#ValveGuide
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

🔧 Upgrade Your Experience with the EverPhone Valve Guide! 🔧
Looking for precision, reliability, and high performance? The EverPhone Valve Guide ensures smooth operation, durability, and an optimized experience for all your devices. 📱
⚙️ Perfect fit for a variety of models 💡 Enhanced performance with top-tier materials 🔒 Built to last – ensuring longevity
Don’t settle for less when you can get the best!
🔗 www.highwaygrm.com
#EverPhone#TechUpgrade#ValveGuide#PrecisionEngineering#TechPerformance#PhoneAccessories#TechInnovation#HighwayGRM#HighwayTruckDXB
0 notes
Link
1 note
·
View note
Photo

#cumminsengine #cummins6ct #valvestem #valveguide #c3925863 https://www.instagram.com/p/CJIjcAFlRIE/?igshid=3oym2ld0bkd0
0 notes
Photo

valve guide 4TNE98 #valveguide #engine #yanmar #4TNE98 #4TNE #forklift #dieselforklifts #rentalforklift https://www.instagram.com/p/CAsGFYWDE8m/?igshid=1i6u6svbkf3s
0 notes
Link
TAEVision 3D Mechanical Design Parts EngineParts Aftermarket @msmotorservice MSMotorservice TRW Automotive KS Kolbenschmidt GmbH Valves ValveTrain ValveGuides ValveCotters ValveSealInserts ValveControlElements ▸ TAEVision Engineering on Pinterest ▸ TAEVision Engineering on Google Photos ▸ TRW Automotive - Valves and Valve Accessories
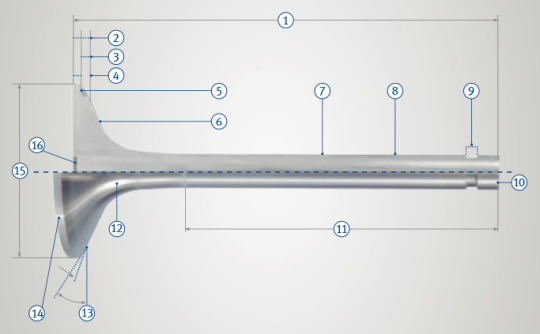
Valves - Dimensions and Technical Terms
1 Total length = L 2 Total valve head thickness 3 Seat height 4 Height of valve seat face 5 Seat armouring (optional) 6 Valve head 7 Skirt diameter = d 8 Valve stem 9 Groove area 10 End face of stem (hardened) 11 Grinding length 12 Throat 13 Valve seat angle = α 14 Head surface 15 Head diameter = D 16 Calotte
Data 187 - Oct 24, 2021
#TAEVision#engineering#3d#mechanicaldesign#parts#engineparts#aftermarket#MSMotorservice#TRW Automotive#KS Kolbenschmidt GmbH#valves#valve train#ValveTrain#ValveGuides#valve guides#ValveCotters#valve cotters#ValveSealInserts#valve seal inserts#ValveControlElements#valve control elements
1 note
·
View note
Photo

گاید دستگاه های راهسازی اصل ژاپن.. 🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵 021-66616500 021-66614900 www.taminghate.com 🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵🇯🇵 قطعات اصل ژاپن را با بهترین قیمت از ما بخواهید. #oemjapan #valveguides #loader #excavators #komatsugenuine #komatsuparts #dumptruck #TGCO #tgcompany #japaneseproducts #komatsu_iran #komatsuagent #komatsu_tehran #oem_komatsu #hd325 #hd465 #hd785 #hd985 #قطعات_ژاپنی #قطعات_اصلی #قطعات_کوماتسو #لوازم_یدکی_اصلی #لوازم_یدکی_راهسازی #تامین_قطعه_کوماتسو #تامین_قطعه_اصلی #تامین_قطعه #نماینده_کوماتسو #کوماتسو #کوماتسو_ایران #کوماتسو_تهران @t.gcompany (at Tehran, Iran) https://www.instagram.com/p/CNhkGN3LCbT/?igshid=uy3xbtuwgm46
#oemjapan#valveguides#loader#excavators#komatsugenuine#komatsuparts#dumptruck#tgco#tgcompany#japaneseproducts#komatsu_iran#komatsuagent#komatsu_tehran#oem_komatsu#hd325#hd465#hd785#hd985#قطعات_ژاپنی#قطعات_اصلی#قطعات_کوماتسو#لوازم_یدکی_اصلی#لوازم_یدکی_راهسازی#تامین_قطعه_کوماتسو#تامین_قطعه_اصلی#تامین_قطعه#نماینده_کوماتسو#کوماتسو#کوماتسو_ایران#کوماتسو_تهران
0 notes
Link

Valve Guides Manufacturer India
0 notes
Text
What You Need To Know When Choosing Valvetrain Components
Of all the engine components that are often changed when modifying an engine, the cam and related components are some of the most critical. Pick the wrong combination of parts and the advantages of all the other engine improvements will be for naught. Ironically, with all the choices available today, deciding on what cam and kit to use is more complicated than ever, so with help from Comp Cams, we will try to eliminate the confusion.
