#Sell ibm
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
HPE 3PAR Maintenance & Support Services | Spectra
Ensure peak performance of your HPE 3PAR storage with Spectra’s expert maintenance and support services. Reliable SLAs, cost-effective plans, and 24/7 assistance available.
#Hpe 3par maintenance#Buy used hpe#Used ibm iseries#Used hpe server#Used dell storage#Sell used hpe#Used dell emc#Used ibm power 10#Ibm server maintenance#Sell ibm
0 notes
Text
Oh hey, look at that! Nokia still sells phones (including modern versions of the early flagship phones I love so much)! They've also expanded to smartphones and tablets over the years, and all the prices I'm seeing are insanely affordable compared to most other mobile tech brands.
So it turns out that when my current phone finally beeps it's last text tone, I really *can* just replace it with a basic old Nokia phone and a tidy lil tablet, and all for fractions of what I paid for the current one!
Now all I need to do is find the desktop computer version of Nokia as a company so I can finally replace my desktop for work.
#does anyone know what desktop computer company sells that could handle both fff14 and 6hrs daily of video conferencing?#i don't need it to have a high storage capacity#i plan to get an external harddrive for all my work files to better secure them#but i DO want to be able to play an mmorpg with the kind of graphics card demand that would have made early ibm engineers cry
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Google antitrust remedy should extinguish surveillance, not democratize it

I'm coming to DEFCON! On FRIDAY (Aug 9), I'm emceeing the EFF POKER TOURNAMENT (noon at the Horseshoe Poker Room), and appearing on the BRICKED AND ABANDONED panel (5PM, LVCC - L1 - HW1–11–01). On SATURDAY (Aug 10), I'm giving a keynote called "DISENSHITTIFY OR DIE! How hackers can seize the means of computation and build a new, good internet that is hardened against our asshole bosses' insatiable horniness for enshittification" (noon, LVCC - L1 - HW1–11–01).

