#Satellite Solar Panels And Array Market Size
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Exhaustive secondary research was done to collect information on the Satellite Solar Panels and Array Market, its adjacent markets, and its parent market. The next step was to validate these findings, assumptions, and sizing with industry experts across the value chain through primary research. Demand-side analyses were carried out to estimate the overall size of the market. Both, top-down and bottom-up approaches were employed to estimate the complete market size. Thereafter, market breakdown and data triangulation were used to estimate the size of segments and subsegments.
#Satellite Solar Panels And Array#Satellite Solar Panels And Array Market#Satellite Solar Panels And Array Industry#Global Satellite Solar Panels And Array Market#Satellite Solar Panels And Array Market Companies#Satellite Solar Panels And Array Market Size#Satellite Solar Panels And Array Market Share#Satellite Solar Panels And Array Market Growth#Satellite Solar Panels And Array Market Statistics
0 notes
Text
Energy Beyond Earth: Growth Opportunities in Space Power Supply Technologies

The space power supply market includes a broad range of solutions, such as solar power systems, batteries, energy storage devices, and power management technologies, all crucial for space applications.The growing need for more dependable and efficient power sources for satellites, spacecraft, and space stations has been the main driver of this market. The increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions in space exploration is being met by advancements in space power technology, including sophisticated solar panels and high-capacity energy storage devices. Key companies like Airbus and Rocket Lab USA dominate the fiercely competitive space power supply business. Additionally, industry and consumer preferences are being shaped by the increased focus on sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and long-duration space missions, which is driving businesses to invest in cutting-edge technology and creative power solutions. In order to satisfy the needs of satellite operations and space exploration, this dynamic market is always changing.
What is the market size and growth forecast for the global space power supply sector?
The Space Power Supply Market was valued at $9,449.9 million in 2024 and is projected to reach $14,787.0 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 4.58% during the forecast period (2024–2034).

What are space power supply products, and what are the types of space power supply products available in the space power supply market?
Space power supply products are essential components designed to provide reliable energy solutions for spacecraft, satellites, and other space systems. The primary types of space power supply products include solar power systems, which harness solar energy to power space missions; solar cells, which are responsible for converting sunlight into electricity; and solar arrays/panels, which consist of interconnected solar cells to provide the necessary power output. Battery systems are crucial for storing energy to ensure continuous power during periods without sunlight, and power management and distribution (PMAD) systems control the distribution of power within space systems, ensuring stability and efficiency. These products play a pivotal role in supporting long-duration space missions, satellite operations, and deep space exploration. As space missions expand, advancements in solar power systems, solar cells, and battery technologies are increasingly vital to meeting the growing energy demands of the space power supply market.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ’s):
What are the major market trends and drivers?
The space power supply market is being driven by several key trends and market drivers. Growing satellite deployments, particularly with mega-constellations such as Starlink and Amazon Kuiper, are expected to continue influencing demand for advanced space power solutions. Investments in space-based solar power systems (SBSP) are also on the rise, which will propel innovation in energy solutions for long-duration space missions. Additionally, advancements in multi-junction solar cells, the development of thin-film and flexible solar cells, and efficiency improvements in solar panels are key trends shaping the future of space power supply, enhancing the performance and sustainability of space missions.
What are the opportunities for growth in the market?
The space power supply market presents several growth opportunities driven by emerging trends. The impact of mega-constellations, such as Starlink, will significantly increase the demand for solar cells, especially as satellite deployments expand. The growing market for CubeSats and small satellites also presents a major opportunity, as these satellites require efficient and reliable power solutions. Solar power's expanding role in deep space exploration missions further boosts demand for advanced solar power systems. Strategic collaborations between governments and private space companies will also foster innovation and investment, driving growth in the space power supply sector.
What are the major market trends and drivers?
The space power supply market is being driven by several key trends and market drivers. Growing satellite deployments, particularly with mega-constellations such as Starlink and Amazon Kuiper, are expected to continue influencing demand for advanced space power solutions. Investments in space-based solar power systems (SBSP) are also on the rise, which will propel innovation in energy solutions for long-duration space missions. Additionally, advancements in multi-junction solar cells, the development of thin-film and flexible solar cells, and efficiency improvements in solar panels are key trends shaping the future of space power supply, enhancing the performance and sustainability of space missions.
Who are the major players in the space power supply market?
AZUR SPACE Solar Power GmbH
Spectrolab
Rocket Lab USA
SHARP CORPORATION
Shanghai Institute of Space Power-Sources
MicroLink Devices, Inc.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL)
Order a free sample PDF of Space Power Supply Market Intelligence Study, published by BIS Research!
Learn more about Aerospace Vertical. Click Here!
Conclusion
The space power supply market is experiencing steady growth driven by increasing demand for efficient and reliable power solutions across satellites, space exploration missions, and launch vehicles. Thanks to developments in energy storage and solar power technology, satellites continue to be the largest application segment. The market serves a wide range of space missions and technological requirements with its varied segmentation by orbit, satellite type, and components. To satisfy the increasing demands of the industry, major firms from all over the world are actively developing. The market is anticipated to keep growing as space missions get more intricate and sustainability becomes more of a priority, becoming increasingly important to satellite operations and space exploration in the future.
0 notes
Text
Google Project Loon Market Size, Share, Development, Growth and Demand Forecast 2021 to 2025
Project Loon is a research and development project being developed by X (formerly Google X), which consists of a network of balloons equipped with routers at the edge of space. The aim of the project is to provide internet to everyone in the world. It is a known fact that many areas in the emerging and developed regions across the globe are deprived of a proper internet access.
Project Loon intends to connect people in rural and remote areas by making use of a network of internet-powered balloons traveling on the edge of space.
Google thinks its internet balloons will be a $10 billion business. Each balloon is equipped with LTE antennas capable of covering around 80 kilometers on the ground, a 100W solar panel array that charges a battery for nighttime operations, and additional antennas to relay traffic to other balloons.
Get Sample Reports Here - https://www.kennethresearch.com/report-details/google-project-loon-market/10065254
Assuming all the mechanisms of the project are functioning as planned, every single person can have access to internet. Loon's Use of Renewable Energy is an added advantage as it will greatly influence and inspire future projects. It creates an interplay between solar energy to keep the balloon functional while using wind energy to define its motor controls. With the constant connectivity to the each other through the internet collaboration between people across the globe will become much easier. The main problem with the Project Loon is the certainty of eventual hardware failure. If a Loon balloon fails, it can either remain up in the air floating, making it difficult to bring down or it might go down in unwanted areas as they can't be reached. Another concern over this project is internet privacy. As the project gives Google more power over a wider range of consumer behaviour the information obtained can become a security issue if it is shared with Government agencies.
Increasing the volume of internet users would invariably increase traffic on the world's leading search engine, Google Search. The increase in search users implies that more ads will be displayed which in turn result in profits for Google. Given the rising number of the mobile internet subscriptions and also the ever-increasing growth in the world population, the need for access to the internet is going to increase even more. The growing population, changing consumer internet habits and multiple developments via Internet-of-Things could drive the demand for a full-time easy access to the internet from every corner of the globe, which could be made possible by implementing Project Loon to its full potential.
Google has already run tests with several different telecoms. It has conducted test runs with Vodafone in New Zealand, Telstra in Australia, and Telefonica in Latin America - and is working on commercial deals with other new network operators. Google will split the revenue from any new customers with the telecommunications company providing the LTE spectrum.
SpaceX and Facebook are also working on similar projects and could be the potential competitors to Google. Facebook is the only company that has started testing its project by the use of unmanned aerial vehicles unlike SpaceX, which plans to provide a similar internet access facility by the use of a fleet of satellites.
Report Contents
Global Market segments
Global Market Drivers, Restraints and Opportunities
Global Market Size & Forecast 2016 to 2022
Supply & Demand Value Chain
Global Market - Current Trends
Competition & Major Companies
Technology and R&D Status
Porters Five Force Analysis
Strategic and Critical Success Factor Analysis of Key Players
Regional Analysis
North America
Latin America
Western Europe
Eastern Europe
Asia Pacific
Middle East and Africa
US and Canada
Mexico
Brazil
Argentina
Rest of Latin America
EU5 (Germany, France, Italy, Spain, U.K.)
Nordic Countries (Denmark, Finland, Norway, and Sweden)
Benelux (Belgium, The Netherlands, and Luxembourg)
Rest of Western Europe
Russia
Poland
Rest of Eastern Europe
China
India
Japan
Australia and New Zealand
Rest of Asia Pacific
GCC countries (Saudi Arabia, Oman, Qatar, Bahrain, UAE and Kuwait)
South Africa
North Africa
Rest of Middle East and Africa
Report Highlights
This report is an elaborate aggregation of primary inputs from industry experts and participants across the supply chain. It provides details on market segmentation which is derived from several product mapping exercises, macroeconomic parameters and other qualitative and quantitative insights. The impact of all such factors is delivered across multiple market segments and geographies.
Detailed Historical Overview (Market Origins, Product Launch Timeline, etc.)
