#cal osha compliance training
Text
OSHA Workplace Safety Training, Consultancy: PCS Safety, California
PCS Safety: Providing quality workplace safety services Company & training including OSHA training to public/private sectors in California and throught United States..
Cal OSHA safety training for Workers – cal osha training coursesA Mandate: The Cal OSHA training module ensures that cal osha safety training workers are eligible for workplace safety osha citation for their positions regardless of industry. Its Known as california safety training
osha citation response Importance of Safety Work Permit by PCS safety Inc - osha certification California A safe system of work permit is an effective vehicle for communicating critical safety information. Safe Lifting Poster- Employers are encouraged to post this guide osha license to help workers follow OSHA’s ergonomic compliance and meet OSHA’s mandatory training requirement.
osha 40 hours- 40 hour hazwoper
labor law posters california - First Aid Compliance for Your first aid training Workplace California Forklift Certification Requirements for Employers workplace first aid What is PSM – Process Safety Management Program, is it Important
Injury and Illness Prevention (IIP) Program Plan Kit : Under Title 8 of the California Code of Regulations (T8CCR) Section 3203, every California employer is required to have a documentable llness injury preventino program kit. At PCS Safety, Inc., osha injury and illness prevention program our Injury and Illness Prevention Plan Kit injury and illness prevention program osha will help you prepare and meet the legal requirements. The first step is conducting injury illness prevention program california the OSHA Inspections & Citation Representation, injury illness prevention program Citation & Appeals.
CAL-OSHA COMPLIANCE TRAINING
Cal OSHA Compliance Training : The Safety Program or Illness and Injury Prevention Program as required by Cal OSHA training requirements must encompass the following elements:
1)Compliance 2) Communication 3) Hazard Assessment 4) Accident/Exposure Investigation 5) Hazard Correction 6) Training and Instruction 7) Record-keeping Compliance is cal osha training courses something every organization with one or more employees must comply with all of the above-mentioned requirements. Cal OSHA Training materials (e.g., interactive videos, online training, and more) that address the topics required by OSHA, are vital documents that you need to prepare, as well as emergency response plans.
#"llness injury preventino program kit#osha injury and illness prevention program#injury and illness prevention program osha#illness prevention program#injury illness prevention program california#injury illness prevention program#cal osha training requirements#cal osha compliance training#cal osha training courses#cal osha training materials#cal osha safety training#cal osha training#california safety training#safety work permit#safe lifting poster#labor law posters California#first aid compliance#california forklift certification requirements#process safety management program
1 note
·
View note
Text
California farmworkers say they were fired for leaving jobs in heat. Could a bill prevent that?
Agricultural workers are 35 times more likely to die from heat-related stress than workers in other industries, according to the National Institutes of Health.
Cortese and advocates say the bill is designed to promote employer compliance with added financial pressure and circumvent Cal-OSHA understaffing. Agricultural employers are already required to provide shade, hydration access, rest breaks and heat illness prevention training, per a 2005 California law.
But all too often, Cortese said, employers fail to comply. One in six farmworkers reported not receiving the minimum number of rest breaks, according to a 2022 study from the UC Merced Community and Labor Center.
“The laws are fine,” Cortese said. “They’ve been on the books for 19 years. We just want them enforced, and we’re going to insist on them being enforced.”
Jorge Santana, one of the now-called “Yolo Six” farmworkers, said he called Cal-OSHA repeatedly to report concerns about heat safety the day the workers were let go. Santana, 61, didn’t hear back from an inspector until three weeks later.
0 notes
Text
Workers Compensation Insurance for Roofers In California
Introduction
Workers' compensation insurance is essential for high-risk professions such as roofing. Given the inherent dangers associated with roofing work, it is crucial for roofing companies in California to understand and comply with workers' compensation regulations. This article explores the key elements of workers' compensation insurance for roofing companies in California, including legal requirements, coverage options, challenges, and best practices.
Legal Requirements
In California, employers are required to carry workers' compensation insurance for all employees, including part-time, temporary, and seasonal workers. This mandate is particularly important for roofing companies due to the high-risk nature of the work.
Key Points:
Mandatory Coverage: Roofing companies must provide workers' compensation coverage for all employees, regardless of the duration or nature of their employment.
Compliance with State Laws: The California Department of Industrial Relations (DIR) and the Division of Workers' Compensation (DWC) oversee compliance with workers' compensation regulations. Roofing companies must adhere to these regulations to avoid penalties and ensure employee protection.
Reporting and Record-Keeping: Employers are required to report work-related injuries and illnesses promptly and maintain accurate records.
Coverage Options
Roofing companies in California have several options for obtaining workers' compensation insurance. These include purchasing a policy from a private insurance carrier, utilizing the state's assigned risk pool for high-risk employers, or self-insuring if the company meets specific financial criteria set by the DIR.
Key Points:
Private Insurance: Many roofing companies prefer private insurance for its flexibility and variety of available policies.
State Compensation Insurance Fund (SCIF): SCIF is a state-run program that provides workers' compensation insurance, especially for businesses that have difficulty obtaining coverage through private insurers.
Self-Insurance: Larger companies with substantial financial stability might choose to self-insure. This option requires state approval and a demonstration of financial capability.
Challenges for Roofing Companies
Roofing companies face unique challenges in managing workers' compensation insurance:
High Risk of Injury: Roofing is a high-risk occupation with potential hazards such as falls, tool injuries, and exposure to extreme weather conditions.
