#Salesforce data from primary storage
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
What Is a Cloud Solution?

In today’s dynamic digital environment, cloud solutions have become the backbone of modern enterprise technology. As organizations continue to transition away from traditional IT infrastructure, the demand for scalable, flexible, and efficient computing has pushed cloud-based services to the forefront. But what exactly is a cloud solution, and why has it become so essential for businesses of all sizes?
Understanding the Fundamentals of a Cloud Solution
A cloud solution refers to any on-demand service, application, or resource that is delivered via the internet. Unlike traditional computing, which relies on physical servers and local infrastructure, cloud computing enables users to access technology services—such as storage, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—remotely through a cloud provider.
These solutions are typically hosted in data centers and offered through providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and others. They provide seamless access, cost efficiency, and powerful processing capabilities that are far superior to legacy systems.
Types of Cloud Solutions
To fully understand what a cloud solution entails, it’s crucial to explore its different deployment and service models:
Public Cloud
A public cloud is a cloud environment owned and operated by a third-party provider. These services are delivered over the internet and shared across multiple organizations. Examples include AWS, Azure, and GCP. Public cloud solutions are ideal for businesses that want to eliminate the cost of hardware purchases and reduce IT complexity.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization and can be hosted either on-premises or through a third-party service. It offers enhanced control, security, and customization. Enterprises with strict compliance requirements often opt for private cloud environments.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines both public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This model provides flexibility, scalability, and better deployment options while meeting both operational and regulatory needs.
Multi-Cloud
Multi-cloud refers to the use of more than one cloud service provider. Businesses adopt this strategy to avoid vendor lock-in, increase resilience, and optimize workloads based on performance, cost, and location.
Cloud Service Models
There are three primary cloud service models:
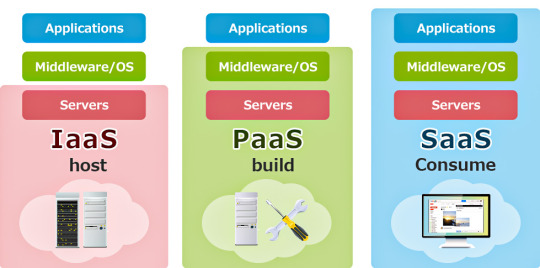
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS delivers fundamental IT resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking through the internet. Businesses can scale up or down based on demand. It eliminates the need to invest in physical hardware, making it a popular choice for startups and enterprises alike.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a framework for developers to build and deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. It includes tools, libraries, and development environments, enhancing productivity and innovation.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS offers ready-to-use applications accessible through a web browser. Common examples include Microsoft 365, Salesforce, Dropbox, and Google Workspace. SaaS eliminates the need for installation, maintenance, and upgrades, delivering a seamless experience to end-users.
Benefits of Cloud Solutions
Embracing cloud solutions provides a multitude of benefits that empower businesses to operate more efficiently and competitively.
1. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud services allow organizations to scale resources up or down based on real-time demands. Whether it’s increasing storage capacity or deploying new applications, everything is done instantly without physical constraints.
2. Cost Efficiency
One of the most attractive advantages of cloud computing is its pay-as-you-go model. Companies only pay for what they use, eliminating the high capital expenditures associated with traditional IT.
3. Business Continuity
Cloud providers offer robust disaster recovery and backup solutions. In the event of a failure, data can be quickly restored, ensuring minimal downtime and business continuity.
4. Enhanced Collaboration
Cloud platforms enable real-time collaboration among teams, regardless of their physical location. File sharing, communication tools, and synchronized data ensure that everyone is working with the most current information.
5. Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Providers manage the underlying infrastructure, including software updates and security patches. This ensures that businesses always have access to the latest features and protections without manual intervention.
6. Security and Compliance
Leading cloud providers invest heavily in security, including encryption, threat detection, and compliance certifications (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001). While concerns still exist, many cloud environments offer superior protection compared to on-premise systems.
Key Use Cases of Cloud Solutions
Cloud solutions serve as the foundation for numerous modern applications and services:
Data Storage & Backup: Secure, scalable cloud storage for large volumes of structured and unstructured data.
Big Data Analytics: Process massive datasets quickly with AI and ML-powered analytics platforms.
Web Hosting: Flexible and reliable hosting services with global reach and redundancy.
Application Development: Cloud-based development environments enhance speed and reduce time to market.
E-commerce: Powering online stores with scalability during peak seasons and integrated payment systems.
Remote Work: Enabling a distributed workforce with access to tools and files anytime, anywhere.
Challenges and Considerations in Cloud Adoption
While cloud solutions offer numerous advantages, there are some challenges businesses must address:
Data Security and Privacy
Data stored in the cloud can be vulnerable to breaches if not adequately secured. Organizations must implement encryption, access control, and security policies to protect sensitive information.
Compliance Requirements
Industries such as finance and healthcare have strict data regulations. Choosing a cloud provider that supports relevant compliance standards is essential.
Latency and Downtime
Although rare, outages do occur. Businesses should assess service level agreements (SLAs) and build redundancy into their cloud architecture.
Vendor Lock-in
Dependence on a single cloud provider can limit flexibility. A multi-cloud strategy may help mitigate this risk.
Future of Cloud Solutions
The future of cloud computing is incredibly promising, driven by advancements in AI, machine learning, edge computing, and quantum computing. Businesses are investing in cloud-native architectures, leveraging microservices, containers, and serverless computing to enhance performance and agility.
As 5G technology matures, the integration of IoT and edge cloud will revolutionize industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics by enabling real-time processing closer to data sources.
Conclusion
A cloud solution is far more than just a buzzword—it is a transformative technology that is reshaping the digital landscape. From cost efficiency and agility to security and innovation, cloud computing empowers businesses to thrive in a competitive market. Whether you're a startup looking to scale or an enterprise seeking digital transformation, adopting the right cloud strategy can unlock unparalleled growth.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Cloud Computing Tutorial for Beginners
Introduction Think of a world where you can use your files, run applications, or even write software without carrying around a high-end computer. That's cloud computing magic — a revolutionary technology that's redefining the manner in which we interact with computers and the web. Be a student, an entrepreneur, or a geek; learning cloud computing opens doors to endless possibilities. In this simple-to-get-start tutorial, we'll de-mystify what cloud computing is, how it works, the main models and services, and why it matters in today's digital age.
What is Cloud Computing? Cloud computing is the provision of computer services — including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence — over the internet ("the cloud") to provide faster innovation, elastic resources, and economies of scale. In straightforward terms, rather than executing software or storing information on your local computer or server, you use a distant system that you access via the internet.
Key Features • On-demand self-service: Compute resources can be provisioned by end-users without human intervention. • Broad network access: Services are made available from anywhere on internet-enabled devices. • Pooling of resources: Cloud providers employ multi-tenant models to host several customers. • Rapid elasticity: Resources can be scaled up or down rapidly depending on demand. • Measured service: You only pay for what you use.
Why Cloud Computing? • Economical: No investment in costly hardware or infrastructure. • Scalable: Simply scale your resources as your needs expand or contract. • Reliable: Cloud providers offer strong disaster recovery and backup solutions. • Accessible: Work anytime, anywhere. • No maintenance: Cloud providers handle updates, security patches, and so forth.
Types of Cloud Deployment Models There are three primary deployment models in cloud computing: 1. Public Cloud • They are offered on the public internet and are used by numerous users. • Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
• Suitable for: Small and medium-sized businesses, start-ups, or individuals who need instant access to assets. 2. Private Cloud • Reserved for a single organization. • Either on-premises deployed or by a third-party provider. • Provides greater control and security but is expensive. 3. Hybrid Cloud • Ties public and private clouds together for greater flexibility. • Businesses can have sensitive data on a private cloud and use public cloud for less sensitive processes.
Cloud Service Models Cloud computing services are mostly classified into three models: 1. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) • Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. • You control the operating system, applications, and data. • Example: AWS EC2, Google Compute Engine. Usage: Storing web site hosting, running virtual machine executions, and backup data storage.
2. PaaS (Platform as a Service) • Provides a platform to customers to write, run, and host applications without the burden of infrastructure management. • Example: Google App Engine, Heroku. Use case: Developing apps fast without worrying about the hardware or operating system. 3. SaaS (Software as a Service) • Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription model. • Example: Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Dropbox. Use case: Having access to software like email, file storage, or CRM without installing it locally. Real-World Examples •Netflix uses AWS to provide videos to hundreds of millions of customers across the globe. •Dropbox allows users to save and share documents through cloud storage. •Salesforce offers a cloud-based CRM application to manage business relationships. •Zoom hosts its video conferencing website on the cloud with high availability. Main Cloud Providers Some of these companies own the marketplace in the cloud: •Amazon Web Services (AWS): Most used and veteran cloud platform. •Microsoft Azure: Biggest in hybrid cloud and enterprise cloud. •Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Focused on data analytics and machine learning. •IBM Cloud, Oracle Cloud, Alibaba Cloud: Other prominent ones. Everyone provides similar essential services but differing tools and cost structures.
Getting Started with Cloud Computing Follows is a step-by-step way in which you can begin to try cloud computing as a beginner: Step 1: Sign Up for a Free Tier Free tiers are provided by all the big cloud providers. For instance: • tAWS Free Tier provides EC2, S3, Lambda, etc. • tAzure Free Account provides $200 credits. • tGoogle Cloud Free Tier provides Compute Engine and BigQuery. Step 2: Explore Basic Services • Install a Virtual Machine (VM): Start a minimal server using EC2 (AWS) or Compute Engine (GCP). • Install Cloud Storage: Store data in S3 (AWS) or Google Cloud Storage. • Test a SaaS App: Mess around with applications such as Google Docs or Trello. Step 3: Learn by Projects Mess around with small projects such as: • Serving a static web page. • Creating a to-do application with Firebase. • Hosting a chatbot on Azure.
