#ElectronicStabilityControl
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
In this video, we explore the core elements that contribute to a car's 5-star safety rating, from sophisticated crash management systems and airbags to electronic stability control and pedestrian safety measures. Learn how Global NCAP sets these benchmarks and the engineering behind each safety feature that helps keep us safe on the road.
If you’re interested in speaking with our experts from Scania, Mercedes, and Nissan, and scheduling a personalized career plan, call us at +91-9342691281 or register here: https://bit.ly/3NY8hTI
#CarSafety#GlobalNCAP#5StarSafety#VehicleSafety#SafetyRating#CrashTesting#Airbags#ElectronicStabilityControl#SafetyStandards#AutomotiveSafety#RoadSafety#CrashTest#EngineeringInnovation#CarTech#SkillLync#finiteelementanalysis#cae#youtube#mechanicalengineering#solidworks#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Electronic Stability Control: How Chassis Control Ensures Safety?
July 26, 2024
by dorleco
with no comment
eMOBILITY CONTROLS
Edit
Introduction
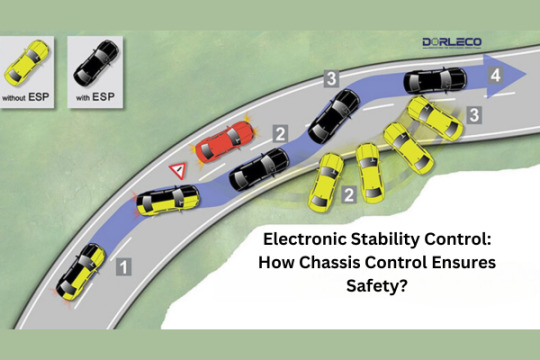
When it comes to automotive technology, safety is paramount. ESC, or electronic stability control, is one of the biggest advancements in automotive safety. This cutting-edge technology is designed to prevent skids and loss of control when driving in hazardous conditions or quickly. We will go over the concept of electronic stability control in this introduction, as well as how it effectively regulates a car’s chassis to ensure safety.
Understanding Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
Electronic stability control, sometimes referred to as ESC or ESP (Electronic Stability Program), is a state-of-the-art safety feature that is currently standard on most modern cars. Helping drivers maintain control of their vehicles is its main goal, particularly in challenging driving conditions.
Considering Vehicle Stability
Vehicle stability is necessary for safe driving. Vehicle instability can lead to hazardous situations like sliding, rollovers, or loss of control, especially in slick conditions like rain, snow, or uneven road surfaces. ESC was developed as a solution to these issues and significantly reduce the risk of accidents caused by instability.
How Electronic Stability Control Works
ESC uses a combination of sensors, microprocessors, and actuators to continuously analyze the vehicle’s behavior and adjust in real time to preserve stability. Here is how it works:
Sensor Inputs: The ESC gathers data on the mechanics of the vehicle from a range of sensors, including wheel speed, steering angle, yaw rate, and lateral acceleration. These sensors provide continuous feedback to the ESC system.

