#devops tra
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
DevOps & Site Reliability Engineering (SRE): The Future of Scalable Tech Careers
The tech industry is evolving, and with it, the demand for professionals who can bridge the gap between development and operations. DevOps and Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) are no longer just buzzwords; they are essential practices for building resilient, scalable systems.
DevOps focuses on collaboration, automation, continuous integration, and delivery.
SRE takes it a step further by applying software engineering principles to operations, focusing on system reliability, uptime, and performance.
These roles are essential in cloud-native environments where infrastructure must scale rapidly and services must remain highly available.
0 notes
Text
MCA Specialisations: Which One is Right for You?

MCA is considered one of the most preferred postgraduate courses by aspirants who intend to work in the rapid growth of computers and technology. As industries continue to digitise quickly, there is a growing demand for MCA graduates, particularly in IT, banking, healthcare and e-commerce.
However, selecting the right MCA specialisation is essential for your career choice. Whether you want to be a software developer, data scientist, cybersecurity expert, or IT consultant, choosing the best specialisation can give you an edge.
In this blog post, we will discuss the most popular MCA courses, career opportunities, and how to choose the best option for you.
1. MCA in Software Development
Software Development is the perfect choice if you love coding and want to develop innovative software solutions. This major develops the skills to build websites and applications, database design and management, programming languages, software engineering, etc.
Key Subjects:
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
Web and Mobile App Development
Database Management Systems (DBMS)
Cloud Computing
Software Testing and Quality Assurance
Career Opportunities:
Software Developer
Full-Stack Developer
Application Engineer
Web Developer
Cloud Software Engineer
This specialisation is perfect for those who enjoy problem-solving and have a knack for writing efficient code.
2. MCA in Data Science & Big Data Analytics
As data-driven decision-making revolutionises the modern business era, data science and prominent data analytics professionals are in great demand. This MCA specialisation trains students in machines, statistical modelling, data analysis, and artificial intelligence.
Key Subjects:
Data Mining and Warehousing
Machine Learning and AI
Predictive Analytics
Deep Learning
Big Data Technologies (Hadoop, Spark)
Career Opportunities:
Data Scientist
Machine Learning Engineer
Business Intelligence Analyst
Data Engineer
If you love working with numbers and extracting insights from large datasets, this specialisation is an excellent choice.
3. MCA in Cyber Security & Ethical Hacking
Cyber threats are growing, and cybersecurity is one of the most pivotal areas in IT. This specialisation trains students to secure digital assets, discover vulnerabilities and defend networks from attackers.
Key Subjects:
Network Security
Ethical Hacking
Cryptography
Information Security Management
Digital Forensics
Career Opportunities:
Cyber Security Analyst
Ethical Hacker
Information Security Consultant
Security Architect
It is the best field for cybersecurity lovers and ethical hackers to protect the digital world.
4. MCA in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is changing the IT landscape, making it a high-grossing career choice. This specialisation trains students to design, implement and manage applications and services that are built on cloud-based systems.
Key Subjects:
Cloud Architecture
Virtualisation Technologies
AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure
DevOps Practices
Cloud Security
Career Opportunities:
Cloud Solutions Architect
Cloud Security Analyst
DevOps Engineer
Cloud Engineer
This specialisation is for you if you want to manage and optimise cloud platforms.
5. MCA in Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
This specialisation is part of a series on the innovations made possible by the AI/ML revolution, which makes industries in health, finance and beyond work differently when they are on. This specialisation encompasses designing intelligent systems that can learn and adapt.
Key Subjects:
Neural Networks
Deep Learning
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Robotics & Automation
AI-driven Business Solutions
Career Opportunities:
AI Engineer
Machine Learning Scientist
NLP Engineer
Robotics Engineer
This specialisation provides endless opportunities for those fascinated by automation and intelligent computing.
6. MCA in Blockchain Technology
How blockchain is changing the way we look at things in business. The MCA specialisation trains students to develop secure and decentralised applications.
Key Subjects:
Blockchain Fundamentals
Smart Contracts Development
Cryptography and Distributed Ledger Technology
Decentralised Applications (DApps)
Career Opportunities:
Blockchain Developer
Cryptocurrency Analyst
Smart Contract Developer
Blockchain Consultant
Blockchain is a path to embrace if you are an enabler of disruptive technology and decentralisation.
7. MCA in Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT, or the Internet of Things, encapsulates connecting natural physical elements with the web, helping create competent answers for homes, medical help, and industrial automation. This specialisation includes networking, data analytics, and embedded systems.
Key Subjects:
IoT Architecture and Protocols
Embedded Systems
Wireless Sensor Networks
IoT Security
Career Opportunities:
IoT Developer
Embedded Systems Engineer
Smart Home Automation Specialist
IoT Security Analyst
This specialisation is excellent if you love innovation and working with smart devices.
8. MCA in IT Management
IT Management is for those who wish to get the best of both worlds of technology and business. It focuses on IT project management, enterprise / solution and business intelligence.
Key Subjects:
IT Strategy and Governance
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Business Analytics
IT Risk Management
Career Opportunities:
IT Manager
Business Analyst
Technology Consultant
IT Project Manager
This specialisation is ideal for those looking to take on leadership roles in the IT sector.
9. MCA in Game Development
The Game Development industry is on the rise, and there is an immensely high demand for professionals in this domain. These specialisations include game design, graphics programming, and immersive technology.
Key Subjects:
Game Engine Programming (Unity, Unreal)
AR/VR Development
Computer Graphics
Game Testing and Debugging
Career Opportunities:
Game Developer
AR/VR Developer
Game Designer
Simulation Engineer
This specialisation can be a dream career path for those passionate about gaming and creativity.
How to Choose the Right MCA Specialisation?
Choosing the right MCA specialisation depends on several factors, including:
Your Interests: What excites you the most? Coding, security, AI, or management?
Career Goals: Do you want to be a developer, data scientist, or IT manager?
Industry Demand: Research job market trends to identify high-demand fields.
Skillset: Align your technical strengths with the specialisation that suits you.
Final Thoughts
There are various specialisations in an MCA, all leading to different careers. The right specialisation for you would be the one that helps you realise your career goals, be it software development, cybersecurity, AI engineering, etc. Research the top MCA colleges and career prospects before deciding, but most importantly, go for the field you are interested in. If you choose the right MCA specialisation, you can build a successful and rewarding career in the tech industry. Whether you're aiming to get into the best MCA colleges or already exploring top MCA colleges, making an informed choice can set the stage for a bright future.
0 notes
Text
Ansible Là Gì? Cách Cài Đặt Ansible trên Ubuntu 22.04
Ansible là một công cụ tự động hóa mã nguồn mở mạnh mẽ, đơn giản và dễ học. Nó được sử dụng để tự động hóa việc cấu hình và quản lý hệ thống, triển khai ứng dụng và nhiều tác vụ khác. Ansible giúp giảm thiểu công sức và thời gian cần thiết để quản lý một số lượng lớn máy chủ, từ vài máy đến hàng nghìn máy.

Tại sao Ansible lại phổ biến?
Ansible có nhiều ưu điểm khiến nó trở thành một lựa chọn phổ biến trong giới DevOps:
Đơn giản: Ansible sử dụng cú pháp YAML đơn giản và dễ đọc, giúp người dùng dễ dàng viết các playbook (tập lệnh của Ansible).
Không cần cài đặt tác nhân: Ansible không yêu cầu cài đặt bất kỳ tác nhân nào trên các máy chủ được quản lý, giúp đơn giản hóa quá trình cài đặt và bảo trì.
Mạnh mẽ: Ansible có khả năng tự động hóa nhiều tác vụ phức tạp, từ cấu hình hệ thống đến triển khai ứng dụng.
Linh hoạt: Ansible có thể được sử dụng để quản lý nhiều loại hệ điều hành và nền tảng khác nhau.
Cộng đồng lớn: Ansible có một cộng đồng người dùng lớn và tích cực, cung cấp nhiều tài liệu, hướng dẫn và module (thành phần mở rộng của Ansible) hữu ích.
Cách Ansible hoạt động
Ansible hoạt động dựa trên nguyên tắc "push-based", nghĩa là nó kết nối đến các máy chủ được quản lý và thực hiện các tác vụ được chỉ định trong playbook. Ansible sử dụng SSH để kết nối đến các máy chủ, do đó yêu cầu duy nhất là máy chủ quản lý (nơi cài đặt Ansible) có thể kết nối SSH đến các máy chủ được quản lý.