While it seems simplistic, choosing a cam should be based on the intended use of the vehicle and the rpm range of the engine. Additional factors, such as engine modifications, compression ratio, fuel delivery (carburetor or fuel injection), trans type, gearing, vehicle weight, and any power adders (like superchargers or nitrous) must be taken into consideration.
Camshaft Designs Hydraulic Flat Tappet: Used for street and mild race performance under normal circumstances, they perform well, require no maintenance, and are relatively inexpensive. However, they are limited in terms of lobe profile. The break-in procedure and the oil used during that process is critical, so follow the installation instructions to the letter.
Mechanical Flat Tappets: For the ability to operate at higher rpm than hydraulic designs and that classic muscle car mechanical sound “solids” are hard to beat. The proper break-in procedure must be followed and there will be maintenance involved as valve clearances must be adjusted on a periodic basis.
Hydraulic Roller Tappets: (OEM and retrofit) one of the most popular options for street performance and mild racing application, these cams are extremely popular. Hydraulic rollers virtually eliminate maintenance and break-in concerns, they are long lasting, and allow the use of the latest technology in cam lobe profiles.
Mechanical Roller Tappets: For all-out street performance and racing applications these cams are available with the most aggressive lobe profiles and used with the highest valvespring pressure for sustained high-rpm operation.
Valvesprings Selecting the proper valvesprings is important and the best source of what springs should be used will come from the camshaft manufacturer. Stiffer than required and horsepower will be needlessly lost to friction, too light, and valve float and possible engine damage may occur.
Comp advises that once the valvesprings have been installed, it is important to check for coil bind. This means that when the valve is fully open, there must be a minimum of 0.060-inch clearance between the coils of both the inner and outer springs. If this clearance does not exist, you must change either the retainer or the valve to gain more installed height, change to a spring that will handle more lift, or machine the spring seat for extra depth.
In addition, always check for clearance between the retainer and the inside face of the rocker arm (this will be most evident while the valve is on the seat). Also, check for clearance between the retainer and the top of the valveguide/seal at maximum lift.
Pushrods/Rocker Arm Geometry For something as inherently simple as a pushrod they are a critical valvetrain component. They have to be strong enough to resist deflection while being lightweight and their length must be correct to ensure proper rocker arm geometry.
Incorrect rocker arm geometry can cause a host of problems. According to the experts at Comp, if the tip of a roller rocker does not hit in the center, the amount of surface area contacted is reduced. The further away from the center the rocker arm is when it hits, the more likely it is for damage to occur. Two of the most common issues that occur are breaking the roller tip on the end of the rocker and “mushrooming” the valve tip. The pushrod can also end up contacting the edge of the rocker cup, causing unnecessary wear on the pushrod and rocker arm. In addition, if the rocker is not touching the center of the valve it will not be pushing straight down but at an angle, which can induce valveguide wear issues.
