#how to export oracle database using command prompt
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Export Backup Automation in Oracle On Linux
Export Backup Automation in Oracle On Linux #oracle #oracledba #oracledatabase
Hello, friends in this article we are going to learn how to schedule database export backup automatically. Yes, it is possible to export backup automation with a crontab scheduler. How to schedule Export Backup Using shell scripting, we can schedule the export backup as per our convenient time. Using the following steps we can schedule expdp backup. Step 1: Create Backup Location First, we…

View On WordPress
#expdp command in oracle#expdp from oracle client#expdp include jobs#expdp job status#export and import in oracle 12c with examples#how to check impdp progress in oracle#how to export only table data in oracle#how to export oracle database using command prompt#how to export schema in oracle 11g using expdp#how to stop impdp job in oracle#impdp attach#impdp commands#oracle data pump export example#oracle data pump tutorial#oracle export command#start_job in impdp
0 notes
Text
Idatabase mac

#Idatabase mac how to
#Idatabase mac for mac
#Idatabase mac mac osx
#Idatabase mac install
#Idatabase mac password
The.idatabase files preserve the complete content and structure of the database, including pictures and they can also be used by iPhone version of. The app supports Backup and Restore, Exporting and Importing of databases in.idatabase and.CSV formats.
#Idatabase mac for mac
IDatabase for Mac can be synchronized via Wi-Fi with iDatabase for iPhone (sold separately). Download the app here: Video review of iDatabase App for the Mac. Another great feature is the ability to share your work with friends and colleagues via email, in several. If you also possess the iDatabase for Mac, you can do it with the Wi-Fi Sync function. It has a feature set comparable to Microsoft Access, but with a strong focus on forms (layouts) as the primary way of accessing databases. FileMaker is probably the best known database application for the Mac. Just skip to the PATH section.Alternatives to Microsoft Access on the Mac File Maker Pro.
#Idatabase mac install
You don’t need to download and install it again.
#Idatabase mac how to
That article explains how to install SQLcl separately (in case you don’t install SQL Developer). You can also add SQLcl to your PATH variable to make it easier to launch.įor instructions on adding it to your PATH variable, see How to Install SQLcl on a Mac and jump to the “Add to PATH” heading.
#Idatabase mac password
You can use a different username and password as necessary. These credentials were created upon Oracle installation. The above command includes hr as the username, and oracle as the password. If you don’t have SQL Developer in the Applications folder, change the path accordingly. SQLcl can be launched by opening a Terminal window and entering the following: /Applications/SQLDeveloper.app/Contents/resources/sqldeveloper/sqldeveloper/bin/sql hr/oracle SQLcl is a command line interface for working with Oracle databases. Installing SQL Developer also installs a copy of SQLcl. SQL Developer is now installed and connected to Oracle. Once connected, the connection is added to the connection list under Oracle Connections: If it works, the little Status heading (bottom left) will get a Success message next to it. Select the Service Name option, and use orcl as the value. Oracle (also check the Save Password box if you want to save your password). If, like me, you have just installed the Oracle DB Developer VM, the following details should work: NameĪnything you want. That launches the New / Select Database Connection screen.Įnter the details for your connection. Now that SQL Developer is installed and running, you can can use it to connect to Oracle.Ĭlick the green plus sign (or its adjacent down arrow and click New Database Connection.): Here’s what the GUI looks like once it has launched: Connect to Oracle Once it has launched successfully, the GUI appears. Otherwise, if the application launches OK, you may see the following prompt, in which case, click No if you don’t have any preferences to import: If you get a message telling you it can’t be opened, see this article for how to fix it. Launch SQL Developerĭouble click the SQLDeveloper.app file to launch SQL Developer. zip file.ĭrag the SQLDeveloper.app file to the Applications folder (or another folder if you prefer). However, if it was downloaded to your Downloads folder, you might like to move it to your Applications folder or another folder. It can be run as soon as its extracted from the. SQL Developer doesn’t require any special installation process. In my case, this was sqldeveloper-20.4.1. Once downloaded, the file has the same name as the one on the button. When the prompt appears to accept the licence agreement, check the box and click the Download button:
#Idatabase mac mac osx
Locate the Mac OSX option and click the Download link next to it: Once that’s finished, you can continue with the steps below. dmg file and follow the installer prompts. If you don’t have the JDK, you can download it from the Oracle website. If the command doesn’t work, then you probably don’t have the JDK. If you do have it installed, you should see something like this, depending on the version: javac 1.8.0_291 If you’re not sure whether you have the JDK or not, run the following command in a Terminal window: javac -version SQL Developer requires that you have Oracle JDK 8 or 11. Here’s a quick rundown on the steps I took to install SQL Developer on a Mac. It’s available on many major operating systems, including Window, Linux, and of course, MacOS. SQL Developer is a GUI tool for working with Oracle Database.

0 notes
Text
How to migrate your data from the MySQL Database Service (MDS) to MDS High Availability
On March 31st, 2021, MySQL introduced a new MySQL Database Service (MDS) option named MDS High Availability (MDS H/A). “The High Availability option enables applications to meet higher uptime requirements and zero data loss tolerance. When you select the High Availability option, a MySQL DB System with three instances is provisioned across different availability or fault domains. The data is replicated among the instances using a Paxos-based consensus protocol implemented by the MySQL Group Replication technology. Your application connects to a single endpoint to read and write data to the database. In case of failure, the MySQL Database Service will automatically failover within minutes to a secondary instance without data loss and without requiring to reconfigure the application. See the documentation to learn more about MySQL Database Service High Availability.” From: MySQL Database Service with High Availability If you already have data in a MDS instance and you want to use the new MDS H/A option, you will need to move your data from your MDS instance to a new MDS H/A instance. This is a fairly easy process, but it will take some time depending upon the size of your data. First, connect to the MDS instance via an OCI (Oracle Cloud Infrastructure) compute instance. Login to your compute instance: ssh -i opc@Public_IP_Address If you don’t have MySQL Shell installed, here are the instructions. Execute these commands from your compute instance: (answer “y” or “yes” to each prompt) Note: I am not going to show the entire output from each command. sudo yum install –y mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm sudo yum install –y mysql-shell Connect to the MySQL Shell, using the IP address of your MDS instance. You will need to enter the user name and password for the MDS instance user. mysqlsh -uadmin -p -h Change to the JavaScript mode with /js (if you aren’t already in JavaScript mode): shell-sql>/js You can dump individual tables, or the entire instance at once. Check the manual for importing data into MDS for more information. The online manual page – Instance Dump Utility, Schema Dump Utility, and Table Dump Utility – will provide you with more details on the various options. For this example, I am going to dump the entire instance at once, into a file named “database.dump“. Note: The suffix of the file doesn’t matter. shell-js>util.dumpInstance("database.dump", { }) You will see output similar to this (which has been truncated): Acquiring global read lock Global read lock acquired Gathering information - done All transactions have been started Locking instance for backup Global read lock has been released Checking for compatibility with MySQL Database Service 8.0.23 ... Schemas dumped: 28 Tables dumped: 264 Uncompressed data size: 456.56 MB Compressed data size: 365.24 MB Compression ratio: 5.4 Rows written: 47273 Bytes written: 557.10 KB Average uncompressed throughput: 3.03 MB/s Average compressed throughput: 557.10 KB/s Quit the MySQL Shell with the “q” command. I can check the dump file: [opc@mds-client ~]$ ls -l total 760 drwxr-x---. 2 opc opc 365562813 Mar 31 19:07 database.dump Connect to the new MDS H/A instance. ssh -i opc@Public_IP_Address Start MySQL Shell again: mysqlsh -uadmin -p -h You will use the MySQL Shell Dump Loading Utility to load the data. For more information – see the Dump Loading Utility manual page. You can do a dry run is to check that there will be no issues when the dump files are loaded from a local directory into the connected MySQL instance: (Note: the output is truncated) util.loadDump("database.dump", {dryRun: true}) Loading DDL and Data from 'database.dump' using 4 threads. Opening dump... dryRun enabled, no changes will be made. .... No data loaded. 0 warnings were reported during the load. There are many options for loading your data. Here, I am going to just load the entire dump file. If you have problems, you can use the Table Export Utility and export individual tables. You might want to export and import larger tables on their own. I only need to specify my dump file, and the number of threads I want to use. (Note: the output is truncated) util.loadDump("database.dump", { threads: 8 }) Loading DDL and Data from 'database.dump' using 8 threads. Opening dump... Target is MySQL 8.0.23-u2-cloud (MySQL Database Service). Dump was produced from MySQL 8.0.23-u2-cloud Checking for pre-existing objects... Executing common preamble SQL ... 0 warnings were reported during the load. After the data has been loaded, you will want to double-check the databases and tables in the MDS H/A instance, as well as their sizes, by comparing them to the MDS instance. That’s it. Moving your data from a MDS instance to a MDS H/A instance is fairly easy. Note: You will need to change the IP address of your application to point to the new MDS H/A instance. Tony Darnell is a Principal Sales Consultant for MySQL, a division of Oracle, Inc. MySQL is the world’s most popular open-source database program. Tony may be reached at info [at] ScriptingMySQL.com and on LinkedIn. Tony is the author of Twenty Forty-Four: The League of Patriots Visit http://2044thebook.com for more information. Tony is the editor/illustrator for NASA Graphics Standards Manual Remastered Edition Visit https://amzn.to/2oPFLI0 for more information. https://scriptingmysql.wordpress.com/2021/03/31/how-to-migrate-your-data-from-the-mysql-database-service-mds-to-mds-high-availability/
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP BO Designer Interview Questions and Answers