Varied Work Environments: Roofers work in different environments, including residential, commercial, and industrial sites, each with unique safety challenges.
High Turnover: The roofing industry often experiences high employee turnover, complicating record-keeping and claims management.
Cost Management: The cost of workers' compensation insurance can be significant due to the high risk associated with roofing work.
Best Practices
To effectively manage workers' compensation insurance and minimize risks, roofing companies should implement several best practices:
Comprehensive Training: Provide thorough safety training tailored to the specific tasks and environments where employees will work. This includes fall prevention, proper use of tools, and safe handling of materials.
Regular Safety Audits: Conduct regular safety audits of job sites to identify and mitigate potential hazards. Ensure compliance with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards and California's specific safety regulations (Cal/OSHA).
Effective Communication: Maintain open lines of communication with employees to quickly address any safety concerns or incidents. Encourage employees to report unsafe conditions and near-misses.
Accurate Record-Keeping: Keep detailed records of employee training, job assignments, and incident reports to streamline the claims process and ensure compliance with state regulations. Proper documentation is crucial for managing claims efficiently.
Return-to-Work Programs: Implement return-to-work programs to help injured employees transition back to their jobs. These programs can reduce the duration and cost of workers' compensation claims and improve employee morale.
Insurance Review: Regularly review insurance policies to ensure they provide adequate coverage for the company's current operations and adjust as necessary. This includes evaluating different insurance providers to find the best coverage options.
California's Unique Considerations
Medical Provider Network (MPN): Employers in California can establish an MPN, a network of healthcare providers to treat workers injured on the job. Employees generally must choose their treating doctor from the MPN.
Benefit Structure: Understanding California's specific benefits structure, including temporary disability, permanent disability, and medical benefits, is crucial for accurate claims management.
Vocational Rehabilitation: California law includes provisions for supplemental job displacement benefits (SJDB) to help injured workers who cannot return to their previous job.
Conclusion
Workers' compensation insurance is a critical component of managing a roofing company in California. By understanding the legal requirements, exploring coverage options, addressing unique challenges, and implementing best practices, roofing companies can protect their employees and their business. Effective management of workers' compensation not only ensures legal compliance but also contributes to a safer and more productive workforce, ultimately leading to a more successful roofing company.
0 notes
Text
The Importance of a Workplace Violence Prevention Course in California
In today's dynamic work environment, ensuring the safety and well-being of employees is paramount. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is through a comprehensive workplace violence prevention course. In California, where workplace safety regulations are stringent and continuously evolving, such courses are particularly critical. This blog delves into the significance of a workplace violence prevention course in California and how it benefits both employers and employees.
Understanding the Need for a Workplace Violence Prevention Course in California
Workplace violence can manifest in various forms, including physical assaults, threats, harassment, and bullying. California, known for its diverse workforce and industries, is no stranger to these challenges. The state has implemented robust regulations to address workplace violence, making a workplace violence prevention course in California essential for compliance and safety.
Key Components of a Workplace Violence Prevention Course in California
Regulatory Compliance: A workplace violence prevention course in California is designed to ensure that organizations comply with state laws and regulations. This includes understanding Cal/OSHA requirements and other relevant statutes that mandate violence prevention measures.
Risk Assessment and Management: The course provides training on how to conduct thorough risk assessments. This involves identifying potential hazards specific to the workplace, evaluating the likelihood of violence, and implementing strategies to mitigate these risks.
Crisis Response Planning: Effective crisis response is a crucial part of a workplace violence prevention course in California. Employees learn how to respond to violent incidents, including evacuation procedures, communication protocols, and coordination with law enforcement.
Employee Training and Awareness: Raising awareness among employees about the signs of potential violence and how to report concerns is a key focus. A workplace violence prevention course in California equips employees with the knowledge and skills to recognize and respond to threats before they escalate.
Support and Resources: The course also covers how to provide support to victims of workplace violence. This includes offering counseling services, ensuring confidentiality, and providing a supportive environment for recovery.
Benefits of a Workplace Violence Prevention Course in California
Enhanced Safety and Security: The primary benefit of a workplace violence prevention course in California is the enhanced safety and security of the workplace. Employees feel more secure knowing that their employer is proactive in preventing violence and protecting their well-being.
Legal Protection: Compliance with state regulations helps protect employers from legal liabilities. A workplace violence prevention course in California ensures that businesses meet all legal requirements, reducing the risk of lawsuits and penalties.
Improved Employee Morale: When employees know that their safety is a priority, it boosts morale and job satisfaction. A positive and secure work environment leads to higher productivity and employee retention.
Reputation Management: Companies that invest in a workplace violence prevention course in California demonstrate their commitment to employee welfare. This enhances their reputation as responsible and caring employers, which can attract top talent and strengthen customer relationships.
Proactive Prevention: By participating in a workplace violence prevention course in California, organizations take a proactive stance in preventing violence. This proactive approach helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate, creating a safer workplace for all.
Implementing a Workplace Violence Prevention Course in California
For organizations looking to implement a workplace violence prevention course in California, the following steps are essential:
Assess Training Needs: Identify the specific needs of your workplace based on industry, size, and past incidents. Tailor the course to address these unique requirements.
Choose a Reputable Provider: Select a training provider with expertise in California's regulations and a proven track record in workplace violence prevention.
