#FHIR compliant interoperability software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
HL7 Platforms Explained: The Backbone of Healthcare Communication Standards
In today's fast-changing healthcare environment, a healthcare interoperability solution is essential for seamless communication among various medical systems. Hospitals, labs, clinics, and other healthcare providers use many different software applications, devices, and data formats. Without a proper system to connect these, sharing important patient information can become slow, incomplete, or error-prone. This is where HL7 platforms come in as the foundation for making healthcare data flow smoothly and securely.
HL7 platforms are the key technology behind many healthcare interoperability solutions used worldwide. They help different healthcare systems “talk” to each other using common standards, enabling better coordination of care. In this blog, we will explain what HL7 platforms are, why they matter, and how they support modern tools like FHIR compliant interoperability software. We will also show how healthcare organizations benefit by adopting these platforms.

What is an HL7 Platform?
An HL7 platform is a software framework or tool that supports the HL7 standard for healthcare data exchange. HL7 stands for Health Level Seven, which is a set of international standards that define how health information is packaged and shared between computer systems.
These platforms act as translators and routers. They take medical data from one system, convert it into a common HL7 format, and then send it to another system that understands that format. This process allows different applications — such as electronic health records (EHRs), lab systems, and billing software — to exchange information accurately and quickly.
By using an HL7 platform, hospitals and clinics reduce the need for manual data entry, lower errors, and speed up patient care.
Why Are Healthcare Interoperability Platforms Important?
Healthcare is complex, with many stakeholders involved. Different departments and providers often use different software systems. Without a healthcare interoperability solution, these systems work in isolation, which can cause delays and miscommunication.
Healthcare interoperability platforms help solve this problem by connecting systems and enabling them to share data in real time. They improve patient safety by giving doctors access to complete medical histories, test results, and medication lists without delay. This better communication also cuts costs by avoiding duplicate tests and unnecessary procedures.
Moreover, interoperability platforms help healthcare providers meet regulatory requirements for data sharing and privacy. They build trust by ensuring patient information is exchanged securely and only with authorized parties.

How HL7 Platforms Work with FHIR Compliant Interoperability Software
In recent years, HL7 introduced a newer standard called FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources). FHIR simplifies healthcare data exchange by using modern web technologies such as RESTful APIs and JSON/XML formats. This makes integration faster and easier compared to older HL7 versions.
Many healthcare organizations are now adopting FHIR compliant interoperability software alongside traditional HL7 platforms. This software supports both the HL7 standards and FHIR, providing a flexible way to connect new and legacy systems.
HL7 platforms play a vital role in bridging older systems that use classic HL7 messaging with modern applications designed for FHIR. This combined approach helps healthcare providers gradually upgrade their technology without disrupting patient care.
Benefits of Using HL7 Platforms in Healthcare
Using HL7 platforms as part of a healthcare interoperability solution offers several key benefits:
1. Seamless Data Exchange
HL7 platforms ensure smooth and standardized data flow between different healthcare systems, allowing accurate and timely access to patient information.
2. Enhanced Patient Care
Better data sharing leads to improved diagnosis and treatment decisions. Clinicians have full medical histories and test results at their fingertips.
3. Cost Savings
By reducing duplicated tests and manual paperwork, HL7 platforms lower administrative costs and reduce delays in patient care.
4. Regulatory Compliance
These platforms help meet health data exchange regulations and maintain patient privacy by controlling data access and sharing.
5. Support for New Technologies
HL7 platforms work with FHIR and other modern standards, enabling healthcare providers to adopt innovative digital health tools without starting from scratch.
How Helixbeat Supports Your Healthcare Interoperability Needs
Helixbeat offers advanced healthcare interoperability platforms designed to help organizations manage and exchange health data effectively. With our expertise in FHIR compliant interoperability software, we deliver solutions that connect your existing systems and new digital tools.
Our platforms provide secure, scalable, and easy-to-use interfaces that improve collaboration across healthcare teams. Whether you are implementing HL7 messaging or transitioning to FHIR, Helixbeat’s solutions can adapt to your needs.
Contact us today to learn how Helixbeat can help your organization build a robust healthcare interoperability solution that improves patient outcomes and operational efficiency.

FAQs About HL7 Platforms and Healthcare Interoperability
1. What is the main purpose of an HL7 platform?
An HL7 platform standardizes and manages the exchange of healthcare information between different software systems to improve communication and patient care.
2. How does FHIR relate to HL7?
FHIR is a modern standard developed by HL7 that uses web technologies for faster and easier healthcare data exchange compared to older HL7 versions.
3. Why is healthcare interoperability important?
Interoperability allows different healthcare systems to share patient data efficiently, improving care quality, reducing errors, and cutting costs.
4. Can HL7 platforms work with existing hospital software?
Yes, HL7 platforms are designed to integrate with many legacy systems as well as new healthcare applications, enabling smooth data exchange.
5. How does Helixbeat support healthcare interoperability?
Helixbeat provides scalable and secure interoperability platforms, including FHIR compliant software, that connect diverse healthcare systems seamlessly.
#electronic health record systems#electronic medical records software#FHIR compliant interoperability software#healthcare interoperability platforms#hl7 platform
0 notes
Text
How to Choose the Best Healthcare App Development Company
The global healthcare industry is undergoing a digital transformation, and mobile apps are at the forefront of this revolution. From telemedicine and patient engagement to medical records and remote monitoring, healthcare apps have become indispensable for both providers and patients.
But building a secure, compliant, and user-friendly healthcare app is not a simple task. It requires deep domain knowledge, technical expertise, and a clear understanding of healthcare regulations like HIPAA, HL7, and GDPR. That’s why choosing the right healthcare app development company is critical to your project's success.
Whether you’re a hospital, a medical startup, a clinic, or a health tech entrepreneur, this guide will help you make an informed decision when selecting a development partner.
1. Understand Your Project Scope and Goals
Before you start your search, clearly define the goals of your app. Are you building a fitness tracker, a mental health platform, a teleconsultation service, or a full-fledged EHR system?
Knowing your app’s purpose will help you filter out companies that specialize in your required solution. A healthcare software development company with experience in similar projects will understand the user flows, compliance requirements, and performance expectations your app must meet.
2. Look for Industry-Specific Experience
Healthcare is a highly regulated and sensitive domain. Your development partner should not only understand mobile and web technologies but also have industry-specific experience in healthtech.
Check if the healthcare app development company has built apps that involve:
Electronic Health Records (EHR)
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Telemedicine platforms
Health and wellness tracking
Lab report and diagnostic data integration
AI-based health risk assessments
Such experience proves the company is equipped to handle healthcare-specific challenges like patient privacy, interoperability, and clinical data security.
3. Verify Regulatory Compliance Expertise
One of the most critical aspects of healthcare app development is regulatory compliance. A misstep can lead to legal issues, financial penalties, and a loss of user trust.
Ensure the healthcare software development company has a track record of building apps compliant with relevant healthcare standards, such as:
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) – for U.S.-based apps
GDPR – for handling data of European Union citizens
HL7/FHIR – for interoperability between healthcare systems
FDA regulations – for medical device and diagnostic apps
Ask the company how they handle data encryption, secure login, user authentication, and access control.
4. Evaluate Technical Proficiency and Stack
Your healthcare app will need a solid technology stack that ensures performance, scalability, and data security. A trustworthy healthcare app development company will be proficient in the following:
Frontend: React Native, Flutter, Swift, Kotlin for cross-platform and native development
Backend: Node.js, Python, .NET for server-side logic and API integrations
Databases: PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and healthcare-compliant data storage solutions
Cloud & DevOps: AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud with CI/CD pipelines and scalable architecture
Security: SSL/TLS encryption, biometric authentication, multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Ask to see case studies or code samples to assess their engineering standards.

