#Juniper Publishers Reviews
Text
Analysis of Mineral Pigments from the Gnishikadzor Area, Southeastern Armenia

Authored by: Yeghis Keheyan
Abstract
The territory of the Republic of Armenia is very rich with ores and different types of deposits, including resources of natural mineral pigments. They differ by large variation of colours and are represented by painted ores, clays, and earths, among which the most significant is the group of paints with yellow, red and brown shades (ochre). Vayots Dzor Province in South-Eastern Armenia is among the rich areas where painted earths are widely spread. Presence of red and brown ochre are very well visible in the south-western part of the province, in the gorge of the Gnishik River, which is also known as the Noravank Gorge, due to the monastic complex of Noravank located here. Red colour rocks in the area of the Noravank Gorge (Gnishikazdor) represented by the sedimentary strata of the Upper Devonian and are determined by the Famennian Stage (375-359 million years). The samples analysed were taken from the foothills of the Noravank Monastery and analysed by different techniques: Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS); FT-IR spectroscopy; XRD diffraction analysis, which allow to indicate the presence of different elements trough contrast variations (atomic number contrast), to determine spectral ranges where absorption peaks were detected, as well as to perform phase identifications. The results show that the concretion is a hard, compact mass of matter formed by the precipitation of mineral cement within the spaces between particles, and is found in sedimentary rock or soil. It is composed of a carbonate mineral such as calcite; an amorphous or microcrystalline form of silica such as chert, flint, jasper or an iron oxide or hydroxide such as goethite and hematite. Implementation of such kind of study is valuable for the future comparison of similar finds from the nearby prehistoric archaeological contexts, where inhabitants exploited red ochre as a pig.
Keywords: Mineral paints; Red ochre; Areni-1 cave; Vayots Dzor Province; Republic of Armenia
Introduction
The mountains of Armenia conceal deposits of ores. Alaverdi (Northern Armenia) and Kapan (Southern Armenia) localities are rich of copper deposits, molybdenum was found in the southeast (Dastakert deposit), in the central and southeastern areas are iron ore deposits (Hrazdan, Abovyan and Svarants deposits). Besides, there are industrial stocks of aluminium-nepheline-syenites, as well as barite with admixture of gold and silver, the deposits of lead, zinc, manganese, gold, platinum, antimony, mercury, and arsenic. There are also rare earth metals: bismuth, gallium, indium, selenium, thallium, tellurium, rhenium. Tuffs (red, orange, yellow, pink, and black), marble, travertines, limestones, are great as building and finishing materials. Semiprecious and ornamental stones are represented by agates, jaspers, amethysts, beryls, rubies, obsidians, onyxes, turquoise.
The area of the country is also rich with resources of natural mineral pigments, where 17 deposits were registered and studied. They differ by large variation of colours and are represented by painted ores, clays and earths, among which the most significant is the group of paints with yellow, red and brown shades (ochre) [1,2].
The colour shade of ochre depends on the type of the iron oxide chromophore. The red ochre contains mainly haematite (Fe2O3), while the yellowish one is rich in hydrated iron oxide goethite, FeO·OH), [3]. The presence of other minerals, such as clay minerals or some metal oxides, can also influence the colour of the ochre. The classification of ochre can be also made according to the matrix composition of kaolinite (Al2SiO5) (OH)4 and/or gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O), and/or sulphate, [4]). Green earth is a clay pigment consisting of hydrated iron, magnesium, and aluminium potassium silicates. Colour varies from a dark, greyish blue green to a dark, dull yellowish green. The colour of green earth is derived from the presence of the following minerals: glauconite or celadonite. As the yellow and red ochre, the green earth or “terreverte” has been used as a pigment all over the world since ancient times [4,5]. They have been found in artworks all over the world and in any historical period, probably due to their availability, high coloring capacities and stability to the light and to the different weather conditions.
Armenian mineral pigments were also used since the dawn of the human civilization and their exploitation by the local inhabitants continued until 1940, after which they were processed on industrial level [2,6].
Vayots Dzor Province in South-Eastern Armenia is among the rich areas where painted earths are widely spread and are represented by large deposits in Agarakadzor and Yeghegnadzor [6]. Meanwhile presence of red and brown ochre are very well visible in the south-western part of the province, in the gorge of the Gnishik River (Gnishikadzor, “dzor” in Armenian means gorge), which is also known as the Noravank Gorge, due to the monastic complex of Noravank (means New Monastery in Armenian) located here The samples analysed in this article was taken from the foothills of the Noravank Monastery, left from the road, where section of red coloured sediment is exposed during the construction of the road (Figure 1). Red colour rocks in the area of the Noravank Gorge (Gnishikazdor) are represented by the sedimentary strata of the Upper Devonian and are determined by the Famennian Stage (375-359 million years). In this area, they are exposed in the core of the so-called Gnishik anticline, spread in the basin of the middle reaches the Gnishik River. The entire stratum of Devonian deposits here is 385 m thick and is represented by ferruginous dark gray and fractured organogenic limestones, which then turn into sandy limestones with a phosphorite content. Ferruginous quartzites with large impregnations of iron oxides are also exposed in ferruginous sandy limestones, shales with carbonate nodules and rich brachiopod fauna: Productella capetatiformis Abrahamian, Plicatifera meisteri, Cyrtospirifer verneuili, Camarotoechia baitaversis, etc (Figure 2).
First evidence of exploitation of similar red coloured ochre from the area was recorded in Late Chalcolithic horizons of Areni-1 cave, located 7km north from the exposure, 2km northeast from the village of Areni, on the left bank of the Arpa River, near the point of its confluence with the tributary Gnishik and at an elevation of 1070m above the sea level. Areni-1 is a threechambered karstic cave. The excavations here began in 2007 and the major significance of this archaeological site was abundantly clear during the initial excavations when very well preserved Chalcolithic (4,300 – 3,400 BCE) and Medieval (4th –18th centuries CE) occupations were exposed. Areni-1 exhibits a transitional culture between Chalcolithic and EBA, which sheds light on the formation and the early stages of the Kura-Araxes culture in the region. Chalcolithic finds from the first gallery of the cave include numerous large storage vessels, some of which contained human skulls – of two adolescent males and a female. Grape remains and vessels typically used for wine storage, together with the results of chemical analyses of the contents, point to Chalcolithic wine production at the site. The cave had been used for different purposes since the end of the 5th millennium BCE: it was a shelter, a storeroom for food; it was used for wine production and for ritual purposes, including burial. All the data indicate clear social complexity and a ritual/productive area. Its strategic location, suitable climate of the Vayots Dzor Province compared to the surrounding mountainous area, and its numerous watercourses and highly fertile soils, make this area especially suitable for human settlement and agricultural development. Indeed, the oldest leather shoe in Eurasia and one of the oldest pieces of evidence for wine production was discovered in the Areni-1 Cave, dated to the Late Chalcolithic – and wine is still today one of the area’s main products [7-15].
Local red ochre was used by the Chalcolithic inhabitants of the cave in different purposes, i.e., for rock-paintings, in symbolic behavior (for coloring the inner parts of the ritual vessels and clay constructions, the compacted floors, as red ochre was the symbol of blood and revival as well as for decorating basketry and pottery [11,13] (Figure 2).
Experimental
The samples from Gnishikadzor or the Noravank were analysed by different techniques. Below are reported the techniques applied to characterize completely these fabulous stones.
Techniques
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS): SEM-EDS micro-morphological and chemical investigations were carried out by a LEO 1450 VP -INCA 300 scanning electron microscope coupled with a electronic probe for X-ray microanalysis, resolution of 3,5nm with the possibility to analyze nonconductive sample by operating in novacuum conditions. The interfacing with EDS gives the possibility to have qualitative and quantitative composition of elements into area observed. For quantitative analysis this method is not sensible under 0.1% in weight. Electron beam energy is 20keV to allow the detection most of the chemical elements starting from boron. Under these experimental conditions the ancient samples have been analysed without any treatment, by using the apparatus in low vacuum. The observations in backscattered electron allow suggest the presence of different elements trough contrast variations (atomic number contrast).
FT-IR spectroscopy: The FTIR microspectra were collected with a Bruker Optic Alpha-R portable interferometer with an external reflectance head covering a circular area of about 5mm in diameter. The samples were placed directly in front of the objective and spots were selected for analysis. The recorded spectral range was 7500-375cm-1 acquired with 200 scans or more, with a resolution of 4cm-1. Spectra reported in the text, however, show only the spectral range where absorption bands were observed (4000-375cm-1). This analysis is non-destructive and non-invasive. The spectra of powdered samples were obtained using the diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform (DRIFT) module. In addition, very small amounts of samples were dispersed in potassium bromide (KBr, FTIR grade purity, Fluka) at different concentrations (sample/ KBr 1/100 to sample/KBr 1/1000). These were studied by collecting 200 scans or more in the same spectral range and resolution. Fourier-Transform infrared (FTIR) spectra were recorded using an Alpha FT-IR spectrometer (Bruker) equipped with the Diffuse Reflection Infrared Fourier Transform (DRIFT) module in the spectral range 7500-375cm-1 at a resolution of 2cm-1 cumulating at least 200 scans. The powdered samples were dispersed in potassium bromide (KBr), FT-IR grade of purity, Fluka) in excess. Figures reported spectral ranges where absorption peaks were detected
XRD diffraction analysis: The X-ray powder diffraction analysis has been performed in the angular range 10-90° in 2θ with a Panalytical X’Pert Pro MPD diffractometer (Cu Kα radiation, λ=1.54184 Å) equipped with X’Celerator ultrafast RTMS detector. The angular resolution (in 2θ) was 0.001°. A 0.04 rad soller slit, a 1° divergence slit, and a 20mm mask have been used on the incident beam path, while a 6.6mm anti-scatter slit and a 0.04 rad collimator have been used on the diffracted beam path. Phase identification has been performed with the Panalytical High Score Plus software.
Results and Discussion
XRD spectra (Figure 3) show prevalently the presence of ochre. From phase analysis the following chemical composition was evidenced; CaCO3, SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, Al2S2(OH)4.
Different stones from the same locality have been cut off. The stone has been cut and analyzed in all parts by FTIR. It was very hard to cut it. Internal part was grey and white. The spectra obtained is reported and compared in figure 4. At 536cm-1 is hematite band and at 473cm-1 is iron oxide band. Quartz band is at 799cm-1. Infrared spectroscopy was employed to analyze the exterior red surface of the stone samples. In addition, a small stone was cut in order to examine the inner side, which appeared grey and white.
Specular reflectance produces derivative- shaped peaks in the region below 1200cm-1 because of the restrahlen effect [16]. All spectra show intense band with peaks at 1545 and 1418cm-1 assigned to the C-O stretching mode of calcite (sparitic limestone). The features at 880 and 2515cm-1 also belong to calcite and respectively assigned to O-C-O bending and combination mode. The features in the 1200-1000 cm-1 interval confidently suggest the presence of silicates, probably kaolin, characterizes by the peaks at about 3690 and 3620 cm-1 assigned to C-H stretching modes [17]. At the lower frequency range of the spectra reported in figures 5a & 5b, bands are also observed at 545 and 466cm-1, indicating the existence of iron oxides molecules in the samples [18].
The proposed assignment seems supported by the absence of mentioned features in the spectra of clear and dark points of the samples. In the last case infrared analysis shows the presence of calcium carbonate as unique component of the stone. Compares micro-FTIR (a) and DRIFT spectra (b) of a red point of the Noravank stone. Spectral differences observed can be attributed only to the different techniques employed. In fact, DRIFT spectrum confirms the components individuated in reflectance analysis suggesting only a minor content of calcium carbonate with respect to the silicates content. In addition, the DRIFT spectrum of a sample of Armenian bole is also reported (c).
SEM- EDS. The micromorphological analysis, using SEM the image detector with secondary electron resolution in non-in-air conditioning has obtained a very well-defined aspect compared to the petrographic material, with clear crystalline formations of a solid structure is observable figure 6.
Other parts of the same stone were analyzed by SEM to identify the different structures, as tested with the other techniques used figure 7 (Table 1). Various points in the area shown in figure 7 and are analyzed in EDS as reported in table 2. Several EDS analyses were carried out on several areas of the sample, the more significative are reported in table 2.
What was observed at the SEM-EDS is in line with the other types of investigations, while not providing data on the molecular formulations, but only on the composition of elements, it may be useful to consider the morphological and microstructural aspect, where, for example, it is never found its trigonal crystalline habit, but the observation of powdery material, figure 7, could be associated with its presence in conjunction with quartz and other minerals, which would explain the red color felt when handling the stone.
Hematite gave following oxide compositions; FeO 29.8%, Fe2O3 15, MgO 2,6, Al2O3 8.1, CaO 16.55, SiO2 26.7, K2O 0.55, TiO2 0.4%. The concretions with following oxide composition have been detected FeO 5.63, Fe2O3 2.8, MgO 1.55, Al2O3 11.42, CaO 33.34, SiO2 44.4.
A concretion is a hard, compact mass of matter formed by the precipitation of mineral cement within the spaces between particles and is found in sedimentary rock or soil. Concretions form within layers of sedimentary strata that have already been deposited. They usually form early in the burial history of the sediment before the rest of the sediment is hardened into rock. This concretionary cement often makes the concretion harder and more resistant to weathering than the host stratum. They are commonly composed of a carbonate mineral such as calcite; an amorphous or microcrystalline form of silica such as chert, flint, or jasper; or an iron oxide or hydroxide such as goethite and hematite. They can also be composed of other minerals that include dolomite, ankerite, siderite, pyrite, marcasite, barite, and gypsum. Although concretions often consist of a single dominant mineral, other minerals can be present depending on the environmental conditions, which created them. For example, carbonate concretions, which form in response to the reduction of sulfates by bacteria, often contain minor percentages of pyrite. Other concretions formed as a result of microbial sulfate reduction, consist a mixture of calcite, barite, and pyrite.
Conclusion
Implementation of different techniques applied to characterize completely the mineral pigment sample from Noravank is а valuable data, showing a need to conduct similar analyses for the other deposits in the Vayots Dzor Province and all Armenia. Such a study can help to create a reliable database of the mineral pigments of the country and to compare the results with the similar studies of the samples discovered from the archaeological contexts. The mineral pigments, especially, ochre, have been intensively used by prehistoric and historic populations for different purposes, especially in creation of rock-paintings, decorating the pottery and basketry, as well as in rituals. Exploitation of pigments by ancient societies will shed new light on the questions of utilization of mineral resources in the territory of Armenia and the raw-material circulation in the landscape, as well as aspects of symbolic behaviour during the complex ritual games, which took place inside the caves and other sacral spaces. This also can be significant example of benefit achieved by the combination of different scientific disciplines and tools regarding deeper study of the ancient past (Figure 8).
