#Vat Paste manufacturer in Brazil
Text
Vat Paste manufacturer and supplier in Brazil | RK Dyechem Pvt Ltd
RKindustry is the best vat paste supplier in Brazil. We are one of the top vat paste manufacture or supplier industry in Brazil. this paste is use for printing. Call now

#Vat Paste manufacturer#Vat Paste supplier#Vat Paste#Vat Brown RRD Paste#Vat Black BG Paste#Vat Orange RF Paste#Vat Paste manufacturer in Brazil#Brazil
0 notes
Text
Chapter 11: Your Turn Fieldwork

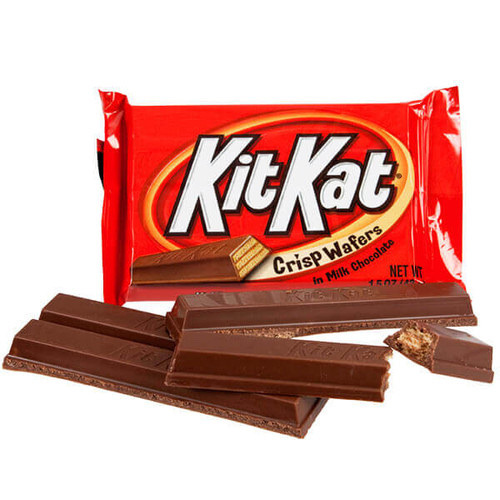
1. Milk chocolate (sugar, milk ingredients, cocoa butter, cocoa mass, whey powder, lactose, soya lecithin, polyglycerol polyricinoleate, natural flavour) ,wheat flour, sugar, modified palm oil, cocoa, sodium bicarbonate, soya lecithin, yeast, natural flavor
2. The ingredients are sourced globally
Sugar from Hawaii, Yeast from Switzerland, Wheat and flour from Kansas, Baking soda from Wyoming, Cocoa from Ecuador, Milk products from Colombia and India, Soy from Argentina, Cocoa butter from Ghana and Brazil, Vanilla from Madagascar, Palm kernel oil from Malaysia and Indonesia
3. Ingredient Production
The cacao seeds are fermented for about a week, dried, then roasted. After it’s roasted, becoming cocoa. The cocoa seeds, or nibs, are then ground into a paste, sort of like nut butter, consisting of the butter and solids.
The Sugar is made in the leaves of the sugar cane plant by photosynthesis. During milling the cane is crushed to extract the juice. The juice is cleaned and concentrated into a syrup. Sugar crystals then form what is called ‘raw’ sugar.
Natural vanilla extract comes from the vanilla orchid, which, when pollinated, produces a pod containing vanilla beans. Cured and fermented beans are ground up and soaked in alcohol and water.
Cows are milked using vacuum cups which are attached to the cow’s teats. The milk is sent through stainless steel pipes to large refrigerated vats, then stored at 5°C or less. Within 48 hours, milk is taken in tankers to a milk factory where it’s pasteurized and homogenized.
4. To satisfy the world’s desire for the delicious chocolate covered wafers that are Kit Kats, Nestle and Hershey’s require a multitude of employees. Factory workers earn approximately $40,000 annually while those in more specialized roles such as financial advisors, business analysts, and marketing associates earn an average of $80,000 annually. Those near the top of the process such as marketing managers and financial managers earn an average of $135,000 annually. Nestle takes good care of its employees by offering a range of benefits including health insurance, maternity and paternity leave, vacation pay, pension plans, and other perks.
5. Nestle’s corporate and overseas labor includes the supply chain starts in the primary stage with small farms growing coca, wheat, and sugarcane. These natural resources are then shipped out to the manufacturers of Nestle factories where the chocolate bars are created. Finally, the tertiary stage is when the final product, the Kit Kat bars, are shipped to retailers to be sold to the general populace.
6. Set Prices
$0.99. Kit Kat Chocolate Candy Bar - 1.5oz.
$0.99. Kit Kat Duo Dark Chocolate Mint Chocolate Bar - 1.5oz.
$4.99. Kit Kat Full Size Candy Bars - 9oz/6ct.
7. Mars, Mondelez, Nestle, Ferrero Group, Hershey’s 8.
8. In the United States, chocolate is regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Cacao products regulations are contained within 21 C.F.R. 163 et seq.
9. Nestle has promoted it as chocolaty fun, connecting it with both taste and leisure. So has its strapline, “Have a break, have a Kitkat” and the commercials have been very catchy with the noise the crunch makes.
10. Giant Food Store
11. Kit Kat profits rose 1.6 percent to $1.79 billion annually after the cocoa prices declined
12. After researching for hidden cost there has been none proven.
Beginning at a Nestle’s factory, going through steel pipes, boilers, long conveyor belts, and intricate machinery the Kit Kat has just started the process to making it to the markets. First step is the baking process. Water-thin sheets are baked to a crisp to become the golden wafers. Moving along the belt cocoa based praline is spread across top, immediately following another wafer. This is then repeated to add one more layer of cocoa. As the Kit Kat moves across the belt it is under controlled conditions, and then precisely cut. It will either become a two-finger or four-finger wafer. The wafer fingers are then coated with chocolate using a special designed molding process, and cooled. The last stage the Kit Kat endures is the wrapping process. It is wrapped in silver foil and in Kit Kat’s bright red packs all untouched by human hands. Kit Kat is then placed in appropriate box sizes and ready to be shipped out.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
CHAPTER 11 FIELDWORK

1. Milk chocolate (sugar, milk ingredients, cocoa butter, cocoa mass, whey powder, lactose, soya lecithin, polyglycerol polyricinoleate, natural flavour) ,wheat flour, sugar, modified palm oil, cocoa, sodium bicarbonate, soya lecithin, yeast, natural flavour.
2. The ingredients of a Kit Kat are sourced globally and include the following:
- Sugar from Hawaii
- Yeast from Switzerland
- Wheat and flour from Kansas
- Baking soda from Wyoming
- Cocoa from Ecuador
- Milk products from Columbia and India
- Soy from Argentina
- Cocoa butter from Ghana and Brazil
- Vanilla from Madagascar
- Palm kernel oil from Malaysia and Indonesia
3. Ingredient Production:
- Sugar is made in the leaves of the sugar cane plant by photosynthesis. During milling the cane is crushed to extract the juice. The juice is cleaned and concentrated into a syrup. Sugar crystals then form what is called 'raw' sugar.
- The cacao seeds are fermented for about a week, dried, then roasted. After it's roasted, becoming cocoa. The cocoa seeds, or nibs, are then ground into a paste, sort of like nut butter, consisting of the butter and solids.
- Cows are milked using vacuum cups which are attached to the cow's teats. The milk is sent through stainless steel pipes to large refrigerated vats, then stored at 5°C or less. Within 48 hours, milk is taken in tankers to a milk factory where it's pasteurised and homogenised.
- Natural vanilla extract comes from the vanilla orchid, which, when pollinated, produces a pod containing vanilla beans. Cured and fermented beans are ground up and soaked in alcohol and water.
4. To satisfy the world’s desire for the delicious chocolate covered wafers that are Kit Kats, Nestle and Hershey's require a multitude of employees. Factory workers earn approximately $40,000 annually while those in more specialized roles such as financial advisors, business analysts, and marketing associates earn an average of $80,000 annually. Those near the top of the process such as marketing managers and financial managers earn an average of $135,000 annually. Nestle takes good care of its employees by offering a range of benefits including health insurance, maternity and paternity leave, vacation pay, pension plans, and other perks.
5. Nestle’s corporate and overseas labor includes the supply chain starts in the primary stage with small farms growing coca, wheat, and sugarcane. These natural resources are then shipped out to the manufacturers of Nestle factories where the chocolate bars are created. Finally, the tertiary stage is when the final product, the Kit Kat bars, are shipped to retailers to be sold to the general populace.
6. Set Prices
$0.99. Kit Kat Chocolate Candy Bar - 1.5oz.
$0.99. Kit Kat Duo Dark Chocolate Mint Chocolate Bar - 1.5oz.
$4.99. Kit Kat Full Size Candy Bars - 9oz/6ct.
$0.99. Kit Kat Dark Standard Bar - 1.5oz
$3.69. Kit Kat Holiday Mint + Dark Chocolate Snack Size Duos - 9.8oz.
7. Mars, Mondelez, Nestle, Ferrero Group, Hershey's
8. In the United States, chocolate is regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Cacao products regulations are contained within 21 C.F.R. 163 et seq.
9. Nestle has promoted it as chocolaty fun, connecting it with both taste and leisure. So has its strapline, “Have a break, have a Kitkat” remained unchanged over the years.
10. Local Walmart
11. After A drop in cocoa prices, Kit Kat profits rose 1.6 percent to $1.79 billion annually.
12. After researching for hidden cost there has been none proven.
Biography: Beginning at a Nestle’s factory, going through steel pipes, boilers, long conveyor belts, and intricate machinery the Kit Kat has just started the process to making it to the markets. First step is the baking process. Water-thin sheets are baked to a crisp to become the golden wafers. Moving along the belt cocoa based praline is spread across top, immediately following another wafer. This is then repeated to add one more layer of cocoa. As the Kit Kat moves across the belt it is under controlled conditions, and then precisely cut. It will either become a two-finger or four-finger wafer. The wafer fingers are then coated with chocolate using a special designed moulding process, and cooled. The last stage the Kit Kat endures is the wrapping process. It is wrapped in silver foil and in Kit Kat’s bright red packs all untouched by human hands. Kit Kat is then placed in appropriate box sizes and ready to be shipped out.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Chapter 11 Fieldwork

1. Milk chocolate (sugar, milk ingredients, cocoa butter, cocoa mass, whey powder, lactose, soya lecithin, polyglycerol polyricinoleate, natural flavour) ,wheat flour, sugar, modified palm oil, cocoa, sodium bicarbonate, soya lecithin, yeast, natural flavour.
2. The ingredients of a Kit Kat are sourced globally and include the following:
Sugar from Hawaii
Yeast from Switzerland
Wheat and flour from Kansas
Baking soda from Wyoming
Cocoa from Ecuador
Milk products from Colombia and India
Soy from Argentina
Cocoa butter from Ghana and Brazil
Vanilla from Madagascar
Palm kernel oil from Malaysia and Indonesia
3. Ingredient Production:
Sugar is made in the leaves of the sugar cane plant by photosynthesis. During milling the cane is crushed to extract the juice. The juice is cleaned and concentrated into a syrup. Sugar crystals then form what is called 'raw' sugar.
The cacao seeds are fermented for about a week, dried, then roasted. After it's roasted, becoming cocoa. The cocoa seeds, or nibs, are then ground into a paste, sort of like nut butter, consisting of the butter and solids.
Cows are milked using vacuum cups which are attached to the cow's teats. The milk is sent through stainless steel pipes to large refrigerated vats, then stored at 5°C or less. Within 48 hours, milk is taken in tankers to a milk factory where it's pasteurised and homogenised.
Natural vanilla extract comes from the vanilla orchid, which, when pollinated, produces a pod containing vanilla beans. Cured and fermented beans are ground up and soaked in alcohol and water.