The Comp tech team advises further that there are a lot of factors involved in determining proper rocker arm geometry. Pushrod length, block deck height, head gasket thickness, rocker arm design, cam base circle size, lifter design, and valve stem length are just a few of these. The only way to account for all factors is to use an adjustable checking pushrod that will allow you to find the exact length of pushrod your setup needs. However, be aware there are different methods of measuring pushrods:
Theoretical Length: This assumes that the pushrod has no oil hole in the end of it. Therefore, the radius at either end is complete, which lengthens the pushrod approximately 0.017 inch in the case of a 5⁄16-inch pushrod with 0.100-inch-diameter oil holes, minimally chamfered.
Actual Length: This is what you would measure if you had a set of calipers large enough to measure over the oil holes at each end of the pushrod. This is the measurement that most people can relate to. Unfortunately, this measurement is affected not only by the diameter of the oil holes but also by the entrance chamfer for each oil hole.
Gauge Length: Although the most difficult to measure (it requires a special-length checking gauge), this measurement is the most reliable. This is because the oil holes and their chamfers are eliminated from the measurement. The only problem is that not all companies use the same gauge diameter. Comp Cams uses a 0.140-inch gauge diameter. All Magnum and Hi-Tech pushrods are measured using this technique.
Comp has developed two methods of measuring pushrods. The first requires the use of their Hi-Tech Pushrod Length Checker. These are marked with a standard length stamped in them. This number represents the gauge length of the part with the two halves screwed completely together. Extending the pushrod one rotation lengthens the gauge length 0.050 inch. For example, a pushrod stamped 7.800 and screwed apart one rotation would be 7.800 inches plus 0.050 inch equal 7.850 inches gauge length.
The second method requires a Comp Magnum Pushrod Length Checker. Once adjusted, you don’t need to have an expensive gauge or a pair of calipers to measure it. You just need a standard-length pushrod to compare it to. Then use a pair of common 6-inch calipers to measure the difference between the two.
Rocker Arms Comp’s techs advise there are three basic ways to increase power through a rocker arm change:
Increase the rocker arm ratio. It’s possible to increase valve lift without ever touching the camshaft by as much as 10 percent by increasing rocker ratio.
Make the rocker arm stiffer. To increase stiffness, there are three options: material, geometry, and the rocker’s holding fixture (mounting style) .The easiest way is to switch to chromoly steel. Although heavier than some other materials, it can offer some design advantages and have much thinner sections than aluminum due to its superior strength density. For the ultimate in high performance, shaft-mounted rockers may be the way to go.
Decrease the moment of inertia. This is the rocker’s resistance to rotation. The higher this measurement, the more valvespring pressure it takes to control the rocker arm instead of the valves—losing rpm and horsepower. The moment of inertia is lowered by lightening the rocker arm’s weight, particularly at areas that are farther from the trunnion (pivot point). Two ways you can do this are by switching to a lighter weight material or by removing mass from the rocker body design.
Rocker arms are available in a variety of materials, designs, and price points, including stamped steel replacements, stamped steel with roller tips, aluminum full rollers, and steel full rollers.
Distributor Gears There are four common types of distributor gears: cast iron, melonized steel, bronze, and composite, which one is used depends on the camshaft (cast-iron flat tappet, ductile iron hydraulic and roller cams, and steel billet cams).
Cast-iron gears should only be used with cast-iron cams.
Melonized gears are heat treated and can be used with all three materials.
Bronze gears are used with billet steel cams (these gears are meant to be sacrificial to save the cam gear, and as a result must be changed regularly).
Composite gears can be used with any cam material.
Oil for Break-In and Hydraulic Roller Lifters When breaking in a flat tappet cam use a specially formulated oil such as Comp Cams PN 1590. Avoid ZDDP additives initially, as they have additional additives that can prevent proper ring seating, and diesel oils should not be used because they no longer have sufficient ZDDP levels to protect the cam initially.
