#Operational Data Management (ODM)
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Commercial Refrigeration Cooling Fans: How High-Efficiency Solutions Boost Performance & Equipment Lifespan?

In industries like cold chain logistics, food processing, and medical refrigeration, reliable freezer operation is non-negotiable. Cooling fans - the unsung heroes of refrigeration systems - directly impact energy efficiency and equipment durability. As an industrial fan manufacturer with 26+ years of expertise, Cooltron breaks down the engineering behind premium freezer cooling fans and reveals how optimized thermal management cuts costs while maximizing uptime.
Why Commercial Freezer Fans Are Your System's Silent Guardians
Continuous freezer operation generates intense heat buildup. Without proper dissipation, this leads to: • Compressor overload (+27% energy waste*) • Premature component failure (85% of refrigeration repairs stem from overheating**) • Safety risks in temperature-sensitive storage
Industry data shows: Low-quality fans account for 62% of unplanned cold storage shutdowns due to motor burnout and corrosion issues.
5 Must-Check Specifications When Selecting Industrial Freezer Fans
CFM & Static Pressure Match airflow (cubic feet/minute) to your unit's BTU output. Pro Tip: Cooltron's engineers provide free CFD simulations to prevent oversizing/undersizing.
Motor Efficiency BLDC motors outperform AC models with:
30-40% lower power consumption
<45 dBA noise levels (meets OSHA workplace standards)
Built-in surge protection
Durability Features Seek IP55-rated aluminum housings and salt spray resistance - critical for seafood processing plants and coastal facilities.
Bearing System Dual ball bearings (60,000+ hour lifespan) vs. sleeve bearings (15,000 hours) = 4X less maintenance.
Certifications UL/CE/ETL listings ensure compliance with US NEC and international electrical codes.
Cooltron's Edge: Engineered for American Industrial Demands
As a 26-year veteran in OEM/ODM manufacturing, we deliver purpose-built solutions:
Precision Fit: 20mm-400mm sizes | 5V-240V voltage compatibility
Smart Integration: PWM speed control syncs with PT100/PTC sensors
Rapid Scaling: 7-day prototype turnaround | 1M+ unit annual capacity
Global Reach: Trusted by 1,000+ clients across North America, Europe, MENA & APAC regions
Case Study: 22% Energy Savings for Midwest Frozen Food Distributor
After upgrading to Cooltron's EC Fan Series: ✓ $18,700 annual power cost reduction ✓ 76% fewer service calls ✓ Full ROI in 11 months "Cooltron's plug-and-play design eliminated retrofitting costs. Their 24/7 Chicago support team sealed the deal." - Maintenance Manager
3 Pro Maintenance Tips from Our Engineers
Monthly: Clean fan blades with compressed air (never water!)
Quarterly: Check amp draw - >10% increase signals bearing wear
Biannually: Test automatic shutoff triggers at 185°F (85°C)
Download our FREE "Fan Product Catalog" or schedule a FaceTime facility audit with our US-based engineers!
0 notes
Text
Why CDISC Standards Matter in Clinical Research
Introduction: Understanding CDISC and Its Role in Clinical Research
The Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC) plays a pivotal role in the world of clinical research, offering standardized data formats to ensure seamless data exchange between different stakeholders. With its global influence, CDISC has transformed how clinical trial data is collected, analyzed, and shared, ultimately improving the quality of pharmaceutical research and development.
What is CDISC? An Overview
CDISC is a nonprofit organization dedicated to developing data standards for clinical trials. These standards streamline the process of sharing data between different organizations, such as pharmaceutical companies, regulatory agencies, and clinical research organizations (CROs). By promoting the use of standardized formats, CDISC aims to facilitate faster, more efficient clinical trials and regulatory submissions.
The Importance of CDISC in Modern Clinical Trials
In today’s fast-paced pharmaceutical and biotech industries, the importance of CDISC standards cannot be overstated. They provide a framework that simplifies data management, reducing errors, and promoting consistency across all stages of clinical trials. As clinical trials become increasingly complex, CDISC standards enable researchers to efficiently manage large volumes of data, ensuring faster results and more accurate insights.
Key CDISC Standards and Their Applications
CDISC has developed several key standards that are widely used in clinical trials. The Study Data Tabulation Model (SDTM) provides a standardized format for tabulating clinical trial data, while the Analysis Data Model (ADaM) supports statistical analysis by structuring data in a consistent way. Additionally, the Operational Data Model (ODM) facilitates the exchange of clinical trial data between different systems. These standards help ensure that data from different sources can be easily integrated and analyzed.
How CDISC Facilitates Regulatory Submission and Compliance
Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA and EMA, have adopted CDISC standards to ensure that clinical trial data is consistent, accurate, and ready for review during regulatory submissions. By using CDISC standards, pharmaceutical companies can streamline their submission processes, reducing the likelihood of delays or rejections. These standards also help ensure that the data meets the specific requirements set by regulatory agencies, making it easier for them to assess the safety and efficacy of new drugs.
The Role of CDISC in Data Quality and Integrity
CDISC standards promote data quality and integrity by providing a structured framework that enhances data consistency, accuracy, and traceability throughout the clinical trial process. With a consistent approach to data management, researchers can easily verify and validate data, ensuring that it meets the required quality standards. This consistency also makes it easier to identify potential issues early on, improving the overall reliability of clinical trial results.
The Future of CDISC: Emerging Trends and Advancements
As clinical trials evolve, CDISC is continuously advancing, integrating new technologies and data formats, such as real-world data (RWD) and artificial intelligence (AI), to improve research outcomes. These advancements will further enhance CDISC’s ability to manage and analyze complex data, leading to faster, more accurate results. With the growing emphasis on precision medicine and personalized treatments, CDISC is poised to play a key role in shaping the future of clinical research.
CDISC Training and Certification: A Key for Professionals
For professionals involved in clinical research, obtaining CDISC certification is an essential step toward mastering industry standards and enhancing career prospects. CDISC offers various training programs and certification opportunities that help individuals stay current with the latest developments in clinical data standards. Certification not only improves one’s skillset but also demonstrates a commitment to quality and professionalism in the field.
Conclusion: The Continuing Impact of CDISC on Clinical Research
The work of CDISC continues to be instrumental in shaping the future of clinical research, ensuring that data is standardized, accessible, and usable across various stakeholders and regulatory entities. As clinical trials become more complex and data-driven, CDISC will remain a key player in improving the efficiency and quality of clinical research worldwide.
0 notes
Text
The Role of Outcome-Driven Metrics in Enhancing Cloud Security Control Strategies

Cloud services adoption surges globally. Many businesses must evolve their security strategies to address emerging challenges.
The global cloud security market was valued at $28.35 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a rate of 13.1% annually from 2023 to 2030. Businesses today face an increasing variety of cyber risks, including advanced malware and ransomware attacks. As companies shift to digital operations and store large amounts of sensitive data in the cloud, they have become key targets for cybercriminals looking to steal or exploit information.