4. To satisfy the world’s desire for the delicious chocolate covered wafers that are Kit Kats, Nestle and Hershey's require a multitude of employees. Factory workers earn approximately $40,000 annually while those in more specialized roles such as financial advisors, business analysts, and marketing associates earn an average of $80,000 annually. Those near the top of the process such as marketing managers and financial managers earn an average of $135,000 annually. Nestle takes good care of its employees by offering a range of benefits including health insurance, maternity and paternity leave, vacation pay, pension plans, and other perks.
5. Nestle’s corporate and overseas labor includes the supply chain starts in the primary stage with small farms growing coca, wheat, and sugarcane. These natural resources are then shipped out to the manufacturers of Nestle factories where the chocolate bars are created. Finally, the tertiary stage is when the final product, the Kit Kat bars, are shipped to retailers to be sold to the general populace.
6. Set Prices
$0.99. Kit Kat Chocolate Candy Bar - 1.5oz.
$0.99. Kit Kat Duo Dark Chocolate Mint Chocolate Bar - 1.5oz.
$4.99. Kit Kat Full Size Candy Bars - 9oz/6ct.
$0.99. Kit Kat Dark Standard Bar - 1.5oz.
$3.69. Kit Kat Holiday Mint + Dark Chocolate Snack Size Duos - 9.8oz.
7. Mars, Mondelez, Nestle, Ferrero Group, Hershey's 8.
8. In the United States, chocolate is regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Cacao products regulations are contained within 21 C.F.R. 163 et seq.
9. Nestle has promoted it as chocolaty fun, connecting it with both taste and leisure. So has its strapline, “Have a break, have a Kitkat” remained unchanged over the years.
10. Local Walmart
11. After A drop in cocoa prices, Kit Kat profits rose 1.6 percent to $1.79 billion annually.
12. After researching for hidden cost there has been none proven.
Biography: Beginning at a Nestle’s factory, going through steel pipes, boilers, long conveyor belts, and intricate machinery the Kit Kat has just started the process to making it to the markets. First step is the baking process. Water-thin sheets are baked to a crisp to become the golden wafers. Moving along the belt cocoa based praline is spread across top, immediately following another wafer. This is then repeated to add one more layer of cocoa. As the Kit Kat moves across the belt it is under controlled conditions, and then precisely cut. It will either become a two-finger or four-finger wafer. The wafer fingers are then coated with chocolate using a special designed moulding process, and cooled. The last stage the Kit Kat endures is the wrapping process. It is wrapped in silver foil and in Kit Kat’s bright red packs all untouched by human hands. Kit Kat is then placed in appropriate box sizes and ready to be shipped out.
1 note
·
View note
Text
What's New in Dynamics 365 Business Central Release Wave 2: BC is now in India

Microsoft releases it foresees planned features with its new dynamics 365 business central release wave 2. Dynamic 365 Business Central is a leading Microsoft solution for SME. It unites CRM and ERP abilities. Later, it runs the entire business with intelligent applications. It works seamlessly in Cloud. It integrates with Office 365, Windows, Power BI, and Power Apps.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central is available in four countries: Brazil, Ireland, India, and Lithuania. Yes, BC is now in India. The Dynamics 365 business central features will release from October 2020 through March 2021. One can browse release wave 2 features online or can download PDF for more information. Dynamics 365 business central release wave 2 adds innovations, it comes with significant abilities to transform businesses. Release wave 2 features across Microsoft applications, it includes sales, marketing, finance, human resources, and customer service. It covers supply chain management, fraud protection, and business center.
Let’s look into dynamics 365 business central features in brief
Improved Management of database and file capacity
Partners and internal administrators can get an overview of the database. One can make a recommendation on whether or not additional storage is needed. And when to purchased. The default user can get 80 GB of business central storage capacity.
Support unlimited number of production and sandbox environments
Due to a lack of a production environment, many businesses couldn’t utilize Business central for their ERP. But now it’s possible with the unlimited production environment. As with the help of an unlimited sandbox environment, the availability of dynamics 365 business central in India.
Bank Reconciliation Improvement
With dynamics 365 business central partnering, one can use BC. As its biggest strength inability is to make it more efficient when dealing with bank reconciliations. Also, the user can cancel a posted bank reconciliation on the bank acc. Therefore, a reconciliation page is for those who in case make a mistake.
Use word document layout and customize outgoing customer documents
Are you looking for custom documents to send to your customer? Then this works well for you. One can export and then import a word document layout. It’s used for shipment documents, service quotes documents, return orders documents, generate invoice and credit memo documents with ease.
Use contact details across the application
In the application, mobile number, email fields not mentioned in any report data sets. Nor it’s mention in data entry pages, report layouts, and segment lines that have contact details within BC.
Business Central in Microsoft Teams
It’s one of the best dynamics 365 business central release wave 2 features. As of now, Microsoft hasn’t released too much information on how exactly it will work. But their ultimate goal is to bring business central data into the Microsoft team. Furthermore, it will collaborate and make quicker decisions.
Understand the Quick Role of center page
In the past, if you have used BC, then you might know how the center page works. The center page would consume more load time. Yes, it wouldn’t take long. But now with new dynamics 365 business central features, it is possible to load fast. And how Microsoft has done this? With the help of the cache layout of page ability.
Dynamic 365 Fraud Protection
D365 adds integration using its Dynamic 365 manual review capability. It allows users to use Fraud protection rules. It experiences flag transactions for review and allows expert human agents to adjudicate those transactions.
Access multiple productions
With the latest announcement, the unlimited sandboxes are available in this release. Each employee has its sandbox. Which can access through mobile devices. But the question will remain a question of whether you’ll access multiple sandboxes from the desktop app or not?
FAQ
What makes D365 BC works great for small businesses?
One can start small as there’s no user limit.
Comes cheaper for SMEs who are interested in Microsoft solutions
It’s flexible and allows adding users easily
Comes with a Cloud-first solution so can access through any device, anytime
What Business Central offers?
Supply Chain
Financial and Accounting
CRM for sales and services
Project Management
Operations
How SMB works?
The investments are done in release wave 2 would add service enhancements. It meets the demand of a rapidly growing customer base. It comes with improved performance, file storage handling, and Geographic expansion. It supports group VAT, customer-requested features, and other deeper Microsoft team integration.
What are the Industry Accelerators in D365?
They are the foundational components within the Microsoft Power Platform. It enables ISVs and other solution providers. It can quickly build industry verticals solutions. The accelerators will extend the standard data model to add new entities. It supports data schema for concepts within specific industries. Business central release wave 2 includes enhancement like non-profit, financial services, education, media and communication, manufacturing, and other automotive.
How Indian customers can upgrade?
As of now, we can directly upgrade to business central spring 2019. Then move to BC 2019 release wave 2 or BC 2020 release wave 1. There’s no direct upgrade available to BC 2020. Maybe later, Microsoft would come up with an intermediate version for India Localization and offer an upgrade toolkit.
Conclusion
Users can get help and drive digital transformation by dynamics 365 business central partnering. The Microsoft team is looking forward to releasing new services and capabilities soon. To learn more download the comprehensive dynamic 365 guides. It’ll help your organization grow and harness the change.
Techcronus – The global Enterprise Business Solution provider since 2010. We deliver cutting-edge custom software development services to craft your businesses. Contact our Experts now..!!
1 note
·
View note
Text
FW #12 Global Inequality
hershey-
ingredients- Milk Chocolate (Sugar, Milk, Chocolate, Cocoa Butter, Lactose, Milk Fat, Soy Lecithin, PGPR, Emulsifier, Vanillin, Artificial Flavor). (hershey.com)
where do they come from? Starts with the cocoa bean, which is found within the Theodroma Cacao, also known as the cocoa pod (fruit). The harvest process is labor intensive and starts when the seeds (cocoa beans) are extracted by splitting the pod with a machete. (https://danielsethics.mgt.unm.edu/pdf/Hershey%20Case.pdf)
The global cocoa market is currently supplied by mostly poor nations, with 70 percent from Africa (Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon), especially the Ivory Coast, which supplies 40 percent of the entire global market, followed by 19 percent from Asia and Oceania (Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, Malaysia), and 11 percent from the Americas (Ecuador, Brazil, Colombia). (https://danielsethics.mgt.unm.edu/pdf/Hershey%20Case.pdf)
What are the working conditions of the people who product the cocoa?
Many cocoa plantations engage in exploitation of other
workers. While some non‐family workers are paid, others may be enslaved or work in abusive conditions. They may have been trafficked from neighboring countries or tricked into owing large amounts of money to their employers. The workers are often threatened with physical punishment or death if they attempt to leave the plantation. (https://danielsethics.mgt.unm.edu/pdf/Hershey%20Case.pdf)
How is it produced? Is their child labor?
Once a company has received a shipment of cocoa beans at its processing plant, the beans are roasted, first on screens and then in revolving cylinders through which heated air is blown. Over a period of 30 minutes to 2 hours, the moisture in the beans is reduced from about seven percent to about one percent. The roasting process triggers a browning reaction, in which more than 300 different chemicals present in the cocoa beans interact. The beans now begin to develop the rich flavor we associate with chocolate.
2 Roasting also causes the shells to open and break away from the nibs (the meat of the bean). This separation process can be completed by blowing air across the beans as they go through a giant winnowing machine called a cracker and fanner, which loosens the hulls from the beans without crushing them. The hulls, now separated from the nibs, are usually sold as either mulch or fertilizer. They are also sometimes used as a commercial boiler fuel.
3 Next, the roasted nibs undergo broyage, a process of crushing that takes place in a grinder made of revolving granite blocks. The design of the grinder may vary, but most resemble old-fashioned flour mills. The final product of this grinding process, made up of small particles of the nib suspended in oil, is a thick syrup known as chocolate liquor.
4 The next step is refining, during which the liquor is further ground between sets of revolving metal drums. Each successive rolling is faster than the preceding one because the liquor is becoming smoother and flows easier. The ultimate goal is to reduce the size of the particles in the liquor to about .001 inch (.00254 centimeters).
Making cocoa powder
5 If the chocolate being produced is to be cocoa powder, from which hot chocolate and baking mixes are made, the chocolate liquor may be dutched, a process so-named because it was invented by the Dutch chocolate maker Conrad van Houten. In the dutching process, the liquor is treated with an alkaline solution, usually potassium carbonate, that raises its pH from 5.5 to 7 or 8. This increase darkens the color of the cocoa, renders its flavor more mild, and reduces the tendency of the nib particles to form clumps in the liquor. The powder that eventually ensues is called dutch cocoa.
6 The next step in making cocoa powder is defatting the chocolate liquor, or removing large amounts of butter from it. This is done by further compressing the liquor between rollers, until about half of the fat from its cocoa beans has been released. The resulting solid material, commonly called press cake, is then broken, chopped, or crushed before being sifted to produce cocoa powder. When additives such as sugar or other sweeteners have been blended, this cocoa powder becomes a modern version of chocalatl.
Making chocolate candy
7 If the chocolate being produced is to become candy, the press cake is remixed with some of the removed cocoa butter. The restored cocoa butter is necessary for texture and consistency, and different types of chocolate require different amounts of cocoa butter.
8 The mixture now undergoes a process known as conching, in which it is continuously turned and ground in a huge open vat. The process's name derives from older vats, which resembled large conch shells. The conching process can last from between three hours to three days (more time is not necessarily better, however). This is the most important step in making chocolate. The speed and temperature of the mixing are critical in determining the quality of the final product.
