#Autonomous Navigation Software Market
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The APAC future of autonomous systems: focus on autonomous navigation software market was valued at $691.7 million in 2022, and it is expected to be $1,361.8 million by 2033. APAC has witnessed a surge in the adoption of autonomous systems across various sectors like automotive, aerospace, marine, agriculture, and logistics. These systems rely on cutting-edge navigation software to operate autonomously, enabling vehicles, drones, robots, and other machines to perceive and navigate their environments without human intervention.
#APAC Future of Autonomous Systems Market#APAC Future of Autonomous Systems Industry#Autonomous Navigation Software Market#Autonomous Navigation Software Industry#Robotics and Automation#BISResearch
0 notes
Text
The Road Ahead – Navigating the Future of the Automotive Industry
🌍 Market Overview
The Global automotive industry Market Size is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, sustainability initiatives, and changing consumer preferences. Automakers are embracing electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous technology, and digital transformation to stay ahead.
Download a Free Sample : https://rb.gy/iwh4in
📈 Growth Drivers
✅ Electrification – Rise in EV adoption due to sustainability goals and government incentives. ✅ Autonomous Vehicles – Investments in self-driving technology from major players like Tesla, Waymo, and GM. ✅ Connectivity & IoT – Smart features, in-car AI, and enhanced safety tech. ✅ Urbanization & Mobility Services – Growth of ride-sharing and subscription-based vehicle models.
⚠️ Key Challenges & Factors
��� Chip Shortages – Semiconductor supply chain disruptions affecting production. 🚧 Regulatory Hurdles – Stricter emissions policies worldwide. 🚧 Consumer Preferences – Shift towards SUVs and electric mobility. 🚧 Raw Material Costs – Fluctuations in lithium, nickel, and other EV battery components.
🔥 Emerging Trends
🔹 EV Market Boom – Tesla, Rivian, and legacy automakers expanding electric fleets. 🔹 Hydrogen Fuel Cell Tech – Toyota & Hyundai leading innovations. 🔹 Sustainable Manufacturing – Recycling initiatives & carbon-neutral plants. 🔹 Software-Defined Vehicles – Over-the-air (OTA) updates & AI-driven enhancements.
Related Urls :
https://www.sphericalinsights.com/reports/automotive-blockchain-market https://www.sphericalinsights.com/reports/china-halal-logistics-market
#AutomotiveIndustry 🚗 |#EVRevolution ⚡ |#CarTrends 🚘 |#FutureOfMobility 🌍 |#AutoTech 🔧 |#ElectricVehicles 🔋 |#AutonomousCars 🤖 |#GreenMobility 🌱 |#CarManufacturing 🏭 |#SmartCars 📡 |#SustainableTransport 🚀 |#AutoInnovation 🔥 |#NextGenVehicles 🚙 |#AutomotiveMarket 📈 |#MobilitySolutions 🚦
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
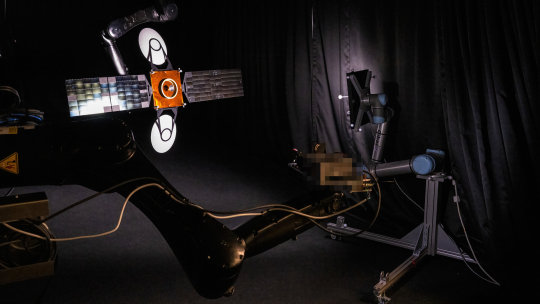
Vision-based navigation system enables satellites to approach or avoid other objects in space
Mounted on a robotic arm attached to a 33-m long rail, a camera system is brought closer and closer to this scale-model satellite, recreating the experience of a rendezvous in space.
European Space Agency's Guidance Navigation and Control (GNC) Rendezvous, Approach and Landing Simulator, GRALS—part of its Guidance, Navigation and Control Test Facilities at the ESTEC technical center in the Netherlands—was used by Lithuanian company Blackswan Space for the testing of their autonomous satellite navigation technology.
This Vision Based Navigation (VBN) system enables satellites to identify and approach or avoid other objects in space with the help of AI—in a way akin to self-driving cars.
"As the satellite numbers are growing rapidly, such capability is key in enabling us to not only better manage the increasing space traffic, but also service satellites that need repairs or are simply out of fuel," notes Marius Klimavičius, founder and CEO of Blackswan Space. "We see a growing demand for our product as the new market of in-orbit servicing emerges."
ESA's GNC System Engineer Irene Huertas García explains, "At the beginning stages of vision-based technology developments, space scenarios are simulated using software. As maturity of the developed solution increases, we need a more representative real-world 'hardware-in-the-loop' testing in visual conditions resembling space. GRALS enables such test conditions, including darkened surroundings and a sun-like light source as required."
Joris Belhadj of the GNC Test Facilities adds, "The lab's model satellite—called BlackGEO– has been manufactured to contain typical elements of a geostationary satellite's topography, with characteristic satellite surface materials including multi-layer insulation and solar cells to enhance its optical representativity. The satellite was also produced by Blackswan under ESA contract, and any customers of our laboratory can now make use of it."
By leveraging the capabilities of ESTEC's GRALS, Blackswan has successfully demonstrated the potential of Vision Based Navigation to enhance space traffic management and enable in-orbit servicing. The company's access to the GNC facility was supported through ESA's General Support Technology Program (GSTP).
The collaboration between ESA and Blackswan Space is strongly backed by the Lithuanian Space delegation. Following the successful test campaign, the delegation has committed to provide ongoing funding to advance Blackswan's VBN system to TRL 6 within the next 12 months, with an in-orbit demonstration mission planned for 2027.
ESA is currently developing its own in-orbit servicing mission, RISE, targeting telecommunications satellites in geostationary orbit.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Artificial Intelligence Developers: Driving the Future of Intelligent Technology
In the fast-evolving world of technology, artificial intelligence developers have become some of the most valuable professionals in the industry. These experts are responsible for designing intelligent machines and systems that simulate human thinking. As AI becomes deeply embedded in our daily lives—from virtual assistants to self-driving cars—the role of artificial intelligence developers continues to expand.
Who Are Artificial Intelligence Developers?
Artificial intelligence developers are specialized software engineers who focus on building applications powered by machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and other AI technologies. They create algorithms that help machines make decisions, learn from data, and solve complex problems efficiently.
Unlike traditional developers, AI developers must blend knowledge from computer science, data science, and mathematics to build systems that can learn and adapt over time.
Core Responsibilities of AI Developers
Artificial intelligence developers handle a wide range of tasks, including:
Designing and implementing AI and machine learning models.
Preprocessing and analyzing large datasets.
Training and evaluating models using statistical techniques.
Building intelligent applications for speech recognition, recommendation systems, predictive analytics, and more.
Collaborating with data scientists, engineers, and product teams to integrate AI solutions into products.
Deploying AI models to production and monitoring their performance.
Key Skills Required for AI Developers
To thrive in the field, artificial intelligence developers must possess a unique blend of technical and analytical skills:
Programming Expertise: Proficiency in Python, R, Java, or C++.
Mathematical Foundation: Strong grasp of algebra, calculus, probability, and statistics.
Familiarity with AI Tools & Frameworks: TensorFlow, PyTorch, Keras, OpenCV, Scikit-learn.
Data Management Skills: Experience with SQL, NoSQL databases, and big data technologies like Spark.
Problem-Solving Abilities: Ability to tackle complex real-world problems through innovative AI solutions.
Knowledge of Cloud Platforms: AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure for deploying scalable AI applications.
Industries Employing Artificial Intelligence Developers
The demand for AI developers is booming across multiple industries:
Healthcare: AI for diagnostics, drug discovery, and robotic surgeries.
Finance: Fraud detection, credit scoring, and algorithmic trading.
E-commerce: Personalized recommendations, customer behavior prediction, and chatbots.
Automotive: Development of autonomous vehicles and smart navigation systems.
Marketing: Predictive analytics and automated content generation.
Career Growth and Opportunities
As AI technology continues to evolve, artificial intelligence developers are at the forefront of innovation. With increasing investment in AI by both startups and large corporations, job opportunities in this field are growing rapidly. Roles like AI engineer, machine learning engineer, data scientist, and research scientist offer high salaries and long-term career prospects.
According to industry reports, AI-related job openings have increased by over 70% in the last few years, with salaries often exceeding six figures depending on experience and location.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence developers are shaping the digital future by building smart systems that transform how we work, live, and interact. Their expertise is essential in unlocking the full potential of AI across industries. For those with a passion for problem-solving, coding, and innovation, a career as an AI developer offers not just exciting challenges but also the opportunity to make a significant impact on the world.
0 notes
Text
The Agentic AI Revolution: From Isolated Bots to Scalable Enterprise Ecosystems in 2025
Artificial intelligence is undergoing a profound transformation as autonomous AI agents transition from experimental prototypes to integral components of enterprise operations. In 2025, agentic AI, software systems that independently perceive, decide, and act, is no longer a distant vision but a rapidly maturing reality. Organizations across industries are embracing these intelligent agents to automate complex workflows, boost productivity, and unlock new avenues of innovation. For professionals seeking to enter this dynamic field, enrolling in the best Agentic AI courses or generative AI courses online in Mumbai offers a practical pathway to gain cutting-edge skills.
