#food_supply
Photo
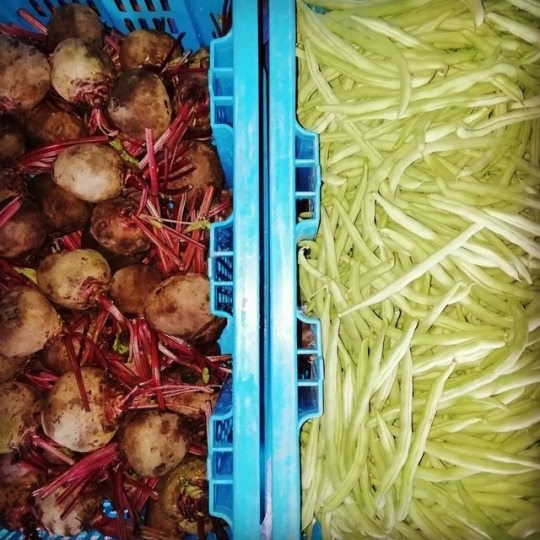

Beetroot & Beans Ready to Delivery. Fresh vegetables for your business. #jayavegi #hill_country #fresh #vegetable #welimada #Srilanka #Beetroot #Beans #vegetable_supply #vegetable_crates #vegetable_for_business #freshness #new #nutrition #keto #healthy #healthyfood #food_supply #vegan #veganfood #red #green #tasty #Jayavegii (at Kaduwela, Sri Lanka) https://www.instagram.com/p/B0kIWOfgNle/?igshid=1x6oquiexr5gz
#jayavegi#hill_country#fresh#vegetable#welimada#srilanka#beetroot#beans#vegetable_supply#vegetable_crates#vegetable_for_business#freshness#new#nutrition#keto#healthy#healthyfood#food_supply#vegan#veganfood#red#green#tasty#jayavegii
0 notes
Text
Let’s Get Scientific: Ecosystems & Biodiversity
Environmental studies cannot be discussed without mention of science. Natural sciences and the scientists that study them are fundamental to understanding how our environment works, how we come to understand the way it works, and how we are affecting it.
In chapters 2 and 3 of Living in the Environment, Miller covers the basics of natural sciences like chemistry, biology, and physics, as they apply to environmental studies. As a chemistry major, most of the information was review, but in order to have a comprehensive understanding of environmental studies the information is critical. Scientists study the natural world through field and laboratory research. Field research allows first-hand observation of forests, oceans, and mountains, examining the extremely complex ecosystems that exist and collecting data that aids humans in interacting with said ecosystems. Laboratory research involves the development of systems that mimic natural ones, and are helpful because they allow for better control of variables.
Some scientific principles, like the law of conservation of energy, help describe why some human behaviors are so harmful to the environment. Energy is divided into two categories: renewable and nonrenewable. Renewable sources of energy, like solar power, wind, moving water, wind, and geothermal energy are replenishable through natural processes. Nonrenewable sources of energy are not replenishable through natural processes on a human time scale, these include oil, coal, natural gas, and nuclear energy. Commercial energy is the 1% of energy that does not come from the sun. The burning of fossil fuels makes up 90% of it.
There are four main systems of earth’s life support system: the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, and biosphere. The atmosphere contains ozone that filters out 95% of UV radiation, and other gasses that help keep the earth warm by trapping heat from the sun. Oceans contain 97% of earth’s water and an enormous amount of biodiversity. The geosphere contains fossil fuels and minerals that are used by humans and other species regularly. Finally, the biosphere is where we live, along with all other life forms.
An important part of the way the world operates is how organisms interact with each other. Organisms are either producers (who make their own nutrients from the environment), consumers (who feed on other organisms for nutrients), or decomposers (who transform waste into nutrients). Ecosystems are sustained through the one-way energy flow (solar energy) and nutrient cycling that happens through these three groups of organisms. Two key indicators are GPP (gross primary productivity) and NPP (net primary productivity). GPP is the rate that energy is converted from solar to chemical by producers and stored in compounds, and NPP is the rate that producers use photosynthesis to produce chemical energy minus the rate they use the stored energy in aerobic respiration.
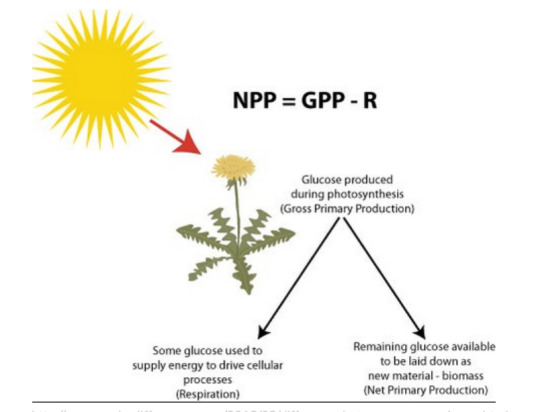
Figure 1. Indicators of productivity. (“How does gross primary productivity differ from net primary productivity?” Socratic Q&A Biology. November 3, 2015. Accessed February 2, 2020.https://socratic.org/questions/how-does-gross-primary-productivity-differ-from-net-primary-productivity)
There are numerous other natural cycles that sustain life on earth, including the water cycle, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and phosphorous cycle. I find cycles to be best understood through diagrams, so below are some helpful graphics.
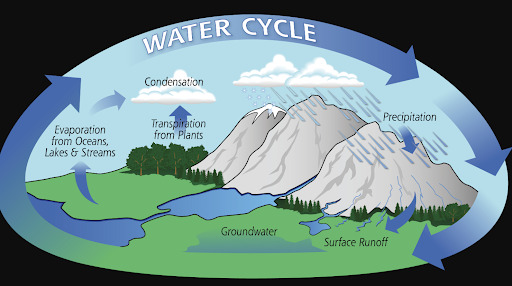
Figure 2. The Water Cycle. (“The Water Cycle.” NASA. Accessed February 2, 2020. https://pmm.nasa.gov/education/water-cycle)

