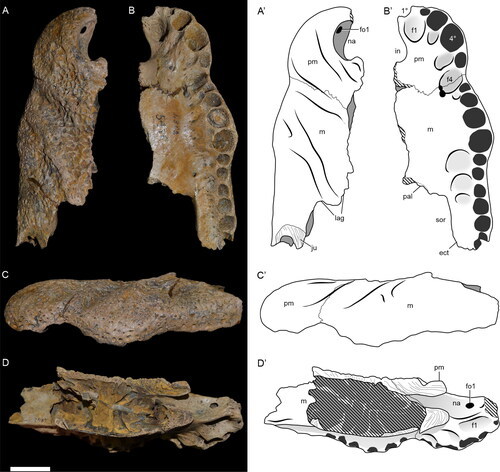
#Arizonasaurus
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
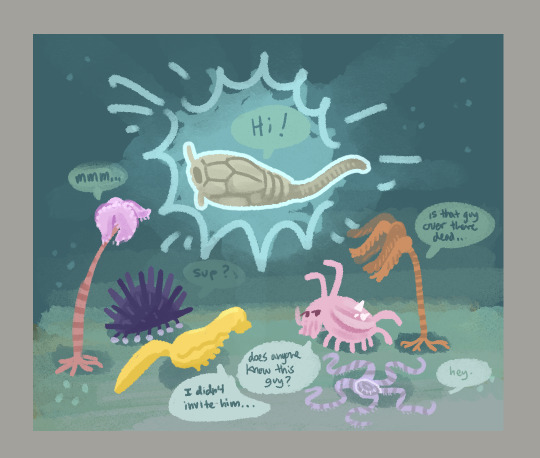




flocking time :)
#my art#paleoart#paleostream#dinocephalosaurus#enoploura#echinoderm#achelousaurus#arizonasaurus#dinosaur
613 notes
·
View notes
Text




Results from the Flocking #paleostream
Dinocephalosaurus, Enoploura, Achelousaurus and Arizonasaurus.
#sciart#paleoart#paleostream#palaeoblr#cretaceous#dinosaur#ceratopsian#arizonasaurus#dinocephalosaurus
332 notes
·
View notes
Text





















Triassic Critters!
251 to 215 million years ago, rising from the ashes of the P-T extinction event and leading into the Mesozoic with pride!
Arizonasaurus - Drepanosaurus - Postosuchus
Herrerasaurus - Nyasasaurus - Eoraptor
Shastasaurus - Nundasuchus - Thalattoarchon
Nothosaurus - Longisquama - Tanystropheus
Broomistega - Triassic Cuddle - Thinaxodon
Mastodonsaurus - Lystrosaurus - Henodus
Plateosaurus - Placerias - Coelophysis
Stickers || Phone Wallpapers Masterlist
Planned or in the works: Silesaurus, Eudimorphodon, Lisowicia, Procompsognathus
#art#my art#paleoart#paleontology#illustration#science#triassic#dinosaur#arizonasaurus#drepanosaurus#postosuchus#herrerasaurus#nyasasaurus#eoraptor#shastasaurus#nundasuchus#thalattoarchon#nothosaurus#longisquama#tanystropheus#broomistega#triassic cuddle#thrinaxodon#mastodonsaurus#lystrosaurus#henodus#plateosaurus#placerias#coelophysis
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
Paleostream 2/03/2024
here are this week's #Paleostream drawings!
today we drew Dinocephalosaurus, Enoploura, Achelousaurus, and Arizonasaurus




#paleoart#paleontology#digital art#artists on tumblr#digital artwork#palaeoart#digital illustration#id in alt text#sciart#paleobr#dinosaur#ceratopsian#archosaurs#echinoderm#Dinocephalosaurus#Enoploura#Achelousaurus#Arizonasaurus#paleostream
170 notes
·
View notes
Text



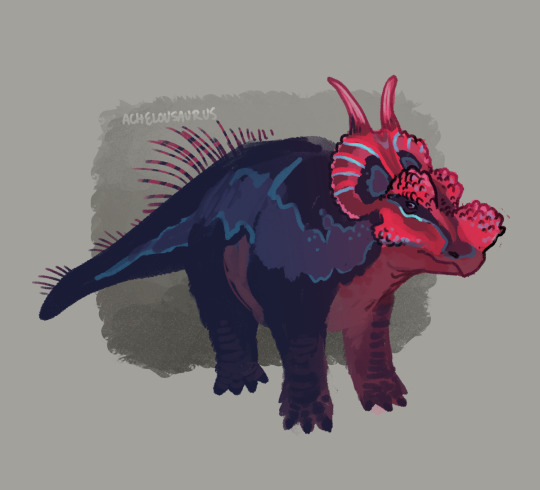
Flocking Together
Dinocephalosaurus/Enoploura
Achelousaurus/Arizonasaurus
#paleoart#prehistory#paleostream#dinocephalosaurus#enoploura#achelousaurus#arizonasaurus#made with krita
47 notes
·
View notes
Link
0 notes
Text
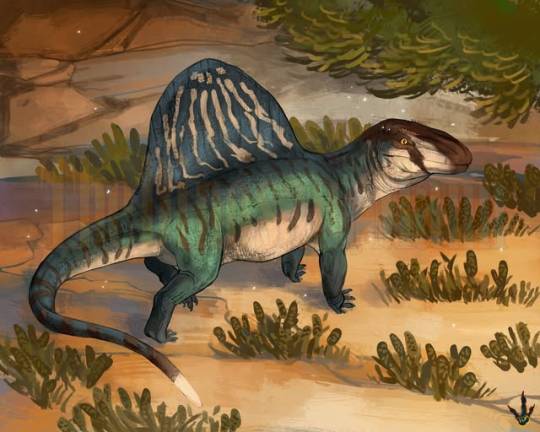