Consumer and Pricing Analysis
Market dynamics of the industry
Market Segmentation
Estimated Market Sizing in terms of volume and value
Recent trends in market and impact
Research Status and Technology Overview
Extensive Industry Structure Coverage
About Kenneth Research
Kenneth Research is a reselling agency providing market research solutions in different verticals such as Automotive and Transportation, Chemicals and Materials, Healthcare, Food & Beverage and Consumer Packaged Goods, Semiconductors, Electronics & ICT, Packaging, and Others. Our portfolio includes set of market research insights such as market sizing and market forecasting, market share analysis and key positioning of the players (manufacturers, deals and distributors, etc), understanding the competitive landscape and their business at a ground level and many more. Our research experts deliver the offerings efficiently and effectively within a stipulated time. The market study provided by Kenneth Research helps the Industry veterans/investors to think and to act wisely in their overall strategy formulation
Contact Us
Name: David
Email : [email protected]
Phone: +1 313 462 0609
1412, Broadway,
21st Floor Suite MA111,
New York, NY 10018
1 note
·
View note
Text
Solar PV Panels Market Tracking Report Analysis 2023-2031
The Solar PV Panels Market was valued at USD 153.07 billion in 2022, and it is anticipated to increase at a CAGR of 9.3% from 2023 to 2031. A solar panel, sometimes referred to as a PV panel, is made up of solar (or photovoltaic) cells that use the sun's light to produce energy. It is constructed from a number of silicon, boron, and phosphorus-based solar cells that are arrayed on the surface in a grid-like arrangement. Globally, the use of solar panels has grown due to the fact that they do not cause any pollution and that their installation aids in reducing the dangerous greenhouse gas emissions.
Get Sample Copy of this Reports@ https://www.econmarketresearch.com/request-sample/EMR005/
Top Key Players:
Market Growth:
The main use of photovoltaic or solar cells is to transform solar energy into an electron flow. These cells generate electricity from solar energy, which is useful for recharging batteries or powering devices. Spacecraft and orbiting satellites were first powered by solar cells. However, in recent years, their use for grid-connected electricity generation has increased. In order to function better, photovoltaic systems seek to maximize production. During the anticipated timeframe, these variables should accelerate market expansion.
Ask for Discount@ https://www.econmarketresearch.com/request-discount/EMR005/
Market Segmentation:
Solar PV Panels Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report, By Technology, By Grid Type, By Application By Region, And Segment Forecasts, 2023 – 2031
Market Drivers - Solar PV (Photovoltaic) panels market:
The industrial sector's rising demand for solar panels is evidence of the public's preference for alternative energy sources over traditional ones. Solar technology and panel installation are receiving significant investment from many sectors throughout the world. The rising number of solar power plants in various industry verticals is the main factor driving the global market for solar panels.
Market Opportunities - Solar PV (Photovoltaic) panels market
Solar cells, often known as photovoltaic cells, are used primarily to transform solar energy into an electron flow. These cells generate electricity from solar energy, which can be used to run devices or top off batteries. Initially, satellites in orbit and spacecraft were powered by photovoltaic cells.
Enquire Before Buy@ https://www.econmarketresearch.com/enquiry/EMR005/
About Us:
Econ Market Research is a one-stop provider of industry research and actionable intelligence. Through our syndicated and consulting research services, we help our clients get solutions to their research requirements. We specialise in industries such as semiconductors and Electronics, Aerospace and Défense, Energy, Automotive and Transportation, Healthcare, Manufacturing and Construction, Media and Technology, Chemicals, and Materials.
Contact Us:
If you have any queries about this report or if you would like further information, please contact us:
E-mail: [email protected]
Phone: (+1) 812 506 4440.
Website:- https://www.econmarketresearch.com
0 notes
Text
SATCOM Equipment Market for Space Is Growing Swiftly Due TO Increasing Demand From End Use Industry
The global SATCOM Equipment Market for Space is projected to grow from USD 2.8 billion in 2019 to USD 7.0 billion by 2025, at a CAGR of 16.8% from 2019 to 2025. The growth of the market across the globe can be attributed to the increasing launch of satellites for applications such as earth observation, communication, and navigation.

Browse 83 market data Tables and 40 Figures spread through 143 Pages and in-depth TOC on "SATCOM Equipment Market - Global Forecast to 2025"
Based on application, the SATCOM equipment market for space is projected to be led by the earth observation & remote sensing segment from 2019 to 2025. According to an article published by SpaceNews in December 2018, the demand for earth observation (EO) is growing, due to a growing focus on analytics from high-resolution and medium-resolution imagery. Technology for analyzing data gathered from EO satellites such as big data analytics is expected to grow four times over the decade.
Browse In-depth Insights: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/space-satcom-equipment-market-177487346.html
The increasing use of CubeSats for earth observation and remote sensing is expected to drive the SATCOM equipment market for space from 2019 to 2025.
Based on satellite type, the CubeSat (0.25U–27U) segment is projected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period. The SATCOM equipment market for CubeSats is expected to grow during the forecast period due to an increase in the volume of CubeSats launched and scheduled for launch during the forecast period. CubeSats are used for a variety of missions, have a small form factor, and cost substantially less to develop and launch in comparison to large satellites. The increase in the launch of CubeSats can be attributed to the rising demand for EO.
North America and Asia Pacific are projected to be high growth potential markets for SATCOM equipment for space during the forecast period.
The SATCOM equipment market for space in the North American region is expected to witness substantial growth during the forecast period due to increased launch and scheduled launch of satellites.
According to an article published in The New York Times in May 2019, SpaceX launched a batch of 60 internet communication satellites, as a part of the Starlink Megaconstellation Project. According to an article published by Future US, Inc., SpaceX has received permission from the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to launch an estimated total of 12,000 Starlink satellites. Major players such as Amazon (US), OneWeb (US), and Telesat (Canada) are also expected to launch satellites during the forecast period.
Key Companies Outlook
Some of the major players in the SATCOM equipment market for space include Airbus SE (Netherlands), Maxar Technologies (US), Mitsubishi Electric Corporation (Japan), General Dynamics Corporation (US), Honeywell International Inc. (US), Harris Corporation (US), ISIS - Innovative Solutions in Space B.V. (Netherlands), and Oxford Space Systems (UK).
Maxar Technologies is ranked second in the SATCOM equipment market for space. Maxar Technologies has been exporting its satellite products for more than 40 years. The company operates its satellite business through its division, MDA, which is a key manufacturer of satellite antennas and communication subsystems. MDA has a global presence and caters to customers from various countries. The antennas offered by MDA cover a wide range of frequencies, including VHF, most of the MHz bands, and EHF up to 90 GHz. It caters to both commercial and military customers. In November 2018, MDA secured two contracts worth USD 11 million from OHB System AG and Tesat-Spacecom GmbH & Co. KG for the supply of multiple advanced communication subsystems.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation secures the third position in the SATCOM equipment market for space. The company has been contributing to space technology since 1960. It has a broad product portfolio and strong business performance. The company is constantly pushing for excellence, with a goal of achieving an operating income ratio of 8%, return on equity of 10% or more, and the ratio of interest-bearing debt to total assets of 15% or less by 2021. The company constantly innovates and brings new technologies to the market, with five new products launched in 2018. In July 2017, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation completed the construction of a facility that is expected to double the satellite component production capacity of the company. The facility is said to undertake the production and testing for solar array panels, structural panels, and other satellite components.
Get Sample Insights: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/requestsampleNew.asp?id=177487346
About MarketsandMarkets™
MarketsandMarkets™ provides quantified B2B research on 30,000 high growth niche opportunities/threats which will impact 70% to 80% of worldwide companies’ revenues. Currently servicing 7500 customers worldwide including 80% of global Fortune 1000 companies as clients. Almost 75,000 top officers across eight industries worldwide approach MarketsandMarkets™ for their painpoints around revenues decisions.
Our 850 fulltime analyst and SMEs at MarketsandMarkets™ are tracking global high growth markets following the "Growth Engagement Model – GEM". The GEM aims at proactive collaboration with the clients to identify new opportunities, identify most important customers, write "Attack, avoid and defend" strategies, identify sources of incremental revenues for both the company and its competitors. MarketsandMarkets™ now coming up with 1,500 MicroQuadrants (Positioning top players across leaders, emerging companies, innovators, strategic players) annually in high growth emerging segments. MarketsandMarkets™ is determined to benefit more than 10,000 companies this year for their revenue planning and help them take their innovations/disruptions early to the market by providing them research ahead of the curve.
MarketsandMarkets’s flagship competitive intelligence and market research platform, "Knowledgestore" connects over 200,000 markets and entire value chains for deeper understanding of the unmet insights along with market sizing and forecasts of niche markets.
Contact: Mr. Aashish Mehra MarketsandMarkets™ INC. 630 Dundee Road Suite 430 Northbrook, IL 60062 USA : 1-888-600-6441
0 notes
Text
Pros and Cons of Solar Energy
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages?
Did you recognize that the energy sun provides to the world for one hour could meet the worldwide energy needs for one year? Undoubtedly, the sun may be a powerful energy source, and albeit we aren't able but to gather a fraction of this energy, yet harnessing this power by installing solar panels can make a big difference to the earth .
While it's been widely criticized for being expensive or inefficient, solar power has now proved to be extremely beneficial - not just for the environment but also for the private economy. Thanks to available solar array grants, also as, the increasingly competitive prices within the market, solar power has become the most source of energy for more and more families. The technology has been drastically improved the last years and has been complemented by solar array storage systems, turning solar into a significantly more efficient source of unpolluted energy.
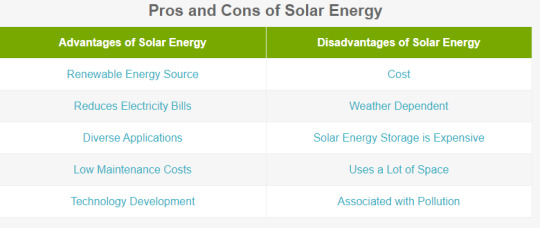
However, there are always downsides regardless of the energy source you select to analyze. Eco Solar Energies has outlined the key advantages and drawbacks of solar energy within the following points:
Advantages of Solar Energy
1. Renewable Energy Source
Among all the advantages of solar panels, the foremost important thing is that solar power may be a truly renewable energy source. It is often harnessed altogether areas of the planet and is out there a day. We cannot run out of solar power , unlike a number of the opposite sources of energy.