To Know More About Juniper Online Journal Material Science Please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/jojms/index.php
For more Open Access Journals in Juniper Publishers please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php
#Juniper Publishers#Material Science#Materials Theory#Structural Materials#Juniper publisher reviews#Juniper publisher journals
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes Mellitus

Authored by Victoria Serhiyenko
Abstract
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω-3 PUFAs) are increasingly being used to prevent cardiovascular diseases (CVD), and cardiac societies recommend the intake of 1g/day of the two ω-3 PUFAs eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acid for primary and secondary prevention of CVD. Clinical trials clearly suggest beneficial effects of ω-PUFAs consumption on lipid metabolism profile, their anti-inflammatory actions; on endothelial activation, which are likely to improve vascular function; antithrombotic and antiatherosclerotic properties. Experimental studies demonstrate direct antiarrhythmic effects, which have been challenging to document in humans. By targeting arterial stiffness and endothelial dysfunction administration of ω-3 PUFAs may prevent atherosclerosis and CVD development. A synergistic interplay showed by ω-3 PUFAs prescription suggest the potential to beneficially impact on fundamental steps involved in the development of preclinical atherosclerosis. We reviewed available evidence of the benefits of ω-PUFAs administration, especially to patients with CVD, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus, including their effects on potential molecular pathways, effects on glucose and lipids metabolism parameters, thrombocyte aggregation parameters and haemostasis, endothelial function, antioxidant/anti-inflammation and antiarrhythmic properties.
Keywords: Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids; Coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis; Diabetes mellitus; Glucose, lipids; Inflammation; Platelets; Haemostasis; Endothelium; Heart rate variability; Arrhythmias; Arterial stiffness
Abbrevations: ω-3 and ω-6 PUFAs: Ω-3 and ω-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids; MetS: Metabolic Syndrome; T2DM: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; CVD: Cardiovascular Diseases; DLP: Dyslipoproteinemia; OS: Oxidative Stress
Go to
Introduction
Numerous studies report salutary effects of ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω-PUFAs), i.e. eicosapentaenoic (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) on cardiovascular diseases (CVD) risk factors. These effects include lowering of serum triglyceride (TG) by reducing of hepatic TG production; lowering of blood pressure (BP) by improving of endothelial cell functution; decreasing of platelet aggregation by reducing of prothrombotic prostanoids; decreasing inflammation via reduction in 4-series leukotrienes (LT) production; protection from arrhythmias by modulation of electrophysiological properties of cardiac myocytes. Systematic meta analysis suggests that high doses of ω-3 PUFAs (~3g/day) produce a small, but significant decrease in systolic blood pressure (SBP) in older and hypertensive subjects [1,2]. The aim of this study was to review the latest evidence about the ω-PUFAs, metabolic syndrome (MetS) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Go to
Discussion
Ω-3 and ω-6 PUFAs are essential fatty acids, as they cannot be synthesized de novo in humans. There are limited data available regarding the exact amount of dietary ω-3 PUFAs consumed by the general population. It is reported that the total daily intake of dietary ω-3 PUFAs in the US is approximately 1.6g. Of this α-linolenic acid (α-LLA) accounts for approximately 1.4g/q.d, and only 0.1–0.2g/q.d. comes from EPA and DHA. The conversion rate from α-LLA to EPA and DHA is variable (0.2-15%). Therefore, in general, the total amount of EPA and DHA available to the body from current dietary patterns is well below the recommended amounts. EPA and DHA didn’t show a significant negative effect on glucose metabolism [3].
Several experimental studies have shown that long-chain ω-PUFAs inhibit the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine and its synthesis in the liver, lead to increased clearance of lipoproteins in the blood, prevent the development of insulin resistance (IR) in experimental diabetes, increase the level of glucose transporter 4 in skeletal muscles, have a positive effect on age related decrease of blood flow in the brain and improve glucose utilization under stress; there isn’t any influence on the development of hypertension (HT) and MetS. Ω-3 PUFAs decrease level of BP, dose-dependent prevent the development of T2DM, IR, contribute to positive changes of blood coagulation parameters; enhance endothelial cell migration and inhibits the proliferation of smooth muscle cells [4]. A meta-analysis of 18 studies found a significant effect of fish oil to lower TG concentrations and increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in the blood; while there were no statistically significant changes in preprandial glucose, glycated hemoglobin A1c, total cholesterol, low density-lipoprotein cholesterol levels. Ω-3 PUFAs may affect the IR and glucose homeostasis by inhibition of IR in the muscle tissue >adipose tissue >>liver, inhibition of insulin secretion, which defer the development of T2DM; and on the state of lipid metabolism (in particular, reduce the concentration of TG, very low density-lipoprotein cholesterol (VLDL-C), increase of HDL-C, improve lipid profile by mixed hyperlipidaemia (HLP), slightly decrease BP, improve endothelial function, have an positive impact on the antioxidant status and inflammatory reactions [5]. Ω-3 PUFAs decrease VLDL assembly and secretion, resulting in diminished TG production, through a decreased sterol receptor element binding protein-1c activity [6,5].
The highly concentrated pharmaceutical preparation Omacor™ (Pronova Biocare, Lysaker, Norway), known as Lovaza™ (Glaxo Smith Kline, St Petersberg, FL, US) in North America is approved by the FDA as an adjunct to diet to reduce very high TG levels (≥500 mg•dL-1) in adults. Each 1-g capsule of ω-3-acid ethyl esters contains ethyl esters of EPA (0.465 g) and DHA (0.375g). Patients take a q.d. dose of 4-g or two 2-g doses (two capsules b.i.d.) [7]. Clinical trials have shown that administration of 4 g•day-1 of Lovaza™ results in a decrease in TG levels of 30-50%; does not affect the efficacy of statins [8,5]. In patients with combined HLP, co-administration of Lovaza™ with statins was a safe and effective means of lowering serum TG, despite the persistent high TG levels when the patients received statins alone [9,5].
The anti-inflammatory actions of marine ω-3 PUFAs are [10]: reduced leucocyte chemotaxis (via decreased production of some chemoattractants (e.g. leukotriene B4 down-regulated expression of receptors for chemoatttactants); reduced adhesion molecule expression and decreased leucocyte-endothelium interaction (via down-regulated expression of adhesion molecule genes [via the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB) (i.e. peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-ɣ (PPAR-ɣ) etc.); decreased production of eicosanoids from arachidonic acid (AA) (via lowered membrane content of AA; inhibition of AA metabolism); decreased production of AA containing endocannabinoids (via lowered membrane content of AA); increased production of ‘weak’ eicosanoids from EPA (via increased membrane content of EPA); increased production of anti-inflammatory EPA and DHA containing endocannabinoids (via increased membrane content of EPA and DHA); increased production of pro-resolution resolvins and protectins (via increased membrane content of EPA and DHA); decreased production of inflammatory cytokines (via down-regulated expression of inflammatory cytokine genes (via NF-kB, i.e. PPAR-ɣ etc.); decreased T cell reactivity (via disruption of membrane rafts (via increased content of EPA and DHA in specific membrane regions).
Ω-3 PUFAs may decrease the risk of atherothrombosis by affecting platelet aggregation and haemostasis. The antithrombotic properties of EPA and DHA have been attributed to the incorporation into platelet phospholipids at the expense of the ω-6 PUFAs, such as AA. An important set of pathways clearly influenced by changes in the ω-3/ω-6 ratio are those for synthesis of eicosanoids. These include the cyclooxygenase (COX), lipoxygenase and cytochrome P450 epoxygenase pathways, for which EPA and DHA compete with AA as a substrate, inhibiting the production of the proaggregatory thromboxane A2 (TXA2) originating from AA. Indeed, the production of TXA2 from platelets stimulated by a variety of agonists decreased by between 60% and 80% after fatty acid supplementation both in vitro and in vivo [11,5]. The mechanism by which ω-3 PUFAs influence endothelial function is mediated by their incorporation into biological membrane phospholipids; this allows modulation of membrane composition and fluidity. The reason lies in the fact that endothelial cell membrane houses caveolae and lipid rafts where several receptors and signaling molecules crucial for cell function are concentrated [12]. Caveolae-associated receptormediated cellular signal transduction includes important pathways such as the, the nitric oxide (NO)/cyclic guanosine monophosphate signaling pathway, the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase and tumor necrosis factor-α/ NF-kB induced COX-2 and prostaglandin E2 activation pathway. By modulating the composition of caveolae, as described for other classes of lipids ω-3 PUFAs may exert their beneficial effects, which include increased NO production and reduced production of proinflammatory mediators [13,12]. In addition to increasing NO production, ω-3 PUFAs decrease oxidative stress.
The incorporation of ω-3 PUFAs in synaptic membranes could potentially influence the autonomic control of the heart. Both nervous tissue and heart tissue have a high content of ω-3 PUFAs (especially DHA) and this may be consistent with the finding that this marine ω-3 PUFAs may modulate cardiac autonomic function as assessed by heart rate variability (HRV) [14]. Thus, ω-3 PUFAs may modulate HRV both at the level of the autonomic nervous system and the heart. Most of the data support that ω-3 PUFAs beneficially modulates cardiac autonomic control thereby possibly reducing the risk of arrhythmias. Accumulating evidence from in vivo and in vitro experiments has demonstrated that ω-3 PUFAs exert antiarrhythmic effects through modulation of myocyte electrophysiology. Ω-3 PUFAs reduce the activity of membrane Na+ channels in cardiomyocytes, thus increasing the threshold for membrane potential depolarization. EPA and DHA also modulate the activity of L-type Ca2+ channels, leading to a reduction in free cytosolic Ca2+ ion, which stabilizes myocyte electrical excitability to prevent fatal arrhythmia. EPA blocks the Na+/Ca2+ channel; however, a single amino-acid point mutation in this channel attenuated the inhibitory effect of EPA. These findings suggested that the cardioprotective effect of ω-3 PUFAs is mediated by direct interaction with membrane ion channels [15].
Ω-3 PUFAs intake has shown to reduce BP especially in HT by interacting with several mechanisms of BP regulation: reduction of stroke volume and heart rate; improvement of left ventricular (LV) diastolic filling; reduction of peripheral vascular resistances; improvement of endothelial-dependent and endothelial-independent vasodilation (stimulation of NO production; reduction of the asymmetric di-methyl-arginine; reduction of endothelin-1; relaxation of vascular smooth muscle cells; metabolic effects on perivascular adipocytes; endothelial regeneration. Mechanisms of HT-related organ damage protection: anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antithrombotic effects; reduction of arterial stiffness; experimental effects on LV hypertrophy and abnormal gene expression; effects on atherosclerotic plaque progression and stability [7]. Ω-3 PUFAs offer a scientifically supported means of reducing arterial stiffness and this may account for some of the purported cardioprotective effects of ω-3 PUFAs [16,17].
Go to
Conclusion
The antiarrhythmic effects of ω-3 PUFAs, which occur by blocking various ion channels, are encouraging. So, cardiovascular benefits of ω-3 PUFAs [7,18] are: antidysrhythmic effects (reduced sudden death; possible prevention of atrial fibrillation; possible protection against pathologic ventricular arrhythmias; improvement in HRV; antiatherogenic effects (reduction in non- HDL-C levels; reduction in TG and VLDL-C levels; reduction in chylomicrons; reduction in VLDL and chylomicron remnants; increase in HDL-C levels; plaque stabilization; antithrombotic effects (decreased platelet aggregation; improved blood rheologic flow); anti-inflammatory and endothelial protective effects (reduced endothelial adhesion molecules and decreased leukocyte adhesion receptor expression; reduction in proinflammatory eicosanoids and LT’s; vasodilation); decreased SBP and diastolic BP. Thus, further research to understand the mechanism of action and confirm the beneficially effect of ω-3 PUFAs on BP profile, artery stiffness and HRV parameters in patiens with MetS, T2DM is needed.
To Know More About Current Research in Diabetes & Obesity Journal Please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/crdoj/index.php
To Know More About Open Access Journals Please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php
0 notes
Text
Is US Patent Policy Strong Enough to Withstand the Winds of Change: A Study of the Need to Change United States Patent Policy

Author by Kent R Acheson
Abstract
The purpose of this case study was to learn how US patent policy requirements differ for the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries, specifically if United States Patent Policy adequately protects intellectual property rights [1] for two divergent industries while still encouraging research and development (R & D) investment sufficient to increase profits and innovation. Data for this study consisted of 38 witness testimonies delivered to US Congress between the years 2005 and 2010 by experts representing the two industries of interest: pharmaceutical and software. Key findings from the data analysis of these 38 testimonies revealed both within industry differences and between industry differences in patent law protection. Within industry differences showed variance based on size of the company and the degree to which they relied on their own R & D. Between industry differences reflected divergent ‘products’ with Pharmaceutical Industries needing long-term protection to recover R & D expenditures that include expenses for human trials research to proceed from patent application to market. Software industry, on the other hand, uses follow-on innovation of others to continue technological advancement by constantly improving upon existing software. The data show that these two industries use patent policy protection in different ways for different reasons. This information will enable Policymakers to develop another form of product protection in lieu of the current patent law to better meet the needs of these two industries rather than try to modify the existing law.
Introduction
Patent law was developed in parts, building on one another with a single purpose in mind of protecting all innovations in a society and this created the basis for patent laws imposed on the current and future generations. Bessen [2,3] stressed that patents may not be valuable in protecting innovation [4-6] but are used solely to diffuse new ideas in the public. Bessen and Maskin [7] had previously highlighted that little research and development (R&D) in the Software Industry is used to gain patent protections and the enforcement issue with patents is difficult, as many patents are issued for products that are not new. Levin [8] and others found much earlier that patents were rated weak at protecting the returns on innovation, far behind the protection gained through lead time and learning curve advantages.
Patent’s role in different industries
The purpose of this qualitative case study was to explore the different requirements for patent policy for the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries. All transcripts from testimonies from the spokespersons representing the two industries introduced to either House between the years 2005 to 2010 concerning the U.S. Patent Reform Bills were collected and analyzed to answer the research question in this case study. The findings could be useful in further adjusting patent policy to encourage innovation for diverse industries, or suggest the creation of another form of idea protection.
A similar problem may be in the type of intellectual property protection that a company chooses to obtain to avoid the constraints of getting a patent and extend the time frame for protection, such as copyright protection that extends protection from the 20 years for a patent to 120 years. Apple Inc. obtained a copyright protection for their popular iPhone [9], which recently lost in a suit against the Federal Government. The landmark decision helps to control copyright creep. Initially when buying an iPhone, Apple Inc. limited the service provider to AT&T and applications had to be bought from the Official Apple Store. Now, however, through a hack on the iPhone, users can choose a different service provider and load other, unofficial, applications not supported by Apple Inc., and hackers are not in violation of Copyright Law.
Policy Makers can use the findings of this study to explore new directions for the United States Patent Policy to optimize advancement of technology in the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries. Historically in the United States, there has been one patent policy. Scholars, academicians, and the United States Government still do not know the ideal amount of IPRs mainly because the objective has been to uphold one uniform policy. This study clarified if further changes were needed for patent policy through a Patent Reform Act, which enables Policy Makers to understand the needs of the Software Industry, or design another form of protection designed specifically for the Software Industry.