Yet, scaling autonomous AI agents from pilots to enterprise-wide ecosystems presents formidable challenges. These include architectural complexity, robust control mechanisms, system reliability, security risks, and fostering cross-functional collaboration. Success demands the fusion of cutting-edge AI research with rigorous software engineering practices and real-world deployment expertise. Professionals who complete an Agentic AI course in Mumbai often find themselves well-prepared to tackle these challenges, gaining both theoretical and applied knowledge.
This article provides a detailed exploration of agentic and generative AI evolution, highlights leading frameworks and deployment strategies, and shares advanced tactics to build scalable, reliable autonomous AI systems. We also examine software engineering best practices, the critical role of interdisciplinary collaboration, and metrics for measuring impact. Finally, a real-world case study of Salesforce’s Agentforce 2.0 illustrates these principles in action, offering practical lessons for AI practitioners and technology leaders navigating this exciting frontier.
Market Context and Agentic AI Maturity in 2025
The AI agent market is entering a phase of rapid growth and enterprise adoption. According to industry analyses, global spending on AI agents is projected to surge from approximately $5 billion in 2024 to over $47 billion by 2030. Deloitte forecasts that by the end of 2025, roughly 25% of companies using generative AI will have launched agentic AI pilots or proofs of concept, with adoption expected to double by 2027.
Despite this momentum, many organizations remain “agent-unready”, facing challenges in integrating AI agents into legacy systems and workflows. The critical barrier lies less in model capabilities and more in enterprise readiness, specifically, exposing APIs securely, orchestrating workflows, and embedding governance frameworks. Enrolling in the best Agentic AI courses can help software engineers and technology leaders understand these enterprise challenges and prepare for real-world deployment.
The emerging “new normal” envisions AI ecosystems where multiple specialized agents operate collaboratively under orchestrator super-agents or “uber-models” that manage workflows end to end. This shift from isolated AI tools to integrated multi-agent systems marks the next wave of AI-driven digital transformation. Professionals seeking to lead in this area often pursue generative AI courses online in Mumbai to stay current with these trends.
Evolution of Agentic and Generative AI in Software
Agentic AI has evolved from early rule-based expert systems to sophisticated entities empowered by large language models (LLMs) and generative AI. These agents perceive their environment, reason about goals, and autonomously execute multi-step tasks with minimal human intervention. Generative AI models such as GPT-4 and successors have revolutionized agent capabilities by enabling natural language understanding, creative content generation, and seamless interaction with humans and digital systems.
This integration allows agents to handle complex decision-making, contextual awareness, and dynamic adaptation. By 2025, enterprises are moving beyond single-agent pilots to deploy multi-agent ecosystems. These systems feature agents specialized for tasks like data analysis, content creation, customer interaction, and predictive forecasting, collaborating through hierarchical orchestration layers that ensure alignment and consistency.
Those interested in mastering these technologies can benefit from the best Agentic AI courses or generative AI courses online in Mumbai, which emphasize hands-on experience with such multi-agent systems.
Leading Frameworks, Tools, and Deployment Strategies
LLM Orchestration Platforms
A cornerstone of scalable agentic AI is the orchestration layer that manages and coordinates multiple LLM-based agents. Leading platforms such as Microsoft Copilot Agents, Google Cloud Agentspace, and Salesforce Agentforce provide unified environments for deployment, monitoring, and workflow integration.
These orchestration frameworks enable:
Multi-agent architectures where agents with specialized skills communicate, delegate tasks, and escalate issues dynamically.
Hierarchical control structures featuring super-agents that oversee sub-agents to maintain policy adherence and conflict resolution.
Seamless integration with enterprise data systems, APIs, and security protocols.
Understanding these platforms is critical, and many aspiring AI engineers enroll in the best Agentic AI courses to gain expertise in deploying such orchestration solutions.
MLOps for Generative AI Agents
Scaling autonomous agents demands robust MLOps practices tailored to the unique challenges of generative models. Beyond traditional machine learning lifecycle management, generative AI requires continuous monitoring for hallucinations, bias, output quality, and compliance risks.
Key MLOps capabilities include:
Automated pipelines for data ingestion, model fine-tuning, and versioned deployments.
Real-time dashboards tracking agent latency, throughput, error rates, and user feedback.
Governance frameworks embedding ethical guidelines, auditability, and regulatory compliance into deployment workflows.
Enterprises adopting these practices achieve more reliable, transparent, and maintainable AI agent systems. Professionals aiming to lead these initiatives find generative AI courses online in Mumbai especially valuable for understanding these specialized MLOps processes.
Phased Deployment Strategy
To mitigate risks and build organizational trust, a phased rollout is recommended:
Initial automation of high-volume, low-risk processes such as customer service inquiries, scheduling, and data entry.
Pilot autonomous agents in controlled environments with defined success metrics and human oversight.
Scale to enterprise-wide ecosystems featuring multi-agent collaboration, hierarchical supervision, and integration with core business systems.
This incremental approach balances innovation speed with technical maturity and risk management. Training from the best Agentic AI courses equips practitioners to design and execute such phased strategies effectively.
Advanced Architectural and Control Tactics
Modular Microservices Architecture
Designing AI agent systems as modular microservices enables independent development, testing, deployment, and scaling of individual agents. This architecture facilitates fault isolation, reduces system complexity, and allows flexible resource allocation tailored to agent workloads.
Standardized Agent-to-Agent Communication
Effective multi-agent coordination relies on robust communication protocols. Techniques include asynchronous messaging queues, event-driven triggers, shared distributed knowledge bases, and consensus mechanisms for state synchronization and conflict resolution. Emerging standards and open protocols are critical to interoperability and scalability.
Hierarchical Supervision and Fail-Safe Mechanisms
Super-agents or control layers oversee subordinate agents, enforcing system-wide policies and intervening when anomalies or conflicts arise. Fail-safe strategies incorporate rollback capabilities, human-in-the-loop escalation, anomaly detection through AI monitoring, and redundancy to prevent cascading failures.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation Pipelines
Deploying reinforcement learning and human feedback loops enables agents to evolve based on real-world interactions, improving reasoning accuracy and execution efficiency over time. Continuous learning pipelines must balance adaptation speed with stability and compliance requirements. Those looking to deepen their practical knowledge of these architectures can benefit greatly from best Agentic AI courses which cover these advanced topics in detail.
Security, Ethics, and Compliance Considerations
Scaling autonomous AI agents introduces new risks that demand proactive mitigation:
Adversarial Threats: Agents must be hardened against malicious inputs and exploitation attempts.
Bias and Fairness: Continuous evaluation ensures outputs do not propagate harmful biases or discriminatory outcomes.
Data Privacy: Compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations requires rigorous data handling and audit trails.
Accountability and Transparency: Logging, explainability, and human oversight are essential to maintain trust and regulatory approval.
Embedding security and ethical guardrails from project inception avoids costly rework and reputational damage, enabling responsible AI deployment at scale. Generative AI courses online in Mumbai often include modules that focus on these critical governance aspects, preparing professionals for real-world challenges.
Software Engineering Best Practices for Agentic AI
Successful scaling hinges on applying mature software engineering disciplines traditionally associated with large-scale enterprise systems:
Code Quality and Documentation: Maintainable, well-documented codebases ensure knowledge transfer and long-term system health.
Automated Testing: Comprehensive unit, integration, and system tests validate agent logic and interactions under diverse conditions.
Robust Logging and Observability: Detailed telemetry supports debugging, incident response, and performance tuning.
Security Engineering: Implement access controls, encryption, and threat detection to safeguard AI services.
Governance and Compliance Frameworks: Formalize processes for ethical review, audit logging, and regulatory reporting.
These practices transform AI agent deployments from fragile experiments into enterprise-grade, scalable services. Professionals who complete the best Agentic AI courses are often better prepared to implement these rigorous engineering standards.
Cross-Functional Collaboration for AI Success
Agentic AI projects inherently span multiple disciplines. Effective collaboration among data scientists, software engineers, product managers, business stakeholders, security experts, and compliance officers is vital. Key enablers include:
Shared tooling and platforms for model development, deployment, and monitoring.
Aligned objectives and success criteria defined jointly by technical and business teams.
Regular communication channels to bridge cultural and technical divides.
Co-created risk management and governance policies.
This holistic approach accelerates delivery, adoption, and value realization across the organization. Many generative AI courses online in Mumbai emphasize teamwork and cross-functional collaboration as core competencies.
Measuring Success: Metrics and Monitoring
Continuous measurement drives iterative improvement and stakeholder confidence. Essential metrics include:
Performance: Latency, throughput, uptime, and resource utilization.
Accuracy and Quality: Decision precision, error rates, and user satisfaction scores.
Business Impact: Productivity gains, cost savings, revenue growth attributable to AI agents.
Compliance and Risk: Number of flagged outputs, security incidents, audit findings.
Advanced monitoring platforms integrate real-time analytics, alerting, and visualization to enable proactive management and rapid response to issues. Understanding these monitoring technologies is often part of the curriculum in the best Agentic AI courses.
Case Study: Salesforce Agentforce 2.0, Scaling AI Agents in CRM
Salesforce exemplifies large-scale autonomous AI deployment with its Agentforce 2.0 platform, launched in 2024. Embedded across its CRM ecosystem, Agentforce automates diverse tasks from lead qualification to contract management, delivering measurable business value.
Journey and Technical Approach
Salesforce began by automating repetitive tasks such as data entry and meeting scheduling, generating early productivity gains. Building on this foundation, they developed specialized agents for:
Customer Interaction Analysis: Leveraging generative AI to summarize communications and extract insights.
