#Liu Gongquan
Photo

Figure 1. Jiang Qingji’s fan calligraphy, UWM Special Collections (cs 000092).
Graduate Research: Chinese Scroll and Fan Work,
Part 11
Today we continue our exploration of calligraphic scripts in Chinese fan work, with further examples of Zheng vs. Qi approaches.
Figure 1 is a fan text written in a cursive script. According to Tai Jingnong (1902-1990), a scholar in Chinese poetry, calligraphy, and painting, cursive scrip first appear in the Han Ju Yan Wooden Slips, which were created from the Han (206 BCE-220 CE) to Jin Dynasty (265-420 CE).The cursive script from this period, such as that found in Monthly and Seasonal Records of Military Supplies from the Kuang-ti South Platoon in the Yung-yüan Era , originated from the hurried writing of the older clerical script (see my last blog).
In this fan, Jiang Qingji (1820-1880) copied a section of A Narrative on Calligraphy by Sun Guoting (646–691, see my blog on Zhang Jian), a very important treatise summarizing the esthetic values of Chinese calligraphy. However, the copying of the text is as far as the similarity goes. For Jiang 敏 in Figure 2 (a), the undulation of the brush breaks the stroke for a staccato thickening-and-thinning effect, whereas Sun’s counterpart in Figure 3 (a) is much more smooth and legato --- a typical characteristic of cursive script canonized by the calligraphic sage Wang Xizhi (303-361 CE, Figure 3 (b)). The variance, angularity, and exaggeration imbue Jiang’s brush with a strong sense of design.
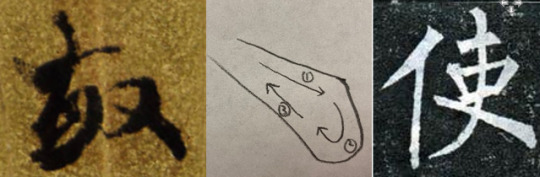
(From left to right):
Figure 2 (a) : Detail from Figure 1
Figure 2 (b): Analysis of the Last Stroke in Figure 2 (a), made by Jingwei Zeng
Figure 2 (c): Detail from The Stele of Xuanmi Pagoda

(From left to right):
Figure 3 (a): Detail from Sun Guoting’s The Manual on Calligraphy
Figure 3 (b): Detail from Wang Xizhi’s On the Seventeenth Day
Figure 3 (c): Detail from Lu Ji’s Recovering from Illness
Figure 3 (d): Detail from Liu Sha Zhui Jian
Jiang’s design is much more apparent in 敏’s last brush (Figure 2 (a)). The brush tip goes rightward first, creates an angle, then makes a circle before it goes back to form a sculptural stroke (see Figure 2 (b)). The bulging monumentality of this stroke is analogous to its counterpart in Figure 2 (c) from the standard writing The Stele of Xuanmi Pagoda --- another calligraphic masterpiece in Chinese history inscribed by Liu Gongquan (778-865) in 841. According to Wang Shizhen (1526-1590), a famous writer and historian in the Ming Dynasty (1368 - 1644), this stele is the most telling example of Liu’s penchant for rippling tendon and bone in his creations. In our fan, Jiang complicated his brush movement by introducing a contrived sculptural design from Liu’s standard writing. Since standard writing can also be called “Zheng” writing in Chinese (see my previous post), contrived design can be seen as the embodiment of Zheng style, a conservative form, relying on established styles and techniques.
The monumentality of Liu’s Zheng style is derived from the Four Masters of Tang (Ouyang Xun, 557-641, Yu Shinan,558-638, Chu Suiliang, 596-658, and Xue Ji, 649-713), whose works are utilized to glorify the peace and prosperity of the dynasty. In Tai Jingnong’s opinion, a calligraphic untrammeled naturalness (Yi, 逸, which is the correlative of Qi, a style of originality, challenging recognized norms) is compromised by this propagandistic self-aggrandizement.
As a matter of fact, the last stroke in Sun’s original work (Figure 3 (a)) exhibits some untrammeled naturalness, as the end of last stroke does not have an obvious sense of design. A much more untrammeled and natural style can be seen in the similar strokes in Wang Xizhi’s On the Seventeenth Day (fourth century, Figure 3 (b)), Lu Ji (261-303)’s Recovering from Illness (ca.303, Figure 3 (c)) and Liu Sha Zhui Jian (ca. 98BC, Figure 3 (d)) --- they are guided by concepts of Yi & Qi.