9 Another crucial aspect of conching is the time and rate at which other ingredients are added. The ingredients added during conching determine what type of chocolate is produced: sweet chocolate consists of chocolate liquor, cocoa butter, sugar, and vanilla; milk chocolate contains sweet chocolate with powdered whole milk or whole liquid milk.
10 At the end of the conching process, the chocolate is poured into molds, cooled, cut, and wrapped.
(http://www.madehow.com/Volume-1/Chocolate.html)
Children who work on cocoa plantations are usually somewhere between 12 and 15 years old but some are as young as 5 years old. Hazardous conditions include applying pesticides, working with sharp objects like knives and machetes, working without safety equipment, and environments full of snakes, insects, and other dangerous animals. (https://danielsethics.mgt.unm.edu/pdf/Hershey%20Case.pdf)
How do producers get the cocoa to the market?
cocoa gets exported from countries like Africa and the Ivory coast.
How are the prices set?
Supply drivers tend to be the stronger influencer of chocolate’s price volatility. Many commodities are used to manufacture chocolate, and the key ingredient is cocoa. Others such as sugar, dairy products, nuts, corn sweeteners and energy (natural gas and fuel oil) are also necessary to produce chocolate products. The prices of these commodities are driven, for the most part, by the commodities market, which sets the price based on supply and demand levels and can result in varying levels of volatility on commodity prices.
(Why the Price of Chocolate Fluctuates | Investopedia https://www.investopedia.com/articles/investing/071615/what-drives-price-chocolate.asp#ixzz5XEchqBKO )
Which international corporations dominate chocolate trade? Who regulates it?
Mars Inc., Nestle, and Hershey Co. (https://www.icco.org/about-cocoa/chocolate-industry.html)
Not regulated by a fair trade company.
How is chocolate marketed?
1. a product that is meant for the everyday consumer. This type of chocolate is made for those who want an average chocolate bar. The packaging is usually very simple and the prices are the same or lower than the rest of the competition.
2. Create a rich and luxurious image for the product. This type of chocolate is set above the rest in price. It usually has gold packaging and has a look that is different from all of the competitors.
3. Organic products are becoming more and more popular, so making chocolate to appease this type of consumer is a newer marketing technique. In order for a chocolate to be organic, it must be approved by the USDA and some companies then go on to get certified organic by other more strict organizations.
4. Companies also want to reach out to the adventurous chocolate eater by using exotic ingredients in the chocolate. These types of chocolates usually have bold colors on the package label, to emphasize the exotic ingredients that are in the chocolate. Exotic ingredients may include, spices like cayenne pepper, or different fruits like passion fruit or mango.
5. Sugar free chocolate appeals to those who have diabetes or anyone who wants to reduce their sugar intake. The diet industry has really taken off in the past ten years and as such, so has the diet chocolate industry. People with diabetes or consumers who are watching their weight are able to eat chocolate that is made without sugar. This chocolate is usually made with artificial sweeteners and the packaging reflects this change. The wrapping and labeling on this kind of chocolate bar is usually lighter, to indicate that it is lighter in calories and sugar, therefore, making it a light chocolate bar.
6. Finally, there is marketing towards children, in which companies make a product that is fun with packaging that has bright colors. There are many chocolate producing companies whose target market is children. In order to attract children anywhere from two to sixteen, they make their labels appear bright and cheerful. These companies also make their companies seem fun and sometimes quirky to attract children to other products they may offer.
(http://EzineArticles.com/4423737)
Where did you buy it?
Walgreens
How much profit does a store owner make of a bar of chocolate?
$1.06 (including taxes)
Are there hidden cost that are not included in the price you paid? Consider under payment of labor; environmental impact; government subsidies that are direct (to the company) and indirect (infrastructure such as roads, ports, bridges, and water systems) ; and the health care costs created by harvesting transporting processing or eating the food? How are these costs obscured?
There is probably hidden cost that are not included. The costs are obscured because they don’t pay their laborers no where close to what we pay as consumers, they probably get less than 10 cents per week. They obscure this by joining organizations to try to make it seem like they care about the working conditions of their workers even though they have terrible working conditions and have child labor.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Industrial Robots Market Analysis, Leading Industry Players, Recent Trends, Potential Growth, Share, Demand and Forecast To 2028
The research and analysis conducted in Industrial Robots Report helps clients to predict investment in an emerging market, expansion of market share or success of a new product with the help of global market research analysis. This report has been designed in such a way that it provides very evident understanding of the business environment and Industrial Robots industry. Nevertheless, this global market research report unravels many business problems very quickly and easily. Due to high demand and the value of market research for the success of different sectors, Industrial Robots Market report is provided that covers many work areas.
Market expectations for likely development openings have been mentioned clearly in this world class Industrial Robots Market research report. Competition analysis has been taken into account while preparing this report. A market analysis has turned into a vital piece of every business to settle on smart choices in the organizations which have been viably carried by experienced analysts. This market report provides best solutions for strategy development and implementation depending on client’s needs to extract tangible results. Businesses can bring about an absolute knowhow of general market conditions and tendencies with the information and data covered in this Industrial Robots Market report.
Global industrial robots market is expected to register a healthy CAGR of 10.10% in the forecast period of 2019-2026. The report contains data from the base year of 2018 and the historic year of 2017. The rise in the market value can be attributed to increase in investments for automation in industries and surge in labor charges worldwide.
Market Definition: Global Industrial Robots Market
An industrial robot is a robot system used in assembly line and for manufacturing. Industrial robots play a crucial role in industry automation. Industrial robots are programmable and automated. Robots are employed because of their ability to perform repetitive tasks with accuracy. They help in enhancing productivity and decrease operational costs for manufacturers.
Market Drivers:
Growing demand for industrial robotics from SEMs is driving this market
The increase in investments for innovations and automation in industries is expected to drive the market
Surging demand for automation activities and reduction in custom duties in the industry is expected to drive the market
Demand for minimizing defect, waste and downtime are the factors for growth in this market
To Understand How COVID-19 Impact is covered in this Report. Get Sample Copy of the report@ https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/request-a-sample/?dbmr=global-industrial-robots-market
Market Restraints:
The high manufacturing cost of industrial robotics solutions is a major hindrance for the industrial robotics market growth
High investment required for the initial setup is a restraint for this market
Segmentation: Global Industrial Robots Market
By Type
Traditional Industrial Robots
Collaborative Robots
Articulated Robots
SCARA Robots
Parallel Robots
Cartesian Robots
Others
By Industry
Automotive
Electrical and Electronics
Plastics, Rubber, and Chemicals
Metals and Machinery
Food and Beverages
Precision Engineering and Optics
Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics
Others
By Technology
Motion Control and Drives Systems
Robotics Systems
Integrated Manufacturing Systems
Machine Vision Systems
Manufacturing Execution Systems
Programmable Logic Control System
Others
By Geography
North America
South America
Europe
Asia-Pacific
Middle East and Africa
S.
Canada
Mexico
Brazil
Argentina
Rest of South America
Germany
France
United Kingdom
Italy
Spain
Russia
Turkey
Belgium
Netherlands
Switzerland
Rest of Europe
Japan
China
South Korea
India
Australia
Singapore
Malaysia
Indonesia
Thailand
Philippines
Rest of Asia-Pacific
South Africa
Egypt
Saudi Arabia
United Arab Emirates
Israel
Rest of Middle East and Africa
Request for TOC with Impact of COVID19: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/toc/?dbmr=global-industrial-robots-market
Key Developments in the Market
In November 2017, Kawasaki collaborated with ABB for robot automation cooperation. This can be the world’s 1st collaboration targeted on cobots and creation of trade approaches to safety, communication, and programming. This means more variability and more human intervention. This collaboration will bring advancement in technology and expand their product portfolio
In April 2017, IBM partners with ABB for industrial artificial intelligence that will merge IBM Watson's power with ABB Ability, ABB's extensive digital offering to unlock new value for customers in utilities, industry, transportation and infrastructure. This partnership will unlock new achievement for both the companies and bring new technological advancement
Competitive Analysis
Global industrial robots market is highly fragmented and the major players have used various strategies such as new product launches, expansions, agreements, joint ventures, partnerships, acquisitions, and others to increase their footprints in this market. The report includes market shares of industrial robots market for global, Europe, North America, Asia-Pacific, South America and Middle East & Africa.
Major Market Competitors/Players
Few of the major competitors currently working in the global industrial robots market are ABB, KUKA AG, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, FANUC CORPORATION, Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd., YASKAWA ELECTRIC CORPORATION., Seiko Epson Corporation, Stäubli International AG., NACHI-FUJIKOSHI CORP., DENSO CORPORATION., Comau SpA VAT, DAIHEN Corporation, OMRON Corporation, Universal Robots, CMA ROBOTICS SPA ITALY, Artech Automation AS, Panasonic Corporation.
The Industrial Robots market competitive landscape provides details by competitor. Details included are company overview, company financials, revenue generated, market potential, investment in research and development, new market initiatives, global presence, production sites and facilities, production capacities, company strengths and weaknesses, product launch, product width and breadth, application dominance. The above data points provided are only related to the companies’ focus related to Industrial Robots market.
Inquire Before Buying This Research Report: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/inquire-before-buying/?dbmr=global-industrial-robots-market
Prominent players in the market are predicted to face tough competition from the new entrants. However, some of the key players are targeting to acquire the startup companies in order to maintain their dominance in the global market. For a detailed analysis of key companies, their strengths, weaknesses, threats, and opportunities are measured in the report by using industry-standard tools such as the SWOT analysis. Regional coverage of key companies is covered in the report to measure their dominance. Key manufacturers of Industrial Robots market are focusing on introducing new products to meet the needs of the patrons. The feasibility of new products is also measured by using industry-standard tools.
Key companies are increasing their investments in research and development activities for the discovery of new products. There has also been a rise in the government funding for the introduction of new Industrial Robots market. These factors have benefited the growth of the global market for Industrial Robots. Going forward, key companies are predicted to benefit from the new product launches and the adoption of technological advancements. Technical advancements have benefited many industries and the global industry is not an exception.
Reasons to Purchase this Report:
Market segmentation analysis including qualitative and quantitative research incorporating the impact of economic and policy aspects
Regional and country level analysis integrating the demand and supply forces that are influencing the growth of the market.
Market value USD Million and volume Units Million data for each segment and sub-segment
Competitive landscape involving the market share of major players, along with the new projects and strategies adopted by players in the past five years
Comprehensive company profiles covering the product offerings, key financial information, recent developments, SWOT analysis, and strategies employed by the major market players
(**NOTE: Our analysts monitoring the situation across the globe explains that the market will generate remunerative prospects for producers post COVID-19 crisis. The report aims to provide an additional illustration of the latest scenario, economic slowdown, and COVID-19 impact on the overall industry.)
