#OrganizationalStructure
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Organizational structure is much more than just a blueprint of who reports to whom; it's the foundation that shapes how a company operates, communicates, and evolves. In this comprehensive exploration of organizational structure design and development, w...
0 notes
Text
An Organizational Breakdown Structure (OBS) is a powerful tool that helps businesses and project teams operate more efficiently by defining roles, streamlining communication, optimizing resources, and improving oversight. Whether managing a small project or overseeing large-scale operations, implementing an OBS can drive productivity, enhance collaboration, and ensure success.
By leveraging an OBS alongside a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), organizations can create a well-coordinated framework that maximizes efficiency and accountability.
If your organization hasn't implemented an OBS yet, now is the perfect time to start!
#ProjectManagement#OrganizationalStructure#BusinessGrowth#OBS#WorkBreakdownStructure#Leadership#Efficiency#ResourceManagement#Communication#Collaboration#RiskManagement#BusinessStrategy#Productivity#CostControl#ContinuousImprovement
0 notes
Text
Departmental Isolation: Silo systems are characterized by the isolation of departments or functional areas within an organization. Each department operates independently, focusing solely on its own goals and objectives without much interaction or collaboration with other departments.
Communication Barriers: Siloed structures often lead to communication barriers between departments. Information sharing is limited, which can result in duplicated efforts, misunderstandings, and missed opportunities for collaboration.
Inefficiencies and Redundancies: Without effective communication and coordination across departments, inefficiencies and redundancies are common. Different departments may develop similar solutions or processes independently, leading to wasted resources and efforts.
Lack of Innovation: Silo systems can stifle innovation as ideas and insights from one department may not reach or be utilized by others. Without cross-pollination of ideas and perspectives, organizations may struggle to innovate and adapt to changing market conditions.
Slow Decision-Making: Decision-making processes can be slow and cumbersome in siloed organizations. Decisions often need to go through multiple layers of hierarchy within each department, leading to delays and missed opportunities.
Customer Experience Impact: Siloed structures can negatively impact the customer experience. Customers may encounter disjointed interactions across different touchpoints of the organization, leading to frustration and dissatisfaction.
Difficulty Implementing Cross-Functional Initiatives: Initiatives that require collaboration and coordination across multiple departments, such as cross-functional projects or strategic initiatives, can be challenging to implement in siloed organizations due to the lack of alignment and cooperation.
Organizational Culture Issues: Siloed structures can perpetuate a culture of division and internal competition rather than collaboration and teamwork. This can lead to decreased employee morale, engagement, and overall job satisfaction.
Risk of Missed Opportunities: Siloed organizations are at risk of missing out on valuable opportunities for growth, innovation, and efficiency improvements that could arise from synergies between different departments and functions.
Need for Integration and Collaboration: To address the limitations of silo systems, organizations must prioritize integration and collaboration across departments. This can involve breaking down silos, fostering a culture of openness and communication, and implementing processes and technologies that facilitate cross-functional collaboration.
0 notes
Link
1 note
·
View note
Text
Profit Motive: A Comprehensive Guide to its 10 Impact

The profit motive is a critical driver in the world of business. The force propels entrepreneurs to innovate, businesses to compete, and economies to grow. But the profit motive is not just about making money. It's about creating value, improving efficiency, and contributing to societal progress. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the many facets of the profit motive, from its role in different economic systems to its ethical implications and impact on the economy.
Understanding the Profit Motive
What is the Profit Motive?

Understanding The Profit Motive What Is The Profit Motive? The profit motive is the incentive that drives businesses and entrepreneurs to strive for maximum profits. It's the heartbeat of economic activity, pushing individuals and companies to innovate, compete, and create wealth. The profit motive is the driving force behind the economic activity of businesses. The desire to profit motivates entrepreneurs to take risks, innovate, and strive for efficiency. The profit motive is the engine that powers the market economy, driving businesses to produce goods and services that consumers want and need. What is a Profit Motive Example? Profit Motive in Entrepreneurship Consider a tech entrepreneur who develops a groundbreaking app. Their primary goal? This profit motive pushes them to innovate, improve the app, and outperform competitors. The entrepreneur's profit motive is not just about making money. It's about creating customer value, improving the user experience, and positively impacting society. Profit Motive in E-commerce Sales In e-commerce, businesses strive to increase their average order value and customer retention rates, driven by profit. But the profit motive in e-commerce is not just about maximizing profits. It's about understanding customer needs, providing excellent customer service, and building long-term customer relationships.
The Profit Motive in Different Economies
What Type of Economy is the Profit Motive? Profit Motive in Capitalism In a capitalist economy, the profit motive reigns supreme. Private ownership and free markets allow businesses to strive for profit maximization, driving economic growth and innovation. But capitalism is not just about making profits. It's about creating customer value, improving efficiency, and contributing to societal progress. Profit Motive in Market Economy In a market economy, the profit motive guides businesses to efficiently respond to market forces, producing goods and services that consumers desire. The profit motive in a market economy is not just about making profits. It's about understanding market trends, responding to consumer needs, and creating customer value. What is the Profit Motive of Marxism? Contrasting Profit Motive and Marxist Economics In Marxist economics, the profit motive is often criticized for leading to exploitation and inequality. Instead, the focus is on collective ownership and meeting societal needs. But Marxist economics is not just about rejecting the profit motive. It's about promoting social justice, equality, and the common good.
The Profit Motive and Competition

