#Calculation of Standard Deviation in Ungrouped Data
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Calculation of Standard Deviation in Individual, Discrete & Continuous Series | Statistics
In this article, we will discuss about Calculation of Standard Deviation in Individual, Discrete & Continuous Series and measures of dispersion in Statistics. How to calculate Standard deviation Standard Deviation Standard deviation Measures of Dispersion in Statistics is the measure of the dispersion of statistical data. The standard deviation formula is used to find the deviation of the data…
View On WordPress
#Calculation of Standard Deviation#Calculation of Standard Deviation in Continuous Series#Calculation of Standard Deviation in Discrete Series#Calculation of Standard Deviation in Grouped Data#Calculation of Standard Deviation in Individual Series#Calculation of Standard Deviation in Ungrouped Data#How to Calculate Standard Deviation#How to Calculate Standard Deviation in Continuous Series#How to Calculate Standard Deviation in Discrete Series#How to Calculate Standard Deviation in Individual Series#Measures of Dispersion Statistics#Standard Deviation
0 notes
Text
In statistics, we have studied the classification of data into a grouped and ungrouped frequency distribution. These data can be pictorially represented using different graphs such as bar graphs, frequency polygons and histograms and so on. Also, we know that the three measures of central tendencies are mean, median and mode. In this article, we will discuss how to find the mean of the grouped data using different methods such as direct method, assumed mean method and step deviation method with many solved example.
Table of Content:
Mean
Standard deviation
Standard deviation of grouped data
Interpretation of Standard deviation
Steps to Calculate Standard Deviation for Grouped Data
Standard deviation of Grouped Data Example
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Read more HERE
0 notes
Link

1. Introduction
Introduction: Why Economics?, Meaning and Definitions of Economics, Economic and Non-economic Activities, Economic Groups, Introduction: Statistics, Meaning and Definition of Statistics, Importance of Statistics in Economics, Limitation of Statistics, Key Points, Question Bank, Very Short Answer Type Questions, Short Answer Type Questions, Long Answer Type Questions, Higher Order Thinking Skills [HOTS], Value Based Questions, Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
2. Collection of Data
Introduction, Meaning of Collection of Data, Types of Data (Sources of Data), Methods of Collecting Primary Data, Questionnaire and Schedule, Census and Sample Investigation Techniques, Sampling and Non-Sampling Errors, Sources of Secondary Data, Census of India And NSSO, Key Points, Question Bank, Very Short Answer Type Questions, Short Answer Type Questions, Long Answer Type Questions, Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS), Value Based Questions, Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
3. Organisation of Data
Introduction, Meaning and Definition of Classification, Objectives of Classification, Methods of Classification, Variable, Statistical Series, Individual Series, Discrete Series (Ungrouped Frequency Distribution or Frequency Array), Continuous Series or Grouped Frequency Distribution, Types of Continuous Series, Bivariate Frequency distribution, General Rules for Constructing a Frequency Distribution, or How to prepare a frequency distribution?, Key Points, Question Bank, Very Short Answer Type Questions, Short Answer Type Questions, Long Answer Type Questions, Numerical Questions, Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs), Value Base Questions, Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
4. Presentation of Data : Tabular Presentation
Introduction, Textual Presentation of Data (Descriptive Presentation), Tabular Presentation of Data, Objectives of Tabulation, Essential Parts of Table, Type of Table, Solved Examples, Key Points, Question Bank, Very Short Answer Type Questions, Short Answer Type Questions, Long Answer Type Questions, Numerical Questions, Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS), Value Based Questions, Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
5. Presentation of Data : Diagrammatic Presentation
Introduction, Utility or Advantages of Diagrammatic Presentation, Limitations of Diagrams, General Principles/Rules for Diagrammatic Presentation, Types of Diagrams, Bar Diagram, Pie Diagram, Key Points, Question Bank, Very Short Answer Type Questions, Short Answer Type Question, Long Answer Type Question, Numerical Questions, Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS), Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
6. Presentation of Data: Graphic Presentation
Introduction, Advantages of Graphic Presentation, Construction of a Graph, False Base Line (Kinked Line), Types of Graphs, Limitation of Graphic Presentations, Key Points, Question Bank, Very Short Answer Type Questions, Short Answer Type Questions, Long Answer Type Questions, Numerical Questions, Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS), Multiple Choice Question (MCQs).