Cài đặt Ansible trên Ubuntu 22.04
Để cài đặt Ansible trên Ubuntu 22.04, bạn có thể thực hiện theo các bước sau:
Cập nhật danh sách gói:Bash sudo apt update
Cài đặt các gói phụ thuộc:Bash sudo apt install software-properties-common
Thêm kho lưu trữ Ansible PPA:Bash sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ansible/ansible
Cập nhật lại danh sách gói:Bash sudo apt update
Cài đặt Ansible:Bash sudo apt install ansible
Kiểm tra cài đặt:Bash ansible --version Nếu bạn thấy thông tin về phiên bản Ansible, nghĩa là bạn đã cài đặt thành công.
Cấu hình Ansible
Sau khi cài đặt Ansible, bạn cần cấu hình nó để có thể quản lý các máy chủ. Hai thành phần quan trọng cần cấu hình là:
Inventory: File chứa danh sách các máy chủ được quản lý.
Playbook: File chứa các tập lệnh tự động hóa.
1. Inventory
File inventory mặc định của Ansible nằm tại /etc/ansible/hosts. Bạn có thể tạo một file inventory mới hoặc sử dụng file mặc định.
Ví dụ, để quản lý hai máy chủ có địa chỉ IP là 192.168.1.10 và 192.168.1.20, bạn có thể thêm chúng vào file inventory như sau:
Ini, TOML[webservers] 192.168.1.10 192.168.1.20
Bạn cũng có thể nhóm các máy chủ lại với nhau:
Ini, TOML[webservers] 192.168.1.10 192.168.1.20 [databases] 192.168.1.30
2. Playbook
Playbook là một file YAML chứa các tập lệnh tự động hóa. Ví dụ, để cài đặt Apache trên hai máy chủ webservers, bạn có thể tạo một playbook có tên install_apache.yml như sau:
YAML--- - hosts: webservers become: true tasks: - name: Cài đặt Apache apt: name: apache2 state: present
Để chạy playbook này, bạn sử dụng lệnh sau:
Bashansible-playbook install_apache.yml
Kết luận
Ansible là một công cụ tự động hóa mạnh mẽ và dễ sử dụng, giúp đơn giản hóa việc quản lý và cấu hình hệ thống. Hy vọng bài viết này đã giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về Ansible và cách cài đặt nó trên Ubuntu 22.04.
Nguồn tham khảo: https://thuegpu.vn/ansible-la-gi-cach-cai-dat-ansible-tren-ubuntu-22-04/
1 note
·
View note
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] Written by experienced Agile coaches, SPCTs, and a SAFe(R) Fellow, this guide is packed with real-world examples, use cases, and anecdotes, and offers valuable guidance to help you avoid common pitfalls and successfully implement SAFe(R)Key FeaturesUnderstand how to tailor SAFe(R) practices to meet your organization's needsAvoid common mistakes encountered while adopting SAFe(R) at team, ART, and portfolio levelsDiscover practical tips and best practices to plan teams, ARTs, events, and Lean Portfolio ManagementBook DescriptionThe Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe(R)) is widely recognized as an eff ective methodology for implementing Agile practices at the Enterprise level. However, the complexity of SAFe(R) can make it challenging for Teams and organizations to determine which practices can be safely adapted to their unique needs. Although SAFe(R) is a framework rather than a set of rules, promoting adaptation, it's crucial to understand why SAFe(R) practices are designed the way they are along with the consequences of modifying them.The SAFe(R) Coaches Handbook is a comprehensive resource that goes beyond a how-to guide, providing a deep understanding of SAFe(R) principles and practices. The chapters are designed in a way to teach you how to successfully implement SAFe(R) in your organization and eff ectively manage the Team's Backlog while avoiding common pitfalls. You'll discover optimal ways to create SAFe(R) Teams and run successful Events. You'll also learn how to plan Agile Release Trains (ARTs), manage the ART Backlog, conduct PI Planning, and grasp the importance of Value Stream Identifi cation in driving value delivery.By the end of this book, you'll be armed with practical tips and advice to help you successfully customize the Scaled Agile Framework to your Enterprise's needs while preserving the aspects that make it work successfully.What you will learnDiscover how to set up Agile Teams to attain maximum effectivenessAvoid common mistakes organizations make with SAFe(R)Find out how to set up the Agile Release TrainDiscover common mistakes enterprises make that affect the success of the ARTUnderstand the importance of Value Streams and learn how to work with them successfullyStart using the best ways to measure the progress of Teams and ARTs at an Enterprise levelRecognize the impact of successful SAFe(R) adoption on Enterprise strategy and organizational structureWho this book is forIf you're a SAFe(R) Practice Consultant (SPCT), Scrum Master/Team Coach, or Release Train Engineer tasked with implementing SAFe(R) within an organization, you'll find this book indispensable. It offers valuable insights into aspects of SAFe(R) and helps ensure success in delivery and execution with practical uses you can adopt. Product owners and product managers will also benefit from this book by gaining a deeper understanding of how to function effectively within a SAFe(R) environment. A basic understanding of SAFe(R), agile, and DevOps is recommended to get the most out of this book.Table of ContentsThriving the Digital AgeBuilding the TeamAgile Team Iteration and PI ExecutionTeam Backlog ManagementTeam Iteration EventsBuilding the Agile Release TrainRelease Trains Day-to-DayART Backlog ManagementEvents for the TrainPI EventsEnterprise StrategyBuilding Your PortfolioEstablishing Lean BudgetsPortfolio Backlog ManagementMeasuring ProgressLeadership AlignmentEmbracing Agility and Nurturing Transformation Publisher : Packt Publishing (28 July 2023) Language : English Paperback : 332 pages
ISBN-10 : 1839210451 ISBN-13 : 978-1839210457 Item Weight : 580 g Dimensions : 23.5 x 19.1 x 1.76 cm Country of Origin : India [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
Master DevOps: Your Complete Guide and Roadmap | DevOps Online Training

Introduction to DevOps
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, the need for streamlined and efficient software development practices has never been greater. Enter DevOps—a culture, philosophy, and set of practices that bring development (Dev) and operations (Ops) together to improve collaboration, integration, and automation throughout the software development lifecycle. DevOps is not just a buzzword; it's a transformative approach that enables organizations to deliver high-quality software faster and more reliably. If you're looking to build a career in this field, DevOps Online Training is your gateway to mastering the skills required to excel in this domain.
What is DevOps?
DevOps is a combination of practices, tools, and cultural philosophies designed to increase an organization's ability to deliver applications and services at high velocity. By breaking down the traditional silos between development and operations teams, DevOps fosters a culture of collaboration, where both teams work together throughout the entire software development lifecycle. This collaboration leads to faster development, more frequent deployment of updates, and higher overall software quality.
At its core, DevOps emphasizes automation, continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), and monitoring. The goal is to minimize manual intervention, reduce errors, and improve the efficiency of software development and deployment. Through DevOps Online Training, you can learn how to implement these practices in real-world scenarios, making you an invaluable asset to any tech organization.
How DevOps Works
DevOps is built on a set of principles and practices that enable organizations to build, test, and deploy software rapidly and efficiently. Here's how DevOps works in practice:
1. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Continuous Integration (CI) is the practice of merging code changes frequently, often multiple times a day, into a shared repository. Automated testing is then conducted to identify and resolve issues early in the development process. Continuous Deployment (CD) takes this a step further by automatically deploying code changes to production after passing the CI pipeline. Together, CI/CD reduces the time between writing code and delivering it to customers, ensuring that software updates are released frequently and reliably.
2. Automation
Automation is a critical component of DevOps. From building and testing code to deploying and monitoring applications, automation helps streamline the entire software development lifecycle. By automating repetitive tasks, teams can focus on more strategic activities, such as optimizing code and improving system performance. Automation tools like Jenkins, Ansible, and Puppet are commonly used in DevOps to create efficient, repeatable processes.
3. Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is the practice of managing and provisioning computing infrastructure through machine-readable scripts rather than manual processes. This approach allows teams to automate the setup and configuration of environments, ensuring consistency across development, testing, and production stages. Tools like Terraform and AWS CloudFormation are popular choices for implementing IaC.
4. Monitoring and Logging
Effective monitoring and logging are essential to maintaining the health and performance of applications in a DevOps environment. By continuously monitoring systems and capturing logs, teams can identify and resolve issues before they impact end-users. Tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and ELK Stack are widely used for monitoring and logging in DevOps.
5. Collaboration and Communication
DevOps is as much about culture as it is about technology. A key aspect of DevOps is fostering a culture of collaboration and communication between development, operations, and other stakeholders. This collaboration ensures that everyone is aligned with the project's goals and that issues are addressed quickly. Tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Jira facilitate communication and collaboration in a DevOps environment.