If you are even slightly plugged into the doings and goings on in this tired old world of ours, then you have heard that Google has lost its antitrust case against the DOJ Antitrust Division, and is now an official, no-foolin', convicted monopolist.
This is huge. Epochal. The DOJ, under the leadership of the fire-breathing trustbuster Jonathan Kanter, has done something that was inconceivable four years ago when he was appointed. On Kanter's first day on the job as head of the Antitrust Division, he addressed his gathered prosecutors and asked them to raise their hands if they'd never lost a case.
It was a canny trap. As the proud, victorious DOJ lawyers thrust their arms into the air, Kanter quoted James Comey, who did the same thing on his first day on the job as DA for the Southern District of New York: "You people are the chickenshit club." A federal prosecutor who never loses a case is a prosecutor who only goes after easy targets, and leave the worst offenders (who can mount a serious defense) unscathed.
Under Kanter, the Antitrust Division has been anything but a Chickenshit Club. They've gone after the biggest game, the hardest targets, and with Google, they bagged the hardest target of all.
Again: this is huge:
https://www.thebignewsletter.com/p/boom-judge-rules-google-is-a-monopolist
But also: this is just the start.
Now that Google is convicted, the court needs to decide what to do about it. Courts have lots of leeway when it comes to addressing a finding of lawbreaking. They can impose "conduct remedies" ("don't do that anymore"). These are generally considered weaksauce, because they're hard to administer. When you tell a company like Google to stop doing something, you need to expend a lot of energy to make sure they're following orders. Conduct remedies are as much a punishment for the government (which has to spend millions closely observing the company to ensure compliance) as they are for the firms involved.
But the court could also order Google to stop doing certain things. For example, since the ruling finds that Google illegally maintained its monopoly by paying other entities – Apple, Mozilla, Samsung, AT&T, etc – to be the default search, the court could order them to stop doing that. At the very least, that's a lot easier to monitor.
The big guns, though are the structural remedies. The court could order Google to sell off parts of its business, like its ad-tech stack, through which it represents both buyers and sellers in a marketplace it owns, and with whom it competes as a buyer and a seller. There's already proposed, bipartisan legislation to do this (how bipartisan? Its two main co-sponsors are Ted Cruz and Elizabeth Warren!):
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/25/structural-separation/#america-act
All of these things, and more, are on the table:
https://www.wired.com/story/google-search-monopoly-judge-amit-mehta-options/
We'll get a better sense of what the judge is likely to order in the fall, but the case could drag out for quite some time, as Google appeals the verdict, then tries for the Supreme Court, then appeals the remedy, and so on and so on. Dragging things out in the hopes of running out the clock is a time-honored tradition in tech antitrust. IBM dragged out its antitrust appeals for 12 years, from 1970 to 1982 (they called it "Antitrust's Vietnam"). This is an expensive gambit: IBM outspent the entire DOJ Antitrust Division for 12 consecutive years, hiring more lawyers to fight the DOJ than the DOJ employed to run all of its antitrust enforcement, nationwide. But it worked. IBM hung in there until Reagan got elected and ordered his AG to drop the case.
This is the same trick Microsoft pulled in the nineties. The case went to trial in 1998, and Microsoft lost in 1999. They appealed, and dragged out the proceedings until GW Bush stole the presidency in 2000 and dropped the case in 2001.
I am 100% certain that there are lawyers at Google thinking about this: "OK, say we put a few hundred million behind Trump-affiliated PACs, wait until he's president, have a little meeting with Attorney General Andrew Tate, and convince him to drop the case. Worked for IBM, worked for Microsoft, it'll work for us. And it'll be a bargain."
That's one way things could go wrong, but it's hardly the only way. In his ruling, Judge Mehta rejected the DOJ's argument that in illegally creating and maintaining its monopoly, Google harmed its users' privacy by foreclosing on the possibility of a rival that didn't rely on commercial surveillance.
The judge repeats some of the most cherished and absurd canards of the marketing industry, like the idea that people actually like advertisements, provided that they're relevant, so spying on people is actually doing them a favor by making it easier to target the right ads to them.
First of all, this is just obvious self-serving rubbish that the advertising industry has been repeating since the days when it was waging a massive campaign against the TV remote on the grounds that people would "steal" TV by changing the channel when the ads came on. If "relevant" advertising was so great, then no one would reach for the remote – or better still, they'd change the channel when the show came back on, looking for more ads. People don't like advertising. And they hate "relevant" advertising that targets their private behaviors and views. They find it creepy.
Remember when Apple offered users a one-click opt-out from Facebook spying, the most sophisticated commercial surveillance system in human history, whose entire purpose was to deliver "relevant" advertising? More than 96% of Apple's customers opted out of surveillance. Even the most Hayek-pilled economist has to admit that this is a a hell of a "revealed preference." People don't want "relevant" advertising. Period.
The judge's credulous repetition of this obvious nonsense is doubly disturbing in light of the nature of the monopoly charge against Google – that the company had monopolized the advertising market.
Don't get me wrong: Google has monopolized the advertising market. They operate a "full stack" ad-tech shop. By controlling the tools that sellers and buyers use, and the marketplace where they use them, Google steals billions from advertisers and publishers. And that's before you factor in Jedi Blue, the illegal collusive arrangement the company has with Facebook, by which they carved up the market to increase their profits, gouge advertisers, starve publishers, and keep out smaller rivals:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jedi_Blue
One effect of Google's monopoly power is a global privacy crisis. In regions with strong privacy laws (like the EU), Google uses flags of convenience (looking at you, Ireland) to break the law with impunity:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/15/finnegans-snooze/#dirty-old-town
In the rest of the world, Google works with other members of the surveillance cartel to prevent the passage of privacy laws. That's why the USA hasn't had a new federal privacy law since 1988, when Congress acted to ban video-store clerks from telling newspaper reporters about the VHS cassettes you took home:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Video_Privacy_Protection_Act
The lack of privacy law and privacy enforcement means that Google can inflict untold privacy harms on billions of people around the world. Everything we do, everywhere we go online and offline, every relationship we have, everything we buy and say and do – it's all collected and stored and mined and used against us. The immediate harm here is the haunting sense that you are always under observation, a violation of your fundamental human rights that prevents you from ever being your authentic self:
https://www.theguardian.com/technology/blog/2013/jun/14/nsa-prism
The harms of surveillance aren't merely spiritual and psychological – they're material and immediate. The commercial surveillance industry provides the raw feedstock for a parade of horribles, from stalkers and bounty hunters turning up on their targets' front doors to cops rounding up demonstrators with location data from their phones to identity thieves tricking their marks by using leaked or purchased private information as convincers:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/12/06/privacy-first/#but-not-just-privacy
The problem with Google's monopolization of the surveillance business model is that they're spying on us. But for a certain kind of competition wonk, the problem is that Google is monopolizing the violation of our human rights, and we need to use competition law to "democratize" commercial surveillance.
This is deeply perverse, but it represents a central split in competition theory. Some trustbusters fetishize competition for its own sake, on the theory that it makes companies better and more efficient. But there are some things we don't want companies to be better at, like violating our human rights. We want to ban human rights violations, not improve them.
For other trustbusters – like me – the point of competition enforcement isn't merely to make companies offer better products, it's to make companies small enough to hold account through the enforcement of democratic laws. I want to break – and break up – Google because I want to end its ability to bigfoot privacy law so that we can finally root out the cancer of commercial surveillance. I don't want to make Google smaller so that other surveillance companies can get in on the game.
There is a real danger that this could emerge from this decision, and that's a danger we need to guard against. Last month, Google shocked the technical world by announcing that it would not follow through on its years-long promise to kill third-party cookies, one of the most pernicious and dangerous tools of commercial surveillance. The reason for this volte-face appears to be concern that the EU would view killing third-party cookies as anticompetitive, since Google intended to maintain commercial surveillance using its Orwellian "Privacy Sandbox" technology in Chrome, with the effect that everyone except Google would find it harder to spy on us as we used the internet:
https://www.thebignewsletter.com/p/googles-trail-of-crumbs
It's true! This is anticompetitive. But the answer isn't to preserve the universal power of tech companies large and small to violate our human rights – it's to ban everyone, especially Google, from spying on us!
This current in competition law is still on the fringe, but the Google case – which finds the company illegally dominating surveillance advertising, but rejects the idea that surveillance is itself a harm – offers an opportunity for this bad idea to go from the fringe to the center.
If that happens, look out.
Take "attribution," an obscure bit of ad-tech jargon disguising a jaw-droppingly terrible practice. "Attribution" is when an ad-tech company shows you an ad, and then follows you everywhere you go, monitoring everything you do, to determine whether the ad convinced you to buy something. I mean that literally: they're combining location data generated by your phone and captured by Bluetooth and wifi receivers with data from your credit card to follow you everywhere and log everything, so that they can prove to a merchant that you bought something.
This is unspeakably grotesque. It should be illegal. In many parts of the world, it is illegal, but it is so lucrative that monopolists like Google can buy off the enforcers and get away with it. What's more, only the very largest corporations have the resources to surveil you so closely and invasively that they can perform this "service."
But again, some competition wonks look at this situation and say, "Well, that's not right, we need to make sure that everyone can do attribution." This was a (completely mad) premise in the (otherwise very good) 2020 Competition and Markets Authority market-study on "Online platforms and digital advertising":
https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5fa557668fa8f5788db46efc/Final_report_Digital_ALT_TEXT.pdf
This (again, otherwise sensible) document veers completely off the rails whenever the subject of attribution comes up. At one point, the authors propose that the law should allow corporations to spy on people who opt out of commercial surveillance, provided that this spying is undertaken for the sole purpose of attribution.
But it gets even worse: by the end of the document, the authors propose a "user ID intervention" to give every Briton a permanent, government-issued advertising identifier to make it easier for smaller companies to do attribution.
Look, I understand why advertisers like attribution and are willing to preferentially take their business to companies that can perform it. But the fact that merchants want to be able to peer into every corner of our lives to figure out how well their ads are performing is no basis for permitting them to do so – much less intervening in the market to make it even easier so more commercial snoops can get their noses in our business!
This is an idea that keeps popping up, like in this editorial by a UK lawyer, where he proposes fixing "Google's dominance of online advertising" by making it possible for everyone to track us using the commercial surveillance identifiers created and monopolized by the ad-tech duopoly and the mobile tech duopoly:
https://www.thesling.org/what-to-do-about-googles-dominance-of-online-advertising/
Those companies are doing something rotten. In dominating ads, they have stolen billions from publishers and advertisers. Then they used those billions to capture our democratic process and ensure that our human rights weren't being defended as they plundered our private data and put us in harm's way.
Advertising will adapt. The marketing bros know this is coming. They're already discussing how to live in a world where you can't measure clicks and you can't attribute actions (e.g. the world from the first advertisements up until the early 2000s):
https://sparktoro.com/blog/attribution-is-dying-clicks-are-dying-marketing-is-going-back-to-the-20th-century/
An equitable solution to Google's monopoly will not run though our right to privacy. We don't solve the Google monopoly by creating competition in surveillance. The reason to get rid of Google's monopoly is to make it easier to end surveillance.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/08/07/revealed-preferences/#extinguish-v-improve

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#google#antitrust#monopolies#remedies#ad-tech#competition#power#doj v google#attribution
1K notes
·
View notes
Note
Tell us, why do you think Commodore failed?
Hoooooo boy... take this with a grain of salt, but here's how I see things based on my incomplete knowledge of the history. I need to do more research on this front, read a few of the books from folks who were there, but here goes nothing:
So, during the calculator wars of the early/mid 1970s, Texas Instruments was knocking competitors out of the game left and right by charging through the nose for the chips they sold. Commodore was one of their customers, and was nearly put out of business as a result. Jack Tramiel's solution was to buy MOS Technologies, effectively putting an end to CBM's reliance on TI's semiconductors because they could suddenly produce their own for much of their big ticket items.
Fast forward to 1981, and Commodore's VIC-20 is in a price war with Texas Instruments' TI-99/4A home computer. Jack kept lowering the price, and TI kept having to do the same to compete, so they were selling at a loss -- against a wildly popular home computer at the time. Jack, ever-vindictive in his motives (business is war, as he liked to say), cut the price of the VIC-20 at a CES show, which killed TI as a competitor in that segment in the market, but he did so at great cost to Commodore.
The way he cut the prices on the VIC also included peripherals, which the various vendors relied on to make their profits. They charged back those losses to Commodore. The result tipped the balance to diminish Jack's position in the company, and Irving Gould ousted him. Jack jumped ship with his sons and went to go work for Atari, selling the ST series machines, which would go on to compete with the Commodore Amiga series.
The problem was that Jack was the big force behind giving the company direction, especially when guiding advertising. The C64 sold itself, which was a blessing and a curse. It meant Commodore never really had to try all that hard to make good ads for it, so when they had to work harder to push later products, they kinda sucked at it. This really hurt the Amiga out of the gate, because nobody knew how to sell this golden child they just acquired, meaning it took many years to find its legs in the market.
Weird side projects continued to build up, and company focus was lost. Engineers churned out some amazing products, but without a guiding force at the top steering the company, and advertising dropping the ball in selling the powerful machines they were creating, the company was already in a slow death spiral. The IBM PC compatibles had already taken hold of much of the market, and were continuing to chip away at Commodore's market share, which wasn't helped by Jack himself fighting the company he founded on the side of Atari. The ST and the Amiga were fighting for the scraps left behind by IBM's juggernaut platform.
Commodore was a dead man walking from the moment Jack just had to get revenge on TI for trying to screw him out of the market in the 70s. It's just that nobody knew what the repercussions would be when he did that...
31 notes
·
View notes
Text