The Profit Motive And Competition What is the Profit Motive and Competition? The Interplay of Profit Motive and Business Competition The profit motive and competition go hand in hand. Businesses compete to maximize profits, leading to better products, lower prices, and improved efficiency. But competition is not just about making profits. It's about improving products and services, meeting customer needs, and contributing to societal progress.
The Ethical Dimensions of Profit Motive
Is Profit Motive Good or Bad? The Positive Impact of Profit Motive The profit motive can drive innovation, job creation, and economic growth. It encourages businesses to improve their products and services, benefiting consumers and the economy. But the profit motive is not just about making money. It's about creating value, improving efficiency, and contributing to societal progress. Potential Downsides and Exploitation in Business However, unchecked profit motives can lead to unethical business practices and exploitation. It's crucial to balance profit motives with ethical considerations. But unethical business practices are not just about making profits. They're about exploiting workers, harming the environment, and undermining societal values. What is an Example of a Bad Profit Motive? Unethical Business Practices Driven by Profit Motive An example of a lousy profit motive could be a company that exploits its workers or harms the environment to increase profits. But the wrong profit motive is about more than just making money. It's about disregarding ethical standards, harming stakeholders, and undermining societal values.
Profit Motive in Different Business Structures
What are Profit Motive and Non-Profit Motive? Profit Motive in For-Profit Organizations The profit motive drives for-profit organizations. They aim to maximize profits to provide returns to their owners or shareholders. But the profit motive in for-profit organizations is not just about making money. It's about creating customer value, improving efficiency, and contributing to societal progress. The Role of Non-Profit Motive in Charitable Organizations Non-profit organizations, on the other hand, are driven by a mission rather than profit. They reinvest surplus funds into their mission rather than distributing it to owners or shareholders. But the non-profit motive is not just about rejecting the profit motive. It's about promoting social justice, equality, and the common good.
The Impact of Profit Motive on the Economy
How Does Profit Motive Affect the Economy? Profit Motive and Wealth Creation The profit motive drives businesses to create wealth, contributing to economic growth and prosperity. But wealth creation is not just about making profits. It's about improving products and services, meeting customer needs, and contributing to societal progress. Profit Motive and Job Creation By striving to maximize profits, businesses can also create jobs and contribute to economic expansion. But job creation is not just about making profits. It's about improving products and services, meeting customer needs, and contributing to societal progress.
Profit Motive and Employee Benefits

Profit Motive And Employee Benefits Profit-Sharing Plans and Employee Compensation How Profit Motive Influences Employee Benefits The profit motive can have a significant impact on employee benefits. Businesses driven by profit are often motivated to invest in their employees, recognizing that a happy, healthy, and motivated workforce can contribute to increased productivity and, ultimately, higher profits. It can lead to the implementation of comprehensive benefits packages, including health insurance, retirement plans, and even profit-sharing schemes. The Role of Profit-Sharing Plans in Business Profit-sharing plans are a prime example of how the profit motive can directly benefit employees. These plans distribute a portion of a company's profits among its employees, aligning the workforce's interests with the business's financial success. It provides employees with a substantial share of the profits they helped to generate and fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to the company's success.
Profit Motive and Taxation
Corporate Tax and Profit Motive How Profit Motive Influences Corporate Tax Strategies The profit motive can also influence a company's approach to taxation. Businesses seeking to maximize profits may employ various strategies to minimize their tax liabilities, such as taking advantage of tax credits, deductions, and incentives. While these strategies are legal and often encouraged by tax policy, they illustrate how the profit motive can drive businesses to optimize all aspects of their operations, including their tax planning. Personal Income Tax and Profit Motive The Interplay of Profit Motive and Personal Income Tax On a personal level, the profit motive can influence decisions about income and taxation. For example, profit-motivated entrepreneurs may reinvest earnings into their businesses to fuel growth and minimize income tax liability. It illustrates how the profit motive can shape financial decision-making at both the corporate and individual levels.
Profit Motive and Business Efficiency
The Role of Profit Motive in Business Efficiency Profit Motive and Cost Reduction The desire for profit can drive businesses to become more efficient and reduce costs. It could involve streamlining operations, investing in technology, or finding more cost-effective suppliers. Businesses can increase their profit margins by reducing costs, demonstrating how the profit motive can improve business efficiency. Profit Motive and Sales Increase Similarly, the profit motive can drive businesses to increase sales. It could involve expanding into new markets, launching new products, or investing in marketing and advertising. By increasing sales, businesses can boost their profits, further illustrating the influential role of the profit motive in driving business growth and success.
Profit Motive and Market Forces

