#VR Training for Manufacturing
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
n recent years, virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a groundbreaking tool in various industries, transforming how we learn, work, and interact with technology. In India, one company that stands out in this burgeoning field is Simulanis Solutions. Renowned for its innovative approach, Simulanis Solutions is revolutionizing the way we approach training and industrial education through cutting-edge virtual reality training solutions
#VR Training Solutions#Immersive VR Training#VR-Based Learning Solutions#Virtual Reality Training Programs#VR Employee Training#Industrial VR Training#Corporate VR Training Solutions#VR Simulation Training#Virtual Reality Skill Development#VR Training for Healthcare#VR Training for Manufacturing#Custom VR Training Solutions#VR Safety Training#Interactive VR Training#VR Training for Education#Augmented and VR Training Solutions#Virtual Reality for Workplace Training#VR-Based Soft Skills Training#Immersive Training Technologies#Realistic VR Training Solutions
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Use Cases of VR in Manufacturing Safety Training
Virtual reality (VR) technology has been a game-changer for various industries, including manufacturing. It is proving to be an effective tool for enhancing safety training in a manufacturing environment. In this article, we'll explore how VR can be used in manufacturing safety training and highlight some of its key use cases.
How to Use VR in Manufacturing Safety Training
Complex Assembly and Maintenance Procedures
Complex Assembly and Maintenance Procedures
VR can be a valuable tool for training employees on complex assembly procedures. With VR simulations, trainees can disassemble and reassemble virtual components, gaining a deep understanding of the machinery's functionalities. This practical, hands-on element of VR-based training ensures that employees can perform these tasks efficiently and safely when faced with real equipment.
Hazardous Material Handling
Manufacturing processes often involve handling hazardous equipment. Immersive VR manufacturing training programs can simulate high-risk scenarios involving the safe handling, storage, and disposal of hazardous materials. Employees can practice using safety gear and emergency response procedures without the real-world risk of accidents or chemical exposures.
Emergency Response Drills
VR can recreate emergencies such as fires, chemical spills, or equipment malfunctions. Trainees can learn how to react during emergencies via realistic VR simulations. This element of realism enhances employees' ability to react swiftly and effectively in real-life emergencies.
Equipment Familiarization
New equipment or machinery in an industrial setting can introduce safety risks due to unfamiliarity. VR training solutions can help employees familiarize themselves with new equipment before it is installed in the actual workplace. This pre-emptive training can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents during equipment transitions.
Safety Culture and Behavioral Training
VR safety training can also help instill a strong safety culture in your organization. Through immersive VR experiences, employees can learn about the importance of safety and how their behavior impacts it. VR can be used to train employees on the psychology of safety and how their actions can prevent accidents.
Remote Training Opportunities
Manufacturing facilities are often dispersed across multiple locations. VR technology enables remote training, providing consistent safety training to employees working in various parts of the world. This ensures that every worker receives the same level of safety education, irrespective of their location.
Stress Testing Under Extreme Conditions
VR training allows for the creation of scenarios that push the limits of conventional manufacturing safety training. VR can recreate high-pressure scenarios or emergencies, which might be challenging to replicate in real-life training. By exposing employees to these scenarios, manufacturers can better prepare their workforce for high-stress situations, ultimately enhancing their ability to handle crises effectively.
Takeaway Thoughts
Adopting VR technology in manufacturing safety training is a game-changer. As the price of VR equipment and software drops in the near future, we can expect VR to play a pivotal role in ensuring manufacturing safety and reducing workplace accidents. If you're interested in incorporating VR for manufacturing safety training, check out XR Guru's Marketplace, where you can choose from a wide range of customized VR manufacturing solutions. Don't hesitate to contact us to learn more and schedule a free demo today!
Visit: https://www.xrguru.com/subject-area/manufacturing-skills-and-safety
1 note
·
View note
Text
DBH worldbuilding info u're supposed to know
The collection
US is having major issues with sea level rising quickly, making even the wealthy residents deciding not living right on the coast anymore. Polar ice has melted to an extent that rising sea levels have many states struggling to keep the water out of their coastal towns (Magazine)
CyberLife's intention with complex level humanization was to literally make people welcome 'em home like they're family instead of getting creeped about it (Magazine)
VR games are very common by 2038 (Magazine)
The President Cristina Warren is an ex-vlogger with no experience in government that relied on social media and celebrity status to be elected in 2036, originally a republican representative. There's a "rumor" CyberLife helped she getting elected by corrupt means and that's why they're "too close" (Magazine, Gallery, Cut concepts)
Warren got an approval of only 33% due to the sequence of bad decisions (Magazine)
The world's population is 10 billion by 2038 (Magazine)
Obesity is in a record high in Detroit by 2038 (Magazine)
NATO is divided about the Russia vs US conflict in the Arctic, they think everybody can benefit of the region without war but Warren is totally pushing for a conflict (Magazine)
Rare minerals used in synthetizing Thirium got Russia and US biting each other in the North Pole in recent yrs. Android manufacture dominates both the US and Russian economies (Magazine)
Kamski being the one creating Thirium 310 and biocomponents more than a decade ago suggests other areas with these minerals were already explored, the North Pole being the last one (Assumption)
Police is constantly using marketing data to identify criminals (Magazine)
Dating websites usually have less than 5% of women using it (Magazine)
0.4% of world population holds 94% of global wealth by 2038 (Magazine)
By 2038 there's constant propaganda selling Canada as the true land of freedom (Magazine)
No matter how u play as Markus u gonna eventually have event contexts distorted, including fake news. They're called criminal org and terrorists no matter what u do (Observation)
CyberLife developed a nano-android to help combating cancer and diseases that can extend the human life-span even reaching a semi-immortality status - and it's very promising as it was already succesful in doing its task (Magazine)
US life expectancy is 91 by 2038 (Magazine)
By 2038 US got a aging population but not enough young people to support the economy with the unemployment rate at 37.3%, and the "job" area is dominated by androids (Magazine, Observation)
When the rebellion starts the gov consider bringing retirees back to work as the country lack qualified manpower to deal with the withdraw of androids (Cut dialogue)
Only two countries have android industries that rival the United States: Russia and China, they're also in a space race of sorts (Magazine)
Team sports like baseball got at least 1 android per team (Magazine)
An advanced high speed train was completed in 2038, connecting New York and LA in less than 2,5 hrs and there's a high flux of east coast folks going to LA (Magazine)
Suburban prices there have rose 64% and California folks are worried they gonna get pushed out of the region (Magazine)
Detroit is currently in a Red Ice epidemic with it being the easiest route the poor go, either by selling or using it (Magazine)
There was a Red Ice Task Force from 2027 to 2031 that made major arrests and drug seizure during the first epidemic (Gallery, Articles)
Bees are extinct by 2038 and people expect a global famine. CyberLife is already making partnerships to create bee-robots while other groups try finding new alternatives (Magazine)
Environmentalists say the Earth’s environment is beyond repair (Magazine)
Global rainforests have been reduced by 79% since 2000 and coastal corals by 58% (Magazine)
During the events of the game an earthquake kills 10k people in China (Magazine)
CyberLife has partnership with the Department of Defense in the development and supply of military androids, something that started in the early 30s after it was approved to limit human casualties in the battlefield (Magazine, Observation)
In 2031 the US gov ordered 2 million androids for use in the infantry, mostly SQ800 units already being deployed in 2032 replacing human soldiers.