An Arizonasaurus surveying the sunset before a hunt.
by Thedinosaurmann
709 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fossil Crocs of 2024
Another year another list of new fossil crocodilians that greatly expand our knowledge of Pseudosuchia across deep time. Happy to say that this is my third time doing this now, so I'm not going to bog you down with the details and get right into it.
Benggwigwishingasuchus
Our first entry, sorted by geological age of course, is Benggwigwishingasuchus eremicarminis (desert song fishing crocodile) from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) of Nevada. It was a member of the clade Poposauroidea, which some of you might recognize as also containing such bizarre early croc cousins like Arizonasaurus and Effigia. Also notable about Benggwigwishingasuchus is that it was found in the Fossil Hill Member of the Favret Formation. Why is that notable? Well the Fossil Hill Member preserves an environment deposited 10 km off the Triassic coastline and also yielded fossils of animals like Cymbospondylus, the giant ichthyosaur. Despite this however, Benggwigwishingasuchus shows no obvious signs of having been a swimmer or diver. Instead, its been hypothesized that it was simply foraging around the coast and might have been washed out to sea.
Artwork by Joschua Knüppe (@knuppitalism-with-ue) and Jorge A. Gonzalez


Parvosuchus
Fast forward some 5 million years to the Ladinian - Carnian of Brazil, specifically the Santa Maria Formation. Here you'll find the one new genus on the list I did not write the wikipedia page for: Parvosuchus aurelioi (Aurélio's Small Crocodile). With only a meter in length, Parvosuchus is amongst the smallest pseudosuchians of the year and a member of the aptly named Gracilisuchidae. Santa Maria was actually home to multiple pseudosuchians, including the mighty Prestosuchus (and its possible juvenile form Decuriasuchus), the small erpetosuchid Archeopelta and larger Pagosvenator and one more...
Artwork by Matheus Fernandes and Joschua Knüppe


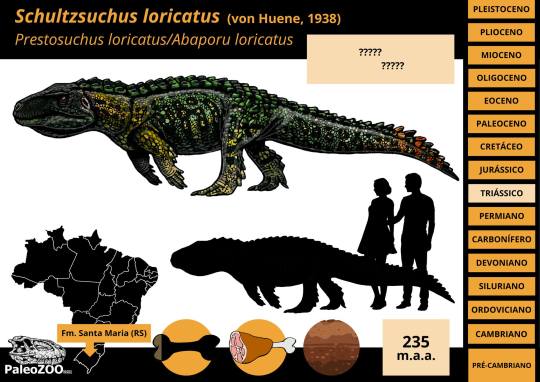
Schultzsuchus
Yup, Santa Maria has been eating good this year. Before the description of Parvosuchus, scientists coined the name Schultzsuchus loricatus (Schultz's Crocodile). Now this one's not entirely new and has long been known under the name Prestosuchus loricatus (by which I mean since 1938). What's interesting is that this new redescription suggests that rather than being a Loricatan, Schultzsuchus was actually an early member of Poposauroidea like Benggwigwishingasuchus. Even if it was no longer thought to be close to Prestosuchus, it was liekly still a formidable predator and among the larger pseudosuchians of the formation.
Artwork by Felipe Alves Elias
Garzapelta
Our last Triassic pseudosuchian and our only aetosaur of the year came to us in the form of Garzapelta muelleri (Mueller's Garza County Shield). It comes from the Late Triassic (Norian) Cooper Canyon Formation of, you guessed it, Garza County, Texas. As an aetosaur, the osteoderms are already regarded as diagnostic, tho unlike some other recent examples there is a little more material to go off from. It's still primarily osteoderms, but at least a good amount and even some ribs.
Artwork by Márcio L. Castro

Ophiussasuchus
Our only Jurassic newcommer is Ophiussasuchus paimogonectes (Paimogo Beach Swimmer Portuguese Crocodile), but arguably you couldn't find a better posterchild for Jurassic crocodyliforms. This new lad is a goniopholidid from the Kimmeridgian to Tithonian Lourinhã Formation, yup, Europe's Morrison. It's anatomy is perhaps not the most exciting, like other goniopholidids it had a flattened, very crocodilian-esque snout and was likely semi-aquatic like its relatives.
Artwork by @manusuchus and Joschua Knüppe
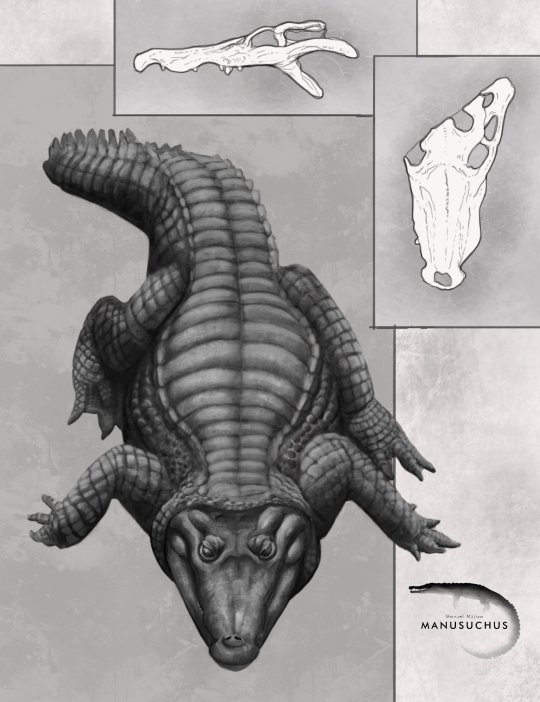

