#SQL Server snapshot backups
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Embracing Snapshot Backups for Multi-Terabyte SQL Server 2022 Environments
In the bustling world of data management, where databases swell beyond the terabyte threshold, traditional backup methodologies stagger under the weight of time-consuming processes. Enter the knight in shining armor: snapshot backups. These backups are not just about speed; they’re a paradigm shift, offering a beacon of hope for quick restoration without the drag. Yet, this shift isn’t just a…
View On WordPress
#fast database restore techniques#multi-terabyte database management#SQL Server backup strategies#SQL Server snapshot backups#storage-level snapshot technology
0 notes
Text
Reliable Website Maintenance Services In India | NRS Infoways
In today’s hyper‑connected marketplace, a website is far more than a digital brochure—it is the beating heart of your brand experience, your lead‑generation engine, and your most valuable sales asset. Yet many businesses still treat their sites as “launch‑and‑forget” projects, only paying attention when something breaks. At NRS Infoways, we understand that real online success demands continuous care, proactive monitoring, and seamless enhancements. That’s why we’ve built our Reliable Website Maintenance Services In India to deliver round‑the‑clock peace of mind, bulletproof performance, and measurable ROI for forward‑thinking companies like yours.
Why Website Maintenance Matters—And Why “Reliable” Makes All the Difference
Search engines reward fast, secure, and regularly updated sites with higher rankings; customers reward them with trust and loyalty. Conversely, a sluggish, outdated, or vulnerable site can cost you traffic, conversions, and brand reputation—sometimes overnight. Our Reliable Website Maintenance Services In India go beyond the basic “fix‑it‑when‑it‑breaks” model. We combine proactive health checks, performance tuning, security hardening, and content optimization into a single, cohesive program that keeps your digital storefront open, polished, and ready for growth.
What Sets NRS Infoways Apart?
1. Proactive Performance Monitoring
We leverage enterprise‑grade monitoring tools that continuously scan load times, server resources, and user journeys. By identifying bottlenecks before they escalate, we ensure smoother experiences and higher conversion rates—24/7.
2. Robust Security & Compliance
From real‑time threat detection to regular firewall updates and SSL renewals, your site stays impervious to malware, SQL injections, and DDoS attacks. We align with global standards such as GDPR and PCI‑DSS, keeping you compliant and trustworthy.
3. Seamless Content & Feature Updates
Launching a new product line? Running a seasonal promotion? Our dedicated team updates layouts, landing pages, and plugins—often within hours—to keep your messaging sharp and relevant without disrupting uptime.
4. Data‑Driven Optimization
Monthly analytics reviews highlight user behavior, bounce rates, and conversion funnels. We translate insights into actionable tasks—A/B testing CTAs, compressing heavy images, or refining navigation—all folded into our maintenance retainer.
5. Transparent Reporting & SLAs
Every client receives detailed monthly reports covering task logs, incident resolutions, and performance metrics. Our Service Level Agreements guarantee response times as low as 30 minutes for critical issues, underscoring the “Reliable” in our Reliable Website Maintenance Services In India.
Real‑World Impact: A Success Snapshot
A Delhi‑based B2B SaaS provider reached out to NRS Infoways after repeated downtime eroded user trust and slashed demo bookings by 18 %. Within the first month of onboarding, we:
Migrated their site to a high‑availability cloud cluster
Deployed a Web Application Firewall (WAF) to fend off bot attacks
Compressed multimedia assets, cutting average load time from 4.2 s to 1.3 s
Implemented weekly backup protocols with versioned restores
Result? Organic traffic climbed 27 %, demo sign‑ups rebounded 31 %, and support tickets fell by half—proving that consistent, expert care translates directly into revenue.
Flexible Plans That Scale With You
Whether you manage a lean startup site or a sprawling enterprise portal, we offer tiered packages—Basic, Professional, and Enterprise—each customizable with à‑la‑carte add‑ons like e‑commerce catalog updates, multi‑language support, or advanced SEO audits. As your business evolves, our services scale seamlessly, ensuring you never pay for overhead you don’t need or sacrifice features you do.
Partner With NRS Infoways Today
Your website is too important to leave to chance. Join the growing roster of Indian businesses that rely on NRS Infoways for Reliable Website Maintenance Services In India and experience the freedom to innovate while we handle the technical heavy lifting. Ready to protect your digital investment, delight your visitors, and outpace your competition?
Connect with our maintenance experts now and power your growth with reliability you can measure.
0 notes
Text
Cloud Cost Optimization Strategies: Reducing Expenses Without Sacrificing Performance
As organizations increasingly rely on cloud infrastructure, cloud cost optimization has become a top priority. While cloud services offer flexibility and scalability, they can also lead to unexpected expenses if not managed properly. The challenge is to reduce cloud costs without compromising performance, security, or availability.
This blog explores proven strategies for cloud cost optimization, helping businesses maximize ROI while maintaining efficiency.
1. Understanding Cloud Cost Challenges
Before optimizing costs, it’s essential to understand where cloud spending can spiral out of control:
🔴 Common Cost Pitfalls in Cloud Computing
Underutilized Resources – Idle virtual machines (VMs), storage, and databases consuming costs unnecessarily.
Over-Provisioning – Paying for computing power that exceeds actual demand.
Lack of Monitoring – Poor visibility into usage patterns and billing leads to inefficiencies.
Data Transfer Costs – High egress charges from excessive data movement between cloud services.
Inefficient Scaling – Failure to implement auto-scaling results in overpaying during low-demand periods.
💡 Solution? Implement cloud cost optimization strategies that ensure you're only paying for what you need.
2. Cloud Cost Optimization Strategies
✅ 1. Rightsize Your Cloud Resources
Analyze CPU, memory, and storage usage to determine the appropriate instance size.
Use cloud-native tools like:
AWS Cost Explorer
Azure Advisor
Google Cloud Recommender
Scale down or terminate underutilized instances to cut costs.
✅ 2. Implement Auto-Scaling and Load Balancing
Use auto-scaling to dynamically adjust resource allocation based on traffic demands.
Implement load balancing to distribute workloads efficiently, reducing unnecessary resource consumption.
🔹 Example: AWS Auto Scaling Groups ensure instances are added or removed automatically based on demand.
✅ 3. Optimize Storage Costs
Move infrequently accessed data to low-cost storage tiers like:
Amazon S3 Glacier (AWS)
Azure Cool Storage
Google Cloud Coldline Storage
Delete obsolete snapshots and redundant backups to avoid unnecessary costs.
✅ 4. Use Reserved Instances & Savings Plans
Reserved Instances (RIs) – Prepay for cloud resources to get discounts (e.g., up to 72% savings on AWS RIs).
Savings Plans – Commit to a specific usage level for long-term discounts on cloud services.
💡 Best for: Organizations with predictable workloads that don’t require frequent scaling.
✅ 5. Leverage Spot Instances for Cost Savings
Spot Instances (AWS), Preemptible VMs (GCP), and Low-Priority VMs (Azure) offer discounts up to 90% compared to on-demand pricing.
Ideal for batch processing, big data analytics, and machine learning workloads.
🚀 Example: Netflix uses AWS Spot Instances to reduce rendering costs for video processing.
✅ 6. Monitor and Optimize Cloud Spending with Cost Management Tools
Track real-time usage and spending with:
AWS Cost Explorer & Trusted Advisor
Azure Cost Management + Billing
Google Cloud Billing Reports
Set up budget alerts and anomaly detection to prevent unexpected cost spikes.
✅ 7. Reduce Data Transfer and Egress Costs
Minimize inter-region and cross-cloud data transfers to avoid high bandwidth charges.
Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) like Cloudflare, AWS CloudFront, or Azure CDN to reduce data movement costs.
💡 Pro Tip: Keeping data in the same region where applications run reduces network charges significantly.
✅ 8. Optimize Software Licensing Costs
Use open-source alternatives instead of expensive third-party software.
Leverage Bring-Your-Own-License (BYOL) models for Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, and SAP workloads to save costs.
✅ 9. Implement FinOps (Cloud Financial Management)
FinOps (Financial Operations) integrates finance, engineering, and IT teams to manage cloud spending effectively.
Establish spending accountability and ensure that each team optimizes its cloud usage.
✅ 10. Automate Cost Optimization with AI and Machine Learning
AI-powered cost optimization tools automatically analyze and recommend cost-saving actions.
Examples:
CloudHealth by VMware (multi-cloud cost management)
Harness Cloud Cost Management (AI-driven insights for Kubernetes and cloud spending)
💡 AI-driven automation ensures cost efficiency without manual intervention.
3. Best Practices for Sustainable Cloud Cost Management
🔹 Set up real-time budget alerts to track unexpected spending. 🔹 Regularly review and adjust reserved instance plans to avoid waste. 🔹 Continuously monitor cloud resource usage and eliminate redundant workloads. 🔹 Adopt a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategy to optimize pricing across different providers. 🔹 Educate teams on cloud cost optimization to promote a cost-conscious culture.
Conclusion
Effective cloud cost optimization isn’t just about cutting expenses—it’s about achieving the right balance between cost savings and performance. By implementing AI-driven automation, rightsizing resources, leveraging cost-effective storage options, and adopting FinOps practices, businesses can reduce cloud expenses without sacrificing security, compliance, or performance.
Looking for expert cloud cost optimization solutions? Salzen Cloud helps businesses maximize their cloud investment while ensuring performance and scalability.
0 notes
Text
What Is Amazon EBS? Features Of Amazon EBS And Pricing

Amazon Elastic Block Store: High-performance, user-friendly block storage at any size
What is Amazon EBS?
Amazon Elastic Block Store provides high-performance, scalable block storage with Amazon EC2 instances. AWS Elastic Block Store can create and manage several block storage resources:
Amazon EBS volumes: Amazon EC2 instances can use Amazon EBS volumes. A volume associated to an instance can be used to install software and store files like a local hard disk.
Amazon EBS snapshots: Amazon EBS snapshots are long-lasting backups of Amazon EBS volumes. You can snapshot Amazon EBS volumes to backup data. Afterwards, you can always restore new volumes from those snapshots.
