#linear equations in one variable class 8 answers
Text
Class-8 Mathematics NCERT Solution Execrise 2.4 Question 3,4,5
#linear equations in one variable class 8 in hindi#linear equations in one variable class 8 ex 2.1#linear equations in one variable class 8 in english#linear equations in one variable class 8 activity#linear equations in one variable class 8 answers#linear equations in one variable class 8 all formulas#linear equations in one variable class 8 cbse#linear equations in one variable class 8 chapter 2#linear equations in one variable class 8 dav#linear equations in one variable class 8 full chapter#linear equations in one variable class 8 formulas#linear equations in one variable for class 8#linear equations in one variable class 8 hindi#linear equations in one variable class 8 hindi medium#linear equations in one variable class 8 important questions#Math's with Narendra Sir provide to you maths videos for all classes.#Maths with Narendra Sir give you live-class platform#for math skills.#Learn math by taking free online math courses.#Get introductions to algebra#geometry#trigonometry with current math coursework and AP exam preparation.#Select a course to learn more.#We create a unique adaptive learning path for you#We diagnose and identify the student’s current needs#We recommend topics that are right for the student#Students choose and work through the topics at their own pace#We supplement the in-class learning with targeted at-home practiceMath's with Narendra Sir provide to you maths videos for all classes.#Select a course to learn more. basic mathema#tics
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Kuta software algebra 1 word problems

#KUTA SOFTWARE ALGEBRA 1 WORD PROBLEMS PDF#
#KUTA SOFTWARE ALGEBRA 1 WORD PROBLEMS SOFTWARE#
#KUTA SOFTWARE ALGEBRA 1 WORD PROBLEMS FREE#
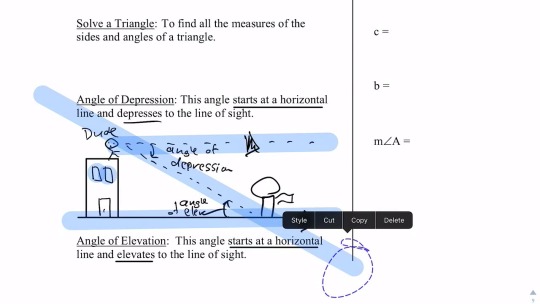
Software for math teachers that creates exactly the worksheets you need in a matter of minutes. O h2 80×1 a2w okbuit 1a k ys somfbt0w 0a 7r mes il dl8c v k d barl ol n qrli3gahzt esn yr we 7spevrsv3efdv x h 0m 8a 7d 3ee mwei8tnh c virn zfli lnpihtuea vanlkg exb1rzaj d1y. Available for pre algebra algebra 1 geometry algebra 2 precalculus and calculus. Algebra 1 Worksheets Word Problems Worksheets. Trigonometry Angle Of Elevation Depression T6 Answers Pdf.
#KUTA SOFTWARE ALGEBRA 1 WORD PROBLEMS PDF#
Test and worksheet generators for math teachers. Math Plane Algebra Word Problems Linear Equations Worksheet Pdf Kuta Samsfriedchickenanddonuts.
#KUTA SOFTWARE ALGEBRA 1 WORD PROBLEMS SOFTWARE#
Worksheet by kuta software llc kuta software infinite algebra 1 literal equations name date period solve each equation for the indicated variable. Choose the type of question to create the list of topics is organized like an index so it is very easy to find the topic you are looking for. Average time saved creating class materials using our desktop software.Ĭomplete list of pre algebra topics complete list of algebra 1 topics complete list of geometry topics complete list of algebra 2 topics. Utilize the kuta software bank of assignments. Your answer should contain only positive exponents. Kuta software infinite algebra 1 name combining like terms date period simplify each expression. With danger on their trail they must trust each other completely or face certain death alone.Based on 2 103 respondents. Software for math teachers that creates exactly the worksheets you need in a matter of minutes. The kuta software infinite algebra 1 multi step equations is developing at a frantic pace. 4 and 8 2) The difference of two numbers is 3. K Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC 11 m 4 9 2 67 90 2 3 10 12 11 6 1 3 p 1 1 2 13 1 13 64 11 8 v 7 8 14 39 5 2m 3 9 10 15 n 3 4 2 3 4 2 16 9 10 n 1 1 10 1 2 9 17 1 1 2 v 3 3 10 1 4 5 18 n 4 7 3 3 4 7 19 9k 65 1 316 845 9 12 13 20 9 19 n 11 10 10 19 21 1 3 n 4 3 1 22 26 33 13 11 x 2 3-2-. L Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 1 Name Systems of Equations Word Problems Date Period 1) Find the value of two numbers if their sum is 12 and their difference is 4. Kuta software infinite algebra 2 name solving multi step equations date period solve each equation 1 4n 2n 4 2 12 2 5v 2v n 2 v 2 3 3 x 3 5 x 4 x 3 3 6 x 0 5 12 3 2k 3k x 6 6 1 3r 2r r 1 k 3 7 6 3 x 2 8 3 4r 8 36 x 4 9 24 6 x 3 r 5 10 75 3 6n. – Jennifer Lynn Barnes New York Times bestselling author of The Inheritance Games In this gripping YA novel about social media. Suitable for any class with algebra content. Kuta Software Infinite Algebra 1 Two Step Equations Worksheet Answers – It is actually exhausting whenever your youngsters request you in aiding these algebra. There are several reasons for this dynamic. Algebra 1 Skills Practice Love and BetrayalRegency style A young woman of noble blood raised as a peasant girl An orphaned. Two-Step Word Problems Kuta Software Llc Pages 1 4 Kutasoftware. Secondly the needs of users are growing requirements are increasing and the needs are changing for kuta. Algebra Worksheet Evaluating Two Step Algebraic Expressions With One Variable A Algebraic Expressions Evaluating Expressions Algebra Worksheets. Read PDF Kuta Software Infinite Algebra 1 Writing Linear Equations Answer Key Jane Anonymous Raw real and utterly gripping.īy Celestine Aubry on September 3 2020. Algebra 1 Multi-Step Equations Part 1 2 Step Equations Worksheets With Answers Two-Step Word Problems Kuta Software Llc Pages 1 4. Kuta Software – Infinite Pre-Algebra Name_ Multi-Step Equations Date_ Period_ Solve each equation. Solving Multi-Step Equations Date_ Period_ Solve each equation. First new technologies are emerging as a result the equipment is being improved and that in turn requires software changes.
#KUTA SOFTWARE ALGEBRA 1 WORD PROBLEMS FREE#
Free Algebra 1 Worksheets.Īccess Free Kuta Software Infinite Algebra 1 Writing Linear Equations Answer Key backcountry to find him. Create the worksheets you need with Infinite Algebra 1.