🎄💾🗓️ Day 16: Retrocomputing Advent Calendar - Tandy 1000🎄💾🗓️
Tandy's 1000, sold by Tandy Corporation in 1984 via its RadioShack stores, was a low-cost home computer designed to be compatible with IBM PC software. It shipped with an Intel 8088 processor, 128 KB of RAM, expandable to 640 KB, and had better-at-the-time graphics and sound than many of the standard PCs. The 1000 had the Tandy Graphics Adapter, or TGA, and the more superior SN76496 or NCR 8496 sound chips. The built-in joystick port also made it desirable for gamers and home users. Different models were produced, each with improved hardware, before being discontinued in 1993. One of the main selling features was its compatibility with IBM-PC, the MS-DOS operating system, and expansion slots for peripheral devices.
And check out our guide! Tandy 1000 Keyboard to USB with CircuitPython. https://learn.adafruit.com/tandy-1000-keyboard-to-usb-with-circuitpython
Have first computer memories? Post’em up in the comments, or post yours on socialz’ and tag them #firstcomputer #retrocomputing – See you back here tomorrow!
#retrocomputing#tandy1000#vintagecomputers#1980scomputers#ibmpccompatible#firstcomputer#tandycorporation#radioshack#int8088#msdos#pcgaming#nostalgiatech#oldschoolgaming#classictech#retrogaming#computermemories#vintagepc#pcretro#techhistory#throwbacktech#joystickport#tandygraphics#80scomputing#retrotechnology#techthrowback#earlypcs#computerhistory#retrohardware
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
The story of Microsoft's meteoric rise and IBM's fall has been on my mind lately. Not really related to any film, but I do think we're overdue for an updated Pirates of Silicon Valley biopic. I really think that the 80's and 90's had some wild stories in computing.
If you ask the average person what operating system your computer could have they'd say that if it's a PC it has Windows, and if it's a Mac it has macOS. All home computers are Macs or PCs, but how did it get this way?
In the 70's everyone was making home computers. Tandy was a leather supply goods company established in 1919, but they made computers. Montgomery Ward was a retail chain that decided to make their own store brand computers. Commodore, Atari, NEC, Philips, Bally and a million other assorted companies were selling computers. They generally couldn't talk to each other (if you had software for your Tandy it wouldn't work on your Commodore) and there was no clear market winner. The big three though were Tandy (yeah the leather company made some great computers in 78), Commodore and Apple.
IBM was the biggest computer company of all, in fact just the biggest company period. In 1980 they had a market cap of 128 billion dollars (adjusted for inflation). None of these other companies came close, but IBM's success was built off of mainframes. 70% of all computers sold worldwide were IBM computers, but 0% of it was from the home market.
IBM wanted to get into this growing and lucrative business, and came up with a unique plan. A cheap computer made with commodity parts (i.e. not cutting edge) that had open architecture. The plan was that you could buy an IBM Personal Computer (TM) and then upgrade it as you please. They even published documentation to make it easy to build add ons.
The hope was that people would be attracted to the low prices, the options for upgrades would work for power users, and a secondary market of add ons would be created. If some 3rd party company creates the best graphics card of all time, well you'd still need to buy an IBM PC to install it on.
IBM was not in the home software business, so they went to Microsoft. Microsoft produced MS-DOS (based on 86-DOS, which they licensed) but did not enforce exclusivity. That meant that Microsoft could sell MS-DOS for any of their competitors too. This was fine because of how fractured the market was. Remember, there were a lot of competitors, no one system dominated and none of the competitors could share software. Porting MS-DOS to every computer would have taken years, and by that point it would be outdated anyways.
IBM saw two paths forward. If the IBM PC did well they would make a ton of money. Third party devs like Microsoft would also make a lot of money, but not as much as IBM. If it failed, well then no one was making money. Either way the balance of power wouldn't change. IBM would still be at the top.
IBM however did not enjoy massive profits. It turns out that having cheap components and an open architecture where you could replace anything would... let you replace anything. A company like Compaq could just buy their own RAM, motherboards, cases, hard drives, etc. and make their own knockoff. It was easy, it was popular, and it was completely legal! Some people could order parts and build their own computer from scratch. If you've ever wondered why you can build your own computer but not your own tv or toaster, this is why. IBM had accidentally created a de facto standard that they had no control over.
In 1981 IBM's PC was worth 2.5% of the marketshare. By 1995 IBM PC compatibles were 95% of the marketshare, selling over 45 million units and IBM had to share the profits with every competitor. Apple is the only survivor of this time because the Macintosh was such an incredible piece of technology, but that's a different story for a different time.
And Microsoft? Well building an OS is much harder than putting together a few hardware components, so everyone just bought MS-DOS. With no exclusivity agreement this was also legal. That huge marketshare was now the basis for Microsoft's dominance.
IBM created a computer standard and gave the blueprints to every competitor and created a monopoly for Microsoft to boot. And that's why every computer you buy either is made by Apple with Apple software, or made by anyone else with Microsoft software. IBM is back where they started, having left the home computer business in 2005.
It's easily the biggest blunder in computer history. Other blunders have killed companies but none were quite as impactful as this one.
This story, and many others I know of, I first read in "In Search of Stupidity", a book authored by a former programmer and product manager that was able to see a lot of this first hand. I make no money advertising this book, I just had a great time reading it.
#software#hardware#microsoft#ibm#apple#tandy#nec#compaq#Wordstar#borland#ashton-tate#lotus#Ms-dos#windows#word#excel#access#commodore#atari#philips#bally#In search of stupidity#macintosh#montgomery ward#pirates of silicon valley
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
watching a Vib-Ribbon playthrough and I’m VERY surprised at how clear some parts of the tutorial are. This would’ve been before vocaloid, and the Daisy Bell program sung by an IBM-7094 would’ve been just around 38 years old. So how I see it, these devs made a coherent vocal synth ~4 years and a few months BEFORE Lola and Leon and on top of that, made a game that runs on literally less than 2 MB of RAM- since the whole selling point of Vib-Ribbon was that you could put your own music discs into the console and play a custom level. idk. silly musical bunny is neat to me.
10 notes
·
View notes
Quote
Everything Musk: Tesla, X, Starlink, SpaceX, The Boring Company, Neuralink Musk is a malignant, metastasizing tumor on democracy. What do we do with cancer? Whatever it takes. Cut it out, irradiate it and and blast it with chemo. We consumers are the aggressive treatment for Musk, and we have to deprive him of the very things he craves: power and money. That means we should punish any brand or company that partners with the South African Nazi. If you have a Tesla, get rid of it. If you own Tesla stock, sell it. If you’re a Starlink customer and have an alternative, use it. If you are in a position to decide on vendors for your employer or business, don’t award business to Tesla, Starlink, SpaceX, X, The Boring Company or Neuralink. Delete your X account. I know many people have kept their accounts to stay up to date on what the Nazi contingent is doing. You need to recognize that Musk is monetizing your attention and his clout in the White House. Business Insider claims advertisers, once concerned with the hate espoused on the platform, are returning to the platform. According to Ad Age, Comcast, IBM, Disney, Warner Bros. Discovery, and Lionsgate Entertainment have resumed advertising on President Elon’s hate forum. Interesting note: earlier this month, X settled with Trump for $10 million over Twitter banning his account following the January 6th Capitol insurrection. If that seems like a straight-up bribe, that’s because it is. If citizens want to know what DOGE is doing, they have to have an X account. This is a massive conflict of interest and one that is serving Apartheid Clyde well. When Musk purchased then-Twitter, he paid $44 billion for the platform. Most on Wall Street agree he over-paid for the asset. He also took on $13 billion in debt when he bought the platform. Why? Because billionaires don’t want to spend their own money when they can so easily spend someone else’s. In this case, Morgan Stanley, Bank of America, Barclays, Mitsubishi and others lent Musk the money. Until very recently, that debt was known as the worst buyout for banks since the 2008 financial crisis because the acquisition was WAY overvalued. Given Musk’s new role as President of the United States and him using X as the only official communication channel for the federal government, X’s debt is now worth par — meaning the company isn’t worth less than he paid for it. Funny how rigging the system works, huh?
Wall of Shame - by Denise Conroy - Bridges To Burn
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’m still thinking about the IBM sponsored MASH 80’s Office AU and I remembered the one ad I was bummed I had to cut from the comp cuz it’s not really office related, so here, for your viewing pleasure, is Alan Alda trying to sell you a computer for your classroom
81 notes
·
View notes
Text
BEIJING (Reuters) - After quitting the education industry last August due to China's crackdown on private tutoring, He Ajun has found an unlikely second life as an unemployment influencer.
The Guangzhou-based vlogger, 32, offers career advice to her 8,400 followers, charting her journey through long-term joblessness. "Unemployed at 31, not a single thing accomplished," she posted last December.
He is now making around 5,000 yuan ($700) per month through ads on her vlogs, content editing, private consultations and selling handicrafts at street stalls.
"I think in future freelancing will be normalised," said He. "Even if you stay in the workplace, you'll still need freelancing abilities. I believe it will become a backup skill, like driving."
China is under instruction to unleash "new productive forces", with government policies targeting narrow areas of science and technology including AI and robotics.
But critics say that has meant weak demand in other sectors and risks leaving behind a generation of highly educated young people, who missed the last boom and graduated too late to retrain for emerging industries.
A record 11.79 million university graduates this year face unprecedented job scarcity amid widespread layoffs in white-collar sectors including finance, while Tesla, IBM and ByteDance have also cut jobs in recent months.
Urban youth unemployment for the roughly 100 million Chinese aged 16-24 spiked to 17.1% in July, a figure analysts say masks millions of rural unemployed.
China suspended releasing youth jobless data after it reached an all-time high of 21.3% in June 2023, later tweaking criteria to exclude current students.
Over 200 million people are currently working in the gig economy and even that once fast-growing sector has its own overcapacity issues. A dozen Chinese cities have warned of ride-hailing oversaturation this year.
Redundancies have even spread to government work, long considered an "iron rice bowl" of lifetime employment.
Last year Beijing announced a 5% headcount reduction and thousands have been laid off since, according to official announcements and news reports. Henan province trimmed 5,600 jobs earlier this year, while Shandong province has cut nearly 10,000 positions since 2022.
Meanwhile, analysts say China's 3.9 million vocational college graduates are mostly equipped for low-end manufacturing and service jobs, and reforms announced in 2022 will take years to fix underinvestment in training long regarded as inferior to universities.
China currently faces a shortage of welders, joiners, elderly caregivers and "highly-skilled digital talent", its human resources minister said in March.
Yao Lu, a sociologist at Columbia University, estimates about 25% of college graduates aged 23-35 are currently in jobs below their academic qualifications.
Many of China's nearly 48 million university students are likely to have poor starting salaries and contribute relatively little in taxes throughout their lifetimes, said one Chinese economist who asked not to be named because of the sensitivity of the issue.
"Although they cannot be called a 'lost generation', it is a huge waste of human capital," the person said.
'DOING THREE PEOPLE'S JOBS'
Chinese President Xi Jinping in May urged officials to make job creation for new graduates a top priority. But for younger workers unemployed or recently fired, the mood is bleak, nine people interviewed by Reuters said.
Anna Wang, 23, quit her state bank job in Shenzhen this year due to high pressure and frequent unpaid overtime. For a salary of about 6,000 yuan per month, "I was doing three people's jobs," she said.
Her ex-colleagues complain about widespread pay cuts and transfers to positions with unmanageable workloads, effectively forcing them to resign. Wang now works part-time jobs as a CV editor and mystery shopper.
At a July briefing for foreign diplomats about an agenda-setting economic meeting, policymakers said they have been quietly urging companies to stop layoffs, one attendee told Reuters.
Olivia Lin, 30, left the civil service in July after widespread bonus cuts and bosses hinted at further redundancies. Four district-level bureaus were dissolved in her city of Shenzhen this year, according to public announcements.
"The general impression was that the current environment isn't good and fiscal pressure is really high," she said.
Lin now wants a tech job. She has had no interview offers after a month of searching. "This is completely different from 2021, when I was guaranteed one job interview a day," she said.
REDUCED STIGMA
Shut out of the job market and desperate for an outlet, young Chinese are sharing tips for surviving long-term unemployment. The hashtags "unemployed", "unemployment diary" and "laid off" received a combined 2.1 billion views on the Xiaohongshu platform He uses.
Users describe mundane daily routines, count down the days since being fired, share awkward chat exchanges with managers or dole out advice, sometimes accompanied by crying selfies.
The increasing visibility of jobless young people "increases broader social acceptance and reduces stigma surrounding unemployment", said Columbia's Lu, allowing otherwise isolated youth to connect and "perhaps even redefine what it means to be unemployed in today's economic climate".
Lu said unemployed graduates understood blaming the government for their plight would be both risky and ineffective. Rather, she said, they were more likely to slip into "an internalisation of discontent and blame" or "lying flat".
He, the influencer, thinks graduates should lower their ambitions.
"If we have indeed entered 'garbage time', then I think young people could accumulate skills or do something creative, such as selling things via social media or making handicrafts."
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
500. The 1984 Olympics Sports Illustrated Preview Issue (July 18, 1984) Part 1.

