Studi Bug / ♓️ sun / ♏️ rising / ♊️ moonFormer IB student M21 / Current Pre-MD/PhDHL App. Math (6), English (7), History (6), Art (5)SL Physics (6), Spanish (6)B.S. Biochemistry/BME Researcher
Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Writing Notes: Children's Dialogue
Language is extremely complex, yet children already know most of the grammar of their native language(s) before they are 5 years old.
BABBLING
Babbling begins at about 6 months and is considered the earliest stage of language acquisition
By 1 year babbles are composed only of the phonemes used in the language(s) they hear
Deaf babies babble with their hands like hearing babies babble using sounds
FIRST WORDS
After the age of one, children figure out that sounds are related to meanings and start to produce their first words
Usually children go through a holophrastic stage, where their one-word utterances may convey more meaning
Example: "Up" is used to indicate something in the sky or to mean “pick me up”
Most common first words (among the first 10 words uttered in many languages): “mommy,” “daddy,” “woof woof,” “no,” “bye,” “hi,” “yes,” “vroom,” “ball” and “banana”
WORD MEANINGS
When learning words, children often overextend a word’s meaning
Example: Using the word dog to refer to any furry, four-legged animal (overextensions tend to be based on shape, size, or texture, but never color)
They may also underextend a word’s meaning
Example: Using the word dog to refer only to the family pet, as if dog were a proper noun
The Whole Object Principle: When a child learns a new word, (s)he is likely to interpret the word to refer to a whole object rather than one of its parts
SYNTAX
At about two years of age, children start to put words together to form two-word utterances
The intonation contour extends over the two words as a unit, and the two-word utterances can convey a range of meanings:
Example: "mommy sock" = subject + object or possessive
NOTE: Chronological age is NOT a good measure of linguistic development due to individual differences, so instead linguists use the child’s mean length of utterance (MLU) to measure development
The telegraphic stage describes a phase when children tend to omit function morphemes such as articles, subject pronouns, auxiliaries, and verbal inflection
Examples: "He play little tune" or "Andrew want that"
Between 2;6 and 3;6 a language explosion occurs and children undergo rapid development
By the age of 3, most children consistently use function morphemes and can produce complex syntactic structures:
Examples: "He was stuck and I got him out" / "It’s too early for us to eat"
After 3;6 children can produce wh-questions, and relative pronouns
Sometime after 4;0 children have acquired most of the adult syntactic competence
PRAGMATICS
Deixis: Children often have problems with the shifting reference of pronouns
Children may refer to themselves as "you"
Problems with the context-dependent nature of deictic words: Children often assume the hearer knows who s/he is talking about
AUXILIARIES
In the telegraphic stage, children often omit auxiliaries from their speech but can form questions (with rising intonation) and negative sentences
Examples: "I ride train?" / "I not like this book"
As children acquire auxiliaries in questions and negative sentences, they generally use them correctly
SIGNED LANGUAGES
Deaf babies acquire sign language in the same way that hearing babies acquire spoken language: babbling, holophrastic stage, telegraphic stage
When deaf babies are not exposed to sign language, they will create their own signs, complete with systematic rules
IMITATION, REINFORCEMENT, ANALOGY
Children do imitate the speech heard around them to a certain extent, but language acquisition goes beyond imitation
Children produce utterances that they never hear from adults around them, such as "holded" or "tooths"
Children cannot imitate adults fully while acquiring grammar
Example:
Adult: "Where can I put them?" Child: "Where I can put them?"
Children who develop the ability to speak later in their childhood can understand the language spoken around them even if they cannot imitate it
NOTE: Children May Resist Correction
Example: Cazden (1972) (observation attributed to Jean Berko Gleason) – My teacher holded the baby rabbits and we patted them. – Did you say your teacher held the baby rabbits? – Yes. – What did you say she did? – She holded the baby rabbits and we patted them. – Did you say she held them tightly? – No, she holded them loosely.
Another theory asserts that children hear a sentence and then use it as a model to form other sentences by analogy
But while analogy may work in some situations, but certainly not in all situations:
– I painted a red barn. – I painted a barn red. – I saw a red barn. – I saw a barn red.
Children never make mistakes of this kind based on analogy which shows that they understand structure dependency at a very young age
BIRTH ORDER
Children’s birth order may affect their speech.