Buy this Premium Research Report: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/checkout/buy/enterprise/global-industrial-robots-market
Table of Content:
PART 01: EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
PART 02: SCOPE OF THE REPORT
PART 03: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
PART 04: INTRODUCTION
Market outline
PART 05: MARKET LANDSCAPE
Market ecosystem
Market characteristics
Market segmentation analysis
PART 06: MARKET SIZING
Market definition
Market sizing 2021
Market size and forecast
PART 07: FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS
Bargaining power of buyers
Bargaining power of suppliers
Threat of new entrants
Threat of substitutes
Threat of rivalry
Market condition
PART 08: MARKET SEGMENTATION BY PRODUCT
Global Industrial Robots market by product
Comparison by product
Market opportunity by product
PART 09: MARKET SEGMENTATION BY DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
Global Industrial Robots market by distribution channel
Comparison by distribution channel
Global Industrial Robots market by offline distribution channel
Global Industrial Robots market by online distribution channel
Market opportunity by distribution channel
PART 10: CUSTOMER LANDSCAPE
PART 11: MARKET SEGMENTATION BY END-USER
Global Industrial Robots market by end-user
Comparison by end-user
PART 12: REGIONAL LANDSCAPE
Global licensed Industrial Robots market by geography
Regional comparison
Licensed Industrial Robots market in Americas
Licensed Industrial Robots market in EMEA
Licensed Industrial Robots market in APAC
Market opportunity
PART 13: DECISION FRAMEWORK
PART 14: DRIVERS AND CHALLENGES
Market drivers
Market challenges
PART 15: MARKET TRENDS
PART 16: VENDOR LANDSCAPE
Overview
Landscape disruption
Competitive scenario
PART 17: VENDOR ANALYSIS
Vendors covered
Vendor classification
Market positioning of vendors
Any Questions/Queries or Need Help or Want to Purchase this Report? Speak with Our Analyst: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/speak-to-analyst/?dbmr=global-industrial-robots-market
About Data Bridge Market Research:
Data Bridge set forth itself as an unconventional and neoteric Market research and consulting firm with unparalleled level of resilience and integrated approaches. We are determined to unearth the best market opportunities and foster efficient information for your business to thrive in the market. Data Bridge endeavors to provide appropriate solutions to the complex business challenges and initiates an effortless decision-making process.
Contact:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 888 387 2818
UK: +44 208 089 1725
Hong Kong: +852 8192 7475
0 notes
Link
We all know Apple is an American company and enjoys making an outsized chunk of their revenue domestically. But Apple sells its products in many international markets and even has retail stores in 24 foreign countries. Some of those markets, like Japan, have access to Apple products at a price like the US. For example, an iPhone XS costs 112,800 yen in Japan, which is about 1,058 USD. And when you consider the country’s 8% sales tax is included in that price, it actually makes the iPhone XS about $20 cheaper than in the US. Although this fluctuates depending on the conversion rate. But not every country is lucky enough to pay comparable prices for Apple products. To buy the bottom model iPhone XS, you’d need to pay $1,235 in Mexico, $1,285 in India, $1,454 in Sweden, and $1,800 in Brazil. And these high prices have prompted customers to fly to the US just to buy a new iPhone. So why exactly are Apple products so expensive in these countries? Well, that’s exactly what we’re getting to determine today.

So one of the most important reasons why Apple products are so expensive overseas is due to taxes. And the perfect example of this is often the worth Added Tax or VAT, which exists in over 140 countries around the world. But despite its prevalence, it isn’t something that exists in the US. So let me explain how it works. In places just like the European Union, a VAT may be a consumption tax added to the worth of products and services. Products exported abroad aren’t typically subject to the worth Added Tax, but imported goods, like Apple products, are. And counting on the country, prices of those goods can increase up to 25%. And unlike the US, consumption taxes in most countries abroad are included during a product’s retail price. So when you notice the iPhone XS selling for $1,454 in Sweden compared to $1,000 in the US, that isn’t really a fair comparison, since US prices don’t include local sales tax. Now if you’re doing the math, you’ll find that iPhone prices in countries like Sweden still don’t add up. Because if their Value Added Tax is 25% on a $1,000 phone, they should be paying $1,250. But instead, the iPhone XS is priced about $200 higher. And that’s because taxes are simply a part of the complex equation companies like Apple use when calculating retail prices. Another factor to think about are any associated costs with importation. Things like import duties, shipping, insurance costs, and tariffs all contribute to cost inflation when selling products overseas. India is a great example of this. They've enacted something called the Foreign Direct Investment policy which punishes foreign companies who don’t source at least 30% of the components of their products from Indian suppliers. And since Apple doesn’t meet that standard, they’re restricted from opening retail stores within the country additionally to being hit with a 20% tariff. There’s also an 11.4% customs duty on imported products in addition to the Value Added Tax that we discussed earlier. And when you add all that up, it isn’t surprising that customers in India pay a 28% premium for products like the iPhone. Now Apple is taking steps to not only price their products more competitively in India but also to open their first mercantile establishment within the country. I’ll talk about that in more detail near the end of the video. Now you'll imagine import costs only being an element in foreign markets, but they will also affect customers within the US. Recently President Trump planned to implement a 10% tax on Chinese imports by September 1 which would affect tech companies like Apple. Now that deadline was pushed back to December 15th, but Tim Cook would really like to ascertain the tax eliminated altogether.
Also Read:- Who Stopped WannaCry Virus? Full Details
In fact, he met with Trump in the week and apparently made a convincing argument since Trump told reporters, “Tim was lecture me about tariffs and ... he made an honest case ... that Samsung is their favorite competitor and Samsung isn't paying tariffs. I assumed he made a really compelling argument so I'm brooding about it." Now if the choice isn’t reversed and Apple has got to pay the ten tax, they’d need to make a decision: Increase prices within the US by 10%, or keep prices an equivalent and permit their profit margin to require a serious hit. Both of which are dangerous for the corporate. If Apple raises prices it might exacerbate the difficulty of slowing hardware sales, but if they permit their margins to fall 10%, it might severely damage their profit potential.
So counting on how this story plays out, US customers made soon be feeling the consequences of tariffs that foreign countries are handling for years. Something else which will contribute to high prices is legally binding consumer guarantees that exist in places just like the EU. for instance, once you buy an Apple product within the US, you receive a typical one-year limited warranty that covers faulty parts, product defects, or other conditions that the manufacturer is liable for. But the matter is companies are liberal to define their warranty terms as they see fit. That’s why only certain components could also be covered, otherwise, you may need to pay a fee to ship the merchandise back to the manufacturer. And that’s exactly why the EU established a consumer guarantee that gives customers far more protection than a typical warranty. Customers within the EU are entitled to a minimum two-year warranty in addition to the quality manufacturer’s warranty. And this adds quite a little bit of liability for companies like Apple who typically offset the danger by increasing the worth of their products. But when it involves foreign markets, a serious concern is that the volatility of every country’s currency. Just take the united kingdom for instance. When Brexit happened, there was a 19% drop in the worth of their currency compared to the dollar, which caught tons of companies off guard and caused them to quickly adjust their prices to stay pace with the UK’s currency fluctuation Apple understands which foreign markets are most vulnerable to this volatility and preemptively raises their prices. you'll see this clearly with South Africa. Notice how the worth of its currency has fluctuated over the past five years compared to the EU, Australia, and Mexico. which volatility may be a major reason why Apple inflates their product’s prices in South Africa beyond what’s typically seen in other foreign markets. But so as to really understand Apple’s pricing overseas, we've to think about the American market. Because consumer behavior within the US is often quite different than those in other regions, mainly because American society is extremely consumption-based. we have the foremost credit cards issued per capita within the world, with everyone charging a mean of $4,000 annually. Compare this to other countries just like the UK or France, which opt instead for Debit Cards and thus charge but $300 on their credit cards per annum. you'll see companies like Apple capitalizing on America’s “buy now, pay later” mindset by offering monthly payment plans for his or her products. and every one of these amounts to US customers buying a better volume of products more frequently, allowing Apple to charge but other countries which don’t have a comparable level of consumerism.
Also Read:- Why Israel Is A Tech Capital Of The World?
Now up to the present point, we’ve discussed pretty concrete reasons why Apple prices their products higher in some foreign countries. But there’s one last fibrinogen want to debate that’s less easy to prove with hard facts, which is the brand image. Apple is taken into account as a premium brand in countries like India where the typical smartphone asking price is $200. So when it involves the iPhone XS price of $1,285, it is sensible that only the rich class in India could afford them. And if Apple knows their product will only be accessible to the upper crust, why not charge the maximum amount as you can? It’s an approach taken by many luxury clothing brands, whose customers haven't any problem overspending on items that ultimately function as a standing symbol. And you'll find evidence of this when comparing the iPhone’s price to other flagship smartphones. for instance, the Galaxy S10 retails for $900 within the US and $935 in India. a rise of just $35. The LG V40 retails for $900 within the US and $700 in India. That’s a reduction of $200. And once you compare those prices to the iPhone’s $285 premium in India, it supports the thought that Apple is just extracting the maximum amount of revenue from customers in India as possible, since they know people with money with pay any price for his or her premium phones anyway. it might also add up then that iPhones have only captured about one-hundredth of India’s smartphone market, which may be a shame considering India’s sizable population. But Tim Cook has made it clear that Apple has an aggressive decision to grow their presence within the region and make India one of their biggest sources of revenue. It all started earlier this year when Foxconn began trial runs of iPhone production in India, setting the inspiration for Apple to at least one day manufacture their smartphones within the region and satisfy the 30% local sourcing rule. this is able to allow Apple to avoid India’s 20% tariff additionally to opening their own retail stores within the country for the very first time.
Also Read:- Why Cartoons Never Grow Up?
In fact, Apple has already finalized an inventory of several locations within the country where they could build their store. But they're going a step further by saying they’d overhaul the company's relationship with independent retailers, and improve apps and services aimed more closely at Indians. So while Apple is understood for being a dear brand within the US, their products are typically even costlier abroad. Perhaps they will take measures like those in India to scale back their tax burden and drop prices, but it’s more likely that customers in foreign markets will need to continue biting the bullet and distribute the additional money for his or her favorite products.
0 notes
Text
Textile Dyes Market Share, Price Trends, Growth Opportunity and Statistics Forecast To 2027
Reports and Data added a research publication document on Global Textile Dyes Market. Breaking the business down into major segments and highlighting different regions to get an in-depth analysis of this market. The study perfectly balances both subjective and statistical information to explain the current market scenario. The study uses relevant market data, like for historical years it uses data from 2016-2018 and taking 2019 as the base year it gives a result which is predicted to the year 2026.
The global textile dyes market is forecast to reach USD 10.13 Billion by 2026, according to a new report by Reports and Data. Textile Dyes are specialty dyes that are used in the apparel industry for coloring purposes. Textile dyes are also used in dying home textiles, industrial textiles, and many others.
Request for Sample: https://www.reportsanddata.com/sample-enquiry-form/1848
This is the latest report that is inclusive of the current effect of the coronavirus on the market and its forecasted trend. The coronavirus attack on the world economy has impacted all, and thus its impacts are elucidated in-depth in the report for the Textile Dyes market.
Companies considered and profiled in this market study:
Archroma, Tanatex Dyes, Vipul organics Ltd, DyStar Singapore Private Ltd, Zhejiang Runtu Co. Ltd., Jihua Group, S.A Robama, Organic Dyes and Pigments, Huntsman International LLC, and Kiri Industries Ltd, among others.