Michigan also announced the purchase of 5k auxiliary androids to assist law enforcement department but following the 2029 Android Act they can't use weapons (PlayStation Blog)
U.S. Army soldiers are equipped with advanced equipment to keep up with their android "subordinates" (Gallery)
Stock exchange falls 10% on fear of Arctic conflict by 2038 (Magazine)
68% of men prefer sex with an android to a human woman and with 52% of men saying they’ve tried the experience at least once (Magazine)
CyberLife currently got around 120 million androids across the globe and some people suspect they're using 'em to spy on people (Magazine)
There are at least 200k military android units already in service across the US military by 2038 and the gov is buying more for the Arctic conflict, an effort to double the infantry size (Magazine)
The US Army is 60~80% android, with humans mainly as commanders and strategists but they tend to use complex AIs to help with assistance (Magazine)
Sales of android intimate partners are very high as lotta men and women prefer living with an android than a human partner (Magazine)
Birthrate is at record low, population decline is said to be irreversible, marriage is in decline as traditional families become “thing of the past” and the divorce rate only increases (Magazine, News, Observation)
US is currently in an "antidepressant epidemic" due to the constant contact with technology, with people even lacking emotional development (Magazine)
The AX400 price is $899 by 2038 (Magazine)
5% of the music market is produced by human musicians. An android boyband Here4U is favorite to win Best Act, Best Video at global music awards - which are human record awards (Magazine, News)
Scientists found "alien" life on Titan: microorganisms living hundreds of kilometers below the surface, in an ocean of salt water protected by a thick layer of ice. The machine-i-forgot-the-name was sent in 2019 (Magazine)
Lute turtles, polar bears, mountain gorillas, african elephants and several species of tiger are extinct by 2038, with CyberLife now making some sorta android zoos (Magazine)
Canada is an android-free zone they don't sell or have any laws about it there as they don't permit androids inside 'em borders (Magazine)
CyberLife has recently released a tech demo of a quaterback android, something that got the Anti-Android Fan Group pissed (Magazine)
There's some sorta quantum magnet being studied that got the potential of cleaning carbon from the air (Magazine)
The Anti-Automation League and CrowneCars representants are in a discussion about ethical decision-making capability of autonomous cars (Magazine)
CyberLife has made a new quantum supercomputer, capable of one billion billion operations per second used to calculate the probability of mass extinction events (Magazine)
Hackers targeting systems like solar panels for ransom seems to be common thing (Magazine)
NASA announced the launch of a five android crew to explore Io (first time it's a full-machine crew). The journey will last three years (Magazine)
CyberLife is a trillionaire company by 2038, they were already billionaires a decade before (Magazine)
The first android ever officially released by CyberLife was the ST200 Chloe, costing 65k in 2024. By 2027 they already had 1mi androids sold (PlayStation Blog)
[continues on the next reblog]
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
It used to be that when BMW would refit a factory to build a new car, the only way the automaker could check if the chassis would fit through the production line was to fly a team out and physically push the body through the process, making note of any snags.
Now, process engineers can simply run a simulation, sending a 3D model of the car through a near-identical digital twin of the factory. Any mistakes are spotted before the production line is built, saving time and money.
Such is the power of the industrial metaverse. Forget sending your avatar to virtual meetings with remote colleagues or poker nights with distant friends, as Mark Zuckerberg envisioned in 2021 when he changed Facebook’s name to Meta; the metaverse idea has found its killer app in manufacturing.
While the consumer version of the metaverse has stumbled, the industrial metaverse is expected to be worth $100 billion globally by 2030, according to a World Economic Forum report. In this context, the concept of the metaverse refers to a convergence of technologies including simulations, sensors, augmented reality, and 3D standards. Varvn Aryacetas, Deloitte’s AI strategy and innovation practice leader for the UK, prefers to describe it as spatial computing. “It’s about bridging the physical world with the digital world,” he says. This can include training in virtual reality, digital product design, and virtual simulations of physical spaces such as factories.
In 2022, Nvidia—the games graphics company that now powers AI with its GPUs—unveiled Omniverse, a set of tools for building simulations, running digital twins, and powering automation. It acts as a platform for the industrial metaverse. “This is a general technology—it can be used for all kinds of things,” says Rev Lebaredian, vice president of Omniverse and simulation technology at Nvidia. “I mean, representing the real world inside a computer simulation is just very useful for a lot of things—but it’s absolutely essential for building any system that has autonomy in it.”
Home improvement chain Lowe’s uses the platform to test new layouts in digital twins before building them in its physical stores. Zaha Hadid Architects creates virtual models of its projects for remote collaboration. Amazon simulates warehouses to train virtual robots before letting real ones join the floor. And BMW has built virtual models for all its sites, including its newest factory in Debrecen, Hungary, which was planned and tested virtually before construction.
To simulate its entire manufacturing process, BMW filled its virtual factories with 3D models of its cars, equipment, and even people. It created these elements in an open-source file format originated by Pixar called Universal Scene Description (OpenUSD), with Omniverse providing the technical foundation for the virtual models and BMW creating its own software layers on top, explains Matthias Mayr, virtual factory specialist at BMW.
“If you imagine a factory that would take half an hour to walk from one side to the other side, you can imagine it’s also quite a large model,” Mayr says. Hence turning to a gaming company for the technology—they know how to render scenes you can run through. Early versions of the virtual factory even had gaming-style WASD keyboard navigation, but this was dropped in favor of a click-based interface akin to exploring Google Street View in a browser, so anyone could easily find their way.
BMW also uses Omniverse for collaboration on car design and customization visualizations for customers, but a key benefit is being able to model production lines. New cars mean a new assembly process, but refitting a factory is a daunting process. Previously, key information was held in silos—production crews understood details of the assembly process, external suppliers had specs of new parts or machinery, architects had detailed building plans—and costs would pile up for every delay or mistake. “The later you find a problem, the worse it is,” says Lebaredian.
Now, problems are worked out virtually, with a central location for standardized data to be held. There’s still a critical human element: Mapping a facility requires sending a laser scanner strapped to a person running through a factory to capture point cloud data about how everything is arranged. Design engineers also need to create a 3D model of every stage of a car as it’s assembled. This level of detail allows BMW to virtually test the assembly process, complete with simulations of robotics, machines, and even human workers, as BMW has data tracking how long it takes employees to assemble a part.
The main idea is to avoid errors—does that machine even fit there?—but the system also enables optimization, such as moving a rack of components closer to a particular station to save steps for human assemblers. “You can optimize first and gain a lot of efficiency in the first production, and in the construction phase, you have fewer mistakes,” Mayr says. “It’s less error prone.”
Omniverse being a Nvidia platform, AI is naturally next. BMW is already layering in generative AI to help with navigation of its virtual models—they’re so massive that finding a particular point in the digital factory can still require asking a human expert for directions. But the aim is to use AI to optimize production lines too. “Because you have the whole data available, not just for one plant, it will be able to make good suggestions,” says Mayr—lessons learned in one factory could more easily be applied to others.
And then there’s robotics and other autonomous systems. Here, Omniverse can offer a digital space for testing before deploying in the real world, but it can also generate synthetic training data by running simulations, just as driverless car systems are trained with virtual video footage generated by AI. “Real-world experience isn’t going to come mostly from the real world—it comes from simulation,” says Lebaredian.
Aryacetas predicts that the biggest impact from the industrial metaverse will be embodied or physical AI—in other words, robots. “Robots aren’t fully there yet, but they’re rapidly training up to understand the physical world around them—and that’s being done because of these underlying spatial computing technologies,” he says.
The future of the metaverse isn’t avatars in a virtual world; it’s digital twins teaching industrial robots how to step out into the physical one.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Submitted via Google Form: Follow Up - Keeping Obsolete Technology
Right.. sorry about that. There seems to be a big confusion what I really want in that question about not removing obsolete technology. Basically, none of the restricted to hobbyists. I'm aware of that - but that is not at all what I want in my world. Everything should still be mainstream. There aren't really much safety features that would steer a manufacturer to not produce phonographs the way they used to (and I absolutely do mean models without USB drives). Phonographs need to be readily available on the market exactly just as they did previously and still being mainstream. You should be able to walk into any general A/V store and buy Blu-Ray players and these old-style phonographs. No 'emulators'. You want to buy a Windows 3.1? Go directly to any shop selling Windows products and you can buy one just as easily as you can get the latest model. You go to a game shop, you can find old style Ataris just as well as your latest VR. Vintage cars.. right.. again. No. In fact we shouldn't be calling it 'vintage' because that means cars that have been around for a long time, not newly manufactured models. Manufacturers should be readily continuing creating new cars with the same old technology, only with added safety features that make them road legal. And these should also be mainstream cars on the modern market, side by side in a car store with your modern vehicles. And maybe just next door is your horse/buggy store and a bicycle store. All mainstream transportation options. Cycling is still popular as a main transport option in some places like Netherlands. Picture a place just like that includes horse/buggy. Any time someone looks on a main road, they should be able to see electric vehicles, bicycles, and horse/buggies.
Ebonwing: Producing every iteration of technology ever created at scale forever is going to be staggeringly expensive and will only get more so the longer that happens. Additionally, you mention that you want phonographs to be without USB drives–so none of the technology is upgraded to be compatible with more modern tech? That just seems inconvenient for customers, and when things are inconvenient to customers someone may just step up and create a more convenient model, which people may then be more inclined to buy.
It’s your world; you can do whatever you want with it, but a lot of people will possibly find this immersion-breaking and I have a hard time thinking of ways to make this plausible.