Although damaging cam lobes isn’t an issue, break-in oil should also be used with roller lifters to protect the internal components. Avoid thick, high-viscosity oil with hydraulic lifters, 10W-40 is generally recommended. Heavier oil can make them noisy.
Selecting camshafts and related components is made much easier by selecting complete assemblies. This a retrofit hydraulic roller kit for a Ford.
When installing any cam the proper assembly lube is essential along with a dedicated break-in oil.
Although they do require care when breaking in, hydraulic flat tappets, such as Comp Cams High Energy Hydraulic lifters, are reliable and affordable for street applications.
A step up from hydraulic flat tappets are retrofit hydraulic rollers. They will require shorter pushrods, and roller rockers are a wise addition.
There are many Chevrolet trucks with roller lifter blocks that were equipped with flat tappets from the factory. Comp Cams offers all the components to install OEM-style rollers, including the “spider” lifter guides and cam thrust plate.
Here are the Comp rollers and guides in place. The guides ensure the rollers are always properly aligned with the cam lobes.
In a factory GM roller block the sheetmetal retainer attaches to threaded bosses cast in the block.
For aftermarket rollers tie bars between pairs of lifters prevent them from becoming misaligned with the cam.
Comp Cams’ Magnum double roller timing set features a three keyway crank sprocket for “straight up” cam timing or 4-degree advance/retard.
An alternative to sprockets and chain, Comp offers this dual idler gear drive.
When converting to a roller cam some method of controlling cam endplay must be included. This thrust bearing uses shims to position it in close proximity to the timing cover.
Comp Cams suggests 0.004-0.010 inch of camshaft endplay. An alternative to the shimmed bearing is the “file to fit” nylon button.
A critical measurement is installed valve retainer height as it impacts spring tension. Here it is being measured with a snap gauge.
The snap gauge is then measured with a dial caliper.
Note the step in the valve retainer, it contacts the damper inside the spring. This is an important factor when measuring valvespring pressure.
When high-pressure triple valvesprings are used with flat tappet cams it’s advisable to remove the inner coil or substitute lighter springs when breaking in the cam.
Valvesprings should be checked at open and closed heights to ensure pressures are correct.
If necessary, shims can be added below the valvesprings to bring them to the proper installed height. These are from Comp Cams and come in 0.015, 0.030, and 0.060-inch thickness.
Pushrods require some method of keeping them aligned with the rocker arms—it may be by the size of the pushrod hole in the head, guided rockers, or guideplates, as seen here. Note this engine is also equipped with screw-in rocker studs.
Comp Cams High Energy Steel Rocker Arms are excellent replacements for street use. They feature a long slot for higher-than-stock lift camshafts and come with grooved pivot balls for enhanced lubrication.
Comp Cams offers a variety of replacement rocker arms in steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
Comp Cams offers a variety of replacement rocker arms in steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
Another version of the Magnum steel rocker uses a guided roller that keeps it centered over the valve stem, eliminating the need for guideplates.
An extremely affordable performance street and moderate race use option are Comp’s High Energy Die Cast Aluminum roller rocker arms. They have a needle bearing fulcrums and roller tips. They are available for GMC, Chevrolet, Ford, and Oldsmobile applications.
An extremely affordable performance street and moderate race use option are Comp’s High Energy Die Cast Aluminum roller rocker arms. They have a needle bearing fulcrums and roller tips. They are available for GMC, Chevrolet, Ford, and Oldsmobile applications.
For the ultimate in durability, Comp offers Ultra Pro Magnum rocker arms. Investment cast from stainless steel these rockers are built to handle up to 7,000 rpm, feature hardened roller tips, an oversized trunnion, and precision-sorted needle bearings that easily stand up to the abuse of the high load valvesprings needed to handle increased lift and rpm.
Many engine builders believe the most effective way to increase horsepower is by replacing stud-mounted rockers with a shaft-mounted rocker system to increase mounting stiffness and valvetrain stability.