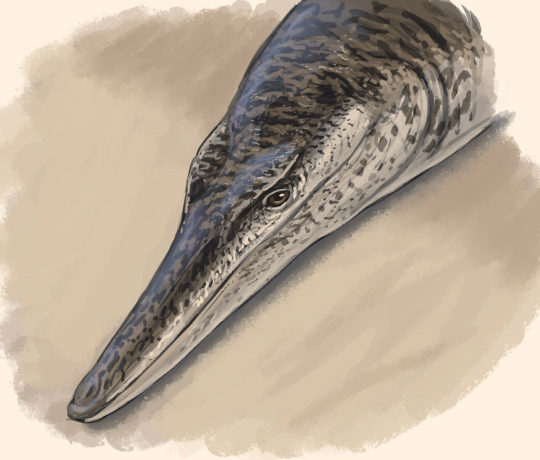
Enalioetes
Another quintessential group of Jurassic crocodyliforms are the metriorhynchoids, however, 2024's only new addition to this clade was actually Cretaceous, specifically from the earliest Cretaceous (Valanginian) of Germany. Like Schultzsuchus, Enalioetes schroederi (Schroeder's Sea Dweller) is new in name only, as fossil material has been found at the latest in 1918 and given the name Enaliosuchus "schroederi" in 1936. This kickstarted a whole series of taxonomic back and forth until the recent redescriptoin finally just gave it a new name and settled things (for now). Looking back I realize that I really need to take the time and fix up the Wikipedia page. Tho I've written its current status, I was kinda limited by being on vacation and never dived into the description section.
Artwork by Joschua Knüppe and Jackosaurus


Varanosuchus
Another Early Cretaceous crocodyliform is Varanosuchus sakonnakhonensis (Monitor Lizard Crocodile from the Sakon Nakhon Province), described from Thailand's Sao Khua Formation. It lived around the same time as Enalioetes, but otherwise couldn't have been more different. Where Enalioetes was fully marine, Varanosuchus was more a land dweller as evidenced by the deep skull and long, slender legs. At the same time, some other features, like its more robust limbs compared to its kin, might suggest that Varanosuchus could have still spent some time in the water like some modern lizards. Tho one might be reminded of Parvosuchus from earlier, Varanosuchus is a much more recent example of small terrestrial croc-relatives, the atoposaurids, which are much closer to todays crocodiles and alligators.
Artwork once again by Manusuchus

Araripesuchus manzanensis
Yet another example of a small, gracile land "crocodile" comes to us in the form of Araripesuchus manzanensis (Araripe Basin Crocodile from the El Manzano Farm). And once again, it belonged to a completely different group, this time the notosuchian family Uruguaysuchidae. Now Araripesuchus is well known as a genus, in part due to the work of Paul Sereno and Hans Larsson (who popularized the names "dog croc" and "rat croc" for two species). Tangent aside, A. manzanensis is known from the upper layers of Argentina's Candeleros Formation, corresponding to the Cenomanian (earliest Late Cretaceous). The same locality also yielded A. buitreraensis, from which A. manzanensis can be distinguished on account of its blunt molariform teeth in the back of its jaw. This dentition, which corresponds to a durophageous diet of hardshelled prey, could explain how it coexisted with the related A. buitrensis at the same locality, allowing the two to occupy different niches. There is a neat little animation done for this animal you can watch here.
Artwork by Gabriel Diaz Yantén

Caipirasuchus catanduvensis
We're staying in South America but moving to Brazil's Adamantina Formation for our next entry: Caipirasuchus catanduvensis (Caipiras Crocodile from Catanduva). This one is a little more recent, tho the age of the Adamantina Formation is a bit of a mess far as I can tell, ranging anywhere from the Turonian to the Maastrichtian. One could also argue that C. catanduvensis is part of the "lanky small croc club" that Parvosuchus, Varanosuchus and A. manzanensis belong to, but I feel that the very short snout helps it stand out from that bunch more easily. Anyhow, Caipirasuchus catanduvensis is a member of Sphagesauridae, related to Armadillosuchus, and herbivorous. What's really interesting tho is that the internal anatomy suggests the presence of resonance chambers not unlike that of hadrosaurs, possibly suggesting that these animals were quite vocal. This could also explain why baurusuchids appear to have had very keen hearing.
Artwork by Joschua Knüppe and Guilherme Gehr


Epoidesuchus
We're staying in the Adamantina Formation for our last Mesozoic croc of the year, Epoidesuchus tavaresae (Tavares' Enchanted Crocodile). Tho also a Notosuchian like Araripesuchus and Caipirasuchus, this one belongs to the family Itasuchidae (or the subfamily Pepesuchinae depending on who you ask), which stand out as being rare examples of semi-aquatic members of this otherwise largely terrestrial group. Epoidesuchus was fairly large for its kin and had long, slender jaws. Like I said, Epoidesuchus and its relatives were likely more semi-aquatic than other notosuchians, something that might explain the relative lack of semi-aquatic neosuchians across Gondwana. They aren't absent mind you, but noticably rarer than they are in the northern hemisphere.
Artwork by Guilherme Gehr

