#PostgreSQL Database tutorial
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
0 notes
Text
youtube
#nest js#nestjs framework#nestjs project#nestjs development#nestjs#typescript development#typescript class#typescript tutorial#typescript#youtube#video#codeonedigest#microservices#microservice#typeorm#orm#object relation mapping#postgres tutorial#postgres database#postgresql#postgres#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Journey to AWS Proficiency: Unveiling Core Services and Certification Paths
Amazon Web Services, often referred to as AWS, stands at the forefront of cloud technology and has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals leverage the power of the cloud. This blog serves as your comprehensive guide to understanding AWS, exploring its core services, and learning how to master this dynamic platform. From the fundamentals of cloud computing to the hands-on experience of AWS services, we'll cover it all. Additionally, we'll discuss the role of education and training, specifically highlighting the value of ACTE Technologies in nurturing your AWS skills, concluding with a mention of their AWS courses.

The Journey to AWS Proficiency:
1. Basics of Cloud Computing:
Getting Started: Before diving into AWS, it's crucial to understand the fundamentals of cloud computing. Begin by exploring the three primary service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Gain a clear understanding of what cloud computing is and how it's transforming the IT landscape.
Key Concepts: Delve into the key concepts and advantages of cloud computing, such as scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and disaster recovery. Simultaneously, explore the potential challenges and drawbacks to get a comprehensive view of cloud technology.
2. AWS Core Services:
Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): Start your AWS journey with Amazon EC2, which provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud. Learn how to create virtual servers, known as instances, and configure them to your specifications. Gain an understanding of the different instance types and how to deploy applications on EC2.
Simple Storage Service (S3): Explore Amazon S3, a secure and scalable storage service. Discover how to create buckets to store data and objects, configure permissions, and access data using a web interface or APIs.
Relational Database Service (RDS): Understand the importance of databases in cloud applications. Amazon RDS simplifies database management and maintenance. Learn how to set up, manage, and optimize RDS instances for your applications. Dive into database engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and more.
3. AWS Certification:
Certification Paths: AWS offers a range of certifications for cloud professionals, from foundational to professional levels. Consider enrolling in certification courses to validate your knowledge and expertise in AWS. AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner, AWS Certified Solutions Architect, and AWS Certified DevOps Engineer are some of the popular certifications to pursue.
Preparation: To prepare for AWS certifications, explore recommended study materials, practice exams, and official AWS training. ACTE Technologies, a reputable training institution, offers AWS certification training programs that can boost your confidence and readiness for the exams.
4. Hands-on Experience:
AWS Free Tier: Register for an AWS account and take advantage of the AWS Free Tier, which offers limited free access to various AWS services for 12 months. Practice creating instances, setting up S3 buckets, and exploring other services within the free tier. This hands-on experience is invaluable in gaining practical skills.
5. Online Courses and Tutorials:
Learning Platforms: Explore online learning platforms like Coursera, edX, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning. These platforms offer a wide range of AWS courses taught by industry experts. They cover various AWS services, architecture, security, and best practices.
Official AWS Resources: AWS provides extensive online documentation, whitepapers, and tutorials. Their website is a goldmine of information for those looking to learn more about specific AWS services and how to use them effectively.
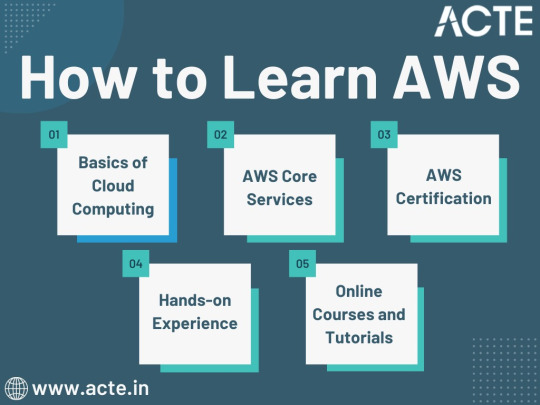
Amazon Web Services (AWS) represents an exciting frontier in the realm of cloud computing. As businesses and individuals increasingly rely on the cloud for innovation and scalability, AWS stands as a pivotal platform. The journey to AWS proficiency involves grasping fundamental cloud concepts, exploring core services, obtaining certifications, and acquiring practical experience. To expedite this process, online courses, tutorials, and structured training from renowned institutions like ACTE Technologies can be invaluable. ACTE Technologies' comprehensive AWS training programs provide hands-on experience, making your quest to master AWS more efficient and positioning you for a successful career in cloud technology.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
DBMS Tutorial for Beginners: Unlocking the Power of Data Management
In this "DBMS Tutorial for Beginners: Unlocking the Power of Data Management," we will explore the fundamental concepts of DBMS, its importance, and how you can get started with managing data effectively.
What is a DBMS?
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a software tool that facilitates the creation, manipulation, and administration of databases. It provides an interface for users to interact with the data stored in a database, allowing them to perform various operations such as querying, updating, and managing data. DBMS can be classified into several types, including:
Hierarchical DBMS: Organizes data in a tree-like structure, where each record has a single parent and can have multiple children.