Solar energy are going to be accessible as long as we've the sun, therefore sunlight are going to be available to us for a minimum of 5 billion years when consistent with scientists the sun goes to die. 2. Reduces Electricity Bills
Since you'll be meeting a number of your energy needs with the electricity your system has generated, your energy bills will drop. what proportion you save on your bill are going to be hooked in to the dimensions of the system and your electricity or heat usage. For example, if you're a business using commercial solar panels this switch can have huge benefits because the massive system size can cover large chunks of your energy bills. Moreover, not only will you be saving on the electricity bill, but there's also an opportunity to receive payments for the excess energy that you simply export back to the grid through the Smart Export Guarantee (SEG). If you generate more electricity than you employ (considering that your solar array system is connected to the grid).
3. Diverse Applications
Solar energy are often used for diverse purposes. you'll generate electricity (photovoltaics) or heat (solar thermal). solar power are often wont to produce electricity in areas without access to the energy grid, to distil water in regions with limited clean water supplies and to power satellites in space. Solar energy also can be integrated into the materials used for buildings. shortly ago Sharp introduced transparent solar power windows.
4. Low Maintenance Cost
Solar energy systems generally don’t require tons of maintenance. you simply got to keep them relatively clean, so cleaning them a few of times per annum will do the work . If unsure , you'll always believe specialized cleaning companies, which supply this service from around 70,000 to Rs 1,20,000 per kW Most reliable solar array manufacturers offer 20-25 years warranty. Also, as there are not any moving parts, there's no wear and tear. The inverter is typically the sole part that must be changed after 5-10 years because it's continuously working to convert solar power into electricity and warmth (solar PV vs. solar thermal). aside from the inverter, the cables also need maintenance to make sure your solar energy system runs at maximum efficiency. So, after covering the initial cost of the system , you'll expect little or no spending on maintenance and repair work. 5. Technology Development Technology within the solar energy industry is consistently advancing and enhancements will intensify within the future. Innovations in physics and nanotechnology can potentially increase the effectiveness of solar panels and double, or maybe triple, the electrical input of the solar energy systems. Disadvantages of Solar Energies 1.Cost
The initial cost of buying a system is fairly high. This includes paying for solar panels, inverter, batteries, wiring, and therefore the installation. Nevertheless, solar technologies are constantly developing, so it's safe to assume that prices will go down within the future.
2. Weather Dependent Although solar power can still be collected during cloudy and rainy days, the efficiency of the system drops. Solar panels are hooked in to sunlight to effectively gather solar power . Therefore, a couple of cloudy, rainy days can have a clear effect on the energy system. you ought to also take under consideration that solar power can't be collected during the night. On the opposite hand, if you furthermore may require your water heating solution to figure in the dark or during wintertime, thermodynamic panels are an alternate to think about .:
3. Solar Energy Storage is Expensive Solar energy has got to be used directly , or it are often stored in large batteries. These batteries, utilized in off-the-grid solar systems, are often charged during the day in order that the energy is employed in the dark . this is often an honest solution for using solar power all day long but it's also quite expensive. In most cases, it's smarter to only use solar power during the day and take energy from the grid during the night (you can only do that if your system is connected to the grid). Luckily your energy demand is typically higher during the day so you'll meet most of it with solar power .
4. Uses A Lot of Space
The more electricity you would like to supply, the more solar panels you'll need, as you would like to gather the maximum amount sunlight as possible. Solar PV panels require tons of space and a few roofs aren't large enough to suit the amount of solar panels that you simply would really like to possess . An alternative is to put in a number of the panels in your yard but they have to possess access to sunlight. If you don’t have the space for all the panels that you
simply wanted, you'll choose installing fewer to still satisfy a number of your energy needs.
5. Associated With Pollution Although pollution associated with solar power systems is way less compared to other sources of energy, solar power are often related to pollution. Transportation and installation of solar systems are related to the emission of greenhouse gases. There also are some toxic materials and unsafe products used during the manufacturing process of solar photovoltaic systems, which may indirectly affect the environment. Nevertheless, solar power pollutes far but other energy sources. Make The Transition to Solar Energy Today!
There are pros and cons to solar energy, but if this article has sparked your interest, you can check out our Website that will help you find the best solar panels for your home. We cover everything from roof suitability, solar panel type, cost, how to save with solar panels, and maintenance.
Has this sparked your interest in solar energy? Eco Solar Energies best Solar Panel Contractors can help you find your best deal! Simply fill in the contact form or Call us we will get back to you with best solar power solutions or Free Cost Estimation.
#solar power system#solar companies in mohali#solar lighting installation Punjab#solar panel cost#Best Solar Company in Hoshiarpur#Best Solar Company in jalandhar#Best Solar Company in moga#Best Solar Company in mohali#solar panels for home#solar company in punjab#solar panels Installation Online#off grid inverter Installation#best solar company#Solar Water Heating System#solar off grid system price#commercial solar systems#solar power solutions Near Me
0 notes
Text
These hyper-efficient solar panels could actually live on your roof soon
The clean energy boffins in their labs are always upping the theoretical limit on how much power you can get out of sunshine, but us plebes actually installing solar cells are stuck with years-old tech that’s not half as good as what they’re seeing. This new design from Insolight could be the one that changes all that.
Insolight is a spinoff from the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, where they’ve been working on this new approach for a few years — and it’s almost ready to hit your roof.
Usually solar cells collect sunlight on their entire surface, converting it to electricity at perhaps 15-19 percent efficiency — meaning about 85 percent of the energy is lost in the process. There are more efficient cells out there, but they’re generally expensive and special-purpose, or use some exotic material.
One place people tend to spare no expense, however, is in space. Solar cells on many satellites are more efficient but, predictably, not cheap. But that’s not a problem if you only use just a tiny amount of them and concentrate the sunlight on those; that’s the Insolight insight.
Small but very high-efficiency cells are laid down on a grid, and above that is placed a honeycomb-like lens array that takes light and bends it into a narrow beam concentrated only on the tiny cells. As the sun moves, the cell layer moves ever so slightly, keeping the beams on target. They’ve achieved as high as 37 percent efficiency in tests, and 30 percent in consumer-oriented designs. That means half again or twice the power from the same area as ordinary panels.
Certainly this adds a layer or two of complexity to the current mass-manufactured arrays that are “good enough” but far from state of the art. But the resulting panels aren’t much different in size or shape, and don’t require special placement or hardware, such as a concentrator or special platform. And a recently completed pilot test on an EPFL roof was passed with flying colors.
“Our panels were hooked up to the grid and monitored continually. They kept working without a hitch through heat waves, storms and winter weather,” said Mathiu Ackermann, the company’s CTO, in an EPFL news release. “This hybrid approach is particularly effective when it’s cloudy and the sunlight is less concentrated, since it can keep generating power even under diffuse light rays.”
The company is now in talks with solar panel manufacturers, whom they are no doubt trying to convince that it’s not that hard to integrate this tech with their existing manufacturing lines — “a few additional steps during the assembly stage,” said Ackermann. Expect Insolight panels to hit the market in 2022 — yeah, it’s still a ways off, but maybe by then we’ll all have electric cars too and this will seem like an even better deal.
from RSSMix.com Mix ID 8176395 https://techcrunch.com/2019/02/19/these-hyper-efficient-solar-panels-could-actually-live-on-your-roof-soon/ via http://www.kindlecompared.com/kindle-comparison/
0 notes
Text
These hyper-efficient solar panels could actually live on your roof soon
The clean energy boffins in their labs are always upping the theoretical limit on how much power you can get out of sunshine, but us plebes actually installing solar cells are stuck with years-old tech that’s not half as good as what they’re seeing. This new design from Insolight could be the one that changes all that.
Insolight is a spinoff from the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, where they’ve been working on this new approach for a few years — and it’s almost ready to hit your roof.
Usually solar cells collect sunlight on their entire surface, converting it to electricity at perhaps 15-19 percent efficiency — meaning about 85 percent of the energy is lost in the process. There are more efficient cells out there, but they’re generally expensive and special-purpose, or use some exotic material.
One place people tend to spare no expense, however, is in space. Solar cells on many satellites are more efficient but, predictably, not cheap. But that’s not a problem if you only use just a tiny amount of them and concentrate the sunlight on those; that’s the Insolight insight.
Small but very high-efficiency cells are laid down on a grid, and above that is placed a honeycomb-like lens array that takes light and bends it into a narrow beam concentrated only on the tiny cells. As the sun moves, the cell layer moves ever so slightly, keeping the beams on target. They’ve achieved as high as 37 percent efficiency in tests, and 30 percent in consumer-oriented designs. That means half again or twice the power from the same area as ordinary panels.
Certainly this adds a layer or two of complexity to the current mass-manufactured arrays that are “good enough” but far from state of the art. But the resulting panels aren’t much different in size or shape, and don’t require special placement or hardware, such as a concentrator or special platform. And a recently completed pilot test on an EPFL roof was passed with flying colors.
“Our panels were hooked up to the grid and monitored continually. They kept working without a hitch through heat waves, storms and winter weather,” said Mathiu Ackermann, the company’s CTO, in an EPFL news release. “This hybrid approach is particularly effective when it’s cloudy and the sunlight is less concentrated, since it can keep generating power even under diffuse light rays.”