Licorice: Some old tech has made a comeback. You can buy vinyl records and record players nowadays in mainstream entertainment stores. People have decided that vinyl gives them an experience Spotify just can’t match. I’ve noticed Polaroid instamatic cameras making a comeback too, recently. And of course some old tech - physical books, for example - has never gone away.
If you want a world in which old and new tech exist alongside each other and are equally popular, you are going to have to give your people a reason for making these choices. There are reasons some people still drive horses and buggies (religious reasons; as a hobby) but there’s also a reason why the car has overwhelmingly replaced the horse and buggy as the main form of transport in every part of the world where people can afford it. Imagine the daily commute to work in a horse and buggy. How long would that take? And who’s going to look after the horse for nine hours while you’re in the office? Cars don’t need that level of care. And in fact, the daily commute as we know it really only became possible after mass public transport - i.e., the train - was invented.
Capitalism depends on new tech ousting old tech. Since the days of the Tulip Bubble investors have staked their money on a new or improved product replacing an earlier version and bringing them big profits as a result. Without this kind of incentive, people aren’t going to invest in inventions, and so most inventions will never see the light of day.
Of course, if you want your world to be the way you describe, you can do it. I can’t imagine what such a world would look like, but I can’t say it isn’t possible. It would almost certainly look very different from our own, economically, socially, and maybe politically.
Addy: For cars... the reason old cars look so boxy to us is
1) metal shaping was a lot more expensive, so there was a huge cost to making things round
2) aerodynamics modeling wasn't as well-developed or as much of a priority. Gas mileage gets huge improvements from the more rounded forms we have today.
Horse + buggy would not be able to maintain modern road speeds. Also doesn't have like... any safety features. Also, horses poop and need to eat and exercise. If you've got a countryside estate, that's one thing (or if you base a carriage/taxi service out of the countryside), but in a city? The logistics make it impractical. Bikes are easy to store, and they don't get startled and bolt.
Even for buggies, you have centuries of development of wagons, and then many, many types of carriages and buggies. Landau, phaeton (single or double), gig, sulky… all from different regions, companies, and generations. And then many more types of carriage besides. Are those all being sold, like how all models of all car companies are still being sold? Or USB drives, are they still selling 8 MB USB drives? Not 8 GB, 8 MB - those first came out under 25 years ago.
The thing about technology is that it is a tool that serves a purpose. If something else serves that purpose better, faster, and at a lower cost, then simple prioritization and cost-benefit analysis (by consumers!) means that the better, cheaper, more effective choice will be chosen.
That's also why we see inefficient things preserved by hobbyists - they're people who care enough about the history of the thing that they're willing to put up with its inefficiencies.
So in your world, if you're looking for why people would keep obsolete (and I say obsolete because they're sub-optimal at their original intended purpose) things around, I'd say to look at what benefit these objects serve.
Like for Windows computers, as in your example, what would a 3.1 version give that a more recent (say 5-10 years) version can't? For the companies, what money are they making that is worth the cost of upkeep and production? Because keeping old products viable takes money. Getting them to work on modern hardware, patching up security flaws, customer support, manufacture, etc - those all take money. How are the companies making a profit off of these products?
CRT TVs are very, very good at producing images with little lag, to the point that they're still used and prized by Smash players. The thing is, CRT TVs require a very complex assortment of manufacturing steps and tools to make, and it's no longer profitable to produce them. So people stopped making them. Since their production is so capital-intensive, it's... exceedingly unlikely that we'll ever see a new CRT TV being made.
Also, what's the scope of this? Does this pervade society, or is it mostly a wealth/entertainment thing? Are there farmers using plows, or are they using tractors? How common is homespun fabric? Are there still wooden sailing ships alongside modern cargo ships (and if so, how do they make enough of a profit for it to be worth it)? Do riverboats still use coal to power steam engines? Are they maintaining historical metallurgy, or are they using modern alloys? For radios, are people still using vacuum tubes and 1800s wiring, or are they putting modern materials inside of an 1800s-looking shell? (There would be SIGNIFICANT audio quality differences)
Because there's a difference between a 1970s car and a 1970s-looking car with a modern engine and modern piping. A farmer who uses an animal-drawn plow will live a harder life than a farmer who uses a tractor.
There's also a difference between novelty experiences (like horse-drawn carriages, which I've seen in some towns during the holiday season) and everyday experiences. There's also a difference between shared community historical pieces (like having a local library with old computer models available to use) and having those pieces commonly used by the everyday person. At the end of the day, a person only has so much space in their home, and they only have so much money to spend.
So when looking at this, I have a couple questions I'd recommend throwing at your world.
What does this tradition achieve/do for the community? What is its purpose? People don't do things for no reason; there's always some kind of motive.
What's the scope? Playing old computer games is one thing, designing infrastructure to support vastly different modes of transport is another. Semi trucks do not play well with horses or pedestrians. (Are there separate roads, such as cars only for long distances?)
Also, things like cars. Are companies required to support every edition of every car they've ever produced? Because many old cars fundamentally are not safe, just due to how they're built. Safety tweaks were added over time, so it can be difficult to separate where one era ends and the next era begins. There's no distinct line
Also also are they still selling the Ford Pinto? Because that car would legitimately catch on fire if it got rear-ended
Why are people supporting this? How does it benefit them? Personal enrichment is a valid answer here, but what motivates people to spend money on older versions of things?
If someone wants to play a modern video game, an old 128 MB computer won't cut it.
Why are companies maintaining this? Keeping up all of that capital tied up is going to be incredibly expensive. What's their trade-off?
If you want to make this world work, go for it! It seems like an interesting idea. Just remember that the big thing about having something be mainstream is that the people involved have to think that it's worth it. Applying that at a small scale, like a library archive system thing, is very different than applying that to the average person.
How can you have a world like this? You get people invested and you make the money worth it. It's how you do that that's the issue. Companies, in the modern day (and the back-then) produce objects that people will buy. They continue to produce those objects so long as ○ people still want to buy them ○ the company makes money off of people buying them (income>expenses) ○ the company can't make more money doing something else (opportunity cost). If you've got two job offers, one that pays $10 and one that pays $50, and they're in a similar location and a similar amount of work, what would keep you from taking the $50 job? If you took the $10 job, you'd be missing out on an extra $40 – that's opportunity cost. The money you could be making if you did something different.
So how are you convincing your mainstream culture, individual by individual, to take the $10 option?
Wootzel: It crossed my mind that one potential explanation for this kind of technological society is if most world powers have 1) Patent laws that severely limit the number of patents that people as a whole can obtain (either with a numerical limit, or really broad application of what is considered too similar to another patent) and 2) Strict laws against any kind of manufacturing without patents.
As the others have explained at length, I still don’t know if this would be sufficient explanation to make it really believable that some truly obsolete technology would still be made alongside newer stuff. It’s probably impossible to make an old car as safe as a new one (unless it only looked old on the outside and was made of different materials, and even then), and old computers generally have security vulnerabilities that could make them hugely risky for any purpose other than hobbyist use.
But! If a mix of tech levels is what floats your boat, nobody will tell you that you can’t just do it anyway. There probably isn’t any way to make a world like this pass as real-world plausible, but there’s nothing wrong with embracing the wackiness and doing it anyway. That’s what fiction is for. When you have elements in your world that probably wouldn’t ever occur in real life, it comes down to how you present them. Don’t try too hard to justify what you’re doing, and if your audience sees you cheerfully rolling with it, they’ll likely cheerfully roll with you.
10 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Sony PLM-A35 Glasstron on PC Format (2000-11)
Translation in English:
Take a properly folded 507 monitor
and put it in your pocket...