Crowe [10] and others stated that a case study design is most appropriate when little is known of a phenomenon in its natural context. A case study is “used to generate an in-depth, multifaceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context” (p. 1). The Pharmaceutical Industry has a profitable track record using the existing Patent Law to protect their R&D investments. The Software Industry is comparatively new and therefore their issues are only just now becoming obvious. Case law is outside the boundaries of this study.
The multiple dimensions of the phenomenon of the nature of protecting intellectual property rights in the Software Industry property and the Pharmaceutical Industry are worthy of study to allow all voices to be heard, including large corporations from both software and pharmaceutical companies, generic drug companies, and smaller software startups. After carefully examining all relevant transcripts, these diverse opinions can be given venue to state their needs.
Methodology and main results
The research question addressed in this study was: How do the patent policy requirements differ for the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries? From the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries’ objectives and needs for the United States Patent Policy to address, the questions spotlighted the sufficiency and effectiveness of the United States Patent Policy.
The focus of this study has two parts, they are:
1. What is the evidence United States Patent Policy adequately protects Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs) for both the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries?
2. How does the United States Patent System encourage companies to make R&D investment in the Software and the Pharmaceutical Industry?
The first research question dealt with the effectiveness of the United States Patent Policy in protecting IPRs in two industries: software and pharmaceutical. The second research question related to how companies invest in R&D with support of the United States Patent Policy. The study explored the ability of the United States Patent Policy to foster innovation with satisfactory IPR protection to encourage R&D spending focusing on two specific industries. The Software Industry experiences a sequential and complementary nature of innovations, building on previous discoveries; and may not use the patent policy in effect in the United States. If patent policy does not consider the different requirements within the Pharmaceutical Industry and is too lax then enough R&D spending will not be invested and technological advancements, including new medications, may come to the market slower or not at all.
The scope of the study is to understand how the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries use the patent system and how better to adjust the patent system to optimize technological advancement. As discussed in assumptions, because of the nature of the source of data and the possible bias that was not fully known, the assumptions may or may not have had a credible or dependable basis and may therefore have biased the findings. Qualitative designs such as the case study have inherent limitations that may threaten validity, they may lack rigor and they may not be generalizable. These limitations may be mitigated with transparency in data analysis and reporting. Crowe 5 and others explains on page 8 “seeking potential, alternative explanations, and being explicit about how interpretations and conclusions were reached, helped readers to judge the trustworthiness of the case study report.
Evidence from various sources highlight the United States Patent system does not work as intended and needs a solution to continue or increase innovative activity. The principal problem deals with innovative activity that is sequential in nature and innovative activity that involves much R&D investment to bring a product to market. Sequential inventions build on previous breakthroughs and do not require much R&D investment. Secrecy would hinder follow-on discoveries of sequential innovative products.
This study used a content analysis of witness [11] testimonies to Congress on the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries from the years 2005 to 2010, and the possibility to develop more than one patent policy to accommodate different sectors of the economy. The study concentrated on software and pharmaceutical companies, as these two industries are most at odds with each other, and have prevented the passage of the Patent Reform Act of 2005 through 2010. The Patent Reform Act of 2010 [12,13] is the result of non-passage of the 2009 Act, as was each successive year from 2005. The stance of the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries remained relatively unchanged in their requirements, but the patent reform acts changed to incorporate the majority opinion of industry. The most important recommendations of the Federal Trade Commission (FTC 11) and National Academies of Sciences (NAS) studies that were first introduced in 2005 by Senator [14] Lamar Smith were considered.
The purpose of this descriptive analysis was to examine the current United States Patent Policy and the proposed changes to United States Patent Policy, and answer the research question – How do the patent policy requirements differ for the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries? This study will help decide if the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries effectively use the U.S. Patent Policy through protecting Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs) and encouraged investment research and development (R&D). The qualitative case study was the most suitable approach to study the issues and answer the research questions because it explored real-life experiences of industries looking to patent Intellectual Property (IP).
Data and Sample Statistics
Data were collected and analysis began using the Content Analysis Guide developed for this study. The testimonies of the BSA representatives, other computer software witnesses, Computing Technology Industry Association, PhRMA representatives, other generic pharmaceutical representatives, and the Generic Pharmaceutical Association, Biotechnology Industry Association (BIO), Intellectual Property Owners Association (IPO) [15-18], and venture capital organizations were included in this study. The IPO was included because IPO members represent 30% of patent applications at the USPTO and include members from the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries, among others. The study included Venture capitalists because some members of BSA [19] and other smaller software companies began with venture capital dollars. Each data point was examined for inclusion of any reference to R&D, including duration and support for R&D, the need for patent protections [20,21], and future needs for patent policy.
The 38 documents submitted to the congressional hearings were analyzed. Documents relating to software and pharmaceutical companies reviewed were not ambiguous but very clear and straight forward following a consistent format, so that anyone conducting another study would reach the same conclusions. They all stated who authored the document, who the document represented, who presented opinion to Congress, their position on the patent reform act, and agreements and disagreements with specific points of the patent reform act. No ambiguity existed and no information required subjective judgments to interpret the information reported. The nature of the data supported the reliability of the findings.


Cisco, Hewlett-Packard, and other big high-tech companies began pushing for reform legislation to limit the number of patent infringement lawsuits and therefore the amounts paid in damages. The United States Patent and Trademark Office’s (USPTO) proceedings’ transcript from the public hearings showed the patent policy needs for BSA’s principle member and founder Microsoft. The public hearing titled Use of the Patent System to Protect Software Related Inventions took place in 1994 at the San Jose Convention Center, California, and at the Crystal Forum in Arlington, Virginia. A brief summary of Microsoft’s speech follows. Microsoft (BSA) recommended that patent protection allow an accused infringer to identify readily the activity forbidden under the claim. The success of a particular claim in meeting these objectives may depend less on the form and more on claim substance and the supporting details.
BSA represents a large base of computer software and hardware companies in the United States. Phelps (2005) from Microsoft Corporation stated that BSA does not want the patent holder to have automatically injunctive relief. Injunctive relief occurs when the courts rule an infringement occurred and automatically issue a ruling to stop the infringer from continuing operations. From the congressional hearing in 2005 on harmonization and other matters, Phelps for BSA supports publication in 18 months. Phelps [39] expressed support for establishing a post grant opposition procedure and supported third-party opportunity to alert USPTO to questionable patents during review. Phelps also supported allowing third parties the opportunity to suggest relevant prior art to examiner during review, supported a limit on damages for willful infringement to include only egregious behavior, and supported limiting damages to only the contributing, patented piece of the invention and not the market value of the whole product, as it is now.
In a congressional hearing in 2005, Simon [40] from Intel , a BSA representative, stated the patent system is difficult to maneuver because of many pieces that comprise computers and software contain “potentially hundreds of patents [that] may be relevant to a particular computer or software technology” [40]. The primary way to challenge a patent under current law is through costly litigation. Intel suggests Congress create a balanced post grant opposition enabling third parties to challenge issued patents that includes a post grant opposition of 2 years from patent grant or 1 year from receiving notice of patent infringement. Simon also encouraged Congress to create a second window to make the post grant review meaningful. Simon suggested a limit on patent application continuations and for the court not to issue a continuation on any claim broader than the broadest claim previously published or issued. BSA suggested a stay on the lower court’s decision in interlocutory appeals before final determination by the Federal Circuit Court of Appeals. Micron Technology, Inc., a non-BSA member, suggested the same patent law reforms as BSA.
In a congressional hearing in 2006, Chandler [41] of Cisco (BSA) suggested a second window triggered by receipt of an infringement complaint. During the first window, the patent issues with thousands or millions of parts making the effectiveness of the patent examination questionable. Chandler (2006) encouraged Congress to make changes to remove venue shopping, and prevent suits from worldwide damages in United States Courts like the Microsoft and AT&T case. The only patent policy need described on the BSA website dated 1994 had no updates, which is understandable because United States Patent Policy has not changed significantly for more than 50 years and the proposed changes have not made it into law. The agreement with the Patent Reform Act was from the most influential voice for the Software Industry; nevertheless, there were disagreements within the Software Industry mainly arising from smaller companies and individual inventors. Software companies wanted patent reform by Congress but differences remained among large software companies and smaller organizations. An overhaul of the patent system and other measures to promote tech development efforts are top priorities of the Business Software Alliance, Cisco, Hewlett-Packard, and other big high-tech companies . BSA members began pushing for reform legislation to limit the number of patent infringement lawsuits, and therefore, the amounts paid in damages.
In an article in PC World dated March 9, 2008, patent reform leads a list of five legislative priorities expressed by BSA in 2008. The opinion article stated that BSA members want Congress to approve the Patent Reform Act but the legislation stalled in the United States Senate because of objections from inventors, pharmaceutical companies and some small tech (computer software) firms. In addition the article proclaimed, more than 170 California businesses and organizations oppose the Patent Reform Act in its current form. They mention that research to stay competitive is both expensive and risky, but strong protections from patent policy attract the necessary investments to commercialize a new product. This is especially the case for the hundreds of smaller, venture capital-backed firms in the state, of which many spun from California’s world-class research universities and private research institutes. According to GlaxoSmithKline, California Wireless and Mi5 Networks in paragraph eight on page one of Gross [42] (2008), the Patent Reform Act “would increase costs to obtain and maintain patents, undermine patent certainty, incentivize infringement, and weaken the enforceability of patent rights and intellectual property protections.”
Dr. Myhrovold [43-45] started Dynamical Systems, a software company, in 1984 that Microsoft bought in 1986. He worked with Microsoft from 1986 to 2000 (14 years). Myhrovold retired from Microsoft in 2000 to start another company, Intellectual Ventures, which files more than 300 patents a year making it the 25th largest inventing organization in America. Dr. Myhrovold stated “[Software is] a complex topic…and it’s all about company culture and how companies use patents” (Perspectives on Patents [46,47]. Continuing Dr. Myhrovold stated “…for most tech companies patents have never been important; they have never been a way to make money” (p. 76, para. 2), and “…patents are, at best, a distraction and most tech companies have made a deliberate decision to ignore the patent system” (p. 76, para. 5). Many other non-BSA members agreed with Myhrovold.
Defensive patenting by software companies explains if a company holds enough patents then this company can steal another product company’s ideas with impunity, but the problem enters when the other entity does not create a product to attack (Myhrovold, 2006, p. 77, para 3). These are the battle lines in the patent reform debate with universities, small inventors and pharmaceutical companies whose lifeblood is the patent system on one side, and companies who decide to infringe or at least do not care about infringing on the other side. Dr. Myhrovold is a witness from the vantage point of a Microsoft senior executive in the 1990s who discussed this role with other firms in the earlier rounds of patent reform debate.
Technology companies exaggerate the problem when over the last 20 years patents have remained in last place of lawsuits for the three forms of idea protection: trademark, copyright, and patents. A study of four high-tech companies that are active in the patent reform debate paid out $3.7 billion in patent lawsuit settlement from 1993 to 2005, but those same four companies earned $1.4 trillion in revenue over the same period making the sums for infringement only 0.26% of revenues on average. The company with the highest number of lawsuits experienced sums for infringement at only 0.51% of revenues. “Patent trolls” are companies that do not market a product but only the idea for a product. Companies that do not produce a product comprise only 2% of the patent infringement lawsuits. Software companies like to blame an innocuous group of patent troll companies when they themselves perform the same litigious practices blamed on trolls. Myhrovold stated the need to embrace the trend to make the alternate resolutions more like a court trial by creating a separate Patent Court, much like the Tax Court, Bankruptcy Court, or Divorce Court to try only specific cases.
Inter Digital is a technology and software company that disagrees with BSA’s proposed changes to patent law. Inter Digital’s Bernstein summarized the differences in the Software industry on page 220 last paragraph at the 2007 congressional hearings: “…the IT industry is absolutely not united in its support for mandatory apportionment, post grant opposition, expansive USPTO rulemaking authority, and interlocutory appeals fall outside the realm of patent ‘reform’.” Bernstein continues by expressing how such an action would degrade patent rights and increase litigation for smaller innovators. The weakening of legitimate patents would protect a few corporate giants and increase the number of lawsuits Bernstein (2007), [48,49].
An article by Mc Dougall [50] and Chabrow (2006), [51,52] in InformationWeek explains the problems as they perceive them with the Patent Reform Act from other software and computer companies. Hans Hxu, founder of online gift registry Felicite.com, says the industry’s large players want the appearance of IP openness but do not practice it. “IBM patents almost everything they do, and then they sit on it, which does not encourage innovation” (Microsoft Agenda, para. 3) says Hxu, a McKinsey consultant although other critics suggest the sellers’ moves cement their advantages when they face rising [53] competition from startups. In an August 2005 essay, Harvard Law School professor and tech entrepreneur James Moore argued the collaborative patent review proposed by IBM, Microsoft, and others would result in fewer patents issued because it would give examiners more ammunition to shoot down patent applications. “If fewer patents are issued, but existing patents are not revoked, IBM and Microsoft win because they already possess vast existing portfolios,” Moore writes (Microsoft Agenda, para. 4). Some Web 2.0 companies dismiss IBM’s argument that business-method patents protect obvious ideas. “Everything is obvious after someone has done it,” says a spokesperson for online movie renter Netflix (Microsoft Agenda, para. 5), which has patents on its queue-ordering system--and is suing Blockbuster for allegedly copying the system.
Small tech companies are taking matters into their own hands, forming patent cooperatives through which they share IPRs. Search company Wink shares in Creative Commons, a group that encourages sharing of copyrights and open source licenses, but there is a line between sharing and protecting intellectual property that creates competitive advantage, says Wink’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Michael [54,55] Tanne. “When companies have invested in the development of technologies, they really ought to be able to protect it,” Tanne says (Microsoft Agenda, para. 6). Resolving these issues will influence developing and commercializing tech innovations. Too many lengthy and expensive legal battles will persuade IT departments to stick with familiar technology, and this is something tech vendors should consider as they take one another to court.
The largest and best known pharmaceutical companies in the Pharmaceutical Industry represented by Pharmaceuticals Researchers and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA), Biotechnology Industry Organization (BIO), and the Professional Inventors Alliance disagree with the weakening of patent protection and the long, time frame proposed for patent reexamination. High R&D characterizes these industries and the Pharmaceutical Industry realizes a shortened patent protection because patent protection begins before FDA approval. This shortens patent protection to commercialize the product to the remaining years.