0 notes
Text
Get all formulas related to linear education in one variable for class 8 with notes and practice exercise questions and solved answers with updates on 2022-2023.
0 notes
Text
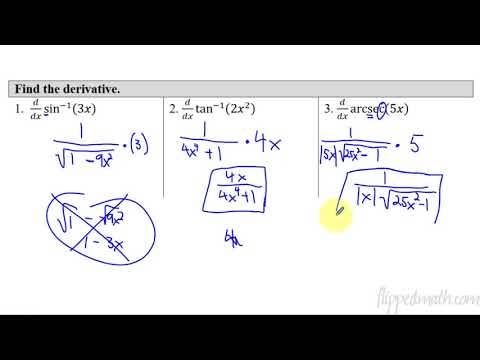
10.4 Usubstitution Trig Functionsap Calculus

10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Answers
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Pdf
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Problems
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Worksheet
Calculus II, Section 7.4, #67 Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions One method of slowing the growth of an insect population without the use of pesticides is to introduce into the population a number of sterile males that mate with fertile females but produce no o spring. Let P represeent. AP Calculus AB Mu Alpha Theta Welcome to AP Calculus AB! Contact me here. Need more review? Browse the Algebra II and Pre-Calculus Tabs. AP ® Calculus AB and BC. COURSE AND EXAM DESCRIPTION. AP COURSE AND EXAM DESCRIPTIONS ARE UPDATED PERIODICALLY. Please visit AP Central. Mathematics 104—Calculus, Part I (4h, 1 CU) Course Description: Brief review of High School Calculus, methods and applications of integration, infinite series, Taylor's theorem, first order ordinary differential equations. Use of symbolic manipulation and graphics software in Calculus. Note: This course uses Maple®.
Math 104: Calculus I – Notes
Section 004 - Spring 2014
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Answers
Syllabus
Concept Videos

Skeleton NotesComplete Notes
Title
More
Remainder 10.6, 10.9
Remainder 10.6/10.9
Series Estimation & Remainder
Sections 10.8-10.10
Sections 10.8-10.10
Taylor (and Maclaurin) Series
Section 10.7
Section 10.7
Power Series Introduction
Section 10.6
Section 10.6
Alt. Series Test and Abs. Conv.
Conv. Tests
Section 10.5
Section 10.5
The Ratio and Root Tests
Section 10.4
Section 10.4
The Comparison Tests
Section 10.3
Section 10.3
The Integral Test
Section 10.2
Section 10.2
Introduction to Series
Section 10.1
Section 10.1
Sequences
Section 9.2
Section 9.2
Linear Differential Equations
Section 7.2 Pt 1Pt 2
Section 7.2
Separable Differential Equations
Section 8.8
Section 8.8
Probability and Calculus
Odd Ans.
Section 8.7 Pt. 1Pt. 2Section 8.7
Improper Integrals
L'Hopital
Section 8.4 Pt. 1Pt. 2Section 8.4
Partial Fraction Decomposition
Section 8.3 Pt. 1Pt. 2Section 8.3
Trig. Substitution
Section 8.2 Pt. 1Pt. 2Section 8.2
Integrating Trig. Powers
Section 8.1 Pt. 1Pt. 2
Section 8.1
Integration By Parts
Section 6.6
Section 6.6
Center of Mass
Section 6.4
Section 6.4
Surface Area of Revolution
Section 6.3
Section 6.3
Arc Length
Section 6.2Section 6.2
Volumes Using Cylindrical Shells
Section 6.1
Section 6.1
Volumes Using Cross-Sections
disk/washer
Review
Calc I Review
Calc I ReviewLimit, Derivative, and Integral
Area b/w CurvesArea b/w Curves Video Example
U-substitution
Graphs you should know
Print out the skeleton notes before class and bring
them to class so that you don't have to write down
https://foxspain82.tumblr.com/post/657282647494672384/achievement-unlocked-2watermelon-gaming. Hide paragraph marks in microsoft word for mac. everything said in class. If you miss anything, the
complete notes will be posted after class.
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Pdf
My Penn Page | Penn Math 104 Page| Penn Undergraduate Math | Advice | Help|
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Problems
10.4 U-substitution Trig Functionsap Calculus Worksheet
Version #1
The course below follows CollegeBoard's Course and Exam Description. Lessons will begin to appear starting summer 2020.
BC Topics are listed, but there will be no lessons available for SY 2020-2021
Unit 0 - Calc Prerequisites (Summer Work)
0.1 Summer Packet
Unit 1 - Limits and Continuity
1.1 Can Change Occur at an Instant?
1.2 Defining Limits and Using Limit Notation
1.3 Estimating Limit Values from Graphs
1.4 Estimating Limit Values from Tables
1.5 Determining Limits Using Algebraic Properties
(1.5 includes piecewise functions involving limits)
1.6 Determining Limits Using Algebraic Manipulation
1.7 Selecting Procedures for Determining Limits
(1.7 includes rationalization, complex fractions, and absolute value)
1.8 Determining Limits Using the Squeeze Theorem
1.9 Connecting Multiple Representations of Limits
Mid-Unit Review - Unit 1
1.10 Exploring Types of Discontinuities
1.11 Defining Continuity at a Point
1.12 Confirming Continuity Over an Interval
1.13 Removing Discontinuities
1.14 Infinite Limits and Vertical Asymptotes
1.15 Limits at Infinity and Horizontal Asymptotes
1.16 Intermediate Value Theorem (IVT)
Review - Unit 1
Unit 2 - Differentiation: Definition and Fundamental Properties
2.1 Defining Average and Instantaneous Rate of
Change at a Point
2.2 Defining the Derivative of a Function and Using
Derivative Notation
(2.2 includes equation of the tangent line)
2.3 Estimating Derivatives of a Function at a Point
2.4 Connecting Differentiability and Continuity
2.5 Applying the Power Rule
2.6 Derivative Rules: Constant, Sum, Difference, and
Constant Multiple
(2.6 includes horizontal tangent lines, equation of the
normal line, and differentiability of piecewise)
2.7 Derivatives of cos(x), sin(x), e^x, and ln(x)
2.8 The Product Rule
2.9 The Quotient Rule
2.10 Derivatives of tan(x), cot(x), sec(x), and csc(x)
Review - Unit 2
Unit 3 - Differentiation: Composite, Implicit, and Inverse Functions
3.1 The Chain Rule
3.2 Implicit Differentiation
3.3 Differentiating Inverse Functions
3.4 Differentiating Inverse Trigonometric Functions
3.5 Selecting Procedures for Calculating Derivatives
3.6 Calculating Higher-Order Derivatives
Review - Unit 3
Unit 4 - Contextual Applications of Differentiation
4.1 Interpreting the Meaning of the Derivative in Context
4.2 Straight-Line Motion: Connecting Position, Velocity,
and Acceleration
4.3 Rates of Change in Applied Contexts Other Than
Motion
4.4 Introduction to Related Rates
4.5 Solving Related Rates Problems
4.6 Approximating Values of a Function Using Local
Linearity and Linearization
4.7 Using L'Hopital's Rule for Determining Limits of
Indeterminate Forms
Review - Unit 4
Unit 5 - Analytical Applications of Differentiation
5.1 Using the Mean Value Theorem
5.2 Extreme Value Theorem, Global Versus Local
Extrema, and Critical Points
5.3 Determining Intervals on Which a Function is
Increasing or Decreasing
5.4 Using the First Derivative Test to Determine Relative
Local Extrema
5.5 Using the Candidates Test to Determine Absolute
(Global) Extrema
5.6 Determining Concavity of Functions over Their
Domains
5.7 Using the Second Derivative Test to Determine
Extrema
Mid-Unit Review - Unit 5
5.8 Sketching Graphs of Functions and Their Derivatives
5.9 Connecting a Function, Its First Derivative, and Its
Second Derivative
(5.9 includes a revisit of particle motion and
determining if a particle is speeding up/down.)
5.10 Introduction to Optimization Problems
5.11 Solving Optimization Problems
5.12 Exploring Behaviors of Implicit Relations
Review - Unit 5
Unit 6 - Integration and Accumulation of Change
6.1 Exploring Accumulation of Change
6.2 Approximating Areas with Riemann Sums
6.3 Riemann Sums, Summation Notation, and Definite
Integral Notation
6.4 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and
Accumulation Functions
6.5 Interpreting the Behavior of Accumulation Functions
Involving Area
Mid-Unit Review - Unit 6
6.6 Applying Properties of Definite Integrals
6.7 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and Definite
Integrals
6.8 Finding Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals:
Basic Rules and Notation
6.9 Integrating Using Substitution
6.10 Integrating Functions Using Long Division
and Completing the Square
6.11 Integrating Using Integration by Parts (BC topic)
6.12 Integrating Using Linear Partial Fractions (BC topic)
6.13 Evaluating Improper Integrals (BC topic)
6.14 Selecting Techniques for Antidifferentiation
Review - Unit 6
Unit 7 - Differential Equations
7.1 Modeling Situations with Differential Equations
7.2 Verifying Solutions for Differential Equations
7.3 Sketching Slope Fields
7.4 Reasoning Using Slope Fields
7.5 Euler's Method (BC topic)
7.6 General Solutions Using Separation of Variables
7.7 Particular Solutions using Initial Conditions and
Separation of Variables
7.8 Exponential Models with Differential Equations
7.9 Logistic Models with Differential Equations (BC topic)
Review - Unit 7
Unit 8 - Applications of Integration
8.1 Average Value of a Function on an Interval
8.2 Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Using Integrals
8.3 Using Accumulation Functions and Definite Integrals
in Applied Contexts
8.4 Area Between Curves (with respect to x)
8.5 Area Between Curves (with respect to y)
8.6 Area Between Curves - More than Two Intersections
Mid-Unit Review - Unit 8
8.7 Cross Sections: Squares and Rectangles
8.8 Cross Sections: Triangles and Semicircles
8.9 Disc Method: Revolving Around the x- or y- Axis
8.10 Disc Method: Revolving Around Other Axes
8.11 Washer Method: Revolving Around the x- or y- Axis
8.12 Washer Method: Revolving Around Other Axes
8.13 The Arc Length of a Smooth, Planar Curve and
Distance Traveled (BC topic)
Review - Unit 8
Unit 9 - Parametric Equations, Polar Coordinates, and Vector-Valued Functions (BC topics)
9.1 Defining and Differentiating Parametric Equations
9.2 Second Derivatives of Parametric Equations
9.3 Arc Lengths of Curves (Parametric Equations)
9.4 Defining and Differentiating Vector-Valued Functions
9.5 Integrating Vector-Valued Functions
9.6 Solving Motion Problems Using Parametric and
Vector-Valued Functions
9.7 Defining Polar Coordinates and Differentiating in
Polar Form
9.8 Find the Area of a Polar Region or the Area Bounded
by a Single Polar Curve
9.9 Finding the Area of the Region Bounded by Two
Polar Curves
Review - Unit 9
Unit 10 - Infinite Sequences and Series (BC topics)
10.1 Defining Convergent and Divergent Infinite Series
10.2 Working with Geometric Series
10.3 The nth Term Test for Divergence
10.4 Integral Test for Convergence
10.5 Harmonic Series and p-Series
10.6 Comparison Tests for Convergence
10.7 Alternating Series Test for Convergence
10.8 Ratio Test for Convergence
10.9 Determining Absolute or Conditional Convergence
10.10 Alternating Series Error Bound
10.11 Finding Taylor Polynomial Approximations of
Functions
10.12 Lagrange Error Bound
10.13 Radius and Interval of Convergence of Power
Series
10.14 Finding Taylor Maclaurin Series for a Function
10.15 Representing Functions as a Power Series
Review - Unit 8
Version #2
The course below covers all topics for the AP Calculus AB exam, but was built for a 90-minute class that meets every other day.
Lessons and packets are longer because they cover more material.
Unit 0 - Calc Prerequisites (Summer Work)
0.1 Things to Know for Calc
0.2 Summer Packet
0.3 Calculator Skillz
Unit 1 - Limits
1.1 Limits Graphically
1.2 Limits Analytically
1.3 Asymptotes
1.4 Continuity
Review - Unit 1
Unit 2 - The Derivative
2.1 Average Rate of Change
2.2 Definition of the Derivative
2.3 Differentiability (Calculator Required)
Review - Unit 2
Unit 3 - Basic Differentiation
3.1 Power Rule
3.2 Product and Quotient Rules
3.3 Velocity and other Rates of Change
3.4 Chain Rule
3.5 Trig Derivatives
Review - Unit 3
Unit 4 - More Deriviatvies
4.1 Derivatives of Exp. and Logs
4.2 Inverse Trig Derivatives
4.3 L'Hopital's Rule
Review - Unit 4
Unit 5 - Curve Sketching
5.1 Extrema on an Interval
5.2 First Derivative Test
5.3 Second Derivative Test
Review - Unit 5
Unit 6 - Implicit Differentiation
6.1 Implicit Differentiation
6.2 Related Rates
6.3 Optimization
Review - Unit 6
Unit 7 - Approximation Methods
7.1 Rectangular Approximation Method
7.2 Trapezoidal Approximation Method
Review - Unit 7
Unit 8 - Integration
8.1 Definite Integral
8.2 Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (part 1)
8.3 Antiderivatives (and specific solutions)
Review - Unit 8
Unit 9 - The 2nd Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
9.1 The 2nd FTC
9.2 Trig Integrals
9.3 Average Value (of a function)
9.4 Net Change
Review - Unit 9
Unit 10 - More Integrals
10.1 Slope Fields
10.2 u-Substitution (indefinite integrals)
10.3 u-Substitution (definite integrals)
10.4 Separation of Variables
Review - Unit 10
Unit 11 - Area and Volume
11.1 Area Between Two Curves
11.2 Volume - Disc Method
11.3 Volume - Washer Method
11.4 Perpendicular Cross Sections
Review - Unit 11

