#IoT Division
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
IoT development solutions for hospitals in South Africa Revolutionize healthcare in South Africa with Mobiloitte's IoT Development Solutions tailored for hospitals. Our cutting-edge technology enhances patient care, streamlines operations, and improves resource management. Monitor equipment, ensure patient safety, and reduce costs with our user-friendly solutions. Embrace innovation and deliver world-class healthcare. Partner with Mobiloitte, your trusted South African IoT development experts.

#IoT Development Solutions#Integrating IoT#IoT Services#IoT & Emerging Technologies#IoT Solutions for Smart Applications#IoT Division#Product Development Channel#IoT Automation Solutions#IoT systems#IoT Solutions for Education#iot in gaming#iot in biotechnology#iot solutions for hotels#iot in hospitality industry#smart home iot solutions#iot solutions for transportation#blockchain iot app development company#blockchain iot software development company#IoT application development services
0 notes
Text
What has Google killed lately
IoT products.
Last year, the teams responsible for Pixel hardware and Android software were merged into one division, and Google today announced a “voluntary exit program” for employees working in the Platforms & Devices group.
SVP Rick Osterloh sent out a memo to employees this morning about the “voluntary exit program,” and the company confirmed to 9to5Google that this is happening.
This program applies to US employees working on Platforms & Devices, which includes Android (Auto, TV, Wear OS, XR), Chrome, ChromeOS, Google Photos, Google One, Pixel, Fitbit, and Nest. Google has many people around the world working on these products, but today’s announcement is just for those stateside.
Meanwhile, this is not a company-wide offer that applies to Search, AI, or other groups, though Alphabet’s new CFO last October said “driving further efficiencies” was a key priority.
Separately, software and hardware were already two very large organizations, with some overlap. Now that things have settled in recent months, employees have a better idea of their roles. Osterloh said the division received questions about the possibility of voluntary exits since the Pixel-Android merger. Not offering people the option to leave in advance was a complaint about how Google handled past layoffs.
The memo frames this exit program as being beneficial for those who might not be aligned or passionate about the combined organization’s mission or are having difficulty with their roles, and hybrid working requirements.
In leaving Google, employees will get a severance package, with more details internally coming soon. From what we learned, this change does not coincide with any product roadmap changes.
Before the merger, the Google hardware division last January switched to a functional organization model where there is one team (and leader) for teams like hardware engineering across Pixel, Nest, and Fitbit. At the same time, a few hundred roles were cut. The broader unification in April was designed to “speed up decision-making” internally.
In offering this program today, Google wants employees “to be deeply committed to our mission and focused on building great products, with speed and efficiency.” The statement also makes reference to “tremendous momentum” and “so much important work ahead.” Google’s full statement is below.
The Platforms & Devices team is offering a voluntary exit program that provides US-based Googlers working on this team the ability to voluntarily leave the company with a severance package. This comes after we brought two large organizations together last year. There’s tremendous momentum on this team and with so much important work ahead, we want everyone to be deeply committed to our mission and focused on building great products, with speed and efficiency.
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
So here's something that someone said to me a few days ago which seems kind of obvious once you've heard it, but which merits mention nonetheless: In the past, before the world wars, inventions were made primarily by individual inventors or small groups of inventors looking to apply them to actual human concerns; now, new technologies come about largely through industrial r & d divisions, and were made specifically to boost shareholder value. The present seems bewildering and the future unknowable and kind of horrifying because huge sociotechnical transformations like AI and IoT are being driven not by actual human concerns or desires, but purely by the interests of capital. Human agency is no longer in the driver's seat, and we are going somewhere that most of us very much do not want to go. It's the difference between the late-Victorian inventor-hero and cyberpunk.
Anyways, we need to seize the means of invention.
320 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is a Foundry? Why It’s the Key to Chip Manufacturing

In the heart of the global electronics industry lies a quiet giant—the semiconductor foundry. While companies like Apple, NVIDIA, and Qualcomm design the chips that power your favorite devices, it's the foundries that physically bring those designs to life. But what exactly is a foundry, and why is it so critical to chip manufacturing?
What is a Semiconductor Foundry?
A semiconductor foundry, or simply "foundry," is a manufacturing facility that fabricates integrated circuits (ICs). These ICs, also known as microchips or chips, are the brains behind modern electronics—everything from smartphones and laptops to cars and industrial machinery.
Foundries specialize in manufacturing chips designed by other companies, a business model known as pure-play foundry. For example, TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company) is the world’s largest and most advanced foundry, producing chips for tech giants without competing with them in design.
There are also IDMs (Integrated Device Manufacturers) like Intel, which both design and manufacture their own chips. However, the pure-play foundry model has become dominant due to the increasing complexity and cost of chip manufacturing.
The Role of a Foundry in Chip Manufacturing
Chip design is only half the equation. Once a design is finalized using software and simulations, it must be turned into physical silicon wafers through a meticulous and highly precise process involving:
Photolithography: Transferring microscopic circuit patterns onto silicon.
Etching and Deposition: Carving and layering materials to form transistors and interconnects.
Ion Implantation: Modifying electrical properties at the atomic level.
Packaging and Testing: Encasing chips and validating their performance.
This process takes place in ultra-clean, billion-dollar facilities where even a speck of dust can ruin a chip. Foundries provide the scale, expertise, and cleanroom environments necessary to execute this complex task at nanometer precision.
Why Foundries Are the Key to the Chip Industry
Enabling Innovation Through Specialization Foundries allow fabless companies (those that only design chips) to focus on innovation without the burden of operating expensive fabrication plants. This division of labor has accelerated technological progress.
Advanced Process Technology Leading foundries invest billions into R&D and process nodes (like 5nm, 3nm, or 2nm technology), pushing the boundaries of performance and power efficiency.