Advantages of the Amazon Elastic Block Store
Quickly scale
For your most demanding, high-performance workloads, including mission-critical programs like Microsoft, SAP, and Oracle, scale quickly.
Outstanding performance
With high availability features like replication within Availability Zones (AZs) and io2 Block Express volumes’ 99.999% durability, you can guard against failures.
Optimize cost and storage
Decide which storage option best suits your workload. From economical dollar-per-GB to high performance with the best IOPS and throughput, volumes vary widely.
Safeguard
You may encrypt your block storage resources without having to create, manage, and safeguard your own key management system. Set locks on data backups and limit public access to prevent unwanted access to your data.
Easy data security
Amazon EBS Snapshots, a point-in-time copy that can be used to allow disaster recovery, move data across regions and accounts, and enhance backup compliance, can be used to protect block data storage both on-site and in the cloud. With its integration with Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager, AWS further streamlines snapshot lifecycle management by enabling you to establish policies that automate various processes, such as snapshot creation, deletion, retention, and sharing.
How it functions
A high-performance, scalable, and user-friendly block storage solution, Amazon Elastic Block Store was created for Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2).Image credit to AWS
Use cases
Create your cloud-based, I/O-intensive, mission-critical apps
Switch to the cloud for mid-range, on-premises storage area network (SAN) applications. Attach block storage that is both high-performance and high-availability for applications that are essential to the mission.
Utilize relational or NoSQL databases
Install and expand the databases of your choosing, such as Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL, Cassandra, MongoDB, and SAP HANA.
Appropriately scale your big data analytics engines
Detach and reattach volumes effortlessly, and scale clusters for big data analytics engines like Hadoop and Spark with ease.
Features of Amazon EBS
It offers the following features:
Several volume kinds: Amazon EBS offers a variety of volume types that let you maximize storage efficiency and affordability for a wide range of uses. There are two main sorts of volume types: HDD-backed storage for workloads requiring high throughput and SSD-backed storage for transactional workloads.
Scalability: You can build Amazon EBS volumes with the performance and capacity requirements you want. You may adjust performance or dynamically expand capacity using Elastic Volumes operations as your needs change, all without any downtime.
Recovery and backup: Back up the data on your disks using Amazon EBS snapshots. Those snapshots can subsequently be used to transfer data between AWS accounts, AWS Regions, or Availability Zones or to restore volumes instantaneously.
Data protection: Encrypt your Amazon EBS volumes and snapshots using Amazon EBS encryption. To secure data-at-rest and data-in-transit between an instance and its connected volume and subsequent snapshots, encryption procedures are carried out on the servers that house Amazon EC2 instances.
Data availability and durability: io2 Block Express volumes have an annual failure rate of 0.001% and a durability of 99.999%. With a 0.1% to 0.2% yearly failure rate, other volume types offer endurance of 99.8% to 99.9%. To further guard against data loss due to a single component failure, volume data is automatically replicated across several servers in an Availability Zone.
Data archiving: EBS Snapshots Archive provides an affordable storage tier for storing full, point-in-time copies of EBS Snapshots, which you must maintain for a minimum of ninety days in order to comply with regulations. and regulatory purposes, or for upcoming project releases.
Related services
These services are compatible with Amazon EBS:
In the AWS Cloud, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud lets you start and control virtual machines, or EC2 instances. Like hard drives, EBS volumes may store data and install software.
You can produce and maintain cryptographic keys with AWS Key Management Service, a managed service. Data saved on your Amazon EBS volumes and in your Amazon EBS snapshots can be encrypted using AWS KMS cryptographic keys.
EBS snapshots and AMIs supported by EBS are automatically created, stored, and deleted with Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager, a managed service. Backups of your Amazon EC2 instances and Amazon EBS volumes can be automated with Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager.
EBS direct APIs: These services let you take EBS snapshots, write data to them directly, read data from them, and determine how two snapshots differ or change from one another.
Recycle Bin is a data recovery solution that lets you recover EBS-backed AMIs and mistakenly erased EBS snapshots.
Accessing Amazon EBS
The following interfaces are used to build and manage your Amazon EBS resources:
Amazon EC2 console
A web interface for managing and creating snapshots and volumes.
AWS Command Line Interface
A command-line utility that enables you to use commands in your command-line shell to control Amazon EBS resources. Linux, Mac, and Windows are all compatible.
AWS Tools for PowerShell
A set of PowerShell modules for scripting Amazon EBS resource activities from the command line.
Amazon CloudFormation
It’s a fully managed AWS service that allows you describe your AWS resources using reusable JSON or YAML templates, and then it will provision and setup those resources for you.
Amazon EC2 Query API
The HTTP verbs GET or POST and a query parameter called Action are used in HTTP or HTTPS requests made through the Amazon EC2 Query API.
Amazon SDKs
APIs tailored to particular languages that let you create apps that interface with AWS services. Numerous well-known programming languages have AWS SDKs available.
Amazon EBS Pricing
You just pay for what you provision using Amazon EBS. See Amazon EBS pricing for further details.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#AmazonEBS#ElasticBlockStore#AmazonEC2#EBSvolumes#EC2instances#EBSSnapshots#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#Govindhtech
0 notes
Text
"Top Disaster Recovery Services of 2024 Revealed! From Microsoft Azure to CrashPlan, discover the best solutions for swift recovery, flexibility, and unmatched support. Read more at Tech Radar now."
Best Disaster Recovery Service of 2024
Best Disaster Recovery Service of 2024
Disaster recovery services (DR) and disaster recovery as a service providers (DRaaS) are crucial for ensuring business continuity in the face of potential data loss and system failures. These services enable businesses to store and recover their data in the event of software or hardware failure, as well as protect against the growing threat of malware and ransomware attacks.
Not all disaster recovery solutions are created equal. While some companies offer backup software with file syncing capabilities, data recovery can be challenging when data is fragmented across different systems and applications. This is where disaster recovery as a service providers come in, utilizing native or hybrid clouds to ensure the seamless recovery of both data and critical systems.
In this article, we will take a look at the best disaster recovery services and DRaaS providers currently available, highlighting their key features, benefits, and target audience. Whether you are a small business or a large enterprise, there is a disaster recovery solution tailored to your specific needs.
Best for Enterprises: Microsoft Azure Site Recovery
When it comes to software solutions, Microsoft is a giant in the industry. Their Azure Site Recovery platform offers enterprise-level disaster recovery with automated protection and recovery in the cloud. This solution is suitable for larger firms and supports Hyper-V, VMware, and physical servers. It also offers integration with System Center and SQL Server AlwaysOn, ensuring seamless recovery and minimal disruption. Microsoft Azure Site Recovery is a powerful, comprehensive solution for enterprise-level disaster recovery needs.
Best for Orchestration: Zerto
Zerto is a disaster recovery service that stands out for its advanced orchestration and automation capabilities. It can work with any storage or hypervisor and offers integrations with VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V. This solution allows for the transfer of workloads and assets between public, private, and hybrid clouds, providing flexible disaster recovery options. While the pricing may be on the higher end, Zerto is an excellent choice for large organizations looking for sophisticated orchestration and automation features.
Best for Swift Recovery: Arcserve UDP Cloud Direct
Arcserve UDP Cloud Direct is a disaster recovery service that promises swift recovery in the event of an outage. It replicates your network in the cloud and provides VPN access to your recovered environment, ensuring business continuity without any additional expenses. With built-in security protocols and data encryption, you can be confident that your information is protected. Arcserve UDP Cloud Direct is a simple and effective solution for mid to large organizations with an IT team.
Best for Flexibility: Carbonite
Carbonite offers a flexible disaster recovery service that allows businesses to backup and recover anything from individual files to whole applications. It supports local and cloud backups, as well as the ability to restore to existing or new hardware without additional software installation. Carbonite's central hub enables easy management and custom backup policies, ensuring a streamlined recovery operation. While the backup process can be slow at times, Carbonite is a reliable and flexible solution for businesses of all sizes.
Best for Support: Ekco Disaster Recovery
Ekco Disaster Recovery provides a secure and supportive disaster recovery solution, offering instant recoveries and specialist help. In addition to backing up your files and systems, Ekco Disaster Recovery provides access to skilled engineers who can assist with various technical issues. With a snapshot of your data and systems turned into virtual environments, you can continue working during moments of crisis. While the pricing plans are not readily available, Ekco Disaster Recovery is ideal for businesses that struggle with complex technology and require ongoing support.
Best for Small Business: CrashPlan
CrashPlan is a comprehensive backup and recovery solution designed for small businesses. It offers competitive pricing and combines data backup with recovery, ensuring the protection of important files. CrashPlan's mobile access feature allows you to retrieve files anytime, anywhere. While it doesn't backup files by type, CrashPlan stores everything and offers full encryption to keep your data secure. As a trusted solution used by TechRadar, CrashPlan is a reliable option for small businesses.
In conclusion, selecting the right disaster recovery service is crucial for safeguarding your business continuity. With options tailored to enterprises, orchestration, swift recovery, flexibility, support, and small businesses, there is a solution available to meet your specific needs. Whether you choose Microsoft Azure Site Recovery, Zerto, Arcserve UDP Cloud Direct, Carbonite, Ekco Disaster Recovery, or CrashPlan, you can rest assured that your data and systems are protected in the event of a disaster.
Sponsored by RoamNook
RoamNook is an innovative technology company specializing in IT consultation, custom software development, and digital marketing. Their main goal is to fuel digital growth for businesses of all sizes. With their expertise and solutions, businesses can confidently navigate the ever-changing digital landscape and ensure their data and systems are secure. Partner with RoamNook to take advantage of their cutting-edge technologies and drive your digital growth forward.
