#here are some commonly used software development methodologies:
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How Fast Can You Get Certified with Online QA Classes?
In today’s digital-first job market, Quality Assurance (QA) professionals play a crucial role in ensuring software products meet required standards before reaching users. As software testing becomes more integrated with agile and DevOps workflows, the demand for QA testers with up-to-date skills and certifications has grown rapidly. For those looking to quickly transition into this high-demand career, Online QA classes present a flexible and fast-track option.
But just how quickly can you get certified by taking QA classes online? Let’s explore the factors that influence certification timelines, what to expect from a course, and how to strategically plan your path to a QA certification.
Understanding QA Certifications: What They Are and Why They Matter
Quality Assurance certifications validate your knowledge of testing methodologies, tools, frameworks, and best practices. They demonstrate to employers that you are competent in identifying bugs, writing test cases, using automation tools, and ensuring software reliability.
Commonly Pursued QA Certifications:
ISTQB (International Software Testing Qualifications Board) Foundation Level
Certified Software Tester (CSTE)
Certified Agile Tester (CAT)
Certified Software Quality Analyst (CSQA)
Automation Tools Certifications (e.g., Selenium WebDriver, JMeter)
These certifications range from beginner to advanced levels, each requiring a specific depth of training and preparation.
Factors That Affect How Fast You Can Get Certified
The speed at which you can get certified with QA training and placement depends on several key factors:
1. Your Current Skill Level
Beginner: If you’re starting from scratch with no technical background, expect to spend more time learning the fundamentals typically 10–14 weeks.
Intermediate/Advanced: If you already have some experience in IT or QA, you may fast-track your learning and complete a certification course in 4–8 weeks.
2. Course Type and Structure
Self-Paced Courses: These allow you to move quickly if you’re motivated. Fast learners can complete content in 4–6 weeks, while others may take 12–16 weeks.
Instructor-Led Courses: These are scheduled weekly (often 2–3 sessions per week) and usually last 8–12 weeks. They offer more guidance but less flexibility.
Bootcamp or Accelerated Programs: Some QA training programs offer intensive 3–6 week courses focused specifically on passing certification exams.
3. Hours You Dedicate Weekly
Full-Time (20–30 hrs/week): You can complete a full QA course and prep for certification in 4–6 weeks.
Part-Time (10–15 hrs/week): You’ll likely need 8–12 weeks to be certification-ready.
Minimal Time (5–7 hrs/week): Expect 3–4 months to complete your training and prepare thoroughly.
4. Certification Exam Requirements
Some certifications, such as ISTQB Foundation, require passing a timed multiple-choice test. Others may require hands-on experience or a project. Make sure your course aligns with these requirements and offers exam prep.
Sample Timeline: Getting QA Certified in 6–12 Weeks
Here’s what a typical fast-track certification journey might look like for someone taking online QA classes:
Week 1–2: Foundations of QA
Learn about the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) and Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC)
Understand the roles of manual and automated testing
Introduction to QA terminologies, defect lifecycle, types of testing
Week 3–4: Core Manual Testing Skills
Writing test plans, test cases, and bug reports
Functional, regression, smoke, and integration testing
Using defect tracking tools (e.g., JIRA, Bugzilla)
Week 5–6: Automation Basics (Optional but Advantageous)
Introduction to Selenium or other tools like Postman for API testing
Writing simple automation scripts
Executing test scripts and interpreting results
Week 7–8: Advanced Concepts and Certification Prep
Test management tools like TestRail or Zephyr
Agile methodologies and DevOps integration
Mock tests, exam strategies, practice scenarios
Week 9–10: Take the Certification Exam
Schedule and sit for the ISTQB Foundation or other relevant certification
Review results and obtain your certificate
Note: This timeline can be adjusted based on your pace, prior experience, and course format.
Advantages of Online QA Classes for Faster Certification
1. Flexible Scheduling
Online QA classes give you the freedom to study on your schedule. Whether you're a student, working professional, or stay-at-home parent, you can plan your study hours around your lifestyle.
2. Accelerated Learning Paths
Many platforms offer crash courses or intensive bootcamps focused on getting you certified fast, sometimes in just 30 days.
3. Hands-On Practice
Good online courses offer real-world assignments, access to test environments, and practical projects to make learning efficient and exam-oriented.
4. Recorded Sessions and Study Material
You can revisit complex topics through recorded lectures, study guides, and downloadable resources, allowing for quicker retention and better preparation.
5. Access to Expert Mentors
Instructor-led QA training often includes mentor support and Q&A sessions, which can clarify doubts quickly and help you prepare faster for exams.
Online QA Class Formats: Which One Is Right for You?
1. Self-Paced Learning
Best for motivated learners who want to move at their own speed.
Courses are often modular, include videos, readings, and quizzes.
Suitable for those balancing jobs or other commitments.
2. Live Instructor-Led Training
Scheduled sessions with live interaction.
Offers accountability, mentorship, and group discussions.
Ideal for beginners or those who benefit from structured environments.
3. Blended Learning
Combines the best of both self-paced and instructor-led learning.
Offers flexibility with real-time support when needed.
Great for learners who want control with some guidance.
Can You Get a Job Right After Certification?
Yes, especially if your QA classes include job placement support. Many training programs now come with:
Resume writing assistance
Mock interviews
Job search help
Live project experience
While certification adds value to your resume, employers also value hands-on experience, communication skills, and familiarity with modern tools. A good QA training program often includes mini-projects or access to real-time environments to make you job-ready immediately after certification.
Real-World Examples: How Fast People Got Certified
Case Study 1: College Graduate with No IT Background
Took an 8-week instructor-led QA course online
Spent 10–12 hours weekly studying
Cleared ISTQB Foundation in 9 weeks
Landed a junior QA tester job within 3 months
Case Study 2: Working Professional Transitioning from Support Role
Opted for a self-paced QA course
Dedicated 15 hours/week after work
Got certified in 5 weeks
Added test automation tools to resume and got promoted internally
Tips to Get Certified Faster with Online QA Classes
1. Choose a Course with Exam Focus
Pick a course that aligns directly with your target certification (like ISTQB). Make sure it includes exam simulations or practice tests.
2. Follow a Study Plan
Create a weekly study schedule with dedicated time slots for lectures, practice, and revision.
3. Practice with Tools
Install QA tools like Selenium, JIRA, or Postman on your local machine and practice daily. This will help solidify your understanding.
4. Join QA Forums or Study Groups
Online communities can answer your questions quickly and offer support. You’ll also find study partners to stay motivated.
5. Stay Consistent
Don’t let gaps stretch your timeline. Even 1 hour a day can keep you on track.
Certification Is Just the Start: What Comes Next?
Once you’re certified, you can start applying for QA roles like:
Manual QA Tester
Automation Tester (Junior)
QA Analyst
Test Engineer
As you gain experience, consider pursuing advanced certifications or learning new tools like Cypress, TestNG, or performance testing tools like LoadRunner.
Final Thoughts
So, how fast can you get certified with online QA classes? With the right strategy and consistent effort, it’s absolutely possible to become certified in as little as 4–8 weeks, even with no prior background. Online QA classes offer the flexibility, resources, and support needed to fit certification into your busy life.
Whether you're switching careers, boosting your current skills, or trying to land your first job in tech, a QA certification earned online can be your launchpad. The key is to choose a high-quality course, set a disciplined study schedule, and take advantage of all available resources.
Key Takeaways:
You can get QA certified in as little as 4–8 weeks, depending on your background and course format.
Online Quality assurance training and placement offer flexibility, hands-on training, and faster certification paths.
Look for courses that align directly with certifications like ISTQB or CSTE.
Stay consistent, practice regularly, and leverage job support services to maximize your success.
0 notes
Text
Dimensional Control Survey Procedure

Dimensional Control Survey Procedure: Ensuring Precision in Complex Projects
Introduction In the world of large-scale construction, engineering, and fabrication, precision is more than a goal—it's a necessity. Whether you’re working on an offshore platform, a manufacturing plant, or a shipbuilding project, even the smallest misalignment can result in costly delays, structural failures, or rework. That’s where the dimensional control survey procedure comes into play. This method is used to precisely measure and verify the spatial location of components and structures, ensuring everything fits together as designed. This article explores the core elements of the dimensional control survey procedure, its importance, the tools involved, and the step-by-step process that ensures projects meet the tightest tolerances for dimensional accuracy.