Scalability and Global Supply Foundries serve a wide range of industries: consumer electronics, automotive, medical, aerospace, and more. Their capacity and scalability make them vital to maintaining the global tech supply chain.
Geopolitical and Economic Importance Countries now consider foundries as strategic assets, essential for national security and economic resilience. Supply chain disruptions in recent years have spotlighted their critical role.
Conclusion
Foundries are the unsung heroes of the digital era. While designers craft the vision for future chips, it’s the foundries that make those visions a reality with unmatched precision and scale. As chip demands surge across AI, IoT, and 5G, the importance of foundries in the semiconductor ecosystem will only grow.
Whether you're holding a smartphone or driving a smart vehicle, chances are a chip built in a foundry is powering the experience—quietly but powerfully behind the scenes.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Boeing F-15EX completes first phase of integrated testing
Fernando Valduga By Fernando Valduga 09/14/2023 - 11:00am in Military
The F-15EX recently completed the first phase of its initial operational test and evaluation (IT&E) program with the launch of an AGM-158 joint air-surface missile (JASSM), the highest-range air-to-ground missile in the U.S. Department of Defense combat inventory.
The JASSM has a range of about 230 miles, according to a U.S. Air Force information leaflet.
The F-15EX is the first U.S. Air Force aircraft to undergo an integrated program of tests and evaluations. The combination of the IOT&E and DOT&E effort is unique to the program, in that the existing test data of the legacy F-15C/D and F-15E can be compared with the data from the new EX, with a special focus on the new features unique to EX, such as its advanced processor and fly-by-wire control system. The EX also has more weapon stations than the F-15E, allowing it to carry more war material.
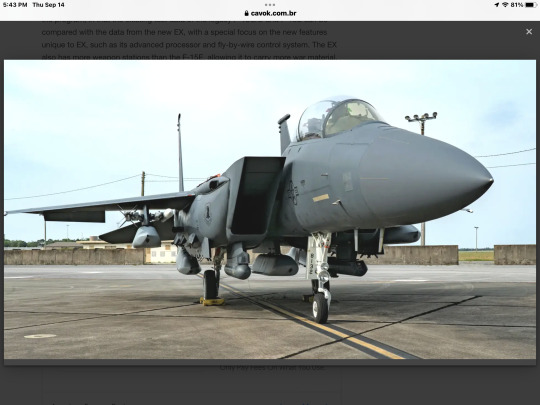

In November 2022 tests, the F-15EX demonstrated that it can carry up to 12 AIM-120 AMRAAM air-to-air missiles.
“Proving the ability of the F-15EX to employ three JASSMs after witnessing the validation of the air-to-air domain paper with a load of 12 AMRAAM that it can fire is incredible,” said Major Calvin Conner, commander of the F-15 division of the 85º Test and Evaluation Squadron. "The firepower that four F-15EX jets bring to a combatant commander is tremendous."
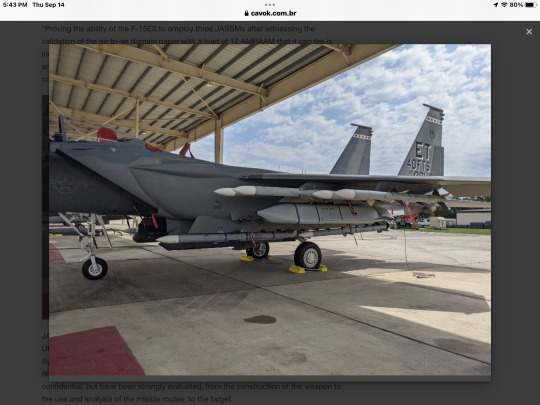

JASSM was launched during the Combat Hammer exercise, held at Hill Air Base in Utah in August. The shot was performed simultaneously with the 53ª Wing Weapon System Evaluation Program, which required a collaborative effort between the 83º and 86º Fighter Weapon Squadrons. The details of the shot - the targets, ranges, etc. - are confidential, but have been strongly evaluated, from the construction of the weapon to the use and analysis of the missile routes, to the target.
"This test shows innovation and results in the rapid delivery of state-of-the-art capabilities to the fighter. That's exactly what our fighters need from us," said Mark Sears, vice president of Boeing Fighters. "The F-15EX is the most affordable and immediate way to renew the capacity and upgrade the capabilities of the U.S. Air Force and we are ready to deliver additional aircraft later this year."
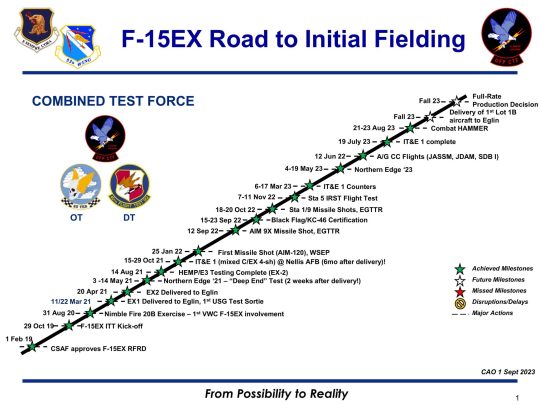
With Phase I of the F-15EX IT&E completed, the data from this phase will be analyzed for the final report to guide a total production decision determination in the coming months.