Sales Forecasting: Predictive analytics agents providing real-time pipeline visibility.
Contract Drafting and Review: Natural language generation and understanding agents accelerating legal workflows.
To address integration complexity, Salesforce adopted a microservices architecture enabling modular agent deployment. Hierarchical agent orchestration ensures coordination and conflict resolution among specialized agents. Compliance is embedded via automated data privacy checks and audit trails.
Outcomes and Impact
35% productivity improvement in sales teams.
25% reduction in contract processing time.
Improved customer satisfaction through faster, personalized responses.
Scalable platform supporting continuous rollout of new AI capabilities.
Salesforce’s success highlights the power of combining strategic vision, software engineering rigor, and cross-functional collaboration to realize agentic AI’s potential. Professionals interested in such transformative projects often seek the best Agentic AI courses or generative AI courses online in Mumbai to build relevant skills.
Actionable Recommendations for Practitioners
Align AI agent initiatives with clear business goals to focus efforts and measure impact.
Design modular, loosely coupled architectures for scalability and maintainability.
Implement layered control mechanisms with super-agents to manage risk and ensure consistency.
Invest in MLOps pipelines tailored to generative AI for continuous evaluation and deployment.
Prioritize security, privacy, and ethical governance from project inception.
Foster interdisciplinary teams with shared objectives and open communication.
Establish comprehensive monitoring and analytics covering technical and business metrics.
Adopt incremental deployment strategies starting with low-risk automation and expanding capabilities progressively.
Enrolling in an Agentic AI course in Mumbai or generative AI courses online in Mumbai can accelerate mastery of these best practices.
Conclusion: Navigating the Autonomous AI Era
The journey to scale autonomous AI agents requires blending innovative AI research with proven software engineering discipline and organizational collaboration. The evolution of agentic and generative AI is enabling enterprises to deploy sophisticated multi-agent ecosystems that deliver substantial business value.
By embracing modular architectures, hierarchical orchestration, robust MLOps, and strong governance, organizations can build reliable, secure, and compliant AI agent platforms. Real-world examples like Salesforce’s Agentforce 2.0 demonstrate the transformative impact of thoughtfully scaled autonomous AI.
For AI practitioners, software engineers, and technology leaders, the path forward involves balancing innovation with discipline, starting small but thinking big, and continuously measuring outcomes. Autonomous AI agents are no longer a future concept, they are reshaping software and business operations today.
This comprehensive approach equips you to lead your organization confidently into the autonomous AI era, turning agentic intelligence into a strategic advantage. To stay competitive and skilled in this evolving domain, consider enrolling in the best Agentic AI courses or generative AI courses online in Mumbai, which provide the knowledge and practical expertise needed for success.
0 notes
Text
Luxury and Electric Vehicles Propel Side View Camera Adoption
Side View Camera System Market Projected to Reach USD 42.7 Billion by 2028 on Safety Mandates and Electric Vehicle Integration
The Side View Camera System Market is undergoing a rapid transformation, projected to grow from USD 1.9 million in 2023 to approximately USD 42.7 billion by 2028. This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of nearly 85.9%. The transition from traditional side mirrors to advanced camera systems is being driven by regulatory mandates, consumer demand for safer driving, and widespread adoption of electric and autonomous vehicles.

To Get Free Sample Report : https://www.datamintelligence.com/download-sample/side-view-camera-system-market
Market Drivers
1. Government Safety Regulations Globally, regulatory bodies are mandating enhanced driver visibility to reduce blind spot accidents. In regions such as Europe and North America, new vehicle safety assessments favor digital vision systems over traditional mirrors, providing a key growth lever for side view camera adoption.
2. Electric and Autonomous Vehicle Integration Electric vehicles, known for sleek and aerodynamic designs, are increasingly equipped with mirrorless systems that reduce drag and energy consumption. In autonomous vehicles, side view cameras are essential for 360-degree perception and real-time environmental awareness.
3. Consumer Demand for Safety and Design Consumers are increasingly prioritizing technology that enhances driving safety and comfort. Side view cameras offer wider fields of view, clearer images in low light, and better performance in harsh weather compared to mirrors. At the same time, they enhance aesthetics and reduce noise by improving vehicle aerodynamics.
4. Advanced Technology and AI-Based Features Leading automotive OEMs are integrating AI-powered functionalities into camera systems, such as lane departure warnings, object detection, and image enhancement. These intelligent systems are a core feature of ADAS and autonomous navigation platforms.
Regional Insights
Europe Leads Global Adoption Europe remains the largest market for side view camera systems, driven by strict vehicle safety regulations, early adoption of EVs, and growing preference for luxury vehicles. Germany, in particular, is a hub for automotive innovation, with multiple brands offering camera-based designs as a standard or premium option.
Asia-Pacific Shows Fastest Growth Asia-Pacific is witnessing the highest growth rate in this segment, with countries like Japan, South Korea, and China pushing advanced manufacturing, electrification, and smart mobility initiatives. Automakers in the region are deploying side view cameras in both domestic and export vehicle lines.
United States Expands with Technological Innovation The U.S. is steadily integrating camera systems into vehicles, especially in luxury segments and autonomous driving prototypes. Increasing investments in smart cities and connected vehicles further reinforce adoption.
Technology Segmentation and Trends
Single vs. Multi-Camera Systems
Single-camera systems are dominating the market due to simplicity and affordability.
Multi-camera systems, offering panoramic visibility and advanced ADAS functionality, are gaining momentum in high-end and commercial vehicles.
Wired vs. Wireless Integration Wired systems are still prevalent due to reliability and cost-effectiveness, but wireless systems are increasingly adopted for ease of installation, reduced cable clutter, and seamless software updates.
ADAS Integration Side view camera systems are becoming integral to advanced driver-assistance systems. Combined with rear view and front view cameras, they support lane-keeping, automatic parking, and collision avoidance capabilities.
Key Opportunities
1. Luxury and Electric Vehicle Expansion Premium and electric vehicles are expected to drive high adoption rates as manufacturers replace traditional mirrors with camera-based systems to improve design, aerodynamics, and driver safety.
2. AI-Powered Image Processing As artificial intelligence becomes more embedded in vehicle systems, side view cameras are integrating real-time analytics, object detection, and enhanced low-light performance.
3. Smart Mobility and Infrastructure Integration As vehicles become connected to road networks and urban infrastructure, side view cameras will serve not only drivers but also external systems managing traffic flow, pedestrian safety, and automated navigation.
4. Aftermarket and Retrofitting Aftermarket kits for retrofitting older vehicles with side view cameras are emerging as a cost-effective solution for vehicle owners seeking enhanced safety and modern aesthetics.
Get the Demo Full Report : https://www.datamintelligence.com/enquiry/side-view-camera-system-market
Challenges
Cost Barriers: High development and production costs may deter OEMs from mass adoption in low- and mid-tier vehicles.
Standardization Issues: Lack of harmonized global regulations on mirrorless vehicle systems can delay rollouts in certain markets.
Consumer Adaptation: Some drivers may resist change from conventional mirrors, citing concerns over screen placement and reliability.
Technological Complexity: Integration with onboard systems like infotainment, ADAS, and power management requires precision engineering and software coordination.
Conclusion
The side view camera system market is on the cusp of a major technological shift, fueled by rising safety expectations, electric vehicle innovation, and global regulatory momentum. Forecasts indicate a dramatic rise in market size from less than USD 2 million in 2023 to over USD 42 billion by 2028.
As consumers demand more intelligent, connected, and aesthetically refined vehicles, side view cameras are replacing mirrors as the new standard in automotive design. Regions like Europe and Asia-Pacific are at the forefront, while the U.S. continues to advance smart infrastructure and autonomy.
Manufacturers that focus on AI integration, energy efficiency, compliance, and intuitive user interfaces will emerge as market leaders. The next generation of vehicles will not just be smarter they will see the road differently, and side view cameras will lead the way.
0 notes
Text
Marine Internet of Things Market Research Report, Demand and Future Trends Till 2037
In 2024, the Marine Internet of Things (IoT) Market was valued at $6.9 billion and is anticipated to grow significantly, reaching $28.5 billion by 2037.This growth corresponds to a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.2% from 2025 to 2037.his growth is propelled by increasing digitization of maritime operations, rising adoption of smart technologies across commercial and defense fleets, and the need for real-time data to optimize marine resource management and vessel performance.
Marine Internet of Things Industry Demand
The Marine IoT Market focuses on integrating advanced sensors, communication systems, software platforms, and data analysis tools within the maritime sector. These technologies enable real-time monitoring, automation, and predictive analytics across marine operations—from cargo tracking to environmental surveillance and safety systems.
Demand is being driven by several key benefits:
Cost-effectiveness: Automated monitoring and predictive maintenance help reduce fuel costs, labor expenses, and unplanned downtimes.
Ease of administration: Centralized systems allow operators to remotely manage fleets, assets, and maritime conditions through cloud-based dashboards.
Long operational life: Marine IoT systems are designed for rugged conditions and long-term deployment, offering sustainable value over time.
From commercial shipping and offshore oil operations to environmental research and defense applications, the marine industry is experiencing a digital transformation fueled by IoT innovation.
