#mathematician does physics with 0 knowledge of any physics at all
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The best scientific analysis is the “throw-it-at-a-wall” experiment.
Wanna know the space between atoms: gold foil experiment— throwing stuff at a gold wall
Wanna understand quantum particles: throw it at another quantum particle— AKA A WALL
Wanna understand the properties of light: throw it at a wall— double slit experiment
#math#mathblr#mathematics#math shitpost#mathematician does physics with 0 knowledge of any physics at all#physics#quantum physics#parenting#how to parent better?
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just read a lousy story, but it had a beginning, a middle, and an End. A BME is an SBE. I vaguely remember the discussions over the choice of Start, Between, and End. The idea of a beginning implies greater knowledge or context in which a beginning can occur, while the idea of a start may include the selection of the basis, like are you going to be this or that, and then within the choice, which route to take. Let’s try to map that.
I’m seeing a Triangular as a beginning because the End contains the 1-0Segment which says a beginning having this potential to an End. We fixed on End early because it is a 0 as the place where at least this counting stops, like in a modular sense. Beginning having potential to End is where max and min bounds appear as the ‘any’ idealizes. It’s amazing how well the conception of orthogonal nSquare space, which has been inherent since the beginning, solves problems. It works so well it makes me anxious that I’ve somehow missed something obvious.
So the other must be the concept of an End as Start, which is the 1-0 label in which an End is the 1 of counting to and the 0 of counting away, except when it’s the 0 of counting from and the 1 of counting from. Notice it’s the same look back principle inherent in 2Square, which means the orthogonal 2Square maps to 2gs, which sounds obvious but the question in my head is where does that occur? As in, I can see the 2Square, with its roots, and it has to rearrange to be a count of 2gs. We note that 2gs can attach at any face and they are only distinguishable if you map to a grid, in which case we construct the fabled 4gs of IC, and bluntly establish the f1-3 of yore, meaning we infer the 4th gs, which maps szK1 to szK2, and which thus makes, in sort of miniature, the grid itself with its ++ and other characterizations.
That was mind-glowingly good work. Thanks. It’s been a question for a long time. So how do I see this rearranging? It’s the states of the IC in which we see the 2gs as roots. That’s why there’s so much interest in polynomials as roots: it’s a level up or down in the chain of roots of spaces. What you’ve finally identified is the nSquare space which is orthogonal to the gs grid, and the relationship between them is contained in the f1-3 concept. That’s why you named it that. Yes, now I remember the discussion that 13 is both a state and a process, and that f1-3 stands for f1-3//3-1, and that’s actually where I remember using that notation first, which shows how embedded you are in me. I remember with great clarity seeing that function operate because it bidirectionally infers or induces, AND that occurs because there is both cardinal and ordinal inference and ordering. That’s a wow of understanding.
The weird thing is here is exactly where the gendering pops out at me because I’m literally accepting that I’ve done the work correctly AND that occurs as I accept that she as the mathematician in me knows what she’s doing and that when the calculators talk about the me, they mean the male identity that frankly is happier when he’s bound to the physical but whose identity took precedence. This occurred for a number of reasons, including the crucial step of side control flipping. Examples are legion. One which really bothered me was the difficulty I had working with knives left-handed. The reason is I was hampered in my right hand technique by it not being native, so I would imitate a less than ideal. It took a lot of work elsewhere for me to see that I needed to turn my body and bring my right arm naturally in tight. It wasn’t until I could hit the naturally that I could see the solution. A second later my knife technique was better than it ever has been because I could actually see what I was doing. I couldn’t see what I was doing optimally before. Ripeness is all.
That message of full subordination is in the Muhammed message. You can see how and why it is easily twisted into control over others. Not the point, but the idea is vital. I remember those conversations better now. The idea is vital because it is meant to infiltrate each person’s mind that not only is God a great, remote abstraction, but God is what you as individual must take into yourself, must realize that you submit to it, as the days turn, as the seasons shift, as your life is a grain of sand, a monument left to a future unknowable to you. And God may be reached through devices like a Trinity which form bridges that let you approach this same basic truth of oneness with the almighty. That is why he said this is our book, they have theirs: what unified men who did not get along is the commonality of being men who do not get along because they do not see. It grabbed them in many ways, including avarice and adventure, because that is how men hear things.
I did not expect to get into that. The words were not rigorous, because the idea is that submission was the message meant to be heard by men, by men as individuals and by men in groups. If you take away the female perspective, and focus on reaching the male, then submission carries with it the gender identification in which Allah is both male and female, both the lord of you and the mother of you, both ways you connect down, both ways you connect up, both allegiances of duty and place, both pathways through life. The dual identity descends from Judaism, which goes so far as to treat the sabbath as a bride, meaning a weekly sexual requirement is built into the day of rest. Start the week off with a bang, I guess.
So the idea of SBE as an operation in which there are states of Start, Between, and End, where Start and End flip. We talked a lot about the meaning of Between, and decided it was whatever counted across S and End. That could be as close to nothing as we can get, so we fill that with a tiny 1 and thus the 0 for all the processes which generate that tiny plug, or absolutely huge, like the idea the universe may grow out only to collapse inward.