6. Security in DevOps (DevSecOps)
As security becomes increasingly important in software development, DevOps practices have evolved to include security as a core component. DevSecOps integrates security into every stage of the software development lifecycle, ensuring that security vulnerabilities are identified and addressed early in the process. By adopting DevSecOps practices, organizations can build more secure applications without compromising on speed and agility.
The Roadmap to Becoming a DevOps Engineer
Becoming a DevOps engineer requires a combination of technical skills, practical experience, and a deep understanding of DevOps principles. Here's a step-by-step roadmap to guide you on your journey:
1. Understand the Basics of DevOps
Before diving into specific tools and technologies, it's important to understand the fundamental principles of DevOps. Learn about the core concepts of CI/CD, automation, IaC, and monitoring. DevOps Online Training can provide you with a solid foundation in these areas, helping you grasp the essential elements of DevOps.
2. Gain Proficiency in Programming and Scripting
A strong foundation in programming and scripting is essential for a DevOps engineer. Start by learning a programming language like Python, Ruby, or Go, as well as scripting languages like Bash or PowerShell. These skills will enable you to automate tasks, write custom scripts, and work with various DevOps tools.
3. Master Version Control Systems
Version control systems (VCS) like Git are critical to DevOps practices. Learn how to use Git for version control, branching, and merging code. Understand how to collaborate with other developers using GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket. Version control is a fundamental skill that every DevOps engineer must possess.
4. Get Hands-On with CI/CD Tools
CI/CD is at the heart of DevOps, so gaining hands-on experience with CI/CD tools is crucial. Learn how to set up and configure Jenkins, CircleCI, or Travis CI to automate the build, test, and deployment processes. DevOps Online Training often includes practical labs and exercises that allow you to practice using these tools in real-world scenarios.
5. Learn About Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
IaC is a key practice in DevOps, enabling teams to manage and provision infrastructure programmatically. Familiarize yourself with IaC tools like Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, and Ansible. Learn how to write scripts that automate the creation and configuration of infrastructure, ensuring consistency across environments.
6. Develop Cloud Computing Skills
Cloud computing is an integral part of DevOps, as it provides the scalability and flexibility needed for modern software development. Gain proficiency in cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Learn how to deploy applications to the cloud, manage cloud resources, and work with cloud-based DevOps tools.
7. Enhance Your Automation Skills
Automation is a cornerstone of DevOps, so it's essential to master automation tools and techniques. Learn how to automate tasks using tools like Jenkins, Puppet, and Chef. Understand how to create automated workflows that integrate with other DevOps tools and processes.
8. Learn About Monitoring and Logging
Effective monitoring and logging are crucial for maintaining the health of applications in a DevOps environment. Familiarize yourself with monitoring tools like Prometheus and Grafana, as well as logging tools like the ELK Stack. Learn how to set up monitoring dashboards, create alerts, and analyze logs to identify and resolve issues.
9. Embrace DevSecOps Practices
Security is a critical aspect of DevOps, and understanding DevSecOps practices is essential for a successful career in this field. Learn how to integrate security into the CI/CD pipeline, conduct security testing, and implement security best practices throughout the software development lifecycle.
10. Gain Practical Experience
Theory alone is not enough to become a proficient DevOps engineer. Hands-on experience is crucial. Work on real-world projects, contribute to open-source DevOps projects, or participate in internships. Practical experience will help you apply the skills you've learned and build a portfolio that showcases your expertise.
11. Obtain DevOps Certifications
Certifications can validate your skills and make you stand out in the job market. Consider obtaining certifications like AWS Certified DevOps Engineer, Google Cloud DevOps Engineer, or Microsoft Certified: Azure DevOps Engineer Expert. These certifications demonstrate your proficiency in DevOps practices and tools.
12. Stay Updated with Industry Trends
The field of DevOps is constantly evolving, with new tools and practices emerging regularly. Stay updated with industry trends by reading blogs, attending conferences, and participating in online communities. DevOps Online Training programs often include updates on the latest trends and tools in the industry.
13. Build a Strong Professional Network
Networking is important in any career, and DevOps is no exception. Join DevOps communities, attend meetups, and connect with other professionals in the field. Building a strong network can lead to job opportunities, collaborations, and valuable insights.
14. Prepare for DevOps Interviews
As you near the end of your learning journey, it's time to prepare for DevOps interviews. Practice common DevOps interview questions, participate in mock interviews, and review your projects and experiences. DevOps Online Training programs often include interview preparation sessions to help you succeed in landing your first DevOps job.
Conclusion
DevOps is a powerful approach that has revolutionized the way software is developed, tested, and deployed. By fostering collaboration between development and operations teams and leveraging automation, CI/CD, and cloud computing, DevOps enables organizations to deliver high-quality software at a rapid pace. Whether you're just starting your career or looking to transition into the field, DevOps Online Training can provide you with the skills and knowledge needed to succeed as a DevOps engineer.
By following the roadmap outlined in this article, you can develop the technical expertise, practical experience, and industry knowledge required to excel in DevOps. Remember to stay updated with the latest trends, build a strong network, and continuously improve your skills.
#devops#devopsonlinetraining#devops engineer#DevOps Roadmap#web development#development#software#Continuous Integration#Continuous Deployment#Cloud Computing#Automation#Software Development#IT Training#cicd#it training institute#it training courses#it training classes
0 notes
Text
Cron Job là gì? Cách thiết lập và quản lý Cron Job

Trong thế giới quản lý hệ thống và tự động hóa, cron job là một công cụ không thể thiếu, việc hiểu rõ cron job là gì cũng như cách thức hoạt động của nó sẽ giúp bạn tiết kiệm thời gian và tối ưu hóa công việc hàng ngày. Hãy cùng khám phá cách hoạt động của cron job và cách sử dụng nó trong quản lý hệ thống của bạn!
1. Cron Job là gì?
Cron job là một khái niệm quan trọng trong quản lý hệ thống và lập lịch tự động hóa các tác vụ trên hệ điều hành Linux. Đây là một công cụ mạnh mẽ cho phép người dùng lên lịch để chạy các lệnh hoặc script vào những thời điểm cụ thể hoặc định kỳ mà không cần sự can thiệp thủ công.
Cron job đặc biệt hữu ích trong các kịch bản như tự động sao lưu dữ liệu, gửi email thông báo, kiểm tra hệ thống hoặc chạy các báo cáo định kỳ. Đối với các quản trị viên hệ thống, lập trình viên và DevOps, hiểu rõ về cron job là một kỹ năng cần thiết.
2. Cấu trúc của Cron Job
Cron job được định nghĩa trong một file gọi là crontab (viết tắt của "cron table"). Mỗi dòng trong crontab đại diện cho một cron job và có cấu trúc như sau:
* * * * * command_to_be_executed
Cấu trúc này được chia thành 5 trường đại diện cho phút, giờ, ngày trong tháng, tháng và ngày trong tuần. Mỗi trường có thể nhận các giá trị cụ thể hoặc ký tự đại diện để biểu thị sự lặp lại.
Phút (* * * * *) - Từ 0 đến 59
Giờ (* * * * *) - Từ 0 đến 23
Ngày trong tháng (* * * * *) - Từ 1 đến 31
Tháng (* * * * *) - Từ 1 đến 12
Ngày trong tuần (* * * * *) - Từ 0 đến 6 (với 0 là Chủ Nhật)
Ví dụ, cron job sau sẽ chạy một script vào lúc 3 giờ 15 phút mỗi ngày:
15 3 * * * /path/to/script.sh
3. Thiết lập và quản lý Cron Job
��ầu tiên bạn cần có một máy chủ chạy hệ điều hành Linux để bắt đầu thiết lập. Bạn có thể trải nghiệm dịch vụ máy chủ ảo VPS Linux miễn phí của chúng tôi tại đây.
3.1. Truy cập và chỉnh sửa crontab
Để tạo hoặc chỉnh sửa cron job, bạn sử dụng lệnh crontab:
Mở crontab để chỉnh sửa:
crontab -e
Xem các cron job hiện tại:
crontab -l
Xóa tất cả các cron job:
crontab -r
3.2. Ví dụ về Cron Job
Chạy một script mỗi ngày vào lúc 0h00:
0 0 * * * /path/to/backup.sh
Chạy một lệnh mỗi thứ Hai vào lúc 9 giờ sáng:
0 9 * * 1 /path/to/weekly_report.sh
Chạy một script mỗi 15 phút:
*/15 * * * * /path/to/check_status.sh
3.3. Các ký tự đặc biệt trong cron job
Ký tự *: Biểu thị mọi giá trị có thể, chẳng hạn như * * * * * nghĩa là mọi phút, mọi giờ, mọi ngày.