Figure 4. Titian’s Danaë
The contrast between premeditated design (Zheng) and the untrammeled naturalness (Yi & Qi) can be seen in the Western art, too. In Titian’s famous work Danaë (figure 4), the body of the woman to the left is derived from Michelangelo's female figure in the sculpture at the Medici Chapel entitled Night, possessing a great designing effect and sculpturality (similar to Jiang and Liu’s Zheng style); on the contrary, the white satin under her body is sketched by the bold slash of the brush (similar to Wang, Lu, and Liu Sha Zhui Jian’s Yi & Qi style), suggesting an unbridled idiosyncrasy, thereby foretelling the arrival of Baroque art.

(From left to right):
Figure 5 (a): Fu Shan’s imitation of Wang Xizhi’s Letter Written in the First Lunar Month
Figure 5 (b): Liu Sha Zhui Jian

(From left to right):
Figure 6 (a): from Figure 5 (a)
Figure 6 (b): from Figure 5 (b)
Figure 6 (c): from Figure 5 (a)
Figure 6 (d): from Figure 5 (b)
Figure 6 (e): from Figure 5 (a)
Figure 6 (f): from Figure 5 (b)
Fu Shan (1607-1684), who was the master for Qi’s style, considered premeditated Zheng’s design as a bete noire and he preferred untrammeled naturalness in his art. In Figure 5 (a), though it is Fu’s imitation of Wang Xizhi’s work, it bares greater resemblance to the wooden slip Liu Sha Zhui Jian in Figure 5 (b). Fu and Liu Sha Zhui Jian employed an unmodulated linearity (Figure 6 (a) and (b)), an untrammeled leisure (the “丿” in Figure 6 (c) and (d)), and an unembellished naturalness (the last horizontal line in Figure 6 (e) and (f)). Both of them epitomized Qi & Yi concepts.
It is worthwhile mentioning that Fu never had the chance to see Liu Sha Zhui Jian, which was excavated in 1906-1907 (see my previous Zheng Xiaoxu’s post), around three hundred years after Fu’s time. The striking similarity between Fu’s work and Liu Sha Zhui Jian testifies Fu’s inimitable capacity to imagine the broken part of the art history by tracing the path of calligraphic evolution.
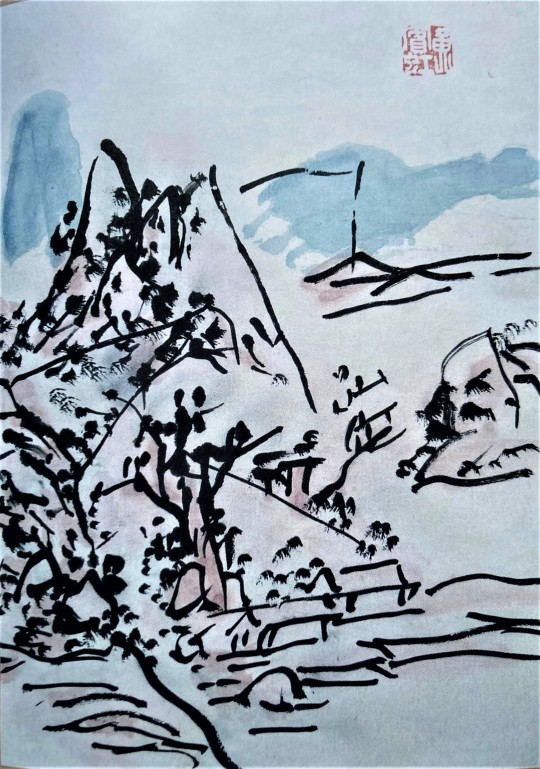

