#kubernetes controller manager
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
#kubernetes controller manager#kubernetes controller golang#kubernetes controller explained#kubernetes controller example#kubernetes controller development
0 notes
Photo

Upbound Spaces brings managed control planes to self-hosted computing environments Upbound Inc., the startup behind the popular open-source Crossplane project, today announced a new self-hosting feature for its flagship control plane technology, enabling users to deploy managed control planes in self-managed computing environments. Upbound Spaces enables customers with rigorous compliance and data sovereignty requirements to benefit from the company’s Crossplane control plane technology. The launch of […] The post Upbound Spaces brings managed control planes to self-hosted computing environments appeared first on SiliconANGLE. https://siliconangle.com/2023/09/06/upbound-spaces-brings-managed-control-planes-self-hosted-computing-environments/
#Cloud#NEWS#The-Latest#applications#cloud-native technologies#control plane#Crossplane#internal development platforms#Kubernetes#managed control planes#managed environments#multicloud#self-hosted environments#Upbound#Upbound Spaces#Mike Wheatley#SiliconANGLE
0 notes
Text
What is Argo CD? And When Was Argo CD Established?

What Is Argo CD?
Argo CD is declarative Kubernetes GitOps continuous delivery.
In DevOps, ArgoCD is a Continuous Delivery (CD) technology that has become well-liked for delivering applications to Kubernetes. It is based on the GitOps deployment methodology.
When was Argo CD Established?
Argo CD was created at Intuit and made publicly available following Applatix’s 2018 acquisition by Intuit. The founding developers of Applatix, Hong Wang, Jesse Suen, and Alexander Matyushentsev, made the Argo project open-source in 2017.
Why Argo CD?
Declarative and version-controlled application definitions, configurations, and environments are ideal. Automated, auditable, and easily comprehensible application deployment and lifecycle management are essential.
Getting Started
Quick Start
kubectl create namespace argocd kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
For some features, more user-friendly documentation is offered. Refer to the upgrade guide if you want to upgrade your Argo CD. Those interested in creating third-party connectors can access developer-oriented resources.
How it works
Argo CD defines the intended application state by employing Git repositories as the source of truth, in accordance with the GitOps pattern. There are various approaches to specify Kubernetes manifests:
Applications for Customization
Helm charts
JSONNET files
Simple YAML/JSON manifest directory
Any custom configuration management tool that is set up as a plugin
The deployment of the intended application states in the designated target settings is automated by Argo CD. Deployments of applications can monitor changes to branches, tags, or pinned to a particular manifest version at a Git commit.
Architecture
The implementation of Argo CD is a Kubernetes controller that continually observes active apps and contrasts their present, live state with the target state (as defined in the Git repository). Out Of Sync is the term used to describe a deployed application whose live state differs from the target state. In addition to reporting and visualizing the differences, Argo CD offers the ability to manually or automatically sync the current state back to the intended goal state. The designated target environments can automatically apply and reflect any changes made to the intended target state in the Git repository.
Components
API Server
The Web UI, CLI, and CI/CD systems use the API, which is exposed by the gRPC/REST server. Its duties include the following:
Status reporting and application management
Launching application functions (such as rollback, sync, and user-defined actions)
Cluster credential management and repository (k8s secrets)
RBAC enforcement
Authentication, and auth delegation to outside identity providers
Git webhook event listener/forwarder
Repository Server
An internal service called the repository server keeps a local cache of the Git repository containing the application manifests. When given the following inputs, it is in charge of creating and returning the Kubernetes manifests:
URL of the repository
Revision (tag, branch, commit)
Path of the application
Template-specific configurations: helm values.yaml, parameters
A Kubernetes controller known as the application controller keeps an eye on all active apps and contrasts their actual, live state with the intended target state as defined in the repository. When it identifies an Out Of Sync application state, it may take remedial action. It is in charge of calling any user-specified hooks for lifecycle events (Sync, PostSync, and PreSync).
Features
Applications are automatically deployed to designated target environments.
Multiple configuration management/templating tools (Kustomize, Helm, Jsonnet, and plain-YAML) are supported.
Capacity to oversee and implement across several clusters
Integration of SSO (OIDC, OAuth2, LDAP, SAML 2.0, Microsoft, LinkedIn, GitHub, GitLab)
RBAC and multi-tenancy authorization policies
Rollback/Roll-anywhere to any Git repository-committed application configuration
Analysis of the application resources’ health state
Automated visualization and detection of configuration drift
Applications can be synced manually or automatically to their desired state.
Web user interface that shows program activity in real time
CLI for CI integration and automation
Integration of webhooks (GitHub, BitBucket, GitLab)
Tokens of access for automation
Hooks for PreSync, Sync, and PostSync to facilitate intricate application rollouts (such as canary and blue/green upgrades)
Application event and API call audit trails
Prometheus measurements
To override helm parameters in Git, use parameter overrides.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#ArgoCD#CD#GitOps#API#Kubernetes#Git#Argoproject#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#govindhtech
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
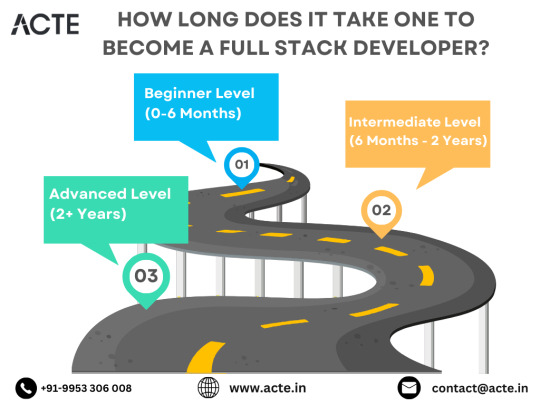
The Roadmap to Full Stack Developer Proficiency: A Comprehensive Guide
Embarking on the journey to becoming a full stack developer is an exhilarating endeavor filled with growth and challenges. Whether you're taking your first steps or seeking to elevate your skills, understanding the path ahead is crucial. In this detailed roadmap, we'll outline the stages of mastering full stack development, exploring essential milestones, competencies, and strategies to guide you through this enriching career journey.

Beginning the Journey: Novice Phase (0-6 Months)
As a novice, you're entering the realm of programming with a fresh perspective and eagerness to learn. This initial phase sets the groundwork for your progression as a full stack developer.
Grasping Programming Fundamentals:
Your journey commences with grasping the foundational elements of programming languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. These are the cornerstone of web development and are essential for crafting dynamic and interactive web applications.
Familiarizing with Basic Data Structures and Algorithms:
To develop proficiency in programming, understanding fundamental data structures such as arrays, objects, and linked lists, along with algorithms like sorting and searching, is imperative. These concepts form the backbone of problem-solving in software development.