The company is now in talks with solar panel manufacturers, whom they are no doubt trying to convince that it’s not that hard to integrate this tech with their existing manufacturing lines — “a few additional steps during the assembly stage,” said Ackermann. Expect Insolight panels to hit the market in 2022 — yeah, it’s still a ways off, but maybe by then we’ll all have electric cars too and this will seem like an even better deal.
0 notes
Text
My DIY Solar Power Setup – Free Energy for Life
It is pretty well known at this point that Mr. Money Mustache is enamored with solar power. Besides the obvious Sci-Fi coolness of it (Electricity, Satellites, Futuristic Robots!) and the eco-friendliness of it (energy with zero noise or pollution), in the last five years the money side of things has finally matured, so that solar power is now the cheapest way to make electricity – even before you account for the added bonus of any available subsidies and the benefits of pollution-free living.
A Watt of Solar Panels: From $100+ to under fifty cents (2017) in less than my lifetime (image source cleantechnica). And the 2017 number for the blue side of the graph hit over 95,000 MW.
It works for individuals: In many cases, if you can get a good rack of solar panels on your roof, your monthly savings will be equivalent to making an investment that performs better than the stock market. But the numbers look even better as your solar setup becomes larger, like if you’re running a solar energy utility or a community solar farm.
Related: In recent Colorado Energy Bids, Solar energy is the cheapest option, even when backed by battery storage (Vox).
The fun part of this for me has always been the physics. Ever since I learned how much energy the Sun shines onto our planet’s surface (about 16,000 times more energy than all of humanity consumes, even with our current bloated habits), I have been certain that a mostly-solar-electric world was inevitable. The only obstructions were human inertia and politics, which are temporary. Physics is forever.
For example, consider the following map showing the tiny amount of our deserts we would need to cover with solar panels to replace all energy consumption (electricity, oil, gas, nuclear, hydro, wind, etc)
Fig. 1: Tiny land area required to power all of humanity. (image source)
And it’s actually even better than that: the image above assumes an old-school solar panel efficiency of 8%, whereas 18% is now a standard rate. So you can cut the black dots in half again, and then chop a few more times to account for the other existing clean energy sources.
And of course, you don’t have to concentrate the panels and run giant power lines everywhere as implied by the map. You can stick solar panels virtually anywhere and they will start working like little employees for you, tirelessly cranking out energy (which is equivalent to money) and automatically.
Which is of course the real subject of this article.
My DIY Solar Project
The new solar array at the MMM HQ workshop generates more than enough power to run the whole property year-round, plus charge the electric cars of the various members.
So naturally, I have always wanted to have my own solar power farm. Until now, various excuses kept me from getting it done: no great places to put panels on the roof of my main house, slightly unfavorable local regulations, but mainly a lack of knowledge of exactly what to buy and how to install it.
I vowed that whenever I finally got this project done, I’d write up a report to you, to spare you some of the research and time consumption that I had to go through.
So let’s get into it!
Part One: Show me the Money
As you can see from the picture above, I’ve started by building a relatively small solar array. There are twelve panels, each about 40 x 60 inches. Each one generates 300 watts of electricity when the sun shines, and when you run the numbers for my climate, the whole setup will crank out about 6100 kWh/year of electricity, a chunk which is worth about $732 per year at average US power prices.
Pretty amazing – enough energy to run my coworking space and Mrs. MM’s adjacent retail store… from a chunk of pretty black glass that is about the same size as a single car parking space!
Meanwhile, the wholesale cost of this equipment broke down roughly like this:
12 solar panels at $130 each: $1656 (a total of 3600 watts at 46 cents per watt)
12 Optimizer modules (which increase power output during partial shade): $650
One SolarEdge 6 kW Inverter (converts the DC current from the panels to AC for the grid): $1102
Various brackets, mounting racks, bolts, and wiring stuff: $460
So my total cost, due to the very good luck of having a friend who is both a dedicated Mustachian and the owner of a booming solar company, was $3900.
That’s the best case, but even after you add normal profit margins plus a 30% tariff that The Donald recently levied on solar panels (and remember the panels are thankfully only half the cost of the system), you can still buy a similar Complete kit for $6000 including shipping.
When you’re measuring the annual return on your investment (or “payback period”), there’s only one thing that matters on the cost side: price per watt. I ended up building this system at about $1.08 per watt, which is low by today’s standards but will soon sound high.
And remember, there are usually tax incentives to cut this cost further – you can take 30% off the top of this cost due to the US Federal “Investment Tax Credit (ITC)“, and possibly more from your state and local government or utility.
The Great Solar Journey to Durango
Last year, I met a badass Mustachian entrepreneur named John. He was in Longmont to visit some family here, but his real home base is in Durango, Colorado where he runs a successful solar installation company called Shaw Solar. There are a million stories that need to be told about this man, but for now we’ll start with this one.
Knowing how long I had been interested in a do-it-yourself solar project, John decided to step up and help me get it done at last. We went over technical details, calculations, strategies, and costs. All of this culminated in me taking a spectacular roadtrip to Durango along with another local friend, in May of 2017.
It was quite a trip, for much more than the acquisition of solar panels and advice. Durango is a stunning little town, and it turned out that John lives in a community of equally impressive siblings and friends – for example his brother Charles who DIY-renovated a 50,000 square foot school over a 20-year period, which has now become the jewel of Durango’s downtown.
Time For the Build
I drove back from this trip full of confidence and energy… only to end up storing the solar panels for months in my studio building as I worked to finish higher-priority parts of the Headquarters building, then waited for the time and motivation to plow through the building permit application.
It took another visit from John to really kickstart the project, and once we worked through it I realized my worry was completely unfounded – if you know what you’re doing, a simple solar array can be completely installed by two people in a less than a day’s work. Here’s what we ended up doing.
Step Zero: Research and Permit
Begin with the end in mind. The amazing Kari Spotts (LPC’s lead of renewable power metering) helps me swap in a new dual-flow electric meter at the successful completion of this project.
This is the part that stops most people before they even begin. The quickest shortcut is that if you’re not interested in these details, find someone who is, to catapult you through it. But if you have enough curiosity to learn the details, here they are:
How big a system should I build? In general, the bigger, the better. The cost per watt goes down as your system grows, making it a higher annual yield on the investment.
“I don’t live in Colorado. How much juice will I get out of it where I live?” This part is fun: The National Renewable Energy Lab runs a great, free calculator called PVWatts that does it all for you: factoring in average weather and solar angles in your area, even allowing you to specify solar panels placed at any crazy angle you like. (In other words, your house doesn’t have to have a perfect South-facing roof).
“Do I need some of those Tesla Powerwall Batteries too?” No. Unless you’re building an off-the-grid cabin, in almost all cases you will want to “grid-tie” your solar array, so you can effectively sell your surplus electricity back to the power company (and thus, other nearby customers), cleaning up your whole town and saving the huge cost of batteries. The Powerwall works great if you want protection from power outages, however, and can even pay for itself if you live somewhere with a smart grid that allows day/night price arbitrage.
“How do I get a permit to build this thing?” Your city’s building department probably has a page describing how to apply. For example, here’s the one for Longmont. The trickiest part is generating a “one-line diagram”, but I cheated by just photoshopping my own details into the example provided with my city, leading to this result, which they approved without question.
Step One: Layout
I had a nice, simple roof that was already facing South, tilted up at a 30 degree angle, which is just about perfect for solar panels. But you can also put them on other slopes or flat roofs, and they still work surprisingly well.
I needed two rails for each row of panels, and the rails get supported by “L”-shaped brackets bolted into the roof. So I ended up with this configuration:
Laying out support brackets, rails, panels, and power inverter.
Important consideration: Because I was putting this on a garage roof (technically “unoccupied space”), I was able to squeeze them all the way to the roof edge. If you are installing on a house, your city’s fire code may require that you leave a 3 foot walking access around the edges. Sometimes it’s wise to think outside the box: a garage roof, a standalone ground-mounted rack if you have lots of unused land, or creating the new workshop/carport/garden shed you’ve always wanted in the sunniest part of your yard.
2: Install your Brackets and Rails
Once you figure out where to put the long “lines” shown above, you measure them out and snap chalk lines right over top of your existing roof material. Then, use some sturdy 2.5″ lag bolts and washers to hold down the L-shaped brackets that come with the solar racking kit. Pre-drill each hole, and inject in some “Through the Roof” sealant with a normal caulk gun before driving in those bolts – this creates a permanent watertight seal. (There are also special brackets to accommodate different roof styles like tile and metal).
Once the brackets are in, you simply use the supplied slide-in bolts and nuts to attach the long rails, straighten them up nicely, and lock it down. Doing all of this with a cordless impact driver makes it quick and clean.
3: Bolt down and connect the Optimizers if you’ve Got ‘Em
These are just little flat boxes that you connect to the top of each pair of rails, about 6″ from the eventual right edge of each solar panel. There’s one optimizer for each panel, and it acts like a babysitter – monitoring output from the panel, compensating for voltage changes when necessary (such as when shade hits that panel). You’ll notice that each optimizer has four wires protruding from it, and there’s one optimizer for each panel. This will make sense in the next step.
Optimizer mounting (face down), plus a good shot of the connections between roof, brackets, and rails.
Once all the optimizers are in place, you connect each pair of longer wires together with the incredibly convenient fast-click connectors. The positive and negative wires have differently shaped connectors so you can’t accidentally reverse them.