5. Check Their Portfolio and Case Studies
Reviewing the portfolio of a healthcare app development company is a must. This will help you understand the types of solutions they've built, the industries they've served, and the challenges they've solved.
Ask for client testimonials, live demos, or app store links. Pay close attention to:
Design aesthetics and user interface quality
App speed and responsiveness
Security features and data protection methods
Integration with third-party APIs (e.g., pharmacy APIs, diagnostic labs, payment gateways)
This due diligence gives you confidence in their ability to deliver a healthcare-grade product.
6. Ensure UI/UX Expertise in Healthcare Design
A great app isn’t just functional—it must be easy to use for patients, doctors, and admins alike. Healthcare users range from tech-savvy Gen Z to elderly patients, so the interface needs to be intuitive, accessible, and inclusive.
Choose a healthcare software development company with skilled UI/UX designers who understand healthcare workflows, patient-centric design, and WCAG accessibility guidelines. Features like larger buttons, simplified navigation, and voice commands can improve engagement significantly.
7. Post-Launch Support and Maintenance
Healthcare apps require ongoing support to fix bugs, release updates, comply with new laws, and add features. Ask the company:
Do they offer post-launch support?
How do they handle emergency updates?
What are their SLAs for response and resolution?
A dependable healthcare app development company should be your long-term partner, not just a one-time vendor.
8. Check Pricing and Engagement Models
Pricing should be transparent and flexible. Many companies offer multiple engagement models such as:
Fixed-price (for well-defined projects)
Time and material (for agile, evolving projects)
Dedicated teams (for long-term partnerships)
Make sure the pricing aligns with your budget and allows scalability as your app grows. Also, ask about hidden costs related to hosting, licensing, or third-party APIs.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the best healthcare app development company is a strategic decision that can make or break your healthtech venture. From regulatory compliance and technical expertise to UX design and post-launch support, every aspect must be evaluated carefully.
A reliable healthcare software development company will not only help you build a compliant and scalable app but also empower your business with digital tools that improve patient care, operational efficiency, and health outcomes.
Take your time, ask the right questions, and choose a development partner that truly understands the complexity and responsibility of working in the healthcare space.
For more information, visit us: -
Software Application Development for Logistics
Best Fintech App Developers
App to Buy Groceries
0 notes
Text
Why eClinicalWorks Software Integration is the Future of Smart Healthcare?
In today’s fast-paced healthcare environment, integrating systems is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. Healthcare providers using ECW EMR and ECW EHR platforms need seamless connectivity to other systems to optimize operations and improve patient care. That’s where eClinicalWorks integration steps in, offering powerful tools to unify various aspects of clinical workflows. From lab systems and medical devices to billing and patient portals, eClinicalWorks integration software makes everything work better together.

What Services Are Covered Under eClinicalWorks Integration?
eClinicalWorks integration services cover a broad range of functions to meet the growing needs of modern healthcare providers. These services empower practices to build a unified and efficient clinical environment.
1. Patient Management Integration: Connects appointment scheduling and patient demographics to ECW EHR systems for a streamlined front-desk experience.
2. Revenue Cycle Automation: Syncs ECW EMR with billing software, automating claim submissions and reducing delays in reimbursements.
3. Lab System Connectivity: Ensures lab reports are automatically delivered into patient records within eClinicalWorks software.
4. E-Prescription Integration: Links ECW to pharmacy networks, making prescription management faster and error-free.
5. Imaging System Integration: Transfers radiology images and reports directly into the patient chart in the ECW platform.
These integrations are designed not only to save time but also to reduce manual errors and data fragmentation across departments.
How Does eClinicalWorks Software Improve Healthcare Workflows?
The beauty of eClinicalWorks software lies in how it simplifies data movement while increasing visibility across teams. It supports structured decision-making by consolidating all clinical data in one place. When the right data is accessible at the right time, outcomes improve naturally. Additionally, by integrating ECW EMR with various systems, providers eliminate redundant documentation and manual entries. This reduces the administrative burden and allows clinicians to focus more on patient care.
How Do Medical Imaging Platforms Integrate With ECW EHR?
Medical imaging plays a crucial role in diagnostics. Integrating these platforms into ECW EHR can enhance clinical accuracy and reduce turnaround times.
Real-Time Access: Images and reports are available instantly inside the patient’s ECW chart.
Reduced Manual Transfers: Eliminates the need for uploading or scanning documents manually.
Streamlined Diagnostics: Radiologists and primary care providers share synchronized data, improving collaboration.
Improved Documentation: Images are tagged and stored automatically in the patient’s electronic chart.
Standardized Communication: Data is shared in standardized formats, enhancing interoperability across platforms.
These features contribute to more efficient and informed medical decisions, benefiting both providers and patients.
What Role Does Laboratory System Integration Play?
Connecting lab systems with ECW EMR software allows for faster clinical action and improved patient satisfaction. eClinicalWorks integration services ensure that lab results are imported directly into the EHR, flagged for provider review, and recorded in the patient's history—all without human intervention. This not only improves turnaround times but also significantly reduces the possibility of transcription errors.
How Do eClinicalWorks Integration Services Support Compliance and Security?
Compliance is a key concern for any healthcare provider. ECW EHR integration is developed to comply with industry standards like HL7 and FHIR. It also ensures HIPAA-compliant data sharing. Whether you're integrating eClinicalWorks software with payment platforms or lab systems, the process respects patient confidentiality and secures sensitive data.
Conclusion:
eClinicalWorks integration is redefining how practices operate, communicate, and care for patients. Whether it’s connecting eClinicalworks EMR software with lab platforms or automating your billing process, eClinicalWorks integration software delivers a reliable, scalable, and secure solution. With the right eClinicalWorks integration services, healthcare providers can streamline operations, minimize risks, and provide better, faster, and smarter patient care.
0 notes
Text
Pioneering the Future of Healthcare Revenue Cycle Management with AI Agents
With escalating healthcare costs and increasingly complex reimbursement models, providers face significant challenges in optimizing Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) while delivering exceptional patient care. Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents—sophisticated software systems powered by machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and robotic process automation (RPA)—are transforming RCM by streamlining processes, minimizing errors, and enhancing outcomes. This blog explores the transformative role of AI agents in RCM, with a deep dive into their deployment in ambulatory healthcare settings, and highlights VerdureRCM’s leadership in driving innovation.

The Role of AI Agents in RCM
AI agents autonomously execute tasks, analyze intricate datasets, and make informed decisions with minimal human oversight. In RCM, they address inefficiencies in critical areas such as patient scheduling, insurance verification, medical coding, billing, claims processing, and payment collections. By integrating seamlessly with Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems and adhering to interoperability standards like Health Level Seven International (HL7) and Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR), AI agents ensure secure, real-time data exchange. This integration reduces manual intervention, enhances accuracy, and fosters a cohesive revenue cycle, enabling providers to focus on patient care.
