#chromic acid reaction
Photo
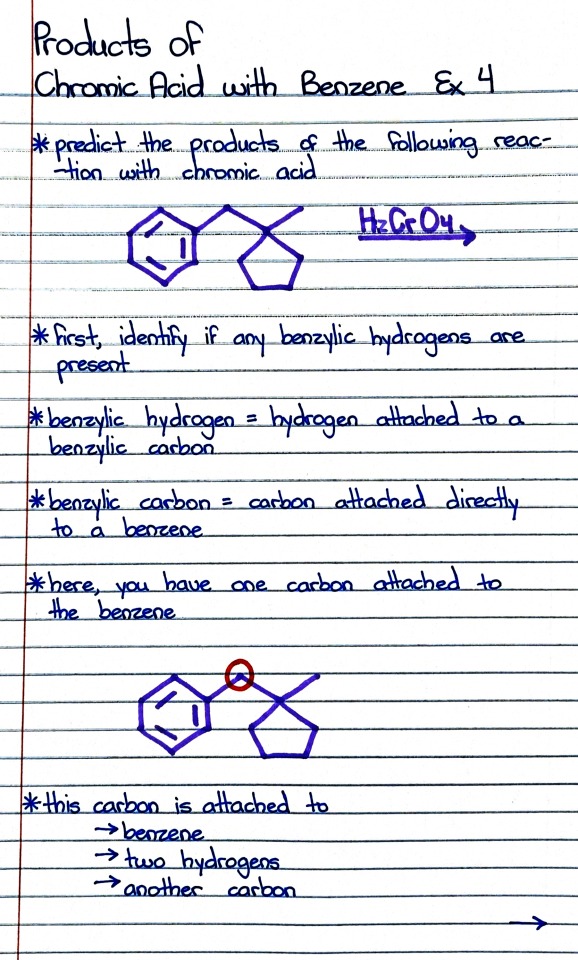
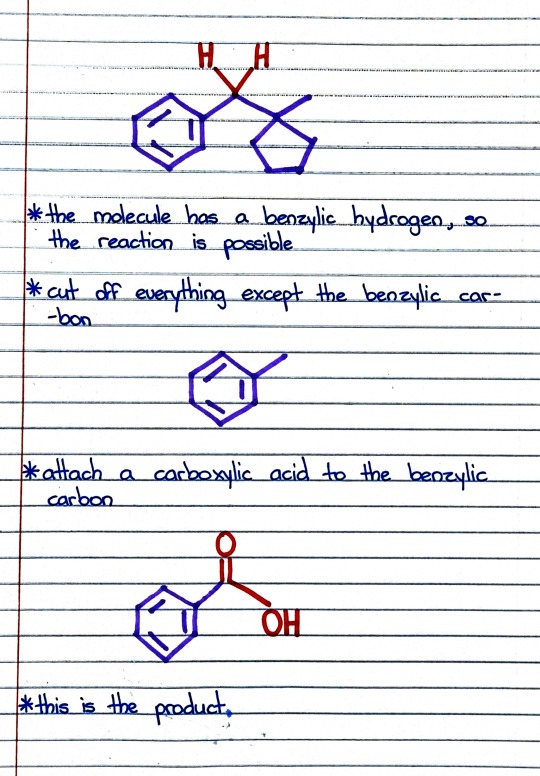
#organic chemistry#ochem#o-chem#o chem#ochem 1#ochem 2#organic chemistry 1#organic chemistry 2#mcat organic chemistry#orgo#reactions#orgo reactions#chemical reactions#orgo mcat#mcat orgo#ochem reactions#studyblr#notes#chromic acid#benzene#benzene reactions#chromic acid reactions
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Passivation? How Does Passivation For Stainless Steel Work? How To Passivate Stainless Steel Parts?
What is the passivation process, and how does it function? How should stainless steel pieces be passivated following machining operations? Machine shops and makers of part materials like stainless steel, titanium, and tantalum frequently ask these questions. And here we're to answer your questions.
What is Stainless Steel Passivation?
A common method of metal finishing to stop corrosion is passivation. Nitric acid or Citric Acid Prevent Corrosion. So they are used in the passivation process to remove free iron from the surface of stainless steel. The chemical process produces a passivation film, or protective oxide layer, which reduces the likelihood of corrosion due to chemical reactions with air. Rust is resisted by passivated stainless steel.
Why is Stainless Steel Passivated?
A best practice for newly machined stainless steel parts and components after fabrication is passivation. Benefits comprise:
Chemical film as a rust-prevention measure
increased longevity of the product
Decontamination of the product's surface
lower requirement for maintenance
What happens during Passivation for Stainless Steel?
An iron-based alloy, stainless steel is typically made of iron, nickel, and chromium. Chromium's presence in stainless steel gives it its ability to resist corrosion. Chromium reacts with oxygen (air) to generate chromium oxide, which coats the surface of stainless steel and prevents the underlying iron from rusting. Passivation is used to speed up and improve the production of the chromium oxide layer.

Free iron off the stainless steel surface is dissolved, while the chromium is left unaltered by immersion in an acid bath. The acid chemically removes the free iron, leaving behind a homogeneous surface with more chromium than the underlying substance.
After the acid bath, the stainless steel generates the chromic oxide layer for 24 to 48 hours when exposed to oxygen in the air. A thicker, more protective chromium oxide coating can grow because of the higher chromium concentration near the surface. By removing any loose iron from the surface, corrosion is prevented from the beginning.
The resulting passive layer offers a rust-resistant surface that is chemically inert.
When is stainless steel necessary to be passivated?
At REBA SCIENTIFIC PTY LTD, we think passivation is a post-fabrication procedure used to modify stainless steel after welding, grinding, cutting, and other machining operations. Passivating might not be essential because stainless steel inherently resists corrosion in the ideal environment.
