#FrameInterpolation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
3LCD Epson Home Cinema 3700 projector Review

In fact, the 3LCD Epson Home Cinema 3700 (EH-TW6700 in Europe) began a continuation of a series of low-cost models for home theater and home entertainment. As known, in 2015, Epson introduced Epson Home Cinema 2040/2045 (1920x1080, 2200 ANSI lm) and 740HD (1280x720, 3000 ANSI lm) projectors are all priced well under $ 1,000. Then, in 2017, the company expanded this series with 3100/3700 models. The Epson 3700 costs $ 200 more compared to 3100 and has a built-in speaker. Both models have almost identical specs and design.

Compared with previous Epson 2040/2045, Epson 3700 provides higher brightness, better contrast and color accuracy, an increased zoom range (1.6x instead of 1.2x), and an extended vertical / horizontal lens shift range. In addition, it supports advanced features, including Super Resolution mode, gamma adjustment, picture-in-picture mode, and manual adjustment of the convergence of three chips. In fact, this set of functions corresponds to the functionality of Epson 3900. But the Epson 3900 costs $ 500 more. Of course, this factor significantly affects the choice of the projector. Projector supports 2D to 3D conversion and two color modes in 3D. One mode provides a higher brightness, but has a slight green bias. The other mode provides more natural colors, but with a lower brightness. For comparison, many models of this price segment have only maximum brightness by default for loss compensation in 3D glasses. The stereoscopic image uses the frame interleaving mode. Model supports any RF glasses. Additionally, model has a VGA input and two HDMI inputs, one of which supports an MHL connection. The USB port (type A) provides connectivity for external media and an optional Wi-Fi adapter.
Epson Home Cinema 3700
Projector provides dynamic contrast ratio of 70,000: 1 (full on/off) without auto iris and darkening using software algorithms. In fact, such a contrast corresponds to level of the DLP projectors of this price segment. But, of course, without the traditional for the DLP technology, the rainbow effect. Model brightness reaches of 3000 ANSI lm. It provides a high-quality image even in a room with scattered daylight and the excellent 3D image quality, despite the brightness loss due to 3D glasses. The projector has two built-in stereo speakers of 10 W.

As know, Epson 3700 has a Throw Ratio of 1.34: 1 - 2.17: 1 (D:W). Its throw distance ranges from 6,2 to 17 ft, and image size from 40" to 180". Projector provides 100" diagonal screen at distance of lens between 9,5 and 16 ft.

Projector has a good 1.6: 1 zoom and convenient manual lens shift adjustment, which reaches of ±24% and ±60% horizontal & vertical, respectively. Keystone Correction reaches of ±30 degrees (Auto) and ±30 degrees (Slide bar) horizontal & vertical, respectively. Epson Image Enhancement Technology (Super Resolution Technology) visually increases the image detail and is designed for high-quality content (for example, from Blu-ray discs).

Additionally, the frame interpolation function provides a 60 fps effect for content with 24 fps and improves the playback quality of highly dynamic scenes.
Features, Pros & Cons
Projector uses Epson 3LCD 3-chip technology, Epson Polysilicon TFT Active Matrix, 0.61- inch wide panel with MLA. The color saturation and black level provide a sufficiently high image quality. Epson Home Cinema 3700 has 4 preset color modes, including Dynamic, Bright cinema, Natural and Cinema. The range of brightness values for different modes (High, Medium and Eco) varies from 2306 to 3438 for Dynamic, from 1653 to 2465 for Bright cinema, from 1736 to 2588 for Medium and from 1635 to 2439 for Eco. Bright Cinema mode provides fairly accurate color rendering on a 225" screen in a darkened room or on a 140" screen with moderate lighting. Dynamic mode is well suited for presentations, providing an acceptable quality at a maximum brightness of 3700 lm. Lens in the long focus reduces the brightness by only 8% compared to the wide-angle mode. The brightness uniformity reaches of 86%. Of course, the color brightness corresponds to the brightness of the white due to use of 3LCD technology. Unfortunately, Input lag is 28 ms without frame interpolation, but reaches 105 when on. Pros - very good picture quality; - remote control with backlight; - high contrast; - two color modes for 3D; - two built-in stereo speakers of 10 W; - zoom of 1.6: 1; - very low brightness reduction in the long-focal position of the lens; - two HDMI inputs (including MHL); - support of Picture-in-Picture, Full HD 3D, Geometric Correction and Frame Interpolation. Cons - relatively high noise level; - delay in automatic iris control; - noise during Auto Iris work; - very high Input lag with Frame Interpolation; - both color modes in 3D have drawbacks (distortion of color rendering or insufficient brightness); - the controversial placement of speakers on back panel. This video illustrates a very high image quality directly on the beige wall without a screen. Read the full article
#3LCDEpsonHomeCinema3700projector#EpsonEH-TW6700#EpsonHomeCinema2040#EpsonHomeCinema2045#EpsonHomeCinema3100#EpsonHomeCinema740HD#EpsonImageEnhancementTechnology#EpsonPolysiliconTFTActiveMatrix#FrameInterpolation#GeometricCorrection#KeystoneCorrection#Picture-in-Picture#SuperResolutionTechnology
0 notes
Text
What is refresh rate in modern TVs