AI Agents in Ambulatory Healthcare
Ambulatory healthcare settings—outpatient clinics, urgent care centers, and specialty practices—operate in a high-volume, fast-paced environment where efficient RCM is essential for financial stability and patient satisfaction. AI agents are uniquely equipped to address the distinct challenges of these settings, where rapid turnaround times, accurate billing, and transparent patient interactions are critical. Below, we explore how AI agents are deployed to optimize RCM in ambulatory care:
1. Streamlined Patient Intake and Scheduling
AI agents revolutionize patient registration by automating data entry and performing real-time insurance eligibility checks. In ambulatory settings, where same-day or walk-in appointments are common, AI instantly verifies coverage by cross-referencing patient data with payer databases. This reduces registration errors, shortens patient wait times, and prevents claim denials due to coverage discrepancies. For instance, AI can alert staff to outdated insurance information during intake, ensuring issues are resolved before services are provided, which is crucial in high-traffic clinics.
2. Automated Prior Authorization for Outpatient Procedures
Many ambulatory services, such as diagnostic imaging, physical therapy, or specialty treatments, require prior authorizations, which can delay care and burden staff. AI agents automate this process by identifying treatments needing approval, extracting relevant clinical data from EHRs, and submitting requests to payers. In urgent care or specialty clinics, AI tracks authorization statuses in real time, escalates delays, and ensures compliance with payer-specific guidelines. This accelerates approvals, reduces administrative overhead, and enables patients to receive timely care, enhancing both operational efficiency and patient experience.
3. Intelligent Coding for Diverse Services
Ambulatory care encompasses a broad spectrum of services, from routine check-ups to complex procedures like endoscopies or cardiac stress tests, each requiring precise medical coding. AI agents leverage NLP and ML to analyze clinical documentation and assign accurate, compliant codes in seconds, even for specialized fields like oncology or orthopedics. By continuously learning payer-specific coding rules and regulatory updates, AI minimizes errors that lead to claim denials. In high-volume settings, where coding backlogs can delay reimbursements, AI’s speed and precision ensure steady cash flow and reduce audit risks.
4. Proactive Denial Management
Claim denials are a persistent challenge in ambulatory care due to diverse payers, varied services, and stringent documentation requirements. AI agents analyze historical claims data to predict and prevent denials by identifying potential issues—such as incomplete documentation or mismatched codes—before submission. Post-submission, AI monitors claim statuses, prioritizes follow-ups, and automates resubmission processes. This is particularly valuable in smaller clinics with limited staff, where AI frees administrators to focus on patient-facing tasks rather than navigating payer disputes.
5. Enhanced Patient Financial Engagement
In ambulatory settings, patients expect clear, convenient financial interactions, as bills are often issued shortly after visits. AI agents generate real-time cost estimates based on insurance coverage and service codes, empowering patients with transparency about their financial responsibilities. Additionally, AI delivers personalized billing reminders via preferred channels like text or email, improving collection rates. By reducing billing confusion and fostering trust, AI enhances patient satisfaction, which is critical in competitive ambulatory markets where patient retention drives revenue.
6. Scalable Operations for Growing Practices
Ambulatory providers, especially those expanding to multiple locations or adding specialties, require RCM solutions that scale seamlessly. AI agents, hosted on cloud-based platforms, adapt to increased patient volumes and complex workflows without sacrificing efficiency. For example, a multi-site orthopedic practice can rely on AI to standardize RCM processes across locations while accommodating unique payer contracts or service mixes. This scalability supports growth, ensuring financial performance remains robust as practices expand.
These applications highlight how AI agents cater to the dynamic, patient-centric nature of ambulatory healthcare, where operational efficiency, financial accuracy, and positive patient experiences are intertwined. By automating repetitive tasks and providing actionable insights, AI empowers ambulatory providers to navigate financial complexities while prioritizing clinical excellence.
VerdureRCM: Leading AI-Driven RCM Innovation
VerdureRCM is redefining RCM by harnessing AI agents to optimize efficiency and elevate patient experience. With expertise equivalent to 250,000 person-years, VerdureRCM’s platform addresses longstanding RCM challenges, setting a new benchmark for healthcare financial operations.
Key AI-Powered Solutions
1. Real-Time Eligibility Verification
AI agents instantly verify insurance coverage, cross-referencing patient data with payer policies to prevent claim denials, improving cash flow and financial transparency for patients.
2. Automated Prior Authorization
AI streamlines prior authorizations by identifying required treatments, submitting requests, and tracking approvals, reducing delays and ensuring timely care.
3. Intelligent Medical Coding
Using NLP and ML, AI agents analyze clinical documentation to generate accurate, compliant codes quickly, minimizing audit risks with explainable coding decisions.
4. Scalable Cloud Infrastructure
VerdureRCM’s cloud-based platform supports practices of all sizes, adapting to growing patient volumes while maintaining operational efficiency.
Benefits for Healthcare Providers
1. Increased Revenue, Lower Costs
AI reduces claim denials, accelerates reimbursements, and automates labor-intensive tasks, freeing resources for patient care and infrastructure investments.
2. Enhanced Efficiency
Automation of coding and authorizations enables staff to focus on patient engagement and clinical decision-making, streamlining operations.
3. Improved Patient Experience
Real-time cost insights and faster approvals foster financial clarity and trust, strengthening patient-provider relationships.
4. Data-Driven Decisions
AI analyzes claims and trends, providing insights to optimize RCM strategies and ensure compliance.
Why VerdureRCM Leads the Industry
1. Deep Expertise
VerdureRCM combines technical innovation with extensive RCM knowledge, addressing real-world challenges effectively.
2. Security and Compliance
Adhering to HIPAA and using advanced encryption, VerdureRCM ensures data security and regulatory compliance.
The Future of RCM with VerdureRCM
As healthcare faces rising costs and regulatory complexity, AI agents will play a growing role. VerdureRCM is poised to lead, expanding AI capabilities and interoperability to reduce denials and enhance efficiency. Its vision is for AI to orchestrate RCM end-to-end, aligning with trends in healthcare automation. Partnering with VerdureRCM empowers providers to achieve financial stability and deliver patient-centered care.
Conclusion
VerdureRCM’s AI-driven approach marks a turning point in RCM, automating workflows, reducing errors, and providing actionable insights. Rooted in expertise and innovation, it leads the healthcare technology sector. As AI reshapes healthcare finance, VerdureRCM is the trusted partner for providers aiming to optimize revenue cycles and embrace a more efficient, patient-focused future.
0 notes
Text
Basics of Medical and Health Software Development

Medical and health software development is a rapidly growing field that blends technology with healthcare to improve patient outcomes, optimize hospital systems, and enhance access to medical services. This post introduces the key concepts, technologies, and challenges involved in developing health-based applications.
What Is Medical Software?
Medical software refers to any application that is designed for use in diagnosing, treating, monitoring, or managing health conditions. Examples include:
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Systems
Telemedicine Platforms
Patient Monitoring Systems
Mental Health Apps
Diagnostic and Imaging Tools
Mobile Health (mHealth) Applications
Key Features of Medical Software
Data Security: Protection of patient data is critical (HIPAA, GDPR).
Interoperability: Integration with hospital systems and other platforms.
Real-time Monitoring: For devices and remote patient care.
Accessibility: Intuitive UI for all users including doctors and patients.
Compliance: Adhering to medical regulations and certifications.
Technologies Used in Development
Frontend: React, Angular, Flutter (for mobile apps)
Backend: Node.js, Django, .NET
Databases: PostgreSQL, MongoDB, FHIR-compliant databases
APIs: HL7, FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources)
AI/ML: For diagnostics, predictive analysis, and personalization
Steps to Build a Basic Health App
Define Purpose: Identify the health problem the app addresses.
Understand Regulations: Learn about data protection and compliance laws.
Design UX: Create intuitive, accessible user interfaces.
Develop Core Features: Include scheduling, tracking, reminders, records, etc.
Test Thoroughly: Ensure accuracy, security, and usability.