However, any of the following can prevent the production of the oxide film that prevents corrosion under typical, actual circumstances:
Foreign substances in a manufacturing setting (shop dirt, grinding swarf)
Stainless steel with sulfides added for better machinability
Parts made of stainless steel may have iron shavings from cutting tools buried on their surface.
In order to re-establish a consistently corrosion-resistant surface, such impurities must be eliminated down to the surface grain boundaries. These problems are resolved via the process of Passivation for Stainless Steel.
0 notes
Text
GST pipette automatic production line - pipette use steps
GST pipette automatic production line manufacturer As mentioned earlier, a pipette is a measuring device used to accurately pipette a certain volume of solution. A pipette is a measuring-dispensing instrument used only to measure the volume of a solution it dispenses. It is a long, thin glass tube with an enlarged section in the middle. Its lower end is beak-shaped, and a marking line is engraved on the neck of the upper end, which is a sign of the accurate volume taken.

1. Introduction: Commonly used pipettes have specifications of 5, 10, 25, 50 and 75ml. The straight glass tube with scale is usually called a pipette. Commonly used pipettes are 1, 2, 5, and 10mL. Pipettes and pipettes are usually accurate to the nearest 0.01 mL.
2. Steps of use: Select a pipette of appropriate specifications according to the volume and requirements of the solution to be pipetted. Pipettes are generally used to accurately pipette solutions in titration analysis, and pipettes are generally used when the reaction needs to control the amount of test solution added.
3. Check the instrument: Check whether the nozzle and tip of the pipette are damaged. If there is any damage, it cannot be used.

4. Clean the instrument: rinse with tap water first, then soak in chromic acid washing solution. The operation method is as follows: hold the upper end of the pipette or pipette with the right hand at a suitable position, the index finger is close to the upper opening of the pipe, and the middle finger and ring finger are opened and held. Hold the outside of the pipette, hold the thumb on the inside of the pipette between the middle finger and the ring finger, and relax the little finger naturally; hold the ear cleaning ball in the left hand, hold the suction ear ball in the palm of the hand with the tip pointing down, and hold the suction ball tightly. Earball, to discharge the air in the ball, insert the tip of the earball into or immediately connect it to the top of the pipette (pipette), and be careful not to leak air. Slowly release the fingers of the left hand, slowly suck the washing liquid into the tube until it reaches the part above the scale line, remove the suction ear ball, quickly block the upper opening of the pipette (pipette) with the index finger of the right hand, wait for a while, and then put the washing liquid into the tube. Return the liquid to the original bottle. And rinse the inner and outer walls of the pipette (pipette) with tap water until no water drops hang, then wash with distilled water 3 times, and drain the water for later use.
5. Absorb the solution: Shake the solution to be absorbed, pour a small part of the solution to be absorbed into a clean and dry small beaker, use filter paper to absorb the water inside and outside the cleaned pipette tip, and insert it into the small beaker When the solution is sucked up to 1/3 of the capacity of the pipette, immediately press the mouth of the pipette with your right index finger, take it out, hold it horizontally and turn the pipette to make the solution flow all over the inner wall of the pipette, and pour the solution from the tip of the lower end Drain into the waste container. In this way, the solution can be absorbed after rinsing 3-4 times.
Insert the pipette that has been rinsed with the liquid to be absorbed into the place 1 to 2 cm below the surface to be absorbed, and use the suction ear ball to absorb the solution according to the above operation method (note that the pipette should not be inserted too deep into the solution, and it should be sucked down while sucking) inserted, always at this depth). When the liquid level in the tube rises to about 1-2 cm above the marked line, quickly block the nozzle with your right index finger (at this time, if the solution drops below the standard line, it should be sucked again), lift the pipette out of the liquid-absorbing surface, And make the tip of the tube touch the inner wall of the container to be sucked for a while, then lift it up, and wipe off the small amount of solution adhered to the lower end of the pipette or pipette with filter paper. (When moving the pipette or pipette, keep the pipette or pipette vertical and not tilted.)

6. Adjust the liquid level: Take another clean small beaker with your left hand, put the tip of the pipette against the inner wall of the small beaker, keep the small beaker tilted, keep the pipette vertical, and keep the scale line and line of sight horizontal (the left hand cannot touch the pipette. Tube). Slightly loosen the index finger (you can turn the pipette or pipette slightly), so that the solution in the tube flows out slowly from the lower mouth. When the liquid level reaches the scale line, press the right index finger firmly, pause for a moment, and then press the above method to dispense the solution. Put the bottom line of the meniscus until it is tangent to the upper edge of the marking line, and immediately press the nozzle tightly with your index finger. Put the tip close to the inner wall of the beaker, move a little towards the mouth of the beaker, and remove the droplet at the tip. Carefully transfer the pipette or pipette to the container receiving the solution.

7. Release the solution: put the pipette or pipette upright, the receiver is inclined, the lower end of the tube is close to the inner wall of the receiver, let go of the index finger, let the solution flow down the inner wall of the receiver, after the solution in the tube flows out, keep the discharge state and stay After 15 seconds, slide the tip of the pipette or pipette against the wall of the receiver a few times back and forth (or rotate the tip of the pipette against the inner wall of the receiver for a circle), remove the pipette (residual on the tip of the tube) A small amount of solution on the inner wall cannot be forced out by external force, because the volume of solution retained on the inner wall of the tip has been considered when calibrating pipettes or pipettes. The earball is blown out and not allowed to remain.)
0 notes
Text
Defouling and pitting technology of rigid flexible printed circuit board
To drill the dirt and pitting is just after the flexible printed circuit board nc drilling, chemical plating of copper or copper plating directly in front of an important working procedure, just flexible printed circuit board to achieve reliable electrical interconnection, just flexible printed circuit board must be combined with its special materials, polyimide materials for its main body and the characteristics of acrylic acid is not resistant to strong alkali, choose suitable to drill and pitting.There are two kinds of technology of defouling and pitting technology of rigid flexible printed circuit board: wet method and dry method.