Ký tự ,: Sử dụng để tách các giá trị, ví dụ 0 12,18 * * * chạy vào 12 giờ và 18 giờ.
Ký tự -: Dùng để biểu thị một khoảng giá trị, ví dụ 0 9-17 * * 1-5 chạy mỗi giờ từ 9 giờ đến 17 giờ từ thứ Hai đến thứ Sáu.
Ký tự /: Biểu thị khoảng thời gian, ví dụ */10 * * * * nghĩa là chạy mỗi 10 phút.
4. Ưu điểm và hạn chế của Cron Job là gì?
Khi sử dụng cron job sẽ mang lại những lợi ích vượt trội, tuy nhiên vẫn còn những hạn chế nhất định.
Ưu điểm
Tự động hóa mạnh mẽ: Cron job giúp tự động hóa nhiều tác vụ lặp đi lặp lại mà không cần can thiệp thủ công.
Linh hoạt: Với khả năng tùy chỉnh thời gian và ngày chạy, cron job có thể đáp ứng hầu hết các yêu cầu về lập lịch.
Hiệu quả: Giảm thiểu sai sót và tối ưu hóa thời gian làm việc của con người, đặc biệt trong quản lý hệ thống.
Hạn chế
Cấu hình phức tạp: Cấu trúc cú pháp của cron có thể gây khó khăn cho người mới bắt đầu.
Thiếu khả năng quản lý trực quan: Không có giao diện đồ họa mặc định, việc quản lý cron job hoàn toàn thông qua dòng lệnh.
Giới hạn trong việc xử lý lỗi: Nếu một cron job gặp lỗi khi chạy, hệ thống không có cơ chế tự động xử lý hoặc cảnh báo trừ khi được cấu hình riêng.
5. Câu hỏi thường gặp về Cron Job
Cron Job có thể chạy nếu hệ thống bị tắt không?
Trả lời: Không, Cron Job chỉ chạy khi hệ thống đang hoạt động. Nếu hệ thống bị tắt tại thời điểm lịch trình, Cron Job sẽ không chạy và sẽ không tự động chạy khi hệ thống được bật lại.
Làm thế nào để xóa một cron job?
Trả lời: Để xóa một Cron Job, bạn có thể mở tệp crontab bằng lệnh crontab -e, sau đó xóa dòng tương ứng với công việc mà bạn muốn loại bỏ.
Tôi có thể chạy một cron job mỗi giây không?
Trả lời: Không, Cron không hỗ trợ việc chạy các tác vụ mỗi giây. Thời gian nhỏ nhất mà Cron có thể lên lịch là mỗi phút.
Cron job có thể chạy một lệnh phức tạp không?
Trả lời: Cron Job có thể chạy các lệnh phức tạp, nhưng nếu lệnh cần xử lý nhiều bước hoặc yêu cầu quản lý trạng thái, bạn nên viết một kịch bản (script) và chạy kịch bản đó thông qua Cron Job.
Tổng kết
Cron job là một công cụ quan trọng trong việc tự động hóa các tác vụ định kỳ trên hệ thống Linux. Hiểu rõ cron job là gì, cách cấu hình và quản lý cron job sẽ giúp bạn tiết kiệm thời gian, giảm thiểu lỗi và tối ưu hóa hoạt động của hệ thống. Mặc dù có một số hạn chế, nhưng với sự hỗ trợ của các công cụ bổ sung, cron job vẫn là một phần không thể thiếu trong quản lý hệ thống hiện đại.
Hy vọng bài viết này đã cung cấp cho bạn những thông tin cơ bản và kỹ thuật cần thiết để bắt đầu với cron job. Hãy thử áp dụng và tối ưu hóa công việc của bạn với công cụ mạnh mẽ này!
Nguồn: https://suncloud.vn/cron-job-la-gi
0 notes
Text
Donne e tecnologia: cresce il lavoro femminile nei settori hi-tech ma i tassi restano bassi

Il mondo della tecnologia sta assistendo a una profonda trasformazione, che si manifesta in diversi cambiamenti sia dal lato dei consumatori che da quello delle aziende. Uno degli aspetti più cruciali di questo mutamento è, per esempio, la crescente presenza femminile nei settori hi-tech. McKinsey & Company ha recentemente evidenziato questo trend, specificando però che se l'Europa riuscisse a raddoppiare la percentuale di lavoratrici donne in campo tecnologico, portandola al 45% entro il 2027, potrebbe godere di un aumento del PIL fino a 600 miliardi di euro. Un valore che sottolinea un potenziale economico inesplorato rappresentato proprio dalle donne nell'industria tecnologica. Donne e lavori ad alta tecnologia: la situazione attuale Rispetto al passato, la presenza di donne nelle aziende hi-tech è aumentata nel giro di pochi anni, evidenziando una tendenza nuova e di assoluto interesse per l'economia globale. In realtà, però, a questo trend positivo corrispondono valori non ancora particolarmente elevati, con una presenza femminile nei settori STEM (Scienza, Tecnologia, Ingegneria e Matematica) tuttora considerata critica. Attualmente, infatti, solo il 38% dei laureati in materie STEM è donna e questo dato si riflette direttamente nella composizione della forza lavoro tecnologica, dove solo il 22% delle posizioni è occupato per l'appunto da professioniste. Nel caso di ruoli più specifici, come DevOps e Cloud, poi la percentuale si riduce all'8%, mostrando come vi sia ancora un netto predominio maschile in questi ambiti. Va inoltre osservato che nelle posizioni di maggior rilievo, le figure femminili rappresentano una vera e propria eccezione: stando a dati EIGE del 2018, infatti, a livello dirigenziale nelle ITC europee era possibile trovare solo un 25% di donne, percentuale che scende al 17% se si guarda agli amministratori delegati. Corsi STEM: una bassa partecipazione femminile Ma perché, nonostante i segnali positivi, le donne sono ancora sottorappresentate nei settori tecnologici in Europa? McKinsey identifica alcuni momenti cruciali del percorso formativo e professionale in cui le donne perdono terreno: durante la transizione dall'istruzione primaria e secondaria all'università, per esempio, la percentuale di donne nei corsi STEM scende infatti di 18 punti percentuali. Inoltre, durante il passaggio dall'università al mondo del lavoro, si verifica una diminuzione ulteriore del 15%. Guardando all'uso delle nuove tecnologie nel mondo lavorativo, però, si nota come alcuni ambiti siano molto più gettonati tra le donne, che di conseguenza sono più presenti in alcuni settori specifici, come il social networking (50%) e l'e-commerce (46%). Molto più basso, invece, il loro coinvolgimento in ruoli tecnologici di rilievo, come sviluppatori e ingegneri dei dati, nei quali la percentuale si ferma al 22%. Considerando l'aumento della richiesta di queste professioni all'interno delle aziende, potrebbe tuttavia essere molto interessante per le donne che si avvicinano al mondo del lavoro guardare a tali posizioni con maggiore interesse. Lo sviluppo di servizi digitali come quelli di intrattenimento, sempre più diffusi a livello globale, ha portato infatti a un rapido incremento nelle assunzioni di sviluppatori e altri professionisti capaci di progettare e dare vita a siti web e applicazioni mobili che permettono, per esempio, di giocare in rete agli svaghi tipici dei casino e di approfondire strategie e regole del poker e degli altri passatempi, una tipologia di lavoro che oggi risulta a netta prevalenza maschile ma che può rappresentare un importante sbocco anche per le ragazze che decidono di studiare queste materie. Proiezioni e obiettivi per il 2027 Guardando al futuro, McKinsey prevede che, al ritmo attuale, la percentuale di donne in professioni tech in Europa raggiungerà il 21% entro il 2027, ma suggerisce al tempo stesso di intervenire affinché la tendenza possa essere migliorata, al fine di sfruttare appieno il potenziale femminile nel settore tecnologico. Secondo la nota società di consulenza, bisognerebbe in particolare agire su alcuni punti fondamentali, che tocchino sia il lavoro in senso stretto che le fasi precedenti all'ingresso sul mercato professionale. In primis occorrerebbe, infatti, supportare le donne nella loro affermazione lavorativa in ambito hi-tech, fornendo strumenti di sostegno adeguati, inoltre andrebbe migliorata la flessibilità all'interno delle aziende, un tema che riguarda non soltanto il mercato della tecnologia ma un po' l'intera organizzazione economica, dal momento che le donne risultano ancora oggi maggiormente frenate rispetto agli uomini dalle responsabilità di caregiving, maternità in primis. In quest'ottica, la soluzione più efficace potrebbe essere quella di garantire il ricorso al lavoro a distanza, e orari più flessibili. In ultima analisi, non bisogna sottovalutare la bassa partecipazione femminile alle materie STEM, quindi adottare misure per rafforzare questa presenza già in ambito accademico. In sostanza, le proposte di McKinsey offrono una roadmap per spingere ancora più in alto la presenza femminile nel settore della tecnologia e puntare al raggiungimento della parità di genere nei prossimi anni. Sbloccare il potenziale delle donne nei ruoli tech non solo contribuirà all'equità di genere, ma porterà anche benefici economici considerevoli per l'Europa. Rendere il settore tecnologico più accessibile e inclusivo per le donne è un passo essenziale verso un futuro in cui il talento femminile svolge un ruolo centrale nella definizione delle tecnologie del domani. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
2020, retrospective in quattro punti
È stato un anno strano e difficile, segnato dalla piaga del COVID-19, ma personalmente lo ricorderò come un anno pieno di opportunità. Il tempo libero regalato dal confinamento mi ha permesso di dedicarmi a progetti che (forse) non avrei mai realizzato altrimenti e immergermi senza distrazioni in nuove esperienze.