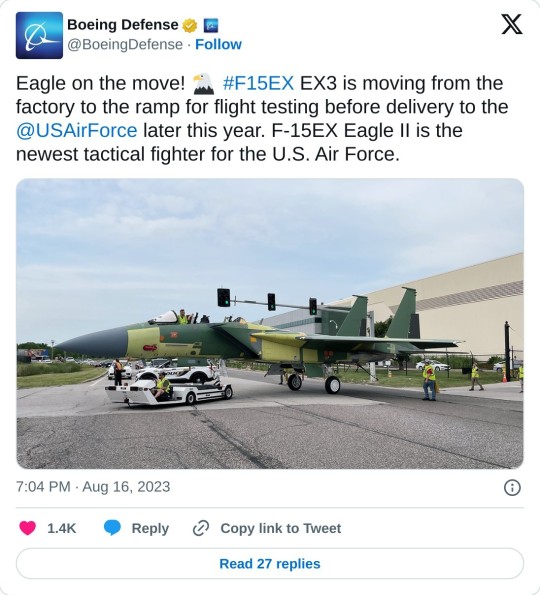
The U.S. Air Force plans to buy 104 F-15EX fighters, although this number could rise to 110 if some changes to the 2024 fiscal year defense bill are enacted.
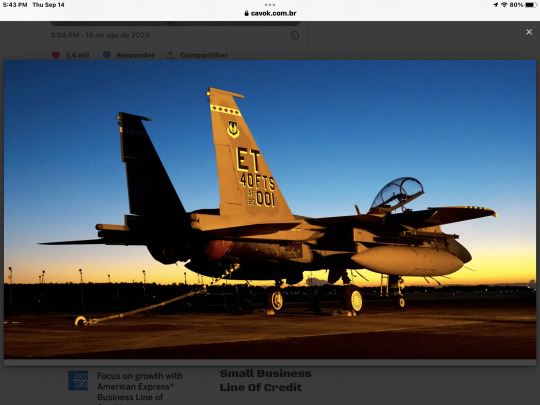
Boeing begins delivering fighters with combat capability to U.S. Air Force squads later this year.
Tags: Military AviationBoeingF-15EXUSAF - United States Air Force / U.S. Air Force
Sharing
tweet
Fernando Valduga
Fernando Valduga
Aviation photographer and pilot since 1992, he has participated in several events and air operations, such as Cruzex, AirVenture, Daytona Airshow and FIDAE. He has work published in specialized aviation magazines in Brazil and abroad. Uses Canon equipment during his photographic work throughout the world of aviation.
Related news
F-35A Lightning II fighter of the Republic of Korea Air Force (RoKAF). (Photo: Liz Lutz / Lockheed Martin)
MILITARY
Approved the purchase of 25 more F-35 fighters by South Korea
14/09/2023 - 08:37
MILITARY
Airbus delivers first C295 aircraft to India
13/09/2023 - 19:18
HELICOPTERS
Lockheed Martin offers Black Hawk to request new medium helicopter from the United Kingdom
13/09/2023 - 18:59
Arrival of the first B-52 at the Boeing unit in San Antonio, Texas, for AESA radar installation.
MILITARY
Raytheon delivers first AESA radar to Boeing for B-52 modernization
09/13/2023 - 16:00
The high-altitude, long-lived RQ-4D Phoenix unmanned aircraft are launched and controlled from Sigonella Air Base in Sicily. (Photo: NATO)
MILITARY
UKRAINE: NATO Drone Unit provided hundreds of flight hours collecting critical information
09/13/2023 - 14:00
BRAZIL
IMAGES: How the FAB is acting in support of those affected by the flood in RS
09/13/2023 - 1:00 PM
10 notes
·
View notes
Text



Looking forward to China’s industrial development prospects in the next 10 years
Looking forward to China's industrial development in the next 10 years, analysis and predictions can be made based on existing development trends, policy orientations and the global economic environment:
Industrial upgrading and structural optimization:
China will continue to promote the upgrading of its industrial structure from labor-intensive to technology- and capital-intensive. Mid- to high-end manufacturing will be the key development direction, including aerospace, high-end equipment, new energy vehicles, new materials and other fields. With the deepening implementation of the "Made in China 2025" strategy and subsequent planning, China will accelerate the in-depth integration of industrialization and informatization, and promote the development of emerging industries such as intelligent manufacturing and the industrial Internet. Innovation drive and technological progress:
Against the background of intensified global technological competition, China will further increase investment in technological innovation, especially in fields such as 5G, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), quantum information, and biotechnology, to enhance the core competitiveness of the industry. Industry 4.0 related technologies and digital transformation will become mainstream. Enterprises will improve production efficiency and product quality through automation and intelligent transformation, and achieve personalized customization and flexible production. Green and sustainable development:
Environmental protection policies are becoming stricter, and low-carbon economy and circular economy will have a profound impact on the path of industrial development. China's industry will be committed to energy conservation and emission reduction, clean production, and the development of green manufacturing systems, such as new energy, energy-saving and environmental protection equipment and services.
Globalization and industrial chain reconstruction:
Taking into account the rise of trade protectionism and the adjustment trend of global supply chains, Chinese industry will actively build independent and controllable industrial and supply chains, seek a higher position in the global value chain, and enhance international competitiveness. While low-end industries are being transferred, China will strengthen international cooperation in some areas, actively participate in the global industrial division of labor, and build international brands and multinational companies. Talent training and system reform:
Facing the challenge of aging, China will pay more attention to the cultivation and introduction of talents, improve the quality of the labor force, especially the construction of highly skilled talent teams, to support the development needs of high-end industries. Deepen institutional reform, create a better business environment, encourage innovation and entrepreneurship, promote the development of small, medium and micro enterprises, and stimulate market vitality. To sum up, in the next ten years, China's industry will focus on high-quality development, focus on technological innovation, industrial chain upgrading, green development and improvement of global competitiveness, and strive to achieve the leap from a manufacturing country to a manufacturing power. At the same time, we will also respond to the challenges brought about by changes in the internal and external environments, continue to deepen reforms, and ensure the stable and healthy development of the industrial economy.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
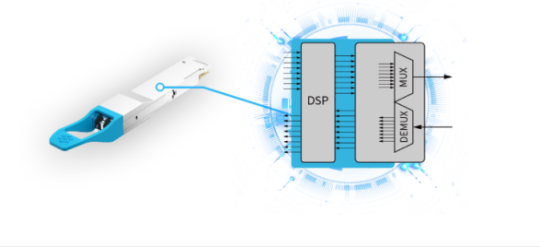
Closer Look at 400G QSFP-DD Optical Transceiver Module
Recent years have seen the evolution towards the 5G, Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing, increasing pressure on data centers to ramp up both network capacity to 400G and driving providers to search for new solutions to achieve their 400G Data Center Interconnects (DCIs). 400G QSFP-DD optical transceiver module is becoming one of the most popular cutting-edge 400G DCI solutions. This article will provide a basic understanding of QSFP-DD optical transceiver modules.