Figure 7: Huang Binhong’s Landscape Painting
Fu’s Qi legacy is carried on by Huang Binhong (1865-1955), an extraordinary Chinese modern landscape painter whose brushwork is characterized by raw, unmodulated, and untrammeled naturalness. The brushwork of Huang’s painting in Figure 7 bears a strong correlation to Fu’s brush in Figure 5 (a) and the satin of Danaë in Figure (4)---they are ad-libbed in the spur of the moment, implying an ephemeral yet highly-spiritualized transcendentalism.
According to The Petty Sayings of Painting, a famous thesis on Chinese painting esthetics, Chinese landscape painting is similar to the writing of cursive and running script --- the creation should not be restrained by rigor and workmanship (i.e., premeditated design, or Zheng). Dong Yuan’s (c. 934-962) interplay of voids and solids (see Figure 8, Dong’s The Rivers of Xiao and Xiang), Mi Fu’s (1051-1107) smoky mountains improvised by horizontal dots, Mi’s son Mi Youren’s (1074-1153, or 1086-1165) The Ink Play of Cloudy Mountains (see Figure 9), and Huang Gongwang’s (1269-1354) withered trees and lean mountains (see Figure 10, Huang’s Nine Submits after the Snow) exhibit a feeling of untrammeled naturalness. On the contrary, “only the vulgar artisans will deliberately create the meticulous paintings in order to please the audiences’ eyes.” The paintings made by this pleasing servitude is “drab and dour.”

Figure 8. Dong Yuan’sThe Rivers of Xiao and Xiang

Figure 9. Mi Youren’s The Ink Play of Cloudy Mountains

Figure 10. Huang Gongwang’s Nine Submits after the Snow
Yi & Qi also happens under Cezanne’s (1839-1906) hands. In Montagne Sainte-Victoire (Figure 11), Cezanne did not choose a refined brush to design remote mountains; instead, he created a simple calligraphic line as his abstract rendition of the landscape. For all these artists, mastering a skill of unpremeditated and sophisticated disegno (Zheng) is not difficult (and indeed, they did so when they were young); what challenged them most was how to get rid of formulaic design and create a free, simple, and impromptu Yi & Qi effect. By doing this, they presented their own characters rather than representing the rules and regulations of traditional and formulaic style.

Figure 11. Cezanne’s Montagne Sainte-Victoire
View more posts from the Zhou Cezong Collection of Chinese scroll and fan work.
– Jingwei Zeng, Special Collections graduate researcher.
#graduate research#Jingwei#Chinese calligraphy#Chinese fans#Chinese art#Chinese paintings#Chinese history#art history#calligraphy#calligraphers#Zheng style#Qi style#Jiang Qingji#Sun Guoting#Liu Gongquan#Wang Xizhi#Lu Ji#Liu Sha Zhui Jian#Fu Shan#Titian#Michelangelo#Huang Binhong#Dong Yuan#Mi Fu#Mi Youren#Huang Gongwang#Paul Cezanne#Zhou Cezong Collection#Tse-Tsung Chow Collection
36 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Liu Gongquan,Tang Dynasty
548 notes
·
View notes
Photo

New Post has been published on https://freenews.today/2021/02/12/two-arrests-two-outcomes-tell-a-tale-of-xi-jinpings-china/
Two Arrests, Two Outcomes Tell a Tale of Xi Jinping’s China