Engage Employees: Involve employees in the training process. Encourage participation and feedback to ensure the course is relevant and effective.
Monitor and Evaluate: Regularly review the effectiveness of the course and make necessary adjustments. Continuous improvement ensures that the training remains relevant and impactful.
Conclusion
Investing in a workplace violence prevention course in California is a strategic move that benefits both employers and employees. By fostering a culture of safety and compliance, organizations can create a secure and supportive work environment. As workplace violence remains a pressing issue, the importance of proactive prevention through comprehensive training cannot be overstated. A workplace violence prevention course in California is not just a regulatory requirement; it is a commitment to the safety and well-being of every employee.
0 notes
Text
Learn about our hr compliance software at PCS!
Practice Compliance Solutions offers efficent, easy-to-use hr compliance software to clients looking to strengthen their practice's hipaa compliance standards. Contact us today to learn more!
Practice Compliance Solutions
10212 Chesterton Drive, Dallas, TX 75238
(844) 738-0624
https://www.linkedin.com/company/optometric-business-solutions/about/
https://www.yelp.com/biz/practice-compliance-solutions-dallas?adjust_creative=xZR1D5sIhOfqTpbo8Ul3ow&utm_campaign=yelp_api_v3&utm_medium=api_v3_phone_search&utm_source=xZR1D5sIhOfqTpbo8Ul3ow
1 note
·
View note
Text
Learn about our safety compliance software at PCS!
Practice Compliance Solutions offers consistent, comprehensive safety compliance software, updated constantly, in a user-friendly app. With broad knowledge in a range of core areas of compliance, we give you the freedom that comes with trusting the experts. Contact us today!
Practice Compliance Solutions
10212 Chesterton Drive, Dallas, TX 75238
(844) 738-0624
https://www.linkedin.com/company/optometric-business-solutions/about/
https://www.yelp.com/biz/practice-compliance-solutions-dallas?adjust_creative=xZR1D5sIhOfqTpbo8Ul3ow&utm_campaign=yelp_api_v3&utm_medium=api_v3_phone_search&utm_source=xZR1D5sIhOfqTpbo8Ul3ow
1 note
·
View note
Text
Learn about compliance management solutions at PCS
Practice Compliance Solutions offers consistent, comprehensive compliance management solutions, updated constantly, in a user-friendly app. With broad knowledge in a range of core areas of compliance, we give you the freedom that comes with trusting the experts. Contact us today!
Practice Compliance Solutions
10212 Chesterton Drive, Dallas, TX 75238
(844) 738-0624
https://www.linkedin.com/company/optometric-business-solutions/about/
https://www.yelp.com/biz/practice-compliance-solutions-dallas?adjust_creative=xZR1D5sIhOfqTpbo8Ul3ow&utm_campaign=yelp_api_v3&utm_medium=api_v3_phone_search&utm_source=xZR1D5sIhOfqTpbo8Ul3ow
1 note
·
View note
Text
Learn about PCS's compliance software!
At Practice Compliance Solutions, our compliance software ensures doctors that any patient-sensitive information is safely stored and shared. To make your practice legally sound, visit Practice Compliance Solutions today!
Practice Compliance Solutions
10212 Chesterton Drive, Dallas, TX 75238
(844) 738-0624
https://www.linkedin.com/company/optometric-business-solutions/about/
https://www.yelp.com/biz/practice-compliance-solutions-dallas?adjust_creative=xZR1D5sIhOfqTpbo8Ul3ow&utm_campaign=yelp_api_v3&utm_medium=api_v3_business_search&utm_source=xZR1D5sIhOfqTpbo8Ul3ow
1 note
·
View note
Text
Learn about PCS's hipaa compliance solutions!
With hipaa compliance solutions from PCS, learn how to ensure that sensitive patient information stays confidential, every time it’s transferred and anywhere it’s stored.
Practice Compliance Solutions
10212 Chesterton Drive, Dallas, TX 75238
(844) 738-0624
https://www.linkedin.com/company/optometric-business-solutions/about/
https://www.yelp.com/biz/practice-compliance-solutions-dallas?adjust_creative=xZR1D5sIhOfqTpbo8Ul3ow&utm_campaign=yelp_api_v3&utm_medium=api_v3_business_search&utm_source=xZR1D5sIhOfqTpbo8Ul3ow
1 note
·
View note
Text
Learn about compliance audits at PCS!
A PCS compliance audit is unique in that it reviews not only the medical record, but also the billing and payment associated with each patient encounter. You will receive an overall summary analysis of the recurring documentation and patient management issues as well as an in-depth review of each patient visit. Visit us online to learn more!
Practice Compliance Solutions
10212 Chesterton Drive, Dallas, TX 75238
(844) 738-0624
https://www.linkedin.com/company/optometric-business-solutions/about/
https://www.yelp.com/biz/practice-compliance-solutions-dallas?adjust_creative=xZR1D5sIhOfqTpbo8Ul3ow&utm_campaign=yelp_api_v3&utm_medium=api_v3_business_search&utm_source=xZR1D5sIhOfqTpbo8Ul3ow
1 note
·
View note
Text
Best Cal OSHA in San Diego
MAS Safety Services specialize in the Analysis and Training of Safety Compliance with Visual Energy Source Shutdown Procedures and Confined Space. As a Complete Safety Compliance Company we are able to deliver the full scope of services to fit your needs. We offer best Cal OSHA in San Diego.