I'm totally late, but aren't we all having a little bit of Olympic withdrawal? This was a big magazine for me as a kid, big. My mom got it for me at the thrift store in 1994 when I was 10 because at the time I collected old issues of Sports Illustrated for the figure skating articles. This issue was massive, about five hundred pages. Five hundred pages of ads and photos I still remember 30 years later.

Like this Levi's ad! I still remember the lady in her maternity jeans, and how the kids couldn't wear riveted Levi's to school because they'd scratch up the desks.

There were several extended profiles of athletes that were expected to win big in Los Angeles, such as Carl Lewis.


Carl Lewis: mall lover.
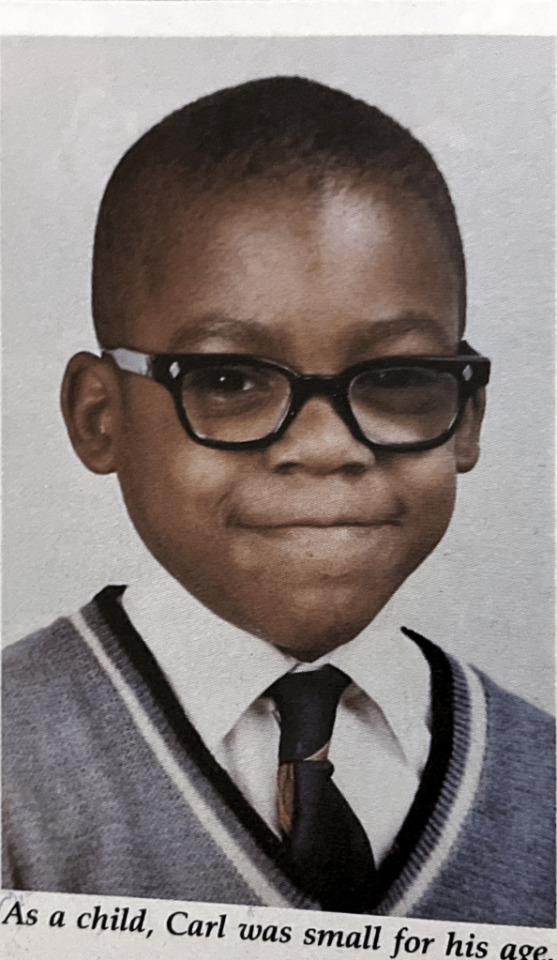

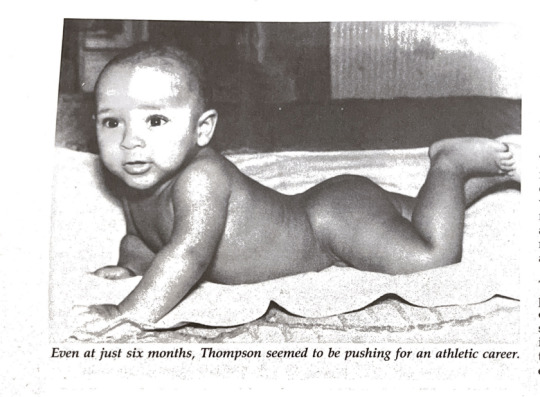
Embarrassing baby photos of the athletes were a common occurrence.

I forgot to mention the Renault Fuego when I did that write up on Renault's short lived visit in the States.

I thought the Chrysler Laser was a thing in Canada, and we in the U.S. had the Plymouth Laser. No! We had the Chrysler first for a couple of years and then we had the Plymouth for a few years? That Lee Iacocca made things so confusing. I've mentioned before that I grew up alongside my niece and when we were in high school, she bought a used green Laser, and I was so jealous.

Autoweek went looking for one of the special 1984 Olympic edition GMC Jimmys, but couldn't find one.

I love that its a heartwarming story about how Bill Toomey almost didn't win the 1968 decathlon, and then its just ...screwdrivers at Sears.
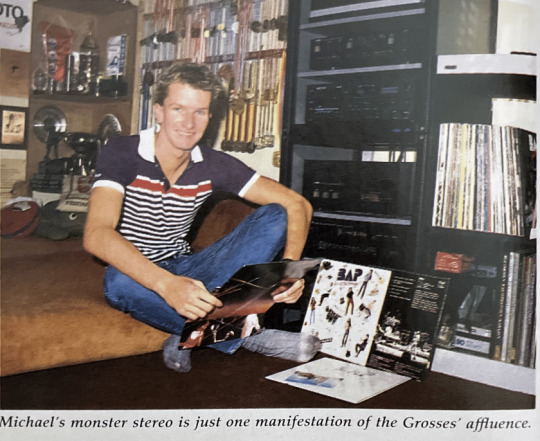

I've spent thirty years trying to figure out what album German swimmer Michael Gross has against his stereo. Bap? Rap? I'm gonna eBay image search it. Okay, so it is a German album by Bap.


1984 was definitely the first 'puter Olympics. Not the first internet Olympics like Atlanta or Nagano, but one where computers were definitely advertised. Looks like the closest Sears Business Systems Center to me was in Virginia Beach where a Shake Shack is today.


When I was a kid looking at this ad, I thought that was the real Charlie Chaplin, and he was still alive in 1984 selling IBM PCJr computers with those awful keyboards. Clint from LGR called the space bar a "gooey celery stick".

This was a sweet section about athletes reminiscing about their time during the first Olympics held in LA back in 1932. The hop step and jump is what we would call the triple jump today. The Sports Illustrated vault is absolute garbage now, but you can still read the text from the other athletes profiled. Ellen Preis the Frencer from Austria had a heck of a story:
ELLEN PREIS AUSTRIA FENCING, INDIVIDUAL FOIL
When we arrived in the United States, we met the mayor of New York. I can't remember his name [it was Jimmy Walker], but I remember he made a lot of funny jokes. He took us to Sing Sing, which was both interesting and a great shock. We sat in the electric chair. It felt awful. Afterward we saw criminals on Death Row, and I felt very sorry for them. Then they took us to a laboratory, and we saw 42 jars containing the brains of criminals who had died in the chair. I was very young, and it made a strong impression.
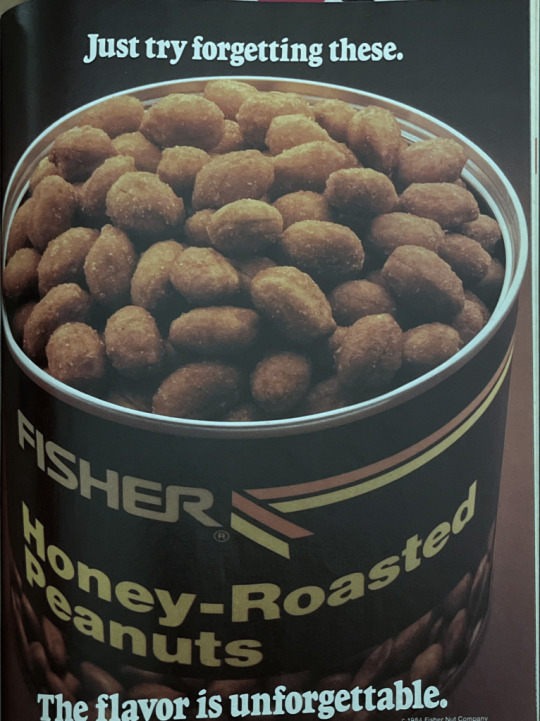