Modern television uses the latest innovative technologies. As a result, their description contains a large number of technical terms and concepts. As a consequence, many users often confuse them. In addition, the description from companies often contains a marketing component, which additionally distorts objective information.
Refresh rate and FPS
The confusion with the screen refresh rate and frame rate due to the same unit of measurement (frames per second) and the similarity of their physical values (information density per unit of time) well illustrates this problem. But they characterize different values. The screen refresh rate corresponds to the maximum number of frames played by the TV per second. In other words, a screen with a frequency of 60 Hz reproduces the image 60 times per second. In fact, the refresh rate of the LCD screen characterizes the frequency of the signals coming to the matrix with information about the color change of the pixels. That is, this value characterizes the objective ability of the device to reproduce frames. Thus, a 50 Hz screen displays the 60 FPS video with lossy. Frame frequency or Frames Per Second (FPS) or Frame Rate or Frame Frequency characterizes the number of frames replaced per second in video content, that is, the shooting technology. This concept was first used by photographer Eadweard Muybridge, who experimented with chronophotographic shooting the moving objects with several cameras. Thus, the difference between these values can be formulated as follows: FPS characterizes the number of frames per second of a video content, and the screen refresh rate determines the possibility of its playback on a particular TV screen. Of course, the optimal choice requires taking into account this aspect. Probably, an expensive display with a frequency of 100 Hz and above will be unnecessarily redundant for playing 25 FPS video content. The video at the end illustrates in detail the difference between these specs.
Modern TVs
In general, modern LED TVs use IPS matrices or their modifications. They provide good color rendering up to 99% and wide viewing angles of 178 ° vertically and horizontally. The response of the modern IPS matrix is about 5 ms. Thus, it plays a maximum of 1000 ms / 5 ms = 200 frames per second. But really, the response time can reach 7 milliseconds. Today, manufacturers install 3 types of matrixes on TVs: - matrix with a frequency of 60 fps; - matrices with a frequency of 120 fps (most common); - matrix with a frequency of 240 fps (usually in expensive models). Today video content for various standards supports: - 1080i - interlaced standard with a frame rate of 25 or 30 (29.97) fps; - 1080p - standard with progressive scanning, allowing the use of 24, 25, 30, 50 or 60 fps; - 720p - standard with progressive (line-by-line) scanning, allowing the use of 50 or 60 fps; - SD - standard digital television 50 or 60 fps; - Analog signal - 25 fps.
Frame interpolation
Refresh rate directly affects the smooth reproduction of high-dynamic scenes and the screen flickering. Accordingly, its increase improves smoothness and reduces flicker. Today, companies solve this task by hardware or by using special processing algorithms (frame interpolation).

Frame interpolation forms additional intermediate frames in video content. Today, almost all segment leaders use their own technologies. The list of indices and technologies of dynamic scenes from different companies includes: - Clear motion rate (CMR), Picture Quality Index (PQI) – Samsung;

- Picture Mastering Index (PMI) - LG; - Perfect Motion Rate (PMR) - Philips; - Motionflow XR – Sony;