Io, sviluppatore
Ho cambiato due lavori quest'anno ma finalmente sono riuscito a trovarne uno che mi soddisfa. Proprio grazie alla mia esperienza lavorativa attuale, sento di non essere più semplicemente una persona che scrive codice, ma uno sviluppatore vero e proprio. Ho ancora molto da imparare, ma è innegabile, guardando indietro, il livello di esperienza che ho acquisito nell'ultimo anno.
Queste nuove conoscenze, unite alla grande quantità di tempo libero e la volontà di portare avanti un mio progetto, mi ha portato a migliorare la mia abilità in Python e imparare Typescript e React in modo da creare una mia app. È stato un lungo viaggio pieno di ostacoli e frustrazione, ma anche di grandissima soddisfazione una volta superate le difficoltà. Creare un'app è dannatamente difficile e sono ancora invischiato nei tortuosi labirinti del DevOps, ma una versione dell'app rozza ma comunque completa e funzionante è già in attesa di essere esaminata da Google, per poter così lanciare un test interno.
C'è ancora tanto lavoro da fare, ma sono orgoglioso di aver portato a termine il mio primo progetto di ampio respiro. E per il nuovo anno, oltre a finire i lavori per l'app, ho già in programma di intraprendere i primi passi per realizzare il mio sogno ormai da anni, ovvero creare un videogioco.
Videogiochi: mistero e avventura
Proprio quando iniziava il confinamento e intanto avevo una settimana completamente libera nel passaggio da un lavoro all'altro, ho deciso di provare quella visual novel di cui tanto parlavano, Danganronpa. Dire che mi ha rapito e ammaliato è riduttivo, mi sono immerso a capofitto nel primo capitolo (Danganronpa: Trigger Happy Havoc) finendolo in una settimana scarsa dedicandoci ben 41 ore di gioco! Anche gli altri capitoli li ho divorati con immenso piacere, complice la storia di mistero coinvolgente e i personaggi curati nei minimi dettagli, per arrivare all'apice della serie nel capitolo finale (Danganronpa V3: Killing Harmony). Ma ho già speso molte parole sulla serie in un altro post.
Al momento sto finendo Control, che mi ha assorbito nella sua affascinante ambientazione paranormale. Mi sono addentrato anche nella zona di confine tra videogioco e film giocando al sorprendente Erica e alle avventure grafiche di Quantic Dreams, Heavy Rain e Beyond: Two Souls. Altre piacevoli sorprese sono state il surreale puzzle game Superliminal e il sovversivo The Last of Us.
Ci sono anche state delusioni, in particolare la serie Nonary Games di cui avevo sentito parlare benissimo ma ho trovato pessima a livello tecnico e non particolarmente intrigante a livello di storia. Sotto le aspettative è stato Persona 4 Golden, che ho giocato con piacere ma mi ha emozionato meno del 5 e in generale meno di quanto pensassi.
Ad ogni modo, quest'anno mi ha dato molto tempo e opportunità per espandere i miei orizzonti in ambito videoludico!
Serie TV: lacrime di gioia e tristezza
Anche se i videogiochi hanno rubato la maggior parte del mio tempo libero, non sono mancate le serie TV (che guardo soprattutto durante i pasti).
Ho iniziato con il botto grazie a Zoey’s Extraordinary Playlist, che mi ha fatto piangere ed emozionare come forse nessun'altra serie ha fatto prima. La premessa è molto originale e piacevole e la serie riesce a farti affezionare a tutti i personaggi.
Altre serie molto belle sono state il documentario sui videogiochi High Score, la serie fuori dagli schemi sui supereroi The Boys e la graziosa e commovenete sitcom Parks and Recreation.
La grande delusione è stata Lovecraft Country, con una partenza molto buona che però finisce per scadere nel banale e nel politically correct.
Libri: riflessioni profonde
La rivelazione di quest'anno è stato Jordan B. Peterson, intellettuale con idee in controtendenza (seppur conservative) e con grandi capacità oratorie. Si può non essere d'accordo con lui, ma non si può non rispettare la sua abilità dialettica. Il suo libro più famoso, 12 Rules for Life, mi ha preso moltissimo. È talmente ricco di saggezza che non può che arricchire chiunque, qualunque sia il suo cammino di vita, e probabilmente necessita più di una lettura per essere compreso appieno.
Tornando invece alla narrativa, mi è piaciuta tantissimo la serie di Dirk Gently (Dirk Gently’s Holistic Detective Agency e The Long Dark Tea-Time of the Soul - probabilmente il miglior titolo mai creato), che ho trovato molto simpatica e arguta. Ho provato anche a rileggere The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy ma l'ho abbandonato, non mi ha preso come una volta.
E per finire ho concluso l’anno continuando la lettura di The Circle, che si sta rivelando molto promettente!
Qui la lista completa di esperienze di quest'anno.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Devops Engineers In Demand
DEVOPS ENGINEERS IN DEMAND
The stiff competition between the various IT organizations has raised the emergence of creating an equilibrium between the agility and responsiveness of the organization and also a stability in the infrastructure. To achieve these ends , various devops practices can be used to make this task accomplishable. In order to reduce the failure rates , companies have adopted devops practices and are in the hunt for hiring people with such expertise.
The devops salary report gathered from puppet labs is an evidence of the scope that this skill possesses. The ratio of the salary earned (range of salary being 1L dollars/year) of devops engineers to IT professionals is 58 to 47.This clearly indicates that more number of devops engineers are paid higher when compared to IT Professionals.
Organizations are adopting devops practices because they want better quality, faster delivery and collaboration. They believe that people with this skill set can make an IT firm stronger and give them an upper hand against their competitors. The future of IT lies in inculcating devops within an IT framework and employing more and more Devops engineers in order to enhance profit maximization and sustainability of an organization .People with this specialization are required in almost every sector, be it financial services ,insurance, telecommunication, retail manufacturing ,transportation or healthcare. The diligence underlying the principles and practices of devops is what makes it the most sought for skill in this era and majority of the IT organizations presume that the balance in the organization can be restored by the devops engineers because of their ability to focus on intricate problems and solve them and also bring the whole organization under one umbrella. Therefore this is a golden career path for anyone aspiring a tremendous and positive career graph with more crests and less troughs.
Contact Us- 9686502645
No:44/1, 3rd Floor, Above Punjabi Food Corner & My Choice J.P. Nagar 7th Phase, (Opp to Brigade Millennium) Bangalore - 560078.