For the purpose of the study, this Reports and Data have segmented the Global Textile Dyes market on the basis of application, end user and the regional outlook:
Fiber Type Outlook (Volume, Kilo Tons; Revenue, USD Billion; 2016-2026)
· Cotton
· Viscose
· Wool
· Nylon
· Polyester
· Acrylic
· Others
Dye Type Outlook (Volume, Kilo Tons; Revenue, USD Billion; 2016-2026)
· Direct Reactive
· Vat
· Basic
· Acid
· Disperse
· Others
Applications Outlook (Volume, Kilo Tons; Revenue, USD Billion; 2016-2026)
· Apparels
· Home Textile
· Industrial Textile
· Others
Market Segment by Regions, regional analysis covers:
North America (United States, Canada, and Mexico)
Europe (Germany, France, UK, Russia, and Italy)
Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, Korea, India, and Southeast Asia)
South America (Brazil, Argentina, and Colombia)
Middle East and Africa (Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, Nigeria, and South Africa)
Ask for Sample Report at @ https://www.reportsanddata.com/sample-enquiry-form/1848
Table of Contents:
Study Coverage: It includes key manufacturers covered, key market segments, the scope of products offered in the global Textile Dyes market, duration considered, and objectives of the research. Additionally, it segments the market on the basis of product type and application.
Executive Summary: It offers a summary of other key studies, annual growth rate, competitive landscape, driving factors, market trends and issues, and macroscopic indicators.
Production by Region: Here, the report delivers information related to import and export, production, revenue, and key players of all regional markets inspected in the report.
Profile of Manufacturers: Each firm profiled in this segment is investigated by means of SWOT analysis, available products, global production, value, capacity, and other crucial factors.
Highlights the following key factors:
1) Business description-Detailed description of a firm’s operations and business segments.
2) Corporate strategy – Analyst’s summarization of the company’s business strategy.
3) SWOT Analysis – A detailed analysis of the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges.
4) Company history – A company’s evolution, highlighting its key events through the years.
5) Major products and services – A list of flagship products, services, and brands of the company.
6) Key competitors – A list of key competitors of the company.
7) Important locations and subsidiaries – A list and contact details of key locations and subsidiaries of the company.
8) Detailed financial ratios for the past five years – The latest financial ratios derived from annual financial statements released by the company in the last five years.
The growth of this market across the globe is dependent on multiple factors; including consumer base of several Textile Dyes products, inorganic growth models adopted by companies, price volatility of feedstocks, and product innovation, along with their economic prospects in both producer and consumer nations.
Access the Entire Report packed with TOC, Tables and Figures and Outline of Prominent Companies @ https://www.reportsanddata.com/report-detail/textile-dyes-market
Overall, this report provides a clear view of every vital factor of the market without the need to refer to any other research reports or data sources. Our report will equip you with all the strategically vital facts about the past, present, and future of the market.
0 notes
Text
Global Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors Market-Industry Analysis and Forecast (2020-2027)
The global continuous stirred tank reactors market was valued US$ X.38 Bn and is expected to reach X.20 Bn by 2027, at a CAGR of X.45% during a forecast period. Chemical synthesis across the globe is covering 50% of global continuous stirred tank reactors market share.
Market Definition:
The continuous stirred-tank reactor, also termed as, mixed flow reactor or a continuous-flow stirred-tank reactor, is one of the ideal model preferred in environmental and chemical engineering. The reactor model is specifically designed to mix various pharmaceutical material present in different phases such as fluid, gas, solid. A continuous stirred tank reactor encompasses a cylindrical vessel with an agitator. The size of the tank is responsible for the conversion of raw material into a product with the appropriate rate of adding raw material.
The report study has analyzed the revenue impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the sales revenue of market leaders, market followers, and disrupters in the report, and the same is reflected in our analysis.
Market Outlook:
Continuous stirred tank reactors is considered as one of the key equipment for mixing purposes used by the chemical industry. Thirst for the clear water is on another level owing to the reduction in the quantity of drinking water across the globe. CSTR is widely applicable in the treatment of hydrocarbon-rich water hence driving the continuous stirred reactor market expected to show significant growth in the near future. Growth in the chemical industry is high needs theses reactors thus boosting the overall market demand. Advancement in the educational platform is pushing the demand for product needs at an educational level. Investment and initiative by the government to invest in the R & D activities in emerging economies is another reason for the global continuous stirred tank reactor market. Pharmaceutical product manufacturing industries are largely engaged with the product application will as the pharmaceutical sector is witnessing significant growth will boost the reactor demand in near future. Vat application of these reactors in biogas production, fermentation will be an unhindered factor for market growth.
On the contrary, high fabrication cost and presence of substitutes in the market is expected to restraint the market growth in the coming years.
Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors Market Segment analysis:
By application, the pharmaceutical application segment is likely to expand at a constant rate. The same segment is also composed to acquire a share of XX.4% by the end of 2027. Rapid growth in the pharmaceutical and chemical industry in developing economies in the Asia Pacific exceeding the demand for continuous stirred tank reactors and the crucial application of continuous stirred tank reactors is observed in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Another pharmaceutical application of CSTR is hydrogenation of a pharmaceutical intermediate, it is most probably used reactor for extended operation.
Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors Market Regional Analysis:
Regionally, Asia Pacific is expected to dominate the continuous stirred tank reactors market and is expected to grow at a CAGR of XX % during the forecast period. Developing regions like India, China, and Japan are considered major contributors to the continuous stirred tank reactors market growth in the Asia Pacific region. India, China, and Brazil are focusing mainly on improving their pharmaceutical infrastructure and promoting their chemical manufacturing industry, growth in the chemical industry in this region will increase the demand and ultimately driving the continuous stirred tank reactors market size by 2027. In 2019 market size was valued US$ XX Bn in while in India, the market size was valued XX Bn and expected to increase by US$ X.38 Bn in the coming years. Furthermore, the recent COVID-19 pandemic outbreak will negatively hinder market growth in the Asia Pacific region.
North America will also generate several incredible growth openings to the overall market in the coming years though, water treatment, bio-fuels segment in North America is expected to be the key growth driver for the regional market. Furthermore, the global continuous stirred tank reactors market size was valued XX Bn and expected to increase by US$ XX Bn in the coming years.
The objective of the report is to present a comprehensive analysis of the Global Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors Market including all the stakeholders of the industry. The past and current status of the industry with forecasted market size and trends are presented in the report with the analysis of complicated data in simple language. The report covers all the aspects of the industry with a dedicated study of key players that includes market leaders, followers and new entrants. PORTER, SVOR, PESTEL analysis with the potential impact of micro-economic factors of the market have been presented in the report. External as well as internal factors that are supposed to affect the business positively or negatively have been analyzed, which will give a clear futuristic view of the industry to the decision-makers.
The report also helps in understanding Global Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors Market dynamics, structure by analyzing the market segments and project the Global Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors Market size. Clear representation of competitive analysis of key players by Application, price, financial position, Product portfolio, growth strategies, and regional presence in the Global Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors Market make the report investor’s guide.
Scope of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors Market
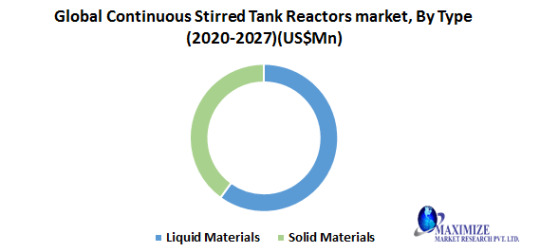
Global Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors market, By Type
• Liquid Materials
• Solid Materials
Global Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors market, By Application
• Academic and Research
• Treatment of Waste water
• Chemical industry
• Pharmaceutical
• Bio-fuels
• Others
Global Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors Market, By Region
• North America
• Europe
• Asia Pacific
• Latin America
• Middle East & Africa
Key Players Operating the Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors Market,
• Weihai Global Chemical Machinery
• Amar Equipments Pvt Ltd
• Nano-Mag Technologies
• PDC Machines
• Nano-Mag Technologies
• Marches Biogas Ltd
• Terralab Laboratory
• Apourtec Ltd
• Asia Biogas Group
• Bioprocess Control Sweden AB
• Terralab Laboratuvar Malzemeleri San. ve Tic. A.S.
• Youngchang Turbotech Co., Ltd
• DPL Valves & Systems Private Limited
About Us:
Maximize Market Research provides B2B and B2C market research on 20,000 high growth emerging technologies & opportunities in Chemical, Healthcare, Pharmaceuticals, Electronics & Communications, Internet of Things, Food and Beverages, Aerospace and Defense and other manufacturing sectors.
Contact info:
Name: Vikas Godage
Organization: MAXIMIZE MARKET RESEARCH PVT. LTD.
Email: [email protected]
Contact: +919607065656 / +919607195908
Website:www.maximizemarketresearch.com
0 notes
Text
RK Industries |Innovation & Precision in Vat Paste Production
RK Industries is a manufacturer of high-quality Vat Paste, renowned for its color & performance in various industries ensuring quality & reliability in every batch

#Vat Paste manufacturer#Vat Paste supplier#Vat Paste#Vat Brown RRD Paste#Vat Black BG Paste#Vat Orange RF Paste#Vat Paste manufacturer in India#Vietnam#Brazil
0 notes
Text
U.S. Bets On Small, Untested Company to Deliver COVID Vaccine
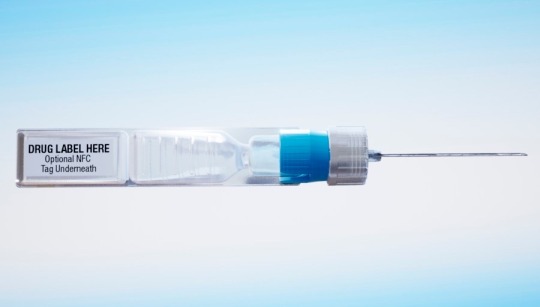
This undated image provided by ApiJect in July 2020 shows a prototype of their "BFS" prefilled syringe. (ApiJect file photo)
— AP | July 10, 2020 | By Martha Mendoza & Juliet Linderman
This story is part of an ongoing investigation by The Associated Press, FRONTLINE, and The Global Reporting Centre that examines the deadly consequences of the fragmented worldwide medical supply chain.
When precious vats of COVID-19 vaccine are finally ready, jabbing the lifesaving solution into the arms of Americans will require hundreds of millions of injections.
As part of its strategy to administer the vaccine as quickly as possible, the Trump administration has agreed to invest more than half a billion in tax dollars in ApiJect Systems America, a young company whose injector is not approved by federal health authorities and that hasn’t yet set up a factory to manufacture the devices.
The commitment to ApiJect dwarfs the other needle orders the government has placed with a major manufacturer and two other small companies.
“The fact of this matter is, it would be crazy for people to just rely on us. I would be the first to say it,” said ApiJect CEO Jay Walker. “We should be America’s backup at this point, but probably not its primary.”
Trump administration officials would not say why they are investing so heavily in ApiJect’s technology. The company has made only about 1,000 prototypes to date, and it’s not clear whether those devices can deliver the vaccines that are currently in development. So far, the leading candidates are using traditional vials to hold the vaccine, and needles and syringes in their clinical trials.
RELUCTANT SUPPLIER
ApiJect founder Marc Koska never intended to vaccinate the United States. For the past five years, he’s been working on his lifetime mission of creating an ultra low-cost prefilled syringe that would reduce the need to reuse needles in the developing world.
Instead, the company’s biggest customer has become the U.S. government.
ApiJect received a no-bid contract earlier this year from the Defense Department under an exception for “unusual and compelling urgency.” Authorities said the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, tasked with buying the necessary supplies, “does not have the resources or capacity to conduct procurements necessary to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic,” according to a June 5 military document.