Figure 3. The Carbon Cycle. (“The Carbon Cycle.” UCAR Center for Science Education. Accessed February 2, 2020. https://scied.ucar.edu/carbon-cycle)

Figure 4. The Nitrogen Cycle. (“Nitrogen Cycle.” studyACS. December 21, 2017. Accessed February 2, 2020. https://www.studyacs.com/blog-nitrogen-cycle-37.aspx)
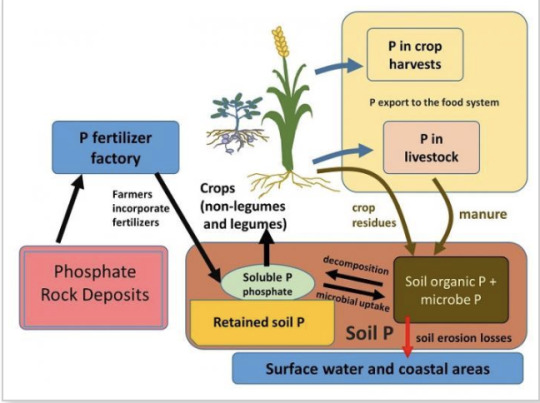
Figure 5. The Phosphorus Cycle. (“The Phosphorus Cycle and Human Management of Soils.” InTeGrate. January 11, 2018. Accessed February 2, 2020. https://serc.carleton.edu/integrate/teaching_materials/food_supply/student_materials/1176)
Chapter four examines the importance of biodiversity, “the variety of life on earth” [1]. There are four components to biodiversity, species diversity, genetic diversity, ecosystem diversity, and functional diversity. Species diversity deals not only with the number of different species in an ecosystem (richness) but also their comparative abundance (evenness). Genetic diversity is the variety of different genes in a species. Ecosystem diversity refers to the presence of many different biological communities, such as deserts, oceans, mountains, and forests. Functional diversity is the variety of natural processes within ecosystems.
Within an ecosystem, species play different roles, termed their “ecological niche,” which can be either broad (for generalists) or narrow (for specialists). Species are classified as native, nonnative, indicator, or keystone to an ecosystem. While definitions of native and nonnative are rather straightforward, indicator species warn of changes in environmental conditions, and keystone species are those that are fundamental to the ecosystem--without them, there is a great risk of collapse.
Earth’s biodiversity is ultimately determined by the balance between speciation (formation of new species) and extinction which are entirely dependent on our changing environmental conditions.
Chapter five discusses how species interact, including predator-prey relationships, parasitism, mutualism, and commensalism, and how populations work, examining births, deaths, immigration, and emigration. A big idea communicated in the chapter is that “no population can escape natural limiting factors and grow indefinitely” [2], reminding us that humans are just as vulnerable as other species, especially considering the projected outcomes of our environmentally degrading behaviors.
Chapter seven studies how climate affects biodiversity. Climate, unlike weather, is the “general pattern of atmospheric conditions in a given area” [3] over a long period of time. Differences in climate have a great impact on the types and locations of deserts, grasslands, forests, and mountains. After going through all the world’s major terrestrial ecosystems, the book reveals that humans are degrading about 60% of them.

