#Types of Variability in Pipetting
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Details of basic cell culture methods and operation steps
Preparations for receiving cells
1. Recording Key Cell Information
When receiving a cell line in the lab for the first time, several pieces of information related to the cell line should be organized and recorded. These details are crucial for ensuring successful cell propagation, expansion, cryopreservation, and storage. It is strongly recommended to document the following information before starting cell expansion: (1) Background information (2) Subculturing (3) Cryopreservation (4) Cell line storage.
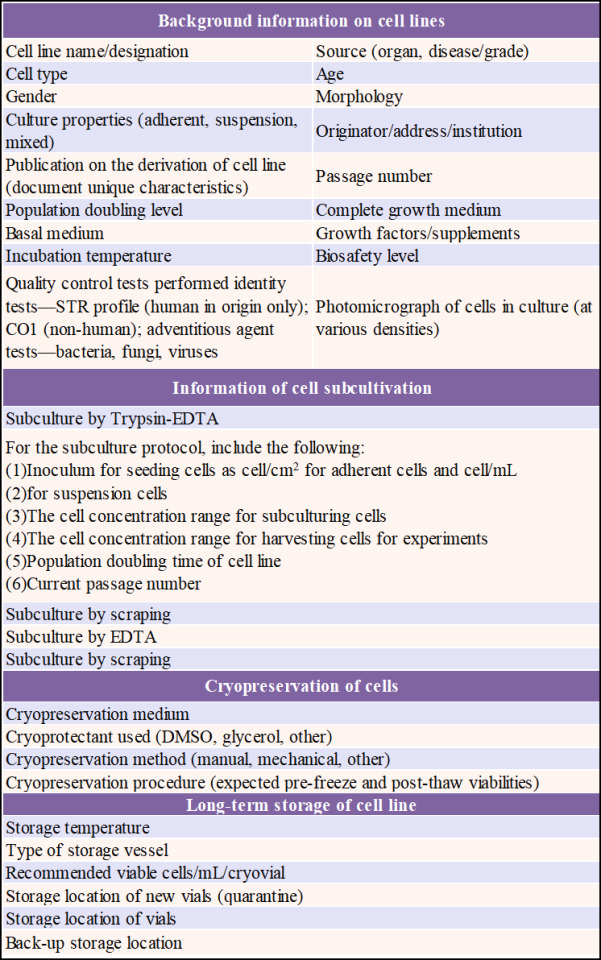
Table 1. Information to Record Regarding Cell Lines[1].
During cell culture, continuous cell lines may undergo changes. Numerous studies have demonstrated the various effects of long-term culture on the morphology, development, and gene expression of cell lines, such as variability in cell growth, leading to cell contamination and other issues. Therefore, it is crucial to establish a seed stock of low-passage cells when the cell line is first received in the laboratory.
2.Morphological Observation of Cultured Cells
Monitoring and recording the morphology and behavior of cells is crucial. It is recommended to routinely and carefully examine cultured cells before subculturing to assess their status and health. Observations of cell morphology can help researchers determine:
(1) Cell morphology: Are the cells healthy or deteriorating (such as cellular senescence or necrosis)?
(2) Is there any evidence of contamination?
(3) Differentiation of cell types and assessment of cell density.
Most cell cultures grow in either suspension or adherent conditions. However, in some cases, a mixed population of suspension and adherent cells may be observed.
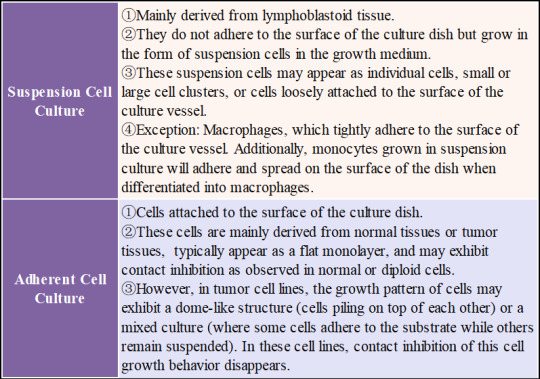
Table2. Cell culture growth type.
Based on morphology, cultured cells can be classified into three basic categories: fibroblast-like, epithelial-like, and lymphoblastoid-like.
Figure 1. General Characteristics and Morphologies of Cultured Cells[1].
The specific operation of receiving cells
Using a T25 culture flask as an example. First, check the color of the culture medium and inspect for any leakage. Then, observe the cell condition under an inverted microscope and capture images at different magnifications to rule out contamination or poor cell condition. After confirming the cells are in good condition, disinfect the outer surface of the cell flask and place it in the incubator for a few hours (depending on cell density) to stabilize the cell state.
Adherent cells: When the cell growth density exceeds 80%, passaging can be performed as needed. If the confluence is less than 80%, perform a partial medium change by removing half of the original medium and adding an equal amount of fresh complete medium. Continue culturing until the cell density exceeds 80%, then proceed with passaging.
Suspension cells: Transfer the liquid from the culture flask to a centrifuge tube and centrifuge at 500g for 5 minutes. Gently discard the supernatant. Resuspend the cell pellet at the bottom of the tube in 10 mL of complete medium by gentle pipetting. Transfer the suspension to a new culture flask and incubate overnight. Perform subculturing based on cell density and growth status.
Cell counting: Dilute the cell suspension to 200-2000 cells per milliliter in a serum-free medium. Add an equal volume of 0.4% trypan blue solution to 10-100 µl of the cell suspension. Mix gently and count the cells using a hemocytometer. Living cells can reject trypan blue and remain translucent, while dead cells will be stained blue. It is also more convenient to directly use a cell counter for counting.
Figure 2. Trypan Blue Staining Image[2].
Selection of Appropriate Cell Culture Media
Selecting the appropriate culture medium is crucial for the success of cell culture. Different types of cells have varying growth requirements and specific culture conditions. First, the nutrients in the culture medium are essential for maintaining cell growth and metabolism. Different types of cells require various amino acids, sugars, vitamins, inorganic salts, lipids, and other nutrients to meet their physiological needs. If the culture medium lacks necessary nutrients, cells may be unable to grow and divide normally, and this can even lead to cell death[3][4].
When selecting the appropriate culture medium, prioritize the culture conditions provided by the cell source company. If the source is uncertain, you can refer to the recommended medium for the corresponding cell type from ATCC.

Table 3. Common cell culture systems.
Secondly, growth factors and hormones in the culture medium play an important role in regulating cell growth and differentiation. These growth factors can promote cell proliferation, development, and differentiation, and play a key role in cell signaling pathways. Different types of cells require specific growth factors and hormones to maintain their particular functions and characteristics. For example, neurotrophic factors are often added to the culture medium for neural cells to promote growth and synapse formation; fetal bovine serum is commonly added to the medium to provide the growth factors, proteins, and other essential components needed by the cells.
In addition, antibiotics can be added when necessary to prevent contamination and protect the cells. For example, double antibiotics (penicillin/streptomycin) or even triple antibiotics (penicillin, streptomycin, amphotericin B) can be used to inhibit the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi. Penicillin-streptomycin is effective in inhibiting the growth of most Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, while amphotericin B can be used to prevent fungal and yeast contamination.
Cell Passage Operation Steps
Over time, the number of cells will increase, but space and resources are limited. Therefore, when cells reach a certain density, it's time to provide them with a larger living space to continue proliferating.
Figure 3. Passaging Workflow Diagram.
Using a T25 culture flask as an example, the common steps for cell passaging are as follows:
(1)Remove the cells from the incubator and observe them under a microscope. If the confluence exceeds 80%, proceed with passaging.
(2)Preparation: Prewarm the culture medium and PBS in a 37°C water bath. Place the consumables needed for passaging (e.g., pipettes, pipette tips, T25 culture flasks) in a biosafety cabinet, sterilize them with UV light for 30 minutes, and ensure proper ventilation. Disinfect the trypsin, prewarmed medium, and PBS with 75% ethanol before placing them in the biosafety cabinet.
(3)Aspirate the old culture medium from the flask, rinse the cells with 5 mL of PBS, and then aspirate the PBS.
(4)Add 1 mL of trypsin, gently shake the flask to ensure the trypsin fully covers the cells, and incubate it in a 37°C incubator for 30 seconds to 2 minutes (the actual incubation time may vary depending on the cell line used).
(5)Observe under a microscope, and when ≥90% of the cells have detached, add a volume of complete medium containing serum equal to twice the volume of the trypsin to stop the digestion. Pipette the surface of the cell layer several times to disperse the cells into a single-cell suspension.
(6)Centrifuge at 500 g for 3~5 minutes, then resuspend the cell pellet in complete medium containing serum.
(7)Distribute the cell suspension into culture flasks according to the desired passaging ratio, add fresh complete medium, gently shake the flask to evenly distribute the cells, and label it accordingly.
(8)Observe the cell density and condition under a microscope, then return the cells to the incubator. When using trypsin for passaging animal cells, several factors need to be considered. Trypsin has proteolytic activity that can affect various physiological and metabolic functions of the cells.
Tips: The Best Method for Passaging Cells Using Trypsin
Before adding trypsin, wash the cells with Ca2+ and Mg2+-free saline/PBS to remove these ions (Ca2+, Mg2+ and serum in the solution can reduce trypsin activity).
Use the lowest concentration and volume of trypsin to detach cells from the surface of the culture flask.
If possible, use the trypsin solution at room temperature or lower to reduce enzyme endocytosis.