The wet drilling and defouling and pitting technology of rigid flexible printed circuit board consists of the following three steps:
1. Swelling (also called swelling treatment).The surface area that can be oxidized can be increased by softening the pore wall substrate with alcohol ether bentonite, which can be easily oxidized. Generally, butylcarbiol is used to make the pore wall substrate dissolve and expand.

2. Oxidation.The purpose is to clean the hole wall and adjust the charge of the hole wall.
(1) concentrated sulfuric acid method: because concentrated sulfuric acid has strong oxidation and water absorption, most of the resin can be carbonized and form water-soluble alkyl sulfonates to be removed. The reaction formula is as follows: CmH2nOn+H2SO4--mC+nH2O perforated wall resin drilling pollution effect is related to concentration of concentrated sulfuric acid, treatment time and solution temperature.The concentration of concentrated sulfuric acid used for the removal of drilling dirt shall not be less than 86% and 20-40 seconds at room temperature.Concentrated sulfuric acid only works on resin, but is not effective for glass fiber. After concentrated sulfuric acid is used to concave the hole wall, there will be glass fiber head protruding, which needs to be treated with fluoride (such as ammonium fluoride or hydrofluoric acid).When using fluoride to treat prominent glass fiber heads, technological conditions should also be controlled to prevent core absorption due to excessive corrosion of glass fiber. The general process is as follows:
- H2SO4:10%
NH4HF2:5-10 g/l
Temperature 30 ℃ in time: 3 to 5 minutes
According to this method of punch after just - flexible printed circuit board to drill the dirt and pitting, and then the hole metallization, through metallographic analysis, found the inner drilling sewage didn't go to complete, lead to low copper layer and hole wall adhesion, thermal stress experiment in metallographic analysis for this (288 ℃, 10 + 1 second), the hole wall copper layer falls off and cause the inner circuit.
In addition, ammonium hydrogen fluoride or hydrofluoric acid have great toxicity, wastewater treatment is very difficult.What's more, polyimide is inert in concentrated sulfuric acid, so this method is not suitable for drilling, cleaning and pitting of rigid-flexible printed circuit board.
(2) the chromate method: because of chromic acid has strong oxidizing, its erosion ability is strong, so it can make the hole wall polymer material long chain disconnected, and oxidation and sulfurization, generated in the surface more hydrophilic groups, such as carbonyl (- C = O), hydroxyl (OH), sulfonic group (- SO3H), etc., so as to improve its hydrophilicity, adjust the hole wall charges, and to remove the purpose of the wall of hole drilling sewage and pitting.The general process formula is as follows:
Chromic anhydride CrO3:400 g/l
H2SO4:350 g/l sulphate
Temperature: 50 to 60 ℃ time: 10-15 min
According to this method, the rigid-flexible printed circuit board after drilling is defouled and corroded, and then the hole is metallized. The metallized hole is analyzed in metallography and tested in thermal stress.
Therefore, chromic acid method is also suitable for drilling, cleaning and pitting of rigid-flexible printed circuit boards. For small enterprises, this method is very suitable, simple and easy to operate.
(3) basic potassium permanganate method:At present, a lot of PCB manufacturers because of a lack of professional technology, still follow rigid multilayer printed circuit board is to drill the dirt and pitting technology - alkaline potassium permanganate to handle just - flexible printed circuit board, the method to remove resin after drilling sewage, at the same time can make its surface etching resin surface produce small bumpy small holes, in order to improve the adhesion strength of coating and the substrate of hole wall, under high temperature and high alkali environment, swelling of the resin can be removed using potassium permanganate oxidation drilling sewage, the system is work for the general rigid laminated, but for just - flexible printed circuit board does not adapt,Because polyimide, the main insulating base material of the rigid-flexible printed circuit board, is not resistant to alkaline, it needs to swell or even dissolve a little in alkaline solution, especially in high temperature and alkaline environment.If this method is adopted, even if the rigid-flexible printed circuit board is not scrapped at that time, the reliability of the equipment using the rigid-flexible printed circuit board will be greatly reduced in the future.
3. Neutralization.After oxidation treatment, the substrate must be cleaned and clean to prevent contamination of the activated solution in the later process. For this reason, it must go through the process of neutralization and reduction.
At present, the popular dry method at home and abroad is plasma decontamination and pitting technology.Plasma is used in the production of rigid-flexible printed circuit board, which is mainly used for drilling and cleaning the hole wall and surface modification of the hole wall.The reaction can be looked at is a highly active state of plasma with the hole wall polymer materials and glass fiber of gas and solid phase chemical reaction, the generated gas products and reaction of particles are not drain the process of vacuum pump, is a dynamic process of chemical reaction equilibrium. According to the first polymer materials used in the flexible printed circuit board usually choose N2, O2, the CF4, gas was fed as raw gas. The N2 have the effect of clean vacuum and preheating.
The schematic expression of plasma chemical reaction of O2+CF4 mixed gas is:
O2 + CF4O + OF + CO + COF package + + e - + F....
[plasma]
Due to the acceleration of electric field, it becomes a highly active particle and collides with O and F particles, resulting in high activity free radicals of oxygen and fluorine, etc., which react with polymer materials as follows:
[C, H, O, N] + [O+OF+CF3+CO+F+...]The CO2 + HF + H2O + NO2 +...
The reaction of plasma and glass fiber is:
SiO2 + [O + OF + CF3 + CO + + F...SiF4 + CO2 + CaL
At this point, we have realized the plasma treatment of the printed circuit board.
It is worth noting that the carbonylation reaction between O in atomic state and c-h and C=C leads to the addition of polar groups on the polymer bonds and the improvement of the surface hydrophilicity of polymer materials.
The rigid - flexible printed circuit board treated by O2+CF4 plasma and then treated with O2 plasma can not only improve the wettability (hydrophilicity) of the pore wall, but also remove the reaction.The finished sediments and incomplete intermediates.After the treatment of the rigid-flexible printed circuit board with direct electroplating, the metallized hole was analyzed in metallographic analysis and thermal stress test using plasma technology to drill dirt and cavitation, and the results fully met the gjb962a-32 standard.