Gartner forecasts that the combined markets for IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS will grow by over 17% annually through 2027. This remarkable expansion underscores the urgency for businesses to transition from traditional security methods to more advanced, cloud-native solutions. Conventional approaches often fall short in safeguarding dynamic cloud environments, emphasizing the need for innovative strategies.
To secure cloud-native and SaaS solutions effectively, organizations must focus on platform configuration and identity risk management. These elements form the cornerstone of modern cloud security. Addressing these areas requires a shift in both security approaches and spending models, ensuring alignment with evolving threats. Furthermore, security metrics must move beyond technical performance to demonstrate their relevance to business outcomes.
The cloud, far from being just a storage solution, represents a sophisticated web of interconnected services. This complexity calls for a refined approach to measuring the impact of security investments. Security and risk leaders should adopt outcome-driven metrics (ODMs) to assess the efficiency of their cloud security measures. ODMs empower leaders to align their efforts with organizational goals, offering actionable insights into their security posture.
By customizing ODMs, businesses can better manage risks, enhance cloud security strategies, and achieve results that support overall objectives. In this blog, we will delve into key ODMs that guide future investments in cloud security, ensuring robust protection and meaningful outcomes.
Key Features and Benefits of Outcome-Driven Metrics

Emphasis on Tangible Results
Outcome-driven metrics prioritize measurable outcomes like fewer incidents, reduced risks, and enhanced operational resilience.
For instance, ODMs don’t just count firewalls but assess how they minimize successful cyber attacks. They evaluate key performance indicators, such as shorter threat detection times, faster response rates, and lower incident severity.
This approach tracks outcomes like fewer data breaches, quicker recovery times, and lower overall security costs due to efficient controls. ODMs ensure that security efforts produce valuable, actionable results that enhance the organization’s resilience and performance.
Alignment with Business Objectives
ODMs integrate security goals with broader organizational priorities to ensure strategic alignment and meaningful impact.
This connection ensures security efforts support business growth, compliance, and customer trust. For example, safeguarding customer data not only prevents breaches but also strengthens brand reputation and meets regulatory requirements.
By translating technical outcomes into business-centric insights, ODMs bridge the gap between security teams and decision-makers. This alignment also helps justify security investments to executives by highlighting their contributions to achieving business goals.
Maximizing Cost-Value Efficiency
ODMs evaluate the cost-value balance of security measures to ensure optimal resource allocation and impactful investments.
Businesses can prioritize initiatives that offer the highest return on investment in risk reduction and operational benefits. For example, high-impact controls receive more funding, while less effective measures are reassessed.
This approach optimizes security budgets, ensuring every dollar spent maximizes protection and minimizes vulnerabilities. It enables organizations to strengthen their overall security posture with precision and efficiency.
Tailored Cloud Security Metrics
Cloud environments require dynamic, outcome-driven metrics to allocate resources effectively and address unique security needs.
Unlike fixed budgets, ODMs guide spending based on specific risks and requirements for various cloud services. For instance, mission-critical applications might need advanced encryption and robust identity management compared to less sensitive workloads.
Cloud-specific ODMs measure how controls like encryption, access management, and monitoring contribute to achieving desired security outcomes. This ensures cloud assets and data remain well-protected while enabling efficient resource utilization.
How to Implement Outcome-Driven Metrics (ODM) in Your Business?

Implementing outcome-driven metrics requires a systematic approach to ensure security measures align with desired outcomes and organizational objectives. Below is a detailed guide to implementation:
Develop Initial Processes and Supporting Technologies
Begin by defining critical security processes and mapping them to the technologies supporting these functions.
For instance, technologies like XDR and EDR underpin endpoint protection, while vulnerability scanners support vulnerability management. Similarly, IAM systems and directory services play a vital role in authentication.
This structured framework ensures each security process has a robust technological backbone, providing the foundation for precise measurement and management. It also helps streamline efforts, enabling teams to focus on impactful areas.
Identity Business Outcomes and ALign ODMs
The next step involves linking security processes to specific business goals and identifying desired results for each process.
For example, in endpoint protection, outcomes may include high deployment coverage and effective threat detection. Metrics could track endpoints actively protected and threats mitigated.
Similarly, in vulnerability management, scan frequency and addressing high-severity risks are critical. Desired outcomes may include percentages of systems scanned and vulnerabilities resolved. This alignment ensures security measures directly support organizational priorities.
Recognize Risks and Dependencies
Understanding risks and dependencies is crucial to managing potential failures and minimizing operational disruptions.
Each process depends on specific technologies, and their failure could jeopardize security efforts. For example, endpoint protection relies on XDR and EDR solutions, while vulnerability management depends on scanners.
Assessing these dependencies enables better contingency planning, ensuring uninterrupted operations and consistent protection against evolving threats. This proactive step mitigates vulnerabilities arising from system failures.
Define ODM for Key Processes
Develop clear and actionable metrics that measure the effectiveness of each security process in achieving its intended outcomes.
For instance, endpoint protection metrics could include the percentage of endpoints actively safeguarded and the average threat detection time. Vulnerability management metrics measure systems scanned, remediation timelines, and resolved high-severity vulnerabilities.
These metrics provide quantifiable insights, enabling organizations to assess progress and refine strategies for improved outcomes.
Evaluate Readiness and Mitigate Risks
Finally, assess the organization’s readiness to adopt outcome-driven metrics and identify risks that could impact implementation.
Ensure the necessary infrastructure, expertise, and resources are in place to monitor and act on ODM insights. Address challenges like data accuracy issues, resistance to change, or integration with existing processes through strategies like phased adoption and training.
This step ensures a smoother transition and maximizes the effectiveness of ODMs in aligning security investments with business objectives.
Implementing outcome-driven metrics transforms security management by focusing on measurable results that directly impact organizational goals. With advancements in technology, AI-driven insights enhance the value of ODMs by automating processes and improving decision-making accuracy.
Organizations leveraging these metrics effectively can achieve superior protection and align security efforts with strategic outcomes. Connect with our experts to explore how ODMs can empower your cybersecurity strategy.
Examples of Outcome-Driven Metrics

Outcome-driven metrics offer measurable insights that demonstrate the real-world impact of security initiatives. Below are some key examples:
Mean Time to Detect (MTTD)
MTTD highlights the average time taken to identify a security threat, focusing on faster detection to mitigate risks.
A reduced MTTD minimizes the damage caused by prolonged threats. For instance, organizations can compare current detection times with targeted benchmarks to monitor improvement.
Regular reporting on this metric may include actionable insights, such as areas needing improvement and how enhanced processes or tools can accelerate detection. Faster identification leads to reduced exposure and a more robust security posture.
Mean Time to Respond (MTTR)
MTTR tracks how quickly an organization contains and resolves incidents, aiming to limit the extent of a breach.
This metric emphasizes operational readiness by showcasing how swift responses can prevent critical disruptions or data losses. Reporting should cover the number of prevented breaches and how internal collaboration or automated solutions can further reduce response times.
Reducing MTTR strengthens resilience by demonstrating the organization’s ability to neutralize threats promptly and efficiently.
Phishing Click-Through Rate
This metric evaluates employee susceptibility to phishing attempts, focusing on awareness and preparedness against social engineering attacks.
A lower click-through rate reflects an informed workforce capable of identifying and avoiding malicious links or emails. Organizations can use simulations and trend reports to measure progress and identify vulnerable groups needing additional training.
Implementing regular phishing tests alongside educational programs enhances overall resistance, making the organization less prone to attacks exploiting human errors.
Security Return on Investment (ROI)
Security ROI quantifies the financial benefits of cybersecurity measures compared to the costs, offering a clear value assessment.
This metric helps illustrate how investments reduce downtime, decrease customer complaints, and lower insurance premiums. Organizations can highlight these savings alongside tangible improvements, such as fewer breaches or reduced recovery costs.
By presenting ROI data in monetary terms, security teams can effectively communicate their value to business leaders and justify future investments.
Outcome-driven metrics like these ensure that security efforts align with strategic goals while delivering measurable value. They empower organizations to focus on actionable outcomes, building trust and demonstrating the effectiveness of their cybersecurity programs.
Practical Examples of Outcome-Driven Metrics for Cloud Security