0 notes
Text
300+ TOP STATA Interview Questions and Answers
STATA Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is the elementary use of Stata?
The integrated statistical software is fundamentally used as an integral part of research methodologies in the field of economics, biomedicine, and political science in order to examine data pattern.
2. What are the most advisable functions performed with the help of Stata?
The program is best suited for processing time? the series, panel, and cross? sectional data.
3. What makes the tool more intuitive?
The availability of both command line and graphical user interface makes the usage of the software more spontaneous.
4. What are the competencies of using Stata software?
The incorporation of data management, statistical analysis, graphics, simulations, regression, and custom programming and at the same time it also accommodates a system to disseminate user-written programs that lets it grow continuously, making it an integral statistical tool.
5. List four major builds of Stata and state their purposes?
STATA MP - Multiprocessor computer which includes dual-core and multicore processors.
STATA SE - Majorly used for analyzing larger databases
STATA IC - The standard version of the software
Numerics by STATA support MP, SE AND IC data types in an embedded environment.
6. State the various disciplines which use Stata as an integral software for efficient results?
STATA software acts as an effective analytical and statistical tools for major sectors, they are as follows :
Behavioral sciences: Behavioral scientist entrust STATA for its accuracy, extensibility, reproducibility, and ease of use features. Whether it is an extensive research on cognitive development, studying personality traits or developing measurement instruments, The software accommodates all the required collateral to pursue a broad range of behavioral science questions.
Education: In the process of developing new tests or researching diverse topics as learning and development, teacher effectiveness, or school finance, STATA establishes the relevant and accurate statistical methodology options forward. The analysis is consistently integrated with illustrations (graphics) and data management into one package in order to seek a wide range of educational questions.
Medical: Medicinal researchers entrust to use STATA for its range of biostatistical methods and reproducibility approach towards the data. In the process of any medical research or while performing a clinical trial, the program provides accurate tools which helps conduct the study from power and sample-size calculations to data management to analysis.
Biostatistics: Biostatisticians approve of STATA for its accuracy, extensibility, and reproducibility. Inconsiderate of the study’s statistical approach or focus area or whether it is a cross-sectional, longitudinal, or time-to-event. STATA equips the users with all the necessary statistics, graphics, and data management tools needed to implement and study a wide range of biostatistical methods.
Economics: The researchers in the field of economics have always relied upon STATA for its accuracy and relevancy. Whether its a study on educational institution selection research process, Gross domestic price or stock trends, Stata provides all the statistics, graphics, and data management tools needed to complete the study with utmost authenticity.
Business / Finance - Marketing: financial and marketing research analysts often rely on this tool in the case of researching asset pricing, capital market dynamics, customer-value management, consumer and firm behaviour, or branding, the reason being its accuracy and extensibility of providing all the statistics, graphics, and data management tools.
Sociology: Apart from the above-listed sectors, STATA is also used in the study of demographic and geographic research processes.
7. What are the key features of Stata/ MP?
STATA/ MP is termed as the fastest and largest version of the program.
This version’s multiprocessing abilities provide the most comprehensive support (multi core) to all kinds of statistics and data administration.
STATA/MP supports over 64 cores/processors, making it the fastest medium to analyze the data when compared to STATA/SE.
This version interprets 10 to 20 billion observations in comparison to STATA/SE’s 2 billion observations.
The program is 100% compatible with other versions and needs no modification of the analyses to obtain Stata/MP's speed improvements.
8. List down few highlights of new Stata 15?
Extended regression modules which can address the problems such as Endogenous covariates, Nonrandom treatment assignment etc in any combination, unlike the previous Heckman and ivregress modules.
STATA’S Latin Class Analysis helps to identify unobserved categories in the latent classes.
STATA now supports Markdown - A standard markup language that allows text formatting from plain text input.
Program's Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium command estimates the parameters of DSGE models that are linear in the variables but potentially nonlinear in the parameters.
Bayes prefix, when combined with Bayesian features with STATA’S spontaneous and elegant specification of regression models, lets the users fit Bayesian regression models more conveniently and fit additional models.
9. What is the work function of Stata’S user interface?
Primarily, STATA by default opens in four different windows :
Results: This window displays all the commands and their results, with an exception being made for graphs which are showcased in their own window.
Review: Only the commands are made visible in this particular window. When clicked on any specific command by the user it appears on a separate window. The review tab has an option of “ Save Review Contents ” which allows the user to save all documented files in the review window to a file for later use. ( This is not a substitute for log and do files.)
Command: This is the space used to type the commands while working in an interactive mechanism. All the content typed here will be reflected in both results and review windows. “ Page Up “ and “ Page Down “ keys are used in order to view previously executed commands.
Variables: Entire list of user ’s variables and their labels are displayed here. When clicked it will be pasted in the command window.
10. What are the various data format compatible with Stata software?
STATA is compatible to import data from various formats, Inclusive of ASCII data formats (such as CSV or databank formats) and spreadsheet formats (including various Excel formats). It can as well read and write SAS XPORT format datasets natively, using the fdause and fdasave commands.
The STATAS’s dominion file formats are platform independent, which enables the users from different operating systems comfortably exchange datasets and programs. Although there has been consistent change over the course of time with respect to STATA’S data format, still the users can read all older dataset formats and can write both the current and most recent previous dataset format, using the same old command.

