#Hosni Mubarak
Text

3 notes
·
View notes
Link
0 notes
Text
2012-Life imprisonment

Former Egyptian President Hosni Mubarak is sentenced to life imprisonment for his role in the killing of demonstrators during the 2011 Egyptian revolution.
0 notes
Text
Downsized: New York Times replaces Thomas Friedman with ChatBot Cairo Taxi Driver
By Yuval Weiss
Last Updated 5/15/2023 at 11:45 PM
Manhattan: In a cost-cutting move described as Boomer Abuse Bold & Decisive, the New York Times decided today to replace longtime pundit Thomas Friedman’s weekly column with the transcripts of a Cairo Taxi Driver Chatbot. “This is really about eliminating the Middle Man.” explained editor Joseph Kahn. “For the last 40 years, Mr. Friedman has based…

View On WordPress
#Ahmed the Chatbot Taxi Driver#Barack Obama#Bibi#Bill Clinton#Binyamin Netanyahu#Cairo#chatbot#Egypt#Hosni Mubarak#Israel#Israeli Politics#King Hussein#New York Times#The World is Flat#Thomas Friedman#Yuval Weiss
0 notes
Text

The Arab Spring had a significant impact on Egypt, with widespread protests and consequent regime change. The impact of the Arab spring still affects Egypt in several ways today, for example:
The Arab Spring led to overthrow of President Hosni Mubarak after 30 years in power, and subsequently, his successor, President Mohamed Morsi, was also ousted. This political instability has left Egypt in a fragile political state, with frequent protests and disruptions to the economy.
Also, the Arab Spring brought about a sense of social empowerment among egyptians, creating a more vocal and politically active society. However, it also led to tensions between different groups, including religious and ethnic minorities, and between secular and Islamists.
Overall, the Arab Spring has left a lasting impact on Egypt, and the country continues to face challenges related to governance, economics and social cohesion.
0 notes
Text
Israel Says It Should Mediate Peace in Sudan, the Sudanese People Disagree
Israel has offered to mediate the conflict raging in Sudan. This piece at Mondoweiss explains its interest, why Sudan finally and fully joining the Abraham Accords is so important to Israel, and how this whole episode is about sidelining the will of the Sudanese people, both in their fight for democracy and their solidarity with the Palestinians.

View On WordPress
#Abdalla Hamdok#Abdel-Fattah Al-Burhan#Abraham Accords#al-Qaeda#Benjamin Netanyahu#Donald Trump#Hemedti#Hosni Mubarak#Joe Biden#Khartoum#Libya#Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo#Mohammed Morsi#Omar al-Bashir#Osama Bin Laden#Palestinians#Rapid Support Forces#Sudan#Three No&039;s#United Arab Emirates
0 notes
Text

Hàppy 79th birthday hosni Mubarak on January 1 2008ad rat year
0 notes
Note
hey could I ask where I could learn more about the arab spring? I can’t find many resources and most of them are very American. I’m asking partially because my parents mentioned a massacre that happened at a mosque around that time, but I can’t find much of that? They used to study in Egypt which is why they were horrified to hear about the brutality those years ago. Sorry if this sounds disrespectful you can ignore it if so. I just want to better understand the unrest in Egypt that I assume is still ongoing today with Sisi
hi sweetheart <3 this isn't disrespectful at all don't worry
unfortunately i don't really have any specific resources i can point you towards that aren't riddled with usamerican propaganda or leave out key details but i remember reading this article from a while back and it was pretty succinct. read it with a discerning eye and lmk if you have any further questions about the points they raised
the massacre your parents are referencing is probably the Rabaa massacre which happened in august of 2013, the biggest massacre in modern egyptian history. military and police forces killed an estimated 1000 protestors, most of whom were supporters of the muslim brotherhood, some others were simply opposed to the military regaining power.
the main key points you need to understand about egypt's modern history, contemporary history, and the arab spring as a whole, are the following:
egypt had been effectively ruled by a military ruling class since the 50's. nasser's presidency oversaw anti-imperialist policies and policies favoring the working class, but he basically laid out groundwork for 70+ years of military dictatorship
anwar al saddat's presidency involved lots of dramatic changes to our domestic and foreign policies, namely privatization of many sectors, introducing neoliberalism to the country, signing the camp david agreements with israel
mubarak's presidency was essentially a 30 years long continuation of sadat's neoliberalism and corruption, things got worse by the day for your average working class egyptian
the 2011 25th of january revolution in egypt was sparked due to worsening living conditions, and protests igniting many of the neighboring countries. namely tunisia, where street vendor mohammed bouazizi self immolated in protest of harassment he had been receiving from government officials.