Deploy and Monitor: Use cloud platforms for scale and monitor performance.
Challenges in Health Software Development
Compliance Complexity: Medical regulations vary by country and region.
Data Sensitivity: Requires encryption, secure access, and audit logs.
Integration with Legacy Systems: Many hospitals use outdated software.
Continuous Testing: Bugs in health apps can be dangerous.
Real-World Examples
Epic Systems: EHR platform used by hospitals worldwide.
MyChart: A patient portal for managing health data and appointments.
Teladoc: A telemedicine app connecting doctors and patients remotely.
Calm, Headspace: Mental wellness and therapy tools.
Useful Tips for Beginners
Start small—build a medication reminder or step tracker app.
Learn the basics of health data standards like FHIR and HL7.
Work with healthcare professionals for domain insights.
Focus on user privacy and ethical programming practices.
Conclusion
Developing medical and health software is both rewarding and challenging. It requires a blend of technical knowledge, legal awareness, and a strong sense of responsibility. With the right approach, programmers can create impactful solutions that improve lives and reshape healthcare delivery.
0 notes
Text
EHR and EMR Development: How to sail through Challenges and craft Intuitive, Compliant Systems
Today, digital transformation in healthcare is the buzzword; and, Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Electronic Medical Records (EMR) systems are must-haves for healthcare providers embracing digitization. These platforms play a vital role in streamlining patient information and improving care coordination. However, EHR and EMR involve significant challenges ranging from usability issues to stringent compliance requirements. Let’s take a sneak peek into the key roadblocks of creating intuitive and compliant EHR and EMR systems and how to overcome challenges in healthcare software development.
The Stumbling Blocks of EHR and EMR Software Development and ways to resolve them

Complex Compliance Regulations
Healthcare being one of the most regulated industries, any healthcare application must comply with industry standards and data protection laws of the region/s where the app operates. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act or HIPAA in the U.S. and General Data Protection Regulation or GDPR in Europe, are examples of regional privacy laws. Such laws have been designed to safeguard patient data and must be integrated into every healthcare software.
What are the consequences of not being compliant?
Healthcare providers not adhering to regulatory compliances are subject to hefty penalties if any data breach takes place. Here’s an example!
Anthem, one of the largest health insurance companies in the U.S., experienced a massive data breach In February 2015 that exposed the personal data of nearly 79 million people. The breach occurred when cybercriminals gained access to Anthem's IT system through a phishing attack on an employee, allowing them to steal sensitive data over several weeks. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office for Civil Rights (OCR) investigated the breach under the HIPAA violation. Anthem agreed to a settlement of $16 million with the OCR and had to sign an agreement to implement corrective actions to improve data security and prevent future breaches. Anthem also faced multiple class-action lawsuits from affected individuals, leading to a $115 million settlement in 2017, marking it the largest data breach settlement in history for that time.
How to mitigate such challenges during health application development?
Compliance-first approach: Implement security and privacy features like multi-factor authentication, encryption, and secure cloud storage from the onset of development.
Automated audits: Build automated auditing tools within the system to continuously monitor and log access to patient data, enabling easy compliance checks.
Regular updates: Stay up-to-date with changing regulations and adapt the system accordingly.
2. Ensuring Interoperability
For EHR and EMR systems to be truly effective, they must be interoperable: be able to seamlessly communicate with existing healthcare systems in a medical facility, such as laboratory systems, billing software, and other healthcare providers' EHR/EMR platforms regardless of the platform or software used. Lack of interoperability can lead to fragmented patient data, care delays, and inefficiencies.
Overcoming the Challenge:
Open APIs and standards: Leverage open APIs and standardized communication protocols like HL7, FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), and DICOM to facilitate smooth data exchange between different systems.
Modular architecture: Use a modular approach to allow easy integration with third-party applications and services, ensuring flexibility as healthcare organizations adopt new technologies.
3. Designing for User Experience
Healthcare professionals often experience frustration when using poorly designed EHR/EMR systems, which can be counterintuitive and slow. This reduces their productivity, increases the likelihood of errors, and even contributes to burnout.
Overcoming the Challenge:
User-centered design: Engage healthcare professionals early in the design phase to understand their workflow and needs. Conduct usability testing to refine interfaces for efficiency and ease of use.
Streamlined UI: Simplify the user interface by focusing on essential features, minimizing unnecessary clicks, and ensuring quick access to the most-used functions.
Mobile-first design: Given the rise of mobile devices in healthcare, ensure that your system is mobile-responsive and works seamlessly across different devices.
4. Data Migration and System Integration
Healthcare organizations transitioning from paper-based records or older EMR/EHR systems face the challenge of migrating vast amounts of data. Ensuring that this data is correctly transferred, cleaned, and integrated without loss is crucial.
Overcoming the Challenge:
Data validation tools: Build validation tools to verify the accuracy and integrity of migrated data, ensuring that essential information like patient history, medications, and test results are preserved.
Custom migration solutions: Tailor data migration solutions to the specific needs of healthcare organizations, ensuring that legacy systems integrate smoothly with the new system.
Testing phases: Conduct multiple testing phases during migration to identify and address potential issues before going live.
5. Maintaining System Scalability and Performance
As healthcare organizations grow and patient data increases, EHR/EMR systems need to scale while maintaining optimal performance. A sluggish system can disrupt clinical workflows and compromise care quality.
Overcoming the Challenge:
Cloud infrastructure: Go for scalable cloud-based infrastructure, allowing the system to handle fluctuating data volumes without compromising performance.
Load balancing and caching: Implement load balancing and caching mechanisms to manage traffic spikes and ensure that the system remains responsive, even during peak usage periods.
Ongoing performance audits: Monitor system performance regularly and make necessary adjustments to support scalability.
6. Facilitating Real-Time Data Access
Real-time data access is essential in emergency care scenarios, where clinicians need immediate access to patient information to make swift, life-saving decisions. However, balancing the need for rapid data retrieval with the complexity of handling large datasets in HER and EMR systems presents unique challenges. The data needs to be retrieved quickly without sacrificing accuracy or overwhelming the system's resources. To address these challenges, various strategies can be employed to enhance real-time performance. However, achieving real-time performance in EHR/EMR systems while managing large data sets can be challenging.
Overcoming the Challenge:
Optimized database management: Use advanced database management techniques, such as indexing and partitioning, to ensure that queries are processed quickly.
Edge computing: Leverage edge computing to bring data processing closer to the point of care, reducing latency and enabling faster access to critical patient information.
Efficient algorithms: Implement algorithms optimized for real-time data processing, reducing delays in retrieving and displaying information.
In a Nutshell
By prioritizing compliance, interoperability, user experience, data migration, scalability, and real-time access, healthcare providers can create intuitive and compliant EHR and EMR systems. Embracing new technologies and collaborating closely with healthcare experts and experienced software development professionals will ensure that these systems continue to evolve to meet the needs of modern healthcare environments.
0 notes
Text
Hospital Software Integration: Overcoming Common Challenges

In today's digitally-driven healthcare landscape, the integration of hospital software has become essential for optimizing patient care delivery, streamlining workflows, and improving operational efficiency. However, while the benefits of integration are clear, healthcare organizations often face common challenges when implementing and integrating hospital software solutions. Let's explore these challenges and strategies for overcoming them to ensure successful integration.
Compatibility Issues: One of the most common challenges in hospital software integration is compatibility issues between different systems and platforms. Healthcare organizations often use a variety of software applications for Electronic Health Records (EHR), billing, scheduling, and other functions, each with its own data formats and protocols. Integrating these disparate systems can be challenging, as they may not be designed to work together seamlessly.
