#Migration testing
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Migration Testing Lab | +971 554747210
0 notes
Text
What to Expect During Migration Testing at Labs in Ajman: A Step-by-Step Guide | +971 554747210
In the UAE’s rapidly evolving market, ensuring the safety and compliance of packaging materials is paramount. Migration testing plays a crucial role in verifying that food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic packaging does not release harmful substances into the product. For businesses operating in the region, understanding what to expect during migration testing at labs in Ajman can streamline the process and help achieve compliance efficiently.
This comprehensive step-by-step guide explains the migration testing process at Ajman labs, highlighting key stages, requirements, and best practices to prepare for successful testing outcomes.
Understanding Migration Testing
Migration testing assesses whether chemicals or contaminants transfer from packaging materials to the product contained within. It’s vital for products that come into contact with packaging—especially food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics—to ensure consumer safety and meet regulatory standards.
Ajman’s migration testing lab use advanced analytical methods to simulate real-world conditions and detect potentially harmful substances migrating from packaging materials. The tests ensure compliance with UAE regulations, GCC standards, and international guidelines.
Step 1: Preparation and Sample Submission
The migration testing process begins with proper preparation and submission of samples.
Sample Selection
Choose packaging materials that accurately represent the product’s actual packaging, including all components like lids, seals, films, and adhesives.
Documentation
Provide detailed information about the product and packaging, including:
Type of product (food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, etc.)
Nature of product contact (liquid, solid, fatty, acidic)
Intended storage conditions and shelf life
Production batch number and supplier details
Lab Submission
Submit the samples along with the documentation to the Ajman migration testing lab. Many labs now offer online submission portals to simplify the process.
Step 2: Preliminary Assessment and Test Planning
Once the lab receives your samples, they conduct a preliminary assessment to plan the testing procedure.
Risk Analysis
The lab experts review your product details to determine the migration risks associated with your packaging material.
Test Scope Definition
Based on the product-contact type and regulatory requirements, the lab defines the scope of testing, which may include:
Overall migration testing (total migration of substances)
Specific migration testing (targeted chemicals such as heavy metals, plasticizers)
Selection of Simulants
The lab selects appropriate food or product simulants (like water, ethanol, acetic acid) that mimic the real product’s chemical properties to replicate actual contact conditions.
Step 3: Sample Preparation
Before testing, the lab prepares the packaging samples according to standardized procedures.
Cutting and Conditioning
Samples are cut to specified dimensions and conditioned to replicate typical storage conditions.
Contact Simulation
Samples are then exposed to selected simulants for defined times and temperatures to simulate actual use and storage conditions.
Step 4: Conducting Migration Tests
Migration testing involves two main categories:
1. Overall Migration Testing
This test measures the total quantity of all migrating substances released from the packaging into the simulant.
Conducted by immersing or contacting the packaging sample with simulants under controlled temperature and time
After exposure, the simulant is analyzed for total non-volatile residue
2. Specific Migration Testing
This test targets specific hazardous substances, such as:
Heavy metals (lead, cadmium, mercury)
Plasticizers (phthalates)
Formaldehyde and other volatile organic compounds
The lab uses advanced analytical methods such as:
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Step 5: Data Analysis and Interpretation
After testing, the lab analyzes the data to assess migration levels against regulatory limits.
Regulatory Limits Check
Results are compared with UAE and GCC limits, as well as international standards such as EU Regulation No 10/2011 or FDA guidelines.
Compliance Determination
The lab determines whether the packaging material complies with overall and specific migration limits for safe product use.
Step 6: Reporting and Certification
The migration testing lab in Ajman prepares a detailed report documenting:
Test methods used
Sample description and preparation details
Migration test results
Compliance status
Recommendations, if any
The report can be submitted to regulatory authorities or used for product registration and quality assurance.
Step 7: Post-Test Consultation and Support
ISO accredited migration testing labs in Ajman often provide post-test consultation services.
Expert Guidance
Lab specialists help you understand the results, explain compliance requirements, and suggest improvements for packaging materials.
Retesting and Follow-Up
If your samples fail migration testing, labs advise on corrective actions and offer retesting services to verify improvements.
Benefits of Migration Testing at Ajman Labs
Choosing a migration testing lab in Ajman offers several advantages:
ISO Accreditation: Ensures reliable, accurate, and internationally accepted results
Regulatory Compliance: Helps meet ESMA, GCC, and international packaging safety regulations
Advanced Technology: Uses cutting-edge analytical instruments for precise testing
Industry Expertise: Serves diverse industries including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics
Fast Turnaround: Provides timely results to support product launch schedules
Consultative Services: Offers technical support for compliance and packaging improvements
Preparing Your Business for Migration Testing
To ensure smooth testing, businesses should:
Select representative packaging samples carefully
Provide complete and accurate product information
Communicate intended storage conditions and product types clearly
Choose labs with ISO 17025 accreditation for credibility
Plan testing in advance to accommodate lead times
Conclusion
Migration testing at labs in Ajman is an essential step to guarantee the safety of packaging materials used in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic products. Understanding the step-by-step process—from sample submission to test execution and reporting—helps businesses prepare efficiently and achieve regulatory compliance.
Partnering with an ISO accredited migration testing lab in Ajman ensures accurate, reliable results and expert guidance, enabling you to protect consumers and meet UAE and GCC packaging standards confidently.
0 notes
Text
How Migration Testing Labs Help Manufacturers Stay Ahead of Changing Regulatory Standards
In today's globalized market, manufacturing industries face increasingly stringent regulations designed to protect consumer health and the environment. From food packaging to cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, packaging materials must meet specific safety standards to ensure that harmful substances do not migrate into products. One of the key aspects of compliance is migration testing, which helps manufacturers evaluate how materials used in packaging might leach harmful chemicals into their products. Migration analysis labs play a vital role in helping manufacturers stay ahead of evolving regulatory standards by providing critical testing services that ensure both compliance and consumer safety.
In this blog, we will explore the importance of migration testing, the role of migration analysis lab, and how they help manufacturers navigate changing regulatory standards.
What is Migration Testing?
