#blazescompendiumentry
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Blaze's Compendium Entry #9:
Turbo Granny

Warning: Faith and religion are important real life topics, that tackles the culture and way of life of millions of real life people. It is a cultural expression, and must be respected by all means. Here, we use a video-game ( some times) and other media series only to ignite the flame of learning about the matter, using its art when well depicted, but we do this with all due respect to the cultures we talk here, grounded by real life sources, cultures and people. And i mean this with respect. Hope you all enjoy.
Turbo Granny is a somewhat modern Yokai that has been popularized lately by pop culture. In 2024, Turbo Granny has made a resurgence due to the hit anime: Dandadan and her apparition in Shin Megami Tensei V: Vengeance, both happening in the spam of just 4 moths.
But before that she also made cameos in the anime Mob Psycho circa 2018, Hell Teacher in 1997 and was first introduced as a playable monster in Shin Megami Tensei Devil Summoner Soul Hackers in 1997. She was absent from the franchise for some decades, upon her return in 2022 for Soul Hackers 2, which coincided with her debut in the -at the time- new manga Dandadan.
Despite that, its origins are so obscure, that I was enticed to dig deep into the lore of this monster and understand if it is even a real urban legend. And here is what i found.
First information that we have about her is that she hails from the Hyogo region in Japan. Supposedly. Hyogo is a southern Region of Japan, between Okayama and Kyoto. Capital is Kobe. So i started by researching about the area, to see if anything about the Region itself has any connections to the particular legend, but did not found anything. The biggest news on the region in the timeline we are looking after was a big earthquake in 1995.
Both western and Japanese Wikipedia pages for this region did not include any mention about Turbo Granny. SMT VV compendium mentions the specific location: MT. Rokko, that is located in the metropolitan area of Kobe. Could no find anything about Turbo Granny on this specific location as well, at the western web.
Addendum: I know that blog posts are hardly scientific accepted sources. However, since we are dealing with an urban legend that survived via word of mouth, this kind of data gathering is the most optimal.
However, using the key words: 六甲山 妖怪 (Mount Rokko Yokai) I could find more content than before. This particular blog mentions some variations of the Yokai, like the way she is called 100km/h hag in Hokkaido, for example. However it lacked any sources and seems to have more of a comedic purpose. Other sites specifically mentions the highways around Mt. Rokko and their tunnels as specific apparitions spots for this creature, but then again no source of whatsoever.


Highway and tunnel at Mt. Rokko, supposedly where the Turbo Granny legend began.
Other Japan web content, showed me the Yokai has been discussed in forums lately, like this one that mentions its resurgence in pop culture as of lately.
But it also mentioned something about the legend being from the Edo period, that could run faster than a horse. And the user speculates that the modern take evolved from there, when cars were introduced in Japan. They, however, provides no source for this information. (Hold this information with yourself for now)
A common thread in all discussions online about this particular monster, be it on Japanese forums, or blog posts, are the outcomes the encounter with Turbo Granny can lead to. From what I could gather, those are:
1- Nothing happens, the granny just scares you. 2-if she passes your car, you get a curse 3- if you passes her, your car will break down completely in less than a week. (Terrifying)
They also speculate that this legend could be from 2ch, which brings us to the first myth about this legend, it did not in fact originated on 2ch! Since the SMT game Soul Hackers, from 1997. 2ch was created in 1999.
But if you keep going through the Japanese web enough, you find more blog posts talking about this Yokai. For example, this other one.
That mentioned the Turbo Granny, but divided in categories. The blog mentioned that this guy called Toshiro Yamaguchi described a version called 60km/h hag that could just run at the max speed of 60 km/h. The Turbo Granny we know can reach up to 100 km/h. Other blogs mentions 140 km/h or as fastest as the target.
This also became a common thread in all registers of this Yokai.
Still in Japanese web, I forgot to check Japanese wikipedia. It got some interesting results, as some interesting variations, and some lore. But only contained one source: This book:
口敏太郎 『本当にいる日本の「現代妖怪」図鑑』 笠倉出版社" In a direct traanslation:
''Illustrated catalogue of modern yokai from Japan that really exist'' This book was released in 2007, 10 years after the granny being featured in the Soul Hackers game, so it is not a good original source.
Sadly I could not find this book anywhere on the internet, only the illustration it has about the Turbo Grannny:

The Wikipedia article states a bit of lore from the book. Keep in mind that I have to use machine translation, so feel free to correct me:
''鞠つ���をしている最中にひき逃げされた少女の霊が、自動車以上のスピードで道路を疾走する「鞠つきマリちゃん」[1]'' It mentions that it is the ghost of an once a little girl who died after being hit by a car, playing a ball game in the highway or tunnel with friends.
This is an interesting report, but so far is the only place I have found that contains it. It can be just an invention of the author, or just a regional tale. Other sources generally do not touch on the origins of the ghost.
It all gave me the idea to go at Google Books, and check what i could find on the matter.
You see, earlier in the research I was discussing at Discord if this creature could be a SMT OC, which would be huge. That is because the oldest citation about this ghost was from Soul Hackers, in 1997.
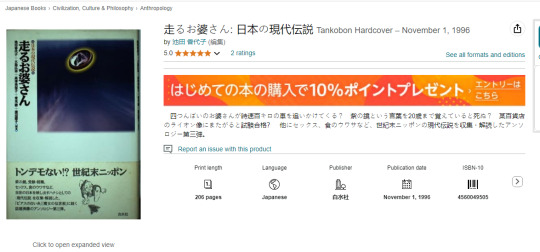
But this was ruled out, going by Google Books, found this book mentioning her at the 29th page, from 1996:
'走るお婆さん: 日本の現代伝說' (Direct translates to: Running Granny: Modern Japanese Folklore)
This book seems to tackle a lot of modern Yokai and Urban Legends in Japan at the mid to late 90s. Its descriptions says:
''A four-legged grandmother chases you in a car at 100 km/h? If you remember the phrase "purple mirror" until you're 20, will you die? If you ride the lion statue in a certain department store, will you pass the exam? Among other urban legends about sex, food and more, the third edition of the anthology that collects and deciphers the modern legends of turn-of-the-century Japan.''
At the 29th page:
(No. 5, June 1994, Issue 6), Kayoko Ikeda's discussion on modern legends titled The Secret of the Running Grandma was published. In that, there are mentions of the Turbo Grandma (with a piece of paper on her back that says 'TURBO' as she rushes by) and the Dash Grandma, who runs along the Tokyo Metropolitan Expressway…"
It also had a mention in the 103rd page:
… There are many modern yokai, like Turbo Grandma, who chase after motorcycles and cars. Also, there are ghosts that get into vehicles, such as in the story of 'The Vanishing Passenger' (The White Thread of the Earring, page 22). These eerie phenomena often manifest when they are reflected in the rear view mirror, often occurring around 2:00 AM…"
This means that we can go even further back, to 1994 as the oldest report of this Yokai. And this book states that it was recorded by a woman called Kayoko Ikeda. I went by her name through Japan web to find her complete list of works, and sure enough I followed the path to the book:
ピアスの白い糸―日本の現代伝説 The white thread- Modern Japanese Urban Legends
Supposdely, this book should mention Turbo Granny, but i can not find it online, nor check its index clearly. There is however, a chapter dedicated to car related Yokai and legends, which can be what we look for. It seems to fit with the page 22, mentioned in the other book.
Ikeda who is a translator of German to Japanese, was involved into it. But could not find much of her work related to Yokai. But she is in fact, an academic.
By this, we can kind of conclude the book White Thread from 1994 was the first recorded instance of Turbo Granny in a book. At least, I personally could not find anything else older than that. The idea of the White Thread book was to report urban legends that were being told around at the time, so it may be just that this was really the first person to write about that.
Similar case happened to the Saci, from our entry #7 in Brazil, which was a popular word of mouth legend up until it started to be recorded in books.
Another name that was hot in this research was of Toshiro/Yoshitaro Yamaguchi (山口敏太郎.). He is a celebrated occultist and urban legends enthusiast in Japan, have written several books, currently also makes videos for the internet discussing the case, but it seems he was a frequent apparition on television shows, and somewhat of an authority in the matter.
For example, Yamaguchi has mentioned the Turbo Granny several times, like this one, where he compares her to other Yokai. But Yamaguchi has published several books, and I lack the Japanese knowledge to verify every one of them, that is assuming I would find it online. But it is clear that he mentioned the creature more than once online.
The other claim I went to check was if the idea of Turbo Granny having an Edo Period ancestor checked. And it kinda surprised me.
By combining Edo period and Turbo Granny in the Japanese web, i was directed to a blog article that aimed to find this originnal legend:
The article traces a parallel to another Yokai: Yama-Uba.
Yama Uba is a yokai that is a monstrous hag, that acts like a witch and often is a sort of Japanese Baba Yaga, or Boggeyman. The connection is interesting, because Yama-Uba is often reported to attack travelers on their ox-cars at roads, and in at least one tale they ran pretty fast for an old hag. The story is called:
''Three Talisman'' (三枚のお札』だろう)
The story is about a monk that was hunt down by the YamaUba, and used its magical talisman to escape. During most of the tale, the Yama Uba was running after him with supernatural speeds.
The author of the article speculates that the parts of the tales showing the Yama Uba running after the travelers, that tried to escape by foot, horse or ox-cars, stuck in the collective mind, and slowly evolved to the imagery of a hag running after cars nowadays.
Yama Uba is a very well documented Yokai, being popular as a bogeyman. There are several tales and folklore regarding her, but it checks out that she indeed had tales about chasing her prey.

Personal theory
Now it is time for that part of my text where I give my personal theory, which is totally my own and based on what I have read and researched. This can be debated and disregarded, but it was my own conclusion. Feel free to disagree with me. And even better, if you are a Japanese citizen who had contact with this legend, let me know and correct me if necessary.
Urban legends are extremely hard to pinpoint, and we can only presume their origins, specially with a big language barrier. But we often can also use deduction and a bit of ''taxonomy'' to co relate myths and folklore that could have birthed the legend, the time and place.
I like to compare this to when a paleontologist finds an incomplete fossil, and have to rely on the closest sibling specimens to try and understand the biology of that animal.
In this case, my Personal theory is that I agree with the said article, and i really think that Yama Uba, and its associated imagery birthed the idea of a hag chasing after vehicles, and people.
If you take a close look, the oldest mention I could find about the Turbo Granny is from 1994, then 1996 and then it appeared again in 1997 in SMT. The idea is that this legend was already been spoken about before the internet exploded, and just slowly was registered. If I had to guess, Id say this legend could have originated by word of mouth in the mountain highways and tunnels of Kobe, in the late 1980s. Those places are naturally where people speed up the most with their cars, and even some times host car meet ups. Initial D is a good example of this culture.


Imagine the big showdown that those two would put up....
Of course, i am not Japanese and i can be completely wrong on that interpretation, but at least the connection with Yokai, and the start of the registration of Turbo Granny is factual and can be assured. It is weird however, that Shigeru Mizuki never registered this Yokai, because even if it appeared as late as 1994, he would probably get to know it. But the man was not all powerful.
I had ran across Japanese people online theorizing the Yokai is a warning against old people causing traffic accidents, but it was just that one person, really. I do not believe much in this theory.
The legend probably spread around Japan during the 90s, appearing in probably occult magazines such as the ones the SMT dev team had access, and the rest is history. Surprisingly Kaneko's commentary on the hag for SH book, has no mention of his sources.

''The ghost of an old woman appears on the highway and runs at full speed. She only overtakes cars without causing any harm, and is more of a frightening presence than a horrifying one. There is also the "Dash Granny" of the same kind. There is also the "100km Granny" which causes accidents in cars that overtake her. It's an old woman running on all fours. There are all kinds of old people, like the Jumping Old Man or the Dash Old Man. Anyway, when you're driving at night, apparently there's one that passes you at incredible speed. Apparently it has the word "Turbo" written on its back, or a piece of paper with that written on it stuck to its back. What's more, it's written in hiragana. Personally, I wrote "Porsche Turbo" on its kimono. Still, old people play a lot of important roles in yokai.'' -Kazuma Kaneko, Soul Hackers Subete (machine translation)
Turbo Granny strikes back: The resurgence of the legend.


Turbo Granny gathered a recent cult following, due to her appearance in pop culture media. SMT was a pioneer in this regard, followed by the after mentioned Hell Teacher manga.
Mob Psycho 100 also featured the Yokai, but due to unforeseen forces, 2024 has became the Turbo Granny year and she is indeed having a brat summer.
When the Dandadan animation hit Netflix at the start of October, the Yokai was instantly recognizable. It became one of the main antagonists and characters of the work, that also dabbles in other Yokai and spirits.
Shin Megami Tensei V: Vengeance not only re added the monster, but also gave her an unique side quest, where you have to hunt down the hag through the pre apocalyptic Tokyo, stop her, and photograph her for an occult magazine.
And finally, my favorite piece of media related to the granny...
In 2017 the Turbo Granny was the star of a Broad Wimax commercial, which is a company that sells internet connection. They commercial was about how their internet speeds were able to be faster than the Turbo Grannyy, and it was starred by a comedian. The whole commercial starts as a documentary, but gets progressively funny.
youtube
Conclusion
As any urban legend, Turbo Granny will forever be a mystery in terms of origins and original sources. We can say for sure this was not invented by Dandadan artist nor Shin Megami Tensei devs, since the legend was around for a long time. It seems people in Japan recognize it as popular as the Slit Mouthed Woman, for instance. This makes this Yokai unique because of how modern and popular it is, through pop culture.
Of course, Dandadan mangaka added his own flavor to the monster, but that is part of the fun.
Honestly it is pretty cool to witness that kind of popularity for a specific Yokai, and watch how the legend slowly evolves and change over time. Who knows?
I hope this put your itch to know this hag's history to sleep!

Turbo Granny at the Soul Hackers for 3DS opening.
Special thanks to Eirikr for the help with the Kaneko commentary!
#Yokai#turbo granny#dandadan#shin megami tensei#kazuma kaneko#japanese folklore#megaten#blazescompendiumentry
95 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blaze's Compendium Entry #10: The Khyah (Cyak, Kack, Khya)

Warning: Faith and religion are important real life topics, that tackles the culture and way of life of millions of real life people. It is a cultural expression, and must be respected by all means. Here, we use a video-game ( some times) and other media series only to ignite the flame of learning about the matter, using its art when well depicted, but we do this with all due respect to the cultures we talk here, grounded by real life sources, cultures and people. And i mean this with respect. Hope you all enjoy.
Also, please note that the Sources for this one will be a bit tricky, since we are talking about a regional and always developing urban legend and cosmology, which is not very well documented in traditional books. In this case we have to turn our attention to personal stories and every day people who lives in this culture.
The Khyah (ख्या) is a mythical creature that is part of the greater Nepali folklore and cosmology. Specifically from the Newar people from the Kathmandu Valley.
Some sources will say that its name means literally ''Ghost'' or ''Haunt'', ''Phantasm'', etc... However i was not able to confirm this. The language spoken by Newar people is the Nepal Bhasa, which is also written in the Devanagari script, just like Hindi. I do not speak this language, so please if you do, reach me out! But in any case, it seems that the word for ''Ghost'' in Newar is ''गुफा'' or ''gupha''. It may be the case that the name: ''Kyah'' got so used to general supernatural occurrences, that it got mixed up. Just like we talked about the Saci in my other post. -This is not uncommon to happen- I used regular online translators to reach this conclusion, but feel free to correct me if i am wrong because i could not consult any native to talk about this matter during my research.
For a bit of context, The Newar are people that historically inhabited the Kathmandu Valley, and the regions around Nepal. As we said before, they speak Newari (Nepal Bhasa). They have 3 major cities, those being Kathmandu, Patan and Bhatgaon. [1] The academic research on the Newar people just started at the early 20th century, the french anthropologist Sylvain, wrote a very famous and complete work called Le Nepal, that was one of the first western written works about the region, and its people. Their religion are mostly Hinduism, Buddhism and there are minorities from other beliefs.
The Newar live in this region since ancient times, way longer before Nepal even existed as a Estate. According to most history books, the Newar would live alone in the region, being sovereigns of the Kathmandu valley up until the Gorgkha Kingdom in 1769. It is very hard to know much about the Newar before that in details, since they are in the region for so long, and mixed so much with other people from around the Nepal, that even their history ends up blending with mythology.
For example: according to the sacred Swayambhu Purana, a Buddhist scripture, the Kathmandu Valley was once a huge lake, Inhabited by Nagas*. That is, until one day the Bodhisattva Manjusri with the help of a powerful sacred sword, sliced the surrounding hills, which in turn made the water flow away. This information is even on Kathmandu government official site!
This myth was later confirmed to have a basis, since NASA themselves found out clues that Kathmandu was in fact, once a huge lake. NASA did not reply me about the Naga thought. Bummer...
*The Swayambhu Purana is a Buddhist text essential to Newar Buddhism. However i sadly could not find a copy online, but there are some summarized versions translated to English, which i am using as guide. For instance the US Wikipedia article, sources books that i also could not find, but i could verify the authors! So... That's something, i guess.

