#CableCalculator
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Cable Size and Safety Compliance: What Australian Electricians Must Know

Electricians must ensure that every installation complies with the AS/NZS 3000 Wiring Rules, which set out the safety principles for electrical systems. Truth be told, undersized cables may lead to overheating, energy loss, or even fire, while oversized cables, although safer, can result in unnecessary costs. With accurate sizing, it basically promotes compliance and cost-effective performance in the long run.
So whether you’re working in residential, commercial, or industrial environments, understanding cable sizing manually or with a cable calculator is essential to your daily work. It ensures your installations are accurate, safe, and aligned with Australian standards.
Why Cable Sizing Matters for Compliance and Safety
When you choose the correct cable size, your system functions efficiently and poses fewer risks to users, structures, or connected devices. The Australian Wiring Standards provide the foundation for safe installations. If you don't comply, you risk inspection failures, rework, or hazards like electric shock or fire. Moreover, when a cable is too small for its current, it generates excess heat, gradually damaging insulation and connected components. This can eventually result in equipment failure or fire hazards.
Meanwhile, using larger cables than necessary may appear safer, but it increases material costs and can make routing more difficult. Overall, a well-sized cable supports efficient operation, complies with safety standards, and helps you manage project costs effectively.
Factors That Affect Cable Sizing
You need to evaluate several interrelated factors when determining the correct cable size. These include:
Current Load: The amount of current the cable carries determines its minimum cross-sectional area. Higher loads require larger cables to handle heat safely.
Voltage Drop: Voltage is lost over distance. Clause 3.6.2 of the Wiring Standard states that the voltage drop should not exceed 5% of the nominal voltage.
Cable Length: Longer runs increase resistance. To maintain voltage levels, you need thicker cables.
Insulation and Installation Conditions: How you install a cable affects its ability to dissipate heat. Cables in conduits or thermal insulation retain more heat, reducing current-carrying capacity.
Environmental Temperature: High ambient temperatures reduce a cable’s current capacity. You may need to apply derating factors.
Type of Conductor: Copper and aluminium conductors differ in resistance. Copper is more conductive, so a smaller size may be enough. Meanwhile, aluminium cables usually require larger diameters.
By using a cable calculator, it helps you factor in all these variables efficiently. With a reliable tool, it will provide a recommended cable size that aligns with safety standards and practical installation requirements.
How to Size Cables the Right Way
Begin by collecting accurate information about the installation. You need to know the current load, voltage, phase type, installation method, run length, and environmental factors. With this information, you can either calculate manually or use a cable calculator.
Manual sizing relies on AS/NZS 3008, which provides current-carrying capacities and correction factors for different installation types and materials. You will need to use formulas such as:
For Single-Phase AC Systems: Vd1 = 2 · L · ( RcosΦ + XsinΦ ) · L
For Three-Phase AC Systems: Vd3 = √3 · I · ( RcosΦ + XsinΦ ) · L
Where:
Vd = voltage drop (volts)
I = current (amps)
R = resistance of the cable (ohms per metre)
X = reactance of the cable (ohms per metre)
cosΦ = power factor of the load
L = one-way cable length (metres)
For three-phase systems, you should also consider additional correction factors. Because these calculations can be complex, many electricians now use digital tools.
Manual Cable Sizing vs. Cable Calculators
Manual methods are dependable when performed correctly but take time and demand precision. For instance, you need to consult tables, apply correction factors, and understand electrical theory. Mistakes in interpretation can also lead to undersized or oversized cables.
Meanwhile, a trusted cable calculator can guide you through data input for load type, run length, voltage, and insulation type. The tool then applies the relevant standards and outputs a recommended size. As a result, it saves you time and reduces the risk of calculation errors.
That said, calculators are only as accurate as the data you provide. You still need to understand the principles behind the numbers and verify the result against AS/NZS standards. The calculator can be a helpful tool but not a substitute for professional judgment.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Sizing Cables
Even experienced electricians can make errors that compromise safety and compliance. One of the most common is underestimating the current load or failing to consider possible future increases. This results in cables that run hot during normal use.
Another oversight involves voltage drop, particularly on long cable runs. Even if the current rating is suitable, a high voltage drop can cause malfunction and inefficiency.
It’s also easy to overlook derating factors. Ignoring ambient temperature, close cable groupings, or incorrect installation types leads to undersized cables. Errors in a cable sizing calculator, like entering the wrong load type or forgetting environmental details, can also affect sizing.
Finally, some electricians neglect to size earth conductors correctly. Earth cables must handle fault currents long enough for protective devices to operate within time limits.
Make Every Wiring Installation Compliant and Efficient
Following the Australian Wiring Standard and applying correct cable sizing supports long-lasting, efficient, and safe installations. When you use a cable calculator wisely and continue refining your knowledge, you reduce the risk of failure and ensure that every job meets the required standard.
With CableHero's innovative online calculators, it takes this further by simplifying complex calculations. We provide reliable calculations tailored to your specific project needs, making compliance faster and more accessible. For more information, visit our website today!
0 notes
Text
Earth Cable Size Calculator UK
Choosing the correct earth cable size is critical for electrical safety. In the UK, this choice depends on factors like fault current, installation type, conductor material, and system voltage. An earth cable size calculator UK helps electricians, engineers, and installers select the right size with confidence. Using the right size not only ensures safety but also compliance with BS 7671 regulations. This guide explains how these calculators work, the formulas involved, and what standards apply in the UK.
Earthing Cable Size Calculation Formula
The Earthing Cable Size Calculation Formula used is based on the adiabatic equation:

Where: S = cross-sectional area (mm²) I = fault current (A) t = fault duration (s) k = constant based on conductor material and insulation This formula is critical in both manual and automated earth cable size calculator UK tools.
Typical K Values for Different Materials (as per IEC 60364-5-54)
MaterialInitial Temp (°C)Final Temp (°C)K Value (A·s½/mm²)Copper (bare)30250226Copper (insulated)90250143Aluminium (bare)30250148Aluminium (insulated)9025094Steel3025050
Earthing Cable Size Standard in the UK
In the UK, the Earthing Cable Size Standard is governed by BS 7671. The minimum size is usually: - 2.5 mm² (if protected against mechanical damage) - 4 mm² (if not protected) This varies depending on installation type and earthing system. Below is a reference table for minimum earthing conductor sizes based on the live conductor: Live Conductor Size (mm²)Minimum Earth Conductor (mm²)Up to 16Same as live conductor16 – 3516 mm²Above 35Half of live conductor size These are general guidelines, and final sizing should still be confirmed using an earth cable size calculator UK.
Earthing Cable Size as Per IEC Standards
IEC 60364 also provides guidance. According to Earthing Cable Size as Per IEC, the same adiabatic equation is applied with material-specific constants. For aluminium, k = 76, and for copper, k = 115 (PVC insulation). IEC standards often supplement BS standards, especially for international projects or installations in commercial buildings.
Size of Earth Wire for Domestic Wiring in SWG
In older installations, SWG (Standard Wire Gauge) was used. In modern UK practice, we use mm². However, for Size of Earth Wire for Domestic Wiring in SWG, here’s a conversion example: SWGmm² (approx)Use Case142.0 mm²Lighting circuits123.3 mm²Small power outlets105.3 mm²Cooker, heavy loads You can use a Wire Gauge Conversion Calculator to switch between SWG and mm².
Factors That Affect Earth Cable Sizing
The size of an earth cable is influenced by many practical and regulatory factors: - Type of earthing system: TN-C-S systems may require larger earth conductors. - Length of cable run: Longer runs may require larger sizes due to resistance. - Material: Copper conducts better than aluminium, so copper cables can be smaller. - Installation method: Enclosed installations may need derating of cable size. - Temperature: Higher ambient temperature reduces current-carrying capacity. All these variables are built into most earth cable size calculator UK tools.
Using Cable Size for Motor Calculator to Support Earth Sizing
Sometimes, earth cable sizing is done in tandem with phase conductor sizing. The Cable Size for Motor Calculator helps determine phase conductors, and the earth is sized in proportion. For example, for a 3-phase motor, if the phase conductor is 25 mm², the earth might be 16 mm² or 10 mm² depending on protection methods. This approach aligns the results of the Cable Size for Motor Calculator with earth cable sizing requirements. Read More. #EarthCableSize, #CableSizeCalculator, #ElectricalWiringUK, #UKCableStandards, #EarthingCalculator, #BS7671, #ElectricalSafety, #GroundingCableSize, #CableSizingUK, #EarthingConductor, #ElectricalEngineering, #UKElectricians, #EarthWireCalculator, #CableInstallationUK, #ElectricianTools Read the full article
#BS7671#CableCalculator#CableSizing#EarthCable#ElectricalEngineering#ElectricalSafety#ElectricianTools#GroundingSystem#UKStandards#wiringregulations
0 notes
Text
Kurama: Taller Than You Thought
We all know YYH’s Kurama is pretty tall. He’s a height-gap boy. But how big is he? Let’s use all the most extreme off-model shots cherry-picked from the manga and anime to find out, using the methodology of the top ‘versus’ debaters on narutoforums’s Meta-Battledome and Star Wars Vs Star Trek!