Microprocessor Analysis: The microprocessor of the ESC system continuously analyses the data from the sensors to determine whether the vehicle is deviating from the driver’s desired course. It compares the actual behavior of the vehicle with the driver’s inputs (such steering wheel position) and the planned trajectory.
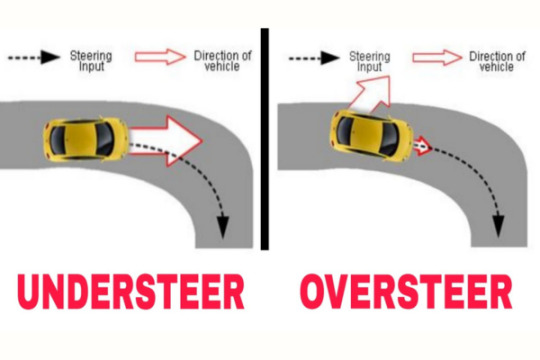
Actuator Response: If the system detects that the vehicle is beginning to skid, understeer — a situation in which the front wheels lose traction and push apart — or overseer — a situation in which the rear wheels lose traction and cause the vehicle to spin — it will take corrective action.
Restoration of Stability: ESC helps the car regain stability by adjusting the brake pressure and engine speed. This allows the driver to maintain control and steer clear of a potentially hazardous scenario. The changes occur almost instantaneously, and the driver is unaware of them.
Safety Guaranteed via Chassis Control
It takes electronic stability control to guarantee road safety. It is an essential component of the chassis control systems, which work together to provide a stable and predictable ride. The phrase “chassis control” describes a collection of technologies that help to keep drivers and passengers safe and avoid accidents, such as the Electronic Stability Control (ESC), the Traction Control System (TCS), and the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS).
Benefits of Electronic Stability Control: How Does Chassis Control Enhance Safety?
Electronic Stability Control (ESC), which has several significant advantages that improve road safety, is frequently a part of automobile chassis control systems. Some of the key advantages of ESC for ensuring safety are as follows:
Prevents Loss of Control: ESC is designed to identify and react to situations, such as sliding or skidding, where a car is in danger of losing control. By adjusting engine power and providing selective braking, ESC reduces the likelihood of accidents caused by a driver losing control of the vehicle.
Enhances Traction: On slick or uneven road surfaces, ESC can increase traction. By adjusting the engine output and braking pressure, it prevents wheel spin and holds the tires firmly on the ground. This comes in especially handy whether it’s icy, snowy, or pouring outside.
Minimizes Understeer and Oversteer: Understeer, or front-wheel slide, and oversteer, or rear-wheel skid, are common causes of accidents during rapid turns or unforeseen maneuvers. In these situations, ESC intervenes to assist the vehicle in maintaining a steady and predictable trajectory by applying the brakes to certain wheels.
Equivalents Additional Safety Systems: ESC works in tandem with Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) and Traction Control Systems (TCS) among other safety systems. When combined, these technologies provide extensive chassis control, making the vehicle responsive and stable in a range of driving conditions.
Reduces Rollover Risk: Electronic stability control (ESC) can also help to reduce the risk of rollovers in top-heavy vehicles such as trucks and SUVs. By preserving stability during quick turns or evasive maneuvers, ESC lowers the risk of the car overturning.
Boosts Driver Confidence: Knowing that the ESC is always monitoring and helping with vehicle stability helps boost driver confidence, especially in challenging driving circumstances. Driving habits could become safer because of this increased confidence.
Smoother Corrections: The vehicle’s behavior is rapidly and gently adjusted by the ESC. Unlike abrupt driver attempts, which can sometimes exacerbate a skid or slide, the ESC’s controlled interventions assist in preventing overcorrection and additional instability.
Electronic Stability Control Drawbacks: How Does Chassis Control Guarantee Safety?
While Electronic Stability Control (ESC) has significantly improved vehicle stability and reduced the risk of collisions, it is important to consider some of its possible limitations and drawbacks:
Cost: ESC is an expensive technology that requires certain actuators, sensors, and microprocessors. As a result, it might make producing and purchasing a car more expensive, which might raise the price of cars with ESC.
Maintenance costs: An ESC may need to be maintained and repaired on occasion, just like any other electrical device. The cost of identifying and fixing issues that develop from malfunctioning ESC system components may be substantial.
False Alarms: ESC systems can sometimes misinterpret the driving environment and initiate interventions when they are not necessary. These false alerts might irritate the motorist and cause a momentary loss of power or control.
Driver Overreliance: Some drivers may become too reliant on the ESC because they mistakenly believe that it will make up for unsafe driving habits. While ESC can sometimes alleviate some situations, driving must still be done with caution and attention.

Limited Effectiveness in Some Terrains: While ESC does a great job on standard highways, it might not work as well in off-road or difficult terrain. Drivers should proceed with caution in these circumstances as the ESC may struggle to keep control.
Tire Wear: ESC interventions may cause tires to wear down more quickly, especially when driving hard or regularly. The cost of operating the car may increase because of having to fix tires more frequently.
Not a Winter Tire Replacement: Not a Winter Tire Substitute Even though ESC can help with control in icy or snowy conditions, winter tires are still required. Nonetheless, drivers in regions with harsh winters should equip their vehicles with the appropriate tires for optimal safety.
Conclusion:
To sum up, Electronic Stability Control (ESC) is a significant technological development in the field of vehicle safety since it is essential to the way chassis control maintains road safety. This technology has completely changed how cars react to changing road conditions and handle them, greatly lowering the chance of collisions brought on by skidding, losing control, or bad weather. Many benefits are provided by ESC, such as preventing loss of control, improving traction, reducing oversteer and understeer, and coordinating with other safety systems.
The possible drawbacks and restrictions of ESC, such as expense, upkeep, sporadic false alarms, and the possibility of driver overreliance, must be acknowledged, though. Technology should be used sensibly and intelligently to mitigate these shortcomings.
Notwithstanding these factors, ESC continues to be a vital component of contemporary car safety, serving as an example of how advanced chassis control systems enhance traffic safety. ESC will surely continue to save lives and improve the safety of drivers, passengers, and pedestrians as it develops and becomes standard in a growing number of vehicles.
1 note
·
View note
Text
FOR SALE 1996 REX PORTABLE T/A 12CY CONCRETE CENTRAL MIX (GRAND FORKS N DAK ) | northdakota.allembru.com
0 notes
Text
Electronic Stability Control: How Chassis Control Ensures Safety?

