#Postgresql documentation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
a day in my life as an web development intern (16/06)
i’m currently interning as a backend developer and am responsible for building an API using Flask(Python) and Postgresql.
09 - 10 = get there, turn on my laptop and open all the apps i need, most of the time it’s PyCharm for coding and Chrome cause I google a LOT. I also spend the first few 15 minutes trying to remember where I am and what I am supposed to do during the dat. and sometimes during this first hour I go get coffee.
10 - 11:30 = for my API, i needed to find a dataset that has all the schools in France with their gps coordinates, and so basically I found a database and wrote a python script to extract the data needed and then try to put a sample into my database.
11:30 - 12:30 = just like the schools, i also needed all the hospitals in france, and when I started looking at the dataset I was going to use for this I realized that there was no way I would get the gps coordinates from this specific dataset.
12:30 - 13:30 = here i went back home and ate a quick lunch.
13:30 - 15:30 = i found a better dataset and so i wrote a script to get the data i wanted from it and also tested putting some data into my database and made sure it worked. this script also involved clinics and nursing homes for the elderly cause I also needed them for my API. 15:30 - 17:00 = around this time I started trying to put all the data I imported from the school and hospital datasets into my database, and at one point I ran into some schools that didn't have a longitude and latitude, and I was like how do I fix that. So I spent around 30 mins googling and trying to write a script that could convert addresses into latitude and longitude, but it wasn't perfect LOL. 17:00 - 17:15 = spoke quickly to my supervisor abt this issue and what could be done about it 17:15 = turn off my laptop and monitors, pack my bag and go home.
as a whole, today was kinda fun ? even tho it was mostly spent struggling and trying to figure out how to do every single thing without using chatgpt (only used it once and it was at a time of dire need so I'm really proud of myself). honestly it's way more fun not using chatgpt cause you get to truly learn how to read documentation and know on your own how things work, and you also learn so much from trying and failing and i personally enjoy it so much !!! but yeah anyways, what's coming is definitely harder than what i've already done, but I've never been more ready. here's to more days of proving to myself over and over again how powerful my brain actually is and how good i am at this.
#i am too lazy to put pictures#study motivation#studyblr#study blog#studyspo#studying#academic weapon#study inspiration#girls in stem#software engineering#study aesthetic
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
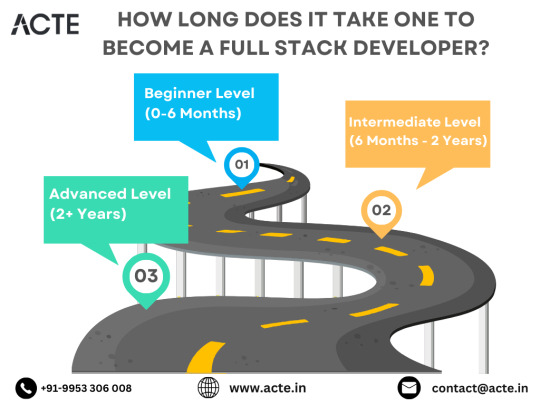
The Roadmap to Full Stack Developer Proficiency: A Comprehensive Guide
Embarking on the journey to becoming a full stack developer is an exhilarating endeavor filled with growth and challenges. Whether you're taking your first steps or seeking to elevate your skills, understanding the path ahead is crucial. In this detailed roadmap, we'll outline the stages of mastering full stack development, exploring essential milestones, competencies, and strategies to guide you through this enriching career journey.

Beginning the Journey: Novice Phase (0-6 Months)
As a novice, you're entering the realm of programming with a fresh perspective and eagerness to learn. This initial phase sets the groundwork for your progression as a full stack developer.
Grasping Programming Fundamentals:
Your journey commences with grasping the foundational elements of programming languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. These are the cornerstone of web development and are essential for crafting dynamic and interactive web applications.
Familiarizing with Basic Data Structures and Algorithms:
To develop proficiency in programming, understanding fundamental data structures such as arrays, objects, and linked lists, along with algorithms like sorting and searching, is imperative. These concepts form the backbone of problem-solving in software development.
Exploring Essential Web Development Concepts:
During this phase, you'll delve into crucial web development concepts like client-server architecture, HTTP protocol, and the Document Object Model (DOM). Acquiring insights into the underlying mechanisms of web applications lays a strong foundation for tackling more intricate projects.
Advancing Forward: Intermediate Stage (6 Months - 2 Years)
As you progress beyond the basics, you'll transition into the intermediate stage, where you'll deepen your understanding and skills across various facets of full stack development.
Venturing into Backend Development:
In the intermediate stage, you'll venture into backend development, honing your proficiency in server-side languages like Node.js, Python, or Java. Here, you'll learn to construct robust server-side applications, manage data storage and retrieval, and implement authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Mastering Database Management:
A pivotal aspect of backend development is comprehending databases. You'll delve into relational databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL, as well as NoSQL databases like MongoDB. Proficiency in database management systems and design principles enables the creation of scalable and efficient applications.
Exploring Frontend Frameworks and Libraries:
In addition to backend development, you'll deepen your expertise in frontend technologies. You'll explore prominent frameworks and libraries such as React, Angular, or Vue.js, streamlining the creation of interactive and responsive user interfaces.
Learning Version Control with Git:
Version control is indispensable for collaborative software development. During this phase, you'll familiarize yourself with Git, a distributed version control system, to manage your codebase, track changes, and collaborate effectively with fellow developers.
Achieving Mastery: Advanced Phase (2+ Years)
As you ascend in your journey, you'll enter the advanced phase of full stack development, where you'll refine your skills, tackle intricate challenges, and delve into specialized domains of interest.