I still haven't forgotten this ad, Fisher. It totally worked.
Part 2 coming soon.
Facebook | Etsy | Retail History Blog | Twitter | YouTube Playlist | Random Post | Ko-fi donation | instagram / threads @thelastvcr | tik tok @ saleintothe90s | TeePublic Store
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Buy Used HPE Servers – Affordable, Certified & High-Performance
Looking for affordable used HPE servers? Browse our selection of certified pre-owned HPE servers with top performance and reliability. Order today!
#NetApp Maintenance#Dell server maintenance#Buy used dell server#Used dell server#Sell ibm#Ibm server maintenance#Used dell emc#Sell used hpe#Used dell storage#Used hpe server#Buy used hpe#Hpe 3par maintenance
0 notes
Text
I love That 70s Episode so much.
I love the little charmed ones + Andy wanting to tag along, I love Phoebe's pink sweater, I love Patty so so much, I love the scene where she meets Phoebe, Phoebe flinging Nicholas' keys into the street, and I love every single one of Penny's lines. "If husbands were supposed to stay married God would have made them live longer." "What's IBM selling at in your time?" "The recipes they learn from me don't come from Betty Crocker, dear." "We're witches, dear. We can do anything."
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Zuckerberg in the dock
I'm on a 20+ city book tour for my new novel PICKS AND SHOVELS. Catch me in PITTSBURGH on May 15 at WHITE WHALE BOOKS, and in PDX on Jun 20 at BARNES AND NOBLE. More tour dates here.