it's important to note here that even before the protests in tunisia, there had been dissent from the egyptian working class, many factory workers went on strikes in protest such as in mahalla
the 2011 revolution was not ideologically coherent, in the sense that everyone, from all different political ideologies joined in, from the Muslim brotherhood to leftist coalitions. this will be important for understanding why it fell short of achieving long term goals. it managed to force hosni mubarak to step down
the MB's candidate, mohammed morsi won the 2012 elections, which sparked a lot of upheaval from leftists, liberals and religious minorities such as copts.
in june of 2013, mass protests broke out against his regime demanding that he step down from power, the us-backed military hijacked the protests and enacted a coup which reinstalled the military regime with sisi as president. protestors of the new regime, whether in support of morsi or not, were massacred in Rabaa and other locations leaving an estimated 1000 protestors dead
it's important to note here that it was later revealed that certain groups which were involved in the 2013 counter-revolution were funded and backed by gulf states (mainly the UAE iirc, i need to fact check that though). there was a marked increase in organized violence from these groups (tamarod was one of them) out of nowhere and it all played out in the military's favor in the end, which isn't a coincidence considering who are their biggest allies in the region. i don't think this was covered in the article above
there has been unprecedented efforts of censorship in the country since then, a complete crackdown on dissent. journalists get jailed for tweeting things opposed to the regime all the time. egyptian prisons (which aren't exactly known to be the most humane) are filled with political prisoners. this current regime is the one the US and their gulf allies backed and endorsed, we get billions of dollars in military aid from the US in exchange for carrying out their imperialist interests in the middle east. as for living conditions, it only gets worse by the day for your average egyptian. most major cities are riddled with slums, inflation is through the roof, unemployment is high, most people can barely afford basic necessities, our infrastructure is in desperate need of maintenance and renovations, our economy is almost entirely financed by the US (even putting military aid aside), the UAE, and saudi arabia. and we're drowning in debt. we take imf loans like, every other month lmfao it's bad
a lot happened within the span of 3 years, this is all not to say that the MB were good, not in the slightest. but the US once again interfering with a foreign country's domestic affairs to secure their interests has resulted in nothing but devastation for the overwhelming majority of the people living here.
as for the arab spring as a whole, i think it's disingenuous when people dismiss its entirety as western backed conflict. even though a lot of it is exactly that (see: libya), especially in countries where the revolutions kind of bled into them rather than already having brewing tensions from working class people suffering worsening conditions. in tunisia and egypt, there was already a lot unrest within their populations over material conditions, which is why i mentioned the mahalla strikes. it's a shame our revolution didn't have more coherent, stronger socialist organizers, it's a shame it was killed and hijacked before we ever got to reap its benefits
#egypt#inbox#phd in yappology over here jesus christ😭#this is as concise as i can summarize everything but do lmk if you have any questions about certain details!#25jan
42 notes
·
View notes
Text

Egyptian security forces dispersed a Gaza solidarity protest outside the headquarters of UN Women in Cairo on Tuesday and detained several activists who took part, according to local media and activists.
Police forces detained most of the protesters, including Mahienour el-Masry, Lobna Darwish, Rasha Azab, Ragya Omran, Mai el-Mahdy, Israa Yusuf and Farida al-Hifny, according to Egyptian activist Ahmed Douma.
During the demonstration, the protesters read a letter addressed to the UN agency for gender equality and women's empowerment, condemning the human rights violations and war crimes affecting women in Gaza and Sudan as a result of the conflicts there.
"Dear UN Women, we are a group of Egyptian women appalled by the atrocities committed against our sisters in Gaza as a result of the Israeli genocidal war on the Palestinian people since 7 October," the letter read.
"We are also appalled by the failure of the UN to protect the two peoples from the ongoing war crimes, especially sexual crimes, and in particular equivocating between the victims and culprits," it added.
The letter accused UN Women of "discriminating against women in Gaza and Sudan" by failing to stand up for them. It also called on the UN agency to carry out investigations into alleged sexual crimes and war crimes against women in the affected areas. Middle East Eye has contacted UN Women for comment.
The police action on Tuesday is not the first time protesters in Egypt have been detained for taking part in protests about Gaza. Egypt has effectively banned protests since President Abdel Fattah el-Sisi came to power over a decade ago, and security forces routinely suppress any anti-government activity.