What is the QSFP-DD Optical Transceiver Module?
Quad small form-factor pluggable-double density (QSFP-DD) is designed with eight lanes that operate at up to 25 Gbps via NRZ modulation or 50 Gbps via PAM4 modulation. It supports data rates of 200 Gbps or 400 Gbps and doubles the density. QSFP-DD is backward compatible with current 40G and 100G QSFPs. It is compliant with IEEE802.3bs and QSFP-DD MSA standards. QSFP-DD is available in single-mode (SM) and multi-mode (MM) fiber optic cables and includes digital diagnostics monitoring (DDM) to monitor parameters such as power, temperature, and voltage.

Types of 400G QSFP-DD Optical Transceiver Module
400G SR8 QSFP-DD
400G SR8 QSFP-DD optical transceiver module is suitable for short-distance interconnection or multi-channel data communication. The transmission rate is up to 425Gbps, and the central wavelength is 850nm. The transmission distance is up to 70m or 100m through multi-mode OM3 and OM4 fiber.
400G DR4 QSFP-DD
400G DR4 QSFP-DD optical transceiver module achieves the transmission over single-mode fiber (SMF) with an MPO-12 connector. It supports a max transmission distance of 500m on SMF.
400G FR4 QSFP-DD
400G FR4 QSFP-DD optical transceiver module supports link lengths of up to 2km SMF with a duplex LC connector. It uses wavelength division multiplexing(CWDM ) technology, eight channels of 53Gbps PAM4 signals on the electrical side, and four channels of 106Gbps PAM4 signals on the optical side, which is twice the rate of the electrical side.
400G LR4 QSFP-DD
400G LR4 QSFP-DD optical transceiver module is designed with a built-in Gearbox chip that multiplexes the two channels' electrical input data into a single-channel outputs signal and then modulates it to the optical receiver end. The digital signal processor (DSP) basis gearbox converts eight channels of 25GBaud PAM4 signals into four channels of 50GBaud (PAM4) over an SMF cable with duplex LC connectors. It supports a transmission distance of up to 10km.
400G LR8 QSFP-DD
The 400GBASE-LR8 optical transceiver module supports link lengths of up to 10km over a standard pair of G.652 SMF with duplex LC connectors.
400G ER8 QSFP-DD
The 400G ER8 QSFP-DD optical transceiver module supports link lengths of up to 40km over a standard pair of G.652 SMF with duplex LC connectors.
400G ER4 QSFP-DD
400G ER4 QSFP-DD optical transceiver module supports link lengths of up to 40km over a standard pair of G.652 SMF with duplex LC connectors. It has only four wavelengths for 4 LAN WDM channels 1295.56/1300.05/1304.58/1309.14nm.
Advantages of 400G QSFP-DD Optical Transceiver Module
Backward compatibility: Allowing the QSFP-DD to support existing QSFP modules (QSFP+, QSFP28, QSFP56, etc.). It provides flexibility for end-users and system designers.
Adopting the 2x1 stacked integrated cage/connector to support the one-high cage connector and two-high stack cage connector system.
SMT connector and 1xN cage design: Enable thermal support of at least 12W per module. The higher thermal reduces the requirement for heat dissipation capabilities of transceivers, thus reducing some unnecessary costs.
ASIC design: Supporting multiple interface rates and fully backward compatible with QSFP+ and QSFP28 modules, thus reducing port and equipment deployment costs.
Applications
400G QSFP-DD optical transceiver module is used in 400G Ethernet, data centers, telecommunications networks, cloud networks, Infiniband interconnects, high-performance computing networks, 5G, 4K video, IoT, etc.
Conclusion
400G QSFP-DD optical transceiver module offers high speed, performance, scalability, and low power in 400G Ethernet. Sun Telecom specializes in providing one-stop total fiber optic solutions for all fiber optic application industries worldwide. Contact us if any needs.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Railcar Mover Market
Railcar Mover Market size was valued at approximately $1524.6 million in 2023. This market is projected to grow to $183.0 million by 2031 with a CAGR of 3.7%.
🔗 𝐆𝐞𝐭 𝐑𝐎𝐈-𝐟𝐨𝐜𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐝 𝐢𝐧𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐭𝐬 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝟐𝟎𝟐𝟓-𝟐𝟎𝟑𝟏 → 𝐃𝐨𝐰𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐚𝐝 𝐍𝐨𝐰
The global railcar mover market is poised for significant growth, driven by increasing demand for efficient rail logistics and advancements in sustainable transport solutions. In 2025, the market is projected to reach approximately USD 1.5 billion, expanding at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.2% through 2033.
This growth is fueled by the expansion of railway networks and the need for flexible railcar handling across industries such as freight, mining, and construction. Electric railcar movers are gaining traction due to their environmental benefits and operational efficiency, with the electric segment expected to reach USD 87.4 million in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 5.0% through 2033.
Key players in the market include Global Railcar Mover Group, Shuttlewagon /Nordco, CRRC, Drapeau, Colmar Technik, Dongda Power, and G. Zwiehoff. These companies are focusing on technological advancements, such as automation and IoT integration, to enhance product offerings and meet the evolving needs of the industry.