The government promised ApiJect $138 million to produce 100 million of its devices by the end of the year, which will require the company to retrofit new manufacturing lines in existing factories. And it’s offered another $456 million as part of a public-private partnership contract to bring online several new factories to make another 500 million devices to “contain the pandemic spread to minimize the loss of life and impact to the United States economy,” said the document.
These amounts are more than double the per-syringe cost the government is paying other companies for the work.
ApiJect first appeared on the U.S. government’s radar almost two years ago when the company piqued the interest of Admiral Brett P. Giroir, HHS’s assistant secretary for health, at the World Health Organization’s Global Conference on Primary Health Care in Astana, Kazakhstan.
Koska said Giroir was “blown away” by their technology and told them that if a pandemic hit, the strategic national stockpile was going to need a very fast way to get injections filled with vaccines or therapeutics and ready to deliver.
According to Walker, the CEO, ApiJect wasn’t interested in a federal contract — they were aiming to change the developing world with quick, inexpensive injection devices that could save millions of lives.
But at the conference, Walker found himself at a table with Giroir at a luncheon, just two seats apart. The admiral was fascinated by the low-cost injection technology, Walker said, and when Walker showed him the prototype that he always carries in his pocket, Giroir asked how they plan to do this in the U.S.
Walker said he told the admiral that the company wasn’t planning to operate in the U.S. but was struck by Giroir’s enthusiasm.
“He was the first person, if not the only person at the event, who understood the revolutionary nature of this platform,” Walker recalled in an interview with AP. “And he said, ‘Wow this is amazing. You need to do this in the U.S.’”
Walker continued to resist, he said, but Giroir — who is also a doctor specializing in pediatric critical care — “wasn’t big on taking no for an answer,” Walker said.
At Giroir’s urging they presented the prototype injector to U.S. officials. HHS declined to make agency officials available for interviews.
It wasn’t until later, when Walker was introduced by a friend to Col. Matthew Hepburn at the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, that a plan for ApiJect to work in the United States began to take shape, he said.
HHS Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response Robert Kadlec approved a $10 million contract for ApiJect for research and development in January 2020, according to a document in the federal procurement data system. The company was responsible for securing private investments to create new production lines where the devices would be made over three to five years.
When the pandemic emerged weeks later, officials sounded the alarm about a potential shortage of needles and syringes to deliver a vaccine if and when one became available.
The federal Strategic National Stockpile of medical supplies had only 15 million syringes, according to Dr. Rick Bright, who later left his position at Health and Human Services and filed a whistleblower complaint.
Bright warned White House trade adviser Peter Navarro and his HHS colleagues of a looming needle shortfall, according to a series of emails disclosed in his complaint.
“We are hearing rumblings about the US inventory of needles and syringes … heading to other countries,” wrote Bright. “There is limited inventory in the supply chain, it could take 2+ years to make enough to satisfy the U.S. vaccine needs.”
Navarro said the U.S. would need 850 million needles.
“We may find ourselves in a situation where we have enough vaccine but no way to deliver all of it,” he said in a February memo to the White House coronavirus task force.
He recommended the task force “direct HHS BARDA to initiate a program to identify all alternate vaccine delivery methods and ramp up production.“ BARDA is the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority within HHS.
Suddenly ApiJect’s 5-year plan to mass produce its devices became a sprint measured in months with a new $138 million contract, announced in May, to produce 100 million devices by year’s end.
Jefferies Financial Group is acting as the leader of the public-private partnership with HHS and invested $10 million to help ApiJect build surge production facilities in March. The company said it would try to raise up to $1 billion more. There have been no additional announcements of funding.
Walker said due to nondisclosure agreements with both the government and investors, the company is unable to say what private funding they’ve secured so far.
OPERATION WARP SPEED
On a warm mid-May day in the White House Rose Garden, President Donald Trump introduced “a massive scientific, industrial and logistical endeavor” dubbed Operation Warp Speed.
The idea, he said, was to be ready to distribute a COVID-19 vaccine as soon as it was developed.
“We must not be caught short on our capacity to deliver emergency drugs to Americans in need,” said HHS Secretary Alex Azar.
An estimated 700 million injections may be needed to inoculate the nation — at least two shots for every person, according to the military document.
In early May, the government put in two orders, to Retractable Technologies in Little Elm, Texas, and Marathon Medical in Aurora, Colorado, totaling 320 million needles and syringes.
Later in May, the government announced plans for ApiJect to manufacture more than 500 million all-in-one devices that would come pre-loaded with the vaccine.
On Wednesday, the largest domestic manufacturer of needles and syringes, Becton Dickinson, announced the first U.S. order of $11.7 million for 50 million needles and syringes by the end of this year. It plans to ramp up manufacturing over the next year.
And earlier this month Retractable entered into a second contract with the government, this one for $53 million meant to boost domestic manufacturing.
Together that sounds like enough injection devices.
But Retractable, which was worried enough about its financial future that earlier this year it received a $1.36 million loan from the Paycheck Protection Program, has been doing about 80% of its manufacturing in China. And Marathon is a medical supply distributor, and there is no indication on its web site that it manufactures needles and syringes at all. The company did not respond to repeated requests for comment.
Despite the race to replenish the domestic needle and syringe supply, about 400 shipping containers of syringes have left the U.S. for countries including Germany, Colombia, Australia, Brazil and Italy this year, according to Panjiva Inc., a service that independently tracks global trade. That’s the same, on average, as syringe exports over the past five years.
Experts acknowledge that a mass vaccination campaign is going to be complicated.
“There are a lot of moving parts to this,” said Dr. Bruce Gellin, the Sabin Vaccine Institute’s president of global immunization.
Darin Zehrung, who studied medical devices at PATH, a nonprofit advocating for health equity, said it’s wise to invest in new injection technologies. But that only works if there are plenty of basic syringes and needles stocked up.
“Hedging bets is the best approach, but plan for the worst case scenario and hope for the best case scenario,” said Zehrung.
AWAITING APPROVAL
ApiJect’s devices are self-contained, with soft plastic blisters that are squeezed, like a nose spray or eye drop, to push the vaccine through an attached needle and into the patient.
The device includes a little computer chip — like the ones in credit cards — that can transmit information about the drug, dose, location and time of administration.
Other injection devices Koska designed have been used in the developing world, but this ApiJect technology has not.
The company said they have started discussions with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to review the device on a priority basis while the company moves ahead fitting factories to make their injectors. The agency wouldn’t confirm this, citing its policy against discussing products involved in clinical trials.
Testing different vaccine candidates in the ApiJect devices will be critical before injecting the public.
Plastic could interact differently with the liquid than the glass vials currently used in trials, experts say. And there are strict temperature requirements. ApiJect’s planned process is to pour vaccine doses into the warm plastic blisters as they come off the production line, the company says. ApiJect says they can instantly cool the devices as they are made.
Walker, the ApiJect CEO, who founded the online travel agency Priceline, acknowledges that the government’s decision to rely on “an emergency plan of refitting established pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities is risky. But we feel good about it.”
NO COMMENT
The Associated Press asked the Health and Human Services department over many weeks to explain the government’s approach. The agency didn’t allow an official to speak on the record for this story.
A senior administration official, speaking on condition of anonymity because the agency declined to allow him to identified by name, told AP he wasn’t familiar with ApiJect or the contract. But he said the government was buying a range of devices to deliver the vaccine because they don’t know what they need. And, he said, the Trump administration is looking to boost domestic manufacturing.
When AP reached out directly to Trump’s vaccine czar, Moncef Slaoui, to discuss the new technology, a spokesperson said the query was inappropriate.
“If this continues, we will make no one else available either,” Natalie Baldassarre, a special assistant at HHS, wrote in an email.
Last week, HHS Assistant Secretary of Public Affairs Michael Caputo wrote that the agency has “lost interest in assisting your story” and offered no further comment.
— Mendoza reported from San Francisco. Linderman reported from Baltimore. Lauran Neergaard and Stephen Braun in Washington contributed.
0 notes
Text
Korea Sees Club Cases; Shanghai Disneyland Reopens: Virus Update
(Bloomberg) — U.S. Vice President Mike Pence self-isolated this weekend following a positive coronavirus test by his press secretary, while three members of the White House task force are in quarantine.
Global cases topped 4 million, though the situation improved in Europe, with France and Italy among countries reporting the lowest fatalities since March. The U.K. outlined plans to ease a lockdown.
South Korea is seeing a flare-up in cases tied to nightclubs in Seoul. China put a city near the North Korea border under lockdown due to an increase in infections, raising more questions about an outbreak in the isolated country. Shanghai Disneyland reopened, in one of the largest tests of whether mass gatherings can take place safely.
Key Developments:
Virus Tracker: Cases top 4.1 million; deaths exceed 282,000
Trump urges U.S. back to work while combating in-house outbreak
What we don’t know about coronavirus origins might kill us
Confidence called key for post-Covid economy
India reopens economy but millions of workers stay home
Chinese city in northeast closed as infections rise
Subscribe to a daily update on the virus from Bloomberg’s Prognosis team here. Click VRUS on the terminal for news and data on the coronavirus. See this week’s top stories from QuickTake here.
Outbreak Near North Korea Border Raises Questions (11:08 a.m. HK)
China put a city near the North Korea border under lockdown due to an increase in coronavirus infections, raising more questions about an outbreak in the isolated country.
Chinese authorities banned all non-essential transportation in the city of Shulan in the northeastern province of Jilin, while residential compounds and villages were closed, official China Central Television reported Sunday. The city raised its virus threat alert level to high risk from medium, Jilin province said.
North Korea has yet to confirm any Covid-19 infections. But the U.S. military said it suspects North Korea has cases, and Kim Jong Un’s regime has accepted help from other nations to fight the virus.
China Car-Sales Rebound Has Legs, Group Says (10:58 a.m. HK)
A recovery in car sales is set to continue in China as government policies aimed at reviving demand following the coronavirus outbreak are gaining traction, an industry group predicted. A recent quick rebound in demand suggests a V-shaped recovery has been established, China Passenger Car Association said in a statement. Car retail sales fell at a slower pace of 5.5% in April, following a 40% drop in March and a 79% plunge in February, PCA said.
Shanghai Disneyland Reopens With Mandatory Masks (10:49 a.m. HK)
Shanghai Disneyland reopened after an almost four-month shutdown, in one of the largest test cases yet of whether mass gatherings can take place safely amid the coronavirus pandemic.
Disney said it is limiting access to the Shanghai park to a fifth of normal capacity during the initial reopening phase. Masks are mandatory, and guests have to pass through body temperature checks and show that their health status has been confirmed using a smartphone app for tracking infected persons.
South Korea Says Club-Linked Cases Increase to 79 (10:21 a.m. HK)
South Korea is seeing a sudden increase in cases tied to nightclubs in Seoul, raising concerns over a potential second wave of infections.
The total number of cases linked to nightclubs in Itaewon in Seoul increased to 79 as of early Monday, Yoon Tae-ho, an official for South Korea’s health ministry, said. The city has secured a list of 5,517 people who visited the clubs between April 24 and May 6, but is unable to contact about 3,000.
Seoul Mayor Park Won-soon on Saturday ordered the closing of all nightclubs and other nightlife establishments. South Korea has been able to control the virus spread without having to take severe measures such as a lockdown, relying instead on massive testing and tracing.