Visit here: https://mas-safety.net/
0 notes
Text
MIPP Matters to Hotels in California and it Should Matter to You too.
First and foremost MIPP is an acronym formulated by the State of California which stands for "Musculoskeletal Injury Prevention Program". We have our own MIPP you can adopt now.
With summer coming to an end and still many making plans to travel to California to take in the best natural and historical sites this side west of the Mississippi, the hotel industry will reach peak capacity as families, backpackers, couples and all wanderlust travelers book up their travel plans in the coming months.
For the hotel industry, business isn’t just good ‐ it’s great. But with occupancy rates climbing higher each year, the hotel industry struggles to maintain the staffing it needs to ensure smooth operations and to meet growing demand for rooms and beds. But with these increased demands, hotel operators and owners must heed Cal/OSHA’s recent regulations requiring them to address the types of repetitive motions and stress‐related injuries commonly sustained by housekeepers. The new law requires employers to implement a written policy and undertake a site‐specific, initial worksite evaluation to identify and address the types of musculoskeletal injuries housekeepers may sustain in their jobs. On top of these regulations, several cities within California, including Oakland and Long Beach, have proposed measures taking these requirements one step further. For instance, Oakland’s initiative, titled “Measure Z,” creates a number of key restrictions on the amount of work a housekeeping employee can perform, including restrictions on the number of hours, square footage they can clean in a day which itself can vary based on the number of rooms they clean in a shift. For the text of Measure Z, click on the link below:
https://www.acvote.org/acvote%E2%80%90assets/02_election_information/PDFs/20181106/en/Measures/22%20%E2%80%90%20Measure%20Z%20%E2%80%90%20City%20of%20Oakland.pdf

Where does one start to ensure compliance with these requirements? With little guidance from the bodies that enacted the ordinance, ensuring compliance can be a confusing undertaking even for the most experienced hotel operators. Keeping this in mind, on the next page we have included a few tips to start thinking about your operations and how they fit within the larger scheme of the new ordinances.
Get a handle of the square footage you’re working with...
Review the drawings of your facility. Create a plan for how you can divide up to the 4,000 square feet requirement. Call each divided spot a “Zone” and assign employees their designated zone. If one zone is undersold or has less turnover in a day, have that employee assist another employee in a zone that is overbooked. Although this may be a bit of a chess game, it is a good start to see how to work the board to ensure your employees are working within requirements.
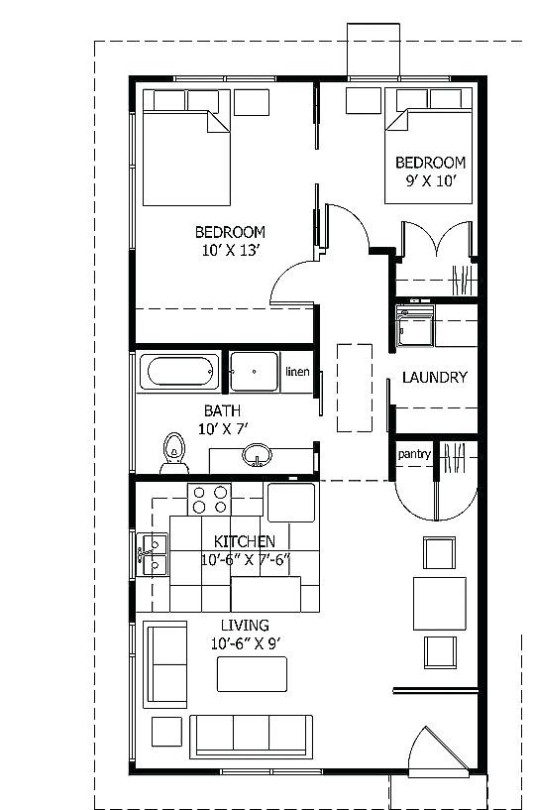
Evaluate the tasks performed by housekeeping employees...
It’s important to evaluate and understand what types of tasks each housekeeping employee accomplishes on a daily basis. Oftentimes housekeeping employees are engaged in a variety of different tasks when they turn over a room. Some housekeepers are also tasked with cleaning some general areas like the bathrooms, the lobby, or conference rooms. But if an employee performs just one or two tasks throughout the day, the risk of a musculoskeletal injury is much higher because of the repetition in performing the same tasks and reduced range of motion required of them. Consider breaking up the employee’s tasks so that they are not focused on long‐term, repetitive motions.
Do you have the right number of staff?
The number of housekeeping staff is critical. As a rule of thumb, if housekeeping employees need to clean more than 4,000 square feet on a routine basis, you probably don’t have enough staff. Of course there are challenges with people calling in sick, the number of rooms that need to be turned over and other elements that may make it infeasible to ensure employees are cleaning less than 4,000 square feet every day. Having on‐call employees or part‐time employees fill in may be a helpful option.
Consider these tips as you contemplate your staffing needs for the summer. Of course, these tips are not intended to be legal advice, and you should consult with an attorney experienced in Cal/OSHA law.
To find out more about Worksite Evaluations and Risk Assessments, Effective MIPP Training and Compliance Solutions, contact Team Accurate by clicking on our logo below.

0 notes
Text
The Significance of Electric Arc Flash Protection Clothing
Arc flash is the exposure to the massive thermal energy released by an arc fault. All employees who work around energized electrical equipment (electricians, maintenance workers, operators, etc.) may get affected by an arc flash occurrence. Arc flashes are a primary hazard in the following types of industries: oil and gas, utility, solar, and wind power generation, paper and pulp manufacturers, hospitals, universities and colleges, food processing and packaging plants, breweries, bakeries, and dairies.