What Is a Dimensional Control Survey? A dimensional control survey is a systematic process used to capture accurate, three-dimensional measurements of physical spaces, structures, or components. These measurements are then compared against design models, drawings, or specifications to ensure alignment, fit-up, and compliance with required tolerances. Unlike traditional surveying methods used in land development or topography, the dimensional control survey procedure focuses on tight tolerances and highly detailed spatial relationships, often in environments where millimeter-level accuracy is required.
Why Dimensional Control Surveys Matter The primary objective of the dimensional control survey procedure is to detect and prevent deviations before they become costly problems. In industries such as oil and gas, shipbuilding, aerospace, and modular construction, parts are often fabricated in one location and assembled in another. If these components don’t align precisely, entire systems can fail to integrate properly. Here’s why dimensional control surveys are essential: • Cost Efficiency: Avoids rework, delays, and material waste by identifying misalignments early. • Improved Safety: Ensures components fit correctly, minimizing structural risks and potential hazards. • Streamlined Assembly: Verifies that parts fabricated off-site will assemble seamlessly onsite. • Quality Assurance: Provides documentation to support compliance with engineering standards and specifications.
Tools and Technology Used The dimensional control survey procedure has evolved significantly with the advancement of technology. Today’s surveyors use high-precision instruments that offer unmatched accuracy and repeatability. Some of the most commonly used tools include: • Total Stations: Robotic or manual instruments that measure angles and distances with high precision. • Laser Scanners: Capture millions of points in three dimensions, creating a dense point cloud of the surveyed environment. • Photogrammetry: Uses overlapping photographs to generate accurate 3D models. • 3D Modeling Software: Converts field measurements into digital representations to compare with design models. • GPS and GNSS: Occasionally used in outdoor or large-area applications, although not suitable for fine tolerance requirements. These tools allow surveyors to achieve incredibly detailed measurements that align closely with digital models and engineering drawings.
Step-by-Step Dimensional Control Survey Procedure
Project Planning and Scope Definition The first step in any dimensional control survey procedure is to define the project scope and objectives. This includes understanding what needs to be measured, the desired tolerances, access constraints, environmental conditions, and the format for deliverables. This planning phase also helps select the right equipment and methodology.
Establishing Control Points Surveyors begin by setting up a reference framework of control points. These are fixed locations that serve as a basis for all subsequent measurements. Accuracy at this stage is crucial, as errors in control point placement can compound throughout the project.
Data Acquisition Using total stations, laser scanners, or photogrammetry, surveyors collect data on the physical locations of key structural components or surfaces. The process varies based on the environment, such as whether the work is indoors, outdoors, at height, or in tight spaces.
Data Processing After collecting the raw data, surveyors process the measurements using specialized software. This step involves converting point clouds or coordinate data into usable 3D models, checking for anomalies, and aligning the data with the project's reference model.
Comparison with Design Models The processed data is then compared with the original design specifications or digital models. Surveyors identify any deviations beyond acceptable tolerances and generate detailed reports. These discrepancies can then be addressed proactively, either through rework or design adjustments.
Reporting and Documentation A comprehensive report is created, outlining the measurement results, any detected deviations, and recommended corrective actions. These reports serve as crucial documentation for quality assurance, regulatory compliance, and future reference.
Re-Survey and Verification (if needed) In some cases, follow-up surveys are conducted to confirm that corrective measures were successful or to monitor ongoing structural changes during a project's lifecycle.
Applications Across Industries The dimensional control survey procedure is used in a wide variety of sectors: • Oil and Gas: Ensures correct alignment of pipelines, platforms, and pressure vessels. • Shipbuilding: Verifies hull form, module alignment, and equipment placement. • Aerospace: Confirms precision in the manufacture and assembly of aircraft components. • Construction: Validates prefabricated parts and modular units before assembly. • Manufacturing: Assesses machine installation and tooling setup with extreme accuracy. No matter the industry, the principles remain the same: measure precisely, compare rigorously, and adjust proactively.
Benefits of Following a Robust Procedure A well-executed dimensional control survey procedure provides several tangible benefits: • Predictability: Reduces guesswork and enhances planning accuracy. • Efficiency: Minimizes delays from misaligned parts or poor fit-up. • Documentation: Creates a permanent record for audits and future inspections. • Flexibility: Allows for real-time adjustments before major errors occur. By sticking to a clear, structured procedure, organizations can maximize both productivity and confidence in their builds.
Conclusion The dimensional control survey procedure is an unsung hero in complex construction and fabrication projects. It acts as a critical checkpoint between design and execution, ensuring that structures are built as planned—with precision, efficiency, and safety in mind. Whether you're assembling offshore rigs, constructing modular buildings, or fabricating aerospace components, this procedure gives teams the confidence that every part will align exactly as it should. Precision isn't just about hitting numbers. It's about delivering peace of mind, reducing risk, and building better—from the ground up.
dimensional #balayage #hairstylist #olaplex #behindthechair #blonde #highlights #wella #hair #embroideryart #rayonthread #vintageneedlework #conroe #conroetx #thewoodlands #houston #texas #conroetexas
1 note
·
View note
Text
Project Management Methodologies: Navigating the Path to Success

Source: BGStock72
In today’s fast-paced business environment, effective project management is more critical than ever. As organizations strive to meet complex demands and deliver projects on time and within budget, understanding various project management methodologies has become essential. This article explores key methodologies, their applications, and how they can enhance project success.
Understanding Project Management Methodologies
Project management methodologies refer to the structured approaches and processes used to plan, execute, and manage projects. These methodologies provide a framework that guides teams in achieving their goals efficiently and effectively. By employing the right methodology, organizations can enhance collaboration, improve communication, and ensure that projects align with their strategic objectives.
The choice of a project management methodology often depends on various factors, including project complexity, team size, stakeholder expectations, and organizational culture.
Here, we will explore some of the most widely used project management methodologies.
1. Waterfall Methodology
The Waterfall methodology is one of the earliest project management approaches. It follows a linear, sequential process where each phase must be completed before the next begins. This methodology is ideal for projects with well-defined requirements and little expected change. Each phase—requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance—has specific deliverables and timelines.
While the Waterfall methodology offers clarity and structure, its rigidity can be a drawback for projects requiring flexibility and adaptability. It is most commonly used in construction and manufacturing projects, where changes are costly and disruptive.
2. Agile Methodology

Agile methodology is a popular approach in software development and other industries that require flexibility and rapid iteration. Unlike the Waterfall model, Agile embraces change and encourages teams to respond to evolving project requirements. Agile emphasizes collaboration, customer feedback, and continuous improvement.
In Agile, projects are divided into smaller, manageable increments called sprints. Each sprint typically lasts two to four weeks, during which teams work on specific features or components. At the end of each sprint, teams review their progress and adjust plans based on stakeholder feedback. This iterative process allows for greater adaptability and ensures that the final product aligns with customer needs.
3. Scrum Framework
Scrum is a subset of Agile methodology, focusing on delivering products in short cycles, called sprints. It provides a structured framework that defines roles, events, and artifacts to enhance collaboration and accountability. Key roles in Scrum include the Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Development Team.
Scrum promotes transparency and inspection, allowing teams to assess their progress regularly. Daily stand-up meetings, sprint planning, and sprint reviews facilitate communication and keep everyone aligned. This methodology is particularly effective in dynamic environments where requirements change frequently.
4. Kanban Methodology

Kanban is another Agile methodology that visualizes work to optimize efficiency and flow. It uses a board (physical or digital) to display tasks, helping teams manage and prioritize work. The Kanban board typically includes columns representing different stages of the project, such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.”
One of the key principles of Kanban is limiting work in progress (WIP) to prevent bottlenecks and improve focus. By visualizing tasks and establishing WIP limits, teams can enhance productivity and ensure smooth project execution. Kanban is particularly effective for teams managing ongoing processes and operations.
5. Lean Project Management
Lean project management focuses on maximizing value while minimizing waste. Originating from manufacturing principles, Lean emphasizes efficiency and continuous improvement. The methodology encourages teams to identify and eliminate non-value-added activities, streamline processes, and deliver quality products.
Lean project management promotes a culture of respect for people, collaboration, and empowerment. Teams are encouraged to contribute ideas for improvement, fostering an environment of innovation. This methodology is beneficial in industries where efficiency and cost reduction are critical.
Choosing the Right Methodology

Selecting the right project management methodology is crucial for project success. Factors to consider include:
Project Size and Complexity: Larger, more complex projects may benefit from structured methodologies like Waterfall, while smaller projects may thrive under Agile or Scrum.
Stakeholder Engagement: If customer feedback and collaboration are essential, Agile methodologies are ideal.
Organizational Culture: Consider the organization’s values and practices. A culture that promotes flexibility and innovation may align better with Agile, while a more traditional environment may prefer Waterfall.