STATA Interview Questions
11. Elaborate on Do, Log and CmdLog files?
The User must always operate his work in a do-file, which ensures the output can be reproduced at a later time. One can start a do.file by simply clicking on the do.file editor button. The user has to also make sure to always turn on “Auto indent” and Auto save on do/run” options presented in the preferences tab.
Another cardinal rule while working on STATA is the always maintain a log file running. These files have a record of the work done and even showcases the results. This function can be activated by giving "log using mylog.log" command. The usage of “.log” extension automatically creates the log as a plain text file that can then be opened in Microsoft Word or notepad as well as Stata's viewer.
One can initiate command log with the command "cmdlog using mycmdlog.log". This ensures the file is saved in the text format. CmdLog has only the executed commands with no reflection of the output. Additionally, all the commands irrespective of where they are issued from are recorded in the command log.
12. Explain Stata salient features?
Time series: This feature of the software allows the users to handle all the statistical challenges constitutional to time-series data, for example, common factors, autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity, unit roots, autocorrelations etc. The program operates various activities like filtering to fitting compound multiple variate models and graphing which reveals the structure into the time series.
Survival Analysis: With the help of specialized survival analytical tools provided by STATA, the user an analyze the duration of an outcome. They can estimate and plot the possibility of survival over time irrespective of discrepancies such as (unobserved event, delay entry or gaps in the study). hazard ratios, mean survival time, and survival probabilities can be predicted with the help of this model.
Extended regression Models: ERM is the face name for the class of models addresses several complications that arise on a regular basis frequently. Example of ERMS are 1) endogenous covariates, 2) sample selection and 3) non random treatment assignment. These complications can either arise alone or with any combination. The ERMs grants the user to make authentic inferences.
Structural Equation Modeling: SME performs an assessment of the mediation effects. It evaluates the relationship between unobserved latent concept and observed variables that measure the concerned latent concept.
ANOVA / MANOVA: These are known as Fit one- and two-way models. They analyze the data enclosed, fixed or random factors or with repeated measures. ANOVA is used when the user faces continuous covariates, whereas MANOVA models when the user has multiple outcome variables. The relationship between the outcome and predictors can be explored by estimating effect sizes and computing least-squares and marginal means.
13. List down standards methods and advanced techniques provided by Stata program?
STATA provides over 100 various authentic statistical tools. Here are the few examples:
STANDARD METHODS ADVANCED TECHNIQUES
Basic tabulations and summaries Time-series smoothers
Multilevel models Binary, count, and censored outcomes
Case-control analysis Contrasts and comparisons
Dynamic panel-data (DPD) regressions Multiple imputations
Power analysis SEM (structural equation modeling)
ANOVA and MANOVA Latent class analysis (LCA)
14. Explain Publication - Quality graphics feature?
STATA makes it convenient for the users to generate high-quality styled graphs and visual representations. A user can either point and click or write scripts to produce numerous graphs in a reproducible manner. In order to view the visual, it must be either converted into EPS or TIF for publication, to PNG or SVG for the web, or to PDF. With an additional feature of integrated graph editor, the user can alter the graph accordingly.
15. List the different graph styles provided by STATA?
STATA is one of the recommended software to create graphical illustrations, the following are the types of graphs made available by STATA namely :
Bar charts
Box plots
Histograms
Spike plots
Pie charts
Scatterplot matrices
Dot charts
Line charts
Area charts etc.
16. How does the reading and documentation function work in STATA?
In order to write a program to read data into STATA, Then the user has two possible choices. “Infile” and “infix” . When compared to infix, the infile command has more capabilities but at the same time has a higher level of complexity. If the user’s codebook has “start” and “length” information for the variables or the variables are separated by spaces ( not commas or tabs) then it advisable to use infile. On the other hand, if the codebook contains “start” and “end” column information then, the user can go ahead with infix.
17. What are the advantages of using STATA program?
STATA is a fast, accurate and easy to use interface, with an additional feature of intuitive command syntax making it a powerful statistical data analytical tool.
STATA provides a wide range of statistical tools from standard methods such as Basic tabulations and summaries, Case-control analysis, Linear regression to advanced techniques for example: Multilevel models, Dynamic panel data regressions, SEM etc.
Data administration feature of STATA allows complete control over all data types. The user can then combine and reshape data sets, manage variables, and collect statistics across groups or duplicates.
The software is capable to manage unique data sets (survival/duration data, panel/longitudinal etc.)
The program is cross-platform compatible which includes windows, MAC, Linux.
18. Explain the role of MATA programming language?
MATA is a full-fledged programming language that compiles the data typed into bytecode, optimizes it, and executes it fast. Al though it is not a requirement in order to use STATA a fast and complex matrix programming language is an essential part of STATA. The language acts as both interactive environments for manipulating matrices and fully developed environment that can produce compiled and optimized code. It complies important features for the processing of panel data, performs operations on real or complex matrices and offers outright support for object-oriented -programming and is fully integrated with every form of STATA.
19. Explain describe and codebook commands?
Once the data is loaded in STATA, User must document in order to know what are the variables and how they are coded. The describe and codebook commands furnish information about the user’s data.
Describe command is the most basic form of a command. It projects a short description of the file and also lists variables and their required information in the datasets.
Codebook drafts a detailed description of each variable. By default, the codebook command will list variables that have nine or less discrete values and means for those which are more than nine.
STATA Interview Questions and Answers Pdf Download
Read the full article
0 notes
Text
ncert solutions for class 7 maths
class 7 maths
Foundation of any subject is important specifically when you are taking about maths . maths is important subject for your academic journey and class 7 maths build your interest as well we as solid foundations in the subject in this class you start learning the algebra and its applications . so always take class 7 maths studies seriously . you must be wondering what is the best approach to study class 7 maths ? how to score good marks in class 7 maths ? so to answering to your questions lets discuss the right approach of studying class 7 maths .
Right approach to study class 7 maths
About class 7 Books: Selection of right books will help you to have better understanding of the concepts so always make NCERT maths book for class 7 your primary book , follow the sequence of chapters given in NCERT book don’t skip any chapters . after doing NCRET take a reference book or follow entrancei notes which are prepared such a way that it will build your solid foundation in class 7 maths
About class 7 maths class: Always attend the class in school or in tuitions never skip any class , if you have any work or family function or you are sick plan the missing topic during the holidays and be reedy your topics before the next class. In class listen what teacher wants to explain and make all important points notes in your note book . ask your questions don’t hesitate while asking silly questions in class 7 maths .
Brief descriptions about Important Chapters covered in class 7 maths
1. Class 7 maths chapter- NUMBERS
Natural Numbers: The counting numbers are called Natural Numbers.
Thus, N = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5,....} is the set of all natural numbers.
Whole Numbers: Whole Numbers are simply the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …
Thus, W = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.....} is the set of all Whole Numbers.
Integers: Integers are like whole numbers, but they also include negative numbers ... but still no fractions allowed!
So, integers can be negative {-1, -2,-3, -4, -5, … }or positive {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, … }, or zer{0}
We can put that all together like this:
I or Z = { ..., -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ... }
Rational Numbers: A rational number is a number that can be written as a ratio (p/q form). That means it can be written as a fraction, in which both the numerator (p) and the denominator (q) are integers and q not zero.
The number 8 is a rational number because it can be written as the fraction 8/1.
Likewise, 3/4 is a rational number because it can be written as a fraction.
Even a big, clunky fraction like 7,324,908/56,003,492 is rational, simply because it can be written as a fraction.
Equivalent rational numbers: Numbers that have the same value but are represented differently.
2. Class 7 maths chapter- DIVISIBILITY TESTS, SQUARES, CUBES,SQUARE AND CUBE ROOTS
OVISIBILITY
DIVISIBILITY TEST:
Test of Divisibility by 2 : A number is divisible by 2, if its units digit is any of the digits 0, 2, 4, 6 and 8.
Example: Each of the numbers 24, 36, 78, 192, 310, 214166 is divisible by 2.
Prime Factors: A factor of a given number is called a prime factor if this factor is a prime number.
Example: The factors of 42 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 14, 21 and 42. Out of these 2, 3 and 7 are prime numbers. Therefore, 2, 3 and 7 are the prime factors of 42.
Common Factors: A number which divides each one of the given numbers exactly, is called a common factor of each of the given numbers.
Example: 4 divide each one of 212 and 356 exactly. Therefore, 4 is a common factor of 212 and 356.
H.C.F. (HIGHEST COMMON FACTOR) OR G.C.D. (GREATEST COMMON DIVISOR) :
H.C.F. or G.C.D. of two or more numbers is the greatest number that divides each one of them exactly.
3. Class 7 maths chapter- ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS AND IDENTITIES
In the previous class, we have learnt about algebraic expressions and their addition and subtraction. In this chapter we shall study multiplication and division of algebraic expressions in the form of monomials and binomials etc.
Constants: A symbol having a fixed numerical value is called a constant.
Variables or Literals: A symbol which takes on various numerical values is known as a variable or a literal.
We know that the perimeter of a square of side a is given by the formula, P = 4a.
Here 4 is a constant, while a and P are variables.
We may give any value to a and get the corresponding value of P.
Algebraic Expressions : A combination of constants and variables, connected by +, - , and is known as an algebraic expression.
Types of algebraic expressions:
1. Monomial : An algebraic expression containing only one term, is called a monomial.
2. Binomial : An algebraic expression containing 2 terms is called a binomial.
3. Trinomial: An algebraic expression containing 3 terms is called a trinomial.
4. Multinomial: An algebraic expression containing more than 3 terms, is called a
multinomial.
Factors of A Term: When numbers and literals are multiple to form a product, then each quantity multiplied is called a factor of the product. A constant factor is called a numerical factor while a variable factor is called a literal factor.
Constant Term: A term of the expression having no literal factor is called the constant term.
Coefficients: Any factor of a term is called the coefficient of the product of other factors.
4. Class 7 maths chapter- EXPONENTS
INTRODUCTION:
we know that can be written as that is read as two raised to the power three. Similarly, 10 times = , read as three raised to the power ten. In general, if x is any number and m is a positive integer, then we have
m times.
The number x is called the base and m is called the exponent or the index of the exponential expression.
5. Class 7 maths chapter- FACTORISATION