On September 17, 2007, The Professional Inventors Alliance expressed through a letter to President Bush the flaws in the Patent Reform Act of 2007. The Patent Reform Act of 2007 did not pass the United States Senate because of the opposition from PhRMA, small inventors, and small tech firms . The letter from the Professional Inventors Alliance expressed that if the Patent Reform Act of 2007 passed into law it would harm the United States’ innovative character because of the inability to enforce patents and would reduce the royalties associated with a patented technology. In 1980, PHRMA’s members invested $2 billion in R&D for new medicines; although, nearly 30 years later (in 2009), PHRMA’s members invested $50.3 billion in R&D out of the $65.2 billion industry-wide total. Pharmaceutical companies rely on government-granted patents to protect their substantial investments in researching and developing new drugs. It takes 10-15 years and costs $800 million on average to bring a new medicine to market. The Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) represents the country’s leading pharmaceutical research and biotechnology companies.
Without patents to protect all the inventions necessary to develop a drug for a limited time, others could simply copy the drugs immediately, offering their versions at a reduced price because they did not incur the high costs to develop the drug. This would seriously affect the pharmaceutical companies’ ability to recoup their costs and reinvest in other research projects. PhRMA stated in 2010 that “a strong patent system is crucial to our economic [56,57] competitiveness, especially in these economically trying times” (PhRMA’s website, 2001, p. 1). The companies in favor and against the Patent Reform Act of 2010 divided into the companies that have favored and opposed the previous patent reform acts, that is, computer software favoring patent reform and pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology companies opposing patent reform. Those opposing and in favor of the patent reform acts through the six years in this study have not changed their needs but, instead, Congress changed trying to create a patent policy agreeable to most patent users.
The large pharmaceutical companies also known as the name brand pharmaceutical companies and the smaller, generic pharmaceutical companies were in general agreement on most issues. Both wanted strong patent protection and both sides were against the Patent Reform Bill [58] of 2005 and 2006 as stated in the congressional hearings on patent reform. The firstinventor- to-file patent system while harmonizing with the large United States trading partners also poses some difficulties and disagreements with United States patentees. The problems lay in the grace period of 1-year and the best mode requirement in the patent application. Harmonizing with other countries’ patent systems as currently written, such as Japan and Europe, would remove the United States grace period of 1 year to file a patent application and would remove the best mode requirement when filing a patent application. The best mode requirement is the descriptive part of the patent application the inventor has to include the inventor’s idea of how best to use or combine the chemicals for complete effectiveness.
The differences between the brand name and generic pharmaceutical companies lay in eliminating the best mode factor of the patent application and the inequitable conduct defense. Brand name pharmaceutical companies say the best mode provision of the patent law is subjective, and therefore should be removed. The generic pharmaceutical companies believe the best mode provision should remain because they cannot copy the patented medication without the recipe or the “best mode” of making the drug. By removing the inequitable conduct defense, brand name pharmaceutical companies will misuse the patent system to the harm of the public and generic pharmaceutical companies. Differences exist between the brand name pharmaceuticals and the generic pharmaceuticals. One example is the issue of patent quality: Best mode. Generic pharmaceuticals want to keep the “best mode” in the patent law language because it lowers cost of medications by allowing generic companies to copy name brand drugs more easily. Ely Lilly [59,60] and PhRMA want to remove the best mode language . The Generic Pharmaceutical Association also has qualms with weakening the inequitable conduct saying that weakening this provision gives brand-name pharmaceutical companies incentive to misrepresent their inventions.
The differences between the brand name and generic pharmaceutical companies lay in eliminating the best mode factor of the patent application and the inequitable conduct defense. Brand name pharmaceutical companies say the best mode provision of the patent law is subjective, and therefore should be removed. The generic pharmaceutical companies believe the best mode provision should remain because they cannot copy the patented medication without the recipe or the “best mode” of making the drug. By removing the inequitable conduct defense, brand name pharmaceutical companies will misuse the patent system to the harm of the public and generic pharmaceutical companies. Differences exist between the brand name pharmaceuticals and the generic pharmaceuticals. One example is the issue of patent quality: Best mode. Generic pharmaceuticals want to keep the “best mode” in the patent law language because it lowers cost of medications by allowing generic companies to copy name brand drugs more easily. Ely Lilly [59,60] and PhRMA want to remove the best mode language . The Generic Pharmaceutical Association also has qualms with weakening the inequitable conduct saying that weakening this provision gives brand-name pharmaceutical companies incentive to misrepresent their inventions.
Together the Case Lawre presented the most comprehensive line of court-led patent reforms, which makes patent reform substantially different in 2010 than 2005. Patent lawyers and the law association, AIPLA [63,64], believe that legislation is not necessary and the court system will eventually find a solution for compromise for the different users of the patent system and will define patent law through successive Case Law. Larger, more market capitalized firms make more noise and are heard more clearly than smaller, less capitalized companies or individual inventors, including companies that specialize in innovation but do not concurrently produce a product, also known as patent trolls. More innovation comes from smaller firms and individual inventors than large entities. The larger software enterprises that often infringe on patents held by companies that do not produce a product (patent trolls) behave similarly to the patent trolls. IBM and Microsoft sit on patents without an accompanying product, when another company discovers something similar the patent surprises the unsuspecting company, and a licensing or royalty agreement can avoid costly litigation. IBM earned over a billion dollars in 2005 solely from license agreements and royalties. Licensing and royalty agreements are another possible direction that companies take to avoid patent infringement suits; however, their use threatens other companies to ransom licensing or royalty agreements but is cheaper and the outcome more certain than litigation.
The Pharmaceutical Industry appreciates the current patent policy and is leery of any changes that would disrupt the current manner in which they use the patent system to optimize patent protection; also the Pharmaceutical Industry like the Software Industry makes the best of the current patent policy . Although pharmaceutical firms have to wait until after drug trials and resulting FDA approval to market the medication, which includes the 20-year patent term and drug approval sometimes lasts as much as 10 years, they too have found ways to evade current patent law to extend the patent length. The Pharmaceutical Industry commonly increases the shortened patent length by adding a known chemical to the patent protected drug therapy, and adds another patent protection term of 20 years by increasing the number of patents on a drug. One specific drug therapy created by a name-brand pharmaceutical firm that a generic company was exploring to copy had patent protection by more than 200 patents spanning 40 years.
Discussion and Conclusions
The specific research questions that framed this qualitative case study were 1. What is the evidence United States Patent Policy adequately protects Intellectual Property Rights [65] (IPRs) for both the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries? 2. How does the United States Patent Policy encourage companies to make research and development (R&D) investment in both the Software Industry and in the Pharmaceutical Industry? Based on the differences on how patent policy should read, issues of effectiveness of the United States Patent Policy to both protect and encourage IPRs and R&D investment should be considered. Patent policy in the United States has remained unchanged for the last 55 years, and has been effective in protecting IPRs and encouraging R&D investment. Pharmaceutical firms have been around many years and have flourished in the current patent policy environment. Only with the creation of the personal computer have software companies entered the scene and have expressed concern for the patent policy changes to reduce the software company’s purposeful infringement. In a few words, the large software companies want to weaken patent protections and reduce their costs to defend against patent infringement lawsuits because big software companies do not care about patents or patent infringement.
Three important findings from this study are
1. The Pharmaceutical and Software Industries use patent policy differently
2. BSA explicitly states they want a strong patent policy, but, in effect, want to weaken the current patent policy, and
3. Differences exist within each industry. Congress has attempted to improve patent law 6 years without success because there is not agreement pleasing all industries, but the principle differences embodied the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries.
Firstly, pharmacy and software use patent policy differently: Pharmacy to protect R&D and Software for defensive purposes. Software Industry (BSA) does not use the patent policy as designed to protect R&D, but to defend against the threat of patent infringement lawsuits. The testimonies to Congress provided evidence to answer my research question of how the patent policy requirements differ between the Software and Pharmaceutical Industries. The testimonies to Congress were clear and straightforward. I did not have to infer the meaning or needs of the witnesses. They clearly stated their position and what they wanted in patent policy. Many people in the Pharmaceutical Industry and smaller software companies specifically stated that larger software and computer companies began calling for patent reform to limit the many patent infringement suits against them. Myhrovold shared his experience working for Microsoft in the late 90s stating that large software companies are not concerned with infringing on another’s patents and the only reason they care at all about patents is to defend against patent infringement lawsuits.
Secondly, the data from congressional testimonies clearly showed that the Software Industry (BSA) verbalized they want a strong patent policy but, instead, they want to weaken the rights of patent holders. This weakening is from: An unlimited post patent review period, placing the burden of proof for infringement on the patent holder (instead of the offender), and limiting the damage awards for infringement to only the infringing part of an innovation. The testimonies clearly stated their position and what they wanted. The previous list clearly communicated to Congress what the Software Industry (BSA) wanted in a patent policy, and refuted by other expert testimonies in the Software Industry.
All BSA representatives stated they wanted strong patent protection, and continued with the above reasons, which amount to weakening a patent holders’ legal rights to their Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs). Many testimonies contrary to BSA stated specifically the reasons BSA wants to limit a patent holders’ IPRs is to stave off patent infringement lawsuits. Myhrovold (2006) shared that patent policy did not enter into Microsoft’s and other BSA members’ culture. Patents are not how software companies protect innovation, but, rather, secrecy, and lead time or economies of scale are more effective to protect innovation in a short product lifecycle industry. Thirdly, the entire Software Industry is not united with BSA, and the entire Pharmaceutical Industry is not united with PhRMA. Differences exist between the two industries and differences exist within each industry, such as difference between larger companies and smaller companies in Software Industry and brand name pharmaceutical versus generic pharmaceutical. Each expert clearly stated what they wanted, why they wanted it, and differences within their respective industries. The witnesses to the congressional hearings succinctly stated that the BSA or PhRMA did not represent the entire industry, and the industry was not united in its desires for patent policy. Siwik [66] said in the exact words that the Pharmaceutical Industry is not united, and based on the non-BSA members’ testimonies with them vehemently disagreeing with BSA’s stance, anyone would reach the same conclusions that BSA is far from united too.
The evidence suggests the two industries use patent policy in different ways. For instance, The Software Industry does not use the patent system to protect intellectual property but rather use the patent system for defensive purposes not so much to protect innovation but to defend against infringement lawsuits. Pharmaceutical industry relies heavily on a patent protection to recover large R&D spending. The evidence was found in examples of how each industry effectively uses the patent system. Based on research of the patent system and the evidence of how each industry uses the patent system, the data would suggest agreement with many of the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and other industries that use the patent system effectively to protect research and development dollars that the system does not need major change. Research shows the answer to the question of how the United States Patent System encourages R&D and promotes innovation; the patent system performs well according to its design. It protects ideas. The current patent policy is effective in protecting innovation and encouraging research and development spending.
For more Open Access Journals please visit our site: Juniper Publishers For more articles, please click on Journal of Organic Medicinal Chemistry
0 notes
Text
A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo- Controlled Study Trial to Evaluate the Potential Effects of Naticol®, Fish Collagen Peptides on Symptoms of Sarcopenia in the Elderly
Abstract
Background: Previous research has shown the potential effects of different doses of specific fish collagen peptides (Naticol®) on muscle mass and muscle function. In addition to these benefits, clinical studies have suggested that ingestion of specific fish collagen peptides (Naticol®) might also have beneficial effects on joint health such as osteoarthritis. Joint health, loss of muscle mass, and loss of muscle function are all symptoms experienced by elderly adults, and especially elderly adults suffering from sarcopenia, suggesting a possible role for Naticol® to help to reduce these symptoms in this vulnerable population.
Aim: The aim of this study was to determine the effect of 24 weeks’ supplementation of Naticol® on symptoms of sarcopenia in an elderly population.
Methods: In a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial 28 elderly adults consumed one 15g sachet of either Naticol® or the Placebo product (maltodextrin) mixed into 20cl of cold water daily before breakfast, for 24 weeks. Symptoms of sarcopenia were assessed using dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) to measure lean body mass, the Short Physical Performance Battery to assess physical performance, the handgrip strength assessment to assess upper body muscle function, and the chair stand test to assess lower body muscle function.
Results: This study showed that 24 weeks of supplementation with Naticol® significantly improved symptoms of sarcopenia compared to placebo, by increasing lean muscle mass and increasing muscular function in the handgrip strength assessment, Short Physical Performance Battery, and Chair Stand Test.
Conclusion: The results of this study demonstrated that daily supplementation of Naticol® (containing fish collagen peptides) in elderly adults can improve symptoms of Sarcopenia, increasing lean muscle mass and increasing both upper and lower body muscle function.
Read More about this Article: https://juniperpublishers.com/jojcs/JOJCS.MS.ID.555850.php
Read More Juniper Publishers Google Scholar: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=rp_7-igAAAAJ&citation_for_view=rp_7-igAAAAJ:LkGwnXOMwfcC
#Juniper Publishers Review#Juniper Publishers in USA#Journal of Case Studies#molecular biology#Biotechnology#caesarean section#Cardiology#blood transfusion
0 notes
Text
Application of (bio) chemical engineering principles and lumping analysis in modelling the living systems
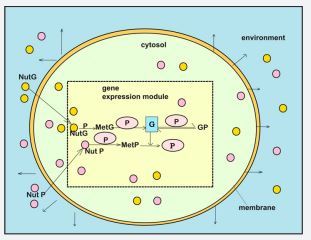
Abstract
The ”whole-cell” simulation of cell metabolic processes under considering a variable-volume modelling framework has been reviewed to prove their advantages when building-up modular model structures of simplified form that can reproduce complex protein syntheses inside cells. The more realistic “whole-cell-variable-volume” (VVWC) approach is reviewed when developing modular kinetic representations of the homeostatic gene expression regulatory modules (GERM) that control the protein synthesis and homeostasis of metabolic processes. The paper review the general concepts of the VVWC modelling, while the cited literature includes past and current experience with GERM linking rules in order to point-out how optimized globally efficient kinetic models for the genetic regulatory circuits (GRC) can be obtained to reproduce experimental observations. Based on quantitative regulatory indices evaluated vs. simulated dynamic and stationary environmental perturbations, the reviewed literature exemplifies with GERM -s from E. coil, at a generic level, how this methodology can be extended:
i) To characterize the module efficiency, species connectivity, and system stability;
ii) To build-up modular regulatory chains of various complexity;
iii) To prove feasibility of the cooperative vs. concurrent construction that ensures an efficient gene expression, system homeostasis, proteic functions, and a balanced cell growth during the cell cycle;
iv) To prove the effect of the whole-cell content ballast in smoothing the effect of internal/external perturbations on the system homeostasis.
Read More About This Article: https://juniperpublishers.com/ctbeb/CTBEB.MS.ID.555566.php
Read More Juniper Publishers Google Scholar Articles: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=nWCnyqYAAAAJ&citation_for_view=nWCnyqYAAAAJ:Se3iqnhoufwC
#biomedical engineering#Juniper Publishers#juniper publisher reviews#biomedical science#Linking GERM-s
1 note
·
View note
Text
Breeding Cowpea Vignaunguiculata l. Walp for Quality Traits
Abstract
Primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) is the most common cause of hypercalcemia in outpatient settings, with an incidence in women of reproductive age of 4.7-6.2 cases per 100,000 persons. When untreated in pregnant women, PHPT can lead to maternal and fetal complications. The authors present a case of a patient with a pre-pregnancy hyperparathyroidism diagnosis: she had worsening symptoms during pregnancy, so was referred for surgery due to failure of clinical treatment to keep the disease under control. Clinical issues, laboratory findings, and relevant therapeutic approaches are discussed.