Cloud Governance ODM
An accurate estimate of activity monitored by cloud infrastructure is vital for robust security. Without detailed tracking of cloud assets, other metrics lose relevance as hidden risks may lurk outside the organization’s visibility and control. These challenges intensify when cloud adoption is primarily driven by business units rather than IT departments, as these units often direct accountability.
For effective cloud governance, visibility into all cloud accounts is crucial. Organizations often monitor only “known cloud accounts,” which may represent only part of their cloud presence. Identifying additional accounts requires compensating controls, such as rigorous approval workflows, expense monitoring, and advanced technical solutions like security service edges and network firewalls. These controls should aim for a holistic view of all active accounts to ensure metric accuracy.
Cloud Account Accountability: Clear ownership ensures accountability for managing account configurations and usage policies.
Cloud Account Usage and Risk: Regular assessments are essential to track account usage and mitigate evolving risks in dynamic cloud environments.
Cloud Operation ODM
Operational security metrics play a pivotal role in securing cloud environments, but their relevance varies based on infrastructure setups. These metrics provide insights into the effectiveness of security measures. However, accurate measurements often depend on the availability of advanced tools. Analyzing these metrics account-by-account or by priority level enhances clarity.
Real-Time Cloud Workload Protection: Critical workloads require real-time runtime monitoring for memory, processes, and other dynamic components.
Runtime Cloud Workload Protection: Non-critical workloads can utilize agentless scanning methods to achieve sufficient security without continuous visibility.
Cloud Identity ODM
Cloud identity management extends beyond user accounts, particularly in IaaS environments, where workloads require their own machine identities and privileges. Effective lifecycle management and governance for these identities are essential. In IaaS environments, identity functions as the primary control for application consumers. Overprivileged identities remain a major concern across cloud providers. Without the right tools, measuring identity can be challenging, necessitating specialized solutions.
Workload Access to Sensitive Data: Machine identities often outnumber user accounts, making privileged workloads a critical area for risk mitigation.
Active Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Users: MFA serves as a fundamental defense for securing user accounts accessing cloud tenants.
Conclusion
Understanding and tracking the cloud services used in an organization is key to effective cloud security and developing meaningful metrics. While some on-premises metrics can be adjusted for cloud use, the unique and fast-changing nature of cloud adoption calls for a fresh approach. Cloud-specific outcome-driven metrics (ODMs) focus on achieving specific security results, rather than simply basing investments on a portion of cloud spending.
Automation is vital for managing these controls in the dynamic cloud environment. Automating tasks like tracking, reporting, and configuration management helps ensure efficiency and accuracy. However, many organizations are cautious about automating fixes in live production environments to avoid disrupting operations. Building strong automation capabilities is often necessary to meet many of these cloud security goals effectively.
With TechAhead, you can be the next leader in the industry. We have been taking the app development services to another level. Because we have the most respected and experienced mobile app developers in the market.
Source URL: The-role-of-outcome-driven-metrics-in-enhancing-cloud-security-control-strategies
#cloud security adoption#outcome-driven metrics for security#cloud security strategies#cloud-native security solutions#cloud security metrics
0 notes
Text
CMSGP: Empowering OEM/ODM Manufacturers in India
India has emerged as a global hub for Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEM) and Original Design Manufacturers (ODM), driven by a unique combination of skilled labor, competitive costs, and an expanding market. In this dynamic landscape, CMSGP (Connected Manufacturing Solutions for the Global Partnership) plays a pivotal role in enhancing the capabilities and competitiveness of OEM and ODM manufacturers across the country.

Understanding OEM and ODM
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
These firms often work under contractual agreements, producing goods that adhere to the specifications of the buying company, allowing brands to leverage existing manufacturing capabilities without incurring the overhead of in-house production.
ODM (Original Design Manufacturer)
ODMs, on the other hand, take on a more comprehensive role by not only manufacturing products but also designing them. They provide a complete package to brands, allowing businesses to enter markets quickly with minimal investment in product development. This is particularly appealing for companies looking to introduce innovative products without the resources to develop them independently.
The Role of CMSGP in Supporting OEM/ODM Manufacturers
CMSGP is committed to fostering growth in the manufacturing sector by providing tailored solutions that enhance operational efficiency, streamline processes, and promote innovation. Here’s how CMSGP supports OEM and ODM manufacturers in India:
1. Streamlining Supply Chains
One of the key challenges OEM/ODM manufacturers face is managing complex supply chains. CMSGP offers advanced supply chain solutions that enable manufacturers to optimize inventory levels, track shipments in real-time, and reduce lead times. This agility is crucial in meeting market demands and ensuring timely delivery of products.
2. Enhancing Product Development
For ODMs, product development is vital to maintaining a competitive edge. CMSGP provides tools and resources that facilitate rapid prototyping and design collaboration. By integrating IoT and digital technologies, manufacturers can innovate more effectively, turning ideas into market-ready products faster than ever.
3. Implementing Smart Manufacturing Solutions
The rise of Industry 4.0 is transforming traditional manufacturing processes. CMSGP assists OEM/ODM manufacturers in adopting smart manufacturing practices, such as automation, data analytics, and IoT integration. These technologies lead to increased productivity, reduced operational costs, and enhanced product quality.
4. Ensuring Quality Control
CMSGP helps implement robust quality control systems that monitor production processes in real-time, ensuring compliance with industry standards and reducing defects.
5. Supporting Regulatory Compliance
In an increasingly regulated environment, navigating compliance requirements can be challenging. CMSGP provides guidance and tools to help OEM/ODM manufacturers understand and meet local and international regulations, thereby minimizing the risk of penalties and ensuring market access.
6. Fostering Sustainable Practices
Sustainability is becoming a significant concern for manufacturers worldwide. CMSGP encourages OEM and ODM manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly practices, such as waste reduction and energy efficiency. By leveraging advanced technologies, businesses can minimize their environmental footprint while improving their bottom line.
Conclusion
As India continues to solidify its position as a leading destination for OEM and ODM manufacturing, the role of CMSGP becomes increasingly important. By providing comprehensive solutions that enhance operational efficiency, promote innovation, and ensure compliance, CMSGP empowers manufacturers to thrive in a competitive landscape.
In this era of rapid technological advancement, OEM and ODM manufacturers must embrace change and adapt to new market realities. With the support of CMSGP, they can navigate these challenges effectively, ensuring sustainable growth and success in the global marketplace. As the manufacturing sector evolves, partnerships with organizations like CMSGP will be key to unlocking the full potential of India’s OEM and ODM capabilities.
0 notes
Text
Leveraging MongoDB with Node.js for Scalable Business Solutions