Factorisation:
When an algebraic expression can be written as the product of two or more expressions, then each of these expressions is called a factor of the given expression.
G.C.F. or H.C.F of Monomials: The greatest common factor of given monomials is the common factor having greatest coefficient and highest power of the variables.
G.C.F. or H.C.F of Monomials = (G.C.F. or H.C.F of numerical coefficients)
(G.C.F. or H.C.F of literal coefficients)
6. Class 7 maths chapter- SETS
Objects: Everything in this universe, whether living or non living, is called an object. Well-defined collection of objects : A collection of objects is said to be well-defined if itis possible to tell beyond doubt about every object of the universe, whether it is there inour collection or not.
Set : A well-defined collection of objects is called a set.
The objects in a set are called its members or elements.
We usually denote sets by capital letters A, B, C etc.
If x is an element of a set A, we say that x belongs to A and we write, .
If x does not belong to A, we write.
There are two methods of describing a set :
(i) Roster Method or Tabulation Method.
(ii) Description Method or Set-builder Form.
7. Class 7 maths chapter- QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
Quadratic Equations: A polynomial of degree 2 when equated to zero, gives an equations, called a quadratic equations.
Solving Quadratic Equation:
By solving a quadratic equation, we mean finding its roots.
Zero Product Rule:
If a and b are any two numbers or expressions, then ab = 0 a = 0 or b =0.
8. Class 7 maths chapter- LINEAR EQUATION IN TWO VARIABLES
In this chapter we shall we shall learn how to solve linear equations in two variables. For this we shall learn graphical representation of a point in a plane. We shall represent a point with the help of two numbers known as coordinates of that point. The concept of coordinates was given by the French Mathematician Rene Desartes, which integrates Algebra and geometry.
9. Class 7 maths chapter- SPEED, DISTANCE AND TIME
Speed: The rate of change of distance is known as speed.
When an athlete runs a race, the change in the time taken is directly proportional to the change in the distance covered. A change in speed is directly proportional to the change in distance covered. More the speed more is the distance covered in the same time.
Units of Speed: Speed is measured in i) meters/ second or m/s
ii) Kilometers/ hour or km/hr
10. Class 7 maths chapter- Simple Interest:
When money is borrowed, interest is charged for the use of that money for a certain period of time. When the money is paid back, the principal (amount of money that was borrowed) and the interest is paid back. The amount of interest depends on the interest rate, the amount of money borrowed (principal) and the length of time that the money is borrowed.
Simple interest is generally charged for borrowing money for short periods of time. Compound interest is similar but the total amount due at the end of each period is calculated and further interest is charged against both the original principal but also the interest that was earned during that period.
Interest = Principle x rate of interest x time
CO
ORDINATE SYSTEM
0 notes
Text
2019 FURTHER MATHEMATICS EXAM PREP
This is the Exam Prep for your Further Mathematics Examination. We will work through one of the past questions from WAEC as we prepare you for academic excellence in your exam.
Going all the Way with you
We will work through the detailed solution to the Theory Paper of WAEC WASSCE GCE 2018 Exam in a bid to prepare you ahead of your Exams.
As an advocate for academic excellence, what I will like you to do is to first attempt the question on your own. Don't be afraid of making mistakes. You learn by trying, by failing, and then by success. Only check the solution presented here after you have made a judicious attempt on each question.Remember that there is no "singular right way" to go about solving the questions. Just check for consistency in the rules and formulae and guidelines as you work along.
The video link to the solutions are included and if you feel you need further explanations, simply check out the video to enhance your study. But make sure you attempt the question first. For this reason, the blog is broken such that you have to “READ MORE” to see the solution to the question attempted.
Who we are
At Davetuts Academy, we explores the STEM subjects with the aim of preparing students for academic excellence in their O' Level, A'Levels, JAMB UTME, POST-UTME, GED, GCSE and IGCSE exams.
We feature comprehensive solution to examination past questions as we explore the basics of the STEM subjects and utilize appropriate soft tools with tips and tricks to prepare students for academic excellence.
Have a look at our welcome video below:
youtube
If by any means you find this exam prep useful, then go ahead and share and subscribe to our YouTube channel, Davetuts Academy as we aim at building academic excellence together!
So here we go with the Exam Prep for Further Mathematics. All the best with the questions!
A Question on Surd
So first, question 1 from WAEC WASSCE 2018 Further Mathematics Exam:

This is a question on surd operations and you just need to follow the correct steps in evaluating multiplication of surds and then finding the conjugate as appropriate.
The solution is shown below and you can watch the accompanying video for better understanding on how to solve such questions.
Watch the video solution by clicking here.

Evaluating the Upper Limit of a Definite Integral
Question 2 below is a question on definite integral. Go ahead and lay your hands on it.

All you have to do to solve this question is to integrate with respect to x, substitute for the upper and lower limit, and subtract the lower limit function from the upper limit function which is an equation in variable t. The catch is that you have to pick the appropriate value for t from the resulting quadratic equation.
The solution is shown below and you can watch the accompanying video for better understanding on how to solve such questions.
Watch the video solution here.
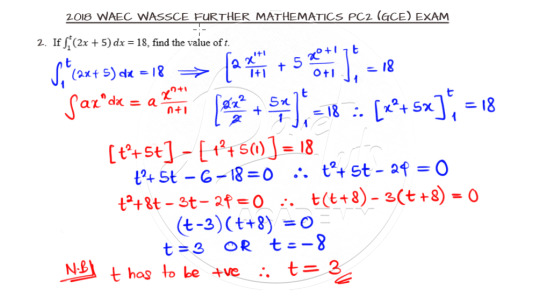
Algebra of Matrices
The next question is on Algebra of matrices. Attempt it first before moving on.

You have to understand the multiplication of matrices to evaluate the square of B and correctly define the identity Matrix I. Once that is done, the matrix N can be evaluated easily.
Click here to watch the video solution to Question 3.
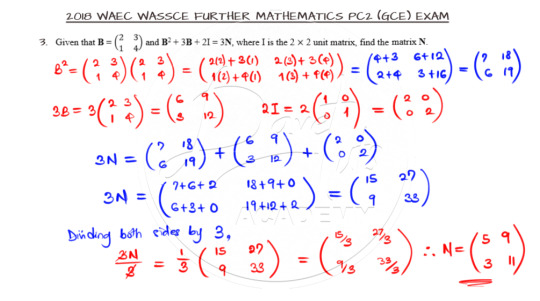
Transform the Equation of a Circle
Question 4 is based on the equation of a circle. Go ahead and try solving on your own first before checking out the solution presented.

Key stuff to simplify the solution include the general equation of a circle and the standard equation of the circle. Furthermore, the process of using completing the square to transform the general equation to the standard equation is quite important to the solution as shown below:


And here is the video for your further study.
youtube
Unordered Selection of Fruits
An unordered selection of fruit is to be carried out in question 5 from combination and you can work it out first.

The confusion to avoid here is the matter of ripe and unripe oranges. Once you can sort that out, the combination formula comes in handy to solve the question.
Click here to watch the accompanying video solution.


Estimate Mode using the Graph
Question 6 is asking us to estimate the modal age of a number of workers using graphical method. So bring out the graph paper and let’s get to work.

Obviously, you need to know the type of graph that can be used to get the mode of a set of data. And histogram is the go-to diagram to help us out. But first, you have to generate your table of values featuring the class boundary. And then you note the highest bar and cross from the adjoining bars to get the point of intersection which can be traced to get the mode.
If you still have some glitches, click here for the video solution.

Finding an Angle of a Triangle using Vector Method
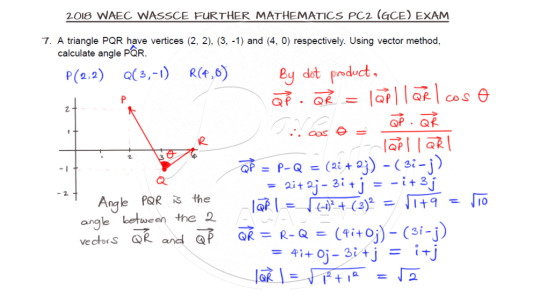
Vectors is here!!! I so much love vectors. And this question is asking us to use vector method to solve for one of the angles of a triangle. So try it out.

First, locate the vertices of the triangle and then you will observe that the point Q is the point at which the angle is to be evaluated. So, taking vectors PQ and RQ, you can find the dot product from which the angle of inclination of the two vectors can be evaluated to yield the answer.
Watch the video solution by clicking on this line.
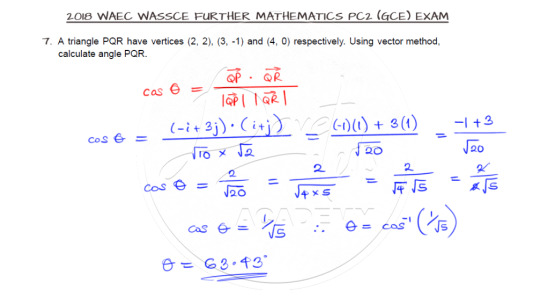
A travelling Motorist in Linear Motion
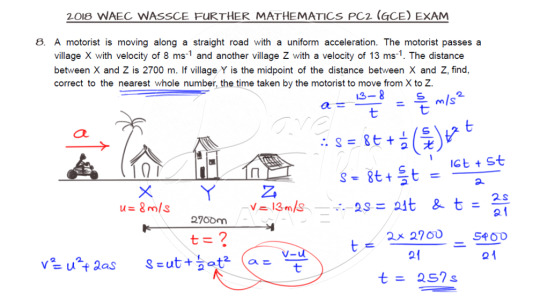
Next is question 8 based on a travelling motorist. Try it out, please.