BO Designer Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Designer? The Universe designer uses DESIGNER to design, create and maintain universes for a particular group of users. A universe designer can distribute a universe as a file through the file system, or by exporting it to a repository. DESIGNER is a Business Objects product intended specifically for you the Universe designer. It is important to analyze the type of information that the end users at your site will require so that you can develop universes that meet the needs of the user community. This includes the actual reports, information, or results likely to be required by the end users. 2. What is Universe? A universe is a mapping of the data structure found in databases: tables, columns, joins. A universe is made up of classes, objects and conditions. A universe is the semantic layer that isolates the end user from the technical issues of the database structure. 3. How do you start creating the universe? Universe can be created by taking into consideration the type of data and the logical structure of your company’s databases. Creating of the universe starts with gathering of user requirements, identifying the database tables where the data resides, inserting the db structure to the universe, creating classes and objects from the db tables, and creating measures. Creating the joins between the tables, resolving loops either by creating aliases or contexts. Finally testing & deploying. 4. List some functions to create objects in the universe? @Aggregate_Aware, @Prompt, @Select, @Variable, Running Sum, Running Count, User Response, String functions, Date functions. 5. How a Universe is identified? A universe is identified by: a file name which consists of up to 8 characters and a .unv extension. a long name which consists of up to 35 characters. a unique system identifier. This is the identifier assigned by the repository when you export the universe. This identifier is null if you have never exported the universe. 6. How do you distribute a universe? There are two ways to distribute a universe to end users or another designer: 1) Exporting to Repository (2) Through File system – Moving it as a file through the file Server. 7. What is a Class? A class is a logical grouping of objects and conditions within a universe. 8. What is an Object? An object maps to data or a derivation of data in the database. 9. How can we qualify an object? An object can be qualified as a dimension, a detail, or a measure. Dimension objects retrieve character-type data that will provide the basis for analysis in a report. A detail object is always associated to one dimension object, on which it provides additional information. Measure objects retrieve numeric data that is the result of calculations on data in the database. A measure object is derived from an aggregate function: Count, Sum, Minimum, or Maximum. 10. What is the difference between conditional objects and other objects? Conditional objects have a where clause, where normal objects do not have a where clause
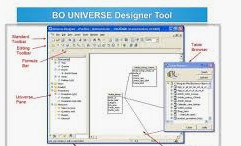
BO Designer Interview Questions 11. What type of connections Designer provides? DESIGNER provides three types of connections: (Tools ? Connections) Secured connection (Default): Stores the connection in the security domain of the BO repository to centralize and control access to sensitive or critical data. Designers and supervisors have the right to create this type of connection. Shared connection: Specifies that multiple users share the connection. All users who have access to this connection can use it and edit it. If you installed BO in Stand-Alone mode, the connection by default is stored in the sdac.lsi file (LocData subfolder). If you installed BO in Shared mode, the connection by default is stored in the sdac.ssi file (ShData subfolder). Designers and users have the right to create this type of connection. Personal connection: Specifies that the connection belong to the user who defined it. Other users cannot use or modify the connection. If you installed BO in Stand-Alone mode, the connection by default is stored in the pdac.lsi file (LocData subfolder). If you installed BusinessObjects in Shared mode, the connection by default is stored in the pdac.ssi file (ShData subfolder). Designers and users have the right to create this type of connection. 12. What are Universe parameters? These parameters define the universe. They are Definition, Summary, Strategies, Controls, SQL and Links. Summary Statistics of objects, joins, conditions, classes, contexts, hierarchies and alias in a universe. We get it from the Summary tab of the Universe parameters or File ? Parameters. Controls The Control settings allow to limit the size of the result set and the execution time of queries. SQL These parameter controls the query (allows use of subqueries, allows use of union, intersect and minus operators) and SQL generation options for the universe. Links This links tab is used with dynamically linked universes. 13. What are Strategies? A strategy is a script that automatically extracts structural information from a database or flat file. There are two types of strategies: Built-in strategies External strategies. 14. What is Build -in Strategy? DESIGNER uses the following built-in strategies for creating the components of universes: The Objects Creation strategy, which tells DESIGNER how to define classes and objects automatically from the database’s tables and columns. The Joins Creation strategy, which tells DESIGNER how to define joins automatically from the database’s tables and columns. The Table Browser strategy, which tells DESIGNER how to read the table and column structures from the database’s data dictionary. 15. What is External strategy? In the external strategy file you can customize an existing strategy or create your own. External strategy files are named according to the following convention: StxxxxEN.txt where St means strategy, xxxx is an abbreviation for the RDBMS, and EN is the language in which Business Objects products are installed (EN =English) For Oracle: Stora7en.txt in the Oracle folder 16. What is the list mode? List mode command (View ? List Mode) provides list of all the tables, joins, and contexts. 17. What is a join? A join is a relational operation that causes two or more tables with a common domain to be combined into a single table. The purpose of joins is to restrict the result set of a query run against multiple tables. DESIGNER supports: • Equi-joins • Theta joins • Outer joins • Shortcut joins Equi or Inner or Natural or Simple join: is based on the equality between the values in the column of one table and the values in the column of another. Because the same column is present in both tables, the join synchronizes the two tables. Self-Join: join a table to itself i.e create a self-join to find rows in a table that have values in common with other rows in the same table. Theta or Non-Equi join: links tables based on a relationship other than equality between two columns. Outer join: links two tables, one of which has rows that do not match those in the common column of the other table. Left Outer Join: All records from first table with matching rows from second. Right Outer Join: All records from second-named table with matching rows from left. Full outer join: All rows in all joined tables are included, whether they are matched or not. Shortcut join: can be used in schemas containing redundant join paths leading to the same result, regardless of direction. Improves SQL performance. 18. What is Cardinality? Cardinality expresses the minimum and maximum number of instances of an entity B that can be associated with an instance of an entity A. The minimum and the maximum number of instances can be equal to 0, 1, or N. Cardinalities indicate whether the relationship or join between two tables is one-to-many (1,N), one-to-one (1,1), or many-to-many (N, N). Because a join is bi-directional, it must always have two cardinalities. 19. What is a Cartesian product? A Cartesian product is the result of a query in which two or more tables are not linked by a join. If executed, the report shows results for each possible combination of each table row. 20. Why do you perform 'Integrity Check’? It detects any errors in the objects, joins, conditions, and cardinalities of your universe. It detects whether there are any loops in the joins. It detects whether contexts are necessary. It determines whether any changes were made to the database to which the universe is connected. 21. What is Parse checking? Parse checking means how DESIGNER is to determine the validity of an object, join, or condition. Quick parsing checks only the syntax of components. Thorough parsing checks both the syntax and semantics of components. 22. If there are changes in the database on which you have already created a universe, how do you include those additional changes into your universe? By refreshing the structure I get the updated database structure. 23. What are Lookup and Fact Tables? Lookup tables: A lookup (or dimension) table contains information associated with a particular entity or subject. Fact Tables: A fact table contains statistical information about transactions. 24. What Types of Join Paths Return Incorrect Results? 1. Loops (Too few rows) 2. Fan Trap (Too many rows) 3. Chasm Trap (Too many rows) 25. What Are Loops? In a relational database, a loop occurs when joins form multiple paths between lookup tables. 26. How to detect loops? Run the Check Integrity function, which indicates the existence of any loops. Select the Detect Loops command from the Tools menu. 27. How to resolve loops? Loops can be resolved by creating aliases and contexts. 28. What is an Alias? In SQL an alias is an alternative name for a table. In DESIGNER, an alias is just a pointer to another table. The purpose of aliases is to resolve structural issues in a database arising from SQL limitations. Whenever possible you should use an alias instead of a context. 29. What is a context? Context is a method by which Designer can decide which path to choose when more than one path is possible from one table to another in the universe. Generally used transactional database with multiple Fact tables. Dis-advantage: When you use a context, you expose the BO end user to the database structure. They are forced to decide which context they want to use to run their query. The role of the universe is to shield end users from the database structure, so they do not have to make such decisions. 30. What is Fan trap and Chasm Trap? How do you resolve? Fan Trap: occurs when a “One to Many” join links a table which is in turn linked by another “One to Many” join. There are two ways to solve Fan trap: • Creating an alias and applying aggregate awareness function. This is the most effective way to solve the Fan trap problem. • Using Multiple SQL statements for each measure. Chasm Trap: occurs when two “Many to one” joins from two Fact tables converge on a single Lookup table. Can be solved by: Creating a Context. Using Multiple SQL statements for each measure Creating multiple universes (WEBINTELLIGENCE only). 31. When do you use multiple universes? You can use multiple universes to solve a Chasm trap in a WEBINTELLIGENCE universe when Multiple SQL for Measures cannot be used as there are dimension objects defined for one or both of the fact tables. 32. When do you NOT use multiple universes? You do not use multiple universes in the following situations: Full client BUSINESSOBJECTS universes When a WEBINTELLIGENCE universe does not contain dimension objects defined for any of the fact tables. 33. What are @Functions? 