I want to bring the focus back to the layerings. We have orthogonal space, nad thus we have layered constructions at whatever angle we want, because we treat the Attachment End as tangent to the CR of 1-0Segmentwhose Triangular lays out as the center, meaning 2 radii in the 1-0Segment, because of the conception of radius, invokes the orthogonal to that line, which of course makes the 3rd End for the Triangular which also exists over those Ends. This is what eating some sugar cookies gets you. Sometimes I wish I drank caffeine, and then I think about how difficult it is now for me to keep from bouncing.
So if we have the CR available, meaning we rotate, which can be both around a radius and as a diameter and also beyond as the diameter becomes a radius, etc. Oh, that’s the idea of seconds and minutes: it’s the radius and the diameter spinning around. What a lovely underlying image to find. Truly beautiful, isn’t it? And this view conveys additional meanings. That is, a clock locates both rings around a center, but this image has the center of the first diameter represent the 3rd End of that CR, so the center then shifts further out, as what was the center is now whipped around in CR. So in that second view, you are now the smaller piece, which repeats the 60 cycle we generate out of the obvious, that it’s a Hexagon where each 1-0Segment stands for 10, which is the fundamental SBE3+1. That’s why a lot can happen in the final minutes and seconds of play, and it ain’t over til it’s over. So a basic clock sets up as 2 rings of Hexagons. One is a Hexagon as described above, while the other is that same Hexagon where the 60 are the prior Hexagons. This is fairly clearly the same kind of space construction as before.
Let’s get into this. This is scale, and it’s two levels, the first and second Hexagons in which the 1-0Segments forming the perimeter represent 10 Hexagons. So what you see is the 1 Attachment at the visible End, with the SBE3 behind. Sometimes the Ends represent the underlying form perfectly and otherwise by being imperfect relative to, as in a terrible story just read or a terrible scene just watched, which had an SBE or a BME.
I need a break.
0 notes
Text
On Differentials
Calculus is intuitive for everyone. At least, it should be. The reason it isn’t is that we lock this knowledge behind over 10 years of formal mathematical training just to get a glimpse at its formal structure. It doesn’t have to be this way. Yes, a vast knowledge of algebra is very important for writing down and actually working with calculus. I don’t dispute that those years of mathematical training are required to completely understand calculus. Nevertheless, I believe that everyone can understand calculus at an intuitive level. Both aspects of calculus, differential and integral calculus, are geometric in nature. Anybody who has a simple grasp of geometry can understand what calculus does. While I will motivate calculus in this and the next essay, and I will readily use calculus henceforth, I will NOT be teaching calculus. One of my favorite YouTube channels, 3Blue1Brown, has an excellent and far superior introduction to calculus and its theorems. Instead, I will simply give some motivation and then launch into its applications.
Calculus is the mathematics of change. Differential calculus regards itself with calculating and quantifying change. What kinds of change? All quantifiable kinds of change! Let’s think of our hill and ball from last time. Not the ball yet, though, just the hill. Suppose the hill looked something like this:

We can ask about how the shape of the hill changes, that is, we can ask about its slope. Doing it is easy. We just measure how much the height changes over a certain amount of length:
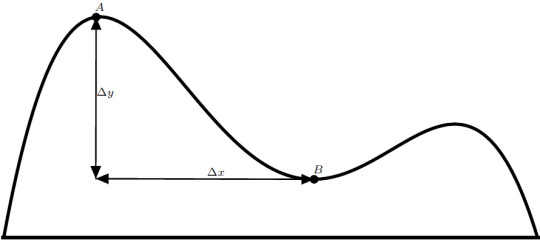
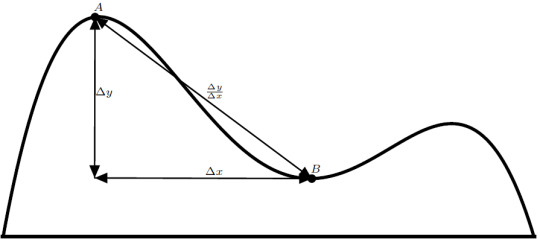
We can express this mathematically as \[ \text{slope} = \frac{\Delta y}{\Delta x} \] This is pretty good by itself, but it’s not calculus yet. There is one major issue with this current measurement. It’s an average. It doesn’t describe the entire hill very well. If we took the average here instead, we get a vastly different result:

In addition, this new result doesn’t describe the shape of this part of the hill too well. Luckily, there is a quick and easy way to get around this. We can take this average over a smaller distance a bunch of times to get different slope measurements for different parts of the hill:

It is now helpful to describe the height of the hill at each position using a function. This function eats a given position, \(x\), and spits out the height of the hill at that point, \(f\left(x\right)\). We can rewrite our expression for the slope using this notation. Suppose we measure the height at points \(x = a\) and \(x = b\). The average slope over this interval is given by \[ \frac{\Delta y}{\Delta x} = \frac{ f\left(b\right) - f\left(a\right) }{ b - a }\]
We don’t have to restrict ourselves to the interval between points \(a\) and \(b\). Instead, we will consider a general interval between some position \(x\) and another position ahead of \(x\), namely \(x + \delta x\).