Designing Scalable Systems:
In the advanced stage, focus shifts to designing scalable systems capable of managing substantial volumes of traffic and data. You'll explore design patterns, scalability methodologies, and cloud computing platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
Embracing DevOps Practices:
DevOps practices play a pivotal role in contemporary software development. You'll delve into continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, infrastructure as code (IaC), and containerization technologies such as Docker and Kubernetes.
Specializing in Niche Areas:
With experience, you may opt to specialize in specific domains of full stack development, whether it's frontend or backend development, mobile app development, or DevOps. Specialization enables you to deepen your expertise and pursue career avenues aligned with your passions and strengths.
Conclusion:
Becoming a proficient full stack developer is a transformative journey that demands dedication, resilience, and perpetual learning. By following the roadmap outlined in this guide and maintaining a curious and adaptable mindset, you'll navigate the complexities and opportunities inherent in the realm of full stack development. Remember, mastery isn't merely about acquiring technical skills but also about fostering collaboration, embracing innovation, and contributing meaningfully to the ever-evolving landscape of technology.
#full stack developer#education#information#full stack web development#front end development#frameworks#web development#backend#full stack developer course#technology
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
java full stack
A Java Full Stack Developer is proficient in both front-end and back-end development, using Java for server-side (backend) programming. Here's a comprehensive guide to becoming a Java Full Stack Developer:
1. Core Java
Fundamentals: Object-Oriented Programming, Data Types, Variables, Arrays, Operators, Control Statements.
Advanced Topics: Exception Handling, Collections Framework, Streams, Lambda Expressions, Multithreading.
2. Front-End Development
HTML: Structure of web pages, Semantic HTML.
CSS: Styling, Flexbox, Grid, Responsive Design.
JavaScript: ES6+, DOM Manipulation, Fetch API, Event Handling.
Frameworks/Libraries:
React: Components, State, Props, Hooks, Context API, Router.
Angular: Modules, Components, Services, Directives, Dependency Injection.
Vue.js: Directives, Components, Vue Router, Vuex for state management.
3. Back-End Development
Java Frameworks:
Spring: Core, Boot, MVC, Data JPA, Security, Rest.
Hibernate: ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) framework.
Building REST APIs: Using Spring Boot to build scalable and maintainable REST APIs.
4. Database Management
SQL Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL (CRUD operations, Joins, Indexing).
NoSQL Databases: MongoDB (CRUD operations, Aggregation).
5. Version Control/Git
Basic Git commands: clone, pull, push, commit, branch, merge.
Platforms: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket.
6. Build Tools
Maven: Dependency management, Project building.
Gradle: Advanced build tool with Groovy-based DSL.
7. Testing
Unit Testing: JUnit, Mockito.
Integration Testing: Using Spring Test.
8. DevOps (Optional but beneficial)
Containerization: Docker (Creating, managing containers).
CI/CD: Jenkins, GitHub Actions.
Cloud Services: AWS, Azure (Basics of deployment).
9. Soft Skills
Problem-Solving: Algorithms and Data Structures.
Communication: Working in teams, Agile/Scrum methodologies.
Project Management: Basic understanding of managing projects and tasks.
Learning Path
Start with Core Java: Master the basics before moving to advanced concepts.
Learn Front-End Basics: HTML, CSS, JavaScript.
Move to Frameworks: Choose one front-end framework (React/Angular/Vue.js).
Back-End Development: Dive into Spring and Hibernate.
Database Knowledge: Learn both SQL and NoSQL databases.
Version Control: Get comfortable with Git.
Testing and DevOps: Understand the basics of testing and deployment.
Resources
Books:
Effective Java by Joshua Bloch.
Java: The Complete Reference by Herbert Schildt.
Head First Java by Kathy Sierra & Bert Bates.
Online Courses:
Coursera, Udemy, Pluralsight (Java, Spring, React/Angular/Vue.js).
FreeCodeCamp, Codecademy (HTML, CSS, JavaScript).
Documentation:
Official documentation for Java, Spring, React, Angular, and Vue.js.
Community and Practice
GitHub: Explore open-source projects.
Stack Overflow: Participate in discussions and problem-solving.
Coding Challenges: LeetCode, HackerRank, CodeWars for practice.
By mastering these areas, you'll be well-equipped to handle the diverse responsibilities of a Java Full Stack Developer.
visit https://www.izeoninnovative.com/izeon/
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
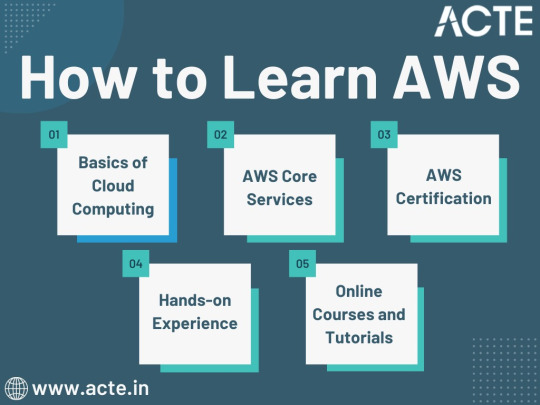
Journey to AWS Proficiency: Unveiling Core Services and Certification Paths
Amazon Web Services, often referred to as AWS, stands at the forefront of cloud technology and has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals leverage the power of the cloud. This blog serves as your comprehensive guide to understanding AWS, exploring its core services, and learning how to master this dynamic platform. From the fundamentals of cloud computing to the hands-on experience of AWS services, we'll cover it all. Additionally, we'll discuss the role of education and training, specifically highlighting the value of ACTE Technologies in nurturing your AWS skills, concluding with a mention of their AWS courses.

The Journey to AWS Proficiency:
1. Basics of Cloud Computing:
Getting Started: Before diving into AWS, it's crucial to understand the fundamentals of cloud computing. Begin by exploring the three primary service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Gain a clear understanding of what cloud computing is and how it's transforming the IT landscape.