In today’s data-driven world, businesses require agile and scalable solutions to manage ever-growing information. The dynamic duo of MongoDB and Node.js offers a powerful combination to address these challenges. This blog delves into how MongoDB, a NoSQL document database, and Node.js, a JavaScript runtime environment, seamlessly integrate to create robust and scalable business solutions.
Why MongoDB? A Document-Oriented Approach
Traditional relational databases (RDBMS) excel in structured data with predefined schemas. However, modern applications often deal with complex, evolving data structures that don’t fit neatly into rigid relational models. MongoDB breaks free from these limitations.
Here’s what makes MongoDB shine:
● Flexible Schema:
MongoDB utilizes a document-oriented approach. Documents are JSON-like structures that can store diverse data types, including arrays and embedded objects. This flexibility allows you to accommodate evolving data models without schema changes, a major advantage for agile development.
● Horizontal Scalability:
MongoDB scales horizontally by sharing data across multiple servers. This allows you to handle increasing data volumes by adding more servers, ensuring your database scales seamlessly with your business growth.
● High Performance:
MongoDB boasts impressive performance due to its in-memory data structures and efficient query execution. This translates to faster read and write operations, crucial for real-time applications.
Why Node.js? The JavaScript Advantage
Node.js brings a unique advantage to the table: JavaScript. As a single-threaded, event-driven environment, Node.js excels at handling a high volume of concurrent requests efficiently. Here’s how it complements MongoDB:
● JavaScript Familiarity
Node.js leverages JavaScript, a widely used language for front-end development. This familiarity empowers developers to work with both back-end and front-end logic using the same language, streamlining development and reducing the learning curve.
● Asynchronous Programming
Node.js’s non-blocking, asynchronous architecture aligns perfectly with MongoDB’s high-performance nature. This enables efficient handling of numerous concurrent requests without compromising responsiveness.
● Rich Ecosystem
The Node Package Manager (npm) provides a vast collection of open-source libraries and frameworks specifically designed for Node.js development. This includes powerful tools for interacting with MongoDB, such as Mongoose, a popular Object Data Modeling (ODM) library.
The Synergy: Building Scalable Solutions
The combined power of MongoDB and Node.js unlocks exciting possibilities for building scalable business solutions. Here are some compelling use cases with technical considerations:
Real-Time Applications
The duo excels in building real-time applications like chat rooms, social media platforms, and collaborative editing tools. MongoDB’s flexibility and Node.js’s event-driven architecture enable seamless data updates and a dynamic user experience.
Technical Considerations
Utilize Socket.IO, a popular real-time communication library for Node.js, to establish bi-directional communication between clients and servers. Implement efficient data serialization techniques (e.g., BSON) to minimize data transfer overhead.
IoT Applications
The ever-growing Internet of Things (IoT) landscape generates vast amounts of unstructured data. MongoDB’s flexible schema and horizontal scalability are ideal for storing and managing sensor data from connected devices, while Node.js facilitates efficient data processing and communication with devices.
Technical Considerations
Explore libraries like Mongoose to simplify data modeling for sensor data. Leverage Node.js’s streaming capabilities to handle high-velocity data streams from IoT devices. Consider implementing authentication and authorization mechanisms to secure communication between devices and the server.
E-commerce Platforms
Modern e-commerce platforms require managing a variety of product information, user data, and purchase histories. MongoDB’s flexibility and scalability cater to the ever-changing needs of e-commerce businesses, while Node.js delivers a robust back-end for handling transactions and user interactions.
Technical Considerations
Utilize MongoDB aggregation pipelines for efficient product search and filtering functionalities. Implement Node.js middleware to handle user authentication, authorization, and shopping cart management. Integrate payment gateways securely using established Node.js libraries.
Security Considerations
While MongoDB and Node.js offer remarkable advantages, security remains a crucial concern. Here are some best practices to follow:
Regular Updates: Maintain up-to-date versions of MongoDB and Node.js to benefit from the latest security patches. Regularly update any installed npm packages to address potential vulnerabilities.
Authentication and Authorization: Implement robust authentication and authorization mechanisms to control user access and prevent unauthorized data modification.
Input Validation: Validate all user input to prevent malicious code injection attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Sanitize and escape any user-provided data before storing it in MongoDB.
Secure Coding Practices: Follow secure coding practices on both the Node.js and database side to minimize security risks. This includes avoiding common vulnerabilities like insecure direct object references (IDOR) and using prepared statements for database queries.
Network Security: Implement network security measures like firewalls and access control lists (ACLs) to restrict unauthorized access to your MongoDB server and Node.js application.
Beyond the Basics: Performance Optimization
Optimizing performance is crucial for maintaining a smooth user experience in large-scale applications. Here are some tips for Node.js and MongoDB performance optimization:
Caching: Utilize caching mechanisms like Redis or Memcached to store frequently accessed data in memory, reducing the load on MongoDB.
Indexing: Create appropriate indexes in MongoDB for frequently used queries to improve query performance.
Profiling: Use profiling tools for both Node.js and MongoDB to identify bottlenecks and optimize code for better efficiency.
To Wrap It Up!
Integrating MongoDB with Node.js for data storage and retrieval presents a multitude of advantages, such as enhanced flexibility, scalability, performance, and robust querying capabilities. Collaborating with a reputable Node.js Development Company such as Force WebTech enables you to maximize the synergies between MongoDB and Node.js, empowering you to create cutting-edge web applications that excel in both performance and user experience. Reach out to Force WebTech now to explore how they can assist you in leveraging MongoDB and Node.js for your upcoming project.
Original Source: https://forcewebtech.com/blog/mongodb-node-js-for-scalable-business-solutions/
0 notes
Text
Gaining Skills in Full-Stack Development Your In-Depth guide for the MERN Stack
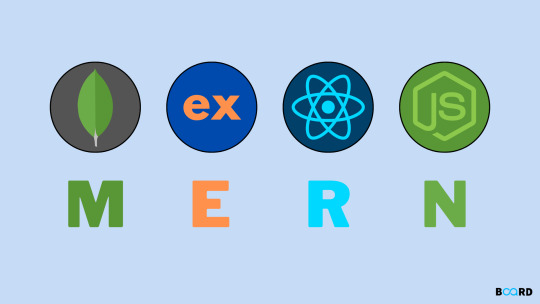
A powerful set of technologies called the MERN stack is employed in the development of dynamic and scalable web applications. It is the perfect option for developers that wish to work with JavaScript for both front-end and back-end development because it includes MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, and Node.js. You will learn the principles of each technology, how they interact with one another, and how to use them to create reliable applications in this course.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
Before diving into MERN stack development, it’s essential to set up your development environment properly. This includes installing Node.js and npm, setting up MongoDB, and configuring your code editor. We'll walk you through each step, ensuring you have all the tools and configurations needed to start building your MERN stack applications.
Building a RESTful API with Express and Node.js
Express and Node.js power a MERN stack application's back end. This section covers handling HTTP requests, managing routes, and building a RESTful API. We'll go over key ideas including managing errors, integrating MongoDB for data storage and retrieval, and middleware.
Using React.js for Front-End Design
The component-based architecture and effective dynamic UI rendering of React.js are well-known. You will gain knowledge about handling user interactions, handling reusable components, and using hooks to manage state. In MERN stack development course advanced topics like Redux for state management in larger applications and React Router for navigation will also be covered.
Connecting the Front-End and Back-End
In a MERN stack application, seamless front-end and back-end integration is essential. This section will walk you through the process of sending HTTP requests from your React components to the Express API using Axios or the Fetch API. You will gain knowledge about managing data retrieval, authentication, and client-server synchronization.
Implementing Authentication and Authorization
Using Authentication and Authorization Security is an essential part of developing websites. We'll go over how to use JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for user authentication and authorization in this section of the course. You'll discover how to manage user sessions, safeguard routes against unwanted access, and develop safe login and registration routes.
Deploying Your MERN Application
The last stage is deployment, which comes once your application is finished. We'll guide you through the process of launching your MERN stack application on an AWS or Heroku cloud platform. You will gain knowledge of setting up environment variables, optimizing your server for production use, and making sure your application is effective and scalable.
Advanced Methods for MERN Stacking
We'll dive into advanced methods and best practices to help you develop your abilities. Performance optimization, real-time functionality implementation using WebSockets, and more efficient data searching with GraphQL are all included in this. These advanced topics will improve your skills as a full-stack developer and get you ready to take on challenging tasks.
Introduction to JavaScript
The foundation of the MERN stack is JavaScript, and efficient development requires an awareness of its contemporary features. We'll go over key JavaScript ideas and ES6+ features like async/await, template literals, destructuring, and arrow functions in this section. These improvements make the code easier to read and maintain while also making it simpler.
The NoSQL Database, MongoDB
A NoSQL database that is document-oriented, MongoDB enables scalable and adaptable data storage. The basics of MongoDB, such as collections, documents, and CRUD functions, will be covered. Additionally, you will learn how to enforce data formats and expedite database operations with Mongoose, an Object Data Modeling (ODM) module for MongoDB and Node.js.
Building and Testing API Endpoints
Developing a strong API is an essential component of every web application. Building and testing API endpoints with Postman-like tools is the main topic of this section. To make sure your API is dependable and error-free, you'll learn how to organize your routes, verify incoming data, and put unit and integration tests in place.
Overview of Component Libraries
Use component libraries like Material-UI or Ant Design to improve your React apps. These libraries include pre-made, editable user interface components that can greatly expedite development and guarantee a unified design. We'll go over how to include these libraries into your project and modify individual parts to suit the requirements of your application.
State Management with Context API and Redux
Effective state management is key to maintaining an organized and scalable React application. We’ll start with the Context API for simple state management scenarios and then move on to Redux for more complex applications. You’ll learn how to set up a Redux store, create actions and reducers, and connect your components to the store using React-Redux.
Handling Forms and Validation
Forms are a critical part of user interaction in web applications. This section covers how to handle form input, manage form state, and implement validation using libraries like Formik and Yup. You’ll learn best practices for creating dynamic and user-friendly forms that enhance user experience.
Real-Time Data with WebSockets
Adding real-time functionalities can significantly enhance user experience in web applications. We'll introduce WebSockets and Socket.io to implement real-time data updates. You’ll learn how to set up a WebSocket server, handle real-time events, and create interactive features such as live chat and notifications.
Using GraphQL with MERN
GraphQL is an alternative to REST that allows for more flexible and efficient data querying. This section will introduce you to GraphQL and how to integrate it with your MERN stack application. You’ll learn how to create GraphQL schemas, write resolvers, and make queries and mutations from your React components.
Testing Your React Components
Testing is an essential part of the development process. This section will cover how to write tests for your React components using testing libraries such as Jest and React Testing Library. You’ll learn how to write unit tests, mock dependencies, and ensure your components behave as expected under various scenarios.
Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD)
Implementing a CI/CD pipeline ensures that your application is tested and deployed automatically whenever you make changes. This section will guide you through setting up CI/CD workflows using services like GitHub Actions or Jenkins. You’ll learn how to automate testing, build processes, and deploy your MERN stack application seamlessly.
Exploring the Ecosystem and Community
The MERN stack has a vibrant and active community that continuously contributes to its ecosystem. This section highlights valuable resources, including forums, documentation, and open-source projects. Engaging with the community can provide support, inspiration, and opportunities to collaborate on exciting projects.
Conclusion
After completing the MERN stack development course in every aspect, you have acquired important information and abilities. Continue developing your own apps, participating in initiatives, and investigating new technologies as you advance. Your newly acquired abilities will be a strong starting point for a profitable full-stack development career. The web development industry is a dynamic and ever-changing field, and with the MERN stack, you're prepared to take on any problem that may arise.
0 notes
Text
Master the Stack: Node.js, Express.js, MongoDB & Netlify