This goes to show how the Newar people are rooted in their mythology, and how this is completely absorbed by even their space and surroundings. Even something as the very foundation of their lands is a hierophany.
This brings us to the Kyah, that we will see can show us a lot about this society.
About the Khyah
The Khyah are supernatural creatures that are hairy, looks like apes, sometimes extremely chubby and have their bodies are totally covered in hair. This description is corroborated my multiple sources, like ''Dietrich, Angela (1998). Tantric healing in the Kathmandu Valley: A comparative study of Hindu and Buddhist spiritual healing traditions in urban Nepalese society. Book Faith India.'' But not only that, the Khyah are also represented in multitudes of paintings and also in costumes for the Yenya Festival. The only thing that can sometimes be different, is that if it will be treated like a Ghost or a more physical creature.

The wealth goddess Lakshmi and two Khyah serving her, in a painting on a Kathmandu temple.
About this painting and sourcing the Khyah appearance:
I have made tireless efforts to pin down the origin of this painting. And many others! This one is present in most of the articles about the Khyah in the internet, even local articles from Nepal itself. However i was not able to pinpoint where it came from. All the sources i found either say this is from a ''temple'' or that it was taken by an individual named: Karrattul. This is not the photographer's name, but instead the name of the profile who uploaded it on the Wikipedia, where it was uploaded in 2012! I tried to reach to Nepali communities and other enthusiasts of History and Mythology, but no one could help me. If you know anything about this painting, please contact me!
For the same reason, it is almost impossible to find sourced materials about the khyah appearance. We know that there are traits like the hair, that keep intact from place to place, but i could not find a central work detailing the creature. We have those paintings from so called temples to trust, and the ceremonial suits used in the Khyah dance.
I will link here a video of a Khyah Dance performance, so you can see the physical traits of this creature are well agreed between the locals.
youtube
The Khyah is popular among children, or at least were at one point. This can be seen in a popular children song sang in Nepal. It depicts the Khyah as a cute and hungry little critter, as the kid in the song is encouraged to give food to it. The Kyah seems never to be satisfied sadly...

A banger...
The Khyah is indeed often treated like a type of ghost. In my personal opinion they are simmilar to Djinn, some kinds of yokai and can be classified generically as a type of monster or apparition, in my view at least. (This means a supernatural creature, that is in between a human and a god like being.) The Newar believe that the Khyah has active participation in events of their daily lives. But they also are not all bad or good, they are multiple entities, some good and some bad. Usually there are white colored Khyah who are good, and black colored Khyah who are bad.
They have their own lives, families, and friends. There are a lot of tales and works related to this creature, not counting personal tales of every day people and their encouters with this little devil. That's how ingrained in the Newar culture the Khyah is.
I was able to track the writings of a Kathmandu Valley denizen, which happened to write about the Kyahk! [3] This person was kind enough to provide a lot of personal information about the regional culture, in their personal website. According to the locals, the Khyah would often live in houses, squares, public spaces, and would regularly interfere with their existence. Not all Khyah are bad, some can protect the households they inhabit, they can bring fortune and good luck. Although, the Khyah fears light, so they have to live in dark corners of the house, like the attic or some empty room.
The Unitedstatian Wikipedia page for Khyah shares some unusual information, that we can not trace to any sources. For instance, they mention that this creature supposedly fears electricity. As interesting as it may seen, the source from this particular information goes to a book called: '' Asian folklore studies, Volume 55. Nanzan University Institute of Anthropology'' Which i was unable to find to read online, and was also unable to find it by its ISBN trackers: 9057890984, 9789057890987. Those took me to another book, called: ''Caturmāsa. Celebrations of Death in Kathmandu, Nepal’'
This one seems to exist, but i also could not find it anywhere online. Google Books has some samples, and it guarantees that the word ''Khyak'' or any variations of sorts, are not on it, which means this is a misinformation. Someone probably interpreted that the fact that Khyah fear light, can also apply to electricity as an energy source. I think you won't be letting your homie Khyah uncomfortable having electricity at your house, don't worry.
Again, according to locals [3] There are two variable Khyah: Black and White. The white are the ones who bring luck, and the Black ones gives you trouble. No matter what kind of this creature you have in your house, you should respect it. They are often revered and well treated. They have their own cozy dark place to hide, like the bhandar and dhkuti. Those are places of the house used to store grains and valuables.
There are other variations according to other local sources sources [3] [4] Those Khyah are usually described as:
-Bārāy Khyāh (बाराय् ख्याः) appears in rooms where girls are kept in seclusion during their rite of passage to adulthood (first period). [5] (Very documented, and easy to track on western sources)
-Bhakun Gwārā Khyāh (भकुं ग्वारा ख्याः), literally football, rolls on the ground to move around. (Most common Khyah, probably the one Kaneko tried to draw! Most commonly seen in regional urban legends. Not very documented in translated to English literature)
-Dhāpalān Khyāh (धापलां ख्याः) is a very hairy Khyah. (Very popular because of that children's song, still sang to this day.)
-Lanpan Khyāh (लँपं ख्याः) blocks people’s way on dark streets. (Not much about this one, really. At least not in western sources. It seems that, along with Bhakun Khyah is probably more of a word of mouth thing)
The relationship with Kawancha

The origin legend for the Khyah goes that, in the distant past, two gods had a baby. They fought to see who had the right to hold the baby, but ended up tearing the child apart. The skin peeled off, revealing just flesh and bones that would separate. The flesh became Khyak, and the bones Kawancha, a skeleton that would be the Anthitesis to the Khyak. This relationship is portrayed in paintings and regional dance festivals. [3]
Also known as Kavam, the skeleton monster seems to be the other half of the Khyah. It is extremely hard to find sources about this, not only because it is a very specific regional folk belief passed down orally, but also because the language barriers. One could in theory go there in person to collect sources about this part of the lore, but it is not an option for me. Someone at Reddit pointed out to me that in some regions, they are not related at all, being just monsters from the same sources. So, their lore seem to vary from place to place.

Painting depicting Kwancha/Kavam and Khyah in Kathmandu. Origin Unknown.
As much as I tried for months, I could not come with a source for this information besides literal oral tradition. But for sure these two are indeed connected in some places. You can see them in several paintings at Kathmandu, and they also have their own dance performance telling their story and painting their relationship. As the Reddit user mentioned, their connection will vary from place to place. Being more of a localized and oral tradition.
youtube
In the performance you can see Khyah and Kwancha performing together, as they show their relationship. Still according to [3], the instrument played in these performances is the Dhimay. Its made from tree bark, and the legend says the gods later created this tool to help control the beings, and communicate with them. In the author's perspective, this was meant to showcase the duality of our universe. This being the real nature of those beings.
Again, I lack written and traceable sources. While the Dhimay is indeed a real instrument, used on those performances, there are almost no mentions of it being related to Khyah or Kwancha in the western internet. This also falls in the category of facts I could not check because of being probably too of a localized oral tradition.
I could at least find some sourced paintings. Like this one, shared by the Twitter user Sanjib Chaudhary Who is an author himself on Nepalese culture.


Kwancha and Khyah are shown in this painting on Jaya Bageshwori temple, in Gaushala.
Also, while Khyah is very well documented in the west, the same can not be said about Kwancha. It is easy to find dances, masks, his Megami Tennsei design (being the most easy result) and paintings about the skeleton monster, but almost nothing on its nature and lore. This means I highly doubt everything the Megaten games say about it to be factual, although they do in fact exist in Nepalese culture.
One thing i noticed is that Kaneko himself could have watched a dance performance of Kwancha and Khyah, or at least seen pictures. Because his Kwancha design for Devil Summoner has the clothing in colors and shapes very similar to some Kwancha performers:


This specific clothing can be seen here: Kawancha (Skeleton) Dance of Bhaktapur कवांचा प्याखं , तौलाछें, भक्तपुर ll Part of Bharab Dance ll
The final point on this part is their origin: Which gods crated them? This rent a space in my brain for free for the last year or so. While I could not find it for sure, this does not mean it is wrong or not factually a belief in their tradition. Buddhism has many gods and entities, and i suspect the ones who created the Khyah accidentally, are just regular Devas.
Modern mentions?
Khyah tales are in the heart of Kathmandu people, and many other Nepal regions. For centuries they dominated the children's tales and late night scare stories of that region. In 1992, Jim Goodman published a book called ''Tales of Old Bhaktapur'' Which complied some folk tales from Nepal.
Sure enough, Khyah makes an appearance in it. At page 28, there is a story about a Khyah haunting a house, and how a boy deals with it. Sadly the book is not openly available on the internet, but google books have some parts readable:

There is also the book: Tales of Kathmandu: folktales from the Himalayan kingdom of Nepal (1980). This book was published by the authors Karna Sakya, Linda Griffith. This book seems to put together many popular folk tales from Nepal, and in the page 105 we have a story called ''The Khya of Marusata.''

Now, as this seems to be the case with every freaking material in this search, this book is not available online, but google books has many parts available. Sadly, we can only see the title of the story. What we can know by a quick google search, is that Marusata is some kind of square in central Kathmandu. I tried to search this tale online, but I could not find. Will try to keep searching for it eventually.
Also, in the books first pages, around 20 or so, Khyah are mentioned too:

It seems to classify Khyah as demons, just like their neighbors Rakshasas. Which is not exactly on the point here, but its interesting nonetheless.
The Khyah are still recognized today, and are well known in the community. But even if the western internet made a good job of preserving its lore and some of their character, their presence is very scarce. By going on Eirikr Kaneko Crib's notes I found that one of the most recent official appearances of the creature online was on the site Local Nepal Today. This seems to be a site dedicated to portray and preserve Nepalese culture and report on situations at the region. It is however, done by foreigners that went to Nepal afterwards. The site seems to be dead, but they do mention their hearings about the Khyah! Here they call it Kack.
The authors compare it to European elves and trolls, which is not exactly a good match. They are more akin to Brownies, Silkies and some kind of Kikimora.
In any way, their description matches most sources, and oral sources alike: They are shy, prefer dark and isolated places, and hate the light. They also comment on the duality between the white Khyah and the black Khyahk.
Most important thought, they mentions talking to an elderly woman in Kathmandu, who shared her own stories about meeting the creature:
''An elderly woman in Kathmandu who saw several kacks – all white ones. The closest encounter was with a quiet, furry fellow who came and sat on her lap! Many of those who’ve seen a kack will tell you how these “little people” would come and sit on the edge of their bed for a while, keeping them half amazed, half in shock the rest of the night. A white kack is friendly – but it can still be a bit scary.''
They also gathered information from old Kathmandu citizens on why the Khyahk tales are vanishing nowadays:
'''Well, old people who grew up in the heart of kack territory – Kathmandu – will usually tell you a simpler reason: kacks are shy creatures and so, since the capital has become crowded and noisy, many have left. Sure kacks can hide and move about by stealth, but there’s a limit. Either way, now it’s no-longer in Kathmandu but in the villages you’ll hear about kacks the most.''
In my personal view, its interesting to connect the vast and accelerated growth of Kathmandu, to the losing of traditions and oral folk tales, which ended up making the Khyah tales vanish bit by bit, becoming isolated to small nearby villages.
This makes me a bit sad, because if there is no one trying to preserve those traditions, it may very well disappear as the times goes on. The internet has this amazing tool to preserve culture, but we do not seem to be using it enough.
In this regard, I am glad that Kazuma Kaneko imortalized Kyahk in the Shin Megami Tensei series, even if they are not regular monsters on the newer games, many people probably had their first encounter with this critter through that.
And that is it! Everything I could gather! Hope you guys enjoyed!

Beware the Kyhak at the feet of your bed!
Thank you for reading through it all. I actually started this research more than 1 year ago, but postponed it multiple times, since I started doing scientific research at college, and other monsters looked way more easy to research.
Stick with me for more deep dives on critters from around the world.
Sources: [1]- "Elements of Newar Social Structure". Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute. Royal Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland.’’ - Christoph Von Furer- Haimendorf, 1956.
[2]- Dietrich, Angela (1998). Tantric healing in the Kathmandu Valley: A comparative study of Hindu and Buddhist spiritual healing traditions in urban Nepalese society. Book Faith India.
[3]- Himalayancultures.com -Personal blog of a Kathmandu citzen that shares a bit about regional folklore and culture. Extremely interesting to see stuff from a personal point of view.
[4]-Archive My Sansar - Regional website about Nepali culture.
[5]- Growing Up: Hindu and Buddhist Initiation Rituals Among Newar Children in Bhaktapur, Nepal, 2008, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. (Pag 174)
[6]- Tales of Old Bhaktapur'' - Jim Goodman (1992)
[7]- Tales of Kathmandu: folktales from the Himalayan kingdom of Nepal (1980)
[8]- Local Nepal Today
#blazescompendiumentry#mythology#blazescompendium#shin megami tensei#kazuma kaneko#nepal#kathmandu#folklore#Newar
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blaze's Compendium Entry #8:Explaining the Origin of ShikiOuji

Note: This post was originally published in April 2024. However, since it is a complete research and dive into this monster, I figured out i could just repost it as a Compendium entry.
As always:
Warning: Faith and religion are important real life topics, that tackles the culture and way of life of millions of real life people. It is a cultural expression, and must be respected by all means. Here, we use a video-game ( some times) and other media series only to ignite the flame of learning about the matter, using its art when well depicted, but we do this with all due respect to the cultures we talk here, grounded by real life sources, cultures and people. And i mean this with respect. Hope you all enjoy.
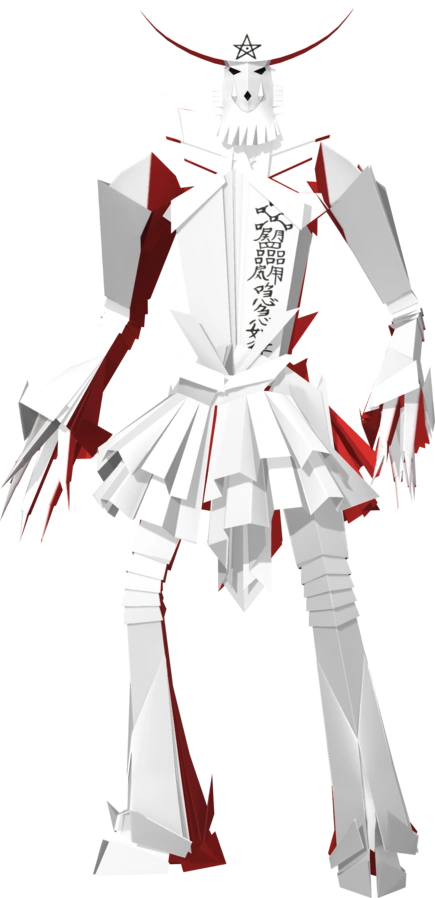
I am sure that, if you played any Megaten game in the last 20 years or so, you ended up seeing this paper dude. His name is always stated as Shiki-Ouji, and he once shared the same design with the Demon called Shikigami.
The weird thing is that when researching Shikigami on my studies, I never found anything about this one so i put some detective work to find out about the origins of Shikiouji, the (yet another) dude who often repels physical damage in Megaten.
The creature is described in many of the series compendium as a powerful Shikigami, that only the most powerful Onmyoji could summon, and they have a vicious temperament.