And thus we move into the Cenozoic and towards the end our or little list. From here on out, say goodbye to Notosuchians or other weird crocodylomorphs and get ready for Crocodilia far as the eye can see.
Ahdeskatanka
The first Cenozoic croc we got is Ahdeskatanka russlanddeutsche (Russian-German Alligator), which despite its name comes from North Dakota, specifically the Early Eocene Golden Valley Formation. Ahdeskatanka is similar to many early alligatorines like Allognathosuchus in being small with rounded, globular teeth that suggest that it fed on hardshelled prey. This would have definitely helped avoid competition in the Golden Valley Formation, which also housed a second, similar form not yet named, a large generalist with a V-shaped snout similar to Borealosuchus and the generalized early caiman Chrysochampsa, also large but with a U-shaped snout.
Artwork by meeeeeeee

Asiatosuchus oenotriensis
We had an alligatoroid, so now its time for a crocodyloid. Asiatosuchus has been recognized from the Late Eocene Duero Basin of Spain for a while now, but now we have a name: Asiatosuchus oenotriensis (Asian Crocodile Belonging To The Land Of Wine). Asiatosuchus is a complex genus, most often not really forming a monophyletic clade and likely representing several distinct or at least successive taxa that form the "Asiatosuchus-like complex". Within this complex, A. oenotriensis is thought to have been close-ish to Germany's Asiatosuchus germanicus.
Artwork by Manusuchus

Sutekhsuchus
Rounding out the trio of major crocodilian clades is Sutekhsuchus dowsoni (Set's Crocodile/God of Deception Crocodile), representing our only gavialoid of the year. Originally described as Tomistoma dowsoni in 1920 based on fossil remains from the Miocene of Egypt, Sutekhsuchus has been at times regarded as distinct and at other times lumped into Tomistoma lusitanica. It was one of several early gavialoids to inhabit the coast of the Tethys during the Miocene and appears to have been most closely related to the genus Eogavialis, clading together just outside of the American and Asian gharials. A fun little personal anecdote, I prematurely learned about this one due to a friend highlighting the name in a study on Eogavialis. Never having heard of "Sutekhsuchus" I took to google scholar, where I found a single result: a reference to the then unpublished description, which naturally I ended up eagerly awaiting.
Artwork by Manusuchus and Joschua Knüppe
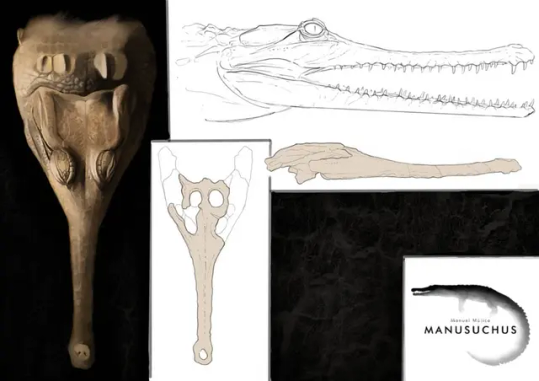

Paranacaiman
Two more and we're done. First, completely arbitrarily, Paranacaiman bravardi (Bravard's Caiman from Parana) from the Miocene Ituzaingo Formation of Argentina. Material of this genus has originally been referred to Caiman lutescens, described in 1912 but now considered a nomen dubium. Paranacaiman is known from limited material only, just the skull table, but that would indicate a "huge" animal. My personal scaling recovered a size of almost 5 meters in length, similar to large black caimans today.
Once again, credit to me

Paranasuchus
Last but not least, Paranasuchus gasparinae (Gasparini's Crocodile from Parana). Coming from the same deposits as Paranacaiman, this one too has been known as a species of Caiman for some time before being assigned its own genus, though it at least got to retain its old species name. Alas, I have not scaled it myself, tho its material is at least more extensive than that of Paranacaiman, including even parts of the snout. A little nitpick because I don't have much to say, but I personally think the name was ill conceived. On its own both Paranacaiman and Paranasuchus are fine names don't get me wrong, but together, coined by the same authors in the same study no less, they strike me as needlessly confusing to non experts. Both are caimans, both are from Parana, so the distinction between "Parana Caiman" and "Parana Crocodile" is entirely arbitrary and doesn't really distinguish them. Not helped by the fact that they are even closely related in the original description. Other than that tho another good addition to our understanding of fossil crocs.
No artwork on this one, but fossil material from Bona et al. 2024
And that wraps up 2024. I hope This post, or my posts throughout the year or even my work on Wikipedia has helped to make these fascinating animals just a little bit more approachable and a massive thanks to all the artists who took their time to create fantastic pieces featuring these incredible animals. Special shout outs to Manusuchus, who diligently illustrated a lot of the featured animals and Joschua Knüppe, who had to listen to me suggest Ahdeskatanka every Sunday for about two months straight now.
Fossil Crocs of 2023
Fossil Crocs of 2022
#paranasuchus#paranacaiman#ahdeskatanka#sutekhsuchus#ophiussasuchus#epoidesuchus#caipirasuchus#araripesuchus#enalioetes#parvosuchus#benggwigwishingasuchus#schultzsuchus#garzapelta#varanosuchus#paleontology#prehistory#palaeoblr#long post#fossil crocs of 2024#paleo#paleonotlogy#crocodilia#crocodylomorpha#pseudosuchia#fossils#2024
259 notes
·
View notes
Text




Doodles from today's flocking paleostream featuring Dinocephalosaurus, Enoploura, Achelousaurus and Arizonasaurus Iced Tea.
137 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why crocodile-line archosaurs are cooler than you think
Pseudosuchian evolution is like really, really underrated. Like people learn a version of "crocodiles have been around for 200 million years" even though pseudosuchians have a super interesting and diverse history. Some forms even converged on the "primitive dinosaur" body plan, despite not being dinosaurs at all!
In rough order of divergence:

Desmatosuchus, an aetosaur

Arizonasaurus, a poposauroid
Shuvosaurus, another poposauroid (not a dinosaur!)