Embark on an Exciting Tech Voyage: Plunge into the Leading Edge of Technology with WhatsOn IT Academy's Deep-Dive Course on February 16, 2024, at 15:00 in BD Time and 9:00 in UK Time. Delve into the vast and modern world of web development, with a comprehensive curriculum that covers everything you need to know about creating robust and resilient RESTful APIs. Elevate your coding abilities by securing your place today for an adventure into the upcoming era of technology! Node.js Fundamentals - Understand Node.js as a JavaScript runtime environment. - Install Node.js and npm, create a project directory, and initialize it. - Revisit basic JavaScript concepts if needed. - Explore using npm to manage dependencies. - Write and run simple Node.js scripts. Building with Express.js - Understand Express.js as a web framework for Node.js. - Learn about routes, handling requests, sending responses. - Create a basic server with Express to serve static files. - Define routes for different URL paths and handle requests accordingly. - Introduce templating engines like EJS or Pug for dynamic content. Connecting to MongoDB - Understand MongoDB as a NoSQL database with document-oriented storage. - Install MongoDB locally or use a cloud service like MongoDB Atlas. - Learn Mongoose as an ODM (Object Data Modeling) library for MongoDB in Node.js. - Connect your Node.js application to the MongoDB database. - Perform Create, Read, Update, delete operations on your MongoDB data using Mongoose. Deployment with Netlify - Understand Netlify as a platform for hosting static websites and web applications. - Explore options like Netlify Functions for serverless functions or static site deployment. - Set up your project for deployment on Netlify. - Push your code to a Git repository and deploy to Netlify. - Verify your application works as expected after deployment. Don't miss this exceptional opportunity to unlock your full potential as a web developer! Secure your spot in this transformative course today and embark on an exciting voyage into the future of technology. Join Now Join WhatsOn IT Academy Facebook Group– Link Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Unveiling the Power of MERN Stack: A Comprehensive Guide
In the ever-evolving landscape of web development, choosing the right technology stack is crucial for building robust and scalable applications. One such powerful and popular stack is the MERN stack, comprising MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, and Node.js. In this blog post, we will dive into the intricacies of each component and explore how they seamlessly work together to create dynamic and feature-rich web applications.
MongoDB:
MongoDB, a NoSQL database, forms the 'M' in MERN stack. Its flexible schema allows developers to store data in a JSON-like format, making it easy to handle and manage large amounts of structured and unstructured data. MongoDB's scalability and high performance make it an ideal choice for applications with rapidly changing data requirements.
Express.js:
Express.js, often referred to as the 'E' in MERN stack, is a minimalistic and flexible Node.js web application framework. It simplifies the process of building robust and scalable web applications by providing a set of features for web and mobile applications. Express.js facilitates the creation of server-side logic, routing, and middleware, streamlining the development process and enhancing the overall performance of the application.
React.js:
React.js, the 'R' in MERN stack, is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces. Developed and maintained by Facebook, React.js enables the creation of interactive and dynamic user interfaces with ease. Its component-based architecture allows developers to build reusable UI components, making the codebase modular and maintainable. React.js also provides a virtual DOM, which enhances the application's performance by minimizing unnecessary updates and rendering only the components that have changed.
Node.js:
Node.js forms the 'N' in MERN stack and serves as the runtime environment for executing server-side JavaScript code. With its non-blocking, event-driven architecture, Node.js enables the development of highly scalable and performant applications. Node.js seamlessly integrates with Express.js, allowing developers to build a complete web application using JavaScript for both the client and server sides.
Building a MERN Stack Application:
To showcase the power of MERN stack, let's walk through the process of building a simple task management application:
a. Setting up the environment:
Install Node.js and npm
Set up a MongoDB database
Create a new React.js application using create-react-app
Initialize an Express.js server
b. Connecting MongoDB with Express.js:
Use Mongoose, an ODM (Object Data Modeling) library, to interact with MongoDB
Define models and schemas for the application's data
c. Building the frontend with React.js:
Create components for tasks, user interface, and interactions
Use React Router for navigation between different views
Fetch and display data from the Express.js API
d. Implementing server-side logic with Express.js:
Set up routes for handling CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations
Implement middleware for authentication and error handling
e. Deploying the MERN stack application:
Choose a hosting provider (e.g., Heroku, AWS, or DigitalOcean)
Configure the deployment environment
Deploy both the frontend and backend components
Conclusion:
The MERN stack provides a powerful and efficient framework for developing modern web applications. MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, and Node.js complement each other seamlessly, enabling developers to build scalable, performant, and feature-rich applications. As you embark on your journey with MERN stack development, explore the vast ecosystem of libraries and tools available to enhance your productivity and create cutting-edge web solutions. Happy coding!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Scaling Up Your Culinary Ventures: Exploring the Advantages of Wholesale Kitchen Scales

Wholesale kitchen scales offer several advantages for culinary ventures, whether you run a restaurant, catering business, bakery, or any other food-related enterprise. These scales are designed to handle large quantities of ingredients accurately and efficiently, making them indispensable tools for any professional kitchen. Let's explore the advantages of using wholesale kitchen scales for your culinary business:
Accurate Measurements: Wholesale kitchen scales are built with high-precision load cells and sophisticated technology, ensuring accurate measurements of ingredients. This precision is crucial for maintaining consistency in recipes and producing high-quality dishes.
Time and Cost Savings: These scales enable faster and more efficient measuring processes. They allow you to measure large quantities of ingredients in a single step, saving time and reducing labor costs.
Bulk Ingredient Handling: Wholesale kitchen scales can handle larger quantities of ingredients, making them ideal for recipes that require bulk measurement. Whether you need to weigh large batches of flour for baking or ingredients for large-scale meal preparation, these scales can handle the task with ease.
Ease of Use: Many wholesale kitchen scales come with user-friendly interfaces and intuitive controls, making them easy to operate even for staff members who may not have extensive technical knowledge.
Digital Integration: Some wholesale kitchen scales have digital interfaces, enabling seamless integration with other kitchen systems and software. This integration can streamline inventory management, recipe scaling, and data analysis.
Portability: Despite their large size, many wholesale kitchen scales are designed to be portable and easy to move within the kitchen or between workstations.
Multi-Functional: Some wholesale kitchen scales offer additional functions, such as converting measurements between units (e.g., grams to ounces) or calculating nutritional information based on ingredient weights.
Consistent Quality: Using wholesale kitchen scales helps maintain consistent quality in your culinary creations. Accurate measurements ensure that each dish meets your desired standard, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Compliance with Regulations: Many culinary businesses are subject to regulatory standards regarding food portioning and labeling. Wholesale kitchen scales ensure that your business complies with these regulations, reducing the risk of fines or penalties.
Scalability: As your culinary business grows, wholesale kitchen scales can easily accommodate increased production demands. Their capacity and efficiency make them suitable for scaling up your operations.
Wholesale kitchen scales are essential tools for any professional kitchen, providing accuracy, efficiency, and scalability. By investing in these scales, you can optimize your culinary processes, reduce waste, and deliver consistent, high-quality dishes to your customers. Whether you are managing a small restaurant or a large-scale catering operation, wholesale kitchen scales can be a valuable asset for your culinary ventures.
0 notes
Link
#advanced analytics ai#Data Solutions#Data Operations#Data Engineering#Operational Data Management (ODM)#Feature Engineering#Data Analytics#Data engineering technologies#Data Science#Data Maturity Assessment#advanced analytics and ai#advanced analytics and data science#advanced analytics companiesadvanced analytics companies#advanced analytics companies#advanced analytics data science#advanced analytics in manufacturing#advanced analytics in retail#advanced analytics industry#advanced analytics services#advanced data engineering
0 notes
Photo