Security forces have detained dozens of pro-Palestine protesters since 20 October, when thousands took part in a rally in Cairo's iconic Tahrir Square, which was the epicentre of the revolution that culminated in the resignation of President Hosni Mubarak in 2011. Following the crackdown on that gathering, protests have been smaller in size and have been quickly dispersed by security officials.
On 30 November, four international activists were detained and held incommunicado for over 27 hours, following a pro-Palestine protest outside the Egyptian foreign ministry in Cairo.
They had staged a rally to demand security clearance for the Global Conscience Convoy, a humanitarian convoy into Gaza planned by Egypt's Journalists' Syndicate, to deliver badly needed aid. Security forces also dispersed a women's pro-Palestine protest in Cairo on 8 March, which coincided with International Women's Day. On 4 April, authorities detained at least 10 protesters at a vigil outside the Journalists' Syndicate in Cairo, denouncing the Egyptian government's role in the siege on Gaza
#egypt#free Palestine#free gaza#I stand with Palestine#Gaza#Palestine#Gazaunderattack#Palestinian Genocide#Gaza Genocide#end the occupation#Israel is an illegal occupier#Israel is committing genocide#Israel is committing war crimes#Israel is a terrorist state#Israel is a war criminal#Israel is an apartheid state#Israel is evil#Israeli war crimes#Israeli terrorism#IOF Terrorism#Israel kills babies#Israel kills children#Israel kills innocents#Israel is a murder state#Israeli Terrorists#Israeli war criminals#Boycott Israel#Israel kills journalists#Israel kills kids#Israel murders innocents
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
U.S. President Joe Biden talked about democracy vs. autocracy a lot in his early days in office. This was an attempt to reinvigorate democracy as a source of American soft power. The Russian invasion of Ukraine was an opportunity to drive home the message of this new geopolitical challenge to surmount. The democracy summits were an attempt to build on Biden’s vision, even though they were flawed in their criteria of which countries to include. Nevertheless, the third democracy summit in Seoul has drowned in the fog of the Israel-Hamas war. The administration’s management of the crisis has acted as a wrecking ball on the framework it was trying to build. While the United States has repeatedly blocked attempts at a permanent cease-fire, China is appealing to the global south by acknowledging the Palestinian right to armed resistance at the International Court of Justice. Allowing the conflict to drag on will keep discrediting the United States, elevate the standing of China and Russia, and undermine the prospects of democracy globally. And current events in Egypt, a historic strategic partner to the United States, showcase the consequences of this inertia.
An initial commitment to democracy in the Middle East came from then-President George W. Bush. In 2005, pressure from Bush’s administration resulted in Egypt’s first competitive presidential election, marking a significant shift in its political landscape. (Before that date, presidents renewed their mandate through referenda.) This first election gave a new life to the first movement that defied then-President Hosni Mubarak’s grip over power, Kifaya (Arabic for “enough”). A new generation became politically engaged, and, according to V-Dem datasets, there was a rise in participation in independent political associations. This new generation led Egypt’s revolution in 2011.
Barack Obama’s speech at Cairo University in 2009 was a rare moment when an American president visiting an Arab country was warmly welcomed. He promised a “new beginning” with the Muslim world after the shocking invasion of Iraq by Bush’s administration. The peak alignment with America’s calls for democracy happened during the Arab Spring of 2011, when the youth in Tahrir Square agitated to overthrow Mubarak with Obama’s support.
When Abdel Fattah al-Sisi took power in 2014, he identified Egypt’s evolving civil society, along with the Muslim Brotherhood, as threats he needed to take down in order to avoid a fate like Mubarak’s. Sisi’s regime has been characterized by a crackdown on dissent, with civil society actors who align with Western values of human rights and democracy labeled as traitors. The United States has come under continuous attack by state-sponsored media as a sponsor of chaos in the region; this propaganda in turn has worked to discredit the Western model of democracy. Meanwhile, former U.S. President Donald Trump’s favorite dictator received little pushback from an administration that did not have democracy on its agenda.
Over the same period, relations with Russia and China have grown stronger. While Mubarak maintained a good relationship with Moscow, Russia’s presence in Egypt mainly came through grain exports and tourism. Since Sisi took power in 2014, Cairo’s pivot toward Moscow was highlighted by the agreement in 2015 for Rosatom to build the first nuclear power plant on Egyptian soil—one of Russia’s most critical strategic wins in the region. Egypt’s reaction to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine involved a provisional agreement to supply rockets to Russia and refusing to block its airspace to Russian fighter jets. Sisi justified this stance when he met American House Intelligence Committee leaders in Cairo: “When the U.S. conditions some of its arms sales and shipments to Egypt, what do you really want me to do?” (Jim Himes, the committee’s ranking member, recounted this interaction with Sisi in an interview with CNN.) The U.S. has, since Obama, been putting conditions to uphold human rights on its aid to Egypt, which is the second-largest recipient of U.S. military assistance after Israel. Although blocks on aid usually involve a small proportion of the $1.3 billion sent annually, China and Russia offer arms deals with no such strings attached.