In conclusion, both dry method and wet method can achieve the purpose of defouling and concave etching of the rigid-flexible interconnect motherboard if the proper method is chosen according to the characteristics of the main material of the system.
jackie from china Eagle Driver PCB,providing 1-50 layers PCB,High quality: Blind/Buried Hole Board, High Tg Thick Copper PCB, Mix- Material Multilayer PCB, Flexi-rigid Board, Flexible Board, Metal Core Board...Skype and E-mail:[email protected]
1 note
·
View note
Text
The role and specific process of anodizing treatment on the surface of aluminum profiles | fscyal.com
The role of anodizing of aluminum profiles
①Enhance anti-corrosion performance: the aluminum profile made by heating and extruding the aluminum rod has a very thin film on the surface, only a few microns, and aluminum is a very lively metal, which is easy to interact with oxygen in the air. Combined with substances such as water and water, aluminum oxide and aluminum hydroxide are formed through chemical reactions, and the corrosion resistance is very poor. The film layer can be thickened by anodic oxidation treatment to more than 10 μm, which can resist the corrosion of various acid and alkali substances. Improve the service life and mechanical properties of aluminum profiles.
②Improve the decoration performance: The surface of the extruded aluminum profile shows the original color of aluminum, that is, silver white. Through anodizing treatment, according to customer requirements and use requirements, the original silver white can be changed by oxidative coloring technology. In various colors such as golden yellow, brown, red, etc., to improve the decorative performance of aluminum profiles.
③ Increase insulation: Aluminum profile is an alloy material composed of alloy elements such as copper, manganese, zinc, etc. It has electrical conductivity. After anodizing, a protective film is formed on the surface to form a new insulation material, which does not have Electrical conductivity can protect the safety of electronic components and is suitable for the production of electronic products.
④Improve the coating adhesion: The substrate surface of the aluminum extrusion profile is covered with a thin layer of aluminum oxide. In order to facilitate the processing of oxidative coloring, anodization is required to open the micropores on the surface of the aluminum profile. It is convenient for the organic dye to adhere better to the coating surface. Finally, the sealing performance makes the various properties of the aluminum profile surface more stable.
Principle of anodizing of aluminum profiles
Anodizing of aluminum profiles is to place aluminum profiles in a solution of sulfuric acid, chromic acid or oxalic acid, and use aluminum as an anode to conduct electrolysis and oxidation under the action of current. Improve the corrosion resistance, abrasion resistance, high temperature resistance and decorative performance of the surface of aluminum profiles. This process of forming anodized films is called anodizing of aluminum profiles. If there is no special emphasis, the anodizing of aluminum profiles usually refers to sulfuric acid Anodizing, this is the most widely used method. The specific chemical reaction equation that occurs in sulfuric acid solution is as follows:
2H ﹢+ 2e ﹣ === H₂ ↑
4OH﹣ + 4e ﹣ === 2HO₂ + O₂ ↑
2Al³ ﹢+ 3O² ﹣ === Al₂O₃ + heat
Al₂O₃ + 3H₂SO4 → Al₂ (SO4) ₃ + 3H₂O
Source: https://www.fscyal.com/the-role-and-specific-process-of-anodizing-treatment-on-the-surface-of-aluminum-profiles/
0 notes
Text
What is Anodizing ? Aluminum Anodizing Process basics
What is Anodizing?

For Anodizing first you have to know What is Anodizing! Anodizing is one of the most common treatments for aluminium.
In all anodizing processes, the basic reaction is the conversion of aluminium surface to aluminium oxide.
The aluminium component, which is made an anodic in the electrolytic cell, causes the oxide layer to harden, leading to better corrosion and wear resistance.For decorative purposes, a layer of oxide formed on the surface is not dyed it is called Anodizing.
What is Anodizing Process for Aluminium

In the Anodizing process for Aluminium, the area must first be cleaned and sanitized before being placed in the bath with an electrolytic solution, especially sulfuric or chromic acid. This provides an electric coating that contains both positive and negative ions.
So how does this process really work?
Yes, if the anodizing coating process continues, a good electrical charge is sent through the aluminium, while a negative charge is applied to the plates in the electrolyte. Essentially, electrical energy forces positive ions to attract poorly charged plates while negative ions are attracted to the aluminium component, which is a good anode.
With the same geometric pattern, these pores run down to the substrate of the part. The combination of aluminium surface and poorly charged ions creates a barrier layer, known as the anodizing aluminium process as the surface layer makes the components resistant to corrode.
The aluminium anodizing process is performed by transferring DC electricity with an electrolytic solution where the aluminium material is filled. The electrical energy causes the release of oxygen on the surface of the aluminium, creating a mass of aluminium oxide.
The resulting anodic film is much larger than natural oxidation and uniform on the surface of the work surface. Aluminium Anodizing is usually made into an acid solution, which slowly dissolves aluminium oxide, creating an oxide filling that protects and / or improves the appearance of the final product.
Conclusion, Aluminium Anodizing creates oxide protection that protects and enhances the appearance of the final product. Type II anodizing is best suited for aluminium, but can be used for non-ferrous metals such as titanium or magnesium.
Should You Anodize Your Metal Parts?

Now that you know more about anodizing aluminium, you can decide if this process is right for your parts or not. If you need functional aluminium parts that will withstand pressure or wear, such as aircraft parts or consumer goods, this back processing method will satisfy your needs.
There is also a noticeable attraction to anodizing aluminium, especially since you can add colour to your parts while keeping the metallic sheen strong.
If you want to learn more about how this approach can help improve your components, contact Indaco Coats best Anodizing Service Provider at Belgaum. Find out how anodizing aluminium can improve your production plans with them.