Website - http://www.blueoceanlearning.com/course/devops-training-bangalore/
0 notes
Text
Tính Năng Chính Của Visual Studio 2015
Cộng tác hiệu quả hơn Kiểm soát mã nguồn toàn diện Tạo các ứng dụng hướng dữ liệu Phát triển phần mềm đa nền tảng Gỡ lỗi và phân tích mã tĩnh LINQ, thực hiện truy vấn, thiết lập hoạt động Cung cấp một loạt các dịch vụ và các lớp Ứng dụng Scalable Workflow Dựa trên các chuẩn giao thức tin nhắn Sửa lỗi nâng cao, kiểm tra một cách tự động và thủ công DevOps với các triển khai tự động và giám sát liên tục Các công cụ và dịch vụ cho các dự án Hỗ trợ Visual Basic C #, F #, C ++, Python, Node.js và HTML / JavaScript
Xem thêm: https://gocchiaseitt.com/visual-studio-2015/

0 notes
Text
Tweeted
El DevOps tras las tiendas MNG o MANGO. Utilizan AWS y Terraform para aprovisionar infraestructura e incluso hacen pruebas unitarias para estos scripts (los de Terraform) https://bit.ly/3PV5tGB
— AlexanderAndrade.Net (@AlexAndradeNet) Jun 2, 2022
0 notes
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] Written by experienced Agile coaches, SPCTs, and a SAFe(R) Fellow, this guide is packed with real-world examples, use cases, and anecdotes, and offers valuable guidance to help you avoid common pitfalls and successfully implement SAFe(R)Key FeaturesUnderstand how to tailor SAFe(R) practices to meet your organization's needsAvoid common mistakes encountered while adopting SAFe(R) at team, ART, and portfolio levelsDiscover practical tips and best practices to plan teams, ARTs, events, and Lean Portfolio ManagementBook DescriptionThe Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe(R)) is widely recognized as an eff ective methodology for implementing Agile practices at the Enterprise level. However, the complexity of SAFe(R) can make it challenging for Teams and organizations to determine which practices can be safely adapted to their unique needs. Although SAFe(R) is a framework rather than a set of rules, promoting adaptation, it's crucial to understand why SAFe(R) practices are designed the way they are along with the consequences of modifying them.The SAFe(R) Coaches Handbook is a comprehensive resource that goes beyond a how-to guide, providing a deep understanding of SAFe(R) principles and practices. The chapters are designed in a way to teach you how to successfully implement SAFe(R) in your organization and eff ectively manage the Team's Backlog while avoiding common pitfalls. You'll discover optimal ways to create SAFe(R) Teams and run successful Events. You'll also learn how to plan Agile Release Trains (ARTs), manage the ART Backlog, conduct PI Planning, and grasp the importance of Value Stream Identifi cation in driving value delivery.By the end of this book, you'll be armed with practical tips and advice to help you successfully customize the Scaled Agile Framework to your Enterprise's needs while preserving the aspects that make it work successfully.What you will learnDiscover how to set up Agile Teams to attain maximum effectivenessAvoid common mistakes organizations make with SAFe(R)Find out how to set up the Agile Release TrainDiscover common mistakes enterprises make that affect the success of the ARTUnderstand the importance of Value Streams and learn how to work with them successfullyStart using the best ways to measure the progress of Teams and ARTs at an Enterprise levelRecognize the impact of successful SAFe(R) adoption on Enterprise strategy and organizational structureWho this book is forIf you're a SAFe(R) Practice Consultant (SPCT), Scrum Master/Team Coach, or Release Train Engineer tasked with implementing SAFe(R) within an organization, you'll find this book indispensable. It offers valuable insights into aspects of SAFe(R) and helps ensure success in delivery and execution with practical uses you can adopt. Product owners and product managers will also benefit from this book by gaining a deeper understanding of how to function effectively within a SAFe(R) environment. A basic understanding of SAFe(R), agile, and DevOps is recommended to get the most out of this book.Table of ContentsThriving the Digital AgeBuilding the TeamAgile Team Iteration and PI ExecutionTeam Backlog ManagementTeam Iteration EventsBuilding the Agile Release TrainRelease Trains Day-to-DayART Backlog ManagementEvents for the TrainPI EventsEnterprise StrategyBuilding Your PortfolioEstablishing Lean BudgetsPortfolio Backlog ManagementMeasuring ProgressLeadership AlignmentEmbracing Agility and Nurturing Transformation Publisher : Packt Publishing (28 July 2023) Language : English Paperback : 332 pages
ISBN-10 : 1839210451 ISBN-13 : 978-1839210457 Item Weight : 580 g Dimensions : 23.5 x 19.1 x 1.76 cm Country of Origin : India [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
Devops va Giai phap Bao mat dot pha voi GKE Autopilot
Các tổ chức đang hiện đại hóa doanh nghiệp với cloud đang tìm kiếm các giải pháp để đơn giản và tự động hóa container orchestration với độ bảo mật, sẵn sàng và khả năng mở rộng cao. dịch vụ GKE Autopilot sẽ sẵn sàng sớm trong năm nay, đây là một cải tiến mới trong phương thức quản lý Kubernetes rằng chúng ta không cần quản lý cụm cluster nữa đồng thời mang lại bảo mật mạnh mẽ và tự động tối ưu tài nguyên sử dụng. (nếu chưa hiểu rõ về GKE Autopilot? kiểm tra tài liệu Autopilot breakout session at Google Cloud Next ‘21, tài liệu này sẽ tóm tắt các tính năng mới của Kubernetes platform có thể làm được)

Đọc thêm tại đây: https://gcloudvn.com/kienthuc/devops-va-giai-phap-bao-mat-dot-pha-voi-gke-autopilot/
Businesss Name: Gimasys Co .ltd
Office: 147-149 Võ Văn Tần, P. 6, Q.3, TP. Hồ Chí Minh 72407
Hotline: 0974 417 099
0 notes
Text
Quel pinguino amato che pensa di avere il mondo

5 vittorie e 5 sconfitte dei primi trent'anni di Linux. Il sistema operativo open source ha cambiato per sempre internet e l'industria del software ma non è riuscito a vincere alcune delle sue sfide più importanti. Trent’anni fa, il 25 agosto del 1991, un giovane studente finlandese mandò una storica email a un gruppo di sviluppatori hobbysti intitolata “Cosa vi piacerebbe vedere di più in Minix?”. Il giovane studente era Linus Torvalds e quell’email è considerata l’atto di nascita di Linux, il sistema operativo open source che da piccolo hobby di un gruppo di giovanissimi hacker all’alba di internet è diventata l’architrave della rete e uno dei tre progetti open source più di successo al mondo oltre che uno dei più grandi. Infatti, il kernel di Linux, cioè il motore del sistema operativo (e la parte comune a tutte le varie distribuzioni gratuite disponibili) è diventato un progetto da poco più di 27.8 milioni di righe di codice, a cui contribuisce un’armata di 14mila sviluppatori sparsi in tutto il mondo.
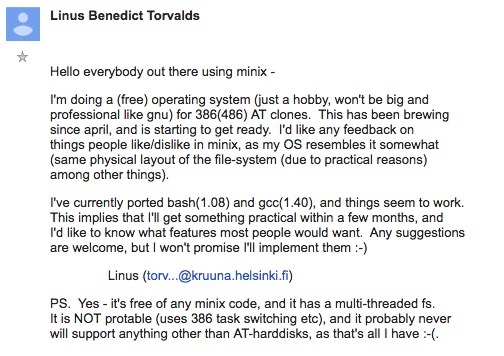
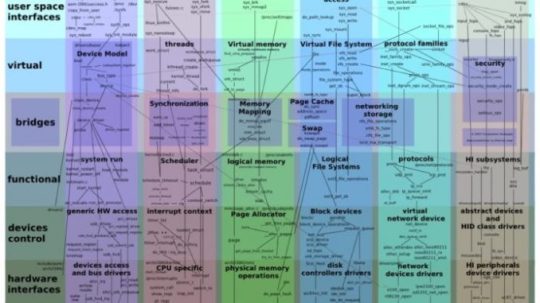
La storica email di Linus Torvalds per presentare la sua versione di Minix. L’idea di chiamare il sistema operativo Linux non è stata sua ma di alcuni volontari. La scelta di Torvalds di sviluppare in maniera free, open e collaborativa il kernel di Linux ha consentito a un altro grande progetto open source, il sistema operativo Gnu, pensato da Richard Stallman ma che non riusciva a decollare, di trovare il suo motore e diventare un rimpiazzo gratuito per Unix, all’epoca “il” sistema operativo (a pagamento) usato sui server e nei centri di calcolo. Trent’anni dopo, però, cos’è successo? Si fa presto a dire che Linux ha vinto: in realtà ha anche perso alcune grandi battaglie. La sua valutazione di mercato era di 3,89 miliardi di dollari nel 2019 (secondo Fortune), il suo valore cresce del 19,2% all’anno (Cagr) e nel 2027 raggiungerò il traguardo dei 15,64 miliardi di dollari. Al tempo stesso, la sua quota di mercato nel settore desktop e portatili è attorno al 2,38%, il doppio di Chrome Os (che non sommiamo perché pur essendo basato su Linux ha uno strato proprietario di servizi di Google) ma molto sotto i due principali sistemi operativi “closed source”: Windows (73%)e macOs (15,4%). Insomma, dopo trent’anni Linux ha sicuramente vinto ai punti ma non per ko. Vediamo perché.