You’ve probably seen this shot, which I have reproduced from CableCalculation’s excellent YYH Character Heights. We know from the English Dub that Bui clocks in at an impressive 9 feet tall, which means Karasu is about 10 feet tall. Indeed, while he doesn’t appear to have a canon height, 10 feet is given as his height on fan wikis. (just don’t look at Sakyo, who is a normal human and about the same height as Bui or Karasu whenever they’re on-panel together).

Youko Kurama and Karasu are exactly the same height in the few shots we get of them side by side. So in the English dub at least, Youko is at 10 feet tall, not 7. Taller than you thought?
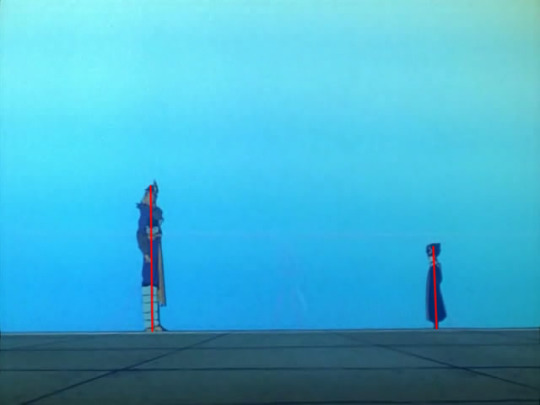

And before you cry ‘off-model!’, this actually works perfectly with the Bui vs Hiei fight. Bui is 1.775x the height of Hiei, making Hiei roughly 155cm or 5��� 1’’ (the English dub says 4’ 11’’ without his hair, but hey, he could be wearing platform shoes!).
Bearing that in mind, we are forced to conclude that either exploding made Karasu smaller, or every time Kurama transforms into Youko he gets taller, since immediately after Kurama returns to ‘normal’ he is 80.5% as tall as Kurama, making him, er, 7 foot 11. His mother would be proud.

Indeed, we see by the end of the series that’s even in human form he’s as tall as Shigure:

(via the super-reliable medium of blurry establishing shots!!)
But how tall is Shigure?
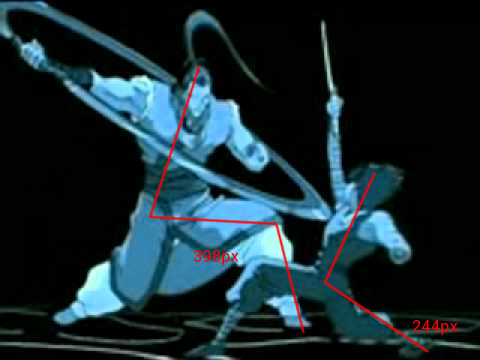
Taking Hiei’s height as 5’ 1’’ (give him those 2’’ platforms!), Shigure appears to be 253cm, or 8’ 3’’. He may be taller than this as he’s hunched over and Hiei is closer to the camera. So Kurama’s human form grows over the course of the series from 5’ 11’’ to 7’ 11’’ to, at bare minimum, 8’ 3’’. He’s a growing boy!
2 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Cable Calculator App
For Android and iOS. Calculate cable sizes in 2 easy steps. Input your design criteria, select from the pre-programmed options, job done!
No more need to remember cable calculation formulas, look up multiple cable rating charts, volt drop formulas, correction factors or Zs values, it’s all programmed in.
0 notes
Text
Earth Cable Size for Lightning Protection
Lightning strikes pose a serious threat to buildings, equipment, and human life. To reduce this risk, an effective lightning protection system is essential. One critical component of this system is the earth cable, which safely channels lightning current into the ground. Choosing the correct earth cable size for lightning protection is vital. This article dives deep into how to select the proper cable size, the factors that influence this decision, and the relevant standards and calculations involved.
Importance of Correct Earth Cable Size for Lightning Protection
When lightning hits a structure, it discharges a high amount of electrical energy in a very short time. If the earth cable size for lightning protection is too small, it can overheat or even melt, causing fire or structural damage. An undersized cable can also result in high resistance, reducing the efficiency of the entire system. On the other hand, a properly sized earth cable ensures that the energy from the strike is safely dissipated into the ground. It reduces step voltage, protects electronic systems, and maintains the integrity of the installation.
Factors Affecting Earth Cable Size for Lightning Protection
There is no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to selecting an earth cable size for lightning protection. Several factors must be considered to determine the optimal size: - Peak lightning current (typically 100 kA for direct strikes) - Duration of current flow - Soil resistivity - Length of the cable - Type of conductor (copper or aluminum) - Installation method (buried or exposed) These variables are all essential in defining the Earthing Cable Size Standard for a given application.
Common Earth Cable Materials and Their Impact on Sizing
Copper is the most commonly used material due to its high conductivity. Aluminum is also used, though it requires a larger cross-section for the same performance. A general guideline is that a copper conductor should have a minimum cross-sectional area of 16 mm² for lightning protection. However, higher-risk areas may require 35 mm² or more. Here’s a quick comparison table: MaterialMinimum Size (IEC Std.)Common ApplicationCopper16 mm²Residential, low riskCopper35 mm²Industrial, high riskAluminum25 mm²Residential backupAluminum50 mm²Industrial systems
Earth Cable Size as Per IEC Standards
According to instrument earthing IEC standard and IEC 62305 (Protection Against Lightning), the minimum earth cable size for lightning protection should meet both mechanical and thermal requirements. The cable must be able to withstand a lightning current of 100 kA peak without damage. The Earthing Cable Size as Per IEC considers both mechanical strength and current-carrying capacity. The conductor should also be corrosion-resistant and compatible with the soil. For example, IEC recommends: - A minimum of 16 mm² copper or 25 mm² aluminum for air-termination and down conductors - A minimum of 35 mm² copper or 50 mm² aluminum for earth conductors where mechanical protection is not ensured These values may be increased depending on soil resistivity or regional codes.
Earth Cable Size Calculation Formula
To calculate the earth cable size for lightning protection, the following simplified formula is often used: S = √(I² × t) / k Where: - S = minimum cross-sectional area (mm²) - I = peak lightning current (A) - t = duration of lightning strike (s) - k = material constant (Copper: 143, Aluminum: 94) Assuming a lightning strike of 100 kA lasting 0.0005s: For copper: S = √(100,000² × 0.0005) / 143 ≈ 29.5 mm² Rounding up, a 35 mm² copper conductor is advisable in high-risk zones. This aligns with values used in most Earth Cable Size Calculators and conforms to Earthing Cable Size Calculation Formula used by engineers.
Importance of Installation Method
The way the cable is installed influences the actual performance. If it is buried directly, it is more likely to corrode, especially if dissimilar metals are in contact. Protective coating or PVC sheath may be necessary. When installed above ground, the cable must be protected from mechanical damage and UV degradation. Instrument earthing standards also recommend that the path to ground should be as straight as possible to avoid impedance from bends.
Earthing Cable Size in Special Applications
In environments like oil refineries, data centers, and substations, earthing systems must also comply with instrument earthing IEC standards. In such sensitive installations, both lightning protection and functional earthing are required. The sizing of these cables might be larger to account for induced voltages, electromagnetic interference, and surge protection. Moreover, tools like Wire Gauge Conversion Calculator are used to compare cable sizes across American Wire Gauge (AWG) and IEC metric standards. This helps in selecting the correct cable when equipment is sourced globally. Read More.....#LightningProtection, #EarthingSystem, #EarthCableSize, #ElectricalSafety, #SurgeProtection, #LightningArrestor, #EarthingCable, #GroundingSystem, #ElectricalDesign, #CableSizing, #LightningGrounding, #ElectricalEngineering, #EarthRod, #EarthingCalculation, #BuildingSafety Read the full article
#CableCalculation#CableSizing#EarthCable#EarthingStandards#Electricaldesign#ElectricalSafety#GroundingSystem#LightningArrestor#LightningProtection#SurgeProtection
0 notes
Video
youtube
Cable Size Calculator
0 notes
Video
youtube
Cable Calc App | Android, iPhone & iPad.
Download for Android: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.procerts.cablecalc
Download for iOS: https://apps.apple.com/gb/app/cable-calc/id1044306956
0 notes
Video
youtube
Cable Size Calculator for iPhone & iPad | Version April 2020
Download for iPhone or iPad: https://apps.apple.com/gb/app/max-zs-values/id498838137
Also available on Andriod: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.procerts.cablecalc&hl=en_GB
0 notes