The importance of proper rocker arm geometry cannot be overstated. At mid lift the roller tip of this rocker arm is centered on the valve stem as it should be.
Comp Cams offers adjustable-length pushrods to establish proper rocker arm geometry. The Hi-Tech versions work like an inside micrometer and will establish the gauge length of the required pushrods.
The Magnum adjustable pushrods establish the actual length of the pushrods needed with the use of a dial caliper.
The Magnum adjustable pushrods establish the actual length of the pushrods needed with the use of a dial caliper.
In some vintage engines, such as this Chrysler Hemi, adjustable pushrods are used with fixed rocker arms.
Because racing engines run at higher-rpm levels with harsh cam profiles, replaceable lash caps may be used to protect the valve stems.
Many engines use shaft-mounted rocker arms. Some, like this FE Ford shown here, have non-adjustable valvetrains so the condition of all components (including the shafts) and valve stem heights have to be within certain specifications.
It is important for new springs to take a heat-set. Upon initial startup, limit rpm to 1,500 to 2,000 until the temperature has reached operating levels. To help the break-in process use Comp Cams Valve Train Assembly Spray.
Selecting the proper distributor gear is dependent on the camshaft material. Comp’s composite gear will work with any of them.
The post What You Need To Know When Choosing Valvetrain Components appeared first on Hot Rod Network.
from Hot Rod Network https://www.hotrod.com/articles/choosing-valvetrain-components/ via IFTTT
0 notes
Text

🚗 Premium Engine Valves & Valve Guides for Maximum Performance! 🔧
Upgrade your engine with top-quality parts from trusted brands! ✅
🔥 Everphone Engine Valves – High durability & precision performance. 🔥 Nittan Engine Valves – Reliable, heat-resistant, and long-lasting. 🔥 Fuji Valve Guides – Perfect fit for smooth engine operation.
Keep your engine running strong with the best components! 💯
📢 Available now! Contact us for more details. 📩 #EngineValves #ValveGuides #AutoParts #HighwayGRM #HighwayTruckDXB
0 notes
Photo

#vr38dett #vr386 #inconel #bigvalve #beryllium #seatring #valveguide (Do-Luck Co.,Ltd.) https://www.instagram.com/p/CD7-sfrnPpw/?igshid=1x23b4h3ltygl
0 notes
Photo

guide valve S4S, S6S #guide #valveguide #Mitsubishi #forklifts #sparepartforklift #montacargas #starpioneerforklift #s4s #s6s https://www.instagram.com/p/B9eRFXyFegt/?igshid=x32f952e1t2j
0 notes
Photo

General Overhaul Cummins 6BT5.9 on process. #globalteknikbppn #workshopbalikpapan #balikpapanku #workshop #repairshop #crankshaft #crankshaftgrinding #centerline #rodcylinder #cylinderhydraulic #surfacegrinding #cylinderhead #spareparts #engineblock #deutz #caterpillar #commonraildiesel #nozzles #fuelinjectionpump #plunger #deliveryvalve #bosch #zexel #valveseat #valveguides #valves #mainbearings #conrod #cummins 6BT5.9#calibration (at Global Teknik Balikpapan) https://www.instagram.com/p/CDkU7vWB4EE/?igshid=1e76cukijk7f4
#globalteknikbppn#workshopbalikpapan#balikpapanku#workshop#repairshop#crankshaft#crankshaftgrinding#centerline#rodcylinder#cylinderhydraulic#surfacegrinding#cylinderhead#spareparts#engineblock#deutz#caterpillar#commonraildiesel#nozzles#fuelinjectionpump#plunger#deliveryvalve#bosch#zexel#valveseat#valveguides#valves#mainbearings#conrod#cummins#calibration