𝐓𝐨𝐩 𝐊𝐞𝐲 𝐏𝐥𝐚𝐲𝐞𝐫𝐬:
Stewart & Stevenson Power Products LLC — ADDA Division | Eastern Lift Truck Co., Inc. | Wiese USA | GNCO, Inc. | MH Equipment Company | EAGLE RAILCAR SERVICES | JSC «Dnipro Railcar Repair and Construction Plant» | GBW Railcar Services
#RailcarMover #RailLogistics #RailIndustry #TracksideSolutions #FreightMobility #RailEquipment #IndustrialTransport #SmartLogistics #TransportInnovation #RailTech #AutomationInRail

0 notes
Text
DESCRIBING THE NOVEL
◊ reference to memory
◊ position and bits
◊ information to its
◊ assembler and compiler
◊ MRB or MRA
◊ format or style
◊ Processor and memory
◊ position where N
◊ word while information
◊ subtraction or division
◊ assembler or compiler
◊ Time before Time
◊ operations and number
◊ Y or it
◊ MEC or IOT
◊ error or tape
◊ operation and maintenance
0 notes
Text
Kalkine Spotlight: S&P/ASX 300 Spotlight on Telstra Group (ASX:TLS) Amid Telecom Infrastructure Growth
Highlights:
Telstra Group continues its national telecommunications leadership across fixed and mobile services.
Expansion of 5G infrastructure and international subsea cable systems support operational reach.
Telstra is listed on the ASX 200 and also appears in the broader s&p/asx 300 index.
Telecommunication Sector Overview with S&P/ASX 300 Relevance Telstra Group (ASX:TLS) operates within the telecommunications sector, providing fixed-line, mobile, internet, and enterprise solutions across Australia and globally. The company is included in both the ASX 200 and the broader s&p/asx 300 index, reflecting its stature among Australia’s most prominent public companies. The s&p/asx 300 captures a wider spectrum of stocks based on float-adjusted market capitalisation, offering insight into the broader Australian equity landscape.
Telstra’s service network spans urban, regional, and remote areas, powered by extensive fibre optics, mobile towers, and satellite communication platforms. Its infrastructure underpins connectivity across various sectors, including education, finance, logistics, and government services. As digitalisation increases across regions, telecommunications remain central to national productivity and information flow.
5G Rollout and Network Expansion Telstra Group continues the rollout of its 5G network across metropolitan and regional zones. The implementation of 5G supports faster mobile data transfer, reduced latency, and improved device connectivity. This expansion strengthens the company's spectrum usage and backhaul transmission efficiency.
The deployment includes upgraded base stations, additional antennas, and core network adjustments. These upgrades accommodate both retail mobile use and enterprise-specific applications such as IoT deployment and machine-to-machine communications. Telstra’s investments in millimetre wave and mid-band spectrum bands support enhanced broadband experiences in high-traffic zones.
International Connectivity and Subsea Infrastructure In addition to domestic coverage, Telstra maintains a global footprint through its international subsea cable systems. These systems link Australia with Asia, the United States, and key Pacific regions, enabling transcontinental data traffic and cloud service integration. The company’s international arm plays a vital role in high-speed cross-border communication.
The Southern Cross and INDIGO cable systems form part of the infrastructure delivering high-capacity data routes. Strategic partnerships in these systems strengthen global bandwidth capacity, serving technology companies, financial firms, and digital content providers. Redundancy and routing diversity within these cables enhance service resilience.
Enterprise and Technology Services Telstra Enterprise serves medium and large businesses through cloud connectivity, managed services, and cybersecurity frameworks. The division supports digital transformation initiatives by enabling secure, scalable, and reliable network access. Services cater to sectors such as healthcare, transportation, mining, and public administration.
The enterprise segment integrates mobile, fixed, and hybrid IT platforms, offering end-to-end connectivity and support. These include software-defined networking, edge computing capabilities, and secure cloud gateways. Telstra’s partnerships with global technology providers support delivery of tailored network solutions across varied industry requirements.
Modernisation Strategy and Digital Innovation Telstra Group continues modernisation initiatives across its network and customer service platforms. Automation, AI integration, and real-time analytics have enhanced digital customer engagement. The company’s self-service portals, mobile apps, and chatbot systems streamline user interactions and fault management.
On the operational side, real-time network diagnostics, AI-enabled predictive maintenance, and centralised monitoring centres contribute to efficiency. Cloud-based support systems also allow for agile product updates, remote diagnostics, and centralised data storage across multiple regions. This modernised approach reflects evolving customer expectations and technology standards.
0 notes
Text
Mobiloitte’ IoT Application Development Services in South Africa Empower homes across South Africa with the future of smart living through Mobiloitte's IoT application development services. Our experts utilize IoT technologies like MQTT, IoT protocols, and cloud integration to create intuitive, energy-efficient, and secure smart home solutions. Experience heightened comfort, convenience, and energy savings. Choose Mobiloitte for cutting-edge IoT applications that enhance lifestyles across the nation.

#IoT Development Solutions#Integrating IoT#IoT Services#IoT & Emerging Technologies#IoT Solutions for Smart Applications#IoT Division#Product Development Channel#IoT Automation Solutions#IoT systems#IoT Solutions for Education#iot in gaming#iot in biotechnology#iot solutions for hotels#iot in hospitality industry#smart home iot solutions#iot solutions for transportation#blockchain iot app development company#blockchain iot software development company#IoT application development services
0 notes
Text
🔬 Igniting Innovation: The Research Culture at Sabaragamuwa University of Sri Lanka
When we think of a university, we often picture lecture halls and exams. But the true essence of higher education lies in the generation of knowledge, and Sabaragamuwa University of Sri Lanka (SUSL) is at the forefront of this mission. SUSL is not just a place for learning — it's a hub of innovation, inquiry, and impactful research.