7. Measures of Central Tendency Arithmetic Mean
Introduction, Meaning and Definition, Objectives and Significance or uses of Average, Requisites or Essentials of an Ideal Average, Types or Kinds of Statistical Averages, Arithmetic Mean (X), Calculation of Arithmetic Mean in Different Frequency Distribution (Additional Cases), Calculation of Missing Value, Corrected Mean, Combined Arithmetic Mean, Mathematical Properties of Arithmetic Mean, Merits and Demerits of Arithmetic Mean, Weighted Arithmetic Mean, List of Formulae, Key Points, Question Bank, Very Short Answer Type Questions, Short Answer Type Questions, Long Answer Type Questions, Numerical Questions, Miscellaneous Questions, Multiples Choice Questions (MCQs).
8. Measures of Central Tendency Median and Mode
Median, Determination of Median, Calculation of Median in Different Frequency Distribution (Additional Cases), Partition Values (Measures of Position or Positional Values based on The principle of Median), Mode (Z), Computation of Mode, Calculation of Mode in Different Frequency Distribution (Additional Cases), Relationship between Mean, Median and Mode, Comparison between Mean, Median and Mode, Choice of a Suitable Average, Typical Illustration, List of Formulae, Key Points, Question Bank, Very Short Answer Type Questions, Short Answer Type Questions, Long Answer Type Questions, Numerical Questions, Miscellaneous Questions, Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS), Value Based Questions, Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
9. Measure of Dispersion
Introduction, Meaning and Definition, Objectives and Significance, Characteristics of Good Measure of Dispersion, Methods of Measurement of Dispersion, Types of Dispersion, Range, Inter-Quartile Range and Quaritle Deviation, Mean Deviation (Average Deviation), Standard Deviation (s), Relationship between Different Measures of Dispersion, Lorenz Curve, Choice of A Suitable Measure of Dispersion, Typical Illustrations, List of Formulae, Key Points, Question Bank, Very Short Answer Type Questions, Short Answer Type Questions, Long Answer Type Questions, Numerical Questions, Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS), Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
10. Correlation
Introduction, Meaning and Definitions, Types of Correlation, Coefficient of Correlation (r), Degree of Correlation, Techniques or Methods for Measuring Correlation, Scatter Diagram (Dotogram Method), Karl Pearson’s Coefficient of Correlation, Spearman’s Rank Correlation, Typical Illustrations, List of Formulae, Key Points, Question Bank, Very Short Answer Type Questions, Short Answer Type Questions, Long Answer Type Questions, Numerical Questions, Miscellaneous Questions, Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS), Value Based Questions, Multiple Choice Questions.
11. Index Numbers
Introduction, Characteristics or Features, Precautions in Constructions of Index Numbers (Problems), Types or Kinds of Index Numbers, Methods of Constructing Price Index Numbers, Simple Index Number (Unweighted), Weighted Index Numbers, Some Important Index Numbers, Significance or Uses of Index Numbers, Limitations of Index Numbers, List of Formulae, Key Points, Question Bank, Very Short Answer Type Questions, Short Answer Type Questions, Long Answer Type Questions, Numerical Questions, Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS), Value Based Questions, Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
12. Mathematical Tools Used in Economics
Slope of a Line, Slope of a Curve, Equation of a line.
13. Developing Projects in Economics
Introduction, Steps Towards Making A Project, Suggested List of Projects.
0 notes
Text
CBSE 11-12th Class Economics Syllabus
CBSE 11th Class Economics 2018-19
Class XI Part A: Introductory Microeconomics Part B: Statistics for Economics Class XII Part A: Introductory Microeconomics Part B: Introductory Macroeconomics
CBSE 12th Class Economics 2019-20
Class XI Part A: Introductory Microeconomics Part B: Statistics for Economics Class XII Part A: Introductory Macroeconomics Part B: Indian Economic Development

Part A: Introductory Microeconomics
Unit 1: Introduction --- 8 Periods Meaning of microeconomics and macroeconomics; positive and normative economics What is an economy? Central problems of an economy: what, how and for whom to produce; concepts of production possibility frontier and opportunity cost. Unit 2: Consumer's Equilibrium and Demand -- 32 Period Consumer's equilibrium - meaning of utility, marginal utility, law of diminishing marginal utility, conditions of consumer's equilibrium using marginal utility analysis. Indifference curve analysis of consumer's equilibrium-the consumer's budget (budget set and budget line), preferences of the consumer (indifference curve, indifference map) and conditions of consumer's equilibrium. Demand, market demand, determinants of demand, demand schedule, demand curve and its slope, movement along and shifts in the demand curve; price elasticity of demand - factors affecting price elasticity of demand; measurement of price elasticity of demand – percentage-change method. Unit 3: Producer Behaviour and Supply 32 Periods Meaning of Production Function – Short-Run and Long-Run Total Product, Average Product and Marginal Product. Returns to a Factor Cost: Short run costs - total cost, total fixed cost, total variable cost; Average cost; Average fixed cost, average variable cost and marginal cost-meaning and their relationships. Revenue - total, average and marginal revenue - meaning and their relationship. Producer's equilibrium-meaning and its conditions in terms of marginal revenue-marginal cost. Supply, market supply, determinants of supply, supply schedule, supply curve and its slope, movements along and shifts in supply curve, price elasticity of supply; measurement of price elasticity of supply - percentage-change method. Unit 4: Forms of Market and Price Determination under Perfect Competition with simple applications.--28 Periods Perfect competition - Features; Determination of market equilibrium and effects of shifts in demand and supply. Other Market Forms - monopoly, monopolistic competition, oligopoly - their meaning and features. Simple Applications of Demand and Supply: Price ceiling, price floor.