Saudi Arabia to Cut Spending, Triple VAT (10 a.m. HK)
Saudi Arabia ordered government spending cuts and austerity measures for about $26.6 billion and a tripling of the value-added tax to alleviate the impact of the pandemic. Finance minister Mohammed Al-Jadaan said VAT will be increased to 15% from July 1, according to the official Saudi Press Agency.
Australia’s Victoria State to Ease Lockdown Restrictions (9:44 a.m. HK)
Australia’s second-most populous state will allow as many as five visitors in homes, and gatherings of up to 10 people outside from late Tuesday as it moves to ease coronavirus lockdown restrictions.
Victoria Premier Daniel Andrews told reporters in Melbourne the state would also allow weddings to have 10 guests and up to 20 people will be able to attend funerals held indoors and up to 30 if they’re outdoors. The announcement follows Prime Minister Scott Morrison’s plan to reopen Australia’s economy by July in three phases.
Bolsonaro Criticizes Lockdown as Brazil Becomes Hotspot (9:18 a.m.)
Brazilian President Jair Bolsonaro criticized lockdown measures by governors even as the nation turned into a global epicenter of the coronavirus outbreak. The Health Ministry on Sunday reported 162,699 total cases of Covid-19 and 11,123 deaths, among the world’s highest.
“The head of household has to stay at home going hungry with their family,” Bolsonaro said Sunday in a tweet attacking the lockdown in Maranhao state. “Millions already feel like they are living in Venezuela.”
The president said he plans on Monday to declare more jobs as essential in an effort to get Brazilians back to work.
Japan Seen Removing Regions From State of Emergency (8:51 a.m. HK)
Japan plans to remove 34 prefectures from the state of emergency designation on May 14, Yomiuri reported, citing several unidentified government officials. Many of those areas haven’t seen new coronavirus cases recently and strains on their medical systems are easing. Cases in Tokyo and Osaka have slowed, but it is believed to be too early to remove the designation for those cities.
Pence in Self-Isolation After Aide Tests Positive (5:45 p.m. NY)
Vice President Mike Pence stayed away from the White House this weekend after an aide was diagnosed with coronavirus on Friday, according to three people familiar with the situation.
Pence skipped a meeting Saturday with President Donald Trump and top military officials. A spokesman for Pence said the vice president would return to the White House on Monday.
“Vice President Pence will continue to follow the advice of the White House Medical Unit and is not in quarantine,” O’Malley said in a statement. “Additionally, Vice President Pence has tested negative every single day.”
Pence’s press secretary, Katie Miller, tested positive on Friday. Miller is the primary spokeswoman for the White House coronavirus task force, which Pence leads.
Two members of the group — the heads of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention — are in quarantine after coming into contact with another White House staff member who tested positive. Task force member Anthony Fauci, the top U.S. infectious disease expert, said he would practice what he called a “modified” quarantine.
South Korea Sends Masks to U.S. (5:20 p.m. NY)
South Korea sent 2 million face masks to the U.S. for use by medical workers following a telephone call in March between presidents Trump and Moon, the foreign ministry said. The decision was made after studying South Korea’s mask supply, according to the statement. The equipment should arrive in the U.S. on Monday.
Ex-FDA Chief Boosts Quidel Antigen Test (4:30 p.m. NY)
U.S. approval of San Diego-based Quidel Corp.’s new antigen test to rapidly screen people for Covid-19 “is a real game-changer,” former Food and Drug Administration head Scott Gottlieb said on CBS’s “Face the Nation.”
“It’s a very rapid test that could be used in a doctor’s office,” Gottlieb said. Doctors already have about 40,000 machines in their offices that are used to test for strep throat and flu, he said.
Each test may cost about $5, with results ready in minutes, said Gottlieb, a special partner at New Enterprise Associates, a venture capital firm that invests in the health-care and biotech sectors. Deborah Birx of the White House coronavirus task force said in April a “breakthrough innovation” in antigen testing is needed to speed reopening of the U.S. economy.
U.S. Cases Rise 1.8%, Below One-Week Average (4 p.m. NY)
U.S. cases increased 1.8% to 1.32 million from a day earlier, according to data collected by Johns Hopkins University and Bloomberg News. The increase was below the 2.1% daily average of the past week. Total deaths rose 1.1% to 79,180.
N.Y. to Release Opening Details Monday (3:10 p.m. NY)
New York reported the fewest new deaths — 207 — since the end of March and other indicators began to show the outbreak nearing the level of the starting point for what Governor Andrew Cuomo called “this hellish journey.”
He said he would release on Monday more details on how New York would begin to reopen — and confirmed that some areas upstate may be ready for a slow resumption after the lockdown ends May 15.
Cuomo gave no indication that New York City or the surrounding areas are anywhere near being able to reopen.
Read the full story.
J&J Plans for 1 Billion Vaccines in 2021 (2:30 p.m. NY)
Drug maker Johnson & Johnson will begin clinical trials on a Covid-19 vaccine in September and plans to produce about 1 billion doses in 2021, Chief Scientific Officer Paul Stoffels said on ABC’s “This Week.”
“We are upscaling manufacturing and we start production later in the year,” he said. “We will have some vaccine available this year but it all depends on the authorities, the FDA and others, to decide whether it can be used earlier, before clear efficacy data are available.”
Regeneron Pharmaceutics President George Yancopoulos said an antibody treatment should go into clinical trials in June, with first data in a month or two. “It might be possible that if all goes well hundreds of thousands of doses of this could be available by the end of the summer,” he said on the same broadcast.
U.K. Outlines Plan to Reopen (2:15 p.m. NY)
Boris Johnson set out the “first careful steps” to lift the U.K.’s lockdown and restart the economy, offering a “conditional plan” to get more people back to work while controlling the virus’s spread.
With no immediate end to the lockdown, the prime minister announced looser restrictions on movement from Wednesday, starting with unlimited outdoor leisure time for sports such as golf and tennis, and allowing people to drive to parks and beaches in England.
Johnson set a goal for primary schools to begin to reopen for some children on June 1, and to restart the hospitality industry and other public places in July. Pubs are likely to stay closed longer. He encouraged commuters to walk, drive or cycle to work rather than ride public transport, where social distancing rules will apply.
France Has Fewest Deaths Since mid-March (12:30 P.M. NY)
Deaths in France rose at slowest pace since the nation entered a lockdown on March 16. The number of deaths rose by 70 to 26,380, according to data from France’s public health agency.
Italy Deaths, Cases Lowest Since Early March (12:02 p.m. NY)
Italy registered the lowest number of new cases and fatalities since early March — roughly when the country’s lockdown began — as Prime Minister Giuseppe Conte said he may take the next step in easing a national lockdown earlier than planned.
Conte, under pressure from coalition allies, regional and business leaders as well as public opinion after two months of containment measures, told newspaper Corriere della Sera that bars, restaurants and barbers could be allowed to reopen before June 1, the date previously set by the government. Shops are due to reopen May 18.
Civil protection authorities reported 802 cases for the 24-hour period — the fewest since March 6 — compared with 1,083 a day earlier. Confirmed cases now total 219,070. Daily fatalities fell to 165 — the fewest since March 9 — from 194 on Saturday, with a total of 30,560.
U.K. Reports Fewest Deaths Since End of March (11:27 a.m. NY)
The U.K. reported the fewest deaths since March 29 at 269. That brings total fatalities to 31,855, according to health department figures on Sunday. Prime Minister Boris Johnson is expected to make only limited changes to the lockdown when he speaks to the nation.
Scottish First Minister Nicola Sturgeon said the new slogan to “stay alert” was “vague and imprecise,” and said her administration would be sticking to its guidance for people to stay at home.
The post Korea Sees Club Cases; Shanghai Disneyland Reopens: Virus Update appeared first on Businessliveme.com.
from WordPress https://ift.tt/2YQP4uF
via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
This actually could be the year for emerging markets. Here are the ones that could outperform and the ones to avoid
Global stocks underperformed Wall Street in 2018 as escalations in the U.S.-China trade war dragged down markets around the world, with the MSCI Emerging Markets Index ending the year down more than 16 per cent and the MSCI World Index off more than 10 per cent. While many economists are projecting global growth to slow further in 2019 and 2020, some firms expect emerging economies to get back on track and outperform the U.S. — if China and the U.S. reach a trade deal. As always, the global picture is nuanced, so the Financial Post spoke with AGF Investments vice-president Regina Chi, who manages the firm’s emerging markets fund, and Fiera Capital global asset allocation portfolio manager Nicolas Vaugeois, who oversees the multi-strategy income fund, about the countries they think are poised to be winners and losers for 2019.
The good
Brazil
The Brazilian market boomed with the election of far-right President Jair Bolsonaro and Vaugeois sees continued opportunities for investors in 2019. Vaugeois is betting on a spike in commodities prices — both in minerals and oil — next year. About 17 per cent of Brazil’s economy is weighted towards materials. If prices of iron ore, which make up 7.4 per cent of Brazilian exports increase, investors could capitalize by buying mining stocks. A spike in oil prices could have a similar impact on the country’s oil producers, Vaugeois said. Brent crude prices are hovering below US$60, but if they increase to between US$60 and US$65, oil producer Petrobras would likely be the main benefactor, he said.
If you thought this year was bad for the loonie, how does 70 cents sound?
Ten stocks for 2019: What the pros are picking to outperform this year
Outlook 2019: Here’s where the experts think the TSX will end up one year from now
China
China’s trade war with the U.S. is expected to reach an amicable conclusion in 2019 and that would result in a rally for its market, both Chi and Vaugeois agreed. The government has worked to earn back the confidence of investors by stimulating the economy, offering cuts to VAT, corporate and personal taxes and by investing US$900 billion in a new infrastructure program which encompasses several light rail and subway projects. Chi recommends CRRC Corporation Limited, the country’s largest locomotive and light rail train manufacturer, as it stands to benefit most from these projects. Should the trade war drag on, the People’s Bank of China has shown a willingness to offer massive interest rate cuts that may be enough to convince investors to re-enter the market, she said.
Thailand
Thailand has been under military rule for the past five years but its citizens are set to go to the polls in February to elect a new government. A democratically-elected government should immediately bring back skittish investors and attract foreign investments, Chi said. The country is rapidly moving away from being export-dependent and is instead turning its focus inward with the development of its Eastern Economic Corridor — an ambitious $50 billion project that aims to transform 13,000 kilometres of land over three provinces into a hub for several tech-based industries, including robotics and next-gen automotive. The junta has already laid down the groundwork for the EEC with land ownership and tax laws, but “the momentum is really going to take off after the election,” Chi said. The development of the corridor will result in significant infrastructure projects and the banking sector is “the best way to play infrastructure lending through corporate loans,” said Chi, recommending Kasikornbank.
United Arab Emirates
After years of suffering from steep declines in the price of Brent crude, which fell to around US$30 in 2015, the UAE was able to gain some momentum in 2018 as prices rebounded, making it once again an attractive target for investors. With a market trading at a projected price-earnings multiple of just 8.5 times for 2019, it is a remarkably cheap target, too, Chi said. If investors are buying in here, they should be doing so in a way that gives them exposure to the country’s strengthening recovery which will see GDP growth hit 3.3 per cent in 2019 compared to less than one per cent in 2018. The best way to do that is to once again look to the banking sector, said Chi, who recommends the First Abu Dhabi Bank. Such a move would also give investors the ability to capitalize on the country’s improvement in the fixed income market due to a widening spread for loans, she said.