Postosuchus, a rauisuchid

Terrestrisuchus, an early crocodylomorph

Neptunidraco, a thalattosuchian

Baurusuchus, a sebecosuchian
Chimaerasuchus, a notosuchian


Simosuchus, another notosuchian

Anatosuchus, a crocoduck notosuchian

Yacarerani, yet another notosuchian
While bird-line archosaurs are fluffier, and have been much more widespread since the Jurassic, pseudosuchians displayed a much wider range of adaptations than we gave them credit for - from fully aquatic thalattosuchians to small terrestrial, herbivorous, armored notosuchians!
243 notes
·
View notes
Text
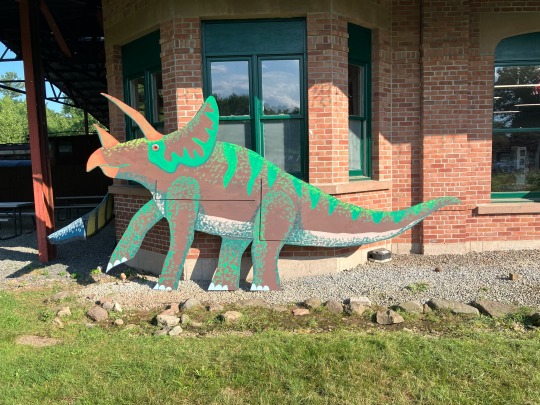










Been crazy busy the last two weeks painting plywood dinosaurs for Dino Weekend at my trolley museum. Finally got to see them on display along the tracks this weekend.
I’ve always loved visiting parks with full-size dinosaur animatronics or statues. The goofier the better. So it’s honestly super cool that I got to create my own little roadside dinosaur park.
I painted each side of the dinosaur with a different design so they’d look different going out on the trolley line vs coming back.
The creatures are:
Dilophosaurus, which may have been the dinosaur that created the Eubrontes fossil tracks found throughout the Connecticut Valley.
Anchisaurus, an early sauropodomorph whose bones were found in East Windsor, CT. They are believed to be the first scientifically-studied dinosaur bones found in North America.
Camarasaurus, because I wanted to include a sauropod that isn’t as well known. This standee is 16 feet tall, so I had to paint it on its side.
Also Triceratops and Stegosaurus, ‘cause you gotta have the classics
Planning on adding more for next year. I’d really like to do more East Coast dinosaurs like Dryptosaurus, Hadrosaurus, and Podokesaurus. And some non-dinosaur prehistoric creatures like Carnufex, Postosuchus, Quetzalcoatlus, Dimetrodon, Arizonasaurus, and Estemmenosuchus.
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
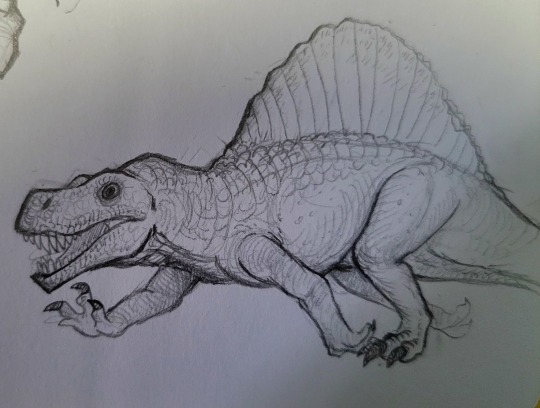