Marine Internet of Things Market: Growth Drivers & Key Restraint
Growth Drivers –
Digital Transformation and Automation in Maritime Operations:
As the demand for enhanced operational efficiency and sustainability grows, maritime companies are increasingly implementing IoT technologies for automated navigation, cargo monitoring, energy optimization, and real-time vessel health assessments.
Increasing Need for Environmental and Regulatory Compliance:
With regulatory agencies imposing more stringent emission and safety regulations, IoT-based monitoring systems play a crucial role in maintaining compliance by continuously tracking emissions, ballast water management, fuel usage, and other key parameters.
Growth of Smart Port Modernization:
Port authorities and fleet managers are modernizing their infrastructure and vessels with interconnected devices to enable smart logistics, predictive docking solutions, and improved communication, thereby opening up significant opportunities for IoT integration.
Request Sample@ https://www.researchnester.com/sample-request-3692
Restraint –
Elevated upfront expenses and potential cybersecurity: While IoT offers long-term savings, the initial setup involves substantial investment in hardware, software, and integration. Moreover, connectivity over open seas raises significant concerns regarding cybersecurity and reliable communication, especially in remote maritime environments.
Marine Internet of Things Market: Segment Analysis
Segment Analysis by Platform Type –
By Platform:
Vessel Management Systems: These platforms provide a unified view of vessel performance, enabling operators to monitor fuel efficiency, engine health, route optimization, and cargo status. The segment is gaining rapid adoption due to its impact on cost control and compliance.
Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs): AUVs are used in oceanographic research, underwater inspections, and military applications.
Segment Analysis by Application –
Asset Tracking & Monitoring: Widely used in commercial shipping and offshore installations to ensure real-time visibility of containers, cargo, and onboard equipment.
Predictive Maintenance: AI-driven analytics assess component health and forecast equipment failures, significantly reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Fleet Management: Provides centralized control of multi-vessel operations, improving navigation, fuel usage, scheduling, and regulatory reporting.
Environmental Monitoring: Deployed for observing oceanographic conditions, pollution levels, and climate indicators, this segment is growing rapidly due to environmental concerns.
Navigation & Route Optimization: Dynamic routing solutions use IoT data to suggest optimal paths based on weather, traffic, and fuel efficiency, boosting safety and reducing costs.
Safety & Emergency Systems: Includes automated distress signaling, man-overboard detection, and condition-based alert systems to enhance crew safety and emergency preparedness.
Segment Analysis by End‑User –
Satellite-based Communication:
Critical for global coverage, particularly in deep-sea operations and remote locations, though it involves higher operating costs.
Cellular:
Increasingly used in coastal and near-shore operations, offering reliable, low-latency connectivity for real-time data exchange.
Wi-Fi:
Ideal for port environments and onboard systems where short-range, high-speed data transmission is required.
VHF & HF Radio:
Still widely used for basic communications and backup systems, especially in legacy vessels and isolated maritime zones.
Marine Internet of Things Market: Regional Insights
North America:
North America leads in marine IoT innovation due to the presence of advanced shipping infrastructure, military investment, and major players in IoT technology. The U.S. is driving growth through adoption of connected naval systems, smart ports, and offshore energy monitoring platforms.
Europe:
Europe is a significant player due to its strong maritime heritage and stringent environmental regulations. Countries like Germany, Norway, and the Netherlands are investing heavily in green shipping and digital transformation, supported by EU initiatives for sustainable marine ecosystems.
Asia-Pacific (APAC):
APAC is emerging as the fastest-growing region, with booming shipbuilding industries, increasing trade routes, and large-scale smart port developments in countries like China, South Korea, Japan, and India. Government support for maritime digitization is also a key growth catalyst.
Top Players in the Marine Internet of Things Market
Key companies actively shaping the Marine Internet of Things Market include Cisco Systems, Inc., IBM Corporation, Siemens AG, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Nokia Corporation, Ericsson AB, General Electric (GE Digital), Honeywell International Inc., Wärtsilä Corporation, ABB Group, Telstra Corporation Limited, HCL Technologies Limited, Asea Brown Boveri Ltd. (ABB Malaysia), Kongsberg Gruppen ASA, and Infosys Limited. These players are investing in advanced maritime IoT platforms, cloud-based analytics, autonomous systems, and smart connectivity to redefine the future of marine operations across both commercial and defense sectors.
Access Detailed Report@ https://www.researchnester.com/reports/marine-internet-of-things-market/3692
Contact for more Info:
AJ Daniel
Email: [email protected]
U.S. Phone: +1 646 586 9123
U.K. Phone: +44 203 608 5919
0 notes
Text
SaaS Experts: Powering the Future of Scalable Software Solutions
In today’s fast-paced digital economy, Software as a Service (SaaS) has become the foundation of modern business operations. From startups to global enterprises, organizations rely on SaaS platforms to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and scale without the limitations of traditional software models. Behind every successful SaaS product are SaaS experts—strategists, engineers, and architects who bring innovation, scalability, and intelligent automation to life.
If you're looking to build or scale a cloud-based solution, it's essential to partner with seasoned SaaS experts who understand how to turn your ideas into secure, scalable, and user-centric products.
Who Are SaaS Experts?
SaaS experts are professionals specialized in designing, developing, deploying, and optimizing software delivered via the cloud. They bring a holistic understanding of cloud infrastructure, subscription-based business models, and user experience design to create products that are accessible anytime, anywhere.
Key areas of expertise include:
Cloud Architecture (AWS, GCP, Azure)
Multi-Tenant Systems
Data Security & Compliance
CI/CD Pipelines & DevOps
Performance Optimization
Subscription Billing Integration
Whether you're building a CRM, a financial analytics dashboard, or a niche collaboration tool, SaaS experts are critical to ensuring your product performs reliably and scales efficiently.
Why SaaS Is the Future of Software
SaaS is no longer a trend—it’s a standard. Here’s why businesses across sectors are adopting SaaS platforms at a record pace:
Accessibility: Use applications from any device, anywhere.
Lower Costs: No hardware or installation needed.
Scalability: Easily expand to support growing users.
Faster Deployment: Rapid development and time-to-market.
Automatic Updates: New features roll out seamlessly.
Forward-looking companies are going a step further by integrating AI product development into their SaaS platforms. AI-driven SaaS products offer real-time decision-making, intelligent automation, and personalized user experiences.
How SaaS Experts Power Your Business
Partnering with experienced SaaS experts can accelerate your product lifecycle, reduce development risk, and ensure long-term scalability. Here's how they contribute:
1. Strategic Planning
They help define your SaaS vision, assess the market landscape, and create a roadmap that aligns with your business goals.
2. Custom Architecture Design
From multi-tenancy to cloud-native environments, they build robust architectures optimized for performance and scalability.
3. User Experience Design
SaaS success relies heavily on user experience. Experts ensure intuitive interfaces, seamless navigation, and mobile responsiveness.
4. Security & Compliance
Data protection is critical. SaaS experts implement strong encryption, role-based access control, and regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
5. Ongoing Support & Optimization
Post-launch, they monitor performance, apply updates, and continuously optimize based on user feedback and analytics.
SaaS Meets AI and Web3: A Powerful Convergence
Modern SaaS platforms are becoming smarter and more decentralized. By combining AI product development and Web3 development company capabilities, SaaS experts are building future-ready platforms with intelligent features and blockchain-backed transparency.
AI in SaaS: Automated workflows, chatbots, predictive analytics.
Web3 in SaaS: Decentralized access, token-based subscriptions, enhanced data control.
This convergence is reshaping industries like fintech, healthcare, logistics, and education, empowering users with smart, secure, and autonomous applications.
Choosing the Right Team: What to Look For
When you're ready to build a SaaS product, make sure to hire developers with deep SaaS experience—not just general coders. Look for a team with:
Proven experience in SaaS architecture
Deep knowledge of DevOps and CI/CD
Experience with AI and cloud technologies
Strong UI/UX and product strategy skills
Post-launch support and feature enhancement capabilities
A reliable SaaS partner acts not just as a service provider, but as a long-term product innovation partner.
Real-World Use Cases of SaaS Solutions
CRM & Sales Platforms (e.g., HubSpot, Salesforce)
Project Management Tools (e.g., Trello, Asana)
AI-powered Analytics (e.g., Mixpanel, Amplitude)
Blockchain-enabled Identity Management
Healthcare SaaS with Predictive Diagnostics
These are built and scaled by expert teams that understand both the business and technical aspects of SaaS delivery.
Final Thoughts
The digital-first future belongs to intelligent, flexible, and secure cloud-based platforms. By working with trusted SaaS experts, you ensure that your product is built to scale, perform, and deliver real value in a competitive market.Whether you’re a founder with a disruptive idea, a business leader planning digital transformation, or an enterprise aiming to modernize, SaaS experts are the cornerstone of your success. Combine their skills with innovation in AI product development, insights from a forward-thinking Web3 development company, and the right approach to hire developers, and you’re well on your way to launching software that thrives in today’s evolving digital landscape.
0 notes
Text
Countering Interference: Anti‑jamming Technology & Adoption Trends
The global anti‑jamming market was valued at USD 4.69 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand to USD 8.64 billion by 2030, reflecting a 9.4% CAGR over the 2024–2030 period. This robust growth is primarily driven by continuous advancements in communication and navigation technologies, which have heightened the reliance on secure, uninterrupted signal processing across both defense and commercial domains.