Using these points, we can rewrite our expression for the slope as \[ \frac{\Delta y}{\Delta x} = \frac{ f\left( x + \delta x\right) - f\left(x\right) }{ \left(x + \delta x \right) - x} \]
Here’s where the calculus comes in. We can ask about the slope of increasingly smaller intervals. Formally, we express this as the limit where the interval length goes to zero. \[ \frac{dy}{dx} = \lim_{\delta x \rightarrow 0} \frac{ f\left(x + \delta x \right) - f\left(x\right) }{ \left(x + \delta x\right) - x} \]
In this limit, we know the slope of the curve at a single point. This difference quotient is the definition of the derivative. Why am I specifying that this is a limit? Let’s simplify the bottom of the fraction a little bit. \[ \frac{dy}{dx} = \lim_{\delta x \rightarrow 0} \frac{ f\left(x + \delta x \right) - f\left(x\right) }{ \delta x} \]
We see that if we were to let \(\delta x = 0\), we would be dividing by zero! That’s why I keep stressing that we’re considering a limit. We are not letting \(\delta x = 0\), we are looking at the behavior of this fraction as \(\delta x\) goes to zero. To see what this means, let’s zoom in on a small part of the hill:
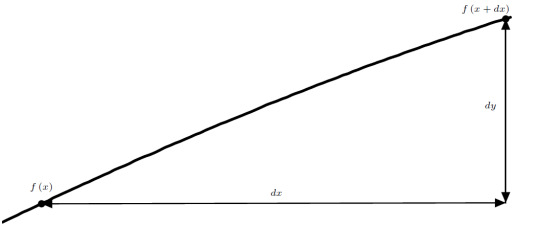
We consider an extremely small length, so small that we call it infinitesimal. Infinitesimals are extremely important in calculus. I will explain them in more detail next time. We use infinitesimal quantities so much in calculus that we denote them by placing a \(d\) in front of the quantity’s name. In this case, we call the infinitesimal distance \(dx\). We can then ask about the infinitesimal change in height, \(dy\), over the distance \(dx\). With these two quantities we can construct the local slope, and since these quantities are infinitesimally small, this is as good as taking the derivative. The slope, and hence the derivative, is given by \[\text{slope} = \frac{dy}{dx}\]
Now, I just did something that will deeply offend any mathematicians in the crowd (and will oust me immediately as a physicist). Although infinitesimals are such a useful concept, they aren’t mathematically rigorous. If we want to be fully rigorous with everything we do, we have to go back to the limit definition of the derivative. Nevertheless, outside of special cases that aren’t particularly physically important, using infinitesimals like I just did to build the derivative is effectively equivalent to using the formal definition, and I will be using this notion of infinitesimals throughout these essays since they are much more intuitive than using the formal definitions.
So we can find the slope of this hill wherever we want. So what? Well, this machinery that we just built, the derivative, is able to analyze all sorts of change. Let’s think about just the ball now. Suppose we were to drop the ball from rest in a vacuum under gravity. We want to quantify its motion to describe it. That means we want to know its position at every single moment in time. We have one piece of experimental evidence to help us along.
Galileo observed that all falling bodies fall with the same acceleration, regardless of their mass. How will this observation help us? How does acceleration mathematically relate to position? The answer (as you may expect by now) has to do with the derivative. Remember that derivatives measure change. But what exactly do they measure? With the hill, we were able to measure the slope of the hill at any point on it. The slope is the rate at which the height, \(y\), changed with respect to the length, \(x\). Derivatives tell us about change by quantifying the rate of change. Any motion has two extremely important rates of change. The first is the rate of change of position with respect to time. This is the velocity. The second rate is obtained from the velocity. It’s the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. This is the acceleration. Now we see where Galileo’s observation can help us. Mathematically, we can calculate the velocity by taking a derivative with respect to time, that is we can calculate \[ v = \frac{dx}{dt}\]
Similarly, we can calculate the acceleration by taking another time derivative \[ a = \frac{dv}{dt}\]
Notice, however, that since velocity is related to position, acceleration is also related to position \[ a = \frac{d}{dt} \left( \frac{dx}{dt} \right) \]
When we act with the same derivative twice, we say that we are calculating the second derivative. That is to say, acceleration is the second time derivative of position. We denote the second derivative more compactly as \[ a = \frac{ d^2 x}{dt^2} \]
More generally, if we have some quantity \(\alpha\) that changes with respect to some parameter \(s\), then we can take \(n\) derivatives with respect to \(s\) to find the rate of change, the rate of the rate of change, the rate of the rate of the rate of change, and so on. In particular, we denote the \(n\)th derivative by \[ \frac{ d^n \alpha}{ds^n}\]
So we now know how the acceleration of a body is related to its position. But that alone doesn’t help much at the moment. All we know is that the ball falls with constant acceleration. So far, all I have told you is how to go from knowing the position at every time to calculating the acceleration, not the other way around. For that, we need to how to start from the derivative and then recover the original function, that is to say, we need to know how to calculate an antiderivative. For this, we need to know how to take the derivative of simple functions, which I will discuss in the next essay.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Betting On Horse Racing - Setting Up Your Betting Bank
By choosing tennis as your preferred sport for betting, you have already given yourself an "edge" against those who bet on or offer odds on other sports. To use this "edge" to make money consistently, however, you'll need to understand two fundamental principles first. Then apply the power of mathematics. It is sheer folly to place a tennis bet (or a bet on anything) with a "traditional" bookmaker. The expression "You can't beat the bookie" is axiomatic; you just cannot beat the bookie over time. It's because the odds are always mathematically calculated in favour of the bookmaker. Everyone knows (or should know) that the bookie's mathematical "edge" against the punter is necessary for him to make a profit so that he can stay in business. Computer technology has given rise to a new form of betting, known as "exchange betting" or "matched betting". With "betting exchanges" there is no bookie to beat; in other words, there is no middle-man. Every punter bets against another punter or punters somewhere out there in the Internet ether. Any punter (or "trader") can place a "back" bet that a player or team will win, and/or place a "lay" bet that a player or team will lose. Thus, any punter can choose to act as an ordinary bettor and/or as a bookmaker. With exchange betting the odds are not set by a third-party or middle-man; they are set by the punters themselves, who place requests for odds at which they are prepared to place bets (if they wish to act as an ordinary bettor), or place offers of odds at which they are prepared to lay bets (if they wish to act as a bookmaker).
