID needs to be accessible from anywhere from the network. Else put your IP of localhost network.host: 0.0.0.0 There is one more thing if you have any dedicated mount pint for data then change the value for #path.data: /path/to/data to your mount point.
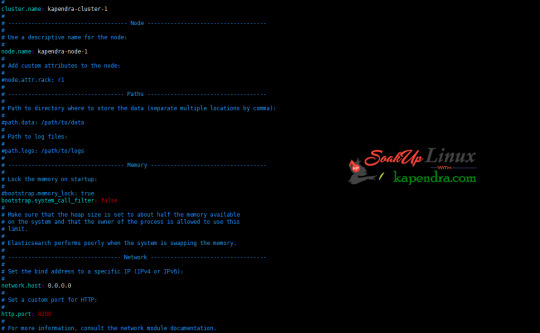
Your configuration should look like the above. Step 8: Starting Elasticsearch Cluster As the Elasticsearch setup is completed. Let the start Elasticsearch cluster with elastic search user so first switch to elastic search user and then run the cluster # su - elasticsearch $ /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch 22278 Step 9: Verify Setup You have all done it, just need to verify the setup. Elasticsearch works on port default port 9200, open your browser to point your server on port 9200, You will find something like the below output http://localhost:9200 or http://192.168.56.101:9200 at the end of this article, you have successfully set up Elasticsearch single node cluster. In the next few articles, we will try to cover a few commands and their setup in the docker container for development environments on local machines. Read the full article
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mastering Elasticsearch in Django: A Comprehensive Guide
"Mastering Elasticsearch in Django: A Comprehensive Guide" would cover a wide range of topics, from the basics to advanced techniques, enabling you to harness the power of Elasticsearch within your Django applications. Here's an outline of what such a guide might include: Chapter 1: Introduction to Elasticsearch and Django
Chapter 2: Setting Up Elasticsearch and Django
Chapter 3: Indexing and Mapping
Chapter 4: Indexing Data from Django Models
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is Solr – Comparing Apache Solr vs. Elasticsearch

In the world of search engines and data retrieval systems, Apache Solr and Elasticsearch are two prominent contenders, each with its strengths and unique capabilities. These open-source, distributed search platforms play a crucial role in empowering organizations to harness the power of big data and deliver relevant search results efficiently. In this blog, we will delve into the fundamentals of Solr and Elasticsearch, highlighting their key features and comparing their functionalities. Whether you're a developer, data analyst, or IT professional, understanding the differences between Solr and Elasticsearch will help you make informed decisions to meet your specific search and data management needs.
Overview of Apache Solr
Apache Solr is a search platform built on top of the Apache Lucene library, known for its robust indexing and full-text search capabilities. It is written in Java and designed to handle large-scale search and data retrieval tasks. Solr follows a RESTful API approach, making it easy to integrate with different programming languages and frameworks. It offers a rich set of features, including faceted search, hit highlighting, spell checking, and geospatial search, making it a versatile solution for various use cases.
Overview of Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch, also based on Apache Lucene, is a distributed search engine that stands out for its real-time data indexing and analytics capabilities. It is known for its scalability and speed, making it an ideal choice for applications that require near-instantaneous search results. Elasticsearch provides a simple RESTful API, enabling developers to perform complex searches effortlessly. Moreover, it offers support for data visualization through its integration with Kibana, making it a popular choice for log analysis, application monitoring, and other data-driven use cases.
Comparing Solr and Elasticsearch
Data Handling and Indexing
Both Solr and Elasticsearch are proficient at handling large volumes of data and offer excellent indexing capabilities. Solr uses XML and JSON formats for data indexing, while Elasticsearch relies on JSON, which is generally considered more human-readable and easier to work with. Elasticsearch's dynamic mapping feature allows it to automatically infer data types during indexing, streamlining the process further.
Querying and Searching
Both platforms support complex search queries, but Elasticsearch is often regarded as more developer-friendly due to its clean and straightforward API. Elasticsearch's support for nested queries and aggregations simplifies the process of retrieving and analyzing data. On the other hand, Solr provides a range of query parsers, allowing developers to choose between traditional and advanced syntax options based on their preference and familiarity.