Read More About This Article: https://juniperpublishers.com/arr/ARR.MS.ID.555690.php
Read More Juniper Publishes Google Scholar Articles: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=l2xTCboAAAAJ&citation_for_view=l2xTCboAAAAJ:k8Z6L05lTy4C
#Juniper Publishers Google scholar#Annals of Reviews & Research#research & reviews journal of life sciences
0 notes
Text
A Novel Methodology for Correction of Cosmetic Problems via Secondary Eyebrow Transplantation - Juniper Publishers

A Novel Methodology for Correction of Cosmetic Problems via Secondary Eyebrow Transplantation - Juniper Publishers
Authored by Yi Jung Lin
Abstract
Eyebrows create a very imperative and noticeable feature of the face. With increasing information, eyebrow transplant has become a prevalent technique. Though it is a small area still requires a lot of precision, knowledge and aesthetic skill regarding anatomy, designing of brows, extraction and implantation technique. In this paper, we performed many cases of eyebrow reconstuction including revision by our own implanter. The cases analyzed in this paper were corrected only by transplantation of occipical donor hair without laser hair removal nor tattoos. This article gives a comprehensive view regarding how to correct previously unsatisfactory eyebrow transplant with special emphasis on several points as hair follicle density, eyebrow shape, entire or partially reconstruction, which has become the most skillful technique.
Keywords: Eyebrow Transplantation; Implanter; Hair Follicle Density; Hypothyroidism
Introduction
Eyebrows are the most communicative feature and form a masterline of the face. It is the orientation fact concerning which all other perspectives and outlines of the face are established. Repairing eyebrows have become a reworthing procedure of hair transplant because of the increasing information and exceptional results. However, eyebrow transplant requires a high degree of skill and experience, not to mention the reconstruction transplant under the condition of previously unsatisfactory eyebrow transplant. With the extensive experience of the author in the field of follicular unit extraction (FUE) and follicular unit transplant (FUT)/strip, especially in aesthetic facial hair restoration, it is feasible to perform high-quality surgical techniques creating satisfactory results and a happy outcomes to patients after previously eyebrow transplant under comprehensive communication.
Procedure evaluation before the transplant
Cosmetic is the most common signs of eyebrow transplant such as inherited absence or insufficient coverage, of a normal appearing eyebrow requiring darker colour or an uneven eyebrow with lack of lateral third or medial portion. The other uncommon indications are trichotillomania, scar due to trauma, burn or tumours, stable alopecia areata, madarosis due to hypothyroidism, leprosy, etc. [1]. Although a correct candidate is one who has accurate expectations, understands limits in density achieved, has a pronounced defect than purely cosmetic purposes and stable or treated disease, the patient still expects a near-perfect surgical result. Even well awaring the difficulties of the reconstruction of eyebrow transplant, after seeing the patients undergoing previous surgery, showing an extremely depressed and anxious state, the authors had to try to deal with the cosmetic problem secondary to previous eyebrow transplant.
Methods
The outline of the eyebrows comes from the arrangement and display of each hair follicle. The qulity and survival rate of the follicles implanted decide the appearance of the eyebrow. FUT/ strip with long hair has long been used using single or small hair grafts for brow transplant [2,3]. Persuing grafts of high quality, Graft quality index (GQI) of grade 1, can present the shape of the eyebrow more accurately. We prefer FUT with long hair to control the qulity of grafts, especially a grade 1 of GQI [4], and only a high surviral rate of hair follicle could show a beautiful outline of eyebrows. We use DIMIS-T 100A of high solution of digital Microscope and Samsung LED monitor for follicle dividing. Despite preparing graft using a dissecting microscope gives the dividing a little slower, however, it is worth the effort and much more perfect.
Case Analysis
Entire reconstruction
The patient received eyebrow transplantation by body hair (leg hair) one year before visiting the clinic. Occasionally, the implanted body hair was too thin and too sparse to connect the original eyebrow hair to present an intact curve. This time, we used the occipital donor hair to make an entire reconstruction. And the result gets more complete than the body hair (Figures 1 & 2).
Partially modified
The patient received eyebrow tattoo before eyebrow transplantion resulting in eyebrow hair lost and fibrosis under eyebrow area noted afterwards. She requested eyebrow implantation and liked it to go unnoticed. After the first implantation, partial eyebrow tail didn’t grow well. We checked the direction and quality of the eyebrow head and made a consecutive curve of the eyebrow. The result of integral contour presented after secondary remodification (Figures 3 & 4).
Shape adjustment
Some patients intend to change their eyebrow shape after transplantation. The stretching points of the eyebrow contour are mostly affected by the spots of brow’s peak. If the peaks’ position beyond the lateral canthus, the patient will appear angry and old look. Trying to enhance both brow heads and closer to the middle nose, it will lower down the arch of the eyebrow’s contour. After adjustment and strengthening the heads of the eyebrows, it would make the face appearing kinder, gentler, and more pleasant (Figures 5 & 6).
Density problem
The contour and shape of the eyebrow are built by several hundred hairs. To implant several hundred hairs onto this limited area is really an arduous and skillful technique. However, the patients often desire the evenly displayed eyebrow hairs without any interspace for the better homogeneous presentation. We used single hair and small 2- hair grafts interspersing in the original hairs, making it look more pleasing and homogeneous (Figures 7 & 8).
Curl direction
Generally, most common problems are related to direction and curl, colour and texture mismatch or lack of regrowth [5]. Despite of the shape design and point location, the curl direction is an important factor to make up the image of the eyebrow. Reverse or crooked direction would damage the smooth curve of the eyebrow. To remedy the interference of the bad curl, we implant more and thicker hairs inside and beside them to ease off the visual effects of the undesired curl directions as much as possible (Figures 9 & 10).
Shaft diameter
Compatible hair qualities are necessary in eyebrow revision, even though it is unreasonable in some case. Selection of shaft diameter is related to the eyebrow even face image before surgery. Thus, selecting compatible shaft diameter is important factor in eyebrow revision. It is more important to check the eyebrow shaft of previous implant by trichoscopy before eyebrow transplant, it could find a better reference for revision [6] (Figures 11 & 12).
Low survival rate
FUE is popular in recent years. Howeveer, unskilled physicians may have undesirable consequences. The patient received FUE eyebrow transplant one year before coming to our clinic. Unfortunately, the implanted follicles from FUE presented extremely low survival rate. And owing to the short shaft of follicle is difficult to orient the hair flow, the hairs growed in odd directions. Because of poor survival rate and different hair flow, it will not present a smooth curve of the eyebrow at all. The affected area is too large for the patient to distinguish between old and new hairs. So, the author has to implant the eyebrows with very high density to facilitate the patient trimming (Figures 13 & 14).
Post-operativecare
The patients are instructed not to wash the face and doing make-up on the periorbital area from the next post-operative day until all crusts have fallen off, about ten days after. After ten days, the implanted hair will start to fall off and nearly all brow transplanted hair fall due to anagen effluvium [7] until two months. Hair regrowth begins at 3-5 months. In next 6-8 months, number increases with more density.
Conclusion
The revision of eyebrow restoration is even more challenging than the virgin eyebrow implantation. The details include low follicle density, peculiar hair curl directions, unnatural looks, unsatisfied shapes, hair qulity and so on after implantation. Inspite of the above, sometimes it still varies regarding the personalities of the patients. To keep careful and conservative communication with the anxious patients is a main determinant before making decision. Overall, with the use of highest standards of techniques and with increasing experience, we provide excellent and beautiful results with patient’s accurate anticipations.
To Know More About JOJ Dermatology & Cosmetics Please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/jojdc/index.php
For more Open Access Journals in Juniper Publishers please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php
#Juniper publishers#Open access Journals#Peer review journal#Juniper publisher reviews#Juniper publisher journals
0 notes
Text
Emulating Natural Morphology in Anterior Crown Fractures: Two Years Follow-up Report - Juniper
Emulating Natural Morphology in Anterior Crown Fractures: Two Years Follow-up Report - Juniper
Authored by Bora korkut
Abstract
Patients may suffer from undesirable aesthetic problems due to color, shape and structural or position abnormalities of anterior teeth. Crown fractures are one the most common reasons of these aesthetic complaints especially in young patients. Creating a conservative as well as powerful restoration against destructive occlusal forces while emulating similar outlook to natural dental tissues is the main objective of treatment of such cases. Direct composite resin restorations are one of the best possible treatment options for the anterior crown fractures. As the dental materials and techniques develop, the clinicians start to learn the physical and optical properties of these materials and use them with proper techniques to create more natural alike as well as long lasting restorations. These restorations are no longer named as 'day savior fillings' today but are called minimally invasive, functional and long lasting 'direct aesthetic restorations' that perfectly emulate natural dental tissues even in anterior area. This article illustrates how to perform a minimally invasive, long lasting, functional and natural alike direct aesthetic restorations in a single visit..
Keywords: Crown fracture; Direct aesthetic restorations; Emulating natural tissues
Objective
Performing a minimally invasive, long lasting, functional and natural alike direct composite resin restorations in a single visit.
Introduction
Aesthetic restoration of lost dental tissues of anterior teeth is a crucial challenge in restorative dentistry. Patients may suffer from undesirable esthetic problems due to color, shape, structural and position abnormalities of anterior teeth. Creating more conservative as well as more powerful restorations against occlusal, lateral and protrusive forces and emulating similar outlook to natural dental tissues is the main objective of up-to- date, contemporary dentistry [1]. An increasing number of dentists prefer minimal invasive and less time-consuming treatment options; as direct resin restorations compared to indirect ceramic restorations for the anterior dental aesthetics [2]. In order to create more natural-looking restorations, clinicians must learn and understand the physical properties of the dental tissues and restorative materials that they use and also interactions of these tissues and materials with light [3]. Various dental materials and techniques have been coming on the scene to improve both functional and aesthetic quality of the restorations. However a few of the esthetic resin materials on the market meet the expectant. The ones having such properties such as simplicity, structural stability, surface polish ability, masking discolorations, surface texturing and simulating natural dental color parameters such as hue, value and chrome are one step ahead [4,5].
Clinical considerations
In this report complex crown fractures due to dental trauma on maxillary right central and lateral incisors were corrected with minimally invasive direct composite resin restorations by using layering technique in a single appointment. The composite resin material used in this case study is a recently developed resin based restorative material, Estelite Asteria (Tokuyama, Japan) designed for emulating natural dental tissues.
Case Report
17 years old female patient applied to the clinic with aesthetic complaints due to dental trauma. He had direct trauma to the maxillary incisors a year ago and had no pain or any other symptoms. According to the intraoral examination complex crown fractures on maxillary right central and lateral incisors were determined (Figure 1,2).
According to the radiographic and vital metric analysis the injured teeth were considered as vital. The periodontal tissues were healthy and oral hygiene was in good condition. The patient' s age and the examinations were both taken into consideration and a conservative approach, minimal invasive direct aesthetic resin restorations were considered as the treatment plan.
Shades selected by using macro dental photography and composite shade samples which are also known as the 'Button Technique. Most appropriate body and translucent shade samples of Estelite Asteria (Tokuyama, Japan) were selected and located on the crown of left central incisor. The body shades were located on the mid-third and the translucent shades were located on the incisal-third of the crown. Then a macro photograph was taken from the labial view by using a professional camera set designed especially for dental photography. The set consist of a body (D700), a macro lens (Macro 100mml), a macro twin flash (MT- 24EX Macro Twin Late Flash), two-sided reflectors and a dual flash bracket mount (Novo Flex Unset). The picture taken was processed in a computer software program called Adobe Photoshop CC (Photoshop CC, Adobe Systems Software). A processed black and white form of the photograph was used to decide the translucent shade. Another processed copy on which contrast was increased and brightness was decreased, was used to decide the body shade (Figure 3). A1B and NE shades (Estelite Asteria, Tokuyama, Japan) were selected. Temporary restorations were prepared for the cracked teeth on a cast model and silicone impression was taken to create a palatal silicone index (Figure 4). Rubber dam was applied on maxillary incisors and canines for maximum isolation (Figure 5). 45 degree deep beveling were done on both incisors to cover the crack lines as minimally invasive preparations (Figure 6. One bottle universal adhesive agent (Bond Force II, Tokuyama, Japan) was used with selective etching. The translucent shade composite resin, NE shade, was used to create the palatal enamel wall. The resin was placed on incisallt on the silicone index and refined by using a composite brushed wetting resin. Then the resin and the silicone index were placed intraoral on the palatal surface of the teeth and polymerized. The index removed and palatal enamel wall was created (Figure 7).
The same resin was used to create marginal enamel walls of the restorations by using kidney-shaped metal matrix bandstand wedges (Figure 8). Body shade composite resin, A1B shade, was used to emulate dentin tissue (Figure 9). Labial surface was restored by using the translucent shade resin (NE) to create the surface enamel layer (Figure 10). In order to avoid overcontouring, composite brush was used with the wetting resin for layering. The surface structure was also created in final surface layering step. The resin used for emulating the enamel surface layer was applied in 3 steps; medial third, distal third and middle third, so that creating the surface grooves, ridges and also incisal notches while layering. The irregular scratches on the surface were emulated by using the composite brush gently without wetting resin (Figure 11).
After polymerization of the last layer, glycerin (Air Barrier, GC, Japan) was applied to whole the restoration surfaces and polymerized for 40 seconds to eliminate the oxygen inhibition layer. The surface cleaned with water spray and dried with air spray. Marginal adaptations and removal of excessive resins were done by a #12 lancet, a fine-grained composite polishing disk (Soflex, 3M, Japan) and interface sandpapers (Epitex, GC, Japan). The labial surface was polished by using only a fine-grained spiral rubber disc (Twist-Dia, light blue) in low speed and in dry condition (Figure 12,13).
The patient was informed about the oral hygiene and informed for recalls for every 6 months (Figure 14).
At 2years recall no sensitivities, fractures, secondary caries lesions were detected on both the teeth and the restorations. Also no discolorations or demarcation lines were detected (Figure 15,16).
On the other hand the micro surface morphology on the central incisor, created with brush touches while layering, was barely may observed. The patient reported that the restorations were fully functional during the time and he was also very satisfied with the aesthetic result. Oral hygiene and periodontal health were also in good condition (Figure 17).
Considering all, in 2 years follow-up the structural integrity, the color stability as well as the aesthetic outlook of the restorations was considered as satisfactory. The patient was called for further follow-ups.