Migration testing is a process that evaluates how chemicals in packaging materials migrate into the products they contain. These chemicals, which may include plasticizers, solvents, inks, heavy metals, and other additives, can leach into food, cosmetics, or pharmaceuticals under certain conditions such as heat, moisture, or time. Migration testing assesses the potential risk these chemicals pose to consumer health.
For example, when packaging materials come into contact with food, migration testing ensures that the substances used in the packaging, such as phthalates or bisphenol A (BPA), do not exceed safe limits. The results from these tests help manufacturers avoid using harmful materials that could lead to product recalls, fines, or harm to their brand reputation.
The Role of Migration Analysis Labs in Regulatory Compliance
Migration analysis labs are specialized facilities that conduct various tests to determine the extent of migration from packaging materials into the product. These labs use a range of methods to simulate real-life conditions and ensure that packaging materials meet safety standards. The role of migration analysis labs in helping manufacturers stay ahead of regulatory changes is multifaceted:
1. Adapting to Evolving Standards
Regulatory standards for packaging materials are constantly evolving to keep up with scientific advancements and consumer safety concerns. Government bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), and the World Health Organization (WHO) regularly update their guidelines and regulations regarding the safe migration of substances from packaging to food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
Migration testing labs are experts in understanding these changing regulations. They are continuously updated on the latest global standards and can help manufacturers ensure that their packaging materials comply with current guidelines. These labs also help manufacturers prepare for upcoming regulatory changes by anticipating new compliance requirements and making necessary adjustments to packaging materials or designs before changes take effect.
2. Providing Customized Testing Solutions
Different industries face different regulatory requirements. For example, food packaging, cosmetics packaging, and pharmaceutical packaging each have unique safety standards and migration limits. A migration testing lab can provide tailored solutions to meet the specific regulatory needs of each industry.
For food packaging manufacturers, migration testing labs may focus on testing the migration of substances that could contaminate food, such as heavy metals, BPA, or other chemicals. In contrast, cosmetics packaging manufacturers may need to test for migration of toxic chemicals that could harm skin or eyes, while pharmaceutical packaging manufacturers are concerned with the potential for leaching of chemicals that could affect drug efficacy or safety.
Migration testing labs customize their testing protocols based on these specific needs and regulatory guidelines, providing valuable insights that help manufacturers stay compliant.
3. Supporting Global Trade and Market Access
As manufacturers expand into global markets, they must comply with various regional regulations. For example, packaging materials approved in the European Union may not meet the standards in the United States or Asia. Migration testing labs help manufacturers navigate the complexities of international trade by ensuring that their packaging materials meet the required safety standards in different regions.
By conducting migration testing and obtaining certifications that prove compliance with international regulations, manufacturers can enter new markets with confidence. Migration analysis labs also ensure that manufacturers are aware of the specific requirements in each region, helping them avoid costly delays, recalls, or penalties due to non-compliance.
4. Preventing Costly Recalls and Liability
One of the biggest risks manufacturers face when it comes to packaging is the potential for a product recall. If migration testing reveals that harmful chemicals are leaching from packaging materials, the manufacturer may face severe financial and reputational consequences. Recalls can be expensive, damage brand trust, and result in legal liability, particularly if consumers are harmed.
By working with migration analysis labs, manufacturers can catch potential issues before they become major problems. Testing packaging materials early in the design and production process helps ensure that harmful substances do not migrate into products, reducing the risk of contamination, recalls, and lawsuits. Additionally, many migration testing labs offer support in meeting the record-keeping and documentation requirements for regulatory compliance, which can further safeguard manufacturers against legal challenges.
5. Identifying New Chemicals and Materials for Safer Packaging
As the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly packaging grows, manufacturers are exploring new materials that are both safe and environmentally friendly. Migration testing labs play a key role in assessing the safety of these new materials.
For example, many manufacturers are turning to biodegradable plastics or plant-based materials, which may behave differently than traditional plastics. Migration testing labs evaluate the migration properties of these materials to ensure they meet safety standards. By conducting comprehensive testing, migration labs help manufacturers identify new, safer packaging solutions that comply with both current and future regulations.
6. Mitigating Environmental Impact
In addition to ensuring consumer safety, migration testing labs help manufacturers meet environmental regulations by assessing the environmental impact of packaging materials. Many regulatory bodies are focusing on the environmental aspects of packaging, such as the use of toxic chemicals and the sustainability of packaging materials.
By conducting migration testing, labs can ensure that packaging materials are not only safe for consumers but also environmentally responsible. Migration testing labs help manufacturers minimize their environmental footprint by identifying packaging materials that are free from harmful chemicals and promoting the use of recyclable or biodegradable alternatives.
7. Providing Certification and Documentation
After conducting migration tests, labs provide detailed reports that document the results of the testing process. These reports are essential for manufacturers to prove that their packaging complies with regulatory standards. Many countries and regions require manufacturers to submit documentation as proof of compliance, especially when seeking certification for entry into global markets.
Migration testing labs provide the necessary certifications and documentation that validate the safety of packaging materials. This ensures that manufacturers can demonstrate compliance to regulatory bodies, thereby reducing the risk of fines or penalties. These reports also help manufacturers maintain transparency and build consumer trust by showing that they have taken the necessary steps to ensure product safety.
Conclusion: Staying Ahead of the Curve
As packaging regulations continue to evolve, manufacturers must stay proactive in ensuring that their materials meet the latest safety standards. Migration testing labs play a crucial role in helping manufacturers stay ahead of changing regulations by providing expert testing, regulatory insight, and customized solutions tailored to the specific needs of various industries.
By partnering with a reputable migration analysis lab, manufacturers can ensure that their packaging materials are safe, compliant, and capable of meeting global standards. This not only helps manufacturers avoid costly recalls and legal liabilities but also gives them a competitive edge in an increasingly regulated global market. As consumer safety and environmental concerns continue to rise, migration testing will remain a vital part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that both manufacturers and consumers are protected from harmful contaminants in packaging materials.
#migration analysis lab#migration analysis#testing labs#testing lab near me#testing lab delhi#migration testing
0 notes
Text
Technology Trends: Advancements Driving Migration Testing Labs in Qatar
In the realm of food safety, migration testing plays a crucial role in ensuring that packaging materials do not transfer harmful substances into consumable products. Qatar, known for its dedication to innovation and excellence, is witnessing significant advancements in migration testing labs. These labs are embracing cutting-edge technologies to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and overall effectiveness. This blog explores the latest technology trends driving migration testing labs in Qatar and their impact on ensuring food safety and quality.