When we talk about Shikigami, the first thing that comes to mind are paper dolls. This is no surprise, since Shikigami are summons Onmyoji binds to paper dolls or talismans, so they could interact with the physical world. This is also because paper is a very easy material to destroy, if things go south. Onmyoji are the equivalent of western sorcerer, that followed the Onmyōdō, a esoteric cosmology. It started in the 6th century in Japan as a divination practice, and evolved from there. I won't go into detail, because this is meant to be a short post. But materials about this practice are abundant on the internet.
The main concept concerning us here is the Shikigami. These are basically some kind of familiar, a spirit or demon if you want, the sorcerer could conjure to protect him or do his biding. The Cultural Alliance Brazil- Japan, which i already mentioned in other posts, states that:
''Shikigami can be Oni or demons, that should serve and protect an Onmyoji. Your abilities would be determined by the abilities of his master.
A Shikigami could assume the form of small animals, birds, etc... One Shikigami from a powerful Onmyoji could possess and control one animal. But only a real powerful Shikigami could possess a person.
When an Onmyoji is fighting another Onmyoji, they employ the use of their Shikigami. Some Onmyoji could spot the enemy Shikigami beforehand, and try to convert it to his side with magical powers. In this game, the converted Shikigami would come back to the old master, and attack with double the force. This pratice was called Shikigami Gaeshi.
Abe no Seimei is said to be the most powerful Onmyoji to ever exist. Some rumors say he had twelve Shikigami, while regular Onmyoji would rarely have more than one Shikigami at the same time.''
So, that is a rough definition of what a Shikigami is.
But, when researching this creature you would not be able to regularly find Shiki-ouji. The fastest method for him to appear, was the English Wikipedia article about Shikigami, which weirdly had this part about Shiki-ouji, but offered no source to it:

Having the kanji to Shikiouji, and some keywords, i found someone at Tumblr who asked the same question 6 years ago, in Eirikr's blog.
From there, Eirikr offered a link to a blog post writing about Izanagi Ryu Shikoku. Ryu Shikoku is an ancient folk religion and pratices from the Kochi prefecture. It is still practiced in the area to this day!
In this belief system there is the tradition of the Shiki-kui masks. Which.. bear a very uncanny resemblance to our paper guy, subject to this post:

These masks would be hang above the place the ceremonies of the Izanagi Ryu take place. They would have magical powers that could repel evil spirits, and non believers from coming to the ceremony and disturbing it. They would also serve as talismans, or paper dolls, in a simmilar vein the regular Shikigami pop image you have in mind.
Since they are used to summon spirits, bind them, and as talismans, these creatures can be, technically called a Shikigami.
With this knowledge in hands, i went to the Japanese web. And sure enough, i found this site: The Nippon Foundation Library. It has an article detailing the paper talismans used by Izanagi No Ryu Onmyoji, and their meanings, powers, and also explained a bit about Shiki-Ouji!
Here is what they have to say: (Please be warned that i do not speak Japanese, and used machine translation. Any corrections are Welcome!)
Shikē Ōji is a spiritual entity invoked by the taisa during prayers for the sick and the "toriwake" ritual to expel evil spirits causing illness or calamity. Its birth is described as abnormal, and due to its excessively violent power, it has no place to reside. Usually, it is sunk in the pond of Tendō-nanta, and summoned only when needed to guard ceremonies, to pray as the guardian deity of ceremonies, or as a prayer deity of Jumon no hakase. There seem to be several types of Shikē Ōji depending on their purpose, such as Takata no Ōji for toriwake, Gotai no Ōji for prayers for the sick, and Ōtaka-shiki for insect prayers. Additionally, talismans such as Sangoku Arashiki, Chimura San Ōji, and Sakago no Ōji are handed down, and it is inferred that they were used according to the content of the prayers, although many details of their usage are unknown.
Using the powerful Shikē Ōji against humans becomes a curse. In Kochi Prefecture, "hitting a ceremony" is widely used to curse people. Many people use this term without understanding its original meaning. "Hitting a ceremony" refers to attacking someone using Shikē Ōji. While Shikē Ōji can benefit people if used for good, it can harm them if used for evil. Talismans of Shikē Ōji, possessing such terrifying power, often have several incisions on them, each containing twelve notches, giving them a rough impression. However, unlike talismans found in mountains and rivers, they do not seem to have incisions for eyes or mouths. In this regard, they are closer to the cutting style of talismans for house gods and sacred gods. Here, one can sense the emphasis on the powerful nature of Shikē Ōji's talismans while also distinguishing them from strange monsters.
So, as you can see there is some key information about the creature here. But the most important ones:
1- It is bind to a talisman, just like other Shikigami. The text here explains it is a paper talisman with notches, just like regular ones used in religious ceremonies.
2-It has a powerful and violent nature, just like the compendium often indicates in Megaten games. It seems hard to tame and use properly without getting hurt.
3-Shiki-Ouji can be powerful and violent, but it seems they dislike being used to hurt people. Instead, they are better employed to use their magic to other deeds. However if you still use them in that regard, they will most likely curse you.
4-Their talismans have twelve notches, no incision for eyes and mouth due to their aggressive nature. This would help to control their interaction with the material world.
I am sure that, if we follow this trail we will find many more sources. Going by key words i found in this text, i found many other sites and books, but since i have no time now to fall a rabbit hole, nor do i speak Japanese... That is it, i think this is a satisfactory answer to where this Megaten Demon came from!
The real forms of Shiki-Ouji
The last thing in want to talk about, is Shiki-Ouji real appearance. Since we have a seemingly wrong impression of they in Megaten, since Kaneko took some artistic freedoms.
First and foremost: From the few things i studies about Shikigami, we know they do not have a real physical form. The paper talismans are just a way to give them physical form. But it was incredibly hard to find a Shiki-Ouji talisman, which was weird because it was so distinguishable. The main reason being that: Shiki-Ouji seems not to be believed to be easy or safe to summon, and also their talismans would be destroyed asap after use.
But with the description i got, it would be this one that matches it the most:
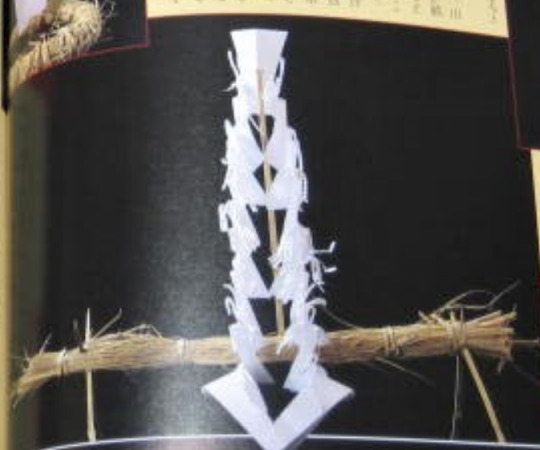

No eyes, or mouth. Twelve Notches, six from each side, and some incisions. Very similar to a regular talisman found in other types of ceremony. Just as the text suggested.
I got this picture from this book:
Tosa, Monobe Village: Shapes of the Gods
Monoba being the village where most of these rituals came from. The book is from 1999, and contains many pictures of actual talismans.
You can see that, aside from the head shape, Kaneko took some freedom with this design. The sources state that Shikiouji talismans should not have a face, nor limbs, since it was too powerful, and should have 12 notches. For some reason, Kaneko drew it in a human-like form, but the face still resembled the Shiki-kui masks. The earlier design of the demon was even more closely resembling the masks:


Shiki-ouji earlier design from Devil Summoner (1996). It was later repurposed as the demon Shikigami. It is almost an exact match to this talisman. I can not however identify the original source.
Shiki-Ouji current design by itself could have been based on this one talisman in specific, at least some parts of it like the head with horned-shaped appendages:

By the looks of it, its face could turn inside out, just like the Megaten Demon can do.
It was sourced by the National Museum of Japanese History, but the post went down. The low quality image of the talisman can still be seen on google, but the link is dead, unfortunately. It seems that this item is still in possession of the Museum in Japan. Kaneko could have seen it in pictures, or in person. This one seems NOT to be displaying a Shiki-Ouji thought.
Maybe the Kaneko take is that Shiki-Ouji was summoned with limbs, and facial features and became much more stronger as a result? We may never know...
And finally there is also an occult book that i found in Amazon Japan that is called: Exploring Izanagi No Ryu: ShikiOuji.
It is supposedly a manual on how to practice Izanagi no Ryu, and magics. I could not find the book online, just the summary. But it mentioned nothing about Shiki-Ouji. Probably has some sort of tutorial to summon it, in fact i was able to find many of those tutorials on the Japanese web.

Now, that is it. I think this puts to rest a little bit of mystery involving the origins of this specific demon. Kaneko sure took some freedoms, but it is still one of the more popular and recognizable characters in the series.
Final considerations:
This most likely is the answer to its origin, but i am not some sort of owner of all truths, so feel free to correct me in anything i said wrong. I am still an amateur scholar, and even if i do know a lot about mythology and ancient religions because i read many books and study a lot of hours of my days, i am by no means a specialist in Japanese Mythology specifically, specially Shikigami practices. The reason is that, i find it very difficult and time consuming to research Japanese sources, since i do not speak Japanese. I will one day, try my best since there are a lot of good Yokai to cover in future Scientific Papers.
I can, however, guarantee that i did my best possible effort in a deep search!
And i have spent a lot of time looking through pictures of Shikigami talismans, and i found some really cute. Like this one. What a whimsical little fella...

#shin megami tensei#atlus#kazuma kaneko#blazescompendium#megaten#mythology#japanese folklore#japanese mythology#shikigami#megami tensei#smt#blazescompendiumentry
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blaze's Compendium Entry #6: Helmet is required to deal with the Muh Shubuu.

Warning: Faith and religion are important real life topics, that tackles the culture and way of life of millions of real life people. It is a cultural expression, and must be respected by all means. Here, we use a video-game series only to ignite the flame of learning about the matter, using its art when well depicted, but we do this with all due respect to the cultures we talk here, grounded by real life sources, cultures and people. And i mean this with respect. Hope you all enjoy.
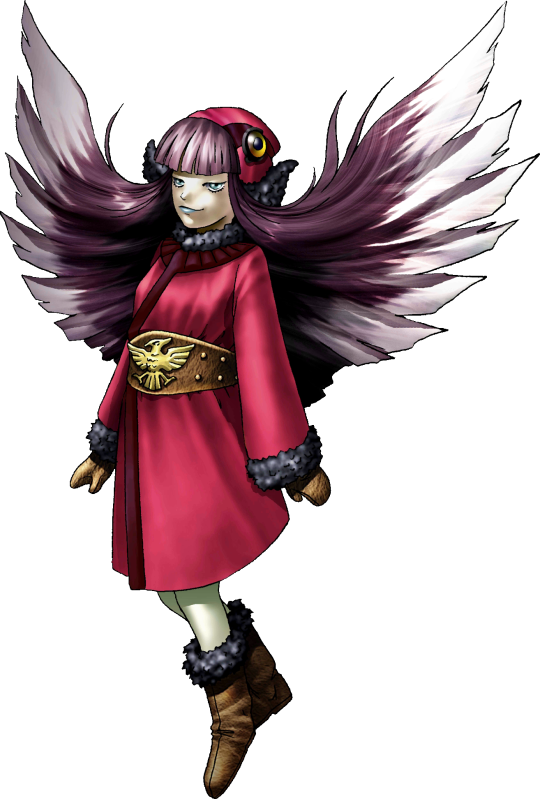
Moh Shubuu, or Moh Shuvuu is a fantastical creature from the Buryati Folclore, nomadic people from Asia in a region between Siberia and Mongolia. Their are treated like a Mythological bird, that is born when a young girl or young woman dies by violent means, without knowing true love. (This can imply chastity, but it will vary in how explicit it says it). Normally, Moh Shubuu will attack man that she could seduce using her young girl looks, bringing the victim to isolated areas of the desert and killing them with a blow to their head, using their ominous sharp beak. Then she would proceed to suck and consume the brain matter out of the person.... Yikes.
According to sources (as always, will be in the boton) There are other ways for a Moh Shubuu to be born, we will explore those later.
This is one of those legends that, finding a single western source on it is way harder than actually understanding it. Not even Wikipedia is of any help here (That is, if it was of any help, any time). The only real English source i was able to locate was a book: ''Christian Demonology and Popular Mythology, Central European, 2006''. Although this book was a verifiable source, it was not from much help because of the biased view of the tale, from a Christian perspective. Which is not exactly wrong. There's whole fields of theology dedicated to this , but we gotta exercise the Methodological Agnosticism here, which means i can't analyze a culture going from other completely biased point of view, but rather try to see by the eyes of said people considering their time and space, which is also not a easy task by any means.

Moh Shubuu hides her beak with her hands, and sleeves.
The book offers little to no insight about more than what is commonly associated with the Moh Shubuu. The western internet is filled with texts and people talking about this legend, in the way i told above. But the creature name gets a bit confusing. Usually, in the west people call it Moh Shuvuu, but it seems this is a western way of spelling the name, which is actually Moh Shubuu or Moh Shubuun. This means literally somehting like ''Evil Bird'' According to most sources, but i was unable to independent verify this claim. So, take it with a bit of salt. I am sure though, that this could not be so much far away from what it really is.
Going by Muh Shubuun or Moh Shubuu makes it more easier to research it, in Russian the name is spelled like: Муу шубуун. In using this language, there is a good amount of sources going from sites that talk about mythology, to museum pages in general, to books. This did not surprised me, because Buryatia being part of Russian territory for centuries now, and Moh Shubuu being a relatively obscure, and oral folklore, makes it very niche to research indeed. Specially from a culture which is in high danger of disappearing. [2]
But by far, the most complete work in Buryatian culture research i was able to find, comes from a renowned Russian folklorist: Matvey Nikolaevich (1858-1918). His work is extensive and very detailed, he spent his life and career studying and documenting Buryati culture. Matvey was celebrated in his time by his expeditions to Buryati settlements to study their culture, and he was elected in 1888 as a member of the Russian Geographic Society. So much so, that a Museum in Buryatia is named after him, and display many of his belongings and researches there. (Linked source, and Museum)
If you happen to speak Russian, and is interested in learning more about Buryatian Folklore, culture and more i heavily suggests you to read more of Matvey books. As for me, i do not speak Russian, so i am relying in software translations. If you notice anything wrong, please let me know!
I can't go too deep in his work here, because our main goal here is to explore the Muh Shubuu lore. Luckily for us, Matvey catalogued this very tale (along with another multitude of Buryati folklore) in some of his work. Here, i will use as a basis his book:
‘’Хангалов М.Н. Собрание сочинений в 3 т. Т.3. / Под ред. Г.Н.Румянцева.-Улан-Удэ: Изд-во ОАО «Республиканская типография», 2004.- (Reprint)’’
Translated roughly as:
‘’Khangalov M.N. Collected works in 3 vols. T.3. / Ed. G.N. Rumyantsev.-Ulan-Ude: Publishing House of JSC "Republican Printing House", 2004. (Reprint)’’
This work was originally published between 1889 to 1903, in 3 volumes focusing on Buryati Folklore. Sadly, i could not locate this book anywhere on the web, at least not using software translation and all my power to do so, i could not locate a physical copy of easy access for me. But, luckily the book is partially transcribed in many web pages and that's how i guided myself.
So, about the Muh Shubuu!
There are some legends Matvey catalogued about this demon in Buryati folklore, but they vary a bit. This can be because of the nomadic nature of the Buryati people, and how the tale can evolve and change between groups and settlement. But nevertheless, the essence is still the same. Here are some tales that Matvey could comply about the Muh Shubuu:
There is, for instance the tale of a young couple, that went to live in the woods together. Sadly the man dies from illness shortly after, leaving his wife alone and depressed. The woman could not bear the loss of her husband, and was driven into madness. During this time, she decides it is a good idea to consume the dead decaying liver of her late husband. After that, she dies as well.
The woman's soul is back as a Mu Shubuun, because of her terrible act. Still according to this particular legend, this demon can change forms into different types of birds. (like some kind of warebird) But, when she transforms back to her more humanoid form, only the beak will remain. (Some times, this beak is described like her lips) The beak will always be visible, no matter how many times she transforms back.
Another tale tells about a hunter, who was hunting alone in the desert. (or woods, depending on the mood of my translation software) After taking a rest, a young woman approaches him. She starts to kick a conversation, cracking jokes, and getting along with the hunter. He noticed that the woman always tried to hid her lower face with her sleeves, and found it suspicious. He notices this is a Mu Shubuu, and asks her to get logs to the fire he is preparing. She goes, and while she's away, the hunter puts some branches and his stuff into his blanket to give the impression he is sleeping in it.
When the demon returns, she thinks the tired hunter was sleeping already, and she could finally attack. She jumped in the blanked with her beak, stabbing the branches and logs he put inside it, and it got stuck. That's when the hunter shoots the thing down with his gun. After that, he burns the remains in a fire.
This story is particularly interesting, because it involves guns, so it was probably not that old. At least this version, it could have changed with the years, with regular weapons becoming guns, once they were invented and got popular. Or... My translation software got something as an bow and arrow as a gun.
This tale also makes clear that the creature was about to kill the hunter, with her classical ''beak to the head'' and would probably consume his brain matter. But there is evidence Mu Shubuu diet consisted of more than just brains. like the woman in the first tale eating the liver of her husband.

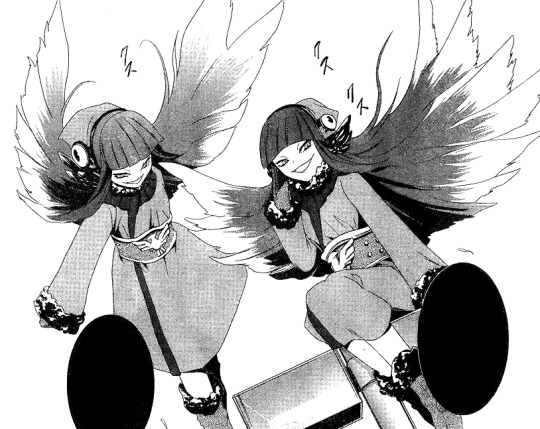
This amazing artwork was made by NATZ they are amazing, and let us use it to illustrate this text. Go check them out! I am a big fan!
In another tale, there is also other person who win in a fight against this demon by getting her stuck in a tree. This seemed to be enough to the creature promise not to bother anyone anymore.
Matvey also complied the information that, some tales described that Mu Shubuu had two ''flints'' with them, usually in their armpits. The right one is a bright red flint, very good looking. The other one is a decayed and rotten tool. The disgusting one is the one to destroy, or take from the creature, because it is linked to her vital forces, it seems. During a fight, Mu Shubuu will try to convince you that the red one is better, but this is a trap. This flint will weaken you instead, making you the easiest prey to this demon.