Firstborns often speak earlier than later-born children, most likely because they get more one-on-one attention from parents.
They favor different words than their siblings.
Whereas firstborns gabble on about animals and favorite colors, the rest of the pack cut to the chase with “brother,” “sister,” “hate” and such treats as “candy,” “popsicles” and “donuts.”
The social dynamics of siblings, it would appear, prime their vocabularies for a reality different than the firstborns’ idyllic world of sheep, owls, the green of the earth and the blue of the sky.
MOTHER'S LEVEL OF EDUCATION
Children may adopt vocabulary quite differently depending on their mother’s level of education.
In American English, among the words disproportionately favored by the children of mothers who have not completed secondary education are: “so,” “walker,” “gum,” “candy,” “each,” “could,” “wish,” “but,” “penny” and “be” (ordered starting with the highest frequency).
The words favored by the children of mothers in the “college and above” category are: “sheep,” “giraffe,” “cockadoodledoo,” “quack quack,” the babysitter’s name, “gentle,” “owl,” “zebra,” “play dough” and “mittens.”
BOYS / GIRLS
One area of remarkable consistency across language groups is the degree to which the language of children is gendered.
The words more likely to be used by American girls than by boys are: “dress,” “vagina,” “tights,” “doll,” “necklace,” “pretty,” “underpants,” “purse,” “girl” and “sweater.”
Whereas those favored by boys are “penis,” “vroom,” “tractor,” “truck,” “hammer,” “bat,” “dump,” “firetruck,” “police” and “motorcycle.”
Tips for Writing Children's Dialogue (compiled from various sources cited below):
Milestones - The dialogue you write should be consistent with the child's developmental milestones for their age. Of course, other factors should be considered such as if the child has any speech or intellectual difficulties. Also note that developmental milestones are not set in stone and each child is unique in their own way.
Too "Cutesy" - If your child characters are going to be cute, they must be cute naturally through the force of their personality, not because the entire purpose of their existence is to be adorable.
Too Wise - It’s true kids have the benefit of seeing some situations a little more objectively than adults. But when they start calmly and unwittingly spouting all the answers, the results often seem more clichéd and convenient than impressive or ironic.
Unintelligent - Don’t confuse a child’s lack of experience with lack of intelligence.
Baby Talk - Don’t make a habit of letting them misuse words. Children are more intelligent than most people think.
Unique Individuals - Adults often tend to lump all children into a single category: cute, small, loud, and occasionally annoying. Look beyond the stereotype.
Personal Goals - The single ingredient that transforms someone from a static character to a dynamic character is a goal. It can be easy to forget kids also have goals. Kids are arguably even more defined by their goals than are adults. Kids want something every waking minute. Their entire existence is wrapped up in wanting something and figuring out how to get it.
Don't Forget your Character IS a Child - Most of the pitfalls in how to write child characters have to do with making them too simplistic and childish. But don’t fall into the opposite trap either: don’t create child characters who are essentially adults in little bodies.
Your Personal Observation - To write dialogue that truly sounds like it could come from a child, start by being an attentive listener. Spend time around children and observe how they interact with their peers and adults. You can also study other pieces of media that show/write about children's behaviour (e.g., documentaries, films, TV shows, even other written works like novels and scripts).
Context - The context in which children speak is crucial to creating realistic dialogue. Consider their environment, who they're speaking to, and what's happening around them. Dialogue can change drastically depending on whether a child is talking to a friend, a parent, or a teacher. Additionally, children's language can be influenced by their cultural background, family dynamics, and personal experiences. Make sure the context informs the dialogue, lending credibility to your characters' voices.
Sources and other related articles: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Writing Notes: On Children
4K notes
·
View notes
Text

i know we joke about cis artists having the weirdest sense of anatomy, but also even when the anatomy is fine, no one seems to want to draw women doing normal things
170K notes
·
View notes
Text






Just to make a point, every time I finished a panel of this I would export it as a PNG on the perceptual setting and use it as a color reference for the next panel
IT'S BAD
PLEASE CHECK YOUR COLOR SETTINGS
EDIT: If you're still having problems, it might help to switch from "Save/Save as" to "Export (as a) Single Layer". Just. Make SURE the box labeled "Expression Color" is set to RGB. I've been messing with this all day, and it looks like this combination of settings will allow exported PNGs to maintain their colors perfectly. To you. So far both Discord and Toyhouse still only display desaturated images and I cannot for the life of me figure out why
87K notes
·
View notes
Text






tutorial for drawing characters with Down syndrome!