Risk Management: Assess the level of risk associated with the project. Methodologies that allow for iterative development and frequent reassessment, such as Agile, may be more suitable for high-risk projects.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of each methodology, organizations can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs.
The Future of Project Management Methodologies
As businesses evolve and project demands change, the landscape of project management methodologies will continue to adapt. Emerging trends such as hybrid methodologies, which combine elements of Agile and traditional approaches, are gaining popularity. These hybrids allow organizations to tailor their project management practices to better suit their unique environments and challenges.
Additionally, advancements in technology and tools will further influence project management methodologies. Tools that support collaboration, automation, and real-time data analysis will become essential for teams aiming to optimize their project outcomes. Embracing these innovations will enable organizations to enhance efficiency, improve communication, and deliver successful projects consistently.
For more insights into project management methodologies and their applications, Enterprise Chronicles remains one of the best magazines to follow. It offers a wealth of knowledge and expertise that can help organizations navigate the complexities of project management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding various project management methodologies is essential for organizations seeking to enhance project success. Each methodology offers unique advantages and challenges, making it vital to choose the right one based on project needs, stakeholder expectations, and organizational culture. By leveraging the appropriate project management methodology, teams can improve collaboration, streamline processes, and ultimately deliver successful projects.
As you explore the world of project management methodologies, remember to stay informed and adaptable. Whether you lean toward Agile, Waterfall, or a hybrid approach, the key to success lies in understanding your project’s requirements and aligning your methodology accordingly. For ongoing insights and updates on project management and industry best practices, be sure to check out Enterprise Chronicles, one of the best magazines in the field.
By embracing the right project management methodologies, organizations can navigate the challenges of today’s business landscape and achieve their strategic goals.
Found this article valuable? Explore more insights in our Enterprise Chronicles.
#business#iso#riskmanagement#cybersecurity#safety#dataprotection#legal#training#security#finance#audit#hr#lgpd#law#datasecurity#tax#gst
0 notes
Text
Process Improvement: The Secret to Boosting Efficiency and Success
In today's fast-paced world, businesses are constantly looking for ways to enhance their operations, improve productivity, and stay ahead of the competition. Enter Process Improvement, a game-changing approach to refining workflows, reducing waste, and achieving better outcomes. Whether you're a startup, a small business, or a global corporation, this concept has something to offer.
If you're new to the term, don't worry! We're here to break it down into simple, relatable terms that will leave you confident about how it can help transform your work and life.
What is Process Improvement?
At its core, Process Improvement is the practice of analyzing and enhancing existing processes to make them more efficient, cost-effective, and reliable. It’s all about identifying pain points, bottlenecks, or unnecessary steps in a workflow and finding better ways to tackle them.
Think of it this way: Imagine you’re baking a cake. The first time you try, you follow the recipe but take a lot of time measuring ingredients, preheating the oven, and cleaning up afterward. Over time, you find ways to streamline the process—pre-measuring ingredients, using tools to speed up mixing, and cleaning as you go. That’s Process Improvement in action!
Why is Process Improvement Important?
Businesses and individuals alike benefit from refining their processes. Here are some key reasons why it matters:
1. Saves Time
Time is money, right? Improving processes means tasks take less time to complete, freeing you to focus on what truly matters.
2. Reduces Costs
By eliminating inefficiencies, you can save resources like materials, labor, and energy. For businesses, this means higher profits.
3. Boosts Productivity
Streamlined workflows enable teams to accomplish more in less time, leading to happier employees and better results.
4. Enhances Quality
Consistently improving processes ensures fewer errors, better products, and more satisfied customers.
5. Encourages Innovation
When you actively look for better ways of doing things, you create a culture of creativity and continuous improvement.
Popular Process Improvement Techniques
There are several tried-and-true methods to improve processes. Here are some of the most commonly used ones:
1. Lean Methodology
Lean focuses on eliminating waste in processes. Waste can be anything that doesn’t add value to the final product or service. For example, reducing overproduction, unnecessary transportation, or excess inventory can significantly cut costs.
2. Six Sigma
Six Sigma aims to minimize errors and variability in processes. It uses data-driven techniques and statistical analysis to achieve near-perfect quality levels.
3. Agile
Though primarily used in software development, Agile principles can be applied to almost any field. Agile emphasizes adaptability and breaking work into smaller, manageable tasks.
4. Kaizen
Kaizen, a Japanese term meaning "continuous improvement," focuses on making small, incremental changes over time that add up to significant results.
5. Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
This technique involves rethinking and redesigning processes from scratch to achieve dramatic improvements in performance.
Steps to Implement Process Improvement
If you’re ready to embrace Process Improvement, here’s a simple step-by-step guide to get started:
Step 1: Identify the Process
Choose a specific process that needs improvement. It could be anything from how customer inquiries are handled to how invoices are processed.
Step 2: Analyze the Current State
Take a close look at how things are currently done. Map out the workflow, gather data, and identify bottlenecks or areas of waste.
Step 3: Set Clear Goals
Define what you want to achieve. Are you looking to save time? Reduce errors? Cut costs? Having a clear goal will guide your efforts.
Step 4: Brainstorm Solutions
Involve your team in brainstorming sessions to come up with potential improvements. Encourage creative thinking and open discussions.
Step 5: Implement Changes
Test the proposed solutions on a small scale before rolling them out company-wide. Monitor the results and make adjustments as needed.
Step 6: Measure Success
Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate the success of your improvements. Celebrate wins and document lessons learned.
Examples of Process Improvement in Action
Here are some real-life scenarios where Process Improvement can make a huge difference:
1. Customer Service
A company noticed long wait times for customer support. By implementing a chatbot for common inquiries, they reduced response times and freed up agents to handle complex issues.
2. Inventory Management
A retail store struggled with overstocked shelves. By adopting a just-in-time inventory system, they minimized waste and improved cash flow.
3. Team Collaboration
A marketing team used multiple tools for project management, leading to confusion. Switching to an all-in-one platform streamlined communication and boosted productivity.
Common Challenges in Process Improvement
While the benefits are clear, Process Improvement isn’t without its challenges. Here’s how to tackle some common obstacles:
1. Resistance to Change
Not everyone loves change. Involve employees early in the process, communicate the benefits, and provide training to ease the transition.
2. Lack of Resources
Improving processes can require time and money upfront. Prioritize high-impact changes that provide the quickest return on investment.
3. Poor Communication
Clear communication is key. Make sure everyone understands the changes and their role in the process.
Tools to Simplify Process Improvement
In today’s digital age, tools can make implementing Process Improvement much easier. Here are some popular ones:
1. Project Management Tools
Platforms like Trello, Asana, and Monday.com help teams manage tasks, deadlines, and communication.
2. Data Analysis Tools
Google Analytics, Tableau, and Power BI provide insights to make data-driven decisions.
3. Workflow Automation
Zapier and Automate.io connect apps and automate repetitive tasks, saving you time.
Final Thoughts
Process Improvement isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a powerful approach that can revolutionize how you work. By identifying inefficiencies, streamlining workflows, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, you can unlock new levels of success and satisfaction.
0 notes
Text
Top Project Management Methodologies: Which One is Right for You?
Choosing the right project management methodology is crucial for ensuring that projects are completed efficiently, within scope, and on time. With a variety of methodologies available, each with its own strengths and best-use scenarios, selecting the one that aligns with your project’s needs can make all the difference. Here’s an overview of some of the top project management methodologies and how to determine which one is right for you:
1. Waterfall Methodology
The Waterfall approach is one of the traditional and most structured methodologies. It follows a linear, sequential design where each phase of the project must be completed before moving on to the next. This method is ideal for projects with clear, unchanging requirements, such as construction or software development projects where each stage (design, coding, testing) must be completed in order.
Best For: Well-defined projects with fixed scopes and strict deadlines.
2. Agile Methodology
Agile is a flexible, iterative approach that allows for constant collaboration and adaptation throughout the project. It breaks projects into smaller, manageable sprints, allowing teams to adjust to feedback or changing requirements as the project evolves. Agile is popular in software development, but it’s increasingly being used across industries where flexibility and adaptability are essential.
Best For: Dynamic projects where requirements may change or evolve, requiring a flexible approach.
3. Scrum
Scrum is a subset of Agile, specifically focused on managing software development projects through short, defined sprints (usually two weeks long). Teams meet daily for quick stand-ups to discuss progress and address any challenges. Scrum focuses on continuous improvement, ensuring that the team delivers value incrementally.
Best For: Complex projects requiring a high degree of collaboration and iteration, especially in software development.