Scalability and Performance
Elasticsearch is designed with scalability in mind from the ground up, making it relatively easier to scale horizontally by adding more nodes to the cluster. It excels in real-time search and analytics scenarios, making it a top choice for applications with dynamic data streams. Solr, while also scalable, may require more effort for horizontal scaling compared to Elasticsearch.
Community and Ecosystem
Both Solr and Elasticsearch boast active and vibrant open-source communities. Solr has been around longer and, therefore, has a more extensive user base and established ecosystem. Elasticsearch, however, has gained significant momentum over the years, supported by the Elastic Stack, which includes Kibana for data visualization and Beats for data shipping.
Document-Based vs. Schema-Free
Solr follows a document-based approach, where data is organized into fields and requires a predefined schema. While this provides better control over data, it may become restrictive when dealing with dynamic or constantly evolving data structures. Elasticsearch, being schema-free, allows for more flexible data handling, making it more suitable for projects with varying data structures.
Conclusion
In summary, Apache Solr and Elasticsearch are both powerful search platforms, each excelling in specific scenarios. Solr's robustness and established ecosystem make it a reliable choice for traditional search applications, while Elasticsearch's real-time capabilities and seamless integration with the Elastic Stack are perfect for modern data-driven projects. Choosing between the two depends on your specific requirements, data complexity, and preferred development style. Regardless of your decision, both Solr and Elasticsearch can supercharge your search and analytics endeavors, bringing efficiency and relevance to your data retrieval processes.
Whether you opt for Solr, Elasticsearch, or a combination of both, the future of search and data exploration remains bright, with technology continually evolving to meet the needs of next-generation applications.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
0 notes
Text

Struggling with slow or inaccurate product searches on your Shopify store? Discover how Elasticsearch with custom filters can supercharge your store’s search performance and improve user experience. 🛒📈 From faster loading to precise results, this blog dives into how to integrate advanced filtering for better conversions. Don’t miss out on this powerful upgrade!
0 notes
Text
ElasticSearch: The Ultimate Guide to Scalable Search & Analytics
Introduction In today’s data-driven world, businesses and developers need efficient ways to store, search, and analyze large volumes of data. This is where ElasticSearch comes in — a powerful, open-source search and analytics engine built on top of Apache Lucene. ElasticSearch is widely used for full-text search, log analytics, monitoring, and real-time data visualization.
In this blog post, we will explore ElasticSearch in-depth, covering its architecture, key features, use cases, and how to get started with it.
What is ElasticSearch?
ElasticSearch is a distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine that allows users to search, analyze, and visualize data in near real-time. It was developed by Shay Banon and released in 2010. Since then, it has become a core component of the Elastic Stack (ELK Stack), which includes Logstash for data ingestion and Kibana for visualization.
Key Features Scalability: ElasticSearch scales horizontally using a distributed architecture. Full-Text Search: Provides advanced full-text search capabilities using Apache Lucene. Real-Time Indexing: Supports real-time data indexing and searching. RESTful API: Provides a powerful and flexible API for integration with various applications. Schema-Free JSON Documents: Uses a schema-free, document-oriented approach to store data in JSON format. Aggregations: Enables advanced analytics through a powerful aggregation framework. Security: Offers role-based access control (RBAC), authentication, and encryption features. Multi-Tenancy: Supports multiple indices, making it useful for handling different datasets efficiently. ElasticSearch Architecture
Understanding ElasticSearch’s architecture is essential to leveraging its full potential. Let’s break it down:
Cluster A cluster is a collection of one or more nodes working together to store and process data. Each cluster is identified by a unique name.
Node A node is a single instance of ElasticSearch that stores data and performs indexing/search operations. There are different types of nodes:
Master Node: Manages the cluster, creates/deletes indices, and handles node management. Data Node: Stores actual data and executes search/indexing operations. Ingest Node: Prepares and processes data before indexing. Coordinating Node: Routes search queries and distributes tasks to other nodes.
Index An index is a collection of documents that share similar characteristics. It is similar to a database in a relational database management system (RDBMS).
Document A document is the basic unit of data stored in ElasticSearch. It is represented in JSON format.