Cairo, too, has been moving closer to Beijing over the past decade, with Chinese investments increasing by more than 317 percent from 2017 to 2022. Because of the growing Chinese maritime presence in Egyptian ports, Egypt anticipates substantial Chinese investments in the Suez Canal region. Besides rapidly growing trade with China, Egypt’s government has had its state media adopt a Chinese propaganda narrative, organized bilateral leadership programs with the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), and allowed for Chinese expansion in the telecommunications sector and cyberspace. Only faint liberal voices within the minimal independent media space challenged the Egyptian official narrative that has championed China as a model of autocratic economic development.
Enclaves of activists and civil society leaders in Egypt and abroad have continued to challenge the Sisi regime, primarily through social media, and to support all those oppressed and imprisoned by him. Their pressures began to yield some results after Biden took office. His administration extended a show of support by highlighting human rights abuses in Department of State reports and withholding a small portion of military aid. Although the United States refused to increase the amount of withheld aid as called for by international human rights organizations, this helped ease some pressure on Egyptian activists. In 2022, and ahead of COP27 in Sharm El-Sheikh, and in an attempt to improve its image in response to the mounting U.S. pressure, Egypt released a considerable number of political prisoners, the issued a national human rights strategy, and establishmed a national dialogue between the regime and the opposition figures who remained inside Egypt. The results of these concessions were minimal, and some, like the human rights strategy and the dialogue, were merely cosmetic maneuvers. Nevertheless, they all happened after incoming U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken openly criticized the arrest of staffers from the Egyptian Initiative for Personal Rights (EIPR) and Biden excluded Egypt from the democracy summits. Egyptian activists understood that any wins, however limited, could be achieved through U.S. support. This was particularly evident in campaigns to release high-profile prisoners like Alaa Abdel Fattah. The war in Gaza has severely compromised this premise.
The Biden administration’s backing of Israel and the repeated American vetoes used in the U.N. Security Council to prevent a permanent cease-fire have slashed the United States’ popularity in Egypt to 9 percent, compared with 46 percent for China, as shown in a survey by the Washington Institute for Near East Policy. The acute rise in anti-American sentiment is not the only result of what the public perceives as hypocrisy and double standards in America’s approach to the conflict. As shown by the survey, a more alarming consequence is the prevalence of distrust in the Western model of democracy and human rights, increasingly perceived as mere rhetorical tools deployed by the United States when human rights align with U.S. interest. Revealing the extent to which this view has been adopted by the public, in its latest release the most famous Egyptian rock band, Cairokee, sang about a double-faced America that doesn’t value Palestinian lives as opposed to those of “white angels.”
What about Europe? Can it pick up America’s slack? Europe once supported democracy and human rights in Egypt, as evidenced by the resolution issued by the European Parliament in 2022 urging EU member states to support a monitoring and reporting mechanism on grave human rights violations in Egypt. But once the war in Gaza began, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen pledged to support Sisi through financial aid packages to mitigate the refugee influx expected from Gaza—and to prevent new waves of migration to Europe.
Arab democracy and human rights advocates made it clear that they parted ways with the Western stance of support for Israel and stood firmly in solidarity with the Palestinians. As a result, human rights organizations have risked support from their partners in the West, and many have become even more isolated in their struggle under repressive regimes. For instance, Germany recently withheld funding for the anti-trafficking program of the Centre for Egyptian Women’s Legal Assistance (CEWLA) as a punishment to its head of the board of trustees, the award-winning human rights defender Azza Soliman, for signing a statement calling for the end of the war in Gaza and supporting the boycotting of the occupation. In solidarity, EIPR stopped all cooperation with the German government. The only winners from the weakening of civil rights organizations in Egypt are the authoritarians.
China and Russia have positioned themselves very well to capitalize on these developments. They did not rely solely on their official statements and positions in support of the ceasefire in the U.N. Security Council, which has already enhanced their image considerably with the Arab public, as detected by the Washington Institute survey. The China in Arabic account on the X platform exemplifies how China is seizing the opportunity to spread anti-American rhetoric. The account spreads pro-Chinese and anti-Western propaganda in Arabic to more than 580,000 followers.