Network DBMS: Similar to hierarchical DBMS but allows more complex relationships between records, enabling many-to-many relationships.
Relational DBMS (RDBMS): The most widely used type, which organizes data into tables (relations) that can be linked through common fields. Examples include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
Object-oriented DBMS: Stores data in the form of objects, similar to object-oriented programming concepts.
Why is DBMS Important?
Data Integrity: DBMS ensures the accuracy and consistency of data through constraints and validation rules. This helps maintain data integrity and prevents anomalies.
Data Security: With built-in security features, DBMS allows administrators to control access to data, ensuring that only authorized users can view or modify sensitive information.
Data Redundancy Control: DBMS minimizes data redundancy by storing data in a centralized location, reducing the chances of data duplication and inconsistency.
Efficient Data Management: DBMS provides tools for data manipulation, making it easier for users to retrieve, update, and manage data efficiently.
Backup and Recovery: Most DBMS solutions come with backup and recovery features, ensuring that data can be restored in case of loss or corruption.
Getting Started with DBMS
To begin your journey with DBMS, you’ll need to familiarize yourself with some essential concepts and tools. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Understand Basic Database Concepts
Before diving into DBMS, it’s important to grasp some fundamental database concepts:
Database: A structured collection of data that is stored and accessed electronically.
Table: A collection of related data entries organized in rows and columns. Each table represents a specific entity (e.g., customers, orders).
Record: A single entry in a table, representing a specific instance of the entity.
Field: A specific attribute of a record, represented as a column in a table.
Step 2: Choose a DBMS
There are several DBMS options available, each with its own features and capabilities. For beginners, it’s advisable to start with a user-friendly relational database management system. Some popular choices include:
MySQL: An open-source RDBMS that is widely used for web applications.
PostgreSQL: A powerful open-source RDBMS known for its advanced features and compliance with SQL standards.
SQLite: A lightweight, serverless database that is easy to set up and ideal for small applications.
Step 3: Install the DBMS
Once you’ve chosen a DBMS, follow the installation instructions provided on the official website. Most DBMS solutions offer detailed documentation to guide you through the installation process.
Step 4: Create Your First Database
After installing the DBMS, you can create your first database. Here’s a simple example using MySQL:
Open the MySQL command line or a graphical interface like MySQL Workbench. Run the following command to create a new CREATE DATABASE my_first_database;
Use the database: USE my_first_database;
Step 5: Create Tables
Next, you’ll want to create tables to store your data. Here’s an example of creating a table for storing customer information:
CREATE TABLE customers ( 2 customer_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, 3 first_name VARCHAR(50), 4 last_name VARCHAR(50), 5 email VARCHAR(100), 6 created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP 7);
In this example, we define a table named customers with fields for customer ID, first name, last name, email, and the date the record was created.
Step 6: Insert Data
Now that you have a table, you can insert data into it. Here’s how to add a new customer:
1 INSERT INTO customers (first_name, last_name, email) 2VALUES ('John', 'Doe', '[email protected]');
Query Data
To retrieve data from your table, you can use the SELECT statement. For example, to get all customers:
1 SELECT * FROM customers;
You can also filter results using the WHERE clause:
SELECT * FROM customers WHERE last_name = 'Doe';
Step 8: Update and Delete Data
You can update existing records using the UPDATE statement:
UPDATE customers SET email = '[email protected]' WHERE customer_id = 1;
To delete a record, use the DELETE statement:
DELETE FROM customers WHERE customer_id = 1;
Conclusion
In this "DBMS Tutorial for Beginners: Unlocking the Power of Data Management," we’ve explored the essential concepts of Database Management Systems and how to get started with managing data effectively. By understanding the importance of DBMS, familiarizing yourself with basic database concepts, and learning how to create, manipulate, and query databases, you are well on your way to becoming proficient in data management.
As you continue your journey, consider exploring more advanced topics such as database normalization, indexing, and transaction management. The world of data management is vast and full of opportunities, and mastering DBMS will undoubtedly enhance your skills as a developer or data professional.
With practice and experimentation, you’ll unlock the full potential of DBMS and transform the way you work with data. Happy database management!
0 notes
Text
Master Flask and PostgreSQL: Step-by-Step Guide
1. Introduction Welcome to this comprehensive tutorial on mastering Flask and PostgreSQL for building database-driven applications. This guide will walk you through the process of creating robust web applications using Flask, a lightweight Python web framework, and PostgreSQL, a powerful open-source relational database management system. What You Will Learn By the end of this tutorial, you…
0 notes
Text
What Is PHP

What Is PHP, and why is It Still Essential in Web Development
PHP (short for Hypertext Preprocessor) is one of the most widely used scripting languages for building websites and web applications. It’s open-source, free to use, and runs on the server, meaning it processes tasks before content reaches your browser. Whether you're logging in to a website, filling out a form, or browsing dynamic content, chances are PHP is working behind the scenes.
In this post, we’ll break down what PHP is, what it’s used for, and why it continues to be a key part of modern web development.
What Is PHP?
PHP is a server-side scripting language that runs on web servers like Apache or Nginx. It helps developers build dynamic websites, meaning the content can change based on user input or data from a database.