WE ARE LOOKING FOR A TRUE GIFT Among SONY's video and multimedia accessories, a device that is as much a technical curiosity as a convenience. The Glasstron glasses are more than just something to wear for a night's reading, but anyone who thinks they're just another gaming controller or VR device is mistaken. The similarity ends there, as this device also has two small screens, but each with a resolution of 180 000 pixels. The question may arise, if it is not a toy, then what is the main function of the new glasses. According to the manufacturer, Glasstron provides a picture as if you were watching a 52" screen from 2 meters away - this is roughly twice the size of large 72 cm TVs. In this case, the story is not about games, but about movies, DVDs and videos. Accordingly, in addition to the high-resolution screen, the glasses also feature a high-quality, built-in dynamic stereo sound system that can be used with two headphones. The Glasstron has traditional composite and S-Video inputs and can display any image that can provide a signal for them. for home video or DVD set, digital camera and camcorder, PlayStation, as well as a computer with a suitable video output. This can be done by an ordinary TV, and for the same price you can get a pretty nice piece, even if it is not from the top category. The question is whether in what cases can glasses costing approximately HUF 200,000 be a good choice compared to a large-screen TV - for example, anywhere and anytime, where and when we don't have a suitable TV set or monitor. If you need an everyday example, the best is a long plane or train journey: 14 hours in a trying session can be quite boring. The traveling manager of our time, on the other hand, just pulls out the portable DVD from the depths of the crocodile skin reticle, connects the Glasstron, which also works from the power supply, and the ideal home theater set is ready. A non-ordinary example would be a photojournalist recording a jungle fight, who can view the material recorded during a long day in good quality in the evening for further selection, without having to carry around a large monitor in his pocket.
After a lot of theory, practice. The Glasstron was supplied with a bunch of different cables, so it was not difficult to connect it to any of the already listed compatible devices, and the live test could immediately follow. Where possible, we used the S-Video input of the glasses for better image quality. The effect is quite convincing, since the barely 1.5 cm screens - since they are located very close to the eyes - fill almost the entire field of vision.
The quality of the movies I watched was also satisfactory, although it was undeniably visible on the screen that it does not provide as sharp an image as a monitor, since the resolution is only 800x225 pixels. This is not such a big problem for moving images, but it can cause problems when separating fine lines, such as text. This resolution was still more than enough to read the subtitles of the Mátrixr DVD, for example, but when we connected the glasses to a computer, there were already problems with sharpness. We tested the usability of Glasstron at several resolutions - the games, for example, worked quite well, but when the text was important, there were already problems: we could comfortably run programs only from the icons on the desktop, since the Start menu was quite noisy. We also ran Word as a basis for comparison, and the 16-point letters were clearly legible on the glasses' LCD at a resolution of 640x480.
The sound of the two earphones was crystal clear during the movies, and the music DVD also sounded in impeccable quality, the built-in AVLS (Automatic Volume Limiter System - Automatic volume control system), which cuts off unpleasant volume spikes that lead to distortions.
The system can provide a really effective film edge, ex. in a comfortable armchair, first, in a staked room. While we're at it, let's talk about comfort. Glasstron is surprisingly light, the weight of 95 grams is dwarfed by old VR helmets, so there would be no obstacle to longer use of the screen. However, there was a unanimous opinion that the Glasstron is quite tiring for the eyes: after half an hour it was nice to have a rest, some people thought it was comfortable for even less time the glasses.
The manufacturer also warns about the strain on the eyes, which is why it does not recommend using the device under the age of 15. The last point of comfort is also important, mobility. Glasstron can be operated both from the mains (it supports several voltages, so it can be used in any country) and from a rechargeable battery. The whole device is light even with the power supply, so it is really comfortable to carry.
Glasstron will certainly be a rather expensive toy for the few, as it can only compete with a large-diameter monitor or TV screen under special circumstances. However, one inevitably stops for a moment to marvel at the technology used: the glasses are feather-light, yet provide excellent sound and convincing image quality, all in a space the size of a vest pocket.
Although it does not protect against the sun, it is just right for DVD
One inevitably stops for a moment to marvel at the technique used.
Pros and cons:
√ Amazing size √ USB connection √ Picture and sound quality X dazzling X For how much?
Opinion: 84%
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
Big Data and AI: The Perfect Partnership for Future Innovations
Innovation allows organizations to excel at differentiation, boosting competitive advantages. Amid the growth of industry-disrupting technologies, big data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) professionals want to support brands seeking bold design, delivery, and functionality ideas. This post discusses the importance of big data and AI, explaining why they matter to future innovations and business development.
Understanding Big Data and AI
Big data is a vast data volume, and you will find mixed data structures because of continuous data collection involving multimedia data objects. A data object or asset can be a document, an audio track, a video clip, a photo, or identical objects with special file formats. Since big data services focus on sorting and exploring data objects’ attributes at an unprecedented scale, integrating AI tools is essential.
Artificial intelligence helps computers simulate human-like thinking and idea synthesis capabilities. Most AI ecosystems leverage advanced statistical methods and machine learning models. Their developers train the AI tools to develop and document high-quality insights by processing unstructured and semi-structured data objects.
As a result, the scope of big data broadens if you add AI integrations that can determine data context. Businesses can generate new ideas instead of recombining recorded data or automatically filter data via AI-assisted quality assurances.
Why Are Big Data and AI Perfect for Future Innovations?
1| They Accelerate Scientific Studies
Material sciences, green technology projects, and rare disorder research projects have provided humans with exceptional lifestyle improvements. However, as markets mature, commoditization becomes inevitable.
At the same time, new, untested ideas can fail, attracting regulators’ dismay, disrespecting consumers’ beliefs, or hurting the environment. Additionally, bold ideas must not alienate consumers due to inherent complexity. Therefore, private sector stakeholders must employ scientific methods to identify feasible, sustainable, and consumer-friendly product ideas for brand differentiation.
AI-powered platforms and business analytics solutions help global corporations immediately acquire, filter, and document data assets for independent research projects. For instance, a pharmaceutical firm can use them during clinical drug formulations and trials, while a car manufacturer might discover efficient production tactics using AI and big data.
2| Brands Can Objectively Evaluate Forward-Thinking Business Ideas
Some business ideas that a few people thought were laughable or unrealistic a few decades ago have forced many brands and professionals to abandon conventional strategies. Consider how streaming platforms’ founders affected theatrical film releases. They have reduced the importance of box office revenues while increasing independent artists’ discoverability.
Likewise, exploring real estate investment opportunities on a tiny mobile or ordering clothes online were bizarre practices, according to many non-believers. They also predicted socializing through virtual reality (VR) avatars inside a computer-generated three-dimensional space would attract only the tech-savvy young adults.
Today, customers and investors who underestimated those innovations prefer religiously studying how disrupting startups perform. Brands care less about losing money than missing an opportunity to be a first mover for a niche consumer base. Similarly, rejecting an idea without testing it at least a few times has become a taboo.
Nobody can be 100% sure which innovation will gain global momentum, but AI and big data might provide relevant hints. These technologies are best for conducting unlimited scenario analyses and testing ideas likely to satisfy tomorrow’s customer expectations.
3| AI-Assisted Insight Explorations Gamifies Idea Synthesis
Combining a few ideas is easy but finding meaningful and profitable ideas by sorting the best ones is daunting. Innovative individuals must embrace AI recommendations to reduce time spent on brainstorming, product repurposing, and multidisciplinary collaborations. Furthermore, they can challenge themselves to find ideas better than an AI tool.
Gamification of brainstorming will facilitate a healthy pursuit of novel product features, marketing strategies, and customer journey personalization. Additionally, incentivizing employees to leverage AI and big data to experiment with designing methods provides unique insights for future innovations.
4| You Can Optimize Supply Chain Components with Big Data and AI Programs
AI can capture extensive data on supply chains and offer suggestions on alternative supplier relations. Therefore, businesses will revise supply and delivery planning to overcome the flaws in current practices.
For instance, Gartner awarded Beijing’s JD.com the Technology Innovation Award in 2024 because they combined statistical forecasting. The awardee has developed an explainable artificial intelligence to enhance its supply chain. Other finalists in this award category were Google, Cisco, MTN Group, and Allina Health.
5| Academia Can Embrace Adaptive Learning and Psychological Well-Being
Communication barriers and trying to force all learners to follow the standard course material based on a fixed schedule have undermined educational institutions’ goals worldwide. Understandably, expecting teachers to customize courses and multimedia assets for each student is impractical and humanly infeasible.
As a result, investors, policymakers, parents, and student bodies seek outcome-oriented educational innovations powered by AI and big data for a learner-friendly, inclusive future. For instance, some edtech providers use AI computer-aided learning and teaching ecosystems leveraging videoconferencing, curriculum personalization, and psycho-cognitive support.
Adaptive learning applications build student profiles and segments like marketers’ consumer categorizations. Their AI integrations can determine the ideal pace for teaching, whether a student exhibits learning disabilities, and whether a college or school has adequate resources.
Challenges in Promoting Innovations Based on Big Data and AI Use Cases
Encouraging stakeholders to acknowledge the need for big data and AI might be challenging. After all, uninformed stakeholders are likely to distrust tech-enabled lifestyle changes. Therefore, increasing AI awareness and educating everyone on data ethics are essential.