hydralisk98′s web projects tracker:
Core principles=
Fail faster
‘Learn, Tweak, Make’ loop
This is meant to be a quick reference for tracking progress made over my various projects, organized by their “ultimate target” goal:
(START)
(Website)=
Install Firefox
Install Chrome
Install Microsoft newest browser
Install Lynx
Learn about contemporary web browsers
Install a very basic text editor
Install Notepad++
Install Nano
Install Powershell
Install Bash
Install Git
Learn HTML
Elements and attributes
Commenting (single line comment, multi-line comment)
Head (title, meta, charset, language, link, style, description, keywords, author, viewport, script, base, url-encode, )
Hyperlinks (local, external, link titles, relative filepaths, absolute filepaths)
Headings (h1-h6, horizontal rules)
Paragraphs (pre, line breaks)
Text formatting (bold, italic, deleted, inserted, subscript, superscript, marked)
Quotations (quote, blockquote, abbreviations, address, cite, bidirectional override)
Entities & symbols (&entity_name, &entity_number,  , useful HTML character entities, diacritical marks, mathematical symbols, greek letters, currency symbols, )
Id (bookmarks)
Classes (select elements, multiple classes, different tags can share same class, )
Blocks & Inlines (div, span)
Computercode (kbd, samp, code, var)
Lists (ordered, unordered, description lists, control list counting, nesting)
Tables (colspan, rowspan, caption, colgroup, thead, tbody, tfoot, th)
Images (src, alt, width, height, animated, link, map, area, usenmap, , picture, picture for format support)
old fashioned audio
old fashioned video
Iframes (URL src, name, target)
Forms (input types, action, method, GET, POST, name, fieldset, accept-charset, autocomplete, enctype, novalidate, target, form elements, input attributes)
URL encode (scheme, prefix, domain, port, path, filename, ascii-encodings)
Learn about oldest web browsers onwards
Learn early HTML versions (doctypes & permitted elements for each version)
Make a 90s-like web page compatible with as much early web formats as possible, earliest web browsers’ compatibility is best here
Learn how to teach HTML5 features to most if not all older browsers
Install Adobe XD
Register a account at Figma
Learn Adobe XD basics
Learn Figma basics
Install Microsoft’s VS Code
Install my Microsoft’s VS Code favorite extensions
Learn HTML5
Semantic elements
Layouts
Graphics (SVG, canvas)
Track
Audio
Video
Embed
APIs (geolocation, drag and drop, local storage, application cache, web workers, server-sent events, )
HTMLShiv for teaching older browsers HTML5
HTML5 style guide and coding conventions (doctype, clean tidy well-formed code, lower case element names, close all html elements, close empty html elements, quote attribute values, image attributes, space and equal signs, avoid long code lines, blank lines, indentation, keep html, keep head, keep body, meta data, viewport, comments, stylesheets, loading JS into html, accessing HTML elements with JS, use lowercase file names, file extensions, index/default)
Learn CSS
Selections
Colors
Fonts
Positioning
Box model
Grid
Flexbox
Custom properties
Transitions
Animate
Make a simple modern static site
Learn responsive design
Viewport
Media queries
Fluid widths
rem units over px
Mobile first
Learn SASS
Variables
Nesting
Conditionals
Functions
Learn about CSS frameworks
Learn Bootstrap
Learn Tailwind CSS
Learn JS
Fundamentals
Document Object Model / DOM
JavaScript Object Notation / JSON
Fetch API
Modern JS (ES6+)
Learn Git
Learn Browser Dev Tools
Learn your VS Code extensions
Learn Emmet
Learn NPM
Learn Yarn
Learn Axios
Learn Webpack
Learn Parcel
Learn basic deployment
Domain registration (Namecheap)
Managed hosting (InMotion, Hostgator, Bluehost)
Static hosting (Nertlify, Github Pages)
SSL certificate
FTP
SFTP
SSH
CLI
Make a fancy front end website about
Make a few Tumblr themes
===You are now a basic front end developer!
Learn about XML dialects
Learn XML
Learn about JS frameworks
Learn jQuery
Learn React
Contex API with Hooks
NEXT
Learn Vue.js
Vuex
NUXT
Learn Svelte
NUXT (Vue)
Learn Gatsby
Learn Gridsome
Learn Typescript
Make a epic front end website about
===You are now a front-end wizard!
Learn Node.js
Express
Nest.js
Koa
Learn Python
Django
Flask
Learn GoLang
Revel
Learn PHP
Laravel
Slim
Symfony
Learn Ruby
Ruby on Rails
Sinatra
Learn SQL
PostgreSQL
MySQL
Learn ORM
Learn ODM
Learn NoSQL
MongoDB
RethinkDB
CouchDB
Learn a cloud database
Firebase, Azure Cloud DB, AWS
Learn a lightweight & cache variant
Redis
SQLlite
NeDB
Learn GraphQL
Learn about CMSes
Learn Wordpress
Learn Drupal
Learn Keystone
Learn Enduro
Learn Contentful
Learn Sanity
Learn Jekyll
Learn about DevOps
Learn NGINX
Learn Apache
Learn Linode
Learn Heroku
Learn Azure
Learn Docker
Learn testing
Learn load balancing
===You are now a good full stack developer
Learn about mobile development
Learn Dart
Learn Flutter
Learn React Native
Learn Nativescript
Learn Ionic
Learn progressive web apps
Learn Electron
Learn JAMstack
Learn serverless architecture
Learn API-first design
Learn data science
Learn machine learning
Learn deep learning
Learn speech recognition
Learn web assembly
===You are now a epic full stack developer
Make a web browser
Make a web server
===You are now a legendary full stack developer
[...]
(Computer system)=
Learn to execute and test your code in a command line interface
Learn to use breakpoints and debuggers
Learn Bash
Learn fish
Learn Zsh
Learn Vim
Learn nano
Learn Notepad++
Learn VS Code
Learn Brackets
Learn Atom
Learn Geany
Learn Neovim
Learn Python
Learn Java?
Learn R
Learn Swift?
Learn Go-lang?
Learn Common Lisp
Learn Clojure (& ClojureScript)
Learn Scheme
Learn C++
Learn C
Learn B
Learn Mesa
Learn Brainfuck
Learn Assembly
Learn Machine Code
Learn how to manage I/O
Make a keypad
Make a keyboard
Make a mouse
Make a light pen
Make a small LCD display
Make a small LED display
Make a teleprinter terminal
Make a medium raster CRT display
Make a small vector CRT display
Make larger LED displays
Make a few CRT displays
Learn how to manage computer memory
Make datasettes
Make a datasette deck
Make floppy disks
Make a floppy drive
Learn how to control data
Learn binary base
Learn hexadecimal base
Learn octal base
Learn registers
Learn timing information
Learn assembly common mnemonics
Learn arithmetic operations
Learn logic operations (AND, OR, XOR, NOT, NAND, NOR, NXOR, IMPLY)
Learn masking
Learn assembly language basics
Learn stack construct’s operations
Learn calling conventions
Learn to use Application Binary Interface or ABI
Learn to make your own ABIs
Learn to use memory maps
Learn to make memory maps
Make a clock
Make a front panel
Make a calculator
Learn about existing instruction sets (Intel, ARM, RISC-V, PIC, AVR, SPARC, MIPS, Intersil 6120, Z80...)
Design a instruction set
Compose a assembler
Compose a disassembler
Compose a emulator
Write a B-derivative programming language (somewhat similar to C)
Write a IPL-derivative programming language (somewhat similar to Lisp and Scheme)
Write a general markup language (like GML, SGML, HTML, XML...)
Write a Turing tarpit (like Brainfuck)
Write a scripting language (like Bash)
Write a database system (like VisiCalc or SQL)
Write a CLI shell (basic operating system like Unix or CP/M)
Write a single-user GUI operating system (like Xerox Star’s Pilot)
Write a multi-user GUI operating system (like Linux)
Write various software utilities for my various OSes
Write various games for my various OSes
Write various niche applications for my various OSes
Implement a awesome model in very large scale integration, like the Commodore CBM-II
Implement a epic model in integrated circuits, like the DEC PDP-15
Implement a modest model in transistor-transistor logic, similar to the DEC PDP-12
Implement a simple model in diode-transistor logic, like the original DEC PDP-8
Implement a simpler model in later vacuum tubes, like the IBM 700 series
Implement simplest model in early vacuum tubes, like the EDSAC
[...]
(Conlang)=
Choose sounds
Choose phonotactics
[...]
(Animation ‘movie’)=
[...]
(Exploration top-down ’racing game’)=
[...]
(Video dictionary)=
[...]
(Grand strategy game)=
[...]
(Telex system)=
[...]
(Pen&paper tabletop game)=
[...]
(Search engine)=
[...]
(Microlearning system)=
[...]
(Alternate planet)=
[...]
(END)
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Coax to fibre media converter