Step 4: Study and Certify Cloud certifications can give your career a boost: • AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner • Microsoft Certified: Azure Fundamentals • Google Cloud Digital Leader These beginner certifications prove your grasp of cloud concepts.
Security in Cloud Security is top of the mind for cloud computing. Even as providers put huge investments in security, end users have some responsibilities too. Shared Responsibility Model: •Cloud provider secures infrastructure. •Customer secures user access, data, and application-level settings. Key Practices: •Employ strong authentication (e.g., multi-factor). •Encrypt data in transit and at rest. •Monitor activity on a regular basis and audit it. •Set proper permissions on users.
Challenges of Cloud Computing The cloud is wonderful, but it's not all sunshine: •Downtime: Disruptions may occur in accessing essential services. •Vendor Lock-in: It is complicated and costly to switch vendors. •Security Risks: Erroneous configuration can compromise security. •Cost Overruns: Pay-as-you-go arrangements become prohibitively expensive if left unmonitored. It's great to be aware of these challenges in order to make smart decisions. The Future of Cloud Computing Cloud computing just keeps improving with fascinating trends such as: •Serverless computing: Code is the focus for developers, while the infrastructure is handled by the provider. •Edge computing: Processing data close to the source (e.g., IoT devices) for enhanced performance. •AI and ML Integration: Cloud platforms allow for powerful tools for model training and deployment. •Multi-cloud strategies: Organizations use multiple providers to avoid dependence on a sole one. Final Thoughts Cloud computing is not a fad buzzword — it's actually the backbone of contemporary digital life. Whether streaming entertainment and smart homes or business applications and mobile phones, the cloud permeates nearly all aspects of everyday life. By learning the basics now, you're setting yourself up to take advantage of one of the greatest technology shifts of the 21st century. If you love development, data, or infrastructure, the cloud has something for you.
0 notes
Text
Explore how ADF integrates with Azure Synapse for big data processing.
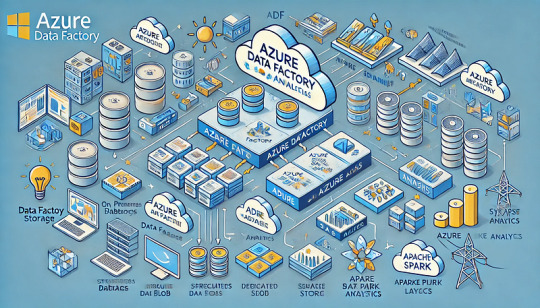
How Azure Data Factory (ADF) Integrates with Azure Synapse for Big Data Processing
Azure Data Factory (ADF) and Azure Synapse Analytics form a powerful combination for handling big data workloads in the cloud.
ADF enables data ingestion, transformation, and orchestration, while Azure Synapse provides high-performance analytics and data warehousing. Their integration supports massive-scale data processing, making them ideal for big data applications like ETL pipelines, machine learning, and real-time analytics. Key Aspects of ADF and Azure Synapse Integration for Big Data Processing
Data Ingestion at Scale ADF acts as the ingestion layer, allowing seamless data movement into Azure Synapse from multiple structured and unstructured sources, including: Cloud Storage: Azure Blob Storage, Amazon S3, Google
Cloud Storage On-Premises Databases: SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL Streaming Data Sources: Azure Event Hubs, IoT Hub, Kafka
SaaS Applications: Salesforce, SAP, Google Analytics 🚀 ADF’s parallel processing capabilities and built-in connectors make ingestion highly scalable and efficient.
2. Transforming Big Data with ETL/ELT ADF enables large-scale transformations using two primary approaches: ETL (Extract, Transform, Load): Data is transformed in ADF’s Mapping Data Flows before loading into Synapse.
ELT (Extract, Load, Transform): Raw data is loaded into Synapse, where transformation occurs using SQL scripts or Apache Spark pools within Synapse.
🔹 Use Case: Cleaning and aggregating billions of rows from multiple sources before running machine learning models.
3. Scalable Data Processing with Azure Synapse Azure Synapse provides powerful data processing features: Dedicated SQL Pools: Optimized for high-performance queries on structured big data.
Serverless SQL Pools: Enables ad-hoc queries without provisioning resources.
Apache Spark Pools: Runs distributed big data workloads using Spark.
💡 ADF pipelines can orchestrate Spark-based processing in Synapse for large-scale transformations.
4. Automating and Orchestrating Data Pipelines ADF provides pipeline orchestration for complex workflows by: Automating data movement between storage and Synapse.
Scheduling incremental or full data loads for efficiency. Integrating with Azure Functions, Databricks, and Logic Apps for extended capabilities.
⚙️ Example: ADF can trigger data processing in Synapse when new files arrive in Azure Data Lake.
5. Real-Time Big Data Processing ADF enables near real-time processing by: Capturing streaming data from sources like IoT devices and event hubs. Running incremental loads to process only new data.
Using Change Data Capture (CDC) to track updates in large datasets.
📊 Use Case: Ingesting IoT sensor data into Synapse for real-time analytics dashboards.
6. Security & Compliance in Big Data Pipelines Data Encryption: Protects data at rest and in transit.
Private Link & VNet Integration: Restricts data movement to private networks.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Manages permissions for users and applications.
🔐 Example: ADF can use managed identity to securely connect to Synapse without storing credentials.
Conclusion
The integration of Azure Data Factory with Azure Synapse Analytics provides a scalable, secure, and automated approach to big data processing.
By leveraging ADF for data ingestion and orchestration and Synapse for high-performance analytics, businesses can unlock real-time insights, streamline ETL workflows, and handle massive data volumes with ease.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/azure-data-factory-training-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
Comprehensive Insights into the CRM All-in-One Software Market: Trends Driving Business Optimization - UnivDatos
According to a new report by UnivDatos Market Insights, the CRM All-in-One Software Market was valued at approximately USD 25 Billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a substantial CAGR of around 13% during the forecast period (2024-2032). This is mainly attributed to increasing acquisitions and strategic partnerships, as well as technological integration, becoming vital trends due to higher demands for products with broader characteristics and the necessity to cover a wider range of consumers. All these moves increase the ability to provide services that are supported by the application of AI, analytics, and automation. For instance, on September 05, 2024, Salesforce (NYSE: CRM), the world's #1 AI CRM, announced it had signed a definitive agreement to acquire Own Company, a leading provider of data protection and data management solutions. Own empowers organizations to ensure the availability, security, and compliance of mission-critical data, while unlocking new ways to gain deeper insights from this data.
Request To Download Sample of This Strategic Report - https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=68215&utm_source=LinkSJ&utm_medium=Snehal&utm_campaign=Snehal&utm_id=snehal
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) Surge in the Market
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) are expected to grow with a significant CAGR in the forecast period (2024-2032). This is mainly because of looking for low-cost and easily implementable strategies that enhance the efficiency of customer management. This segment is in the process of migrating to cloud solutions to reduce expenses and integrate the ability to expand and access remotely as they expand. SMEs prefer intuitive interfaces and automation, aspects that allow them to increase customer interactivity with little fuss involved. Also, the integration of CRM with e-commerce and mobile platforms strengthens them and offers them opportunities to deliver effective customer experience.
For instance, on March 12, 2024, Salesforce announced the general availability of Pro Suite, a flexible, scalable, all-in-one offering to help small businesses get started and scale on the #1 AI CRM. Powered by Salesforce’s Einstein 1 Platform and Data Cloud, Pro Suite helps customers grow their operations with one ready-to-use and easy-to-implement solution.
Here are five examples of government regulations, laws, and legal frameworks that influence the CRM All-in-One Software market:
· General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – European Union. This regulation went into effect on May 25, 2018. It specifies guidelines for the collection, storage and processing of personal information of customers for businesses that operate in the European Economic Area (EEA), and also for those outside the EU who deal with citizens of the EEA.
· In addition, the law regulates the mechanisms for transferring the personal data of EU citizens to third countries. On July 16, 2020, the Court of Justice for the European Union (CJEU) declared the EU-US Privacy Shield invalid and affirmed that the Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) remain a valid transfer mechanism. Simply put, it means that if a business uses CRM or any other software that stores the personal data of EU customers in the US, this software has to rely on the SCCs for data transfers.
· Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) – Canada. This act is the primary data protection law that covers all private sector organizations which manage any type of personal information.
· The Privacy Act 1988 (Privacy Act) – Australia. This law regulates the proper collection, management, storage and disclosure of personal information, both in the private and public sectors.
· California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (CCPA), Colorado Privacy Act, Utah Consumer Privacy Act and Consumer Data Protection Act (Virginia) – are the four primary laws concerning data protection in the US, as this country does not yet have federal data protection legislation.
Ask for Report Customization - https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=68215&utm_source=LinkSJ&utm_medium=Snehal&utm_campaign=Snehal&utm_id=snehal
According to the report, the impact of CRM All-in-One Software has been identified to be high for the Asia-Pacific area. Some of how this impact has been felt include:
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to grow at a notable CAGR in the forecast period (2024-2032) because of increasing demand for streamlined customer management solutions across industries. Adding to this, cloud-based CRM applications are preferred for its portability and minimum client cost and this is best suitable for the countries where the level of IT growth is dissimilar. The use of artificial intelligence to support growth is therefore enhanced by AI for auto insights and customer personalization, which are crucial for customer interactions. Moreover, the continuity with the use of mobile and social media is also considered as the companies can extend their market and operation to new levels and conditions suited for the Asia-Pacific region consumer’s behavior.
On March 1, 2023, Exeevo a global enterprise SaaS leader focused on the Life Sciences industry, announced its expanded partnership with Sanofi SA (NASDAQ: SNY) in China launching their next-generation unified omnichannel OneCRM customer relationship management (CRM) platform. This new solution OneCRM propels Sanofi China to the forefront of intelligent innovation as a digital-first market leader in China. It allows them to deliver outstanding customer experience and corresponding commercial results. Critically, Exeevo’s Omnipresence was the only solution that adhered to Chinese data privacy regulations including the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL).
0 notes
Text
Why Web Applications Are the Future of Digital Transformation