Key Concepts: Delve into the key concepts and advantages of cloud computing, such as scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and disaster recovery. Simultaneously, explore the potential challenges and drawbacks to get a comprehensive view of cloud technology.
2. AWS Core Services:
Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2): Start your AWS journey with Amazon EC2, which provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud. Learn how to create virtual servers, known as instances, and configure them to your specifications. Gain an understanding of the different instance types and how to deploy applications on EC2.
Simple Storage Service (S3): Explore Amazon S3, a secure and scalable storage service. Discover how to create buckets to store data and objects, configure permissions, and access data using a web interface or APIs.
Relational Database Service (RDS): Understand the importance of databases in cloud applications. Amazon RDS simplifies database management and maintenance. Learn how to set up, manage, and optimize RDS instances for your applications. Dive into database engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and more.
3. AWS Certification:
Certification Paths: AWS offers a range of certifications for cloud professionals, from foundational to professional levels. Consider enrolling in certification courses to validate your knowledge and expertise in AWS. AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner, AWS Certified Solutions Architect, and AWS Certified DevOps Engineer are some of the popular certifications to pursue.
Preparation: To prepare for AWS certifications, explore recommended study materials, practice exams, and official AWS training. ACTE Technologies, a reputable training institution, offers AWS certification training programs that can boost your confidence and readiness for the exams.
4. Hands-on Experience:
AWS Free Tier: Register for an AWS account and take advantage of the AWS Free Tier, which offers limited free access to various AWS services for 12 months. Practice creating instances, setting up S3 buckets, and exploring other services within the free tier. This hands-on experience is invaluable in gaining practical skills.
5. Online Courses and Tutorials:
Learning Platforms: Explore online learning platforms like Coursera, edX, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning. These platforms offer a wide range of AWS courses taught by industry experts. They cover various AWS services, architecture, security, and best practices.
Official AWS Resources: AWS provides extensive online documentation, whitepapers, and tutorials. Their website is a goldmine of information for those looking to learn more about specific AWS services and how to use them effectively.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) represents an exciting frontier in the realm of cloud computing. As businesses and individuals increasingly rely on the cloud for innovation and scalability, AWS stands as a pivotal platform. The journey to AWS proficiency involves grasping fundamental cloud concepts, exploring core services, obtaining certifications, and acquiring practical experience. To expedite this process, online courses, tutorials, and structured training from renowned institutions like ACTE Technologies can be invaluable. ACTE Technologies' comprehensive AWS training programs provide hands-on experience, making your quest to master AWS more efficient and positioning you for a successful career in cloud technology.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating the Cloud Landscape: Unleashing Amazon Web Services (AWS) Potential
In the ever-evolving tech landscape, businesses are in a constant quest for innovation, scalability, and operational optimization. Enter Amazon Web Services (AWS), a robust cloud computing juggernaut offering a versatile suite of services tailored to diverse business requirements. This blog explores the myriad applications of AWS across various sectors, providing a transformative journey through the cloud.

Harnessing Computational Agility with Amazon EC2
Central to the AWS ecosystem is Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), a pivotal player reshaping the cloud computing paradigm. Offering scalable virtual servers, EC2 empowers users to seamlessly run applications and manage computing resources. This adaptability enables businesses to dynamically adjust computational capacity, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Redefining Storage Solutions
AWS addresses the critical need for scalable and secure storage through services such as Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) and Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store). S3 acts as a dependable object storage solution for data backup, archiving, and content distribution. Meanwhile, EBS provides persistent block-level storage designed for EC2 instances, guaranteeing data integrity and accessibility.
Streamlined Database Management: Amazon RDS and DynamoDB
Database management undergoes a transformation with Amazon RDS, simplifying the setup, operation, and scaling of relational databases. Be it MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQL Server, RDS provides a frictionless environment for managing diverse database workloads. For enthusiasts of NoSQL, Amazon DynamoDB steps in as a swift and flexible solution for document and key-value data storage.
Networking Mastery: Amazon VPC and Route 53
AWS empowers users to construct a virtual sanctuary for their resources through Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud). This virtual network facilitates the launch of AWS resources within a user-defined space, enhancing security and control. Simultaneously, Amazon Route 53, a scalable DNS web service, ensures seamless routing of end-user requests to globally distributed endpoints.
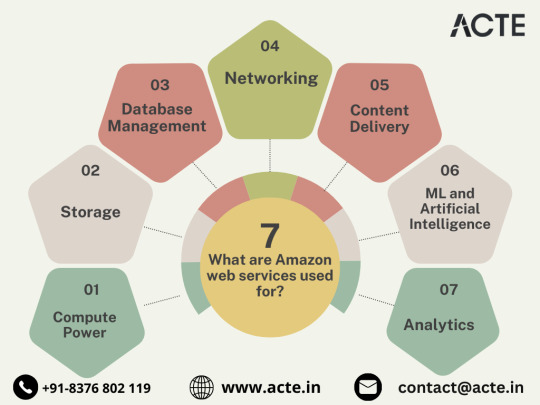
Global Content Delivery Excellence with Amazon CloudFront
Amazon CloudFront emerges as a dynamic content delivery network (CDN) service, securely delivering data, videos, applications, and APIs on a global scale. This ensures low latency and high transfer speeds, elevating user experiences across diverse geographical locations.
AI and ML Prowess Unleashed
AWS propels businesses into the future with advanced machine learning and artificial intelligence services. Amazon SageMaker, a fully managed service, enables developers to rapidly build, train, and deploy machine learning models. Additionally, Amazon Rekognition provides sophisticated image and video analysis, supporting applications in facial recognition, object detection, and content moderation.
Big Data Mastery: Amazon Redshift and Athena
For organizations grappling with massive datasets, AWS offers Amazon Redshift, a fully managed data warehouse service. It facilitates the execution of complex queries on large datasets, empowering informed decision-making. Simultaneously, Amazon Athena allows users to analyze data in Amazon S3 using standard SQL queries, unlocking invaluable insights.