The four dangerous elements of an arc flash are: enormous light, pressure wave, acoustic energy, and thermal energy. An arc flash blast usually lasts less than a second, and leads to an outburst and a flash fire. A flash fire is a rapid moving flame that can be caused by diffuse fuel, such as dust, gas, or a vapour of a flammable liquid. All the five elements must be present in order to produce a flash fire: fuel, a source of ignition, oxygen, a constricted space, and combustion (the action of heating a substance until it burns away rapidly). When a worker is close to the location where the mishap happens, serious burns and even death can occur.
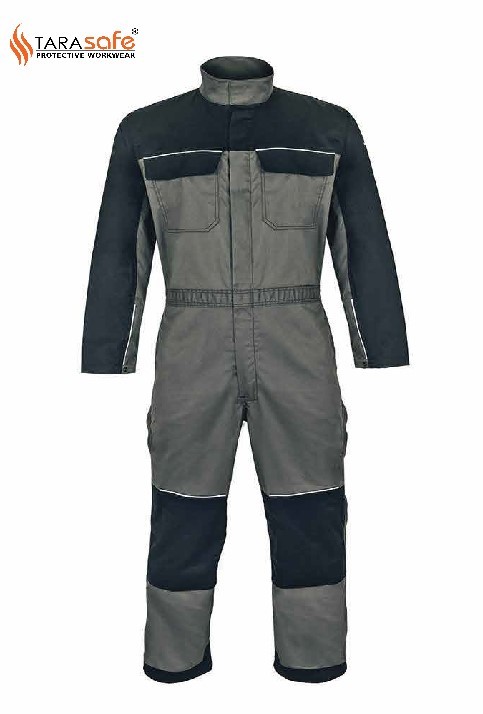

The NFPA 70E Standard demands that all employees wear arc-rated clothing “wherever there is possible submission to an arc flash above the threshold incident-energy level for a second degree burn.”
In order to find the proper Arc Flash clothing for your demand, you have to perform risk assessment to find out what hazards exist at your work place. You also should check if safety ratings of PPE you plan to provide for your workers are in line with the OSHA requirements. It is important for everyone’s knowledge that all arc-rated garments are also flame-resistant, but not all flame-resistant garments are arc-rated. When wearing multiple layers of arc flash safety clothes, it is important to calculate the combined arc-rating of your full outfit to ensure compliance with the NFPA 70E Standard.
Wearing arc-rated garments and PPE is the ultimate line of defence against severe injuries that may be caused by an arc flash. OSHA’s 1910.132 regulation states that “the protective equipment which includes personal protective equipment, shall be provided by the employer at no cost to employees”.
You should always train your team on how to wear their arc-rated PPE properly. The clothing has to be sized properly and be comfortable. The ability to quickly remove clothing that catches fire is also vital as it can prevent the person wearing it from getting severely burned or simply killed.
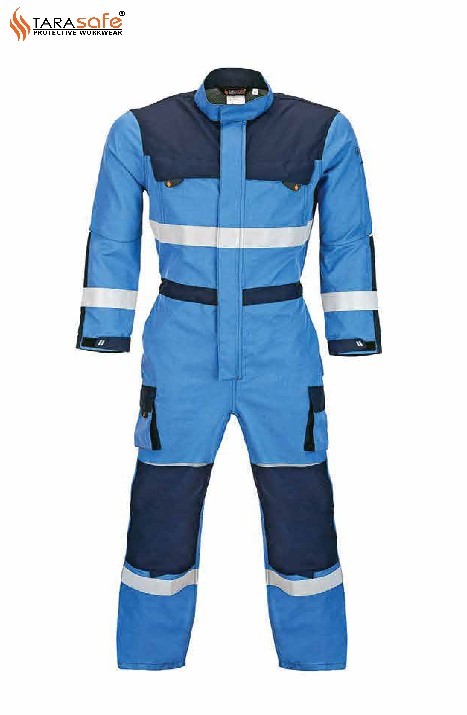

Specially designed Arc protective Clothing from TaraSafe® will help insulate the wearer from heat, resist breaking open of garment and will not ignite or continue to burn when exposed to a high intensity, short duration explosion and electric arc fire. We offer Arc Rated clothing providing protection from 8 - 40 cal/cm2.
For more information visit our website: www.tarasafe.com
About TaraSafe
TaraSafe® specializes in conceptualizing, designing and producing high quality Protective Clothing for various end applications. Today Tarasafe® is the largest manufacturer and supplier of Flame Resistant protective clothing in India, with the distinction of successfully executing supplies of these special garments to various Indian industry giants in the Oil and Metal industries.
Company Name: Tarasafe International Pvt.Ltd.
Address: Dutta Properties, Budge Budge Trunk Road,
P.O. Govindapur, P.S. Maheshtala
Kolkata - 700 141, West Bengal, India
Tel: +91-33-2492-9410/ 7998
Email: [email protected]
Url: https://www.tarasafe.com
0 notes
Text
Anaheim installer Nexus Energy Systems cited by OSHA for fall protection violations
New Post published on http://roofnrays.com/anaheim-installer-nexus-energy-systems-cited-by-osha-for-fall-protection-violations/
Anaheim installer Nexus Energy Systems cited by OSHA for fall protection violations
Cal/OSHA has cited an Anaheim solar panel installation company $193,905 for multiple serious workplace safety hazards including one willful serious accident-related violation, following an investigation of a worker who was seriously injured after they fell from the roof of an Oakland home. Cal/OSHA determined that Nexus Energy Systems did not provide required fall protection for its workers.