In a highly advanced technological environment, competition is very severe for organisations. This has led to the adoption of digital transformation as a strategic foundation for change, as it accelerates productivity improvement, optimizes customers’ satisfaction, and minimises overhead expenses. Among the factors that contribute to this change, the shift to web applications has been defined as one of the primary prerequisites. Since these tools offer unique flexibility, scalability, and accessibility, they remain an essential component of the digital world.
If you’re curious about why web applications are transforming industries worldwide, here are the top reasons you need to know:
1. Accessibility from Anywhere, Anytime

Web applications provide easy accessibility from anywhere as long as the internet connection is available. This is different from other software that needs installation on the host system; a web application can be run from any browser.
Why It Matters: Organizations can encourage the work-from-home model, the multicultural workforce, and customer satisfaction without limitations.
Example: Google Workspace, as well as Slack, have made it easy for employees to be productive and work together, especially when working remotely.
2. Cost-Effective and Easy to Maintain

Web applications cut IT infrastructure costs to a great deal. Unfortunate for desktop applications, they require frequent updates and extensive installation procedures; on the other hand, web apps are updated by their providers, centrally.
Why It Matters: Companies use less money on financial investments in computer equipment and software update charges and can get technical support for customers while guaranteeing that the users will be dealing with the latest version.
Example: Compared to other types of implementation approaches, the application of SaaS offers consistent upgrades that are also time- and cost-efficient — look, for instance, at Salesforce.
3. Enhanced Security

Modern web applications come with robust security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and cloud-based storage, to protect sensitive data.
Why It Matters: It benefits both businesses and end users in the way that users can ensure their data is secure without the need for high levels of automation.
Example: Software as a service, such as Microsoft Azure, has measures that would ensure security in its operations.
4. Scalability to Meet Growing Needs

Web applications are designed to grow with your business. They can handle increasing traffic, expanding features, and additional users without major overhauls.
Why It Matters: They do not have to invest in new tools as they grow; through a symbiotic relationship, the system matures together with the companies.
Example: Web stores implemented with the help of solutions such as Shopify can easily process thousands of transactions per day and work stably.
5. Improved User Experience

Web applications focus on offering intuitive user interfaces and responsive design. Whether accessed from mobile devices, tablets, or desktops, they ensure a consistent and smooth experience.
Why It Matters: Customers and employees respond to clear and easy solutions. A transparent and smooth interaction process increases both the efficiency and the happiness level.
Example: Online banking applications have brought another dimension to the disbursement of finance with fast, customer-friendly applications.
6. Integration with Other Digital Tools

Web applications can be easily connected with other systems like a CRM, ERP, and different analysis tools. The integration is such that it supports the smooth flow of activities.
Why It Matters: Businesses can connect all their tools to automate processes, enhance insights, and eliminate manual work.
Example: Platforms like Zapier and APIs enable data flow between applications, saving time and boosting productivity.
7. Faster Development and Deployment