In some regions, the IT or network infrastructure necessary for big data is unavailable or prone to stability flaws. This issue requires more investments and talented data specialists to leverage AI tools or conduct predictive analyses.
Today’s legal frameworks lack provisions for regulating AI, big data, and scenario analytics. So, brands are unsure whether expanding data scope will get public administrators’ approvals. Lawmakers must find a balanced approach to enable AI-powered big data innovations without neglecting consumer rights or “privacy by design” principles.
Conclusion
The future of enterprise, institutional, and policy innovations lies in responsible technology implementations. Despite the obstacles, AI enthusiasts are optimistic that more stakeholders will admire the potential of new, disruptive technologies.
Remember, gamifying how your team finds new ideas or predicting the actual potential of a business model necessitates AI’s predictive insights. At the same time, big data will offer broader perspectives on global supply chains and how to optimize a company’s policies.
Lastly, academic improvements and scientific research are integral to developing sustainable products, accomplishing educational objectives, and responding to global crises. As a result, the informed stakeholders agree that AI and big data are perfect for shaping future innovations.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What's new in tech 2024?

In 2024, the tech landscape is evolving rapidly, ushering in groundbreaking innovations and transformative advancements across various industries. From artificial intelligence and machine learning to augmented reality and quantum computing, the pace of technological innovation has never been faster. Let's explore some of the key trends and developments shaping the tech industry in 2024.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Continues to Dominate:
AI is at the forefront of technological advancements, driving innovation in numerous sectors such as healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing. In 2024, AI is becoming more sophisticated, with advanced algorithms and deep learning models powering intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and personalized experiences.
Quantum Computing Breakthroughs:
Quantum computing is poised to revolutionize computing power and capabilities, enabling complex calculations and solving problems that are currently infeasible for classical computers. In 2024, we are witnessing significant progress in quantum computing research, with the development of more stable qubits, scalable quantum systems, and practical applications in optimization, cryptography, and drug discovery.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Experiences:
AR and VR technologies are transforming how we interact with digital content and the physical world. In 2024, we are seeing immersive AR and VR experiences becoming increasingly mainstream, with applications in gaming, entertainment, education, training, and remote collaboration. Enhanced AR glasses, immersive VR headsets, and spatial computing platforms are driving innovation in this space.
5G Connectivity and Edge Computing:
The rollout of 5G networks is enabling ultra-fast, low-latency connectivity, paving the way for a new era of interconnected devices and services. In 2024, 5G adoption is accelerating, powering IoT ecosystems, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and real-time streaming experiences. Edge computing, coupled with 5G, is decentralizing computing resources and enabling faster data processing at the network edge.
Sustainable and Green Technologies:
As environmental concerns continue to mount, the tech industry is focusing on developing sustainable and eco-friendly solutions. In 2024, we are witnessing the rise of green technologies, including renewable energy sources, energy-efficient devices, carbon capture technologies, and eco-friendly manufacturing processes. Tech companies are increasingly prioritizing sustainability in their product development and operations.
Cybersecurity and Privacy Measures:
With the growing threat of cyberattacks and data breaches, cybersecurity remains a top priority for organizations and individuals alike. In 2024, there is a heightened focus on enhancing cybersecurity measures, including advanced encryption techniques, threat intelligence, zero-trust architectures, and privacy-enhancing technologies. The adoption of robust cybersecurity practices is essential to safeguarding sensitive data and protecting digital assets.
In conclusion, 2024 promises to be an exciting year for technology, with groundbreaking innovations shaping the future of industries and society as a whole. From AI and quantum computing to AR/VR experiences and sustainable technologies, the tech landscape is evolving rapidly, offering new opportunities and challenges for businesses, consumers, and policymakers alike. Stay tuned as we continue to explore and embrace the latest tech trends in the years to come. Get more interesting updates regard software development solutions.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Integration of AI and Blockchain: All You Need to Know
The convergence of AI and the metaverse
Interestingly, this convergence has its roots in the same hardware that powers it. GPUs, known for rendering rich virtual spaces, are the same workhorses that train AI models. Their parallel computing capabilities not only make them invaluable in AI development, but also in bringing the complex environments of the Metaverse to life. This synergy is evident in the rising value of GPU manufacturers like Nvidia, highlighting the intertwined growth of artificial intelligence and virtual reality technologies.
Looking ahead to 2024, the convergence of AI and the metaverse is shaping up to be a fundamental advance in our technological journey. We are about to witness how AI transforms the act of creation within the metaverse. This year, we predict that AI will evolve beyond its current capabilities, allowing creators to create expansive virtual worlds simply through the power of description. The metaverse will no longer require complex skills in 3D modeling and animation; instead, it will respond to the creative impulses of Human thought, which AI brings to life.
The trust architecture of tomorrow
The year 2023 was a crucible for blockchain, with the industry going through legal challenges and corporate upheavals. These tests, reminiscent of the growing pains of any technological breakthrough, heralded the maturation of blockchain. Amid this legal maelstrom, the essence of blockchain – the digitization of asset ownership – remained resolute and unscathed, continuing its march towards the technological revolution.
We envision blockchain merging into the fabric of the Internet, similar to the invisible but vital protocols that power our emails and instant messages. This convergence will make blockchain assets become a native dialect of the digital realm, essential and, most importantly, invisible to the user. Interacting with blockchain will be as simple as sending an email, with its hidden complexities and omnipresent efficiency and security. In this future, blockchain development services is not just a technology; it is a silent orchestrator of digital trust and ownership.
Synergies between virtual reality and the metaverse
In 2023, virtual reality (VR) has risen to become the next frontier in human-computer interaction, providing unprecedented bandwidth for digital communication and embodying the essence of presence. This leap forward has been driven by advances from major hardware manufacturers, with the launch of Meta Quest 3 and the long-awaited VR headsets from Apple and Nintendo. Every step in this area is not just about technological progress; It is about redefining our own perception and interaction with digital spheres.
Looking ahead to 2024, we are on the brink of a watershed moment in the spatial computing industry. The potential use case of experiencing events like the NBA Finals from the best seats in the stadium, all from the comfort of home, is set to capture the imagination of the masses. This experience, bridging the physical and digital worlds, will likely be a catalyst for widespread adoption among the early majority. The road ahead for virtual reality is long and full of potential, but the convergence of technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain and advanced hardware is setting the stage for a seismic shift.
The cultural and economic impact
In the narrative of our digital evolution, Generation Z emerges as the vanguard of a new cultural epoch. Born in a world where virtuality is as real as the air they breathe, these digital natives are the first to fully immerse themselves in the fruits of technological convergence. His initial, playful and experimental forays into the creation of memes and digital artifacts are nothing more than the prologue to a deeper and more significant change. With AI-powered tools and the metaverse at your fingertips, they don't just use technology; They are reshaping it, subjecting the digital universe to their imagination and whims.
We see these young minds not only embrace but master the art of creation within these new realms. They are the pioneers of a world where user-generated content is not just a hobby but a new economic frontier. In their hands, creativity and innovation become more than expression; They are the keys to unlocking new forms of value and influence. The power once held by a select few over coding and legal complexities is now democratized in the hands of these young creators, heralding a future where the digital realm is limited only by the imagination.
In 2024
As the year 2024 progresses, we find ourselves on the cusp of a transformative era in technology. The integration of AI, blockchain and virtual reality is creating a new digital landscape. This convergence is more than a mere fusion of technologies; It is a revolution in the way we interact with the digital realm. The advancement of AI is redefining creative possibilities in the metaverse, allowing environments to be shaped solely by thought. Blockchain evolves into a fundamental layer of digital trust, making asset ownership part of the fabric of the Internet. Virtual reality, on the brink of a breakthrough, will radically change our sensory experiences in digital spaces.
Fundamentally, this technological synergy is the playing field of Generation Z, who are not only users but active creators and modelers of these areas. Their commitment to these technologies is not just about leisure; It is the forging of a new economic and cultural landscape where imagination is the main currency.