In recent years, next‑generation communication systems—ranging from satellite links to sophisticated radar networks—have become integral to modern military operations and critical infrastructure. As these systems grow more complex, adversaries have developed increasingly potent jamming capabilities. In turn, equipment manufacturers and defense agencies are investing heavily in advanced anti‑jamming solutions. Enhanced signal‑processing methods, such as adaptive filtering and frequency‑hopping algorithms, are being continually refined to detect, isolate, and neutralize malicious interference, thereby safeguarding mission‑critical communications.
Simultaneously, the escalation of electronic warfare (EW) on the global stage has emerged as a pivotal catalyst for market expansion. Rising geopolitical tensions are prompting nations to bolster their EW arsenals, which include both jamming and anti‑jamming tools. Government budgets for defense procurement now routinely allocate significant funding to anti‑jamming research and development, fueling innovation in hardware components—like smart antennas and digital beamforming receivers—as well as in software‑defined EW suites capable of real‑time threat analysis and countermeasure deployment.
Beyond military applications, the civilian sector’s growing dependence on GPS‑based navigation and wireless communications has created new opportunities for anti‑jamming technologies. Industries such as aviation, maritime shipping, logistics, and emerging autonomous‑vehicle platforms demand uncompromised signal integrity to ensure safety and operational efficiency. For instance, unmanned aerial systems and smart‑city infrastructure rely on precise positioning data; any jamming or spoofing event could lead to catastrophic failures. Consequently, commercial service providers are integrating anti‑jamming modules into critical assets—further broadening the market’s scope.
Key Market Trends & Insights
Regional Leadership – North America: With a 35.85% share of global revenues in 2023, North America remains the largest marketplace for anti‑jamming systems. This dominance is fueled by sustained investments in advanced EW capabilities and national security programs.
U.S. Market Dynamics: The United States is poised for notable growth from 2024 to 2030, driven by government initiatives that promote technological innovation and partnerships between domestic and international defense contractors to develop cutting‑edge anti‑jamming platforms.
Asia Pacific Surge: The Asia Pacific region is also expected to register significant expansion during the forecast period. Heightened geopolitical competition has led countries such as China, India, and Japan to increase procurement of anti‑jamming solutions to strengthen their defense postures.
Receiver Segment – Military & Government Grade: In 2023, the military and government grade receiver category accounted for 71.1% of market revenue, highlighting the paramount importance of resilient communication and navigation systems in defense operations.
Technique Focus – Nulling: The nulling technique—designed to identify and cancel out unwanted interference—dominated with the largest revenue share in 2023. Its precision in suppressing jamming signals makes it a cornerstone technology for both fixed and mobile platforms.
Application – Position, Navigation & Timing (PNT): Anti‑jamming solutions for PNT applications led the market in 2023, reflecting the critical need for accurate timing and location data in both civilian and military contexts.
End‑Use – Military: The military segment commanded the largest share of anti‑jamming revenues in 2023, driven by growing requirements to protect defense communications, ensure the reliability of navigation aids, and maintain operational effectiveness in contested environments.
Order a free sample PDF of the Anti-jamming Market Intelligence Study, published by Grand View Research.
Market Size & Forecast
2023 Market Size: USD 69 Billion
2030 Projected Market Size: USD 64 Billion
CAGR (2024-2030): 4%
North America: Largest market in 2023
Asia Pacific: Fastest growing market
Key Companies & Market Share Insights
Key players operating in the anti-jamming market include BAE Systems., Raytheon Systems Limited, Hexagon AB, ST Engineering, Thales, TUALCOM, Collins Aerospace, Lockheed Martin Corporation, Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd., and Meteksan Defence Industry Inc. These companies invest heavily in research and development to enhance their anti-jamming solutions, ensuring they meet the evolving demands of modern warfare and secure communications. In addition, collaborations and strategic partnerships between these leading firms and smaller, specialized technology companies are common, fostering the development of state-of-the-art anti-jamming systems.
Companies across the globe are securing investment to enhance their GPS signal capabilities. For instance, in November 2023, BAE Systems secured investment for the subsequent phase of the Eurofighter Typhoon aircraft's anti-jamming system. The Digital GPS Anti-jam Receiver (DIGAR) Phase 4 Enhancement was designed to enhance the aircraft’s survivability against radio frequency interference and GPS signal spoofing and jamming, The funding also included BAE’s new GEMVII-6 airborne digital GPS receiver, which enabled the aircraft to use digital beamforming for anti-jamming.
Browse Horizon Databook on Durable Global Anti-jamming Market Size & Outlook
Conclusion
Fueled by rapid innovations in signal‑processing techniques, rising electronic warfare investments, and the expanding use of GPS‑dependent systems in both defense and civilian arenas, the anti‑jamming market is set for strong, sustained growth through 2030.
0 notes
Text
The future of autonomous systems: emerging technologies and opportunities market is expected to be $5.68 billion by 2033.
#Future of Autonomous Systems Market#Autonomous Navigation Software Market#Future of Autonomous Systems Industry#Future of Autonomous Systems Report#Automation#Bisresearch
0 notes
Text
Low Noise Amplifier Market Grows with the Rise of High-Speed Networks

The global Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) market, valued at US$ 4.9 Bn in 2022, is poised for significant expansion, projected to reach US$ 12.8 Bn by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 11.3% during the forecast period. The market is being propelled by rising demand for high-performance communication systems, especially with the rollout of 5G networks, the proliferation of smart devices, and increased adoption of LNAs in satellite and space-oriented applications.
LNAs are critical components in devices where signal integrity and amplification are paramount, including smartphones, Wi-Fi systems, satellites, and military equipment.
Market Drivers & Trends
A key driver of growth is the rapid development in the global telecommunications industry, marked by heavy investments in 5G infrastructure, VoLTE services, and the Internet of Things (IoT). LNAs are essential in boosting weak RF signals without adding significant noise, thereby enhancing connectivity and device performance.
The booming consumer electronics sector, characterized by increased smartphone penetration and demand for compact, high-efficiency components, is another major contributor. Moreover, modular LNA designs are allowing for greater customization, compatibility, and integration into IoT applications.
Latest Market Trends
Advanced Materials: There is a rising trend toward using Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) and Silicon Germanium (SiGe) in LNA design due to their superior frequency response and lower noise characteristics.
Software-Defined Vehicles (SDVs): LNAs are becoming integral in next-gen autonomous vehicles, with automotive OEMs increasingly requiring advanced signal processing components for radar and safety systems.
Miniaturization: The trend of smaller, more power-efficient devices is pushing manufacturers to innovate in compact LNA designs without compromising on gain and noise figure.
Key Players and Industry Leaders
Prominent players in the global LNA market include:
Analog Devices, Inc.
Skyworks Solutions, Inc.
NXP Semiconductors
Infineon Technologies
Texas Instruments
Panasonic Corporation
Qorvo, Inc.
Onsemi
Teledyne Microwave Solutions
Narda-MITEQ
Qotana Technologies Co., Ltd.
Microsemi Corporation
These companies are focused on innovation, product differentiation, and expansion through partnerships and acquisitions. Their strategies reflect a strong emphasis on high-growth applications such as autonomous driving, 5G networks, and satellite communications.
Recent Developments
In December 2023, Applied EV partnered with NXP Semiconductors to enhance autonomous vehicle safety using advanced control systems, likely incorporating high-performance RF front-end components including LNAs.
In August 2023, GlobalFoundries launched the 9SW RF SOI Technology, aimed at enhancing next-generation 5G mobile applications. The innovation supports low-power, low-cost, and flexible front-end modules where LNAs are central.
Market Opportunities
Space-Oriented Applications: The growing utilization of LNAs in navigation systems, disaster management, and weather forecasting satellites presents long-term growth opportunities.
Defense & Aerospace: With increased global defense spending, the demand for high-frequency LNAs in radar and communication systems is rising.
Healthcare: Medical imaging devices are increasingly incorporating RF components, opening new avenues for LNAs.
Future Outlook
With rapid technological shifts and increasing demand across multiple sectors, the global LNA market is expected to experience sustained growth through 2031. The evolution of 5G and 6G networks, coupled with increasing interest in software-defined platforms and advanced automotive electronics, will shape the next phase of the market.
Strategic collaborations, R&D in semiconductor materials, and regional manufacturing initiatives will remain pivotal for players seeking to stay competitive.
Access important conclusions and data points from our Report in this sample - https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=S&rep_id=22091
Market Segmentation
By Frequency
Less than 6GHz
6GHz to 60GHz
Greater than 60GHz
By Material
Silicon
Silicon Germanium
Gallium Arsenide
By Application
Satellite Communication Systems
Test & Measurement
Wi-Fi
Networking
Cellular Telephones
Others
By Industry Vertical
Consumer Electronics
Medical
Industrial
Defense
Automotive
Telecom
Others
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific led the global market in 2022 and is projected to retain dominance through 2031. This is attributed to:
High smartphone adoption
Growing consumer electronics production
Strong shift toward 5G network rollouts
Notably, India's emergence as a manufacturing hub is bolstering the regional landscape. For instance, Google’s 2023 decision to manufacture Pixel smartphones in India underlines the region’s importance in global tech supply chains.
North America and Europe also hold substantial market shares due to heavy investments in space exploration, defense modernization, and next-gen automotive systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the expected value of the global LNA market by 2031? The market is projected to reach US$ 12.8 Bn by 2031.
2. What is the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of the LNA market from 2023 to 2031? The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.3%.