Key Technological Advancements in Migration Testing
Migration testing lab in Qatar are at the forefront of adopting advanced analytical instruments and methodologies. These labs leverage state-of-the-art equipment such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) for precise analysis. Moreover, emerging trends in testing methodologies, such as solid-phase microextraction (SPME) and accelerated solvent extraction (ASE), are revolutionizing the way migration testing is conducted. Innovations in packaging materials, including barrier coatings and active packaging, are also influencing analysis techniques, allowing for more accurate assessments of chemical migration.
Impact of Technology on Testing Accuracy and Efficiency
The integration of advanced technologies has significantly enhanced the accuracy and efficiency of migration testing in Qatar. Improved detection limits and sensitivity enable labs to detect even trace amounts of chemical compounds, ensuring comprehensive testing. Furthermore, technological advancements have led to faster turnaround times and increased throughput, allowing labs to handle a higher volume of samples efficiently. Enhanced data analysis and interpretation capabilities provide valuable insights into the composition of packaging materials, facilitating informed decisions regarding food safety.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
While the adoption of new technologies brings numerous benefits, migration testing labs in Qatar face certain implementation challenges. Integrating new technologies into existing infrastructure requires careful planning and investment in equipment and software. Additionally, ensuring that lab personnel are adequately trained to utilize these technologies effectively is essential. Addressing regulatory and compliance requirements poses another challenge, as labs must ensure that their testing methods meet international standards and regulations. However, with proper planning, training, and adherence to best practices, these challenges can be overcome, paving the way for seamless technology implementation.
Future Directions and Potential Innovations
Looking ahead, migration testing labs in Qatar are poised to embrace even more advanced technologies and methodologies. Predictive modeling and artificial intelligence (AI) are expected to revolutionize migration testing by predicting potential migration risks and optimizing testing protocols. Advancements in green chemistry and sustainable testing methods will also play a significant role, aligning with Qatar's commitment to environmental sustainability. Furthermore, collaborative research initiatives and partnerships between academia, industry, and government agencies will drive innovation and accelerate the development of new testing solutions.
Conclusion
The technological advancements driving migration testing lab in Qatar are shaping the future of food safety and quality assurance. By embracing cutting-edge technologies and methodologies, these labs are enhancing their capabilities to detect and analyze chemical migration in packaging materials. Improved accuracy, efficiency, and data analysis empower Qatar to uphold the highest standards of food safety and comply with international regulations. As migration testing labs continue to evolve and innovate, Qatar's commitment to excellence in food safety remains unwavering, ensuring the health and well-being of consumers both locally and globally.
0 notes
Text

Equinox Labs is a leading Food Testing Lab in Mumbai. We ensure accurate food quality testing solutions with the help of a committed team of experts and the latest technology.
Equinox Labs
#EquinoxLabs#foodtestinglaboratoryinMumbai#BestfoodtestinginMumbai#foodtestinglabsinMumbai#Migration testing
0 notes
Text
Does anyone care about them horses…



#horse race tests#whitexcyan#art#artwork#sketch#lineart#drawing#rendering#horse art#had to migrate this to tumblr#horse races#jovial merryment#comely material morning#cyan#superstitional realism#yuri#horse yuri#…
529 notes
·
View notes
Text
i suppose i have always been here / drinking the same water / falling from the sky then floating / back up & down again / i suppose i am something like a salmon / climbing up the river / to let myself fall away in soft / red spheres / & then rotting
Franny Choi, Turing Test
#Franny Choi#Turing Test#Soft Science#presence#water#salmon#rotting#girl rotting#migration#poetry#Asian American literature#Asian American and Pacific Islander Heritage Month#AAPI Heritage Month#Asian Heritage Month#quotes#quotes blog#literary quotes#literature quotes#literature#book quotes#books#words#text
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Can there be an ethical way to exploit a woman for a womb and treat a baby like a commodity?
The global surrogacy industry is experiencing an unprecedented boom, raising ethical concerns across borders. As more couples turn to surrogacy as a path to parenthood, this assisted reproductive technology has evolved into a multi-billion dollar market.
According to recent research, the global surrogacy industry is projected to grow from $21.85 billion in 2024, to $196 billion by 2034. This explosive growth is primarily concentrated in Europe and North America, where surrogacy is legal and regulated.
However, the legal landscape of surrogacy remains a complex patchwork across nations, with some countries embracing it while others maintain strict prohibitions. This inconsistency in regulations has created gray areas.
Scientific research highlights the possibility of abuse arising from gaps in legal frameworks and disputes, whether surrogacy is legal or not. It points to unethical practices such as trafficking of women, coercion of both surrogates and prospective parents by agencies, lack of respect for bodily autonomy or informed consent, ‘sham’ procedures and multiple embryo exchanges.
Cross-Border Exploitation: A Dark Web of Surrogacy
Surrogacy-related abuse often happens in a region formed by three countries: Turkey, Georgia and Northern Cyprus.
While surrogacy remains illegal in Turkey, it’s perfectly legal in its northeastern neighbor Georgia and southern neighbor Northern Cyprus, creating a dangerous legal vacuum that enables exploitation.
The Hope for the Future Association, based in Tbilisi, Georgia, is one of the organizations reporting cases of abuse and illegal surrogacy in the country.
“Our organization has evidence of both Georgian and Turkish citizens being used as surrogate mothers, along with cases of children being transported across borders with falsified documents,” said Tamar Khachapuridze, the association’s director. “We’ve reported these to the prosecutor’s office. Despite a decade-long investigation by Georgian prosecutors, these cases remain collecting dust. It appears someone is working to keep these dark dealings under wraps.”
While surrogacy remains illegal in Turkey, it’s perfectly legal in its northeastern neighbor Georgia and southern neighbor Northern Cyprus, creating a dangerous legal vacuum that enables exploitation.
The Hope for the Future Association, based in Tbilisi, Georgia, is one of the organizations reporting cases of abuse and illegal surrogacy in the country.