0 notes
Link
TAEVision 3D Mechanical Design Parts EngineParts Aftermarket @msmotorservice MSMotorservice TRW Automotive KS Kolbenschmidt GmbH Valves ValveTrain ValveGuides ValveCotters ValveSealInserts ValveControlElements ▸ TAEVision Engineering on Pinterest ▸ TAEVision Engineering on Google Photos ▸ TRW Automotive - Valves and Valve Accessories
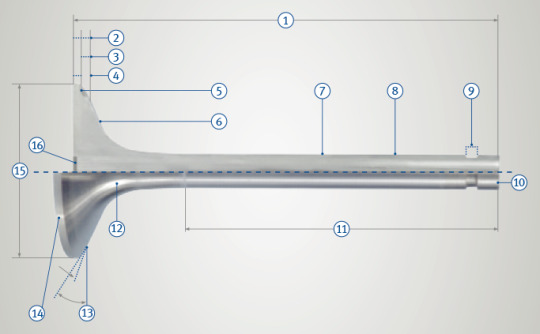
Valves - Dimensions and Technical Terms
1 Total length = L 2 Total valve head thickness 3 Seat height 4 Height of valve seat face 5 Seat armouring (optional) 6 Valve head 7 Skirt diameter = d 8 Valve stem 9 Groove area 10 End face of stem (hardened) 11 Grinding length 12 Throat 13 Valve seat angle = α 14 Head surface 15 Head diameter = D 16 Calotte
Data 187 - Jul 08, 2021
#TAEVision#engineering#3d#mechanicaldesign#parts#engineparts#aftermarket#MSMotorservice#TRW Automotive#KS Kolbenschmidt GmbH#valves#valve train#ValveTrain#valve guides#ValveGuides#valve cotters#ValveCotters#valve seal inserts#ValveSealInserts#valve control elements#ValveControlElements
1 note
·
View note
Text
Mildly Modifying Pontiac’s 455 H.O. To Add Nearly 100 hp Over Factory Gross Rating
To ensure suitable engine operation on unleaded fuel while reducing emissions, GM mandated a maximum compression ratio of 8.5:1 for the 1971 model year. Pontiac responded by essentially increasing the displacement of its otherwise high-compression 1970 Ram Air IV to create the 1971 455 H.O. In its introductory model year as the division’s top engine, the round-port 455ci had a gross rating of 335 hp at 4,800 rpm and 480 lb-ft at 3,200 rpm. The 455 H.O. was carried over for 1972 without any major changes, but the gross output rating was dropped in favor of net values. It was rerated at 300 hp at 4,000 rpm and 415 lb-ft at 3,200 rpm.
Despite only two years in production run, the 455 H.O. is regarded by many Poncho experts as the most versatile street engine Pontiac ever produced. Gobs of low-rpm torque make it quite responsive in normal driving conditions, and it can instantly turn tires into a smoky haze by standing on the throttle. It remains a formidable contender in pure-stock competition, and simply injecting it with a bit of modern technology allows the factory-engineered package to really shine.
Jim Rotella of Omaha has a 1972 Trans Am that’s equipped with a TH400 automatic transmission, 3.08:1 rear axle ratio, air conditioning, and power steering and brakes. When the time came to rebuild its numbers-matching 455 H.O., he reused the important factory-issued components and beefed up the internals to maximize performance without compromising driveability. Here’s how this 455 H.O. generates 433 hp at 4,800 rpm and 517 lb-ft at 3,500 rpm.
Block The number-matching 485428 455ci block with four-bolt main caps was bored 0.030 inch during a previous rebuild. The cylinder walls were clean enough that only an additional 0.010 inch was required during this rebuild, taking the total bore diameter to 4.195 inches. Butler Performance supplied its proprietary long-stroke rotating assembly that includes 4.25-inch forged steel crankshaft and forged H-beam connecting rods from Eagle and forged pistons from Ross. Total displacement measures 469 ci.