Moscow is already cashing in on these gains by hosting Palestinian factions, including Hamas, for reconciliation talks. China sees in the conflict an opportunity to expand its geopolitical role in the region while the United States is bogged down with Iranian proxies in Syria, Iraq, and the Red Sea, and it reaps political wins from the Houthi Red Sea attacks, which spare Chinese vessels and crew members. But those who have gained the most from the anti-American sentiment are the autocratic regimes of the region.
Sisi is relieved to have secured his third presidential term through a sham election. He blocked his main rival, Ahmed Tantawi, from running, and sentenced him after the election to a one-year suspended prison sentence and a ban from running in parliamentary elections for five years. Instead of calling out such violations, Western pressures were focused on mitigating the effects of the war and having an active Egyptian role in the day-after scenario despite its internal vulnerabilities. Nationalist and religious rhetoric has prevailed, even among activists on social media.
The United States needs to move fast to restore its image globally. This requires promptly ending the devastating war in Gaza and adopting a fair and balanced approach to the Middle East conflict. Promoting democracy should be repositioned at the center of American foreign policy to counter the global rise in authoritarianism championed by China and Russia. In parallel, measures should be taken to nudge autocratic allies in the region toward political reform. Economic and trade incentives should be linked to structural economic and political reforms. Judicial reform and unequivocal implementation of the rule of law should be mandated to guarantee the long-term efficacy of economic aid packages, as well as to extend solid support to freedom fighters unwilling to relinquish their struggles for democracy.
Pundits have criticized the Biden administration’s autocracy-vs.-democracy framework as an impractical approach to the geopolitical contest with China. Yet democratization and upholding human rights remain essential soft powers. Autocrats like Sisi already prefer aligning with China, who absolve them from any commitment to human rights. With support for China growing, displays of hard power such as military showdowns and trade wars will become the main arenas for competition.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
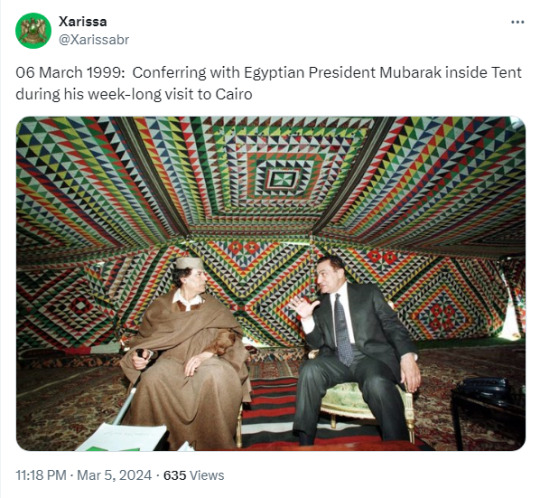
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Results of Arab Spring.
The Arab Spring was a series of anti-government protests, uprisings, and armed rebellions that spread across much of the Arab world in the early 2010s. It began in response to corruption and economic stagnation and was first started in Tunisia. From Tunisia, the protests then spread to five other countries: Libya, Egypt, Yemen, Syria, and Bahrain, where either the ruler was deposed (Zine El Abidine Ben Ali, Muammar Gaddafi, Hosni Mubarak, and Ali Abdullah Saleh) or major uprisings and social violence occurred including riots, civil wars, or insurgencies. Sustained street demonstrations took place in Morocco, Iraq, Algeria, Iranian Khuzestan, Lebanon, Jordan, Kuwait, Oman, and Sudan. Minor protests took place in Djibouti, Mauritania, Palestine, Saudi Arabia, and the Moroccan-occupied Western Sahara.
145 notes
·
View notes
Link
0 notes
Text
contrariwise, there is clear significance to the Emperor Julianus perishing at war with the Magians, and by a spear wound, which the Christians later attributed to their dead god Mercurius
also apparently said Mercurius has recently been attributed with secretly turning Hosni Mubarak to Christendom @_@
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Lev Koufax and John Parker
The Popular Socialist Alliance Party (SPAP) is one of many organizations working in conjunction with the Egyptian Journalists Syndicate to organize the Global Conscience Convoy to the Rafah crossing to Gaza. It was founded in the wake of the Egyptian Revolution of 2011, after the merger of several socialist organizations that faced repression under U.S.-backed dictator Hosni Mubarak.
#Egypt#Cairo#global conscience convoy#SPAP#socialist#OpenRafahCrossing#solidarity#internationalism#class struggle#workers#GazaUnderAttack#John Parker#Struggle La Lucha
4 notes
·
View notes