Exploring Essential Web Development Concepts:
During this phase, you'll delve into crucial web development concepts like client-server architecture, HTTP protocol, and the Document Object Model (DOM). Acquiring insights into the underlying mechanisms of web applications lays a strong foundation for tackling more intricate projects.
Advancing Forward: Intermediate Stage (6 Months - 2 Years)
As you progress beyond the basics, you'll transition into the intermediate stage, where you'll deepen your understanding and skills across various facets of full stack development.
Venturing into Backend Development:
In the intermediate stage, you'll venture into backend development, honing your proficiency in server-side languages like Node.js, Python, or Java. Here, you'll learn to construct robust server-side applications, manage data storage and retrieval, and implement authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Mastering Database Management:
A pivotal aspect of backend development is comprehending databases. You'll delve into relational databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL, as well as NoSQL databases like MongoDB. Proficiency in database management systems and design principles enables the creation of scalable and efficient applications.
Exploring Frontend Frameworks and Libraries:
In addition to backend development, you'll deepen your expertise in frontend technologies. You'll explore prominent frameworks and libraries such as React, Angular, or Vue.js, streamlining the creation of interactive and responsive user interfaces.
Learning Version Control with Git:
Version control is indispensable for collaborative software development. During this phase, you'll familiarize yourself with Git, a distributed version control system, to manage your codebase, track changes, and collaborate effectively with fellow developers.
Achieving Mastery: Advanced Phase (2+ Years)
As you ascend in your journey, you'll enter the advanced phase of full stack development, where you'll refine your skills, tackle intricate challenges, and delve into specialized domains of interest.
Designing Scalable Systems:
In the advanced stage, focus shifts to designing scalable systems capable of managing substantial volumes of traffic and data. You'll explore design patterns, scalability methodologies, and cloud computing platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
Embracing DevOps Practices:
DevOps practices play a pivotal role in contemporary software development. You'll delve into continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, infrastructure as code (IaC), and containerization technologies such as Docker and Kubernetes.
Specializing in Niche Areas:
With experience, you may opt to specialize in specific domains of full stack development, whether it's frontend or backend development, mobile app development, or DevOps. Specialization enables you to deepen your expertise and pursue career avenues aligned with your passions and strengths.
Conclusion:
Becoming a proficient full stack developer is a transformative journey that demands dedication, resilience, and perpetual learning. By following the roadmap outlined in this guide and maintaining a curious and adaptable mindset, you'll navigate the complexities and opportunities inherent in the realm of full stack development. Remember, mastery isn't merely about acquiring technical skills but also about fostering collaboration, embracing innovation, and contributing meaningfully to the ever-evolving landscape of technology.
#full stack developer#education#information#full stack web development#front end development#frameworks#web development#backend#full stack developer course#technology
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Is cPanel on Its Deathbed? A Tale of Technology, Profits, and a Slow-Moving Train Wreck
Ah, cPanel. The go-to control panel for many web hosting services since the dawn of, well, web hosting. Once the epitome of innovation, it’s now akin to a grizzled war veteran, limping along with a cane and wearing an “I Survived Y2K” t-shirt. So what went wrong? Let’s dive into this slow-moving technological telenovela, rife with corporate greed, security loopholes, and a legacy that may be hanging by a thread.
Chapter 1: A Brief, Glorious History (Or How cPanel Shot to Stardom)
Once upon a time, cPanel was the bee’s knees. Launched in 1996, this software was, for a while, the pinnacle of web management systems. It promised simplicity, reliability, and functionality. Oh, the golden years!
Chapter 2: The Tech Stack Tortoise
In the fast-paced world of technology, being stagnant is synonymous with being extinct. While newer tech stacks are integrating AI, machine learning, and all sorts of jazzy things, cPanel seems to be stuck in a time warp. Why? Because the tech stack is more outdated than a pair of bell-bottom trousers. No Docker, no Kubernetes, and don’t even get me started on the lack of robust API support.
Chapter 3: “The Corpulent Corporate”
In 2018, Oakley Capital, a private equity firm, acquired cPanel. For many, this was the beginning of the end. Pricing structures were jumbled, turning into a monetisation extravaganza. It’s like turning your grandma’s humble pie shop into a mass production line for rubbery, soulless pies. They’ve squeezed every ounce of profit from it, often at the expense of the end-users and smaller hosting companies.
Chapter 4: Security—or the Lack Thereof
Ah, the elephant in the room. cPanel has had its fair share of vulnerabilities. Whether it’s SQL injection flaws, privilege escalation, or simple, plain-text passwords (yes, you heard right), cPanel often appears in the headlines for all the wrong reasons. It’s like that dodgy uncle at family reunions who always manages to spill wine on the carpet; you know he’s going to mess up, yet somehow he’s always invited.
Chapter 5: The (Dis)loyal Subjects—The Hosting Companies
Remember those hosting companies that once swore by cPanel? Well, let’s just say some of them have been seen flirting with competitors at the bar. Newer, shinier control panels are coming to market, offering modern tech stacks and, gasp, lower prices! It’s like watching cPanel’s loyal subjects slowly turn their backs, one by one.
Chapter 6: The Alternatives—Not Just a Rebellion, but a Revolution
Plesk, Webmin, DirectAdmin, oh my! New players are rising, offering updated tech stacks, more customizable APIs, and—wait for it—better security protocols. They’re the Han Solos to cPanel’s Jabba the Hutt: faster, sleeker, and without the constant drooling.
Conclusion: The Twilight Years or a Second Wind?
The debate rages on. Is cPanel merely an ageing actor waiting for its swan song, or can it adapt and evolve, perhaps surprising us all? Either way, the story of cPanel serves as a cautionary tale: adapt or die. And for heaven’s sake, update your tech stack before it becomes a relic in a technology museum, right between floppy disks and dial-up modems.
This outline only scratches the surface, but it’s a start. If cPanel wants to avoid becoming the Betamax of web management systems, it better start evolving—stat. Cheers!
#hosting#wordpress#cpanel#webdesign#servers#websites#webdeveloper#technology#tech#website#developer#digitalagency#uk#ukdeals#ukbusiness#smallbussinessowner
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating the DevOps Landscape: Opportunities and Roles
DevOps has become a game-changer in the quick-moving world of technology. This dynamic process, whose name is a combination of "Development" and "Operations," is revolutionising the way software is created, tested, and deployed. DevOps is a cultural shift that encourages cooperation, automation, and integration between development and IT operations teams, not merely a set of practises. The outcome? greater software delivery speed, dependability, and effectiveness.

In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the essence of DevOps, explore the key technologies that underpin its success, and uncover the vast array of job opportunities it offers. Whether you're an aspiring IT professional looking to enter the world of DevOps or an experienced practitioner seeking to enhance your skills, this blog will serve as your roadmap to mastering DevOps. So, let's embark on this enlightening journey into the realm of DevOps.