Use trypsin to treat the cells for the shortest time possible to avoid over-digestion, which may affect the cells.
Use trypsin inhibitors, such as complete medium containing serum, to neutralize and terminate trypsin activity, then centrifuge to remove the trypsin.
After the cells have detached, immediately centrifuge to remove the trypsin from the surface of the culture flask.
Product Recommendation
DMEM (High Glucose, L-Glutamine, Pyruvate, Phenol Red, no HEPES)
Commonly used media for cell culture.
DMEM (Low Glucose, L-Glutamine, Pyruvate, Phenol Red, no HEPES)
Commonly used media for cell culture.
RPMI 1640 (L-Glutamine, Phenol Red, no HEPES)
Commonly used media for cell culture.
BM-Cyclin
Effectively inhibit and eliminate mycoplasma contamination commonly found in cell culture.
Penicillin-Streptomycin
Dual antibiotics can effectively control contamination caused by many types of bacteria.
0.25% Trypsin-EDTA (1x), phenol red
Used for cell dissociation, routine cell culture passaging, and primary tissue dissociation to disperse tissues or adherent cells into single cells.
References
[1] 1.Reid YA. Best practices for naming, receiving, and managing cells in culture. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2017 Oct;53(9):761-774. [2] Aung S M, et al. Live and dead cells counting from microscopic trypan blue staining images using thresholding and morphological operation techniques[J]. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2019, 9(4): 2460. [3] Jessica Cox, et al. Co-occurrence of Cell Lines, Basal Media and Supplementation in the Biomedical Research Literature. Journal of Data and Information Science. 2020, Vol. 5. Issue (3) : 161-177. [4] Lee JT, et al. Cell culture medium as an alternative to conventional simulated body fluid. Acta Biomater. 2011 Jun;7(6):2615-22.
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Choose the Right Pipette for Your Laboratory Needs?
While you are in a laboratory or research setting, pipettes are used for accurate and precise liquid handling. They are indispensable tools included in any laboratory, this is followed by choosing the right pipette which can be reliable and efficient throughout the experiment procedure.
This also ensures the suitable pipette calibration which can play a major role in maintaining the required precision and accuracy of the volume of liquid dispensed by the pipette. This can further improve the chances of getting reliable experiment results in the laboratory settings.
This blog will guide you through the key considerations for selecting the perfect pipette for your specific laboratory needs. Along with this you would also get an overview on the key points to consider while choosing suitable pipette for your experiment procedure.
Types of Pipettes for Laboratory needs
Several types of pipettes are available at Microlit, which can be a suitable addition to your experimental procedures. They each have their strengths and weaknesses, let’s have a look.
Air Displacement Pipette
While working in a laboratory, you may observe that the air displacement pipette is the most common type. They can also play a significant role in maintaining air pressure to aspirate and dispense liquids. So, it becomes more suitable for aqueous solutions but not ideal for viscous or volatile liquids. There are sub category to air displacement pipettes, such as
Micropipettes
They are used for dispensing microliter volumes, which can be suitable for molecular biology, biochemistry, and other micro-scale applications. If you are using micropipettes, then they can be a suitable addition to use them for their versatility in variable volume measurement.
Macropipettes
Apart from the usage of micropipettes, macropipettes can be a perfect addition for dispensing milliliter volumes. They can also maintain the accuracy and precision of the results while liquid handling, throughout the laboratory works.
Positive Displacement Pipettes
Pipettes used for laboratory needs are equipped with the micropipette technology, these are also attached with a piston that directly helps in dispensing the liquid. Further, this can play an essential role in transferring viscous, volatile, and sticky liquids.
Along with this, it can also provide an enhanced accuracy and precision compared to air-displacement pipettes for these specific liquids. These can elevate the overall experience of experiment procedures and also improve the chances of getting accurate results throughout the procedure.
Multichannel Pipettes
If you are thinking that you would have to change pipettes for various use cases, but this is not with multichannel pipettes. It can have multichannel pipettes, which can be attached in the experiment procedures, these can range between 8 to 12.
These can also allow simultaneous dispensing into multiple wells or tubes. Through which it can be crucial for high-throughput assays and cell culture, further enhancing the experiment standards and saving much time while you are in the laboratory.
Repeating Pipettes
Pipettes are not only used altogether, there is also a need of repeating pipettes as per the need through the experiment procedures. These liquid handling instruments are designed for repetitive dispensing of the same volume.
These are also useful for dispensing aliquots of reagents, which also enhances the experiment procedures. Further, it also makes the process of deriving experiment results seamless. But these pipettes can be time consuming, which may also affect the experiment procedure.
Electronic Pipettes
Among all the pipette types, there are electronic pipettes which make an evolution in pipette usage through the experiment. These electronic pipettes are equipped with programmable features, increased precision, and reduced pipetting force.
While you are in a laboratory, you may observe that the electronic pipettes can play a significant role in minimizing the risk of RSI. Further, as they are particularly beneficial for complex protocols, it can elevate your experiment procedures and support seamless liquid handling.
Key Features to Consider while choosing the Right Pipette
Along with the types of pipettes used in the experiment as per the laboratory needs, there are various key features that can be considered while choosing the suitable pipette for experiment.
Volume range
There are pipettes of various ranges available that can be a useful aspect while choosing the right one for you. This is to ensure that the pipette’s volume range matches your needs during an experiment. Along with this, you may also need to check the liquid levels as required through the experiment.
Accuracy and Precision
While choosing the right pipettes for your laboratory, you can look for pipettes with high accuracy, which can ensure that you get the closest value of the liquid required. Along with this, precision is equally important, as it improves the reproducibility of measurements.
These can be expressed as percentage, so this can be easy to understand, further this can also wither off the confusion while you are conducting the experiment. With the enhanced accuracy and precision, you will get the accurate required results, without any hassle.
Ergonomics
When you are working in a laboratory, for several hours and with the repetitive usage of pipettes, this can elevate the chances of strain on the wrist and hand. So, while choosing the suitable pipette for you, consider a few parameters in check such as pipette weight, shape, and plunger force.
This can play a significant role in supporting you throughout the experiment procedures and when you choose ergonomic pipettes for experiment. These can also support you through the experiment, further preventing the liquid loss, minimizing strain.
Calibration and Maintenance
Maintaining accuracy can be a crucial part in an experiment, for this regular calibrating would be a necessary step while conducting an experiment. For achieving the required accuracy in the experiment, you should choose pipettes that are easy to calibrate and maintain. As this can also follow a seamless experiment and the quick procedures.
Making the Right Choice
Choosing the right pipette can be a crucial decision for you as a lab technician, so carefully consider your specific requirements. These include the types of liquids you will be working with, the required accuracy and precision, and your budget.
Don���t hesitate to consult Microlit, they are equipped with experienced colleagues and pipette suppliers you are waiting for. Investing in high-quality pipettes will improve your work quality and lab efficiency.
#liquid handling#liquid handling instrument#micropipette#micropipette price#pipettes#electronic pipettes#micropipette technology
0 notes
Text
Micropipette Guide 2024: Types, Applications and More

Micropipettes or pipettes, are instruments used to measure liquid ranging between volumes of 1-10000 µl and transfer it from one sample container to another. This is a basic liquid-handling instrument for almost all scientific laboratories.
Types of Micropipettes
There is no 1 way to classify micropipettes. It can vary in a number of ways.
1. Number of Channels
Single Channel Micropipettes
A single-channel micropipette has only 1 channel to aspirate and dispense the liquid. It means you can handle only one sample at a time.
Multi-Channel Micropipettes
Multi-channel micropipettes can handle 8, 12 or 16 samples in one go. It can attach multiple tips at the same time and you can get the work done faster especially if working in high-throughput labs.
2. Volume Adjustment
Fixed Volume Micropipettes Here the volume a pipette can aspirate and dispense remains the same and you don’t have the option to adjust or choose between a range. They offer consistent and accurate results for repetitive pipetting.

Variable Volume Micropipettes
Variable volume pipettes give you the flexibility to choose the volume you want to pipette (within the given range). You need to set the volume manually on the dial. High-performance pipettes also come with a volume lock feature for enhanced safety and reliability.

3. Operating Mechanism
Mechanical Pipettes
These are the standard pipettes widely used in all laboratories. Mechanical micropipettes operate on a piston-driven system, where users manually set the desired volume using a dial and apply thumb pressure on the plunger to aspirate and dispense liquids.

Electronic Micropipettes
Electronic micropipettes are more expensive than mechanical ones because they have digital controls, programmability and eliminates the element of human error to a certain extent. It has an electronic display and is ideal for high-throughput labs where reproducibility is paramount.
Components of Micropipette
Plunger
The plunger is one of the main components of the micropipette. Use your thumb to press down on the plunger to aspirate and dispense the liquid.
Then, with a firmer push, sometimes called the “blow-out stop,” it ensures a thorough expulsion of any remaining liquid, guaranteeing accurate measurements—a two-step process of liquid control.
Ergonomics are a key point here since lab professionals will be pipetting repeatedly for long hours. A low-force mechanism which does not require excessive plunge force, will minimize the RSI.
Volume Adjustment Dial
By twisting the volume adjustment dial, you dictate the micropipette’s plunger movement, determining your experiment’s liquid dosage. In micropipettes with adjustable volumes, this feature offers precise measurement control, no matter how small or large the quantity is.