Source: https://www.techradar.com/best/best-disaster-recovery-service&sa=U&ved=2ahUKEwia1MWrjuSEAxVNMlkFHfaMCIYQxfQBegQIBhAC&usg=AOvVaw2um8RgrcAmITMgAl5M02Lm
0 notes
Text
MySQL NDB Cluster Backup & Restore In An Easy Way
In this post, we will see, how easily user can take NDB Cluster backup and then restore it. NDB cluster supports online backups, which are taken while transactions are modifying the data being backed up. In NDB Cluster, each backup captures all of the table content stored in the cluster. User can take backup in the following states: When the cluster is live and fully operational When the cluster is live, but in a degraded state: Some data nodes are down Some data nodes are restarting During read and write transactions Users can restore backups in the following cluster environments: Restore to the same physical cluster Restore into a different physical cluster Restore into a different configuration cluster i.e. backup taken from a 4 nodes cluster and restore into 8 data nodes cluster Restore into a different cluster version Backups can be restored flexibly: Restore can be run locally or remotely w.r.t the data nodes Restore can be run in parallel across data nodes Can restore a partial set of the tables captured in the backup Use cases of Backup & Restore: Disaster recovery - setting up a cluster from scratch Setup NDB Cluster asynchronous replication Recovery from user/DBA accidents like dropping of a table/database/schema changes etc During NDB Cluster software upgrade Limitations: Schemas and table data for tables stored using the NDB Cluster engine are backed up Views, stored procedure, triggers and tables/schemas from other storage engine like Innodb are not backed up. Users need to use other MySQL backup tools like mysqldump/mysqlpump etc to capture these Support for only full backup. No incremental or partial backup supported. NDB Cluster Backup & Restore concept in brief: In NDB Cluster, tables are horizontally partitioned into a set of partitions, which are then distributed across the data nodes in the cluster. The data nodes are logically grouped into nodegroups. All data nodes in a nodegroup (up to four) contain the same sets of partitions, kept in sync at all times. Different nodegroups contain different sets of partitions. At any time, each partition is logically owned by just one node in one nodegroup, which is responsible for including it in a backup.When a backup starts, each data node scans the set of table partitions it owns, writing their records to its local disk. At the same time, a log of ongoing changes is also recorded. The scanning and logging are synchronised so that the backup is a snapshot at a single point in time. Data is distributed across all the data nodes, and the backup occurs in parallel across all nodes, so that all data in the cluster is captured. At the end of a backup, each data node has recorded a set of files (*.data, *.ctl, *.log), each containing a subset of cluster data.During restore, each set of files will be restored [in parallel] to bring the cluster to the snapshot state. The CTL file is used to restore the schema, the DATA file is used to restore most of the data, and the LOG file is used to ensure snapshot consistency.Let’s look at NDB Cluster backup and restore feature through an example:To demonstrate this feature, let’s create a NDB Cluster with below environment.NDB Cluster 8.0.22 version 2 Management servers 4 Data nodes servers 2 Mysqld servers 6 API nodes NoOfReplicas = 2 If you are wondering how to setup a NDB Cluster, then please look into my previous blog here. Step 1:Before we start the cluster, let’s modify the cluster config file (config.ini) for backup. When backup starts, it create 3 files (BACKUP-backupid.nodeid.Data, BACKUP-backupid.nodeid.ctl, BACKUP-backupid.nodeid.log) under a directory named BACKUP. By default, this directory BACKUP created under each data node data directory. It is advisable to create this BACKUP directory outside the data directory. This can be done by adding a config variable ‘BackupDataDir’ to cluster configuration file i.e. config.iniIn the below example, I have assigned a path to ‘BackupDataDir‘ in config.ini:BackupDataDir=/export/home/saroj/mysql-tree/8.0.22/ndbd/node1/data4Step 2: Let’s look at the cluster from the management client (bin/ndb_mgm): Step 3: As cluster is up and running so let’s create a database, a table and do some transactions on it. Let’s insert rows into table ‘t1’ either thru sql or thru any tools. Let’s continue the rows insertion thru sql to have a significant amount of datas in the cluster. Let’s check the rows count from table ‘t1’. From the below image, we can see that table 't1' has ‘396120’ rows in it. Step 4: Now issue a backup command from the management client (bin/ndb_mgm) while some transactions on the table ‘t1’ was going on. We will delete rows from table ‘t1’ and issue a backup command in parallel. While delete ops is going on, issue a backup command from the management client: Let’s check the new row count from table ‘t1’ after all the delete ops finished. From the below image, we can see that now the table ‘t1’ has ‘306120’ rows. Let’s look at the files backup created. As we have assigned a path to backup files so let’s discuss about these files in brief. From the above image, we can see that, for each backup, one backup directory is created (BACKUP-backupid) and under each backup directory, 3 files are created. These are:BACKUP-backupid-0.node_id.Data (BACKUP-1-0.1.Data):The above file contains most of the data stored in the table fragments owned by this node. In the above example, 1 is the backupid, 0 is a hardcoded value for future use. 1 is node_id of the data node 1. BACKUP-backupid.node_id.ctl (BACKUP-1.1.ctl): The above file contains table meta data i.e. table definitions, index definitions.BACKUP-backupid.node_id.log (BACKUP-1.1.log):This file contains all the row changes that happened to the tables while the backup was in progress. These logs will execute during restore either as roll forward or roll back depends on whether the backup is snapshot start or snapshot end. Note:User can restore from anywhere i.e. doesn’t have to be from any particular data node. ndb_restore is an NDB API client program, so can run anywhere that can access the cluster. Step 5: Upon successfully completion of a backup, the output will looks like below: From the above image, Node 1 is the master node who initiate the backup, node 254 is the management node on which the START BACKUP command was issued, and Backup 1 is the 1st backup taken. #LogRecords ‘30000’ indicate that while backup was in progress some transaction was also running on the same table. #Records shows the number of records captured across the cluster. User can see the backup status also from the “cluster log” as shown below:2021-01-12 15:00:04 [MgmtSrvr] INFO -- Node 1: Backup 1 started from node 2542021-01-12 15:01:18 [MgmtSrvr] INFO -- Node 1: Backup 1 started from node 254 completed. StartGCP: 818 StopGCP: 855 #Records: 306967 #LogRecords: 30000 Data: 5950841732 bytes Log: 720032 bytesSo this concludes our NDB Cluster backup procedure. Step 6:We will now try to restore the data from the backup taken above. Let’s shutdown the cluster, cleanup all the files except the backup files and then start the cluster with initial (with no data).Let’s restore the backup to a different cluster. From the below image, we can see that data node Id’s are different from the cluster where backup was taken. Now let’s see if our database ‘test1’ is exist in the cluster or not after initial start. From the above image, we can see that, database ‘test1’ is not present. Now let’s start our restore process from the backup image #1 (BACKUP-1). The NDB restore works in this flow: It first restore the meta data from the *.ctl file so that all the tables/indexes can be recreated in the database. Then it restore the data files (*.Data) i.e. inserts all the records into the tables in the database. At the end, it executes all the transaction logs (*.log) rollback or roll forward to make the database consistent. Since restore will fail while restoring unique and foreign key constraints that are taken from the backup image so user must disable the index at the beginning and once restore is finished, again user need to rebuild the index. Step 7:Let’s start the restoration of meta data.Meta data restore, disable index and data restore can execute at one go, or can be done in serial. This restore command can be issued from any data node or can be from a non-data node as well.In this example, I am issuing meta data restore and disable index from Data Node 1 only for once. Upon successful completion, I will issue the data restore.Data Node 1: shell> bin/ndb_restore -n node_id -b backup_id -m --disable-indexes --ndb-connectstring=cluster-test01:1186,cluster-test02:1186 –backup_path=/path/to/backup directory -n: node id of the data node from where backup was taken. Do not confuse with the data node id of the new cluster.-b: backup id (we have taken backup id as ‘1’)-m: meta data restoration (recreate table/indexes)--disable-indexes: disable restoration of indexes during restore of data--ndb-connectstring (-c): Connection to the management nodes of the cluster.--backup_path: path to the backup directory where backup files exist. The results of above meta restore from data node 1 is shown below: Let’s start the data restore on the Data Node 1. Data Node 1:shell> bin/ndb_restore -n node_id -b backup_id -r --ndb-connectstring=cluster-test01:1186,cluster-test02:1186 –backup_path=/path/to/backup directory Below, I am trying to capture the logs from the data restore run results as it started and then at the end. From the above image, we can see that restore went successful. Restore skips restoration of system table data. System tables referred to here are tables used internally by NDB Cluster. Thus these tables should not be overwritten by the data from a backup. Backup data is restored in fragments, so whenever a fragment is found, ndb_restore checks if it belongs to a system table. If it does belong to a system table, ndb_restore decides to skip restoring it and prints a 'Skipping fragment' log message.Let’s finish all the remaining data restore from the other data nodes. These data restore can be run in parallel to minimise the restore time. Here, we don’t have to pass -m, --disable-indexes again to restore command as we need to do it only once. With the first restore completion, it has already created tables, indexes etc so no need to recreate it again and will also fail. Once all the data are restored into the table(s), we will enable the indexes and constraints again using the –rebuild-indexes option. Note that rebuilding the indexes and constraints like this ensures that they are fully consistent when the restore completes.Data Node 2:shell> bin/ndb_restore -n node_id -b backup_id -r --ndb-connectstring=cluster-test01:1186,cluster-test02:1186 –backup_path=/path/to/backup directoryData Node 3:shell> bin/ndb_restore -n node_id -b backup_id -r --ndb-connectstring=cluster-test01:1186,cluster-test02:1186 –backup_path=/path/to/backup directoryData Node 4:shell> bin/ndb_restore -n node_id -b backup_id -r --ndb-connectstring=cluster-test01:1186,cluster-test02:1186 –backup_path=/path/to/backup directory Ndb restore (ndb_restore) is an API, it needs API slots to connect to cluster. Since we have initiated 3 ndb_restore programme in parallel from Data node ID 4, 5 and 6 so we can see from the below image that ndb_restore took API ID: 47, 48 and 49. Let’s see the results from the remaining data nodes. Since all the ndb_restore API finished successfully, we can see that the API ID that it had taken to connect the cluster has been released. The last step is to rebuild the index. This can also done from any data nodes or from any non-data nodes but only once.Data Node 1:shell> bin/ndb_restore -n node_id -b backup_id --rebuild-indexes --ndb-connectstring=cluster-test01:1186,cluster-test02:1186 –backup_path=/path/to/backup directory--rebuild-indexes: It enables rebuilding of ordered indexes and foreign key constraints. Step 8:So we have finished our restoration steps. Let’s check the database, table, rows count in table etc .. So database ‘test1’ is already created. Now we can see that table ‘t1’ has been created and the row count#306120 which is also matching with our backup image (look at Step# 4).So this concludes our NDB Cluster backup and restore feature. There are many more options user can pass to both backup (START BACKUP) and restore (ndb_restore) programme based on the requirements. In the above example, I have selected the basic minimum options user might need for backup and restore. For more information on these options, please refer to NDB Cluster reference manual here. https://clustertesting.blogspot.com/2021/01/mysql-ndb-cluster-backup-restore-in.html
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to perform storage migration in a Hyper-V failover cluster
Case
You have a Hyper-V cluster and you need to migrate virtual machine disk files and other disk-based clustered objects (such as paging files and snapshots) from an old storage repository to a new storage repository. This could mean migration between storage LUNs of the same storage system or between storage LUNs of different storage systems which are attached to the same hypervisor cluster. The migrated virtual machine disks may be of type .vhd, .vhdx, .vhdx shared or .vhds (VHD Set).