Key Technologies for DevOps:
Version Control Systems: DevOps teams rely heavily on robust version control systems such as Git and SVN. These systems are instrumental in managing and tracking changes in code and configurations, promoting collaboration and ensuring the integrity of the software development process.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): The heart of DevOps, CI/CD tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, and CircleCI drive the automation of critical processes. They orchestrate the building, testing, and deployment of code changes, enabling rapid, reliable, and consistent software releases.
Configuration Management: Tools like Ansible, Puppet, and Chef are the architects of automation in the DevOps landscape. They facilitate the automated provisioning and management of infrastructure and application configurations, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
Containerization: Docker and Kubernetes, the cornerstones of containerization, are pivotal in the DevOps toolkit. They empower the creation, deployment, and management of containers that encapsulate applications and their dependencies, simplifying deployment and scaling.
Orchestration: Docker Swarm and Amazon ECS take center stage in orchestrating and managing containerized applications at scale. They provide the control and coordination required to maintain the efficiency and reliability of containerized systems.
Monitoring and Logging: The observability of applications and systems is essential in the DevOps workflow. Monitoring and logging tools like the ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) and Prometheus are the eyes and ears of DevOps professionals, tracking performance, identifying issues, and optimizing system behavior.
Cloud Computing Platforms: AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are the foundational pillars of cloud infrastructure in DevOps. They offer the infrastructure and services essential for creating and scaling cloud-based applications, facilitating the agility and flexibility required in modern software development.
Scripting and Coding: Proficiency in scripting languages such as Shell, Python, Ruby, and coding skills are invaluable assets for DevOps professionals. They empower the creation of automation scripts and tools, enabling customization and extensibility in the DevOps pipeline.
Collaboration and Communication Tools: Collaboration tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams enhance the communication and coordination among DevOps team members. They foster efficient collaboration and facilitate the exchange of ideas and information.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): The concept of Infrastructure as Code, represented by tools like Terraform and AWS CloudFormation, is a pivotal practice in DevOps. It allows the definition and management of infrastructure using code, ensuring consistency and reproducibility, and enabling the rapid provisioning of resources.

Job Opportunities in DevOps:
DevOps Engineer: DevOps engineers are the architects of continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. They meticulously design and maintain these pipelines to automate the deployment process, ensuring the rapid, reliable, and consistent release of software. Their responsibilities extend to optimizing the system's reliability, making them the backbone of seamless software delivery.
Release Manager: Release managers play a pivotal role in orchestrating the software release process. They carefully plan and schedule software releases, coordinating activities between development and IT teams. Their keen oversight ensures the smooth transition of software from development to production, enabling timely and successful releases.
Automation Architect: Automation architects are the visionaries behind the design and development of automation frameworks. These frameworks streamline deployment and monitoring processes, leveraging automation to enhance efficiency and reliability. They are the engineers of innovation, transforming manual tasks into automated wonders.
Cloud Engineer: Cloud engineers are the custodians of cloud infrastructure. They adeptly manage cloud resources, optimizing their performance and ensuring scalability. Their expertise lies in harnessing the power of cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud to provide robust, flexible, and cost-effective solutions.
Site Reliability Engineer (SRE): SREs are the sentinels of system reliability. They focus on maintaining the system's resilience through efficient practices, continuous monitoring, and rapid incident response. Their vigilance ensures that applications and systems remain stable and performant, even in the face of challenges.
Security Engineer: Security engineers are the guardians of the DevOps pipeline. They integrate security measures seamlessly into the software development process, safeguarding it from potential threats and vulnerabilities. Their role is crucial in an era where security is paramount, ensuring that DevOps practices are fortified against breaches.
As DevOps continues to redefine the landscape of software development and deployment, gaining expertise in its core principles and technologies is a strategic career move. ACTE Technologies offers comprehensive DevOps training programs, led by industry experts who provide invaluable insights, real-world examples, and hands-on guidance. ACTE Technologies's DevOps training covers a wide range of essential concepts, practical exercises, and real-world applications. With a strong focus on certification preparation, ACTE Technologies ensures that you're well-prepared to excel in the world of DevOps. With their guidance, you can gain mastery over DevOps practices, enhance your skill set, and propel your career to new heights.
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Journey to Devops
The concept of “DevOps” has been gaining traction in the IT sector for a couple of years. It involves promoting teamwork and interaction, between software developers and IT operations groups to enhance the speed and reliability of software delivery. This strategy has become widely accepted as companies strive to provide software to meet customer needs and maintain an edge, in the industry. In this article we will explore the elements of becoming a DevOps Engineer.
Step 1: Get familiar with the basics of Software Development and IT Operations:
In order to pursue a career as a DevOps Engineer it is crucial to possess a grasp of software development and IT operations. Familiarity with programming languages like Python, Java, Ruby or PHP is essential. Additionally, having knowledge about operating systems, databases and networking is vital.
Step 2: Learn the principles of DevOps:
It is crucial to comprehend and apply the principles of DevOps. Automation, continuous integration, continuous deployment and continuous monitoring are aspects that need to be understood and implemented. It is vital to learn how these principles function and how to carry them out efficiently.
Step 3: Familiarize yourself with the DevOps toolchain:
Git: Git, a distributed version control system is extensively utilized by DevOps teams, for code repository management. It aids in monitoring code alterations facilitating collaboration, among team members and preserving a record of modifications made to the codebase.
Ansible: Ansible is an open source tool used for managing configurations deploying applications and automating tasks. It simplifies infrastructure management. Saves time when performing tasks.
Docker: Docker, on the other hand is a platform for containerization that allows DevOps engineers to bundle applications and dependencies into containers. This ensures consistency and compatibility across environments from development, to production.
Kubernetes: Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform that helps manage and scale containers. It helps automate the deployment, scaling, and management of applications and micro-services.
Jenkins: Jenkins is an open-source automation server that helps automate the process of building, testing, and deploying software. It helps to automate repetitive tasks and improve the speed and efficiency of the software delivery process.
Nagios: Nagios is an open-source monitoring tool that helps us monitor the health and performance of our IT infrastructure. It also helps us to identify and resolve issues in real-time and ensure the high availability and reliability of IT systems as well.
Terraform: Terraform is an infrastructure as code (IAC) tool that helps manage and provision IT infrastructure. It helps us automate the process of provisioning and configuring IT resources and ensures consistency between development and production environments.
Step 4: Gain practical experience:
The best way to gain practical experience is by working on real projects and bootcamps. You can start by contributing to open-source projects or participating in coding challenges and hackathons. You can also attend workshops and online courses to improve your skills.