Figure 6. The major impacts that humans have on terrestrial ecosystems (Miller, G. Tyler. Living in the Environment. National Geographic Learning/Cengage Learning, 2018.)
Chapter eight dives into the subject of aquatic biodiversity, specifically why aquatic ecosystems are so important. Marine ecosystems provide a number of ecosystem and economic services, such as production of oxygen, water purification, nutrient cycling, food, energy, recreation, and employment. One very timely mention the book makes is the growing threat of ocean acidification. In my sophomore year of high school, I remember learning the chemical equation that represents this process. It was one of the first times I had seen an environmental issue represented so physically and plainly to my understanding. When carbon dioxide reacts with ocean water, carbonic acid is formed which is detrimental because it decreases the amount of carbonate ions available for the formation of coral reefs and the shells and skeletons of organisms.
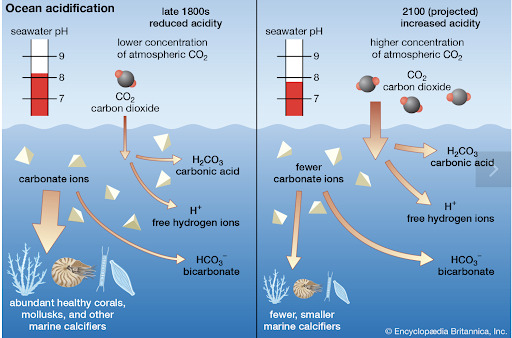
Figure 7. The process of ocean acidification. (Rafferty, John P. “Ocean Acidification.” Encyclopedia Britannica. January 30, 2020. Accessed February 2, 2020. https://www.britannica.com/science/ocean-acidification)
Other major threats to aquatic biodiversity are coastal development, runoff of pollutants, overfishing, and invasive species. Freshwater systems are also incredibly important, providing many ecosystem and economic services similar to marine systems, but one major new service is the provision of drinking water, which is a huge issue, especially politically.
In order to sustain aquatic biodiversity, I believe we must control emissions of carbon dioxide to prevent further damage to coral reefs, reduce fishing subsidies, and pass more laws protecting aquatic environments, unlike the Trump administration’s action that I referenced last week that did the opposite. While scientists lead the way, citizens and lawmakers must follow closely behind.
Word Count: 1040
Question: Is it accurate to say that many people who don’t believe in climate change are simply under-educated in the natural sciences, or does the problem run deeper than that?
[1] Miller, G. Tyler. Living in the Environment. 19th ed. (Boston: Cengage Learning, 2018) 79.
[2] Miller, Living in the Environment, 114.
[3] Miller, Living in the Environment, 145.
0 notes
Text
Day Four
March, 28th, 2019
Today my lack of nutrition has really begun to take a toll on me, I’ve been experiencing some really painful headaches throughout the day and its really been causing me to lack focus at school, however, I was lucky enough to receive some free treats from some kind classmates at school which definitely boosted my energy and mood.
For breakfast this morning I made myself some porridge with cut up banana slices. I quite enjoyed this meal and it kept me feeling full, and somewhat more nutritious.