Instead of just showing static pages, PHP allows for things like:
Displaying personalized user dashboards
Submitting and processing forms
Handling logins and registrations
Connecting to databases and fetching content
Key Features of PHP:
Server-Side Execution: Code runs on the server and sends the result to the browser.
Database Friendly: Easily connects with databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQLite.
Form Handling: Collects and processes data from HTML forms.
Session Management: Tracks users across pages (great for logins and shopping carts).
Platform Independent: Works on Windows, macOS, Linux—pretty much anywhere.
Large Community & Resources: Tons of tutorials, tools, and frameworks like Laravel.
What Is PHP Used For?
PHP is used for building all kinds of websites—from small personal blogs to full-scale eCommerce platforms. Let’s look at the common ways developers use PHP:
1. Dynamic Website Content
PHP helps create websites that change depending on who is visiting or what they’re doing. Think of personalized greetings, product recommendations, or updating shopping cart totals without refreshing the page.
2. Working With Databases
Need to store user data, products, or blog posts? PHP connects smoothly with databases like MySQL to save and fetch information, making it easy to manage large websites.
3. Handling Forms
When users fill out a form—say, to sign up or contact you—PHP processes that data. It checks if everything’s filled out correctly and then stores or emails the info.
4. User Sessions
PHP helps websites remember who you are as you move between pages. This is essential for things like staying logged in or remembering items in your cart.
5. Security and Automation
PHP allows you to add basic security layers, like input validation, data encryption, and access control. It’s also used for sending emails, generating PDF invoices, or even auto-posting to social media.
Is PHP Frontend or Backend?
PHP is strictly a backend language. While it works alongside frontend tools like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, PHP runs on the server. It handles all the logic behind the scenes—things like checking passwords, fetching data, or updating user info.
Why PHP Still Matters Today
Even with new languages and frameworks entering the scene, PHP remains highly relevant. It powers big names like Facebook (originally built on PHP), WordPress, and Wikipedia. Plus, frameworks like Laravel have modernized PHP, making development faster and cleaner.
In short, PHP is still a reliable, powerful choice—especially for developers building secure, data-driven websites.
Conclusion
PHP might not always be in the spotlight, but it's still the backbone of the web. It’s fast, flexible, and works well with almost anything. If you're planning to build a dynamic website or web application, learning PHP is a solid first step—and it’s not going anywhere anytime soon.
0 notes
Text
Master SQL in 2025: The Only Bootcamp You’ll Ever Need

When it comes to data, one thing is clear—SQL is still king. From business intelligence to data analysis, web development to mobile apps, Structured Query Language (SQL) is everywhere. It’s the language behind the databases that run apps, websites, and software platforms across the world.
If you’re looking to gain practical skills and build a future-proof career in data, there’s one course that stands above the rest: the 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL.
Let’s dive into what makes this bootcamp a must for learners at every level.
Why SQL Still Matters in 2025
In an era filled with cutting-edge tools and no-code platforms, SQL remains an essential skill for:
Data Analysts
Backend Developers
Business Intelligence Specialists
Data Scientists
Digital Marketers
Product Managers
Software Engineers
Why? Because SQL is the universal language for interacting with relational databases. Whether you're working with MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, or Microsoft SQL Server, learning SQL opens the door to querying, analyzing, and interpreting data that powers decision-making.
And let’s not forget—it’s one of the highest-paying skills on the job market today.
Who Is This Bootcamp For?
Whether you’re a complete beginner or someone looking to polish your skills, the 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL is structured to take you through a progressive learning journey. You’ll go from knowing nothing about databases to confidently querying real-world datasets.
This course is perfect for:
✅ Beginners with no prior programming experience ✅ Students preparing for tech interviews ✅ Professionals shifting to data roles ✅ Freelancers and entrepreneurs ✅ Anyone who wants to work with data more effectively
What You’ll Learn: A Roadmap to SQL Mastery
Let’s take a look at some of the key skills and topics covered in this course:
🔹 SQL Fundamentals
What is SQL and why it's important
Understanding databases and tables
Creating and managing database structures
Writing basic SELECT statements
🔹 Filtering & Sorting Data
Using WHERE clauses
Logical operators (AND, OR, NOT)
ORDER BY and LIMIT for controlling output
🔹 Aggregation and Grouping
COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX
GROUP BY and HAVING
Combining aggregate functions with filters
🔹 Advanced SQL Techniques
JOINS: INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, FULL
Subqueries and nested SELECTs
Set operations (UNION, INTERSECT)
Case statements and conditional logic
🔹 Data Cleaning and Manipulation
UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT statements
Handling NULL values
Using built-in functions for data formatting
🔹 Real-World Projects
Practical datasets to work on
Simulated business cases
Query optimization techniques
Hands-On Learning With Real Impact
Many online courses deliver knowledge. Few deliver results.
The 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL does both. The course is filled with hands-on exercises, quizzes, and real-world projects so you actually apply what you learn. You’ll use modern tools like PostgreSQL and pgAdmin to get your hands dirty with real data.
Why This Course Stands Out
There’s no shortage of SQL tutorials out there. But this bootcamp stands out for a few big reasons:
✅ Beginner-Friendly Structure
No coding experience? No problem. The course takes a gentle approach to build your confidence with simple, clear instructions.