La mappa del kernel di Linux (fonte Wikipedia) Le 5 grandi vittorie 1 – Il sistema operativo più diffuso oltre al pc Linux ha sdoganato l’idea che possa esistere un sistema operativo open. Nel mondo del software questa è stata la seconda grande rivoluzione dopo quella di Microsoft degli anni Settanta (cioè che il software ha più valore dell’hardware). L’importanza di essere aperti fin nei dettagli (e non fornire solo delle Apie delle specifiche di sviluppo per le terze parti) è la ricetta segreta del successo di Linux e la cosa che gli ha permesso di essere estremamente efficace per la costruzione di strumenti sofisticatissimi. Non a caso Linux è la piattaforma standard per una marea di apparecchi e strumenti digitali oltre ai pc e ai server: dal router di casa all’auto della Tesla, dalla webcam alle fotocamere digitali. Il mondo dell’embedded è quasi totalmente Linux e questo è possibile perché tutti hanno potuto lavorare al suo sviluppo e verificare che funzioni. Oggi i grandi sviluppano linguaggi di programmazione (Go, Swift), framework, middleware open source per continuare a sfruttare il valore di essere open. L’apertura completa è la versione “fatta bene” della cosiddetta Api Economy, che invece si basa sul monopolio dei servizi esposti dai fornitori. 2 – Linux è Gnu L’idea del free software o del software open arriva prima di Linux: Richard Stallman è stato il suo ideologo ma non è riuscito a trasformarla in una proposizione vincente sul mercato. C’è riuscito Torvalds con Linux, che ha ridato vita al progetto Gnu di Stallman diventandone il motore e insieme ad Apache è il vero grande diffusore dell’idea del free software (ma non chiedetelo a Stallman perché lui vi dirà di no). Linux ha sdoganato l’idea che i software open non sono solo degli hobby ma anche degli strumenti scientifici e industriali sofisticati. 3 – Internet ama Linux L’infrastruttura di internet è storicamente basata su server Unix e sistemi di routing dei dati che hanno utilizzato Unix o altri sistemi operativi proprietari. Tuttavia, è con l’arrivo di Linux che si è sviluppato il “vero” paradigma di internet: senza Linux milioni di startup non avrebbero potuto entrare in affari, da piccolissimi provider che hanno portato per la prima volta la connettività nelle case di milioni di persone negli anni Novanta ai primi servizi e aziende online.

Linux (logo da Wikipedia) Per esempio, il motore di ricerca di Google esisterebbe solo come tesi di dottorato se non fosse stato possibile riciclare migliaia e migliaia di vecchi pc con Linux per trasformarli nella prima, grande “server farm”. Se Microsoft o Apple volessero sviluppare da zero Linux dovrebbero investire almeno 14,7 miliardi di dollari in stipendi di programmatori per riuscirci. 4 – Un mondo standard Trent’anni fa, quando è nato Linux, c’erano decine di versioni di Unix incompatibili tra loro. È una fase dello sviluppo della tecnologia che viene chiamato “guerra degli Unix” e che ha segnato profondamente quella storia che non si studia sui banchi di scuola o all’università, e tuttavia è critica per lo sviluppo di interi settori industriali oggi dipendenti dal digitale. Linux ha introdotto una varietà di possibili utilizzi con un unico sistema operativo sempre aperto e compatibile, a cui tutti hanno potuto contribuire. Qualcosa di più di uno standard aperto. 5 – Il futuro del cloud L’idea di “macchine virtuali” è molto vecchia, è nata negli anni Sessanta in Ibm. E quella di internet come sistema operativo è dei geni di Sun Microsystems (“The network is the computer“). Ma se guardiamo a tutte le tecnologie del cloud che negli ultimi cinque anni hanno radicalmente trasformato internet, cioè i container e i microservizi, l’unico punto in comune è che sono tutte basate su Linux. La piattaforma creata da Torvalds è quella che permette anche la trasformazione nel modo con il quale si costruisce il software online e offline: DevOps, Ci/Cd (le pratiche combinate di integrazione continua e distribuzione continua del software) e tutti i flussi di lavoro e le tecnologie che oggi permettono il funzionamento di servizi come Google Cloud e Netflix si basano su innovazioni rese possibili, in ultima analisi, da Linux. Le 5 sconfitte di Linux Le sconfitte di Linux sono politiche, non tecnologiche. Ma non per questo bruciano meno. E in alcuni casi ci vuole un attimo per capire perché il sistema operativo nato per essere il campione del mondo open source sia in realtà diventato lo strato gratuito di alcune delle più grandi piattaforme proprietarie 1 – Pochissimo mercato desktop Nonostante lo sforzo dei volontari e la passione europea (soprattutto in Germania) per l’uso dei sistemi operativi e dei software open source per la pubblica amministrazione, in realtà Linux non ha mai sfondato nel mondo dei personal computer, cioè dei sistemi operativi per la produttività personale. La sua quota di mercato è relativamente molto piccola ed è poco diffuso. Ed è un vero peccato, perché ci sono distribuzioni mirate che sono più facili da usare di Windows, ambienti con desktop manager e gestori del sistema strutturati per essere come, se non meglio, di quelli di macOS. Però alla fine chi compra un pc lo fa con Windows già caricato a bordo, oppure prende un Mac. Che, oggi, con il nuovo chip proprietario Apple Silicon, è diventato un po’ meno compatibile con Linux di prima (ma non temete: la community ci sta lavorando). In conclusione: la promessa di avere Linux nei personal computer della metà degli utenti del pianeta non si è realizzata. Peccato. 2 – Non è più veramente “open” Linux ha perso anche una battaglia ideologica molto importante: il sistema operativo “open” e “free” per definizione, alfiere di un sistema in cui tutti possono vedere il codice sorgente del software e modificarlo a piacimento, è diventato la base di una serie di piattaforme chiuse. E questo non è un bene. La licenza di distribuzione e d’uso di Linux non è stata pensata per impedire che, per esempio, Google lo usi sui suoi server e sui telefoni Android, Amazon sul suo cloud, Ibm sui suoi server. Però gli utilizzatori di Linux in questo caso lo sfruttano per costruire piattaforme proprietarie. Il lavoro gratuito di migliaia e migliaia di sviluppatori volontari è stato usato per arricchire i proprietari del codice e Linux è diventato (anche) una commodity che fa il gioco dei big tech, senza ricevere niente in cambio. 3- L’influenza (negativa) dei big del tech Chi sono i più grandi contributori del codice del kernel di Linux e delle varie componenti open source? La leggenda vuole che siano studenti e giovani programmatori volontari di tutto il pianeta che, mossi dalla loro etica, si dedicano gratuitamente al grande progetto “open”. Non è più così. La realtà invece è che grandi aziende come Intel, Ibm, Samsung, Oracle, Google, Amazon e da qualche tempo anche Microsoft (ma non dimentichiamoci di Hp e decine di altri) pagano i loro dipendenti per lavorare in orario di ufficio a Linux e completare una serie di componenti del kernel e di altre parti del sistema operativo open. Diventando anche responsabili di determinate aree o di nuovi progetti. Lo scopo? È riassunto nel vecchio detto: “Se non puoi combatterli, unisciti a loro“.