In conclusion, Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands as an all-encompassing cloud computing platform, empowering businesses to innovate, scale, and optimize operations. From adaptable compute power and secure storage solutions to cutting-edge AI and ML capabilities, AWS serves as a robust foundation for organizations navigating the digital frontier. Embrace the limitless potential of cloud computing with AWS – where innovation knows no bounds.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
🚀 Professional Database Designer | Expert in ERD & Data Modeling 🚀
Struggling to visualize your database structure? I create clear, efficient Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs) that simplify complex data and improve your system’s performance.
🔹 Tailored ERD designs for your unique business needs 🔹 Support for Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL & more 🔹 Scalable and optimized database models 🔹 Detailed documentation & expert consultation included
Let’s turn your data into a powerful asset!
👉 Hire me on PeoplePerHour now: https://www.peopleperhour.com/hourlie/professional-database-designer-erd/524486
DatabaseDesign #ERDDesign #DataModeling #DataArchitecture #DatabaseExpert #SQLDatabase #DataManagement #TechSolutions #PeoplePerHour #FreelancerLife #ITConsulting #BusinessIntelligence #DataDriven #SoftwareDevelopment #CustomDatabase #DataEngineering #DatabaseConsultant #TechFreelancer #DatabaseOptimization #DataVisualization #SystemDesign #CloudDatabase #TechSupport
0 notes
Text
Top Tools and Technologies Every Full Stack Java Developer Should Know
In today's fast-paced software development landscape, Full Stack Java Developers are in high demand. Companies seek professionals who can work across both the frontend and backend, manage databases, and understand deployment processes. Whether you're just starting your career or planning to upskill, mastering the right set of tools and technologies is key.
If you're considering a full stack java training in KPHB, this guide will help you understand the essential technologies and tools you should focus on to become industry-ready.

1. Java and Spring Framework
The foundation of full stack Java development starts with a deep understanding of Core Java and object-oriented programming concepts. Once you’ve nailed the basics, move to:
Spring Core
Spring Boot – simplifies microservices development.
Spring MVC – for building web applications.
Spring Security – for handling authentication and authorization.
Spring Data JPA – for database operations.
Spring Boot is the most widely adopted framework for backend development in enterprise applications.
2. Frontend Technologies
A full stack Java developer must be proficient in creating responsive and interactive UIs. Core frontend technologies include:
HTML5 / CSS3 / JavaScript
Bootstrap – for responsive designs.
React.js or Angular – for building dynamic SPAs (Single Page Applications).
TypeScript – especially useful when working with Angular.
3. Database Management
You’ll need to work with both relational and non-relational databases:
MySQL / PostgreSQL – popular SQL databases.
MongoDB – a widely used NoSQL database.
Hibernate ORM – simplifies database interaction in Java.
4. Version Control and Collaboration
Version control systems are crucial for working in teams and managing code history:
Git – the most essential tool for source control.
GitHub / GitLab / Bitbucket – platforms for repository hosting and collaboration.
5. DevOps and Deployment Tools
Understanding basic DevOps is vital for modern full stack roles:
Docker – for containerizing applications.
Jenkins – for continuous integration and delivery.
Maven / Gradle – for project build and dependency management.
AWS / Azure – cloud platforms for hosting full stack applications.
6. API Development and Testing
Full stack developers should know how to develop and consume APIs:
RESTful API – commonly used for client-server communication.
Postman – for testing APIs.
Swagger – for API documentation.
7. Unit Testing Frameworks
Testing is crucial for bug-free code. Key testing tools include:
JUnit – for unit testing Java code.
Mockito – for mocking dependencies in tests.
Selenium / Playwright – for automated UI testing.
8. Project Management and Communication
Agile and collaboration tools help manage tasks and teamwork:
JIRA / Trello – for task and sprint management.
Slack / Microsoft Teams – for communication.
Final Thoughts
Learning these tools and technologies can position you as a highly capable Full Stack Java Developer. If you're serious about a career in this field, structured learning can make all the difference.
Looking for expert-led Full Stack Java Training in KPHB? ✅ Get industry-ready with hands-on projects. ✅ Learn from experienced instructors. ✅ Job assistance and certification included.
👉 Visit our website to explore course details, check out FAQs, and kickstart your journey today!
0 notes
Text
What Does a Java Developer Do? Everything You Should Know Before Hiring

One of the most popular programming languages worldwide, Java powers everything from smartphone apps to business applications. Hiring Java developers could be a good option if you want to create an application that is secure, scalable, and effective. What do Java developers actually do, and why should you choose them for your project?
We will go over the main duties of a Java developer in this article, along with what you should know before hiring one. Knowing what to look for in a Java developer will help you make an informed hiring decision, regardless of how big or small your company is.
Understanding the Role and Responsibilities of a Java Developer
The Core Responsibilities of a Java Developer
You want people who are experts at utilizing Java to create reliable programs when you hire Java developers. Writing, testing, and maintaining the code that runs different kinds of software is the core responsibility of a Java developer. This covers everything from large-scale enterprise systems to desktop and mobile applications.
Writing code that follows best practices and is clear, effective, and well-documented is the responsibility of Java developers. To make sure the software satisfies user demands and business goals, they work with cross-functional teams that include designers and system architects. They are also adept at debugging, troubleshooting, and performance and scalability optimization of programs.
Java Developer Skills You Should Look For
It's crucial to assess Java developers' competence in a number of crucial areas before hiring them. The following are the fundamental abilities a Java developer needs to have:
Core Java: To create applications, one must have a thorough understanding of Java syntax, libraries, and APIs.
Frameworks and Tools: Knowledge of well-known frameworks, such as Spring and Hibernate, helps expedite development and increase the scalability of applications.
Database Knowledge: Java developers should know how to link databases with Java apps and feel at ease dealing with databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB.