✅ Practice-Driven Learning
Learning by doing is at the heart of this course. You’ll write real queries, not just watch someone else do it.
✅ Lifetime Access
Revisit modules anytime you want. Perfect for refreshing your memory before an interview or brushing up on a specific concept.
✅ Constant Updates
SQL evolves. This bootcamp evolves with it—keeping you in sync with current industry standards in 2025.
✅ Community and Support
You won’t be learning alone. With a thriving student community and Q&A forums, support is just a click away.
Career Opportunities After Learning SQL
Mastering SQL can open the door to a wide range of job opportunities. Here are just a few roles you’ll be prepared for:
Data Analyst: Analyze business data and generate insights
Database Administrator: Manage and optimize data infrastructure
Business Intelligence Developer: Build dashboards and reports
Full Stack Developer: Integrate SQL with web and app projects
Digital Marketer: Track user behavior and campaign performance
In fact, companies like Amazon, Google, Netflix, and Facebook all require SQL proficiency in many of their job roles.
And yes—freelancers and solopreneurs can use SQL to analyze marketing campaigns, customer feedback, sales funnels, and more.
Real Testimonials From Learners
Here’s what past students are saying about this bootcamp:
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “I had no experience with SQL before taking this course. Now I’m using it daily at my new job as a data analyst. Worth every minute!” – Sarah L.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “This course is structured so well. It’s fun, clear, and packed with challenges. I even built my own analytics dashboard!” – Jason D.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “The best SQL course I’ve found on the internet—and I’ve tried a few. I was up and running with real queries in just a few hours.” – Meera P.
How to Get Started
You don’t need to enroll in a university or pay thousands for a bootcamp. You can get started today with the 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL and build real skills that make you employable.
Just grab a laptop, follow the course roadmap, and dive into your first database. No fluff. Just real, useful skills.
Tips to Succeed in the SQL Bootcamp
Want to get the most out of your SQL journey? Keep these pro tips in mind:
Practice regularly: SQL is a muscle—use it or lose it.
Do the projects: Apply what you learn to real datasets.
Take notes: Summarize concepts in your own words.
Explore further: Try joining Kaggle or GitHub to explore open datasets.
Ask questions: Engage in course forums or communities for deeper understanding.
Your Future in Data Starts Now
SQL is more than just a skill. It’s a career-launching power tool. With this knowledge, you can transition into tech, level up in your current role, or even start your freelance data business.
And it all begins with one powerful course: 👉 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL
So, what are you waiting for?
Open the door to endless opportunities and unlock the world of data.
0 notes
Text
Code Across the Stack: A Deep Dive into Full Stack Development
In the evolving world of web and software development, professionals who understand both the front-end and back-end aspects of applications have become invaluable. These professionals, known as full stack developers, have the unique capability to “code across the stack,” handling everything from user interfaces to server logic and databases. Whether you're building a simple blog or a complex enterprise-level platform, having a grasp of full stack development is increasingly essential.
What Does Full Stack Development Involve?
At its core, full stack development refers to the ability to develop both the client-side (front end) and server-side (back end) portions of an application. This includes, but is not limited to:
Front-End Development: This deals with everything users see and interact with in their browser. It includes HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, along with frameworks like React, Vue.js, or Angular.
Back-End Development: This manages the server, database, and application logic. Common tools and languages include Node.js, Python, Ruby, Java, PHP, and frameworks like Express or Django.
Database Management: From SQL databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL to NoSQL options like MongoDB, understanding how to store and manage data efficiently is key.
Version Control and Deployment: Tools like Git, GitHub, Docker, and CI/CD pipelines help manage code changes and automate deployment.
Being proficient in all these areas enables a developer to understand the full picture and effectively build scalable, secure, and user-friendly applications.
Why Full Stack Developers Are in High Demand
Companies today look for agility. Hiring a single person who can manage both ends of development means more flexibility, faster turnaround, and better coordination. Full stack developers can jump in wherever needed, making them a strategic asset to startups and enterprises alike.
Some benefits of becoming a full stack developer include:
Versatility: You’re not limited to just the front or back end. You can contribute wherever needed.
Higher Salary Potential: Skilled professionals who understand multiple layers of development often command higher salaries.
Broader Career Opportunities: From tech startups to established corporations, full stack developers are needed in virtually every sector.
Better Project Insight: Knowing the entire stack helps in architectural decisions and better communication with team members.
How to Become a Full Stack Developer
Breaking into full stack development may seem daunting at first, but it’s completely achievable with the right resources and mindset. A full stack developer course can be one of the most effective ways to build your skill set systematically.
A well-designed full stack developer course typically includes:
Foundational Web Technologies: HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript.
Front-End Frameworks: React.js, Angular, or Vue.js.
Back-End Development: Node.js, Express, or Django.
Database Integration: SQL and NoSQL databases.
Project-Based Learning: Real-world applications that mimic actual workplace environments.
Soft Skills and Deployment: Git, version control, DevOps basics, and deployment strategies.
By the end of such a course, learners are often able to build and deploy complete applications from scratch.