Web application building and deployment are faster than conventional software development. Today there is a great number of frameworks and cloud services that allow implementing agile development processes.
READ MORE- https://www.precisio.tech/why-web-applications-are-the-future-of-digital-transformation/
#technology#web design#web development#software development#digitalmarketing#it services#information technology
0 notes
Text
SaaS-Based vs Cloud-Based: What’s the Difference?
Two terminologies that often get tossed around are saas cloud applications (Software as a Service) and Cloud-Based. While they might seem interchangeable, these terms represent distinct facets of the digital space, each offering a unique set of advantages and applications.
The cloud is a space where data and applications float effortlessly, accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. It’s a virtual space that eliminates the need for physical infrastructure, allowing businesses and individuals to store, process, and access their information without the constraints of physical servers.
At its core, Cloud-Based refers to the delivery of computing services – from storage to processing power – over the internet. It is a comprehensive umbrella term encompassing a variety of services, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and, of course, Software as a Service (SaaS).
This offers virtualized computing resources over the internet. Companies can rent virtual machines and other resources rather than investing in and maintaining physical servers.
A level up, PaaS provides a platform allowing developers to build, deploy, and scale applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for users to install, maintain, or update the software on their devices.
SaaS-Based takes center stage when it comes to delivering specific software applications through the cloud. This means users can access software applications without the hassle of installation, updates, or maintenance. Popular examples include Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Salesforce.
One of the key advantages of SaaS-Based solutions is accessibility. Users can access applications from any device with an internet connection, fostering collaboration and flexibility.
Forget the days of manual updates. SaaS applications are maintained and updated by the service provider, ensuring users always have access to the latest features and security patches.
SaaS offers scalability on demand. Whether a business is growing rapidly or experiencing a temporary surge, SaaS applications can adapt to changing needs without requiring significant infrastructure investments.
While SaaS-Based and Cloud-Based are interconnected, the difference lies in their scope and application. Cloud-Based serves as the overarching model, providing the infrastructure and platforms, while SaaS-Based refines the experience, focusing specifically on delivering software applications smoothly.
When choosing between the two, it’s crucial to assess your needs. If you’re seeking a complete solution that encompasses infrastructure, platforms, and software, then Cloud-Based might be your go-to. However, if your primary goal is smooth access to specific applications without the burden of maintenance, then SaaS-Based is the star of the show.
In conclusion, understanding the complexities of SaaS-Based vs. Cloud-Based is crucial in navigating the digital space.. As technology continues to advance, these terms will undoubtedly evolve, but for now, they remain essential in shaping how we interact with, access, and leverage digital tools and cloud-saas solutions.
0 notes
Text
Cloud services

Cloud services have become essential for individuals and businesses looking to store, manage, and process data efficiently. At its core, cloud services computing provides access to shared computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, and software, over the internet. This eliminates the need for businesses to invest in expensive infrastructure or manage complex IT systems on-site.
Types of Cloud Services
Cloud services come in three primary models, each serving different needs:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This is the most basic form of cloud service, providing virtualized computing resources like servers, storage, and networks. Companies can scale up or down according to their needs, reducing costs. Popular examples of IaaS include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS provides a platform allowing developers to build, test, and deploy applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. This accelerates development cycles and ensures scalability. Services like Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure offer PaaS solutions.
Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers fully functional software applications over the internet. Users can access these services via a web browser without installing or maintaining them. Examples include Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Salesforce.
Benefits of Cloud Services
Cost-Efficiency: One of the biggest advantages of cloud services is the reduction in hardware costs. Businesses pay only for the resources they use, which reduces the need for large upfront investments in IT infrastructure.
Scalability: Cloud services allow businesses to scale their operations rapidly. As demand grows, companies can easily increase their computing power, storage, or bandwidth, ensuring they can handle growth without disruption.
Flexibility and Accessibility: Since cloud services are accessible over the internet, employees can work from anywhere, facilitating remote work and collaboration. This flexibility has become particularly crucial in today’s globalized business environment.
Security and Reliability: Leading cloud providers invest heavily in security measures such as encryption, identity management, and regular updates, ensuring data protection. Additionally, cloud services often come with disaster recovery plans, minimizing the risk of data loss.
Conclusion
Cloud services have transformed the way businesses operate, offering unmatched flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. As companies continue to innovate and expand, cloud computing remains a critical tool in navigating the modern digital landscape. Embracing cloud services can streamline operations, enhance security, and foster growth in an increasingly competitive world.
0 notes
Text
Embrace the Future: Exploring the Power and Potential of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has emerged as a meaningful change in today's quickly expanding technology landscape, transforming the way individuals and organizations manage and use IT resources. The flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness that come with having access to computing power, storage, and apps via the internet instead of local servers or personal devices are unmatched. This article explores the fundamentals of cloud computing, as well as its advantages, important models, and potential applications going forward.

Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of numerous services over the internet, including data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software. The "cloud" symbolizes the internet, and the technology enables users to access and store data on remote servers rather than on local hard drives or servers. This shift from traditional on-premises IT infrastructure to cloud-based services offers several advantages.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing
1. Cost Efficiency:
One of the primary advantages of cloud computing is cost efficiency. Businesses no longer need to invest heavily in physical infrastructure, hardware, and maintenance. Cloud service providers offer a pay-as-you-go model, allowing companies to pay only for the resources they use. This model significantly reduces capital expenditure and operational costs.
2. Scalability and Flexibility:
Cloud computing provides unmatched scalability and flexibility. Businesses can quickly scale up or down based on their needs without worrying about over-provisioning or under-provisioning resources. This flexibility is crucial for managing varying workloads and meeting the demands of peak periods.
3. Accessibility and Collaboration:
With cloud computing, data and applications are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility promotes collaboration, as teams can work together in real-time, regardless of their geographical location. Cloud-based tools and platforms facilitate seamless communication and project management.
4. Disaster Recovery and Data Backup:
Cloud service providers typically offer robust disaster recovery and data backup solutions. In the event of hardware failure, natural disasters, or cyberattacks, businesses can quickly restore their data and resume operations. This resilience is critical for maintaining business continuity.
5. Security:
Contrary to common concerns, cloud computing can enhance security. Reputable cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and regular security audits. They also ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations, offering a higher level of security than many on-premises solutions.
Cloud Computing Models
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It offers fundamental infrastructure such as virtual machines, storage, and networks. Users can rent these resources on a pay-as-you-go basis. Popular IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS):
PaaS offers a platform that allows developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure. It provides tools and services for application development, including operating systems, databases, and development frameworks. Examples of PaaS providers are Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS):
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access these applications through web browsers, eliminating the need for installation and maintenance. Common SaaS applications include customer relationship management (CRM) systems like Salesforce, email services like Gmail, and productivity tools like Microsoft Office 365.
The Future of Cloud Computing
1. Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies:
As businesses continue to leverage cloud computing, many are adopting hybrid and multi-cloud strategies. A hybrid cloud combines on-premises infrastructure with cloud services, offering the best of both worlds. Multi-cloud strategies involve using services from multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and enhance redundancy.
2. Edge Computing:
Edge computing is an emerging trend that complements cloud computing. It involves processing data closer to its source, at the "edge" of the network, to reduce latency and improve performance. This is particularly important for applications requiring real-time processing, such as IoT devices and autonomous vehicles.
3. AI and Machine Learning Integration:
Cloud computing is driving the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into various applications. Cloud platforms offer AI and ML services that enable businesses to build intelligent applications without investing in specialized hardware. This democratization of AI and ML is accelerating innovation across industries.
4. Enhanced Security Measures:
As cyber threats evolve, cloud providers are continuously enhancing their security measures. Advanced encryption, zero-trust architectures, and AI-driven security analytics are some of the innovations ensuring that cloud environments remain secure. Businesses can expect even more robust security features in the future.
5. Sustainable Cloud Solutions:
With increasing awareness of environmental impact, cloud providers are focusing on sustainability. Green cloud computing initiatives aim to reduce the carbon footprint of data centers through energy-efficient practices and renewable energy sources. This shift towards eco-friendly cloud solutions aligns with global sustainability goals.
Conclusion:
The IT environment has been completely changed by cloud computing, which provides many advantages such increased security, scalability, affordability, and accessibility. Businesses using cloud technology should anticipate more advancements and developments that will shape the cloud computing landscape in the future. AI and edge computing to hybrid and multi-cloud techniques integration, the possibilities are vast. By leveraging cloud computing, businesses can stay competitive, agile, and prepared for the challenges of tomorrow. Embrace the future with cloud computing and unlock the full potential of your digital transformation journey.
0 notes
Text
Demystifying the Cloud: An Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has become a ubiquitous term in today's digital world. But for those unfamiliar with the concept, it can sound a bit nebulous. This article aims to shed light on what cloud computing is and how it can benefit your organization. For better understand for cloud computing you can goto the simcolab.
What is Cloud Computing?