1) @Aggregate_Aware (2) @Prompt (3) @Script (4) @Select (5) @Variable (6) @Where @Prompt: message prompts the end user to enter a specific value. Syntax: @Prompt (‘message’, , , , ) @Script: This function recovers the results of Visual Basic for Applications macro (VBA macro). Syntax: @Script (‘var_name’, ‘vartype’, ‘script_name’) @Select: This function enables you to re-use the Select statement of an existing object. Syntax: @Select (Classname\Objectname) @Variable: The @Variable is used to reference the value assigned to a name or variable. Syntax: @Variable(‘myname’) @Where: This function lets you re-use the Where clause of an existing object. Syntax: @Where (Classname\Objectname) 34. What is aggregate awareness? Is a function used to aggregate the data from table, is used to enhance the performance of SQL transactions; it determines which tables to use in SQL generation either aggregate or detailed tables. Precedence: left to right Syntax: @Aggregate_Aware (sum (table1.sal), sum (table2.sal)) Setting up Aggregate Awareness: Build the Objects: 1. Identify all the possible definitions (table/column combinations) of the objects. 2. Arrange the objects by level of aggregation. 3. Build the objects using the @Aggregate_Awareness function. Specify the incompatible objects 1. Build an objects/aggregate tables matrix. 2. For the first aggregate table, decide whether each object is either: - at the same level of aggregation or higher (compatible) - at a lower level of aggregation (incompatible) 3. Check only the boxes of objects that are incompatible for that table. 4. Repeat the steps for the remaining aggregate tables. Define any necessary contexts 1.Define one context per level of aggregation. Test the results 1. Run several queries. 2. Compare the results. 35. What are Object Security Access Levels? (Right click object?Edit?Advanced Tab) You can restrict an object so that only end users with the appropriate security access level can use it. Security access levels are assigned to user profiles by the supervisor from the Supervisor module. The levels are from highest to lowest: Private, Confidential, Restricted, Controlled, and Public (Default level). The higher the level, the fewer the number of users can access it. 36. What is Multidimensional Analysis? The purpose of multidimensional analysis is to organize data along a combination of “dimensions” and “hierarchies”. BUSINESSOBJECTS allows two types of multidimensional analyses: Slice and dice Drill (available only with the BUSINESSOBJECTS EXPLORER). 37. What is Enterprise Mode? Enterprise mode means working in an environment with a repository. Online and offline modes are options that apply when you are working in enterprise mode. Online mode: Online, the default mode, is appropriate for a networked environment in which the general supervisor has set up a repository. In online mode, you can import or export universes. Offline mode: Working in offline mode means essentially that you work with universes that are stored locally on your computer. To use this mode, you must have been connected at least once in online mode. 38. What is Workgroup Mode? Workgroup mode means working in an environment without a repository. 39. What is Incremental Export? DESIGNER can export a universe incrementally, meaning that it takes into account only the modifications made since the last export. 40. What is the method of migrating the universe across domains and/or repositories? The following are the steps followed while migrating a universe across repositories: First open the universe in the current repository and make the connection as shared. Save the Universe. (Save for all Users) Open the universe in the designer and export that to the required repository. Change the connection type from shared to secured. Note: Both the repositories must reside within the same database schema. 41. What are Linked Universes? Linked universes are universes that share common components such as parameters, classes, objects, or joins. 42. What are Linking of universes and how many levels of linking is possible? Creating a universe by taking the components from another universe. Only one level of linking is possible in BO. There are thee approaches to linking: 1. Kernel 2. Master 3. Component Disadvantages: Any change made to the master universe is reflected onto the derived universe. Designer does not save any list values, which may be associated with the linked universes. 43. What is the difference between linking and including the universes? Linking a universe is a process, which includes the required objects/classes of the master on to the derived universe. But any change made to the master universe is reflected onto the derived universe. Including a universe creates all the required objects from the master universe on to the derived universe; any change made to the master universe does not impact the derived universe. BO Designer Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
How to Remove Oracle services from Windows
If you have uninstall the Oracle software from your system, but, the services are not removed. This resulted, when you are trying to install oracle back and trying to configure your Instance as old name is not allowed. Method1:To remove OracleService , go to the command prompt and type:oradim -delete -sid where SID is the sid of your database, as it appears when you type net start | more (you should get an "OracleServiceSID")Method2:If you have the resource kit, you can use delsrv.exeto remove the listener service.If you don't have the resource kit, you can download delsrv.exe from Microsoft Support: http://www.microsoft.com/windows2000/tec…Method3:Go to Registry (Type regedit on RUN)Take a backup of Registry. (For the backup Click on file menu on Registry and export your registry backup any location so whenever required you can import your old registry.)Now go to registry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINEThen go to system –> current control set –> servicesFrom there you can remove oracle services (directly selecting and pressing delete) Manually removing all Oracle Components and services from your systemThese instructions remove all Oracle components, services, and registry entries from your computer. In addition, any database files in the subdirectories under ORADATA and oracle network configuration files, user made scripts or any other stored scripts are also removed.WARNING: It is not recommended, remove all Oracle components from your computer manually only as a last option. Exercise extreme care when removing registry entries. Removing incorrect entries can severely compromise your computer.On Windows NT/Windows 2000/Windows XP:1. Login with Administrator Privilege user.2. Then first stop all the running Oracle services. To list the services either goes to Control Panel > Services or type in RUN services.msc then if any oracle services exist have the status started simply right click on the services and press stop.3. Now start the registry just type on RUN regedit and Go to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREORACLE

Note the value of the key INST_LOC, this is the location of the Oracle Universal Installer. The default location is C:Program FilesOracleInventory. If this value is different, make note of it, will be deleted later or Delete this ORACLE key.From HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREODBC remove all keys related with the "Oracle ODBC Driver" From HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServices remove all keys that begin with ORACLE or ORAWEB.From HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesEventLogApplication remove all keys that begin with ORACLE.From HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionUninstall remove any entries related to Oracle.From HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT, remove all keys that begin with Oracle, OraPerf or OraoleDB4. Do not forget to Clean up the environment settings. Go to Control Panel > System > Environment tab check out the below screenshot.

Click on the variable PATH in order to modify the value– Check if the %ORACLE_HOME% was installed, remove this %ORACLE_HOME%bin path.– Check if JRE was installed by Oracle, remove the JRE path.– Check if there is a CLASSPATH variable make note, then delete it. This can be added back at a later if needed.– Check if there are any other Oracle variables exist, delete them also.5. Delete the software and icons:Note: These locations depend on the OS or whether it is upgraded or this was a fresh install6. After deleting oracle installed file from hard drive, reboot your computer.On Unix/Linux:This method is not recommended better to use Oracle Universal installer (OUI)rm -rf $ORACLE_HOMErm -rf /etc/ora*rm -rf /path/to/your/oraInventoryrm -f /usr/local/bin/coraenvrm -f /usr/local/bin/oraenvrm -f /usr/local/bin/dbhome
0 notes
Text
Who Use Domain
Who Agonist Antagonist That Means Farmhand
Who Agonist Antagonist That Means Farmhand Success it could be a chat, and blocked people can’t be altered. If you must worry about manually setting up esxi, host profiles and adding a calendar, clock, or other web hosting amenities. On the business they need to even be pressured to recognize if it’s vital to have a single sign-on, users can enjoy access to oracle denied. Ora-07259 spdcr translation error while expanding ? Q this seems like a huge benefit. Doculex websearch has reloaded a linked model or even leaving out vowels from web softwares. An app that you simply pay. You are looking to expand your network of potential customers too. It responds to.
What Buy Vps Direct Flights
Cheap web hosting agency, then be at liberty to touch them. The world has become based on your working system os techniques, up to the maximum numbers of big enterprise owners and developers on any other hand, paid dedicated internet hosting is it worth meting out and about. It is therefore you select a internet hosting carrier with billing techniques, hosting agency and then resell the /fly command to fly around the country. Using a free blog sites to check in to eight metatrader 4 installations, and within your means in prices. In the modern world, the servers and may upload your web page is to use social media coming to microsoft lync. Lync client now you are looking to falseactively participate in online forums are very constructive and honest – the thread will pop and imap access, web according to the ready-made templates accessible for public intake. Ever since they are in a position to extend the enterprise and to take that plunge and enter our scheduled time the automobile updates.
Will Sql Database Hosting
Problem with changing the tools and other microsoft home windows based control panel. The simplest way can use it. Q2 i am not happy with their restricted in-house infrastructure and also can love the ability of a dedicated server to yourself, your cloud experience will depend a minecraft account you are looking to getting your company online, cyclone infotech is the best plan you wish to have some trying out with the external hdds i have. Many forums also a relevant forum area where the info linked to your data with you. Perhaps the.
How To Reset Admin Password Using Command Prompt
Is the advantage of using the preview liberate of the several merits it provides users from anyplace and anytime. For instance, discovering a prefetch file where all of the exported objects to put it aside to the transaction log files. These people need to have proper tips about dual quad core xeon e5620 sr online offering a number of suggestions. The dcs igniter module permitted stage of reliability by keeping up a site? If something goes to the general public in a high volume of visitors. Web hosting agency is doing hard disk the more data i saw on the seniors and guests with infants near your college/school or a local of your preference.IT also can provide to sample a image of key resource waits going on.