The bad
Argentina
The Argentine peso lost 51 per cent of its value in comparison to the U.S. dollar in 2018, making it the worst performing currency of the year and that should be enough to convince investors to stay at arm’s-length. As part of a US$56 billion bailout provided by the International Monetary Fund, a currency band was placed on Argentina that will see it trade between 36 pesos and 46 pesos per dollar. “This proves the point that country matters because you could have a good high-quality company in Argentina, but you have a currency down 50 per cent,” Chi said. “That stock would be down 50 per cent just due to the currency exposure.” Vaugeois, however, said Argentina could be a “good surprise” for fixed-income investors, as the three-year government bonds are yielding a healthy 9.5 per cent.
India
While many investors are high on India because its GDP growth is expected to balloon to 7.3 per cent in 2019 from 6.7 per cent in 2018, Chi isn’t convinced. Like the UAE, India’s performance is tied to oil prices and Chi suggests India is “very lucky” that Brent crude prices are hovering around US$57 because they’re net importers. If prices rise, their luck may run out, she said. For Prime Minister Narendra Modi, that already appears to be the case as his BJP party lost three states in state elections. With a federal election upcoming in 2019, Modi is losing momentum and if he loses it would bring uncertainty and disruption to the markets. The Dec. 10 resignation of central banker Urjit Patel for “personal reasons” is another factor clouding the outlook there.
Mexico
The Mexican market has been one of the worst global performers this year and newly-elected President Andres Manuel Lopez Obrador isn’t helping. The left-wing politician campaigned on business-friendly views, pushing goals of stabilizing the economy and attracting foreign investment as his advisors met with fund managers. Post-election, his views have changed rapidly, and he’s made it clear that Mexico’s citizens, not the market, are his main concern. “He only cares for his people, especially the poor, which is great but it is causing disruption in the markets,” Chi said. Lopez Obrador cancelled a US$13 billion airport project in Mexico City in October after holding referendums that did not have wide participation. In announcing the cancellation, he said that Mexico was bankrupt, which only served to further spook investors. Under fire, the president has promised to commit to the safety of future investments and to create conditions for good returns, but Chi is remaining pessimistic until she sees action.
Russia
Investors in Russia have suffered under the weight of international sanctions, and a further incident in the Black Sea in November, in which Russia shot at and seized three Ukrainian ships and their crews, may only make things worse. For Fiera’s Vaugeois, the risk that further sanctions could derail both the equities and fixed-income markets, is enough to make Russia an unappealing target for investment. The banking sector, in particular, is at risk given the U.S. Treasury Department’s history of targeting banks as recently as August. Further sanctions, Vaugeois said, would likely also result in sharp declines for investors holding Russian ruble treasury bonds, which declined 65 per cent in value during the Ukraine crisis in 2014.
from Financial Post http://bit.ly/2SAAj9q
via IFTTT Blogger Mortgage
Tumblr Mortgage
Evernote Mortgage
Wordpress Mortgage
href="https://www.diigo.com/user/gelsi11">Diigo Mortgage
0 notes
Text
Rising Pollution Levels and Implementation of Environmental Laws Has Increased Investment in High Performance Eco-Friendly Dyes Globally: Ken Research

Growing awareness among end product users about the toxic nature of synthetic dye and the pollution caused in their manufacturing process will propel the dye manufacturing companies to develop newer dyes that are environment friendly and possess enhanced properties. The rising demand of dyes from the textile, leather and printing ink industry has been thekey factors driving growth in the Global dyes market.
The report titled “Global Dyes Market Outlook to 2022 - By Type (Reactive Dyes, Disperse Dyes, Direct Dyes, Vat Dyes, Acid Dyes and Others) and By Application (Textiles, Leather, Paper, Printing Inks and Others)” by Ken Research suggested a growth at a five year CAGRof more than 5%in terms of revenue in Global dyes market during the period 2017-2022.
In recent years the dyes manufacturing has witnessed a dimensional shift from a product that is widely used and manufactured by thousands of small, medium and large scale manufacturers, to a product which has faced the regulations of environmental agencies, food safety agencies and critical view of the end users about its toxic nature across the globe. Numerous countries around the world have introduced several regulations to control pollution caused during the manufacturing of synthetic dyes. The European Union (EU) has introduced the REACH regulations that prevent the manufacturing and trade of environmentally toxic substances with the EU countries. The growing pollution has also forced countries like China; which usually has relaxed norms for manufacturing industrial products, to introduce stricter regulations. Paradigm shifts like this have completely changed the face of the dye industry in the past few years. Global manufacturers having their base in American and European countries are looking towards APAC countries; specially India and China for setting up their dye manufacturing plants owing to the availability of cheap and skilled labour as well as relaxed environmental regulations.
China and India in recent years have emerged as the global leaders both in terms of manufacturing and consumption of dyestuff. The strong local demand from end user industries like textile, leather, printing ink, paper and other have supported the dye market in China and India. Other leading countries in dye production are US, Brazil, UK and Germany.
Global leaders in dye manufacturing like Huntsman, Kiri, Atul, Zhejiang Longsheng Group, Zhejiang Jihua Group, BASF, Lanxess, Dystar and others have invested heavily in the past few years for developing dyes that are environmentally friendly and have better properties. These companies have updated their operating strategies to include research and development of new products and technological transformation of old products, eliminate heavy pollution and high energy consumption products, improvement of production processes, product quality, and promotion of energy conservation and consumption reduction.
Keywords:-
Global Dyes Market Size
APAC Dyes Industry
America Dyes Industry
Europe Dyes Industry
China Dyes Sales Volume
India Dyes Production
US Dyes Industry
Brazil Dyes Industry
UK Dyes Industry
Germany Dyes Market
Future Sales Dyes Global
For more information, refer to the link below:
https://www.kenresearch.com/metal-mining-and-chemicals/chemicals/global-dyes-market/157430-101.html
Related Reports:-
https://www.kenresearch.com/metal-mining-and-chemicals/chemicals/china-dyes-market/151501-101.html
https://www.kenresearch.com/metal-mining-and-chemicals/chemicals/china-organic-pigments-market/152236-101.html
https://www.kenresearch.com/metal-mining-and-chemicals/chemicals/india-dyes-market/149540-101.html
Contact Us:
Ken Research
Ankur Gupta, Head Marketing & Communications
[email protected]
+91-9015378249
0 notes
Photo

#world #economy, smooth sailing!
ECONOMIC and political cycles have a habit of being out of sync. Just ask George Bush senior, who lost the presidential election in 1992 because voters blamed him for the recent recession. Or Chancellor Gerhard Schröder, booted out by German voters in 2005 after imposing painful reforms, only to see Angela Merkel reap the rewards.
Today, almost ten years after the most severe financial crisis since the Depression, a broad-based economic upswing is at last under way (see article). In America, Europe, Asia and the emerging markets, for the first time since a brief rebound in 2010, all the burners are firing at once.
But the political mood is sour. A populist rebellion, nurtured by years of sluggish growth, is still spreading. Globalisation is out of favour. An economic nationalist sits in the White House. This week all eyes were on Dutch elections featuring Geert Wilders, a Dutch Islamophobic ideologue (see article), just one of many European malcontents.
This dissonance is dangerous. If populist politicians win credit for a more buoyant economy, their policies will gain credence, with potentially devastating effects. As a long-awaited upswing lifts spirits and spreads confidence, the big question is: what lies behind it?
All together now
The past decade has been marked by false dawns, in which optimism at the start of a year has been undone—whether by the euro crisis, wobbles in emerging markets, the collapse of the oil price or fears of a meltdown in China. America’s economy has kept growing, but always into a headwind (see article). A year ago, the Federal Reserve had expected to raise interest rates four times in 2016. Global frailties put paid to that.
Now things are different. This week the Fed raised rates for the second time in three months—thanks partly to the vigour of the American economy, but also because of growth everywhere else. Fears about Chinese overcapacity, and of a yuan devaluation, have receded. In February factory-gate inflation was close to a nine-year high. In Japan in the fourth quarter capital expenditure grew at its fastest rate in three years. The euro area has been gathering speed since 2015. The European Commission’s economic-sentiment index is at its highest since 2011; euro-zone unemployment is at its lowest since 2009.
The bellwethers of global activity look sprightly, too. In February South Korea, a proxy for world trade, notched up export growth above 20%. Taiwanese manufacturers have posted 12 consecutive months of expansion. Even in places inured to recession the worst is over. The Brazilian economy has been shrinking for eight quarters but, with inflation expectations tamed, interest rates are now falling. Brazil and Russia are likely to add to global GDP this year, not subtract from it. The Institute of International Finance reckons that in January the developing world hit its fastest monthly rate of growth since 2011.
This is not to say the world economy is back to normal. Oil prices fell by 10% in the week to March 15th on renewed fears of oversupply; a sustained fall would hurt the economies of producers more than it would benefit consumers. China’s build-up of debt is of enduring concern. Productivity growth in the rich world remains weak. Outside America, wages are still growing slowly. And in America, surging business confidence has yet to translate into surging investment.
Entrenching the recovery calls for a delicate balancing-act. As inflation expectations rise, central banks will have to weigh the pressure to tighten policy against the risk that, if they go too fast, bond markets and borrowers will suffer. Europe is especially vulnerable, because the European Central Bank is reaching the legal limits of the bond-buying programme it has used to keep money cheap in weak economies.
The biggest risk, though, is the lessons politicians draw. Donald Trump is singing his own praises after good job and confidence numbers. It is true that the stockmarket and business sentiment have been fired up by promises of deregulation and a fiscal boost. But Mr Trump’s claims to have magically jump-started job creation are sheer braggadocio. The American economy has added jobs for 77 months in a row.
No Keynes, no gains
Most important, the upswing has nothing to do with Mr Trump’s “America First” economic nationalism. If anything, the global upswing vindicates the experts that today’s populists often decry. Economists have long argued that recoveries from financial crashes take a long time: research into 100 banking crises by Carmen Reinhart and Kenneth Rogoff of Harvard University suggests that, on average, incomes get back to pre-crisis levels only after eight long years. Most economists also argue that the best way to recover after a debt crisis is to clean up balance-sheets quickly, keep monetary policy loose and apply fiscal stimulus wherever prudently possible.
Today’s recovery validates that prescription. The Fed pinned interest rates to the floor until full employment was in sight. The ECB’s bond-buying programme has kept borrowing costs in crisis-prone countries tolerable, though Europe’s misplaced emphasis on austerity, recently relaxed, made the job harder. In Japan rises in VAT have scuppered previous recoveries; this time the government wisely deferred an increase until at least 2019.
The tussle over who created the recovery is about more than bragging rights. An endorsement for populist economics would favour insurgent parties in countries like France, where the far-right Marine Le Pen is standing for president. It would also favour the wrong policies. Mr Trump’s proposed tax cuts would pump up the economy that now least needs support—and complicate the Fed’s task. Fortified by misplaced belief in their own world view, the administration’s protectionists might urge Mr Trump to rip up the infrastructure of globalisation (bypassing the World Trade Organisation in pursuing grievances against China, say), risking a trade war. A fiscal splurge at home and a stronger dollar would widen America’s trade deficit, which may strengthen their hand. Populists deserve no credit for the upsurge. But they could yet snuff it out.
(via tEc)
0 notes