Tip Ejector
Keep your hands and micropipette clean by disposing of used tips promptly. Utilize the convenient tip ejector button to effortlessly remove micropipette tips, ensuring a fuss-free and contamination-free experiment environment.
Tip Cone The tip cone, also known as the shaft, is the crucial component of a micropipette where the disposable tip is inserted. Its primary function is to ensure a snug fit for the tip, ensuring precision in measurements and preventing air leakage. Its adaptable shape accommodates various sizes and styles of tips, allowing for versatile and secure usage without concerns of detachment or disruptions.
Calibration Screw Inside the micropipette lies a crucial component, the calibration screw. This is what makes accuracy possible. Twisting this tiny screw adjusts the liquid output, fine-tuning the micropipette’s performance. Regular checks and tweaks, as advised by the manufacturer, ensure precision in your measurements, keeping everything flowing smoothly.
Applications of Micropipettes in Laboratory
Micropipettes are used to measure any small amount of liquid samples for testing and research. They are crucial in lab settings like molecular biology and diagnostics, precisely transferring tiny liquid volumes, facilitating diverse experiments. Mastery of their principles is key to effective scientific research and analysis.
Some common applications include:
1. Molecular Biology 2. Biochemistry 3. Cell Culture 4. Microbiology 5. Analytical Chemistry 6. Clinical Diagnostics 7. Pharmaceutical Research
How does a Micropipette work?
Micropipettes operate on the principle of air displacement. They consist of a plunger connected to an internal piston, which moves to two distinct positions: Filling Position: When the plunger is depressed to the first stop, the internal piston displaces a volume of air equal to the desired volume shown on the volume indicator dial. This creates a vacuum, drawing the liquid into the tip. Dispensing Position: The second stop on the plunger is used solely for dispensing the contents of the tip without drawing in additional air.
How to use a micropipette?
1. Start with choosing the right micropipette and micropipette tips
Select the one that is best for your application. While pipettes are similar in the way they function, what sets them apart is the accuracy and precision of the measurement, ergonomics and general durability of the instrument.
Set the volume based on your requirement and ensure the tips match the volume of the pipettes.
2. Attach the micropipette tip to the micropipette
Don’t use excessive force here because good quality pipettes will be quick and seamless to attach to the tips and should provide a leak-proof seal.Immerse the pipette in the liquid at 90 degrees Be mindful of your posture and keep the position upright. Aspirate and dispense 2-3 times before actually measuring the liquid
3. Forward or Reverse Pipetting
First let’s talk about forward pipetting:To aspirate the liquid in the tip, press the plunger to the first stop. Immerse the pipette tip vertically in the liquid. Slowly release the plunger while the tip is immersed. The liquid will be aspirated into the pipette tip. To dispense the liquid, place the tip on the inner wall of the receiving vessel at a steep angle Slowly press the plunger to the first stop to dispense the liquid. To empty the tip completely, press the plunger to the second stop.
Now for reverse pipetting
The reverse technique is suitable for dispensing reagents/solutions that have high viscosity or a tendency to foam easily. It is also recommended for dispensing very small volumes.To aspirate the liquid in the tip, press the plunger to the second stop and immerse the pipette tip vertically in the liquid. Slowly release the plunger while the tip is immersed. The liquid will be aspirated into the pipette tip. To dispense the liquid, place the tip on the inner wall of the tube at a steep angle. Slowly press the plunger to the first stop. Finally, eject the tip and dispose it off
Calibration of Micropipettes
Calibration is conducted through gravimetric testing, which involves weighing the amount of pure water delivered in a single operation of the pipette. The obtained mass is divided by the density of water to determine its volume. Variable volume pipettes should undergo testing at three or more points across their designated range, typically at maximum volume, 50% of maximum volume, and the lower limit of their range.
Here’s a general guide on how to calibrate a micropipette:
1. Gather MaterialsMicropipette(s) to be calibrated Appropriate pipette tips Distilled water or a calibration solution Weighing balance with appropriate accuracy (usually in milligrams) Gloves and lab coat for safety
2. Prepare the Micropipette Ensure the micropipette is clean and free from any residue. Attach a fresh and compatible pipette tip to the micropipette.
3. Pre-Wet the Pipette Tip (Optional) For some micropipettes, pre-wetting the tip with the liquid being used can help ensure accuracy. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding pre-wetting.
4. Prepare the Calibration Solution Use distilled water or a calibration solution recommended by the micropipette manufacturer.
Ensure the calibration solution is at room temperature to minimize density variations.
5. Set the Micropipette to the Desired Volume Adjust the micropipette to the volume you want to calibrate (e.g., if calibrating a 10-100 μL micropipette, set it to 50 μL).
6. Dispense Liquid into a Weighing Boat or Container Dispense the liquid from the micropipette into a weighing boat or a container placed on a weighing balance.
Note down the initial weight (W1) of the liquid dispensed.
7. Weigh the Dispensed Liquid Carefully weigh the liquid dispensed using the weighing balance. Ensure the balance is calibrated and accurate.
Record the final weight (W2) of the liquid.
8. Calculate the Dispensed Volume Subtract the initial weight (W1) from the final weight (W2) to determine the weight of the liquid dispensed (W).
Convert the weight of the liquid dispensed to volume using the density of the liquid or the known density of the calibration solution.
Calculate the actual volume dispensed using the formula:

9. Compare with Expected Volume Compare the calculated volume dispensed with the expected volume (e.g., 50 μL for a 10-100 μL micropipette). Calculate the percent error to assess the accuracy of the micropipette calibration:

10. Adjust if Necessary If the percent error is within an acceptable range (typically ±2-5%), the micropipette is calibrated. Otherwise, adjustments may be needed. Consult the micropipette’s user manual for instructions on how to adjust the volume settings. Adjust carefully and recheck the calibration until the desired accuracy is achieved.
11. Record Calibration Data Keep a record of the calibration process, including the micropipette serial number, date of calibration, volume settings, calibration solution used, measured weights, calculated volumes, and any adjustments made.
12. Final Checks After calibration, perform a final check to ensure the micropipette is dispensing accurately and consistently across the volume range.
When is micropipette calibration required?
Micropipette calibration is typically required in the following situations:
Initial Use
New micropipettes should be calibrated before their initial use to ensure accuracy and precision.
Scheduled Calibration
Regular calibration intervals are recommended to maintain the accuracy of micropipettes over time. The frequency of calibration depends on factors such as the frequency of use, the criticality of the measurements, and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
After Maintenance or Repair
Calibration should be performed after any maintenance or repair work on the micropipette to verify that it meets the required specifications.
Change in Operating Conditions
If there is a significant change in the operating conditions, such as temperature or altitude, recalibration may be necessary to account for these factors’ effects on the micropipette’s performance.
Compliance Requirements
Laboratories may have regulatory or quality assurance requirements that mandate regular calibration of micropipettes to ensure traceability and compliance with standards.
Where do we get the best micropipette for the lab?
When purchasing a micropipette for your lab, consider key factors such as accuracy, precision, ergonomics, and ease of maintenance. Research the brands and models, compare specifications, and read user reviews to make an informed decision. Evaluate additional features like adjustable volume settings and compatibility with automation systems. Set a budget and balance costs with desired features. Check warranty coverage and customer support options for added peace of mind.
Cleaning and Maintenance of Micropipettes
1. External CleaningRemove and Clean the Tip Ejector: Begin by detaching the tip ejector and giving it a thorough wipe-down.
Wipe Down All Exposed Surfaces: Take a lint-free cloth or tissue and carefully wipe all visible parts of the micropipette, including the body, buttons, operating rod, and tip holder. Be diligent in cleaning any scuffs, marks, or accumulated debris in hard-to-reach areas.
Use a Brush for Stubborn Debris: If there are persistent stains or dirt, consider using a soft-bristled brush to gently scrub the affected areas.
Reassemble and Allow to Dry: Once the exterior surfaces are clean, reattach the tip ejector and ensure it is securely in place. Leave the pipette to air dry completely before further use. Final Wipe with Cleaning Solution: Finish the cleaning process by wiping down the outer surfaces once more with a cleaning solution to remove any remaining residue. Allow the alcohol to evaporate fully before returning the pipette to service.
2. Internal Cleaning
Cleaning the inside of a pipette should be handled by trained personnel to avoid incorrect reassembly, which can damage the micropipette and affect its performance, leading to decreased accuracy and potential leakage.Disassemble the Micropipette: Carefully take apart the pipette, placing the upper part in a clean, dry area.
Wipe with Alcohol-Coated Wipes: Use alcohol-coated wipes to thoroughly clean the entire interior, including the body, connecting nut, tip holder, O-ring, seal, and the stainless steel surface of the piston. Ensure the piston is completely dry to prevent corrosion.
Allow Alcohol to Evaporate: Let the alcohol evaporate fully from the interior of the pipette. Check for Lubrication Needs: Refer to the instruction manual to determine if any parts, like the piston assembly and seals, require lubrication. Follow the manual’s guidance for reassembly, ensuring proper alignment and placement of components.
Maintaining Micropipettes
When the pipette is not in use it should be stored in an upright position. The pipette should be inspected prior to use each day for any dust or contamination on outside surfaces. Special attention should be given to the tip cone. No solvent other than isopropanol should be used to clean the pipette. If the pipette is used daily, an internal parts inspection should be performed every three months.
Choosing the right micropipette for your applicationEnsure that the micropipette can accommodate the desired range of liquid volumes for your pipetting needs.