You end up connecting inverters to each other, and each panel only to its host inverter, like this:
Inverter to panel connections
If you have two lines of panels as I do, connect the far end of one line to the far end of the next line, so you end up with a long series of optimizers where both ends terminate with a loose wire on the end closest to your inverter.
Grounding is Important: Using the supplied grounding screw terminals, connect all the rails together with bare 10AWG copper wire. From that last terminal, you’ll be running a length of the same size wire down to the inverter.
4: Install the Solar Panels!
The bottom of each panel has two long output wires. Use clips and/or zip ties to keep the cables tidy so they don’t dangle onto the roof too much.
This step is better with two people, especially on a steep roof. Starting at the furthest corner from the location of your inverter, connect each the panel’s wires to the matching ones on its host inverter. Set the panels down straight, and use the click-in clamps that come with the racking system to clamp down the panel using your cordless drill/driver.
By the end of this step, you’ll have one or more tidy lines of panels with just two powerful-looking DC wires poking out the end, with connectors to go.
You’re now ready to build the final run of wire, which will enter a metal conduit and travel through your roof, down the side of your house, and into the inverter.
5: The Home Run:
Drill a 1″ hole in your roof and put a roof boot over top of it, tucked under the upper course of shingles. From there, your goal is to provide a protected path to get the high voltage DC wires to from the panels, down to the inverter.
My city required 3/4″ metal rigid conduit, which gave me the opportunity to learn about the various fittings and connectors that are part of working with conduit. I also bought a conduit bending tool, since there are many more outdoor electrical projects still on the docket for the MMM HQ building.
I ran a length of metal conduit up from the inverter and just beyond the roof boot, then transitioned to a downward-facing connector to some flexible conduit, just to keep the wires covered until they get under the panels. All three conductors including the ground are running through this tube. If doing it again, I’d suggest using a different conduit box for that transition. Also, you can switch from a bare ground wire to a stranded, insulated ground at that point – much easier to pull through!
6: Mounting The Inverter and Connecting it all to the Grid:
The part that sounds the most mysterious is actually one of the most simple:
Hang the inverter on the wall using the supplied bracket and a few screws
Connect the conduit and pull in the DC wires from the solar panels into the inverter’s connection box. On this Solaredge unit, there are nice spring clip terminals.
Do the same on the other side of the connection box, running a length of 10/3 household wiring (for outputs up to 40 amps) right into the breaker box, as if you were hooking up any other 240 volt circuit.
Inverter mounting, including the conduit going up through the roof (left), out to the main breaker box (right), required warning stickers (red), and how it’s hooked up inside (bottom)
7: Get it all Inspected and Power it Up!
The inspector will probably have a nitpick or two with your work. Stay strong and make any required corrections, and pass that inspection. Then you flip on the AC breaker, the DC power switch, the inverter’s main power switch, and poke through the menu systems to make sure everything is set to run the way you like it.
For this Solaredge system, I had to run a “Pairing” step with the power optimizers (see manual), and add a TP-Link Wireless Repeater/Bridge to allow the inverter’s wired Ethernet connection to join my existing property-wide Wi-Fi network. Which happens to be the the spectacularly good Google Mesh Wi-fi system.
So What’s Next?
From this point on, it’s all on automatic pilot. The system generates electricity every day, which reduces the Headquarters power bill down to zero. In winter, the days are shorter so we might consume more than we produce. But in summer, a large surplus will more than make up for it.
My inverter from Solaredge comes with a really nice monitoring features, available from both a phone app and any browser. Plus, you can share a public version of your page with anyone. Here’s one I made for the MMM-HQ array.
At the time of writing, I’ve had the system online for 27 mostly-January days, including a couple of writeoffs where the panels were covered in snow. It has still averaged about 10 kWh of electricity production per day, which is more than the average consumption of the whole facility. Put another way, the 265 kWh of electricity is enough to power an electric car for roughly 1000 miles of driving.
The monitoring tool also estimates about 410 lbs of CO2 emissions prevented, which is 0.2 tons or about $4.00 worth at current carbon cleanup rates. If you happen to care about running a carbon-neutral life (or business) as I do, this means the carbon offset makes your solar electricity about 15% more valuable in your mental accounting.
I can also double or triple the number of panels on this particular system (once I decide on a good place to put them) without changing the inverter or any of the grid-tie connections, which will greatly improve my annual return on investment. It’s just a LEGO-like plug and play to connect more panels to an existing rack of them, plus the inverter has a second set of inputs if you are running in some wires from a string of panels you have placed somewhere else.
My power company pays out a check for any overall surplus at the end of each year, purchasing the power at a wholesale rate. But many regions are more solar-friendly than this, giving you a full retail or even higher rate for solar-generated electricity as an incentive to go green.
The Final Word:
Solar energy is strangely fun to produce – most people report satisfaction far beyond just the monetary benefits. It gets you out there rooting for the Sun, and for your fellow humankind to follow suit and start harvesting it alongside you. So if you’ve been considering getting it done, the time is good.
Thanks again to John Shaw (shawsolar.com) for all the help with this project. If you have questions about the details or the industry in general, please put them in the comments and both John and I should be able to weigh in.
And if you happen to own a home or business around Durango, CO, contact Shaw Solar directly and tell ’em who sent you!
Rough Edges Alert: I’ve started by publishing this article in an unpolished form, so If you see incorrect details, please let me know and I’ll clean it up over time after publication.
from Finance http://www.mrmoneymustache.com/2018/02/07/diy-solar-power/ via http://www.rssmix.com/
0 notes
Text
Metamaterial Market Research Report Analysis
Metamaterials Market
Growth opportunities in the Metamaterials Market look promising over the next six years. This is mainly due to their increasing demand for modeling & simulation to perform the various operation in industrial sectors and rising employment across major end-use sectors, including medical, aerospace and defense, consumer electronics, and automotive.
Request for a FREE Sample Report on Metamaterials Market
Metamaterials Market Dynamics (including market size, share, trends, forecast, growth, forecast, and industry analysis)
Key Drivers
Several prominent drivers stimulating the growth of the global metamaterials market include the increasing preference to implement these materials across several information and technology applications, augmenting demand for mirroring and reproducing of the devices for industrial purposes, and the surging emphasis on the introduction of effective solar power solution. Also, the mounting focus to employ the material across several healthcare and biomedical operations is strengthening the metamaterials market size. The material is further utilized for power plants, smart metamaterial antennas for 5G networks and satellites, and mechanically scanned array platforms for self-driving cars & drones will supplement the market share. However, as per the metamaterials market research, insufficient knowledge, excessive research, and design cost for successful execution in real-time functions and complexities concerned with design and fabrication may hinder the market growth.
Vertical Segment Drivers
Based on the Vertical, Aerospace and Defense is projected to expand at a higher CAGR during the forecast period. This is primarily attributed to their largest market size in terms of value. They mainly require customized solutions for communication. Also, the majorly endorsed metamaterial-based equipment are antennas, protective layers, windscreens, EMC shielding, and cloaking devices. These antennas can be applied for safe communications in the defense sector as they can be tuned to different bandwidths. Thus, the rising need for bandwidth and demand for secure communication further bolsters the market growth.
Application Segment Drivers
Based on the Application, Communication Antenna and Radar (BeamSteering) is expected to witness a faster CAGR during the forecast period. This is because of their soaring demand applications such as satellite communication, Wi-Fi routers, radar communication, and 5G communications.
Metamaterials Market’s leading Manufacturers:
· Mediwise
· Nanohmics Inc
· Echodyne Corp
· JEM Engineering
· Kymeta Corporation
· MetaShield LLC
· Multiwave Technologies AG
· TeraView Limited.
· Metamagnetics
· Kymeta Corporation
Metamaterials Market Segmentation:
Segmentation by Technology
· Electromagnetic
· Terahertz,Photonic (Optical)
· Tunable
· Frequency Selective Surface
· Other
Segmentation by Application
· Communication Antenna and Radar (BeamSteering)
· Sensors
· Solar Panel and Absorbers
· Display
· Medical
· Imaging
· Windscreen
· Other
Segmentation by Vertical
· Automotive
· Aerospace and Defense
· Consumer Electronics
· Medical
· Energy and Power
· Other
Segmentation by Region:
· North America
o United States of America
o Canada
· Asia Pacific
o China
o Japan
o India
o Rest of APAC
· Europe
o United Kingdom
o Germany
o France
o Spain
o Rest of Europe
· RoW
o Brazil
o South Africa
o Saudi Arabia
o UAE
o Rest of the world (remaining countries of the LAMEA region)
About GMI Research
GMI Research is a market research and consulting company that offers business insights and market research reports for large and small & medium enterprises. Our detailed reports help the clients to make strategic business policies and achieve sustainable growth in the particular market domain. The company's large team of seasoned analysts and industry experts with experience from different regions such as Asia-Pacific, Europe, North America, among others, provides a one-stop solution for the client. Our market research report has in-depth analysis, which includes refined forecasts, a bird's eye view of the competitive landscape, key factors influencing the market growth, and various other market insights to aid companies in making strategic decisions. Featured in the 'Top 20 Most Promising Market Research Consultants' list of Silicon India Magazine in 2018, we at GMI Research are always looking forward to helping our clients to stay ahead of the curve.
Media Contact Company Name: GMI RESEARCH Contact Person: Sarah Nash Email: [email protected] Phone: Europe – +353 1 442 8820; US – +1 860 881 2270 Address: Dublin, Ireland Website: www.gmiresearch.com
0 notes
Text
Journal - 26 Extraordinary Architectural Projects Across China
China is no stranger to great architecture. Within the last decade, the country has emerged as the globe’s largest construction market, and as a result, many noteworthy modern projects have been built. The winners’ gallery of last year’s A+Awards, the world’s largest awards program for architecture and building-products, form indisputable proof of China’s rise: An incredible 26 projects across the country were recognized in a plethora of categories. With the 8th Annual A+Awards now open for entries, it is anticipated that many Chinese firms will once again take the spotlight through new and innovative works.