#blockchain#blockchain development#blockchain development company#blockchain development service#blockchain technology
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Asset Reliability Software Market Size, Key Players & Market Growth Drivers
Global Asset Reliability Software Market Overview The Global Asset Reliability Software Market is experiencing significant expansion, with an estimated market size of USD 4.2 billion in 2024 and projected to reach approximately USD 8.1 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.4% during the forecast period. This growth is driven by the increasing need for predictive maintenance, asset performance management, and digital transformation across industries such as manufacturing, energy, utilities, and transportation. Enterprises are increasingly adopting asset reliability software to enhance operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and maximize the lifecycle value of physical assets. The integration of IoT sensors, AI-based analytics, and cloud computing into asset management platforms is streamlining real-time monitoring and predictive diagnostics. The demand for enterprise asset management (EAM) solutions is further fueled by rising maintenance costs and the need to comply with stringent regulatory frameworks regarding safety and operational reliability. Global Asset Reliability Software Market Dynamics Drivers: Key market drivers include the growing adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, increased demand for centralized asset performance platforms, and the shift toward condition-based maintenance. Organizations are investing in real-time asset health monitoring and failure prediction systems to reduce unplanned downtimes. Restraints: High initial implementation costs and lack of skilled professionals to manage complex software platforms pose significant challenges. Additionally, small and medium enterprises (SMEs) often struggle with budget constraints and legacy system integration. Opportunities: Emerging economies offer untapped potential for market players due to increased infrastructure investments and growing awareness of asset reliability benefits. Government initiatives promoting digital transformation and smart industrial ecosystems are further expected to create favorable conditions for market growth. Technology and Sustainability: The convergence of AI, machine learning, and edge computing is revolutionizing the asset reliability software space. Sustainability goals are driving the adoption of green asset management practices, minimizing environmental impact, and maximizing resource efficiency. Regulations encouraging predictive maintenance practices and safety compliance are also accelerating software deployments across sectors. Download Full PDF Sample Copy of Global Asset Reliability Software Market Report @ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/download-sample?rid=375966&utm_source=PR-News&utm_medium=387 Global Asset Reliability Software Market Trends and Innovations Key innovations shaping the asset reliability software market include the integration of digital twins, cloud-native solutions, and mobile-enabled platforms. Digital twins allow real-time simulation and performance forecasting of assets, enabling proactive maintenance and operational decision-making. Cloud-based deployment models are enabling greater scalability, remote accessibility, and lower upfront infrastructure costs. AI-driven failure prediction models, natural language processing (NLP) interfaces, and AR/VR-based asset training tools are also gaining traction. Strategic partnerships between software vendors and IoT providers are creating holistic solutions that combine asset condition monitoring, lifecycle analytics, and remote diagnostics. Vendors are focusing on modular solutions, offering flexibility to scale based on organizational needs. Global Asset Reliability Software Market Challenges and Solutions Challenges: Major obstacles include integration with legacy systems, data silos, and lack of interoperability across platforms. Additionally, cybersecurity threats to cloud-hosted asset data present ongoing risks. Rising pricing pressures and customization demands further challenge solution providers. Solutions: Cloud-native platforms with robust API frameworks are addressing integration challenges.
Standardized data formats and open-source protocols are improving interoperability. Cybersecurity enhancements, such as end-to-end encryption and zero-trust architecture, are safeguarding asset data. Vendors are offering tiered pricing models to cater to varied organizational scales and budgets, making asset reliability solutions more accessible. Global Asset Reliability Software Market Future Outlook The market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, fueled by advancements in AI-powered diagnostics, smart sensors, and digital infrastructure development. As more industries embrace predictive maintenance and intelligent asset monitoring, asset reliability software will become central to achieving operational excellence and ESG goals. Companies prioritizing lifecycle value, energy efficiency, and compliance will increasingly rely on advanced reliability tools to gain a competitive edge. Looking ahead, the integration of sustainability analytics, carbon tracking, and prescriptive maintenance will further enhance software capabilities, making the asset reliability software market a critical component of the global industrial digitalization landscape. Key Players in the Global Asset Reliability Software Market Global Asset Reliability Software Market are renowned for their innovative approach, blending advanced technology with traditional expertise. Major players focus on high-quality production standards, often emphasizing sustainability and energy efficiency. These companies dominate both domestic and international markets through continuous product development, strategic partnerships, and cutting-edge research. Leading manufacturers prioritize consumer demands and evolving trends, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Their competitive edge is often maintained through robust R&D investments and a strong focus on exporting premium products globally. Schneider Electric SA eMaint K26Vesta Partners LLC IBM Corporation Oracle Corporation Ramco Systems Infor IFS AB ABB Ltd. SAP SE Get Discount On The Purchase Of This Report @ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ask-for-discount?rid=375966&utm_source=PR-News&utm_medium=387 Global Asset Reliability Software Market Segments Analysis and Regional Economic Significance The Global Asset Reliability Software Market is segmented based on key parameters such as product type, application, end-user, and geography. Product segmentation highlights diverse offerings catering to specific industry needs, while application-based segmentation emphasizes varied usage across sectors. End-user segmentation identifies target industries driving demand, including healthcare, manufacturing, and consumer goods. These segments collectively offer valuable insights into market dynamics, enabling businesses to tailor strategies, enhance market positioning, and capitalize on emerging opportunities. The Global Asset Reliability Software Market showcases significant regional diversity, with key markets spread across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. Each region contributes uniquely, driven by factors such as technological advancements, resource availability, regulatory frameworks, and consumer demand. By Industry Vertical By End-User By Application By Geography • North America• Europe• Asia Pacific• Latin America• Middle East and Africa For More Information or Query, Visit @ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/product/asset-reliability-software-market/ About Us: Verified Market Research Verified Market Research is a leading Global Research and Consulting firm servicing over 5000+ global clients. We provide advanced analytical research solutions while offering information-enriched research studies. We also offer insights into strategic and growth analyses and data necessary to achieve corporate goals and critical revenue decisions. Our 250 Analysts and SMEs offer a high level of expertise in data collection and governance using industrial techniques to collect and analyze data on more than 25,000 high-impact and niche markets.
Our analysts are trained to combine modern data collection techniques, superior research methodology, expertise, and years of collective experience to produce informative and accurate research. Contact us: Mr. Edwyne Fernandes US: +1 (650)-781-4080 US Toll-Free: +1 (800)-782-1768 Website: https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ Top Trending Reports https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ko/product/fertilizer-additives-market/ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ko/product/liquid-fertilizers-market/ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ko/product/non-protein-nitrogen-market/ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ko/product/beta-glucan-market/ https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ko/product/food-amino-acids-market/
0 notes
Text
AI and VR for Better Employee Learning

Introduction
Training employees has always been crucial, but today’s workplaces need smarter, more engaging ways to upskill teams. That’s where AI and VR step in. By blending intelligent automation with immersive learning environments, companies can now deliver training that’s not only effective but also enjoyable.
In this blog, we’ll explore how AI and VR are changing employee learning, making it more personalized, hands-on, and results-driven.
Why Traditional Training Falls Short
Most traditional training methods—like manuals, slideshows, or even in-person sessions—can feel outdated. They often lack interaction, real-time feedback, and adaptability. Employees may end up forgetting what they learned or struggle to apply it in real situations.
Enter AI and VR—technologies that bring training to life in real time and context.
How AI and VR Improve Learning Outcomes
1. Immersive Real-World Simulations
Using VR, employees can step into realistic job scenarios:
Practice safety procedures in virtual factories
Train customer service in simulated stores
Rehearse complex tasks without any real-world risk
2. Personalized Learning Paths
AI can track performance and customize content:
Identify strengths and weaknesses
Adapt lessons based on progress
Suggest refresher modules when needed
3. Engaging, Hands-On Learning with AI and VR
AI and Virtual Reality together make learning interactive and fun:
Gamified modules with real-time feedback
Performance scoring and dynamic challenges
Hands-on practice instead of passive reading
4. Scalable Training Across Locations
Whether you have 10 employees or 10,000, AI and VR offer scalable solutions:
Train remote teams simultaneously
Maintain consistent training quality across branches
Reduce the cost and time of physical workshops
5. Data-Driven Insights
With AI, companies can track learning metrics:
Time spent on tasks
Mistakes and improvements
Completion rates and success scores
This data helps refine the training process and improve future outcomes.
Real-World Examples of AI and VR in Employee Training
Healthcare
Surgeons practice procedures in VR while AI offers performance feedback, helping them improve precision and safety before working on real patients.
Manufacturing
Factory workers use VR to learn machine operations, while AI identifies areas needing more practice, reducing accidents and downtime.
Retail
Employees in retail environments engage in role-play scenarios with virtual customers. AI assesses soft skills like communication and problem-solving.
Aviation
Pilots and ground crew train in high-risk simulations using VR. AI monitors stress levels and decision-making to improve response under pressure.