Verify if the micropipette features a universal tip cone to accommodate various types of pipette tips.
Check if the micropipette is autoclavable at the necessary temperature to ensure proper sterilization.
Check if the micropipette is UV resistant so that they can be kept inside the hood even when the UV mode is on.
Assess the ergonomic design of the micropipette for smooth and comfortable handling during use. Confirm if the micropipette is calibrated to guarantee precise dispensing of liquids.
Evaluate the accuracy and precision of the micropipette’s readings to ensure compliance with ISO standards.
Ergonomics is a key factor in choosing a pipette because repetitive strain injury is common amongst lab personnel who pipette regularly. Low-force tip ejection and minimal plunge force are crucial.
Accumax Lab Devices specializes in manufacturing high-precision liquid handling instruments for top-tier laboratories worldwide. With a focus on innovation, it offers an advanced range of micropipettes designed to enhance user experience within real-world laboratory settings. Especially our range of FAB and FAB LF pipettes, which are specially designed for accuracy and precision with excellent ergonomics to elevate your pipetting experience like never before.
Micropipette FAQs
1. Can I use any brand of pipette tips with my micropipette?
Whether you can use any brand of pipette tips with your micropipette depends on its tip cone design. If your micropipette has a universal tip cone, it means it’s compatible with a wide range of international pipette tip brands, as long as they’re suitable for your micropipette’s volume capacity.
2. What’s the best way to sterilize my pipette before use?
To clean your micropipette before using it, first, check if it can be sterilized using an autoclave. If it can, follow the instructions in the manual to know the right temperature and duration for sterilization. Make sure to consider the type of liquid you’ll be using it for.
3. Is there a simple way to check if my micropipette is calibrated correctly?
Set it to the usual volume, then dispense water five times. Weigh what you piped out on a scale. If it matches up nicely with the ISO standard, your micropipette is good to go. If not, it’s time for a recalibration.
4. How frequently should I recalibrate my micropipette?
For regular use, it’s good to check your micropipette’s calibration every 3 to 6 months. Following the ISO 8655 standard, it’s recommended to have it calibrated annually.
5. How to adjust the volume of a micropipette?
To adjust the volume on your micropipette, look for the display showing numbers indicating the volume range. If you have a fixed-volume micropipette, the range is predetermined. However, if you have a variable volume micropipette, you can adjust it within the given range by using the rotational dial located at the top of the micropipette plunger. Alternatively, you can consult the manual for specific instructions on changing the volume.
6. Why is it important to avoid touching the tips of the micropipette?
When you touch the tips of a micropipette, you risk transferring oils and other substances from your fingers onto them. This can interfere with the accuracy of volume measurements and potentially contaminate your samples. To maintain precision and avoid contamination, it’s best to handle the micropipette tips only with the instrument itself.
7. What happens if I release the plunger of the micropipette too quickly?
Releasing the micropipette plunger too quickly can lead to inadequate liquid draw up and dispensing, causing potential inaccuracies in your measurements.
8. What should I do if my micropipette isn’t working right?
If your micropipette isn’t working properly, it’s time for some troubleshooting. Start by double-checking if it’s properly calibrated and if the volume setting is correct. Ensure that the pipette tips are securely attached and not damaged. If the issue persists, you might need to clean or maintain the micropipette according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If all else fails, it might be time to consult with a colleague or contact technical support for further assistance.
9. Can my micropipette handle different types of liquids?
Your micropipette is designed to handle a variety of liquids, whether they’re watery solutions, viscous substances, or even oils. As long as you’re using the appropriate tip size and technique, your micropipette can smoothly pipette different types of liquids.
This blog originally posted here: Micropipette Guide 2024: Types, Applications and More
0 notes
Text
Enhancing Cell Culture Research with Mediray NZ's Advanced Plate Solutions
Introduction:
In the realm of biomedical research, cell culture plays a pivotal role in understanding cellular behavior, disease mechanisms, and drug responses. However, the efficacy of such research heavily depends on the quality of tools and equipment utilized. Among these, cell culture plates are fundamental components, providing the necessary environment for cell growth and experimentation. Mediray NZ, a leading provider of laboratory equipment, offers cutting-edge solutions like the 12-well and 48-well cell culture plates, revolutionizing the landscape of cellular research.
Understanding Cell Culture Plates:
Cell culture plates are essential tools for studying cell behavior in controlled environments. They consist of wells where cells are seeded and cultured under specific conditions. The choice of plate format depends on the experimental requirements, such as cell type, culture volume, and throughput. Mediray NZ recognizes these diverse needs and offers a range of options, including the popular 48 well cell culture plate.
12-Well Cell Culture Plate:
The 12-well cell culture plate is a versatile tool widely used in research laboratories. With its larger well size compared to higher-density formats, such as 24-well or 96-well plates, the 12-well plate allows for easier handling and manipulation of cells. This format is particularly advantageous for experiments requiring a higher volume of cells or complex cellular interactions. Researchers working on applications like tissue engineering, drug screening, or stem cell research often prefer the 12-well plate for its flexibility and ease of use.
Key Features of Mediray NZ's 12-Well Cell Culture Plate:
1. Optimal Well Size: The well size of Mediray NZ's 12-well plate is carefully designed to accommodate a sufficient number of cells while allowing for proper nutrient exchange and gas permeability.
2. Uniform Surface Coating: Consistent surface coating ensures homogeneous cell attachment and growth, minimizing experimental variability.
3. Sterile Packaging: Each plate is individually packaged and sterilized to maintain cell culture integrity and prevent contamination.
4. Compatibility: The 12-well plate is compatible with a wide range of cell culture protocols, including microscopy, immunostaining, and biochemical assays.
5. Durability: Constructed from high-quality materials, Mediray NZ's 12-well plates are robust and withstand rigorous experimental conditions.
Applications of 12-Well Cell Culture Plates:
Mediray NZ's 12-well cell culture plates48 well cell culture plate
find applications across various research domains:
1. Drug Discovery: Screening compounds for therapeutic efficacy and toxicity.
2. Cancer Research: Studying tumor growth, metastasis, and drug resistance mechanisms.
3. Developmental Biology: Investigating cellular differentiation and morphogenesis.
4. Neurobiology: Culturing neuronal cells for studying synaptic plasticity and neurodegenerative diseases.
48-Well Cell Culture Plate:
While the 12-well format offers versatility, researchers often require higher throughput for screening assays and optimization studies. The 48-well cell culture plate addresses this need by providing a greater number of wells within the same footprint, enabling researchers to perform multiple experiments simultaneously. This format is ideal for high-content screening, dose-response studies, and parallel experimentation.
Key Features of Mediray NZ's 48-Well Cell Culture Plate:
1. High Throughput: With 48 wells per plate, researchers can conduct large-scale experiments efficiently, saving time and resources.
2. Compact Design: Despite the increased well count, the plate maintains a compact footprint, allowing for easy integration into automated systems and incubators.
3. Clear Well Markings: Well markings are clearly visible, facilitating accurate pipetting and sample identification.
4. Consistent Performance: Each plate undergoes rigorous quality control measures to ensure uniform cell growth and reproducible results.
5. Cost-Effective: The 48-well format maximizes experimental throughput without compromising on quality, making it a cost-effective solution for research laboratories.
Applications of 48-Well Cell Culture Plates:
Mediray NZ's 48-well cell culture plates cater to a wide range of research applications:
1. High-Throughput Screening: Screening libraries of compounds or genetic constructs for various biological activities.
2. Stem Cell Research: Differentiating stem cells into specialized cell types for regenerative medicine and disease modeling.
3. Infectious Disease Studies: Cultivating pathogens for studying host-pathogen interactions and drug susceptibility.
4. Environmental Toxicology: Assessing the effects of chemicals and pollutants on cellular viability and function.
Conclusion:
Mediray NZ's 12-well and 48-well cell culture plates represent advanced solutions for modern biomedical research. With their superior quality, versatility, and performance, these plates empower researchers to push the boundaries of cellular biology and accelerate scientific discovery. Whether investigating fundamental cellular processes or screening potential therapeutics, Mediray NZ's innovative plate solutions provide the foundation for groundbreaking research initiatives.
0 notes
Text
Automated Pipetting System
An automated pipetting system, also known as an automated liquid handling system, is a sophisticated laboratory instrument designed to accurately and precisely dispense and aspirate liquids in a high-throughput and automated manner. These systems are used in a wide range of applications, including genomics, drug discovery, clinical diagnostics, and analytical chemistry. Here are some key features and uses of automated pipetting systems: Liquid Handling: Automated pipetting systems are capable of handling various types of liquids, including reagents, samples, and solvents. They can accurately dispense specific volumes with high precision, reducing the risk of human error and variability in manual pipetting.
0 notes
Text
Adjustable vs. Fixed Volume Micropipettes - Which is Right for Your Lab?
In the precision-centric world of laboratory science, the choice of pipetting tools is crucial to the efficiency and accuracy of experiments. Among the essential tools in any lab are micropipettes, specifically adjustable and fixed volume micropipettes. Each type has its unique advantages, and choosing between them depends on your lab's specific needs. Let's delve into the characteristics of variable volume micropipettes, Microlit micropipettes (a renowned brand known for its precision tools), fixed volume micropipettes, and adjustable micropipettes to help you make an informed decision.