Imagine accessing computing resources like storage, processing power, databases, and even software applications, not from physical servers on-site, but on-demand over the internet. That's the essence of cloud computing. Cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offer these resources as services, eliminating the need for upfront investment in hardware and software.
Why Consider Cloud Computing?
There are several compelling reasons to embrace cloud computing:
Cost Savings: Eliminate the upfront costs of hardware, software licenses, and IT infrastructure management. Pay only for the resources you use with a pay-as-you-go model offered.
Scalability: Easily scale your computing resources up or down to meet fluctuating demands. No more struggling with over- or under-provisioning of resources.
Increased Agility: Cloud computing fosters a more agile environment. New applications and services can be deployed quickly, allowing businesses to adapt to changing market conditions.
Improved Disaster Recovery: Cloud providers offer robust disaster recovery solutions. In the event of an outage, your data and applications remain accessible, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
Platform Independence: Access applications and data from any device with an internet connection. Cloud computing removes the constraints of location and hardware compatibility.
Understanding Cloud Service Models
Cloud computing offers a variety of Cloud service models to cater to different needs. Here's a breakdown of the three main ones:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Rent the fundamental building blocks of computing, such as servers, storage, and networking. This provides the most control and flexibility, but also requires the most technical expertise to manage.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Develop, deploy, and manage applications on a pre-configured platform. PaaS offerings often include tools and services for development, database management, and security.
Software as a Service (SaaS): Access and use software applications directly over the internet. This is the most user-friendly option, as there is no software to install or maintain. Popular examples include Salesforce for CRM and Dropbox for file storage.
Choosing the Right Cloud Deployment Model
Cloud deployment models determine how cloud services are delivered. The three primary models are:
Public Cloud: Resources are shared among multiple users and offered by cloud service providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP. This offers the most cost-effective option, but security and control may be considerations.
Private Cloud: Resources are dedicated to a single organization and can be managed internally or by a third party. This provides the highest level of control and security, but comes at a higher cost.
Hybrid Cloud: A combination of public and private clouds allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both. For instance, public cloud can be used for non-critical workloads, while private cloud can be used for sensitive data and applications.
Security Considerations
Data security and privacy are paramount concerns when considering cloud computing. It's crucial to choose a reputable cloud provider with robust security measures in place. Organizations also need to implement access control protocols and ensure compliance with relevant data privacy regulations.
Cloud Adoption Strategies
Transitioning to the cloud requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key steps:
Identify Cloud-Suitable Workloads: Not all applications and data are suited for the cloud. Evaluate your needs and prioritize workloads that can benefit most from scalability and agility.
Develop a Migration Plan: Craft a comprehensive plan for migrating workloads to the cloud. This includes data migration strategies, security considerations, and testing procedures.
Manage Costs: Cloud service providers offer various pricing models. Carefully monitor your cloud usage and optimize your costs by leveraging features like reserved instances and spot instances.
Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor your cloud environment to identify inefficiencies and optimize resource utilization. Cloud services offer tools and dashboards to help you track performance and costs.
The Future of Cloud Computing

Cloud computing is a rapidly evolving landscape. Emerging trends like serverless computing, which removes server management overhead, and edge computing, which brings processing closer to data sources, will continue to shape the future.
0 notes
Text
Using Azure Data Factory with Azure Synapse Analytics

Using Azure Data Factory with Azure Synapse Analytics
Introduction
Azure Data Factory (ADF) and Azure Synapse Analytics are two powerful cloud-based services from Microsoft that enable seamless data integration, transformation, and analytics at scale.
ADF serves as an ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) or ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) orchestration tool, while Azure Synapse provides a robust data warehousing and analytics platform.
By integrating ADF with Azure Synapse Analytics, businesses can build automated, scalable, and secure data pipelines that support real-time analytics, business intelligence, and machine learning workloads.
Why Use Azure Data Factory with Azure Synapse Analytics?
1. Unified Data Integration & Analytics
ADF provides a no-code/low-code environment to move and transform data before storing it in Synapse, which then enables powerful analytics and reporting.
2. Support for a Variety of Data Sources
ADF can ingest data from over 90+ native connectors, including: On-premises databases (SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, etc.) Cloud storage (Azure Blob Storage, Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage) APIs, Web Services, and third-party applications (SAP, Salesforce, etc.)
3. Serverless and Scalable Processing With Azure Synapse, users can choose between:
Dedicated SQL Pools (Provisioned resources for high-performance querying) Serverless SQL Pools (On-demand processing with pay-as-you-go pricing)
4. Automated Data Workflows ADF allows users to design workflows that automatically fetch, transform, and load data into Synapse without manual intervention.
5. Security & Compliance Both services provide enterprise-grade security, including: Managed Identities for authentication Role-based access control (RBAC) for data governance Data encryption using Azure Key Vault
Key Use Cases
Ingesting Data into Azure Synapse ADF serves as a powerful ingestion engine for structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data sources.
Examples include: Batch Data Loading: Move large datasets from on-prem or cloud storage into Synapse.
Incremental Data Load: Sync only new or changed data to improve efficiency.
Streaming Data Processing: Ingest real-time data from services like Azure Event Hubs or IoT Hub.
2. Data Transformation & Cleansing ADF provides two primary ways to transform data: Mapping Data Flows: A visual, code-free way to clean and transform data.
Stored Procedures & SQL Scripts in Synapse: Perform complex transformations using SQL.
3. Building ETL/ELT Pipelines ADF allows businesses to design automated workflows that: Extract data from various sources Transform data using Data Flows or SQL queries Load structured data into Synapse tables for analytics
4. Real-Time Analytics & Business Intelligence ADF can integrate with Power BI, enabling real-time dashboarding and reporting.
Synapse supports Machine Learning models for predictive analytics. How to Integrate Azure Data Factory with Azure Synapse Analytics Step 1: Create an Azure Data Factory Instance Sign in to the Azure portal and create a new Data Factory instance.
Choose the region and resource group for deployment.
Step 2: Connect ADF to Data Sources Use Linked Services to establish connections to storage accounts, databases, APIs, and SaaS applications.
Example: Connect ADF to an Azure Blob Storage account to fetch raw data.
Step 3: Create Data Pipelines in ADF Use Copy Activity to move data into Synapse tables. Configure Triggers to automate pipeline execution.
Step 4: Transform Data Before Loading Use Mapping Data Flows for complex transformations like joins, aggregations, and filtering. Alternatively, perform ELT by loading raw data into Synapse and running SQL scripts.
Step 5: Load Transformed Data into Synapse Analytics Store data in Dedicated SQL Pools or Serverless SQL Pools depending on your use case.
Step 6: Monitor & Optimize Pipelines Use ADF Monitoring to track pipeline execution and troubleshoot failures. Enable Performance Tuning in Synapse by optimizing indexes and partitions.
Best Practices for Using ADF with Azure Synapse Analytics
Use Incremental Loads for Efficiency Instead of copying entire datasets, use delta processing to transfer only new or modified records.
Leverage Watermark Columns or Change Data Capture (CDC) for incremental loads.
2. Optimize Performance in Data Flows Use Partitioning Strategies to parallelize data processing. Minimize Data Movement by filtering records at the source.
3. Secure Data Pipelines Use Managed Identity Authentication instead of hardcoded credentials. Enable Private Link to restrict data movement to the internal Azure network.
4. Automate Error Handling Implement Retry Policies in ADF pipelines for transient failures. Set up Alerts & Logging for real-time error tracking.
5. Leverage Cost Optimization Strategies Choose Serverless SQL Pools for ad-hoc querying to avoid unnecessary provisioning.
Use Data Lifecycle Policies to move old data to cheaper storage tiers. Conclusion Azure Data Factory and Azure Synapse Analytics together create a powerful, scalable, and cost-effective solution for enterprise data integration, transformation, and analytics.
ADF simplifies data movement, while Synapse offers advanced querying and analytics capabilities.
By following best practices and leveraging automation, businesses can build efficient ETL pipelines that power real-time insights and decision-making.
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/azure-data-factory-training-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
An Insight into SaaS & BaaS: Revolutionizing Everything From Cloud to Cash