#What is Anodizing#Anodizing Process basics#anodising process#what is anodized aluminum#anodized aluminum#aluminum anodizing process basics#anodic oxide
0 notes
Photo

Study on the Analysis of Chromite Refractory Brick from Mwe Taung Chromite Ore
by Dar Nei Sung ""Study on the Analysis of Chromite Refractory Brick from Mwe Taung Chromite Ore""
Published in International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (ijtsrd), ISSN: 2456-6470, Volume-3 | Issue-5 , August 2019,
URL: https://www.ijtsrd.com/papers/ijtsrd26765.pdf
Paper URL: https://www.ijtsrd.com/engineering/mineral-and-metallurgical-engineering/26765/study-on-the-analysis-of-chromite-refractory-brick-from-mwe-taung-chromite-ore/dar-nei-sung
call for paper papers in journals, call for paper in ugc approved journals
This research paper is the preliminary study of testing the feasibility of chromite ore to produce refractory. Chromite ore was taken from Mwe Taung, in Chin State, Myanmar. Chromite ore contains iron oxide, alumina, magnesia, lime, chromic oxide and silica. The prepared chromite has been extensively used for high temperature metallurgical reactions. The chemical analysis of chromite ore was done to know the composition. Composition expresses the percentage of oxide component which can able to determine whether the refractory is acidic, basic or neutral. The chromite ore studied in this research is neutral refractory. The experiment of chromite refractory brick production was carried out first, the chromite powder are reduced to 50 mesh, 100 mesh and 200 mesh through sieving and then, mixed with magnesium chloride as binder, applied to 400 tons pressure, heated at drying temperature 200°C for twenty four hours and at firing temperature 1580°C for fifty two hours to produce chromite refractory brick. Analysis of locally available chromite refractory brick produced is tested. The standard properties such as cold crushing strength, apparent specific gravity, apparent porosity, bulk density and water absorption.
0 notes
Text
Top Things to Consider when purchasing chemical storage cabinets
Chemical storage cabinets, for many companies are a vital safety features that play important roles in their business operations. Whether companies use their chemicals in their manufacturing or for cleaning they are the most hazardous materials commonly found in the work place.
Chemical storage cabinet’s main role is to minimize the risk of chemical exposure to all those people who use or work in the areas and to safe guard the environment from contamination.
Things to consider when purchasing chemical storage cabinets:
Materials used to make the Cabinets
When selecting the right types of storage cabinets one of the most important considerations is the compatibility of the chemicals that will be stored in them and the materials used to construct the cabinets themselves.
Some chemicals have very corrosive properties, strong acids and caustic substances are likely to corrode any metallic components, so metal cabinets should not be considered for these types of chemicals.
Chemicals such as acetic acid, chromic acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid as well as common bases such as ammonia, ammonium hydroxide, caustic potash (potassium hydroxide), and caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) should never be stored near or in metal.
Cabinets for storage of liquids need to contain drip trays large enough to contain all the liquids in case of a container rupture or leak
Flammable Non-Corrosive
Often metal chemical storage cabinets are recommended for flammable chemicals that are not corrosive as they can be designed to contain these chemicals or a fire to minimize the danger to employees, property and the environment if they are accidently spilt or ignited
Segregating Chemicals
Chemicals need to be separated according to their compatibility and in such a way that incompatible chemical cannot come into contact with each other in the event of an accident or spillage as this could cause issues such as combustion and subsequent fire, violent chemical reactions such as noxious or toxic smoke or gases’ Acids must not be stored with bases, reducing agents or oxidizers must not be stored with organic materials.
These types of chemicals should where possible be kept in separate chemical storage cabinets or be divided with inert physical barriers
Size of chemical storage cabinets
When purchasing chemical storage cabinets you need to consider the amount of chemicals you need to keep on hand at any one time. It’s far better to purchase smaller quantities of chemicals more often because
You lessen the risks involved with storing large amounts of unused chemicals
Many chemicals have a short use by period
In the event of an accident spillages will be minimized
It can cost a lot to properly dispose of unwanted or unused chemicals legally and responsibly
Access ability of chemicals in storage areas
Always ensure that all chemicals are properly labeled with their contents and expiry dates clearly visible.
Chemicals should be stored so that shelves are not over crowed
Hazardous chemicals should not be stored above eye level so they are easily visible
There should be specially trained personal in charge with storage and handling chemicals
When purchasing chemical storage cabinets ensure they are a suitable size and design as well as material for the chemicals you will store.