Thank you for choosing Primus Cable as your fiber media converter supplier. If you have any questions about selecting the right fiber media converter or fiber optic media converter for your network, please call or email us. Some also include cooling fans extending the life of network components.Īt Primus Cable, we leverage or nearly 20 years’ experience to provide you the best possible customer service. They often include a redundant power supply and hot swapping functionality. Media converter chassis ensure seamless operation for your network for years. This SFP media converter works with single mode fiber measuring 9/125 and 10/125 microns. It works with multimode fiber measuring 50/125 and 62.5/125 microns. This SFP media converter is designed to handle both single and multimode fiber optic cable. This product is designed to be used to convert a fiber optic (To slink) digital audio signal into a digital coaxial signal. Picture of CTC UNION 20 Port Managed SFP Patching HUB. The MC210CS supports longwave (LX) laser. The Media Converter, 10/100/1000M Gigabit Ethernet, SFP Transceiver Slot is an SFP media converter built to convert 10/100/1000BASE-TX to 1000BASE-FX or vice versa. Converts 100/1000Base -FX Ethernet copper to 100 & 1000Mbps SFP fibre. 3z 1000Base-LX standards, the MC210CS is designed for use with single-mode fiber cable utilizing the SC-Type connector. Primus Cable also supplies SFP fiber media converters which include the transceiver slot. This unit has four transmitting modes and a selectable optical link loss alarm. It supports auto-negotiation in TP port to detect speed and duplex mode automatically. This standard media converter covers a distance up to 10 Kilometers. The Media Converter, Single Mode, Gigabit Ethernet, 10KM, SC Connector is made to handle 10, 100, and 1000BASE-T Gigabit network standards. Our standard media converters are available in both single and multimode varieties. Primus Cable supplies this type of fiber media converter in 10/100BASE Fast Ethernet, 10/1000BASE Gigabit, and 1000BASE Pure Gigabit versions. Standard fiber Ethernet media converters provide the basic data conversion from copper to fiber without including a transceiver within the unit. Media Converter Chassis (compatible with your fiber optic media converter).Primus Cable is proud to offer the following categories of fiber to Ethernet media converter products: They are also used in metropolitan area network (MAN) access and data transport services to enterprise customers. They were introduced to the industry nearly two decades ago and are important in interconnecting fiber optic cabling-based systems with existing copper-based, structured cabling systems. Need Help Finding Media Converters Tripp Lites Media Converters convert a fiber optical signal to a copper Ethernet signal that extends both power (48. run over coaxial cables, but now only twisted pair or fiber optic cables are used. You can also contact our buyer service and get some buying guides.A fiber media converter is a simple networking device that makes it possible to connect two dissimilar media types such as twisted pair with fiber optic cabling. Economical: As media converters integrate fiber and copper networks. We hope to keep every buyer up to date with this fastest moving electronic industry and the latest products trends. Update your electrical products and buy from these credible suppliers with the latest China production technology. They are experienced China exporters for your online sourcing. You can also customize Coaxial To Fiber Converter orders from our OEM/ODM manufacturers. operation types, modes or media types (twisted pair, fibre, coax). Design engineers or buyers might want to check out various Coaxial To Fiber Converter factory & manufacturers, who offer lots of related choices such as cable, fiber optic cable and optical fiber. These products are used to acquire, process, and distribute television, data, voice, security, and traffic control signals over fiber optic, copper, and coax. and 10-Gigabit Ethernet to fibre with commercial and industrial media converters. Amongst the wide range of products for sale choice, Coaxial To Fiber Converter is one of the hot items. They would supply all of your electrical requirements You’re sure to find what you need in our broad selection of electrical & electronics, including electronic components, electrical & Telecommunication equipment and electromechanical devices. Import electrical products from our verified China suppliers with competitive prices. Our electronics supplier database is a comprehensive list of the key suppliers, manufacturers(factories), wholesalers, trading companies in the electronics industry. Sourcing Guide for Coaxial To Fiber Converter:

0 notes
Text
Lucrative Job Opportunities That Students Can Grab After PGDM
In recent years, the PGDM degree has gained a great deal of popularity among management candidates. The primary reason for its popularity is that talented PGDM students have more professional options than MBA students.
The PGDM programme offered by the top PGDM colleges in Odisha is a new generation programme that prepares students in the actual application of management abilities. As the times have changed, more and more job functions have become specialised in fields of management, resulting in the birth of new PGDM specialisations.
Please visit ODM Business School right away for more information about PGDM courses in Odisha.

Talent Manager
• It is the responsibility of talent managers to communicate and negotiate successfully with the organisation's emerging talent.
• For effective results, talent managers should be able to distribute tasks based on the abilities available.
• Talent managers are expected to create and maintain a robust network of connections within the sector for the purpose of identifying commercial prospects.
• Talent managers are required to have comprehensive and current knowledge of their particular domains and industries.
• Talent managers are supposed to mentor and advise talent on career-impacting personal and professional decisions.
• Talent managers are expected to collaborate with a wide variety of individuals inside an organisation.
Salary and Benefits
• Freshmen will likely earn between four and six lakhs rupees each year.
• Experienced professionals would earn between six and eight lakhs per year.
Retail Manager
• Retail managers are responsible for the daily operations of a business with the objective of maximising earnings while minimising expenses.
• Retail managers are accountable for overseeing the daily operations of a store or department within an organisation.
• It is the responsibility of the retail managers to guarantee that promotions are executed accurately and in accordance with the company's standards and to ensure that all employees are working toward the day's goal.
• Retail managers are accountable for managing and motivating a workforce in order to boost productivity.
• Retail managers are expected to analyse sales numbers and anticipate future sales, as well as analyse and evaluate patterns for planning purposes.
• Retail managers are expected to record sales numbers, analyse data, and plan forward using information technology.
• Retail managers are responsible for ensuring that quality, customer service, and health and safety standards are met.
• The retail managers are expected to routinely walk the sales floor to identify consumers, fix urgent issues, and handle transactions as necessary.
• Retail managers are expected to remain informed of retail industry market trends.
• Retail managers must comprehend impending customer initiatives and keep an eye on the competition.
• Retail managers are expected to initiate improvements to enhance the industry's business.
• Retail managers are needed to coordinate promotional operations with local publications and the community in specific areas.
Salary and Benefits
• Fresh PGDM graduates will earn approximately between six and eighty lakhs per year.
• Experienced professionals would earn between eight and twelve lakhs per year.