Step 5: Get certified:
Getting certified in DevOps can help you stand out from the crowd and showcase your expertise to various people. Some of the most popular certifications are:
Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA)
AWS Certified DevOps Engineer
Microsoft Certified: Azure DevOps Engineer Expert
AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner
Step 6: Build a strong professional network:
Networking is one of the most important parts of becoming a DevOps Engineer. You can join online communities, attend conferences, join webinars and connect with other professionals in the field. This will help you stay up-to-date with the latest developments and also help you find job opportunities and success.
Conclusion:
You can start your journey towards a successful career in DevOps. The most important thing is to be passionate about your work and continuously learn and improve your skills. With the right skills, experience, and network, you can achieve great success in this field and earn valuable experience.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating the DevOps Landscape: A Beginner's Comprehensive
Roadmap In the dynamic realm of software development, the DevOps methodology stands out as a transformative force, fostering collaboration, automation, and continuous enhancement. For newcomers eager to immerse themselves in this revolutionary culture, this all-encompassing guide presents the essential steps to initiate your DevOps expedition.

Grasping the Essence of DevOps Culture: DevOps transcends mere tool usage; it embodies a cultural transformation that prioritizes collaboration and communication between development and operations teams. Begin by comprehending the fundamental principles of collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement.
Immerse Yourself in DevOps Literature: Kickstart your journey by delving into indispensable DevOps literature. "The Phoenix Project" by Gene Kim, Jez Humble, and Kevin Behr, along with "The DevOps Handbook," provides invaluable insights into the theoretical underpinnings and practical implementations of DevOps.
Online Courses and Tutorials: Harness the educational potential of online platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity. Seek courses covering pivotal DevOps tools such as Git, Jenkins, Docker, and Kubernetes. These courses will furnish you with a robust comprehension of the tools and processes integral to the DevOps terrain.
Practical Application: While theory is crucial, hands-on experience is paramount. Establish your own development environment and embark on practical projects. Implement version control, construct CI/CD pipelines, and deploy applications to acquire firsthand experience in applying DevOps principles.

Explore the Realm of Configuration Management: Configuration management is a pivotal facet of DevOps. Familiarize yourself with tools like Ansible, Puppet, or Chef, which automate infrastructure provisioning and configuration, ensuring uniformity across diverse environments.
Containerization and Orchestration: Delve into the universe of containerization with Docker and orchestration with Kubernetes. Containers provide uniformity across diverse environments, while orchestration tools automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Integral to DevOps is CI/CD. Gain proficiency in Jenkins, Travis CI, or GitLab CI to automate code change testing and deployment. These tools enhance the speed and reliability of the release cycle, a central objective in DevOps methodologies.
Grasp Networking and Security Fundamentals: Expand your knowledge to encompass networking and security basics relevant to DevOps. Comprehend how security integrates into the DevOps pipeline, embracing the principles of DevSecOps. Gain insights into infrastructure security and secure coding practices to ensure robust DevOps implementations.
Embarking on a DevOps expedition demands a comprehensive strategy that amalgamates theoretical understanding with hands-on experience. By grasping the cultural shift, exploring key literature, and mastering essential tools, you are well-positioned to evolve into a proficient DevOps practitioner, contributing to the triumph of contemporary software development.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How a Web Development Company Builds Scalable SaaS Platforms
Building a SaaS (Software as a Service) platform isn't just about writing code—it’s about designing a product that can grow with your business, serve thousands of users reliably, and continuously evolve based on market needs. Whether you're launching a CRM, learning management system, or a niche productivity tool, scalability must be part of the plan from day one.
That’s why a professional Web Development Company brings more than just technical skills to the table. They understand the architectural, design, and business logic decisions required to ensure your SaaS product is not just functional—but scalable, secure, and future-proof.
1. Laying a Solid Architectural Foundation
The first step in building a scalable SaaS product is choosing the right architecture. Most development agencies follow a modular, service-oriented approach that separates different components of the application—user management, billing, dashboards, APIs, etc.—into layers or even microservices.
This ensures:
Features can be developed and deployed independently
The system can scale horizontally (adding more servers) or vertically (upgrading resources)
Future updates or integrations won’t require rebuilding the entire platform
Development teams often choose cloud-native architectures built on platforms like AWS, Azure, or GCP for their scalability and reliability.
2. Selecting the Right Tech Stack
Choosing the right technology stack is critical. The tech must support performance under heavy loads and allow for easy development as your team grows.
Popular stacks for SaaS platforms include:
Frontend: React.js, Vue.js, or Angular
Backend: Node.js, Django, Ruby on Rails, or Laravel
Databases: PostgreSQL or MongoDB for flexibility and performance
Infrastructure: Docker, Kubernetes, CI/CD pipelines for automation
A skilled agency doesn’t just pick trendy tools—they choose frameworks aligned with your app’s use case, team skills, and scaling needs.
3. Multi-Tenancy Setup
One of the biggest differentiators in SaaS development is whether the platform is multi-tenant—where one codebase and database serve multiple customers with logical separation.
A web development company configures multi-tenancy using:
Separate schemas per tenant (isolated but efficient)
Shared databases with tenant identifiers (cost-effective)
Isolated instances for enterprise clients (maximum security)
This architecture supports onboarding multiple customers without duplicating infrastructure—making it cost-efficient and easy to manage.
4. Building Secure, Scalable User Management
SaaS platforms must support a range of users—admins, team members, clients—with different permissions. That’s why role-based access control (RBAC) is built into the system from the start.
Key features include:
Secure user registration and login (OAuth2, SSO, MFA)
Dynamic role creation and permission assignment
Audit logs and activity tracking
This layer is integrated with identity providers and third-party auth services to meet enterprise security expectations.
5. Ensuring Seamless Billing and Subscription Management
Monetization is central to SaaS success. Development companies build subscription logic that supports:
Monthly and annual billing cycles
Tiered or usage-based pricing models
Free trials and discounts
Integration with Stripe, Razorpay, or other payment gateways
They also ensure compliance with global standards (like PCI DSS for payment security and GDPR for user data privacy), especially if you're targeting international customers.
6. Performance Optimization from Day One
Scalability means staying fast even as traffic and data grow. Web developers implement:
Caching systems (like Redis or Memcached)
Load balancers and auto-scaling policies
Asynchronous task queues (e.g., Celery, RabbitMQ)
CDN integration for static asset delivery
Combined with code profiling and database indexing, these enhancements ensure your SaaS stays performant no matter how many users are active.
7. Continuous Deployment and Monitoring
SaaS products evolve quickly—new features, fixes, improvements. That’s why agencies set up:
CI/CD pipelines for automated testing and deployment
Error tracking tools like Sentry or Rollbar
Performance monitoring with tools like Datadog or New Relic
Log management for incident response and debugging
This allows for rapid iteration and minimal downtime, which are critical in SaaS environments.