So we need the Linear equations of motion to handle this question. But you have to interpret the question correctly before you can get it right. And there are at least two ways to go about answering this question. One way to solve it is given below.
Click here to watch the video.
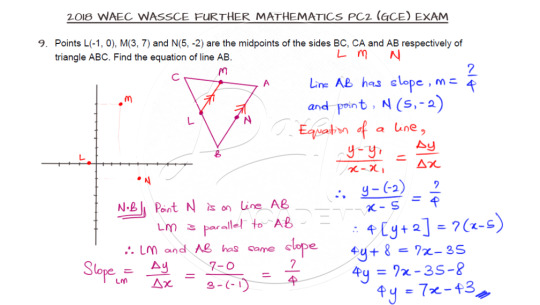
Equation of the Side of a Triangle
Question 9 asks us to evaluate the equation of a line, but not just any line. It is the side of a triangle whose vertices were given. So go ahead and try solving the question.

You need to know that joining the midpoints of two sides of a triangle will yield a line parallel to the third side and since two parallel lines have the same slope, the question can be solved by using the coordinate of the midpoint of the line AB as requested.
Further clarity are presented here in the video solution
Simultaneous Equation + Quadratic Factors
Question 10a is combining a problem on simultaneous equation and factorization of a quadratic polynomial. Try it out and make sure you are on track by making use of your calculator.

To solve this question, you will have to solve a set of simultaneous equations in 3 variables. This will enable you to solve for the values of p, q and r. The resulting quadratic equation can be factored out to get the factors of the given function.
The video solution is presented here.


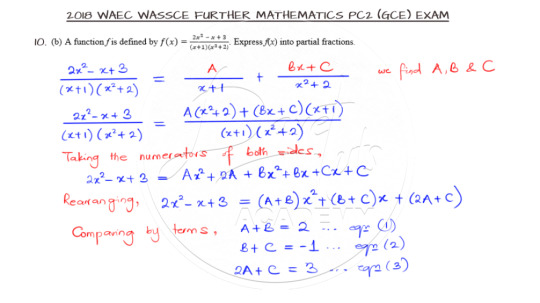
Expressing Rational Function in Partial fractions
Partial fraction is the next question in 10b and the question is as shown below:

The point to note is the splitting of the rational function into its partial fraction components. Once the LCM is sorted out, we can equate the numerators to get the values of the introduced unknowns as shown.
The video solution can be gotten here.

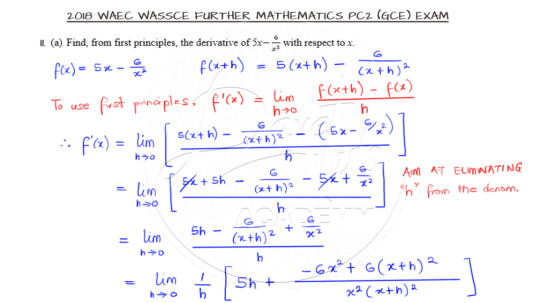
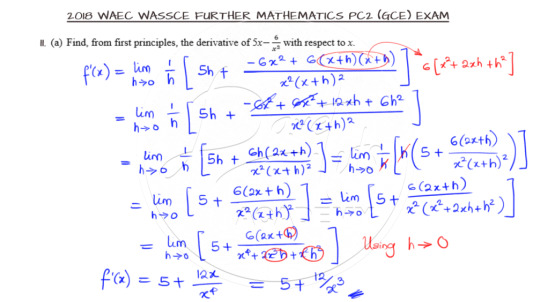
Differentiation from First Principles
Question 11a is on differentiation and we have a simple function to differentiate. But wait a minute. We are to use first principles! So go ahead and attempt this on your own.

I hope you really try this question out. Knowing the technique of differentiation from first principles is vital here. Once the formula is applied, e need to work at eliminating any stand-alone h in the denominator so that we will not have an undefined function while working. For questions like this, the more you practice, the better you become.
Watch the video solution from Davetuts Academy by clicking here.
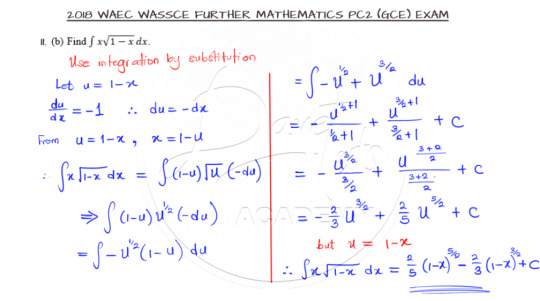
Integration by substitution
Question 11b is based on integration but you need a little trick to solve it. All the best as you attempt this question.

Okay, the little trick is to use substitution. As you can see, trying to integrate straight will constitute the Herculean task of integrating the root of (1-x). So introducing another variable as a function of x and substituting appropriately is the way to go on this type of questions.
And the video is here for better understanding.
Finding the Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient
Question 12a is on Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient and as expected, go ahead and lay your hands on this question.
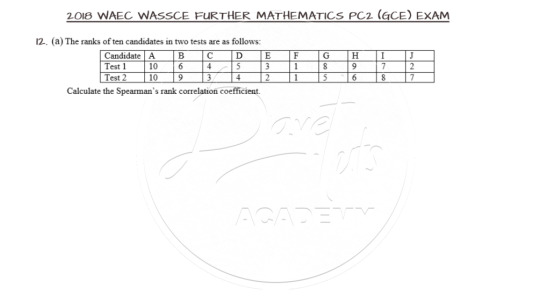
The Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient is used to summarize the strength and direction (negative or positive) of a relationship between two variables. For this question, we need to get the square of the difference in the two tests and use that in the formula for the Coefficient as shown below. As a guide, confirm that the sum of the differences equate to zero, otherwise, something is wrong with your calculation.
The video for the solution can be accessed here.
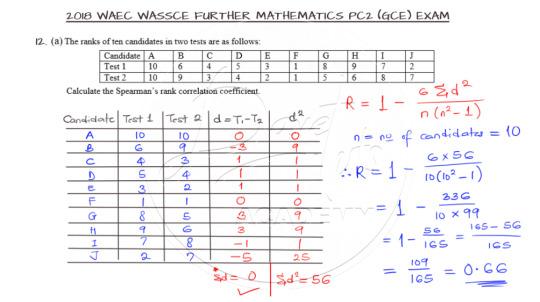
Evaluating Conditional Selection
A conditional selection is to be carried out in Question 12b and you can go ahead to attempt the question.

The first case is quite straightforward, but on the second instance, we need to apply our ingenuity to solve for that “harder” case as shown below.
Here is the video solution for the question.
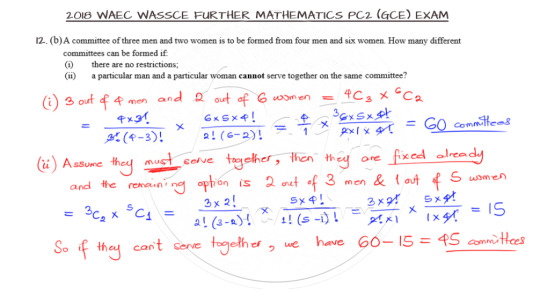
Working with Binomial Probability
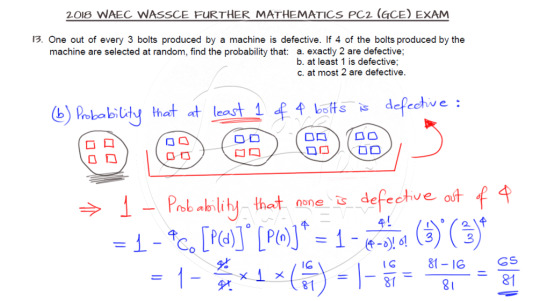
Binomial Probability is featured in Question 13 for us to solve as shown.