The Self-Taught vs. Structured Learning Debate
While some individuals opt to learn through tutorials, forums, and trial-and-error, many prefer the structure and guidance that a comprehensive full stack developer course provides. The benefits of enrolling in a structured program include:
Mentorship: Direct access to instructors who can help resolve doubts.
Accountability: A schedule that keeps you on track.
Certification: Proof of your skills, which can be valuable when job hunting.
Networking Opportunities: Connecting with other learners and professionals.
Final Thoughts
Coding across the stack is more than a technical skill—it’s a mindset. It’s about seeing the big picture, understanding how different parts of a system interact, and being able to build solutions that are both user-friendly and technically sound. Whether you're just starting your tech journey or looking to enhance your skill set, investing time in a full stack developer course can be a strategic move.
In today’s digital economy, full stack developers are more than coders—they’re problem-solvers, creators, and the glue that holds development teams together. If you’re passionate about technology and ready to take on the challenge, there’s no better time to dive into the world of full stack development.
0 notes
Text
Full Stack in Action: Real Projects That Make You Job-Ready
When learning full stack web development, tutorials and theoretical knowledge only get you so far. The real transformation happens when you apply that knowledge to build actual, functioning projects — the kind that mimic real-world scenarios, solve real problems, and impress hiring managers.
That’s what Full Stack in Action: Real Projects That Make You Job-Ready is all about. It’s not just about writing code — it’s about crafting solutions from front end to back end, and gaining confidence as a future-ready developer.
Why Real Projects Matter in Full Stack Learning
Let’s be honest — coding exercises are great for understanding syntax, but they don’t prepare you for building and deploying scalable applications. Real projects test your ability to:
Collaborate on multiple layers of development
Make design decisions that balance user experience and performance
Work with databases, APIs, version control, and cloud hosting
Handle bugs, test features, and make improvements
Think like a product developer, not just a coder
By working on real-world applications, learners of full stack web development can experience what it’s like to build something end-to-end — from designing responsive front-end interfaces to integrating robust back-end systems.
What Does “Full Stack” Really Involve?
A full stack web development professional is someone who understands both client-side and server-side technologies. That includes:
Front-End (Client Side): HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, Angular, or Vue.js — everything users interact with.
Back-End (Server Side): Node.js, Express.js, Django, Ruby on Rails, or PHP — logic, data handling, and server functions.
Databases: MySQL, MongoDB, PostgreSQL, Firebase, etc.
Version Control: Git and GitHub for collaboration.
Deployment: AWS, Heroku, Netlify, or Vercel for going live.
Real Projects That Boost Your Portfolio
Here are some practical, engaging project ideas that can elevate your resume and make you stand out during interviews:
1. E-Commerce Website (Amazon Clone)
Front-end: Product listing, cart, search, filtering
Back-end: Inventory management, payment integration, user accounts
Skills: React, Node.js, MongoDB, Stripe API
2. Job Portal
Features: Job listing, company dashboard, resume uploads
Focus: Authentication, dynamic content, admin interface
Tech stack: Angular, Express.js, MongoDB, REST APIs
3. Blog Platform with CMS
Users can write, edit, delete posts; comments and likes
Admin panel with roles and permissions
Stack: Django, PostgreSQL, Bootstrap
4. Real-Time Chat Application
Features: Live messaging, rooms, media sharing
Use: Socket.io, WebSocket, Firebase
Front-end: React with Redux
5. Online Learning Management System (LMS)
Modules: Course enrollment, quiz system, certificates
Back-end logic: Role-based access, scoring, session tracking
Stack: MERN (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js)
6. Portfolio Website with Blog Integration
Personal project showcasing your skills and experience
Includes projects, blog, contact form, testimonials
Deployed on: Netlify or GitHub Pages
How Real Projects Make You Job-Ready
Employers today are not just hiring coders — they want developers who can think critically, adapt quickly, and build scalable applications. Real-world projects offer:
Proof of Work: Showcases your skills beyond certificates
Problem Solving Experience: Bugs, deployment errors, and design challenges help you grow
Project Ownership: Build something you can confidently talk about during interviews
Adaptability: Exposure to a range of tools and technologies
Soft Skills You Build Along the Way
Working on full stack web development projects also enhances several key soft skills:
Time management and meeting deadlines
Communication and documentation
Collaboration via Git and project management tools
Presentation skills when demonstrating projects to peers or recruiters
Ready to Get Started?
Whether you're self-taught, bootcamp-trained, or currently pursuing a computer science degree, adding real-world applications to your portfolio is the smartest way to prepare for a developer role. Don’t wait for the “perfect time” — start simple, iterate, and keep building.
Final Thoughts
Full Stack in Action: Real Projects That Make You Job-Ready isn’t just a catchy phrase — it’s a mindset. It’s about learning by doing and embracing the messy, exciting, and rewarding journey of creating something functional and meaningful.
So take that leap. Pick a project, define your stack, and start building. Because the best way to learn full stack web development — and to get hired — is to show what you can build, not just what you know.