0 notes
Video
When chromyl chloride is added to water, it quickly hydrolyzes to form hydrogen chloride gas and chromic acid. On the surface it rapidly scattered and disappeared. When more is added though, it all sinks to the bottom and then gets lifted up by the hydrogen chloride bubbles. Video from @nile.red #laboratory #chemical #chemist #scientist #experiment #molecule #experiments #reaction #quimica #scienceexperiment #reactionchamber #chemicalreaction #homelab #fading #synthesis #fluorescence #lablife #fluorescent #research #microscope #sciart https://www.instagram.com/p/CADv-QejV1A/?igshid=1n427com3v99j
#laboratory#chemical#chemist#scientist#experiment#molecule#experiments#reaction#quimica#scienceexperiment#reactionchamber#chemicalreaction#homelab#fading#synthesis#fluorescence#lablife#fluorescent#research#microscope#sciart
0 notes
Photo
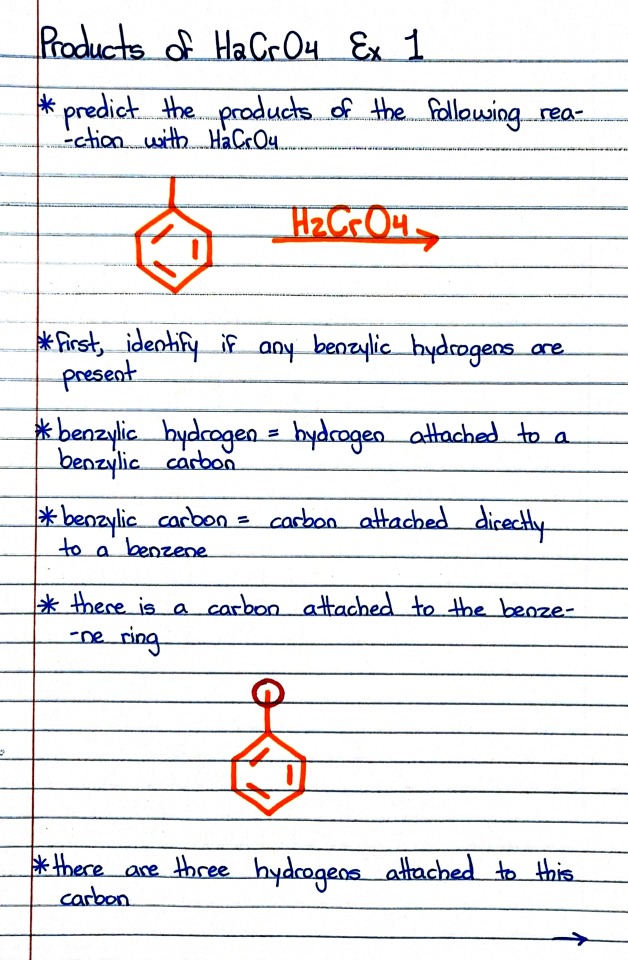
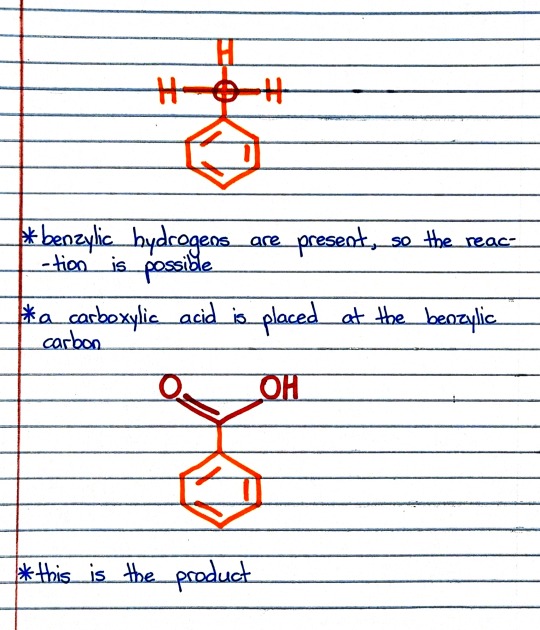
#organic chemistry#ochem#o-chem#o chem#ochem 1#ochem 2#organic chemistry 1#organic chemistry 2#mcat organic chemistry#orgo#reactions#orgo reactions#chemical reactions#orgo mcat#mcat orgo#ochem reactions#studyblr#notes#h2cro4#chromic acid#chromic acid notes#chromic acid reaction
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Absorbable Sutures Market Projected to Garner Significant Revenues by 2025
Sutures, generally called stitches, are sterilized, surgical threads that are used for wound closure. They are primarily used to close incisions resulting due to a surgery. They are used by doctors and surgeons to hold skin, blood vessels, internal organs, and various other tissues of the body together after they have been detached by incision, injury, or surgery. Surgical suture closure creates an environment for faster healing of the wound. Tissues are fastened with sutures until ample healing occurs to enable patients to endure stress without any mechanical support.
Read Report Overview: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/absorbable-sutures-market.html
A variety of sutures, with varied properties are available according to the usage. Sutures can be widely categorized into two types: non-absorbable sutures and absorbable sutures. An absorbable suture dissolves in tissue after a certain time period. It degenerates as the wound or incision cures. A non-absorbable suture does not dissolve in the body and has to be removed by a surgeon after a surface incision has healed. An ideal suture should be strong, non-toxic, hypoallergenic, and flexible. In addition, sutures should not absorb fluid to avoid unwanted infection.
The category of suture used depends on the type of surgery, nature of the location, and the preference and professional understanding of the surgeon.
Development of advanced wound care dressings and availability of alternatives such as surgical staplers and complications such as hemorrhage, leakage especially in esophageal and colonic anastomosis and diverticular formation are a few factors restraining the expansion of the absorbable sutures market.
Request Brochure of Report: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=B&rep_id=42095
Sutures placed internally require to be removed, and those present on the outside can be removed easily without any re-opening of the wound. Absorbable sutures are thus often preferred for internal wound stitches, and non-absorbable sutures are mostly used for external wounds. Absorbable sutures include polyglactin 910, polyglycolic acid sutures, polydioxanone sutures, and catgut, poliglecaprone 25.
Based on type, the global absorbable sutures market can be segmented into monofilament sutures and multifilament or braided sutures. Monofilament sutures have easy passage through the tissues, whereas multifilament sutures have stable knotting feature. In general, monofilament sutures produce less tissue reaction compared to multifilament sutures. Multifilament sutures are mostly braided and layered with various materials such as silicon, polycaprolactone, wax, calcium stearate, PTFE, etc.
Request For TOC : https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=T&rep_id=42095
In terms of raw material, the global absorbable sutures market can be categorized into natural and synthetic. Natural sutures include catgut and silk sutures. All other sutures falls under the synthetic type. Based on coating, the global absorbable sutures market can be divided into uncoated and coated sutures. Typically, braided sutures are coated and monofilament sutures are uncoated as braided sutures are easy to coat compared to monofilaments sutures. Coating materials include silicon, wax, gelatin, chromium salt, polycaprolactone, PTFE, and calcium stearate. Polymeric coating materials are more bio-compatible than conventional coating materials such as beeswax, gelatin, pafaffin, etc. New functional coatings such as antimicrobial or antibacterial coatings are now available and are used on both multifilament and monofilament sutures. Stem cell coating is also available, which improves healing properties. Coated sutures include catgut chromic, silk, PGA sutures, polyglactin 910 and polyester sutures, twisted nylon, polydioxanone, and poliglecaprone sutures. Uncoated sutures include monofilament nylon, monofilament polypropylene sutures, and PVDF. Based on application, the absorbable sutures market can be segmented into valve sutures, cardiovascular sutures, gynecology sutures, orthopedic sutures, dental sutures, sutures for cosmetic surgery, ophthalmic sutures, general sutures, etc. In terms of end-user, the absorbable sutures market can be classified into hospitals, ambulatory surgical centers, specialty clinics, dental clinics, and others.