Profit Motive And Market Forces The Interplay of Profit Motive and Market Forces How Profit Motive Responds to Supply and Demand The profit motive is intrinsically linked to the fundamental market forces of supply and demand. Businesses, driven by the desire to maximize profits, respond to changes in these forces. For instance, if a product's demand increases, a profit-motivated business would increase production to meet this demand and capitalize on the potential for increased sales and profits. Profit Motive and Price Determination Price determination is another area where the profit motive and market forces intersect. Businesses aim to set prices to maximize profits, considering production costs, competition, and consumer willingness to pay. This dynamic pricing strategy, driven by the profit motive, plays a crucial role in the efficient functioning of markets.
Profit Motive and Innovation
The Role of Profit Motive in Business Innovation How Profit Motive Drives Innovation The profit motive can be a powerful catalyst for innovation. In their quest for increased profits, businesses are incentivized to develop new products, improve existing ones, or find more efficient production methods. This drive for innovation benefits businesses in terms of potential profit growth and contributes to societal progress by introducing new technologies, products, and services. Profit Motive and Risk Management Innovation often involves risk, and the profit motive plays a role here too. Businesses must balance the potential profits from an innovative idea with the risks involved in its development and implementation. This risk management aspect of the profit motive encourages businesses to make calculated decisions that can lead to sustainable profit growth.
Profit Motive in the Global Economy
The Impact of Profit Motive on Global Trade How Profit Motive Influences International Business In the global economy, the profit motive influences international business decisions. Companies seeking to maximize profits may enter foreign markets, source materials from overseas, or establish international partnerships. These decisions, driven by the profit motive, contribute to the interconnectedness of the global economy and can lead to economic growth and development in different parts of the world. Profit Motive and Corporate Social Responsibility As businesses operate globally, they also face increasing scrutiny regarding their social and environmental impact. Here, the profit motive must be balanced with corporate social responsibility. Companies recognize that long-term profitability is linked to sustainable and ethical business practices. This shift represents an evolution of the profit motive, incorporating a broader range of considerations beyond immediate financial gain.
Profit Motive and Consumer Behavior
The Influence of Profit Motive on Consumer Choices How Profit Motive Shapes Product and Service Offerings The profit motive significantly influences the range of products and services available to consumers. Businesses, driven to maximize profits, strive to offer products and services that meet consumer needs and preferences. This dynamic interaction between the profit motive and consumer behavior shapes the marketplace, leading to diverse offerings catering to various consumer needs and tastes. Profit Motive and Customer Experience The profit motive also impacts the customer experience. Businesses recognize that providing a positive customer experience can increase customer loyalty, repeat business, and positive word-of-mouth, boosting profits. As such, the profit motive can drive businesses to invest in customer service, user-friendly interfaces, and other aspects of the customer experience.
Profit Motive and Social Impact
The Role of Profit Motive in Social Entrepreneurship Balancing Profit Motive and Social Impact In recent years, the concept of social entrepreneurship has gained traction. Social entrepreneurs balance the profit motive with the desire to make a positive social impact. They build businesses that aim to solve social problems or meet societal needs while generating profits. This approach represents a new way of thinking about the profit motive, demonstrating that businesses can be both profitable and socially responsible. Profit Motive and Social Innovation The profit motive can also drive social innovation. Businesses, particularly those in the social enterprise sector, are motivated to develop innovative solutions to social problems in their quest for profits. It can lead to developing products and services that generate profits and contribute to societal well-being.
Profit Motive and Sustainability
The Intersection of Profit Motive and Environmental Sustainability Profit Motive and Sustainable Business Practices The profit motive can play a significant role in promoting environmental sustainability. Businesses increasingly recognize that sustainable business practices can lead to cost savings, improved brand reputation, and increased customer loyalty – all of which can boost profits. This realization drives businesses to adopt energy efficiency, waste reduction, and sustainable sourcing practices, demonstrating how the profit motive can contribute to environmental sustainability. Profit Motive and Green Innovation Similarly, the profit motive can spur green innovation. In their quest for profits, businesses are motivated to develop innovative, profitable, and environmentally friendly products and services. It can lead to the development of green technologies, renewable energy solutions, and other innovations contributing to environmental sustainability.
Profit Motive and Corporate Governance

Profit Motive And Corporate Governance The Role of Profit Motive in Corporate Governance Profit Motive and Shareholder Value The profit motive plays a significant role in corporate governance, particularly in the context of shareholder value. Companies are often driven to maximize shareholder value, typically increasing profits. This focus on profit maximization can influence a wide range of corporate governance decisions, from strategic planning and risk management to executive compensation and dividend policies. Profit Motive and Corporate Ethics However, the pursuit of profits must be balanced with ethical considerations. Corporate governance mechanisms, such as codes of conduct, ethics committees, and whistleblower policies, can ensure that the profit motive does not lead to unethical or illegal behavior. This balance between profit maximization and ethical conduct is critical to good corporate governance.
Profit Motive and Economic Policy
The Influence of Profit Motive on Economic Policy Profit Motive and Tax Policy The profit motive can influence economic policy, particularly tax policy. Governments often use tax incentives to motivate businesses to invest, create jobs, or undertake specific activities. These incentives are based on the understanding that the profit motive drives businesses and will respond to opportunities to increase their profits. Profit Motive and Regulatory Policy The profit motive also plays a role in regulatory policy. Governments must balance the desire to foster a business environment that maximizes profit with the need to protect consumers, workers, and the environment. This balance is often achieved through regulations that set standards for business conduct while allowing businesses to earn profits.
Profit Motive and the Future of Business
The Evolving Role of Profit Motive in Business Profit Motive and the Triple Bottom Line The role of the profit motive in business is evolving. More and more businesses are adopting the triple bottom line concept, emphasizing profits (the traditional bottom line) and social and environmental performance. This approach recognizes that businesses can pursue profits while contributing to social and environmental well-being. Profit Motive and Business Model Innovation The profit motive is also driving business model innovation. Businesses are exploring new ways to generate profits while creating value for customers, employees, and society. Read the full article
#BusinessEthics#BusinessRisk#ConsumerBehavior#CorporateCulture#CorporateGovernance#CorporateStrategy#EconomicDevelopment#GlobalEconomy#GovernmentRegulation#HumanResources#IndustryDynamics#Innovation#MarketForces#OrganizationalStructure#ProfitMotive#SocialImpact#Sustainability#TechnologicalAdvancements
0 notes
Text
Organizational Structure
Start Any Business provides expert guidance on designing an effective organizational structure for your company. Our services ensure a well-defined hierarchy, clear roles, and efficient workflows tailored to your business needs. Benefit from our tailored solutions to optimize productivity, enhance communication, and support your business growth.
Read More: https://www.startanybusiness.ae/organizational-structure/
startanybusiness #uae #dubai #organizationalstructure #businessstructure #companyhierarchy #corporateorganization #teamstructure #managementlevels #businesshierarchy #organizationaldesign #companystructure #orgchart #corporategovernance #teamdynamics #workplacestructure #businessorganization #operationalefficiency