Shards and Replicas Shards: An index is divided into smaller pieces called shards, which allow ElasticSearch to distribute data across multiple nodes. Replicas: Each shard can have one or more replicas to ensure high availability and fault tolerance. Use Cases of ElasticSearch
ElasticSearch is widely used in various industries. Here are some key use cases:
Full-Text Search ElasticSearch’s powerful text analysis and ranking make it ideal for implementing search functionalities in websites, e-commerce platforms, and applications.
Log and Event Analytics Companies use ElasticSearch to analyze logs generated by applications, servers, and security systems. It helps in real-time monitoring, identifying errors, and optimizing system performance.
Business Intelligence & Data Visualization ElasticSearch powers data analytics dashboards like Kibana, enabling businesses to analyze trends and make data-driven decisions.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Organizations use ElasticSearch for threat detection and cybersecurity monitoring by processing security logs.
IoT and Real-Time Data Processing ElasticSearch is widely used in IoT applications for processing sensor data in real-time, making it an excellent choice for IoT developers.
Continue to the Next Step by clicking here
Best Practices for Using ElasticSearch
To get the best performance from ElasticSearch, consider the following best practices:
Proper Indexing Strategy: Use optimized index mapping and data types to improve search performance. Shard Management: Avoid excessive shards and keep a balanced shard-to-node ratio. Use Bulk API for Large Data Ingestion: Instead of inserting data one by one, use the Bulk API for batch inserts. Optimize Queries: Use filters and caching to improve query performance. Enable Security Features: Implement role-based access control (RBAC) and encryption. Monitor Performance: Use Elastic Stack monitoring tools to keep track of ElasticSearch cluster health. Challenges & Limitations
Despite its advantages, ElasticSearch has some challenges:
Memory Usage: Requires careful memory tuning and management. Complex Query Syntax: Can be difficult to master for beginners. Data Consistency: ElasticSearch follows an eventual consistency model, which may not be ideal for all applications.
0 notes
Text
Argus: El Ojo que Nunca Parpadea en la Seguridad de Redes
En el vasto y turbulento océano del tráfico de red, donde paquetes de datos navegan sin descanso, acechan amenazas invisibles: intrusos, anomalías y actividades sospechosas que buscan explotar vulnerabilidades. Para los profesionales de la ciberseguridad, la vigilancia constante no es una opción, sino una necesidad. Aquí es donde Argus (Audit Record Generation and Utilization System) entra en…
#Ciberseguridad#Elasticsearch#Herramientas de Ciberseguridad#Puertos IP#Splunk#Trafico de Red#Wireshark
0 notes
Text
How to Install Elasticsearch 8 on Ubuntu 24.04
This article explains how to install Elasticsearch 8 on Ubuntu 24.04. Elasticsearch is a robust, open-source search and analytics engine designed to handle large volumes of data in real time. Built on the Apache Lucene library, it offers a distributed, scalable, and high-performance platform for full-text search, structured search, and analytics. It integrates seamlessly with other components…
0 notes
Text







#DidYouKnow How Open Source Fuels Cloud Innovation! 🚀☁️
Swipe left to explore!
💻 Explore insights on the latest in #technology on our Blog Page 👉 https://simplelogic-it.com/blogs/
🚀 Ready for your next career move? Check out our #careers page for exciting opportunities 👉 https://simplelogic-it.com/careers/
#didyouknowfacts#knowledgedrop#interestingfacts#factoftheday#learnsomethingneweveryday#mindblown#openstack#ceph#ansible#prometheus#elasticsearch#opensource#cloud#cloudstrategy#didyouknowthat#triviatime#makingitsimple#learnsomethingnew#simplelogicit#simplelogic#makeitsimple
0 notes
Text
Is AWS Elasticsearch Developer’s True Hero?

Elasticsearch is a free open source search engine, which is used for log analytics, full-text search, application monitoring and more. It makes easy to deploy, operate and scale Elasticsearch clusters in the AWS Cloud. We can get direct access to the Elasticsearch APIs. It provides Scalability, Availability and Security for the workload process run.