Variable Volume Micropipettes
Variable volume micropipettes are versatile tools that allow researchers to adjust the volume of liquid dispensed, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. This adjustability is particularly beneficial in experimental setups that require different volumes or in labs with varied pipetting needs. Variable volume micropipettes ensure that you can perform multiple tasks with the same pipette, reducing the need for multiple fixed volume pipettes and saving space and resources.
Microlit Micropipette
Microlit is a brand known for its high-quality, ergonomic pipettes designed to provide accurate and precise liquid measurement with reduced user fatigue. They offer both adjustable and fixed volume micropipettes, catering to the diverse needs of laboratories. Microlit micropipettes are engineered with user comfort in mind, featuring lightweight designs and easy volume adjustments. Their products are an excellent choice for labs looking for reliable, ergonomic pipetting solutions.
Fixed Volume Micropipettes
Fixed volume micropipettes are designed to dispense a specific volume of liquid. These pipettes offer simplicity and speed, as they eliminate the need to adjust the volume for each use, making them ideal for repetitive tasks requiring the same volume. Fixed volume micropipettes are known for their reliability and consistency, providing precise measurements every time. They are particularly useful in high-throughput settings where the same procedure is repeated multiple times.
Adjustable Micropipettes
Adjustable micropipettes combine the versatility of variable volume pipettes with the precision and ease of use characteristic of fixed volume models. They allow for quick adjustments of the dispensed volume, catering to a broad range of tasks within a single experiment. Adjustable micropipettes are perfect for labs that handle complex protocols requiring different volumes but still demand the precision and accuracy that fixed volume pipettes offer.
Which is Right for Your Lab?
Choosing between adjustable and fixed volume micropipettes depends on your lab's specific needs:
For Versatility and Broad Application Range: If your lab performs a wide variety of experiments that require different volumes, variable volume or adjustable micropipettes are the way to go. They offer the flexibility needed to accommodate diverse protocols.
For Repetitive Tasks and High Throughput: If you're working in an environment where speed and consistency are paramount, and the tasks involve repetitive pipetting of the same volume, fixed volume micropipettes offer the efficiency and reliability you need.
For Precision and Comfort: Brands like Microlit offer both adjustable and fixed volume micropipettes designed with ergonomic features to reduce fatigue and improve accuracy, making them a good choice regardless of the type you choose.
In conclusion, the decision between adjustable and fixed volume micropipettes should be guided by the specific requirements of your laboratory. Consider the nature of your experiments, the importance of versatility versus speed, and the ergonomic needs of your team. By carefully assessing these factors, you can select the pipetting tools that will best support your research and ensure the success of your lab's operations.
#variable volume micropipettes#microlit micropipette#fixed volume micropipettes#adjustable micropipettes
0 notes
Link
FirstSource provides different types of Pipettes from CAPP & Scientifique. If you want to learn the practices of Enhancing the pipetting then consider these points.
0 notes
Text
How to Improve Pipetting Techniques
One of the widely recognized normal operations done in the laboratories is Pipetting. This technique is both an estimating strategy and the movement utilized for transporting little volumes of liquid. Tasks done can become a routine. However, it is basic to take after prescribed procedures with such little specimen volumes and even trifling mix-ups impact the consequences.
youtube
Averting statistical anomalies in data sets
If you are gathering information for the pre-market authorization accommodation to the FDA to fulfill canny companion commentator, factual anomalies can annihilate the certainty estimation of an informational index. Numerous wellsprings of factors exist when taking care of microliter volumes of fluid for exploratory examination. To begin with, intra operator changeability, it is the level of fluctuation that exists over different informational indexes performed by a similar person. The inter-operator variability is the difference level that exists between different administrators playing out an indistinguishable undertaking. These both fluctuation resources can essentially affect trust in the information.
Different kinds of Pipetting Variability
Intra-operator Variability:
The variance of intra operator in standard fluid dealing with is presented through contrasts in pipettes or moment variances in the method. Likewise, while you pipet into a microplate, an administrator may not hold the pipette vertical that leads to contrasts in fine weight of pipette tip. Subsequently, little variances can be seen in the measure of administered fluid. So also, the administrator may not contact the pipette tip against the well divider with different pipetting into the same microplate. They can affect trail readout while these sources result in picoliter or nano contrasts in the aliquot volume.
Inter-operator Variability:
The change in inter-operator in the standard fluid is presented through contrasts in administrator method. One such precedent is the weight connected to a pipette while apportioning fluid. The last level of the solitary step of pipetting includes pushing air through the tip to remove any staying fluid. A few administrators may apply a sufficient measure of weight others may apply weight or oust the fluid too quickly. These both distinctions can result in unique readouts when information is obtained. When the factual examination is connected, these deviations will convert into decreased certainty esteems may be falling great underneath the benchmark of 99.7%.
Techniques to attain confidence interval of 99.7% in liquid handling
An administrator's method is just as exact as the instrument he/she is utilizing. Therefore, an individual pipette ought to be utilized while reproducing tests or for a given trial. Although the exactness of the pipette might be inadequate, the fluctuation level will stay consistent crosswise over repeats and informational collections. Likewise, pipettes ought to be legitimately kept up. This incorporates standard cleaning and administration by a guaranteed expert. Exactness and accuracy need to be computed between planned administrations by estimating the heaviness of a known fluid aliquot. These means can enhance the outcomes got in fluid approaching processes. Even though the instrument mistake is normal, administrator blunder is considerably bigger and unavoidable issue when managing fluid. Few arrangements exist to battle these wellsprings of mistake. Initially, prepare and retrain your staff all the time which directs for appropriate pipetting to go far in decreasing slip-ups. Like, when required survey administrator methods at normal interims will recommend remedial activities. Also running the dummy plates for these appraisals may devour expensive reagents. However, it's superior to advocating distant information focuses on an analyst.
Electronics Pipettes
These are the valuable device in annihilating blunders in techniques of pipetting. The exactness of electronic pipettes and reproducibility far surpass that of manual pipettes, including pipettes with multichannel. Both of the variability pipetting i.e.., intra-and inter-operator fluctuation is decreased to a reasonable level. For whatever length of time, it takes a workforce to precisely program these pipettes. The measure of fluid administered will without a doubt be more exact than that of manual instruments. Administrators can just turn a handle or press a catch to be guaranteed that volumes of aliquot will be inside acknowledged vacillation to the coveted amount. Furthermore, electronic instruments are better than manual pipettes as far as productivity, which diminishes administrator strain. And also guarantees that fluids are administered in an opportune way.
Electronic pipettes are an essential and viable arrangement in fighting poor certainty interims. The 99.7% benchmark certainty interim never again lays two standard deviations outside the mean when in the hands of legitimately prepared professionals.
youtube
youtube
#How to Improve Pipetting Techniques#Types of Variability in Pipetting#Learn about manual and electronic pipettes
0 notes
Text
Automated Pipetting Systems Market is Predicted to See Lucrative Gains Over 2021-2026 Covid-19 Analysis
"
<a href=https://www.reporthive.com/request_sample/2802504 target=""""_blank"""" rel=""""noopener""""> Get Sample Report<a href=https://www.reporthive.com/checkout?currency=single-user-licence&reportid=2802504 target=""""_blank"""" rel=""""noopener""""> Buy Complete Report<a href=https://www.reporthive.com/request_customization/2802504 target=""""_blank"""" rel=""""noopener""""> Request for Customization
A new market study is released on Automated Pipetting Systems Market 2021 with data Tables for historical and forecast years represented with Chats & Graphs with easy to understand detailed analysis. The report also sheds light on present scenario and upcoming trends and developments that are contributing in the growth of the market. In addition, key market boomers and opportunities driving the market growth are provided that estimates for Global Automated Pipetting Systems Market till 2026. The authors of the Automated Pipetting Systems Market report have piled up a detailed study on crucial market dynamics, including growth drivers, restraints, and opportunities. Automated Pipetting Systems Market report carries out research and analysis of the market for a particular product/service which includes the investigation into customer inclinations. It performs the study of various customer capabilities such as investment attributes and buying potential. This market report involves feedback from the target audience to understand their characteristics, expectations, and requirements. The report provides new and exciting strategies for upcoming products by determining the category and features of products that the target audiences will readily accept. The global Automated Pipetting Systems market research report collects data about the target market such as pricing trends, customer requirements, competitor analysis, and other such details.
>>Get technical analysis | Request a FREE PDF Sample Copy @ https://www.reporthive.com/request_sample/2802504
Research objectives: Post-COVID analysis on market growth and size (growth potential, opportunities, drivers, industry specific challenges and risks). To study and analyze the global Automated Pipetting Systems market size by key regions / countries, product type and application, historical data from 2015 to 2021 and forecast to 2026. The study covers the current Automated Pipetting Systems market size and its growth rates based on 5-year records with a company overview of key players / manufacturers:
Eppendorf, Gilson international, Biotek Instruments, Thermo Scientific, Mettler Toledo Analytical Instruments, Agilent Technologies, ...