Solution: To overcome compatibility issues, healthcare organizations should invest in hospital software solutions that offer flexible integration capabilities and support industry-standard protocols such as HL7 and FHIR. Working closely with software vendors and IT specialists can help identify compatibility issues early in the integration process and develop customized solutions to ensure smooth interoperability between systems.
Data Security Concerns: Data security is a top priority in healthcare, and integrating hospital software solutions raises concerns about the security and privacy of patient information. Healthcare organizations must ensure that data exchange between integrated systems is secure and compliant with regulatory standards such as HIPAA and GDPR. Failure to address data security concerns adequately can lead to breaches, compliance violations, and reputational damage.
Solution: Implementing robust security measures such as encryption, access controls, and audit trails is essential for safeguarding patient data during hospital software integration. Healthcare organizations should conduct thorough risk assessments and engage with software vendors who prioritize data security and compliance. Regular security audits and employee training programs can help maintain a culture of security awareness and mitigate the risk of data breaches.
Workflow Disruptions: Hospital software integration can disrupt existing workflows and processes, causing confusion and resistance among staff members. Healthcare providers may encounter difficulties adapting to new systems or changes in their workflows, leading to decreased productivity and morale. Resistance to change and a lack of training can further exacerbate workflow disruptions and hinder the success of integration initiatives.
Solution: Effective change management is critical for minimizing workflow disruptions during hospital software integration. Healthcare organizations should involve key stakeholders, including frontline staff, in the integration process from the outset and communicate transparently about the goals and benefits of integration. Providing comprehensive training and support resources to staff members can help alleviate concerns and build confidence in using new systems. Additionally, implementing phased rollout plans and soliciting feedback from end-users can help identify and address workflow issues proactively.
Cost and Resource Constraints: Hospital software integration projects can be costly and resource-intensive, requiring investments in software licenses, hardware infrastructure, and IT personnel. Healthcare organizations operating on limited budgets may struggle to allocate sufficient resources to integration initiatives, leading to delays or compromises in project scope and quality.
Solution: To address cost and resource constraints, healthcare organizations should conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses and prioritize integration projects based on their potential impact on patient care and operational efficiency. Exploring alternative funding sources such as grants, partnerships, or government incentives can help offset integration costs and accelerate project implementation. Additionally, outsourcing certain integration tasks to experienced third-party vendors or consultants can provide cost-effective solutions and access to specialized expertise.
In conclusion, hospital software integration offers significant benefits for healthcare organizations, but it also presents common challenges that must be addressed to ensure successful implementation. By adopting proactive strategies such as addressing compatibility issues, prioritizing data security, managing workflow disruptions, and addressing cost constraints, healthcare organizations can overcome these challenges and unlock the full potential of integrated hospital software solutions. Embracing hospital software integration as a strategic investment in patient care delivery and operational excellence is essential for staying competitive and meeting the evolving needs of patients and providers in today's dynamic healthcare environment.
#HMS#hmssoftware#hospitalsoftware#HealthcareManagementsystem#Healthcare#HospitalManagementSystem#HospitalManagement#BSA#GrapesHMS#MIS#EMR#GrapesIDMR#Grapes#HealthcareManagementSystemsoftware#Software#SoftwareSolution#Doctor#PatientRegistration#IPDManagement#OPDManagement#IDMR#Labmanagement#NursingStation#Dietmanagement#MRDManagement#BloodBank#Linenmanagement#HRManagement#Pharmacy#Radiology
0 notes
Photo

Health Information Exchange
Integrate your software with Health Information Exchanges securely and in HIPAA compliant manner through Mirth Connect.
visit- https://wi4.org/services/hl7-interoperability/mirth-connect/ Call (470) 830-0294
#ldap #mirth #mirthsupport #mirthbywi4 #mirthconnect #FHIR #HL7interface #hl7 #SSL
1 note
·
View note
Text
FHIR Server Fusion: Advanced Healthcare Interoperability Solution for Seamless Data Exchange
Helixbeat’s FHIR Server Fusion enables secure, standardized healthcare data exchange across systems. Enhance interoperability, improve patient care, and streamline clinical workflows with this scalable and efficient healthcare interoperability solution built on FHIR standards.
#healthcare interoperability solution#FHIR compliant interoperability software#healthcare interoperability platforms#hl7 platform
0 notes
Photo

Significance of Mobile Health Apps Testing Today and Tomorrow
From retail to banking to e-commerce industries, there are applications that cover a wide range of services we use daily. The healthcare sector has also started to launch mobile app platforms across the health care delivery cycle, forming a voluminous medical app market.
Mobile health apps and devices are truly making a strong impact in the healthcare sector, as they can easily diagnose disease and prevent the likelihood of developing death-defying medical conditions like diabetes or heart disease.
The market of mHealth (mobile health) app has been growing with the adoption of new workflows, technologies, and new business models that are transforming healthcare. With the growing adoption of mobile in this sector, the business opportunity for mHealth apps is also growing exponentially.
Market Scenario and Statistics
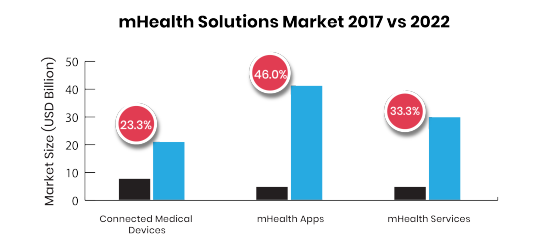
The global mHealth app market is estimated at US$28.320 bn in 2018 and is expected to reach up to US$102.35 bn by 2023. (source-Research and Market)
Over 318,000 health apps exist on the top app stores, nearly double the number of apps available in the year 2015 with approx. 200 or more apps being added every day (IQVIA).
These statistics speak that progressively more healthcare providers offer mobile applications to their patients, which ultimately makes the interaction between provider and patient much simpler. An increase in the coverage of mobile cellular networks and the growing accessibility of patient education technology in emerging economies have churned out better prospects for the mobile health market.
Types of mHealth applications
Healthcare Professional Finders
Symptom Checkers
Condition Education and Management
Self-Monitoring
Managing Clinical and Financial Records
Rehabilitation Programs
Remote Patient Monitoring
Prescription Filling and Compliance (Adherence)
Challenges, challenges everywhere
With the exponential growth of mHealth applications, delivering a secure and high-quality working app has become a necessity for user retention. Healthcare is sensitive to changes and innovations as lives are literally at stake. This extra cautiousness creates roadblocks, which may cause difficulties in creating a new healthcare application.
Challenges in the mHealth apps that cause a focus on Quality Assurance:
Meeting Usability Expectations
It does not matter whether your enterprise’s goal is as determined as creating a mobile version of health records or as humble as a recommendation with healthcare professional finders, the app should be convenient to use. Each mobile health app can influence several stakeholders, including caregivers, care team members, insurers, patients, admin staff, and more. The application should support their workflows easily, so QA specialists need to get a clear picture of basic user requirements.
Security and Privacy of the Devices, Data, and Apps
The need to safeguard software from breaches, malicious attacks, and nasty viruses, could disturb the whole development team. In healthcare, there is an answer to cope with such incidents: compliance with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). If the mobile health app is compliant with this legislative regulation, then it is secured.
HIPAA act focuses on the security and privacy of health data and requires added knowledge of the vertical. In particular, QA specialists should thoroughly study the Act to assure that the test is consistent with each section of the regulation applicable to the specific product.