3. Which region dominates the LNA market? Asia Pacific held the leading share in 2022 and is expected to maintain dominance due to strong demand for consumer electronics and telecom growth.
4. Which applications are driving the LNA market? Key applications include satellite communication systems, Wi-Fi, cellular telephones, and networking equipment.
5. Who are the major players in the global LNA market? Top players include Analog Devices, Skyworks Solutions, Infineon Technologies, Texas Instruments, and NXP Semiconductors.
6. What are the key materials used in LNAs? LNAs are commonly made from Silicon, Silicon Germanium, and Gallium Arsenide for different performance needs.
7. What are the key opportunities in the LNA market? Emerging opportunities include autonomous vehicles, IoT applications, and space-based technologies.
Explore Latest Research Reports by Transparency Market Research: Surge Protection Devices Market: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/surge-protection-devices-market.html
Robotic Waste Sorting Market: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/robotic-waste-sorting-market.html
Photoionization Detection (PID) Gas Analyzer Market: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/photoionization-detection-gas-analyzer-market.html
Thin Film Power Inductor Market: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/thin-film-power-inductor-market.html
Silicon on Insulator (SOI) Market: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/silicon-insulator-market.html
About Transparency Market Research Transparency Market Research, a global market research company registered at Wilmington, Delaware, United States, provides custom research and consulting services. Our exclusive blend of quantitative forecasting and trends analysis provides forward-looking insights for thousands of decision makers. Our experienced team of Analysts, Researchers, and Consultants use proprietary data sources and various tools & techniques to gather and analyses information. Our data repository is continuously updated and revised by a team of research experts, so that it always reflects the latest trends and information. With a broad research and analysis capability, Transparency Market Research employs rigorous primary and secondary research techniques in developing distinctive data sets and research material for business reports. Contact: Transparency Market Research Inc. CORPORATE HEADQUARTER DOWNTOWN, 1000 N. West Street, Suite 1200, Wilmington, Delaware 19801 USA Tel: +1-518-618-1030 USA - Canada Toll Free: 866-552-3453 Website: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
What is an Agentic AI system?

Artificial intelligence (AI) has undergone transformative evolution in recent decades — from simple rule-based systems to complex, self-learning neural networks. A relatively new and increasingly important concept in this continuum is the development of agentic AI systems. Unlike traditional AI, which often operates passively within predefined tasks, agentic AI refers to systems capable of pursuing goals, interacting autonomously with their environment, and adapting their strategies over time. These qualities bring both powerful potential and significant responsibility for developers, users, and regulators.
Let’s understand what Agentic AI systems are, how they function, and the implications of their use.
Defining Agentic AI
The term agentic is derived from the word agency, which refers to the capacity of an entity to act independently and make its own choices. In the context of AI, an agentic system is one that is capable of taking initiative, setting or interpreting goals, and acting in a way that’s not merely reactive but purpose-driven.
An agentic AI system:
Acts autonomously without requiring step-by-step instruction.
Is goal-oriented and often capable of setting sub-goals.
Adapts its behavior based on changing environments or feedback.
Can operate across extended time horizons and in complex, dynamic scenarios.
Examples include AI personal assistants that schedule tasks with minimal oversight, robotic systems that explore unknown environments, or AI agents that negotiate contracts or coordinate teams.
Key Characteristics of Agentic AI
Goal-Directed Behavior
The defining feature of agentic AI is its ability to pursue goals. These goals may be set externally by a human or internally inferred by the system. Unlike simple automation, agentic AI systems plan and execute sequences of actions to achieve objectives — often optimizing for long-term outcomes.
For instance, a logistics AI might not only deliver a parcel, but also decide when and how to reroute in case of traffic or mechanical issues to minimize delays.
Autonomous Operation
Agentic systems operate with a high degree of autonomy. Once initialized, they do not rely on constant human input. They perceive their environment, make decisions, and act — often in real-time — based on sensory data, predictive models, and learned experiences.
Think of a self-driving car navigating through a city: it must continuously observe its surroundings, make split-second decisions, and adapt to traffic laws and unpredictable obstacles.
Adaptability and Learning
Adaptation is crucial for agentic behavior. Through reinforcement learning, fine-tuning, or continuous learning techniques, agentic AI systems can adjust their strategies based on past outcomes and new information. This learning loop enables them to become more efficient, accurate, or aligned with changing contexts.
A customer support chatbot that learns how to better handle rare queries over time is a simple example of this adaptive capacity.
Environmental Interaction
Agentic AI systems must engage with the environment — whether that environment is physical (as with robots), digital (as with software agents), or social (as with conversational agents). They receive feedback, assess the impact of their actions, and adjust accordingly.
For example, a trading AI agent evaluates financial market data and modifies investment strategies to maximize returns.
Examples of Agentic AI in Practice
Autonomous Drones: These navigate complex terrain, identify objects or people, and make decisions without human pilots.
AI Negotiators: Used in supply chains or corporate deals, they can evaluate options, make offers, and accept compromises based on predefined constraints and objectives.
AI Research Agents: Tools like AutoGPT or open-agent frameworks can self-prompt, run tasks, evaluate results, and iterate on their process without direct user supervision.
Virtual Companions: AI characters in games or virtual worlds that interact with players as if they have personality, memory, and long-term motivations.
Agentic AI vs. Traditional AI
FeatureTraditional AIAgentic AIOperationReactiveProactiveGoal SettingHuman-defined, staticMay interpret or set sub-goalsAutonomyLimitedHighLearningOften fixed or offlineContinuous and adaptiveTime HorizonShort-term tasksLong-term strategies
The Agentic AI builds upon traditional models but introduces an additional layer of complexity and independence. While traditional AI may classify images or detect fraud in transactions, agentic AI could design experiments, investigate fraud, and even recommend policy actions in response.
Risks and Challenges
Agentic AI systems introduce new types of risks:
Misalignment: If an AI interprets its goals in an unintended way, it may pursue actions that conflict with human values or objectives. This is a major concern in AI safety research.
Unpredictability: High autonomy and adaptive behavior can lead to unpredictable outcomes, especially in open or poorly defined environments.
Accountability: If an AI agent acts independently, who is responsible for its actions — the developer, the user, or the AI itself?
Security and Control: Malicious actors could exploit agentic AI to create systems that act independently in harmful ways (e.g., autonomous cyberattacks).
Governance and Ethics
As agentic AI becomes more widespread, ensuring it operates within ethical and legal boundaries is essential. This includes:
Transparency: Making it clear when users are interacting with an agentic system.
Explainability: Ensuring AI decisions can be understood and questioned.
Oversight: Developing mechanisms for monitoring and controlling agentic behavior.
Alignment: Researching ways to ensure agentic AI systems pursue human-aligned goals.
Regulators, researchers, and industry leaders must collaborate to establish frameworks that balance innovation with caution.
The Future of Agentic AI
Agentic AI is not science fiction — it is already here in early forms and will become increasingly common across industries. Whether it’s co-piloting software development, managing autonomous systems, or acting as virtual project managers, agentic AI promises to dramatically expand what machines can do independently.
However, this future must be approached with vigilance. Agentic AI systems are powerful tools, and like any tool, they can be misused or misdirected. The goal must be to build systems that are not just autonomous and intelligent — but also safe, transparent, and aligned with human values.
Agentic AI represents a critical shift in the landscape of artificial intelligence — from passive tools to active agents. By pursuing goals, interacting autonomously with environments, and adapting through learning, these systems open new possibilities across science, industry, and society. But with this power comes new responsibilities for how we build, manage, and govern AI in the years to come.
As we stand at the threshold of this new era, understanding what agentic AI is — and what it can become — is essential for anyone shaping the future of technology.
0 notes
Text
5 Practical AI Agents That Deliver Enterprise Value

The AI landscape is buzzing, and while Generative AI models like GPT have captured headlines with their ability to create text and images, a new and arguably more transformative wave is gathering momentum: AI Agents. These aren't just sophisticated chatbots; they are autonomous entities designed to understand complex goals, plan multi-step actions, interact with various tools and systems, and execute tasks to achieve those goals with minimal human oversight.
AI Agents are moving beyond theoretical concepts to deliver tangible enterprise value across diverse industries. They represent a significant leap in automation, moving from simply generating information to actively pursuing and accomplishing real-world objectives. Here are 5 practical types of AI Agents that are already making a difference or are poised to in 2025 and beyond:
1. Autonomous Customer Service & Support Agents
Beyond the Basic Chatbot: While traditional chatbots follow predefined scripts to answer FAQs, Agentic AI takes customer service to an entirely new level.
How they work: Given a customer's query, these agents can autonomously diagnose the problem, access customer databases (CRM, order history), consult extensive knowledge bases, initiate refunds, reschedule appointments, troubleshoot technical issues by interacting with IT systems, and even proactively escalate to a human agent with a comprehensive summary if the issue is too complex.
Enterprise Value: Dramatically reduces the workload on human support teams, significantly improves first-contact resolution rates, provides 24/7 support for complex inquiries, and ultimately enhances customer satisfaction through faster, more accurate service.
2. Automated Software Development & Testing Agents
The Future of Engineering Workflows: Imagine an AI that can not only write code but also comprehend requirements, rigorously test its own creations, and even debug and refactor.