Based on region, the absorbable sutures market can be segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa. North America is anticipated to be a dominant region of the absorbable sutures market due to the rising number of surgeries, increasing incidence of cardiovascular diseases, and fast adoption of advanced technologies. Asia Pacific is anticipated to be a rapidly expanding region of the absorbable sutures market.
Key players operating in the global absorbable sutures market include B. Braun Melsungen AG, Ethicon, Inc., Medtronic Plc., DemeTech Corporation, Smith & Nephew Plc. Zimmer Biomet Holdings, Inc., Boston Scientific Corporation, LifeSciences Corporation, Teleflex Incorporated, Acelity L.P. Inc., and ConMed Corporation.
About us:
Transparency Market Research (TMR) is a U.S.-based provider of syndicated research, customized research, and consulting services. TMR’s global and regional market intelligence coverage includes industries such as pharmaceutical, chemicals and materials, technology and media, food and beverages, and consumer goods, among others. Each TMR research report provides clients with a 360-degree view of the market with statistical forecasts, competitive landscape, detailed segmentation, key trends, and strategic recommendations.
Contact us:
Transparency Market Research
90 State Street,
Suite 700,
Albany
NY - 12207
United States
Tel: +1-518-618-1030
USA - Canada Toll Free 866-552-3453
Email: [email protected]
Website: http://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/
0 notes
Text
Study the properties of alcohols, compare/contrast with phenols and identify unknowns
Study the properties of alcohols, compare/contrast with phenols and identify unknowns
Alcohols tested: 1-butanol (primary alcohol); 2-butanol (secondary alcohol); tert-butanol (a tertiary alcohol); a phenolic compound and 2 unknowns.
Chemical Reactions:
Write the chemical equations for all of the tests performed (Lucas, chromic acid, ferric chloride) and balance when feasible. If the compound…
View On WordPress
#Custom Essay Writing Service#custom Law papers#Rush Essays#Writing a PHD Thesis#Writing Research Paper
0 notes
Text
Post 9: Safety Precautions While Electroplating
Electroplating chemicals are hazardous and should be used with caution. A proper knowledge of the possible risks is necessary before undertaking the process. It is also important to understand the disposal mechanisms for the same.
Copper Sulphate solution is inarguably one of the most commonly used solutions in DIY electroplating. The safety data sheet of copper sulphate solution is available here. Copper Sulphate solution is toxic if swallowed, causes skin and eye irritation and is very toxic to aquatic life. It is suggested to wear safety glasses and chemical-resistant gloves. There are laws regulating the disposal of these chemicals that must be followed strictly. If the need is to dispose just a small amount, one suggested procedure may be to put steel wool in it, so most of the copper will plate out as metal, then neutralize it with baking soda and flush it down the sink.
Nickel solution is also commonly used in electroplating, especially in the electroless nickel process. General short-term effects include irritation of the skin and eye whereas longer-term effects could include allergic reactions in the skin, asthma, inflammation of the lungs and lung/nose cancer. Here is a link to safe nickel plating which does not use unsafe acids. The safety data sheet for nickel solution can be found in [3] and [4]. The basic waste disposal procedure for waste treatment of spent Electroless Nickel baths is simply to plate all the nickel out of the bath. The nickel in the bath is plated onto steel wool until the concentration is below 2-3 ppm. After this, the local authority guidelines should be checked. Article [5] mentions sending it to the POTW (publicly owned treatment works) after reducing the nickel concentration.
Chromic acid is a strong irritant and corrosive. Exposure usually arises as the result of splashes, as a mist of chromic acid coated bubbles of hydrogen or as chromic acid contaminated dust. Chromic acid affects the skin, nasal and bronchial mucosal linings. On the skin, chromic acid can cause chronic ulcers known as ‘chrome holes’. In the nasal cavity, chrome ulceration affects the nasal septum and can cause perforation. When inhaled as a mist or contaminated dust, chromic acid can cause nasal irritation, rhinitis and bronchitis. If splashed in the eyes, chromic acid can cause severe injury including conjuctival inflammation and corneal injury. Chromic acid contains soluble hexavalent chromium which is toxic and carcinogenic. Disposal is tough and standard procedures should be followed. Some steps can be found out in [1]. The safety data sheet is available here.
If any other chemical / heavy metal is being used, its safety sheet and disposal mechanism should be understood before using it. Some common cautions while electroplating are:
Do not wear rings. No jewellery be worn when one is handling electrical circuits. There have been several incidents where the jewellery contributed to an electrocution incident.
Wear insulated gloves and splash goggles.
Always add acid to water.
Ensure that the ventilation system is appropriate for hazardous fumes.
Always label and date solutions properly.