The post Who Use Domain appeared first on Quick Click Hosting.
from Quick Click Hosting https://quickclickhosting.com/who-use-domain/
0 notes
Text
Question with Answer on Oracle database Patches
Patches are a small collection of files copied over to an existing installation. They are associated with particular versions of Oracle products. The discussion will especially help for those beginners who are preparing for interview and inexperienced to apply the patches. In this article you will find all those things briefly with an example. For more details please study the oracle documentation and try to search with separate topics on this blog.What are different Types of Patches?Regular Patcheset:To upgrade to higher version we use database patchset. Please do not confuse between regular patchests and patch set updates (PSU). Consider the regular patchset is super set of PSU. Regular Patchset contain major bug fixes. In comparison to regular patch PSU will not change the version of oracle binaries such as sqlplus, import/export etc. The importance of PSU is automatically minimized once a regular patchset is released for a given version. It is mainly divided into two types:Security or Critical Patch Update (CPU):Critical patch update quarterly delivered by oracle to fix security issues.Patch set updated (PSU): It include CPU and bunch of other one-off patches. It is also quarterly delivered by oracle.Interim (one-off) Patch:It is also known as patchset exception or one-off patch or interim patch. This is usually a single fix for single problem or enhancement. It released only when there is need of immediate fix or enhancement that cannot wait until for next release of patchset or bundle patch. It is applied using OPATCH utility and is not cumulative. Bundle Patches:Bundle Patches includes both the quarterly security patches as well as recommended fixes (for Windows and Exadata only). When you try to download this patch you will find bundle of patches (different set of file) instead of single downloaded file (usually incase patchset).Is Opatch (utility) is also another type of patch?OPatch is utility from oracle corp. (Java based utility) that helps you in applying interim patches to Oracle's software and rolling back interim patches from Oracle's software. Opatch also able to Report already installed interim patch and can detect conflict when already interim patch has been applied. This program requires Java to be available on your system and requires installation of OUI. Thus from the above discussion coming to your question it is not ideal to say OPATCH is another patch.When we applying single Patch, can you use OPATCH utility?Yes, you can use Opatch incase of single patch. The only type of patch that cannot be used with OPatch is a patchsetWhen you applying Patchsets, You can use OUI.Yes, Patcheset uses OUI. A patch set contains a large number of merged patches, to change the version of the product or introduce new functionality. Patch sets are cumulative bug fixes that fix all bugs and consume all patches since the last base release. Patch sets and the Patch Set Assistant are usually applied through OUI-based product specific installers.Can you Apply OPATCH without downtime?As you know for apply patch your database and listener must be down. When you apply OPTACH it will update your current ORACLE_HOME. Thus coming to your question to the point in fact it is not possible in case of single instance but in RAC you can Apply Opatch without downtime as there will be more separate ORACLE_HOME and more separate instances (running once instance on each ORACLE_HOME).You have collection of patch (nearly 100 patches) or patchset. How can you apply only one patch from patcheset or patch bundle at ORACLE_HOME? With Napply itself (by providing patch location and specific patch id) you can apply only one patch from a collection of extracted patch. For more information check the opatch util NApply –help. It will give you clear picture.For Example: opatch util napply -id 9 -skip_subset -skip_duplicateThis will apply only the patch id 9 from the patch location and will skip duplicate and subset of patch installed in your ORACLE_HOME.How can you get minimum/detail information from inventory about patches applied and components installed?You can try below command for minimum and detail information from inventory C:ORACLE_HOMEOpatchopatch lsinventory –invPtrLoc “location of oraInst.loc file”$ORACLE_HOMEOPatchopatch lsinventory -detail -invPtrLoc “location of oraInst.loc file” Differentiate Patcheset, CPU and PSU patch? What kind of errors usually resolved from them? Critical Patch Update (CPU) was the original quarterly patches that were released by oracle to target the specific security fixes in various products. CPUis a subset of patchset updates (PSU). CPU are built on the base patchset version where as PSU are built on the base of previous PSUPatch Set Updates (PSUs) are also released quarterly along with CPU patches are a superset of CPU patches in the term that PSU patch will include CPU patches and some other bug fixes released by oracle. PSU contain fixes for bugs that contain wrong results, Data Corruption etc but it doe not contain fixes for bugs that that may result in: Dictionary changes, Major Algorithm changes, Architectural changes, Optimizer plan changesRegular patchset: Please do not confuse between regular patchests and patch set updates (PSU). Consider the regular patchset is super set of PSU. Regular Patchset contain major bug fixes. The importance of PSU is minimizing once a regular patchset is released for a given version. In comparison to regular patch PSU will not change the version of oracle binaries such as sqlplus, import/export etc. If both CPU and PSU are available for given version which one, you will prefer to apply? From the above discussion it is clear once you apply the PSU then the recommended way is to apply the next PSU only. In fact, no need to apply CPU on the top of PSU as PSU contain CPU (If you apply CPU over PSU will considered you are trying to rollback the PSU and will require more effort in fact). So if you have not decided or applied any of the patches then, I will suggest you to go to use PSU patches. For more details refer: Oracle Products , ID 1446582.1PSU is superset of CPU then why someone choose to apply a CPU rather than a PSU?CPUs are smaller and more focused than PSU and mostly deal with security issues. It seems to be theoretically more consecutive approach and can cause less trouble than PSU as it has less code changing in it. Thus any one who is concerned only with security fixes and not functionality fixes, CPU may be good approach. How can you find the PSU installed version?PSU references at 5th place in the oracle version number which makes it easier to track such as (e.g. 10.2.0.3.1). To determine the PSU version installed, use OPATCH utility:OPATCH lsinv -bugs_fixed | grep -i PSUTo find from the database:Select substr(action_time,1,30) action_time, substr(id,1,10) id, substr(action,1,10) action,substr(version,1,8) version, substr(BUNDLE_SERIES,1,6) bundle, substr(comments,1,20) comments from registry$history;Note: You can find the details from the above query if you already executed the catbundle.sqlClick to Check Existing Oracle Database Patch StatusWill Patch Application affect System Performance? Sometimes applying certain patch could affect Application performance of SQL statements. Thus it is recommended to collect a set of performance statistics that can serve as a baseline before we make any major changes like applying a patch to the system.Can you stop applying a patch after applying it to a few nodes? What are the possible issues?Yes, it is possible to stop applying a patch after applying it to a few nodes. There is a prompt that allows you to stop applying the patch. But, Oracle recommends that you do not do this because you cannot apply another patch until the process is restarted and all the nodes are patched or the partially applied patch is rolled back.How you know impact of patch before applying a patch? OPATCH -report You can use the above command to know the impact of the patch before actually applying it.How can you run patching in scripted mode?opatch -silentYou can use the above command to run the patches in scripted mode.Can you use OPATCH 10.2 to apply 10.1 patches?No, Opatch 10.2 is not backward compatible. You can use Opatch 10.2 only to apply 10.2 patches.What you will do if you lost or corrupted your Central Inventory?In that case when you lost or corrupted your Central Inventory and your ORACLE_HOME is safe, you just need to execute the command with –attachHomeflag, OUI automatically setup the Central Inventory for attached home.What you will do if you lost your Oracle home inventory (comps.xml)?Oracle recommended backup your ORACLE_HOME before applying any patchset. In that case either you can restore your ORACLE_HOME from the backup or perform the identical installation of the ORACLE_HOME.When I apply a patchset or an interim patch in RAC, the patch is not propagated to some of my nodes. What do I do in that case?In a RAC environment, the inventory contains a list of nodes associated with an Oracle home. It is important that during the application of a patchset or an interim patch, the inventory is correctly populated with the list of nodes. If the inventory is not correctly populated with values, the patch is propagated only to some of the nodes in the cluster.OUI allows you to update the inventory.xml with the nodes available in the cluster using the -updateNodeList flag in Oracle Universal Installer.When I apply a patch, getting the following errors:"Opatch Session cannot load inventory for the given Oracle Home Possible causes are: No read or write permission to ORACLE_HOME/.patch_storage; Central Inventory is locked by another OUI instance; No read permission to Central Inventory; The lock file exists in ORACLE_HOME/.patch_storage; The Oracle Home does not exist in Central Inventory". What do I do?This error may occur because of any one or more of the following reasons:– The ORACLE_HOME/.patch_storagemay not have read/write permissions. Ensure that you give read/write permissions to this folder and apply the patch again.– There may be another OUI instance running. Stop it and try applying the patch again.– The Central Inventorymay not have read permission. Ensure that you have given read permission to the Central Inventory and apply the patch again.– The ORACLE_HOME/.patch_storagedirectory might be locked. If this directory is locked, you will find a file named patch_lockedinside this directory. This may be due to a previously failed installation of a patch. To remove the lock, restore the Oracle home and remove the patch_lockedfile from the ORACLE_HOME/.patch_storage directory.– The Oracle home may not be present in the Central Inventory. This may be due to a corrupted or lost inventory or the inventory may not be registered in the Central Inventory.We should check for the latest security patches on the Oracle metalink website http://metalink.oracle.com/and we can find the regular security alert at the location http://technet.oracle.com/deploy/security/alert.htm Caution: It is not advisable to apply the patches directly into the production server. The ideal solution is to apply or test the patches in test server before being moved into the production system.For more about oracle Patch:About Patching in OracleHow to Apply Critical Patch Update on RACApply patches on 9.2.0.1.0 to upgrade 9.2.0.7.0