0 notes
Photo

"The Innovator's Dilemma" is a book written by Clayton M. Christensen, a Harvard Business School professor and management consultant. The book explores why successful companies often struggle to stay competitive in the face of disruptive technologies and markets. Through a series of case studies and analysis, Christensen offers insights and strategies for companies to navigate these challenges and avoid falling into the "innovator's dilemma" trap. In "The Innovator's Dilemma," Christensen explains how established companies often fail to innovate and adapt in the face of new technologies and changing market conditions. He argues that companies can become too focused on their existing customer base and current products, which can prevent them from investing in new and potentially disruptive technologies. This can lead to a "dilemma" where companies are unable to adapt to changing market demands, and are eventually surpassed by more innovative and agile competitors. Go to operationsinsider.com to read the full summary including the key takeaways of this book. Link for summaries or purchase in BIO Like❤️/Share✅/comment👇/follow👉@operationsinsider #opex #operationsinsider #wasteattack #waste #ClaytonMChristensen #TheInnovatorsDilemma #disruptiveinnovation #businessstrategy #technologydisruption #organizationalstructure #risktaking #experimentation #businessmodels #competitiveadvantage #marketdemands #casestudies #computerindustry #diskdrivemanufacturing #steelindustry #customerneeds #newtechnologies #jobtobedone #managementconsultant #HarvardBusinessSchool #successfulcompanies #innovation #agility #leadership #managementtheory #booksummary (hier: Samsung Digital City Suwon Korea) https://www.instagram.com/p/Co6UkvsI59C/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#opex#operationsinsider#wasteattack#waste#claytonmchristensen#theinnovatorsdilemma#disruptiveinnovation#businessstrategy#technologydisruption#organizationalstructure#risktaking#experimentation#businessmodels#competitiveadvantage#marketdemands#casestudies#computerindustry#diskdrivemanufacturing#steelindustry#customerneeds#newtechnologies#jobtobedone#managementconsultant#harvardbusinessschool#successfulcompanies#innovation#agility#leadership#managementtheory#booksummary
0 notes
Link
"Organisation constrains architecture; architecture constrains strategy."
0 notes
Text
The Venn diagram is interesting. It could be more complex since other relationships could be included/shown in the diagram. I am thinking of the options.
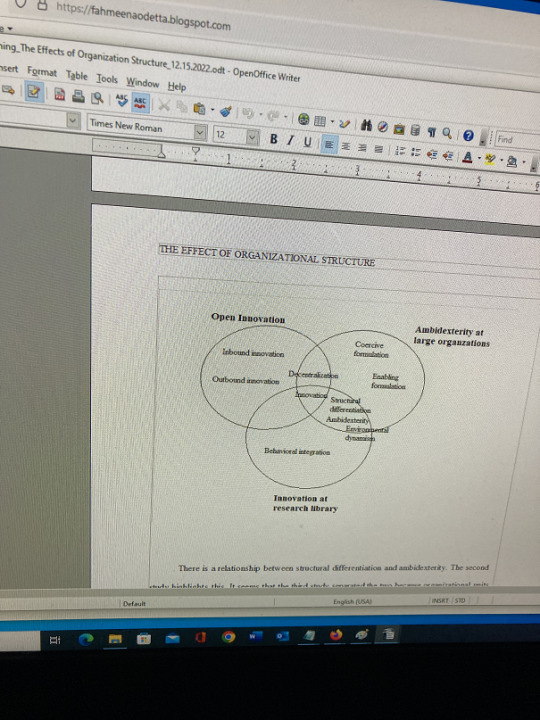
0 notes
Photo

Just some thoughts from earlier this morning… what you would do- paying someone to do some house work (my case from this morning is ironing-used the time when was still chill and cool) for about an hour or two until you dealing with business matters or you would do it yourself?! Point of time management and organization- so what would you considered doing?! #entrepreneuralife #entrepreneuralmindset #housekeepingwork #ironing #timemanegement #motivationalwork #organizationalskills #organizationalstructure #organizationalstrategy https://www.instagram.com/p/CRi_kpMp_Vo/?utm_medium=tumblr
#entrepreneuralife#entrepreneuralmindset#housekeepingwork#ironing#timemanegement#motivationalwork#organizationalskills#organizationalstructure#organizationalstrategy
0 notes
Link
CORPORATE STRUCTURING – CHOOSE AN APPROPRIATE FORM OF BUSINESS ENTITY
Read our blog here : https://bit.ly/3tXPbAm
#corporate#organizationalstructure#Limitedpartnership#startupindia#Bostonfiancialadvisorygroup#outsource#profitability#financialadvisory#businesses#bostonfinancialgroup#startupbusiness#financialeducation#payrolls#us#california#financialservices#taxes#outsourcingsolutions#outsourcingservices#accounting
0 notes
Text
Organizational structure is much more than just a blueprint of who reports to whom; it's the foundation that shapes how a company operates, communicates, and evolves. In this comprehensive exploration of organizational structure design and development, w...
0 notes
Text
Family Dollar - A Failure in Organizational Structure
Now that we’ve talked about a company that has a great organizational culture, let’s talk about a company that doesn’t do as well at motivating its employees.