DISCLAIMER... please keep in mind that this is an introductory drawing tutorial and has some generalizations in it, so not every “X is Z” statement will be true for Actual People. it's more of an overview of features that are common in people with Down syndrome, not meaning to imply that every person with DS has all of them 👍👍 thanks
if you draw any characters using this feel free to tag me!!
35K notes
·
View notes
Text
I thought it would be an hour of listening to screaming and looking at pictures of draculas, but it was so much for frightening than fathomed
130K notes
·
View notes
Text




Compiled some basic information I know about drawing fat characters for beginners since I've been seeing more talk about absence of really basic traits in a lot of art lately.
Morpho Fat and Skin Folds on Archive.org (for free!)
124K notes
·
View notes
Text

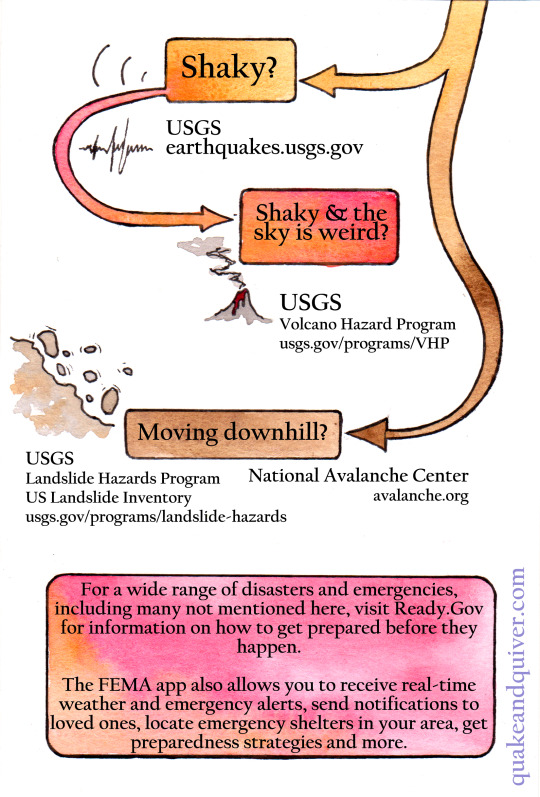
Noticed something a little funky in the world around you and want to figure out what's up? Especially if there might be something you ought to be doing about it? Not sure what information sources to trust these days? If you're in the US, federal agencies like NOAA, USGS, EPA and more collect massive amounts of scientific data every day, much of which is publicly available online - if you know where to look.
A PDF version with clickable links is available for free on my itchio page (quakeandquiver); I'll add a direct link in a reblog.
33K notes
·
View notes
Text

tweet
Something like this would be so colossally helpful. I'm sick and tired of trying to research specific clothing from any given culture and being met with either racist stereotypical costumes worn by yt people or ai generated garbage nonsense, and trying to be hyper specific with searches yields fuck all. Like I generally just cannot trust the legitimacy of most search results at this point. It's extremely frustrating. If there are good resources for this then they're buried deep under all the other bullshit, and idk where to start looking.