Solution
For best practice designs of Hyper-V clusters, you should review the following article: https://stefanos.cloud/kb/how-to-deploy-a-hyper-v-cluster-with-powershell/. Also you can purchase my e-book on Hyper-V cluster design best practices. https://stefanos.cloud/blog/windows-failover-clustering-design-handbook/ To migrate virtual machine storage, you should use the Hyper-V cluster storage migration feature. Via Failover Cluster Manager Follow the steps below in the Failover Cluster Manager console. - Open the Hyper-V cluster manager console and click on the VM whose storage you need to migrate between cluster disks (volumes). Right-click on the VM and choose command "Move --> Virtual Machine Storage".

On the upper section, choose either the entire source VM or some of the associated storage files which you wish to migrate (source). Then drag and drop the selected rows to the lower section into the target folder of the target cluster volume (target). After completing the drag and drop operation, you should see a summary of the before (source) and after (target) storage repository for the dragged storage entities, as shown in the example below.
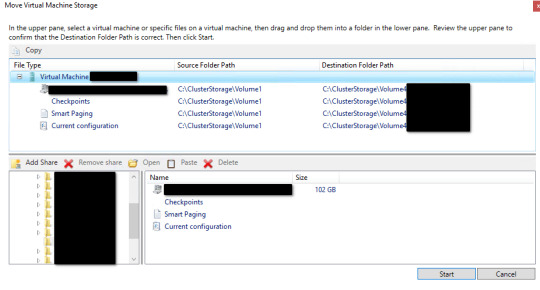
When you are ready click "Start" and observe the storage migration status in the Failover Cluster Manager console as well as by observing network traffic in the Windows File Explorer, from the source storage volume to the target volume. The storage migration initiation should be shown inside the Failover Cluster Manager, next to the VM record whose storage migration has started.

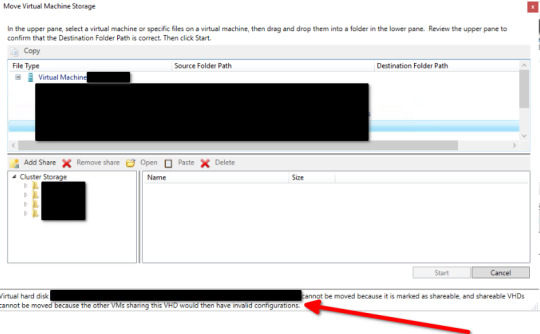
You should repeat the above steps for all virtual machines whose storage you wish to migrate. Via Powershell You can achieve the same Hyper-V virtual machine storage migration with the following example Powershell cmdlet. Move-VMStorage "SourceVM" -VirtualMachinePath D:MyVMsConfig -SnapshotFilePath D:MyVMsSnapshots -SmartPagingFilePath D:MyVMsSmartPaging -VHDs @(@{"SourceFilePath" = "C:MyVMsDisk1.VHDX"; "DestinationFilePath" = "D:MyVMsDisksDisk1.VHDX"}, @{"SourceFilePath" = "C:MyVMsDisk2.VHDX"; "DestinationFilePath" = "D:MyVMsDisksDisk2.VHDX"}) Storage migration of shared vhdx or vhds disks If you try to migrate a storage disk which is configured as a shared disk (either in .vhds VHD Set or .vhdx shared format) you will encounter the following blocking error and the storage migration will not be able to continue. Virtual hard disk C:ClusterStorage.vhdx cannot be moved because it is marked as shareable and shareable VHDs cannot be moved because the other VMs sharing this VHD would then have invalid configurations.
Shared disks are part of a guest WFC cluster If the shared disks to be migrated to another storage LUN are part of a Windows Failover Cluster (WFC) in a guest cluster fashion, for example in a SQL Server guest cluster configuration, then you need to carry out the following steps. - Shut down both guest cluster nodes (hosts). - Remove the shared VHDX/VHDS file from the second guest cluster node.
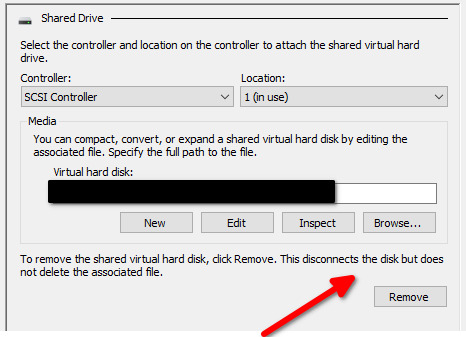
- Re-configure the VHDX/VHDS file to become a non-shared file. There is no official way to convert from VHDS to VHDX but only a workaround. Follow the steps below for this conversion from VHDS to VHDX.- Shutdown all the guest cluster VMs using the vhdx/vhds disk in question and detach the disk. - Copy/backup *.vhds and *.ahdx - Rename *.ahdx to *.vhdx - Use the Starwind V2V Converter too to convert to vhd or vhdx. - Re-attach the disk and verify functionality in your WFC cluster. - Power on the guest cluster node 1. - Perform the storage migration of the shared disks from guest cluster node 1. - Shut down node 1 again. - Re-configure the VHDX/VHDS file again to become a shared file and add it back to guest cluster node 2. - Power on both guest cluster nodes. Shared disks are not part of a guest WFC cluster In this case, you need to carry out the following steps. - Shut down the VM to which the shared disk in question is attached. - Remove the shared disk in question from the VM. This will detach the disk from the VM but it will not delete the actual disk file/data.
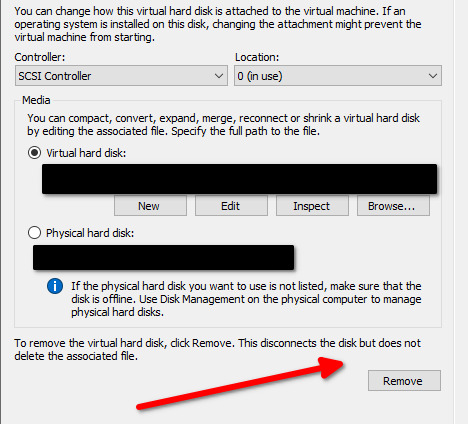
- Re-add the disk to the VM but this time choose the disk to be a non-shared disk.
- Power on the VM and perform the storage migration from the WFC console.
Sources
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/hyper-v/move-vmstorage?view=windowsserver2022-ps https://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/Azure/en-US/27ccf285-e5c3-4819-8f9c-82784b8ba71a/convert-vhdset-to-vhdx?forum=winserverhyperv Read the full article
#failovercluster#hyper-v#livemigration#Microsoft#Powershell#Storage#storagemigration#vhdset#vhds#vhdx#virtualmachines
0 notes
Text
5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable Processors Boost SQL Server 2022

5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable Processors
While speed and scalability have always been essential to databases, contemporary databases also need to serve AI and ML applications at higher performance levels. Real-time decision-making, which is now far more widespread, should be made possible by databases together with increasingly faster searches. Databases and the infrastructure that powers them are usually the first business goals that need to be modernized in order to support analytics. The substantial speed benefits of utilizing 5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable Processors to run SQL Server 2022 will be demonstrated in this post.
OLTP/OLAP Performance Improvements with 5th gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors
The HammerDB benchmark uses New Orders per minute (NOPM) throughput to quantify OLTP. Figure 1 illustrates performance gains of up to 48.1% NOPM Online Analytical Processing when comparing 5th Gen Intel Xeon processors to 4th Gen Intel Xeon processors, while displays up to 50.6% faster queries.
The enhanced CPU efficiency of the 5th gen Intel Xeon processors, demonstrated by its 83% OLTP and 75% OLAP utilization, is another advantage. When compared to the 5th generation of Intel Xeon processors, the prior generation requires 16% more CPU resources for the OLTP workload and 13% more for the OLAP workload.
The Value of Faster Backups
Faster backups improve uptime, simplify data administration, and enhance security, among other things. Up to 2.72x and 3.42 quicker backups for idle and peak loads, respectively, are possible when running SQL Server 2022 Enterprise Edition on an Intel Xeon Platinum processor when using Intel QAT.
The reason for the longest Intel QAT values for 5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable Processors is because the Gold version includes less backup cores than the Platinum model, which provides some perspective for the comparisons.
With an emphasis on attaining near-real-time latencies, optimizing query speed, and delivering the full potential of scalable warehouse systems, SQL Server 2022 offers a number of new features. It’s even better when it runs on 5th gen Intel Xeon Processors.
Solution snapshot for SQL Server 2022 running on 4th generation Intel Xeon Scalable CPUs. performance, security, and current data platform that lead the industry.
SQL Server 2022
The performance and dependability of 5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable Processors, which are well known, can greatly increase your SQL Server 2022 database.
The following tutorial will examine crucial elements and tactics to maximize your setup:
Hardware Points to Consider
Choose a processor: Choose Intel Xeon with many cores and fast clock speeds. Choose models with Intel Turbo Boost and Intel Hyper-Threading Technology for greater performance.
Memory: Have enough RAM for your database size and workload. Sufficient RAM enhances query performance and lowers disk I/O.
Storage: To reduce I/O bottlenecks, choose high-performance storage options like SSDs or fast HDDs with RAID setups.