Family Dollar, similar to other dollar stores, tends to do well in profits and its upward profits can be seen in its stocks, as the Family Dollar Stores (FDO) stock is up about 4% in the past year. However, the employees are not happy with their workplace and benefits. Not only do the employees receive poor pay, but they also have to work long hours to make up for the lack of staff. In order to cover the store’s extended hours with their tight budgets, managers are constantly struggling at work. Most employees are unable to take on a second job due to the long hours, and therefore have to struggle with their living expenses.
Our opinion: As mentioned in previous posts, it is easy to see how the employees are the core of any business. A business is able to prosper only if its employees are happy enough to unleash their full creative potential. An organizational structure doesn’t have to be all providing towards the employees, but it should be ethical and able to help them feel comfortable at work. What Family Dollar does with its low pay and long hours is not only unethical but disadvantageous for the company in the long run.
Reference: McClay, R. (2015, August 17). Think Amazon's Bad? Here are 6 Companies with Worse Culture. Retrieved May 13, 2020, from https://www.thestreet.com/investing/stocks/6-companies-with-worse-workplaces-than-amazon-13257755
0 notes
Text
Building Effective Organizations: Understanding Structure, Authority, and Span of Control

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Profit Motive: A Comprehensive Guide to its 10 Impact

The profit motive is a critical driver in the world of business. The force propels entrepreneurs to innovate, businesses to compete, and economies to grow. But the profit motive is not just about making money. It's about creating value, improving efficiency, and contributing to societal progress. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the many facets of the profit motive, from its role in different economic systems to its ethical implications and impact on the economy.
Understanding the Profit Motive
What is the Profit Motive?

Understanding The Profit Motive What Is The Profit Motive? The profit motive is the incentive that drives businesses and entrepreneurs to strive for maximum profits. It's the heartbeat of economic activity, pushing individuals and companies to innovate, compete, and create wealth. The profit motive is the driving force behind the economic activity of businesses. The desire to profit motivates entrepreneurs to take risks, innovate, and strive for efficiency. The profit motive is the engine that powers the market economy, driving businesses to produce goods and services that consumers want and need. What is a Profit Motive Example? Profit Motive in Entrepreneurship Consider a tech entrepreneur who develops a groundbreaking app. Their primary goal? This profit motive pushes them to innovate, improve the app, and outperform competitors. The entrepreneur's profit motive is not just about making money. It's about creating customer value, improving the user experience, and positively impacting society. Profit Motive in E-commerce Sales In e-commerce, businesses strive to increase their average order value and customer retention rates, driven by profit. But the profit motive in e-commerce is not just about maximizing profits. It's about understanding customer needs, providing excellent customer service, and building long-term customer relationships.
The Profit Motive in Different Economies
What Type of Economy is the Profit Motive? Profit Motive in Capitalism In a capitalist economy, the profit motive reigns supreme. Private ownership and free markets allow businesses to strive for profit maximization, driving economic growth and innovation. But capitalism is not just about making profits. It's about creating customer value, improving efficiency, and contributing to societal progress. Profit Motive in Market Economy In a market economy, the profit motive guides businesses to efficiently respond to market forces, producing goods and services that consumers desire. The profit motive in a market economy is not just about making profits. It's about understanding market trends, responding to consumer needs, and creating customer value. What is the Profit Motive of Marxism? Contrasting Profit Motive and Marxist Economics In Marxist economics, the profit motive is often criticized for leading to exploitation and inequality. Instead, the focus is on collective ownership and meeting societal needs. But Marxist economics is not just about rejecting the profit motive. It's about promoting social justice, equality, and the common good.
The Profit Motive and Competition