🧠 Why Research Matters
Research is the cornerstone of progress. It’s how we solve problems, innovate technologies, and improve quality of life. SUSL recognizes this and has embedded a strong research-oriented culture across all faculties. From Computing and Technology to Agriculture, Social Sciences, and Applied Sciences, the university promotes both theoretical and applied research that contributes to national and global development.
🏛 Centers and Institutes of Research
SUSL hosts a variety of dedicated research centers and institutes that support academic inquiry and real-world innovation. These include:
Research and Publication Division – Coordinates university-wide research efforts.
Faculty Research Committees – Every faculty promotes research in its respective discipline.
International Relations Office (IRO) – Facilitates collaborative research projects with foreign institutions.
These entities not only fund and monitor research activities but also publish journals, host conferences, and connect students with external grants.
🔗 Explore research divisions and initiatives: 👉 SUSL Research Division
👩💻 Research in the Faculty of Computing
As a Computing undergraduate at SUSL, I’ve seen how the faculty empowers students to conduct real-world research in areas such as:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Data Science and Big Data
Cybersecurity
Software Engineering
Internet of Things (IoT)
Undergraduate students are required to complete a final-year research project, which is reviewed by both academics and industry professionals. Some students even get the chance to present their work at local and international conferences.
🔗 Find more info about the Faculty of Computing: 👉 Faculty of Computing
🌱 Sustainability and Agricultural Research
SUSL’s Faculty of Agricultural Sciences is another area where research shines. From sustainable farming to food security and climate-resilient crops, the faculty collaborates with ministries, NGOs, and international bodies to address global agricultural challenges.
Students are encouraged to get involved in field research, lab analysis, and policy-based studies, contributing meaningfully to the future of farming in Sri Lanka.
🔗 Learn more about agricultural studies: 👉 Faculty of Agricultural Sciences
🌏 Collaborations and Global Impact
SUSL has partnered with international universities in Japan, Germany, Australia, and China, enabling joint research programs, staff exchanges, and access to international funding.
These collaborations make SUSL students globally competitive and expose them to diverse research methodologies and advanced technologies.
🔗 View university’s international efforts: 👉 International Office – SUSL
🏆 Recognition and Publication
SUSL encourages publication in peer-reviewed journals, participation in symposiums, and submission of projects to national research exhibitions. Students and academics regularly win awards and recognition for their innovative contributions.
Furthermore, SUSL publishes its own academic journals which include research papers authored by both faculty and students.
🔗 Read about achievements and research events: 👉 SUSL Events & News
✨ Final Thoughts
The research culture at Sabaragamuwa University is not only thriving — it is empowering. Whether you're a student looking to explore your curiosity or an academic aiming to make a difference, SUSL offers the tools, mentorship, and platform to grow.
As a proud student here, I’ve seen how ideas turn into innovations and how research changes lives. And this is just the beginning.
🔗 Visit the official SUSL website: 👉 https://sab.ac.lk/
1 note
·
View note
Text

Multi-Core Optical Fiber: Redefining Bandwidth in a Compact Package | Fibrecross
The digital age has ushered in unprecedented demand for high-speed, high-capacity networks. From remote collaboration and cloud gaming to massive IoT deployments, our appetite for data only grows. Traditional single-core optical fibers—while reliable—are straining under this weight. Enter multi-core optical fiber (MCF), a technology that crams multiple light-carrying paths into one thin strand of glass, dramatically boosting capacity without demanding more duct space.
The Essentials of Multi-Core Fiber
Imagine a single-lane road suddenly becoming a multi-lane expressway inside the same tunnel. That’s the core idea: instead of one light-guide at the center, an MCF embeds several—often 4, 7, or 12—within the same cladding. Each “lane” (core) carries its own data stream, enabling space-division multiplexing (SDM) and multiplying total throughput.
Key design points include:
Core Arrangement: Symmetrical patterns (e.g., hexagonal clusters) ensure mechanical stability and uniform performance.
Crosstalk Control: Adequate spacing or refractive-index trenches keep light in its lane, minimizing interference.
Standard Footprint: Most MCFs retain the familiar 125 µm outer diameter so they fit existing cables and connectors—with the right adapters.

Why Networks Are Racing to Adopt MCF
Skyrocketing Traffic Video streaming, virtual reality, and 5G backhaul are pushing fiber links to their theoretical limits. MCF offers a near-term upgrade path without overhauling network routes.
Urban and Subsea Constraints In congested city ducts or undersea trenches, ripping and re-laying cable is prohibitively expensive. Adding cores, not cables, solves the space puzzle.
Energy and Cost Savings Fewer fiber strands and transceivers translate into lower power bills and reduced hardware expenses—an attractive proposition for sustainability-minded operators.
Future-Proofing As networks evolve toward software-defined, spatially multiplexed architectures, MCF becomes a foundational building block rather than a niche experiment.
Technical Hurdles and How They’re Being Solved
Splicing and Alignment Joining multiple cores requires sub-micron precision. Next-generation splicers with rotational alignment and real-time feedback are making installations smoother.
Connectors and Fan-In/Fan-Out Converting between single-core equipment and MCF requires fan-in/fan-out modules. Advances in 3D-printed waveguides and silicon photonics are paving the way for plug-and-play adapters.
Optical Amplification Standard EDFAs serve only one core. Researchers are developing multi-core amplifiers that pump all channels simultaneously, ensuring balanced gain across the fiber.
Standards and Ecosystem International bodies are defining MCF specs for core count, spacing, and performance metrics. As more vendors sign on, compatibility headaches will diminish.

What’s Next for Multi-Core Fiber?
The journey of MCF has only just begun. Here are some emerging directions to watch:
Higher Core Counts Beyond 12 cores, experimental fibers with 19, 36, or more lanes are under laboratory evaluation—each promising exponential capacity growth.