Challenges and Considerations in AI and VR
While AI and VR offer powerful benefits, companies must consider:
Upfront costs for hardware and content creation
Ensuring employees are comfortable with new tech
Data security and privacy, especially with AI tracking
The Future of Workplace Learning Using AI and VR
As more organizations adopt AI and VR, we can expect:
Fully immersive onboarding programs
On-the-job guidance through smart wearables
Continuous micro-learning through AI-driven platforms
These technologies will make learning a seamless part of everyday work, not a one-time event.
Conclusion
AI and VR are no longer futuristic buzzwords—they’re here, and they’re transforming how employees learn. From hands-on practice to intelligent coaching, these tools are helping companies build stronger, smarter teams. If you want to keep your workforce competitive, now’s the time to invest in better training.
Want to explore how AI and VR can supercharge your employee learning programs? Contact Modnexus for tailored solutions that work.
0 notes
Text
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping industries and enhancing training methodologies. Among the pioneering virtual reality companies in India, Simulanis stands out, particularly in major cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Noida. This blog will delve into what makes Simulanis a leader in the VR sector and how it is revolutionizing the way we approach virtual reality training in India.
#VR Training Solutions India#Virtual Reality Training Programs#VR-based Employee Training India#Immersive VR Training India#Virtual Reality for Industrial Training#VR Safety Training India#Corporate VR Training India#VR Skill Development India#VR Training for Manufacturing#Virtual Reality for Workforce Training#VR Simulations for Training India#VR Training for Healthcare India#Virtual Reality in Education India#VR for Skill Enhancement India#Interactive VR Training India#VR for Corporate Training India#Virtual Reality Safety Simulations India#VR Training Platforms India#Virtual Reality for Emergency Response#Next-gen VR Training India
0 notes
Text
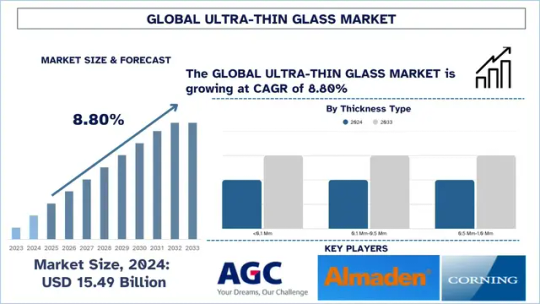
Ultra-Thin Glass Market Report, Size, Share & Analysis 2025-2033
According to the UnivDatos, as per their “Ultra-Thin Glass Market” report, the global market was valued at USD 15.49 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of about 8.80% during the forecast period from 2025 - 2033 to reach USD billion by 2033.
The global Ultra-Thin Glass Market is witnessing huge growth, being boosted by industries in the electronics, healthcare, and automotive sectors that now require materials that provide precision, lightness, and higher functionality. Being uniquely thin at usually less than 1 mm in thickness, ultra-thin glass finds applications necessitating strength while being flexible and transparent. Their importance is lent to the nascent high-design applications from foldable smartphones to transparent displays to medical imaging systems. The consumer electronics industry seems to be the largest end-user area with promising growth in diagnostics, wearables, and micro-optics, forcing the market toward higher integration, smarter sustainability, and technical excellence.
Growing Demand for Foldable & Flexible Displays Drives Market Expansion
The demand for foldable and flexible display technologies, the ultra-thin glass market continues to grow. As top tech companies push the boundaries of innovation, foldable smartphones, bendable tablets, and rollable TVs are slowly fading out of the prototype phase. For example, Samsung's Flex In & Out™ Flip and Rollable Flex™, announced at CES 2024, are basically allowing 360-degree folding and scaling of form factors using ultra-thin glass, really setting the direction for the upcoming years for the industry. Ultra-thin glass opens possibilities for such cutting-edge innovations. It provides durability, touch sensitivity, and optical clarity whilst remaining sufficiently flexible under stress. Usually ranging from 30 to 100 µm in thickness, ultra-thin glass is considered the premium material for next-generation displays due to its better scratch resistance and can withstand environmental hazards when compared with polymer films. The growing demand from end-users for slimmer, lighter, and more immersive devices, OEMs and display manufacturers continue to heavily invest in roll-to-roll processing, surface coatings, and laser-cutting technologies, trying to enhance yield and break down cost barriers.
Latest Trends in the Ultra-Thin Glass Market
Increased Investment in AR/VR and Micro displays
One more accelerating trend includes the use of ultra-thin glass in AR, VR, and XR systems. Spatial computing and wearable displays have entered critical positions in gaming, healthcare, training, and defense. Lightweight, high-resolution micro displays are therefore in demand. Ultra-thin glass, especially below 0.2 mm in thickness, is crucial for providing 3500+ resolution on OLED-on-silicon panels, as has recently been demonstrated by companies such as Samsung Display. These glasses give adequate thermal and optical results and maintain ultralight weight, paramount for comfort during prolonged wear and for an immersive experience.
Access sample report (including graphs, charts, and figures): https://univdatos.com/reports/ultra-thin-glass-market?popup=report-enquiry
Lead-Free and Eco-Friendly Glass Compositions
Environmental sustainability is becoming an increasing consideration in the area of ultra-thin glass. Resin manufacturers are veering away from old formulations with lead or otherwise containing harmful substances in favor of environmentally friendly, lead-free alternatives. Now the products contain oxides of barium, boron, and bismuth and certify RoHS and green building certifications without compromising on the actual performance. For example, manufacturers in Europe and Japan have taken the green road, developing an ultra-thin glass that is fully recyclable and equipped with anti-reflective and anti-fingerprint technologies for use in both consumer electronics and architectural applications. This trend has increasingly gone into development amidst ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) policies to promote clean, safer supply chains.
Emerging Opportunities in Medical & Diagnostic Imaging
The medical and diagnostic sectors are expansively developing a market for ultra-thin glass applications in the areas of imaging systems, smart sensors, and interfaces for transparent shielding. Diagnostic imaging is an ever-expanding field due to the rising burden of chronic illnesses, an aged population, and precision medicine-related applications requiring lightweight optically advanced materials, integrated displays in devices such as digital X-rays, portable ultrasound, and point-of-care imaging.
Ultra-thin glass is layer-built onto touch-enabled glass interfaces in imaging machines, thus enhancing user-friendliness from a clinician and infection-control standpoint. This maintenance of portability goes hand in hand with mobile X-ray units and portable imaging booths-without sacrificing the thin-glass screen's durability and clarity, especially in emerging markets like India, Brazil, and Southeast Asia. The design emphasis is now shifting towards a modular, patient-friendly diagnostic environment wherein the demand is for glass that is as functional as it is aesthetic. From the views of hospitals and laboratories, this glass finds ultra-thin double-use in observation panels, diagnostic monitors, and control displays at the intersection of safety, usability, and form.
Transparent Innovation: Ushering in a Multi-Sectoral Revolution
The future of the ultra-thin glass market lies in a cross-sector innovation where electronics meet medicine and architecture meet sustainability, with design and regulation as the other end of the spectrum. As demand builds for smarter, lighter, and greener products, ultra-thin glass will keep playing a prominent role.
This 18-20-micron-thick material is sculpting modern engineering with the utmost thinness, strength, and optical clarity in foldable OLED displays, XR wearables, shielded diagnostic rooms, and solar-integrated windows. Strategic partnerships-cum-alliance-building between the glass processor and the electronics OEM sector, and rising investments in cleanroom-compatible production facilities, are expected to uplift the market in the coming years.
As industries world over metamorphose, ultra-thin glass shall emerge as a critical enabler, balancing technology, transparency, and sustainability harmoniously.
Contact Us:
UnivDatos
Contact Number - +1 978 733 0253
Email - [email protected]
Website - https://univdatos.com/
Linkedin- https://www.linkedin.com/company/univ-datos-market-insight/mycompany/
0 notes
Text
How AR/VR Integration is Being Adopted by Web Development Companies
The internet is no longer limited to 2D experiences. With the rise of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technologies, websites are becoming more immersive, interactive, and engaging than ever before. These advanced visual experiences are no longer confined to games or niche apps—they're making their way into mainstream web development.
Forward-thinking Web Development Company teams are now offering AR/VR integration as part of their service stack. Whether it’s for product visualization, virtual showrooms, education, or real estate, AR/VR elements are redefining how users interact with brands online.
Let’s explore how web development companies are implementing these technologies and what it means for the future of the web.