Elasticsearch architecture
The AWS Elasticsearch Service Architecture is very dynamically to allow create instances, remove instances, change instance sizes, change storage configuration and customize to make other changes. This Elasticsearch allows to search and analyse the data log. It consists of three components.
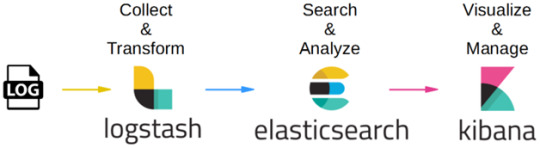
Logstash – is used to collect and transferred to the Elasticsearch.
Elasticsearch –facilitates search and analyze with the logs stored in it. It acts as a database.
Kibana –Kibana enables the data visualization on the dashboard that uses ELK stack. This tool provides a quick insight of the documents using visualization Kibana’s dashboard contains interactive diagrams, geospatial data, and graphs to visualize complex queries that let you search, view, or interact with the stored data. Kibana helps you to perform advanced data analysis and visualize your data in a variety of tables, charts, and maps.
Get started with an Elastic Cluster with AWS
First, create an AWS account and follow the following steps to claim your domain.
Tap on to “Create a new domain”
Select on the appropriated Deployment type and select the Elasticsearch version. Click Next.
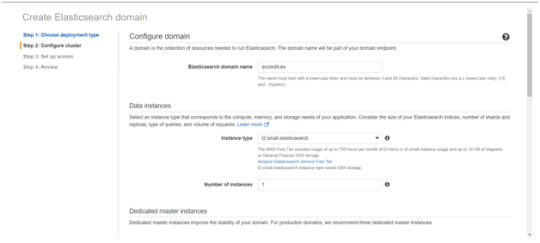
Enter a domain name and choose the Instance type in the prompt page and Click Next.
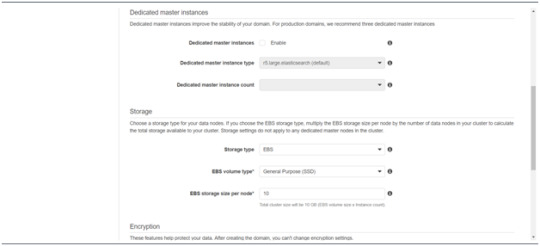
Follow to enter the “Dedicated master instances”
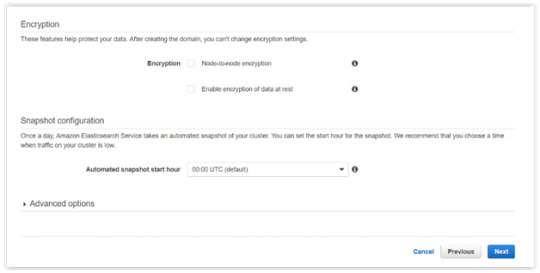
Click Next.
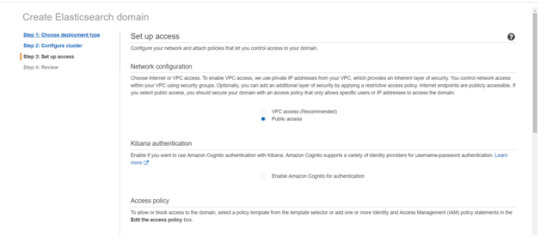
After the Cluster Configuration, you will be taken to the Set up access part. In the Setup access part, enable the specific set of users who can access your ElasticSearch cluster. There are two options — VPC access and Public access. Once you select one of the options and confirm your entries your new cluster is created.
Things to consider
1. Expandable
Amazon Elasticsearch Service provides to monitor your cluster through Amazon CloudWatch metrics.
We can change the cluster in various size from top or bottom within single clicks in the AWS management console or via a single API call.
There is a customizable setting available based on the range of instance types and storage options including SSD-powered EBS volumes.
2.Integrations
Many integrations available in the AWS Elasticsearch such as Kibana for data visualization, Amazon CloudTrail is used to audit API calls configure in AWS ES domains and integrate with Amazon Amazon S3, Amazon Kinesis, and Amazon DynamoDB for loading streaming data into Amazon ES.