IT Project Manager
• The IT project managers are responsible for managing the organisation's resources and motivating the team to meet tight deadlines under duress.
• The IT Project Managers are responsible for monitoring the execution of assigned work, establishing deadlines, and delegating duties to the project team while eliminating potential risks.
• The IT Project Managers are expected to complete the project in accordance with the plan that serves the organisation's best interests.
• The IT project managers are responsible for initiating the project by assessing its viability and establishing budgets, teams, and resources.
• IT project managers are responsible for establishing goals and objectives, defining responsibilities, and managing schedules and deadlines in accordance with client specifications.
• The IT project managers are expected to identify, lead, and encourage the internal and external stakeholder organisations comprising the project team.
• It is the responsibility of the IT project managers to manage the projects by organising the project team to keep them on schedule and within budget constraints.
• It is the responsibility of the IT project managers to monitor and control operations by tracking the project's progress.
• It is the responsibility of the IT project managers to bring the project to a close, including evaluating the project's viability and the problems associated with its execution.
Salary and Benefits
• New graduates will likely earn between six and eight lakh rupees per year.
• Experienced professionals would earn between eight and twelve lakhs per year.
Conclusion
In the recent five to ten years, the majority of students have opted for PGDM courses in Odisha over MBA. This demand is a result of the industry's great job options for PGDM students. PGDM courses are constantly in line with industry requirements compared to MBA degrees. The PGDM programme emphasises skill-based learning, which is required by modern industries, particularly for management professionals. The competency-based approach is the next big thing in management education, and PGDM has always been known to give this from the beginning.
0 notes
Text
AMD Launches Ryzen Embedded V3000 Series Processors

AMD introduced the Ryzen Embedded V3000 Series processors, adding the high-performance “Zen 3” core to the V-Series portfolio to deliver reliable, scalable processing performance for a wide range of storage and networking system applications. With greater CPU performance1, DRAM memory transfer rate, CPU core count3 and I/O connectivity when compared to the AMD Ryzen Embedded V1000 series, the new AMD Ryzen Embedded V3000 Series processors deliver the performance and low-power options required for some of the most demanding 24x7 operating environments and workloads. Now shipping to leading embedded ODMs and OEMs, AMD Ryzen Embedded V3000 processors address the growing demands of enterprise and cloud storage, as well as data center network routing, switching and firewall security features. AMD Ryzen Embedded V3000 processors can power a variety of diverse use-cases ranging from virtual hyper-converged infrastructure to advanced systems at the edge. Rajneesh Gaur, corporate vice president and general manager, Embedded Solutions Group, AMD, said, “We designed AMD Ryzen Embedded V3000 processors for customers seeking a balance of high-performance and power-efficiency for a wide range of applications in a compact BGA package. AMD Ryzen Embedded V3000 processors deliver a robust suite of features with advanced benefits required for superior workload performance in enterprise and cloud storage and networking products.”

AMD Ryzen Embedded V3000 processors are available in four-, six- and eight-core configurations with low thermal design power (TDP) profiles spanning from 10W to 54W for storage and networking systems to enable an exacting balance of performance and power efficiency in a compact design. The new AMD Ryzen Embedded V3000 processor family enables system designers to leverage a single board design for a wide range of system configurations, with ball grid array (BGA) packaging and low thermal dissipation for the creation of more versatile, flexible designs that ease system integration. Shane Rau, research vice president, Computing Semiconductors, IDC, said, “Storage and networking require a different balance of data processing performance, data movement, power management and thermal management than traditional compute. Processors for storage and networking require compute, memory and I/O capabilities balanced for rack space utilization, power efficiency and low heat dissipation in space-constrained environments. The market for storage and networking will demand x86-compatible processors optimized for core data center and edge infrastructure systems and processor vendors offering them will help their OEM customers significantly expand their system TAM while leveraging their existing investments in the x86 ecosystem.”
AMD Ryzen Embedded V3000 Series Processor Overview
Model TDP Range CPU Core / Thread Count CPU Base Freq. GHz CPU Boost Freq. GHz (Up to) L2 CPU Cache L3 CPU Cache Max DDR5 throughput (MT/s) (Up to) PCIe Gen4 Lanes Ethernet Ports Junction Temp. V3C48 35-54W 8 / 16 3.3 GHz 3.8 GHz 4 MB 16 MB 4,800 20L 2x10 Gb 0-105C V3C44 35-54W 4 / 8 3.5 GHz 3.8 GHz 2 MB 8 MB 4,800 20L 2x10 Gb 0-105C V3C18I 10-25W 8 / 16 1.9 GHz 3.8 GHz 4 MB 16 MB 4,800 20L 2x10 Gb -40-105C V3C16 10-25W 6 / 12 2.0 GHz 3.8 GHz 3 MB 16 MB 4,800 20L 2x10 Gb 0-105C V3C14 10-25W 4 / 8 2.3 GHz 3.8 GHz 2 MB 8 MB 4,800 20L 2x10 Gb 0-105C Additional Key Benefits Linux OS support with upstreamed Ubuntu and Yocto drivers Planned product availability up to 10 years, providing customers with a long-lifecycle support roadmap Available security capabilities include AMD Memory Guard4for defending against unauthorized memory access, and AMD Platform Secure Boot5 to mitigate for firmware advanced persistent threats (APTs) Read the full article
0 notes
Text
What are the types of storage servers?
The gadget is reliable with maximum storage space. The storage server is a type of server used to keep, secure, store, and manage digital files and folders. The purpose of a built server is limited to ample data storage and access to the data on a shared network. It can also be termed a file server. The storage server serves as a central point for data storage and access.
The local client nodes' access is through GUI and FTP control panel. It serves as a backup server for data storage.
The integral part of direct-attached storage (DAS), network-attached storage (NAS), and many more. The server is used to manage, secure, and store the digital access of data and files is called a storage server.
Types of storage
The storage server is of two types – dedicated and non-dedicated servers.
The dedicated server exclusively uses a file server with specific workstations for reading and writing the database. The disk array formation is the result of data file storage. The technology is developed to operate multiple disk drives together as a unit. A disk array has a cache (faster than a magnetic disk) and advanced storage visualization and RAID. The type of disk array used is dependent on the storage network.
Once a machine is configured and made public on the network, users can start accessing the available storage space on the storage server by 'mapping' the drives on their computers. After mapping, the computer's operating system identifies the storage server as an additional drive. If the network configuration is done precisely, all computers are granted permission to create, modify and execute files directly from the server while adding extra shared storage space to each connected computer.
USI has provided customers with the ODM/JDM/EMS Server, Storage, NAS, and SSD product and manufacturing service. We offer the L10 system design service, which includes the M/B, Firmware BIOS & BMC, Sub-card (Backplane, Add-on card, etc.), and enclosure & thermal design and system integration.
Server
In USI, customers will have both the ODM/JDM server products developing and the EMS server board build service. We offer the L10 server system design service, which includes the server M/B, Firmware BIOS & BMC, Sub-card (Backplane, Add-on card, etc.), enclosure & thermal design, and system integration. The customer's NPI will be managed in the Taiwan factory, and the mass production will be handled in the China factory, Shenzhen, and Kunshan, for the board and system build.
Strengths
10+ years of Server MB, Cards, ODM/JDM design experience
Intel x86 platform hardware, BMC, and BIOS development talent expert
Total solution on system integration validation
Certification and Regulatory Service
Advanced SMT manufacturing, assembly, test process
World Wide Logistic and Service
0 notes