Mode-Multiplexed MCF Combining spatial cores with few-mode transmission inside each core could unlock even greater data densities, albeit with more complex signal processing.
Integrated Photonic Interfaces Photonic chips capable of routing, switching, and amplifying multi-core signals on a single silicon die will accelerate deployment in data centers and metro networks.
Green Networking As operators chase carbon-neutral goals, MCF’s efficiency gains—fewer lasers per bit—will become a core selling point.
Final Thoughts
Multi-core optical fiber represents a paradigm shift: instead of adding more cables, we add more lanes inside the same cable. For network architects wrestling with capacity crunches in crowded cities or deep beneath the ocean, MCF offers a smart alternative—one that leverages existing infrastructure while delivering tomorrow’s bandwidth today.
Whether you’re planning a hyperscale data center interconnect, upgrading metro rings, or building the next generation of submarine links, multi-core fiber deserves a central place in your strategy. Its blend of performance, efficiency, and scalability makes it uniquely suited to tackle the data deluge head-on—without bringing your network to a standstill.
0 notes
Text
Turning City Plans into Immersive 3D Vector Maps for Architecture Firms

3D Vector Maps for Architecture Firms
City planning has always been a critical process in shaping the urban experience. Whether it’s designing efficient transportation systems, allocating green spaces, or planning high-rise complexes, architecture firms rely heavily on visual tools to communicate ideas and envision development. Today, one tool stands out for its precision and immersive quality 3D Vector Maps.
By turning traditional 2D city plans into detailed 3D Map Illustration, architecture firms can visualize space, scale, and infrastructure with unmatched clarity. Let’s explore how immersive 3D vector maps are revolutionizing Architecture Illustration and what benefits they offer in modern urban planning.
What Are 3D Vector Maps?
3D vector maps are high-resolution digital representations of geographic and structural data, built using vector graphics rather than raster images. Unlike pixel-based maps, vector maps are scalable, editable, and interactive, making them perfect for dynamic architectural and urban projects.
When combined with 3D map illustration techniques, these maps evolve into layered, immersive models that allow stakeholders to zoom in, rotate, and explore city layouts in real-time. The result? More accurate planning, better client presentations, and fewer errors in execution.
From 2D City Plans to 3D Map Illustrations
Traditional city plans are often presented in 2D layouts—flat representations that show zoning, roadways, infrastructure, and plot divisions. That’s where 3D Map Illustration steps in.
Visualize elevations and topography
Place buildings and landmarks in spatial context
Simulate sun paths and shadows
Overlay zoning codes, utilities, and traffic systems
The transition is not merely aesthetic—it’s practical. 3D vector maps help architecture firms move beyond abstract drawings and into the realm of realistic, data-driven design.
Benefits for Architecture Firms
1. Enhanced Architecture Illustration
Instead of hand-drawn sketches or static renders, firms can offer clients an immersive tour through their proposed designs.
Features like interactive flyovers, real-time rendering, and zoomable details bring life to static plans. Whether for urban redevelopment or a new skyscraper, 3D map illustrations improve comprehension and engagement.
2. Improved Client Communication
Clients who aren’t trained in reading technical drawings often struggle to understand 2D plans. 3D Map Illustration translate those complex designs into accessible visuals. Architecture firms can now walk clients through every street, park, and tower in a proposed development using virtual maps.
This interactive communication eliminates ambiguity and builds trust, accelerating decision-making and approvals.
3. Faster Design Iterations
Need to move a residential block? Add a highway? Change the zoning layout? With 3D Vector Maps, edits can be made quickly without redrawing from scratch.
This saves time in the design phase and encourages more experimentation—ultimately leading to better urban solutions.
4. Integration with Smart City Technologies
Modern cities are embracing data-driven planning, and 3D Vector Maps serve as the foundation for smart city development. These maps can integrate with GIS (Geographic Information Systems), real-time traffic data, environmental sensors, and IoT devices to offer predictive insights.
Architecture firms that adopt 3D map illustration workflows position themselves at the forefront of smart city initiatives.
Key Use Cases
Urban Redevelopment
When city planners aim to revitalize an old district, 3D Map Illustration provide a clear before-and-after view. Historical data can be layered with new designs, showing how existing infrastructure adapts to modern needs.
Master Planning
Large-scale projects like university campuses, industrial zones, or sports complexes benefit from 3D Vector Maps by simulating how people, vehicles, and services will interact with the environment.
Infrastructure Design
Bridges, tunnels, and highways require detailed spatial planning. Vector-based 3D maps allow architects and engineers to understand gradients, elevation changes, and traffic flow in a visual context.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Mapping out water bodies, green spaces, and elevation levels helps firms predict the environmental impact of development. 3D map illustration tools can model drainage systems, erosion patterns, and sunlight distribution to guide sustainable designs.
Tools and Technologies Behind 3D Vector Mapping
The creation of 3D Vector Maps typically involves several software tools and data sources, such as:
GIS Data: Geographic Information Systems provide the base data, including terrain, land use, and infrastructure.
CAD Software: Tools like AutoCAD or Civil 3D help convert technical drawings into scalable 3D geometry.
3D Modeling Platforms: Software like SketchUp, Rhino, or Blender are used to build detailed models.
Vector Graphics Engines: Applications like Adobe Illustrator or Figma (with 3D plugins) allow designers to craft vector-based illustrations.
Rendering Engines: For lifelike visualization, rendering tools like Lumion or Twinmotion bring the 3D maps to life.
The seamless integration of these tools ensures architecture firms can deliver precise, visually engaging, and editable 3D visuals.
How to Get Started with 3D Map Illustration
If your architecture firm is ready to embrace 3D Map Illustration, here’s a step-by-step approach to get started:
Step 1: Collect Accurate Base Data
Precision at this stage ensures your vector map is accurate.