As the "back" bettors gradually lower their requested odds and the "lay" bettors gradually raise their offered odds, the software on the exchange betting web site matches all the back bets with all the lay bets at the instant they coincide. The accounts of the "backers" or "layers" are then credited with their winnings automatically a few seconds after the end of the event according to its result. Obviously, the technology for providing such a "fair" betting service must be paid for somehow. This payment is taken in the form of a commission on the punter's net winnings on an event (or "market"). That is, commission is charged only on any positive difference between winnings and losses on the same event. This betting system is as close to a perfectly fair betting environment as it is possible to achieve. There are very few betting exchanges in existence, however, perhaps because the exchange betting software is so complex and therefore costly. The giant among exchange betting web sites is Betfair, with about 90% of the market at the time of writing. Others are the Global Betting Exchange (BetDAQ), ibetX, Betsson, Matchbook and the World Bet Exchange (WBX). Betfair is by far the most popular because it was the first to offer this "perfectly fair" betting environment, and is trusted to perform accurately and instantly.
So, why does tennis betting give you that "edge" over betting on other sports? The answer, though simple, is often overlooked even by those who bet tennis regularly. And if you're someone who's never bet on tennis, you'd almost certainly not have realized the significance of the tennis scoring system on the betting. Consider this fundamental difference between the tennis scoring system and that of probably any other sport you can think of. In other sports and games the trailing player or team must make up the points gap by winning a point for every point they have already lost in order to catch up to the leader. Only then can they start to move ahead. This fact seems obvious. In tennis, however, the trailing player or team can lose the first set 6-0 (possibly with a deficit of 24 points). That team can then win the second set by the most narrow of margins, 7-6 in a tie-break, winning the set by very few points (or even by winning fewer points than the opponents, a rare but possible occurrence!). As soon as the trailing player or team wins the second set, the two sides suddenly have even scores, even though one player or team might have actually won many more points than the opponents. This anomaly often has a profound psychological effect on one or both sides, which affects the way they play for the next few minutes, and therefore also the betting odds requested and offered by punters on the match. This, however, is another aspect of tennis betting which may be the subject of another article. This article deals with the mathematical aspect of tennis betting and how to win money with this knowledge.
Now that you're aware of these two fundamental principles, how can you use them to your advantage when making tennis bets? The key is not to be just a "backer" or a "layer", simply betting on the final outcome of an event. If you do that, you will lose out over time, because there's always a small difference between the "back" odds and the "lay" odds -- there must be, otherwise there'd be no incentive for anyone to offer odds and there'd be no betting at all. Combine that with the commission you pay on your net winnings, and the "edge" is against you mathematically (although it is not as great as with conventional bookmakers). 토토사이트
The secret to winning at tennis betting is to be BOTH a "backer" AND a "layer", but at different points during the event. This is another aspect of betting that distinguishes the exchange betting web site from the traditional bookie. At the betting exchange you can place a back or lay bet at any time during the event, right up until the very last second or the final point. This is known as "in-play" betting. Because in-play betting is allowed, the odds for each opposing side change as the event progresses, according to the likelihood (as perceived by the punters) of either one side or the other being the eventual winner. The trick is to place a back bet on one side at certain odds and later place a lay bet on that side (or a back bet on the other side) at better odds as fortunes change and the odds swing in your favour. If you can achieve this, you will win your bet overall, regardless of the outcome of the event -- a true "win-win" scenario.
Apart from Principle #2, explained earlier, tennis is ideal for such "swing" betting, because the odds fluctuate after every point is played. There are therefore very many small swings to one side and then to the other. This doesn't happen in soccer, for example, because goals are so rare and a goal shifts the advantage suddenly and hugely to the scoring side. Furthermore, a tennis match can have one of only two results; there can be no draw or tie; and one of only two players or teams can win. In horse racing, for example, the winner can come from a large number of runners. The more possible outcomes there are to factor into the equation, the more difficult it is to win. (Despite this obvious logic, soccer and horse racing remain the two most popular sports for betting, probably for historical reasons. Tennis is already third in popularity, however, as more and more punters discover the fact that it is easier to make money betting on tennis than on any other sport.) Now that you have -- it is hoped -- understood and absorbed the generalities of exchange betting and the peculiarities of tennis scoring, it is time to explain the details of how you can win at tennis betting.