Modification of Software
Database Design: Make sure your query execution plans, indexes, and database schema are optimized. To guarantee effective data access, evaluate and improve your design on a regular basis.
Configuration Settings: Match your workload and hardware capabilities with the SQL Server 2022 configuration options, such as maximum worker threads, maximum server RAM, and I/O priority.
Query tuning: To find performance bottlenecks and improve queries, use programs like Management Studio or SQL Server Profiler. Think about methods such as parameterization, indexing, and query hints.
Features Exclusive to Intel
Use Intel Turbo Boost Technology to dynamically raise clock speeds for high-demanding tasks.
With Intel Hyper-Threading Technology, you may run many threads on a single core, which improves performance.
Intel QuickAssist Technology (QAT): Enhance database performance by speeding up encryption and compression/decompression operations.
Optimization of Workload
Workload balancing: To prevent resource congestion, divide workloads among several instances or servers.
Partitioning: To improve efficiency and management, split up huge tables into smaller sections.
Indexing: To expedite the retrieval of data, create the proper indexes. Columnstore indexes are a good option for workloads involving analysis.
Observation and Adjustment
Performance monitoring: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) and pinpoint areas for improvement with tools like SQL Server Performance Monitor.
Frequent Tuning: Keep an eye on and adjust your database on a regular basis to accommodate shifting hardware requirements and workloads.
SQL Server 2022 Pricing
SQL Server 2022 cost depends on edition and licensing model. SQL Server 2022 has three main editions:
SQL Server 2022 Standard
Description: For small to medium organizations with minimal database functions for data and application management.
Licensing
Cost per core: ~$3,586.
Server + CAL (Client Access License): ~$931 per server, ~$209 per CAL.
Basic data management, analytics, reporting, integration, and little virtualization.
SQL Server 2022 Enterprise
Designed for large companies with significant workloads, extensive features, and scalability and performance needs.
Licensing
Cost per core: ~$13,748.
High-availability, in-memory performance, business intelligence, machine learning, and infinite virtualization.
SQL Server 2022 Express
Use: Free, lightweight edition for tiny applications, learning, and testing.
License: Free.
Features: Basic capability, 10 GB databases, restricted memory and CPU.
Models for licensing
Per Core: Recommended for big, high-demand situations with processor core-based licensing.
Server + CAL (Client Access License): For smaller environments, each server needs a license and each connecting user/device needs a CAL.
In brief
Faster databases can help firms meet their technical and business objectives because they are the main engines for analytics and transactions. Greater business continuity may result from those databases’ faster backups.
Read more on govindhtech.com
#5thGen#IntelXeonScalableProcessors#IntelXeon#BoostSQLServer2022#IntelXeonprocessors#intel#4thGenIntelXeonprocessors#SQLServer#Software#HardwarePoints#OLTP#OLAP#technology#technews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Microsoft Sql Server Vss Writer 9.0 Download
Microsoft Sql Server Vss Writer Download
Microsoft Vss Writer For Sql Server 2017 Download
Microsoft Sql Server Vss Writer 9.0 Download Windows 10
Microsoft Sql Server Vss Writer 9.0 Download Full
Microsoft Sql Server Vss Writer 9.0 Download Free
9.0.21022 2 9.0.30729 2 Microsoft SQL Server VSS Writer 9.00.1399.06 2 9.00.2047.00 2 Microsoft SQL Server Native Client 9.00.2047.00 2 6.20.1099.0 2 WebFldrs XP 9.50.6513 1 Microsoft SQL Server VSS Writer 9.00.2047.00 1 SQLXML4 9.00.2047.00 1 9.00.2047.00 1 9.00.2047.00 1 9.3.4035.00 1 9.3.4035.00 1 9.00.4035.00 1 Microsoft SQL Server VSS.
SQL Server 2014 Service Pack 3 (SP3) and cumulative update (CU) builds. Cumulative update name. Knowledge Base number. SQL Server 2014 SP3 CU4 + Security Update. January 12, 2021.
Where can I download the Sql Server VSS Writer? It was deleted somehow. SQL Server VSS writer is not available as a separate download. Instead you will need to obtain from.

-->
Applies to: SQL Server (all supported versions)
The SQL Writer Service provides added functionality for backup and restore of SQL Server through the Volume Shadow Copy Service framework.
The SQL Writer Service is installed automatically. It must be running when the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) application requests a backup or restore. To configure the service, use the Microsoft Windows Services applet. The SQL Writer Service installs on all operating systems.
Purpose

When running, Database Engine locks and has exclusive access to the data files. When the SQL Writer Service is not running, backup programs running in Windows do not have access to the data files, and backups must be performed using SQL Server backup.
Use the SQL Writer Service to permit Windows backup programs to copy SQL Server data files while SQL Server is running.
Microsoft Sql Server Vss Writer Download
Volume Shadow Copy Service
The VSS is a set of COM APIs that implements a framework to allow volume backups to be performed while applications on a system continue to write to the volumes. The VSS provides a consistent interface that allows coordination between user applications that update data on disk (writers) and those that back up applications (requestors).
Microsoft Vss Writer For Sql Server 2017 Download
The VSS captures and copies stable images for backup on running systems, particularly servers, without unduly degrading the performance and stability of the services they provide. For more information on the VSS, see your Windows documentation.
Note
When using VSS to backup a virtual machine that is hosting a Basic Availability Group, if the virtual machine is currently hosting databases that are in a secondary state, starting with SQL Server 2016 (13.x) SP2 CU2 and SQL Server 2017 (14.x) CU9 those databases will not be backed up with the virtual machine. This is because Basic Availability Groups do not support backing up databases on the secondary replica. Prior to these versions of SQL Server, the backup would fail with an error.
Microsoft Sql Server Vss Writer 9.0 Download Windows 10
Virtual Backup Device Interface (VDI)
SQL Server provides an API called Virtual Backup Device Interface (VDI) that enables independent software vendors to integrate SQL Server into their products for providing support for backup and restore operations. These APIs are engineered to provide maximum reliability and performance, and support the full range of SQL Server backup and restore functionality, including the full range of hot and snapshot backup capabilities. If a third-party vendor application requests a snapshot (VSS) backup, the SQL Writer Service calls the VDI API functions in order to perform the actual backups. Note that the VDI API is independent of VSS and is frequently used in software solutions that do not employ VSS APIs.
Permissions
The SQL Writer service must run under the Local System account. The SQL Writer service uses the NT ServiceSQLWriter login to connect to SQL Server. Using the NT ServiceSQLWriter login allows the SQL Writer process to run at a lower privilege level in an account designated as no login, which limits vulnerability. If the SQL Writer service is disabled, then any utility which in relies on VSS snapshots, such as System Center Data Protection Manager, as well as some other 3rd-party products, would be broken, or worse, at risk of taking backups of databases which were not consistent. If neither SQL Server, the system it runs on, nor the host system (in the event of a virtual machine), need to use anything besides Transact-SQL backup, then the SQL Writer service can be safely disabled and the login removed. Note that the SQL Writer service may be invoked by a system or volume level backup, whether the backup is directly snapshot-based or not. Some system backup products use VSS to avoid being blocked by open or locked files. The SQL Writer service needs elevated permissions in SQL Server because in the course of its activities it briefly freezes all I/O for the instance of SQL Server.
Features
Microsoft Sql Server Vss Writer 9.0 Download Full
SQL Writer supports:
Full database backup and restore including full-text catalogs
Differential backup and restore
Restore with move
Database rename
Copy-only backup
Auto-recovery of database snapshot

SQL Writer does not support:
Log backups
File and filegroup backup
Page restore
Remarks
Microsoft Sql Server Vss Writer 9.0 Download Free
The SQL Writer service is a separate service from the SQL Server engine and is shared across different versions of SQL Server and across different instances of SQL Server on the same server. The SQL Writer service file ships as part of the SQL Server installation package and will be marked with the same version number as the SQL Server engine it ships with. When a new instance of SQL Server is installed on a server or an existing instance is upgraded, if the version number of the instance being installed or upgraded is higher than the version number of the SQL Writer service that is currently on the server, that file will be replaced with the one from the installation package. Note that if the SQL Writer service was updated by a Service Pack or Cumulative Update and a RTM version of SQL Server is being installed, it is possible to replace a newer version of the SQL Writer service with an older one, provided that the installation has a higher major version number. For example, the SQL Writer service was updated in SQL Server 2016 (13.x) SP2 CU2. If that instance is upgraded to SQL Server 2017 (14.x) RTM, the updated SQL Writer service will be replaced with an older version. In this case, you would need to apply the latest CU to the new instance in order to get the newer version of the SQL Writer service.
0 notes
Text
Veeam Certified Engineer 2021 VMCE2021 Exam Questions
VMCE2021 exam is a new Veeam Certified Engineer 2021 exam replacement of VMCE2020 which will be retired on October 31, 2021. PassQuestion new cracked Veeam Certified Engineer 2021 VMCE2021 Exam Questions to help you pass the VEEAM VMCE2021 exam smoothly. After using high quality Veeam Certified Engineer 2021 VMCE2021 Exam Questions, you will understand the topics of the VEEAM VMCE2021 exam easily. The VMCE2021 Exam Questions and Answers will address your shortcomings and improve your skills to help you become the VEEAM certified Engineer quickly.Make sure that you are using all of our Veeam Certified Engineer 2021 VMCE2021 Exam Questions multiple times so you can ensure your success in the real exam.
Veeam Certified Engineer 2021
The VMCE certification is documented proof that an administer or engineer has the necessary level of expertise to protect an organization’s data with Veeam Availability Suite. It is a great investment for an IT professional looking to increase productivity, reduce operation costs, propel personal career advancement and achieve industry recognition.
The VMCE certification validates your knowledge and skills to perform a wide array of tasks with Veeam solutions. In addition, it confirms that you hold the necessary level of technical expertise to implement, configure and manage Veeam Availability Suite correctly.The VMCE 2021 Exam is now available. VMCE 2020 Exam is expected to retire October 31, 2021. The passing score for the VMCE exam is 70%.The VMCE 2021 exam has 50 questions in 75 minutes.