8. Preparing for Scale from a Product Perspective
Scalability isn’t just technical—it’s also about UX and support. A good development company collaborates on:
Intuitive onboarding flows
Scalable navigation and UI design systems
Help center and chatbot integrations
Data export and reporting features for growing teams
These elements allow users to self-serve as the platform scales, reducing support load and improving retention.
Conclusion
SaaS platforms are complex ecosystems that require planning, flexibility, and technical excellence. From architecture and authentication to billing and performance, every layer must be built with growth in mind. That’s why startups and enterprises alike trust a Web Development Company to help them design and launch SaaS solutions that can handle scale—without sacrificing speed or security.
Whether you're building your first SaaS MVP or upgrading an existing product, the right development partner can transform your vision into a resilient, scalable reality.
0 notes
Text
CNAPP Explained: The Smartest Way to Secure Cloud-Native Apps with EDSPL

Introduction: The New Era of Cloud-Native Apps
Cloud-native applications are rewriting the rules of how we build, scale, and secure digital products. Designed for agility and rapid innovation, these apps demand security strategies that are just as fast and flexible. That’s where CNAPP—Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform—comes in.
But simply deploying CNAPP isn’t enough.
You need the right strategy, the right partner, and the right security intelligence. That’s where EDSPL shines.
What is CNAPP? (And Why Your Business Needs It)
CNAPP stands for Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform, a unified framework that protects cloud-native apps throughout their lifecycle—from development to production and beyond.
Instead of relying on fragmented tools, CNAPP combines multiple security services into a cohesive solution:
Cloud Security
Vulnerability management
Identity access control
Runtime protection
DevSecOps enablement
In short, it covers the full spectrum—from your code to your container, from your workload to your network security.
Why Traditional Security Isn’t Enough Anymore
The old way of securing applications with perimeter-based tools and manual checks doesn’t work for cloud-native environments. Here’s why:
Infrastructure is dynamic (containers, microservices, serverless)
Deployments are continuous
Apps run across multiple platforms
You need security that is cloud-aware, automated, and context-rich—all things that CNAPP and EDSPL’s services deliver together.
Core Components of CNAPP
Let’s break down the core capabilities of CNAPP and how EDSPL customizes them for your business:
1. Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Checks your cloud infrastructure for misconfigurations and compliance gaps.
See how EDSPL handles cloud security with automated policy enforcement and real-time visibility.
2. Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)
Protects virtual machines, containers, and functions from attacks.
This includes deep integration with application security layers to scan, detect, and fix risks before deployment.
3. CIEM: Identity and Access Management
Monitors access rights and roles across multi-cloud environments.
Your network, routing, and storage environments are covered with strict permission models.
4. DevSecOps Integration
CNAPP shifts security left—early into the DevOps cycle. EDSPL’s managed services ensure security tools are embedded directly into your CI/CD pipelines.
5. Kubernetes and Container Security
Containers need runtime defense. Our approach ensures zero-day protection within compute environments and dynamic clusters.
How EDSPL Tailors CNAPP for Real-World Environments
Every organization’s tech stack is unique. That’s why EDSPL never takes a one-size-fits-all approach. We customize CNAPP for your:
Cloud provider setup
Mobility strategy
Data center switching
Backup architecture
Storage preferences
This ensures your entire digital ecosystem is secure, streamlined, and scalable.
Case Study: CNAPP in Action with EDSPL
The Challenge
A fintech company using a hybrid cloud setup faced:
Misconfigured services
Shadow admin accounts
Poor visibility across Kubernetes
EDSPL’s Solution
Integrated CNAPP with CIEM + CSPM
Hardened their routing infrastructure
Applied real-time runtime policies at the node level
✅ The Results
75% drop in vulnerabilities
Improved time to resolution by 4x
Full compliance with ISO, SOC2, and GDPR
Why EDSPL’s CNAPP Stands Out
While most providers stop at integration, EDSPL goes beyond:
🔹 End-to-End Security: From app code to switching hardware, every layer is secured. 🔹 Proactive Threat Detection: Real-time alerts and behavior analytics. 🔹 Customizable Dashboards: Unified views tailored to your team. 🔹 24x7 SOC Support: With expert incident response. 🔹 Future-Proofing: Our background vision keeps you ready for what’s next.
EDSPL’s Broader Capabilities: CNAPP and Beyond
While CNAPP is essential, your digital ecosystem needs full-stack protection. EDSPL offers:
Network security
Application security
Switching and routing solutions
Storage and backup services
Mobility and remote access optimization
Managed and maintenance services for 24x7 support
Whether you’re building apps, protecting data, or scaling globally, we help you do it securely.
Let’s Talk CNAPP
You’ve read the what, why, and how of CNAPP — now it’s time to act.
📩 Reach us for a free CNAPP consultation. 📞 Or get in touch with our cloud security specialists now.
Secure your cloud-native future with EDSPL — because prevention is always smarter than cure.
0 notes
Text
Secure Your Hybrid Cloud with Windows Server 2022 Standard
Building a Fortress: The Future of Hybrid Cloud Security with Windows Server 2022
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, securing your hybrid cloud environment is more critical than ever. Windows Server 2022 Standard emerges as a robust foundation, blending innovative security features with flexible management capabilities to empower businesses of all sizes. This powerful server OS is designed to meet the complex demands of modern IT infrastructure, ensuring your data remains protected while maintaining seamless connectivity across on-premises and cloud environments.
One of the standout features of Windows Server 2022 Standard is its secured-core server capabilities. This technology integrates hardware, firmware, and software security measures to create a resilient fortress against cyber threats. By leveraging features like Secure Boot, hardware root of trust, and virtualization-based security, organizations can significantly reduce the attack surface and safeguard critical assets from malicious intrusions.
Furthermore, Windows Server 2022 enhances multi-layer security through advanced threat protection mechanisms. It offers improved encryption protocols, real-time security monitoring, and streamlined patch management, enabling IT teams to identify vulnerabilities and respond swiftly to emerging threats. This comprehensive security approach ensures that your hybrid cloud remains resilient against increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.
Managing hybrid environments has never been easier thanks to the improved hybrid server management tools integrated into Windows Server 2022. The platform provides a unified management experience, allowing administrators to control both on-premises and cloud resources efficiently. Features like Azure Arc integration facilitate seamless deployment, monitoring, and updating of servers across diverse environments, reducing operational complexity and boosting productivity.
For organizations leveraging containerization, Windows Server 2022 offers significant improvements in windows containers. Enhanced support for Kubernetes, improved isolation, and faster container startup times help developers deploy applications swiftly and securely. This ensures that your development pipeline remains agile and responsive to market needs, all while maintaining a high level of security.