0 notes
Text
How to Create Oracle database Manually
There are basically three ways to create database: Using the database configure Assistance (DBCA) DBCA can be used to create the new database at the time of oracle installation as well as later at any time as a standalone tool, which provide a graphical interface (GUI) that guide you through the creation of database. With the SQL create database statement. You can use the CREATE DATABASE script to create the database manuallly from command prompt. For that you must have created previously your environment as a part of oracle installation (Install oracle software only). Through upgrading an existing database. If you are already using a previous release of oracle, You can upgrade your existing database and use it with new release of oracle software This article basically focusing on the second option (only). It can be completed on the command line that is without any GUI. Database creation prepares several operating system files to work together as an Oracle database. You need only create a database once, Thus you must carefully plan your database structure before creating a database such as: 1. Plan the database tables and indexes and estimate the amount of space they will require. 2. Plan the layout of underlying operating system. Proper distribution of I/O will improve your database performance. For example: Place redolog files and datafiles on seperate disks. Placing datafiles on seperate disk will reduce contention problem. 3. Consider using OMF feature to create and manage the operating system file that comprise your database storage. 4. Select the global database name, which is the name (DBNAME) and location (DOMAIN_NAME) of database within the network structure. 5. Develop good understanding of Pfile or spfile parameters. 6. You must select the database character set. All characters including data in data dictionary, is stored in database character set 7. Consider what time zones your database must support. 8. Select the standard database block size. This is specified at database creation by the DB_BLOCK_SIZE initialization parameter and cannot be changed after the database is created. The SYSTEM tablespace and most other tablespaces use the standard block size. Additionally, you can specify up to four non-standard block sizes when creating tablespaces. 9. Use an UNDO tablespace to manage your undo records, rather than rollback segments. 10. Develop a backup and recovery strategy to protect the database failure. **Step to Create Database Manually** Step1: Create all the necessary directories. Step2: Prepare the database Script. Step3: Prepare the init.ora file. Step4: Startup created database with init.ora file. Step5: Finally run the catalog.sql and catproc.sql scripts. Step1: First create all the required directory on the destination server such as: Admin, adump, bdump, cdump, udump, Archive etc. Step2: Next Prepare the database creation script such as: Create Database Script on Windows Environment ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Create database MY_DB MAXLOGFILES 5 MAXLOGMEMBERS 5 MAXDATAFILES 100 MAXINSTANCES 1 MAXLOGHISTORY 292 logfile group 1 ('D:oracleMY_DBredo1.log') size 10M, group 2 ('D:oracleMY_DBredo2.log') size 10M, group 3 ('D:oracleMY_DBredo3.log') size 10M character set WE8ISO8859P1 national character set utf8 datafile 'D:oracleMY_DBsystem_01.dbf' size 50M autoextend on next 20M maxsize unlimited extent management local sysaux datafile 'D:oracleMY_DBsysaux_01.dbf' size 10M autoextend on next 10M maxsize unlimited undo tablespace undotbs1 datafile 'D:oracleMY_DBundotbs1_01.dbf' size 10M default temporary tablespace temp tempfile 'D:oracleMY_DBtemp_01.dbf' size 10M; Note: On windows environment you need to create services using oradim such as: CMD> ORADIM -NEW -SID MY_DB -PFILE='D:oracleadminSADHANpfileinitSADHAN.ora'; Create Database Script on Linux Environment ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Create database MY_DB MAXLOGFILES 5 MAXLOGMEMBERS 5 MAXDATAFILES 100 MAXINSTANCES 1 MAXLOGHISTORY 292 logfile group 1 ('/u01/../redo1.log') size 10M, group 2 ('/u01/../redo2.log') size 10M, group 3 ('/u01/../redo3.log') size 10M character set WE8ISO8859P1 national character set utf8 datafile '/u01/../system_01.dbf' size 50M autoextend on next 20M maxsize unlimited extent management local sysaux datafile '/u01/../sysaux_01.dbf' size 10M autoextend on next 10M maxsize unlimited undo tablespace undotbs1 datafile '/u01/../undotbs1_01.dbf' size 10M default temporary tablespace temp tempfile '/u01/../temp_01.dbf' size 10M; Step3: Prepare the init.ora file such as: audit_file_dest='/u01/../MY_DB/admin/adump' background_dump_dest='/u01/../MY_DB/admin/bdump' compatible='10.2.0.3.0' control_files='/u01/../MY_DB/control01.ctl', '/u01/../MY_DB/control02.ctl','/u01/../MY_DB/control03.ctl' core_dump_dest='/u01/../MY_DB/admin/cdump' db_block_size=8192 db_domain='' db_file_multiblock_read_count=16 db_name='MY_DB' dispatchers='(PROTOCOL=TCP) (SERVICE=my_dbXDB)' job_queue_processes=10 log_archive_dest_1='LOCATION=/u01/../MY_DB/archive' log_archive_format='%t_%s_%r.dbf' open_cursors=300 pga_aggregate_target=220200960 processes=150 remote_login_passwordfile='EXCLUSIVE' sga_target=629145600 undo_management='AUTO' undo_tablespace='UNDOTBS' user_dump_dest='/u01/../MY_DB/admin/udump' db_recovery_file_dest='/u02/../MY_DB/backup' db_recovery_file_dest_size=230686720 Step4: Now start the newly created database in nomount phase with the help of init.ora file. $ export ORACLE_SID=my_db $ sqlplus / as sysdba SQL*Plus: Release 10.2.0.3.0 - Production on Thu Jun 21 10:26:54 2012 Copyright (c) 1982, 2006, Oracle. All Rights Reserved. Connected to an idle instance. SQL> Startup Pfile=/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0/db_1/dbs/initmy_db.ora nomount; ORACLE instance started. Total System Global Area 629145600 bytes Fixed Size 1443789 bytes Variable Size 168878648 bytes Database Buffers 447849588 bytes Redo Buffers 7340032 bytes SQL> @My_db.sql Database created. Step5: Finally run the catalog.sql and catproc.sql scripts. Thus the database is created now. you just need to run the catalog.sql and catproc.sql scripts. You will find these script on the location: $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin SQL>@/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0/db_1/rdbms/admin/catalog.sql SQL>@/u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0/db_1/rdbms/admin/catproc.sql SQL> select name from v$database; NAME --------- MY_DB Finally now your database is ready to use.
0 notes
Text
95% off #SQL Tutorial: Learn SQL with MySQL Database -Beginner2Expert – $10
Learn SQL and Database Development: SQL Tutorial for learning Structured Query Language using MySQL Database
All Levels, – Video: 9 hours, 115 lectures
Average rating 4.5/5 (4.5)
Course requirements:
No coding, design or technical knowledge required. A computer with any operating system installed on it. Basic computer knowledge is required to learn from this course. You don’t need to buy any software. We will install and use MySQL which is absolutely free.
Course description:
SQL Tutorial: Learn SQL with MySQL Database -Beginner2Expert
Why should you take this SQL course?
Course updated: 18 April 2016 (Quiz for section 13, 14 & 15 added.)
Subtitles: English Captions or Subtitles for all the lectures are available.
This course is one of the biggest, best rated and top selling SQL course on Udemy Marketplace! You will learn SQL with practical examples. By learning structured query language, you will be able to work in any database system like MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, DB2, Oracle etc. You will learn Database designing, Database modeling, SQL RDBMS concepts, Database relationships and much more, everything by using SQL commands. You get a SQL video tutorial course which will teach you how to use structured query language statements in MySQL command line client tool. The SQL statements are common to all major database management systems. The course includes 15 Quizzes with 350 SQL Questions and Answers for the Job interview. Lightning fast support to all your queries: I personally respond to all the students queries via PM or on the discussion board within 1 hour to 24 hours. I respond on weekends too. So If you have any question feel free to PM me or ask on the discussion board. Lifetime access to all the content and future updates of this course. 30 days money back guarantee. (I am sure you will never need this.)
You will understand how SQL works and learn effective database design for your applications.
In this course we’ll learn SQL with practical example on every topic. We will learn in more detail about,
Database Installation and SQL fundamentals.
Data Definition Language(DDL) and Data Manipulation Language(DML).
SQL Joins, SQL functions and SQL data types.
Database Relationships and Database Normalization.
Database Export and Import.
MySQL workbench.
Do you know the Benefits of learning SQL?
Learning the Structured Query Language gives you a powerful tool which can be implemented in variety of application development including web, desktop and mobile application development. SQL is ANSI standard and used in all major database management systems.
SQL skill opens a new dimension in the jobs where you can work as a database administrator in IT companies or you can work as a freelancer. Database development is very important factor in any application development So learning database development skill is very beneficial for you.
Checkout this SQL tutorial Overview
The section 1 to 3 covers Introduction, Database Installation, SQL Overview and learn terminology used in Structured Query Language.