The Profit Motive And Competition What is the Profit Motive and Competition? The Interplay of Profit Motive and Business Competition The profit motive and competition go hand in hand. Businesses compete to maximize profits, leading to better products, lower prices, and improved efficiency. But competition is not just about making profits. It's about improving products and services, meeting customer needs, and contributing to societal progress.
The Ethical Dimensions of Profit Motive
Is Profit Motive Good or Bad? The Positive Impact of Profit Motive The profit motive can drive innovation, job creation, and economic growth. It encourages businesses to improve their products and services, benefiting consumers and the economy. But the profit motive is not just about making money. It's about creating value, improving efficiency, and contributing to societal progress. Potential Downsides and Exploitation in Business However, unchecked profit motives can lead to unethical business practices and exploitation. It's crucial to balance profit motives with ethical considerations. But unethical business practices are not just about making profits. They're about exploiting workers, harming the environment, and undermining societal values. What is an Example of a Bad Profit Motive? Unethical Business Practices Driven by Profit Motive An example of a lousy profit motive could be a company that exploits its workers or harms the environment to increase profits. But the wrong profit motive is about more than just making money. It's about disregarding ethical standards, harming stakeholders, and undermining societal values.
Profit Motive in Different Business Structures
What are Profit Motive and Non-Profit Motive? Profit Motive in For-Profit Organizations The profit motive drives for-profit organizations. They aim to maximize profits to provide returns to their owners or shareholders. But the profit motive in for-profit organizations is not just about making money. It's about creating customer value, improving efficiency, and contributing to societal progress. The Role of Non-Profit Motive in Charitable Organizations Non-profit organizations, on the other hand, are driven by a mission rather than profit. They reinvest surplus funds into their mission rather than distributing it to owners or shareholders. But the non-profit motive is not just about rejecting the profit motive. It's about promoting social justice, equality, and the common good.
The Impact of Profit Motive on the Economy
How Does Profit Motive Affect the Economy? Profit Motive and Wealth Creation The profit motive drives businesses to create wealth, contributing to economic growth and prosperity. But wealth creation is not just about making profits. It's about improving products and services, meeting customer needs, and contributing to societal progress. Profit Motive and Job Creation By striving to maximize profits, businesses can also create jobs and contribute to economic expansion. But job creation is not just about making profits. It's about improving products and services, meeting customer needs, and contributing to societal progress.
Profit Motive and Employee Benefits

Profit Motive And Employee Benefits Profit-Sharing Plans and Employee Compensation How Profit Motive Influences Employee Benefits The profit motive can have a significant impact on employee benefits. Businesses driven by profit are often motivated to invest in their employees, recognizing that a happy, healthy, and motivated workforce can contribute to increased productivity and, ultimately, higher profits. It can lead to the implementation of comprehensive benefits packages, including health insurance, retirement plans, and even profit-sharing schemes. The Role of Profit-Sharing Plans in Business Profit-sharing plans are a prime example of how the profit motive can directly benefit employees. These plans distribute a portion of a company's profits among its employees, aligning the workforce's interests with the business's financial success. It provides employees with a substantial share of the profits they helped to generate and fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to the company's success.
Profit Motive and Taxation
Corporate Tax and Profit Motive How Profit Motive Influences Corporate Tax Strategies The profit motive can also influence a company's approach to taxation. Businesses seeking to maximize profits may employ various strategies to minimize their tax liabilities, such as taking advantage of tax credits, deductions, and incentives. While these strategies are legal and often encouraged by tax policy, they illustrate how the profit motive can drive businesses to optimize all aspects of their operations, including their tax planning. Personal Income Tax and Profit Motive The Interplay of Profit Motive and Personal Income Tax On a personal level, the profit motive can influence decisions about income and taxation. For example, profit-motivated entrepreneurs may reinvest earnings into their businesses to fuel growth and minimize income tax liability. It illustrates how the profit motive can shape financial decision-making at both the corporate and individual levels.
Profit Motive and Business Efficiency
The Role of Profit Motive in Business Efficiency Profit Motive and Cost Reduction The desire for profit can drive businesses to become more efficient and reduce costs. It could involve streamlining operations, investing in technology, or finding more cost-effective suppliers. Businesses can increase their profit margins by reducing costs, demonstrating how the profit motive can improve business efficiency. Profit Motive and Sales Increase Similarly, the profit motive can drive businesses to increase sales. It could involve expanding into new markets, launching new products, or investing in marketing and advertising. By increasing sales, businesses can boost their profits, further illustrating the influential role of the profit motive in driving business growth and success.
Profit Motive and Market Forces