Enter the 8th Annual A+Awards
Showcased below, last year’s Chinese A+Award winners form a celebration of contemporary design ideas throughout the country. From hospitality and sports projects to commercial pop-ups, offices and education spaces, these projects represent an incredible diversity of design approaches and construction methods. Built across a range of scales, they bring an incredible array of contemporary architectural concepts to life. As you consider which of your latest projects to submit for this year’s program, get inspired by China’s best modern architecture:
Boolean Operator by MARC FORNES / THEVERYMANY, China Commercial-Pop-Ups & Temporary, Jury Winner, 2019
For the event of the Jinji Lake Biennial, New York-based studio MARC FORNES / THEVERYMANY installed a large-scale outdoor pavilion on the elevated plaza of the Suzhou Center. Its undulating enclosure interrupts the usual traffic as an unexpected, emergent environment.
Xinglong Bookstore by MUDA-Architects, China Unbuilt Commercial, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
The bookstore’s design takes the idea of “a book falling from the sky” as the starting point of the story, and the architectural form is taken from book. Through this metaphor, the team hoped that people can walk into the building to read themselves, and to complete a journey of self-discovery in a peaceful environment.
Tibet Intangible Cultural Heritage Museum by Shenzhen HuaHui Design, Tibet, China Architecture +Art, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
Tibet is considered to be a holy place close to the sky, with the Potala Palace and Jokhang Temple being pilgrims’ destinations. The team’s basic design concept of “Heavenly Road” is consistent with the most unique natural and cultural genes in Tibet. The concept of “heavenly road” is embodied at three levels.
Play Stack Shenyang by CLOU architects, Shenyang, China Commercial-Shopping Center, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
Designed to be a shopping mall as a playground, ‘Play Stack’ is a kid’s themed mall with piled up boxes containing playful elements. Terraced volumes, connecting staircases and a large roof deck are threaded into a continuous exterior ‘play scape’ path.
Swirling Cloud: Pavilion for BJFU Garden Festival by SUP Atelier, Haidian, Beijing, China Architecture +Ceilings, Popular Choice Winner & Jury Winner, 2019
Located in a grove in the campus of BJFU, the “pavilion of clouds” is a bamboo structure built for 2018 “Bamboo Garden Festival”, and the project was commissioned by the faculty of BJFU. Covering an area of approximately 120 square meters, the pavilion serves as a hub for information during the festival and turns into a flexible place for recreation and gathering when the event is over.
3D Printed Pedestrian Bridge by XWG Archi-Studio, Beijing, Shanghai, China Architecture +Technology, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
Inspired by the ancient Anji Bridge in Zhaoxian, China, this bridge adopts the structure of a single arch to bear the load. The 3D printing concrete system is independently developed by Professor Xu Weiguo’s team. It integrates technologies such as digital architectural design, printing path generation, operation control system, printing tool, concrete material, etc.
123+ Kindergarten by OfficeOffCourse, Shanghai, China Institutional-Kindergartens, Popular Choice Winner, 2019 Architecture +Learning, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
The 123+ kindergarten is located in a newly built shopping center. It adopts the Montessori method of education, which views the child as one who is naturally eager for knowledge and capable of initiating learning in a supportive, thoughtfully prepared learning environment.
Dongsi 5Lmeet by DAGA Architects, Beijing, China Commercial-Coworking Space, Popular Choice Winner & Jury Winner, 2019
The Dongsi 5Lmeet was an abandoned soy sauce factory surrounded by the old gray-tiled buildings. It is not far from the historical Duan Qirui Prime Minister’s Office, and next door is a residential development that’s been there for decades. 5Lmeet was made to be an innovative space in an old community.
Louis Vuitton by Nathan Allan Glass Studios, Beijing, China Architecture +Glass, Jury Winner, 2019
As Louis Vuitton’s flagship store in Beijing China, this high end retail store features a storefront section that was completely renovated with custom kiln formed glass. 32 panels of various sizes, totaling over 1000 square feet of glass, were formed, safety tempered, and installed. The custom design was produced using a special “Freeform Series” production process, which creates deep 3D patterned glass.
Exhibition Center of Longquan National Archaeological Park of China by OfficeOffCourse, Longquan, Lishui, China Architecture +Glass, Popular Choice Winner, 2019 Cultural-Gallery, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
Historically, Longquan celadon is a type of green-glazed Chinese ceramic, known as celadon or green ware, produced from about AD950-AD1550. The national Archaeological Park is built to preserve the Longquan historical kiln conservation sites in Dayao village.
X-House by asap/ adam sokol architecture practice, Beijing, China Architecture +Metal, Jury Winner, 2019
Situated in Beijing’s tallest residential structure, the X-House is a showcase business and residential space for an international entrepreneur. Designed to accommodate business meetings, banquets, guests, and other functions, the space features a 1000-bottle wine cellar, tasting room, and spa bathrooms.
Chishui Danxia World Natural Heritage Visitor Center by West-line Studio, Chishui, Zunyi, China Architecture +Stone, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
This tourist center welcomes visitors to the Danxia World Natural Heritage Site in Chishui region, a popular tourist attraction. The project includes the basic facilities for tourists and is located at the entrance of the scenic area in a V-shaped canyon.
Shenzhen Energy HQ by BIG, Shenzhen, China Commercial-Office – High Rise (16+ Floors), Popular Choice Winner, 2019
Shenzhen Energy HQ is a complex high-rise building comprising office spaces and public functions. The building is based on an efficient and well-designed floor plan, enclosed by a skin specifically optimized and modified to reduce solar heat gain.
“The Shadow Garden” of World Horticulture Expo in Yangzhou by OfficeOffCourse, Yangzhou, China Architecture +Landscape, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
The Shadow Garden is one of the five satellite pavilions located in the first completed phase of 2021 World Horticulture Expo site in Yangzhou. Based on the scheme, this expo reflects the beauty of local landscape and plants as well as its programmatic requirement which is an educational place. The design aims to generate a new relationship between landscape and architecture.
Village Lounge of Shangcun by SUP Atelier, Jixi, China Architecture +Community, Jury Winner, 2019
The village lounge in Shangcun turned the ruined courtyard into a public space, providing leisure, multi-used community space for both local residents and tourists.
VITA-The Fortune Bridge by Arizon Design, Zhengzhou, China Transportation-Transportation Infrastructure, Popular Choice Winner & Jury Winner, 2019
As the main lead into the Shopping Boulevard, the bridge represents the architect’s hope of providing youngsters with emotional support. It is thus referred to as “the Fortune Bridge”.
Bozhou Stadium by Yuan Ye Architects/China Construction Engineering , Bozhou, China Sport & Recreation-Stadium/Arena, Jury Winner, 2019
Bozhou Stadium abstracts the inverted trapezoidal form from Han Dynasty architecture and utilizes it as the basic geometric form of the building. It also uses the square pool along the shape as the “base” to ground the building form and emphasize the purity of the building. Inspired by the local armor of the warriors of the Han Dynasty, the architectural skin simulates the folding of the armor’s surface with a continuous triangular folding surface.
Vanke Emerald Park by Lacime Architects, Chongqing, China Sport & Recreation-Recreation Centers, Jury Winner, 2019
In Vanke Park, the outer frame, column and cornice of the main building are all designed with an oblique section. The horizontal lines of the floor intersect with the inclined planes between the columns, which increases the requirement for construction accuracy. The square main building is surrounded by water on three sides, and the columns of the outer frame fall on the water.
Yunmen Montain all-seasons Resort by ATAH, Qingzhou, Weifang, China Sport & Recreation-Recreation Centers, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
The Yunmen Mountain all-seasons Resort is located at the Qilu Mountain Region. Although the local city of Qingzhou is famous for its history and vernacular architecture, visitors can immediately feel the presence of the vast nature when immersed in the mountains. Hence, the design concept is based on integration into the mountains and nature, rather than cultural expression or history.
Hangzhou Haishu School of Future Sci-Tech City by LYCS Architecture, Hangzhou, China Institutional-Primary & High Schools, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
Traditional school planning in modern Chinese cities usually provides students and children with an adult-scale campus environment at an excessively early stage. Facing these phenomenon, the architects aimed to subversively break these conventions in school planning and offer children with space of their own scale and age in which they could enjoy living and studying.
Hengdian Hotel by gad, China Hospitality-Unbuilt Hospitality, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
The hotel is located in the center of Hengdian City, the “Chinese Hollywood.” The site is surrounded by three sides by mountains which are also forested. The design concept is building the image of the contemporary private residence through the arrangement of courtyards which are based on the space of the local famous private residence called Lu Residence, or “the Folk Forbidden City”.
Dreaming Someone by WAY Studio, Beijing, China Hospitality-Restaurants, Jury Winner, 2019
WAY Studio recently completed the “Aye by Meeting Someone” restaurant in Beijing to explore spatial performance and provide a transient surreal experience to visitors. The spherical entrance, the infamous rabbit hole, crashes into the wall and creates ripples on the exterior façade. Designed with computational scripting, the façade has become a juxtaposition between technology and craftsmanship, linking modernity with tradition.