148K notes
·
View notes
Text


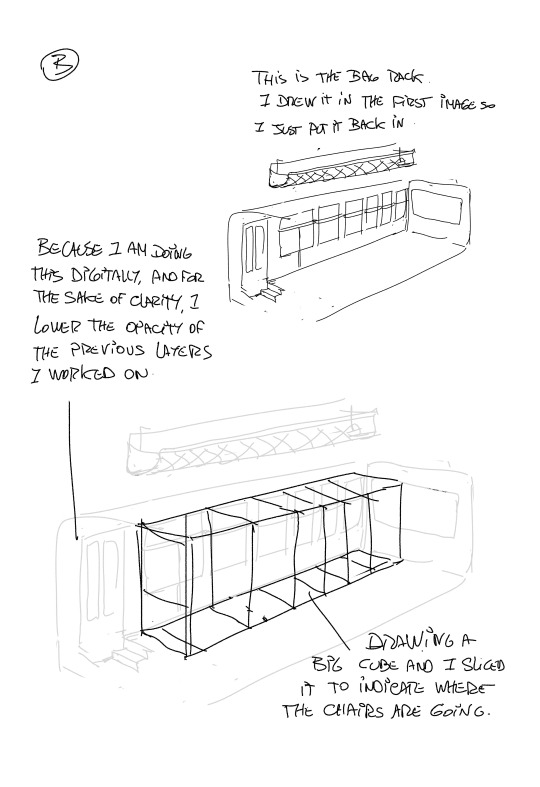
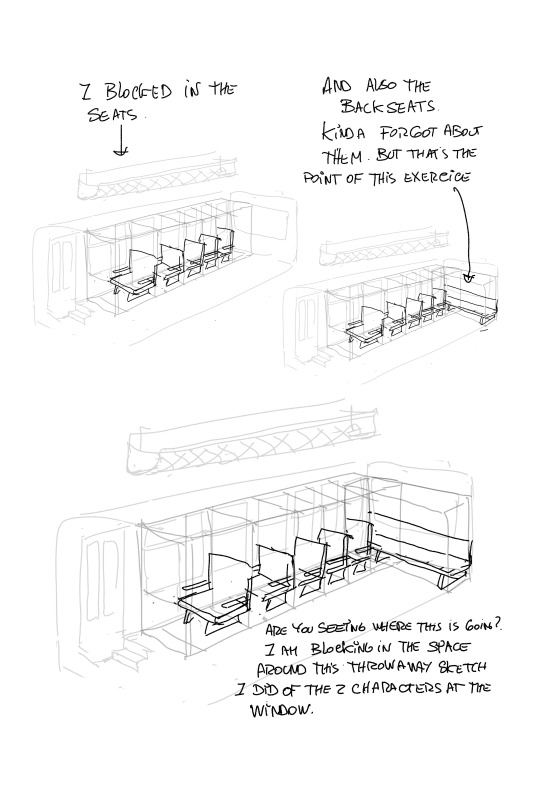

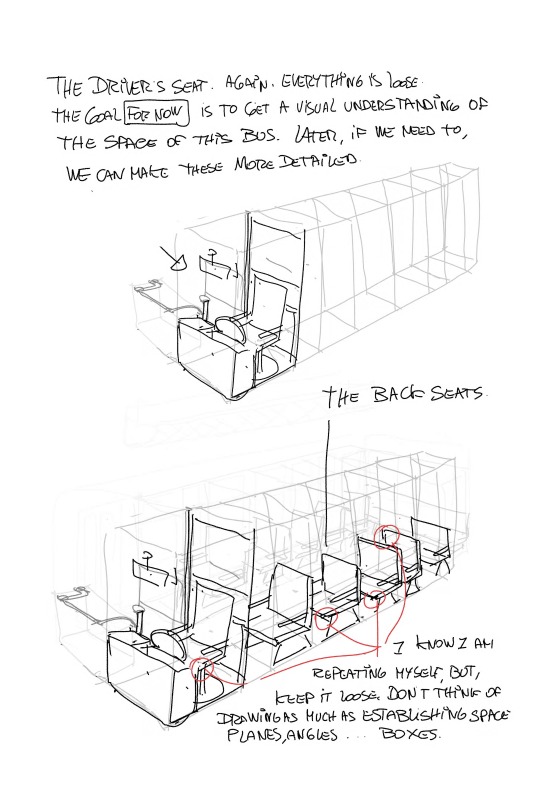



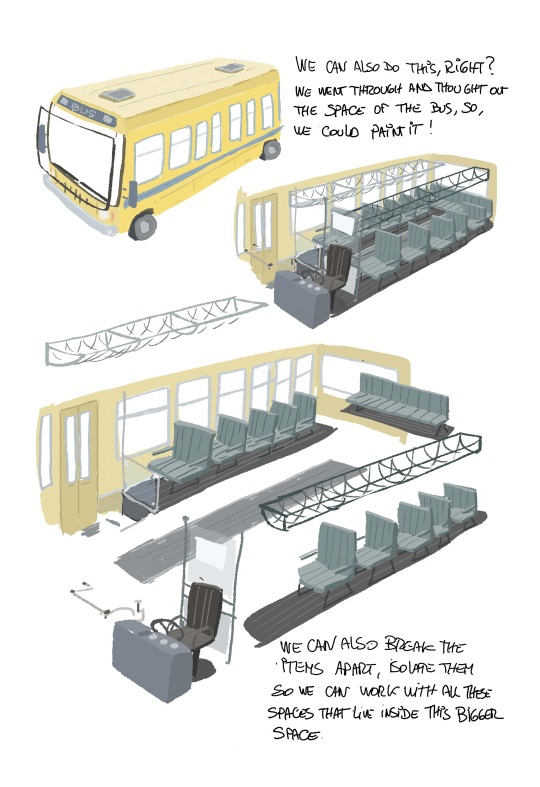
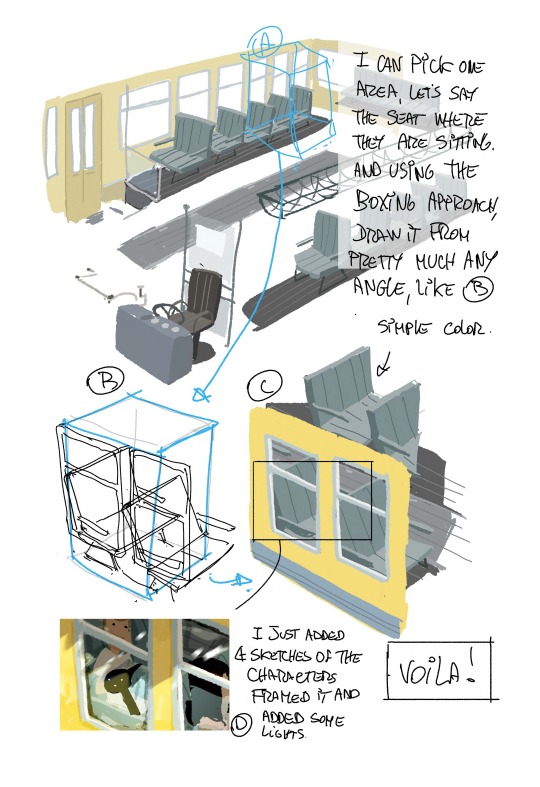




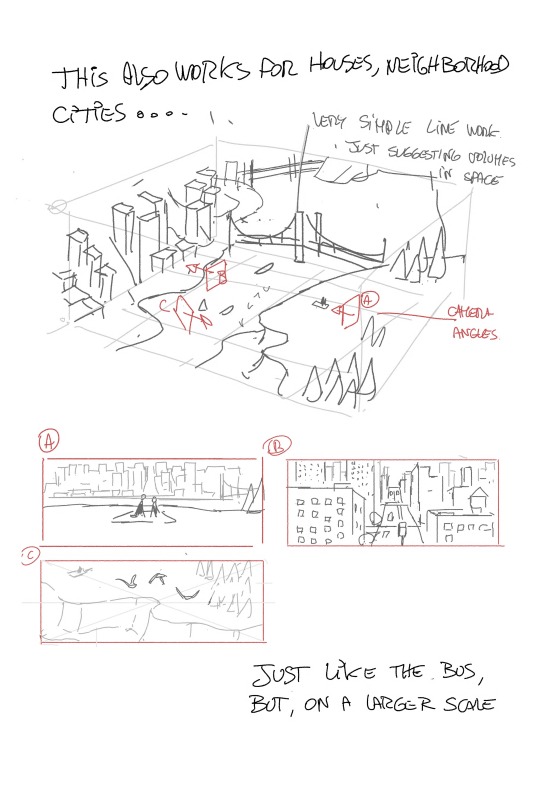
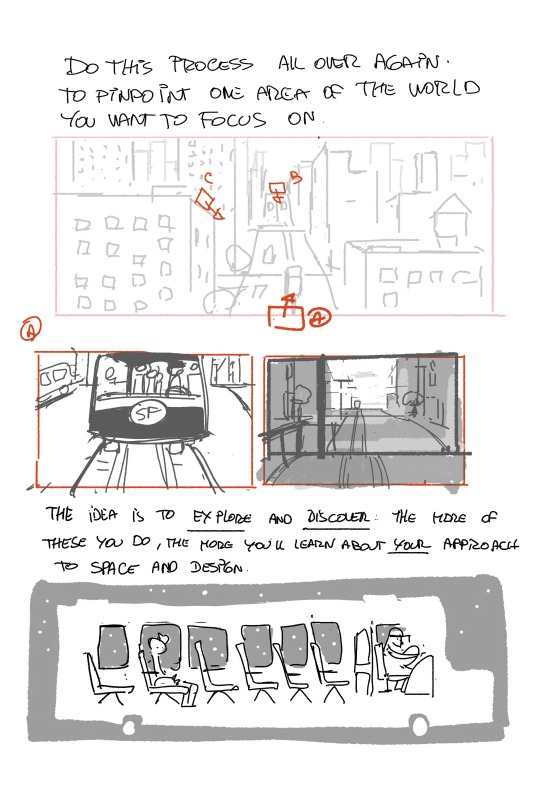
More notes on World building. I have a bunch more about HOW to use the skills,boarding for exploration. color. lighting and eventually how to find you voice as an artist ( which,yeah..I mean..I guess EVERYBODY has advice on that). Any other topics I should cover??
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
how to wake up earlier
sleep is a challenge for many people. after vacations or intensive projects or even a couple rounds of staying up late playing video games, we've all messed up our sleep schedules before. this is a guide on how to wake up earlier and get healthier sleep. please let me know if you'd like more posts like this. wishing love and prosperity to all <3
the night/day before:
choose a bedtime that's 9-10 hours before your wake up time. make sure you're in bed at this time. if you don't fall asleep immediately (which you won't, the first couple of times) read or journal until you feel sleepy.