Monstrous little Arizonasaurus
While it might be confused for Dimetrodon, this Triassic menace is more alike a proper reptile, and built much more lizard-like than Dimetrodon. This style is starting to grow on me, the bold lines and details make me adore drawing these prehistoric beasties.
#art#artwork#artists on tumblr#dinosaur#doodle#paleoart#prehistoric#reptile#lizard#arizona#mesozoic#creature art#creature#animal#paleontology#stylized
136 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sailed Animals
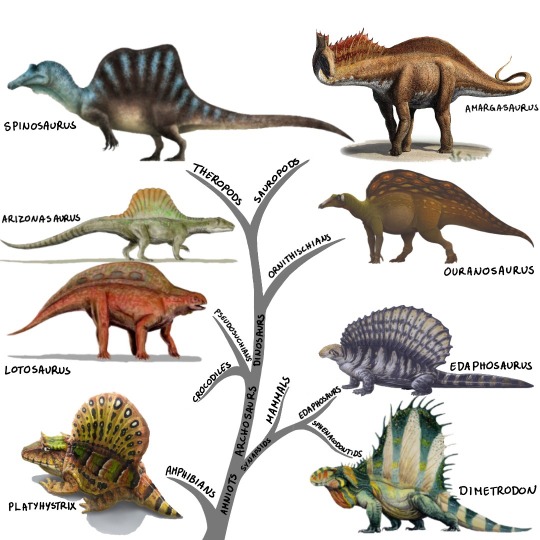
(Sailed animals and their relationships. Art by: Platyhystrix - Gabriel Uguento, Dimetrodon - Rob Soto, Edaphosaurus - Sean Closson, Arizonasaurus, Lotosaurus - Nobo Tamura, Spinosaurus - Liam Elward, Ouranosaurus - Scott Reid, Amargasaurus - Sergey Krasovskiy)
Okay, what I actually wanted to do, was write something about the Permian, and I will be doing that at some point - however, I got side tracked by Dimetrodon and Edaphosaurus and their sails, so here we are.
You see, I‘m a big fan of convergent evolution and especially when the evolution converges to some very specific and bizarre feature that we don‘t fully understand, like big sails on the backs of animals.
As you can see in the picture above, sails have evolved independently from each other many times. Some of the earliest instances come from the late Carboniferous and early Permian and include the amphibian Platyhystrix (I had no idea that there were sailed amphibians, that‘s so cool) and of course the famous carnivorous Dimetrodon and its plant-eating cousin Edaphosaurus. Edaphosaurus and Dimetrodon are often mistaken for reptiles or even dinosaurs. They were neither, but instead they were synapsids, the same group that includes us mammals.
The next time we see sails is during the Triassic in the crocodile-related Pseudosuchians, like the carnivorous Arizonasaurus or herbivorous Lotosaurus. I‘m not entirely sure, if the sails evolved only once in this group, or multiple times, because it is hard to find information on that (I really wish those croc-cousins would get the same attention as dinosaurs).
But speaking of dinosaurs: They of course also had sails. Most famous for it is Spinosaurus and its relatives, but other groups of dinosaurs also evolved sails. Those included the sauropods (the long-necked giant herbivores) like Amargasaurus (well, maybe?), as well as the Ornithopods (duck-billed dinosaurs and their relatives) like Ouranosaurus.
Now you might think that we have a clear lack of sailed animals at the moment, but don’t worry: there are still animals with sails! And somehow I was completely unaware of this until I started looking into it. We still have the Crested Chameleon, some species of basilisks, sail-fin dragons and the sailfish (although from what I understand its sail works differently then the ones of the lizards).

The sails of all these animals are made up from long extensions of the vertebrae. It is assumed that those bones were covered in tissue, spanning open a sail. We can be pretty certain of this, because there have been fossils found, where the bones had broken and then healed back together while the animal was still alive, clearly showing that they must have been held in place by something (Rega et al, 2012).
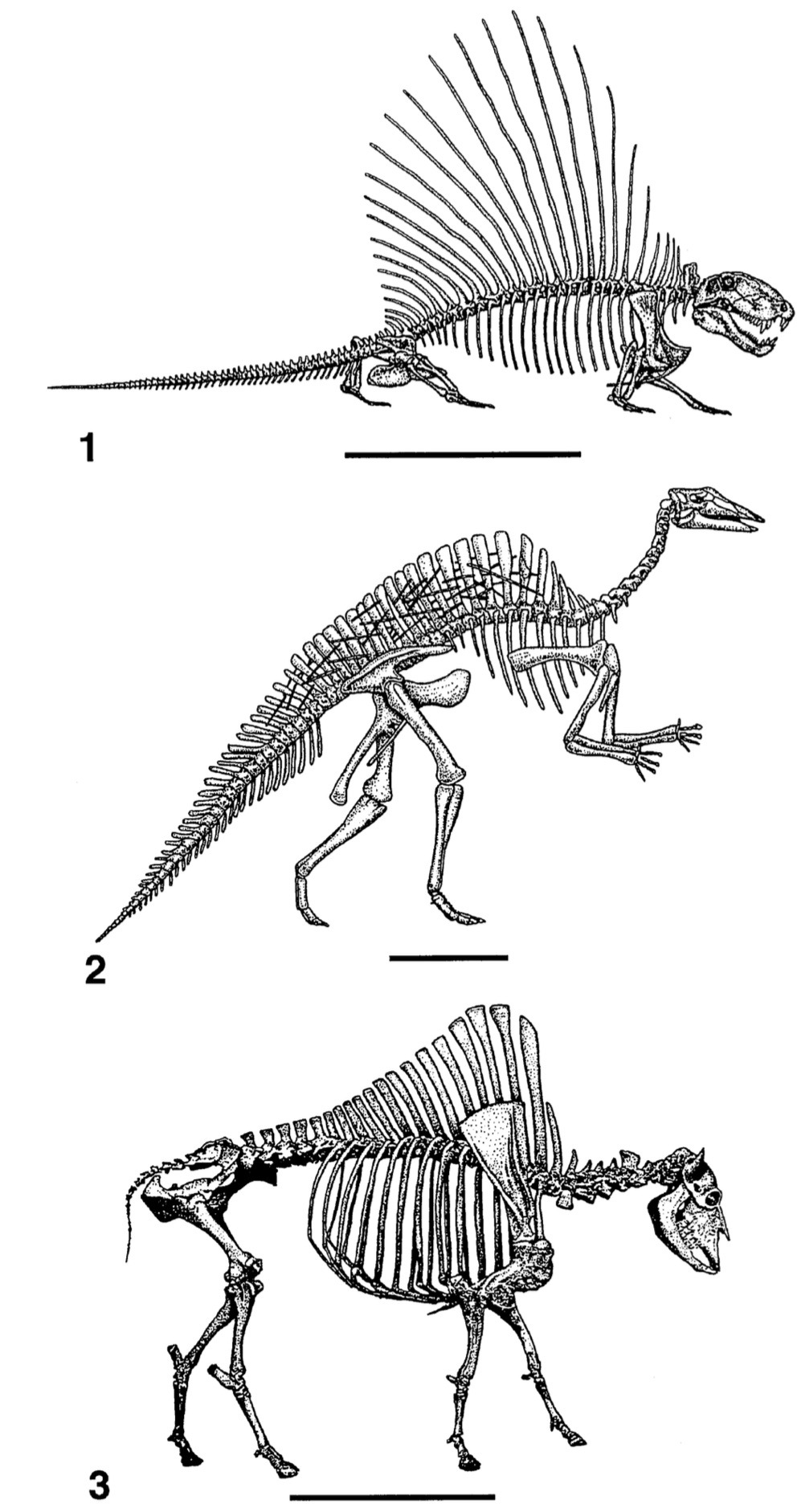
(skeletons of Dimetrodon, Ouranosaurus and a bison, Bailey 1997)
For different animals these bones can look very different though: For the synapsids like Dimetrodon they were very thin, while they were thicker and flatter in dinosaurs. In that way, they looked a lot more similar to the vertebrae of modern humped animals like bisons. This is why in the 90s there were some suggestions that those dinosaurs didn‘t have sails, but instead had big humps on their back for energy storage or maybe for insulation to keep a constant body temperature (Bailey, 1997).
The idea never really caught on, but we did this amazing illustration of a humped spinosaurus out of it. I know, we‘ve probably all seen our fair share of Spinosaurus reconstructions, but I have never seen a chonky one, and I don‘t know how to feel about it.
(humped Spinosaurus, Bailey 1997)
The big questions that remains is of course: why sails? what were they good for? The most common answer you get is either display or thermoregulation.
The sails being a display structure is a very intuitive answer. If you‘re carrying around a giant billboard-like structure on your back, it would only make sense to advertise something on it. You could use it to impress the opposite sex with fancy colors, intimidate rivals because it makes yourself look a lot bigger or signal to other animals that you are the same/a different species.
One thing that I always think about, but never see mentioned, especially in the case of the herbivorous sailed animals, is mimicry. Edaphosaurus and Dimetrodon lived at the same time, so could it not be, that Edaphosaurus had sails to make themselves look like big scary Dimetrodons to keep other predators away? Similar to how we have many harmless insects pretending to be wasps today? It would of course not explain why Dimetrodon had a sail, but it could give the herbivores a reason to have one.
The other big reason for sails is thermoregulation. Especially cold-blooded animals could have used their sails like solar panels, pointing them towards the sun and collecting heat (Bramwell & Fellgett, 1973). Alternatively, the sails could have been used to cool the animal down by positioning them in the direction of winds (Bennett, 1996).
The only problem with thermoregulation is, that its viability depends on whether the animals in question were endothermic or ectothermic (warm- or cold-blooded). And for pretty much all the sailed animals this is a heated (pun intended) debate.