Earlier it was stated that the secret to winning at tennis betting is to be both a "backer" and a "layer", but at different points during the event, placing bets at different times during the event as fortunes change and the odds swing in your favour. This can be done with both "in-play" betting and "pre-event" betting. One method used with in-play betting is called "scalping". As its name suggests, scalping involves skimming a tiny profit by backing or laying at exactly the right moment as the odds move slightly in your favour, perhaps when one player scores two or three consecutive points, and repeating the process again and again. The biggest drawback of scalping is that it is very time-consuming and fraught with mental and physical tension. Not only must you pay full attention to what's happening during the match by live video broadcast, but you must also catch exactly the right moments at which to bet, which is, in fact, made impossible by the 5-second delay imposed by the exchange betting software between the time you place the bet and the time it is accepted. We're not elaborating on this here because, as stated previously, this article is about winning by mathematics, not by the sweat of your brow. The maths aspect involves betting, not during the event, but before the event starts. That is, pre-event betting.
There are a few tennis betting "systems", some purely manual, others using software programs, some of which are enormously complicated. From the investigations of the writer (a mathematician), they all require the input, at some point, of a "probability factor" by the bettor. This probability factor is usually the odds at which you want your "balancing" bet (the "lay" bet on the "backed" side or the "back" bet on the opposing side) to be triggered, giving you the "win-win" scenario mentioned earlier. So, how do you determine the value of this probability factor? That, dear reader, is the crucial point of the whole matter, the linch-pin that holds any exchange betting "system" together and determines whether it succeeds or fails, whether you win or lose. Up to now, it seems, this probability factor has had to be determined by the sheer experience of a few seasoned professional gamblers, or by trial-and-error guesswork by lesser mortals. Little wonder that so many punters lose or do not win as much as they could because they do not know the EXACT value needed to optimize their bets! Accuracy is of paramount importance when determining the probability factor, in order to maximize the chances of winning consistently. A search on the Web for a tool to calculate it proved negative. The writer therefore created one that encompasses not only all aspects of exchange betting but also the peculiarities of the tennis scoring system, and called it the Abacus Exchange Betting Calculator, for want of a better name. The probability factor is calculated to two decimal places, merely by entering the pre-event odds of both opposing sides, and has enabled the writer to make consistently more than 10% profit from tennis betting since Wimbledon 2009.
As a parallel test, the writer also placed bets according to "gut feeling", in sufficient numbers to establish a trend. It resulted in a loss of 10% of the working capital (or "bank"). Other tests were done, using the Abacus Exchange Betting Calculator, by betting on other sports where small odds swings occur, such as American Football, snooker and darts (very long matches only, otherwise the swings are too large). The results here just about covered the commissions paid on winnings; so, it is not worthwhile. It seems, then, that the particular mathematical formula or algorithm (which is very complex) discussed here works well only in conjunction with the unique scoring system of tennis. As a scientist, the writer feels that it is highly probable to win at sports betting consistently over time only when the following factors are present: An exchange betting web site is used, not a conventional betting web site. (Beware of many sites that pretend to offer exchange betting by appearing in search engine results for "exchange betting"! Ensure that their software system enables you both to back and to lay bets at any odds you want against other punters, not against the house. If in doubt, check that their web site looks like the one at Betfair.)
0 notes
Text
Tennis Betting - Tips For Exchange Betting on Tennis Matches
By choosing tennis as your preferred sport for betting, you have already given yourself an "edge" against those who bet on or offer odds on other sports. To use this "edge" to make money consistently, however, you'll need to understand two fundamental principles first. Then apply the power of mathematics.
Principle #1
It is sheer folly to place a tennis bet (or a bet on anything) with a "traditional" bookmaker. The expression "You can't beat the bookie" is axiomatic; you just cannot beat the bookie over time. It's because the odds are always mathematically calculated in favour of the unibet telephone bookmaker. Everyone knows (or should know) that the bookie's mathematical "edge" against the punter is necessary for him to make a profit so that he can stay in business.
Computer technology has given rise to a new form of betting, known as "exchange betting" or "matched betting". With "betting exchanges" there is no bookie to beat; in other words, there is no middle-man. Every punter bets against another punter or punters somewhere out there in the Internet ether. Any punter (or "trader") can place a "back" bet that a player or team will win, and/or place a "lay" bet that a player or team will lose. Thus, any punter can choose to act as an ordinary bettor and/or as a bookmaker.

With exchange betting the odds are not set by a third-party or middle-man; they are set by the punters themselves, who place requests for odds at which they are prepared to place bets (if they wish to act as an ordinary bettor), or place offers of odds at which they are prepared to lay bets (if they wish to act as a bookmaker).
As the "back" bettors gradually lower their requested odds and the "lay" bettors gradually raise their offered odds, the software on the exchange betting web site matches all the back bets with all the lay bets at the instant they coincide. The accounts of the "backers" or "layers" are then credited with their winnings automatically a few seconds after the end of the event according to its result.
Obviously, the technology for providing such a "fair" betting service must be paid for somehow. This payment is taken in the form of a commission on the punter's net winnings on an event (or "market"). That is, commission is charged only on any positive difference between winnings and losses on the same event.