Digital transformation is no longer a buzzword. It has become a reality, a necessity. In this rapidly evolving technological landscape, businesses are tirelessly trying to remain agile, innovative, and customer-centric. In this endeavour, Software as a Service (SaaS) and Banking as a Service (BaaS) have emerged as powerful platforms, driving the next wave of the digital revolution.
What is SaaS?
Software as a Service (SaaS), is a kind of cloud computing that provides users with access to software applications over the Internet. These applications are hosted on a cloud and managed by the service provider, relieving users from the need to install, manage, or update the software on their local servers or computers.
Why is SaaS the Future and Why is it Used?
The potential of SaaS stretches far beyond ease of use. By eliminating the need for hardware acquisition, provisioning, and maintenance, it significantly reduces upfront costs. Flexible payments make it an affordable solution for businesses of all sizes. It also provides scalable usage, allowing companies to scale up or down based on their requirements.
Moreover, automatic updates ensure users always have access to the latest features and security measures. Its accessibility from any internet-connected device makes it a perfect fit for today’s remote working culture. Given these advantages, it is no surprise that SaaS is being hailed as the future of software delivery.
SaaS Integration and the SaaS Business Model

SaaS platforms are designed for seamless integration into the existing IT infrastructure. It enables businesses to focus on their core competencies, leaving software-related issues to the SaaS provider.
The SaaS business model primarily relies on subscription-based revenue, with clients paying a fixed amount periodically to access the service. This ensures a steady revenue stream for providers and makes budgeting easier for clients.
On-Premise Vs SaaS: Why SaaS is Superior?
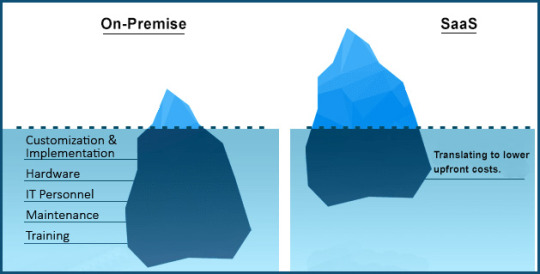
On-premise software comes with substantial initial costs, including hardware, software licenses, and installation, not to mention the ongoing costs of maintenance, updates, and IT staff.
SaaS, on the other hand, is subscription-based, translating to lower upfront costs. The fact that it is maintained by the service provider further eliminates the need for maintenance and IT staffing costs. Also, SaaS solutions are scalable, customizable, accessible from anywhere, and always up-to-date, making them the superior choice for most businesses.
SaaS Products and Companies we all know
The SaaS market is crowded with many players, each one offering its unique value proposition. Top global SaaS companies include Salesforce, known for its customer relationship management (CRM) software; Adobe, with its creative and multimedia software suite; Microsoft, offering a range of productivity tools and business solutions; and Google, with its robust G Suite of Office applications.
The Role of IaaS and PaaS along with SaaS
In the cloud computing realm, SaaS is one of the three primary service models, along with Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS).
IaaS virtualized computing resources over the internet. IaaS provides physical and virtual resources that are used to build a cloud. These resources include servers, network hardware, storage, and data center space. Users can rent these resources as per their needs, thereby saving on the capital expenditure that would have been incurred if they were to set up their own infrastructure. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure are some of the examples of Iaas.
PaaS delivers a platform for users to develop, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with application development. The PaaS provider manages the responsibility of housing the software and hardware components on their own infrastructural setup. As a result, developers can focus more on writing the code and the business logic, and less on managing hardware, software updates, and other routine IT management tasks. Examples of PaaS include Google App Engine, Heroku, and IBM Cloud Foundry.
SaaS delivers software applications over the web. IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the Internet, and PaaS provides a platform for the creation and deployment of applications. Together, these models comprise the backbone of cloud computing, each serving distinct purposes but also complementing each other.
SaaS Uses in Different Sectors
Digital Marketing
Marketing teams leverage SaaS to automate tasks, streamline workflows, create content and improve campaign effectiveness. SaaS tools assist in email marketing, social media management, customer relationship management (CRM), and various forms of analytical tracking. These tools enable marketers to measure campaign effectiveness, user engagement, and return on investment in real time.
Human Resource
HR professionals use SaaS for recruitment processes, streamline employee onboarding, assist in performance tracking, and even manage payroll. The advantage of these solutions lies in their ability to centralize data, allowing for seamless management and offering employees user-friendly self-service options. This promotes HR efficiency and boosts employee satisfaction.
Financial Sector
HR professionals use SaaS for recruitment processes, streamline employee onboarding, assist in performance tracking, and even manage payroll. The advantage of these solutions lies in their ability to centralize data, allowing for seamless management and offering employees user-friendly self-service options. This promotes HR efficiency and boosts employee satisfaction.
Education Sector
In education, SaaS facilitates online learning, course management, and collaboration among students and teachers. By providing extensive learning resources and a platform for interactive learning, SaaS tools enhance both teaching methodologies and the overall learning experience.
Healthcare
SaaS in healthcare provides numerous benefits, from improving patient care to optimizing operational processes. Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems, telehealth platforms, patient portals, and medical billing software are common SaaS applications in healthcare. They help streamline workflows, improve data accessibility, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Retail
In the retail sector, SaaS solutions offer a multitude of tools to improve both the customer experience and the retailer’s operations. E-commerce platforms, inventory management systems, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools, and analytics software are some of the SaaS solutions used in this sector. They help businesses optimize their supply chain, gain customer insights, and manage their online presence effectively.
What is BaaS?
Banking as a Service (BaaS) is a model where financial services capabilities are provided over the Internet via APIs. With BaaS, fintech companies, retailers, and other businesses can integrate banking services into their own products, without the need to establish a full-fledged bank.
Why is BaaS the Future of Banking?
BaaS holds the promise of a more inclusive and innovative financial services sector. Enabling non-banks to offer financial services, encourages competition, promotes innovation and potentially leads to better services for consumers. As customer expectations evolve, the demand for integrated, seamless financial services will only grow, making BaaS an increasingly attractive proposition.
How Does BaaS Work and How is it Used?
BaaS operates through APIs, which allow third parties to access banking services such as payments, transfers and account management on their platforms. Managed by a licensed bank, this infrastructure saves businesses from building complex banking functions from scratch.
Primarily utilized by fintech firms, BaaS facilitates services like digital wallets, payment gateways, and lending platforms. As we all know there is no finance without technology nowadays. This synergistic integration of existing platforms provides a smooth and convenient customer experience. Any business can leverage BaaS to integrate banking services, differentiate itself in the market, and enhance customer service.
BaaS Integration with Other Technologies
BaaS can be integrated with other technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain to offer advanced financial solutions. For example, AI can be used for personalized banking services, machine learning for predictive analysis in lending decisions, and blockchain for secure, transparent transactions. These integrations enhance the capabilities of BaaS platforms, opening up new paths for innovation.
The Intersection of SaaS and BaaS

SaaS and BaaS are both service-based models, delivering…..
To read the full article: https://dsb.edu.in/an-insight-into-saas-baas-revolutionizing-everything-from-cloud-to-cash/?utm_source=tumblr&utm_medium=tumblr&utm_campaign=Saas+and+BaaS
#ai#jobs#india#blockchain#chatgpt#gpt 4#fintech#education#google#banking#saas#saas technology#saasmarketing#saas solutions#b2b saas#automation#baas#financial#investing#finance
0 notes
Text
5 Most Important Salesforce Integrations for Your CRM Platform