- Active Motion & Resolution(AMR) - Toshiba; - Backlight scanning BLS - Panasonic; - Clear Motion Index (CMI) - Thomson; - Subfield Motion - Samsung plazma. Unfortunately, companies use different index calculation methods. Accordingly, TVs without an index of dynamic scenes reproduce an image with a frame rate of the input signal, without its correction or improvement. But today, such models are found only in the budget segment.
Indices of dynamic scenes
TVs with an index of dynamic scenes 100 improve the image by adding 1 frame between the existing two (frame interpolation). Usually, additional virtual frames are identical to the original. In this case, increasing the frequency reduces flicker. Thus, a 60 Hz matrix with an index of 100 visualizes an improvement only for video content with a frequency of less than 60. The index of dynamic scenes 200 is virtually identical to the previous, but uses an improved image processing algorithm by the processor. TVs with a 120 Hz matrix typically support a 400-600 index. They generate 2-3 additional frames between the original ones. The format of the generated frames (identical or different) depends on the processing algorithm. Given the use of identical processors for the indices 100 and 400, it can be assumed that they are identical. Additionally, models with such indices necessarily use local dimming. Theoretically, this technology provides an improvement even for UHD, but many users do not confirm this in their feedback and comments. Models with with support for 800-1200 index use expensive matrices and high-performance processors that provide frame analysis and the creation of new intermediate real frames. According to TV owners, the visualization of improved playback of high-dynamic scenes is present between models with indices 100 and 200, but disappears at indices 400 or 600. Therefore, many experts consider the indexing to be partially marketing. Of course, interpolation requires perfect processing algorithms. Otherwise, inaccurate conversion or generation of intermediate frames reduces the quality of the final image due to digital artifacts. Therefore, increasing the frequency significantly increases the requirements for processing algorithms.
Features
Unfortunately, some companies incorrectly use the concept of 200 Hz. Honest dynamic image enhancement technology uses motion interpolation, generating additional frames. Other a cheaper and less efficient technology uses Scanning Backlight technology, which reduces motion blur. Such TVs with pseudo 200 Hz mode and Scanning Backlight technology actually provide frame refreshing only with 100 Hz. In this case, the control system divides the screen into three parts horizontally and periodically on / off backlight. Next, the TV adds a dark rectangle to the image on the screen, that moves across the screen at a frequency of 100 times per second, creating the illusion of playback with 200 Hz. Periodically dimming the backlight reduces the blurring effect of a moving object, increasing the sharpness of the contours in intermediate frames. Additionally, this technology reduces power consumption. But, of course, Scanning Backlight is radically different from the real frequency of 200 Hz and has significant drawbacks. In particular, it reduces the overall brightness of the image and increases the flicker of the screen. The test mode of such images illustrates the difference between real 200 Hz and Scanning Backlight.

Although, of course, the lower cost partially compensates for this nuance.
Conclusion
Today, models of the world's leading electronics companies, including Samsung, LG and Sony, provide real 200 fps with the help of powerful high-performance video processors. Such TVs correctly form up to three intermediate frames between consecutive frames of a standard 50 Hz video content. As a result, the 200 Hz provides excellent detail even for the complex maneuver of a football player or fast boxer attack.