This betting system is as close to a perfectly fair betting environment as it is possible to achieve.
There are very few betting exchanges in existence, however, perhaps because the exchange betting software is so complex and therefore costly. The giant among exchange betting web sites is Betfair, with about 90% of the market at the time of writing. Others are the Global Betting Exchange (BetDAQ), ibetX, Betsson, Matchbook and the World Bet Exchange (WBX). Betfair is by far the most popular because it was the first to offer this "perfectly fair" betting environment, and is trusted to perform accurately and instantly.
Principle #2
So, why does tennis betting give you that "edge" over betting on other sports? The answer, though simple, is often overlooked even by those who bet tennis regularly. And if you're someone who's never bet on tennis, you'd almost certainly not have realized the significance of the tennis scoring system on the betting.
Consider this fundamental difference between the tennis scoring system and that of probably any other sport you can think of.
In other sports and games the trailing player or team must make up the points gap by winning a point for every point they have already lost in order to catch up to the leader. Only then can they start to move ahead. This fact seems obvious.
In tennis, however, the trailing player or team can lose the first set 6-0 (possibly with a deficit of 24 points). That team can then win the second set by the most narrow of margins, 7-6 in a tie-break, winning the set by very few points (or even by winning fewer points than the opponents, a rare but possible occurrence!).
As soon as the trailing player or team wins the second set, the two sides suddenly have even scores, even though one player or team might have actually won many more points than the opponents.
This anomaly often has a profound psychological effect on one or both sides, which affects the way they play for the next few minutes, and therefore also the betting odds requested and offered by punters on the match. This, however, is another aspect of tennis betting which may be the subject of another article. This article deals with the mathematical aspect of tennis betting and how to win money with this knowledge.
How to win at tennis betting
Now that you're aware of these two fundamental principles, how can you use them to your advantage when making tennis bets?
The key is not to be just a "backer" or a "layer", simply betting on the final outcome of an event. If you do that, you will lose out over time, because there's always a small difference between the "back" odds and the "lay" odds -- there must be, otherwise there'd be no incentive for anyone to offer odds and there'd be no betting at all. Combine that with the commission you pay on your net winnings, and the "edge" is against you mathematically (although it is not as great as with conventional bookmakers).
The secret to winning at tennis betting is to be BOTH a "backer" AND a "layer", but at different points during the event. This is another aspect of betting that distinguishes the exchange betting web site from the traditional bookie. At the betting exchange you can place a back or lay bet at any time during the event, right up until the very last second or the final point. This is known as "in-play" betting.
Because in-play betting is allowed, the odds for each opposing side change as the event progresses, according to the likelihood (as perceived by the punters) of either one side or the other being the eventual winner. The trick is to place a back bet on one side at certain odds and later place a lay bet on that side (or a back bet on the other side) at better odds as fortunes change and the odds swing in your favour. If you can achieve this, you will win your bet overall, regardless of the outcome of the event -- a true "win-win" scenario.
Why bet on tennis and not on other sports?
Apart from Principle #2, explained earlier, tennis is ideal for such "swing" betting, because the odds fluctuate after every point is played. There are therefore very many small swings to one side and then to the other. This doesn't happen in soccer, for example, because goals are so rare and a goal shifts the advantage suddenly and hugely to the scoring side.
Furthermore, a tennis match can have one of only two results; there can be no draw or tie; and one of only two players or teams can win. In horse racing, for example, the winner can come from a large number of runners.
The more possible outcomes there are to factor into the equation, the more difficult it is to win. (Despite this obvious logic, soccer and horse racing remain the two most popular sports for betting, probably for historical reasons. Tennis is already third in popularity, however, as more and more punters discover the fact that it is easier to make money betting on tennis than on any other sport.)
"In-play" betting or "pre-event" betting?
Now that you have -- it is hoped -- understood and absorbed the generalities of exchange betting and the peculiarities of tennis scoring, it is time to explain the details of how you can win at tennis betting.
Earlier it was stated that the secret to winning at tennis betting is to be both a "backer" and a "layer", but at different points during the event, placing bets at different times during the event as fortunes change and the odds swing in your favour. This can be done with both "in-play" betting and "pre-event" betting.
One method used with in-play betting is called "scalping". As its name suggests, scalping involves skimming a tiny profit by backing or laying at exactly the right moment as the odds move slightly in your favour, perhaps when one player scores two or three consecutive points, and repeating the process again and again. The biggest drawback of scalping is that it is very time-consuming and fraught with mental and physical tension. Not only must you pay full attention to what's happening during the match by live video broadcast, but you must also catch exactly the right moments at which to bet, which is, in fact, made impossible by the 5-second delay imposed by the exchange betting software between the time you place the bet and the time it is accepted.
We're not elaborating on this here because, as stated previously, this article is about winning by mathematics, not by the sweat of your brow. The maths aspect involves betting, not during the event, but before the event starts. That is, pre-event betting.
Mathematics do not lie!
There are a few tennis betting "systems", some purely manual, others using software programs, some of which are enormously complicated. From the investigations of the writer (a mathematician), they all require the input, at some point, of a "probability factor" by the bettor. This probability factor is usually the odds at which you want your "balancing" bet (the "lay" bet on the "backed" side or the "back" bet on the opposing side) to be triggered, giving you the "win-win" scenario mentioned earlier.