To understand the structure of Automated Pipetting Systems market by identifying its various subsegments. Focuses on the major players of the global Automated Pipetting Systems Market, to define, describe, and analyze the value, market share, market competitive landscape, SWOT analysis, and development plans in the coming years. To analyze the Automated Pipetting Systems Market with respect to individual growth trends, future prospects, and their contribution to the total market. Analyze competitive developments such as expansions, agreements, new product launches and acquisitions in the market to better understand the pre and post COVID scenario. Reporthive has released an updated research report highlighting the title Global Automated Pipetting Systems Market Research Report 2021, which presents a modern market growth outlook as well as the forecast forecast along with the Investment Rate (ROI) as a whole., with a developing CAGR close to XX% throughout the 2019-2026 period. The file studies the revenue of the Automated Pipetting Systems industry in the global market, especially in the North of the United States, China, Europe, Southeast Asia, Japan and India, with production, consumption, income, import and export in those areas. Market by Automated Pipetting Systems Type: Multi-Channel, Single-Channel Market by Automated Pipetting Systems Application: Biological Fields, Chemical Fields, Medical Fields, Others Automated Pipetting Systems Geographic Market Analysis: The report provides information on the Automated Pipetting Systems market area, which is subdivided into subregions and countries. In addition to the market share in each country and sub-region, this chapter of the report also provides information on profit / growth opportunities and also mentions the share according to the impact of COVID-19 for each region, country, and sub-region. * North America (Mexico, USA, Canada) * Europe (Netherlands, Germany, France, Belgium, UK, Russia, Spain, Switzerland) * Asia Pacific (China, Australia, Japan, Korea, India, Indonesia, Thailand, Philippines, Vietnam) * Middle East and Africa (Turkey, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, United Arab Emirates, South Africa, Israel, Nigeria) * Latin America (Brazil, Chile, Argentina, Colombia, Peru). Reason for purchasing this report: - It offers research and analysis of changing serious situations. - For the improvement of expert choices in organizations, it offers systematic information with essential organizational viewpoints - It helps to understand the important parts of the key elements. - The report explains the major key factors of the market, for example, drivers, limitations, models and openings. - It offers a provincial survey on the global Automated Pipetting Systems market along with the business profiles of some partners. - It offers tremendous information on the introduction of new elements that will impact the advancement of the Global Automated Pipetting Systems
>>> Direct purchase Our report (Edition 2021) Below @ https://www.reporthive.com/checkout?currency=single-user-licence&reportid=2802504
TOC Highlights: Chapter 1. Introduction: The Automated Pipetting Systems research work report covers a concise introduction to the global market. This segment provides assessments of key participants, a review of Automated Pipetting Systems industry, outlook across key areas, financial services, and various difficulties faced by Automated Pipetting Systems Market. This section depends on the Scope of the Study and Report Guidance. Chapter 2. Outstanding Report Scope: This is the second most significant chapter, which covers market segmentation along with a definition of Automated Pipetting Systems. It characterizes the whole scope of the Automated Pipetting Systems report and the various features it is describing. Chapter 3. Market Dynamics and Key Indicators: This chapter incorporates key elements focusing on drivers [Includes Globally Growing Automated Pipetting Systems frequency and Increasing Investments in Automated Pipetting Systems], Key Market Restraints[High Cost of Automated Pipetting Systems], opportunities [Arising Markets in Developing Countries] and introduced in detail the arising trends [Consistent Innovate of New Screening Products] development difficulties, and influence factors shared in this latest report. Chapter 4. Type Segments: This Automated Pipetting Systems market report shows the market development for different kinds of products showcased by the most far-reaching organizations. Chapter 5. Application Segments: The analysts who composed the report have completely assessed the market capability of key applications and perceived future freedoms. Chapter 6. Geographic Analysis: Each provincial market is deliberately examined to understand its current and future development, improvement, and request situations for this market. Chapter 7. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Global Automated Pipetting Systems Market: 7.1 North America: Insight On COVID-19 Impact Study 2021-2026 7.2 Europe: Serves Complete Insight On COVID-19 Impact Study 2021-2026 7.3 Asia-Pacific: Potential Impact of COVID-19 (2021-2026) 7.4 Rest of the World: Impact Assessment of COVID-19 Pandemic Chapter 8. Manufacturing Profiles: The significant players in the Automated Pipetting Systems market are definite in the report based on their market size, market served, products, applications, regional development, and other variables. Chapter 9. Estimating Analysis: This chapter gives price point analysis by region and different forecasts. Chapter 10. North America Automated Pipetting Systems Market Analysis: This chapter includes an appraisal on Automated Pipetting Systems product sales across major countries of the United States and Canada along with a detailed segmental viewpoint across these countries for the forecasted period 2021-2026. Chapter 11. Latin America Automated Pipetting Systems Market Analysis: Significant countries of Brazil, Chile, Peru, Argentina, and Mexico are assessed apropos to the appropriation of Automated Pipetting Systems. Chapter 12. Europe Automated Pipetting Systems Market Analysis: Market Analysis of Automated Pipetting Systems report remembers insights on supply-demand and sales revenue of Automated Pipetting Systems across Germany, France, United Kingdom, Spain, BENELUX, Nordic, and Italy. Chapter 13. Asia Pacific Excluding Japan (APEJ) Automated Pipetting Systems Market Analysis: Countries of Greater China, ASEAN, India, and Australia & New Zealand are assessed, and sales evaluation of Automated Pipetting Systems in these countries is covered. Chapter 14. Middle East and Africa (MEA) Automated Pipetting Systems Market Analysis: This chapter centers around Automated Pipetting Systems market scenario across GCC countries, Israel, South Africa, and Turkey. Chapter 15. Research Methodology The research procedure chapter includes the accompanying primary realities, 15.1 Coverage 15.2 Secondary Research 15.3 Primary Research Chapter 16. Conclusion >> [With unrivaled insights into the Automated Pipetting Systems market, our industry research will help you take your Automated Pipetting Systems business to new heights.] <<
>>>> For more customization, connect with us at @ https://www.reporthive.com/2802504/enquiry_before_purchase
Why Report Hive Research: Report Hive Research delivers strategic market research reports, statistical surveys, industry analysis and forecast data on products and services, markets and companies. Our clientele ranges mix of global business leaders, government organizations, SME’s, individuals and Start-ups, top management consulting firms, universities, etc. Our library of 700,000 + reports targets high growth emerging markets in the USA, Europe Middle East, Africa, Asia Pacific covering industries like IT, Telecom, Semiconductor, Chemical, Healthcare, Pharmaceutical, Energy and Power, Manufacturing, Automotive and Transportation, Food and Beverages, etc. Contact Us: Report Hive Research 500, North Michigan Avenue, Suite 6014, Chicago, IL – 60611, United States Website: https://www.reporthive.com Email: [email protected] Phone: +1 312-604-7084"
0 notes
Text
Pipettes and Accessories Market Growth Opportunities, Share & Competitive Landscape Report To 2026

The global pipettes and accessories market size was valued at US$ 1.3 billion in 2017 and is expected to witness a CAGR of 4.0% over the forecast period (2018 – 2026).
Pipettes are used in biotechnology, pharmaceutical, and chemical laboratories in order to transfer certain volume of liquids. Micropipettes are important in molecular biology experiments, which require microliter amounts of solutions whereas serological pipettes are used in microbiology laboratories to prepare cell cultures that require media preparations of milliliter volumes. Volume transfers with sterile cultures and solutions using instruments such as micropipettes and serological pipettes are one of several types of routine techniques performed in a laboratory. Pipette designs such as electronic pipetting, ultralight pipettes, plungers positions in more user-friendly configurations, and reducing frictional forces help in reducing strain.
Download the PDF brochure: https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/insight/request-pdf/2322
Increasing research and development in the field of pharmaceuticals and biotechnology due to high prevalence of infectious diseases and cancer are the major factors driving the pipettes and accessories market growth. According to 2012 European Union Industrial R&D Investment Scoreboard, the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors represented 17.7% of business R&D expenditure in the world.
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly focusing on conducting research and development activities as well as outsourcing such activities to academic and private research institutes. This in turn is increasing demand for liquid handling systems such as pipettes. Pharmaceutical companies are also increasingly outsourcing their research activities to privately-owned Contract Research Organizations (CRO) to maintain their presence in the growing pharmaceutical and biotechnology market. For instance, in May 2018, Ritter Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a manufacturer of novel therapeutic products entered into an agreement with Medpace, a CRO to conduct the first of two pivotal Phase 3 clinical trials for RP-G28 among patients with lactose intolerance.
Pipettes and Accessories Market Restraints
Pipettes are extensively used for various applications and are thus exposed to various types of reagents and specimens. They can introduce quality-specific concerns regarding precision and accuracy and can also lead to safety risks, particularly while working with hazardous chemicals or specimens with a high infection risk. Furthermore, high cost of electronic pipettes can be a negative factor for the market growth. For instance, the cost of the Xplorer plus electronic single channel pipette with charging adapter is around US$ 1000. This product may not be affordable for several laboratories due to its high price. However, manual pipettes tend to be more economical, though they produce greater variability, particularly for highly sensitive or expensive pipetting applications.
Browse Complete Report For More Information @ https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/market-insight/pipettes-and-accessories-market-2322
0 notes
Text
A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right Liquid Handling Instrument
In any laboratory setting, liquid handling is a critical process that directly impacts the accuracy, efficiency, and reliability of experiments. Whether it's for research, diagnostics, or pharmaceutical development, choosing the right liquid handling instrument is essential for precise results. With a variety of options available, selecting the best one for your needs can be overwhelming. This guide will help you navigate the key factors to consider when choosing the right liquid handling instrument.
Accuracy and Precision
Accuracy refers to how close the measured volume is to the true volume, while precision relates to the reproducibility of measurements. Both factors are critical in maintaining the quality of your experiments.
For routine tasks, manual pipettes may suffice as long as they’re calibrated regularly.
For high-precision tasks like genomic sequencing or drug discovery, electronic pipettes provide better consistency and reduce human variability.