Exam Objectives
Describe Veeam Availability Suite components usage scenarios and relevance to your environment.
Effectively manage data availability in on-site, off-site, cloud and hybrid environments.
Ensure both Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs) are met.
Configure Veeam Availability Suite to ensure data is protected effectively.
Adapt with an organization’s evolving technical and business data protection needs.
Ensure recovery is possible, effective, efficient, secure and compliant with business requirements.
Provide visibility of the business data assets, reports and dashboards to monitor performance and risks.
View Online Veeam Certified Engineer 2021 VMCE2021 Free Questions
Which Vepdm Backup & Replication feature component is able to utilize Microsoft SQL Server transaction log backups for point-in-time restore? A.U-AIR Microsoft SQL Recovery wizard B.Instant Recovery C.Full VM Restore D.Veeam Explorer for Microsoft SQL Answer:D
You want to deploy an On-Demand Sandbox. While creating the application group, which sources can be used to add virtual machines to the Application Group? (Choose three.) A.Backup Copy in Backup repository B.Replica on non-Cloud Connect VMware vSphere host C.Replica on Cloud Connect VMware vSphere host D.Backup in Cloud Repository E.Storage Shapshot F.Backup on Backup Repository Answer:BEF
Which of the following statements is true regarding the Veeam Backup & Replication integration with supported Storage Systems for VMware vSphere are true? (Choose three). A.On storage accesses through NFS, VMs with snapshots will be skipped from Backup from Storage Snapshots B.Veeam Backup & Replication can backup virtual machines from a supported secondary storage array C.On storage accessed through NFS, VMs with snapshots can be protected with Backup from Storage Snapshots D.When Backup from Storage Snapshots is performed, VMware shapshot is never utilized E.Enabling Backup from Storage Snapshots for all backup jobs are not recommended Answer:ABE
Which procedure is used to finalize replica failback? A.Migrate to production B.VMware Storage vMotion C.Replica failback does not need to be finalized D.Commit failback E.Quick Migration Answer:D
In the event a VMware VM configuration file (VMX) is missing and a restore is needed, what Veeam restore process is the best choice for this situation? A.VM file restore B.Instant disk recovery C.Instant VM recovery D.Virtual disk restore Answer:A
Sometimes snapshots are "lost" by vCenter. What tool finds and removes those lost snapshots? A.CLI Snapshot Removal Tool B.Snapshot Hunter C.Snapshot Extractor D.Veeam ONE Orphaned VM Reporter Answer:B
0 notes
Text
Tìm hiểu về AWS Elastic Block Store (EBS)? Giới hạn tối đa AWS EBS?
Có bài viết học luyện thi AWS mới nhất tại https://cloudemind.com/ebs/ - Cloudemind.com
Tìm hiểu về AWS Elastic Block Store (EBS)? Giới hạn tối đa AWS EBS?
Khi làm việc với AWS, một trong những dịch ko thể thiếu được xếp vào dạng xóa mù cloud ko thể ko xem qua đó là nhóm dịch vụ về lưu trữ trong đó có EBS (Elastic Block Store). Đây là một dạng dịch vụ lưu trữ dữ liệu dạng block, có nghĩa là dữ liệu lưu vào các block khác nhau, khi có sự thay đổi dữ liệu là thay đổi các block này. Bài này chúng ta cùng hiểu kỹ hơn về EBS nhé. EBS sử dụng trong những use cases nào? Giới hạn của EBS là gì? Ưu nhược điểm của AWS EBS…
Giới thiệu AWS EBS
EBS là loại dịch vụ thuộc nhóm về lưu trữ. EBS được thiết kế để sử dụng cùng với EC2 để tạo nên một máy ảo trên cloud gọi là EC2 instances. Một máy chủ trên cloud sẽ được phân biệt phần tính toán và bộ nhớ riêng với phần lưu trữ. EC2 cung cấp cho bạn lựa chọn về vCPU và RAM, còn EBS cung cấp khả năng lưu trữ như HDD/SSD. Vậy EC2 và EBS xem như là perfect couple để tạo nên một bộ đôi ăn ý và phổ biến nhất. (Ngoài EBS, EC2 còn có thể làm việc với nhiều loại lưu trữ khác như EFS hay Instance Store nhưng trong bài này Kevin chỉ cover về EBS loại hình phổ biến và dễ sử dụng nhất).
internet
EBS là loại hình lưu trữ phổ biến cho nhiều loại workload ứng dụng thiên về xử lý giao dịch transactional hay cần khả năng đọc ghi throughput cao. Có rất nhiều ứng dụng có thể cài trên EBS ví dụ như web server, database (sql và nosql), enterprise application, containers, big data analytics, media processing hay các chương trình thiên về machine learning, file system…
Thậm chí EBS còn có thể chịu các workload mà tần số truy suất tính bằng single-digit-milisecond (độ trễ tính bằng 1 ký số ví dụ như: 1 milisecond 9 milsecond) như các DB đòi hỏi performance cao như SAP HANA hay các ứng dụng cần thông lượng throughput cực cao tính bằng Gigabyte/s như phân tích dữ liệu Hadoop.
EBS có tính persistent hiểu nôm na là có tính tồn tại, khi máy chủ EC2 stop hay thậm chí terminated (xóa bỏ) thì phân vùng EBS vẫn còn tồn tại. Điều này ngược với loại hình storage có tên là Instance Store.
EBS có scope hoạt động là AZ specific, có nghĩa là EBS khi tạo ra sẽ ảnh hưởng trên một AZ, và dữ liệu EBS được sao lưu trong AZ đó.
EBS Snapshot là một tính năng cho phép sao lưu EBS đến Amazon S3 tự động thông qua lifecycle policy.
Lợi ích chính của EBS
High performance – EBS là loại dịch vụ lưu trữ phù hợp với một dải rộng các workload từ các ứng dụng web server, dịch vụ lưu trữ file hay tới các workload nặng như phân tích dữ liệu lớn, machine learning hay xử lý media…
EBS volume sử dụng cho EC2 R5b instance có thể hỗ trợ throughput tới 60Gbps và 260K IOPS
HDD EBS-backed EC2 phù hợp các workload về big data hay analytics, data warehouse…
High Available & Durable – Protect failure when replicating within AZ, offering 99,999% availability (five 9s). Bạn có thể kết hợp sử dụng với DLM (Data Lifecycle Management) để backup dữ liệu tăng tính available của dữ liệu.
Durability 99.8% – 99.9%
For high durable volume (io2) provide 99.999%
Cost effective – Chi phí đôi khi ko phải là lúc nào cũng có lợi nhất khi bàn tổng thể một giải pháp nhưng phần lớn các dịch vụ AWS ra đời sau luôn có tỷ số giá trên hiệu năng (p/p) luôn tốt hơn, đem lại lợi ích cho người dùng. Cụ thể AWS ra loại hình lưu trữ gp3 mới hơn gp2 với chi phí thấp hơn 20% cho phép bạn có IOPS mạnh hơn và hiệu năng mạnh hơn.
Virtually unlimited scale – Bạn có thể dễ dàng scale EBS tính đến hàng Petabytes mà không ảnh hưởng hay gián đoạn đến ứng dụng. EBS vì có AZ Specific nên muốn provision vùng EBS ở AZ khác bạn dễ dàng sử dụng thông qua tính năng EBS Snapshot (rồi provision ở AZ khác với bản snapshot đã có).
Secure – EBS tạo mới được mã hóa mặc định để đảm bảo data compliance. EBS hỗ trợ mã hóa data at rest và in-transit. EBS cũng work rất tốt với các hệ thống quản lý khóa của AWS như KMS và ko ảnh hưởng tới performance của EBS. Điều này rất tuyệt.