Part B: Statistics for Economics
In this course, the learners are expected to acquire skills in collection, organisation and presentation of quantitative and qualitative information pertaining to various simple economic aspects systematically. It also intends to provide some basic statistical tools to analyse, and interpret any economic information and draw appropriate inferences. In this process, the learners are also expected to understand the behaviour of various economic data. Unit 1: Introduction 07 Periods What is Economics? Meaning, scope, functions and importance of statistics in Economics Unit 2: Collection, Organisation and Presentation of data 27 Periods Collection of data - sources of data - primary and secondary; how basic data is collected, with concepts of Sampling; Sampling and Non-Sampling errors; methods of collecting data; some important sources of secondary data: Census of India and National Sample Survey Organisation. Organisation of Data: Meaning and types of variables; Frequency Distribution. Presentation of Data: Tabular Presentation and Diagrammatic Presentation of Data: (i) Geometric forms (bar diagrams and pie diagrams), (ii) Frequency diagrams (histogram, polygon and ogive) and (iii) Arithmetic line graphs (time series graph). Unit 3: Statistical Tools and Interpretation 66 Periods (For all the numerical problems and solutions, the appropriate economic interpretation may be attempted. This means, the students need to solve the problems and provide interpretation for the results derived.) Measures of Central Tendency- mean (simple and weighted), median and mode Measures of Dispersion - absolute dispersion (range, quartile deviation, mean deviation and standard deviation); relative dispersion (co-efficient of range, co-efficient of quartile-deviation, co-efficient of mean deviation, co-efficient of variation); Lorenz Curve: Meaning, construction and its application. Correlation – meaning and properties, scatter diagram; Measures of correlation - Karl Pearson's method (two variables ungrouped data) Spearman's rank correlation. Introduction to Index Numbers - meaning, types - wholesale price index, consumer price index and index of industrial production, uses of index numbers; Inflation and index numbers.
Part C: Developing Project in Economics 20 Periods
The students may be encouraged to develop projects, as per the suggested project guidelines. Case studies of a few organisations / outlets may also be encouraged. Under this the students will do only ONE comprehensive project using concepts from both part A and part B. Some of the examples of the projects are as follows (they are not mandatory but suggestive): (i) A report on demographic structure of your neighborhood. (ii) Changing consumer awareness amongst households. (iii) Dissemination of price information for growers and its impact on consumers. (iv) Study of a cooperative institution: milk cooperatives, marketing cooperatives, etc. (v) Case studies on public private partnership, outsourcing and outward Foreign Direct Investment. (vi) Global warming. (vii) Designing eco-friendly projects applicable in school such as paper and water recycle. The idea behind introducing this unit is to enable the students to develop the ways and means by which a project can be developed using the skills learned in the course. This includes all the steps involved in designing a project starting from choosing a title, exploring the information relating to the title, collection of primary and secondary data, analysing the data, presentation of the project and using various statistical tools and their interpretation and conclusion.