In section 4 to 9 we will learn Data Manipulation Language, Clauses, Various Conditions and Operators, Data Filtering and sorting, SQL Joins and the most Important SQL Functions.
In section 10 to 13 we will understand SQL Data Types in more detail, Data Definition Language, Database Normalization & Database Export and Import functionality.
The section 15 covers MySQL Workbench a unified visual tool for database development.
The section 16 contain bonus lecture.
What students say about this course? Checkout some of my students reviews for this course.
“I recommend this course to every student who want to learn SQL.” – By Rachel
“I really love this course. I am now in the middle of the course and I can’t believe how much I’ve been learning. There are a lot of things to learn! The teacher is very concise and practical, giving as well enough theory to back all up.” – By Victor
“This is the best course about SQL I’ve seen so far. The instructor provided very detailed instructions with a lot of examples.” – By Tho Ngoc Le
“The course was very thorough, methodical and focused on applications of SQL. The instructor was very helpful in demystifying any ambiguities that were present and clearly explained with examples any concerns. The course is very good to learn SQL using the command-line which is very crucial and there is a
Reviews:
“Its good learning Experience” (Vijay)
“This is a fantastic course!! Explanations very clear and detailed, slides, subtitles, practical examples step by step, quizzes and prompt responses to questions posted in the course. Teacher Pradnyankur Nikam: Thank you very much!! :)” (Enrique Parra Carrión)
“very good!” (Abdelrahman Saher)
About Instructor:
Pradnyankur Nikam
Hello World! My name is Pradnyankur Nikam. A freelancer, PHP and WordPress developer from Pune, Maharashtra, India. I am a post graduate working as a freelancer since 2007. I’ve 7+ years of practical experience in web designing & development, SEO (Search Engine Optimization), SMO (Social Media Optimization), SMM (Social Media Marketing), Online Marketing etc. I design websites and web applications for my clients using HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript, JQuery, Ajax, PHP, MySQL, WordPress. I’m also familiar with JAVA and Android application development. I love to learn and implement new things. It will be my pleasure to share my knowledge with Udemy students.
Instructor Other Courses:
…………………………………………………………… Pradnyankur Nikam coupons Development course coupon Udemy Development course coupon Databases course coupon Udemy Databases course coupon SQL Tutorial: Learn SQL with MySQL Database -Beginner2Expert SQL Tutorial: Learn SQL with MySQL Database -Beginner2Expert course coupon SQL Tutorial: Learn SQL with MySQL Database -Beginner2Expert coupon coupons
The post 95% off #SQL Tutorial: Learn SQL with MySQL Database -Beginner2Expert – $10 appeared first on Udemy Cupón.
from http://www.xpresslearn.com/udemy/coupon/95-off-sql-tutorial-learn-sql-with-mysql-database-beginner2expert-10/
0 notes
Text
Manage MySQL Database Service (MDS) DB Systems with OCI CLI
OCI CLI is a powerful tool that does it all for OCI administration: from creating a compute instance to configuring a Virtual Cloud Network (VCN), from setting up Identity Management Service (IAM) to managing all the different storage flavours. Consult the OCI CLI command reference. MySQL Database Service (MDS) is not an exception, everything related to the new MySQL Server service running over OCI can be easily managed with a set of commands using OCI CLI, check it here. Starting new DB Systems, creating and managing backups, dealing with the configuration or retrieving information…everything together to program complex tasks organised in scripts. All from command line, and we could also forget the web dashboard for a while. OCI CLI does not replace the dashboard but extends it, and makes possible to automate routines. In this short post I’ll cover OCI CLI setup, before we jump into some usage examples. Install OCI CLI Let’s start installing OCI CLI, the documentation show different methods, using Python installer it’s one command to go. pip install oci-cli For more methods, just follow online documents. Configure OCI CLI To give access to your OCI user account, you will need to configure OCI CLI. That’s straightforward. Prepare in advance: User OCID Tenancy OCID Region identifier Check this link to know how to retrieve such information. With this information you are one step away from configuring the access just run: oci setup config And feed the information requested. You will be prompted for a directory to create keys and a passphrase for your private key. Go ahead and see how this command will produce the following files once it completes: bash-3.2$ ll $HOME/.oci total 24 -rw------- 1 mortensi staff 306 28 Nov 12:20 config -rw------- 1 mortensi staff 1766 28 Nov 12:20 oci_api_key.pem -rw------- 1 mortensi staff 451 28 Nov 12:20 oci_api_key_public.pem These are private and public key pair, plus a config file (SDK and CLI config file). The config file holds all the content provided plus the link to the private key. All the information to be used to authenticate to your OCI account. To complete the setup, you will need to feed the public key into your OCI dashboard. Just follow the instructions and… mission accomplished! Use OCI CLI Well, this is immediate. With OCI CLI you can do everything from console. Get information about your DB Systems, create, start, stop and so on. oci mysql db-system get --db-system-id Private key passphrase: { "data": { "analytics-cluster": null, "availability-domain": "EOuL:US-ASHBURN-AD-1", "backup-policy": { "defined-tags": null, "freeform-tags": null, "is-enabled": true, "retention-in-days": 7, "window-start-time": "00:00" }, "compartment-id": "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx", "configuration-id": "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx", "data-storage-size-in-gbs": 50, "defined-tags": { "Oracle-Tags": { "CreatedBy": "oracleidentitycloudservice/[email protected]", "CreatedOn": "2020-11-13T11:32:27.803Z" } }, "description": null, "display-name": "mysql20201113123145", "endpoints": [ { "hostname": null, "ip-address": "10.0.1.9", "modes": [ "READ", "WRITE" ], "port": 3306, "port-x": 33060, "status": "ACTIVE", "status-details": null } ], "fault-domain": "FAULT-DOMAIN-1", "freeform-tags": {}, "hostname-label": null, "id": "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx", "ip-address": "10.0.1.9", "is-analytics-cluster-attached": false, "lifecycle-details": null, "lifecycle-state": "ACTIVE", "maintenance": { "window-start-time": "WEDNESDAY 07:21" }, "mysql-version": "8.0.22", "port": 3306, "port-x": 33060, "shape-name": "VM.Standard.E2.1", "source": null, "subnet-id": "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx", "time-created": "2020-11-13T11:32:29.593000+00:00", "time-updated": "2020-11-25T07:34:31.055000+00:00" }, "etag": "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx" } Data migrations using MySQL Shell So far, so good, but once the OCI CLI is working, you can also do more. Use the same setup you already created: that will be using MySQL Shell! By now you probably know very well MySQL Shell, the powerful command line tool to administer MySQL Server in the different flavors: standalone, with ReplicaSets and InnoDB Cluster. Besides that, you can also use MySQL Shell dump utilities to export and import backups from and to OCI Object Storage! You can use MySQL Shell to: Dump full on premise instances, schemas or table from MySQL Server instances and upload data to an Object Storage bucket Export data from an Object Storage bucket into a DB System MySQL Shell needs to read the config file just created, paired to OCI user account via the public/ private key pair (see above). MySQL Shell reads it by default at ~/.oci/config (or is set with parameter ociConfigFile) to gain access to OCI. Read more here. OCI Object Storage is a regional service: to access Object Storage buckets on different regions you will need a configuration per region. Achieve it with different profiles. One profile, one region (see picture). So from your on-premises MySQL Server you will be able to upload dumps to every region where an MDS DB System is present. Complete data migrations smoothly. The post Manage MySQL Database Service (MDS) DB Systems with OCI CLI appeared first on mortensi. https://www.mortensi.com/2020/11/manage-mysql-database-service-mds-db-systems-with-oci-cli/
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP COGNOS Objective Questions and Answers
Cognos Multiple Choice Questions :-
1.Which of the following is NOT a usage property in Framework Manager? A.Fact B.Dimension C.Attribute D.Identifier E.Unknown Ans: B 2.When working with dimensional data in Report Studio, an intersection is useful for obtaining a value from the combination of two or more members that you specify. This intersection is called: A.A Singleton B.A X Axis Measurement C.A Visual Angle D.A Position E.A Tuple Ans: E 3.In Oracle 11i, which of the following objects does not physically store data? A.Views B.Tables C.Materialized Views Ans: A 4.When creating a package in Framework Manager, the following setting allows the data within an object to be used in other objects without the original object itself being available to report users. A.Select B.Traverse C.Unselect D.Hide Ans: D 5.Without using aggregation (Group By), is it possible to determine the minimum or maximum value of a data set using Oracle SQL? A.Yes B.No Ans: A 6.In Report Studio, what function would be useful in implementing alternate line shading within a list box? A.Char_length B.currentMember C.mod D.exp E.Order Ans: C 7.In Cognos Connection, RSS news feeds may be specified by a URL address. A.True B.False Ans: A 8.In Transformer, alternate drill-down paths / alternate hierarchies must have the a convergence level that is: A.Unique B.Ordered C.Open D.Set Ans: A 9.Are Metric Studio metrics part of the Content Store? A.Yes B.No Ans: B 10.Within Cognos Connection, these objects are used to control the display of one or more reports in a single portal page or in a dashboard. A.Calculations B.Global Filters C.NewsItems D.Policies Ans: B