Profit Motive And Market Forces The Interplay of Profit Motive and Market Forces How Profit Motive Responds to Supply and Demand The profit motive is intrinsically linked to the fundamental market forces of supply and demand. Businesses, driven by the desire to maximize profits, respond to changes in these forces. For instance, if a product's demand increases, a profit-motivated business would increase production to meet this demand and capitalize on the potential for increased sales and profits. Profit Motive and Price Determination Price determination is another area where the profit motive and market forces intersect. Businesses aim to set prices to maximize profits, considering production costs, competition, and consumer willingness to pay. This dynamic pricing strategy, driven by the profit motive, plays a crucial role in the efficient functioning of markets.
Profit Motive and Innovation
The Role of Profit Motive in Business Innovation How Profit Motive Drives Innovation The profit motive can be a powerful catalyst for innovation. In their quest for increased profits, businesses are incentivized to develop new products, improve existing ones, or find more efficient production methods. This drive for innovation benefits businesses in terms of potential profit growth and contributes to societal progress by introducing new technologies, products, and services. Profit Motive and Risk Management Innovation often involves risk, and the profit motive plays a role here too. Businesses must balance the potential profits from an innovative idea with the risks involved in its development and implementation. This risk management aspect of the profit motive encourages businesses to make calculated decisions that can lead to sustainable profit growth.
Profit Motive in the Global Economy
The Impact of Profit Motive on Global Trade How Profit Motive Influences International Business In the global economy, the profit motive influences international business decisions. Companies seeking to maximize profits may enter foreign markets, source materials from overseas, or establish international partnerships. These decisions, driven by the profit motive, contribute to the interconnectedness of the global economy and can lead to economic growth and development in different parts of the world. Profit Motive and Corporate Social Responsibility As businesses operate globally, they also face increasing scrutiny regarding their social and environmental impact. Here, the profit motive must be balanced with corporate social responsibility. Companies recognize that long-term profitability is linked to sustainable and ethical business practices. This shift represents an evolution of the profit motive, incorporating a broader range of considerations beyond immediate financial gain.
Profit Motive and Consumer Behavior
The Influence of Profit Motive on Consumer Choices How Profit Motive Shapes Product and Service Offerings The profit motive significantly influences the range of products and services available to consumers. Businesses, driven to maximize profits, strive to offer products and services that meet consumer needs and preferences. This dynamic interaction between the profit motive and consumer behavior shapes the marketplace, leading to diverse offerings catering to various consumer needs and tastes. Profit Motive and Customer Experience The profit motive also impacts the customer experience. Businesses recognize that providing a positive customer experience can increase customer loyalty, repeat business, and positive word-of-mouth, boosting profits. As such, the profit motive can drive businesses to invest in customer service, user-friendly interfaces, and other aspects of the customer experience.
Profit Motive and Social Impact
The Role of Profit Motive in Social Entrepreneurship Balancing Profit Motive and Social Impact In recent years, the concept of social entrepreneurship has gained traction. Social entrepreneurs balance the profit motive with the desire to make a positive social impact. They build businesses that aim to solve social problems or meet societal needs while generating profits. This approach represents a new way of thinking about the profit motive, demonstrating that businesses can be both profitable and socially responsible. Profit Motive and Social Innovation The profit motive can also drive social innovation. Businesses, particularly those in the social enterprise sector, are motivated to develop innovative solutions to social problems in their quest for profits. It can lead to developing products and services that generate profits and contribute to societal well-being.
Profit Motive and Sustainability
The Intersection of Profit Motive and Environmental Sustainability Profit Motive and Sustainable Business Practices The profit motive can play a significant role in promoting environmental sustainability. Businesses increasingly recognize that sustainable business practices can lead to cost savings, improved brand reputation, and increased customer loyalty – all of which can boost profits. This realization drives businesses to adopt energy efficiency, waste reduction, and sustainable sourcing practices, demonstrating how the profit motive can contribute to environmental sustainability. Profit Motive and Green Innovation Similarly, the profit motive can spur green innovation. In their quest for profits, businesses are motivated to develop innovative, profitable, and environmentally friendly products and services. It can lead to the development of green technologies, renewable energy solutions, and other innovations contributing to environmental sustainability.
Profit Motive and Corporate Governance