turn your devices off or put them away at least 30 minutes (ideally 2 hours) before your bedtime. if you have any devices that stay on overnight, make sure they aren't within arms reach and notifications are turned off. if you're using your phone as an alarm make sure it's on the other side of your room, so that you have to walk to turn your alarm off in the morning.
make sure dinner is a light, satisfying meal. don't eat after dinner, as this can lead to acid reflux and interrupted sleep.
avoid caffeine and sugary drinks in the afternoon and evening. keep your caffeine intake under 400mg per day.
sleep with your curtains or blinds open. this will help adjust your circadian rhythm to the day/night cycle.
find a relaxing hobby you can do before bed. some ideas include crochet, knitting, reading, journaling or building puzzles. these are well known in helping with stress management and can help you unwind before you go to sleep.
create a relaxing night routine. make sure you feel clean and comfortable by the time you go to sleep.
make use of a lavender scent before you go to bed. whether it's a linen spray, incense, a candle or an oil diffuser. lavender is calming and can help you feel sleepy, especially if you learn to associate it with sleep.
in the morning:
get out of bed the second you wake up. you need to get up, turn off your alarm and stay out of bed.
make your first activity of the day one you enjoy. your skincare routine, cooking a nice breakfast, a warm shower or even sitting on the couch watching netflix is an option. there's no shame in what you choose to do first thing in the morning, even if it's not productive. if it gets you out of bed, it's the right choice.
expose yourself to sunlight as soon as possible in the morning. just 10 minutes could help your circadian rhythm adjust. if it's dark in the mornings because of the weather or the different seasons, turn your lights on.
other tips:
avoid pulling all-nighters or taking naps. staying up all night is bad for your health, full stop. lack of sleep weakens your immune system and ruins your focus during the day. taking naps regularly can impair the sleep schedule you've been working so hard to build. however, if you're really tired, a 20 minute nap is better than a cup of coffee.
make your mental health and stress management a priority. depression, anxiety and stress result in poor sleep. they can be managed with a well balanced lifestyle and professional intervention.
having a well balanced diet can improve your general health as well as your sleep. make sure you aren't skipping meals. have of each meal should be fruits and vegetables, a quarter grains (preferably wholegrain) and a quarter protein. eat as much variety as possible.
stay well hydrated. the common recommendation of 8 glasses a day is a good goal. staying hydrated can help you stay more alert during the day.