Discussion
Ever increasing aesthetic demands of the patients require better dental materials and application techniques and also more clinical experience and knowledge. Natural-looking as well as functional and stable dental restorations may only be created only with the combination of these headlines. Natural dental tissues demonstrate translucency, opalescence, and fluorescence that must be imitated by the chosen restorative material in order to emulate the natural [6,7]. Especially translucency is recently accepted to have a key role in shade match of the restorative materials with natural dental tissues. Translucency is defined as the amount of light that passes through the dental tissues and may vary according to one of the parameters of color, value [8]. If the value of a tooth or dental material is high, lighter reflect from the surface, resulting in low translucency [9]. Taken this into consideration, some dental manufacturers have developed some new generation of aesthetic composite resins to emulate the natural dental tissues better than ever.
In the case presented a recently produced Estelite Asteria (Tokuyama, Japan) was used as the composite resin material which has supra-nano inorganic spherical fillers. Although this resin has an advantage for using as two-step layering, in this case conventional three-step layering was used to mimic the natural dental tissue layers. The composite brush manipulation was very easy and effective while layering as the consistency of the resin was soft enough. It is a fact that the composite layering procedures under reflector light takes much longer time that might be a problem. But the working time of the shades of this resin was also long enough. The polymerizing time for the shades used in this study was 10 seconds that is an advantage for the clinician. The natural surface morphology was emulated with gentle brush touches while surface layering. As the method used for layering depends on not creating over-contouring, the polishing procedures for restoration surfaces only done by a fine grained spiral polishing disc (Twist Dia, light blue). The surface texture created by composite brush hits could only be protected by using this polishing procedure [10]. This polishing material also creates a very shiny surface that is also very resistant to discolorations. Smooth adaptation between resin and dental tissues and having no micro-leakage due to the enhanced physical properties of the resin such as low polymerization shrinkage may describe having no sensitivities or secondary caries at 2 years recall [11]. As the correct indication of the case is an indispensable condition for direct anterior resin restorations, the stability of the restorations depends on having no devastating occlusal forces. The restorations were fully functional during the 2 years time and had no fractures as a result of that [12]. The enhanced fracture resistance of the composite resin might also positively affect the strength of the restorations. Also the glycerin (Air Barrier, GC, Japan) used for enhancing the physical properties of the surface layer made a positive effect on creating a more resistant surface layer to potential fractures and discolorations [13]. The loss in micro surface morphology on the central incisor that was created with brush touches may be related to the erosive or abrasive pattern of patient's diet and brushing style. It may be due to the surface roughness of the restoration which is related to the physical properties of the resin used. However that loss was insignificant for the aesthetic outlook in speaking distance. The patient was very satisfied with the durability, aesthetic outlook and especially the color harmony and gloss of the restorations. The specific spherical fillers and enhanced optical properties of the resin [14], the button technique used for selection of the shades [15], overcontour less layering technique [8,16] and detailed polishing procedures [17] are possibly played the key roles in this aesthetic outcome.
For years the anterior direct resin restorations compared to the indirect veneers and accepted as a loser in general. They were blamed as weak especially about durability and color resistance. However before criticizing, everyone must self-criticize him/ herself and ask the question: if these direct restorations were done correctly or not? Like all dental procedures, direct composite resin restorations have some indications and contra-indications. These can be aliened as; proper occlusal relations [18], correct shade selection [19], good isolation [20], good adhesion [21], detailed polishing [22], frequent recalls [18,21] quality materials [18] and also clinical experience. These are like rings of a circle and if one of them breaks, then the whole restoration fails. If the direct composite resin restorations were performed by taking these into consideration, the success rate of these restorations would definitely increase.
Conclusion
As a conclusion although 2 years times still a short term to evaluate, with correct indication, quality material and proper technique the direct resin restorations were seemed to be highly long lasting, color resistant and aesthetic under the conditions of this follow-up case study If direct restorations with composite resins are done by the rules, they are obviously one of the best treatment options for today's dentistry.
For more Open Access Journals in Juniper Publishers please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/aboutus.php
For more articles in Open Access Journal of Dentistry & Oral Health please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/adoh/index.php
To know more about Open Access Journals please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/journals.php
#Juniper Publishers Review#Juniper Publishers group#Restorative Dentistry#dental sciences#peer reviewed journals
0 notes
Text

⋆⠀⠀&.⠀⠀٬⠀⠀(⠀⠀ARSENIC.⠀⠀)⠀...⠀is the first full album (lp) by south korean girl group, letalis. the album was released in both digital and physical form by south korean entertainment company, apricus culture on october 29, 2014.
the album was supported by performances of the title track, "POISON" and two additional promotional singles, "FOR THE THRILL" and "CHECK IT". as the group's first full-length album, ARSENIC received mixed reviews despite its overwhelming commercial success. the group promoted the album for a total of five weeks through music show performances, two seoul concerts, five fanmeetings, and several variety show appearances. the album's title track, "POISON" received a total of 8 music show wins while "CHECK IT" amassed 2 towards the later end of promotions.
despite the album's popularity, critics published mostly lukewarm reviews of the album. most prominently, a common critique was the "repetitive" sentiment shared by critics in both korea and abroad. despite critical favorites "REBOUND", "CHECK IT", "LOVE/OR", and "BAD GIRL" receiving praise for the involvement of contributing members naryun, jiseo, and melanie, other songs were heavily criticized for their recurring themes, genres, and structure. regardless, the group's fanbase would propel the album and its promotional singles onto the gaon and billboard global charts, solidifying the "bread and butter" of letalis' musical character.

⠀*⠀SECTION ONE⠀:⠀the tracklist.
ʬ.ʬ.⠀001:⠀ ⠀٬⠀⠀ REBOUND
ʬ.ʬ.⠀002:⠀⠀٬⠀⠀ FOR THE THRILL⠀
ʬ.ʬ.⠀003:⠀⠀٬⠀⠀ POISON* (title)⠀
ʬ.ʬ.⠀004:⠀⠀٬⠀⠀ GINGER TRUFFLE
ʬ.ʬ.⠀005:⠀⠀٬⠀⠀ DRIP⠀
ʬ.ʬ.⠀006:⠀⠀٬⠀⠀ LIGHT ME UP⠀
ʬ.ʬ.⠀007:⠀⠀٬⠀⠀ CHECK IT
ʬ.ʬ.⠀008:⠀⠀٬⠀⠀ LOVE/OR
ʬ.ʬ.⠀009:⠀⠀٬⠀⠀ MISS.ME
ʬ.ʬ.⠀010:⠀ ⠀٬⠀⠀ GUN
ʬ.ʬ.⠀011: ⠀ ⠀٬⠀⠀ BAD GIRL⠀
ʬ.ʬ.⠀012:⠀ ⠀٬⠀⠀ MINDURZ
ʬ.ʬ.⠀013:⠀ ⠀٬⠀⠀ GLASSSY

⠀*⠀SECTION TWO⠀:⠀the physical album.


⋆⠀⠀&.⠀⠀٬⠀⠀two versions of arsenic were available for purchase upon initial release. the group would go on to record the entire album in japanese for a limited edition special release in 2015 as part of their debut anniversary celebration.
ʬ.ʬ.⠀STANDARD VERSION: contains one disc, one photobook (featuring 100 photos), one of four unit posters, one of seven member-written letters, one of seven random photocards, one group poster, and one of three random stickers.
ʬ.ʬ.⠀TONEDEAF VERSION: contains one disc, one photobook (featuring 111 photos), one of four unit posters, one of seven member-written letters, two of seven random photocards, one of seven individual mini-poster, one of two random group posters, three stickers, and one fandom charm.

ㅤ*ㅤSECTION THREEㅤ:ㅤthe styling.

sticking to the general idea of their previous era, the members each had a personal hand in their own looks. each stage built off the individual tastes of each member while holding on to their cohesiveness. easily one of their most identifiable eras solely off the styling.

ㅤ*ㅤSECTION FOURㅤ:ㅤthe notes.
a fan favorite era
one of their more iconic albums, def a top three vitalis staple album
people either loved or hated this era (including the girls themselves). there were a lot of mixed reviews among critics and it wasn't secret to the girls.
weird animosity between emmy and juniper starts here. no one really knows why but they were regularly exchanging not-so nice words about each other to anyone who cared enough to listen.
one of their encore stages went viral after they used voice changing microphones with shuffled effects (entirely emmy's idea). still one of the highest viewed encores of all time, a letalis fandom staple video as well. several members were in tears from laughter (emmy, jiseo, naryun) while others were completely stoic (naira, juniper). ironically, this video pretty much sums up their public dymanic pretty well.
lots of controversy surrounding the tracks on the album. towards the end of the promotional period, the girls were visibly tired of performing "for the thrill" which was unanimously voted in a fan poll posted to melanie's fancafe as being the fans' least favorite b-side off the album.
despite how well the title track, "poison" did, some of the girls voiced their varying opinions on what they would chosen instead. snowballed into a weird scandal where they were accused of suffering from "celebrity disease". never ended up being addressed but apricus did tighten the reigns on what the girls were allowed to say/bring up during the rest of the promotions.
the true beginning of the core writers and producers that usually appear on letalis albums. also the beginning of the naryun and trenton rumors (that would eventually be entirely true). it wasn't lost on the public that letalis was gonna stick to what works so these same writers and producers in different arrangement are a staple to their discography.
miss. me randomly went viral in 2020 around the time challenges became a regular occurrence. so in between the challenges for the album they were promoting at the time, they were suffering through doing cute little hand choreo for the song.
naryun, melanie, and emmy gained their first credits on this album!
announced their first asian tour after the end of promotions. cute little 15-show tour, mostly in large theaters and arenas, nothing crazy but a precious memory for all the girls.
# ⋆⠀⠀ʬ.ʬ.⠀⠀٬⠀⠀(⠀⠀&.⠀⠀)⠀...⠀DISCOGRAPHY.#ficnetfairy#fictional kpop company#fictional kpop oc#fictional kpop idol#fictional kpop community#fictional idol group#fictional characters#fictional idol community#fictional idol addition#fictional idol oc#fictional idol company#fictional kpop soloist#fake kpop gg#fake kpop girl group#fake kpop group#fake kpop idol#fake oc#kpop au#idol kpop#kpop#kpopidol#kpop gg#oc kpop gg
22 notes
·
View notes
Note
I'm not saying adults insisting they only need to read YA books and watch children's cartoons is leading to this culture wide phobia of sex which in turn is becoming a useful vector for the increasing spread of fascism except that is exactly what I'm saying.
Im not that anon but want to expand on their thought, if they're saying what I think they are.
I thought of this more when seeing an old post of someone saying their English teacher should have let them write a report on Divergent instead making them read 1984. Someone commented supporting the OP, saying that they never read Divergent, but 1984 is problematic. Iirc, the commenter referred to Winston (I think that's the protag in 1984; sorry I haven't reread it in years) as a creep. I can't remember is this specific commenter called Winston a misogynist, but that's a common complaint I hear when people say they don't like 1984.
The screenshot of that post also had other screenshots, including the twt posts of YA authors saying that the classics were problematic. It's a sentiment I keep seeing around book twt before I deactivated my account but still on booktube as well, and it's always booktubers who also read and rant about Colleen Hoover, because they know her name gets clicks. Or booktubers that do those videos titled "I read [old/popular/controversial] series so you don't have to".
Sorry, sliding off topic a bit. Going back to what anon said, YA books tend to be more sanitized. They're supposed to be written for a 15-19 audience, so sex and gore aren't supposed to be explicit. There are YA books with sex scenes. 2 I read recently have sex scenes, but they aren't explicit. One uses mostly poetic language and infers to what's happening, and the other essentially fades to black after they get into bed, as they're touching and then picks up the next morning. (One of these YA books had a big controversy on booktube a few years ago for being problematic, though. Gee, wonder why /s)
But for the most part, often for people who enjoy urban fantasy or romances but not steamy scenes, they may go for YA, since it's usually more "PG". Unfortunately, some people get it in their head that this makes YA inherently "better", that adult books that are being more explicit are only doing it to get more sales, when YA tbh has a tighter hold on it marketing-wise.
Okay, I'm not published (yet), but I've been studying it when I need to take a break from writing to see what course is best for me and what I want to write. YA is becoming oversaturated in the market, so it's not as big a "money making genre" for debut authors as it might have been once (and I'd argue that even in the past when YA was smaller, you still had to be lucky, known, or connected to get that 6-figure check for a debut YA novel). YA is more likely to get scrutinized, considering its supposed to he for a younger audience, so a YA author wanting to push boundaries is going to receive more push-back than an adult lit author.
Now pushback happens in adult lit, too, like Ava Reid saying her editor or publisher (I forget who) told her that Juniper&Thorn might be too dark. (I've read it. Yes, it's dark, but bad reviews I saw for the book blew it way out of proportion. If you (gen) like lyrical/poetic narration and gothic horror, I highly suggest it).
But it feels like there's more of a push to keep YA books "clean". You can find some outliers, but like the YA I mentioned above, those outliers in YA that push boundaries can get wrapped in controversy and called problematic.
And for whatever reason, some people on booktube say this is a good thing and say "think of the children!"
They will say censorship is bad but then advocate for sanitized YA to be read instead of classics, because the classics are "bad" and "teach bad things" and "should be left in the past". They advocate for censorship without realizing they are advocating for censorship. It's exhausting, and as someone who wants to be published and does enjoy a lot of YA, it makes me feel discouraged. I don't think I'm "pushing boundaries" at all in my writing or saying anything new, but I'm very sure it's not sanitized enough for most publishers, especially if I wanted to try for one of the beg houses in the US.
Tl;dr One of the major problems in this anti-intellectualism is capitalism.
.
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Spin Coating of Thymol Blue Indicator on F-SnO2 Glass to fabricate a Novel Sensor Electrode in Potentiometric Acid-Base Titration
Authored by: Nasser M Abu Ghalwa
Abstract
This study deals with the investigation for preparation of conductive glass / thymol blue TB sensor electrode by spin coating of the thymol blue (TB) indicator on conductive glass formed from F-SnO2, and it’s using as indicator electrode in potentiometric acid-base titration in aqueous solution at 298K. The change of the open circuit potential with pH (E-pH) curve is linear with slope of 0.052V/dec at 298K. The standard potential of the above electrode E0, was determined with respect to the SCE as reference electrode. The recovery percentage for potentiometric acid-base titration using G/TB as indicator electrode was calculated.