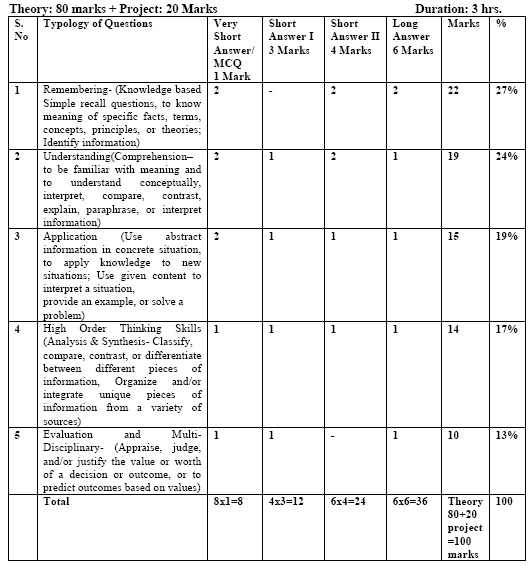
Suggested Question Paper Design
CBSE March 2019 Examination
CBSE 2018-19 Syllabus

Part A: Introductory Microeconomics
Unit 1: Introduction 8 Periods Meaning of microeconomics and macroeconomics; positive and normative economics What is an economy? Central problems of an economy: what, how and for whom to produce; concepts of production possibility frontier and opportunity cost. Unit 2: Consumer's Equilibrium and Demand 32 Periods Consumer's equilibrium - meaning of utility, marginal utility, law of diminishing marginal utility, conditions of consumer's equilibrium using marginal utility analysis. Indifference curve analysis of consumer's equilibrium-the consumer's budget (budget set and budget line), preferences of the consumer (indifference curve, indifference map) and conditions of consumer's equilibrium. Demand, market demand, determinants of demand, demand schedule, demand curve and its slope, movement along and shifts in the demand curve; price elasticity of demand - factors affecting price elasticity of demand; measurement of price elasticity of demand – percentage-change method. Unit 3: Producer Behaviour and Supply 32 Periods Meaning of Production Function – Short-Run and Long-Run Total Product, Average Product and Marginal Product. Returns to a Factor Cost: Short run costs - total cost, total fixed cost, total variable cost; Average cost; Average fixed cost, average variable cost and marginal cost-meaning and their relationships. Revenue - total, average and marginal revenue - meaning and their relationship. Producer's equilibrium-meaning and its conditions in terms of marginal revenue-marginal cost. Supply, market supply, determinants of supply, supply schedule, supply curve and its slope, movements along and shifts in supply curve, price elasticity of supply; measurement of price elasticity of supply - percentage-change method. Unit 4: Forms of Market and Price Determination under Perfect Competition with simple applications. 28 Periods Perfect competition - Features; Determination of market equilibrium and effects of shifts in demand and supply. Other Market Forms - monopoly, monopolistic competition, oligopoly - their meaning and features. Simple Applications of Demand and Supply: Price ceiling, price floor.
Part B: Introductory Macroeconomics
Unit 5: National Income and Related Aggregates 28 Periods Some basic concepts: consumption goods, capital goods, final goods, intermediate goods; stocks and flows; gross investment and depreciation. Circular flow of income (two sector model); Methods of calculating National Income - Value Added or Product method, Expenditure method, Income method. Aggregates related to National Income: Gross National Product (GNP), Net National Product (NNP), Gross and Net Domestic Product (GDP and NDP) - at market price, at factor cost; Real and Nominal GDP. GDP and Welfare Unit 6: Money and Banking 15 Periods Money - meaning and supply of money - Currency held by the public and net demand deposits held by commercial banks. Money creation by the commercial banking system. Central bank and its functions (example of the Reserve Bank of India): Bank of issue, Govt. Bank, Banker's Bank, Control of Credit through Bank Rate, CRR, SLR, Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate, Open Market Operations, Margin requirement. Unit 7: Determination of Income and Employment 27 Periods Aggregate demand and its components. Propensity to consume and propensity to save (average and marginal). Short-run equilibrium output; investment multiplier and its mechanism. Meaning of full employment and involuntary unemployment. Problems of excess demand and deficient demand; measures to correct them - changes in government spending, taxes and money supply. Unit 8: Government Budget and the Economy 15 Periods Government budget - meaning, objectives and components. Classification of receipts - revenue receipts and capital receipts; classification of expenditure – revenue expenditure and capital expenditure. Measures of government deficit - revenue deficit, fiscal deficit, primary deficit their meaning. Unit 9: Balance of Payments 15 Periods Balance of payments account - meaning and components; balance of payments deficit-meaning. Foreign exchange rate - meaning of fixed and flexible rates and managed floating. Determination of exchange rate in a free market.