“Our organization has evidence of both Georgian and Turkish citizens being used as surrogate mothers, along with cases of children being transported across borders with falsified documents,” said Tamar Khachapuridze, the association’s director. “We’ve reported these to the prosecutor’s office. Despite a decade-long investigation by Georgian prosecutors, these cases remain collecting dust. It appears someone is working to keep these dark dealings under wraps.”
Khachapuridze cited a particularly alarming case involving a Turkish surrogate mother. After undergoing embryo transfer in Georgia, she was reportedly transported to Thailand three months before giving birth, where she delivered a baby intended for a single Chinese man.
This case directly violates Georgian law, which explicitly prohibits embryo transfer or any surrogacy procedures for women from foreign countries.
When we obtained the case number from Khachapuridze’s files and approached the Georgian Prosecutor’s Office with written questions about the existence and content of the investigation, our written inquiries and follow-up calls went unanswered.
Rusudan Nanava, a Tbilisi-based lawyer handling surrogacy cases, explained the wall of silence: “I doubt you’ll get any information from the prosecutor’s office. Criminal cases, especially those involving surrogacy, are treated with the highest level of confidentiality.”
Georgia’s Legislative Tug of War: Balancing Ethics and Economics
In a significant policy shift, the Georgian government is grappling with proposed legislation that could fundamentally reshape the country’s surrogacy landscape. The move comes amid growing concerns over human trafficking and exploitation in the industry.
“We’re seeing cases of law abuse, including human trafficking,” said independent member of parliament Tamar Kordzaia. “While the government pushes for change through surrogacy laws, I believe we could address these issues through other regulatory measures.”
The controversial bill, introduced in June 2023, would effectively end commercial surrogacy in Georgia, permitting only altruistic arrangements. This shift would bar foreign couples—who currently make up 95 percent of intended parents—from accessing Georgian surrogacy services, restricting the practice to Georgian citizens only.
However, Kordzaia remains skeptical about the bill’s future, which has yet to take effect.
“This is moving at a glacial pace, despite the government’s ability to fast-track legislation when it wants to,” she said. “The economic implications are severe—both for medical facilities and the women who rely on surrogacy income. I suspect the bill will ultimately be withdrawn.”
In a country where 11.5 percent of women aged 18-65 live below the absolute poverty line, surrogacy has become a lifeline for many Georgian women struggling to make ends meet. Their stories paint a stark picture of economic desperation intersecting with the global fertility market.
Take Teona, a 42-year-old teacher and domestic violence survivor, who turned to surrogacy twice a decade ago. “As a woman, I wanted to help another woman who couldn’t have children,” she said, her voice tinged with both pride and pragmatism. “Of course, there was financial motivation. My main goal was to buy my own apartment, and I did it—for my child’s future.”
Dr. Keti Gotsiridze, director of the Reproductive Health Center of the Chachava clinic, one of Georgia’s well-established health institutions, said according to the data research of her clinic, surrogacy practice contributes $300 million a year to health tourism. Gotsiridze said 90 percent of their clients are foreigners. Surrogate mothers are paid 25-30 thousand Euros; Chachava works with an average of 300-400 surrogate mothers a year.
For the time being, it seems that the new legislation to change the practice of surrogacy in Georgia has been shelved due to economic concerns. However, the question of how to prevent human trafficking, which has also emerged with the abuse of the existing law, remains unanswered.
Cross-Border Surrogacy Investigation Closes With No Charges Filed
A prosecutorial investigation has revealed an alleged surrogacy trafficking network spanning Turkey, Georgia and Northern Cyprus, highlighting the devastating human cost of unregulated fertility treatments.
The case began on Sept. 3, 2021, when Turkey’s Health Ministry received an anonymous tip about “F. IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) Center,” a fertility clinic in Istanbul’s affluent Beşiktaş district. According to the whistleblower, the clinic was targeting vulnerable young women, including minors, from the working-class neighborhood of Ümraniye with promises of financial gain through surrogacy.
The scheme was elaborate: Women were provided with fertility drugs to use at home for durations ranging from two to 12 days. They were then allegedly trafficked to Georgia and Northern Cyprus using forged documents, with all expenses covered by the network. The fertility medications were reportedly sourced from pharmaceutical warehouses and distributed through a café in Üsküdar, serving as a front for the operation.
Despite the gravity of these allegations, the investigation faced significant hurdles. After a year-long probe, authorities could only identify one suspect, known as A.A., who allegedly recruited the women. The café implicated in the scheme closed its doors just one month before police surveillance began.
When we reached out to M.K., the lawyer who owned the café, he confirmed his ownership but denied any knowledge of the fertility drug distribution, claiming he was also a victim in the scheme.
Another crucial lead emerged regarding Dr. S.T., who allegedly treated the women at “F. IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) Center” and later deleted their medical records. However, police terminated the investigation, citing lack of evidence and the doctor’s clean criminal record.
When reached for comment, Dr. S.T. denied all allegations, dismissing the claims made in the investigation as baseless.
The case took another turn when the Istanbul Public Prosecutor’s Office dismissed the case in January 2023. The Provincial Health Directorate appealed, arguing that “the investigation was inadequate” and “the material and moral elements of the crime have not been fully established.” Nevertheless, on May 31, 2023, the Istanbul 7th Criminal Court of Peace rejected the appeal without explanation.
The case remains closed, leaving crucial questions unanswered about the fate of these young Turkish women, the conditions they endured, and the clinics involved in Georgia and Northern Cyprus. The Ministry of Health has remained silent on queries about similar reported cases, raising concerns about the scale of this cross-border surrogacy trade.
A Cross-Border Underground Surrogacy Network
A police raid in Istanbul in 2019 exposed a sophisticated trafficking network spanning Turkey, Georgia and Northern Cyprus. The operation revealed a complex web involving a Northern Cypriot ringleader and two Moldovan accomplices who coordinated the trafficking of Turkish women for surrogacy purposes.
During the raid, police discovered large quantities of fertility drugs. According to detained suspects’ testimonies, these hormones were supplied by the Northern Cypriot kingpin and administered to potential surrogate mothers recruited from Turkey. The women were then trafficked to clinics in both Northern Cyprus and Georgia, with one prominent facility identified as “IVF Tours Georgia” in Tbilisi.