Salesforce integration helps businesses organize everything and control key business processes from a single platform. This enables the seamless integration and execution of operations related to marketing, sales, finance, project management, human resources, and accounting. Additionally, the Salesforce integration services assist in tying together various departments into a single program. This blog will teach you about the Salesforce integration tools built into your CRM platform, which also increase workforce productivity.
There are excellent integration tools that turn Salesforce's potential into a limitless experience for businesses of all sizes and technical proficiency levels. However, the user and technical interfaces of these top Salesforce integration products range greatly. For instance, they vary in terms of target audiences, data storage methods, and programming languages.
Particular integration tools are easy to set up and use. To make the procedure simpler, they frequently come with pre-set templates. However, some tools are quite complex and require technical knowledge. Generally speaking, the platform enables you to connect to various systems, including external ERP, marketing automation, accounting, computer telephony, email training, social media, and IT service tools, to improve employee and customer engagement. Continue reading to discover more about Salesforce integration and productivity-boosting integration options for your business.
What Does Integration with Salesforce Mean?
Every organization has a unique set of needs, and each solution functions differently. These have business logic, security, visual representation, and data storage and are designed in various languages. Additionally, Salesforce integration develops and manages improved API-based communication between apps and CRM.
Integration with Salesforce provides adequate access and data analysis. It assists directors and managers in every stage of decision-making. All businesses should concentrate on effective integration tools because these resources can deliver the best results.
Your Workforce Productivity will Increase Thanks to These 5 Salesforce Integrations
When businesses spend significant time on non-core tasks rather than essential components, workforce productivity suffers significantly. For instance, increasing sales is the primary responsibility of sales reps. Although it aids them in their selling process, data updating, task scheduling, and email synchronization are not their primary tasks. The sales representatives can save time by automating tasks with the integration tools. Some of them are mentioned below.
1- Integration of Salesforce and Gmail with Ebsta
Gmail and Salesforce are widely used in business. They must integrate their digital tools if they want to increase productivity. Salesforce users use CRM to manage customer data, workflow, activity, data exchange, and reporting with one third-party system, like marketing platforms, to support related activities. Ebsta serves as a link between the two platforms and gives Gmail access to Salesforce functionality.
Salesforce can be used to track email openings, email templates, and follow-up tasks while syncing the Google Calendar and Email with Ebsta. Additionally, the integration with Google Calendar ensures event synchronization on demand. Thus, by integrating Gmail and Salesforce with Ebsta, meeting scheduling, email delivery, email capture, email sending, and creating a personalized workflow can all be done effectively.
2- Use Quip to Improve Team Collaboration
Team conversations, documents, and spreadsheets are all included under one roof in the cutting-edge productivity package Quip. It enables your team to work together more effectively to complete tasks. An interactive, connected, the connected solution is made possible by Quip Salesforce integration. As a result, fewer emails are sent, fewer meetings are held, and more growth opportunities to meet customer demands.
With Salesforce integration services, you can expand your opportunities and improve your decision-making. Quip also aids in report analysis by offering a thorough understanding and disseminating up-to-date information in Meetups.
3- Use ToutApp's Auto-Log Email Feature
With ToutApp, sending personalized emails to contacts and leads is simpler. You can track the activity of the leads to find out what functions well in Salesforce CRM. Top Salesforce integration tools like ToutApp increase sales productivity by generating emails more quickly. Additionally, it permits follow-ups on business email promotions. With the aid of such a tool, sales representatives can nurture leads and send the appropriate content to prospects at the appropriate time.
Users can call prospects directly from Salesforce thanks to the dialer and phone built-in to the platform. This marketing tool supports lead conversion while assisting with work prioritization and content improvement.
4. Post-Chat Feedback Using Getfeedback
Customers now need real-time feedback in addition to real-time help. Your team can provide adequate chat support in real-time with Salesforce Chat. However, the team must consider how customers interact to assess performance metrics like customer effort and course modification if customers are unhappy.
You can use branded surveys to collect customer feedback in real time through Getfeedback integration with Salesforce. While pushing responses from customers into Salesforce, it contextualizes them to produce insights and increase productivity.
5. Use Icertis to manage the Contract Lifecycle
Companies that require basic contract management to support contract portfolios can use specific Salesforce contract management capabilities.
However, you will require something more than Salesforce if you are required for management aspects of the contract life cycle, such as data analysis, reporting, tools, and ERP system interaction. You are not utilizing the system without combining Salesforce with a powerful contract management platform.
Your sales team can create, view, approve, and collaborate on contracts inside Salesforce, thanks to the integration between Salesforce and Icertis. This aids in accelerating the flow of contracts, improving productivity, and fostering the expansion of your business. Additionally, it improves sales by relieving sales representatives of tiresome administrative duties.
Users may submit contract requests through Salesforce objects, monitor progress updates, and manage the contract lifecycle. The Salesforce and Icertis integration speeds up, secures, and optimizes business operations. As a result, you can increase the contract's processing efficiency while increasing revenue, lowering risks, and managing costs.
A Conclusion
Salesforce integration aids in increasing productivity levels and achieving an unbeatable position in the cutthroat market. Effective time management is the key to productivity, and you can do this by using Salesforce integration tools. A small modification to business procedures can significantly improve workforce effectiveness. Integrating these powerful tools with Salesforce can save time and help you achieve your goals more quickly.
0 notes
Text
#Salesforce Data Storage Management Best Practices#Salesforce data storage best practices#Data Growth in Salesforce#data growth in Salesforce.#Data Growth#standard practices for Salesforce data storage management#Salesforce data archival strategy.#Salesforce Data Storage Management#DataArchiva Native Archiving#Salesforce data archiving#DataArchiva External Archiving#Salesforce data from primary storage#Salesforce data with DataArchiva.#Salesforce reporting#Storage Usage Page#compliance archiving in Salesforce#Compliance Archive
1 note
·
View note
Text
Demystifying Cloud Computing Services: Unleashing the Power of the Cloud
Introduction:
In today's digital age, businesses are increasingly relying on technology to drive innovation and stay ahead of the competition. Among the many technological advancements, cloud computing has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing the way organizations store, process, and access data. In this blog, we will explore the world of cloud computing services, including leading providers like Oracle Cloud, Microsoft Cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Cloud, as well as the benefits of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms.
Cloud Computing: A Brief Overview Cloud computing refers to the delivery of on-demand computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, and software, over the internet. Instead of maintaining costly on-premises infrastructure, organizations can leverage the scalability and flexibility of the cloud to scale their operations seamlessly. Cloud computing offers three primary service models: Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
Oracle Cloud: Unleashing Enterprise-Grade Cloud Solutions Oracle Cloud is a comprehensive cloud platform that caters to the specific needs of enterprise organizations. It provides a wide range of services, including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, along with industry-specific solutions. Oracle Cloud stands out with its high-performance infrastructure, advanced security features, and support for hybrid cloud deployments. With capabilities like Autonomous Database and Oracle Functions, businesses can accelerate their digital transformation journey while ensuring data integrity and compliance.
Microsoft Cloud: Empowering Productivity and Collaboration Microsoft Cloud, known as Microsoft Azure, is a robust cloud computing platform that offers a vast array of services. From virtual machines and storage to AI and machine learning tools, Azure provides organizations with the building blocks to create, deploy, and manage applications seamlessly. With services like Azure DevOps and Azure Active Directory, businesses can streamline their development processes and enhance collaboration across teams. Microsoft Cloud's integration with popular productivity tools like Office 365 further enhances its value proposition.
Amazon Web Services (AWS): The Pioneers of Cloud Computing Amazon Web Services, commonly referred to as AWS, is a leading player in the cloud computing market. AWS offers a wide range of services, including compute power, storage, and databases, enabling businesses to build scalable and resilient applications. With AWS Lambda and Amazon Elastic Container Service, developers can embrace serverless architecture and microservices. Additionally, AWS provides a rich ecosystem of managed services, such as Amazon RDS and Amazon Redshift, to handle specific use cases efficiently.
Google Cloud: Innovating with AI and Data Analytics Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is Google's cloud computing offering, providing a robust infrastructure for building and deploying applications. GCP's strengths lie in its data analytics and machine learning capabilities, powered by services like BigQuery and Google Cloud AI. By leveraging Google's extensive experience in these domains, organizations can unlock valuable insights from their data and build AI-powered applications. GCP's serverless offerings, such as Google Cloud Functions and Google Cloud Run, provide seamless scalability for applications.
SaaS Platforms: Streamlining Business Processes Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms offer ready-to-use applications hosted in the cloud, eliminating the need for organizations to develop and maintain their software. SaaS platforms, like Salesforce, Workday, and Zendesk, provide a wide range of enterprise applications, including customer relationship management (CRM), human resources management, and customer support. By adopting SaaS platforms, businesses can reduce costs, enhance productivity, and focus on their core competencies, leaving the software management to the experts.
Conclusion:
Cloud computing services have transformed the way businesses operate, enabling them to scale, innovate
#cloud computing#cloudplatform#oraclecloud#microsoftcloud#amazon web services#googlecloud#saas platform
0 notes
Text
How Much Do You Really Know About Cloud Services