Profit Motive And Corporate Governance The Role of Profit Motive in Corporate Governance Profit Motive and Shareholder Value The profit motive plays a significant role in corporate governance, particularly in the context of shareholder value. Companies are often driven to maximize shareholder value, typically increasing profits. This focus on profit maximization can influence a wide range of corporate governance decisions, from strategic planning and risk management to executive compensation and dividend policies. Profit Motive and Corporate Ethics However, the pursuit of profits must be balanced with ethical considerations. Corporate governance mechanisms, such as codes of conduct, ethics committees, and whistleblower policies, can ensure that the profit motive does not lead to unethical or illegal behavior. This balance between profit maximization and ethical conduct is critical to good corporate governance.
Profit Motive and Economic Policy
The Influence of Profit Motive on Economic Policy Profit Motive and Tax Policy The profit motive can influence economic policy, particularly tax policy. Governments often use tax incentives to motivate businesses to invest, create jobs, or undertake specific activities. These incentives are based on the understanding that the profit motive drives businesses and will respond to opportunities to increase their profits. Profit Motive and Regulatory Policy The profit motive also plays a role in regulatory policy. Governments must balance the desire to foster a business environment that maximizes profit with the need to protect consumers, workers, and the environment. This balance is often achieved through regulations that set standards for business conduct while allowing businesses to earn profits.
Profit Motive and the Future of Business
The Evolving Role of Profit Motive in Business Profit Motive and the Triple Bottom Line The role of the profit motive in business is evolving. More and more businesses are adopting the triple bottom line concept, emphasizing profits (the traditional bottom line) and social and environmental performance. This approach recognizes that businesses can pursue profits while contributing to social and environmental well-being. Profit Motive and Business Model Innovation The profit motive is also driving business model innovation. Businesses are exploring new ways to generate profits while creating value for customers, employees, and society. Read the full article
#BusinessEthics#BusinessRisk#ConsumerBehavior#CorporateCulture#CorporateGovernance#CorporateStrategy#EconomicDevelopment#GlobalEconomy#GovernmentRegulation#HumanResources#IndustryDynamics#Innovation#MarketForces#OrganizationalStructure#ProfitMotive#SocialImpact#Sustainability#TechnologicalAdvancements
0 notes
Text
SOLUTION AT Academic Writers Bay View attached explanation and answer. Let me know if you have any questions.OutlineAbstract•The proposal on process improvement is designed to assess the concepts of balancedscorecard, vision, mission, values, and best practices for improving and monitoring in St.Mary’s Medical CenterIntroduction•St. Mary’s Medical Center is one of the largest medical facilities in Huntington. It isamong the biggest healthcare facilities in West Virginia.•The main purpose of this paper is to assess the facility’s organizational structure, mission,vision, finances, learning and growth, evidence-based monitoring and improving andvalues of St. Mary’s Medical Center.Existing Organizational Structure•St. Mary’s Medical Center’s organization structure provides an outlay of how differenthealthcare tasks are assigned, coordinated, monitored and directed in the quest to ensureorganizational targets and objectives are adequately achieved.•The chief executive officer and the president form the St. Mary’s cabinet, designed todefine the organization’s clinical approaches and implement the new initiates and achieveshort-term and long-term goals.Mission and Vision of St. Mary’s Medical Center•The mission of St. Mary’s Medical Center is to make the healing process of God knownto the world by improving the health of the people it serves.•Their vision is to achieve a healthier future for all.Finances•To upgrade the field of finance, St Mary’s Medical Centre needs to adopt an improvedepic free electronic system for handling the hospital records.Internal processes•Competency in research is one of the strengths of St Mary’s medical center. Having thepatient’s interest at the core is among the virtues at St Mary’s medical center.Customer Satisfaction•St. Mary’s Medical center is committed to advance care services through establishingelectronic health record system.Evidence-Based and Best-Practice for Monitoring & Improving•The evidence-based process improvement for St. Mary’s Medical Center will be assessedusing a balanced scorecard.St. Mary’s Medical Center Values•St. Mary’s Medical Center is committed to exercise or rather instill all-inclusive valuesand strive to improve its relationship with patients.Conclusion•St Mary’s Medical Center is a leader in providing critical care medicine in the US.•The facility can ensure patient satisfaction by conducting review assessments frompatients receiving care services.ReferencesAnderson, L., & Slonim, A. (2017). Perspectives on the strategic uses of concept mapping toaddress public health challenges. Evaluation and Program Planning, 60, 194-201. doi:10.1016/j.evalprogplan.2016.08.011El-Jardali, F., & Fadlallah, R. (2017). A review of national policies and strategies to improvequality of health care and patient safety: a case study from Lebanon and Jordan. BMCHealth Services Research, 17(1). doi: 10.1186/s12913-017-2528-1Goś, K. (2015). The key advantages and disadvantages of matrix organizationalstructures. Studia i Materiały, (2/2015 (19)), 66-83. http://dx.doi.org/10.7172/17339758.2015.19.5Melnyk, B. M., Gallagher-Ford, L., & Fineout-Overholt, E. (2016). Implementing the evidencebased practice (EBP) competencies in healthcare: a practical guide for improvingquality, safety, and outcomes. Sigma Theta Tau.Mulhall, J., Trost, L., Brannigan, R., Kurtz, E., Redmon, J., & Chiles, K. et al. (2018).Evaluation and Management of Testosterone Deficiency: AUA Guideline. Journal OfUrology, 200(2), 423-432. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2018.03.1151Cost-Benefit AnalysisNameCapella UniversityHealth Care Quality, Risk, and Regulatory ComplianceAssessment 3Date2AbstractCost-benefit analysis, abbreviated as CBA, is an approach most corporations employ to analyzethe available decisions. The personnel designed to analyze the organization conducts CBA byadding up the gains of a specific situation after which he or she deducts the costs attributed totaking up the decision. The personnel further develop a model designed to place or rather assigncosts to the intangible assets.
St. Mary’s Medical Center has opted to use Electronic HealthRecords (EHR) to heighten and streamline performance and operations. Data is available in thefacility’s premises among the personnel when an unforeseen risk arises. Studies have shown thatusing EHR lowers the risks associated with data overloading as well as privacy of healthcareinformation. This paper is thus entirely about the CBA of St. Mary’s Medical Center. Theprimary purpose is to support the recommendations that pertain to finances needed to developcomplex information technology and ensure the sustainability and effectiveness of EHR.Keywords: Cost Benefit Analysis, Electronic Health Record, St. Mary’s Medical Center3The Cost-Benefit Analysis Process and AnalysisManagers in an organization conduct a CBA before embarking on new projects. Theanalysis entails factoring in the revenue and expenses to be realized upon implementing or ratherexecuting the proposed project. The findings extracted from the CBA are entirely used todetermine the project’s financial feasibility and gauge whether the company should opt for analternative project. CBA helps to exclude the opportunity costs attributed to establishing a wholenew EHR without incurring flaws in the process of making decisions (Asche et al., 2020). Bydefinition, opportunity costs refer to the alternative benefits realized from choosing an alternativeoption.When an organization considers opportunity costs, such helps project managers assessand estimate the possible benefits of undertaking an alternative choice (Asche et al., 2020).Opportunity costs do not encompass the benefits realized from the initial choice. To achieveerror-free implementation of the EHR system that will encompass complex IT systems, St.Mary’s Medical Center’s managers will be required to perform a CBA process. An in-depth CBAanalysis begins with the compilation of a list of elements that covers costs and the presumedbenefits to be realized from implementing a whole new EHR in the healthcare facility. St. Mary’sMedical center will incur the cost of training workers to align with the risk financingrecommendation that calls for implementing a complex IT system.The primary cost included in CBA is the risk financing recommendation’s direct cost tobe incurred from direct labor. The healthcare facility will solicit labor from the existing and hiredworkers. They will be expected to handle the system and ensure its success. For instance, theywill be required to feed in the records and medical history of the patients available in the EHRsystem. Indirect cost to be incurred in implementing the EHR system includes electricity needed4to operate the system, management’s overhead costs, and other utility costs to facilitateimplementing of the project.On the other hand,… CLICK HERE TO GET A PROFESSIONAL WRITER TO WORK ON THIS PAPER AND OTHER SIMILAR PAPERS CLICK THE BUTTON TO MAKE YOUR ORDER
0 notes