regular exercise can improve quality of sleep. exercise during the day if possible, but definitely not within 2 hours of your bedtime.
make a list of reasons why you want to wake up early. read this every night before you go to bed and first thing in the morning. make sure your reasons are important enough to motivate you.
if you're struggling to adjust to a new sleep schedule because your current sleep schedule is so far off, adjust your bed/wake times in 30 minute increments. this can make the adjustment more comfortable.
stay as consistent as possible. try to keep the habits you've built, even over vacations or exam seasons. discipline will eventually become a habit.
only drink in moderation, alcohol can do serious damage to your circadian rhythm. alcohol generally is bad for you and should not be overconsumed.
if you're having persistent issues with sleep, reach out to a doctor or a sleep specialist who can help you.
finally, be kind to yourself. you can't force yourself to sleep, and stressing about it will only make sleeping properly more difficult. change comes gradually, and you can achieve anything you set your mind to as long as you're consistent.
~*
i hope you're having a lovely day. if you have anymore tips for achieving a healthy sleep schedule, please let me know. i would love to hear it.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
how to create a good night routine
it's important to take time to maintain yourself and prepare for bed every day. often we get caught up with life events and neglect ourselves in the process. this results in a messy sleep schedule and undue stress. each evening is a chance to work at consistency and self care, and we miss out when we rush our night routines.
planning:
figure out how much time you have, realistically. do you eat dinner with your family at a certain time? do you go to the gym with someone in the evenings? what time do you need to be in bed? ideally you would have at least an hour to wind down for bed.
write out a schedule. make sure you have enough time to prep for your night routine, clean up and do your skincare and hair care routines, prepare for the next day and wind down for bed.
make sure you have everything you need. use product that you already have before buying new stuff, but make sure you have the essentials you need to carry out your routine comfortably.
example schedule:
8.00pm - 8.10pm: get everything together, turn off the big lights, choose music for the evening
8.10pm - 8.40pm: shower, moisturize body
8.40pm - 9.10pm: skincare, hair care
9.10pm - 9.30pm: pack bags for the next day, choose outfit
9.30pm - 10.00pm: read, get into bed
a note on adjusting your schedule:
if your schedule doesn't work well, don't force yourself to fit into it. your schedule should work for you and you should change it whenever necessary to make sure it does. it's important to remember that you are the priority here and this is your time to take care of yourself.
~*
hello my loves. this is a follow up post to how to wake up earlier. i believe that having a good day starts the night before. if you have any essential steps in your night routine that i haven't mentioned here, please let me know. wishing love and prosperity to all <3
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
MCAT Review
Describe the mechanism of action and regulation of the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase, including the role of its various subunits, cofactors, and allosteric regulators. How does this enzyme contribute to the overall process of cellular respiration and energy production in the cell?
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) is a complex enzyme that plays a key role in the overall process of cellular respiration and energy production in the cell. The enzyme catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA, which is an important step in the process of converting glucose to ATP.
The enzyme is composed of multiple subunits, including E1 (pyruvate dehydrogenase), E2 (dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase), and E3 (dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase). The E1 subunit contains a thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) cofactor, which binds to and activates pyruvate. The E2 subunit contains a lipoic acid cofactor, which participates in the transfer of the acetyl group from the E1 subunit to the E2 subunit.
The activity of PDH is regulated by a number of factors, including allosteric regulators and covalent modification. One of the key allosteric regulators of PDH is its end product, acetyl-CoA. When the levels of acetyl-CoA in the cell are high, it binds to PDH and inactivates the enzyme, preventing the buildup of acetyl-CoA and maintaining a balance in the cell’s energy metabolism.
PDH also undergoes covalent modification by phosphorylation, which is catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK). This phosphorylation inactivates the enzyme and can be reversed by the action of pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase (PDP). PDK is activated by high levels of acetyl-CoA, NADH and ATP and repressed by ADP, AMP, Ca2+ and pyruvate.
Overall, PDH plays a crucial role in the process of cellular respiration by converting pyruvate to acetyl-CoA, which is then used in the citric acid cycle to generate ATP. Its activity is carefully regulated to maintain a balance in the cell’s energy metabolism.
9 notes
·
View notes