Introduction
Safety comes first in the field of vehicle technology. Electronic Stability Control (ESC) is one of the most important developments in increasing vehicle safety. This state-of-the-art device is intended to avoid skids and loss of control when making rapid movements or in challenging driving situations. In this introduction, we will discuss the idea of electronic stability control and how it successfully controls a vehicle’s chassis to maintain safety.
Understanding Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
Modern cars now come equipped with electronic stability control, also known as ESC or ESP (Electronic Stability Program), which is a cutting-edge safety technology. Its major objective is to help drivers keep control of their cars, especially in difficult driving situations.
Considering Vehicle Stability
Driving safely requires a stable vehicle. Especially under slick circumstances like rain, snow, or uneven road surfaces, a vehicle losing stability can result in dangerous scenarios like sliding, rollovers, or loss of control. To overcome these problems and greatly lower the danger of accidents brought on by instability, ESC was created.
The Operation of Electronic Stability Control
A mixture of sensors, microprocessors, and actuators is used by ESC to continuously monitor the behavior of the vehicle and make modifications in real time to maintain stability. This is how it goes:
Sensor Inputs: The ESC collects information from a variety of sensors, such as wheel speed, steering angle, yaw rate, and lateral acceleration, concerning the dynamics of the vehicle. The ESC system receives continual feedback from these sensors.
Microprocessor Analysis: To assess whether the vehicle is departing from the driver’s intended course, the ESC system’s microprocessor continuously examines the data from the sensors. It contrasts actual vehicle behavior with the projected trajectory and the driver’s inputs (such as steering wheel position).
Actuator Response: The system initiates corrective action if it notices that the car is starting to skid, understeer (where the front wheels lose traction and push wide), or overseer (where the rear wheels lose traction and cause the car to spin).
Restoration of Stability: By altering the engine speed and brake pressure, ESC aids in regaining the vehicle’s stability, enabling the driver to keep control and avoid a potentially dangerous situation. The driver is not aware of these modifications, which take place nearly instantly.

Ensuring Safety through Chassis Control
In order to ensure road safety, electronic stability control is essential. It is a crucial part of the chassis control systems, which cooperate to offer a steady and predictable driving experience. The term “chassis control” refers to a group of technologies, including the Traction Control System (TCS), the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), and the Electronic Stability Control (ESC), all of which help to keep drivers and passengers safe and prevent accidents.
Electronic Stability Control Benefits: How Chassis Control Promotes Safety?
Vehicles’ chassis control systems often include Electronic Stability Control (ESC), which has a number of important benefits that increase road safety. The following are some of the main benefits of ESC for assuring safety:

Disadvantages of Electronic Stability Control: How Chassis Control Ensures Safety?
Although Electronic Stability Control (ESC) has substantially increased vehicle stability and decreased the danger of accidents, it’s vital to take into account some of its potential drawbacks and restrictions:
Cost: ESC is a sophisticated technology that calls for specialized microprocessors, actuators, and sensors. As a result, it may raise the price of manufacturing and acquiring a car, perhaps increasing the cost of ESC-equipped vehicles.
Costs of maintenance: Just like any other electronic device, an ESC may occasionally need to be maintained and repaired. The expense of diagnosing and resolving problems that arise when ESC system components malfunction may be high.
False Alarms: On occasion, ESC systems might interpret driving conditions incorrectly and start interventions when they aren’t required. These erroneous warnings may result in a brief loss of power or control and can annoy the driver.
Driver Overreliance: Some motorists could become unduly reliant on the ESC in the mistaken belief that it will make up for unsafe driving habits. While ESC can sometimes reduce certain situations, it cannot take the place of cautious and careful driving.
Limited Effectiveness on Some Terrains: While ESC is quite effective on normal highways, it might not be as effective in off-road or difficult terrain. Drivers should use caution in these circumstances since ESC may struggle to maintain control.
Tire Wear: ESC interventions, particularly when driving aggressively or frequently, may result in increased tire wear. This may lead to more frequent tire repairs, raising the car’s running expenses.
Not a Substitute for Winter Tires: Not a Replacement for Winter Tires ESC can aid in maintaining control in icy or snowy situations, but winter tires are still necessary. For maximum safety, drivers in areas with severe winters should nevertheless outfit their cars with the proper tires.

Conclusion:
In conclusion, Electronic Stability Control (ESC) stands as a remarkable technological advancement in the realm of automotive safety, playing a pivotal role in how chassis control ensures safety on the road. This system has revolutionized the way vehicles handle and respond to dynamic driving conditions, significantly reducing the risk of accidents caused by loss of control, skidding, or adverse weather conditions. ESC offers a multitude of advantages, including preventing loss of control, enhancing traction, mitigating understeer and oversteer, and working in harmony with other safety systems.
However, it is essential to acknowledge the potential disadvantages and limitations of ESC, such as cost, maintenance, occasional false alarms, and the risk of driver overreliance. These drawbacks should be addressed through responsible and informed use of the technology.
Despite these considerations, ESC remains a cornerstone of modern vehicle safety, exemplifying how cutting-edge chassis control systems contribute to road safety. As ESC continues to evolve and become standard in an increasing number of vehicles, it will undoubtedly continue to save lives and enhance the safety of drivers, passengers, and pedestrians alike.
#ElectronicStabilityControl#ChassisControl#SensorInputs#electricvehicle#Dorleco#sustainableemobility#Evs#BatteryManagement
0 notes