On December 6, three installers were working to install solar panels at the Oakland residence when one of the workers lost his footing and fell 15 feet onto the concrete driveway, suffering a broken wrist and jaw. None of the workers were wearing fall protection.
“Falls from roofs are often deadly, and that is why employers must protect their employees from fall hazards and provide effective training,” said Cal/OSHA deputy chief of enforcement Debra Lee. “This employer was aware of these dangers and ignored its responsibility to address them.”
Cal/OSHA cited Nexus Energy Systems for five violations, three of which were related to the December accident. The violations include:
A willful serious accident-related violation as the employer failed to provide fall protection.
Two serious violations for the employer’s failure to provide training and ensure compliance with fall protection measures.
Two general violations for the employer’s failure to implement an effective heat illness protection plan and an injury and illness prevention program that identifies and corrects hazards specific to the worksite.
Cal/OSHA also cited the employer for two additional violations stemming from an incident that investigators learned had taken place the previous September, when a worker suffered electrical burns while connecting solar panels to an energized breaker box. Cal/OSHA noted one serious continuing violation for failing to provide insulated gloves or tools while working on energized equipment, and a general violation for the employer’s failure to investigate the industrial accident and take measures to correct safety hazards.
A violation is classified as serious when there is a realistic possibility that death or serious harm could result from the actual hazard created by the violation, and violations are classified as accident-related when the injury, illness or fatality is caused by the violation. A willful violation is cited when the employer is aware of the law and violates it nevertheless, or when the employer is aware of the hazardous condition and takes no reasonable steps to address it.
All employers in California are required to have an effective written injury and illness prevention program, a safety program to identify, assess and control hazards in the workplace. Cal/OSHA has online tools and publications to guide employers on how to establish an effective safety program. Cal/OSHA’s resources on fall protection include a safety and health factsheet, residential fall protection training and a construction safety pocket guide.
News item from the California Department of Industrial Relations; Cal/OSHA
0 notes
Text
California Cannabis: Breaking Down the CDPH Permanent Regulations
The State of California finally adopted permanent cannabis regulations earlier this month. In a series of posts, we’re going to cover the highlights of each agency’s permanent rules so that you know what big changes to expect during 2019. This post will cover the main changes (in our opinion) regarding the California Department of Public Health Manufactured Cannabis Safety Branch’s (“CDPH-MCSB”) permanent regs. Without further ado:
No more Farm Bill hemp-CBD ingredients or additives. It’s no secret that the California Department of Health Food and Drug Branch (“FDB”) has an issue with hemp-CBD. Specifically, an FAQ that issued from FDB last year made clear that FDB prohibits hemp-CBD in “Food” for humans and pets. Now, CDPH-MCSB is following suit (indirectly). Pursuant to new regulation 40175(c), “a manufacturer licensee shall only use cannabinoid concentrates and extracts that are manufactured or processed from cannabis obtained from a licensed cannabis cultivator.” What this means is that using Farm Bill hemp-CBD as an ingredient or addictive to cannabis manufactured products is not allowed unless it comes from a licensed cannabis cultivator. The protections of the Farm Bill won’t apply.
Owners and financial interest holders. I recently wrote about how it’s unclear as to how far the state will now go in finding and vetting entity owners and entity financial interest holders, especially since the Bureau of Cannabis Control (“BCC”) articulates in its rules that it intends to locate and vet every human possible in pretty much any ownership structure. But what about MCSB? MCSB entity owner regulations now state that “if the owner . . . is an entity, then the chief executive officer and members of the board of directors of the entity shall be considered owners,” and for financial interest holders, MCSB rules mandate only that “financial interest holders shall be disclosed on the application for licensure.” On balance, the BCC’s owner and financial interest holder rules are much more aggressive than MCSB, and the BCC’s comments to its owner and financial interest holder rules was that all agencies would apply the same standards for vetting. However, this clearly isn’t going to be the case if stakeholders go off of a plain reading of the law. Though it will be strange, the MCSB will very likely stick to its minimal vetting requirements while the BCC goes full bore on retailer, distributor, and lab owners and financial interest holders.
Changes in ownership. Again in contrast with the BCC, the MSCB is going to be much easier on changes in ownership of licensees. Under BCC regulations, if there’s a full buy-out of all existing owners, the entity can no longer operate while the change of ownership is being reviewed and processed by the BCC. The MCSB however has no such standard, at least not one that’s codified under the new regs. Specifically, for any changes of ownership or changes to financial interest holders, the MCSB expects the following protocol:
“The licensee shall notify the [MCSB] of the addition or removal of an owner through [the agency’s online system] within 10 calendar days of the change; Any new owner shall submit the information required [by law]; The [MCSB] shall review the qualifications of the new owner in accordance with [state law] and these regulations to determine whether the change would constitute grounds for denial of the license. The [MCSB] may approve the addition of the owner, deny the addition of the owner, or condition the license as appropriate, to be determined on a case-by-case basis; An owner shall notify the [MCSB] through [the state agency’s online system] of any change in their owner information . . . within 10 calendar days of the change; and a licensee shall notify the [MCSB] through [the state’s online system] of any change in the list of financial interest holders . . . within 10 calendar days of the change.”