Keywords: Potentiometry; Thymol blue; Sensor; Conducting glass; Titration; Indicator electrode
Introduction
Chemical sensors are devices that convert the concentration of target compounds into an analytical signal. The term analytical implies the concept of measurability. Then a chemical sensor converts the information about the presence of target compounds into a measurable quantity [1]. Chemical sensors play a big role in checking the environment we live in, contributing information on industrial production processes, quality management of food stuffs and beverages, detection and analysis of some ions and many other applications [2]. Transparent conducting oxides possess a unique combination of optical transparency and metallic conductivity in a single material. Their properties are widely exploited in a host of energy, optical, and electrical applications [3-5]. SnO2 is a wide band-gap semiconductor with a band gap of 3.6eV and was the first transparent conducting oxides to receive significant commercialization. It exhibits good transparency and can be easily n-type doped. Degenerate carrier densities can be achieved by doping with fluorine [6,7]. Potentiometric titrations are the basic chemistry laboratory technique for the quantitative analysis of substances with unknown concentrations using standard solutions of known concentration. The substance with unknown concentration and the standard solution are termed analyte and titrant respectively [8]. This method widely used in different fields such as the food industry, scientific research, and chemical, clinical and pharmaceutical laboratories. Titrimetric procedures based on a detection of the endpoint, i.e., the point at which volumetric titration is completed, are successfully employed over a wide range of concentrations and are popular because of their simplicity, speed, accuracy and good reproducibility [9]. Recently, many studies developed some types of electrodes in potentiometric acid base titration [10-13]. Thymol blue (thymolsulphonephthalein) is used as a pH indicator. A solution of thymol blue exhibits three form (red color), Neutral form (yellow color) and basic form (blue color) show Figure 1 [14].hone radiation can lead to adverse effects [10-16]. Thus, the public concern is that increasing the frequency of the radiation will also increase the effects of the radiation [14-16].
The aim of this study for preparing a spin coating of thymol blue indicator TB on conducting glass formed from F-SnO2 to prepare a new modified electrode sensor (glass / indicator electrode), for used in potentiometric acid base titration.
Experimental
Chemicals
The chemicals used in potentiometric titrations and preparation the electrode was tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), Thymol blue (TB), hydrochloric acid, ammonia, Acetic acid, phosphoric acid, sodium hydroxide, sulfuric acid, citric acid and disodium phosphate. The chemicals are of analytical pure grade (Merck) Where the F-SnO2 glass from (Sigma Aldrich).
Synthesis of Materials
Preparation of Hydrolyzed TEOS
A mixture of 2. ml of absolute ethanol, 0.86ml of 0.1M of HCl were added to 2.5ml of TEOS under stirring. The obtained solution was kept under stirring at room temperature until a homogeneous clear solution was obtained. The solution was aged at least for 24 hours before used in the coating process. The hydrolyzed TEOS solution was used as a host matrix for the indicators.
Preparation of Indicators
Indicators solution (1×10-2M) thymol blue indicator (TB) were prepared using absolute ethanol as solvent.
Stock solution of indicators
The sample solution was prepared by mixing 1ml of blank hydrolyzed TEOS solution and 1ml for each indicator.
Preparation of Silica-immobilized Thin Films
Substrate Cleaning
Glasses were activated by concentrated H2SO4 for 24 hours, then washed with distilled water and ethanol. The surface was finally rubbed with cleaning paper.
Preparation of glass/TB electrodes using Spin coating method
All thin films layers prepared in this work were made by spinning three drops of the solutions onto a clean glass slide. The coating process was performed using the spin coater machine at 900rpm spinning speed for 1 min. period time. To obtain multilayers of thin films a subsequent spin coating method was performed after gradually drying of the previous layer at room temperature for 24 hours, then dried at 80oC for another 48 hours. And repeat the spin coating two or three time. Where the conducting substrate is usually conducting glass, consisting of glass coated with a thin layer of F-doped SnO2.
Sensor design of potentiometric cell
The potential of the indicator electrode relative to that of the reference electrode was measured on a digital multimeter model YDM 302C (China). Potentials were measured to ±5mv. The potential of Thymol blue, sensor indicators electrodes was measured vs. a saturated calomel electrode (SCE). The error in the measurement of the potential due to liquid- junction potentials in these electrolytes is estimated to be about 0.001V.
The solution in a beaker is stirred by means of a magnetic stirrer. The electrodes (indicator and reference) were dipped slowly into aqueous solution (acid or reductant). After the steady state potential was attained, the titration of the acid was carried out by addition of 1ml of the base to the acidic solution, waiting until the steady potential is established and then measured. The potential variation depends on the type of the base, the progress of neutralization process and on the initial concentration of the acid to be titrated. The results were reproducible to satisfactory value of ±5 mV for potential measurements. The process of addition of the titrant was repeated until the equivalence point was reached.
The E-pH relation of Thymol blue electrode:
The E-pH relation of Thymol blue electrode
According to Figure 2 the change of the open circuit potential (E) of the G/ TB indicator electrode with pH . The E-pH plot of the G/TB indicator electrode fits straight line with slope of 53.11mV at 298K. This value is close to the magnitude of the term 2.303RT/F at the corresponding temperature (59.1mV at 298 K). This value is close to the magnitude of the term 2.303RT/F (where: R gas constant, T absolute temperature and F Faraday constant) at the corresponding temperature (59.1mV at 288K). From Figure 2 the E0 value of the sensor electrode, i.e., the potential at [H+] = 1, is computed as 279.1mV relative to the saturated calomel electrode and can determination by:
This equation is applicable for the reversible behavior of working electrode. From the developed Nernst equation, we indicate that working electrodes can be used as pH-indicator. At high or low pH, the electrode indicates pH less than true value as pH glass electrode, it may be due to damage in electrode or existence of alkali metal ions in solution too.
The response time of the sensor
In general, the response time was defined as the time of sensor’s output reach to 90% of the equilibration after the measurement was started, especially to electrochemical sensors [15-17]. Figures 3a-3e show the response time of the G/TB sensor at different concentration of phosphoric acid, acetic acid, Hydrochloric acid, ammonia and NaOH respectively. Response time, in the range of (100-450) seconds was achieved, which rendered the sensor highly practical.
Effect of temperature on the response characteristics:
The importance of temperature measurement when performing pH measurements has already been mentioned in reference to slope correction. Temperature also has an effect of both pH buffers and solutions, as the hydrogen ion activity will increase with increasing pH [18].
The Thymol blue sensor response was evaluated at different temperatures, Figure 4. At lower temperatures, like 288K, the slope of the sensor was about 33.54mV/decade and the sensor would be used for pH measurements in the range from (2-11). However, when the temperature of the test solutions was adjusted to 298K, the slope significantly increased to 53.11mV/decade. By raising the temperature to 313K and 323 K the slope increased to 54.11mV/ decade and 59.75mV/decade respectively. Figure 4 shows the square of the correlation coefficient (r2) for pH measurements using the solid-state sensor, at different temperatures, as compared to pH values obtained by a conventional pH electrode (Hanna Instruments HI 1131 pH combination electrode) was found to change as the temperature increases where as r2 values for measurements at 283K, 298K, 308K, and 318K were 0.9655, 0.9386, 0.9482, 0.9876, respectively. This indicates that better results could be obtained at 298K due to easy and settable to use without heating.
The relation between conventional glass PH electrode and G/ TB indicator electrode
All potential values were converted with respect to the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE). During experiments, pH was also monitored with a commercial glass electrode that was calibrated daily using commercial standard buffer solutions (2-9) [19]. Figure 5 represents the correlation between the conventional glass PH electrode and G/Thymol blue indicator electrode, it can be easily recognized that excellent correlation between the results obtained by the solid-state pH sensor and the conventional glass pH electrode could be achieved. The slope of this relation was 0.947 and the r2 was 0.947. This indicate that G/TB indicator electrode potential values are closed to the values of conventional glass pH electrode.
Potentiometric of weak acids against NaOH
Figures 6a & 6b represent the potentiometric titration of 0.1M NaOH with different concentrations of acetic acids and phosphoric acid. The variation of G/TB electrode potential at 298K with the different volumes of standard 0.1M NaOH followed typical potentiometric titration curves. These curves show slight decrease in potential (to more negative values) with the addition of the titrant. Where Figure 6c show the potentiometric titration between the volume of 0.1M standard HCl against ammonia. The variation of the TB electrode potential at 298K with the different volumes of standard HCl followed typical potentiometric titration curves. These curves show slight increase in potential (to more positive values) with the addition of the titrant.
Location of endpoints
Figure 7a represent ΔE/ΔV against V plot for the potentiometric titrations of CH3COOH and H3PO4 with 0.1 M standard NaOH. From the plots the values of end points were determined. The obtained results and calculated values of (R%) are listed in Tables 1 & 2 for acetic acid and phosphoric acid respectively. The values of pKa for different concentration of acetic acid and phosphoric acid were calculated using the method of half neutralization as shown in Table 3. There are two jumps in the titration of phosphoric acid with NaOH using G/TB sensor. i.e two end points appear by using this electrode. The obtained values of pKa for the investigated bases are close to the previously reported values. Where Figure 7b represent ΔE/ΔV against V for the potentiometric titrations of ammonia and 0.1M standard HCl respectively. From the plots the values of end points are determined.
Finally, the values of pKb for different concentration of ammonia can be determined using the method of half neutralization. They are listed in Table 3 for the tested bases. The obtained values of pKb for the investigated bases are close to the previously reported values.
Conclusion
This study investigated the preparation of the modified electrodes of type glass/ thymol blue G/TB and their use as sensor indicator electrodes in the potentiometric acid-base titrations in aqueous solution at 298K. E-pH curve is linear with slope of 0.053.1V/decade for the G/BTB electrode at 298K. This value is close to the theoretical value 2.303RT/F (0.059V at 298K) and the recovery percentage for potentiometric acid-base titration using G/TB as indicator electrode was calculated.
i. On other hand the standard potential of the tested electrode, E0, is computed as 279mV with respect to SCE as reference electrode. Acetic acid, phosphoric acid, hydrochloric acid and ammonia were successfully potentiometric titration with NaOH as titrant in aqueous medium at 298K. Finally, this study is applied in different temperatures like 283K, 298K, 308K, and 318K were the correlation coefficient (r2) 0.9655, 0.9383, 0.9482, 0.9876, respectively.
To Know More About Juniper Online Journal Material Science Please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/jojms/index.php
For more Open Access Journals in Juniper Publishers please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php
#Juniper Publishers#Material Science#Materials Theory#Structural Materials#Juniper publisher reviews#Juniper publisher journals
0 notes
Text
Anti-hyperglycemic Effect and Regulation of Carbohydrate Metabolism by Phenolic Antioxidants of Medicinal Plants against Diabetes

Authored by HP Gajera
Introduction
Background
Diabetes mellitus is a carbohydrate metabolism disorder of endocrine system due to an absolute or relative deficiency of insulin secretion, action, or both [1]. The disorder affects more than 100 million people worldwide and it is predicted to reach 366 million by 2030. The non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM, type 2) is the most prevalent form globally which is associated with elevated postprandial hyperglycemia. The occurrence of NIDDM 2 has been shown an alarming increase during the last decade (http//www.who.Int/diabetes/en/).
Plant derivatives with reported hypoglycaemic properties have been used in folk medicine and traditional healing systems. Very few of these traditional antidiabetic plants have received proper scientific or medical scrutiny despite recommendations by WHO. Ayurveda and other Indian traditional approaches have described more than 800 plants in the Indian subcontinent, known to possess antidiabetic potentials. These require to be effectively studied and in fact only few of them have been characterized for their mechanistic action [2,3]. Pancreatic α-amylase, is a key enzyme in the digestive system and catalyses the initial step in hydrolysis of starch to maltose and finally to glucose. Degradation of this dietary starch proceeds rapidly and leads to elevated post prandial hyperglycemia. It has been shown that activity of HPA in the small intestine correlates to an increase in post-prandial glucose levels, the control of an important aspect in treatment of diabetes [4]. Hence, retardation of starch digestion by inhibition of enzymes such as α- amylase would play a key role in the control of diabetes.
The discovery of specific high-affinity inhibitors of pancreatic α-amylase for the development of therapeutics has remained elusive. Inhibitors currently in clinical, use for example, acarbose, miglitol, and voglibose, are known to inhibit a wide range of glycosidases such as α-glucosidase and α-amylase. Because of their non specificity in targeting different glycosidases, these hypoglycemic agents have their limitations and are known to produce serious side effects. Therefore, the search for more safer, specific, and effective hypoglycemic agents has continued to be an important area of investigation with natural extracts from readily available traditional medicinal plants offering great potential for discovery of new antidiabetic drugs [5]. Ponnusamy et al. [6] studied on antidiabetic medicinal plants for human pancreatic amylase inhibitory effect in vitro and found that pancreatic α-amylase lower the levels of post perandial hyperglycemia via control of starch breakdown. The probable mechanism of action of the above fractions is due to their inhibitory action on HPA, thereby reducing the rate of starch hydrolysis leading to lowered glucose levels. Phytochemical analysis revealed the presence of alkaloids, proteins, tannins, cardiac glycosides, flavonoids, saponins and steroids as probable inhibitory compounds.
Anti-hyperglycemic effect of natural phenolic antioxidants
Advanced molecular studies showed that methanol extract of black jamun plant modulate the expression of glucose transporter (Glut-4), peroxisome proliferator activator receptor gamma (PPARγ) and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3 kinase) comparable with insulin and rosiglitazone [7]. Evaluation of black jamun containing antidiabetic poly herbal formulation in alloxan induced diabetic rats also showed significant hypoglycemic activity, positive glucose tolerance activity and reduced lipid peroxidation in various organs compared to that of the diabetic control animals [8]. Meshram et al. [9] studied on hypoglycaemic action of black jamun seeds. The possible mechanism by which extracts bring about its may be by affecting the activity of glucoamylase or by increasing the glycogen biosynthesis. Thus, the significant inhibition of glucoamylase suggests that the active hypoglycaemic compound present in methanolic extracts of jamun seeds does not necessarily require the presence of functioning of β-cells for its favourable action seen in type-I. It means the methanol extracts of black jamun seeds may act in a variety of diabetic conditions with or without functioning of pancreatic β-cells.
Hasan et al. [10] studied DPPH radical scavenging activity of black jamun seed extracted in methanol. It has been determined that the antioxidant effect of plant products is mainly due to radical scavenging activity of phenolic compounds such as flavonoids, polyphenols, tannins, and phenolic terpenes [11]. Liang & Yi [12] identified hydrolysable tannins (ellagitannins) extracted from black jamun fruit showed a very good DPPH radical scavenging activity and ferric reducing/antioxidant power. The results are promising and indicating the utilization of the fruit of black jamun as a significant source of natural antioxidants.