To verify whether this clinic continues to engage with Turkish women five years after the raid, we conducted an undercover investigation. Posing as potential surrogates from Turkey, we contacted “IVF Tours Georgia” via email. The response was swift and telling: Not only did they accept our inquiry, but they immediately began discussing financial arrangements and medical screenings. This exchange revealed a striking fact: Despite Georgian law restricting surrogacy to Georgian citizens, the clinic openly offered services to Turkish nationals, highlighting the persistent nature of this illegal cross-border trade.
Lack of Oversight Fuels Surrogacy Concerns in Northern Cyprus
In Northern Cyprus, a growing surrogacy industry operates within a complex web of legal ambiguity and insufficient oversight, despite having well-crafted regulations. Former health minister (2018-2019) and Republican Turkish Party MP Filiz Besim warns that human trafficking cases persist due to inadequate supervision.
“While we have meticulously drafted laws permitting surrogacy, the lack of oversight remains a critical issue,” Besim said. “Our unique position outside international law, due to our unrecognized status, has created vulnerabilities that are being extensively exploited. This has led to the emergence of illicit international networks involved in human, women, and child trafficking.”
Deputy Besim emphasizes that women—particularly from Caucasian countries—are being brought from abroad as surrogate mothers in violation of laws. He notes that due to insufficient oversight, questions remain about the agreements, facilitators, and conditions under which these women are transported.
Our anonymous field interviews and observations reveal serious concerns about surrogacy practices stemming from the country’s lack of oversight. A troubling gray area has emerged where low-income women face potential exploitation. Women may be pressured into surrogacy due to financial hardship, raising ethical concerns about the commodification of women’s bodies and children’s rights.
International organizations like U.N. Women have voiced similar concerns about surrogacy practices in regions like Northern Cyprus, citing these risks and inadequate oversight. They stress the importance of protecting surrogate mothers through proper safeguards: ensuring they are fully informed, free from coercion, and fairly compensated for the risks they undertake
Surrogacy became legal in Northern Cyprus in August 2016 under the Law Regulating Human Cell, Tissue, and Organ Transplantation Rules. A new, more robust bill was drafted in April 2023, though Parliament has yet to convene to discuss these changes.
Northern Cyprus has emerged as Europe’s leading destination for reproductive treatments. The industry’s prominence is evident in everyday encounters in the capital, Lefkoşa, where stories of successful surrogacy arrangements—including a recent case involving a European couple—are commonplace.
While official statistics remain undisclosed, artificial intelligence analysis estimates approximately 500 surrogacy arrangements occur annually in Northern Cyprus. According to LaingBuisson, a London-based healthcare market research firm, the country handles about 11 percent of all egg donation treatments in Europe.
Social Media’s Underground Surrogacy Market
Despite legal bans and restrictions, a thriving underground surrogacy market in Turkey continues to operate in plain sight. There are numerous advertisements openly seeking surrogate mothers on social media platforms such as Instagram and Facebook.
In one of these advertisements, we wrote to a woman who said she could be a surrogate mother, with a request to have a child. Ten years ago in Turkey, the woman said she had been a surrogate mother once and explained how the process would work and offered us two methods to help her conceive:
“The child could be from my egg and your husband’s sperm. Would you be okay with that after birth? We’d never need to know each other. We wouldn’t even need a transfer. We could handle it ourselves – inject your husband’s sperm directly into my uterus. Or, we could select healthy eggs and have your and your husband’s eggs transferred to me.”
Most alarmingly, she assured us that certain private clinics would perform these procedures clandestinely, promising there would be “no issues” with birth certificates—a clear indication of document fraud.
The desperation of infertile couples seeking parenthood through these illegal channels may be understandable, but the risks are severe. These back-alley procedures not only endanger the health of all parties involved but also expose them to serious legal consequences. The combination of medical risks and criminal liability creates a potential storm of challenges for vulnerable individuals.
The Delicate Balance: Finding a Legal Middle Ground
Is there a way to craft ideal legislation that prevents exploitation while acknowledging the deep human desire for parenthood? Attorney and professor Dr. Özlem Yenerer Çakmut believes the answer lies in nuanced regulation rather than absolute prohibition.
“We can’t simply ignore the profound yearning of those who dream of experiencing not just parenthood, but the entire journey—from pregnancy to birth,” Yenerer explained. “These are couples who want more than adoption; they want to be part of every moment, every milestone.”
“The challenge lies in striking a delicate balance between regulation and prohibition,” she continued. “A blanket ban isn’t the answer, especially in societies where having children carries immense social and cultural weight. While we can’t legitimize illegal practices, we can work toward meaningful legislation that protects all parties involved while acknowledging these deeply human desires.”
There is also a section of the world strongly opposed to surrogacy. At its forefront stands the Casablanca Declaration, a document signed by 100 experts from 75 countries in March 2023, calling for a universal ban on surrogacy practices.
Leading this charge is Olivia Maurel, herself born through surrogacy in 1991, who has emerged as one of the movement’s most compelling voices.
“Standing against surrogacy means advocating for its universal abolition,” Maurel declared with conviction born of personal experience. “This isn’t just about abstract principles—it’s about defending the fundamental rights of women and children, about protecting human dignity in its most basic form. Surrogacy, by its very nature, undermines these essential values.”
For some, surrogacy represents a last resort in their journey to parenthood. A 46-year-old woman living in Georgia, who chose to remain anonymous, shared the challenging aspects of this process. After having her uterus and ovaries removed due to health issues, she and her husband decided to pursue surrogacy six years ago.
The woman described maintaining close contact with the surrogate mother both before the transfer and throughout the pregnancy. “I monitored her doctor visits, tests and medications regularly. I ensured she maintained a healthy diet, and I was present during the birth. I was with my baby from the moment of delivery.”
Despite being a challenging and costly process, she pursued surrogacy to fulfill her dream of motherhood. “If surrogacy is the only path to becoming a mother, you must give it your all, learn to manage your emotions, and stay focused on your goal. The difficulties and pain are temporary; the love for a child is permanent,” she said.
E.U. Redefines Surrogacy Regulations
Recent legal scholarship challenges the traditional binary approach of outright bans versus complete legalization. Instead, experts advocate for a nuanced international framework that transcends cultural and moral absolutes while protecting fundamental human rights. This perspective emphasizes the critical need for comprehensive national legislation in countries where surrogacy exists, whether legal or not, to safeguard the rights of both women and children.