Labeling. Labeling is still just as intense and comprehensive as it was under the emergency regulations. Now though, manufacturers need to ensure that, if a product container is separable from the outer-most packaging (e.g., a container placed inside of a box), the product container includes the following: (1) For edible cannabis products, topical cannabis products, suppositories, or orally-consumed concentrates, all information required for the primary panel except for cannabinoid content, and (2) for inhaled products (e.g., dab, shatter, and wax), the universal symbol (which is the black triangle with a cannabis leaf and an “!” with “CA” underneath). We also now (finally) have specific labeling requirements for pre-roll and packaged flower that didn’t exist before outside of the statute, itself. Overall, there are additional technical change requirements for labeling, including the weight of the product now needing to be in metric and U.S. customary units, specific labeling for flavoring in line with federal law, and more specific labeling restrictions for cannabinoid content.
Packaging. Until 2020, manufacturers are off the hook for providing child resistant packaging (“CRP”). Until then, retailers will bear the burden of CRP through the continued use of CRP exit packaging. Once CRP for manufacturers kicks in though, they’ll need to adhere to a litany of requirements, including compliance with the Poison Prevention Packaging Act of 1970 Regulations.
New product definitions. Via the permanent regulations, MCSB has introduced a number of newly defined terms, which is ultimately better for licensees so that confusion doesn’t abound as product development continues. For example, we now have as recognized definitions like:
“Infused pre-roll,” which means “a pre-roll into which cannabis concentrate (other than kief) or other ingredients have been incorporated”;
“Kief,” which means “the resinous trichomes of cannabis that have been separated from the cannabis plant”; and
“Orally-consumed concentrate,” which means “a cannabis concentrate that is intended to be consumed by mouth and is not otherwise an edible cannabis product. ‘Orally-consumed concentrate’ includes tinctures, capsules, and tablets . . .”
OSHA training. Given that cannabis remains federally illegal, people often think that violating one federal law somehow gives you a license to violate every federal law, which is entirely untrue. Under the permanent MCSB regulations:
“for an applicant entity with more than one employee, the applicant employs, or will employ within one year of receiving a license, one supervisor and one employee who have successfully completed a Cal/OSHA 30-hour general industry outreach course offered by a training provider that is authorized by an OSHA Training Institute Education Center to provide the course.”
Clearly, safety and federal compliance in the workplace still applies, even to cannabis operators, which is now demoralized under the permanent MCSB rules.
Changes to operations that now require state approval. As the state moves along with licensing and enforcement, it was inevitable that certain licensee actions would first require state approval. What this usually means is that major changes to your business or SOPs can’t go down without the state’s blessing, which can take weeks or months to secure. Specifically, for the MCSB, licensees will now have to report to and clear with the state the following action items before the licensee pulls the trigger on them (all to the tune of a $700 change application fee, which is non-refundable):
the addition of any closed-loop extraction method;
the addition of any other extraction method that necessitates a substantial or material alteration of the premises;
the addition of infusion operations if no infusion activity is listed in the current license application on file with the [MCSB] (you’ll also have to tell the state about “any changes to the product list on file with the [MCSB] and provide a new product list within 10 business days of making any change” to the products you’re making”); or
a substantial or material alteration of the licensed premises from the current premises diagram on file with the [MCSB].
Importantly, a “substantial or material alteration” includes: “the removal, creation, or relocation of an entryway, doorway, wall, or interior partition; a change in the type of activity conducted in, or the use of, an area identified in the premises diagram; or remodeling of the premises or portion of the premises in which manufacturing activities are conducted.” Be advised!
California Cannabis: Breaking Down the CDPH Permanent Regulations posted first on http://ronenkurzfeld.blogspot.com
0 notes
Text
California Cannabis: Breaking Down the CDPH Permanent Regulations
The State of California finally adopted permanent cannabis regulations earlier this month. In a series of posts, we’re going to cover the highlights of each agency’s permanent rules so that you know what big changes to expect during 2019. This post will cover the main changes (in our opinion) regarding the California Department of Public Health Manufactured Cannabis Safety Branch’s (“CDPH-MCSB”) permanent regs. Without further ado:
No more Farm Bill hemp-CBD ingredients or additives. It’s no secret that the California Department of Health Food and Drug Branch (“FDB”) has an issue with hemp-CBD. Specifically, an FAQ that issued from FDB last year made clear that FDB prohibits hemp-CBD in “Food” for humans and pets. Now, CDPH-MCSB is following suit (indirectly). Pursuant to new regulation 40175(c), “a manufacturer licensee shall only use cannabinoid concentrates and extracts that are manufactured or processed from cannabis obtained from a licensed cannabis cultivator.” What this means is that using Farm Bill hemp-CBD as an ingredient or addictive to cannabis manufactured products is not allowed unless it comes from a licensed cannabis cultivator. The protections of the Farm Bill won’t apply.