It's been more than a decade in the making, but Facebook – or, if you prefer, Meta – is going on trial for antitrust violations, with the highest possible stakes and the worst possible evidence (for Facebook).
The Big Tech On Trial blog was started to follow the Google antitrust case, the biggest antitrust case of the century, which was barely noticed by most of the press. Partly that was down to the 40 year period in which antitrust was not enforced, a prolonged induced coma that caused the press's antitrust muscles to waste away. Partly, it was because Judge Amit Mehta was comically deferential to Google's demands for secrecy about the trial and its exhibits, which added complexity and obscurity to the proceedings. Despite this, the DoJ prevailed, and Mehta ruled that "Google is a monopolist, and it has acted as one to maintain its monopoly." Now, Google faces break-up, and Trump's DoJ has confirmed that it will seek nothing less:
https://www.nytimes.com/2025/03/07/technology/trump-google-search-antitrust.html
The Biden administration may have been run by a president who'd spent his career kowtowing to giant, predatory corporations, but the left of the Democratic coalition forced him to install the most skilled and aggressive antitrust enforcers in generations:
https://pluralistic.net/2025/04/10/solidarity-forever-2/#oligarchism
They racked up an impressive series of wins, but too many of their cases were unfinished when the Democrats lost the election through a series of unforced errors that have left the country – and the world – teetering on the brink of a whole Bronze Age prophesy's worth of omnishambolic polycrises. There are so many important and good things imperiled by the Mad King presidency, and the DOJ and FTC's groundbreaking antitrust cases are certainly among them.
In some ways, this is normal. Vicious, criminal corporate bosses have long employed a delay/deny/defer strategy to draw out the antitrust cases against them, betting that a change in government will let them off the hook. This worked for Amway, which drew out its FTC prosecution for being a pyramid scheme until Richard Nixon resigned and was replaced by Gerry Ford, who had been the congressman to Amway founders Jay Van Andel and Rich DeVos. Ford ordered the FTC to let Amway off, so the FTC crafted the "Amway rule," which defines a list of of ruinously exploitative and dishonest tactics that are nevertheless legal. Every pyramid scheme since has been designed to fit within the confines of this rule. Whenever you hear from an old classmate hoping to sell you "leadership coaching," essential oils, tights, or any other gewgaw, know that they are the progeny of Gerry Ford and the Amway rule.
This delaying tactic also works for antitrust. When the DoJ sued IBM for its monopoly tactics, the company spent billions procuring delays. The case lasted for 12 years, from 1970-1982, and in each of those 12 years, the IBM spent more on outside counsel to fight the US government than the DoJ spent on all the lawyers fighting all the antitrust cases in the country. They called it "antitrust's Vietnam," and (unlike the actual Vietnam war) it paid off. After Reagan was elected, he ordered the DoJ to let IBM off the hook, and the company lived to monopolize another day.
Microsoft pulled off this gambit too, drawing out the proceedings and appeals after it was convicted of illegal monopolization. They delayed the process until GW Bush was elected, and then Dubya ordered his enforcers to drop their opposition to Microsoft's appeal, and the company got off scot free.
So the big question now is, "Will Trump let Facebook walk?" There's not really any question that Facebook is guilty as hell, but Trump is practitioner of "boss politics." He's made it clear that, guilty or not, he is willing to protect you if you suck up to him. He's created several channels that corporations and individuals can bribe him: there's the Trump memecoin, a virtual tipjar for the Oval Office. There's his bizarre gambit of suing companies he wishes to demand fealty from (like Disney), inviting the companies settle the suits for tens of millions of dollars more than is reasonable, as a way to legally shuffle eight-figure bribes into the president's personal bank account.
Appropriately enough, Trump inaugurated his bribery program with his inauguration, soliciting million dollar "donations" to the inauguration fund from corporate leaders seeking favors from his government. Big Tech bosses – including Zuck – broke all land-speed records in the race for their checkbooks. But Trump isn't an "honest politician" (in the Heinlein sense of "he stays bought"). Last week, Trump lopped $733 billion off Apple's market cap, which was a hell of a way to thank CEO Tim Cook for his $1m "donation."
Zuck's got other ways to bribe Trump, of course. His pivot-to-culture-war-bullshit announcement – in which he declared an end to Meta's "feminine" use of fact checkers and moderation policies – was a naked gift to Trump, a guarantee that Trump and his henchmen could lie about anything from Haitians eating dogs to gay barbers being members of fearsome international terrorist gangs without threat of moderation or correction on Meta's platforms. For a compulsive liar like Trump, any relaxation of fact checking is a naked bribe:
https://www.lemonde.fr/en/economy/article/2025/01/12/mark-zuckerberg-wants-more-masculine-energy-and-less-diversity-policy_6736961_19.html
So, will Trump's FTC take Facebook down? It's hard to say. On the one hand, Trump claims to have fired the two Democratic FTC commissioners, Alvaro Bedoya and Rebecca Slaughter. A unanimous Supreme Court ruling makes it clear that the president doesn't have the legal authority to fire FTC commissioners without cause, and Bedoya and Slaughter still consider themselves to be on the job, though they've been locked out of the building and their email:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Humphrey%27s_Executor_v._United_States
The weak GOP rump on the Commission are far from the best America has to offer. On his first day, Trump FTC Chair Andrew Ferguson killed a swathe of investigations and enforcement actions, walking away from the FTC's fights on things like "surveillance pricing" and "predatory pricing." In their place, Ferguson instituted a snitch-line where FTC employees could rat each other out for "wokeness":
https://prospect.org/politics/2025-01-24-executive-action-reaction-day-4/
But despite this, Ferguson has also indicated that he will selectively carry on the unprecedented work of Biden's FTC. For example, he affirmed that his FTC would continue to use the Biden era merger guidelines, which put far stricter limits on corporate mergers than we've seen since the 1980s. And he's publicly declared that he will fight Meta to the bitter end, praising the FTC lawyers on the case as "some of the best" in the agency:
https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2025-03-17/ftc-has-the-resources-to-take-on-big-tech-chairman-says
Writing for Big Tech on Trial, antitrust litigator Brendan Benedict lays out the stakes and odds in the case:
https://www.bigtechontrial.com/p/zuckerberg-on-the-stand-the-trial
One thing is clear from Benedict's excellent, comprehensive piece: there is a lot of extremely damning evidence against Meta. Some of this evidence comes from company insiders, like the whistleblower Sarah Wynn-Williams, whose tell-all memoir of her decade running Facebook's foreign policy team is filled with stomach churning revelations about top management's deliberate, ugly, vicious disregard for its users and the world:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250391230/carelesspeople/
Meta did Wynn-Williams a huge favor by forcing her into arbitration and securing a legally binding order requiring her to cease publicly commenting on her book, a move that triggered massive, worldwide interest in her book (it's why I picked it up!). This, in turn, led to Wynn-Williams being invited to testify before Congress, where her revelations about Zuckerberg's shameless, endless sucking up to the Chinese government and Xi Jinping caught the interest of Trumpland stalwarts like Josh Hawley and Chuck Grassley:
https://www.techpolicy.press/transcript-former-exec-sarah-wynnwilliams-testifies-on-facebooks-courtship-of-china/
Assuming this political will persists, Trump's FTC will have to prove that Meta deliberately set out to create and maintain a monopoly. In this regard, they will be greatly aided by the best possible witness for the prosecution: Mark Zuckerberg and his giant, flapping fucking mouth. Zuckerberg has repeatedly, explicitly confessed, in writing, in economic and legal terms, to pursuing a growth strategy based on blatantly illegal anticompetitive actions. As Careless People makes clear, Zuck is an arrogant, out-of-touch crank who cannot stop tripping over his own dick.