Volume Range and Flexibility
Different experiments require varying volumes of liquid to be transferred, so selecting an instrument with an appropriate volume range is important.
Micropipettes are ideal for small volumes (1-1000 μL), making them perfect for applications like PCR and enzyme assays.
Bottle-top dispensers can handle larger volumes and are useful for bulk liquid handling tasks, such as transferring reagents or buffers.
Opt for an instrument that offers flexibility in volume range to accommodate various experimental needs.
Ergonomics and User Comfort
Frequent pipetting can lead to repetitive strain injuries, especially in high-volume laboratories. Ergonomics play a major role in ensuring that the instrument is comfortable and easy to use over extended periods. When choosing a liquid handling instrument:
Look for lightweight designs and comfortable grips, especially if it’s a manual pipette.
Electronic pipettes with minimal button pressing can reduce strain on your hands.
Consider features like adjustable volume dials, which make it easier to switch between different volumes with ease.
Automation and Throughput Needs
If your lab requires high throughput or your experiments involve repetitive tasks, investing in an automated liquid handler could be worthwhile. Automation reduces the risk of human error, increases reproducibility, and frees up lab technicians to focus on more complex tasks. However, for labs with limited budgets or smaller workloads, semi-automated pipetting systems can offer a good balance between manual and automated handling.
Contamination Control
Cross-contamination can ruin experiments, especially in sensitive applications like molecular biology or microbiology. Choosing the right type of pipette can help minimize contamination risks:
Disposable tips are a must for avoiding sample carryover.
Some pipettes come with filter tips to prevent aerosols from contaminating samples or pipettes.
Positive displacement pipettes are ideal for handling viscous, volatile, or dense liquids where contamination is a higher risk.
Cost Considerations
Budget is always a factor, but it’s essential to weigh the cost of the instrument against the potential benefits it can offer. While manual pipettes are more cost-effective, investing in electronic or automated systems can improve accuracy, reduce human error, and save time in the long run. Consider the return on investment (ROI) when purchasing advanced equipment.
Maintenance and Calibration
Regular maintenance and calibration are crucial for ensuring that your liquid handling equipment continues to perform accurately. Instruments with easy-to-maintain designs or self-calibration features can save time and resources. Additionally, some manufacturers offer calibration services, which can be a valuable support option.
Conclusion
Choosing the right liquid handling instrument is more than just picking a tool off the shelf—it’s about understanding the demands of your specific lab work, considering factors like accuracy, volume range, ergonomics, and contamination control. By carefully evaluating these elements, you can select an instrument that not only meets your current needs but also adapts to future demands, helping you achieve consistent and reliable results in the lab.
Whether you’re running simple assays or conducting complex research, the right liquid handling tool can make all the difference.
#liquid handling instrument#manual pipettes#electronic pipettes#liquid handling equipment#type of pipette#micropipettes
0 notes
Note
Hi Julia! Do you have any tips for working with 96 well plates? My cell concentrations are all over the place because I suck at pipetting evenly.
Hi there! Aaaahhh 96 wells plates. the bane of my existence. let’s see what we can do here!
Vortex your cell suspension often. Cells settle quickly, so I usually vortex my sample after each plate. However I recommend you vortexing your sample after every row/column/8 or 12 pipettes as a start until you’re more comfortable.
Use a multi-channel pipette if applicable. These’ll increase your speed and hopefully reproducibility. You’ll have to pour your sample into a sterile trough (so vortexing is out of the question), but you can create multiple tubes of cell suspension/plate and vortex those before pouring into the trough.
Pipette into the plate randomly. Meaning instead of pipetting all of row 1 (or column A), etc in an orderly fashion, try pipetting in a random pattern (A1, then B5, then H8, etc). I do this for when each column is a different variable (ex. treatment concentration), so in case my cell suspension does settle halfway through, certain treatments aren’t going to have different cell concentrations. Also it’s kind of fun to create interesting patterns :D
Do everything the same. Aspirate in the same spot and depth per well, dispense in the same spot and depth (and speed) per well, vortex at the same speed and duration, etc. The more things that are kept consistent, the more likely the results will also be consistent.
If you’re having issues with cells clumping around the edges of the well, you can try pipetting a bit of warm sterile 1X PBS into the empty spaces between the wells (and then aspirate them away after your cells have adhered). I’ve found that magically encourages the cells to spread out more, and is kind of a god-send if you need to do any type of visual analyses. Also avoid swirling the plate afterwards, as this may push the cells into the edges. You can gently tilt the plate side to side as an alternative if you want to give the cells one last good mix.
Maybe even play around with the cell concentration. Every cell line/type behaves differently, and some cells need a minimum concentration in order to grow, and some cells also stop growing after a certain concentration. All these cellular kinetics may affect your downstream applications (like a cell viability assay, count, etc). You can try plating higher concentrations, or lower concentrations, and see what happens.
Practice practice practice. Everything takes time to master, even pipetting into plates. No one starts anything perfectly, so know it’s ok to make some mistakes in order to grow as a scientist. You’ll get the hang of 96-well plates soon enough if you keep at it :)
Hope this helps! If not, let me know and let’s see what else we can do! Good luck!
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pipettors Market Price Trends and Key Raw Material Analysis 2018-2025
January 9, 2019: The Global Pipettors market is expected to grow at a substantial CAGR in the years to come. A pipettor, commonly termed as a “pipette” or “pipet” is a laboratory tool generally used in biology, chemistry, and medicine to dispense measured volume of liquid. Pipettes basically work by creation of partial vacuum above the chamber that holds the liquid and selectively releases this vacuum to draw up and give out according to the preferred volume. Pipettors dispensing between 1 and 1000µl are known as micropipettes whereas macropipettes dispense a greater volume.
In the market, there are several designs of pipettors available such as manual, electronic, single channel or multi channel pipettes. They designed for efficiency when working with changing tubes, plates, and dishes. Pipettors are designed for different purposes such as improving accuracy and decreasing the risk of repetitive motion.
Request a Sample Copy of This Report @ https://www.millioninsights.com/industry-reports/pipettors-market/request-sample
Global pipettors market is segmented on the basis of product, application and geography. Based on product, the pipettors industry is segmented into variable-volume, fixed-volume, single-channel, multi-channel and so on. Based on application, the pipettors market is segmented into hospitals, pharmaceuticals & biotech companies, clinical diagnostic labs, environmental, government agencies, process control industries and so on. Based on geography, the pipettors industry is segmented into North America, China, Europe, Japan, India, Southeast Asia and Latin America.
View Full Report with TOC @ https://www.millioninsights.com/industry-reports/pipettors-market
Market Segment:
Geographically, this report is segmented into several key Regions, with production, consumption, revenue (million USD), market share and growth rate of Pipettors in these regions, from 2013 to 2025 (forecast), covering
North America
Europe
China
Japan
Southeast Asia
India
Global Pipettors market competition by top manufacturers, with production, price, revenue (value) and market share for each manufacturer; the top players including
Eppendorf
Capp ApS
Nichiryo
Hamilton
Sartorius
Thermo Fisher
Labnet
Kimble-Chase
Sarstedt
Aptaca
On the basis of the end users/applications, this report focuses on the status and outlook for major applications/end users, consumption (sales), market share and growth rate for each application, including
Pharmaceutical and biotech companies
Hospitals
Clinical diagnostic labs
Government agencies
Environmental
Process control industries
Table of Contents
1 Pipettors Market Overview
2 Global Pipettors Market Competition by Manufacturers
3 Global Pipettors Capacity, Production, Revenue (Value) by Region (2013-2018)
4 Global Pipettors Supply (Production), Consumption, Export, Import by Region (2013-2018)
5 Global Pipettors Production, Revenue (Value), Price Trend by Type
6 Global Pipettors Market Analysis by Application
7 Global Pipettors Manufacturers Profiles/Analysis
8 Pipettors Manufacturing Cost Analysis
9 Industrial Chain, Sourcing Strategy and Downstream Buyers
10 Marketing Strategy Analysis, Distributors/Traders
11 Market Effect Factors Analysis
12 Global Pipettors Market Forecast (2018-2025)
For More Details Visit @ million insights
#pipettors market#pipettors market size#pipettors market share#Pipettors Market Scope#pipettors#laboratory equipment
0 notes
Text
Automated Liquid Handling Market Analysis- KBV Research
Automated Liquid Handling systems have contributed to the rearrangement of research workflows, which has further led to off-putting the manual efforts that are typically involved in liquid transfer operations. Automated liquid handling reflects a set of equipment and instruments that are used for handling liquids and implementing functions relating to liquid transfer within a clinical and research arena.
Intuitive interfaces of automated liquid handling systems enable operators of any skill level to perform their daily tasks effortlessly and with confidence. The systems provide full control of a highly flexible automation. Automated liquid handling systems reduce time spent on repetitive pipetting tasks. They offer systems that are best suitable for medium or high applications along with meeting multiple liquid handling requisites which include channels, liquid volumes, or microplate type. Decreasing sample contamination and improving accuracy in bioassays is possible with these systems.
Manual intervention into research often comes coupled with errors and is not reproducible. It further creates supplementary bottlenecks within the encompassed research experiment when try-outs are not satisfactorily reproduced. These concerns have highlighted the adoption of automated liquid handling systems since their implementation ensures error-free reproducible results.
Click Here For Free Insights
Why are ALH systems crucial?