Version Control Systems: Collaboration and code maintenance require familiarity with Git or other version control systems.
Testing and Debugging: To guarantee code quality, Java developers should be proficient in both developing unit tests with frameworks like JUnit and debugging.
How Java Developers Contribute to Your Team
Depending on the requirements of your project, Java developers can participate in a number of ways. A Java developer will concentrate on the server-side, developing APIs, and overseeing database interactions when working on a web application. Java developers are necessary to create Android apps with Java or Kotlin for mobile applications.
Additionally, they support the integration of third-party services, speed optimization of the application, and adherence to security best practices. Building scalable solutions that can expand with your company is made possible in large part by Java developers.
Java developers are frequently assigned to create enterprise-level software solutions, customer-facing platforms, or mission-critical apps that support internal systems for tech businesses.
How to Hire Java Developers
It's critical to have a clear idea of the skill set needed and the expected salary when you are preparing to hire Java developers. To determine the competitive pay for Java developers in your area or globally, use a salary benchmarking tool. Remember that prices may differ based on location, experience, and level of proficiency with particular frameworks.
Take into account your team's size and composition as well. You may want to look for engineers who can handle a variety of duties if you are hiring for a startup or small team. However, you might want Java engineers with more specialized knowledge of particular frameworks or technologies if you are growing.
Conclusion: Why You Should Hire Java Developers
Hiring Java developers is a wise move if you want to create scalable, effective, and secure apps in today's tech-driven environment. For software firms looking to maintain an advantage in a cutthroat market, their proficiency in developing reliable backend systems, creating clear and effective code, and integrating with different technologies is priceless.
You can make an informed choice and select the best candidates to advance your projects by knowing the responsibilities and abilities of Java developers and using a salary benchmarking tool to match market rates. Hire software developers with Java experience if your company wants to create innovative apps that improve user experience, scalability, and performance.
0 notes
Text
🚀 How to Deploy MongoDB on Ubuntu VPS (5 Minute Quick-Start Guide)
This article demonstrates how to deploy MongoDB on Ubuntu VPS. This guide walks you through the step-by-step process of deploying MongoDB on an Ubuntu VPS (Ubuntu 20.04 or 22.04). What is MongoDB? MongoDB is a NoSQL, open-source, document-oriented database designed for high performance, scalability, and flexibility. Unlike traditional relational databases (like MySQL or PostgreSQL), MongoDB…
0 notes
Text
DBMS Tutorial for Beginners: Unlocking the Power of Data Management
In this "DBMS Tutorial for Beginners: Unlocking the Power of Data Management," we will explore the fundamental concepts of DBMS, its importance, and how you can get started with managing data effectively.
What is a DBMS?
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a software tool that facilitates the creation, manipulation, and administration of databases. It provides an interface for users to interact with the data stored in a database, allowing them to perform various operations such as querying, updating, and managing data. DBMS can be classified into several types, including:
Hierarchical DBMS: Organizes data in a tree-like structure, where each record has a single parent and can have multiple children.
Network DBMS: Similar to hierarchical DBMS but allows more complex relationships between records, enabling many-to-many relationships.
Relational DBMS (RDBMS): The most widely used type, which organizes data into tables (relations) that can be linked through common fields. Examples include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
Object-oriented DBMS: Stores data in the form of objects, similar to object-oriented programming concepts.
Why is DBMS Important?
Data Integrity: DBMS ensures the accuracy and consistency of data through constraints and validation rules. This helps maintain data integrity and prevents anomalies.
Data Security: With built-in security features, DBMS allows administrators to control access to data, ensuring that only authorized users can view or modify sensitive information.
Data Redundancy Control: DBMS minimizes data redundancy by storing data in a centralized location, reducing the chances of data duplication and inconsistency.
Efficient Data Management: DBMS provides tools for data manipulation, making it easier for users to retrieve, update, and manage data efficiently.
Backup and Recovery: Most DBMS solutions come with backup and recovery features, ensuring that data can be restored in case of loss or corruption.
Getting Started with DBMS
To begin your journey with DBMS, you’ll need to familiarize yourself with some essential concepts and tools. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Understand Basic Database Concepts
Before diving into DBMS, it’s important to grasp some fundamental database concepts:
Database: A structured collection of data that is stored and accessed electronically.
Table: A collection of related data entries organized in rows and columns. Each table represents a specific entity (e.g., customers, orders).
Record: A single entry in a table, representing a specific instance of the entity.
Field: A specific attribute of a record, represented as a column in a table.
Step 2: Choose a DBMS
There are several DBMS options available, each with its own features and capabilities. For beginners, it’s advisable to start with a user-friendly relational database management system. Some popular choices include:
MySQL: An open-source RDBMS that is widely used for web applications.
PostgreSQL: A powerful open-source RDBMS known for its advanced features and compliance with SQL standards.
SQLite: A lightweight, serverless database that is easy to set up and ideal for small applications.
Step 3: Install the DBMS
Once you’ve chosen a DBMS, follow the installation instructions provided on the official website. Most DBMS solutions offer detailed documentation to guide you through the installation process.
Step 4: Create Your First Database
After installing the DBMS, you can create your first database. Here’s a simple example using MySQL:
Open the MySQL command line or a graphical interface like MySQL Workbench. Run the following command to create a new CREATE DATABASE my_first_database;
Use the database: USE my_first_database;
Step 5: Create Tables
Next, you’ll want to create tables to store your data. Here’s an example of creating a table for storing customer information:
CREATE TABLE customers ( 2 customer_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, 3 first_name VARCHAR(50), 4 last_name VARCHAR(50), 5 email VARCHAR(100), 6 created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP 7);
In this example, we define a table named customers with fields for customer ID, first name, last name, email, and the date the record was created.