4. Kanban
Kanban is a visual methodology that uses a board to track tasks through different stages of completion. Unlike Agile and Scrum, Kanban doesn’t use sprints but instead allows for continuous workflow. It emphasizes limiting work in progress, ensuring that teams don’t overextend themselves.
Best For: Projects that require a continuous flow of work and teams that need to visualize task progress.
5. Lean Project Management
Lean methodology focuses on maximizing value while minimizing waste. It aims to create efficient workflows by identifying unnecessary tasks and eliminating them. Lean is commonly used in manufacturing but is also applied to other industries that aim to optimize efficiency.
Best For: Teams looking to streamline processes, reduce waste, and increase efficiency.
6. PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments)
PRINCE2 is a process-based methodology widely used in the UK and other parts of Europe. It divides projects into multiple stages and provides a structured framework for managing risks, quality control, and scope. PRINCE2 emphasizes detailed documentation and defined roles and responsibilities.
Best For: Large, complex projects with a need for clear roles, structured processes, and heavy documentation.
7. Critical Path Method (CPM)
CPM is a technique used to predict project duration by identifying the longest sequence of tasks (critical path) that must be completed on time for the entire project to be finished by the due date. CPM is valuable in projects where timely completion is critical, and tasks are interdependent.
Best For: Projects with tight deadlines where task scheduling is key.
8. Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a methodology aimed at improving the quality of processes by identifying and eliminating defects or inefficiencies. Often combined with Lean principles, Six Sigma uses data-driven techniques to improve performance and minimize variability.
Best For: Projects where quality control and precision are essential, especially in manufacturing or service industries.
How to Choose the Right Methodology?
When deciding on the right project management methodology, consider the following:
Project Size and Scope: Smaller projects may benefit from simpler methodologies like Kanban or Lean, while larger projects may require the structure of PRINCE2 or Waterfall.
Team Structure: Agile or Scrum may work better for teams that thrive on collaboration and flexibility. Waterfall may be better suited for teams that prefer clearly defined stages.
Client or Stakeholder Involvement: If your project requires frequent feedback or has evolving requirements, Agile is likely the best fit.
Timeline: For projects with fixed deadlines, methodologies like CPM or Waterfall are effective in managing time-sensitive tasks.
Industry-Specific Needs: Some industries may have preferred methodologies, such as Lean for manufacturing or Agile for software development.
Ultimately, the best methodology depends on the unique needs of your project and team. It’s also possible to combine elements from different methodologies to create a hybrid approach that works best for your specific project.
Are you ready to take your project management skills to the next level? Join our OTHM Level 7 Diploma in Project Management at Edubex! This comprehensive program will equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to master top project management methodologies and excel in leadership roles.
Enroll today and start your journey towards becoming a certified project management expert. Take charge of your career and manage projects with confidence and efficiency!
0 notes
Text
How to Become a Software Engineer
Becoming a software engineer is an exciting journey that combines creativity, problem-solving, and technical skills. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you navigate this path.

1. Understand the Basics
What is Software Engineering? Software engineering involves designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software systems. It's crucial to understand the fundamental concepts, including algorithms, data structures, and programming paradigms.
2. Choose Your Educational Path
Formal Education: A bachelor’s degree in computer science, software engineering, or a related field is the most common route. Some universities offer specialized programs focusing on software development.
Self-Directed Learning: If traditional education isn’t for you, consider online courses or coding bootcamps. Websites like Coursera, edX, and Udacity offer excellent resources.
3. Learn Programming Languages
Start with the Basics: Familiarize yourself with languages like Python, Java, or JavaScript. These languages are widely used and provide a solid foundation.
Expand Your Skills: As you progress, learn additional languages and frameworks (e.g., C++, Ruby on Rails, React) that are relevant to your interests or the industry you wish to enter.
4. Gain Practical Experience
Build Projects: Start small by creating personal projects. This not only solidifies your understanding but also builds your portfolio.
Contribute to Open Source: Participating in open-source projects helps you gain real-world experience and connect with other developers.
5. Understand Software Development Methodologies
Familiarize Yourself with Agile and DevOps: Understanding methodologies like Agile or DevOps is crucial, as these are commonly used in the industry.
6. Networking and Community Engagement
Join Developer Communities: Engage with online forums, local meetups, or tech conferences. Networking can lead to job opportunities and collaborations.
Follow Industry Trends: Stay updated with the latest technology trends by reading blogs, listening to podcasts, and participating in discussions.
7. Prepare for Job Applications
Build a Strong Resume: Highlight your projects, relevant experience, and technical skills. Tailor your resume for each job application.
Practice Interview Skills: Prepare for technical interviews by solving coding challenges on platforms like LeetCode or HackerRank.
8. Continuous Learning
Stay Curious: The tech industry is ever-evolving. Keep learning new languages, frameworks, and tools to remain competitive.
Conclusion
Becoming a software engineer requires dedication and continuous learning. By following these steps, you can build a successful career in this dynamic field.
#SoftwareEngineering #Coding #Programming #TechCareers #LearnToCode #SoftwareDevelopment #CareerAdvice #OpenSource #TechCommunity #ContinuousLearning
0 notes
Text
Custom Application Development Services in India

Custom application development has emerged as a crucial solution for businesses seeking tailor-made software to meet their unique operational needs. In India, the demand for custom software solutions has grown exponentially due to the availability of highly skilled developers, cutting-edge technology, and cost-effective services. Whether it’s a startup or an established enterprise, businesses are increasingly turning to the best custom software development services in India for customized, scalable, and reliable applications.
Why Choose Custom Application Development Services? Off-the-shelf software solutions may cater to general needs but often fall short when it comes to addressing specific business requirements. Custom applications, on the other hand, are designed to meet the particular demands of a company, ensuring that every function, process, and user experience is optimized.
Some of the key benefits include:
Personalized Solutions: Custom software is designed specifically for your business, making it highly efficient and easier to integrate with existing systems. Scalability: As your business grows, custom applications can be modified and scaled without the limitations often found in standard software. Enhanced Security: Custom applications provide greater control over security features, reducing vulnerabilities that are commonly associated with widely-used software. The Role of the Best Custom Software Development Services in India India has established itself as a global leader in IT and software development, with a strong focus on providing innovative and high-quality custom application development services. The best custom software development services in India offer solutions across a range of industries, including healthcare, finance, education, and eCommerce.
Here are some reasons why India is preferred for custom software development:
Expertise: Indian developers are known for their expertise in modern programming languages, development frameworks, and agile methodologies, ensuring that your project is in capable hands. Cost-Effectiveness: One of the primary reasons businesses opt for custom application development in India is the cost advantage. High-quality services are available at a fraction of the price when compared to Western counterparts, without compromising on quality. Timely Delivery: Most Indian companies adhere to strict timelines and deliver projects on time, ensuring that your business doesn't experience any unnecessary delays. End-to-End Services: From consulting and planning to development and maintenance, the best custom software development services in India provide comprehensive solutions tailored to your specific business needs. Key Features to Look for in Custom Software Development Services When selecting a custom application development service, it’s important to keep in mind certain key features that can make a significant difference in the outcome of your project.
Deep Industry Knowledge: Ensure that the development team has experience in your industry, as this will help them better understand your specific requirements. Communication & Collaboration: Strong communication is crucial during the development process. Look for a company that promotes transparency and keeps you involved in every stage of the project. Post-Development Support: A good custom software development service will offer ongoing support and maintenance to ensure that the application functions smoothly even after the project is delivered. Innovation & Flexibility: The development team should be open to incorporating new technologies and features that may arise during the development process, providing the flexibility to evolve with your business. How to Choose the Best Custom Software Development Company in India Selecting the best custom software development company in India requires careful consideration of several factors. Here are some tips to help you make the right choice:
Portfolio & Testimonials: Review the company's portfolio and previous projects to assess their expertise. Client testimonials and case studies can offer valuable insights into their quality of work. Technical Proficiency: Ensure the development team is proficient in the latest technologies and tools that are relevant to your project. Clear Project Management: A good development company will have a structured approach to managing projects, including regular updates, milestone tracking, and an open channel for feedback. Flexible Pricing Models: Choose a company that offers flexibility in its pricing models, whether it’s a fixed price, hourly rate, or a dedicated team model. This allows you to select the option that best fits your budget and project scope. The Future of Custom Application Development in India With the rapid pace of technological advancements, custom application development in India is only set to grow further. Innovations in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are shaping the future of custom applications. Indian developers are keeping pace with these changes, ensuring that they can deliver future-ready solutions that can adapt to evolving business needs.