Amid this contentious landscape, the European Parliament Council took decisive action on Jan. 23, 2024, reaching a provisional agreement to classify exploitative surrogacy practices as human trafficking. The measure was formally adopted on May 27, 2024.
The new framework imposes strict penalties on those who exploit women through forced surrogacy or deceptive practices, while establishing comprehensive support systems for victims. E.U. member states must implement these protections into their national legislation within two years.
The production of this investigation is supported by a grant from the IJ4EU fund. The International Press Institute (IPI), the European Journalism Centre (EJC) and any other partners in the lJ4EU fund are not responsible for the content published and any use made out of it.
This reporting was supported by the International Women’s Media Foundation’s Howard G. Buffett Fund for Women Journalist
About Seda Karatabanoğlu and Zeynep Yüncüler
Seda Karatabanoğlu graduated with a bachelor's degree from Istanbul University's Faculty of Communication in Turkey and a master's degree in European studies and international relations at l'Université Paul-Valéry in France. She worked at Cumhuriyet Newspaper. Her articles have been published on many online platforms such as Euronews Turkish and DW Turkish. Currently residing in France, she continues her work as an independent journalist.
Zeynep Yüncüler is a graduate of Izmir University of Economics, where she studied in the Media and Communication Department. She worked at Milliyet Daily, 'Artı 1' TV, BirGün Daily, ‘Artı Tv’ and Punto24, an independent journalism platform in Turkey. She also served as the secretary for the Journalists’ Union of Turkey's Istanbul branch. She was honored with the best interview award (2016) by the Progressive Journalists’ Association (ÇGD). Currently, she is a freelancer.
#International surrogacy is big business#Surrogacy-related abuse#The Hope for the Future Association#Türkiye#Georgia#Northern Cyprus#The economic implications are severe—both for medical facilities and the women who rely on surrogacy income#Meaning the increasing demand for surrogacy relies on poor women#People so wrapped up in having a biological child they don't think of what consequences the kid will face later on#Health risks tied to genetic history#Legal issues if the paperwork around birth and migration to the country of the purchasing parents are shady#I monitored her doctor visits and tests and medications regularly. I ensured she maintained a healthy diet#Can you imagine doing someone such a big favor just to have them breathe down your neck for nine months?
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thomas wiki pages but they're designed with a more Wikipedia-ish format

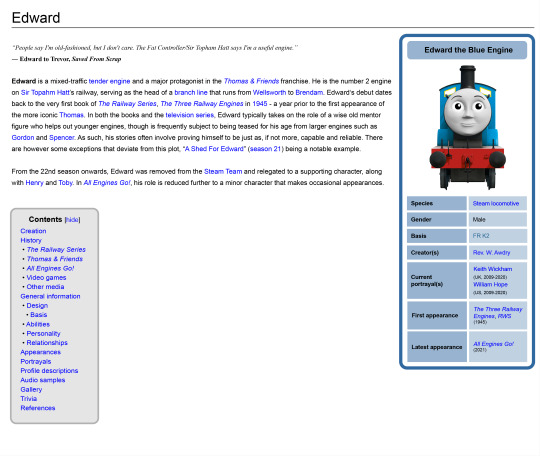
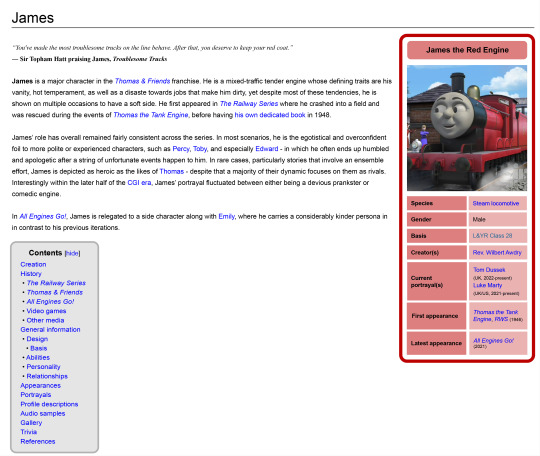

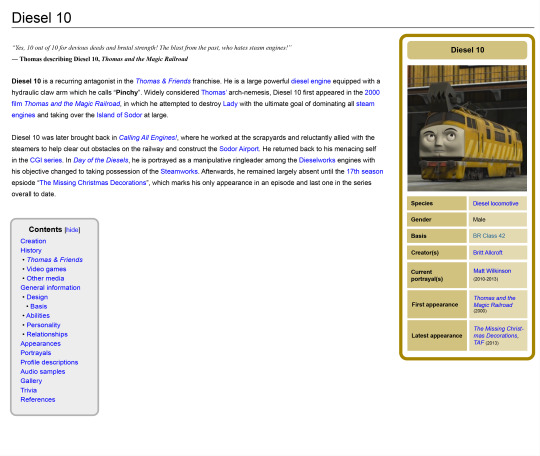
#ttte#thomas and friends#ttte thomas#thomasthetankengine#ttte edward#edwardtheblueengine#ttte james#jamestheredengine#ttte emily#emilythestirlingengine#ttte diesel 10#experiment#test#mockup design#im aware that this has a tad less personality but the basic point is to put out all the info in a professional manner#and unbiased as possible#its kinda sad that the official wiki is practically locked within Fandom as there's not a whole lot of free alternatives to migrate over to
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Migration Testing Labs in Abu Dhabi Support Pharmaceutical Packaging Safety? | +971 554747210
Pharmaceutical packaging plays a crucial role in protecting medicines from contamination, degradation, and tampering, ensuring that drugs maintain their efficacy and safety throughout their shelf life. With the rapid growth of the pharmaceutical industry in the UAE and the wider GCC region, regulatory bodies have tightened standards to ensure that pharmaceutical packaging materials meet strict safety requirements.
One key aspect of pharmaceutical packaging safety is migration testing — the assessment of potential transfer of harmful substances from packaging materials into medicines. Migration testing labs in Abu Dhabi have become indispensable partners for pharmaceutical manufacturers, importers, and regulators aiming to guarantee packaging safety and compliance.