Buryat knife with a suspension, a tube, a pouch, a flint. Silver, coral, malachite, mahogany, leather, hardened steel, corals, chasing, punching, forging. I dont know, but maybe this legends of a ''flint'' could be referring to the tools here.
There is also the implication that there are male Mu Shubuun as well! According to Matvey there was a tale about a forest where lots of Mu Shubuun inhabited, and they always caused mayhem in the region, attacking and eating people's brains.
One day, a warrior decided to go there, and was (surprise surprise) attacked by a Mu Shubuun. In this story, the flint version was accounted for, and the warrior win the fight taking the ugly looking flint from the demon. But, she ends up fleeing.
The man follows the creature trail up to a well, where he found not only the female Mu Shubuun that attacked him, but a male Mu Shubuun. It was the male that convinced the guy not to harm them, explaining that attacking humans was an habit of the female Mu Shubuun only. As a way to apologize, the couple of demons teach the man how to defend himself from their relatives, using magical phrases. I could not translate them very well using software, but in Russian it goes as:
‘’Хадалан долон - Хадалаевы семеро
Хамнагахи найман - Хамнагановы восьмеро’’


Female and (possible) male Mu Shubuun from the game Blood Brothers. I like this interpretation very much, because of the bloody beak.
This tales are interestng, because they are very small but they manage to convey a lot about this creature, which is sadly not very much available to western sources. It is evident that in Buryatia, this is a relatively known folkloric tale, and in Russia and Eurasia it was spread by books and the internet, much before the demon was explored in the Shin Megami Tensei series.
For instance, the Irkutsk City Museum, in Russia has a page dedicated to Buryati culture, and also shows some Mu Shubuun texts. Irkutsk is not in Buryatia, rather is a bit north, after the Baikal lake that separates Buryatia from the rest of Russia. But it is close enough to have some cultural connections.
(Again, i am not going too deep into the Buryati belief system as a whole. Not only because that's not the foccus here, but because it would need much more research. If you want me to talk about more of this culture in the future, let me know!)
Much is talked about the Buryatian Shamanism when talking about the Buryatian folklore. This was present in Matvey's work, as well in official government sources as the Irkutsk Museum. This Shamanistic culture often deals with lots of problematic spirits. Those are usually translated as bad spirits, ghosts, or even demons. This means our little devil bird girl is not alone in this pantheon. Just to be brief about some other Buryatian mystical creatures:
Ada: A spirit that manifests itself as a small crature with only one eye, and one teeth. Their mouth is on her lower jaw. Can appear as a dog, children or even inflate itself as a balloon. (This one is specifically creepy, and it is also cited by Matvey works)
Anakhai: Also spotted on the before told sources, this is a cyclop-like creature that attacks children.
Ezykhe: A spirit that causes harm to domestic animals. Usually it appears as a decaying old hag, that steals cow's milk. This can cause malnutrition to calfs, and even death of livestock.
The Buryati usually are practitioners of Tengrism. This is a belief system that is sustained by the relationship with the Earth, being protected by it and the ancient spirits. It is interesting that, in some sources the Tengrists believe that the skeleton is sacred, because it stores a part of the Soul. They went as far as to not damage animal bones during sacrificial rituals. So, since Mu Shubuun has to break open the skull to eat its prey's brain, i wonder if it is seen as a even more evil act by them. [sourced by Buryati Religion and Society’ from Lawrence Krader, 1954]
As is the case with any culture, we need to know a bit of the time and place to understand the collective consciousness that give birth to such myths. The Buryatia territory as a place and the way of life of the Buryati people is essential to this mixture. For instance, being nomadic people that relies a lot in livestock and surviving the harsh Eurasian deserts and the SIberian tundra, the worst fears would often be dictated by those essential pillars of their lifes.
A creature that can slowly kill your livestock? A predatory demon that kills you alone in the desert, sucking your brains? Those were real fears. It is hard to dive deeper into Buryati culture in this text, because it is just a crop honestly, but is also very important to remind ourselves that the Buryati are a diverse people, and some behaviors, tales and even words can change from place to place.
There is definitively a lot to learn from their culture, and a lot to preserve. Being endangered to disappear, it is always interesting to spread the word to more people that could study and preserve Buryati history.
If you are interested, i can recommend also the paper ‘’Buryati Religion and Society’ from Lawrence Krader, published originally in 1954. It is not perfect, and it is pretty old, but it is a good start! It is one of the few English sources about Buryatian culture out there.
Mu Shubuun is a very interesting case of a regional folklore making a trip from it's mother culture and ending up appearing in pop culture. Even with UN classifying the Buryati language to be highly in risk to be extinct, this predatory bird devil ended up in games and known in many parts of the world. In SMT for instance, she ranked 9th as the most popular demon in recent years, as well is a recurrent character in almost every franchise release since the 1990s.
Kazuma Kaneko's design is great for me, because it interprets the beak as disguised as the creature hair, or is it hair and just looks like a beak? That is the magic of his take on the creature. I am just curious on how he got to this specific folklore in the first place.


Kaneko took inspiration from Buryati female clothes when designing Mu Shubuun appearance! Very neat. SMT Moh Shubuu lacks the beak, but its hair its styled like a bird's beak, head and wings in a very cool nod to its nature.
It is fascinating to think this happened, but it got me thinking that Mu Shubuun was a product of a culture, and real people that lived by this for centuries. As the warning says in the start of the text, we can use popular media to spark a flame of interest in the matter, but this has to be done with all due respect.
The next paragraphs are based on my personal opinions upon studying this tale extensively. But you feel free to disagree with me, or even correct me!
In my personal belief, Mu Shubuun is one of those Folkloric cautionary tales. Not only not to wander alone in the desert, which could be fatal by very real means, but also that violence against the more vulnerable could have consequences. In the case of Young Woman, this could end up as a Muh shubuu coming to enact her revenge.
Another personal observation of mine: The creature carrying flints reminded me of the old Korean tradition of young virgin woman carrying daggers in her clothes (usually in their arms as well), so they could commit suicide if endangered to be sexually harassed. [1] This could be nothing related, but i thought about it immediately after noticing the flint trope with Moh Shubuu.
As why the bird connection, i really can't say for sure. Probably because raptor birds could be menacingly common, around. But i should study Buryati culture deeper in order to be more accurate about it. End of my personal opinions
Be any reason why this tale survived centuries and ended up here, in the internet, videogames, and other works, is a mystery to me. Maybe the idea of a vengeful spirit taking her grudge on male society is alluring to some, maybe it was because Kazuma Kaneko really did an amazing design, and maybe it is because there is something about regional tales, folklore and beliefs that really fascinate some of us. Some distortions may have occurred in the way, but it is also part of this process. To me, it is important that Buryati traditions and culture can be preserved, and for many, Mu Shubuun is the link to this cosmos. That is a very interesting thing, and i am quite fascinated by it as well.
Thank you for reading up until here!

Sources:
-Matvey, Collected works Volume 3, pages 25 to 26 (reprinted in 2004) - (Хангалов М.Н. Собрание сочинений в 3 т. Т.3. / Под ред. Г.Н.Румянцева.-Улан-Удэ: Изд-во ОАО «Республиканская типография», 2004.- С.25-26’’)
-Irkutsk City Museum
-Buryati Religion And Society, Lawrence Krader 1954. (Sadly paywall...)
[1] - Korean Perceptions of Chastity ceptions of Chastity, Gender Roles, and Libido; F , Gender Roles, and Libido; From Kisaengs to the Twenty First Century (This one is just to back my claim about similarities)
[2]- The troubled state of the Buryati language today, Dulma Batorova
#blazescompendium#blazescompendiumentry#buryati#mongolia#shin megami tensei#kazuma kaneko#atlus#megami tensei#folklore#mythology
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blaze's compendium entry #7: Never deny tobacco to the Saci Pererê

The Saci painted by Newton Cavalcanti to a stamp collection, 1974
Warning: Faith and religion are important real life topics, that tackles the culture and way of life of millions of real life people. It is a cultural expression, and must be respected by all means. Here, we use a video-game ( some times) and other media series only to ignite the flame of learning about the matter, using its art when well depicted, but we do this with all due respect to the cultures we talk here, grounded by real life sources, cultures and people. And i mean this with respect. Hope you all enjoy.
I can finally talk a bit about my home country myths after a brief trip around other countries mythical creatures. The Saci is an extremely popular creature in Brazilian Folklore, and if you are Brazilian i am absolute sure you have encountered its fabulous tales already.
The Saci is (regrettably) not represented in the Megaten game series, as most of characters from my Compendium series. But i want to pop this bubble going forward, and not be exclusively tied to this games, since Mythology is a much more expansive subject, and i like to use Megaten just as a welcoming gate to more casual audiences!
The Saci Pererê is a Brazilian folkloric creature, akin to the trickster ''gnome'' archetype, not considered an evil creature by any means, but very mischievous and a prankster. Normally depicted as a black skinned toddler smoking a pipe, red cap, and some times red clothing. It's most striking feature is his only leg, which he uses to jump around in a surprisingly agile manner. His mischief deeds are many, like he would tie horse's manes, startle them, move objects inside people's homes, etc... His most known power is his control of wind currents. He can summon small sized typhoons, in which the creature can ride on to flee or use to fight if he needs to.
The Saci is hyperactive and fast, always doing something. Some people can interpret this creature as malevolent since its mischief and pranks can cause serious problems, like stealing the breaks of a carriage. However, that's not exactly the truth. The Saci is, almost always portrayed as neutral creture, and it has been since it's inception into the public consciousness. As we can see, some times it can be treated as a little devil, but it's a beloved figure nonetheless.
The name Saci Perere cames from a theorized corruption of the Tupi Guarani words: Caa Cy Perereg, which means ''Jumping Evil Eyes''. That's stated on the book ''Saci Perere: An Inquiry Result''. I was not able to verify it independently because i do not speak Tupi, and i was also unable to find online translators. But, this wording is also verified by the book ''Geography of the Brazilian Myths'' by the legendary Brazilian folklorist Camara Cascudo, so it seems legit. There will be a lot of this book in this subject, because it is such a complete work and a vital piece of research for anyone getting into the topic. [2], [1]
Cascudo does a great scholar work, going as far as giving dis-ambiguity of the Saci from other myths, and even animals that could be related to the legend.
Context: The Tupi Guarani, or just Guarani are the biggest native population living in the territory of Brazil today. They live more from the central region to the south and south-east, relatively far away form the Amazon forest in the northern regions. In general they are polytheists, and today are around 57.000,00 people. [This is sourced by the IBGE, Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics]
But, even being a very popular creature in the local folklore, and even transcending the boundaries of its homeland some times, (as we will see ahead) the Saci has a relatively recent history. It's impossible to pinpoint exactly who and how this legend started. But we know it started on the southern and south-eastern most regions of the country, but there's no mention of it on the old fables from native people, which makes scholars think that the Saci is not that old as its relatives of the regional folklore.
A fact that corroborates this assertion is that, besides being a very popular folklore in Brazil, Saci is absent form any mentions to ancient sources, starting to appear more from the 18th century and above. [1]
The name Saci is not stranger to Folklore in the region though. Saci is also the name of a bird, Tapera Naevis, which has a related myth according to the Brazilian National Museum. The Saci bird is treated sometimes like a demon, that can confuse travelers with its singing. Another local legend has that this bird can suck the dead's souls. Al tough both of those claims are backed, i personally did not hear about it until researching for this topic. [1]
This particular bird its said to be seen as a bad omen to this day, in the Amazon region. This is pretty far away from where the folkloric Saci was born, but it seems that a common association with the bird is that it asks for tobacco to its pipe, just like the Saci does. This animal has the habit to sing during night times, so the legend says that it means it wants tobacco. If you actually replies to it, its said the bird will come after your promisse. [1]
This particular bird can also be connected to another folkloric tale, this time from the northern regions of Brazil, a witch called the Matinta-Pereira. This is a particular demonic witch, that can transform itself into the Saci bird, (Tapera Naevis) to get offerings from residents of villages. When her demands are not met, she causes bad things to happen. She also wears a red hat, and her name also bears the ''Perereg'' wording from before. Scholars believe that this is because this bird sometimes jumps in one leg, and has red feathers in their heads, which would also make senses with the Saci! I personally could not find any visual registry about it, but i am sure most of birds some times do this kind of stuff. [1]
The Matinta eventually became a generic name for haunting and supernatural ocurrences in the Northern regions, while the Saci became a thing in the southern regions. The Matinta became more associated with its cursed singings, as the book mentioned before says: ''It trespasses villages with its haunting screams. It will not attack or go after people, thought.'' [1] It kinda resembled me personally of the European Banshee, which also caused misfortune and disasters, and possesses a terrifying cry.


The Saci bird and the Matinta-Pereira witch. (Art i got from Wikipedia, can't find the artist ): )
But this is just one, of the whole ''Birds named as Saci''. There is also the Romococcyx Phasianellus known colloquially as ''Peixe Frito'' (Fried Fish) and inhabits most of Brazilian territory. It has myths around its singing. [1]
If you got interested in this whole rabbit hole of folkloric birds, there's a lot to go on around the world myths! Just some time ago we made an article about the Muh Shubbuu from the Buryati people!
Notably the Saci shares its notoriety and Brazilian legends Pantheon with other similar trickster spirits, like the Caipora and the Curupira. Both are protectors of the nature, both of those are tricksters, and both also asks for tobacco in some legends! Although, the Saci is not a protector of nature, his only goals are to cause mischief. In more recent times, Saci is treated like he's a friend of those two, but this has more of a childish connotation, when teaching about national folklore to children.
The Saci also has spawned some relatives in neighbor countries. In Uruguay there is the Yasi Yatere, which is kind of a gnome with a magical wand. It can shape shift, and it usually kidnaps woman. When its wand is taken, much like the brazilian Saci with its hat, its powers ceases and it becomes weak. It's described in great detail in the book ''Supersticiones y Lendas'', from Juan B Ambrosetti. [1], [3]
In Argentina the Yasi is described mixing the features of its cousins from the region. It is also a dwarf type of gnome, but it's red and also carry a magical wand that protects its powers. They also would kidnap children to play with them, but they would go insane after that. It is also described by Ambrosetti. But also mentioned in a letter of a European missionary called José Guevara. [1]. [3]
Many of these features that the Saci and the Yasi shares comes mostly from European legends, the old archetype of a monster that can be tamed by taking it's belongings. Like the Vouivre from France with its carbuncle. The Saci wears its distinct red hat, that its often taken as the source of its power, so capturing a Saci involves capturing his hat. This could have a Portuguese influence. [1] Theres myths in Portugal, like the so called ''Pesadelo'' which is a creature that when having its hat stolen, could be controlled by the assailant.[1]
-Interesting fact that i have found many sources for this Portuguese myth, and other books mentioning it, but when talking with a friend from Portugal, he could not recognize this specific legend. If you are also Portuguese, and know about it, please let me know!
The 1924 book from F.C Maytzhusen: ''Pigimeos en Leyendas de los Guarnies'' Roughly translated as ''Gnomes in Guarany legends'' tells that the own Gurani people from the region had already its own myths about small magical people living in the woods, which some scholars attribute to an ancient memory of a small stature tribe that potentially lived around. This concept probably mixed very well with the before cited European beliefs, brought by the invaders. [4]
As you can see, it's like the already established lore about native gnome myths got fused with the European equivalents, such as like: The haunting trickster spirits of the woods, small size, agile and mischievous. In the book Geography of Brazilian Myths, the author makes a lot of comparisons to Djins, Imps, Faes, Fairies, and in fact i believe the Saci can absolutely fit in any of those ''races'' of mythic creatures, specially a Djinn or Yokai.
But in that book, the author fixates on the European Kobold being it's main ''ancestry''. The Kobold is like a Goblin, gnome and other whimsical forest creatures like the Brownies, Knockers and Silkies. Kobolds are a bit more versatile than its relatives, being told to live in houses, mining sites, and even boats. The boat ones used to smoke pipe! Kobold are individuals and can be mischievous, haunting and tormenting Humans that don't do their will. Just like their possible Brazilian relatives, the Kobold encounters are not usually fatal.