In the years to come, we can expect more businesses to look for the best custom software development services in India to build applications that are not only efficient and scalable but also innovative and aligned with future technology trends.
Conclusion Custom application development in India offers businesses the opportunity to create unique software tailored to their specific needs. With expertise, innovation, and cost-effectiveness, India continues to be the go-to destination for companies worldwide. By choosing the best custom software development company in India, businesses can ensure that they receive a high-quality product that is scalable, secure, and customized to their operations.
For reliable and comprehensive custom application development services, Webstep is here to help you achieve your business goals.
0 notes
Text
Introduction to Software Engineering

Software engineering is a field focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software systems. It involves applying engineering principles to create software that is reliable, efficient, and meets user requirements. Here are some key aspects:
**Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC):** The process of software development typically includes phases such as planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
**Software Design:** This involves defining the architecture and components of the software system. Techniques like object-oriented design, design patterns, and UML diagrams are commonly used.
**Coding:** Writing the actual source code in programming languages like Java, C++, Python, or JavaScript. Code must be clear, maintainable, and efficient.
**Testing:** Ensuring the software works as intended through various testing methods like unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and acceptance testing.
**Project Management:** Managing the software development process involves scheduling, budgeting, risk management, and ensuring the project meets its goals. Methodologies like Agile, Scrum, and Waterfall are commonly used.
**Maintenance and Support:** After deployment, software needs to be maintained to fix bugs, update features, and ensure compatibility with evolving technologies.
**Software Engineering Principles:** These include principles like modularity, abstraction, encapsulation, and separation of concerns, which help in creating well-structured and maintainable software.
**Ethics and Professionalism:** Software engineers must adhere to ethical standards, such as ensuring user privacy and data security, and producing reliable and safe software.
TCCI Computer classes provide the best training in online computer courses through different learning methods/media located in Bopal Ahmedabad and ISCON Ambli Road in Ahmedabad.
For More Information:
Call us @ +91 98256 18292
Visit us @ http://tccicomputercoaching.com/
#computer engineering course in Iscon Ambli Road-Ahmedabad#computer engineering course in bopal-Ahmedabad#IT engineering course in Ahmedabad#software engineering course in bopal-Ahmedabad
0 notes
Text
Skills Required for QA Professionals in QA Automation
Here are some essential skills required for QA Automation:
Programming Languages: Proficiency in at least one programming language such as Java, Python, JavaScript, or others commonly used in test automation.
Test Automation Tools/Frameworks: Experience with popular automation frameworks like Selenium WebDriver, Appium (for mobile testing), or tools like Cypress, TestComplete, or Robot Framework.
Version Control Systems: Knowledge of version control systems like Git for managing test scripts and collaborating with teams.
Web Technologies: Understanding of web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) to interact with elements on web applications.
API Testing: Ability to automate testing of APIs using tools like Postman, RestAssured, or libraries in programming languages.
Database Skills: Basic knowledge of SQL for verifying data integrity and performing backend testing.
Testing Concepts: Strong understanding of software testing concepts, types of testing (functional, regression, load, etc.), and best practices.
CI/CD Tools: Familiarity with Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, or GitLab CI for automating test execution.
Problem-Solving Skills: Ability to analyze complex problems and provide solutions within the automation framework.
Communication: Good communication skills to collaborate with developers, testers, and other stakeholders.
Agile Methodology: Understanding of Agile practices and how automation fits into Agile development cycles.
Attention to Detail: Thoroughness in writing test scripts, handling edge cases, and ensuring comprehensive test coverage.
These skills collectively enable QA Professionals to effectively create, execute, and maintain automated test suites that ensure the quality and reliability of software applications. Learn QA Automation Skills to pave your way to becoming a successful QA professional.
#automation testing#automation testing tools#automation testing training#automation training#tech trends#technology#software testing#qa automation
0 notes
Text
Next-Gen DevOps Certifications: Preparing for the AI-Driven IT Landscape
The rapid evolution of technology continues to transform the IT industry, pushing the boundaries of what's possible and creating new opportunities for professionals. One of the most significant shifts in recent years is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into DevOps practices. As AI-driven tools become more prevalent, the need for specialized knowledge and skills grows, making next-gen DevOps certifications crucial for IT professionals aiming to stay ahead in the AI-driven IT landscape.
The Intersection of DevOps and AI
DevOps, a set of practices that combines software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops), has always focused on automating and integrating the processes between software development and IT teams. The goal is to improve collaboration and productivity by automating workflows and continuously measuring application performance. AI enhances these processes by introducing advanced capabilities such as predictive analytics, intelligent automation, and machine learning algorithms that can analyze vast amounts of data to make informed decisions.
The Need for Next-Gen DevOps Certifications
As AI becomes more embedded in DevOps workflows, traditional skills and knowledge are no longer sufficient. IT professionals need to understand how AI can be applied to optimize DevOps processes, from continuous integration and delivery to monitoring and incident management. This is where next-gen DevOps certifications come into play.
Next-gen DevOps certifications focus on equipping professionals with the skills needed to leverage AI tools and methodologies. These certifications cover a range of topics, including AI and machine learning fundamentals, AI-driven automation, data analytics, and the ethical considerations of using AI in IT operations.
Key Certifications to Consider
Several certification programs have emerged to address the growing demand for AI-integrated DevOps skills. Here are some of the most valuable certifications for professionals looking to excel in the AI-driven IT landscape:
Certified DevOps Engineer – AI and Machine Learning (CDE-AML): This certification focuses on the integration of AI and machine learning in DevOps practices. It covers the use of AI for predictive analytics, automated testing, and intelligent monitoring.
AI for DevOps Professionals Certification: Offered by leading organizations like the Linux Foundation, this certification provides a comprehensive understanding of how AI can enhance DevOps processes. It includes modules on AI-driven automation, data analysis, and AI tools commonly used in DevOps.
Google Cloud Professional DevOps Engineer: This certification emphasizes the use of Google Cloud's AI and machine learning services to streamline DevOps workflows. It covers infrastructure automation, continuous delivery, and performance monitoring using AI.
Microsoft Certified: Azure DevOps Engineer Expert: Focused on Microsoft's Azure platform, this certification teaches professionals how to implement DevOps practices using Azure's AI and machine learning tools. It includes training on automated testing, continuous integration, and delivery pipelines. Preparing for the Future
To prepare for the AI-driven IT landscape, professionals should not only pursue next-gen DevOps certifications but also engage in continuous learning. Here are some steps to help you stay ahead:
Stay Updated with AI Trends: Regularly read industry blogs, attend webinars, and participate in forums to stay informed about the latest advancements in AI and DevOps.
Hands-On Practice: Gain practical experience by working on projects that integrate AI into DevOps workflows. Use platforms like GitHub to collaborate with others and learn from real-world scenarios.
Join Professional Communities: Engage with communities of like-minded professionals. Platforms like LinkedIn, Reddit, and specialized forums provide opportunities to network, share knowledge, and learn from experts in the field.
Invest in Training: Enroll in courses and workshops offered by reputable training providers. Wiculty Learning Solutions, for instance, offers a range of programs designed to help professionals acquire the latest skills in AI and DevOps. Conclusion
The integration of AI into DevOps is revolutionizing the IT landscape, creating a demand for professionals who possess both DevOps expertise and AI knowledge. Next-gen DevOps certifications are essential for those looking to thrive in this evolving environment. By staying updated, gaining hands-on experience, and engaging in continuous learning, IT professionals can position themselves at the forefront of the AI-driven IT landscape, ensuring they are well-prepared for the future.
0 notes
Text
Accelerating transformation: The impact of automation on cloud migration

Cloud computing has become the bedrock of modern businesses. The ability to store, manage, and access data and applications remotely has revolutionized the way organizations operate. However, the journey to migration of an organization’s digital assets, applications, data, and workloads from conventional on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based platforms isn’t always straightforward.
Cloud migration involves meticulous planning, resource allocation, and implementation strategies. This is where automation plays a pivotal role in accelerating the process.
Gartner predicts 60% of data center infrastructure teams will have relevant automation and cloud skills by 2027
In this blog we will explore the profound implications of automation in accelerating the rapid migration to cloud infrastructure.
Benefits of automated cloud migration
Due to the rising complexities in the migration process, leveraging automation becomes paramount. By integrating automated tools and methodologies, organizations can streamline their migration projects, achieving faster, more accurate, and reliable outcomes. Here are some key benefits:
1. Efficiency improvements
Automation streamlines tasks, optimizing processes and resource utilization for faster completion during cloud migration. By eliminating manual intervention, organizations can achieve greater efficiency and reduce the time required for migration.