Investing in the right licensing is crucial to unlock the full potential of Windows Server 2022 Standard. For competitive pricing and licensing options, explore the windows server 2022 standard license price. This license provides the essential features needed to build a secure, scalable, and efficient hybrid cloud environment.
In conclusion, Windows Server 2022 Standard is more than just an operating system; it’s a strategic enabler for modern enterprises aiming to harness the power of hybrid cloud while maintaining the highest security standards. Embrace this innovative platform to future-proof your IT infrastructure, safeguard your data, and empower your business to thrive in a digital-first world.
0 notes
Text
Migrating Virtual Machines to Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization with Ansible Automation Platform
As enterprises modernize their infrastructure, migrating traditional virtual machines (VMs) to container-native platforms is no longer just a trend — it’s a necessity. One of the most powerful solutions for this evolution is Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization, which allows organizations to run VMs side-by-side with containers on a unified Kubernetes platform. When combined with Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform, this migration can be automated, repeatable, and efficient.
In this blog, we’ll explore how enterprises can leverage Ansible to seamlessly migrate workloads from legacy virtualization platforms (like VMware or KVM) to OpenShift Virtualization.
🔍 Why OpenShift Virtualization?
OpenShift Virtualization extends OpenShift’s capabilities to include traditional VMs, enabling:
Unified management of containers and VMs
Native integration with Kubernetes networking and storage
Simplified CI/CD pipelines that include VM-based workloads
Reduction of operational overhead and licensing costs
🛠️ The Role of Ansible Automation Platform
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform is the glue that binds infrastructure automation, offering:
Agentless automation using SSH or APIs
Pre-built collections for platforms like VMware, OpenShift, KubeVirt, and more
Scalable execution environments for large-scale VM migration
Role-based access and governance through automation controller (formerly Tower)
🧭 Migration Workflow Overview
A typical migration flow using Ansible and OpenShift Virtualization involves:
1. Discovery Phase
Inventory the source VMs using Ansible VMware/KVM modules.
Collect VM configuration, network settings, and storage details.
2. Template Creation
Convert the discovered VM configurations into KubeVirt/OVIRT VM manifests.
Define OpenShift-native templates to match the workload requirements.
3. Image Conversion and Upload
Use tools like virt-v2v or Ansible roles to export VM disk images (VMDK/QCOW2).
Upload to OpenShift using Containerized Data Importer (CDI) or PVCs.
4. VM Deployment
Deploy converted VMs as KubeVirt VirtualMachines via Ansible Playbooks.
Integrate with OpenShift Networking and Storage (Multus, OCS, etc.)
5. Validation & Post-Migration
Run automated smoke tests or app-specific validation.
Integrate monitoring and alerting via Prometheus/Grafana.
- name: Deploy VM on OpenShift Virtualization
hosts: localhost
tasks:
- name: Create PVC for VM disk
k8s:
state: present
definition: "{{ lookup('file', 'vm-pvc.yaml') }}"
- name: Deploy VirtualMachine
k8s:
state: present
definition: "{{ lookup('file', 'vm-definition.yaml') }}"
🔐 Benefits of This Approach
✅ Consistency – Every VM migration follows the same process.
✅ Auditability – Track every step of the migration with Ansible logs.
✅ Security – Ansible integrates with enterprise IAM and RBAC policies.
✅ Scalability – Migrate tens or hundreds of VMs using automation workflows.
🌐 Real-World Use Case
At HawkStack Technologies, we’ve successfully helped enterprises migrate large-scale critical workloads from VMware vSphere to OpenShift Virtualization using Ansible. Our structured playbooks, coupled with Red Hat-supported tools, ensured zero data loss and minimal downtime.
🔚 Conclusion
As cloud-native adoption grows, merging the worlds of VMs and containers is no longer optional. With Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization and Ansible Automation Platform, organizations get the best of both worlds — a powerful, policy-driven, scalable infrastructure that supports modern and legacy workloads alike.
If you're planning a VM migration journey or modernizing your data center, reach out to HawkStack Technologies — Red Hat Certified Partners — to accelerate your transformation. For more details www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
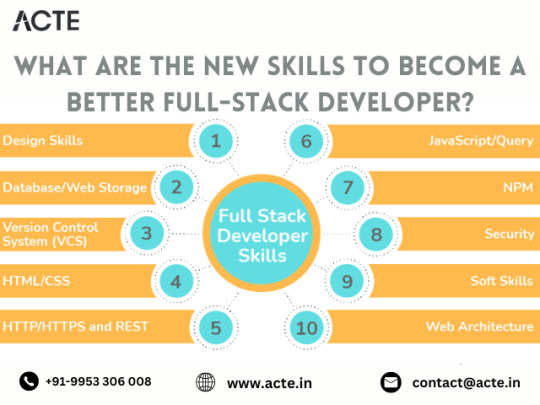
Elevating Your Full-Stack Developer Expertise: Exploring Emerging Skills and Technologies
Introduction: In the dynamic landscape of web development, staying at the forefront requires continuous learning and adaptation. Full-stack developers play a pivotal role in crafting modern web applications, balancing frontend finesse with backend robustness. This guide delves into the evolving skills and technologies that can propel full-stack developers to new heights of expertise and innovation.

Pioneering Progress: Key Skills for Full-Stack Developers
1. Innovating with Microservices Architecture:
Microservices have redefined application development, offering scalability and flexibility in the face of complexity. Mastery of frameworks like Kubernetes and Docker empowers developers to architect, deploy, and manage microservices efficiently. By breaking down monolithic applications into modular components, developers can iterate rapidly and respond to changing requirements with agility.
2. Embracing Serverless Computing:
The advent of serverless architecture has revolutionized infrastructure management, freeing developers from the burdens of server maintenance. Platforms such as AWS Lambda and Azure Functions enable developers to focus solely on code development, driving efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Embrace serverless computing to build scalable, event-driven applications that adapt seamlessly to fluctuating workloads.
3. Crafting Progressive Web Experiences (PWEs):
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) herald a new era of web development, delivering native app-like experiences within the browser. Harness the power of technologies like Service Workers and Web App Manifests to create PWAs that are fast, reliable, and engaging. With features like offline functionality and push notifications, PWAs blur the lines between web and mobile, captivating users and enhancing engagement.
4. Harnessing GraphQL for Flexible Data Management:
GraphQL has emerged as a versatile alternative to RESTful APIs, offering a unified interface for data fetching and manipulation. Dive into GraphQL's intuitive query language and schema-driven approach to simplify data interactions and optimize performance. With GraphQL, developers can fetch precisely the data they need, minimizing overhead and maximizing efficiency.