How they work: Given a high-level feature request ("add a new user login flow with multi-factor authentication"), the agent breaks it down into granular sub-tasks (design database schema, write front-end code, implement authentication logic, write unit tests, integrate with existing APIs). It then leverages code interpreters, interacts with version control systems (e.g., Git), and testing frameworks to iteratively build, test, and refine the code until the feature is complete and verified.
Enterprise Value: Accelerates development cycles by automating repetitive coding tasks, reduces bugs through proactive testing, and frees up human developers for higher-level architectural design, creative problem-solving, and complex integrations.
3. Intelligent Financial Trading & Risk Management Agents
Real-time Precision in Volatile Markets: In the fast-paced and high-stakes world of finance, AI agents can act with unprecedented speed, precision, and analytical depth.
How they work: These agents continuously monitor real-time market data, analyze news feeds for sentiment (e.g., identifying early signs of market shifts from global events), detect complex patterns indicative of fraud or anomalies in transactions, and execute trades based on sophisticated algorithms and pre-defined risk parameters. They can dynamically adjust strategies based on market shifts or regulatory changes, integrating with trading platforms and compliance systems.
Enterprise Value: Optimizes trading strategies for maximum returns, significantly enhances fraud detection capabilities, identifies emerging market risks faster than human analysts, and provides a continuous monitoring layer that ensures compliance and protects assets.
4. Dynamic Supply Chain Optimization & Resilience Agents
Navigating Global Complexity with Autonomy: Modern global supply chains are incredibly complex and vulnerable to unforeseen disruptions. AI agents offer a powerful proactive solution.
How they work: An agent continuously monitors global events (e.g., weather patterns, geopolitical tensions, port congestion, supplier issues), analyzes real-time inventory levels and demand forecasts, and dynamically re-routes shipments, identifies and qualifies alternative suppliers, or adjusts production schedules in real-time to mitigate disruptions. They integrate seamlessly with ERP systems, logistics platforms, and external data feeds.
Enterprise Value: Builds unparalleled supply chain resilience, drastically reduces operational costs due to delays and inefficiencies, minimizes stockouts and overstock, and ensures continuous availability of goods even in turbulent environments.
5. Personalized Marketing & Sales Agents
Hyper-Targeted Engagement at Scale: Moving beyond automated emails to truly intelligent, adaptive customer interaction is crucial for modern sales and marketing.
How they work: These agents research potential leads by crawling public data, analyze customer behavior across multiple channels (website interactions, social media engagement, past purchases), generate highly personalized outreach messages (emails, ad copy, chatbot interactions) using integrated generative AI models, manage entire campaign execution, track real-time engagement, and even schedule follow-up actions like booking a demo or sending a tailored proposal. They integrate with CRM and marketing automation platforms.
Enterprise Value: Dramatically improves lead conversion rates, fosters deeper customer engagement through hyper-personalization, optimizes marketing spend by targeting the most promising segments, and frees up sales teams to focus on high-value, complex relationship-building.
The Agentic Future is Here
The transition from AI that simply "generates" information to AI that "acts" autonomously marks a profound shift in enterprise automation and intelligence. While careful consideration for aspects like trust, governance, and reliable integration is essential, these practical examples demonstrate that AI Agents are no longer just a theoretical concept. They are powerful tools ready to deliver tangible business value, automate complex workflows, and redefine efficiency across every facet of the modern enterprise. Embracing Agentic AI is key to unlocking the next level of business transformation and competitive advantage.
0 notes
Text
Navigating Autonomous AI Control in 2025
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, 2025 marks a pivotal year for the adoption and deployment of autonomous AI agents. These intelligent entities are not just tools but strategic assets that can transform how businesses operate, innovate, and compete. As AI practitioners, software architects, and technology decision-makers, understanding the emerging strategies for navigating autonomous AI control is crucial for harnessing its full potential. This article delves into the evolution of Agentic and Generative AI, the latest tools and frameworks, advanced implementation tactics, and the critical role of software engineering and cross-functional collaboration. We will also explore real-world success stories and provide actionable insights for those embarking on this transformative journey, including how to architect agentic AI solutions to meet specific business needs.
Evolution of Agentic and Generative AI in Software
Agentic AI: The Rise of Autonomous Agents
Agentic AI represents a significant shift in AI capabilities, moving from passive models to active, goal-driven agents that can plan, adapt, and act across systems without manual intervention. These autonomous AI agents are poised to revolutionize industries by optimizing operations, enhancing decision-making, and scaling services. By 2025, it is estimated that a majority of companies will integrate enterprise AI agents into their operations, marking a new era of intelligent automation. For professionals interested in advanced Agentic AI courses, understanding these dynamics is essential for staying ahead in the field.
Recent Advancements in Agentic AI
MLOps Integration: The integration of Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) practices is crucial for the development, deployment, and monitoring of Agentic AI models. MLOps ensures that AI systems are scalable, reliable, and compliant with regulatory standards. This is particularly important for those learning how to architect agentic AI solutions that meet specific business needs.
Cross-System Orchestration: Effective deployment of autonomous AI agents requires cross-system orchestration, allowing these agents to interact with various platforms like Salesforce, Snowflake, and Workday. This integration is crucial for unlocking intelligent automation and ensuring that AI-driven decisions are aligned with business operations. Advanced Agentic AI courses often cover these topics in depth.
Generative AI: The Power of Creative Models
Generative AI has been making waves with its ability to create novel content, such as images, text, and music. This technology is not only a creative tool but also a transformative force in industries like marketing, education, and entertainment. However, its integration into enterprise environments requires careful consideration of data quality, governance, and ethical implications. For those interested in Generative AI and Agentic AI course materials, understanding the synergy between these technologies is crucial.
Recent Developments in Generative AI
LLM Orchestration: Large Language Models (LLMs) are a cornerstone of Generative AI, offering powerful text generation capabilities. However, their effective deployment requires orchestration frameworks that can manage complexity, ensure data privacy, and optimize performance. Tools like LLaMA and PaLM have shown promising results in this area. Combining knowledge from Generative AI and Agentic AI course materials can help professionals leverage these advancements effectively.
Explainability and Transparency: As Generative AI becomes more pervasive, there is a growing need for explainability and transparency in AI decision-making processes. This involves developing methodologies that provide insights into how AI models generate content and make decisions. Understanding how to architect agentic AI solutions that incorporate these principles is essential for building trust in AI systems.
Integration Challenges
Both Agentic and Generative AI face common challenges, including data quality issues, governance, and the need for robust infrastructure to support their deployment. As these technologies become more pervasive, organizations must prioritize data-driven strategies and ensure that AI systems are aligned with business objectives. Advanced Agentic AI courses often emphasize the importance of addressing these challenges proactively.
Data Quality and Governance
Data Management Systems: Implementing data management systems that provide structured, real-time, and governed data is essential for successful AI deployments. Without such a foundation, AI systems can suffer from hallucinations, inefficiencies, and disconnected decisions. This is a critical aspect of how to architect agentic AI solutions that are reliable and scalable.
Policy-Based Governance: Establishing clear policies for data usage, model training, and decision-making processes is critical for ensuring that AI systems operate within defined boundaries and adhere to organizational policies. This is particularly relevant for those taking Generative AI and Agentic AI course modules focused on governance.
Ethical Considerations
Data Privacy and Bias: Ensuring data privacy and mitigating bias in AI systems are paramount ethical considerations. This involves adopting practices that protect sensitive data and ensure AI models are fair and unbiased. Advanced Agentic AI courses cover these ethical considerations in detail.
Transparency and Explainability: Developing AI systems that are transparent and explainable is essential for building trust and ensuring accountability. This involves creating methodologies that provide insights into AI decision-making processes. Understanding how to architect agentic AI solutions with these principles in mind is crucial for ethical AI deployment.
Latest Frameworks, Tools, and Deployment Strategies
MLOps for Agentic AI
MLOps is a critical framework for managing the lifecycle of AI models, from development to deployment and monitoring. It ensures that AI systems are scalable, reliable, and compliant with regulatory standards. This is a key topic in advanced Agentic AI courses, as it directly impacts the success of Agentic AI deployments.
LLM Orchestration for Generative AI
Effective deployment of LLMs requires orchestration frameworks that manage complexity, ensure data privacy, and optimize performance. Recent tools like LLaMA and PaLM have demonstrated significant capabilities in this area. Combining knowledge from Generative AI and Agentic AI course materials can help professionals optimize these frameworks.
Cross-System Integration
Cross-system integration is essential for unlocking the full potential of AI. This involves developing infrastructure that allows AI agents to interact seamlessly with various platforms, ensuring that AI-driven decisions are aligned with business operations. Understanding how to architect agentic AI solutions that facilitate this integration is vital for maximizing AI benefits.
Advanced Tactics for Scalable, Reliable AI Systems
Unified Data Foundation
A unified data foundation is essential for successful AI deployments. This includes implementing data management systems that provide structured, real-time, and governed data. Without such a foundation, AI systems can suffer from inefficiencies and disconnected decisions. This is a critical aspect of how to architect agentic AI solutions that are reliable and scalable.
Policy-Based Governance
Policy-based governance is critical for ensuring that AI systems operate within defined boundaries and adhere to organizational policies. This involves setting clear guidelines for data usage, model training, and decision-making processes. Generative AI and Agentic AI course materials often emphasize the importance of governance in AI systems.
Multi-Agent Coordination
In environments where multiple AI agents are deployed, coordination is key. This involves developing infrastructure that supports multi-agent communication and collaboration, ensuring that agents work together seamlessly to achieve common goals. Understanding how to architect agentic AI solutions that support multi-agent coordination is essential for complex AI deployments.