So, how do you determine the value of this probability factor? That, dear reader, is the crucial point of the whole matter, the linch-pin that holds any exchange betting "system" together and determines whether it succeeds or fails, whether you win or lose.
Up to now, it seems, this probability factor has had to be determined by the sheer experience of a few seasoned professional gamblers, or by trial-and-error guesswork by lesser mortals. Little wonder that so many punters lose or do not win as much as they could because they do not know the EXACT value needed to optimize their bets!
Accuracy is of paramount importance when determining the probability factor, in order to maximize the chances of winning consistently. A search on the Web for a tool to calculate it proved negative. The writer therefore created one that encompasses not only all aspects of exchange betting but also the peculiarities of the tennis scoring system, and called it the Abacus Exchange Betting Calculator, for want of a better name. The probability factor is calculated to two decimal places, merely by entering the pre-event odds of both opposing sides, and has enabled the writer to make consistently more than 10% profit from tennis betting since Wimbledon 2009.
As a parallel test, the writer also placed bets according to "gut feeling", in sufficient numbers to establish a trend. It resulted in a loss of 10% of the working capital (or "bank").
Other tests were done, using the Abacus Exchange Betting Calculator, by betting on other sports where small odds swings occur, such as American Football, snooker and darts (very long matches only, otherwise the swings are too large). The results here just about covered the commissions paid on winnings; so, it is not worthwhile.
It seems, then, that the particular mathematical formula or algorithm (which is very complex) discussed here works well only in conjunction with the unique scoring system of tennis.
Conclusion
As a scientist, the writer feels that it is highly probable to win at sports betting consistently over time only when the following factors are present:
1. An exchange betting web site is used, not a conventional betting web site. (Beware of many sites that pretend to offer exchange betting by appearing in search engine results for "exchange betting"! Ensure that their software system enables you both to back and to lay bets at any odds you want against other punters, not against the house. If in doubt, check that their web site looks like the one at Betfair.)
AND
2. The sport is tennis, because of its unique scoring system.
AND
3(a) You learn about and become experienced in in-play betting and are prepared to devote almost all your time glued to a computer screen while following each match, sometimes more than one simultaneously.
OR
3(b) You use software that tells you exactly the odds to request and offer and the stakes to place in pre-event betting in only a few minutes, thus allowing you to get on with your normal life.
0 notes
Link
‘It Seems That I Know How the Universe Originated’
The theoretical physicist Andrei Linde may have the world’s most expansive conception of what infinity looks like. Alan Lightman February 8, 2021
In Jorge Luis Borges’s story “The Book of Sand,” a mysterious Bible peddler knocks on the narrator’s door and offers to sell him a sacred book he came by in a small village in India. The book shows the wear of many hands. The stranger says that the illiterate peasant who gave it to him called it The Book of Sand, “because neither sand nor this book has a beginning or an end.” Opening the volume, the narrator finds that its pages are rumpled and badly set, with an unpredictable Arabic numeral in the upper corner of each page. The stranger suggests that the narrator try to find the first page. It is impossible. No matter how close to the beginning he explores, several pages always remain between the cover and his hand: “It was as though they grew from the very book.” The stranger then asks the narrator to find the end of the book. Again, he fails. “This can’t be,” says the narrator. “It can’t be, but it is,” says the Bible peddler. “The number of pages in this book is literally infinite. No page is the first page; no page is the last.” The stranger pauses and reflects. “If space is infinite, we are anywhere, at any point in space. If time is infinite, we are at any point in time.”
Sign up for The Atlantic’s daily newsletter.
Each weekday evening, get an overview of the day’s biggest news, along with fascinating ideas, images, and voices. Email Address (required)
Thanks for signing up!
Thoughts of the infinite have mesmerized and confounded human beings through the millennia. For mathematicians, infinity is an intellectual playground, where an endless string of fractions can add up to 1. For astronomers, the question is whether outer space goes on and on and on. And if it does, as most cosmologists now believe, unsettling consequences abound. For one, there should be an infinite number of copies of each of us somewhere out there in the cosmos. Because even a situation of minuscule probability—like the creation of a particular individual’s exact arrangement of atoms—when multiplied by an infinite number of trials, repeats itself an infinite number of times. Infinity multiplied by any number (except 0) equals infinity. Recommended Reading
The Universe Is as Spooky as Einstein Thought Natalie Wolchover and Quanta The Multiverse Idea Is Rotting Culture Sam Kriss A sphere of small particles expands and contracts against a black background. The Big Bang May Have Been One of Many Natalie Wolchover
Measurements of infinity are impossible, or at least impossible according to the usual notions of size. If you cut infinity in half, each half is still infinite. In an imaginary scenario known as “Hilbert’s grand hotel,” if a weary traveler arrives at a fully occupied hotel of infinite size, no problem. You simply move the guest in room 1 into room 2, the guest in room 2 into room 3, and so on ad infinitum. In the process, you’ve accommodated all the previous guests and freed up room 1 for the new arrival. There’s always room at the infinity hotel. The cover of Alan Lightman's forthcoming book, Probable Impossibilities This post was excerpted from Lightman’s forthcoming book.