Step 6: Insert Data
Now that you have a table, you can insert data into it. Here’s how to add a new customer:
1 INSERT INTO customers (first_name, last_name, email) 2VALUES ('John', 'Doe', '[email protected]');
Query Data
To retrieve data from your table, you can use the SELECT statement. For example, to get all customers:
1 SELECT * FROM customers;
You can also filter results using the WHERE clause:
SELECT * FROM customers WHERE last_name = 'Doe';
Step 8: Update and Delete Data
You can update existing records using the UPDATE statement:
UPDATE customers SET email = '[email protected]' WHERE customer_id = 1;
To delete a record, use the DELETE statement:
DELETE FROM customers WHERE customer_id = 1;
Conclusion
In this "DBMS Tutorial for Beginners: Unlocking the Power of Data Management," we’ve explored the essential concepts of Database Management Systems and how to get started with managing data effectively. By understanding the importance of DBMS, familiarizing yourself with basic database concepts, and learning how to create, manipulate, and query databases, you are well on your way to becoming proficient in data management.
As you continue your journey, consider exploring more advanced topics such as database normalization, indexing, and transaction management. The world of data management is vast and full of opportunities, and mastering DBMS will undoubtedly enhance your skills as a developer or data professional.
With practice and experimentation, you’ll unlock the full potential of DBMS and transform the way you work with data. Happy database management!
0 notes
Text
What is Django? A Complete Guide for Beginners

Django is a high-level Python web framework that enables rapid development of secure and maintainable websites. It follows the model-template-view (MTV) architectural pattern and encourages clean, pragmatic design. Popular among developers for its scalability, reusability, and simplicity, Django helps build full-stack web applications with minimal code. Designed to handle backend logic, database interactions, URL routing, and more, Django is ideal for both startups and enterprise-level projects. If you're looking to learn web development in 2025, Django is one of the top Python frameworks for beginners, thanks to its rich documentation, strong community support, and compatibility with modern tools like REST APIs, PostgreSQL, and frontend libraries like React
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Hiring Django Developers in 2025
If you’re building a scalable, secure, and high-performing web application in 2025, Django remains one of the best frameworks to use. But to unlock its full potential, you need to hire Django developers who understand how to use this Python-based framework to meet your business goals.

Why Choose Django in 2025?
Django is still a top choice for web development in 2025 due to:
Rapid Development: Built-in admin panel, ORM, and modular architecture
Scalability: Used by companies like Instagram, Spotify, and NASA
Security: Protection against XSS, CSRF, and SQL injections
Community Support: A mature and well-documented ecosystem
When Should You Hire a Django Developer?
You should hire Django developers if:
You need to build a custom web application or CMS
You’re planning a secure eCommerce site
You require API development for mobile/web apps
You want a high-performance MVP or startup product
You need a secure backend for SaaS or enterprise software
Key Skills to Look For
Before hiring, make sure the Django developer is skilled in:
Python programming
Django framework (ORM, views, forms, templates)
REST APIs (DRF — Django REST Framework)
Front-end integration (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React/Angular)
Database systems (PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQLite)
Version control (Git)
Deployment (Docker, AWS, CI/CD)
Hiring Options: Freelancer vs Agency
Option Pros ConsFreelancer Cost-effective, flexible Limited availability, may lack team supportAgency (like Oodles)Scalable, full-stack team, support & QASlightly higher cost
If you want a full-cycle development solution with guaranteed timelines and post-launch support, hiring through an agency is ideal.
Interview Questions to Ask
Here are a few practical questions you can ask during the interview:
What’s the difference between a Django model and a Django form?
How would you handle user authentication in Django?
Explain the role of middleware in Django.
What are signals in Django and when should you use them?
How do you optimize Django for performance?
How Much Does It Cost to Hire Django Developers in 2025?
Freelancers: $20 — $60/hour (based on location & experience)
Agencies: $25 — $100/hour (comes with project managers, QA, and design support)
Dedicated Developer (Full-Time): $2000 — $6000/month
Outsourcing to countries like India gives you access to highly skilled developers at lower cost without compromising quality.
Where to Find Django Developers?
Freelance Platforms: Upwork, Freelancer, Toptal
Developer Marketplaces: Turing, Arc, Gun.io
Agencies: Oodles — Hire Django Developer
Job Boards: StackOverflow, GitHub Jobs, Remote OK
✅ Final Thoughts
Hire Django developers in 2025 is about more than just technical skills. You need someone who understands your business vision, works well with your team, and builds secure, scalable web applications with future growth in mind.
Whether you’re launching a new product, upgrading your tech stack, or expanding your backend, make sure you hire a Django developer who brings value from day one.
Looking to hire Django experts? Partner with Oodles for experienced Django developers who deliver quality, speed, and security.
0 notes
Text
Learning Full Stack Development: A Journey from Frontend to Backend
In the ever evolving world of technology, full stack development has emerged as one of the most in demand and versatile skill sets in the software industry. Whether you're a beginner stepping into the coding universe or an experienced developer looking to broaden your horizon, learning Full Stack Development Online can be a game changer. This blog post will guide you through what it means to be a full stack developer, why it's valuable, and how to start your journey effectively.

What is Full Stack Development?
Full stack development refers to the ability to work on both the frontend (client-side) and backend (server-side) of a web application. A full stack developer is someone who can manage the entire development process from designing user interfaces to handling databases and server logic.
Frontend: Everything the user interacts with HTML, CSS, JavaScript, frameworks like React or Angular.
Backend: Everything behind the scenes server logic, databases, APIs, and authentication using languages like Node.js, Python, Java, or PHP.
Why Learn Full Stack Development?
High Demand: Companies value developers who can handle multiple aspects of development.
Better Problem Solving: Understanding both sides helps you debug and improve applications more efficiently.
More Opportunities: Freelancing, startups, or product building all benefit from full stack skills.
Autonomy: Build complete apps by yourself without relying on multiple specialists.