In this blog, we explore how migration testing lab in Abu Dhabi support pharmaceutical packaging safety, their testing methods, and why they are vital for protecting consumer health and meeting stringent regulatory standards.
What is Migration Testing in Pharmaceutical Packaging?
Migration testing is a specialized process that measures the transfer of chemical substances from packaging materials—such as plastics, adhesives, inks, and coatings—into the pharmaceutical products they contain. This is essential because contaminants migrating into medicines can compromise drug stability, alter therapeutic efficacy, and potentially harm patients.
Pharmaceutical packaging migration testing assesses both overall migration (total mass transfer of substances) and specific migration (individual hazardous chemicals like heavy metals, plasticizers, or monomers). The testing ensures that any migration falls within safe limits as defined by international regulations such as the European Pharmacopoeia, USP, and local authorities like the UAE’s Ministry of Health and Prevention (MOHAP).
Why is Migration Testing Critical for Pharmaceutical Packaging?
Pharmaceutical products have highly sensitive compositions and strict purity requirements. Even minimal contamination from packaging materials can:
Cause chemical degradation or reduced potency of drugs
Trigger adverse reactions or toxicity in patients
Lead to microbial contamination if packaging integrity is compromised
Result in product recalls, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage for manufacturers
Therefore, rigorous migration testing is mandatory to ensure that packaging materials used for pharmaceuticals do not release harmful substances that could impact product safety or patient health.
How Migration Testing Labs in Abu Dhabi Support Pharmaceutical Packaging Safety
Abu Dhabi hosts several advanced migration testing laboratories equipped with cutting-edge technology and expert personnel trained specifically for the pharmaceutical sector. Here is how these labs support pharmaceutical packaging safety:
1. Compliance with International and Regional Standards
Migration testing labs in Abu Dhabi follow internationally recognized standards such as:
European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.)
United States Pharmacopeia (USP) <661>, <661.1>, and <661.2>
ICH Q3D guidelines for elemental impurities
ISO 10993 for biocompatibility
GCC and UAE MOHAP regulations
By aligning testing protocols with these standards, Abu Dhabi labs help pharmaceutical companies meet global regulatory expectations and facilitate smooth market access both locally and internationally.
2. Advanced Analytical Techniques
Pharmaceutical packaging migration testing requires high sensitivity and accuracy to detect trace contaminants. Abu Dhabi labs employ sophisticated analytical methods such as:
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) for organic compound migration
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) for plasticizers and other chemical additives
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) for heavy metal analysis
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) for polymer characterization
These advanced techniques ensure precise identification and quantification of migrating substances.
3. Customized Testing Protocols for Pharmaceuticals
Different pharmaceutical products—tablets, capsules, injectables, liquids—have varying interactions with packaging materials. Abu Dhabi migration testing labs tailor test protocols by:
Selecting relevant food or pharmaceutical simulants to mimic drug formulations
Setting temperature and time parameters reflecting actual storage and usage conditions
Assessing both primary packaging (blister packs, bottles) and secondary packaging (cartons, labels)
Customized testing increases the accuracy of migration results, providing reliable safety data.
4. Expertise in Material Compatibility and Risk Assessment
Abu Dhabi labs provide consultancy services to pharmaceutical companies on packaging material selection based on migration test outcomes. They conduct risk assessments to identify potential migration issues early in product development, helping manufacturers choose compatible materials that minimize migration risks.
5. Quality Assurance and Regulatory Documentation Support
Accredited migration testing labs in Abu Dhabi issue detailed reports and certificates that comply with UAE MOHAP and international regulatory requirements. This documentation is essential for product registration, regulatory audits, and quality assurance.
Benefits of Using Migration Testing Labs in Abu Dhabi for Pharmaceutical Packaging
Local Regulatory Expertise and Fast Turnaround
Abu Dhabi labs understand the nuances of local regulations and can provide timely test results, speeding up product approvals and market launches in the UAE and GCC region.
Cost-Effective Testing Solutions
Local labs reduce logistics costs and provide competitive pricing for migration testing, making it accessible for both large pharma companies and SMEs.
Ensuring Patient Safety and Brand Integrity
Thorough migration testing guarantees the safety and efficacy of medicines, protecting patients and reinforcing manufacturer credibility in a competitive market.
Challenges Addressed by Migration Testing Labs in Abu Dhabi
Pharmaceutical packaging faces several challenges that migration testing labs help resolve, including:
Complex packaging materials: Modern pharmaceutical packaging often uses multi-layer laminates and innovative polymers whose migration behaviors require expert analysis.
Stringent safety thresholds: The pharmaceutical sector demands extremely low migration limits, necessitating high-precision testing instruments.
Regulatory variability: Labs guide companies through differing international regulations, helping harmonize compliance strategies.
Conclusion
Migration testing is a cornerstone of pharmaceutical packaging safety. It ensures that packaging materials do not compromise drug quality or patient health through harmful chemical migration. Migration testing labs in Abu Dhabi offer the expertise, technology, and regulatory knowledge essential to meet this challenge.
By partnering with these accredited labs, pharmaceutical manufacturers in Abu Dhabi and the broader UAE market can ensure their packaging materials comply with strict safety standards, accelerate regulatory approvals, and maintain high-quality products that safeguard consumers.
0 notes
Text
Why Migration Testing is Crucial for Plastic Packaging Manufacturers in Ajman? | +971 554747210
Plastic packaging plays a vital role in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries in Ajman. However, manufacturers must ensure that their packaging materials do not compromise product safety. Migration testing is a critical process that helps plastic packaging manufacturers verify that harmful substances do not transfer from packaging materials into the products they contain. This blog explores why migration testing is essential for plastic packaging manufacturers in Ajman and how it supports compliance with international safety standards.
Understanding Migration Testing
Migration testing evaluates the extent to which chemicals from plastic packaging migrate into food, beverages, and other consumer products. The process ensures that substances such as plasticizers, stabilizers, and residual monomers remain within permissible limits, reducing the risk of contamination.
Plastic packaging manufacturers in Ajman must comply with various regulatory standards, including:
European Union (EU) food contact regulations
United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) standards
Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) safety guidelines
ISO and ASTM international safety standards
By conducting migration testing, manufacturers can prevent potential health risks and avoid regulatory penalties.