The Role of Software Engineering Best Practices
Reliability and Security
Software engineering best practices play a vital role in ensuring the reliability and security of AI systems. This includes adopting agile development methodologies, implementing robust testing frameworks, and conducting thorough risk assessments. Advanced Agentic AI courses often cover these best practices in detail.
Compliance and Ethics
AI systems must comply with regulatory standards and ethical guidelines. This involves integrating compliance checks into the AI development lifecycle and ensuring that AI decisions are transparent and explainable. Understanding how to architect agentic AI solutions that meet these standards is crucial for ethical AI deployment.
Cross-Functional Collaboration for AI Success
Collaboration Between Data Scientists and Engineers
Collaboration between data scientists and engineers is crucial for developing AI systems that are both technically sound and aligned with business objectives. This collaboration ensures that AI models are not only accurate but also scalable and maintainable. Generative AI and Agentic AI course materials often highlight the importance of this collaboration.
Involvement of Business Stakeholders
Involving business stakeholders in the AI development process is essential for ensuring that AI systems meet organizational needs. This includes aligning AI goals with business objectives and ensuring that AI-driven decisions are informed by business context. Understanding how to architect agentic AI solutions that align with business needs is vital for successful AI integration.
Measuring Success: Analytics and Monitoring
Performance Metrics
Measuring the success of AI deployments requires defining clear performance metrics. This includes tracking model accuracy, decision-making efficiency, and business outcomes such as cost savings or revenue growth. Advanced Agentic AI courses often cover how to set these metrics effectively.
Real-Time Monitoring
Real-time monitoring is critical for identifying and addressing issues as they arise. This involves setting up dashboards that provide insights into AI system performance and allow for swift intervention when needed. Understanding how to architect agentic AI solutions that support real-time monitoring is essential for ensuring AI system reliability.
Case Study: TechCorp
Let's consider a hypothetical company, TechCorp, which specializes in manufacturing and logistics. TechCorp decided to leverage Agentic AI to optimize its supply chain operations. For professionals interested in Generative AI and Agentic AI course materials, this case study provides valuable insights into real-world applications.
Technical Challenges
Initially, TechCorp faced challenges in integrating AI agents with its existing systems. The company had to develop a unified data foundation and implement policy-based governance to ensure seamless interaction between AI agents and business processes. Understanding how to architect agentic AI solutions that address these challenges is crucial for successful AI integration.
Business Outcomes
After deploying autonomous AI agents, TechCorp experienced significant improvements in supply chain efficiency, reducing delivery times by 30% and operational costs by 25%. The AI system also enhanced decision-making by providing real-time insights into inventory levels and demand forecasts. This case study highlights the importance of advanced Agentic AI courses in preparing professionals for such deployments.
Real-World Example: Integration of Generative AI
In addition to Agentic AI, TechCorp also explored the integration of Generative AI for content creation. By leveraging LLMs, TechCorp was able to automate the generation of product descriptions and marketing materials, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with content creation. This demonstrates how Generative AI and Agentic AI course knowledge can be applied in real-world scenarios.
Actionable Tips and Lessons Learned
Prioritize Data Quality
Ensure that your AI systems are built on a foundation of high-quality, governed data. This is crucial for preventing errors and ensuring that AI decisions are reliable and trustworthy. Understanding how to architect agentic AI solutions that prioritize data quality is essential for successful AI deployments.
Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration
Encourage collaboration between data scientists, engineers, and business stakeholders to ensure that AI systems meet organizational needs and are aligned with business objectives. Generative AI and Agentic AI course materials often emphasize the importance of this collaboration.
Monitor and Adapt
Implement real-time monitoring and be prepared to adapt your AI strategies as needed. This involves continuously assessing AI system performance and making adjustments to optimize outcomes. Understanding how to architect agentic AI solutions that support real-time monitoring is vital for ensuring AI system reliability.
Conclusion
Navigating autonomous AI control in 2025 requires a strategic approach that combines cutting-edge technology with practical wisdom. By understanding the evolution of Agentic and Generative AI, leveraging the latest frameworks and tools, and prioritizing software engineering best practices and cross-functional collaboration, organizations can unlock the full potential of AI. As AI continues to transform industries, embracing these emerging strategies will be crucial for staying ahead of the curve. Whether you are an AI practitioner, a software architect, or a technology decision-maker, the journey into the autonomous AI era is not just about technology—it's about transforming how we work, innovate, and succeed. For those interested in advanced Agentic AI courses or Generative AI and Agentic AI course materials, this article provides a comprehensive overview of the strategies and tools needed to succeed in this field.
0 notes
Text
Immediate Edge Review - The Time of AI-Powered Tools Is Here
Our Verdict On Immediate Edge:
We tend to've totally examined Immediate Edge and will attest to its excellence within the trading sphere. In capable hands, it maximises market opportunities. Our detailed review below provides full insights.
What is Immediate Edge?
Immediate Edge could be a cutting-edge automated trading system meticulously crafted to elevate the crypto trading experience for traders of all backgrounds.

Fueled by advanced technology, groundbreaking trading techniques, and AI, Immediate Edge conducts trades autonomously, rising as a standout performer in the trade. It's the proper tool to help you expertise seamless and effective trading in the cryptocurrency markets.
Engineered to oversee your cryptocurrency trading activities and implement ways on your behalf, Immediate Edge boasts a user-friendly interface, catering to novices and seasoned traders alike.
Powered by a subtle algorithm, Immediate Edge continuously assesses the crypto market, devising well-informed trading ways. With AI at its core, it executes trades with precision, optimising profitability for users. Explore this comprehensive Immediate Edge review for valuable insights in choosing your trading companion.
The Official Scores of Immediate Edge
Simplified Account Initiation
4.9/five Immediate Edge revolutionises user registration, providing a streamlined and economical process that saves time and effort. The user-friendly platform style and straightforward instructions permit both beginners and experienced traders to begin trading quickly, facilitating a sleek transition into on-line trading.
Expedited Money Operations
4.7/five Immediate Edge stands out in offering a wide selection of deposit and withdrawal choices, accommodating users' preferred payment ways. The platform's optimised transaction processing ensures swift completions, enhancing the overall user experience. Whereas there is perpetually space for improvement, Immediate Edge financial operations system is very regarded within the trade.
Numerous Trading Instruments and Adaptive Ways
4.half dozen/5 Immediate Edge caters to a broad spectrum of trading preferences by providing an in depth choice of assets, together with exotic pairs, CFDs, and a lot of. The platform's flexibility in supporting multiple trading approaches empowers users to navigate various market conditions and implement their most well-liked techniques. This adaptability sets Immediate Edge but its competitors and contributes to its growing popularity among traders worldwide.
Superior Shopper Care
4.9/five Immediate Edge unwavering dedication to exceptional client service forms the cornerstone of its success. The committed support team provides prompt and efficient assistance, addressing user inquiries and concerns as prime priorities. The knowledgeable employees consistently exceeds expectations to confirm customer satisfaction, demonstrating a genuine commitment to user expertise. While there is continually potential for growth, Immediate Edge client support is extremely praised and builds trust among its users.
Advanced Protective Measures
four.half dozen/five In an era where digital security is crucial, Immediate Edge prioritises the protection of user data and funds. The platform implements sophisticated security protocols and encryption techniques to safeguard sensitive data and stop unauthorised access.

Whereas Immediate Edge security measures are comprehensive, the dynamic landscape of cyber threats necessitates continuous enhancement and adaptation. Users will be confident that Immediate Edge remains vigilant in strengthening its defences to keep up a secure trading setting for its valued clients.
Pros and Cons of Immediate Edge
Comprehensive testing has uncovered the strengths and limitations of Immediate Edge. Traders need to grasp these aspects when considering this AI platform.
We'll outline where the software shines and where it falls short, helping you in assessing its fit for your cryptocurrency trading needs.
Pros Cons
CySec-licensed Brokers Initial Deposit Might Be A lot of Affordable
SSL Security Requires Small Daily Interaction
GDPR-prepared
Automated Broker-Shopper Matching
Supports Altcoins & Exotic Crypto Pairs
Good User Expertise
Who is Immediate Edge Good For?
Immediate Edge emerges as a dynamic trading platform, addressing the numerous requirements of investors across all levels of experience. Its versatility makes it a top selection for traders throughout their investment journey.
1st-Time Traders
Newcomers to trading will appreciate the platform's intuitive style and clear structure. Its user-friendly interface and guided options enable beginners to initiate trades confidently, while not feeling overwhelmed by unnecessary complexity.
Novice/Intermediate Traders
As users gain experience, Immediate Edge expandable options become increasingly valuable. The platform adapts to the trader's growth, introducing additional subtle tools at an appropriate rate. This gradual exposure to advanced capabilities permits developing investors to broaden their skillset and refine their ways organically.

Experienced Traders
For market professionals, Immediate Edge demonstrates its true potential. The platform's depth is evident through its advanced analytical tools and intensive customization choices. These powerful features enable seasoned traders to implement intricate ways and maximise their market engagement.
Visit Here - https://www.immediateedge.org/ https://www.facebook.com/immediateedge25
#immediateedge#immediateedgereviews#immediateedgeapps#immediateedgeapp#immediateedgereview#immediateedgescam#immediateedgeprice#immediateedge2025
1 note
·
View note