Higher Earning Potential: Multi-skilled developers often command higher salaries.
Skills You Need to Master
Here’s a breakdown of core skills needed for a full stack developer to study in a well reputed Software Training Institutes:
Frontend:
HTML, CSS, JavaScript: The building blocks of any website.
Frameworks: React.js, Vue.js, or Angular.
Responsive Design: Making websites mobile-friendly using CSS frameworks like Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS.
Backend:
Languages: Node.js, Python (Django/Flask), Ruby, Java, or PHP.
Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB.
APIs: RESTful and GraphQL.
Authentication & Security: JWT, OAuth, HTTPS.
Tools & Platforms:
Version Control: Git and GitHub.
Deployment: Heroku, Vercel, Netlify, AWS, or Digital Ocean.
CI/CD & Testing: Basic knowledge of pipelines and automated testing.
How to Start Learning Full Stack Development

Pick a Language Stack: For beginners, the MERN stack (MongoDB, Express, React, Node.js) is a popular and well-supported option.
Follow a Roadmap: Stick to a structured learning plan. Many websites like roadmap.sh offer visual guides.
Build Projects: Start simple (to-do list, portfolio website) and gradually work on more complex applications like blogs, chat apps, or e-commerce platforms.
Use Online Resources: Leverage free and paid courses on platforms like free Code Camp, Udemy, Coursera, and YouTube.
Join Communities: Participate in developer communities on GitHub, Reddit, or Discord to get feedback and stay motivated.
Tips for Staying on Track
Be patient: Full stack development takes time. Don’t rush.
Practice consistently: Code every day, even for a short time.
Document your journey: Start a blog or GitHub repo to share your progress and projects.
Stay updated: Web development technologies evolve. Follow tech blogs, newsletters, and changelogs.
Final Thoughts
Learning full stack development is an investment in your future as a developer. It empowers you to understand the bigger picture of software development and opens doors to a wide range of career opportunities. Start small, be consistent, and enjoy the process before you know it, you'll be building fully functional web apps from scratch.
0 notes
Text
Inside the World of Full Stack Development: Crafting Seamless Digital Experiences
In today’s fast-paced digital age, the demand for adaptable, versatile developers has reached an all-time high. As businesses continue to evolve in a technology-driven landscape, the role of full stack developers has emerged as a pivotal force in shaping seamless digital experiences. From the front-end visuals to the back-end functionality, these professionals orchestrate entire applications with precision and efficiency.
But what does it really mean to live inside the world of full stack development?
Understanding the Full Stack Ecosystem
Full stack development refers to the ability to work on both the front end and back end of web and software applications. While front-end development focuses on user interface (UI) and user experience (UX), the back end includes server logic, databases, APIs, and integration systems.
To craft a seamless digital experience, a full stack developer must have a working command over multiple layers of technology. A few core components include:
Front-end technologies such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, or Angular.
Back-end development using tools like Node.js, Python, Ruby, or Java.
Database management with MySQL, MongoDB, or PostgreSQL.
Version control systems like Git for code management.
Server and deployment practices using Docker, Kubernetes, or AWS.
But mastering tools isn’t enough. What truly sets apart today’s developers is how they learn and apply these skills in real-time environments.
Project-Based Full Stack Learning: The Key to Practical Expertise
Traditional learning models often focus too much on theory. But in the evolving tech ecosystem, practical exposure wins the race. This is where project-based full stack learning steps in.
Instead of merely learning syntax or reading documentation, learners build actual applications that reflect real-world use cases. This method:
Encourages hands-on coding from day one.
Teaches students how different components interact in a live environment.
Helps learners grasp error handling, debugging, and optimization organically.
Boosts confidence and provides a portfolio to showcase in interviews.
In short, it bridges the gap between conceptual understanding and workplace application.
Solving Real-World Challenges with Java
A core part of being a well-rounded full stack developer is problem-solving. And Java, being one of the most stable and widely-used programming languages, plays a crucial role in that journey.
Real-time problem-solving with Java introduces developers to scenarios where high-performance, secure, and scalable systems are required. Think of things like:
Building payment gateways
Developing REST APIs for e-commerce platforms
Creating server-side logic for mobile applications
Ensuring thread safety and memory management in multi-user systems
Using Java in full stack development isn’t just about writing back-end logic; it’s about integrating robust performance and security within scalable architectures. And when these solutions are executed in real-time, they provide a rich learning ground for both novices and seasoned developers.
Why Full Stack Development Matters Today
Crafting seamless digital experiences isn't simply about attractive interfaces. It's about delivering responsive, secure, and optimized platforms that feel effortless to users.
Here’s why full stack development has become a cornerstone in the tech world:
Efficiency: One person can handle both front and back-end, reducing development time and communication gaps.
Flexibility: Developers can switch roles depending on project needs.
Comprehension: Better understanding of how components interact improves debugging and integration.
Value: Companies save costs while ensuring faster delivery and consistency.
In fact, many startups and small businesses now prefer hiring full stack developers over segmented teams, as they can iterate rapidly and pivot when needed.
Building a Career Inside the Full Stack World
To thrive in this space, aspiring developers must combine technical skills with the right mindset. Here’s what helps:
Focus on end-to-end project development. Not just coding snippets, but building from concept to deployment.
Practice debugging in live environments. Mistakes are your best teachers.
Engage in real-time problem-solving with Java and other back-end tools.
Join developer communities. Platforms like GitHub, Stack Overflow, and Dev.to offer immense collaborative learning.
Stay updated. The tech world evolves fast — full stack developers must keep up.