In preparation for a long day I had a few mid morning snacks which are not pictured. I snacked on a hard boiled egg and one of my banana oat cookies quickly in between classes.
For lunch I had the same old rice and chickpeas again. This meal is starting to get old but it’s still very easy to make and I enjoy the taste of it.

Today during one of my evening courses, my class and I had a wonderful surprise of fresh baked goodies from one of our generous classmates. We also got to enjoy some fresh homemade chai tea. This was a wonderful treat and the flavor of everything immediately boosted my mood! It’s shocking how much food effects your moods and the way you feel throughout the day.
For supper this evening I made two scrambled eggs and had a couple pieces of toast. Although I feel that I’ve had a lot of eggs and bread during this challenge, I am still not sick of it.

Looking back on my meals today I am again very grateful to have access to the foods that I do. Having incredibly convenient access to several different supermarkets , even some with different price ranges, is a very key factor for the nutritious diet I am able to maintain. I am also very fortunate to be able to have access to produce from farms, such as the eggs I’ve been enjoying over the past few days. In more remote areas of the country, and even the world, some individuals may not have the same luxury.
Socioeconomic factors, as well as access to transportation services play a big role in food access. Individuals from low income families in rural locations may not have access to supermarkets and well supplied gardens and farms like I do, This may drastically limit their food consumption choices to whatever they physically can find in their areas. The food they have access to may not be nutritious, but it may be all they have.
I am very eager to be completing this challenge in just three days! I feel as though this experience will definitely make me more appreciative and conscious of how lucky I am to have such a variety of food sources available for myself and my family. This is something I will never take for granted.
See you all on day five!
Food Access: https://serc.carleton.edu/integrate/teaching_materials/food_supply/student_materials/1063
Dimensions of Food Security: https://wocatpedia.net/wiki/Definition_and_Dimensions_of_Food_Security
0 notes
Text
Food Supplies Factories Should Get More Operational Relaxation: Parle
#Food_Supplies Factories Should Get More Operational Relaxation: #Parle
Considering a better food and consumables supply in the COVID-19 lockdown period, India’s leading FMCGmajor, Parle suggested that restrictions on a number of workers in factories located in green and amber zones, specially for food products companies. The company mentioned, that there is s acute need for relaxation for operational efficiency of manufacturing factories as meeting demand will…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Photo

Delevered Fresh Vegetables with safety transportation #vegetable #transport #food_deliver #food #fresh #hill_country #healthy #new #welimada #bogahakumbura #farm #cultivation #24hours_fresh #jayavegi #food_supply #freshness #vegetable_crates (at Colombo, Sri Lanka) https://www.instagram.com/p/Bui3xbsASoW/?utm_source=ig_tumblr_share&igshid=1x8j2apk4xjw6
#vegetable#transport#food_deliver#food#fresh#hill_country#healthy#new#welimada#bogahakumbura#farm#cultivation#24hours_fresh#jayavegi#food_supply#freshness#vegetable_crates
0 notes
Photo

#seed #potatoes #potato_production #agriculture #agri #Srilanka #welimada #bogahakumbura #soil #rich #cultivation #roots #fresh #freshness #organic #upcountry #market #potato #seedlings #feeling #grow #food #product #food_deliver #food_supply #vegetable_supply #vegetable (at Jayavegi) https://www.instagram.com/p/Bybjh41gDU9/?igshid=10rcyp8y4z9dx
#seed#potatoes#potato_production#agriculture#agri#srilanka#welimada#bogahakumbura#soil#rich#cultivation#roots#fresh#freshness#organic#upcountry#market#potato#seedlings#feeling#grow#food#product#food_deliver#food_supply#vegetable_supply#vegetable
0 notes
Text
United States To Procure Processed Food Supplies Worth USD 3 Billion
#United_States To Procure Processed #Food_Supplies Worth USD 3 Billion
The US will purchase $3 billion worth of dairy, meat and produce from farmers and ranchers starting early next week, President Donald Trump announced.
“The USA will be purchasing, from our farmers, ranchers & speciality crop growers, $3 billion worth of dairy, meat & produce for food lines & kitchens,” US President Donald Trump tweeted.
The President noted that the government purchase was part of…
View On WordPress
0 notes