5. Unlocking Potential with Jamstack Development:
Jamstack architecture empowers developers to build fast, secure, and scalable web applications using modern tools and practices. Explore frameworks like Gatsby and Next.js to leverage pre-rendering, serverless functions, and CDN caching. By decoupling frontend presentation from backend logic, Jamstack enables developers to deliver blazing-fast experiences that delight users and drive engagement.
6. Integrating Headless CMS for Content Flexibility:
Headless CMS platforms offer developers unprecedented control over content management, enabling seamless integration with frontend frameworks. Explore platforms like Contentful and Strapi to decouple content creation from presentation, facilitating dynamic and personalized experiences across channels. With headless CMS, developers can iterate quickly and deliver content-driven applications with ease.
7. Optimizing Single Page Applications (SPAs) for Performance:
Single Page Applications (SPAs) provide immersive user experiences but require careful optimization to ensure performance and responsiveness. Implement techniques like lazy loading and server-side rendering to minimize load times and enhance interactivity. By optimizing resource delivery and prioritizing critical content, developers can create SPAs that deliver a seamless and engaging user experience.
8. Infusing Intelligence with Machine Learning and AI:
Machine learning and artificial intelligence open new frontiers for full-stack developers, enabling intelligent features and personalized experiences. Dive into frameworks like TensorFlow.js and PyTorch.js to build recommendation systems, predictive analytics, and natural language processing capabilities. By harnessing the power of machine learning, developers can create smarter, more adaptive applications that anticipate user needs and preferences.
9. Safeguarding Applications with Cybersecurity Best Practices:
As cyber threats continue to evolve, cybersecurity remains a critical concern for developers and organizations alike. Stay informed about common vulnerabilities and adhere to best practices for securing applications and user data. By implementing robust security measures and proactive monitoring, developers can protect against potential threats and safeguard the integrity of their applications.
10. Streamlining Development with CI/CD Pipelines:
Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines are essential for accelerating development workflows and ensuring code quality and reliability. Explore tools like Jenkins, CircleCI, and GitLab CI/CD to automate testing, integration, and deployment processes. By embracing CI/CD best practices, developers can deliver updates and features with confidence, driving innovation and agility in their development cycles.
#full stack developer#education#information#full stack web development#front end development#web development#frameworks#technology#backend#full stack developer course
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why You Should Hire Developers Who Understand the Future of Tech
Whether you’re launching a startup, scaling your SaaS product, or building the next decentralized app, one thing is clear—you need the right developers. Not just any coders, but skilled professionals who understand both the technical and strategic sides of digital product building.
In today’s fast-evolving tech landscape, the need to hire developers who are agile, experienced, and forward-thinking has never been greater. From blockchain to AI to SaaS, the right team can turn your business vision into a scalable, future-proof product.
Why Hiring Developers is a Strategic Move, Not Just a Task
In-house or outsourced, full-time or fractional—hiring developers is not just about filling a technical role. It’s a strategic investment that determines:
The speed at which you go to market
The quality of your product
The ability to scale your infrastructure
The cost-effectiveness of your development cycle
When you hire developers who are aligned with your business goals, you're not just building software—you’re building competitive advantage.
The Types of Developers You Might Need
Your hiring approach should depend on what you're building. Here are some common roles modern businesses look for:
1. Frontend Developers
They create seamless and engaging user interfaces using technologies like React, Angular, or Vue.js.
2. Backend Developers
These developers handle the logic, databases, and server-side functions that make your app run smoothly.
3. Full-Stack Developers
They handle both front and back-end responsibilities, ideal for MVPs or lean startups.
4. Blockchain Developers
Crucial for any web3 development company, they specialize in smart contracts, dApps, and crypto integrations.
5. AI Engineers
As AI product development continues to grow, developers with machine learning and automation skills are increasingly in demand.
6. DevOps Engineers
They ensure your systems run efficiently, automate deployment, and manage infrastructure.
Depending on your project, you may need to hire developers who are specialists or build a blended team that covers multiple areas.
The Modern Developer Stack: More Than Just Code
Today’s development goes far beyond HTML and JavaScript. You need developers familiar with:
Cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP)
Containers & orchestration (Docker, Kubernetes)
APIs & microservices
Version control (Git, GitHub, Bitbucket)
Security best practices
Automated testing & CI/CD
The goal isn’t just to write code—it’s to build secure, scalable, and high-performance systems that grow with your business.
SaaS Products Need Specialized Developer Expertise
If you're building a SaaS platform, the development process must account for:
Multi-tenant architecture
Subscription billing
Role-based access
Uptime and monitoring
Seamless UX and product-led growth
That’s where experienced saas experts come in—developers who not only write clean code but understand SaaS metrics, scale, and user behavior.
Hiring the right SaaS development team ensures your platform can evolve with user needs and business growth.
Web3: The Future of App Development
More and more businesses are looking to create decentralized applications. If you’re building in the blockchain space, you need to hire developers who are familiar with:
Ethereum, Polygon, Solana, or other chains
Smart contract development (Solidity, Rust)
Wallet integrations and token standards
DeFi and DAO protocols
Collaborating with a seasoned web3 development company gives you access to specialized talent that understands the nuances of decentralization, tokenomics, and trustless systems.
AI-Driven Applications: Why You Need Developers with ML Skills
From personalized recommendations to intelligent chatbots, AI product development is becoming an essential feature of modern apps. Developers with AI and machine learning knowledge help you:
Implement predictive analytics
Automate workflows
Train custom models
Use data more effectively
If your project involves building intelligent features or analyzing large datasets, hiring developers with AI experience gives you a distinct edge.
In-House vs Outsourced: What’s Right for You?
Many businesses face the choice: Should we build an in-house team or hire externally? Here’s a quick breakdown:
Criteria
In-House Team
Outsourced Developers
Control
High
Medium to High (depending on provider)
Cost
Higher (salaries + overhead)
More flexible, often cost-effective
Speed to Hire
Slower
Faster (especially with an agency/partner)
Specialized Skills
Limited
Broader talent pool
Scalability
Moderate
High
For many startups and growing businesses, the best solution is to partner with a development agency that gives you dedicated or on-demand talent, while letting you stay lean and focused.
What to Look for When Hiring Developers
To make the most of your investment, look for developers who:
Have a proven portfolio of completed projects
Are fluent in your tech stack
Can communicate clearly and collaborate cross-functionally
Understand business logic, not just code
Are committed to continuous learning
Whether you’re hiring freelancers, building an internal team, or partnering with a service provider—vetting for these traits is key to long-term success.
Final Thoughts: Hire Smart, Build Faster
Tech moves fast—and the companies that keep up are the ones with the right talent by their side.
Choosing to hire developers who understand modern trends like Web3, AI, and SaaS is no longer optional. It’s the difference between building something that merely works—and building something that lasts, grows, and disrupts.