Under Mr. Xi, the party’s traditionally suspicious stance against businesspeople who are politically active or outspoken has worsened. Wang Gongquan, a former venture capitalist who financed advocacy for more liberal social and political policies, was among the first high-profile individuals jailed after Mr. Xi came to power. Ren Zhiqiang, a retired real estate tycoon, was sentenced last year to 18 years in prison after he repeatedly criticized Mr. Xi’s policies, including the government’s mishandling of the early days of the coronavirus outbreak.
In private chatrooms and behind closed doors, some people are asking what signal Beijing is sending to the private sector by arresting Mr. Sun. Outspoken and generous, Mr. Sun is in some ways the model of the civic-minded businessman the party extols. He has built a town — Dawu City — around his company’s campus in rural Hebei Province, complete with a hospital with 1,000 beds.
“My dream,” he once said, “is to build a modern city in the countryside.”
Mr. Sun, 66, was born in Xushui, in Hebei Province, about a two-hour drive south of Beijing. He joined the People’s Liberation Army after graduating from middle school. He left the army eight years later and moved back to his hometown to work at the state-owned Agricultural Bank of China.
A curious and restless soul, he studied college law and took Chinese literature courses in his spare time. In 1985, he quit his banking job and started a business with 1,000 chickens and 50 pigs. His company, Dawu Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Group, now employs about 9,000 people, many from nearby villages.
As his business grew, Mr. Sun sought out liberal intellectuals in Beijing. By the spring of 2003, he was becoming a voice for farmers and entrepreneurs’ rights, giving speeches at top Chinese universities.
After irritating the authorities, he was arrested on accusations of illegal fund-raising. His new friends leapt to his defense. Legal scholars argued that the law he was accused of violating had been written in a way that gave the authorities broad discretion to charge businessmen who fell out of favor.
Liu Xiaobo, the human rights activist who later became a Nobel Peace Prize laureate and who died in prison in 2017, explained then that Mr. Sun “poses a tremendous challenge for the current system.” As an entrepreneur, wrote Mr. Liu, Mr. Sun despised bribery, had the financial resources to act independently and had the courage to speak up and urge political reform.
Source
0 notes
Text
书法字典大全Pro-练字必备
By: Farig Technology Co. Ltd.
[sc name=”ads1″]
Category: Education
Release Date: 2019-05-07
Current Version: 1.0.2
Adult Rating: 4+
File Size: 15.31 MB
Compatibility: Requires iOS 9.0 or later.
Copyright: Farig Technology Co. Ltd.
Price: $2.99
Description:
1. Covering the works of famous calligraphy such as Wang Xizhi, Wang Xianzhi, Yan Zhenqing, Liu Gongquan, Ouyang Xun, Yan Liang, Zhao…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo

Tranquillity
Chengdu Wu Hou Shrine - China
Wuhou Temple (Memorial Temple of Marquis Wu) is dedicated to Zhuge Liang, the Marquis Wu (Wuhou) of Kingdom of Shu in the Three Kingdoms Period (220 - 280).
Zhuge Liang was the personification of noble character and intelligence. Memorial architectures erected in many places after his death include a famous one in Chendu.
Located in the south suburb of Chengdu, the temple covers 37,000 square meters (398,277 square feet). The date of its establishment is unclear, only that it was built next to the temple of Liu Bei, the emperor of Shu. It was combined with the Temple of Liu Bei at the beginning of the Ming Dynasty; consequently, the entrance plaque reads 'Zhaolie Temple of Han Dynasty' (Zhaolie is the posthumous title of Liu Bei). The current temple was rebuilt in 1672. Surrounded by old cypresses and classical red walls, it evokes nostalgia.
The main body of the temple is divided into five sections, the Gate, the second Gate, the Hall of Liu Bei, the corridor, and the Hall of Zhuge Liang, all of which run south to north. Inside, clay sculptures of Shu Emperor and ministers stand together, making them a special feature.
The most valuable cultural relic here is the stele set up in 809. This huge stele 367-centimeter (144-inch) high and 95-centimeter (37-inch) wide is called the Triple-Success Stele. The three successes are: an article written by Pei Du, a famous minister of the Tang Dynasty who served four emperors in succession, calligraphy by Liu Gongquan, one of the most brilliant calligraphers in Chinese history, and a statement about the morality and achievements of Zhuge Liang.
Taken with the Sony A7RII
www.kirkhillephotography.com
www.instagram.com/kirkhillephotography/
www.facebook.com/Kirkhillephotography
#landascape#photo#photography#travel#peace#china#Chengdu Wu Hou Shrine#sony#Wallpaper#High#Resolution
0 notes