0 notes
Text
Your Investment Guide to Building a Home Depot Clone App

In today’s digitally driven world, consumers expect to shop for everything—from light bulbs to lumber—without stepping foot into a store. Home improvement giants like Home Depot have revolutionized this experience by offering powerful eCommerce and mobile platforms. But what if you want to create a similar app? This comprehensive guide outlines everything you need to know—from features to budget—about building your own Home Depot clone app.
Why Build a Home Depot-Like App?
The global home improvement market is booming, and online sales are at the heart of its growth. According to market reports, digital commerce for home products, tools, and furniture is growing annually. An app like Home Depot not only makes buying more convenient but also supports inventory checks, professional services booking, and customer assistance—all from a smartphone.
If you're aiming to tap into this market with a custom app, understanding the investment structure is critical.
Key Features Your Home Depot Clone App Needs
To compete in this space, your app must deliver a seamless shopping experience. Here are the must-have features:
1. User-Friendly Interface
Easy navigation
Smart search with filters
Category-wise product display
2. Product Catalog & Inventory Management
Real-time updates
Barcode scanning
Bulk product uploads
3. Secure User Authentication
Social login options
Multi-factor authentication
4. Shopping Cart & Checkout
One-click cart management
Multiple payment gateways
Real-time delivery charges and taxes
5. Order Tracking
Live updates
Estimated delivery times
6. Loyalty Programs & Offers
Reward points
Special discounts for members
7. Customer Support Integration
Live chat, email, or call support
FAQs and chatbot help
8. DIY Tips & Video Tutorials
Engaging multimedia content to help users with their home projects
9. AR Integration
Let users visualize furniture or fixtures in their space using Augmented Reality
Technology Stack for a Home Depot Clone App
Choosing the right tech stack ensures scalability and high performance. Here's a suggested stack:
Frontend: React Native (for cross-platform), Swift (iOS), Kotlin (Android)
Backend: Node.js, Python (Django/Flask)
Database: MongoDB, PostgreSQL, Firebase
Cloud: AWS, Google Cloud
APIs: Google Maps API (for store locations), Stripe/PayPal API (for payments)
Partnering with experienced tech teams like IMG Global Infotech ensures you get industry-standard technologies and clean code architecture.
Cost Breakdown: What Will You Spend?
The cost of developing a Home Depot clone app depends on various factors including feature complexity, development location, and chosen technology. Here’s an approximate breakdown:
1. UI/UX Design
Wireframes, mockups, user testing
Estimated Cost: $3,000 – $6,000
2. Frontend & Backend Development
App interface and logic
Estimated Cost: $15,000 – $30,000
3. Third-Party Integrations
Payment gateways, maps, AR features
Estimated Cost: $3,000 – $8,000
4. Admin Panel Development
Dashboard for product and order management
Estimated Cost: $5,000 – $10,000
5. Testing & QA
Bug fixing, device compatibility
Estimated Cost: $2,000 – $5,000
6. Deployment & Maintenance
App store submissions, post-launch support
Estimated Cost: $2,000 – $5,000
✅ Total Estimated Cost: $30,000 – $60,000+
For a highly scalable and feature-rich version with AR, loyalty programs, and custom CRM integration, costs may go up to $80,000 or more.
Timeline for Development
Depending on complexity, a Home Depot clone app can take 4 to 8 months to develop. A minimum viable product (MVP) may be launched sooner, allowing you to test the market and iterate.
How Can IMG Global Infotech Help?
If you're planning to invest in developing a Home Depot clone app, choosing the right technology partner is critical. IMG Global Infotech brings:
✅ Years of experience in custom eCommerce app development
✅ Expert developers skilled in latest tech stacks
✅ Transparent pricing with scalable engagement models
✅ End-to-end service—from ideation to post-launch support
Their team understands the home improvement domain, offers tailored solutions, and ensures your app is not just functional but competitive.
Final Thoughts: Is It Worth It?
Absolutely, if done strategically. The rising demand for online hardware and home improvement products presents a prime opportunity for growth. With a well-researched app model, strong development team, and future-ready features, your app can become the next big name in this niche.
Investing in a Home Depot clone app in 2025 can unlock new customer segments, increase sales, and give your brand a strong digital footprint. Get started with a professional partner likeIMG Global Infotech to turn your vision into a robust reality.
#ecommerce developers#ecommerce website development#hire ecommerce developers#ecommerce#ecommerce app development#software development#online fashion shopping#fashion design software#online shopping clothes#online clothing shop#online clothing store#online shopping
0 notes
Text
youtube
#youtube#video#codeonedigest#microservices#microservice#docker#nodejs module#nodejs express#node js#nodejs#node js training#node js express#node js development company#node js development services#node js developers#node js application#postgres database#postgres tutorial#postgresql#postgres#docker image#docker container#docker tutorial#dockerfile#docker course
0 notes
Text
Why Should You Choose PHP for Web Development Services?

In the ever-evolving digital landscape, choosing the right technology for web development is crucial. PHP remains one of the most preferred programming languages for building dynamic and scalable websites. Here’s why PHP should be your top choice for web development services.
1. Open-Source and Cost-Effective
PHP is an open-source scripting language, which means it’s free to use. Businesses can save on licensing fees while still benefiting from a robust, high-performing framework for their web applications.