A 21 anni, Torvalds era un vero geek e come tale si è comportato: ha creato il suo sistema operativo, lo ha messo in Rete e ha chiesto ai suoi simili di partecipare al suo sviluppo. Parliamo di Linux, ovviamente (foto: AFP) Intel, Ibm, Microsoft e tutti gli altri vogliono che Linux vada nella direzione tecnologica che conviene a loro, che supporti le loro tecnologie e hardware, che insomma sia un sistema fatto a loro immagine e somiglianza. Così, i Linux Day (e gli Install Day), i vecchi appassionati che girano a fare proseliti e insegnare ai “newbie” come installare Ubuntu o la Debian e le altre attività della community di volontari (compresi gli adesivi gratuiti che gli studenti appiccicano sul coperchio del loro pc) sono diventati una specie di facciata folkloristica. 4 – Spaghetti code L’espressione, chiariamolo subito, è provocatoria e palesemente esagerata: “spaghetti code” era il termine usato negli anni Settanta e successivi per indicare programmi il cui codice sorgente era confuso e confusionario, soprattutto per l’uso del goto al posto dei costrutti della programmazione strutturato. Lo sviluppo di Linux gestito ancora da Linus Torvalds è fantastico, ma non così il mondo delle distribuzioni e soprattutto la documentazione per gli utenti finali. Là regna il caos. Accanto ad alcune distribuzioni “maggiori” che curano particolarmente la documentazione, c’è un vero e proprio spezzatino in cui trovare la tecnologia o l’informazione che serve diventa un incubo. Senza contare che le distribuzioni e i software open collegati vanno a mode: per un periodo hanno centinaia di sviluppatori e poi vengono abbandonate, lasciando gli utenti finali nei pasticci. 5 – Il kernel sbagliato Quando Linus Torvalds ha deciso di creare Linux, era all’università e l’ha fatto in polemica con un famoso professore di sistemi operativi, Andrew S. Tanenbaum, una specie di superstar del settore nonché il creatore del sistema operativo “didattico” Minix, che era una alternativa accademica nettamente migliore di Unix. Al centro della scelta per l’architettura di Linux fatta da Torvalds c’è stata quella di sviluppare un kernel di tipo monolitico (anche se poi modularizzato). Invece, Tanenbaum aveva e ha dimostrato che l’approccio opposto, cioè con un micro-kernel, è superiore e avrebbe reso Linux molto più efficace e più adatto sia ai processori multicore (che nel 1991 non erano ancora una opzione) e in prospettiva per i servizi distribuiti nel cloud. Linux ha vinto una battaglia che sarebbe stato meglio aver perso. Read the full article
#apple#chrome#cloudcomputing#Debian#elettronica#ElettronicaOpenSource#google#ibm#informatica#intel#Internet#kernel#LinusTorvalds#Linux#macos#microsoft#Minix#opensource#telecomunicazioni#Ubuntu#windows
0 notes
Text
Cron Job là gì? Cách thiết lập và quản lý Cron Job

Trong thế giới quản lý hệ thống và tự động hóa, cron job là một công cụ không thể thiếu, việc hiểu rõ cron job là gì cũng như cách thức hoạt động của nó sẽ giúp bạn tiết kiệm thời gian và tối ưu hóa công việc hàng ngày. Hãy cùng khám phá cách hoạt động của cron job và cách sử dụng nó trong quản lý hệ thống của bạn!
1. Cron Job là gì?
Cron job là một khái niệm quan trọng trong quản lý hệ thống và lập lịch tự động hóa các tác vụ trên hệ điều hành Linux. Đây là một công cụ mạnh mẽ cho phép người dùng lên lịch để chạy các lệnh hoặc script vào những thời điểm cụ thể hoặc định kỳ mà không cần sự can thiệp thủ công.
Cron job đặc biệt hữu ích trong các kịch bản như tự động sao lưu dữ liệu, gửi email thông báo, kiểm tra hệ thống hoặc chạy các báo cáo định kỳ. Đối với các quản trị viên hệ thống, lập trình viên và DevOps, hiểu rõ về cron job là một kỹ năng cần thiết.
2. Cấu trúc của Cron Job
Cron job được định nghĩa trong một file gọi là crontab (viết tắt của "cron table"). Mỗi dòng trong crontab đại diện cho một cron job và có cấu trúc như sau:
* * * * * command_to_be_executed
Cấu trúc này được chia thành 5 trường đại diện cho phút, giờ, ngày trong tháng, tháng và ngày trong tuần. Mỗi trường có thể nhận các giá trị cụ thể hoặc ký tự đại diện để biểu thị sự lặp lại.
Phút (* * * * *) - Từ 0 đến 59
Giờ (* * * * *) - Từ 0 đến 23
Ngày trong tháng (* * * * *) - Từ 1 đến 31
Tháng (* * * * *) - Từ 1 đến 12
Ngày trong tuần (* * * * *) - Từ 0 đến 6 (với 0 là Chủ Nhật)
Ví dụ, cron job sau sẽ chạy một script vào lúc 3 giờ 15 phút mỗi ngày:
15 3 * * * /path/to/script.sh
3. Thiết lập và quản lý Cron Job
Đầu tiên bạn cần có một máy chủ chạy hệ điều hành Linux để bắt đầu thiết lập. Bạn có thể trải nghiệm dịch vụ máy chủ ảo VPS Linux miễn phí của chúng tôi tại đây.
3.1. Truy cập và chỉnh sửa crontab
Để tạo hoặc chỉnh sửa cron job, bạn sử dụng lệnh crontab:
Mở crontab để chỉnh sửa:
crontab -e
Xem các cron job hiện tại:
crontab -l
Xóa tất cả các cron job:
crontab -r
3.2. Ví dụ về Cron Job
Chạy một script mỗi ngày vào lúc 0h00:
0 0 * * * /path/to/backup.sh
Chạy một lệnh mỗi thứ Hai vào lúc 9 giờ sáng:
0 9 * * 1 /path/to/weekly_report.sh
Chạy một script mỗi 15 phút:
*/15 * * * * /path/to/check_status.sh
3.3. Các ký tự đặc biệt trong cron job
Ký tự *: Biểu thị mọi giá trị có thể, chẳng hạn như * * * * * nghĩa là mọi phút, mọi giờ, mọi ngày.
Ký tự ,: Sử dụng để tách các giá trị, ví dụ 0 12,18 * * * chạy vào 12 giờ và 18 giờ.
Ký tự -: Dùng để biểu thị một khoảng giá trị, ví dụ 0 9-17 * * 1-5 chạy mỗi giờ từ 9 giờ đến 17 giờ từ thứ Hai đến thứ Sáu.
Ký tự /: Biểu thị khoảng thời gian, ví dụ */10 * * * * nghĩa là chạy mỗi 10 phút.
4. Ưu điểm và hạn chế của Cron Job là gì?
Khi sử dụng cron job sẽ mang lại những lợi ích vượt trội, tuy nhiên vẫn còn những hạn chế nhất định.
Ưu điểm
Tự động hóa mạnh mẽ: Cron job giúp tự động hóa nhiều tác vụ lặp đi lặp lại mà không cần can thiệp thủ công.
Linh hoạt: Với khả năng tùy chỉnh thời gian và ngày chạy, cron job có thể đáp ứng hầu hết các yêu cầu về lập lịch.
Hiệu quả: Giảm thiểu sai sót và tối ưu hóa thời gian làm việc của con người, đặc biệt trong quản lý hệ thống.
Hạn chế
Cấu hình phức tạp: Cấu trúc cú pháp của cron có thể gây khó khăn cho người mới bắt đầu.
Thiếu khả năng quản lý trực quan: Không có giao diện đồ họa mặc định, việc quản lý cron job hoàn toàn thông qua dòng lệnh.
Giới hạn trong việc xử lý lỗi: Nếu một cron job gặp lỗi khi chạy, hệ thống không có cơ chế tự động xử lý hoặc cảnh báo trừ khi được cấu hình riêng.
5. Câu hỏi thường gặp về Cron Job
Cron Job có thể chạy nếu hệ thống bị tắt không?
Trả lời: Không, Cron Job chỉ chạy khi hệ thống đang hoạt động. Nếu hệ thống bị tắt tại thời điểm lịch trình, Cron Job sẽ không chạy và sẽ không tự động chạy khi hệ thống được bật lại.
Làm thế nào để xóa một cron job?
Trả lời: Để xóa một Cron Job, bạn có thể mở tệp crontab bằng lệnh crontab -e, sau đó xóa dòng tương ứng với công việc mà bạn muốn loại bỏ.
Tôi có thể chạy một cron job mỗi giây không?
Trả lời: Không, Cron không hỗ trợ việc chạy các tác vụ mỗi giây. Thời gian nhỏ nhất mà Cron có thể lên lịch là mỗi phút.
Cron job có thể chạy một lệnh phức tạp không?
Trả lời: Cron Job có thể chạy các lệnh phức tạp, nhưng nếu lệnh cần xử lý nhiều bước hoặc yêu cầu quản lý trạng thái, bạn nên viết một kịch bản (script) và chạy kịch bản đó thông qua Cron Job.
Tổng kết
Cron job là một công cụ quan trọng trong việc tự động hóa các tác vụ định kỳ trên hệ thống Linux. Hiểu rõ cron job là gì, cách cấu hình và quản lý cron job sẽ giúp bạn tiết kiệm thời gian, giảm thiểu lỗi và tối ưu hóa hoạt động của hệ thống. Mặc dù có một số hạn chế, nhưng với sự hỗ trợ của các công cụ bổ sung, cron job vẫn là một phần không thể thiếu trong quản lý hệ thống hiện đại.
Hy vọng bài viết này đã cung cấp cho bạn những thông tin cơ bản và kỹ thuật cần thiết để bắt đầu với cron job. Hãy thử áp dụng và tối ưu hóa công việc của bạn với công cụ mạnh mẽ này!
Nguồn: https://suncloud.vn/cron-job-la-gi
0 notes