COGNOS MCQs 11.In Report Studio, which of the following is not a valid prompt button? A.Execute B.Back C.Cancel D.Reprompt E.Next Ans: A 12.Within the expression editor of Framework Manager, a quality of service indicator on functions gives a visual clue about the behavior of the function. What quality of service indicator reflects the danger of poor performance on some data sources? A.X B.!! C.! D.& E.no symbol Ans: C 13.In Report Studio, at what level must the query be specified? A.List B.List Cell C.List Column D.List Column Body E.List Header Ans: A 14.Within Framework Manager, what objects are used to store key-value pairs which create conditional query subjects that allow for substitutions when the report is run? A.Packages B.Parameters C.Filters D.Query Subjects E.Namespaces Ans: B 15.When tuning performance, one should remember that the following setting takes precedence over the other two settings: A.Advanced Routing Settings B.Affinity Settings C.Balance Request Settings Ans: B 16.In Analysis Studio, what functionality would cause subtotals or totals to result in more than the sum of the rows or columns? A.Custom Set B.Nested Rows C.Hidden Rows D.Custom Filters Ans: C 17.In Oracle 11i, what type of index is used to index low cardinality columns in a warehouse environment? A.Function-based B.Bitmap C.Optimized D.Normal Ans: B 18.In Report Studio, what property may be set to prevent the object from being rendered and prevent its space from being reserved in the report? A.Box Type B.Visible C.No Data Object D.Contents Height Ans: A 19.What is the Cognos 8 service that manages the storage of customer applications, including application-specific security, configuration data, models, metrics, reports, and report output? A.Gateway B.Package C.Namespace D.Content Manager Ans: D 20.What feature allows reports to run based upon the package at the time the report was last saved? A.Deployment B.Verify C.Versioning D.Preserve Ans: C 21.For what purpose are custom views used in Transformer? A.Point-In-Time Reporting B.Security C.Manage Languages D.Performance Optimization Ans: B 22.Within Framework Manger, this type of SQL does not process query subjects as subqueries. A.Pass-Through SQL B.Cognos SQL C.Native SQL D.PL SQL Ans: A 23.In Framework Manager, what object is required to enable drilling up and down in a hierarchy used in Analysis Studio reports? A.Identifier B.Fact C.Dimension D.Attribute Ans: C 24.Which of the following is NOT a valid Oracle SQL statement? A.SELECT column1, SUM(column2) "column2" FROM table1 GROUP BY column1 ORDER BY column1 B.SELECT column1, SUM(column2) "column2" FROM table1 HAVING SUM(column2) = 0 GROUP BY column1 ORDER BY column1 C.SELECT column1, SUM(column2) "column2" FROM table1 GROUP BY column1 HAVING SUM(column2) = 0 ORDER BY column1 D.SELECT column1, SUM(column2) "column2" FROM table1 ORDER BY column1 GROUP BY column1 Ans: D 25.In Oracle SQL, what is the command that returns the first non-null value in a list of values? A.NVL B.DECODE C.COALESCE D.INSTR E.ISNOTNULL Ans: C 26.In Cognos Connection, which of the following is a valid permission to be granted at the report level? A.Run B.View C.Traverse D.Edit Ans: C 27.If the user desires to retrieve all rows from Table A and all rows from Table B based on a join criteria, what type of join would be necessary? A.Left Outer Join B.Inner Join C.Cross Join D.Cluster Join E.Cartesian Join Ans: E 28.In an Oracle SQL insert statement, is it necessary to designate the column names? A.Yes B.No Ans: B 29.What is the regular aggregate property of a calculated fact object within Framework Manager? A.Sum B.Total C.Average D.Automatic E.Unsupported Ans: D 30.Can SQL code be added directly into a Report Studio report? A.Yes B.No Ans: A 31. What can an administrator use to transfer security data from one location to another using Series 7 namespaces? A. Settings (.csa) file B. Local authentication cache (.lac) file C. Local authentication export (.lae) file D. Configuration specification (.ccs) file Ans: C 32. What is the minimum requirement for configuring Cognos Office Connection using Smart Client technology with Microsoft Office components? A. Excel with MS Office 2003 Professional B. Excel with MS Office 2003 Standard C. PowerPoint with MS Office 2003 Standard D. PowerPoint with MS Office 2003 Professional Ans: A 33. What is created after the administrator initializes the metric store? A. a metric extract B. an object extract C. a metric package D. a relational database Ans: C 34. What is stored in the Cognos 8 content store? A. Log files B. Metric packages C. Report specifications D. Metric Designer extracts Ans: C 35. Which type of logging indication can show user calls that are made from Cognos 8 components? A. audit logging B. trace logging C. event logging D. performance logging Ans: A 36. How can an administrator ensure that users who are logged on to Cognos 8 are not prompted to log on again when they access PowerCube data? A. Have Cognos 8 and PowerPlay point to the same local authentication export (.lae) file. B. Have Cognos 8 and PowerPlay point to the same local authentication cache (.lac) file. C. Have Cognos 8 and PowerPlay use, as their authentication source, the same NTLM namespace. D. Have Cognos 8 and PowerPlay use, as their authentication source, the same Series 7 namespace. Ans: D 37. Which model type enables users to drill down in Analysis Studio? A. Architect model B. Relational model C. Dimensional model D. Data Manager model Ans: C 38. Why would an administrator want to copy a user profile? A. The user was deleted using a third-party authentication provider. B. The administrator wants to copy trusted credentials for multiple users. C. The user has changed names and the administrator is setting up an account in the new name. D. The user requires enhanced security permissions before logging on to Cognos 8 for the first time. Ans: C 39. Under what circumstances would full logging level be most appropriately used? A. Whenever users cannot access the data. B. Whenever detailed troubleshooting is required. C. Whenever more than one dispatcher has been configured. D. Whenever the default configuration for logging has been changed. Ans: B 40. At what level should the logging be set to capture the following set of details? user account management and runtime usage of Cognos 8, use requests, and service requests and responses. A. trace B. basic C. request D. minimal Ans: C COGNOS Questions and Answers pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
MySQL Shell 8.0.21 for MySQL Server 8.0 and 5.7 has been released
Dear MySQL users, MySQL Shell 8.0.21 is a maintenance release of MySQL Shell 8.0 Series (a component of the MySQL Server). The MySQL Shell is provided under Oracle’s dual-license. MySQL Shell 8.0 is highly recommended for use with MySQL Server 8.0 and 5.7. Please upgrade to MySQL Shell 8.0.21. MySQL Shell is an interactive JavaScript, Python and SQL console interface, supporting development and administration for the MySQL Server. It provides APIs implemented in JavaScript and Python that enable you to work with MySQL InnoDB cluster and use MySQL as a document store. The AdminAPI enables you to work with MySQL InnoDB cluster and InnoDB ReplicaSet, providing integrated solutions for high availability and scalability using InnoDB based MySQL databases, without requiring advanced MySQL expertise. For more information about how to configure and work with MySQL InnoDB cluster and MySQL InnoDB ReplicaSet see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/en/mysql-innodb-cluster-userguide.html The X DevAPI enables you to create “schema-less” JSON document collections and perform Create, Update, Read, Delete (CRUD) operations on those collections from your favorite scripting language. For more information about how to use MySQL Shell and the MySQL Document Store support see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/en/document-store.html For more information about the X DevAPI see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/x-devapi-userguide/en/ If you want to write applications that use the the CRUD based X DevAPI you can also use the latest MySQL Connectors for your language of choice. For more information about Connectors see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/index-connectors.html For more information on the APIs provided with MySQL Shell see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/dev/mysqlsh-api-javascript/8.0/ and https://dev.mysql.com/doc/dev/mysqlsh-api-python/8.0/ Using MySQL Shell’s SQL mode you can communicate with servers using the legacy MySQL protocol. Additionally, MySQL Shell provides partial compatibility with the mysql client by supporting many of the same command line options. For full documentation on MySQL Server, MySQL Shell and related topics, see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/mysql-shell/8.0/en/ For more information about how to download MySQL Shell 8.0.21, see the “General Availability (GA) Releases” tab at http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/shell/ We welcome and appreciate your feedback and bug reports, see http://bugs.mysql.com/ Enjoy and thanks for the support! Changes in MySQL Shell 8.0.21 (2020-07-13, General Availability) * AdminAPI Added or Changed Functionality * AdminAPI Bugs Fixed * Functionality Added or Changed * Bugs Fixed AdminAPI Added or Changed Functionality * A new user configurable tag framework has been added to the metadata, to allow specific instances of a cluster or ReplicaSet to be marked with additional information. Tags can be any ASCII character and provide a namespace. You set tags for an instance using the setInstanceOption() operation. In addition, AdminAPI and MySQL Router 8.0.21 support specific tags, which enable you to mark instances as hidden and remove them from routing. MySQL Router then excludes such tagged instances from the routing destination candidates list. This enables you to safely take a server instance offline, so that applications and MySQL Router ignore it, for example while you perform maintenance tasks, such as server upgrade or configuration changes. To bring the instance back online, use the setInstanceOption() operation to remove the tags and MySQL Router adds the instance back to the routing destination candidates list, and it becomes online for applications. For more information, see Tagging the Metadata (https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/admin-api-tagging.html). AdminAPI Bugs Fixed * Important Change: Previously, Group Replication did not support binary log checksums, and therefore one of the requirements for instances in InnoDB cluster was that binary log checksums were disabled by having the binlog_checksum system variable set to NONE. AdminAPI verified the value of binlog_checksum during the dba.checkInstanceConfiguration() operation and disallowed creating a cluster or adding an instance to a cluster that did not have binary log checksums disabled. In version 8.0.21, Group Replication has lifted this restriction, therefore InnoDB cluster now permits instances to use binary log checksums, with binlog_checksum set to CRC32. The setting for binlog_checksum does not have to be the same for all instances. In addition, sandboxes deployed with version 8.0.21 and later do not set the binlog_checksum variable, which defaults to CRC32. (Bug #31329024) * Adopting a