The Importance of Migration Testing for Plastic Packaging Manufacturers
Ensuring Compliance with Safety Regulations
Verifies that packaging materials meet regional and global safety standards.
Reduces the likelihood of product recalls due to non-compliance.
Protecting Consumer Health
Prevents contamination from hazardous chemicals such as bisphenol A (BPA), phthalates, and heavy metals.
Ensures that plastic packaging remains safe for prolonged food contact.
Enhancing Product Quality and Shelf Life
Prevents unwanted interactions between packaging and product contents.
Ensures that food and beverages maintain their intended taste and quality.
Improving Market Access for Exporters
Facilitates smooth trade by meeting international compliance requirements.
Increases acceptance of Ajman’s plastic packaging in global markets.
How Migration Testing is Conducted in Ajman’s Laboratories
Ajman’s testing laboratories follow globally recognized methodologies to conduct migration testing. The key steps include:
1. Selection of Packaging Materials
Identification of plastic materials used in food and beverage packaging.
Assessment of high-risk materials that require extensive testing.
2. Simulation Testing Under Real-World Conditions
Exposure of packaging materials to food simulants under different temperature and humidity conditions.
Analysis of migration levels to ensure compliance with regulatory thresholds.
3. Analytical Testing Techniques
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) for detecting volatile organic compounds.
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) for analyzing heavy metal contaminants.
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) for assessing polymer compositions.
4. Evaluation of Test Results and Certification
Comparison of findings against regulatory migration limits.
Issuance of compliance certificates required for product approvals.
Challenges in Migration Testing for Plastic Packaging Manufacturers
Keeping Up with Evolving Regulations
Frequent updates in food safety laws necessitate ongoing compliance efforts.
High Testing Costs for Small Manufacturers
Migration testing can be expensive, posing challenges for small-scale producers.
Ensuring Consistency Across Different Batches
Manufacturers must implement strict quality control measures to maintain compliance in mass production.
Future Trends in Migration Testing for Plastic Packaging
Ajman’s laboratories are embracing innovative technologies such as AI-powered testing, real-time migration monitoring, and eco-friendly packaging alternatives. These advancements will help manufacturers streamline testing processes and ensure safer packaging solutions.
Conclusion
Migration testing is a crucial requirement for plastic packaging manufacturers in Ajman to ensure product safety, regulatory compliance, and market expansion. By working with accredited laboratories and adopting the latest testing methodologies, manufacturers can enhance their product quality and protect consumer health. As Ajman continues to grow as a manufacturing hub, migration testing will remain a fundamental aspect of safe and sustainable plastic packaging production.
0 notes
Text
It's okay.
#Meta Knight#I love Meta's JP VA so much#Starlyteart#A short one but hey sometimes you just need Meta Knight to tell you it's okay#Also was testing a new program Windows is forcing me to migrate to#Anyone who knows where the audio is from might be screaming at me
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating Regulatory Requirements: Migration Testing in Qatar's Business Landscape
In Qatar's bustling business landscape, regulatory compliance is paramount, particularly in industries where product safety is of utmost concern. Migration testing lab in Qatar play a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with these regulations, thereby upholding public health standards and bolstering consumer trust. This blog post delves into the intricacies of regulatory compliance in migration testing and its crucial significance within Qatar's business environment.

Qatar's Regulatory Landscape: An Overview:
To comprehend the regulatory framework in Qatar, it's imperative to grasp the entities responsible for governing product safety standards. Qatar's regulatory bodies, including the Ministry of Commerce and Industry and the Qatar General Organization for Standardization (QS), enforce stringent regulations aligned with international standards. Compliance with these regulations is vital for businesses aiming to access global markets and assure consumers of product safety.
The Role of Migration Testing Labs in Regulatory Compliance:
Migration testing labs serve as invaluable allies for businesses navigating regulatory requirements. These labs offer expert guidance, conduct comprehensive testing, and provide certification services to ensure adherence to international standards. By partnering with migration testing labs, businesses can streamline their compliance efforts and demonstrate their commitment to regulatory standards.
Challenges in Regulatory Compliance for Businesses:
Despite the importance of regulatory compliance, businesses in Qatar often face challenges in meeting these requirements. Common hurdles include a lack of awareness about regulatory frameworks, resource constraints, and the complexity of compliance procedures. Overcoming these challenges requires proactive measures, including education, resource allocation, and strategic planning.
Best Practices for Ensuring Regulatory Compliance:
Effective compliance management requires businesses to implement best practices and strategies tailored to their specific needs. Establishing robust quality management systems, conducting regular audits, and staying informed about regulatory changes are essential steps. Continuous improvement initiatives and employee training programs also play a pivotal role in maintaining compliance standards.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, navigating regulatory requirements in migration testing is vital for businesses operating in Qatar's dynamic business landscape. Migration testing lab serve as indispensable partners in ensuring compliance with these regulations, thereby safeguarding public health and maintaining consumer trust. By understanding the regulatory landscape, addressing challenges, and implementing best practices, businesses can navigate regulatory requirements effectively and gain a competitive edge in the market.
0 notes
Text


7 Lessons Learned From Making A Viral Video - Paola Baldión
Watch the video interview on YouTube here.
#filmmaking#film#actors#actress#viral video#I am migration#dna test#ancestors#life#real life#ethnicity#cultural heritage#making a video#viral#family#women in film#viral trends#artists#artists on tumblr#art on tumblr#filmmakers on tumblr#cinema#documenting life#culture#history#ancestry#what is my heritage#life lessons
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Watch how Africans populated the earth. Also pay attention to that route out of North East Africa.

#medna#mtdna#human migration#africa#east africa#african#afrakan#kemetic dreams#afrakans#brown skin#brownskin#africans#middle east#south africa#dna#dnangelic#dna activation#dnaedit#dna test#science#sciencenature#scientists#world#cells#social science#social spirit#social security#social software#social skills#asia
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
durkeys :)
#exli speaks#testing out the camera on my new phone... it fucks so HARDD!!#dont mind the sounds of my family shuffling about in the background LMAO#i love seeing the turkeys come around though :) they wander through the city in different flocks and this flock always migrates through#our backyard every few months#its been a while since we saw them though!!#they didnt come at all in the summer- or we didnt see them at least
10 notes
·
View notes