3.Guarantee
It guarantees to provide a secure environment and easy integration with Amazon VPC and VPC security groups. There is an availability to access the Identity and Access Management (IAM) control. It provides authentication for Kibana and Data encryption with node-to-node encryption.
4.Availability
Amazon ES supports the different zones in two geographical locations and various node allocations with a large number of zones in the same region itself. It manages the cluster and notifies the damaged nodes automatically.
Conclusion
This article has covered what AWS Elastic Search means, its benefits, what happens between and how you can use it.
#AWS#Elasticsearch#LogAnalytics#SearchEngine#CloudComputing#DataVisualization#Kibana#Scalability#Security#CloudWatch#AWSIntegration#DataEncryption#VPC#ElasticCluster#API#CloudInfrastructure#TechSolutions#BigData#AWSElasticsearch#ElasticSearchService#DataAnalysis#CloudServices
0 notes
Text

What is AWS Elasticsearch? . . . . for more information and a tutorial https://bit.ly/3CCnSWw check the above link
0 notes
Text
Elasticsearch Observability: Unveiling Hidden Engineering Secrets
youtube
0 notes
Text
SIEM & ELK Stack: Cyber Security Concept
Security is the most important part for any organization, an organization with no security measures, is definitely a noob at its services. Now that we are learning about security there are a lot of different fields into cyber security one of which is SOC Analyst that I have been keen to learn about. So, I was introduced to SIEM to understand how, what, and why it is used in cybersecurity. Let's take a closer look at what SIEM is and how it functions.
In cybersecurity, a SIEM tool provides companies with advanced monitoring and analysis capabilities, allowing them to track infrastructure activities, identify events, and detect threats before they can impact services or products. To better understand, it tracks everything that has been taken place on a certain device where this tool has been installed.

How SIEM Tools Work:
Data Collection: SIEM tools collect log data and security events from various sources across the IT infrastructure. What exactly it collects as logs ? The data collected can be anything from login attempts, file access, network traffic, configuration changes, to application-specific events.
Data Normalization and Correlation: Once the data is collected, the SIEM tool normalizes it, converting different types of logs into a common format. This makes it easier to analyze and correlate data from different sources. The tool then correlates these events to identify patterns that might indicate a security threat. For example, multiple failed login attempts from a single IP address followed by a successful login might trigger an alert for a potential brute-force attack.
Monitoring and Real-Time Analysis: SIEM tools provide real-time monitoring and analysis of the collected data. They continuously track activities on all monitored devices, generating alerts for suspicious or unusual behavior. This real-time capability allows security teams to respond quickly to potential threats, often before they can cause significant damage.
Threat Detection and Response: By analyzing the correlated data, SIEM tools can detect various types of threats, such as malware, insider threats, data exfiltration, and more. When a potential threat is detected, the SIEM tool can generate alerts, trigger automated responses, or initiate workflows for incident response.
Compliance Reporting: SIEM tools often include reporting capabilities that help organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements. They can generate reports on security events, user activities, and other metrics that are required.
There are some rules that are set into SIEM tools for threat detection, few of them are predefined from MITRE & some are set as custom according to user requirements. This tool not just tracks devices logs and events but can also track a user behavior of an employee working on device provided by firm. Which can be later used to analyze any misuse or illegal activities performed via company asset by a user. .
This is the the best article that I found to understand ELK & more about SIEM : ELK-SIEM Blog
To Understand an installation of ELK I would recommend this resource : Install ElasticSearch Logstash and Kibana on Windows 10 (ELK Stack) (Elastic Stack)
There is a lot to talk about this tool and techstack, Later will definitely share insight on SIEM & ELK with detailed understanding of SOC Analyst role that i have been very much interested to learn about.
For now ciao..
0 notes
Text

Struggling to help customers find what they need on your Shopify store? 🛍️ Improve their shopping experience with Custom Search Filters powered by Elasticsearch! 🔍 From lightning-fast results to advanced filtering options, learn how this powerful combo boosts user experience and conversions. 🚀
#Exinent#ShopifyDevelopment#Elasticsearch#eCommerceTips#ShopifyStore#CustomFilters#UXDesign#ShopifyExperts
1 note
·
View note