Owners and financial interest holders. I recently wrote about how it’s unclear as to how far the state will now go in finding and vetting entity owners and entity financial interest holders, especially since the Bureau of Cannabis Control (“BCC”) articulates in its rules that it intends to locate and vet every human possible in pretty much any ownership structure. But what about MCSB? MCSB entity owner regulations now state that “if the owner . . . is an entity, then the chief executive officer and members of the board of directors of the entity shall be considered owners,” and for financial interest holders, MCSB rules mandate only that “financial interest holders shall be disclosed on the application for licensure.” On balance, the BCC’s owner and financial interest holder rules are much more aggressive than MCSB, and the BCC’s comments to its owner and financial interest holder rules was that all agencies would apply the same standards for vetting. However, this clearly isn’t going to be the case if stakeholders go off of a plain reading of the law. Though it will be strange, the MCSB will very likely stick to its minimal vetting requirements while the BCC goes full bore on retailer, distributor, and lab owners and financial interest holders.
Changes in ownership. Again in contrast with the BCC, the MSCB is going to be much easier on changes in ownership of licensees. Under BCC regulations, if there’s a full buy-out of all existing owners, the entity can no longer operate while the change of ownership is being reviewed and processed by the BCC. The MCSB however has no such standard, at least not one that’s codified under the new regs. Specifically, for any changes of ownership or changes to financial interest holders, the MCSB expects the following protocol:
“The licensee shall notify the [MCSB] of the addition or removal of an owner through [the agency’s online system] within 10 calendar days of the change; Any new owner shall submit the information required [by law]; The [MCSB] shall review the qualifications of the new owner in accordance with [state law] and these regulations to determine whether the change would constitute grounds for denial of the license. The [MCSB] may approve the addition of the owner, deny the addition of the owner, or condition the license as appropriate, to be determined on a case-by-case basis; An owner shall notify the [MCSB] through [the state agency’s online system] of any change in their owner information . . . within 10 calendar days of the change; and a licensee shall notify the [MCSB] through [the state’s online system] of any change in the list of financial interest holders . . . within 10 calendar days of the change.”
Labeling. Labeling is still just as intense and comprehensive as it was under the emergency regulations. Now though, manufacturers need to ensure that, if a product container is separable from the outer-most packaging (e.g., a container placed inside of a box), the product container includes the following: (1) For edible cannabis products, topical cannabis products, suppositories, or orally-consumed concentrates, all information required for the primary panel except for cannabinoid content, and (2) for inhaled products (e.g., dab, shatter, and wax), the universal symbol (which is the black triangle with a cannabis leaf and an “!” with “CA” underneath). We also now (finally) have specific labeling requirements for pre-roll and packaged flower that didn’t exist before outside of the statute, itself. Overall, there are additional technical change requirements for labeling, including the weight of the product now needing to be in metric and U.S. customary units, specific labeling for flavoring in line with federal law, and more specific labeling restrictions for cannabinoid content.
Packaging. Until 2020, manufacturers are off the hook for providing child resistant packaging (“CRP”). Until then, retailers will bear the burden of CRP through the continued use of CRP exit packaging. Once CRP for manufacturers kicks in though, they’ll need to adhere to a litany of requirements, including compliance with the Poison Prevention Packaging Act of 1970 Regulations.
New product definitions. Via the permanent regulations, MCSB has introduced a number of newly defined terms, which is ultimately better for licensees so that confusion doesn’t abound as product development continues. For example, we now have as recognized definitions like:
“Infused pre-roll,” which means “a pre-roll into which cannabis concentrate (other than kief) or other ingredients have been incorporated”;
“Kief,” which means “the resinous trichomes of cannabis that have been separated from the cannabis plant”; and
“Orally-consumed concentrate,” which means “a cannabis concentrate that is intended to be consumed by mouth and is not otherwise an edible cannabis product. ‘Orally-consumed concentrate’ includes tinctures, capsules, and tablets . . .”
OSHA training. Given that cannabis remains federally illegal, people often think that violating one federal law somehow gives you a license to violate every federal law, which is entirely untrue. Under the permanent MCSB regulations:
“for an applicant entity with more than one employee, the applicant employs, or will employ within one year of receiving a license, one supervisor and one employee who have successfully completed a Cal/OSHA 30-hour general industry outreach course offered by a training provider that is authorized by an OSHA Training Institute Education Center to provide the course.”
Clearly, safety and federal compliance in the workplace still applies, even to cannabis operators, which is now demoralized under the permanent MCSB rules.
Changes to operations that now require state approval. As the state moves along with licensing and enforcement, it was inevitable that certain licensee actions would first require state approval. What this usually means is that major changes to your business or SOPs can’t go down without the state’s blessing, which can take weeks or months to secure. Specifically, for the MCSB, licensees will now have to report to and clear with the state the following action items before the licensee pulls the trigger on them (all to the tune of a $700 change application fee, which is non-refundable):
the addition of any closed-loop extraction method;
the addition of any other extraction method that necessitates a substantial or material alteration of the premises;
the addition of infusion operations if no infusion activity is listed in the current license application on file with the [MCSB] (you’ll also have to tell the state about “any changes to the product list on file with the [MCSB] and provide a new product list within 10 business days of making any change” to the products you’re making”); or
a substantial or material alteration of the licensed premises from the current premises diagram on file with the [MCSB].
Importantly, a “substantial or material alteration” includes: “the removal, creation, or relocation of an entryway, doorway, wall, or interior partition; a change in the type of activity conducted in, or the use of, an area identified in the premises diagram; or remodeling of the premises or portion of the premises in which manufacturing activities are conducted.” Be advised!
California Cannabis: Breaking Down the CDPH Permanent Regulations posted first on https://centuryassociates.blogspot.com/
0 notes