Silky, Knocker, Kobold and Brownies are just some whimsical European fae that can be the common ancestor to the Saci
While some of those European Fae often smoked, the actual academic theory on why the Saci smoked pipe, it's from the native smoking rituals and culture of the Brazilian Native people, such as the Guarany. In the book before mentioned, the native people from Brazil teached the European invaders how to smoke. This was quick considered to be a sin for some European priests and got demonized by some as well, while it spread quickly between their peers. [1]
The Saci being one legged is not something original in mythology. Going back further in time to the legendary book ''Natural History'' from Pliny the Elder, (i really want to come back to this book one day) where he describes the Monopods, humanoid creatures that had just one leg and a giant feet, which they used to cast refreshing shadows on themselves when it was too hot outside. This creatures were before described in the even older book, Indika from Ctesias, and supposedly spotted in India. Just like the Saci, this creature was extremely agile even if just having one leg. They continued to be believed and continuously described well over the middle ages. [1], [5]

Monopod. A rather Silly guy from Nuremberg Chronicle, 1493
There's no consensus on its origins, but some people say that the first people from the Europe seeing Yoga practitioners in India stand in one leg, or have some kind of parasol confused. We will likely never know, but that goes to show one legged humanoid creatures were already talked about much earlier. [1]
In Chile you also had the Ketronamun from the native people there, a small gnome with just one leg, that appear in myths from almost every part of the Pacific South American coast. [1]
But there were also one legged deities around, take Tezcatlipoca from the Mexica (Aztecs) for instance. Being the god of moon and the stars, and one of the most important beings in the Mexica pantheon, he lost its leg fighting Cipactli. It was also related to the nocturnal wind, another connection with the Saci. But there is no scholar belief that the two were actually connected, they just shared a lot of similarities. [1]

T ezcatlipoca misses his leg, or foot in many depictions!
But How the Saci was actually Born?
As we discussed the Saci Pererê was not cataloged by the first European Invaders of the 16th century. In truth, there are a lot of myths and tales that were properly archived by them, but the Saci is nowhere to be seen. So, scholars deduct the Saci was not that old, being actually born and popularized around the 17th century. [1] But the Saci would just gain character and personality around the 19th century.
The legend much probably, spread by word of mouth from south to north, while it would slowly absorbing local and foreign elements during its trip. From the regional mythical creatures like the Curupira, he inherited the ability to confuse and mislead people. From Caipora he inherited the haunting whistles and its relationship with horses. Its only leg could be from the Bird myths, and also inherited from European folklore as well. Its own red hat also coming from there. [1]
The red hat sometimes its a sign of supernatural entities in Europe. The name ''The One With The Red Hat'' was an euphemism for Satan himself and other devils in Portugal. The Saci some times is treated like a devil, in the Book ''Saci: An Inquiry Result'' at the page 83, there's a tale about the Saci appearing with a sulfur scent, just like demons would normally do. [2]
The Revival and the Controversy of Monteiro Lobato
When we talk about the Saci in Brazil, the elephant in the room is always Monteiro Lobato, an author from the 20th century. Without a doubt, his work was one of the most prolific and known authors if its time, and also dedicated a lot of his work to disseminate national Folklore. There was just one big problem: He was a terrible person. Lobato was a racist, aligned with the United Statian KKK, (yes) and generally treated people, specially black people, very poorly. So, if that was a text oriented only for Brazilians, i'd completely ignore his name, and would focus on the texts. But, for the sake of education of foreign readers, i had to mention him.
In 1917, this (awful) individual published an inquiry in one of the biggest newspapers of the country, searching for personal and regional tales about the Saci, which he planned to catalog and archive. The idea was to protect the national Folklore, since he would argument that we should focus on our own mythology, rather than importing everything from other countries. While the Saci had the ancestry of European Myth, it was a 100% modern Brazilian born legend. This kind of thought is pretty impressive from a racist dipshit, but ok.
Although Lobato did had the idea of collecting tales, they were all brought from other people, regular people, which i prefer to credit. With this rather than him. They published the book ''Saci: An Inquiry Result''. This book would be very important for the Saci lore, because it ended up skyrocketing its dim popularity, making sure he would survive for more centuries.
A funny trivia about this book, is that at the time of its publishing, the newspaper asked its sponsors to make ads using the Saci. Which had some pretty weird art that i rather not show. Thank you Monteiro Lobato for creating our capitalist version of the Dictionaire Infernal, very cool.
[EDIT] Lobato is also the creator of the work ''Sítio do Pica Pau Amarelo'' or roughly translated as Spot of the Yellow Woodpecker. I ended up not talking about it, but this is by far his most famous work that featured the Saci Pererê as one of the main character, as many other folkloric Brazilian entities. This work is often credited as many children's first contact with the Saci, and other folk Brazilian tales. This particular series is about a farm owned by Benta, an elderly woman that lived alone in the countryside. Her friend Nastácia lives along, and is famous for her dishes. She often gets visits of her nephew Lucia, which has the nickname Narizinho. She brings along her doll Emillia, which ends up gaining life and becomes a sort of tomboyish sidekick. They both live adventures along her friends and folkloric creatures.
Much regarded as the ''Brazilian Wizard of Oz'' this work was so popular it got adapted into several comic books and live action shows. The most popular of which aired during the 2000s from 2001 to 2007, and i as a kid often watched it. My favorite character had to be Emilia. (She will be present in the compendium, or a lesser post soon enough)
Al tough, due to Lobato awful nature as a person, the series is often pointed out as racist and problematic, being also written in the early 20th century it was filled with problems, which made a lot of people that grew up with this work depressed by those details. Luckily this is one of the rare occasions where there is an active effort from scholars and fans alike, to separate Sitio's influence on Brazilian culture and Folklore, from the awful person that was Lobato. The book is now on Public Domain, and each new iteration of the story deletes more and more problematic points, and as more decades went by, it gets more safe to consume and mixed with the Brazilian folklore, leaving the author in a sweet side note.
That said, not everybody is ok with this approach as well, and prefer to just abandon the literary work entirely. Which i honestly can't blame them for...

One of the latest iterations of Sitio do Pica Pau Amarelo is a cartoon, produced during the 2010s. Here are Emilia and Lucia.
But, as the 20th century went by and more people went in contact with the Saci tales, now widespread, the once regional myth started to gain the world, and became a symbol of the country culture. For instance, in the 70s and 80s the Saci would be featured in the Japanese anime: Akuma Kun, from the legendary author Shigeru Mizuki, which i already covered many times here. Mizuki is an old acquaintance of us theologians, because he was not only a mangaka, but also a devoted scholar of over the world mythologies. Its studies some times ended up in Brazil, and that's how he got the Saci.
You may know this author from the famous Ge Ge Ge no Kitaro series. Mizuki made some mistakes, but he was one of the most important folklorists of its time, helping to protect and disseminate the folklore of his country. According the author Michael Dylan Foster, in the book ''The book of Yokai'' Mizuki was influenced by folklorists as such Yanagita Kunio (we already mentioned him here as well, for the Obayrion post!) And thanks to Mizuki, most post war Japanese people were thinking of his works, when thinking about Yokai.
But back to the Saci, he was a recurring character in the Akuma Kun manga. The series was about a boy that could control mythical creatures from around the world. Since Akuma Kun got a lot of sequels and reboots, we are talking about Saishinban Akuma Kun, from 1988. There, the Saci makes an appearance! The looks is very faithful, but the hat isn't red, and in the animation the character would have two legs, rather than the only leg always associated with it. Still, he controlled the winds and was very mischievous just like in its home country!


The Saci in Akuma Kun Manga vs Anime
Mizuki's iteration of the Saci also just loses its powers when people take out his pipe, which differs from our regular version, where the hat does that. Besides this fact, Mizuki takes the artistic freedom to make the creature liking Football, which i particularly find funny but a bit stereotypical, and some people did not liked it. Overall, i thought it as a great representation!
Akuma Kun will get a new Anime in 2023. Lets hope that our Brazilian whimsicall friend makes an appearance.
There is much talk on how Mizuki found about the Saci Pererê, and the contact of Japanese with Brazilian folklore. I already explored that on my text on the Pokémon Whimsicott as well. However, the Brazilian Folklore in my opinion resonates very well with Japanese Folklore, so much that a lot of other Japanese artists that came in contact with it ended up using it as inspiration as well. A very known example is from the animator Ype Nakashima, that much probably had contact with Mizuki. The Saci was a character in one of Ype's most beloved works, the animation Piconze.

Although the exagerated details in the Saci, that can be seen as problematic nowadays, this depiction is a product of its time, and i do not agree with it. It's here for the purpose of education.
While the Saci is not from Japan, we can see that it would get along very well with other Yokai, which ends up making it kind of popular with Japanese audiences. Other Brazilian Mythical creatures were also explored by foreigners like the Cuca, Caipora, (which appeared in the Demi Kids series of games, by the way!) The Curupira, and many others!
The Saci vs the Halloween a National Symbol
The Saci Pererê got the status of a national symbol. And as such, it was often used as a counter point to foreign interference in Brazilian culture. Since its rebirth in the 20th century, in an attempt to retrieve its legacy, the creature is often held as a protector of Brazilian culture.
As such, in 2003 it was proposed by Brazilian politics that the Saci should have a national holiday, and it should be commemorated in October 31st, in opposition to the growing Halloween culture around Brazil. The argument was that this was a foreign holiday, not from our country, and we should celebrate the Saci as a symbol of patriotism.
Notoriously, the beef between the Saci and Jack O'Lantern was commemorated in a song, from the 2013 parody metal album ''Metal Folklore'', sang by the Brazilian metal singer Bruno Sutter, acting as his parody Persona the Detonator. The album was pretty well received and brought attention to the concept again, with the song called ''Saci.'' which is a critic to United States imperialism and its forced influence on Brazilian culture. Bruno brought along the famous Punk Rock singer João Gordo to this track, which is a celebrated artist in the country, who even ended up in some Nirvana gigs, back in the 1990s.
I personally got to know Bruno during a concert, and even watched him perform live. The dude is amazing, and you should give it a listen!
You can listen to this particular song on Spotify!
''October 31st is the Saci day!
Do not fool yourself my friend
Halloween is american, which is far away from Brazil
Trick or treat is your fucking mother!
Saci is the red cape warrior!
Saci is a mischievous boy!
The Pumpkin is already shitting itself
Don't fuck with Brazilian Folklore!'' -Some Lyrics from the song

This amazing artwork was provided by my great friend @atmaflare! Here we see the Saci having an argument with Jack O'Lantern, probably saying to him to stay away from his turf.
The comedic and critic nature of the song made it pretty popular at the time, and this canonically beef between the two creatures became somewhat common here. Still, both are dates are celebrated without any major incident! The Saci Day is not a way to attack the culture of Halloween, but to bring attention to our own folklore.
Inside Brazil, Saci is also a major character of the amazing Netflix series ''Invisible City'' which is all about Brazilian Folklore, and supernatural occurrences in a life of a police officer in modern times. Give it a watch!
On Personal Notes
So, in this case the Saci comes from my home country and naturally i grew up with his tales of mischief and supernatural occurrences. In this sense, i have much more of a personal connection to my topic of study for this text, and so i can have my own verdict to it. It's natural for kids here to have contact with this mythical character. Or at least, it was when i was a kid in the early 2000s.
When i was little, the Saci was a particular mythological being that i feared. It was not that he was dangerous in a real sense of the way, but i rather not find it alone in the woods, or be bullied by him.
Still there was a grain of fascination by his figure, because there was the possibility to actually win against the Saci, taking his hat and making him do as our biding. And most of time, his mischief ended up as funny for kids.
Nowadays the Saci is still regarded as one of the most beloved folkloric tales of Brazil, inspiring newer generations of folklorists to protect and share the culture that they belong and grew up with, such as myself. For this reason, the Saci will always stay in the Brazilian collective consciousnesses, not only because of its supernatural powers, its haunting abilities surviving the current age, but also as a symbol of our own home in this planet.
As Camara Cascudo said in his book:
''Today the Devil that is inseparable from tales, from countryman conversations. Vague, haunting, unexpected, malicious, humorous (...) Now, diluted in the memory of those who does not have the spiritual age to fear it anymore.''
Sources and Bibliography:
1- Camara Cascudo: Geografia dos Mitos Brasileiros (Geography of Brazilian Myths)
2- Saci: Resultado de um Inquérito, Monteiro Lobato (Saci: An Inquiry Result)
3- Supersticiones y Lendas'', Juan B Ambrosetti.
4- Pigimeos en Leyendas de los Guarnies, F.C Maytzhusen
5- Natural History, Pliny the Elder
6- The Book of Yokai, Michael Dylan Foster (small Citation)
#blazescompendiumentry#brazilian folklore#folclore brasileiro#saci perere#jack o lantern#pyro jack#megaten#folclore#long post#m#mythology#brazilian mythology#shin megami tensei 2#blazescompendium
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blaze's Compendium Entry #5:
What does the fox say? Ask Cironnup- Kamuy

Warning: Faith and religion are important real life topics, that tackles the culture and way of life of millions of real life people. It is a cultural expression, and must be respected by all means. Here, we use a video-game series only to ignite the flame of learning about the matter, using its art when well depicted, but we do this with all due respect to the cultures we talk here, grounded by real life sources, cultures and people. And i mean this with respect. Hope you all enjoy.
Let's get back to Japan once again, but this time to the northern Island of Hokkaido. There lives the Ainu people. Today we are not only talking about my favorite Megami Tensei creature, but also about very interesting entities, culture and people. Please, sit back and enjoy the ride.
(Please, note that i don't speak Japanese. I had to go over English sources as well use software to translate. If i got anything wrong, let me know!) This time, all sources will be available at the end of the post, since iv used them extensively, it got pretty messy to pin down the exact points, so will list them below)
Cironnup (Also called Chironnup or Chironnupu in Japan) in the Ainu tongue translates to ''Those who we kill many''. And it can be used to describe foxes in general, but also is referred to a Kamuy.
For us to understand what Cironnup is, we first need to dive in the meaning of the word Kamuy, which is very, very interesting.
In the Ainu tradition, Kamuy can be a complex term to translate. It can be defined as a sort of divine spirit, supernatural entity or even a god. The Foundation for Ainu Culture translated it as the word god, when i emailed them about the matter. Its similar to the word Kami, in Shinto Japan. It's a tricky word to translate that has no perfect match in English. But let's go with god.
Sometimes in the modern day Japan, the word can also be translated as Kami, or Hotoke (Spirit). But as their English counterparts, those words don't match 100% correctly the true meaning of the Kamuy word.
The Ainu belief system comes from their relationship with the Kamuy. This belief came from people who have a deep connection with nature, and helped them to survive and thrive in their environment, as well protect them from disasters and other calamities.
The Ainu belief system does not have a central scripture, like the Christians have the Bible. Their views of the Kamuy can be interpreted differently through time and place, but remain somewhat similar. It's good to remember the Ainu is a diverse group. Beliefs, customs and regional dialects can vary from region to region.
But ok, then what is a Kamuy? You ask.
The Kamuy description can vary, but they are spirits, supernatural entities, or gods. They can be attributed to many creatures and objects. In fact, there's Kamuy for diseases, earthquakes, fauna, flora, and more. It's like this belief system comes around the idea that everything and everyone has a soul.
There's not only natural occurred Kamuy, but also the ones that came from man-made objects, like spears, boats.
The relationship between Kamuy and Human are complex. Some Kamuy can provide for Humans, like animals that provide meat and fur, or plants that provide food and remedy. Others can protect and take care of Humans. There's also Kamuy who bring calamities, like diseases such as smallpox. (Sources where keen on Smallpox, it seems it got pretty common in Hokkaido some times.)
Some examples are like the Fire Kamuy, that not only provides heat and cooked food, but also hears Humans and take their pleads to other Kamuy in case they still have not answered. the owl related Kamuy remain outside villages looking after their people.
Another good and very specific example is the Salmon Kamuy. Known as Chep-Kamuy. Salmon was a much needed fish for the Ainu, so they often built their villages next to streams where they could find this fish. Thus the importance.
Kamuy are often portraied as free willed entities. They live their lifes just as we do, and they can be good or evil. Some times they are not eivl, but there can be a conflict of interests between Humans and Kamuy. Being good or bad, Kamuy would only come back to their world once their mission is accomplished in the Human world.
It is said that the Kamuy have their own relatives and friends in their world, so it is at least implied that are many instances of one Kamuy. For example, many Chep-Kamuy living in their world along many Cironnup-Kamuy. For this reason, when a good Kamuy is going home the Ainu offers them hospitality, food, drinks in rituals so they can either thank the entity for what was given.
This way, according to the Ainu, the Kamuy will come back home happy and satisfied, thankful for the Human hospitality. They will tell all their friends and family about how good they were treated on Earth. The Ainu believes that not only the hospitality offered to the Kamuy makes they wanting to come back, but also they could bring more Kamuy along, after telling their relatives about how good they were treated. This also make that specific Kamuy more respected in their world. Both sides having a mutual relationship.
In the case of bad Kamuy, like disease, the tactics were to run away from it. Some Ainu even erasing their own footprints in the snow so they can't be tracked by the malevolent entity. They were also treated with respect, but in more of a fearsome way.
The Kamuy often inhabited animals and plants, for example. So, in the case of wild animals the way a Kamuy go home is when the animal is killed. Hunting deprives a creature of their life, but it is necessary for survival. This act is seen as the Humans liberating a Kamuy back to their world, after have killed their carcass. (In the case of wild animals)
One of the more famous, and important of those rituals were related to the Bear Kamuy. (Kin Un Kamuy) I wont go too deep into it, because it's complex, but basically the Ainu took care of a bear cub for a whole year, even living among them as another member of their society, before slaughtering it with arrows, and eating its meat. This way, the Ainu hope the Kamuy goes to its world grateful for the hospitality and the time it spent with Humans.
-You can remember Teddie from Persona 4 kinda having this motif in his Persona ''Kamuy''.
As you can see, the Kamuy is a fascinating subject. They can be good, bad, they are multitudes, they have families and lifes, their own personalities and interests just like Humans. They can be humble, hateful, have pride or a good sense of humor. They can be related to natural phenomena, animals, plants. There's just a lot to cover about Kamuy.
My note here, but it remembers me a lot of the concept of Jinn and Daemons, from Islamic and Greek pantheons respectively.
BACK TO CIRONNUP, THIS WAS A LONG TURN

Cironnup-Kamuy is the fox deity in this context. Foxes by themselves were called upon many names in the Ainu culture. Cironnup is one of those names. But it could also be Kemakosnekur which means ''light footed god'' according to the Foundation for Ainu Culture.
Cironnup appears in many tales and are generally known to be Kamuy that listens to people's requests, brings food, can protect against illness and foreign enemies. They can appear in premonitory dreams to warn about calamities. But there are some instances of Cironnup doing mischief and evil deeds, like possessing people, transforming into people as disguises.
As in many cultures around the world, foxes are treated like cunning and natural tricksters. But the Ainu had a deep relationship with the foxes, since they were essential to their survival in some times. They could be deceiving, but also could bring good help. This could explain this duality.
The name Cironnup could also be referred to other creatures, it can be names of villages, and could also describe wild beasts. It could describe many other wild animals that were heavily hunted by the Ainu, but slowly the name was more and more associated with the Fox. (The Fox itself could have different names in different regions as well.)
In the specific case of Cironnup, the premonitory nature of it were also brought by some regions using fox skulls as divination tools. They could also be used as guardians for Sea Fishing.