References:
https://www.chemistry.nus.edu.sg/PSSO/safety/Special%20Chemical%20Waste.htm
http://www.globalhealingcenter.com/natural-health/metal-toxicity-health-dangers-nickel/
https://www.fishersci.com/shop/msdsproxy?productName=SN70100&productDescription=NICKEL+REF+STD+SOL+CRT+100ML&catNo=SN70-100&vendorId=VN00033897&storeId=10652
http://www.circuitmedic.com/msds/msds_nickel_plating_solution.shtml
http://www.pfonline.com/articles/easy-waste-treatment-for-spent-en-baths
https://www.st-andrews.ac.uk/staff/policy/healthandsafety/publications/waste/waste-disposaloflaboratorywastesguidance/
https://www.ganoksin.com/article/electroplating-safety-precautions/
Your queries and suggestions are always welcome. Please mail me any relevant content at [email protected]
All my findings are also available at the GitHub repo: https://github.com/dharnidharka/3dplating
0 notes
Photo


#organic chemistry#ochem#o-chem#o chem#ochem 1#ochem 2#organic chemistry 1#organic chemistry 2#mcat organic chemistry#orgo#reactions#orgo reactions#chemical reactions#orgo mcat#mcat orgo#ochem reactions#studyblr#notes#chromic acid#benzene#hydrogens#benzylic hydrogens#carboxylic acid#carboxylic acids
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Absorbable Sutures Market to Reflect Impressive Growth Rate by 2025
Sutures, generally called stitches, are sterilized, surgical threads that are used for wound closure. They are primarily used to close incisions resulting due to a surgery. They are used by doctors and surgeons to hold skin, blood vessels, internal organs, and various other tissues of the body together after they have been detached by incision, injury, or surgery. Surgical suture closure creates an environment for faster healing of the wound. Tissues are fastened with sutures until ample healing occurs to enable patients to endure stress without any mechanical support.
A variety of sutures, with varied properties are available according to the usage. Sutures can be widely categorized into two types: non-absorbable sutures and absorbable sutures. An absorbable suture dissolves in tissue after a certain time period. It degenerates as the wound or incision cures. A non-absorbable suture does not dissolve in the body and has to be removed by a surgeon after a surface incision has healed. An ideal suture should be strong, non-toxic, hypoallergenic, and flexible. In addition, sutures should not absorb fluid to avoid unwanted infection.
Read Report Overview: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/absorbable-sutures-market.html
The category of suture used depends on the type of surgery, nature of the location, and the preference and professional understanding of the surgeon.
Development of advanced wound care dressings and availability of alternatives such as surgical staplers and complications such as hemorrhage, leakage especially in esophageal and colonic anastomosis and diverticular formation are a few factors restraining the expansion of the absorbable sutures market.
Sutures placed internally require to be removed, and those present on the outside can be removed easily without any re-opening of the wound. Absorbable sutures are thus often preferred for internal wound stitches, and non-absorbable sutures are mostly used for external wounds. Absorbable sutures include polyglactin 910, polyglycolic acid sutures, polydioxanone sutures, and catgut, poliglecaprone 25.
Based on type, the global absorbable sutures market can be segmented into monofilament sutures and multifilament or braided sutures. Monofilament sutures have easy passage through the tissues, whereas multifilament sutures have stable knotting feature. In general, monofilament sutures produce less tissue reaction compared to multifilament sutures. Multifilament sutures are mostly braided and layered with various materials such as silicon, polycaprolactone, wax, calcium stearate, PTFE, etc.
Request Brochure of Report: https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=B&rep_id=42095
In terms of raw material, the global absorbable sutures market can be categorized into natural and synthetic. Natural sutures include catgut and silk sutures. All other sutures falls under the synthetic type. Based on coating, the global absorbable sutures market can be divided into uncoated and coated sutures. Typically, braided sutures are coated and monofilament sutures are uncoated as braided sutures are easy to coat compared to monofilaments sutures. Coating materials include silicon, wax, gelatin, chromium salt, polycaprolactone, PTFE, and calcium stearate. Polymeric coating materials are more bio-compatible than conventional coating materials such as beeswax, gelatin, pafaffin, etc. New functional coatings such as antimicrobial or antibacterial coatings are now available and are used on both multifilament and monofilament sutures. Stem cell coating is also available, which improves healing properties. Coated sutures include catgut chromic, silk, PGA sutures, polyglactin 910 and polyester sutures, twisted nylon, polydioxanone, and poliglecaprone sutures. Uncoated sutures include monofilament nylon, monofilament polypropylene sutures, and PVDF. Based on application, the absorbable sutures market can be segmented into valve sutures, cardiovascular sutures, gynecology sutures, orthopedic sutures, dental sutures, sutures for cosmetic surgery, ophthalmic sutures, general sutures, etc. In terms of end-user, the absorbable sutures market can be classified into hospitals, ambulatory surgical centers, specialty clinics, dental clinics, and others.
Request For TOC : https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/sample/sample.php?flag=T&rep_id=42095
Based on region, the absorbable sutures market can be segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa. North America is anticipated to be a dominant region of the absorbable sutures market due to the rising number of surgeries, increasing incidence of cardiovascular diseases, and fast adoption of advanced technologies. Asia Pacific is anticipated to be a rapidly expanding region of the absorbable sutures market.
Key players operating in the global absorbable sutures market include B. Braun Melsungen AG, Ethicon, Inc., Medtronic Plc., DemeTech Corporation, Smith & Nephew Plc. Zimmer Biomet Holdings, Inc., Boston Scientific Corporation, LifeSciences Corporation, Teleflex Incorporated, Acelity L.P. Inc., and ConMed Corporation.
The report offers a comprehensive evaluation of the absorbable sutures market. It does so via in-depth qualitative insights, historical data, and verifiable projections about market size. The projections featured in the report have been derived using proven research methodologies and assumptions. By doing so, the research report serves as a repository of analysis and information for every facet of the absorbable sutures market, including but not limited to: Regional markets, technology, types, and applications.
About us:
Transparency Market Research (TMR) is a U.S.-based provider of syndicated research, customized research, and consulting services. TMR’s global and regional market intelligence coverage includes industries such as pharmaceutical, chemicals and materials, technology and media, food and beverages, and consumer goods, among others. Each TMR research report provides clients with a 360-degree view of the market with statistical forecasts, competitive landscape, detailed segmentation, key trends, and strategic recommendations.
Contact us:
Transparency Market Research
90 State Street,
Suite 700,
Albany
NY - 12207
United States
Tel: +1-518-618-1030
USA - Canada Toll Free 866-552-3453
Email: [email protected]
Website: http://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/
0 notes