(Airflow around an Edaphosaurus, Benett 1996; Can I just point out that this graph, as well as the chonky Spinosaurus were part of actual peer reviewed publications? I do chemistry irl and I‘m a bit jealous that in the papers I write I never get the chance to draw dorky looking synapsids)
Now that we‘ve discussed the reasonable well accepted explanations for sails, let‘s get into some more outlandish ones. Maybe Dimetrodon used its sail to „camouflage among reeds while [it] waited for prey, or as an actual boat-like sail to catch the wind while the animal was in the water“, as stated in multiple papers. I tried to hunt down the original source for this, but the idea comes from a Book by Romer and Price from 1940, and unfortunately I don‘t have access to it. Honestly, I would love to know if they had any actual reasoning for it or if they were just throwing ideas around, because the image of a Dimetrodon floating around on the surface of the water and getting pushed around by winds sounds ridiculous. Similarly, having a giant structure on your back, just so you can camouflage it to look like the background seems like a lot of unnecessary effort. Surely you could just not have the giant structure and it would have the same effect.
For Spinosaurus, there is the idea that they might have used their sails to shade the water while hunting, like a heron bird. I had never heard that before, but I find it a bit strange. Wouldn‘t that mean, that they had to catch fish at a weird angle towards their side? Seems uncomfortable. Of course there are also many ideas that the sails might have helped with swimming or whatever, but I don‘t want to get into the Is-Spinosaurus-aquatic-debate. I‘m pretty sure most of the papers about it would be outdated anyways and the ones that aren‘t will be in approximately 20 minutes.