M50 Art Hotel by MUDA-Architects, China Architecture +Models & Rendering, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
M50 Art Hotel Project is located in Pingle, Sichuan. Pingle Ancient Town is planned to be a music theme town. Therefore, the starting point of this project was around “Music”. In this project, MUDA- Architects strived to explore and activate local culture genes, and to create a landmark building that can inherit the historical context and also is forward-looking.
Boat Rooms on the Fuchun River by The Design Institute Of Landscape & Architecture China Academy Of Art , Hangzhou, China Hospitality-Hotels & Resorts, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
These boat rooms “float” on the west bank of a lake where the resort covers a large area. The concept and shape of the “boat room” take its root in a local social custom from Fuchun.
Dongshang by Imafuku Architects, Beijing, China Hospitality-Bars & Nightclubs, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
Located in Beijing’s central business district, Dongshang is a contemporary Japanese restaurant and bar with a wide selection of sake and Japanese whisky. The vision of the client was to create a Japanese-style venue, while also representing the elements of Chinese culture, as well as featuring natural materials.
One City Development by Aspect Studios, Hubei, China Landscape & Planning-Urban & Masterplans, Popular Choice Winner, 2019
Aspect Studios set out to create a destination that provides a unique response to the public realm of the city and a place that acknowledges the importance of socially orientated space for people. To do this the team drew upon contemporary Wuhan lifestyle and the traditional local mythology of the ‘Phoenix’. The design is structured with a series of diverse spaces, nodes and experiences connected and unified by a fluid gesture and movement.
To be in the running for an iconic A+Awards trophy, publication in “The World’s Best Architecture” book by Phaidon, and a wealth of global publicity on Architizer, make sure your firm enters the 8th Annual A+Awards before the Final Entry Deadline on March 27th, 2020.
Enter the 8th Annual A+Awards
The post 26 Extraordinary Architectural Projects Across China appeared first on Journal.
from Journal https://architizer.com/blog/inspiration/collections/a-architecture-china/ Originally published on ARCHITIZER RSS Feed: https://architizer.com/blog
#Journal#architect#architecture#architects#architectural#design#designer#designers#building#buildings
0 notes
Text
Solar Power is Coming to Space, According to the Airforce
In the race to replace traditional #energy methods with #solar energy, the United States is setting its sights on space. The Airforce Research Laboratory (AFRL) in Albuquerque is currently working on a #space-based solar energy satellite. In collaboration with Northrop Grumman, an American global aerospace and defense technology company, the AFRL is aiming to create a satellite system that will gather #solar energy from space, convert it into radio frequencies, and channel it back down to Earth. The primary goal is that the space-based #solar power project will provide energy for remote military base operations.
The project is known as the Space Solar Power Incremental Demonstration and Research project, or SSPIDR, and will cost more than $100 million to create and launch. AFRL’s Space Vehicles Director, Colonel Eric Felt, told the Albuquerque Journal that “to ensure Department of Defense mission success, we must have the energy we need at the right place at the right time.”
Major Tim Allen stated that the project is primarily to help replace convoy power deliveries used by troops. With the ability to send solar power from space to targeted areas, troops will no longer have to escort power convoys and are more likely to remain safe. The overall goal of the space-based solar system will be reliable, “wireless power transmission,” according to Allen.
Details of the Space-Based Solar Array
Developers of the AFRL space-based solar system are planning on creating a constellation of satellites with solar panels, spanning nearly 10,000-square meters across. The goal is that the solar energy gathered from the space structure can be targeted towards and electronically steered to specific locations. Rachel Delaney, the systems engineer for the space-based solar project, is currently working with a team to develop different demonstrations that will allow them to work out the details for a large-scale prototype.
Some of the biggest challenges Delaney and her team will face involve combating thermal damages that the solar structure may incur, as well as supporting a mammoth solar array of this size in orbit.
Increasing Interest in Space-Based Solar
Beaming solar energy from space back to Earth is not a new concept. In fact, the idea of space-based solar energy production has been around since the 1960s. However, it has not been a technologically realistic nor cost-effective possibility until recently. Part of the AFRL’s challenge in moving forward with space-based solar energy will be to find out just how cost-effective such an idea will be.
The good news is that with space-based solar energy, the solar panels can operate 24/7. According to Ali Hajimiri, an electrical engineering professor at the California Institute of Technology and director of their Space Solar Power Project, space-based solar has access to a constant power source. With no clouds, atmosphere, weather, or other obstructions, solar arrays in space can soak up the sun’s rays without interference or dependence on a day and night cycle.
Space-Based Solar: The Solution to Earth’s Energy Crisis?
Hajimiri, as well as other scientists and leaders that are pushing for space-based solar, are optimistic that we could test the first solar array in space within the next few years. Former NASA scientist, John Mankins, estimates that a space-based solar system could generate a constant flow of nearly 2,000 gigawatts of power. This is a massive upgrade in output compared to Earth’s largest solar production farm in Aswan, Egypt, which only produces 1.8 gigawatts of energy for the region.
If scientists can find a way to build a successfully space-based solar energy system that is both cost-effective and efficient, we could see “virtually limitless and sustainable energy” provided to various markets and cities worldwide, according to Mankins. Mankins warns, however, that other problems, such as geopolitics, could hinder progress.
Even though the AFRL space-based solar system will be used primarily for military operations, Delaney and Allen are hopeful that this solar project will be useful in the future for delivering solar energy to remote areas and other non-military communities around the world. Before long, we may just find that our energy on Earth is provided by space-based solar arrays floating in the atmosphere.
Resources:
https://www.abqjournal.com/1386648/afrl-looks-to-beam-solar-energy-from-space.html
https://www.forbes.com/sites/scottsnowden/2019/03/12/solar-power-stations-in-space-could-supply-the-world-with-limitless-energy/
0 notes
Text
Sailing Among the Stars: How Photons Could Revolutionise Space Flight
https://sciencespies.com/news/sailing-among-the-stars-how-photons-could-revolutionise-space-flight/
Sailing Among the Stars: How Photons Could Revolutionise Space Flight
A few days from now, a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket will lift off from Florida, carrying a satellite the size of a loaf of bread with nothing to power it but a huge polyester “solar sail.”
It’s been the stuff of scientists’ dreams for decades but has only very recently become a reality.
The idea might sound crazy: propelling a craft through the vacuum of space with no engine, no fuel, and no solar panels, but instead harnessing the momentum of packets of light energy known as photons - in this case from our Sun.
The spacecraft to be launched on Monday, called LightSail 2, was developed by the Planetary Society, a US organisation that promotes space exploration which was co-founded by the legendary astronomer Carl Sagan in 1980.
But the idea itself has been around for a lot longer than that.
“In the 1600s, Johannes Kepler talked about sailing among the stars,” Bill Nye, the chief executive of the Planetary Society, told AFP.
Kepler theorised that sails and ships “could be adapted to the heavenly breezes,” and “it turns out, there really is. It’s not just poetry,” said Nye, who is known in the US as the “Science Guy” after the children’s TV show which brought him national fame in the 1990s and who now hosts a Netflix program.
And building a solar sail doesn’t require cutting-edge tech as you might imagine.
It’s essentially a large square of very thin film (less than the width of a human hair), which is also ultra-light and reflective.
It has an area of 32 square meters and is made from Mylar, a brand of polyester that has been on the market since the 1950s.
As photons bounce off the sail, they transfer their momentum in the opposite direction to the bouncing light.
“The bigger and shinier and lower mass the spacecraft, the more of a push it gets,” explains Nye.
The thrust provided by these photons is tiny – but it’s also unlimited. “Once you’re in orbit, you never run out of fuel,” he said.
Japan’s space agency launched a solar sail in 2010, dubbed Ikaros, but others haven’t been able to fully test the concept.
“It’s a romantic idea whose time has finally come,” said Nye. “We hope this technology catches on.”
Unlimited energy Its predecessor was LightSail 1, launched in 2015. But its mission, which lasted a few days, experienced problems and was intended only to test deployment of the sail.
LightSail 2 cost $7 million (roughly Rs. 49 crores), a relative pittance in space mission terms. It is envisaged to remain in orbit for a year, and represents a more definitive proof of concept.
“We want to democratise space exploration,” enthused Nye, who has invited universities and businesses to take up the technology.
A few days after its launch from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, LightSail 2 will open its hinged solar arrays, then deploy the four triangular parts of its sail, which together form a giant square.
For this demonstration, solar panels will provide power for the satellite’s other functions such as photography and ground communications.
As it orbits the Earth, it will begin to increase its altitude thanks to the pressure of solar radiation on the sail.
So what do we see the technology being used for in the near future?
For a start, it could facilitate deep space exploration. Though it starts off much slower than a spaceship powered by fuel, it will continue to accelerate permanently through space, eventually achieving breathtaking speeds.
The other application would be in maintaining a probe at a stationary point in space, which would require corrections to be made infinitely. For example, a telescope that looks out for asteroids in the vicinity of Earth, or a satellite that needs to be fixed in a stationary orbit above the North Pole.
“You’d need an enormous amount of rocket fuel to keep stationary for 10 years. It’s just not practical,” said Nye.
Photons, on the other hand, are unlimited.
As a bonus, said the scientist, “You’ll be able to see it from the ground,” with the naked eye.
#News
0 notes
Text
SATCOM Equipment Market – Opportunities, Challenges & Future Growth Scope Till 2025
The global SATCOM Equipment Market for Space is projected to grow from USD 2.8 billion in 2019 to USD 7.0 billion by 2025, at a CAGR of 16.8% from 2019 to 2025. The growth of the market across the globe can be attributed to the increasing launch of satellites for applications such as earth observation, communication, and navigation.