If you’re ready to build a world-class product with a team that understands both code and strategy, explore partnering with a trusted digital team today.
The future is being written in code—make sure yours is built by the right hands
0 notes
Text
Q-AIM: Open Source Infrastructure for Quantum Computing

Q-AIM Quantum Access Infrastructure Management
Open-source Q-AIM for quantum computing infrastructure, management, and access.
The open-source, vendor-independent platform Q-AIM (Quantum Access Infrastructure Management) makes quantum computing hardware easier to buy, meeting this critical demand. It aims to ease quantum hardware procurement and use.
Important Q-AIM aspects discussed in the article:
Design and Execution Q-AIM may be installed on cloud servers and personal devices in a portable and scalable manner due to its dockerized micro-service design. This design prioritises portability, personalisation, and resource efficiency. Reduced memory footprint facilitates seamless scalability, making Q-AIM ideal for smaller server instances at cheaper cost. Dockerization bundles software for consistent performance across contexts.
Technology Q-AIM's powerful software design uses Docker and Kubernetes for containerisation and orchestration for scalability and resource control. Google Cloud and Kubernetes can automatically launch, scale, and manage containerised apps. Simple Node.js, Angular, and Nginx interfaces enable quantum gadget interaction. Version control systems like Git simplify code maintenance and collaboration. Container monitoring systems like Cadvisor monitor resource usage to ensure peak performance.
Benefits, Function Research teams can reduce technical duplication and operational costs with Q-AIM. It streamlines complex interactions and provides a common interface for communicating with the hardware infrastructure regardless of quantum computing system. The system reduces the operational burden of maintaining and integrating quantum hardware resources by merging access and administration, allowing researchers to focus on scientific discovery.
Priorities for Application and Research The Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) algorithm is studied to demonstrate how Q-AIM simplifies hardware access for complex quantum calculations. In quantum chemistry and materials research, VQE is an essential quantum computation algorithm that approximates a molecule or material's ground state energy. Q-AIM researchers can focus on algorithm development rather than hardware integration.
Other Features QASM, a human-readable quantum circuit description language, was parsed by researchers. This simplifies algorithm translation into hardware executable instructions and quantum circuit manipulation. The project also understands that quantum computing errors are common and invests in scalable error mitigation measures to ensure accuracy and reliability. Per Google Cloud computing instance prices, the methodology considers cloud deployment costs to maximise cost-effectiveness and affect design decisions.
Q-AIM helps research teams and universities buy, run, and scale quantum computing resources, accelerating progress. Future research should improve resource allocation, job scheduling, and framework interoperability with more quantum hardware.
To conclude
The majority of the publications cover quantum computing, with a focus on Q-AIM (Quantum Access Infrastructure Management), an open-source software framework for managing and accessing quantum hardware. Q-AIM uses a dockerized micro-service architecture for scalable and portable deployment to reduce researcher costs and complexity.
Quantum algorithms like Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) are highlighted, but the sources also address quantum machine learning, the quantum internet, and other topics. A unified and adaptable software architecture is needed to fully use quantum technology, according to the study.
#QAIM#quantumcomputing#quantumhardware#Kubernetes#GoogleCloud#quantumcircuits#VariationalQuantumEigensolver#machinelearning#News#Technews#Technology#TechnologyNews#Technologytrends#Govindhtech
0 notes
Text
DevOps for Beginners: Navigating the Learning Landscape
DevOps, a revolutionary approach in the software industry, bridges the gap between development and operations by emphasizing collaboration and automation. For beginners, entering the world of DevOps might seem like a daunting task, but it doesn't have to be. In this blog, we'll provide you with a step-by-step guide to learn DevOps, from understanding its core philosophy to gaining hands-on experience with essential tools and cloud platforms. By the end of this journey, you'll be well on your way to mastering the art of DevOps.

The Beginner's Path to DevOps Mastery:
1. Grasp the DevOps Philosophy:
Start with the Basics: DevOps is more than just a set of tools; it's a cultural shift in how software development and IT operations work together. Begin your journey by understanding the fundamental principles of DevOps, which include collaboration, automation, and delivering value to customers.
2. Get to Know Key DevOps Tools:
Version Control: One of the first steps in DevOps is learning about version control systems like Git. These tools help you track changes in code, collaborate with team members, and manage code repositories effectively.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Dive into CI/CD tools like Jenkins and GitLab CI. These tools automate the building and deployment of software, ensuring a smooth and efficient development pipeline.
Configuration Management: Gain proficiency in configuration management tools such as Ansible, Puppet, or Chef. These tools automate server provisioning and configuration, allowing for consistent and reliable infrastructure management.
Containerization and Orchestration: Explore containerization using Docker and container orchestration with Kubernetes. These technologies are integral to managing and scaling applications in a DevOps environment.
3. Learn Scripting and Coding:
Scripting Languages: DevOps engineers often use scripting languages such as Python, Ruby, or Bash to automate tasks and configure systems. Learning the basics of one or more of these languages is crucial.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Delve into Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation. IaC allows you to define and provision infrastructure using code, streamlining resource management.
4. Build Skills in Cloud Services:
Cloud Platforms: Learn about the main cloud providers, such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Discover the creation, configuration, and management of cloud resources. These skills are essential as DevOps often involves deploying and managing applications in the cloud.
DevOps in the Cloud: Explore how DevOps practices can be applied within a cloud environment. Utilize services like AWS Elastic Beanstalk or Azure DevOps for automated application deployments, scaling, and management.
5. Gain Hands-On Experience:
Personal Projects: Put your knowledge to the test by working on personal projects. Create a small web application, set up a CI/CD pipeline for it, or automate server configurations. Hands-on practice is invaluable for gaining real-world experience.
Open Source Contributions: Participate in open source DevOps initiatives. Collaborating with experienced professionals and contributing to real-world projects can accelerate your learning and provide insights into industry best practices.
6. Enroll in DevOps Courses:
Structured Learning: Consider enrolling in DevOps courses or training programs to ensure a structured learning experience. Institutions like ACTE Technologies offer comprehensive DevOps training programs designed to provide hands-on experience and real-world examples. These courses cater to beginners and advanced learners, ensuring you acquire practical skills in DevOps.

In your quest to master the art of DevOps, structured training can be a game-changer. ACTE Technologies, a renowned training institution, offers comprehensive DevOps training programs that cater to learners at all levels. Whether you're starting from scratch or enhancing your existing skills, ACTE Technologies can guide you efficiently and effectively in your DevOps journey. DevOps is a transformative approach in the world of software development, and it's accessible to beginners with the right roadmap. By understanding its core philosophy, exploring key tools, gaining hands-on experience, and considering structured training, you can embark on a rewarding journey to master DevOps and become an invaluable asset in the tech industry.
7 notes
·
View notes