For the sauropods, the “long-necks“, like Amargasaurus, even less is clear: It is even debated whether the spines on their necks formed sails or horns. If they had horns those might have been a defense structure or just for display. If they had sails - well, then it‘s the same questions as for all the other weirdos.
So yeah, overall, sailed animals were pretty weird, and there is still a lot to learn.
Also “sail“ doesn‘t sound like a word anymore.
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
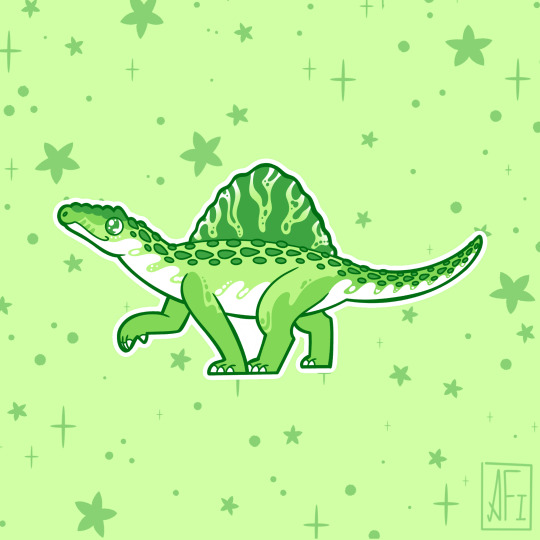
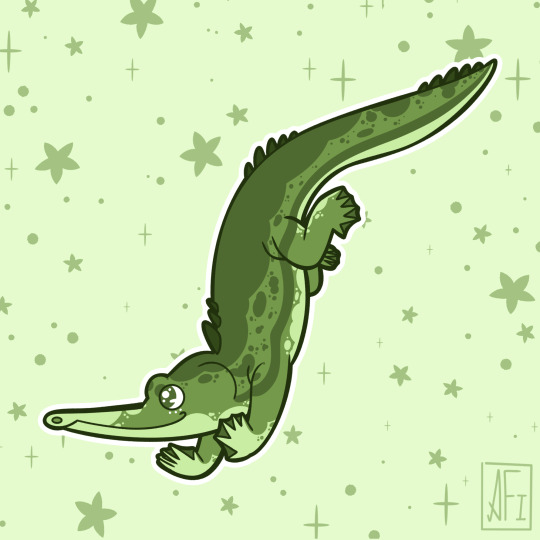
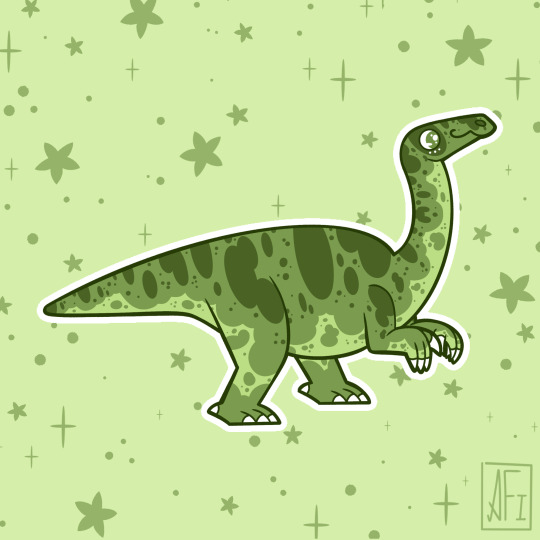
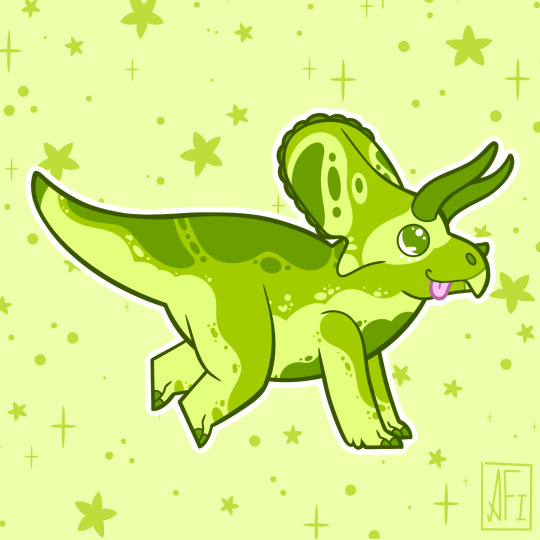
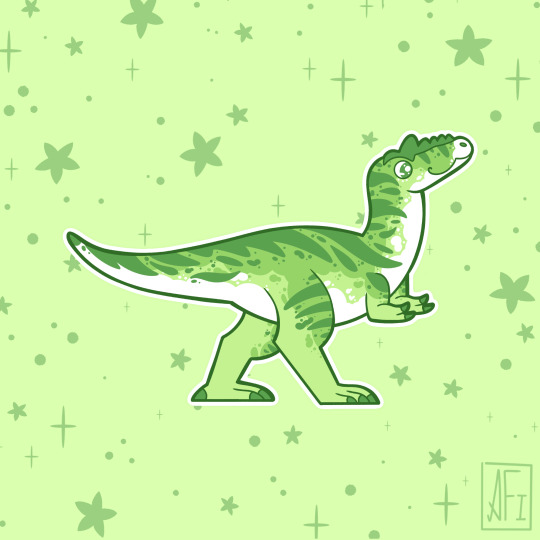











My Mesozoic is Lime Green!
Dromaeosauroides - Ceratosuchops / Baryonyx - Arizonasaurus
Jakapil - Champsosaurus - Plateosaurus
Torosaurus - Alioramus - Dimorphodon
Inawentu - Zalmoxes - Fukuiraptor
Stickers || Phone Wallpapers Masterlist
#art#my art#paleoart#paleontology#science#illustration#dinosaur#Inawentu#Zalmoxes#Fukuiraptor#Dromaeosauroides#Ceratosuchops#Baryonyx#Arizonasaurus#Jakapil#Champsosaurus#Plateosaurus#Torosaurus#Alioramus#Dimorphodon
53 notes
·
View notes
Text


Day #4, a tribute to Arizonasaurus babbitti! * Triassic * Pseudosuchian with a sail! * Medium-sized: ~3m long also one of my favorite extinct animals, but this one is a carnivore! Aaand yes, their fossils have been found in Arizona (who could've guessed?).
(Wikipedia) (Artist)
6 notes
·
View notes