Step 2: Choose the Right Software Stack
Depending on your team’s expertise, choose tools that offer compatibility with 3D modeling and vector-based editing. Look for platforms that support collaborative workflows.
Step 3: Define the Layers
Break the map into logical layers—terrain, roads, utilities, buildings, vegetation, and more. This modular structure makes editing and analysis easier.
Step 4: Model in 3D
Using 3D software, convert your base layers into dimensional models. Apply real-world scales, textures, and lighting to create an immersive experience.
Step 5: Refine and Illustrate
Now comes the creative part—refining your 3D vector map with color coding, annotations, icons, and symbols.
Step 6: Render and Present
Export your map into interactive formats for web, video walkthroughs, or VR presentations. Make sure your output is optimized for both client review and internal decision-making.
The Future 3D Vector Maps
The future of Architecture Illustration lies in immersive, interactive experiences. As augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and real-time rendering become mainstream, 3D map illustrations will evolve from tools of presentation to tools of simulation.
Imagine city planners using VR goggles to explore a new district before laying a brick, or stakeholders manipulating buildings in real-time to optimize space usage. With 3D Vector Maps, that future is already unfolding.
Conclusion
In the competitive world of urban design and architecture, standing out means embracing innovation. 3D Map Illustration and 3D vector maps are no longer optional—they are essential tools that drive clarity, precision, and creativity.
By transforming 2D city plans into immersive 3D experiences, architecture firms can communicate ideas more effectively, design smarter, and contribute to the creation of more livable, sustainable cities. Whether you're designing a neighborhood or reimagining a skyline, it's time to bring your maps to life—one vector at a time.
0 notes
Text
Facilities Management Companies in Saudi Arabia: Driving Operational Excellence and Sustainability
In recent years, the demand for facilities management (FM) services has seen remarkable growth in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. This surge is fueled by rapid urban development, Vision 2030 initiatives, and increasing awareness about the importance of efficient building operations and maintenance. As cities expand and infrastructure projects become more complex, facilities management companies in Saudi Arabia are playing a critical role in ensuring that assets are maintained, environments are safe and sustainable, and operational costs are minimized.
What is Facilities Management? Facilities management encompasses a wide range of services designed to support the functionality, safety, and efficiency of the built environment. These services include hard FM (technical services such as HVAC maintenance, electrical systems, plumbing, etc.) and soft FM (non-technical services like cleaning, landscaping, security, and waste management). The goal of FM is not only to maintain the physical infrastructure but also to enhance the overall experience of those who use the facility—whether they are employees, customers, or residents.
The Role of Facilities Management in Saudi Arabia’s Development Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030—a comprehensive plan to diversify the economy and reduce dependence on oil—has significantly accelerated infrastructure development across sectors such as healthcare, education, tourism, and transportation. Major projects like NEOM, The Red Sea Project, and Qiddiya demand world-class infrastructure and long-term asset management. This has led to a rising demand for professional FM services that can meet international standards and support the Kingdom’s ambitious growth.
Facilities management companies in Saudi Arabia are essential partners in this transformation. They help ensure that buildings and infrastructure are well-maintained, energy-efficient, and compliant with safety regulations. By offering integrated solutions, these companies allow organizations to focus on their core business while leaving the complexity of facility operations to experienced professionals.
Key Players in the Market The Saudi FM market is a mix of local firms and international players. Some of the leading names include:
Musanadah Facilities Management: Known for its integrated FM solutions across government and private sectors.
Initial Saudi Group: Offers a wide range of soft FM services including cleaning, hospitality, and support services.
Engie Solutions: A global energy and services group that operates across the Kingdom, providing sustainable FM solutions.
Emrill Services and Imdaad: Though UAE-based, these firms have started offering services in Saudi Arabia to support the growing market.
Al Fouzan Trading & General Construction Co.: Expanding its FM division in line with real estate development trends.
Technological Integration in FM One of the most notable trends in the Saudi FM industry is the increasing use of technology. Digital platforms are being deployed to manage assets, track maintenance schedules, and monitor energy consumption. Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, AI-driven analytics, and Building Information Modeling (BIM) are being adopted to enhance predictive maintenance and optimize building performance.
Smart cities are a key part of Saudi Arabia’s future, and FM companies are expected to play a vital role in managing these intelligent environments. Automation, remote monitoring, and real-time data analytics are no longer optional—they are essential tools for modern facilities management.
Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility Another critical focus area for FM companies in Saudi Arabia is sustainability. With rising energy costs and increasing environmental regulations, efficient energy use and sustainable practices have become top priorities. Facilities managers are now expected to implement green building strategies, reduce water and energy waste, and promote recycling and eco-friendly practices.
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification is becoming more common in Saudi Arabia, especially for government and commercial buildings. FM providers who understand green building standards and can implement sustainable operations are highly sought after in today’s market.
Challenges Facing the Industry Despite the growth and innovation, FM companies in Saudi Arabia also face several challenges. One of the main issues is the shortage of skilled labor, particularly for technical roles. There is also a need for stronger regulatory frameworks and industry standards to ensure consistent service delivery across the sector.
Moreover, cultural adaptation and client education remain essential. Many organizations in the Kingdom are still transitioning from traditional in-house facility maintenance to outsourcing through professional FM firms. Educating clients on the long-term cost benefits and operational advantages of FM outsourcing is a continuing task.
The Future of FM in Saudi Arabia The facilities management industry in Saudi Arabia is expected to grow steadily over the coming years, driven by continued urban expansion, increased privatization, and the country’s focus on sustainability and quality of life improvements. According to market research, the FM sector in the Kingdom could exceed $50 billion in value by the end of this decade.
Facilities management companies in Saudi Arabia will continue to evolve, integrating more advanced technologies, upskilling their workforce, and aligning their services with national goals. These firms are not only maintaining buildings—they are shaping the way people live, work, and interact within the urban environments of the future.
0 notes