Since multiple variables are affecting the important process in laboratories, choosing the appropriate solution for small volume handling is extremely important. Therefore, numerous labs have turned to automated liquid handling systems to complement improved reliability and increased efficiency to lab processes. One of the key benefits of automated liquid handlers is that they eradicate both person-to-person and day-to-day variability. Further, they generally accomplish this through minimized training that is needed to manually hand out sub-microliter volumes. Automated liquid handles also enable combination with other processing instruments. Through this, automated liquid handlers can be improved to accomplish better results and can be calibrated as per factors like the liquid type.
Types of Automated Liquid Handling Systems
Individual Benchtop Workstation
Individual benchtop workstations are tools that are designed to perform most of the sampling, mixing, and amalgamating liquid samples automatically. Bioresearch laboratories and drug development labs have limited sample contamination and free personnel to perform other tasks by using a multipurpose liquid handling automated workstation. The workstations are capable of measuring samples, add reagents, and ensure that liquids are added to bioassays in a uniform way. In comparison with other liquid handling systems, benchtop workstations are emerging as one of the top selling products across the globe.
ALH in PCR setup
The automation of PCR setup upsurges reproducibility alongside reducing hands-on time. Automated liquid handlers enable rapid and accurate setup of endpoint, real-time, and multiplex PCR experiments. With platform sizes including benchtop and largely integrated workstations, any throughput requirements can be entertained. Automated liquid handlers offer solutions for any PCR automation needs.
ALH in Serial Dilution
Serial dilutions are a commonly used application in a lab. The user pipettes concentrated sample into the desired location and fill a series of additional locations which contain a fixed amount of diluent. Lab automation is the most appropriate choice for simplifying serial dilutions along with assuring utmost accuracy. A multi-channel automated pipettor has the capability of carrying out serial dilutions of eight to twelve samples simultaneously.
ALH in Plate Reformatting
Owing to the surging liquid handling constraints, sample reformatting turns out to be an expensive process. Plate reformatting is the process in which samples are moved from one container to another. The flow must be carefully performed to avoid unnecessary container format changes. Automated liquid handlers are used for compound management. These offer full plate dilutions and reformatting from source plates to assay plates.
Trends & Developments
Liquid handling robots are being used in automating chemical and biochemical laboratories. The robots dispense a specific quantity of reagent, samples, or other liquids into a designated container. Several liquid handling workstations can conduct multiple lab unit operations like sample mixing, transport, manipulation, and incubation. Liquid handling robots are available in the market with customizations using different add-on modules like PCR machines, colony pickers, etc. Manufacturers are emphasizing on developing automated liquid handling workstations to mix, sample, and combine the liquids.
Automated liquid handling systems extend the range from semi-automated multichannel pipettors to room-sized systems. The industry is evolving toward nifty, modular systems for every budget. Similarly, instrumentation, software, and methods are following the trend toward superior user accessibility.
Contact Us:- 244 Fifth Avenue, Suite 1407 New York, N.Y. 10001 United States (U.S) Tel: +1 (646) 661-6066 Email : [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Pipettes and Accessories Market Outlook,Opportunity Analysis And Top Companies
The global pipettes and accessories market size was valued at US$ 1.3 billion in 2017 and is expected to witness a CAGR of 4.0% over the forecast period (2018 – 2026).
Pipettes are used in biotechnology, pharmaceutical, and chemical laboratories in order to transfer certain volume of liquids. Micropipettes are important in molecular biology experiments, which require microliter amounts of solutions whereas serological pipettes are used in microbiology laboratories to prepare cell cultures that require media preparations of milliliter volumes. Volume transfers with sterile cultures and solutions using instruments such as micropipettes and serological pipettes are one of several types of routine techniques performed in a laboratory. Pipette designs such as electronic pipetting, ultralight pipettes, plungers positions in more user-friendly configurations, and reducing frictional forces help in reducing strain.
Increasing research and development in the field of pharmaceuticals and biotechnology due to high prevalence of infectious diseases and cancer are the major factors driving the pipettes and accessories market growth. According to 2012 European Union Industrial R&D Investment Scoreboard, the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors represented 17.7% of business R&D expenditure in the world.
Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly focusing on conducting research and development activities as well as outsourcing such activities to academic and private research institutes. This in turn is increasing demand for liquid handling systems such as pipettes. Pharmaceutical companies are also increasingly outsourcing their research activities to privately-owned Contract Research Organizations (CRO) to maintain their presence in the growing pharmaceutical and biotechnology market. For instance, in May 2018, Ritter Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a manufacturer of novel therapeutic products entered into an agreement with Medpace, a CRO to conduct the first of two pivotal Phase 3 clinical trials for RP-G28 among patients with lactose intolerance.
Download the PDF brochure:
https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/insight/request-pdf/2322
Pipettes and Accessories Market Restraints
Pipettes are extensively used for various applications and are thus exposed to various types of reagents and specimens. They can introduce quality-specific concerns regarding precision and accuracy and can also lead to safety risks, particularly while working with hazardous chemicals or specimens with a high infection risk. Furthermore, high cost of electronic pipettes can be a negative factor for the market growth. For instance, the cost of the Xplorer plus electronic single channel pipette with charging adapter is around US$ 1000. This product may not be affordable for several laboratories due to its high price. However, manual pipettes tend to be more economical, though they produce greater variability, particularly for highly sensitive or expensive pipetting applications.
Pipettes and Accessories Market - Regional Insights
On the basis of region, the global pipettes and accessories market is segmented into North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East, and Africa. North America is the largest market for biotechnology and pharmaceutical research and manufacturing and therefore, demand for pipettes and accessories is the highest in the region. According to a study published by the International Trade Administration in 2016, the U.S. is the major hub for drug manufacturing and is expected to grow considerably in future.
Asia Pacific pipettes and accessories market is expected to witness significant growth over the forecast period. This is owing to increasing clinical trials from biopharmaceutical industry in the region due to easy patient recruitment and availability of skilled professionals to conduct research experiments. This in turn leads to increasing number of research laboratories being set up in the region, thereby propelling demand for pipettes and accessories. For instance, in March 2017, Herbalife Company associated with Syngene established a new research and development lab at Bangalore, India.
According to the India Brand Equity Foundation June 2018 report, Government of India has reduced the approval time for new facilities to propel investments for drug manufacturers under the ‘Pharma Vision 2020’. Such initiatives are expected to attract foreign investors for the development of new manufacturing units, in turn increasing demand for pipettes and accessories during the forecast period.
Click To Reading More On Pipettes and Accessories Market
About Coherent Market Insights:
Coherent Market Insights is a prominent market research and consulting firm offering action-ready syndicated research reports, custom market analysis, consulting services, and competitive analysis through various recommendations related to emerging market trends, technologies, and potential absolute dollar opportunity.
Contact Us:
Mr.Shah Coherent Market Insights 1001 4th Ave, #3200 Seattle, WA 98154 Tel: +1-206-701-6702 Email:[email protected]
Visit our news Website: https://www.coherentwire.com
0 notes
Text
Pipettors Market is set for a Potential Growth Worldwide: Excellent Technology Trends
01th November 2018: This Report Studies the Global Pipettors Market size, industry status and forecast, competition landscape and growth opportunity. This Research Report categorizes the Global Pipettors Industry by Companies, Region, Application, Type and end-use Industry.
Pipettors market is expected to grow at a substantial CAGR in the years to come. A pipettor, commonly termed as a “pipette” or “pipet” is a laboratory tool generally used in biology, chemistry, and medicine to dispense measured volume of liquid. Pipettes basically work by creation of partial vacuum above the chamber that holds the liquid and selectively releases this vacuum to draw up and give out according to the preferred volume. Pipettors dispensing between 1 and 1000µl are known as micropipettes whereas macropipettes dispense a greater volume.
Browse Full Research Report @ https://www.millioninsights.com/industry-reports/pipettors-market
In the market, there are several designs of pipettors available such as manual, electronic, single channel or multi channel pipettes. They designed for efficiency when working with changing tubes, plates, and dishes. Pipettors are designed for different purposes such as improving accuracy and decreasing the risk of repetitive motion.
Global pipettors market is segmented on the basis of product, application and geography. Based on product, the pipettors industry is segmented into variable-volume, fixed-volume, single-channel, multi-channel and so on. Based on application, the pipettors market is segmented into hospitals, pharmaceuticals & biotech companies, clinical diagnostic labs, environmental, government agencies, process control industries and so on. Based on geography, the pipettors industry is segmented into North America, China, Europe, Japan, India, Southeast Asia and Latin America.
Europe is expected to hold the largest share in pipettors industry in the upcoming years. This could be attributed to the expected recovery in food processing, pharmaceutical, and biotechnology industries. Key players operating in the pipettors market are Eppendorf AG, Rainin, Hamilton, Sorensen, USA Scientific, Sartorius, Capp ApS, Nichiryo, Corning, BRAND, Nichiryo Co. Ltd., Hamilton, Kimble-Chase, Mettler Toledo International Inc., Labcon, Socorex Isba S.A, Sarstedt, VISTALAB, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., ECHNOLOGIE, Labnet, BrandTech, Tecan Group Home, Biotix, Bel-Art, Aptaca, Ohaus, Greiner, Scilogex, TPP, PerkinElmer, Bioplas, Argos Technologies, Dragon Laboratory and Gilson.
Get a Sample Copy of This Report @ https://www.millioninsights.com/industry-reports/pipettors-market/request-sample
0 notes