Một số giới hạn của AWS EBS
Maximum volume size: 16TB
Logical data block: 4K
Một EC2 instance có thể attach bao nhiêu EBS? Tùy theo loại instance và OS là gì, thông thường 28, có một số instance type hỗ trợ tới 31, một số khác chỉ 3. Tham khảo thêm: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/volume_limits.html
Tham khảo:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/volume_constraints.html
Xem thêm: https://cloudemind.com/ebs/
0 notes
Text
Migrate Your SQL Server Database to Amazon RDS
Amazon RDS is a web service that provides cloud database functionality for developers looking for a cost-effective and simple way to manage databases. If you’re looking to migrate your existing SQL database to RDS, this is the guide for you. RDS offers six database engines: 1. Amazon Aurora 2. Microsoft SQL Server 3. Oracle 4. PostgreSQL 5. MYSQL 6. MariaDB With RDS, there is no need for you to buy any other rack and stack hardware or install any software.The complexity of moving your existing Microsoft SQL Server to Amazon RDS is mostly determined by the size of your database and the types of database objects which you are transferring. For example, migrating a database which has data sets on the order of gigabytes along with stored triggers and procedures is going to be more complex than migrating a modest database with only few megabytes of test data and no stored procedures or triggers. Why You Might Consider Migrating Your SQL Database to Amazon RDS RDS allows developers to set up database instances in the cloud. Developers are relieved of the complexity of managing and maintenance of the database. Instead, they can focus on developing successful products. There’s one issue, however: There is no file system access. Though this is usually not a huge problem, it becomes a concern if you are trying to restore or create an SQL Server backup (.bak) file. This may sound like a daunting task, but it is in fact quite easy. In this post, we have tried to provide you with some easy steps to migrate your SQL Server database to Amazon RDS: 1. The first step would be to take a snapshot of the source RDS instance. 2. Secondly, you will have to disable automatic backups on the origin RDS instance. 3. Now, create your target database by disabling all foreign key constraints and triggers. 4. Import all the logins into the destination database. 5. The next step is creating the schema DDL with the help of the Generate and Publish Scripts Wizard in SSMS. 6. Next, execute the SQL commands on your target DBA to create your schema. 7. You can use either the bulk copy command (cp) or the Import/Export Wizard in SSMS to migrate your data from the origin database to your target database. Migrate Your SQL Server Database to Amazon RDS 8. Clean up the target database by re-enabling the foreign key constraints and triggers. 9. Again re-enable the automatic backups on the source RDS instance. Thankfully, after experimenting with this process many times, we found a better solution not documented in the AWS documentation. SQL Azure Migration Wizard To save time and avoid errors, we have discovered a new and better solution called the SQL Azure Migration Wizard. With SQL Azure Migration Wizard, the process of migrating databases (or anything including views/tablse/stored procedures) in, out, or between RDS instances is much easier and faster. To migrate your SQL database to Amazon RDS using SQL Azure Migration Wizard, follow these easy steps. Step1: Download the SQLAzureMW Tool Download SQL Azure Migration Wizard on CodePlex. Next, you need to extract the SQLAzureMW.exe file. You can utilize SQL Server Management Studio for connecting your local SQL server and Amazon Web Service RDS instance. But, before doing all this, make sure that you have a good connection to these two servers. Step 2: Begin the Migration Double click on the SQLAzureMW.exe file. A page will appear on your screen and what you now need to do is to select Database as an option under the Analyze/Migrate category. Once you do this, click on the Next button. Step 3: Source Database Tasks Now enter your Source SQL Server Database connection details and click on the Connect button. Choose the source database and click on the button that says ‘Next.’ Then select an option named as ‘Script all database objects’.This option can enable to do the complete migration of the database. But if you don’t want to migrate entire database then you select an option that says ‘Select specific database objects.’ Step 4: Create Scripts Create scripts for all selected SQL server objects. You should save the script on local hard drive and the move ahead by hitting a click on a button ‘Next’. Step 5: Destination Database Process Now you have created a script of your database. You will now be required to enter your RDS SQL Server connection credentials and then connect it. Step 6: Select the Target Database Choose the target database that you would like to migrate. If you have not created any database earlier, then create a new one using Create Database option and go next. Be sure to do a quick check to confirm if there are any errors. Step 7: The Grand Finale You can now verify your SQL Server Management Studio and check all the migrated data. As you can see, SQL Azure Migration Wizard saves a lot of time. You will have to modify settings in your corporate firewall if your database is on-premises. In case your database is already hosted on Amazon Web Services, you can also add an entry to your instance’s security group. Next, what you have to do is simple: launch and prepare an Amazon RDS instance running SQL. Then restore the database from the SQL dump and take note of the current log file name. Now you will use the database dump to start the RDS instance. Once the RDS instance is initialized, you will be required to run the replication stored procedures that are supplied as part of the release to configure the RDS instance. Once your RDS instance matches any changes that have taken place, the application configuration can be modified to use it in preference to the existing version. Summary Thus sums up the process on how to migrate a SQL Server database to Amazon RDS. The process of data migration is not a very complicated process but a very easy one indeed. We hope that this post was useful enough in helping all those who want to migrate their SQL Server Database to Amazon RDS.
#database Management services provider#sql server dba service providers#DBA service providers#remote DBA services providers
0 notes
Text
AWS Enterprise Training for Seasoned Professionals, Get Future Ready Now
Our AWS enterprise training exposes the students to the fundamental and advanced ideas and capabilities of Amazon Web Services. Hundreds of organizations have found our Amazon Web Services training program helpful. They are all satisfied with the assistance and support we provided the in learning the intricacies of the subject with satisfaction. Our AWS Tutorials fulfil the expectations of Enterprises. Stay tuned as we often update Amazon Web Services Tutorials. We assist organizations achieve optimum performance with our training program.
Amazon Web Services is the most significant course in the current scenario due to the increased number of requirements and dependency with attached best in class security. Our AWS group training helped businesses and professionals adapt to the live usage environment and to its difficulties.
1. What exactly is AWS?
Our AWS lesson exposes the reader to the fundamental ideas and capabilities of Amazon Web Services. Our students found the training program helpful, assisting with improved performance on the job. We encourage our students to stay tuned to updates related to AWS and further certifications; for that, join our LinkedIn or Facebook cloud practitioners’ group.
Amazon Web Services is the most significant course in the current scenario due to the increased number of job opportunities and the high compensation pay. We also provide AWS online instruction to all students worldwide through the media. These are the best AWS Tutorials created by our institute's professional teachers.
• What exactly is AWS?
• What exactly are AWS EC2 Instances?
• What exactly is the AWS Management Console?
• What exactly is AWS Lambda?
• What exactly is AWS API Gateway?
• What exactly is AWS Dynamo DB?
• What exactly are AWS Certifications?
• Why is AWS so popular today?
• How will AWS evolve over the next five years?
1. What exactly is AWS?
AWS is an abbreviation for Amazon Web Services. It's a cloud platform created by the e-commerce behemoth Amazon.com.
Governments, businesses, and people may utilize Amazon's cloud computing services to access a powerful cluster of cloud-based services.
2. What exactly is AWS API Gateway?
Amazon Web Services API Gateway is one of the many AWS services available.
Developers may use this platform to build, publish, regulate, and secure APIs.
To access various online services, including Amazon Web Services, you may create an Application Programming Interface (API).
3. What exactly is AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda is a cloud computing service provided by Amazon Web Services. It's an event-driven service that provides serverless processing of codes responding to events such as program messages, user actions, sensor output, and so on. The service manages resources automatically to offer smooth and real-time processing of requests. AWS Lambda joined Amazon Web Services in 2014, and since then, it has seen many improvements, making it most attractive among businesses.
4. What exactly is the AWS Management Console?
The AWS management console is a graphical user interface that enables you to access Amazon Web Services through web browsers via the internet. You may use the management interface to control various Amazon services, including cloud storage and cloud computing. AWS interface is accessible from a mobile device by downloading the AWS Console mobile app.
5. What exactly are AWS EC2 Instances?
Amazon EC2 is a cloud computing service that offers scalable computational power. In other words, AWS's EC2 service provides us with a virtual private computer in the cloud. COMPUTE capacity is the amount of energy needed to run your task in the cloud. The computing power provided by the EC2 service in the form of EC2 Instances is both scalable and dynamic.
6. What exactly is Amazon Dynamo DB?
Amazon Web Services offers Dynamo DB as a database service (AWS).
The dynamo DB is also known as a NoSQL database since it uses JSON queries to interact with the database. Opposed to SQL databases, which utilize SQL-related questions to interact with the database. This database is both versatile and quick and used for applications that need consistency and latency at the millisecond level at any size.
7. What exactly is Amazon Relational Database Services (RDS)?
The DB case is Amazon RDS's basic structural square. A database occurrence is a distinct database circumstance in the cloud. A DB event may include several client-created databases, and you can access them using the same tools and apps as you would with an isolated database example. A DB event may be created and modified using the AWS Command Line Interface, the Amazon RDS API, or the AWS Management Console.
The DB usage comes with computation and memory limits. Its type and size govern these. It's the reason database planning is an essential aspect of server optimization. If your requirements change after some time, you may modify DB cases.
It provides a cost-effective, scalable limit for an industry-standard social database and manages fundamental database organization tasks.
Zones of Monitoring and Availability
Amazon's distributed computing assets are stored in widely accessible server farm offices across the globe (for instance, North America, Europe, or Asia).
Every datum focal region is referred to as a district. You may execute your database event in several Availability Zones, which is known as a multi-AZ organization.
Amazon sets up and maintains an optional backup DB event in a different Availability Zone when you choose this option. Your primary DB example is replicated synchronously across Availability Zones to the auxiliary occurrence to provide information excess, failover support, dispose of I/O solidifies, and minimize inactivity spikes during framework reinforcements.
See High Availability (Multi-AZ) for Amazon RDS for additional information.
Security
A security group controls the entry to a DB event. It does this by granting access to the IP address ranges or Amazon EC2 instances that you specify. Amazon RDS makes use of DB security groups, VPC security groups, and EC2 security groups. In simple words, a DB security gathering regulates access to a DB instance that is not in a VPC; a VPC security gathering controls access to a DB instance that is within a VPC. An Amazon EC2 security gathering contains access to an EC2 instance used with a DB instance. See Security in Amazon RDS for additional information about security gatherings.
Examining an Amazon RDS Database Instance
There are many methods to monitor the presentation and well-being of a DB occurrence.
The free Amazon CloudWatch administration monitors the exhibition and strength of a DB occurrence; execution outlines are shown in the Amazon RDS comfort.
You may subscribe to Amazon RDS events to be notified when changes occur with a database, for example, a DB Snapshot, a DB parameter collection, or a DB security collection.
See Monitoring Amazon RDS for additional information.
Interfaces for Amazon RDS
There are many methods for connecting to Amazon RDS.
Amazon Web Services Management Console
The AWS Management Console is a simple web interface. You may manage your DB events directly from to reassure, with no scripting needed. Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS to get the Amazon RDS assistance.
Amazon RDS Programming
If you are a designer, you can get access to Amazon RDS automatically.
See Amazon RDS Application Programming Interface Reference for additional information.
It is recommended to use AWS Software Development Kits for application development.
The AWS SDKs handle low-level nuances like confirmation, retry logic, and error handling, allowing you to focus on your application logic.
AWS SDKs are available in a variety of languages.
See Tools for Amazon Web Services for additional information.
AWS also provides libraries, test code, educational exercises, and other resources to help you get started quickly.
See Sample Code and Libraries for additional information.
How are Amazon RDS fees calculated?
When using Amazon RDS, you have the option of using on-request DB cases or held DB occurrences.
More information may be found in DB Instance Billing for Amazon RDS.
8. Amazon Web Services Elastic Load Balancer - ELB
Elastic Load Balancer spreads incoming network traffic from applications across many servers, which may be in various Availability Zones.
It aids and improves the fault tolerance of your applications.
It acts as a single point of contact for your customers, ensuring that the application is always accessible.
You may either add or remove instances from the load balancer, which has no effect on your load balancer, and similarly, removing the load balancer has no effect on your Ec2s.
It aids in scaling your load balancer's traffic to your application as it changes over time and also automatically handles the bulk of burden when scaled.
Elastic load balancers have their own DNS domains and are never assigned IP addresses.
We may examine the load balancing activities using DNS.
Load balancer health checks are required to be set up since they bring in the status of the load balancers.
It is essentially the sanity tests that are performed on the servers to determine if they are healthy or sick.