What is AR/VR in the Context of Web Development?
Augmented Reality (AR) enhances real-world environments by overlaying digital content (like 3D models or animations) onto the user’s physical space—typically through their mobile camera or device sensors.
Virtual Reality (VR) immerses users in a completely virtual environment, usually via headsets or 360-degree web experiences.
Web development teams use frameworks and libraries like WebXR, A-Frame, Three.js, and 8thWall to bring these capabilities into standard web browsers—no app downloads required.
Why Businesses Are Embracing AR/VR on the Web
Immersive Product Experiences eCommerce brands are using AR to let customers “try before they buy.” Think virtual try-ons for glasses or placing furniture in your living room using your phone. VR takes it further—allowing virtual walkthroughs of showrooms or product environments. These experiences reduce return rates and increase buyer confidence.
Enhanced Storytelling and Engagement Brands in sectors like travel, entertainment, and education are using VR to offer immersive storytelling. AR adds interactive overlays to real-world maps, guides, or events—making content more memorable and shareable.
Training and Simulation Platforms In industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and aviation, companies are building browser-based simulations for staff training. These immersive tools boost retention, improve safety, and reduce training costs.
How Web Development Companies Are Integrating AR/VR
1. Using WebXR API for Cross-Platform Immersion
The WebXR Device API allows web apps to access AR and VR capabilities directly through the browser. Development teams integrate it to:
Create 360° product viewers
Build interactive virtual tours
Enable headset-based VR experiences
WebXR works on platforms like Oculus, HTC Vive, and even smartphones—making immersive web apps accessible to a wider audience.
2. Leveraging 3D Libraries and Game Engines
Technologies like Three.js, Babylon.js, and Unity WebGL are increasingly used to bring interactive 3D scenes to the browser. Development companies use these tools to:
Design rich, textured environments
Animate product models and avatars
Allow real-time interaction without native apps
These libraries are performance-optimized for web use, ensuring smooth experiences even on mobile devices.
3. Optimizing for Performance and Load Speed
AR/VR assets are often heavy (think 3D models, textures, animations). That’s why experienced developers:
Use lazy loading and asset compression
Integrate CDNs and cache strategies
Optimize rendering pipelines for WebGL
This ensures AR/VR content loads quickly without affecting overall site speed—critical for SEO and user experience.
4. Integrating with CMS and eCommerce Platforms
Modern web development companies are embedding AR viewers and VR tours into CMSs like WordPress, Contentful, or Shopify. This allows non-technical teams to update immersive content without touching code. For example:
Realtors can add new VR property tours through the CMS
Retailers can swap 3D product models in the backend
This modular approach makes immersive content easier to manage and scale.
5. Enabling Mobile-First AR Experiences
Not every user has a VR headset—but almost everyone has a smartphone. Developers are leveraging mobile AR frameworks like 8thWall or ZapWorks to:
Launch camera-based AR experiences
Link immersive content to QR codes or social ads
Deliver AR through progressive web apps (PWAs)
This mobile-first mindset expands the reach of immersive tech beyond niche audiences.
Industries Leading the Charge
Retail & Fashion: Virtual try-ons, interactive fitting rooms
Real Estate: VR property tours, 3D floor plans
Automotive: 360° car viewers and in-showroom AR demos
Healthcare: VR-based patient education and training simulations
Education: Interactive learning modules with VR field trips or lab simulations
As user expectations shift toward experiential content, these use cases are becoming more common across industries.
Conclusion
AR and VR are no longer future tech—they’re part of today’s web. By integrating immersive experiences directly into the browser, developers are transforming static websites into interactive environments that engage users in powerful new ways.
A forward-thinking Web Development Company knows how to harness AR/VR to deliver both wow-factor and functionality. Whether you're looking to boost engagement, reduce bounce rates, or stand out from competitors, immersive tech may be your next big digital move.
0 notes
Text
Virtual Reality in Manufacturing Education: Benefits and Challenges
As manufacturing rapidly evolves with digital transformation, automation, and stricter safety standards, traditional training methods like lectures and manuals are falling short. Virtual reality (VR) is stepping in to revolutionize manufacturing education by offering immersive, hands-on learning in risk-free digital environments. It enables workers to practice complex procedures safely and efficiently. While the benefits are significant—enhanced retention, standardized training, and safety—adopting VR at scale comes with its own set of challenges that organizations must navigate.
The Benefits of VR in Manufacturing Education
Immersive, Risk-Free Learning
One of VR’s greatest strengths is its ability to create high-fidelity, interactive simulations that mirror real-life manufacturing scenarios. Learners can engage in realistic tasks without the fear of injury or equipment damage. This encourages confidence and experimentation, which are essential to skill mastery.
Standardized, Scalable Training
Consistency is critical in industrial training. With VR, every learner—regardless of location or instructor—receives the same content, cues, and assessment metrics. This ensures standardization, especially in global manufacturing operations, where uniform compliance and skills proficiency are non-negotiable.
Faster Knowledge Retention
VR activates multiple senses, leading to improved engagement and memory retention. Learners absorb information faster when they experience it rather than passively read about it. This active learning model has been shown to reduce training time significantly while boosting long-term recall.
Data-Driven Insights
Modern VR platforms offer real-time analytics. Educators and trainers can monitor performance metrics like reaction time, accuracy, and procedural adherence. These insights help identify skill gaps early and tailor learning pathways to individual needs—something nearly impossible in traditional training setups.
Safe Simulation of Rare Scenarios
Certain manufacturing incidents—like chemical spills, fires, or system failures—are difficult and dangerous to simulate in live training. VR can recreate these situations realistically, helping trainees practice responses without compromising safety.
Challenges of Integrating VR into Manufacturing Education
Despite its clear advantages, the integration of VR isn’t without its friction points. Understanding these challenges is essential for successful adoption.
High Initial Investment
While VR training reduces long-term costs, the initial setup—hardware, software development, content customization, and technical support—can be expensive. Many small to mid-sized manufacturers struggle to justify these upfront expenses without a clear ROI roadmap.
Content Relevance and Customization
Generic training modules may not align with specific company processes or equipment. Customizing content for a particular factory setup requires collaboration between subject matter experts and VR developers, which can extend development timelines.
Resistance to Change
Veteran workers accustomed to hands-on, traditional methods may be skeptical of VR-based learning. Overcoming this mindset requires change management strategies, including pilot programs, peer testimonials, and gradual rollout plans.
Technical Barriers
VR systems require a certain level of digital literacy and infrastructure. In regions with limited connectivity and tech skills, implementing VR training at scale can pose difficulties.
The Path Forward: Learning with XR Guru
As the manufacturing sector continues to embrace digital transformation, VR training is emerging as a vital tool in workforce development. The benefits clearly outweigh the challenges—if the right partners are involved.
That’s where XR Guru comes in. With a laser focus on immersive, industry-specific learning, XR Guru offers a comprehensive suite of VR solutions tailored to the unique needs of the manufacturing industry. From safety protocols and machine operation to situational awareness and emergency response, our expertly designed modules bring manufacturing education into the modern age.
In a world where precision, agility, and safety define success on the production floor, VR education—powered by platforms like XR Guru—is not just a supplement. It's a necessity.
For more information, visit: https://www.xrguru.com/virtual-reality-in-manufacturing
0 notes
Text
Revolutionizing Manufacturing: Leveraging Metaverse Technologies for Enhanced Processes

One of the primary applications of the metaverse development in manufacturing is virtual prototyping and simulation. By creating digital replicas of products and production lines, manufacturers can test designs, identify potential flaws, and optimize processes before physical implementation. This not only accelerates the product development cycle but also reduces costs associated with traditional prototyping methods.
In conclusion, the integration of metaverse technologies holds immense potential for revolutionizing manufacturing processes and unlocking a new era of innovation and efficiency. By leveraging virtual prototyping, collaborative design environments, and remote monitoring capabilities, manufacturers can optimize production workflows, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. As the metaverse continues to evolve, its impact on the manufacturing industry is poised to grow, ushering in a new era of connected and intelligent manufacturing. To unlock AR/VR’s potential in manufacturing, partnering with a specialized company is key. DevDen excels here, a metaverse development company. Whether upgrading processes, training, or customer experiences, choose DevDen for an innovative manufacturing journey. Contact us now for a more immersive future.
#vr training solution#vr training#3d product modeling#augmented reality#metaverse#virtual reality#mixed reality#xr development#xr development company#ar development company
0 notes