The Demand for Interoperable Systems and Apps
As healthcare software and app is steady goes into the cloud, even legacy systems follow the trend. Undoubtedly, smaller apps are the first to make the move. The resource acclaimed the necessity for interoperability in such applications, as new health IT technologies, priorities, and procedures, will influence changes in accepted standards for data transfer–Health Level Seven (HL7), Digital Imaging And Communications In Medicine (DICOM) and Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR).
QA specialists have to ensure continuous dialogue between their applications and all other systems that could connect to it, counting huge clinical systems (CRM, ERP, EHR), and an extensive choice of smart medical devices and wearable.
If the testing period won’t be consistent with all industry standards and demands, it will cause high operating costs.
Solutions- How ImpactQA Can Help You?
It is essential that mHealth providers should integrate software testing as a vital component of their digital health strategy.
Our experts completely understand the nuisances of Mobile Health applications involving legacy systems, multiple subsystems, voluminous test data, diverse data sources, and complex authentication systems.
Our QA specialists also offer Healthcare software testing solutions for diverse healthcare players such as hospitals, diagnostic centers, pharma companies, clinical labs, third-party administrators (TPA), medical equipment makers, etc.
We offer the following testing services in the healthcare domain:
Usability Testing
Mobile Apps Testing
Functional Testing
Performance Testing
Security Testing
Interoperability Testing
Systems Integration and Interface Testing
Our committed healthcare application test team has the expertise to cater to the requirements for comprehensive healthcare application tests manually and using test automation tools like Selenium, Appium, Robotium, and QTP. Our proficiency lies in building agile and robust test solutions for health institutions that help them address their need for flexible and cost-effective solutions.
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/impactqa-it-services-pvt-ltd/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Impact_QA
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/ImpactQA/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/impactqa/
P.S. We are always happy to read your comments and thoughts ;)
#ImpactQA#mhealth#mobile health applications#qa#qa testing services#qa testing company#healthcare#mobile health#Software Testing Services#Software Testing Company#software testing tools
0 notes
Text
The evolving data landscape will transform healthcare: here are four trends to watch
The healthcare system generates approximately a zettabyte (a trillion gigabytes) of data each year, which includes both classic data from sources such as EHRs, diagnostics and genetics, as well as newer data sources such as gut biome sensors, wearable devices and environmental monitors, and social media. Consequently, it’s now possible to quantify a person across three dimensions of human existence: biological, environmental and digital/social.
Big tech is leading the way in quantifying our existence, creating tools and technology to track and measure consumers’ weight, heart rate and other traditional health signifiers, as well as their social determinants of health—information on where and how people live, such as what (or if) they eat, their access to travel, how much they exercise and how they socialize. Social determinants account for roughly 60% of human health and well-being, while healthcare accounts for only 10%. In other words, having the data on where and how people live provides the power to influence people’s health status, so as tech companies race to collect and link this information, they’re reshaping how we view and deliver healthcare. Pharma companies—and healthcare stakeholders more broadly—should take note, paying attention to what’s coming, how healthcare delivery could change, and what it means for their vertical.
Data advances abound—and challenges too
As most anyone following business news these days knows, all of the biggest tech players have announced efforts or products to claim a piece of the exploding healthcare data pie, and they’re partnering with traditional stakeholders across the industry to plan their entry. For example, Apple has its FDA-cleared electrocardiogram feature on its Apple Watch; ResearchKit, a software framework for clinical trial apps; Health Records, an app that aggregates existing patient-entered data from its Health app with a user’s electronic medical record data; and a collaboration with Aetna on Attain, an iPhone/Apple Watch app that tracks and rewards users for healthy behaviors. Apple is using its iPhone and other technologies—and even a new Apple credit card—to systematically build a platform to quantify many aspects of human existence, and has implemented methods to assure that the information can be readily shared and accessed if permission is granted.
Other companies such as Amazon and Google have created an integrated suite of offerings (with Amazon acquiring Whole Foods and Google offering hardware like Nest, Google Home and Pixel). These tech companies will have enough data on consumers to gain a holistic view into their lives and to offer targeted solutions to their healthcare needs.
The healthcare industry has already found itself behind the eight ball, and it’s now grappling with the larger question about how data structure, ownership and access will work in the fully integrated healthcare data landscape of the future. Moreover, there are still considerable challenges to using the emerging healthcare data effectively. Some data is messy or is missing altogether, and AI and machine learning systems often lack the necessary training data sets. And, of course, interoperability issues abound. The fragmented nature of healthcare data has led to the formation of data aggregators that sell data to other stakeholders in data marketplaces, and these data marketplaces either aggregate data across different data types or focus almost exclusively on one data type.
For example, the HealthVerity Marketplace contains HIPAA-compliant, de-identified data on more than 300 million U.S. consumers, pulling together medical and prescription claims, lab results, EMRs and other data types from more than 30 data suppliers across the country. Meanwhile, Nebula Genomics offers a blockchain-based network that houses users’ genetic information.
Some of these data marketplaces are starting to partner with each other and form more comprehensive marketplaces, which is a step in the right direction, and other solutions are emerging. For example, Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR), a new web standard that enables healthcare information to be shared electronically, and SMART on FHIR, which are open specifications that can be used to integrate health-related apps with EHRs and other healthcare IT systems, are burning down interoperability barriers.
Big players like Intermountain Healthcare and Partners Healthcare are using SMART on FHIR to build and utilize apps that work seamlessly with their EHR systems—providing better access to data for them and their patients while expanding data collection. Regulators are on board: New rules from CMS and ONC require healthcare providers and insurers to implement open data-sharing technology that will ensure data movement across plans and expand patients’ access to data.
Furthermore, there have been advancements in structuring some of the unstructured data that better describe the “whole person.” For example, the American Medical Association has partnered with UnitedHealthcare to create 22 new ICD-10 codes for social determinants of health (such as food insecurity, access to transportation, and social connectedness) so that researchers can structure information about wellness.
Pharma needs to track—and adapt to—four major data trends
To capitalize on healthcare’s data-driven evolution—and to keep pace with the change—pharma needs to keep an eye on four major trends.
1. New patient segmentation: Payers have a strong incentive to harness all of the data that they can get to ensure that their members are as healthy as possible. As a result, they lead the pack in applying machine learning, big data analytics and even natural language processing (from phone conversations) to segment people by risk.
For example, Anthem has created an integrated data warehouse that holds its claims data along with EHRs, lab results and other necessary data sets—allowing analysts to investigate members’ specific characteristics and determine their risks for emergency medical treatment or unstable health conditions, and creating the ability to segment and target members with offers of health coaching or additional services.
What will this new approach to patient segmentation mean for pharma’s clinical trial design and recruitment? How will it change the way that payers evaluate patient populations for access to drugs? Pharma companies are going to have to modify their clinical trial designs to match new evidence standards that link social determinants of health to outcomes. They’ll also need to consider new dimensions of patient segmentation along the lines of access to travel, food security, social engagement and the like. This will be necessary as payers consider this information in their population health analyses.
2. Care model change: Fueled by data, the healthcare delivery model is beginning to change, shifting the focus from treating sickness to maintaining and encouraging wellness. While there will always be specialty care, the majority of healthcare is moving towards localized health hubs offering social program-like services related to education, prevention and treatment in a retail setting.
For example, Cityblock, a company under the Alphabet umbrella, is partnering with health plans to reach people in neighborhoods with high poverty rates and other social challenges. They collect structured and unstructured data, and synthesize it into dashboards to enable community health practitioners to create personalized overall life wellness plans that address personal habits and social behaviors—ideally heading off health conditions before they start.