Heads The 1972 455 H.O. 7F6 cylinder heads with oversized intake ports and round-shaped exhaust ports were completely rebuilt using bronze valveguides, stainless-steel Ferrea valves in 2.11/1.77-inch, and a multi-angle valve job. Intake and exhaust airflow at 28 inches measures 223 and 177 cfm, respectively. Comp Cams supplied the 987-16 dual valvesprings while ARP supplied the 7/16-inch rocker studs. Combustion-chamber volume measures 100 cc and compression ratio calculates to pump-gas-friendly 9.2:1.
Intake Manifold Beyond minor surfacing to true up the flanges, the cast-aluminum 488945 intake manifold with separate cast-iron exhaust crossover and oversized intake runners was otherwise left as-cast.
Carb While the 1972 455 H.O. used an otherwise typical-for-1972 Quadrajet with an airflow capacity of 750 cfm, the 1971 455 H.O. Quadrajet was quite unique and flowed more than 825 cfm. Rotella uses the rare 1971-spec No. 7041268 carburetor. Its fitted with 74 primary jets, 43 primary metering rods, and CV secondary rods for maximum performance.
Exhaust A pair of reproduction round-port exhaust manifolds with 2.45-inch diameter collectors from Ram Air Reproduction Enterprises replaced the cracked originals.
Distributor The original 1112126 points-type distributor was rebuilt using a high-quality CS-89 contact points set from NAPA. It was recurved to provide 22 degrees of mechanical advance by 3,200 rpm. Peak power was achieved with 34 degrees of total spark lead, and 12 additional degrees of vacuum advance improves efficiency at response in light-throttle conditions.
Camshaft A custom-ground hydraulic roller camshaft from Comp Cams was specifically chosen to complement the intended operating range and convenience accessories. Duration at 0.050 inch measures 224/236 with 0.502/0.520-inch valve lift with Comp Gold series roller rocker arms in 1.5:1 ratio. The lobe separation is 113 degrees with the intake centerline at 109. Comp’s 857-16 hydraulic roller lifters were also employed.
The post Mildly Modifying Pontiac’s 455 H.O. To Add Nearly 100 hp Over Factory Gross Rating appeared first on Hot Rod Network.
from Hot Rod Network http://www.hotrod.com/articles/mildly-modifying-pontiacs-455-h-o-add-nearly-100-hp-factory-gross-rating/ via IFTTT
0 notes
Text

The primary function of a valve guide is to guide the valve stem as it moves up and down during the engine's operation. This ensures that the valve maintains proper alignment with the valve seat, allowing for efficient sealing and combustion in the engine's cylinders. Without functioning valve guides, the engine can experience problems such as poor compression, oil consumption, and decreased performance.

#highwaygrm#highwaytruckdxb#highwaytruck#highwaytruckdubai#autoservices#valveguides#engineprecision#efficiencymatters
0 notes
Link
TAEVision 3D Mechanical Design Parts EngineParts Aftermarket @msmotorservice MSMotorservice TRW Automotive KS Kolbenschmidt GmbH Valves ValveTrain ValveGuides ValveCotters ValveSealInserts ValveControlElements ▸ TAEVision Engineering on Pinterest ▸ TAEVision Engineering on Google Photos ▸ TRW Automotive - Valves and Valve Accessories

Valves - Dimensions and Technical Terms
1 Total length = L 2 Total valve head thickness 3 Seat height 4 Height of valve seat face 5 Seat armouring (optional) 6 Valve head 7 Skirt diameter = d 8 Valve stem 9 Groove area 10 End face of stem (hardened) 11 Grinding length 12 Throat 13 Valve seat angle = α 14 Head surface 15 Head diameter = D 16 Calotte
Data 187 - May 21, 2021
#TAEVision#engineering#3d#mechanicaldesign#parts#engineparts#aftermarket#MSMotorservice#KS Kolbenschmidt GmbH#TRW Automotive#MSMotorservice TRW Automotive KS Kolbenschmidt GmbH#valves#ValveTrain#valve train#ValveGuides#valve guides#ValveCotters#valve cotters#ValveSealInserts#valve seal inserts#ValveControlElements#valve control elements#valves and valve accesories
1 note
·
View note