Top Skills Every Full Stack Developer Should Master
HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript (ES6+)
Front-end frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular
Back-end platforms like Node.js, Java Spring Boot, or Express.js
Databases: SQL & NoSQL
Version Control: Git & GitHub
Web Hosting & Deployment: Heroku, AWS, Netlify
Soft Skills: Communication, Time Management, and Critical Thinking
Final Thoughts
Inside the world of full stack development, the journey is as important as the destination. From learning through project-based full stack learning modules to encountering real-time problem-solving with Java, the process transforms a beginner into a professional equipped to handle dynamic digital challenges.
Crafting seamless digital experiences isn’t just about code — it’s about vision, innovation, and adaptability. Full stack developers are not just builders of websites or apps; they are the architects of digital transformation.
Whether you're a curious beginner or a tech enthusiast looking to upskill, stepping into this world is a decision that will shape not just your career, but the way you understand and influence technology.
0 notes
Text
Boost Your Tech Career with a Comprehensive Java Training and Internship Program

In today’s fast-paced digital world, programming skills are more than just an added advantage—they are essential. Among the myriad programming languages, Java stands out as one of the most robust, versatile, and in-demand languages used across industries, from mobile apps to enterprise-level software. If you're a student, fresher, or even a working professional looking to transition into software development, enrolling in a Java training and internship program can be your golden ticket to a successful IT career.
Why Learn Java?
Java is one of the oldest and most powerful programming languages still actively used today. It runs on billions of devices and serves as the backbone of many enterprise systems, Android apps, web servers, and more. Here's why Java continues to be a top choice for developers and organizations:
Platform Independence: Java is a "write once, run anywhere" language, meaning code written in Java can run on any system with a Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Strong Community Support: With millions of developers worldwide, help, documentation, and updates are always accessible.
Versatile Applications: From banking software to gaming applications and Android development, Java is everywhere.
High Demand: Companies across the globe constantly look for skilled Java developers, making it a highly employable skill.
What is a Java Training and Internship All About?
A Java training and internship is a structured learning program designed to teach both foundational and advanced concepts in Java programming, followed by real-time industry exposure through internships.
This program typically includes:
In-Depth Java Training: Covering topics such as Core Java, OOPs (Object-Oriented Programming), Collections Framework, Exception Handling, Multithreading, JDBC, and GUI programming.
Advanced Java Concepts: Including Servlets, JSP (JavaServer Pages), Spring Framework, Hibernate, RESTful APIs, and Microservices.
Project Development: Hands-on development of live projects to implement what you’ve learned.
Internship Experience: Working with a tech company or development team to gain practical, real-world experience.
Certification: A recognized certificate to showcase your skills to future employers.
Key Skills You’ll Learn
Participating in a Java training and internship program can help you master several critical skills that are valuable in the IT industry. These include:
1. Programming Fundamentals
You will start with understanding how Java works, its syntax, data types, variables, operators, and flow control statements.
2. Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
Java is an object-oriented language. You'll learn about classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, encapsulation, and abstraction—concepts that form the base of modern software development.
3. Database Integration
Using JDBC and ORM tools like Hibernate, you’ll learn how Java applications interact with databases such as MySQL, Oracle, or PostgreSQL.
4. Web Development
You'll gain skills in building Java-based web applications using Servlets, JSP, and frameworks like Spring MVC or Spring Boot.
5. Debugging and Testing
Understand how to debug Java applications, write unit tests using JUnit, and ensure that your code is reliable and efficient.
6. Project Management Tools
Gain experience using Git, GitHub, Maven, and other tools commonly used in development environments.
Benefits of Joining a Java Training and Internship Program
Enrolling in such a program offers multiple advantages beyond just learning how to code.
✅ Structured Learning
The course is designed by experts and follows a curriculum that gradually takes you from beginner to advanced level.
✅ Hands-on Experience
Working on live projects and real-world problems enhances your problem-solving ability and builds your portfolio.
✅ Professional Mentorship
Access to experienced mentors and instructors helps clarify doubts, understand complex topics, and receive valuable career guidance.
✅ Resume Building
The internship experience, along with a certificate of completion, significantly boosts your resume and makes you stand out to employers.
✅ Job Opportunities
Many internship programs have placement assistance or allow top performers to get absorbed into the company itself.
Who Should Join?
This program is suitable for:
Students in B.Tech/BCA/MCA or other CS-related streams who want to strengthen their programming base.
Fresh graduates looking to land their first job in software development.
Working professionals aiming to shift from non-tech roles or other languages into Java-based development.
Freelancers and entrepreneurs who want to build Java-based applications independently.
What a Typical Training and Internship Program Includes
While the details may vary by provider, a good Java training and internship program typically offers:
Component
Details
Duration
8 to 16 weeks
Mode
Online / Offline / Hybrid
Learning Hours
2-3 hours/day or weekend batches
Tools Covered
IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse, GitHub, MySQL, Maven
Projects
E-commerce website, Online Exam Portal, Chat App, etc.
Certification
Yes – with performance evaluation
Placement Support
Resume building, mock interviews, job referrals
How to Choose the Right Program?
When selecting a Java training and internship program, consider the following:
Reputation of the Institution: Choose a training center or ed-tech platform with positive reviews and a proven track record.
Curriculum Quality: Ensure that the course covers both Core and Advanced Java, along with real-time projects.
Internship Opportunities: Look for programs that offer internships with reputed companies.
Post-training Support: Some programs offer job placement help or career counseling—this is a big plus.
Affordability: Check if the program is within your budget and whether it offers EMI or scholarship options.
Real Career Impact
Those who complete the training and internship successfully often find career paths such as:
Java Developer
Backend Developer
Android Developer (Java-based)
Software Engineer
Full Stack Developer
Technical Consultant
With time and experience, you can grow into roles like Team Lead, Solution Architect, or even Product Manager in IT companies.
Final Thoughts
Investing your time and effort in a structured learning program can transform your career path. Java is more than just a programming language—it's a career catalyst. Whether you want to build enterprise software, Android applications, or simply add a valuable skill to your resume, a Java training and internship program provides the knowledge, experience
0 notes