In addition, TVs with a refresh rate of 200 Hz are great for gamers. Unfortunately, all such models belong to the upper price segment. Of course, the refresh rate is one of the important criteria for choosing a TV. Read the full article
#ActiveMotion&Resolution(AMR)#BacklightscanningBLS#ClearMotionIndex(CMI)#Clearmotionrate(CMR)#dynamicscenesindices#FPS#FrameInterpolation#framerate#IPSmatrix#MotionflowXR#PerfectMotionRate(PMR)#PictureMasteringIndex(PMI)#PictureQualityIndex(PQI)#Refreshrate#responsetime#SubfieldMotion
0 notes
Text
Features of settings for Motion-Compensated Frame Interpolation when connecting the TV to a PC
Correct settings when connecting the TV to a PC significantly affect the playback quality. Basically, they depend on the algorithm of video signal processing. Usually, modern LCD TVs of the middle price range provide a frequency of up to 100-200 Hz. An increase in frequency is achieved by interpolation of frames. But companies use different names for this technology. For example, this technology is called True Motion in LG TVs, Motion Plus in Samsung TVs, Perfect Natural Motion in Philips TVs or Real Cinema in Panasonic TVs.
Operation principle
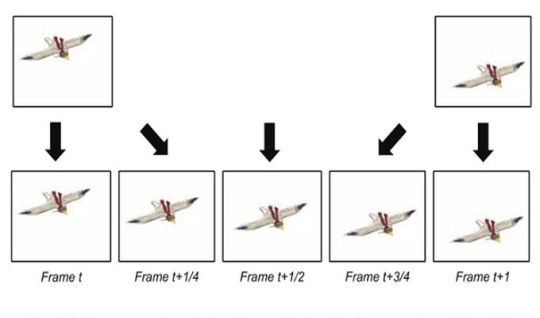
The TV receives input signals with a frequency, for example, 50 Hz, forms an additional intermediate frame from two adjacent frames and then plays back all frames, including the newly formed one.
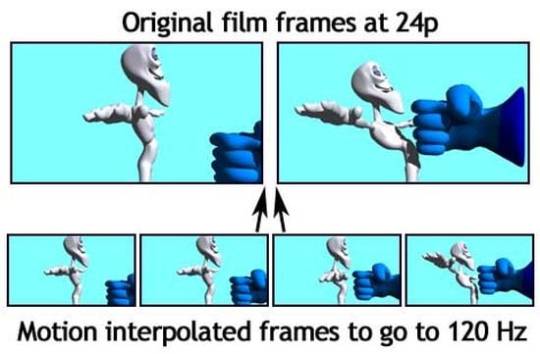
Accordingly, the frequency increases, for example, to 100 Hz. This process is called anti-aliasing and ensures smooth and realistic video playback. Interpolation algorithm reproduces incoming frames with a delay, calculating the offset difference between neighboring frames to create its own intermediate image. CPU calculates scene, object displacement, background and other parameters with the help of appropriate algorithms and creates frame on the basis of these parameters. It's designed to smoothing the transition between neighboring frames at the entrance. This effect becomes noticeable at panoramic shooting with offset of background. The intermediate frame reduces this offset between frames. Interpolation provides the smoother playback, increasing it by 2-4 times.
Playback with PC video card
PC has a video card with a HDMI yield. The maximum frequency of transmission for HDMI cable is 60 Hz in 1080p resolution. Most modern digital movies typically have a frequency ~ 24 frames / second. The video card of PC also generates an intermediate image with the help of video CPU and software. This process is as follows. PC increases a frequency with 24 Hz to 50 Hz. After that, the image is directed to the TV input. TV is trying increase the frequency up to 100 Hz. As a result, the image on the screen starts to "float". It accelerates, slows down or "hangs" for a second. Of course, viewing video in this mode is very inconvenient. The problem is double video processing. Processing algorithms on PC and TV are not synchronized that leads to a chaotic sequence of their work.
Decision
Turning off anti-aliasing in the TV at first glance seems like an obvious solution to this problem. But the TV creates an image with a frequency of 100 Hz, and the computer’s video card only provides up to 50 Hz. Thus, disabling an image processing on a computer is more efficient. This is done as follows. The auto-tuning function of the image frequency at the output of the player is switched. This option ensures that the output frequency matches the original video file frequency. In this mode, the player determines the frame rate at the input (24 Hz) and automatically converts the HDMI video output at this frequency. As a result, the TV receives a video stream at a rate of 24 frames per second without preliminary processing. The anti-aliasing mode on the TV provides image playback without jerks and braking. This method is great for video playback. But the interface and the program will work slowly because of switching the image frequency to 24 Hz. This setting is performed by the videoplayer (for example, the XBMC-player has this function) or using an autofrequency program.
This video demonstrates MCFI operation principle. Read the full article
#FrameInterpolation#MotionPlus#Motion-CompensatedFrameInterpolation#PerfectNaturalMotion#RealCinema#TrueMotion
0 notes
Text
Adjusting the optimal TV settings

Of course, the playback quality is one of the main criteria for choosing a TV. It, in turn, depends on the technical characteristics of the model and on the settings. Some of them are complex and require special equipment for calibration. But many basic settings are easily performed by the user themselves using the settings menu and test pattern. Optimum adjustment of TV settings significantly affects the image quality. Brightness, Sharpness and color / saturation are some of the basic parameters of the image.
Brightness
This value characterizes the maximum possible level of white in the center of the screen, is measured in candelas per square meter (1cd / mВІ = 1nit) and is one of the most important characteristics of a TV. It provides a comfortable viewing in any external lighting, for example, in daylight or electric lighting. A modern TV provides normal image quality with a minimum brightness of 250 cd / square meter or higher. This value should be directly proportional to the screen diagonal. For example, 250 cd / square meter is enough for a 19" model, but a 36" TV requires already 500 cd / square meter. The backlight brightness behind of crystals does not affects on the image brightness. The image brightness depends on the crystals quality, their location and from correct adjust of polarizing filters. Thus, the electronics significantly affects on value of this parameter. Brightness setting regulates primarily black level. Special pattern test image is intended for the correct setting this parameter. All gradations of black should be clearly distinguished. The left diagram corresponds to the correct brightness setting, and the right diagram shows a non-optimal setting of this value.