For pharma companies, the increasingly local and down-skilled care model indicates that it’s time to assess the new influence points for care decisions and to optimize their commercial models appropriately. This tech-enabled care delivery will rely on pathways and rules-based decisions. Pharma will need to identify where and how to influence these predetermined care decisions in a more business-to-business manner. For example, as payers move patients to post-acute sites of care, providers here are gaining the power to switch treatments to generics or drive biosimilar adoption.
3. Evolving engagement dynamics: In the race for access to healthcare data, many former enemies are “frenemies.” Everyone is a potential partner. For example, Pfizer buys cancer data from Flatiron, which is owned by Roche. Roche and Pfizer are competitors. Everyone is cool with this. Meanwhile, the Yoda Project at Yale has direct competitors contributing their data to an open-access platform.
Data-oriented partnerships and alliances are becoming the norm, so pharma companies should consider adding more data-focused roles to their roster. In addition to the chief data officers and chief digital officers being recruited now, they’ll need data alliance/venture teams and data stewards, with savvy data monitoring and licensing experts leading the way on finding and securing valuable data relationships.
4. Using data as an R&D value generator: Increasingly, pharma companies are using new forms of data in new ways, in all parts of their business and throughout their product development cycle. For example, Daphne Koller, a computer science professor at Stanford University, founded Insitro, which is focused on reversing the death spiral of R&D productivity by leveraging machine learning, CRISPR and other techniques to make drug discovery more efficient. Leveraging technologies such as organs on a chip and stem cells, mutating these cells, and phenotyping, Insitro has created a bio-data factory to explicitly enable machine learning. The results have been promising—leading to a partnership with Gilead.
Data is now a strategic asset for pharma companies. As data sources paint a more complete picture of biological function, pharma companies can examine their small molecule libraries for new applications. In addition, they can design new biomarkers (including digital) to create product differentiation and, ideally, to enable earlier read-outs on clinical trials, which will bring products to market sooner and cut development costs. More rich and complete data handled in the right way will enable better and more effective decisions from R&D all the way to commercial.
The race is on to acquire and aggregate data, clean data, structure unstructured data, find new forms of data and generate missing data. In the next decade, navigating the data marketplace will be as critical as navigating the reimbursement landscape was in the past decade. Commercial viability will depend on it.
0 notes
Text
"Google Cloud for Healthcare: new APIs, customers, partners and security updates"
Google Cloud’s goal for healthcare is very much a reflection of Google’s overall mission: to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful. Applying this mission to healthcare means using open standards to help enable data sharing and interactive collaboration, while also providing a secure platform. Just imagine if all healthcare providers could easily, securely and instantaneously collaborate while caring for you. Ultimately, we hope that better flow of data will inspire new discoveries with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), leading to insights that improve patient outcomes.
This week at HIMSS we’re showcasing our progress toward serving this mission through our Google Cloud Platform (GCP), G Suite and Chrome solutions, our work with customers and partners, and our focus on compliance and security.
Unlocking data with the new Cloud Healthcare API
We’ve recently launched the new Cloud Healthcare API, which addresses the significant interoperability challenges in healthcare data. The new API provides a robust, scalable infrastructure solution to ingest and manage key healthcare data types—including HL7, FHIR and DICOM—and lets our customers use that data for analytics and machine learning in the cloud.
As part of our early access launch, we’re already working with a group of customers and partners, including the team at the Stanford School of Medicine. Here’s what Somalee Datta, Ph.D., Stanford School of Medicine Director of Research IT, had to say about our work together:
"Open standards are critical to healthcare interoperability as well as for enabling biomedical research. We have been using the Google Cloud Genomics API for a long time and are very excited to see Google Cloud expanding its offerings to include the new Cloud Healthcare API. The ability to combine interoperability with Google Cloud’s scalable analytics will have a transformative impact on our research community."
Our goal with the Cloud Healthcare API is to help transform the healthcare industry through the use of cloud technologies and machine learning. Healthcare is increasingly moving to the cloud, and the adoption of machine learning will allow the industry to unlock insights that can lead to significant clinical improvements for patients. The Cloud Healthcare API is currently available in an early access release, but over the next year, we plan to roll it out to more customers and partners—let us know if you’re interested.
In addition to the the Cloud Healthcare API, we have a long history of supporting open APIs directly on GCP. Our Cloud Genomics API has provided an implementation of the Global Alliance for Genomics & Health APIs for many years now. Through an API-first approach, we can help healthcare enterprises simplify data interoperability by providing a strong foundation with cloud infrastructure and services. For example, Apigee enables healthcare enterprises to manage and deploy FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) APIs on top of their existing electronic health record systems.
How our healthcare customers are using Google Cloud
Beyond our work on APIs, our approach is to give healthcare customers the tools they need to accelerate projects in areas like population health, personalized medicine and clinical research. At HIMSS we’ll talk in more detail about how our customers are using Google Cloud. Here are a few examples:
M*Modal is working with Google Cloud to reinvent the experience of healthcare and mitigate widespread physician burnout. The collaboration leverages M*Modal’s success in adoption of its physician-assistive, AI-based solutions with Google Cloud’s expertise in AI at scale to align innovation with market needs. M*Modal solutions deliver AI-powered, real-time contextual understanding and more enhanced, actionable insights from clinical data to the doctor directly at the point of care.
Lahey Health is making the move to G Suite for its many benefits, including innovation, scalability, collaboration, security and productivity. From the security perspective, they chose G Suite for our team of dedicated security professionals, malware scanning for early detection of global campaigns, and secure end-to-end infrastructure that has built-in protections across many layers.
The Chilean Health Ministry is using Google Cloud’s Apigee platform to provide a nationwide API-based connectivity to help ensure data, applications and services are easily, yet securely, available when and where needed. This connectivity helps secure access to patient information, regardless of whether it’s needed in one of Chile’s 1,000 remote medical facilities or in one of its connected health centers.
Cleveland Clinicis using Google Cloud’s Apigee platform to realize the full potential of their underlying electronic medical record through FHIR APIs. Using a secure, scalable and industry-grade API platform, Apigee allows Cleveland Clinic to enable, augment and extend functionality of their EHR. It’s also enabling them to run advanced analytics and ML-based predictive models, revealing insights to clinicians that help them deliver improved patient care.
Rush University Medical Center is also using Apigee to enhance many aspects of patient care and patient experience. They're looking to optimize scheduling, identify excess costs, reduce emergency department wait times, reducing readmissions and identifying and predicting cybersecurity threats using Google Cloud's capabilities in AI and ML.
Color is using Variant Transforms—a new open source tool we recently released that helps export genomic variants directly into BigQuery—to discover new capabilities for their cancer diagnostic service. When the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard first brought the GATK Best Practices pipeline to GCP in 2015, it was $45 to analyze a single genome. Since then, Broad has steadily brought down the cost to a little over $5 by optimizing its use of GCP, while maintaining (and even improving) the quality of the output, and has recently made this same pipeline—at the same cost—available to researchers around the world.
Middlesex Hospital and Chapters Health System are using Chrome to provide a secure, future-proof entry point to the cloud, connecting their staff to data-driven systems so they can focus on what’s most important: delivering great patient care.
How we're working with partners
Partners are essential to the work we do with healthcare customers. Here are a few that we’re talking about at HIMSS:
Flex introduced BrightInsight, a secure, managed services platform running on GCP. BrightInsight aggregates data to deliver real-time intelligence and optimize the value of connected drug, device or combination products. It’s designed to support CE-marked and FDA-regulated medical devices, combination products and Software as a Medical Device requirements for pharmaceutical and medtech companies. Flex is partnering with Google Cloud to deliver insights with customizable analytics dashboards that take advantage of our advanced machine learning and AI capabilities.