The first hurdle the FTC will have to clear is the "relevant market" question. For a company to be a monopolist, it has to dominate a given sector. So what's Meta's sector? In its courtroom filings, Meta claims that it competes with the entire internet and on that basis, it is a minor player indeed. Market definition is a thorny problem in Big Tech antitrust cases, because the companies are such sprawling conglomerates that they can claim that they compete with just about everyone:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/12/10/borked/#zucked
But those claims are greatly undermined when the company itself contradicts them, in writing. Back in 2011, Facebook told advertisers that it was "now 95% of all social media in the US."
Zuckerberg – the company's founder and CEO, who controls a majority of its voting stock – then proceeded to pen a series of memos affirming the company's deliberate monopolization strategy. For example, in justifying his decision to purchase Instagram – a company with 12 employees – for $1 billion, Zuckerberg described how "network effects" would keep Facebook from competing with Insta, so he planned on buying the company to capture those network effects and create a market where competitors' "new products won’t get much traction."
Other memos describe the company's deliberate plans to create high "switching costs" to make customers' departure as painful as possible, ensuring that companies with better products will struggle to attract users:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/08/28/talking-hard-work-blues/#hostage-takers
As if that wasn't enough, Zuck sent another memo contrasting Google+ with Instagram, writing, "One thing about startups though is you can often acquire them. I think that is a good outcome for everyone." This was just a restatement of Zuck's longstanding – and again, written – rule of business, "It is better to buy than to compete."
Things are not looking good for Meta. Having failed in a series of increasingly desperate maneuvers to get the case dismissed, the company has fallen back on gambits like writing Trump a check for a million bucks – and hiring Mark Hansen, the trial judge's former clerk, as its courtroom counsel.
Meta is a repeat offender. In 2019, Facebook paid the largest-ever corporate penalty of any kind, $5 billion, for lying about its users' privacy. The reason that settlement was so large? The company had already admitted to lying about user privacy and had made a legally binding promise not to do it again (they did it again) (and again) (and again).
Wynn-Williams called her book "Careless People," but there's plenty of evidence that Zuckerberg's offenses are deliberate, not carelessness. That evidence comes straight from Zuck's own keyboard, in memos where (for example) he discusses "using M&A to build a competitive moat around us on mobile and ads…[let's] spend $1-2 billion over the next couple of years on acquisitions."
Early in Facebook's history, Zuckerberg gave a speech explaining that he didn't want to sell Facebook because "Having media corporations owned by conglomerates is just not an attractive idea to me." Apparently it got more attractive after Zuck started to buy companies by the bushel.
This coincided with Meta increasing both the "ad-load" and the "unconnected posts" (boosted content from accounts you don't follow) in its products. Meta doesn't charge its users money, it charges them attention (which it then sells to advertisers and publishers) The (attentional) price of using Meta products has skyrocketed, at the expense of quality – a textbook proof of monopolization.
The timing of the release of Careless People and the trial couldn't be better (for us – not Meta!). I'm in the middle of Careless People right now (look for my review soon), and I agree with the Trashfuture panel who talked about how validating it was to have my longstanding suspicions that Facebook's many catastrophic blunders had to be the result of a deliberate decision to trade its users', customers' and society's wellbeing for its own profits:
https://www.podbean.com/ep/pb-3c2y8-1879998
Much has been made of Facebook's role in multiple genocides, starting with the Rohinga genocide in Myanmar. The company's maneuvers since then are a mix of Wynn-Williams's "carelessness" and actual malice. Facebook's traumatized moderators call themselves the company's "tonsils" – a sacrificial organ whose role is to absorb pathogens and protect the body corporate:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/04/19/tonsilitis/#mod-traum
Meanwhile, the company touts its laughably bad "genocide filters":
https://pluralistic.net/2022/03/23/false-genocide-negative/#metacrap
Even as it bullies and threatens watchdogs that monitor its moderation systems:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/11/20/sovkitsch/#adobserver
Facebook is a company that spent most of its history in a race to become too big to jail, seeking to shape regulations to keep smaller companies from growing to be competitive threats. This is why Zuckerberg has been such a vocal critic of Section 230, a law that people mistakenly view as a gift to Big Tech:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/03/25/facebook-has-a-facebook-problem/#played-for-zuckers
The company has curried favor with the world's dictators, creating a wave of "Facebook politicians" primarily drawn from the far right, including the brutal dictator of Cambodia:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/25/nationalize-moderna/#hun-sen
But in becoming too big to jail, the company also became too big to care (convenient for a firm whose executive ranks are filled with people who are manifestly lacking in any empathy). Thus the world's dominant social media platform has become a place where anyone who talks publicly about their cancer diagnosis will be bombarded with ads for snake-oil fake cancer cures that will drain their wallets and keep them from seeking life-saving therapy:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/07/13/youre-still-the-product/#targeting
Thus we have a company where insiders routinely use Meta's extensive commercial surveillance apparatus to casually stalk their romantic interests and anyone else they want to know more about:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/07/14/who-watches-the-zuckmen/#pecksniffs
Thus we have a company that systematically defrauded the entire media industry with its "pivot to video," creating a wave of bankruptcies in news organizations around the world, a mass extinction event we're still reeling from today (and then the company tried to do it again, with the disastrous "pivot to metaverse"):
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/18/metaverse-means-pivot-to-video/
Thus we have a company that threatened to walk away from the EU before it would obey the trading bloc's privacy laws:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/09/22/uncivvl/#fb-v-eu
(Ironically, the company insists upon the utmost secrecy when it negotiates with regulators, because nothing is more important than (Meta's) privacy):
https://pluralistic.net/2021/01/27/viral-colonialism/#ico-schtum
Meta's own employees are clearly keenly aware of its toxic nature. It's not just Sarah Wynn-Williams: departing Facebookers' "badge posts" – where they publicly take stock of their careers at Facebook – are a litany of recriminations and regrets:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/12/12/fairy-use-tale/#badge-posts
How will this case go? Well, it's hard to say. The judge – James Boasberg – just rejected a bid by Meta to keep its exhibits secret from the press and the public, seemingly having learned a lesson from Mehta's mistakes in the Google case.
And Meta has undergone spasms of antitrust fervor, like when Apple cut off third-party commercial surveillance by mobile apps, even as Apple spied on its own customers to fuel targeted ads. This prompted Zuckerberg to go on the warpath, telling anyone who'd listen that Apple was a dangerous tech monopoly and that the government really ought to do something about it:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/08/29/chickenized-home-to-roost/#chickenizers-come-home-to-roost
Yup.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2025/04/11/it-is-better-to-buy/#than-to-compete