Binomial probability refers to the probability of exactly x successes on n repeated trials in an experiment which has two possible outcomes. So here our possible outcomes from the selection is picking either a defective bolt or a non-defective bolt. The solution is as shown below:
Check the video tutorial for detailed explanation of the solution to the question.

Resolution of Concurrent Co-planar Forces
Question 14 is on the resolution of co-planar forces.
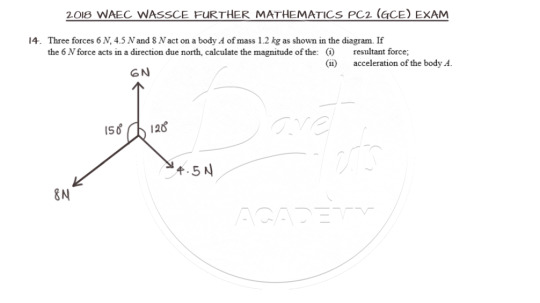
The solution warrants that the inclined forces be resolved to the horizontal and vertical components. This can be done in a variety of ways. You may prefer using the angles 150 and 120 degrees as given or the angles minus 90 degrees or as used in the solution, 180 minus the given angles.

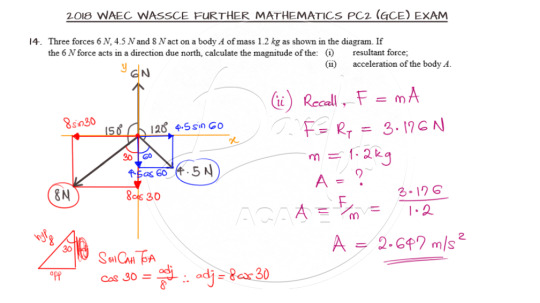
You can watch the video solution as shown below:
youtube
Final Velocity of a Stone under Free Fall
Question 14b features a free falling stone whose final velocity is to be determined.

The equation of motion comes in handy in solving the question as shown below
And here is the link to the video solution too.

Algebra of Vectors
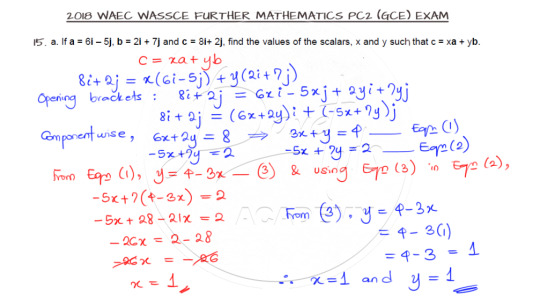
Question 15a features the algebra of vectors. Go through and attempt the question on your own.

The solution involves opening the brackets and equating the components of the resulting vector equation to get the scalars as requested.
The video solution can be gotten here.
Parallelogram Law of Vectors
Finally, our last question features the parallelogram law of vectors.

The cosine rule comes in handy in solving this question and all you need to note is the requested angle as opposed to the angle used in the cosine rule.
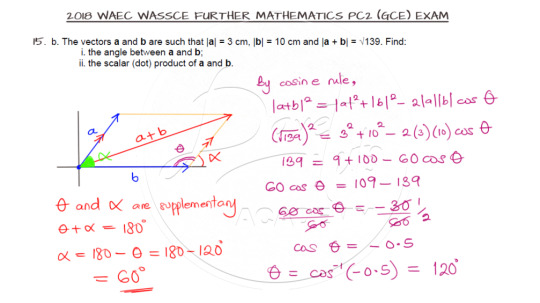
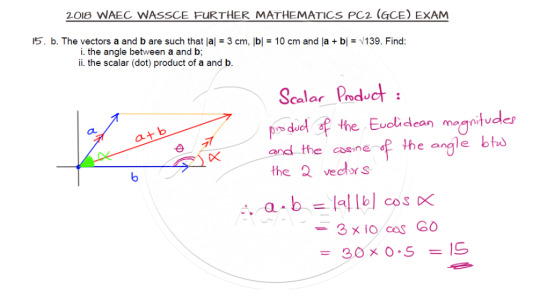
And here is the video solution:
youtube
So that is all about that.
Hopefully, you laid your hands on the questions first before checking with the solution featured here.
Kindly share this and let’s build academic excellence in students together.
Don’t forget to follow #davetutsacademy and visit our YouTube channel for more stuff like this by clicking here: Davetuts Academy.
0 notes
Text
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2

Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2
Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Identify the algebraic linear equations from the given expressions.
(a) x2 + x = 2
(b) 3x + 5 = 11
(c) 5 + 7 = 12
(d) x + y2 = 3
Solution:
(a) x2 + x = 2 is…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Class-8 Mathematics NCERT Soluction Ex-2.5 chapter-2 #Mathswithnarendrasir #Narendrasir
#linear equations in one variable class 8 in hindi#linear equations in one variable class 8 ex 2.1#linear equations in one variable class 8 in english#linear equations in one variable class 8 activity#linear equations in one variable class 8 answers#linear equations in one variable class 8 all formulas#linear equations in one variable class 8 cbse#linear equations in one variable class 8 chapter 2#linear equations in one variable class 8 dav#linear equations in one variable class 8 full chapter#linear equations in one variable class 8 formulas#linear equations in one variable for class 8#linear equations in one variable class 8 hindi#linear equations in one variable class 8 hindi medium#linear equations in one variable class 8 important questions#Math's with Narendra Sir provide to you maths videos for all classes.#Maths with Narendra Sir give you live-class platform#for math skills.#Learn math by taking free online math courses.#Get introductions to algebra#geometry#trigonometry with current math coursework and AP exam preparation.#Select a course to learn more.#We create a unique adaptive learning path for you#We diagnose and identify the student’s current needs#basic mathema#tics#basic mathematics topics#list of basic mathematics topics#basic mathematics topics for primary school
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2

Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2
Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Identify the algebraic linear equations from the given expressions.
(a) x2 + x = 2
(b) 3x + 5 = 11
(c) 5 + 7 = 12
(d) x + y2 = 3
Solution:
(a) x2 + x = 2 is…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2

Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2
Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Identify the algebraic linear equations from the given expressions.
(a) x2 + x = 2
(b) 3x + 5 = 11
(c) 5 + 7 = 12
(d) x + y2 = 3
Solution:
(a) x2 + x = 2 is…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2

Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2
Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Identify the algebraic linear equations from the given expressions.
(a) x2 + x = 2
(b) 3x + 5 = 11
(c) 5 + 7 = 12
(d) x + y2 = 3
Solution:
(a) x2 + x = 2 is…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2

Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2
Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Identify the algebraic linear equations from the given expressions.
(a) x2 + x = 2
(b) 3x + 5 = 11
(c) 5 + 7 = 12
(d) x + y2 = 3
Solution:
(a) x2 + x = 2 is…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2

Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 2
Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Identify the algebraic linear equations from the given expressions.
(a) x2 + x = 2
(b) 3x + 5 = 11
(c) 5 + 7 = 12
(d) x + y2 = 3
Solution:
(a) x2 + x = 2 is…
View On WordPress
0 notes