Part C: Developing Project in Economics 20 Periods
Suggested Question Paper Design
CBSE March 2019 Examination

Note: There will be Internal Choice in questions of 3 marks, 4 marks and 6 marks in both sections (A and B). (Total 3 internal choices in section A and total 3 internal choices in section B).
Guidelines for Project Work in Economics (Class XII)
Students are supposed to pick any ONE of the two suggested projects. The project should be of 30-40 pages (approx), preferably hand-written. Teachers should help the students to select the topic after detailed discussions and deliberations. Teacher should play the role of a facilitator and should supervise and monitor the project work of the student. The teacher must periodically discuss and review the progress of the project. The teacher must play a vital role of a guide in the research work for the relevant data, material and information regarding the project work. Also, the students must be guided to quote the source (in the Bibliography/References section) of the information to ensure authenticity. The teacher must ensure that the students actually learn the concepts related to the project as he/she would be required to face questions related to the project in viva-voce stage of the final presentation of the project. Empirical study based / investing project work may be appreciated. The teacher may arrange a presentation in the classroom of each and every student so that students may learn from each others’ project work. The teacher must ensure that the students learn various aspects of the concept related to the topic of the project work. I. Project (Option One) : What’s Going Around Us The purpose of this project is to – Enable the student to understand the scope and repercussions of various Economic events and happenings taking place around the country and the world. (eg. The Dynamics of the Goods & Services Tax and likely impacts on the Indian Economy or the Economics behind the Demonetisation of 500 and 1000 Rupee Notes and the Short Run and Long Run impact on the Indian Economy or The impact of BREXIT from the European Union etc.) Provide an opportunity to the learner to develop economic reasoning and acquire analytical skills to observe and understand the economic events. Make students aware about the different economic developments taking place in the country and across the world. Develop the understanding that there can be more than one view on any economic issue and to develop the skill to argue logically with reasoning. Compare the efficacy of economic policies and their respective implementations in real world situations and analyse the impact of Economic Policies on the lives of common people. Provide an opportunity to the learner to explore various economic issues both from his/her day to day life and also issues which are of broader perspective. Scope of the project: Student may work upon the following lines: Introduction Details of the topic Pros and Cons of the economic event/happening Major criticism related to the topic (if any) Students’ own views/perception/ opinion and learning from the work Any other valid idea as per the perceived notion of the student who is actually working and presenting the Project-Work. Mode of presentation and submission of the Project: At the end of the stipulated term, each student will present the work in the Project File (with viva voce) to the external examiner. Marking Scheme: Marks are suggested to be given as –

The external examiner should value the efforts of the students on the criteria suggested CBSE Suggestive List 1. Micro and small scale industries 2. Food supply channel in India 3. Contemporary employment situation in India 4. Disinvestment policy 5. Health expenditure (of any state) 6. Goods and Services Tax Act 7. Inclusive growth strategy 8. Human Development Index 9. Self help groups 10. Any other topic II. Project (Option Two): Analyse any concept from the syllabus The purpose of this project is to – Develop interest of the students in the concepts of Economic theory and application of the concept to the real life situations. Provide opportunity to the learners to develop economic reasoning vis-a-vis to the given concept from the syllabus. Enable the students to understand abstract ideas, exercise the power of thinking and to develop his/her own perception To develop the understanding that there can be more than one view on any economic issue and to develop the skill to argue logically with reasoning Compare the efficacy of economic policies in real world situations To expose the student to the rigour of the discipline of economics in a systematic way Impact of Economic Theory/ Principles and concepts on the lives of common people Scope of the project: Following essentials are required to be fulfilled in the project. Explanation of the concept: - Meaning and Definition - Application of the concept - Diagrammatic Explanation (if any) - Numerical Explanation related to the concept etc. (if any) - Students’ own views/perception/ opinion and learning from the topic.. Mode of presentation and submission of the Project: At the end of the stipulated term, each student(s) will present their work in the Project File (with viva voce) to the external examiner. Marking Scheme: Marks are suggested to be given as –

The external examiner should value the efforts of the students on the criteria suggested. CBSE Suggested List: Price Determination Price Discrimination Opportunity Cost Production Possibility Curve Demand and its determinants Supply and its determinants Production – Returns to a Factor Cost function and Cost Curves Monopoly Oligopoly Monopolistic Competition Credit Creation Money Multiplier Central Bank and its functions Government Budget & its Components Budget deficit Exchange Rate Systems Foreign Exchange Markets Balance of payments Any other topic Contact us for tutoring and homework help Read the full article
0 notes