2. High Performance and Scalability
With frameworks like Laravel, CodeIgniter, and Symfony, PHP enables developers to create scalable applications that can grow with business needs. It handles high traffic efficiently, making it ideal for websites of all sizes.
3. Cross-Platform Compatibility
PHP seamlessly integrates with multiple operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS. It supports various databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle, offering flexibility to developers.
4. Fast Development and Easy Maintenance
PHP’s extensive libraries, frameworks, and built-in functionalities accelerate development speed. Additionally, its simple syntax makes it easier to maintain and update applications over time.
5. Strong Community Support
Being one of the most widely used programming languages, PHP boasts an active global community. Developers can access countless tutorials, forums, and documentation to troubleshoot and enhance their web solutions.
6. Security and Reliability
PHP offers robust security features that help protect websites from common threats like SQL injection and data breaches. Frameworks such as Laravel come with built-in security measures, ensuring safer applications.
Conclusion
PHP continues to be a dominant force in web development due to its flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and strong support community. Whether you’re building a startup website or an enterprise-level application, PHP is a reliable choice for seamless web development.
Looking for expert PHP development services? Contact iSyncEvolution to build a high-performing website tailored to your business needs.
1 note
·
View note
Text
DBMS Tutorial Explained: Concepts, Types, and Applications

In today’s digital world, data is everywhere — from social media posts and financial records to healthcare systems and e-commerce websites. But have you ever wondered how all that data is stored, organized, and managed? That’s where DBMS — or Database Management System — comes into play.
Whether you’re a student, software developer, aspiring data analyst, or just someone curious about how information is handled behind the scenes, this DBMS tutorial is your one-stop guide. We’ll explore the fundamental concepts, various types of DBMS, and real-world applications to help you understand how modern databases function.
What is a DBMS?
A Database Management System (DBMS) is software that enables users to store, retrieve, manipulate, and manage data efficiently. Think of it as an interface between the user and the database. Rather than interacting directly with raw data, users and applications communicate with the database through the DBMS.
For example, when you check your bank account balance through an app, it’s the DBMS that processes your request, fetches the relevant data, and sends it back to your screen — all in milliseconds.
Why Learn DBMS?
Understanding DBMS is crucial because:
It’s foundational to software development: Every application that deals with data — from mobile apps to enterprise systems — relies on some form of database.
It improves data accuracy and security: DBMS helps in organizing data logically while controlling access and maintaining integrity.
It’s highly relevant for careers in tech: Knowledge of DBMS is essential for roles in backend development, data analysis, database administration, and more.
Core Concepts of DBMS
Let’s break down some of the fundamental concepts that every beginner should understand when starting with DBMS.
1. Database
A database is an organized collection of related data. Instead of storing information in random files, a database stores data in structured formats like tables, making retrieval efficient and logical.
2. Data Models
Data models define how data is logically structured. The most common models include:
Hierarchical Model
Network Model
Relational Model
Object-Oriented Model
Among these, the Relational Model (used in systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle) is the most popular today.
3. Schemas and Tables
A schema defines the structure of a database — like a blueprint. It includes definitions of tables, columns, data types, and relationships between tables.
4. SQL (Structured Query Language)
SQL is the standard language used to communicate with relational DBMS. It allows users to perform operations like:
SELECT: Retrieve data
INSERT: Add new data
UPDATE: Modify existing data
DELETE: Remove data
5. Normalization
Normalization is the process of organizing data to reduce redundancy and improve integrity. It involves dividing a database into two or more related tables and defining relationships between them.
6. Transactions
A transaction is a sequence of operations performed as a single logical unit. Transactions in DBMS follow ACID properties — Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability — ensuring reliable data processing even during failures.
Types of DBMS
DBMS can be categorized into several types based on how data is stored and accessed:
1. Hierarchical DBMS
Organizes data in a tree-like structure.
Each parent can have multiple children, but each child has only one parent.
Example: IBM’s IMS.
2. Network DBMS
Data is represented as records connected through links.
More flexible than hierarchical model; a child can have multiple parents.
Example: Integrated Data Store (IDS).
3. Relational DBMS (RDBMS)
Data is stored in tables (relations) with rows and columns.
Uses SQL for data manipulation.
Most widely used type today.
Examples: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server.
4. Object-Oriented DBMS (OODBMS)
Data is stored in the form of objects, similar to object-oriented programming.
Supports complex data types and relationships.
Example: db4o, ObjectDB.
5. NoSQL DBMS
Designed for handling unstructured or semi-structured data.
Ideal for big data applications.
Types include document, key-value, column-family, and graph databases.
Examples: MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis, Neo4j.
Applications of DBMS
DBMS is used across nearly every industry. Here are some common applications:
1. Banking and Finance
Customer information, transaction records, and loan histories are stored and accessed through DBMS.
Ensures accuracy and fast processing.
2. Healthcare
Manages patient records, billing, prescriptions, and lab reports.
Enhances data privacy and improves coordination among departments.
3. E-commerce
Handles product catalogs, user accounts, order histories, and payment information.
Ensures real-time data updates and personalization.
4. Education
Maintains student information, attendance, grades, and scheduling.