#pluralistic#ftc#facebook#zuck#mark zuckerberg#antitrust#trustbusting#tripping over your own dick#boss politics antitrust#careless people#Sarah Wynn-Williams
132 notes
·
View notes
Note
If the Commodore 64 is great, where is the Commodore 65?

It sits in the pile with the rest of history's pre-production computers that never made it. It's been awhile since I went on a Commodore 65 rant...
The successor to the C64 is the C128, arguably the pinnacle of 8-bit computers. It has 3 modes: native C128 mode with 2MHz 8502, backwards compatible C64 mode, and CP/M mode using a 4MHz Z80. Dual video output in 40-column mode with sprites plus a second output in 80-column mode. Feature-rich BASIC, built in ROM monitor, numpad, 128K of RAM, and of course a SID chip. For 1985, it was one of the last hurrahs of 8-bit computing that wasn't meant to be a budget/bargain bin option.
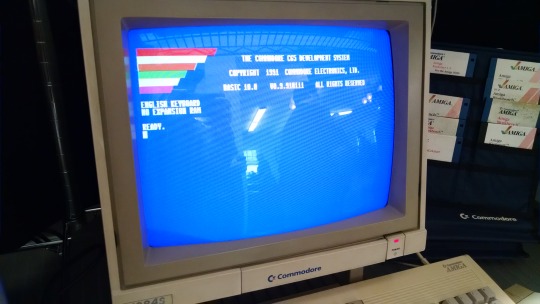
For the Amiga was taking center stage at Commodore -- the 16-bit age is here! And its initial market performance wasn't great, they were having a hard time selling its advanced capabilities. The Amiga platform took time to really build up momentum square in the face of the rising dominance of the IBM PC compatible. And the Amiga lost (don't tell the hardcore Amiga fanboys, they're still in denial).
However, before Commodore went bankrupt in '94, someone planned and designed another successor to the C64. It was supposed to be backwards compatible with C64, while also evolving on that lineage, moving to a CSG 4510 R3 at 3.54MHz (a fancy CMOS 6502 variant based on a subprocessor out of an Amiga serial port card). 128K of RAM (again) supposedly expandable to 1MB, 256X more colors, higher resolution, integrated 3½" floppy not unlike the 1581. Bitplane modes, DAT modes, Blitter modes -- all stuff that at one time was a big deal for rapid graphics operations, but nothing that an Amiga couldn't already do (if you're a C65 expert who isn't mad at me yet, feel free to correct me here).
The problem is that nobody wanted this.
Sure, Apple had released the IIgs in 1986, but that had both the backwards compatibility of an Apple II and a 16-bit 65C816 processor -- not some half-baked 6502 on gas station pills. Plus, by the time the C65 was in heavy development it was 1991. Way too late for the rapidly evolving landscape of the consumer computer market. It would be cancelled later that same year.
I realize that Commodore was also still selling the C64 well into 1994 when they closed up shop, but that was more of a desperation measure to keep cash flowing, even if it was way behind the curve by that point (remember, when the C64 was new it was a powerful, affordable machine for 1982). It was free money on an established product that was cheap to make, whereas the C65 would have been this new and expensive machine to produce and sell that would have been obsolete from the first day it hit store shelves. Never mind the dismal state of Commodore's marketing team post-Tramiel.

Internally, the guy working on the C65 was someone off in the corner who didn't work well with others while 3rd generation Amiga development was underway. The other engineers didn't have much faith in the idea.
The C65 has acquired a hype of "the machine that totally would have saved Commodore, guise!!!!1!11!!!111" -- saved nothing. If you want better what-if's from Commodore, you need to look to the C900 series UNIX machine, or the CLCD. Unlike those machines which only have a handful of surviving examples (like 3 or 4 CLCDs?), the C65 had several hundred, possibly as many as 2000 pre-production units made and sent out to software development houses. However many got out there, no software appears to have surfaced, and only a handful of complete examples of a C65 have entered the hands of collectors. Meaning if you have one, it's probably buggy and you have no software to run on it. Thus, what experience are you recapturing? Vaporware?
The myth of the C65 and what could have been persists nonetheless. I'm aware of 3 modern projects that have tried to take the throne from the Commodore 64, doing many things that sound similar to the Commodore 65.
The Foenix Retro Systems F256K:

The 8-Bit Guy's Commander X16

The MEGA65 (not my picture)
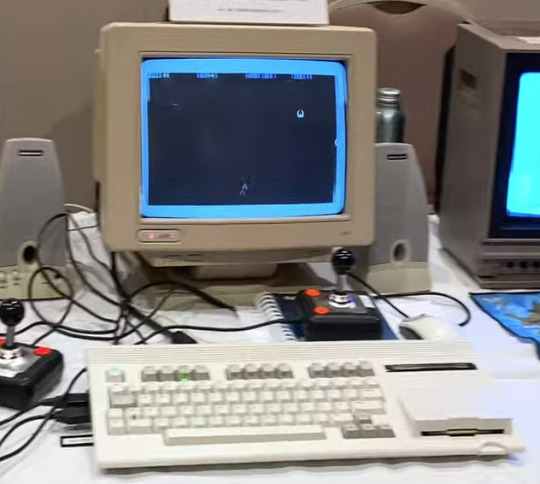

The last of which is an incredibly faithful open-source visual copy of the C65, where as the other projects are one-off's by dedicated individuals (and when referring to the X16, I don't mean David Murray as he's not the one doing the major design work).
I don't mean to belittle the effort people have put forth into such complicated projects, it's just not what I would have built. In 2019, I had the opportunity to meet the 8-Bit Guy and see the early X16 prototype. I didn't really see the appeal, and neither did David see the appeal of my homebrew, the Cactus.
Build your own computer, build a replica computer. I encourage you to build what you want, it can be a rewarding experience. Just remember that the C65 was probably never going to dig Commodore out of the financial hole they had dug for themselves.
262 notes
·
View notes
Note
thank you so much dping that masterlist of william and joeys mpvies, ive been seaeching for q lot of them since weeks but most of the sites where i found them werent very trustworthy, so thank ypu so much I LOVE YOU ALSO QHERE DID YOU BOUGHT THE IBM CD?
You're welcome! I bought my DVD from Amazon, but I'm pretty sure they also sell it on Alternative Cinema and MAYBE Grindhouse.
3 notes
·
View notes