2. Cost savings
One of the significant advantages of automation in cloud migration is the reduction of operational costs. By minimizing manual intervention and enhancing resource efficiency, organizations can achieve cost savings throughout the migration process.
3. Reduction in manual errors
Human errors can have significant consequences during cloud migration, leading to data loss or application failures. Automation reduces the likelihood of manual errors, ensuring the secure and accurate transfer of data and applications to the cloud environment.
4. Accelerated deployment cycles
Automated procedures expedite the deployment of applications and resources, significantly reducing deployment time. This allows organizations to take advantage of the scalability and flexibility offered by the cloud, enabling faster time-to-market for new products and services.
5. Scalability and flexibility
Automation enables easy scaling and swift adaptation to changing needs during cloud migration. Organizations can effortlessly adjust their resources and infrastructure to accommodate growth and changing requirements, ensuring a seamless transition to the cloud.
Tools and technologies for automating cloud migration processes
Several tools and technologies can facilitate the automation of cloud migration processes. Here are some popular ones:
1. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools enable organizations to automate infrastructure provisioning and configuration management. Some widely used IaC tools include:
Terraform: Empowers infrastructure automation through declarative configuration files.
AWS CloudFormation: Simplifies the provisioning of AWS resources using templates.
Azure Resource Manager: Offers templates for resource deployment in Azure.
2. Data migration tools
Data migration is a critical aspect of cloud migration, and several tools are available to facilitate seamless data transfer. Some commonly used data migration tools include:
AWS Database Migration Service: Facilitates the migration of databases to AWS with minimal downtime.
Azure Database Migration Service: Enables organizations to migrate databases to Azure with ease.
Google Cloud Data Transfer Service: Streamlines the process of transferring data to Google Cloud.
3. CI/CD tools
Continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) tools automate the software development process, allowing for efficient application deployment and management. Here are some popular CI/CD tools:
Jenkins: An open-source automation server for continuous integration and delivery.
GitLab CI/CD: Provides a robust platform for the entire DevOps lifecycle.
CircleCI: Offers cloud-based CI/CD for automating the software development process.
Key areas for automation in cloud migration
1. Resource provisioning and configuration
Automating resource provisioning and configuration management is crucial for optimizing cloud migration. By implementing automated procedures, organizations can ensure efficient resource utilization and streamlined configurations.
2. Data migration and transfer
Smooth data migration and synchronization are vital for a successful cloud migration strategy. Automated tools facilitate secure and accurate data transfer, ensuring that vital data is seamlessly moved to the cloud environment.
3. Application deployment and management
Efficient application deployment and management are essential for leveraging the benefits of the cloud. By integrating CI/CD pipelines and containerization tools, organizations can automate application deployment, accelerating deployment cycles and ensuring effective management in the cloud.
Best practices for implementing automation in cloud migration
1. Assessment and planning
Evaluate the current state of infrastructure, applications, dependencies, and interconnections.
Clearly define objectives and expected outcomes from the migration.
Utilize automated assessment tools to identify workloads suitable for migration.
Select the right automation tools and frameworks based on compatibility and requirements.
2. Standardization and templates
Standardize configurations by creating templates and standard configurations.
Develop reusable automation scripts or playbooks for consistent deployment across different environments.
3. Security and compliance
Implement automated security checks and configurations to ensure compliance adherence.
Utilize identity and access management automation for secure resource access.
4. Testing and validation
Implement automated testing for applications to ensure they function properly in the cloud environment.
Develop validation procedures and automated tests to confirm successful migrations.
5. Incremental migration and monitoring
Break down the migration into smaller, manageable chunks to reduce risks and enable iterative improvements.
Implement automated monitoring tools to track performance, detect issues, and optimize resource usage post-migration.
How to identify if automated cloud migration works for your business?
Discovering if automated cloud migration suits your business involves diving into crucial factors. It’s like finding the perfect puzzle piece that fits seamlessly. To unravel this puzzle, peek into your business’s needs, goals, and capabilities, consider the following factors:
Assess your business objectives and evaluate how automation can support them.
Evaluate the complexity and scale of your migration project and determine if automation can streamline the process.
Conduct a risk assessment to identify potential challenges and determine if automation can mitigate them.
Consider the time-to-value and speed of deployment that automation can offer.
Assess the scalability and flexibility that automation can provide to accommodate your business’s future growth.
Evaluate the compatibility of your applications with automation tools and frameworks.
Consider conducting pilot projects or proof of concepts to test the feasibility and effectiveness of automated cloud migration for your business.
Embrace automated cloud migration for hassle-free transformation
Adopting automation isn’t merely an enhancement but a necessity in modernizing infrastructure. It empowers businesses to concentrate on innovation, secure in the knowledge that the foundation of their operations is well-optimized and future-ready.
Are you looking to seamlessly transition your operations to the cloud? Our automated cloud migration services are designed to simplify and expedite the migration process for your business. With our expertise in cloud consulting services, we ensure a smooth transition, optimizing efficiency and minimize disruptions. Excited to tap into the perks of automated cloud migration? Let’s make your transformation effortless starting today.
#Cloud Migration Service#cloud migration AWS#Cloud Automation#Cloud Migration Strategies#Cloud consulting services
0 notes
Text
QA & Test Automation: Career Opportunities

QA and Test Automation careers offer promising opportunities as the demand for robust, bug-free, and efficient software increases. In this article, we will examine the field of QA and Test Automation. We will explore the different job prospects it provides and discuss why choosing a career in this field can be satisfying and fulfilling.
The Role of QA & Test Automation
Before we start exploring career opportunities, let’s first understand the role that QA and Test Automation professionals play in the software development process.
Quality Assurance (QA): QA professionals are responsible for ensuring that software products meet the desired quality and performance standards. They work closely with development teams to identify potential issues, validate functionality, and conduct thorough testing to uncover defects. QA encompasses various types of testing, including functional, non-functional, regression, and performance testing, to name a few.
Test Automation: Test Automation involves the use of automated scripts and testing tools to perform repetitive and time-consuming testing tasks. Automation ensures faster and more efficient testing, allowing QA professionals to focus on complex scenarios and exploratory testing. Test Automation is particularly valuable in Agile and DevOps environments where rapid and continuous testing is essential.
Types of QA Automation Testing
As a Quality Assurance Automation Tester, you will collaborate with diverse testing methodologies to address specific challenges and achieve organizational goals. Automation testing allows you to streamline and enhance the testing process, making it more efficient and reliable. Here are some commonly used types of QA automation testing:
1. Functional Testing
Functional testing is essential for QA automation testing. It checks if the software performs the necessary functions and produces the expected output based on the input. This testing is crucial to ensure that the software behaves as intended and meets the requirements. It includes positive and negative test cases, boundary testing, and equivalence partitioning.
2. Performance Testing
Performance testing is crucial for evaluating how a software application performs under specific workloads and conditions. It falls under nonfunctional testing and aims to identify potential performance issues and ensure consistent and reliable performance. Testers use it to assess response times, system stability, scalability, and resource utilization. Common types of performance testing include load testing, stress testing, and scalability testing.
3. Unit Testing
Unit testing tests individual functions or software components in isolation to ensure they work correctly and meet functional requirements. Automated unit tests verify that code units produce expected output for various inputs. Early identification and addressing of defects contribute to higher code quality and maintainability.
4. Smoke Tests
Smoke tests, also known as “build verification testing,” evaluate the software’s architecture stability. The main goal is to confirm that all major functions of the software work correctly after a new build or release. These tests are fast, high-level checks that determine if the software build is stable for further testing. They play a crucial role in software development and testing, identifying critical issues early on.
5. GUI Testing
GUI testing evaluates the user interface of a software app. QA automation testers use it to validate user interactions like keystrokes, clicks, and touch gestures. It ensures expected responses and consistent user experience. GUI testing also verifies visual elements, layouts, fonts, and colors as per design specs. Automated tools help testers conduct these evaluations efficiently on various platforms and devices.
6. API Testing
API testing evaluates software at its message layer, checks components, and verifies API functionality. It’s useful for testing integrations between software components or services. Testers can evaluate data exchanges, error handling, authentication, and response times. API testing ensures seamless communication between software parts and accurate, secure data transmission.
QA automation testing types serve specific purposes in the software testing process. QA professionals use a combination of these types to assess quality, identify defects, and ensure software meets user expectations. Automation tools and frameworks enable efficient testing, faster development cycles, and more reliable software releases.
Why Choose a Career in QA & Test Automation?