Cironnup calling its Kamuy friends for help? In Japanese this attack is called ''Kitsunebi Aputo'' Which mixes the Kitsunebi flames, with the Ainu word for rain, meaning a rain of a fox fire. Although... Kitsune is a whole different matter.
In my researches i found a Brazilian web page dedicated to Japanese culture. There, i found a story about the author being hunting with an Ainu, and they talked a bit about their relationship with the Cironnup Kamuy.
According to the author, they were out hunting when he noticed footprints in the snow that were from a Fox. He then proceeded to ask the Ainu hunter if they should go after it. But the Ainu stopped the Brazilian hunter, informing him that if they catch the fox first, the Cironnup-Kamuy would certainly go around the woods telling all other animals they were hunting nearby. Because by killing the Fox, the Kamuy would be liberated of the body.
When the fox was indeed caught, they would tie their snouts, so it would keep its mouth shut and wont spoil their hunt. The author did not seemed conclusive if this was a general and normal hunting behavior for the Ainu, but being a first hand account (And written in my own native language) i found it interesting to post here.

Cironnup's beta design for Shin Megami Tensei IV: Apocalypse. It wears some clothing inspired by the Ainu.
The Human Race has a very interesting relationship with foxes in general. Their depictions usually repeats itself through our history, because they are very interesting animals by themselves. Me myself, I've lived my whole life, in a culture where foxes are absent because they are not naturals to the place where i live.
Their relationship with foxes makes me wonder and reflect about it, since the creature does indeed have a duality. While it can be deceiving and cunning, it has also a protective nature, it is strong and some times even lovable. Foxes are also signaled worldwide as an awareness and investigative symbol, which is also portrayed by Cironnup, sometimes presenting danger from far away.
Still worldwide, the foxes are treated like the tricksters of the nature, masters in deceiving and playing pranks.
The Ainu fascinated me not only as a culture, but also in their relationship with the nature, not exactly looking at the world around only as resource, but also with care and respect.
I hope one day i can visit Hokkaido and learn more about the Ainu culture personally.
-Ainu online dictionary Ainu-to-shizen Degitaru-zukan”by Ainu Museum
Sources:
-Akarenga JP (A Hokkaido culture foccused web page)
-Commentary on the book “Karirinka-to-kitsune-no-kamisama” [カリリンカときつねのかみさま] (2012) by Sakiko Yatani Provided by the Foundation of Ainu Culture
-The Foundation of Ainu Culture (Inquired via e-mail)
-Ainu Legends, Cironnup Daisuke Tchê (The tale about the Ainu hunter, in portuguese)
Special thanks go for @researcherposts for helping me reaching the Foundation of Ainu Culture.
Again, if i got anything wrong, please correct me! I will be more than help to fix anything :)
#mythology#ainu culture#Cironnup#Ainu#hokkaido#mythology and folklore#shin megami tensei#atlus#blazescompendium#blazescompendiumentry
100 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blaze's Compendium entry #2: Zhu Tun She: A pig? A snake? Both!?

This is a very mysterious creature, that supposedly has been spotted during the Song Dynasty, in China. (This being between 10th and 13th century)
Zhu Tun She (which means literally something like ''Snake Pig'' in Chinese) was described as a demon or monster snake, but it had four legs and behaved like a pig but violently, making squeaking noises. Some sources say it was covered in scaled and hair.
This specific creature caught my attention some years ago, and was one of the first Megaten Demons that i wanted to research by my own, because i found it very interesting. I ended up going to a Chinese Book Store in my city to research it, but it was relatively unknown even for natives. The internet has surprisingly few information about this demon, and since i do not speak Chinese, there's a huge language barrier. Still, i went on.
The most widely spread tale about Zhu Tun She in the west and Chinese web, is that it appeared during the Song Dynasty attacking peasants and soldiers, and (maybe) sometimes eating them. It was supposedly defeated by an officer who was also a magician, and managed to kill it.
From my initial superficial research in the topic, as well my more detailed one, it seems this creature is not a recurrent one. They are different from more recurrent characters, that have their own tales and whatnot. As far as i could pinpoint, at least, Zhu Tun She had just a small tale from a very specific time period. It's valid thought, that i affirm once again i am not a Chinese speaker, so if the creature appeared in other literary works, i was not able to read nor find it.

Zhu Tun She in Demi Kids. Sorry i stacked them...
The origins of the beast came from the Yijianzhi, a collection of folkloric and fantastic tales written during the Song Dynasty. This series of tales contained originally hundreds of chapters, which were complied by Hong Mai, a prolific writer from the time. Its believed that the first chapter was from around 1161, and the other ones from around 1198.
Hong Mai (1123 - 1202) was an author that decided to collect this old stories in a book. He gave the name Yijianzhi in honor to the author Yijian, which wrote according on tales he himself heard, according to Taoist Texts.
The Yijanzhi by itself is very interesting. It contains multitudes of texts, that travels around a lot of topics. From gods, to ghosts, to revenge stories, kings, fantasy, some bizarre stuff, and most important: Fantastical creatures that inhabit those legends.
In case you want to read the book... I have good and bad news: The good news is that it received a partial translation to English in 2018, i have read this version. It's called Records of The Listener and it's a simple and very rewarding read. There's also a 2007 version of partial translation. Both are properly archived and you can read it online.
The bad news is that, they are just a partial translation, many tales are missing and the Zhu Tun She one is among those missing. We do, however have a summarized version, this version was extracted from me from Chinese sources, but you can also find it on the western web. I used software to translate it, so please forgive me if i get something wrong. (See below)
But before, let's discuss it's origins a bit:
While the source mostly associated with the story, was the elusive Shigeru Mizuki book ''Dictionary of Chinese Demons'', and probably the same Kaneko took it from. There's hardly English sources about this demon, which made it very hard to research about it not being a native Chinese speaker, or at least knowing a bit of the language.
Me and some friends even pondered about it being made up by Mizuki, since it has happened before with other creatures. But with the help of the Chinese Web, i could pin down exactly where this tale was originally from:
-This was present in the book Siqu Quanshu. It's a compendium from the Qing Dynasty that contained some chapters of the Yijian Zhi including this one, you can read in it's entirety online here. (If you can read Chinese. If you can't, i will provide a translation below do not fear.)
The indexation in this book is as follows:
Siqu Quanshu -> Yijian Zhi -> 戊卷03 ( volume 3) - It's unclear how was it's original index in its original source.
(Thanks u/storiesti for helping me finding it)
The compendium in question was commissioned by the emperor Qianlong, and it's how this tales survived. That's important, because many Yijian Zhi chapters simply did not survived to the modern age, and the way some of them did was being republished in works such as that. So, at the very least it was not made up by Mizuki or anyone in the internet.
So... What was this story about then? What was our little piggy's tale?
Here's a brief version of it, translated via software, sorry it was the best i could do:
In the stationed army at Jiankang, there was a officer named Cheng Jun who was very experienced in the "forbidden spells" technique, especially in subduing demon snakes. This incident seems to have happened in the 23rd year of the Shaoxing period. (1130 AD) One evening, when the army was training outside the south gate, a snake suddenly appeared in a bamboo woods. The snake was as thick as a pestle, about three feet long, covered in fur, with four legs, just like a demon. When it appeared, it would make a sound like a pig and chase after people while making this noise, running as if it were going to devour them. People could only panic and flee with no way to deal with it. At this moment, someone nearby found a horse stable and quickly used it to trap the snake, then reported the matter to the commander. The commander immediately sent someone to investigate and also commanded Cheng Jun, who was famous for subduing spirit snakes, to take care of the snake. After a while, Cheng Jun arrived; as soon as he saw it, he recognized the shape of the demon snake under the horse stable. He said, "This is called 'Zhu Tun She', a type of demon snake that kills people once they get entangled by it." After that, Cheng Jun blew air from above the horse stable and began to use his spells. Soon, Cheng Jun commanded someone to open the horse stable, and they saw the demon snake curled up and motionless. Cheng Jun then closed the horse stable again, deeply inhaled as if he was absorbing moonlight, and then blew air from above the stable three more times. Afterwards, Cheng Jun commanded someone to open the horse stable again, and they saw that the demon snake had turned into a puddle of blood.
A.. lot happened here as you can see.

Shigeru Mizuki's depiction of the Zhu Tun She.
It's unclear how common this demon was supposed to be in that tale, since Cheng was able to identify it pretty easily, and was known to defeat monsters like that all the time.
But that is how far it goes, the creature was (to my knowledge) never mentioned again, and made brief appearances in popular media. I don't know how it ended up in Mizuki's table, but he helped to popularize it since most of sources end up in his book. This is of course because it's way more accessible to read a book from the 1990s than an old scroll from 1130s.
Zhu Tun She differs from other critters i'v researched about, because there's few to no nuance in its existence. There's no moral to the tale, there's nothing to explain it as well, it seems like a cryptid from the old world, or just an elaborated fictional tale to amuse the emperor.
My personal theory is that: If it was not made up to amuse the Emperor, it was probably a very weird capybara or something like that. Who knows?
Still it's a very fascinating demon, a creature that would be terrifying to find alone in a bamboo forest for sure. But the best part of this study was to find more about the work where it came from, the Yijian Zhi. This books are simply amazing.
It's a collection of tales from old China, some supernatural, others just common tales. Still, they are very brief and entertaining also shedding some light into old China, full of myths and stories. As i said, there's a partial translation to English available to buy, or read online! Go check it out.
As for our pig friend, i could not find out if it had other apparitions in Chinese folklore, as mentioned before. It seems Zhu Tun She was an very isolated incident, and has only known by us because someone republished the tale many years later.
You see, snakes are beings very present in Human collective consciousness. Snakes were natural predators to early humans, many of us are born with innate fear of snakes. Snake monsters, demons and gods are part of lots of cultures around the world. The Quetzalcoatl in Central America, the Hydra in Greek Mythology, Orochi in Japanese mythology. In Northeastern Brazil there's a tale of a Feathered monster Snake called ''The Lapa's Feathered Snake''. This is just some of them, while many other exist.
As our ancestral predator and a very dangerous creature, snakes ended up taking a lot of space in our minds.
It's possible that other creatures similar to Zhu Tun She have been written, but could be lost to time. Who knows? There's indeed many other snake demons around the world, so our pig friend here is not alone!

I'd like to thank sorenblr for helping me getting attention to this research, and also Atmaflare for literally accompanying me during this research. @sorenblr and @atmaflare thank you!
Hope you all enjoyed!
Sources: -Siqu Quanshu: Some Yijian Zhi tales (Original Chinese book where the tale is currently available, brought from the Yijian Zhi books)
-The Dictionary of Chinese Demons (Shigeru Mizuki, could not find it for buying but its the source parroted throughout the web.)
#mythology#chinese mythology#Yijian zhe#shin megami tensei#megaten#kazuma kaneko#shigeru mizuki#yokai#demons#monster#atlus#blazescompendiumentry
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blaze's Compendium Entry #3: Do not try to steal from Vouivre!

The Vouivre is known to be a Draconic creature from the French folklore. Specifically from the Eastern part of France. The Vouivre is not to be confused with her fellow local dragons such as the Guivre, Wivre or the Melusine. Her differs herself for two key elements: Her almost always feminine humanoid looks (Although, sometimes shes also described as a fierce serpentine dragon) And the jewel in her forehead, called the Carbuncle. This jewel is precious to the Vouivre because it grants her eye sight, and also (according to some sources) heat. It could also be or not be her only eye, depending on the legend.
Vouivres are neutral beings. Generally they don't pick fights with humans, only if provoked or in self defense. Which is fairly common, since the greedy humans try to steal her jewel all the time, which is said to be more valuable than ''any mineral found in any Brazilian mine'' (Jenin Clement, 1884: ''Traditions Populaire de la Cote d'or'')
The jewel received it's name thanks to the Latin world ''Carbunculus'' which meant something like hot coal. That's because, according to the legend, the Vouivre's jewel was hot and bright like hot coal.
It does not help that the Vouivre is usually hoarding lots of gold and treasure in her lairs, which also attracts many unwanted attention. If, the Vouivre needed to fight, fortunately for her she was blessed with such strong flames that she could completely carbonize a human being to ashes. (Faune et Flore de la French Comtee, 1910- Beauquier)
But more often than they would like, the Vouivre would be hunted down during their most vulnerable period: When she had to take off the Carbunkle out of her forehead, and bath or drink water. That's the period she had to protect the Carbuncle, it should not fall into water, it would lose it's fire powers. And although there's few to no sources that state that this would kill the Vouivre, the Faune et Flore de la French Comtee book states at least one instance where removing it for too long would kill the creature. If you consider that the Carbuncle is destroyed after falling into water, it means she would also die.
In most of the tales, the Carbuncle serves as the Vouivre only eye. There's few sources where it is just a jewel embed into the creature's forehead, and in others it was part of a crown she wears. According to some sources as Jenin Clement, 1884: ''Traditions Populaire de la Cote d'or, looking directly to her Carbuncle (or her eyes) would cause confusion, panic and fear, making you completely immobilized.
According to a web page from the Fremch Comtee government, the Carbuncle is ''so valuable that not even all world's gold could afford it.'' This page in question is long dead, but there's some content of it available at the site Blackdrago. Not the most reliable source out there, but at least they saved this page's content. Also saved in Blackdrago, there's also a dead link to an article of the Fremch Comtee government about the origin of the Myth. This page is available at the wayback machine!
Fun fact: Carbuncle is also the name of the infection caused by the Anthrax. Anthrax has its own name meaning ''coal'' (ἄνθρ��ξ) in greek. That´s because the infection causes skin damage that looks like coal. The relation with the Vouivre is probably none, but i thought it was cool enough to put here. Please i can't stress it as much as i want but do not google it!
For those more versed in Mythological beings, demons and mysterious fantastical beings, you may recall the name Carbuncle as another mythical creature from the South American Folklore. The Book of Imaginary Beings, 1975 edition (Jorge Luis Borges) Describes the Carbuncle as a mysterious creature that the 16th century Spanish Conquistadors painted as elusive. A poet-priest called Martin Del Barco claimed to have seen one in Paraguay, and has described it in its 1606 poem ''Argentina'' (If you asked me, it's weird that it was in Paraguay, but was featured in the Poem named Argentina... but, ok.)
The Carbuncle, not only for it's name shared an eerie similarity with the French Vouivre. Martin described it as a ''small animal, with a shining glowing object in it's head, like a glowing coal.'' It's jewel was also sought after, and supposedly very valuable. I wont dive too deep in this creature here and now. The point is that the Vouivre had some similar creatures, even such a distant ''cousin'' as the Carbuncle of South America.