Helps in online learning platforms and academic administration.
5. Telecommunications
Manages user profiles, billing systems, and call records.
Supports large-scale data processing and service reliability.
Final Thoughts
In this DBMS tutorial, we’ve broken down what a Database Management System is, why it’s important, and how it works. Understanding DBMS concepts like relational models, SQL, and normalization gives you the foundation to build and manage efficient, scalable databases.
As data continues to grow in volume and importance, the demand for professionals who understand database systems is also rising. Whether you're learning DBMS for academic purposes, career development, or project needs, mastering these fundamentals is the first step toward becoming data-savvy in today’s digital world.
Stay tuned for more tutorials, including hands-on SQL queries, advanced DBMS topics, and database design best practices!
0 notes
Text
Django & PostgreSQL: Unlock Advanced Database Features
1. Introduction Overview: Django and PostgreSQL are powerful tools that, when combined, enable developers to build robust, scalable, and feature-rich web applications. PostgreSQL offers advanced database features that can enhance your Django projects, such as window functions, common table expressions (CTEs), and full-text search. This tutorial will guide you through integrating Django with…
0 notes
Text
This SQL Trick Cut My Query Time by 80%
How One Simple Change Supercharged My Database Performance
If you work with SQL, you’ve probably spent hours trying to optimize slow-running queries — tweaking joins, rewriting subqueries, or even questioning your career choices. I’ve been there. But recently, I discovered a deceptively simple trick that cut my query time by 80%, and I wish I had known it sooner.

Here’s the full breakdown of the trick, how it works, and how you can apply it right now.
🧠 The Problem: Slow Query in a Large Dataset
I was working with a PostgreSQL database containing millions of records. The goal was to generate monthly reports from a transactions table joined with users and products. My query took over 35 seconds to return, and performance got worse as the data grew.
Here’s a simplified version of the original query:
sql
SELECT
u.user_id,
SUM(t.amount) AS total_spent
FROM
transactions t
JOIN
users u ON t.user_id = u.user_id
WHERE
t.created_at >= '2024-01-01'
AND t.created_at < '2024-02-01'
GROUP BY
u.user_id, http://u.name;
No complex logic. But still painfully slow.
⚡ The Trick: Use a CTE to Pre-Filter Before the Join
The major inefficiency here? The join was happening before the filtering. Even though we were only interested in one month’s data, the database had to scan and join millions of rows first — then apply the WHERE clause.
✅ Solution: Filter early using a CTE (Common Table Expression)
Here’s the optimized version:
sql
WITH filtered_transactions AS (
SELECT *
FROM transactions
WHERE created_at >= '2024-01-01'
AND created_at < '2024-02-01'
)
SELECT
u.user_id,
SUM(t.amount) AS total_spent
FROM
filtered_transactions t
JOIN
users u ON t.user_id = u.user_id
GROUP BY
u.user_id, http://u.name;
Result: Query time dropped from 35 seconds to just 7 seconds.
That’s an 80% improvement — with no hardware changes or indexing.
🧩 Why This Works
Databases (especially PostgreSQL and MySQL) optimize join order internally, but sometimes they fail to push filters deep into the query plan.
By isolating the filtered dataset before the join, you:
Reduce the number of rows being joined
Shrink the working memory needed for the query
Speed up sorting, grouping, and aggregation
This technique is especially effective when:
You’re working with time-series data
Joins involve large or denormalized tables
Filters eliminate a large portion of rows
🔍 Bonus Optimization: Add Indexes on Filtered Columns
To make this trick even more effective, add an index on created_at in the transactions table:
sql
CREATE INDEX idx_transactions_created_at ON transactions(created_at);
This allows the database to quickly locate rows for the date range, making the CTE filter lightning-fast.
🛠 When Not to Use This
While this trick is powerful, it’s not always ideal. Avoid it when:
Your filter is trivial (e.g., matches 99% of rows)
The CTE becomes more complex than the base query
Your database’s planner is already optimizing joins well (check the EXPLAIN plan)
🧾 Final Takeaway
You don’t need exotic query tuning or complex indexing strategies to speed up SQL performance. Sometimes, just changing the order of operations — like filtering before joining — is enough to make your query fly.
“Think like the database. The less work you give it, the faster it moves.”
If your SQL queries are running slow, try this CTE filtering trick before diving into advanced optimization. It might just save your day — or your job.
Would you like this as a Medium post, technical blog entry, or email tutorial series?
0 notes
Text
SQL Online Course with Certificate – Learn SQL Anytime, Anywhere
Boost your data skills with our flexible SQL online course with a certificate, designed for learners of all levels. Whether you're a beginner exploring data for the first time or a professional seeking to validate your SQL expertise, this self-paced course offers a complete learning experience. You'll master SQL fundamentals, database queries, data filtering, joins, subqueries, and more—using platforms like MySQL and PostgreSQL. Learn through step-by-step video tutorials, interactive exercises, and practical assignments. Upon course completion, receive a recognized certificate that you can showcase on your resume or LinkedIn profile to enhance your job prospects in data analysis, business intelligence, and IT. Enroll now and start learning SQL from anywhere, at your own pace.
0 notes