Pursuing a career in QA and Test Automation offers a host of compelling reasons:
High Demand: As software continues to permeate every aspect of our lives, the need for QA and Test Automation professionals has surged. Organizations understand the significance of delivering quality software to gain a competitive edge, leading to a consistent demand for skilled QA experts.
Versatility: QA professionals work across industries, from healthcare to finance to entertainment. This versatility allows individuals to explore diverse domains and industries, making it an exciting and ever-changing career.
Continuous Learning: The dynamic nature of technology ensures that QA professionals are always learning and adapting to new tools, methodologies, and best practices. This keeps the role fresh and challenging.
Problem Solving: QA and Test Automation professionals are essentially digital detectives, hunting for elusive software bugs. This problem-solving aspect of the role can be intellectually stimulating and rewarding.
Career Progression: QA and Test Automation roles often provide clear pathways for career growth. Individuals can progress from junior positions to senior roles, such as QA Lead, Test Automation Engineer, or QA Manager.
Career Opportunities in QA & Test Automation
Now that we understand the importance of QA and Test Automation. Let’s explore the various career opportunities available in this field:
1. QA Tester
QA Testers are responsible for executing test cases, identifying defects, and validating that software applications meet specified requirements. They play a crucial role in maintaining software quality and ensuring bug-free releases.
2. Test Automation Engineer
Test Automation Engineers create, maintain, and execute automated test scripts using testing frameworks and tools. They focus on automating repetitive test cases to improve efficiency and test coverage.
3. QA Analyst
QA Analysts are responsible for analyzing project requirements, creating test plans, and developing test cases. They work closely with development teams to ensure that software is tested comprehensively.
4. QA Lead/Manager
QA Leads and Managers oversee QA teams, manage testing projects, and ensure that testing processes align with project goals. They are responsible for test planning, resource allocation, and quality assurance strategies.
5. Performance Tester
Performance Testers focus on evaluating software applications’ performance under various conditions, including load, stress, and scalability testing. They identify bottlenecks and optimize application performance.
6. Security Tester
Security Testers specialize in identifying vulnerabilities and security risks in software applications. They perform penetration testing and security assessments to ensure that data remains secure.
7. DevOps Engineer
DevOps Engineers bridge the gap between development and operations. They are responsible for automating testing processes, continuous integration, and continuous delivery (CI/CD), ensuring rapid and reliable software deployments.
8. Test Architect
Test Architects design and implement testing frameworks, strategies, and best practices for QA teams. They play a strategic role in optimizing testing processes and ensuring consistent quality.
9. QA Consultant
QA Consultants work as independent experts, providing advice and guidance to organizations seeking to improve their QA practices. They assess current processes, recommend improvements, and implement best practices.
10. Test Environment Manager
Test Environment Managers are responsible for setting up and maintaining test environments that mimic production conditions. They ensure that QA teams have access to the necessary resources for testing.
11. Test Data Analyst
Test Data Analysts focus on managing and maintaining test data, ensuring that QA teams have access to realistic and relevant data for testing purposes.
Salaries in QA & Test Automation
Salaries in the QA and Test Automation field can vary significantly based on factors such as location, experience, and specific job roles. Here’s a general overview of salary ranges:
Entry-Level QA Tester (0–2 years of experience): Entry-level QA testers can expect to earn an average annual salary ranging from ₹3,00,000 to ₹6,00,000.
Intermediate QA Tester (2–5 years of experience): QA testers with a few years of experience typically earn salaries in the range of ₹6,00,000 to ₹9,00,000 per year.
Senior QA Tester (5–8 years of experience): Senior QA testers, who have demonstrated expertise in the field, can command annual salaries ranging from ₹9,00,000 to ₹15,00,000.
Test Automation Engineer: Test automation engineers, who specialize in creating and maintaining automated testing frameworks, can earn salaries between ₹6,00,000 to ₹12,00,000 per year, depending on their experience and skills.
QA Lead/Manager: QA leads or managers responsible for overseeing testing teams and strategies can earn substantial salaries, ranging from ₹10,00,000 to ₹20,00,000 or more annually.
Performance Test Engineer: Performance test engineers, who focus on assessing software scalability and performance, typically earn salaries in the range of ₹6,00,000 to ₹12,00,000 per year.
Automation Test Lead/Manager: Professionals in automation test leadership roles can expect annual salaries ranging from ₹12,00,000 to ₹20,00,000 or higher, depending on their experience and responsibilities.
QA Architect: QA architects, responsible for designing and implementing testing frameworks and strategies, can earn substantial salaries, often exceeding ₹20,00,000 per year.
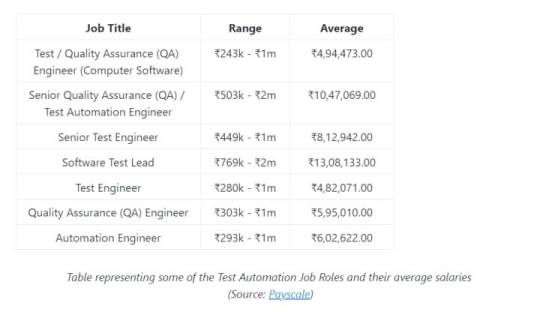
It’s important to note that these salary ranges are approximate and may vary based on factors like the location of the job (metros tend to offer higher salaries), the size and reputation of the company, and the demand for specific skills and expertise. Additionally, professionals with certifications and specialized skills in tools like Selenium, JUnit, TestNG, and performance testing tools may have the opportunity to earn higher salaries in the QA and Test Automation field.
Conclusion
A career in QA and Test Automation is a great way to make a good living while also being challenged and having a variety of opportunities. The importance of QA professionals in the software development process cannot be overstated, and the demand for their expertise continues to grow.
Whether you’re starting your career, transitioning into a new role, or seeking opportunities for career advancement, Test Automation offers a wide array of options. To start your journey in this exciting field and gain a solid foundation in QA and Test Automation, consider enrolling in the expert-led courses offered by Datavalley. Our hands-on training and real-world projects will equip you with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in the world of software testing. Join us today and be a crucial part of the technology industry, where quality and reliability are of utmost importance.
QA & Test Automation Bootcamp
Topics Covered
Software testing fundamentals and best practices
Test case design techniques
Defect tracking and bug reporting
Introduction to test automation
Hands-on with Selenium for web application testing
Understanding CI/CD pipelines, QA role
Who is this ideal for?
Any one Tech or Non-tech with an eye for detail
and an interest in ensuring software quality. Basic
programming, coding
Mini-Project
Automate sample test cases for a web application
using Selenium WebDriver in Java
Job/Career Track:
QA/Automation testing
The Highlights of the Bootcamps
20 hours of immersive learning, spanning two weeks
Practical, hands-on learning
Complete a mini-project
Earn a certificate and showcase it in your profile
Select from four diverse tracks
Sessions on soft skills and communication
Learn from industry experts
Guides to choosing your career path
#datavalley#dataexperts#data engineering#data analytics#data science#power bi#business intelligence#dataexcellence#data analytics course#data science course#automation testing#qa/automation testing#testing engineer
1 note
·
View note
Text
The PMP certification is highly regarded and demonstrates your expertise in project management. Here are some career possibilities you can explore after earning a PMP certification:
Project Manager: This is the most common career path for PMP-certified professionals. You can manage projects in various industries such as IT, construction, healthcare, finance, and more. Project managers are responsible for planning, executing, and monitoring projects to ensure they are completed successfully and on time.
Program Manager: Program managers oversee a portfolio of related projects and initiatives within an organization. They ensure that projects align with strategic goals and coordinate resources to achieve the desired outcomes.
Portfolio Manager: Portfolio managers focus on high-level strategic planning and management of a company's entire project portfolio. They prioritize and allocate resources to different projects and ensure alignment with the organization's objectives.
Agile Project Manager: PMP certification can also be combined with agile methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, to become an Agile Project Manager. This role is essential in IT and software development, where agile practices are commonly used.
IT Manager: PMP-certified professionals with a background in IT can pursue careers as IT managers, overseeing the planning and execution of IT projects, infrastructure upgrades, and software development initiatives.
0 notes
Text

Becoming a professional in equity research requires a combination of knowledge, skills, and experience. Here are some steps you can take to enhance your expertise and become a pro in equity research:
Develop a Strong Foundation: Start by acquiring a solid understanding of financial concepts and principles. Familiarize yourself with accounting, financial statements, valuation techniques, and investment analysis. Consider enrolling in finance or accounting courses or pursuing a degree in finance or a related field.
Gain Practical Experience: Practical experience is crucial in equity research. Look for internships or entry-level positions at financial institutions, investment banks, or asset management firms. This will provide you with hands-on exposure to real-world equity analysis, research processes, and industry dynamics.