Final Fantasy's interpretation of the (Creture) Carbuncle.
Back to the Vouivre:
The window of time to get the Vouivre in her vulnerable state varies according to the region, or tale. Some say is once a year, or even weekly. The book ''The Drac: French tales of Dragons and Demons'' (Felice Holman, Nanine Valen, Stephen Walker - 1975) Tells about a tale where the Vouivre comes out only once a year. Normally the sources agrees it's when there's an important mass, and the people are too busy to care about the creature. This could be at Easter or Christmass (Christmass would be specially told in the Audrey region). In deeply catholic societies, nobody would flee from the church just to hunt the Vouivre. (Oh boy some did)
In tales from Monthier the Vouivre would come out at the eleventh first midnight bell from the clock, during Christmas night. The common sense is that they are generally very intelligent, that's how they know the perfect timing to be alone.
But also on her weak spot was the fact that the Vouivre had very frequent habits, which could mean that someone smart enough would eventually figure out how to reach her. She also had the ability to stun foes, although i just found one source about this skill in the book Jenin Clement, 1884: ''Traditions Populaire de la Cote d'or' Honestly, she's just trying to be alone, hoarding her treasure and caring for her hygiene. I can relate.
According to the book ''Faune et Flore Populaires de la French Comtee'' The name Vouivre came from the Latin word Vipera, which means viper. Vouivre can also means just ''wyvern'' in a general term, and not specifically this tale. Going by the Indo-European root you get to the word ''Gwer'' which means something warm or hot. From there, the word Wyvern comes from. It was meant to refer a fire serpent, or a type of dragon. This relation with the warmth and heat could also explain the Jewel that the Vouivre has, and the relation of this creature with the fire element.
There's some speculation about her name influencing regional dialects. For instance, the Morvan Dialect Glossary has the word Vouavre. This could mean heat or something wet. If the translation goes for the first option, this could theoretically be another association, or even where the original name of this dragon came from. Morvan is a dialect of the region Burgundy and is a french derivative. But i could not find any translator for this dialect, nor any confirmation this word even exists, so take it with a grain of salt.

She could canonically use agi!
There's a lot of places in Eastern France that bears the Vouivre name, that's how popular the legend was there. Many of those places are described in books such as the ones mentioned above (sources will be in the end of the article) are simply too old, some are not even there anymore. But surprisingly you can use google maps to check, and see that still there are many places with the name out there.
During my research, i also found out there's a french movie about this legend, called La Vouivre (1989). Honestly, it seems pretty interesting. It's about a WW1 veteran who became obsessed with the legend. (Just as did i, when i wrote 40ish pages of research for this text) I will take my time to watch it some day, and i will probably post my thoughts here.
Because their tendency to get mugged by Humans, Vouivres tend to like isolated places, where they can live alone and in peace. This could be old monasteries, old castles, caverns, or deep woods. No matter the source, Vouivres always like to be alone, have regular habits and are (mostly) neutral. Some of those locations in Eastern France are so associated with this creature, that it has either named it or became a symbol of this place.
Take for instance The castle of Vaugrenans. (We will be back to it later) The place was destroyed in the 17th century, and now is just ruins in which people said a Vouivre lived. It got so associated with it, there's a sign near it telling about the legend. In this case, the Vouivre was also interpreted as a creature who controlled, and used snakes. This particular feature can be seen in Kaneko's design of the Vouivre, since she has a snake in her body.
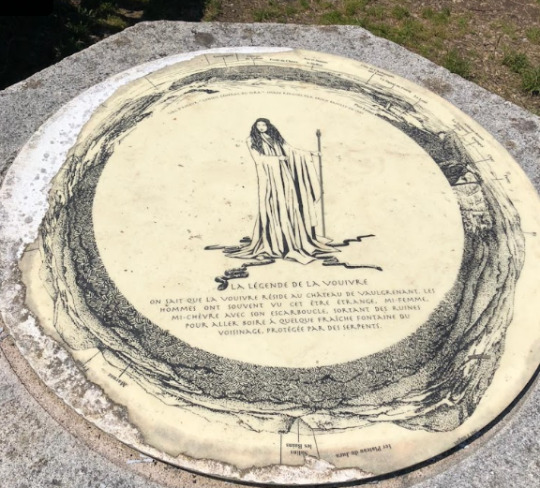

This Picture was taken from Google Maps, you can check by yourself! It depicts the Vouivre from the Vaugrenans Castle ruins.
The Vouivre were also commonly associated with rivers and streams, where supposedly they took their baths and drank water. Some hills, falls and mounds also got associated with it.
At least in one Source they used their feminine looks to seduce the human assailant, and get out of the danger. (Jenin Clement, 1884: ''Traditions Populaire de la Cote d'or').
Most of sources agrees that the Vouivre has bat-like wings, and when flying through the night sky, lets out a flame trail, like a shooting star. The sources like the Faune et Flore de la French Comtee, 1910 states that the creature could reach 2 meters tall.
The book ''The Drac'' Describes some tales of people that tried to actually rob the Vouivre. One man actually succeeded in getting her treasure, but not the Carbuncle. He made home with gold, but ended up dying by a mysterious illness, and the fortune disappeared.
In the Faune et Flore de la French Comtee, 1910 book, there's a legend about a man that succeeded in stealing the Carbuncle and also killing the Vouivre. The man blinded the creature taking the jewel, and had prepared beforehand a pit full of spikes. The man made the dragon fall to her death, and took the Carbuncle. But the thing was so valuable he never managed to sell it, dying without seeing a single coin from it. The treasure vanished not long after his passing.
Another tale from this particular book tells the horrifying story of a poor and hungry family, that ended up trying to steal the Vouivre's treasures to survive. The mother has the not so great idea to invade the dragon's cave with her infant son, while the creature was absent. But they takes too long that the Vouivre gets back before they could leave. In a hurry the mother left the children behind, who got stuck inside the cave when the Vouivre closed it. The mother waited camped in front of the cavern getting help from her neighbors, crying for her son. Exactly one year later, when the Vouivre exited the cave, her children was unharmed and could escape. Honestly, who would invade a dragon's den with a toddler? That's on her.
The legend was also spread from all over Eastern France. Regions such as Burgundy, Niverneeis and Baurbonnais were also prolific Vouivre nests, according to legend.
In the book Faune et Flore de la French Comtee, 1910, the author also compares the Vouivre to two other mythical beings. First: The Basilisk. Some people made this association due to their similar habitats, but the Basilisk being actively violent towards people.
There's a piece direct from page 12:
''...It (The Basilisk) was believed to be close related to the Vouivre. But much more terrible. (...) It inhabited old walls, attics and old houses, and guarded treasures...''
There are some similarities, but those are generic traits of mythological monsters and demons. They could be attributed to any creature, but i found interesting.

The Basilisk, by Kazuma Kaneko.
The other mythological creature discussed in the book that could be related to the Vouivre is the Melusine. Another distant cousin? The Melusine are humanoid creatures, sometimes half fish and half snake. In this book, the author draws parallels to the Vouivre, due to Melusine some times possessing snake-like features.
Much popular in Europe during the 14th century, the myth of the Melusine ended up making appearances in many coat of arms around Europe. Like the Holy Roman Germanic Empire, Escandinavian and the Warsaw City. Although many times treated as a snake, the association with the Vouivre comes from some draconic interpretations. This could be one of the origins, but its unclear.
This was not the only mention of the Melusine relation with the Vouivre. In the book Jenin Clement, 1884: ''Traditions Populaire de la Cote d'or', this also mentioned. They do share similar bodies, but the Melusine lacks the distinct Jewel in her forehead.

The Melusine, as it is portrayed in Shin Megami Tensei: If... by kazuma Kaneko.
There are some surviving records of first hand accounts of people who swear that they saw the creature. According to Faune et Flore de la French Comtee, 1910:
-In 1835 a villager from Jura, in the Dole district was about to go inside a pit where he saw treasure. He supposedly ran away crying in horror and blacked out. He said he had met a Vouivre face to face. Other villagers from that place and time swear they saw the creature as well.
-In 1850 in Augeraus someone actually tried to shoot the thing. According to the account, the demon was naturally unharmed.
Again at the book Jenin Clement, 1884: ''Traditions Populaire de la Cote d'or', There's actual names of People that got involved with the creature, supposedly:
-A couple called Jaquot and Jaquette (There's no way this is real, this is some serious Wario and Waluigi stuff)
-A Man called Nicolas Broreau
According to legend, this man actually survived his encounter while trying to steal from the creature. The creature stunned and seduced him, using her brains to get her jewel back. She even gives him some of her gold, but since he did not made what she demanded, the gold turned into rocks. This was also one of the few instances of sources where the Vouivre had two eyes, and not only the Carbuncle.
Those were the more interesting ones, but there are a lot of cases, and a lot of legends, it's hard to put everything down here. But again, sources will be in the end.
But by far the most interesting story of the Vouivre came from the book Jenin Clement, 1884: ''Traditions Populaire de la Cote d'or'. Here we go back to the castle of Vaugrenans, a chateau in eastern France. We are presented to the owner of the castle, but she was ruined by her beauty and excesses. This turned her into the demon Vouivre, who terrorized the town. She had a son, a knight who fought her to put an end to her destruction. According to this legend, the archangel Michael helped the Knight named George, who ended up killing the Vouivre destroying her Jewel and crushing her with his Horse.
In depression for killing his mother, he asks the Archangel to be punished. Michael burns the man and spread his ashes. He later is reborn as a child again, and was supposedly canonized.
When i first read this story it caught my eye that this is too similar to the Saint George tale, of killing a dragon. The name and everything. This tale could be indeed be a rationalization of the saint's lore. As i said above, this place is indeed known for the Vouivre legend, but there's nothing there indicating that this Saint tale is really associated with it as far as i have gone.
There's also a city in north-western France, called St. Georges du Vievre. This city has a name very closely related to the Vouivre and also depict a Saint George. This village today has less than 1000 people living there, and was first shown in a map in 1164 with his latin name: ''Sanctus Georgus De Wevra''.
Supposedly, Vievra refers to neraby woods called Guevra. This was the name of the place at least at the 11th Century. The name indicates that there was a dragon who ate children living in that place, that according to legend was killed by Saint George. (Probably not the same of his legend, this could be a regionalization of the myth, but all indicates it was just a regular Wyvern) This dragon was a Wyvern, the original meaning of the name Vouivre. Simply a Wyvern. The word could predate Latin, maybe going for more indo-European roots, but honestly it's hard to know.
The emblem of the village is literally Saint George killing a giant snake, which take us back to the original meaning of Vouivre and Wyvern, coming from the Latin word Vipera.

This village, as far as my research has gone, lacks any Vouivre tales or legends. Instead, the name here is merely a recall to its original meaning as the word for viper and Wyvern. This was sourced by the book ''Gentillhomeires des pays de l´eure'' Franck Beaumont, 1999. I've only found articles about it, the book is quite elusive. If you have it, or ever found it let me know!
In conclusion:
As such any local folklore, it's almost impossible to pin down the origins for the myth of the Vouivre. The common theme here is that of ''Risk and Reward'' type of cautionary tale, but also the European fascination with dragons.
Dragon tales were not uncommon at France, and we even already told about the Wivre, Guivre and many others. What makes the Vouivre tales interesting is that she was almost always minding her buisness, when the humans are the ones who cause her trouble. It's also worthy to note how in almost all of the tales there's never a happy ending for those trying to steal from the demon, even when they seems to achieve success in their endeavors to get the treasures from the Vouivre, something goes wrong. It goes to show how some things are just not made for human hands, no matter how much our species try to go over it. There was never pressure to hunt the Vouivre, most of them were not doing anything wrong in their tales, but yet the Humans tried to conquer their power to themselves.
There are many other interesting draconian mythological beings in Europe, and the Vouivre is specially popular in the particular Eastern region of France. It's a good display on how folklore and cultural traditions can influence a community, becoming naming conventions and symbols of that place's history. Today there's many people that fight to preserve this history, and i believed that researching and posting about it would do it's part.
I hope you all enjoyed. Please reblog, like, or interact to the post to spread the Vouivre's tale.
And remember, never try to steal from the Vouivre!
Sources:
Jenin Clement, 1884: ''Traditions Populaire de la Cote d'or''
Faune et Flore de la French Comtee, 1910- Beauquier
The Drac: French tales of Dragons and Demons'' (Felice Holman, Nanine Valen, Stephen Walker - 1975)
About the South American Carbuncle:
The Book of Imaginary Beings, 1975 edition (Jorge Luis Borges)
Note: All the books are in french, and i used software translation to read it. I am not familiar with the French geography, so if i got any place or name wrong, let me know!
#Vouivre#shin megami tensei#devil summoner#mythology#european mythology#french folklore#kazuma kaneko#wyvern#mythology and folklore#folklore#dragons#atlus#Vaugrenans#blazescompendiumentry
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blaze's Compendium entry #1: Dormarth- The Celtic hound

In most of sources, Dormarth is described as some kind of ''Cerberus'' of Celtic Folklore, being described as a guard dog of the gates of underworld on those cultures. And also in most sources, Dormarth's name is referred as meaning ''Death's Door''. This was also replicated in her Shin Megami Tensei appearance.
However, a superficial research into this creature always reveals that it is also called by another names such as ''Dormach'' and ''Dormarch'', and it's more often than not, treated as a hunting dog of sorts.
Speaking into the context of Welsh mythology and folk tales, it's said that the underworld has a king, called Gwynn Ap Nudd. He supposed owns a beast called Dormarch/Dormarth, that follows him during hunts. Specifically, his hunts for lost souls. (See Below the connection to the concept of Wild Hunt).
Gwynn is a very important figure when talking about Dormarth, since this mythical being is closely associated with the later. The so called ''King of Underworld'' is also associated to the concept of Wild Hunt, which is a common sight in European cultures. Famous examples include the Nordic Wild Hunt, with Odin presiding over it. In most of the depictions of the phenomena, hunting dogs are with it. Gwynn's Wild Hunt was no exception.
*It's also worthy to note that, i have focused my efforts on researching Dormarth, and have not gone deep into Gwynn's lore. I will probably do it later as another entry in my compendium series.
It's said in the Black Book of Camarthen, that Gwynn obtained Dormarth from the legendary King Maelgwn Gwynedd. The later really existed, but gained a mythic status in Celtic history. The figure lies buried in Puffin Island, UK.
The Black Book of Camarthen describes Dormarth as a beast with two front legs, only one head, and a tail that has 3 ends. There's no mention of lower legs, or other heads like a Cerberus would have.
To better understand Dormarth's discription and meaning, we have to go back to the first apparition of this creature, in the said Book of Camarthen. It's a 13th century Welsh book, that details poems, legends and folk tales from Wales. It was re released in 1906, and the original was scanned in 2002 and archived online for public view.
Read online
To my knowledge, that's Dormarth oldest written account. The book by itself contains a lot of contents from the time, and i was very interested to keep going with it, but for the topic at hand its already a very satisfactory base. In case you are curious, the 1906 version from J. Evans is available to buy and read online as well!
With the 1906 version as a base, Dormarth the modern author inserts some of his interpretations, and describes Dormarth less as a dog, and more as a sea creature, like a whale. Some authors associate that to the Christianity becoming more and more popular in the region at the time. Although, i could not find any credible sources or reasons to link the facts. Some say that Dormarth was associated to the biblical tale of Jonah and the Whale, which... I don´t really know why. The biggest theory is because, in this newer version, Dormarth is drawn like a whale of sorts (?). That would, in theory, suggest the old 13th century tale was being now interpreted by 20th century Christians. Evans was a christian by a matter of fact, so i can see why this theory exists, but for me its a kinda of stretch. Probably has more to do with his own interpretation of the creature. (Even thought Dormarth is clearly a dog...)
But what about our Fantastical Hound? What does the old texts says about it?
Surprisingly... Not much!
According to the Black Book of Camarthen, Dormarth supposedly inhabits the ''Ar Wybir'' which literally means ''mounting in the clouds.'' -Specifically the ones surrounding mountains. We can presume that's their ''natural habitat''. This also could mean Dormarth manipulates winds, and can fly.
In the book, Gwynn meets the king Gwyddno from Cantre'r Gwaelod (which, by the way has a really interesting tale) an old mythical land that supposedly sank in the ocean just like Atlantis.
At this meeting, there's a dialogue where Gwynn presents his hound, Dormarth. The owner of such creature praises its features, and talks about its role in the Wild Hunt. At the later, Gwynn collected the soul of his fallen soldiers with the help of his hunting dogs, such as Dormarth, which he praised as his best dog. (Good boy, or girl!)
Here's a small part of that poem:
"Handsome my dog, and round bodied, And truly the best of dogs; Dormath was he, which belonged to Maelgwyn. Dormath with the ruddy nose! what a gazer Thou art upon me because I notice Thy wanderings on Gwibir Vynyd."
-Black Book of Camarthen, 13th century
To better understand this fantastical Welsh creatures, we need to be presented to the concept of the Cwn Annwn, this translates itself to simply ''Hounds of Annwn. This said Annwn is another type of netherworld, another dimension, or plane. It's been seen in other traditional Welsh works, such as Maginobion which is a collection of folk tales and texts. This plane is also associated strongly with Gwynn Ap Nudd, since he is the king of the netherworld, mytical beings, fantastical creatures and this kind of stuff.
I need to bring the Cwn Annwn to the topic, because they were strongly associated with the Hild Hunt themselve, being the literal dogs that hunt down souls at this phenomena. We can thereby, conclude that Dormarth is indeed one of the Cwn Annwn, but a notorious one.
The Cwn Annwn also had other duties, such as carry the souls of the dead on their journeys to the after life. (Its often interesting to me how many cultures regards dogs as companions to lost souls, trying to reach heaven, or just guarding heaven. I can think about the Aztec dog of Xolotl, Cerberus, and many other instances.) At the Wild Hunt, they also had the duty to pursue criminals, until they could not run anymore. This is the modern depiction of the Wild Hunt hunting criminals, where before the Christians came, they would hunt anyone! The Christians probably were not satisfied by the idea of the righteous average christian running the risk of being hunt down by a demonic dog, so they nerfed it.
The author John Rhys comments also on the idea that Christianity changed the way Gwyn's Wild Hunt worked, where before Gwynn would hunt any dead soul, now the Wild Hunt was believed to hunt only criminals.
''What Gwynn hunts, is the soul of the dead. But Christianity has narrowed his field a lot, now he only hunts criminals.''
-Rhys on the Christian influency on this old Celtic myth, around page 156 of Studies in Arthurian Legends, 1891.
Note: The British Islands had a lot of Wild Hunt folklore. Actually, Europe had it in general, it was a trope. And hounds were also a common theme. There's cases you can read about from the entirety of the continent, and maybe one day i can bring the Wild Hunt to our compendium, there's a lot of material!
Coming back to Dormarth, since she's not going anywhere here. She's described specifically as a hunter dog helping Gwynn, in what one can only suppose it's the Wild Hunt. Still, at the 1906 version of the Black Book of Camarthen, page 97, there's a drawing of Dormarth. The creature is present in the pages 13 and 14 of the original manuscript, which can also be read online.