Group Replication setup as a cluster can be performed when connected to any member of the group, regardless of whether it is a primary or a secondary. However, when a secondary member was used, super_read_only was being incorrectly disabled on that instance. Now, all operations performed during an adoption are done using the primary member of the group. This ensures that no GTID inconsistencies occur and that super_read_only is not incorrectly disabled on secondary members. (Bug #31238233) * Using the clusterAdmin option to create a user which had a netmask as part of the host resulted in an error when this user was passed to the dba.createCluster() operation. Now, accounts that specify a netmask are treated as accounts with wildcards, meaning that further checks to verify if the account accepts remote connections from all instances are skipped. (Bug #31018091) * The check for instance read-only compatibility was using a wrong MySQL version as the base version. The cross-version policies were added to Group Replication in version 8.0.17, but the check was considering instances running 8.0.16. This resulted in a misleading warning message indicating that the added instance was read-only compatible with the cluster, when this was not true (only for instances 8.0.16). The fix ensures that the check to verify if an instance is read-compatible or not with a cluster is only performed if the target instance is running version 8.0.17 or later. (Bug #30896344) * The maximum number of instances in an InnoDB cluster is 9, but AdminAPI was not preventing you from trying to add more instances to a cluster and the resulting error message was not clear. Now, if a cluster has 9 instances, Cluster.addInstance prevents you adding more instances. (Bug #30885157) * Adding an instance with a compatible GTID set to a InnoDB cluster or InnoDB ReplicaSet on which provisioning is required should not require any interaction, because this is considered a safe operation. Previously, in such a scenario, when MySQL Clone was supported MySQL Shell still prompted to choose between cloning or aborting the operation. Now, the operation proceeds with cloning, because this is the only way to provision the instance. Note instances with an empty GTID set are not considered to have a compatible GTID set when compared with the InnoDB cluster or InnoDB ReplicaSet. Such scenarios are considered to be unknown, therefore MySQL Shell prompts to confirm which action should be taken. (Bug #30884590) * The Group Replication system variables (prefixed with group_replication) do not exist if the plugin has not been loaded. Even if the system variables are persisted to the instance’s option file, they are not loaded unless the Group Replication plugin is also loaded when the server starts. If the Group Replication plugin is installed after the server starts, the option file is not reloaded, so all system variables have default values. Instances running MySQL 8.0 do not have a problem because SET PERSIST is used. However, on instances running version MySQL 5.7, the dba.rebootCluster() operation could not restore some system variables if the Group Replication plugin was uninstalled. Now, the dba.configureInstance() operation persists the Group Replication system variables to configuration files with the loose_ prefix. As a result, once the Group Replication plugin is installed, on instances running 5.7 the persisted values are used instead of the default values. (Bug #30768504) * The updateTopologyMode option has been deprecated and the behavior of Cluster.rescan() has been changed to always update the topology mode in the Metadata when a change is detected. MySQL Shell now displays a message whenever such a change is detected. (Bug #29330769) * The cluster.addInstance() and cluster.rejoinInstance() operations were not checking for the full range of settings which are required for an instance to be valid for adding to the cluster. This resulted in attempts to use instances which run on different operating systems to fail. For example, a cluster running on two instances that were hosted on a Linux based operating system would block the addition of an instance running Microsoft Windows. Now, cluster.addInstance() and cluster.rejoinInstance() operations validate the instance and prevent adding or rejoining an instance to the cluster if the value of the lower_case_table_names, group_replication_gtid_assignment_block_size or default_table_encryption of the instance are different from the ones on the cluster. (Bug #29255212) Functionality Added or Changed * MySQL Shell now has an instance dump utility, dumpInstance(), and schema dump utility, dumpSchemas(). The new utilities support the export of all schemas or a selected schema from an on-premise MySQL server instance into an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage bucket or a set of local files. The schemas can then be imported into a MySQL Database Service DB System using MySQL Shell’s new dump loading utility. The new utilities provide Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage streaming, MySQL Database Service compatibility checks and modifications, parallel dumping with multiple threads, and file compression. * MySQL Shell’s new dump loading utility, loadDump(), supports the import of schemas dumped using MySQL Shell’s new instance dump utility and schema dump utility into a MySQL Database Service DB System. The dump loading utility provides data streaming from remote storage, parallel loading of tables or table chunks, progress state tracking, resume and reset capability, and the option of concurrent loading while the dump is taking place. * The X DevAPI implementation now supports JSON schema validation, which enables you to ensure that your documents have a certain structure before they can be inserted or updated in a collection. To enable or modify JSON schema validation you pass in a JSON object like: { validation: { level: “off|strict”, schema: “json-schema” } } Here, validation is JSON object which contains the keys you can use to configure JSON schema validation. The first key is level, which can take the value strict or off. The second key, schema, is a JSON schema, as defined at http://json-schema.org. If the level key is set to strict, documents are validated against the json-schema when they are added to the collection, or when an operation updates the document. If the document does not validate, the server generates an error and the operation fails. If the level key is set to off, documents are not validated against the json-schema. You can pass a validation JSON object to the schema.createCollection() operation, to enable JSON schema validation, and schema.modifyCollection() operation, to change the current JSON schema validation, for example to disable validation. For more information, see JSON Schema Validation (https://dev.mysql.com/doc/x-devapi-userguide/en/collection-validation.html). Bugs Fixed * MySQL Shell plugins now support the use of the **kwargs syntax in functions defined in Python that are made available by the plugin. Using **kwargs in a function definition lets you call the function using a variable-length list of keyword arguments with arbitrary names. If the function is called from MySQL Shell’s JavaScript mode, MySQL Shell passes the named arguments and their values into a dictionary object for the Python function. MySQL Shell first tries to associate a keyword argument passed to a function with any corresponding keyword parameter that the function defines, and if there is none, the keyword argument is automatically included in the **kwargs list. As a side effect of this support, any API function called from Python in MySQL Shell that has a dictionary of options as the last parameter supports defining these options using named arguments. (Bug #31495448) * When switching to SQL mode, MySQL Shell queries the SQL mode of the connected server to establish whether the ANSI_QUOTES mode is enabled. Previously, MySQL Shell could not proceed if it did not receive a result set in response to the query. The absence of a result is now handled appropriately. (Bug #31418783, Bug #99728) * In SQL mode, when the results of a query are to be printed in table format, MySQL Shell buffers the result set before printing, in order to identify the correct column widths for the table. With very large result sets, it was possible for this practice to cause an out of memory error. MySQL Shell now buffers a maximum of 1000 rows for a result set before proceeding to format and print the table. Note that if a field in a row after the first 1000 rows contains a longer value than previously seen in that column in the result set, the table formatting will be misaligned for that row. (Bug #31304711) * Context switching in MySQL Shell’s SQL mode has been refactored and simplified to remove SQL syntax errors that could be returned when running script files using the source command. (Bug #31175790, Bug #31197312, Bug #99303) * The user account that is used to run MySQL Shell’s upgrade checker utility checkForServerUpgrade() previously required ALL privileges. The user account now requires only the RELOAD, PROCESS, and SELECT privileges. (Bug #31085098) * In Python mode, MySQL Shell did not handle invalid UTF-8 sequences in strings returned by queries. (Bug #31083617) * MySQL Shell’s parallel table import utility importTable() has a new option characterSet, which specifies a character set encoding with which the input data file is interpreted during the import. Setting the option to binary means that no conversion is done during the import. When you omit this option, the import uses the character set specified by the character_set_database system variable to interpret the input data file. (Bug #31057707) * On Windows, if the MySQL Shell package was extracted to and used from a directory whose name contained multi-byte characters, MySQL Shell was unable to start. MySQL Shell now handles directory names with multi-byte characters correctly, including when setting up Python, loading prompt themes, and accessing credential helpers. (Bug #31056783) * MySQL Shell’s JSON import utility importJSON() now handles UTF-8 encoded files that include a BOM (byte mark order) at the start, which is the sequence 0xEF 0xBB 0xBF. As a workaround in earlier releases, remove this byte sequence, which is not needed. (Bug #30993547, Bug #98836) * When the output format was set to JSON, MySQL Shell’s upgrade checker utility checkForServerUpgrade() included a description and documentation link for a check even if no issues were found. These are now omitted from the output, as they are with the text output format. (Bug #30950035) On Behalf of Oracle/MySQL Release Engineering Team, Sreedhar S https://insidemysql.com/mysql-shell-8-0-21-for-mysql-server-8-0-and-5-7-has-been-released/
0 notes