Sharpness
Correct setting of this parameter provides an equally sharp image for any viewing distance. Sharpness test image is designed for adjustment of this parameter. Setup is as follows: - the user is located on a comfortable for him the distance from TV; - the Sharpness test image is displayed on the TV screen.

- its value increases to the maximum or until the appearance of artifacts due to excessive sharpness, which manifests itself as bright halos around objects and thickening for fine lines; - the value is reduced to the disappearance of artifacts. This sharpness is optimal.
Saturation
The correct setting of this parameter is difficult without a special device for calibration. However, this can be done with the help of photographs. It's carried out by the following algorithm. High-quality photos of nature with the different shades of green are displayed on the TV screen.

Green color is the most preferred due to maximum sensitivity of the eyes to it. Additionally, the many TVs reproduce this color with a maximum distortion. Next, the color / saturation value is adjusted before the maximum image realism. User can also to adjust this parameter with the help of high-quality people photos. In this case, the natural skin tone is the criterion of the settings correctness.
Motion-Compensated Frame Interpolation (MCFI)
This technology is designed to smooth out the playback of dynamic scenes and is based on the formation of intermediate frames.

Correct use of frame interpolation is important when connecting the TV to a PC. The maximum playback quality is achieved when anti-aliasing in the TV is turned on and the image processing in the PC is turned off. Adjusting picture settings LG TV is perfectly illustrated in this video. Read the full article
#FrameInterpolation#MCFI#Motion-CompensatedFrameInterpolation#optimalTVsettings#Saturation#Sharpness
0 notes
Text
TV settings

Many consumers pay attention to the differences in the playback quality of TVs in stores. This is especially noticeable during simultaneous work of several TVs on one channel. Unfortunately, modern TV manufacturers primarily are interested in increasing sales. Therefore, the optimal pre-settings are not a priority for some companies. Manufacturers often try to present in their TVs maximally "bright blue" and "red" colors, increasing the brightness of these colors. Marketers know that the buyers majority choose the brightest TVs or models with maximally deep color. However, the most TVs provide the similar playback quality when properly setting. This factor can be useful in choosing the optimal TV.
Main settings
The calibration provades the maximum correct image playback. This method uses a reference image at the TV input. The values of reference image parameters are compared with the image on the screen. Complex Delta E characterizes the deviation degree from standard color. For example, Delta E = 0 corresponds to the ideal setting. The reference colors are very deep, bright and saturated. A calorimeter provides a measure of the color temperature of the output signal. Specialist achieves of the images identity on the screen with reference colors during the calibration process. Only top models usually provide full calibration. Typically, Delta E value after calibration is 2-3. The human eyes do not perceive such distortion. However, this calibration is laborious, requires knowledge and equipment. The TVs are adjusted before the maximum possible identity to international standards. The TV must minimally to distort the original content that is always created on basis of standards or recommendations. Correct playback of the sky at sunset, skin color of actor and the image details provides realness. Abbreviations PAL, NTSC or HDTV are designation of these standards. They contain requirements and recommendations to the video signal parameters and the allowable values of various image parameters. Most of the standards are outdated after the HDTV emergence. Today OLED TVs provide maximum color gamut.
Main technical values
Values of main settings: - color temperature of 6500K (D65); 6500 K is the approximate color temperature of the midday sun. White objects under such light have a certain color. - gamma correction; Gamma coefficient determines the ratio between the numerical value of the pixel and its actual luminosity. Correctly set gamma correction provides proportional reproduction of halftones in the whole range. The recommended value is 2.22 (or 2.4 in the darkened room); - brightness; Brightness provides clarity and saturation of the image in external lighting. The recommended brightness of about 120 cd / sq.m. A list of settings that do not require the use of special hardware settings includes: - Picture Mode (Standard / Dynamic / cinema); - mode of color temperature (cool / normal / warm); - tripping of some settings; - contrast; - brightness; - sharpness; - color / saturation; - Motion-Compensated Frame Interpolation (MCFI). This video shows the image settings of the TV. Read the full article
0 notes