Stanely et al. [13] evaluated the protective effects of gallic acid on brain lipid peroxidation products, antioxidant system, and lipids in streptozotocin induced type II diabetes mellitus. The results showed the beneficial effects of gallic acid on brain metabolism in streptozotocin induced type II diabetic rats. A diet containing gallic acid may be beneficial to type II diabetic patients. Meguro et al. [14] investigated the effects of continuous ingestion of a catechin rich beverage in patients with type 2 diabetes. The significant increase in insulin level was observed to patients fed with green tea containing the catechin. Rizvi et al. [15] evaluated the effect of tea catechins (epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), epigallocatechin (EGC), epicatechin gallate (ECG) and epicatechin (EC)) on markers of oxidative stress in erythrocytes from type 2 diabetics. The relative effectiveness of individual catechins are in the order of EGCG>ECG>EGC>EC. Higher intake of catechin rich food by diabetic patients may provide some protection against the development of long term complications of diabetes. Chlorogenic acid is a major component of coffee that may provide more of an explanation for coffee’s effect on risk for type 2 diabetes. Chlorogenic acid proposed beneficial effects on glucose metabolism. The chlorogenic acid may delay glucose absorption in the intestine through inhibition of glucose-6-phosphate translocase 1 and reduction of the sodium gradient driven apical glucose transport. In vitro studies and animal studies showed that chlorogenic acid derivates can be decreased hepatic glucose output through inhibition of glucose- 6-phospatase [16].
Jung et al. [17] investigated the blood glucose lowering effect and antioxidant capacity of caffeic acid in mice. Caffeic acid induced a significant reduction of the blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin levels than the control group. Increased plasma insulin by caffeic acid was attributable to an antidegenerative effect on the islets. Caffeic acid also markedly increased glucokinase activity and its mRNA expression and glycogen content and simultaneously lowered glucose-6- phosphatase and phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase activities and their respective mRNA expressions, accompanied by a reduction in the glucose transporter 2 expression in the liver. Zhi et al. [18] investigated the antioxidant activity of black jamun leaf extracts. Leaf extracts contained phenolic compounds, such as ferulic acid and catechin, responsible for their antioxidant activity.
Diabetes, when uncontrolled, causes dyslipidemia often followed by atherogenic abnormalities. Balasubashini [19] examined role of ferulic acid (flavonoid) in diabetes induced dyslipidemia. Study demonstrates that ferulic acid lowers the lipid levels in diabetic rats and hence prevents further complications. It has been documented that ferulic acid may lower blood sugar level of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetic mice by enhancing insulin secretion [20]. Diabetic mice was given rice derived ferulic acid for 17 days and results showed that plasma insulin level increased while blood sugar level decreased significantly compared with control [21]. Ferulic acid may be beneficial in Type 2 diabetic and for the management of diabetic complications. Hussain et al. [22] indicated that quercetin can decrease postprandial glucose level after disaccharides loading, which may be mainly attributed to inhibition of α-glucosidase as one of the expected mechanisms for the reduction of plasma glucose. This effect subsequently leads to suppression of postprandial hyperglycemia. Thus, quercetin can be considered as a potential candidate for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Medicines that reduce postprandial hyperglycemia by suppressing the absorption of carbohydrates are shown to be effective for prevention and treatment of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus [23]. Quercetin inhibited in vitro the intestinal α-glucosidase activity [24]. It has been also assumed that quercetin activates tyrosine kinase. Phosphorylation of the specific region of the subunit in insulin receptor (including Tyr- 1158, Tyr-1161 and Tyr-1162) correlates with receptor tyrosine kinase activation and the propagation of the biological actions of the hormone [25].
Correlations between antidiabetic, antiradical and phenolic compounds
Our previous study Gajera et al. [26,27] suggested that antidiabetic activity of fruit parts of black jamun landraces was positively correlated with free radical scavenging activity, nutraceuticals profile and individual phenolic constituents. Total phenols and individual phenolics are positively correlated with antidiabetic and antiradical activities but vary with different level of significances. Individual phenolics - gallic, catechin, ellagic and ferulic acids are highly positively correlated (P0.001) with antidiabetic and free radical scavenging activity. The positive correlation (P0.01) was established for caffeic and chlorogenic acids to scavenge free radicals and α amylase inhibitory activity (antidiabetic) for methanolic extract of black jamun fruit parts. The quercetin was found only in seed and its part kernel fraction of BJLR-6 (very small size fruits) and found to be positively correlated (P0.05) with antidiabetic activity. Among the fruit parts of black jamun land races, seed exhibited maximum seven individual phenolics and total phenols, particularly in their kernel parts. Among the individual phenolics, gallic acid was most diverse phenolic constituents which significantly positively correlated (P0.001) with inhibition of α amylase activity and DPPH radical scavengers followed by catechin, ellagic and ferulic acids in different fruit parts of black jamun land races. The study explained correlation of individual phenolics including flavonoids (ferulic) with α amylase inhibition and free radical scavenging activities in fruit parts of indigenous black jamun landraces.
Muniappan et al. [28] reviewed the black jamun as an antidiabetic plant which contained ellagic acid, glycosides, anthocynine, kampferol, marcein and isoquarcetine; and halt the diastolic conversation of starch into sugar. The phenolic constituents may be contributed directly to the antioxidative action. Consequently, the antioxidant activities of plant/ herb extracts are often explained by their total phenolics and flavonoid contents with good correlation.
To Know More About Current Research in Diabetes & Obesity Journal Please click on:
https://juniperpublishers.com/crdoj/index.php
To Know More About Open Access Journals Please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/index.php
0 notes
Note
omg actually keen to hear ur yellowface thoughts once uve synthesised them... im a chronic rf kuang hater but i also do read her books every time so i would love to know what u thoughtttt
hello omg thank you for asking about this, i would love to know your thoughts too actually!
so it's been a day, i was able to sleep on it... this won't be the most serious review ever but i'll freely share both what i've been mulling over and my thoughts as i type. i think the book is good enough for what i personally thought it would be, which is a silly off-kilter story with a very compelling premise. the bare minimum i initially knew, which is that some white girl stole her dead asian-american friend's work, was enough to intrigue me. what i didn't understand was the hype around how "insane" it is on tiktok (which i will readily admit is where i found out about the book's existence) and i had my hesitations to hold it to that standard. turns out i was right to be hesitant. there was room for so much more. like i understand the pov and insights are deliberately limited and unreliable bc of the main character herself, but here's one example: when juniper made a remark on athena not knowing what it's like to be poor, i expected those thoughts to play a larger role in the story or go a bit deeper, but they were left as few among the many bits and pieces of surface level commentary and somewhat valid criticism against athena and it kind of got lost in the mix. this is such a shame especially because it's clear juniper is big on her own family's dynamics and financial situation, so it could've been such a great comparison point (?) for her to really dig into when it came to her resentment against athena.
i feel like that was the biggest missed opportunity in my eyes because when i read the author bio at the end of the book, i was surprised to find that rf kuang herself is from yale. i didn't know who she was before reading the book, this is my introduction to her and i went in completely blind. knowing a bit of her background now honestly leaves a sour taste in my mouth because this time the story feels too self-referential the way some taylor swift songs can be (and i enjoy tswift btw lol). but i don't know for sure since i still haven't looked into her that much. this is why i would LOVE to know why you're a hater bc i feel we'd have similar reasons
also the buildup to the ending and the ending itself were both so underwhelming that it dampened some of the fun i had in earlier parts of the story. like i was enjoying this white woman going kind of crazy but kuang's stab at the uncanny fell so flat i literally could not stop just thinking about perfect blue 1997 and how i did not pick up the same suspense here. not that they have to be the same at all, i just live like this. also in line with this so much of the book feels chronically online. at first i appreciated how online spaces were so heavily embedded in the story but by the halfway point i was like, um.... i thought this was a satire on the publishing industry, not glimpses of publishing interspersed between losing ur mind over twitter and goodreads LOL.
for now this is all i have to say. fun book! i can tell rf kuang is skilled in her own right. i enjoyed the pacing and the writing style, it was such an easy read and there's nothing wrong with that. nothing i want to take too seriously or sink my teeth too deeply into. people on booktok praise yellowface way too highly that's 10000% for sure
#ans#hope its ok i answer ur ask publicly! let me know if i should take this down lol#but i REALLY want to know why youre a hater bc i truly dont know anything about this author at the moment
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Relationship Between Early Menopause, Estrogens Receptor A Polymorphism, Vitamin D3 Receptor Polymorphisms and Osteoporosis in a Mediterranean Population
Abstract
In order to clarify the role of candidate genes for the osteoporosis related phenotypes, we have investigated among polymorphism of the ESR1 gene and polymorphism of VDR3 gene in the relation to BMD and bone loss in a population of women of the southern Italy who underwent early (35-45 years old) menopause. The bone mineral density of all subjects was measured by Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). Molecular analyses were performed on ERa and VDR3 genes exons using both sequencing and RFLP technology. All women showed an average DEXA value less than -2,5. We have identified polymorphisms in the coding region of ESR1 gene that is well correlated with the bone status of the affected subjects. Vitamin D3 receptor also presents polymorphisms and is evident only in the affected subjects. The identified polymorphism of ESR1 is present only in osteoporotic patients and absent in normal subjects, such as the vitamin D receptor. Furthermore all the subjects that show such polymorphisms have DEXA values lesser than -2.5 showing a relationship between the above polymorphisms and bone loss. This let us to hypothesize that identification of polymorphism of ESR1 and vitamin D3 receptor could be a tool for early diagnosis of osteoporosis in early menopause woman.
Read More about this Article:https://juniperpublishers.com/jojcs/JOJCS.MS.ID.555852.php
Read More Juniper Publishers Google Scholar: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=rp_7-igAAAAJ&citation_for_view=rp_7-igAAAAJ:ufrVoPGSRksC
#Juniper Publishers Google Scholar#Juniper Publishers Review#Journal of Case Studies#SARS-CoV-2 virus#pharmacology#Dermatology
0 notes
Text
I’ve seen other fanfic writers do an AO3 wrap up and tbh I’ve been kind of embarrassed to do one myself because I was only a productive writer from May to October which isn’t even half of the year (thanks to Jedi: survivor, bg3, and everything in my authors notes) but it was also my most productive year for writing fanfic that I wanted to do something so…
Ao3 statistics don’t easily separate by year for a multi chapter fic that I started back in 2021, but I can do a rough estimate of 2023 stats and then reflect on every fic that I’ve written this year. (Edit: by the time I finish writing this we will be a week into 2024 at least)
Almyrah’s AO3 2023 Year In Review:
New fics posted: The Spy and The Actor, Phoenix the Vampire Hunter
Fics updated: The Spy and The Liar: The Movie (6x)
Word count: ~50k
Comment threads: 48
Kudos: 81+
Best comment: @agent-calivide (in Exes and Ohs, chapter 7 of The Spy and The Liar: The Movie)
I have had so much support for my writing this year thanks to the amazing I Expect You To Die fandom and the IEYTD fandom discord in particular. To be honest, you guys really make it hard to be humble with how much love is showered over my fics and I am so grateful for every kudos, comment, and bookmark I’ve received since I started the Celebrity Crush series way back in 2021 when a certain actor lived in my head rent free.
Like I said before the statistics are rough estimates and I think that the best way to celebrate all I’ve done this past year is with words more than numbers and statistics.
The Spy and The Liar: The Movie
This is probably the best fic I’ve ever written! I am so proud of how it has grown beyond ten bullet points to be the 66k story it currently is with more to come. I’ve loved weaving foreshadowing and subtext into the story that I think most people have missed.
It’s also really hard to stay humble as this is the most love I’ve ever gotten on a fic and it has somehow seemingly become the Agent Phoenix/John Juniper fic on ao3. I’ve literally dropped all my other wips for other and bigger fandoms because of how much love and support it’s gotten. Especially because of the people in the fandom discord. Maybe it’s the instant appreciation but I had never been more motivated to write than when y’all shared your love for this fic and the Celebrity Crush series in general.
The Celebrity Crush series and ieytd was the first thing that got me back into writing after going through the most traumatic and violent loss and experience of my entire life back in 2020 (wasn’t even covid related lol). Literally an entire year had passed before I could write again. To know that this story has meant as much to you guys as he has to me has been the greatest gift that could ever been given to me.
Thank you.
The Spy and The Actor
This story wasn’t really supposed to be anything. The first (and only) chapter was written on a whim in one sitting based on a conversation in the fandom discord. Just the third time I’d be rewriting the ieytd 2 with an Agent Phoenix/John Juniper twist…
But then came the comments.
For those that don’t know, the point of the fic was that it was written and published by John Juniper but to come off as a fan thirsting for John instead of John thirsting for Phoenix. At its core it was me roleplaying as John Juniper. And the discord decided to roleplay in the comments as various characters from the games and of course I had to respond in character as John Juniper!
Even when I was a teen I thought roleplay was kinda cringe. But now? I get it, like I get it! I had so much fun roleplaying as John Juniper!!! I’m usually really nice so being able to just let go and be an absolute bitch. I’m so excited to work on the next chapter but I know it’ll have to be when I’ll have time to sit down and roleplay with everyone again.
Phoenix the Vampire Hunter
This was written for Calivide for beta reading a chapter in The Spy and The Liar: The Movie. This is the first fully alternate universe fic I’ve ever written and I absolutely adore the world I’ve created. It’s a sandbox that I’d love to play in more and I’d love for others to play in the sandbox too if they ever feel like it and write their own stories of the world. The ending I have planned leaves the world open for so many possible stories for myself or anyone to explore.
And I promise that I wrote vampire!Juniper before I ever played Baldur’s Gate III and fell in love with Astarion
God this got long but these fics mean so much more to me than simple statistics can tell and I hope people can see why I chose to elaborate on everything.
With 2024 signaling the 10th year of me writing and publishing fanfiction and with last year being so productive, I’m hoping to bring all of last years productivity into the new year as long as the video game industry stops releasing so many good games (I haven’t even gotten to spider-man 2 yet lol)
#Almyrah#ao3 writer#2023 ao3 wrapped#fanfic writing#ieytd#i expect you to die#ieytd fandom#ieytd2#john juniper
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
From Biophilia to Naturalist Intelligence Passing Through Perceived Restorativeness and Connection to Nature
Abstract
This mini review looks at the affective bonds and the cognitive benefits at the basis of the relationship between human beings and Nature, as a solid starting point for an environmental education program aimed to foster naturalist intelligence. Evidences from studies of years of joint research in evolutionary biology and environmental psychology fields show a plausible overlapping between the constructs of Biophilia, Nature fascination and affiliation to life, and the measurable constructs of perceived restorativenesss and connection to Nature. Here we propose a theoretical model showing the role these constructs may play on the development of naturalist intelligence and eventually on pro-environmental behavior, i.e. the final aim of environmental education. In addition, a fresh speculation on the biophilic quality of the school environment as a way to sustain environmental education is proposed. Biophilia, as the evolutionary legacy, and naturalist intelligence, as the potential goal of education, can be considered the two poles of an environmental education journey where perceived restorativenesss and connection to Nature play a significant role.
Read More About This Article: https://juniperpublishers.com/arr/ARR.MS.ID.555604.php
Read More Juniper Publishes Google Scholar Articles: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=l2xTCboAAAAJ&citation_for_view=l2xTCboAAAAJ:tuHXwOkdijsC
#Juniper Publishers Google scholar#Annals of Reviews & Research#research & reviews journal of life sciences
0 notes