Browse 83 market data Tables and 40 Figures spread through 143 Pages and in-depth TOC on "SATCOM Equipment Market - Global Forecast to 2025"
Based on application, the earth observation & remote sensing segment is projected to lead the SATCOM equipment market for space during the forecast period.
Based on application, the SATCOM equipment market for space is projected to be led by the earth observation & remote sensing segment from 2019 to 2025. According to an article published by SpaceNews in December 2018, the demand for earth observation (EO) is growing, due to a growing focus on analytics from high-resolution and medium-resolution imagery. Technology for analyzing data gathered from EO satellites such as big data analytics is expected to grow four times over the decade.
Browse In-depth Insights: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/space-satcom-equipment-market-177487346.html
The increasing use of CubeSats for Earth observation and remote sensing is expected to drive the SATCOM equipment market for space from 2019 to 2025.
Based on satellite type, the CubeSat (0.25U–27U) segment is projected to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period. The SATCOM equipment market for CubeSats is expected to grow during the forecast period due to an increase in the volume of CubeSats launched and scheduled for launch during the forecast period. CubeSats are used for a variety of missions, have a small form factor, and cost substantially less to develop and launch in comparison to large satellites. The increase in the launch of CubeSats can be attributed to the rising demand for EO.
Regional Outlook
North America and Asia Pacific are projected to be high growth potential markets for SATCOM equipment for space during the forecast period.
The SATCOM equipment market for space in the North American region is expected to witness substantial growth during the forecast period due to increased launch and scheduled launch of satellites.
According to an article published in The New York Times in May 2019, SpaceX launched a batch of 60 internet communication satellites, as a part of the Starlink Megaconstellation Project. According to an article published by Future US, Inc., SpaceX has received permission from the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to launch an estimated total of 12,000 Starlink satellites. Major players such as Amazon (US), OneWeb (US), and Telesat (Canada) are also expected to launch satellites during the forecast period.
Key Companies Outlook
Some of the major players in the SATCOM equipment market for space include Airbus SE (Netherlands), Maxar Technologies (US), Mitsubishi Electric Corporation (Japan), General Dynamics Corporation (US), Honeywell International Inc. (US), Harris Corporation (US), ISIS - Innovative Solutions in Space B.V. (Netherlands), and Oxford Space Systems (UK).
Maxar Technologies is ranked second in the SATCOM equipment market for space. Maxar Technologies has been exporting its satellite products for more than 40 years. The company operates its satellite business through its division, MDA, which is a key manufacturer of satellite antennas and communication subsystems. MDA has a global presence and caters to customers from various countries. The antennas offered by MDA cover a wide range of frequencies, including VHF, most of the MHz bands, and EHF up to 90 GHz. It caters to both commercial and military customers. In November 2018, MDA secured two contracts worth USD 11 million from OHB System AG and Tesat-Spacecom GmbH & Co. KG for the supply of multiple advanced communication subsystems.
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation secures the third position in the SATCOM equipment market for space. The company has been contributing to space technology since 1960. It has a broad product portfolio and strong business performance. The company is constantly pushing for excellence, with a goal of achieving an operating income ratio of 8%, return on equity of 10% or more, and the ratio of interest-bearing debt to total assets of 15% or less by 2021. The company constantly innovates and brings new technologies to the market, with five new products launched in 2018. In July 2017, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation completed the construction of a facility that is expected to double the satellite component production capacity of the company. The facility is said to undertake the production and testing for solar array panels, structural panels, and other satellite components.
Get Sample Insights: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/requestsampleNew.asp?id=177487346
About MarketsandMarkets™
MarketsandMarkets™ provides quantified B2B research on 30,000 high growth niche opportunities/threats which will impact 70% to 80% of worldwide companies’ revenues. Currently servicing 7500 customers worldwide including 80% of global Fortune 1000 companies as clients. Almost 75,000 top officers across eight industries worldwide approach MarketsandMarkets™ for their painpoints around revenues decisions.
Our 850 fulltime analyst and SMEs at MarketsandMarkets™ are tracking global high growth markets following the "Growth Engagement Model – GEM". The GEM aims at proactive collaboration with the clients to identify new opportunities, identify most important customers, write "Attack, avoid and defend" strategies, identify sources of incremental revenues for both the company and its competitors. MarketsandMarkets™ now coming up with 1,500 MicroQuadrants (Positioning top players across leaders, emerging companies, innovators, strategic players) annually in high growth emerging segments. MarketsandMarkets™ is determined to benefit more than 10,000 companies this year for their revenue planning and help them take their innovations/disruptions early to the market by providing them research ahead of the curve.
MarketsandMarkets’s flagship competitive intelligence and market research platform, "Knowledgestore" connects over 200,000 markets and entire value chains for deeper understanding of the unmet insights along with market sizing and forecasts of niche markets.
Contact: Mr. Aashish Mehra MarketsandMarkets™ INC. 630 Dundee Road Suite 430 Northbrook, IL 60062 USA : 1-888-600-6441
0 notes
Link
The clean energy boffins in their labs are always upping the theoretical limit on how much power you can get out of sunshine, but us plebes actually installing solar cells are stuck with years-old tech that’s not half as good as what they’re seeing. This new design from Insolight could be the one that changes all that.
Insolight is a spin-off from the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, where they’ve been working on this new approach for a few years — and it’s almost ready to hit your roof.
Usually solar cells collect sunlight on their entire surface, converting it to electricity at perhaps 15-19 percent efficiency — meaning about 85 percent of the energy is lost in the process. There are more efficient cells out there, but they’re generally expensive and special-purpose, or use some exotic material.
One place people tend to spare no expense, however, is in space. Solar cells on many satellites are more efficient but, predictably, not cheap. But that’s not a problem if you only use just a tiny amount of them and concentrate the sunlight on those; that’s the Insolight insight.
Small but very high-efficiency cells are laid down on a grid, and above that is placed a honeycomb-like lens array that takes light and bends it into a narrow beam concentrated only on the tiny cells. As the sun moves, the cell layer moves ever so slightly, keeping the beams on target. They’ve achieved as high as 37 percent efficiency in tests, and 30 percent in consumer-oriented designs. That means half again or twice the power from the same area as ordinary panels.
Certainly this adds a layer or two of complexity to the current mass-manufactured arrays that are “good enough” but far from state of the art. But the resulting panels aren’t much different in size or shape, and don’t require special placement or hardware, such as a concentrator or special platform. And a recently completed pilot test on an EPFL roof was passed with flying colors.
“Our panels were hooked up to the grid and monitored continually. They kept working without a hitch through heat waves, storms and winter weather,” said Mathieu Ackermann, the company’s CTO, in an EPFL news release. “This hybrid approach is particularly effective when it’s cloudy and the sunlight is less concentrated, since it can keep generating power even under diffuse light rays.”
The company is now in talks with solar panel manufacturers, whom they are no doubt trying to convince that it’s not that hard to integrate this tech with their existing manufacturing lines — “a few additional steps during the assembly stage,” said Ackermann. Expect Insolight panels to hit the market in 2022 — yeah, it’s still a ways off, but maybe by then we’ll all have electric cars too and this will seem like an even better deal.
from GreenTech – TechCrunch https://ift.tt/2DXfkHS via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
These hyper-efficient solar panels could actually live on your roof soon
The clean energy boffins in their labs are always upping the theoretical limit on how much power you can get out of sunshine, but us plebes actually installing solar cells are stuck with years-old tech that’s not half as good as what they’re seeing. This new design from Insolight could be the one that changes all that.
Insolight is a spinoff from the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, where they’ve been working on this new approach for a few years — and it’s almost ready to hit your roof.
Usually solar cells collect sunlight on their entire surface, converting it to electricity at perhaps 15-19 percent efficiency — meaning about 85 percent of the energy is lost in the process. There are more efficient cells out there, but they’re generally expensive and special-purpose, or use some exotic material.
One place people tend to spare no expense, however, is in space. Solar cells on many satellites are more efficient but, predictably, not cheap. But that’s not a problem if you only use just a tiny amount of them and concentrate the sunlight on those; that’s the Insolight insight.
Small but very high-efficiency cells are laid down on a grid, and above that is placed a honeycomb-like lens array that takes light and bends it into a narrow beam concentrated only on the tiny cells. As the sun moves, the cell layer moves ever so slightly, keeping the beams on target. They’ve achieved as high as 37 percent efficiency in tests, and 30 percent in consumer-oriented designs. That means half again or twice the power from the same area as ordinary panels.
Certainly this adds a layer or two of complexity to the current mass-manufactured arrays that are “good enough” but far from state of the art. But the resulting panels aren’t much different in size or shape, and don’t require special placement or hardware, such as a concentrator or special platform. And a recently completed pilot test on an EPFL roof was passed with flying colors.
“Our panels were hooked up to the grid and monitored continually. They kept working without a hitch through heat waves, storms and winter weather,” said Mathiu Ackermann, the company’s CTO, in an EPFL news release. “This hybrid approach is particularly effective when it’s cloudy and the sunlight is less concentrated, since it can keep generating power even under diffuse light rays.”
The company is now in talks with solar panel manufacturers, whom they are no doubt trying to convince that it’s not that hard to integrate this tech with their existing manufacturing lines — “a few additional steps during the assembly stage,” said Ackermann. Expect Insolight panels to hit the market in 2022 — yeah, it’s still a ways off, but maybe by then we’ll all have electric cars too and this will seem like an even better deal.
from iraidajzsmmwtv https://tcrn.ch/2DZ13dF via IFTTT
0 notes