That's... Nothing like what Kaneko drew...
The interesting part about Dormarth it's not their features, nor their powers, as with some mythical creatures, but the etymology of its name...
You see, the real origins and meanings of the name Dormarth are uncertain. If you research by your own, you see some people call it Dormarth, while others call it Dormarch, as said earlier. This is because the original work had a bit of paint in the last letters, or it just eroded with time. If you read it as Dormarth, it means something like ''Death's door''. However there's evidence the name was actually written as Dormarch.
I will talk more about the creature's name in a bit. You just need to know now, that over the internet, books, and many sources, usually this being is named either Dormarch or Dormarth. For the scholars of the Breton language, you can notice that Dor= Door, and March = ...horse. Yeah, i will address that eventually, keep reading.
Evidently, if you look deep down into books and overall sources, there's no legend of Dormarth as a guard dog. It's never told for us that Dormarth is one, but still many modern media portray Dormarth as such. Even at her mentions in the Shin Megami Tensei franchise, most of its compendium entries describes her like that.
There's also a lot of online articles connecting Dormarth to the Irish Goddess Callieach. Where most of the times being also depicted as a guard dog, but being side by side with said goddess. This also has no backing from anywhere, there's no citation -as far as i know and had researched- that put those two together.
Talking about it's academics sources, Dormarth is only born and mostly portrayed in Welsh mythology and folkloric literature. But Callieach as mentioned it's an Irish goddess (Albeit sometimes appearing in Welsh and Manx mythology as well) ,and was never present in the works where Dormarth was. Again, as far as my research has gone.
Callieach is a goddess of the winter, also associated with landscape and nature. There's few and almost no room to put a Guard dog of the underworld near her, but i don't eliminate the idea of word of mouth doing this, and being less recorded. Just a theory of mine thought, because i could not find any sources on where this association with this goddess has begun for Dormarth.
It's widely known that Celtic mythology spreads itself by all the Britanic islands, and their ages vary a lot. I could locate Callieach being recorded mentioned at a 8th century poem, but as far as i researched there was again, no mention of Dormarth. It's clear now, that this association has no backing, and it's mostly a misinterpretation of Celtic culture.
*I got curious on where Atlus and most of modern depictions of Dormarth took this idea of it being sided with Callieach, and after an extensive search, i found a 2004 post at Deviantart that make this exact association, and it was the oldest i could get. Since Dormarth first appearance at SMT was from the Raidou novel, in 2007-8, maybe Kaneko got his idea from here? I dont know...
In the book ''Celtic Folklore, Welsh, and Manx'' by Jhon Rhys written in 1901, at page 216 Dormarth is cited by the author, who is pondering if the creature is indeed a Cwn Annwn. Rhys was a very interesting author, because he actually went to research personally, and collected local testimonies and tales from ordinary people. Here it's no diferent, and he tells about a local tale of a business man, that had the unlucky fate of being a town attacked by the so called Cwn Annwn. In this report, Dormarth is not cited directly, but the creature itself is at the glossary in the last pages of the book as well.
At this point deep in the study of this creature, i was a bit walking around in circles, because everything went to dead ends, and my lack of knowledge in Celtic languages certainly did not help me. I've found that some people online really theorized that the interpretation of Welsh myths could really trip over to Ireland, for example and be slightly different, and not very well recorded. This could in theory explain the discrepancies in the descriptions of the creature.
Dormarth is also present in the 1905 book: ''Celtic Myth and Legend'' by Charles Squire. Squire is a very known author from the 20th century, and wrote this very huge and detailed collection of Celtic Mythology. Some things in the book did not aged well, but in the most part is a very usefull book.
Squire cites the poem from the Black Book of Camarthen, which i exhaustively read and talked about here. But, in the bibliography section of the book, you can see where Squire found Dormarth in the first place. It was in a book called ''Studies in Arthurian Legends'', Written in 1891 by John Rhys (You again!).
Time to raise an eyebrow and ask yourself what in the world is Dormarth doing in an academic study of the King Arthur legends? Well, around the page 150ish, Rhys is lecturing us about a poem about Lancelott and Elayne. (The book its available online in its entirety, go check it out if you want to.) In this poem, we are told about the time Lancelott goes to a tournament with the other knights of the Round Table, where a young woman falls in love with him, only to be rejected and later committing suicide. The tale by itself it's interesting, but there's the part that really interests our text, that is the woman's mysterious father.
Rhys explains that her father was a weird man, that was always by a well, described himself as ''King of the Islands'', and devoted himself so much to this title, that according to Rhys reflection, he could not save his own daughter from suicide.
However, what concerns us the most here is that the man was described being always accompanied by some ''beast''. The man stated that this beast belonged to him, and only him and his descendants. The creature was only described this way, as a ''beast''. And supposedly had a powerful roar.
The poem in question was written by Thomas Malory (1405-1475). Malory is important for this research, because of many things, but specifically because of its place on time and space.
He was an English romanticist, living during the 15th century and wrote mainly about King Arthur. His works were based on Gaulish books from the 13th century. He knew much about the folklore and myths of that age.
Back to the poem of Lancelott, the father of the young woman had his own history with King Arthur. The man was keen on fighting Arthur, and had the habit to take away the horses of the knights he defeated. He waited Arthur at his well, with his beast, in hopes to duel with him.
Here, Rhys does his connection with Dormarth:
Malory tells that the beast roared with the strength of 30 hounds. Rhys reflects that maybe Malory was referencing some kind of guard dog with 3 heads, just like Cerberus. It's also cited during this reflection, other mythical dogs from around Europe -page 156-, but ultimately he traces a parallel with the nearest culture, the Welsh.
Rhys interpreted that the figure being the father of Ellayne, is actually a Breton version of Gwyn App Nudd (!!!)
As said before, in his other book from 1901, Rhys tells us more about this modern depiction of Gwynn's Wild Hunt. He even writes about hearing it personally from townsfolk in Cardiganshare.
Gwynn then take us back to the 13th century Black Book of Camarthen. (Notice that Malory was notorious for consuming 13th century works!) Here, back to the original welsh depiction of Dormarth, Rhys explains the problem with the name Dormarth. There's something erased from it in the original book, where it's written Dormach, instead.
Rhys theory on why Dormarth is written with march, and also erased, it's because the original scribe must have been instructed to write it as Dormarth, but ended up writing it as Dormarch. As said before, Dor= door, but March means horse. This probably confused anyone in charge of finishing the book, which made the decision to erase the ''R''. This creates a name with no meaning, thus solving the typo. Still, Rhys assure us it must have been instructed to write it as Dormarth. And he is probably the first author that does that.
But again, if you know the Breton language, you know that ''marth'' is not death. It instead is ''marv''. But Rhys explains that as well: In the also from the 13th century ''Book of Taliessin'' (not to confuse with the Deep Purple album), there's a poem about death, where it's mentioned as ''Marth'', not marv. The academics of the time deduced that Marth is death personified, a way to name Death itself. Rhys supports this idea by the etymology of the word, for example, starting from Latin:
-Mors > mortis > morte>marv>marth
By this idea, Dormarth is had as the personified death at the door of Annwn. To support even more this claim, Rhys describes old sayings from south Cardiganshare, where death was often described as a dog's mouth.
Going even further, Rhys proposes that maybe even English modern expressions like ''in the maws of death''. Or the german expression ''Rachen des Toden'' originated from here.
Rhys concludes:
''Its by this way, that one seeks to understand and the meaning of Dormarth.''
Here is where Dormarth as a guard dog originated. But as a guard dog of Gwynn App Nudd and his domain, not Callieach. At the same book from John Rhys, he also tells us that the Welsh believe that Gynn's hounds are led by a way bigger and fearsome one.
''He's bigger, louder, hunts at night, floating sometimes silently, sometimes devouring a victim that screams.''- Page 158.
So... Let's finish with Dormarth's resume:
Dormarth is one of the hounds of Anwnn, and Gwynn App Nudd in Welsh mythology. Due a gramatical error, its true name its hard to decipher, but it's clearly depicted as the hound that leads Gwynn's wild hunt and probably guards the gates of Annwn. It is the death at Annwn's door for anyone who shall approach.

Sources:
-Black Book of Camarthen (reprint and 13th century version)
-Celtic Folklore, Welsh and Manx - John Rhys
-Celtic Myth and Legend - Squire, Studies in Arthurian Legends - John Rhys.
#celtic mythology#welsh mythology#shin megami tensei#devil summoner#kazuma kaneko#Dormarth#Demons#Mythology#mythology and folklore#atlus games#blazescompendiumentry
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blaze's Compendium Entry #4: Take the long way home, and avoid the Obairyon!

Normally described as a local Yokai in the Niigata prefecture in Japan, this creature supposedly has a childish and mischievous personality, and not always dangerous. This creature was also known as ''Piggyback Demon''
It's main feature, and the thing it is more known for, its their habit to jump in random travelers backs, always screaming ''Obairyon''. If nothing is done to repel it, the person will have to carry this being in their back, in a sort of demonic piggy back ride. Each step, Obairyon gets more and more heavy, eventually becoming unbearable to carry. At this point, the person will probably collapse and the Demon will make fun, and play with the poor victim until it gets bored and go away. Usually this is not fatal, but extremely inconvenient. If you consider yourself a strong person, and would resist more to the crescent mass of Obairyon's body, it will simply start to nimble your head until you eventually give a wrong step.
However, by bringing Obairyon homee and managing to beat him in its own game, lands yourself a very good reward...
If, a person can reach home with the heavy Obairyon, they will be rewarded with the Demon transforming into a heavy bag of gold, making the person instantly rich! But since the creature's torture was so exhausting, that was a very rare case. So, don't go into Niigata's woods trying to get rich, you will probably end up in a wheelchair.
The site yokai.com (which is a great English source and research hub about Yokai) States that people would often use iron bowls in their heads to repel the Obairyon. It would often protect them from the creature's habit to bite their heads, so many villagers started using an iron bowl as an ornament, in order to protect against this Yokai.
Other skills this Yokai can have are more mundane and general,(that is, for a Yokai...) like being invisible. It's also very hard to be removed from a person. It's unknown on what the creature feeds. In my research, i could not find anything about it eating parts of, or whole Human beings.
The name Obairyon, also according to multiple sources including Yokai.com, means something like ''Give me a piggyback ride!'' in the local Niigata prefecture dialect. It also attends by other names, like: bariyon, onbu obake, ubariyon, obusaritei. This big variety in naming is due to regional dialect changes, but their behavior is always the same.
It's origins are very uncertain. As it happens with a lot of Yokai, it's hard to pin down exactly where it started, because usually it's more of a folk and oral tradition. Of course, many Yokai have their origins pretty detailed, some examples being like Nekomata and Karakasa-Obake. But Obairyon is a bit more shrouded in mystery, in this regard.
The most accepted and sourced idea of its origin, according to yokai.com is That the Obairyon tale is an analogy to the duty of raise a children. The creature's childish manner is a direct link to this idea, and it can be seen as ''Those who can resist the weight of raising a children, will be rewarded.'' Those who can endure the Demon's exigences and heavy weight, will prosper with treasure. Just like the parents who can raise their children and endure the weight of helping another human being develop, will also be rewarded with treasures in their lifetime.
As a metaphor to parenthood, Obairyon exigences are abusive and sometimes unbearable, but when reaching home after all the hard work you had, you will notice that your investment was worth the suffering.
Of course, this is only a rough idea. The origins for this particular Yokai are indeed shrouded in mystery.
Being if that's the case about Obairyon's tale, parenthood here is treated in such a sincere way. It's a very complex and delicate phase of Human existence in Earth, that is not always treated with that much needed grain of truth to all of their aspects.

Obairyon being a somewhat popular Yokai, this demon is featured in a multitude of pop culture media. Besides Megami Tensei, Obairyon is well known to appear in the legendary Ge Ge Ge No Kitaro anime franchise. It's not the first time our friend Mizuki appears in one of our Compendium Entries.
As said before, as a local folk legend it's pretty hard to pinpoint the origins of this myth. The language barrier poses a difficulty in trying to identify their first origins and first sources, but as far as my research has gone, Obairyon is a more local tradition incorporated in Yokai Folklore, with no discernible origin date.
So, what i am doing in this text is basically complying every information i could gather from valid sources, so i can bring this local obscure Yokai legend to more people in the world.
But honestly, most of the versions follows the same description, with few to no variations! Obairyon is a very heterogeneous entity. Although it's origins are traced to the Niigata region, there's similar Yokai around Japan, that shares elements of Obairyon's narrative.
For example, there is the Konaki Jijii. This interesting creature has the same habit to harm lone travelers traversing woods. I wont go in details here, because it's not their spotlight, but the major difference from Obairyon is their murderous intent. After getting in the victim's back, this demon will grow heavier and heavier, and eventually it will be fatal for the victim. Konaki was also present in GeGeGe, and you can read more about it here
Obairyon by itself does not change its modus operandi too much, except for sometimes biting people, and its name.
There's also some scholars who divide other Yokais into sub-species of Obairyon, or some term like this (the translation was not that much clear about it) There's for instance the Oigakari from Hiroshima Prefecture, which is described as a shadow being that jumps into people's back. I could not source this one in English, sadly. But it definitively has some similarities. This association was sourced by the work ''Weekly Excite''. I could not find any more about it, so...take it with a grain of salt. The Yokai by itself does indeed exist, i just could not confirm it was once associated with our Piggyback friend from Niigata.

Yo, what's the little guy doing????
There's also the well sourced Oppasho-Ishi from Tokushima, which its said to be related from a Sumo wrestler. Much like Obairyon this peculiar creature jumps into people' backs, getting more and more heavier. The famous 20th century Japanese Folklorist Kunio Yanagita has associated this creature to the Obairyon in his book: ''Yokai Dangi''.
Another writer specialized in Yokai, Kenji Murakami specifies in his book ''Yokai Encyclopedia'' that Obairyon and similar Yokai are normally associated to specific locations, such as paths in the woods, abandoned houses, tunnels and other likely places.
While tracing Obairyon's origins from written accounts and sources is very hard, specially for a non-Japanese speaker, it's very noticeable how common and popular it is in the Yokai culture. Or at least, it is a very diffused legend around Japan. Enough for some scholars to ponder about its relationship with other Yokai, and the true tales that gave it birth.
As said before, Obairyon is the embodiment of hard work. We often see ourselves in situations where our suffering and labor seems to never end, and our way home becomes more and more heavy and distant. But, as it is human to strive and use our spirit to go where we never were meant to go, those who can endure the heavy weight of their journeys will always be blessed by treasures.
The next time you think about giving up on the hard and long path you chose, remember it must be an Obairyon in your back, biting your head. Just focus in reaching to your destination and this suffering will become fruits for your to sow. Who knows? Maybe it transforms into piles of gold.
Or i don't know, it may really be a Demon... In this case, call someone more indicated to help.
Sources:
(Please note that i do not speak Japanese. All those books mentions something that i brought about Obairyon, but i could have mistranslated something because of machine translation. If i did, please send me a message!)
Yokai.com
Yokay Encyclopedia, Kenji Muramaki
Yokai Dangi, Kunio Yanagita.
Inhabitants of the Fantasy World Volume IV, Tatsumi Tada
Dictionary of Myths and Legends, Asakura
#blazescompendiumentry#Yokai#japanese mythology#japanese folklore#Obairyon#demon#mythology#devil summoner#shin megami tensei
21 notes
·
View notes