Expand Your Knowledge: Stay up to date with the latest industry trends, market developments, and economic factors. Read financial news, research reports, and industry publications regularly. Develop a deep understanding of the industries and sectors you are interested in analyzing.
Master Financial Analysis: Develop your financial analysis skills by studying and analyzing
companies' financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Learn how to interpret key financial ratios and indicators, and understand their implications on a company's performance and valuation.
Learn Valuation Techniques: Become proficient in various valuation methodologies used in equity research, such as discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, relative valuation (comparable company analysis), and market multiples. Practice applying these techniques to analyze and value different companies.
Enhance Your Analytical Skills: Sharpen your analytical abilities by working on case studies, financial modeling, and scenario analysis. This will help you develop the ability to critically analyze complex data, identify trends, and make informed investment recommendations.
Utilize Research Tools: Familiarize yourself with research tools and software commonly used in equity research, such as Bloomberg, FactSet, or Capital IQ. These tools provide access to extensive financial data, news, and research reports, enabling you to conduct in-depth analysis efficiently.
Network and Learn from Experts: Engage with professionals in the field of equity research through networking events, industry conferences, or online communities. Connect with experienced analysts or mentors who can provide guidance, share insights, and help you navigate your career path.
Pursue Professional Certifications: Consider obtaining industry-recognized certifications like the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designation. The CFA program covers a broad range of topics relevant to equity research and is highly regarded in the finance industry.
Continuously Learn and Adapt: The field of equity research is dynamic, so it's important to keep learning and adapting to new trends and technologies. Stay curious, explore emerging sectors, and embrace lifelong learning to stay at the forefront of the industry.
Becoming a pro in equity research requires dedication, persistence, and continuous learning. By building a strong foundation, gaining practical experience, and honing your analytical skills, you can position yourself for a successful career in this exciting field.
You Can attend a free workshop on Equity Research organized by Jobaaj Learnings.
Even though you are a student from any background or a working professional, Equity Research has become a must have skill in resumes and will give you a competitive edge in the job interview
Click here to register for free workshop:
youtube
0 notes
Text
#There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question as the best software development methodology for a particular project depends on a num#including the project's size#complexity#team size#and client requirements. That said#here are some commonly used software development methodologies:
0 notes
Text
Digital Self-Sufficiency 101
I’ve noticed that the chaos of 2020 has caused many people to notice that commercially available technologies have grown increasingly intrusive, expensive, and restrictive. Therefore, I thought I would put together some easy ways to maintain privacy and self-sufficiency as much as possible in the digital age.
SOFTWARE IN GENERAL
Using incognito mode or private mode in your browser actually does nothing to prevent your internet service provider from watching your activity. The Tor browser is your easiest option for keeping your search history private.
To keep downloads, system updates, and activity from other applications private, consider using a VPN. Personally, I sometimes use ProtonVPN for this, but some people might find it uncomfortably slow. A proxy server will not provide the same layer of protection but suffices for day-to-day use.
Never reuse passwords, but it is usually okay to choose a common theme for them, and choosing long or uncommon phrases is actually safer than using random strings of characters.
Password managers are also relatively safe. KeePass is a good open-source choice that creates an encrypted password database on your device and so keeps your information entirely private.
Consider switching browsers. Chrome (including Chromium) and Edge both send data to Google and Microsoft respectively. Firefox is heavily customizable, open-source, and focused on privacy; Opera is closed-source but does provide useful features such as a built-in browser VPN.
TrackMeNot is an add-on that performs automated random Google searches, making it much harder for Google to determine your search activity. Also, use an adblocker wherever possible - AdBlock Plus is an effective free choice.
Archive.org is an excellent source of ebooks, journals, music, etc. that allows you to borrow materials and download them or read them online without requiring any personal information.
DRM, or digital rights management, is a form of software used to prevent people from copying files or accessing them outside of certain applications (such as iTunes for music, Adobe Reader for ebooks, etc). It is perfectly legal to remove DRM from works you have purchased, so that you actually own the file and not just a license to access it within a certain framework.
There are several plugins available for the Calibre ebook library that get rid of DRM on book files; this is the one I use. I don’t have iTunes or Spotify, but I’ve heard good things about NoteBurner, and I know that plenty of alternatives exist for DRM removal of music files.
Also, youtube-dl is a useful tool for downloading videos from YouTube. Be careful to use this only on open-source or public domain videos.
LINUX
Linux has advanced astronomically in the past decade -- it is definitely the best option for privacy and security, and is now fairly easy to use.
If you’re just beginning, Ubuntu is a great choice with graphics that will make your PC look and feel a bit like a Mac. You can completely opt out of giving any data to the developers, and it’s by far the most commonly used distro in the Linux community, meaning that most support and apps are developed for it.
Take a test drive! Here is an easy tutorial for how to put Ubuntu on a USB stick and run it on your computer without affecting your Windows system or changing any of your files.
On most hardware, an out of the box Ubuntu installation works fine for browsing the web, watching movies, studying, and day-to-day use -- do test it using a USB before installing it, though.
The best thing about Linux is that you are the absolute dictator of your own computer. The appearance, functionality, and resource management of your system is all up to you. Also, there are hundreds of different operating systems and configurations under the Linux umbrella.
The fact that most viruses and malware are designed to run on Windows offers a degree of protection to Linux users, and those running more obscure distributions are less vulnerable, but security consciousness is still very important. ClamAV is a good open-source antivirus specifically designed to scan for malware targeted at Linux systems, and chkrootkit can detect any rootkits that may be installed on your system.
If you use Linux exclusively, the WINE toolkit can allow you to run programs designed for Windows. It does require some setup but eliminates a lot of compatibility issues (*pointed glance at my online classes*).
WINDOWS
A computer with standard Windows installed will never be all that private or independent, given the limitations hard-coded into the system, but there are still plenty of things you can do.
Don’t use a Microsoft account on your personal computer -- this enables Microsoft to combine data sent from your computer with your personal information. To turn this off, go into Settings, select Accounts, find your own account, and click the “Delete” option.
If you are installing Windows on a computer, don’t connect to the Internet during the setup process. When it asks you to connect to WiFi, click the “I don’t have Internet” option in the bottom left corner -- this will allow you to set up Windows using a local account, bypassing the requirement to create a Microsoft account.
When it comes to protecting your PC from hackers, choose strong passwords and be careful what you click on, and after that Microsoft Defender should do the trick. For the most part, commercial antivirus software is not necessary; any malicious actor worth their salt will be able to circumvent common choices like McAfee or Norton.
The Windows updater includes many invasive features without a way to opt out, and can be disabled. Hit the Windows key + R to bring up the Run menu, type “services.msc” in the text box, and press Enter to open the Services Manager. Find Windows Updates and Windows Update Medic, right-click on both of those, and select “Disable.”
Use caution when electing not to update Windows; oftentimes patches for important security vulnerabilities are incorporated into the updates, and Microsoft doesn’t allow users to select which updates to install.
OS X / iOS
The entire Apple business model is based on hardware that’s far below the industry standard for the price range and software that’s obsolescent from the moment you purchase it. These products are pure fashion over function and are pretty much inseparable from their surveillance software and use restrictions.
HARDWARE
Don’t get a new laptop simply because yours is getting older or slower. Hardware available to the average consumer hasn’t changed significantly in the past decade. If your computer is getting older and feels slower, that’s probably because Windows has grown heavier and less efficient with every update.
Self-sufficiency and durability go together in technology as in all other facets of manufacturing.
SSDs may be slightly faster than conventional hard disk drives, but they don’t have as much storage capacity and will fail more quickly, so for most uses an HDD is probably more practical. Anything that has “flash memory” as its sole form of storage should be avoided.
Entry-level laptops in 2020 are usually worse in terms of design and specifications than they were in 2015. Second-hand options can be a good idea, especially workstations designed for business use (my PC was made in 2012 and is still humming along with no problems).
Swappable batteries are increasingly rare but go a long way to increase the usefulness of a PC while traveling or offline. Also, touchscreens always shorten battery life by at least an hour or two.
Intel Atom processors are common on lower-cost laptops but are very slow and prone to overheating unpredictably.
Also, anything without a fan (look for a visible vent on the underside) can overheat in the summer and is probably indicative of lower processing power.
The vast majority of two-in-one laptops and tablet hybrids are severely underpowered -- the extremely small size prevents the use of proper computer hardware.
Source: am a Linux user and hobbyist programmer who learned most of this using the time-honored Mess Around and Find Out methodology.
12 notes
·
View notes