The main health check answers are as follows:
Response timer:
When checking for output, it should return the status in the time allowed, and if there is no response, it should at least throw the error message in the time permitted.
In the allotted period, either an error or a response should be shown.
Interval: The amount of time it takes to distribute load across the instances.
Healthy Threshold: Any output anticipated to be shown within the specified time, as well as servers that are healthy enough to bring in the load management.
Unhealthy Threshold: If the instances are offline or unresponsive, or if the threshold has been exceeded, the load balancer will fail to handle the load.
Elastic Load Balancing Varieties
Elastic Load Balancing is compatible with three kinds of load balancers:
1.Traditional Load Balancer.
2.Load Balancer for Applications
3.Load Balancer for the network
Load Balancer in the Traditional Style
Classic Load Balancer, like any other load balancer, does basic load balancing across many EC2 instances. It operates in accordance with the OSI model's Transport layer (fourth layer). This was mostly utilized before the implementation of the application load balancer.
Load Balancers for Applications
Application Load Balancers operate according to the OSI model's application layer (the seventh layer). Loads are dispersed and controlled in accordance with the application's use.
Load Balancer for Networks
The Network Load Balancer is excellent for balancing TCP traffic loads.
Instances, containers, microservices, and so on may be targets.
It can handle millions of requests per second while maintaining low latency, guaranteeing excellent network performance.
Load balancers have many key characteristics, including the ability to guarantee high availability across several or a single availability zone by spreading incoming traffic.
In reaction to incoming application load, the request processing capacity is increased.
One of the essential aspects of ELB is the health check, which displays or brings in the status of servers. It guarantees the servers' sanity and status checks. Bringing in or detecting the health of Amazon EC2 instances is ideal.
If any of the EC2 instances are discovered to be unhealthy, the load balancer redirects traffic to other servers rather than the defective or unhealthy servers or EC2 instances.
Security features are implemented in load balancers by adding security groups, NACLs (Network Access control lists), or even VPCs (virtual private clouds).
Load Balancer accepts IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Cloud Watch is a monitoring and management solution that tracks all load balancer data.
Logs obtained by cloud monitor will aid in the diagnosis of any application problems or web traffic.
SSL (secure socket layer) certificates handle load balancer encryption, including public key authentication and offloading SSL (secure socket layer) decryption from application instances.
Load Balancing and Autoscaling services may be coupled to guarantee traffic is properly controlled and balanced while applications and services are in place.
Certifications from AWS
AWS is an abbreviation for Amazon Web Services, which is a collection of cloud computing services offered by Amazon.
An AWS certification validates your ability to manage the services offered by AWS.
Cloud computing has recently grown in popularity among businesses due to its advantages, such as increased productivity and lower costs.
Why has AWS remained so popular up to this point?
AWS, or Amazon Web Services, is a subsidiary business of Amazon.com that provides on-demand cloud computing platforms.
These services are available in sixteen different locations across the globe, and they include EC2 (Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud) and S3 (Simple Storage Services). They provide approximately 70 services, including storage, network, database, analytics, and so on.
What Will AWS Look Like in the Next Few Years?
There is hardly any business out there that does not want to build its own public cloud and is not carefully watching AWS or Amazon Web Services. AWS, with its security, brings customers increased database storage and computational capacity. Furthermore, it offers content distribution and other helpful services to businesses to help them develop. Many businesses are currently using, and millions are moving to Amazon Web Services to build complex applications with increased flexibility and dependability.
0 notes
Photo

What is SQL Service ? SQL service refers to Structured Query Language which provides support to create a snapshot from SQL server with the help of a Volume Shadow copy Service (VSS). Accurate InfoSoft offers SQL Backup Services to its customers which comes with its own benefits. A VSS compliant (SQL writer) is used to enable a third-party backup application to use the framework that can be used to backup files. Our firm provides SQL servers to keep all your personal as well as commercial information safe and sound. For more information click here - https://acsonnet.com/it-outsourcing/sql-backup-services/ Follow our social media links : Facebook -https://www.facebook.com/AccurateInfosoftIndia/posts/172104971599707 Pinterest - https://in.pinterest.com/pin/879116789731598298 Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/p/CQvS5obs19H/?utm_source=ig_web_copy_link
0 notes
Text
Cost-effective disaster recovery for Amazon Aurora databases using AWS Backup
You may have stringent regulatory compliance obligations that require an effective multi-Region disaster recovery (DR) plan to mitigate a Region-wide disaster. AWS offers multiple methods to meet these needs, taking into consideration different factors such as recovery time objective (RTO), recovery point objective (RPO), and costs. In this post, I focus on how to keep costs low while meeting the regulatory compliance obligations of a cross-Region DR strategy for Amazon Aurora databases. AWS offers an array of purpose-built database engines, including relational, key-value, document, in-memory, graph, time series, and ledger databases. When it comes to traditional applications with relational databases on the backend, customers choose Amazon Aurora and Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS). Aurora is a MySQL and PostgreSQL-compatible relational database built for the cloud, which combines the performance and availability of traditional enterprise databases with the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of open-source databases. Amazon RDS is a managed service that supports the MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, and Oracle database engines. Planning your DR strategy RTO and RPO metrics are important when designing a DR strategy. RTO represents how long it takes to return to a working state after a disaster, and RPO represents the amount of data (in time units) you could lose when a disaster happens. Using AWS Backup for a cross-Region snapshot copy If RTO and RPO requirements are less stringent, using a cross-Region snapshot and restore is a cost-effective cross-Region DR strategy to comply with regulatory compliance obligations. You can create snapshots of your source Aurora databases and copy them to a supported AWS Region based on a schedule of your choice using AWS Backup. AWS Backup offers a cost-effective, fully-managed, and policy-based service that enables you to copy snapshots to a different Region without having to worry about writing custom scripts and maintaining them. In addition, AWS Backup can also leverage AWS Organizations to implement and maintain a central view of backup policy across resources in a multi-account AWS environment. To start using AWS Backup for managing a cross-Region snapshot copy, create a scheduled backup plan. You can choose pre-existing templates for the backup plans or build your own plan. Building a new plan from the scratch gives you the flexibility to choose backup windows closely aligning with your RTO and RPO requirements, making use of cron expressions. Make sure you choose a schedule that also aligns with the size of your database. The larger the database, the larger the time it takes to create the snapshot and copy it to a different Region. To enable a cross-Region backup copy, you need to make sure you choose the destination Region in the Generate Copy section of the backup plan. You can also choose a backup vault of your choice in the destination Region. If your DR strategy requires copying the snapshots to a different backup vault in a different AWS account in a different Region, AWS Backup gives you that flexibility as well. However, AWS Backup needs permissions to access the external account to copy to your backup. After you create the plan, assign the database resources to the backup plan. You can use tags to assign the resources to the backup plans for simplicity. Snapshots are charged for their storage along with the cross-Region data transfer costs. To estimate your costs, see AWS Backup pricing. Snapshots are incremental in nature, which means the first snapshot of a DB instance contains the data for the full DB instance and subsequent snapshots of the same DB instance only have the data that changed after your most recent snapshot. Depending on the Regions involved and the amount of data to be copied, a cross-Region snapshot copy can take hours to complete and will be a factor to consider for the RPO requirements. You need to take this into account when you estimate the RPO of this DR strategy. If you have strict RTO and RPO requirements, you should consider a different DR strategy, such as Amazon Aurora Global Database . Using Aurora Global Database Aurora Global Database is designed for globally distributed applications, allowing a single Aurora database to span multiple AWS Regions. It provides disaster recovery from Region-wide outages and enables low-latency global reads by allowing reads from the nearest Aurora cluster. Aurora Global Database uses the dedicated infrastructure in Aurora’s purpose-built storage layer to handle replication across Regions. Dedicated replication servers in the storage layer handle the replication, which allows you to meet enhanced recovery and availability objectives without compromising database performance. Aurora Global Database provides the following benefits: Fast global failover to secondary Regions, typically up to a few minutes, which helps achieve a low RTO Low replication lag across Regions, typically less than 1 second, which helps achieve a low RPO Replication performed by Aurora Global Database has no performance impact on the primary DB cluster Aurora Global Database allows you to achieve good RTO and RPO because of its design, which employs physical storage-level replication. The secondary Region instance of the global database doesn’t replay data-modifying statements. Instead, it performs continuous parallel recovery at the storage level in the secondary Region, enabling it to achieve sub-second latency. This also reduces replication overhead on the primary. With Aurora Global Database, you pay for compute, storage, and replicated write I/O in primary and secondary Regions, along with the data transfer charges from the primary to secondary Region. To Summarize, Aurora Global database can be configured to run nodes in the destination region which would help achieve a better RTO and a faster DR. You can also run the Aurora Global database without a node in the destination region, but that would result in a longer RTO as you would have to spin up a new instance during a Disaster. Carefully estimate the strategy based on your DR goals and pricing. To estimate your pricing, see Amazon Aurora Pricing. Testing your cross-Region DR strategy A good DR strategy needs to be tested to make sure it meets the RTO, RPO, and cost requirements, and any regulatory compliance obligations. Regular testing of your DR strategy helps you identify potential issues or gaps and take corrective action to stay prepared for unforeseen events. For Amazon Aurora Global Database we have recently launched managed planned failover which can be utilized for testing. Conclusion In this post, I explained how to use AWS Backup to create a cross-Region DR strategy for your Amazon Aurora database. The AWS backup based approach is highly cost-effective, employs a backup and restore strategy, and can be designed to comply with cross region backup regulatory requirements. I also explained Aurora Global Database, an Aurora feature which can be utilized when you have strict RTO and RPO requirements. We welcome your feedback and comments. About the author Harish Shenoy is a Senior Technical Account Manager for AWS Enterprise Support. He has been working with various Database technologies for more than a decade . He is a great advocate of automation and has designed and Implemented multiple Database automation tools in his career. He works with Enterprise customers to design, implement and support complex cloud infrastructures. He is a sports enthusiast who enjoys playing Cricket, Ping Pong, Badminton and Tennis . He spends his free time with his wife and a daughter traveling and exploring different places. https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/database/cost-effective-disaster-recovery-for-amazon-aurora-databases-using-aws-backup/
0 notes