Imagia is transforming the way researchers can investigate disease characterization, progression and treatment response.
To address the increased demand for genomics, Kanteron Systems has introduced telegenomics on GCP as an addition to its Precision Medicine Platform.
Client Outlook has integrated their eUnity medical imaging viewer with the new Cloud Healthcare API, enabling them to provide a seamless visualization experience for medical images stored on GCP.
WuXi NextCODE’s massively scalable genomics database management system and clinical and research applications will be available to all Google Cloud users later this year.
And, on the hardware front, with Chrome solutions and technology partnerships, we’re also announcing a new collaboration between Healthcast, Citrix and Chrome OS that aims to provide a more secure and economical approach to data access. In another example, using VMware’s Digital Clinical Workspace and Point of Care solutions with a Chromebook allows users to securely access sensitive data and apps.
How we’re focusing on security and compliance
We can’t talk about improving healthcare without addressing security and compliance. We’re continuing to expand HIPAA compliance coverage across G Suite and GCP. Today, we announced that Google App Engine and Cloud Machine Learning Engine are covered, joining more than two dozen other HIPAA-compliant GCP services
http://ift.tt/2mWH4pB
, including Google Compute Engine, Google Cloud Storage and BigQuery.
Come by and say hello at HIMSS
There have been a lot of developments in our work in healthcare over the last year. We’re excited to be back at HIMSS and looking forward to working with everyone there. Stop by our booth and check out our sessions if you’re at HIMSS this week.
Source : The Official Google Blog via Source information
0 notes
Text
With iOS 11.3, Apple appears to unite sufferers and their healthcare knowledge
New Post has been published on https://takenews.net/with-ios-11-3-apple-appears-to-unite-sufferers-and-their-healthcare-knowledge/
With iOS 11.3, Apple appears to unite sufferers and their healthcare knowledge
Apple has introduced that its upcoming iOS 11.three launch will permit sufferers to view digital medical information (EMRs) and different scientific details about themselves on iPhones and iPads.
Apple’s new Well being Information function makes use of the prevailing Well being app (launched in 2014 on iOS eight) to allow medical services to attach through an API to their EMR methods to share knowledge between suppliers and sufferers.
The brand new Well being Report function is at the moment accessible to the sufferers of 12 hospital methods through the iOS 11.3 beta, in line with Apple.
“Within the coming months, extra medical services will connect with Well being Information providing their sufferers entry to this function,” Apple stated in its announcement.
The medical services which have signed on to beta check the Well being Report function embody:
Final 12 months, constructing on its well being informatics platform, Apple launched HealthKit, a developer API that was a part of the iOS software program improvement package; it allowed third-party builders to create functions that can be utilized by the Well being app.
Final week, Apple introduced the replace to the Well being app with the iOS 11.three beta, enabling cellular customers to see EMRs on their iPhone. The up to date Well being Information part throughout the Well being app brings collectively hospitals, clinics and the prevailing app to make it straightforward for customers to see accessible medical knowledge from a number of suppliers at any time when they select.
John Halamka, CIO at CareGroup Healthcare System and CIO and affiliate dean for academic know-how at Harvard Medical College, stated EMR sharing will generally be solely between healthcare suppliers and generally be supplier to affected person and again to supplier.
In a provider-to-provider state of affairs, a radiologist could share data with a heart specialist, for instance. Within the provider-to-patient-to-provider state of affairs, a doctor could share check outcomes with a affected person and the affected person could then schedule a follow-up appointment.
“Apple is considerably accelerating the provider-to-patient-to-provider strategy with iOS 11.three,” Halamka stated through electronic mail.
The Well being Info Know-how for Financial and Medical Well being (HITECH) Act of 2009 required all healthcare services to roll out EMRs and show by Significant Use requirements that they had been functioning as required.
Whereas Significant Use requirements required each EHR have a affected person portal, the information weren’t simply shared between disparate healthcare services.
“You probably have 5 suppliers, you most likely have 5 portals,” Halamka stated.
Thus, every time a affected person needs to see healthcare data, they need to log into a number of portals.
Apple’s new Well being Information function will allow customers to see their accessible medical knowledge from a number of suppliers, at any time when they select – eliminating the necessity for a number of logins.
Apple just isn’t the one supplier to roll out cellular entry to EMRs.
Westmed Medical Group, a 500 supplier multi-specialty medical group in Westchester County, N.Y. and Fairfield County, Conn., not too long ago rolled out the Bridge Affected person Portal Model 2.zero and the Universe mHealth App from Universe mHealth LLC.
The applying permits sufferers to not solely view their EMRs, ship messages to healthcare suppliers, view lab outcomes and handle appointments and refills, but additionally permits them to pay payments through a PCI-compliant cost service from TrustCommerce. The options can be utilized through an iOS and Android cellular app.
When Westmed initially rolled out the EMR portal in October, it did include just a few “glitches,” in line with Merin Joseph, CIO at Westmed. For instance, some messaging to sufferers was getting caught in spam folders as a result of they had been being marked by electronic mail apps as vendor lists.
“So far as the portal itself, it took time to course of,” Joseph stated. “Proper now, I believe it is working the way it’s designed to and we’ll proceed to work with it to reinforce options.”
Westmed expects to start its advertising marketing campaign this month to let its sufferers know in regards to the options now accessible to them through their good telephones, tablets and laptops.
Apple’s idea is to leverage the Quick Healthcare Interoperability Sources (FHIR) interface, a set of requirements that may quickly be accessible in each main EHR to consolidate lifetime scientific information from completely different suppliers on cellular gadgets, Halamka stated.
“Placing the affected person on the heart of their care by enabling them to direct and management their very own well being information has been a spotlight for us at Cedars-Sinai for a while,” Darren Dworkin, CIO at Cedars-Sinai, stated in an announcement. “We’re thrilled to see Apple taking the lead on this house by enabling entry for customers to their medical data on their iPhones.”
Previously, customers have voiced worry round one thing as private as a medical report being launched in digital type. Healthcare data is arguably probably the most delicate knowledge there’s as a result of as soon as it is disclosed, it may be utilized by cyber criminals for nefarious functions for a lifetime.
A 2016 examine by the Brookings Institute confirmed that since late 2009, the medical data of greater than 155 million People has been uncovered with out their permission by about 1,500 breaches.
The prospect of healthcare knowledge being shared through Apple on cellular gadgets may exacerbate these issues.
Halamka identified, nevertheless, that no knowledge will probably be saved by Apple.
“All knowledge will probably be encrypted and biometrically secured (fingerprint or facial recognition) in your cellphone,” Halamka stated. “Sufferers would resolve what knowledge to share with what apps.”
Sufferers from taking part medical establishments could have data from numerous establishments organized into one view and get common notifications about their lab outcomes, situations, immunizations, medicines, procedures and very important stats. Sufferers will obtain notifications when their knowledge is up to date.
“Streamlining data sharing between sufferers and their caregivers can go a good distance in the direction of making the affected person expertise a optimistic one,” Stephanie Reel, CIO at Johns Hopkins Drugs, stated in an announcement. “That is why we’re enthusiastic about working with Apple to make accessing safe medical information from an iPhone as easy for a affected person as checking electronic mail.”
This story, “With iOS 11.three, Apple appears to unite sufferers and their healthcare knowledge” was initially revealed by Computerworld.
0 notes