Cloud Services Pittsburgh has many advantages for your firm. So that you can stay in touch with your business from anywhere at any time, it enables you to set up what amounts to a virtual office. As more and more people use computers, smartphones, and tablets with an internet connection, finding what you need is much simpler. Both private and public cloud options are available today. Access to a public cloud is universal, thanks to the internet. Private clouds are secure, isolated networks or data centres that only allow authorised users to access their hosted services. The main goal of cloud computing is to make it simple and convenient to get your hands on shared and private computing resources.
What we can do with cloud computing
Businesses no longer need to invest in costly IT equipment or data centres to access applications and data storage; they can lease these services from a cloud provider.
Instead of allocating funds and personnel to maintain an in-house IT network, firms can save money and time by using cloud-computing services.
Providers of Cloud Services Pittsburgh, in turn, can reap substantial cost savings by catering to a large customer base.
An assortment of cloud-based service models
IaaS
IaaS providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) give users a virtual server instance, cloud storage, and application programming interfaces (APIs) so they can more easily migrate their workloads to the cloud (VM). Each user is allotted a certain amount of storage space, which can be used to launch and shut down virtual machines, provide access to data, and alter other settings. To accommodate a wide range of workloads, IaaS providers offer a selection of preconfigured instance sizes (small, medium, big, extra-large) and the option to create your own. Regarding commercial customers, the Infrastructure as a Service cloud architecture is the most analogous to a remote data centre.
PaaS
In the Platform as a Service (PaaS) concept, cloud providers act as a repository for software engineering resources. APIs, web portals or gateway programmes provide users with online access to these programmes. Several PaaS companies also offer to host the product once it is complete, making it useful for post-development testing and other purposes. Lightning Platform from Salesforce, Elastic Beanstalk from Amazon Web Services, and Google App Engine are all examples of popular PaaS Cloud Services Pittsburgh.
SaaS
The term "web services" is commonly used to refer to the software applications distributed via the SaaS model. Customers can use any computer or mobile device with an internet connection to gain access to SaaS apps and services. While using a SaaS model, consumers can access resources like programmes and data stores.
Conclusion
The primary benefit of moving workloads to the Cloud Services Pittsburgh is speeding up the release of dynamically scalable apps. Yet, with so many cutting-edge new services available in the cloud, from machine intelligence to IoT connectivity, developers are increasingly drawn there. You can contact Ceeva if you need cloud services.
0 notes
Text
Salesforce Development Lifecycle: Detailed Phases
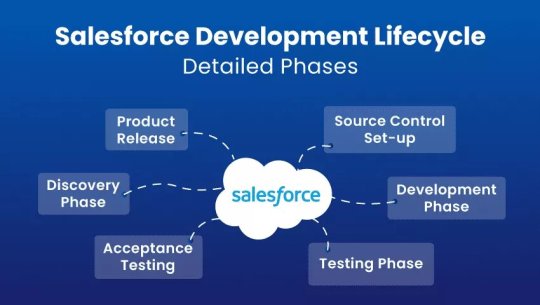
“With great power comes great responsibility.” We all know this. Or at least anyone who has ever heard of Spider man knows these words.
Salesforce as a tool is kind of the all-powerful one in this context. But anyone who knows Salesforce development also fits the bill.
The Salesforce development lifecycle is multi-layered; not only does it require investment, but rather, a commitment from the entire organization to see the development through. The development team will, of course, commit to their role in it, but it is crucial that the organization, who is the client, does so too.
SFDC development life cycle begins with discovery, understanding why a client requires Salesforce, and their exact needs. There are several complex phases that follow, all culminating in project delivery and staff training. Let’s take a look at all the phases of the Salesforce development lifecycle:
Phases of Salesforce application development lifecycle
Generally, development projects are completed in phases, with every phase having a particular goal to achieve. Salesforce Development Lifecycle goes through 6 such phases.
Let us better understand each phase of the Salesforce Development Lifecycle:
1. Discovery Phase
This is the primary phase of Salesforce development. In this phase, the requirements of the department are assembled, analyzed, and decided upon. Later on, these are shared with development teams. Now, several factors are involved in the discovery phase, like the objectives/goals of projects, critical needs, development intricacies, automation needs, reporting, gaps in the previous implementation, APIs, tools, and development approaches.
2. Source Control Set-up
Source control provides you with a tool to help track changes occurring in files. A release manager would kick off a development project and create repositories and branches. Let’s see what these two components are:
Repository
It is sort of like a vessel for version control. Usually used to store away files, and it can track changes in files in real time. A repository is the master storage of files, from which many branches, which contain new elements in development, come out. You can oversee changes, review the work of other developers, and clear up discord by creating different repositories.
Branches
Branches give the developers an autonomous working environment to work on new features away from other development work. Branches allow for parallel development and provide the developers with control changes when products are released for testing. It is favorable to have a separate Git repository for different projects. You can merge all the data later on with the main application. The responsibility falls to the release manager to assign tasks according to the intellect of the developer.
When you create a version control, you can set up a single source of code, manage conflicts, reduce risks, facilitate deployment risks, clarify reduction, and release at a higher rate.
3. Development Phase
Development operations are executed in sandbox environments. Every developer who works in such an environment has a copy of the main production application and the essential configuration info. Developers use these separate environments to write code, modifications, and testing. They may connect with their sandbox using Force.com and transmit metadata to IDE. After all the required changes are made and tested, they are transferred to the Git repository. If a project requires multiple people working on the same code, check the conflicts before you put the code in the repository.
4. Testing Phase
After the development phase comes the testing phase, teams are gathered to conduct top-to-bottom testing sessions where code is moved from the primary repository to the sandbox. Quality Analysts conduct different testing processes in Salesforce application development projects, like unit testing, performance testing, regression testing, visual testing, integration/API testing, load testing, etc.
Most of all, Salesforce application development partners use agile methodology so that any structural changes can be taken care of at this stage. Although, should serious modifications arise, you have to go back to the drawing board (initial development stage).
5. Acceptance Testing
After the stages mentioned above are completed, we come to the acceptance testing phase. User acceptance tests are conducted and carried out by end-users in combination with the development team. In this phase, a release manager creates sandboxes, which the end user then uses for testing. Once the testing is completed and approved, the product is ready to be released. However, if there are changes suggested at this stage, you can take the entire thing back to the initial development phase.
6. Product Release
After undergoing different testing procedures, the product is tested a final time for performance in a sandbox. Here, all the configurations, functionalities, and app data are tested a last time. Here we have to ensure that the solution passes through the service level agreements before being set up in production.
How will CRMJetty help you with the same?
We have been honing our Salesforce development skills for over 16 years now and have built a strong portfolio of clients who have made it in the industry with us. You can count on our expertise with the software, as well as our understanding of your unique needs.
Contact us today to learn more about everything we offer in terms of Salesforce development and get started on your path to success!
Original Blog: https://www.crmjetty.com/blog/sfdc-development-lifecycle-phases/
0 notes