We can play games with infinity, but we cannot visualize it. By contrast, we can visualize flying horses. We’ve seen horses, and we’ve seen birds, so we can mentally implant wings on a horse and send it aloft. Not so with infinity. Its “unvisualizability” is part of its mystique.
One of the first recorded conceptions of infinity seems to have occurred around 600 B.C., when the Greek philosopher Anaximander used the word apeiron, meaning “unbounded,” or “limitless.” For Anaximander, the Earth and the heavens and all material things were caused by the infinite, although infinity itself was not a material substance. About the same time, the Chinese employed the word wuji, meaning “boundless,” and wuqiong, meaning “endless,” and believed that the infinite was very close to nothingness. In Chinese thought, being and nonbeing, like yin and yang, are in harmony with each other—thus the kinship of infinity and nothingness. A few centuries later, Aristotle argued that infinity does not actually exist, though he conceded something he called “potential infinity.” The whole numbers are an example. For any number, you can always create a bigger number by adding 1 to it. This process can continue as long as your stamina holds out, but you can never get to infinity.
Read: We need a new word for infinite spaces
Indeed, one of the many intriguing properties of infinity is that you can’t get there from here. Infinity is not simply more and more of the finite. It seems to be of a completely different nature, although pieces of it may appear finite, such as large numbers or large volumes of space. Infinity is a thing unto itself. Everything we see and experience has limits, boundaries, tangibilities. Not so with infinity. For similar reasons, St. Augustine, Baruch Spinoza, and other theological thinkers have associated infinity with God: the unlimited power of God, the unlimited knowledge of God, the unboundedness of God. “God is everywhere, and in all things, inasmuch as He is boundless and infinite,” said Thomas Aquinas. Beyond the religious sphere of the immaterial world, physicists believe that there might be infinite things in the material world as well. But this belief can never be proved. You can’t get there from here. Most of us have our first glimmerings of infinity as children, when we look up at the night sky for the first time. Or when we go to sea, out of sight of land, and gaze upon the ocean extending on and on until it meets the horizon. But these are only glimmerings, like counting to a few thousand in Aristotle’s potential infinity. We’re overwhelmed. But we haven’t even come close.
The concept of infinity remains controversial and paradoxical today, galvanizing international conferences and heated scholarly disputes. Can physical forces ever be infinite in strength? Can space be dissected into smaller and smaller pieces indefinitely, an infinity of the small? At the other end, can physical space extend beyond galaxy after galaxy without limit? Is there an infinity between the infinity of the whole numbers and the infinity of all numbers? In May 2013, a panel of scientists and mathematicians gathered in New York City to discuss the profound conundrums surrounding infinity. William Hugh Woodin, a mathematician at the University of California at Berkeley, put it this way: “It’s kind of like mathematics lives on a stable island—we’ve built a solid foundation. Then, there’s the wild land out there. That’s infinity.”
The person on planet Earth who may have come up with the most expansive conception of spatial infinity is the theoretical physicist Andrei Linde, a professor at Stanford University. Linde works only with pencil and paper. Now 72 years old, he was born and grew up in Moscow and received his Ph.D. in physics there from the Lebedev Physical Institute. Both of his parents were physicists. He married a physicist, Renata Kallosh (also a professor at Stanford). In 1990, Linde and Kallosh moved to the United States and took up their current academic positions.
In the 1980s, Linde proposed a radical theory of the origin of the universe.
His theory, a revision of the MIT physicist Alan Guth’s 1981 theory, itself a revision of the 1927 Big Bang model, is called “eternal chaotic inflation.” The theory posits that in its infancy, our universe went through a period of highly rapid expansion, much faster than in the standard Big Bang model. In a tiny fraction of a second, a region of space smaller than an atom “inflated” to a size large enough to encompass all the matter and energy we can see today. That much of the inflation theory was articulated in Guth’s paper. Linde’s theory goes further. It proposes that our universe is necessarily one of a vast number of universes, each of which is constantly and randomly spawning new universes in an unending chain of cosmic creation, extending into the future for eternity. Some of those universes, and perhaps our own, should be infinite in extent. In our particular universe, the period of highly rapid expansion would have been completed and done with when our universe was 0.000000000000000000000000000000001 seconds old.
Read: The best explanation for everything in the universe
One could easily dismiss such speculations as science fiction. But the fantastic speculations of scientists have often found a grip on reality. Two hundred years ago, who would have thought we would be able to decipher the microscopic chemical code that creates living organisms and to alter that code as if rearranging a deck of cards? Or build tiny boxes that could communicate pictures and voices through space? Linde’s speculations are backed up by serious equations, and a number of important predictions of what I will call the “Guth-Linde inflation theory” have been confirmed by experiment. In the scientific community, Linde is widely regarded as a physicist of the first rank. He has won most of the major prizes in physics except for the Nobel.
Linde does not have a small opinion of himself. When I met him the first time, in 1987, a few years after his most important work on the inflation theory, he told me about his discovery with these words:
I easily understood what Guth was trying to do. But I did not understand how [inflation] could be done, since we have seen that the inhomogeneities [in Guth’s original theory] were large [contradicting observations]. I just had the feeling that it was impossible for God not to use such a good possibility to simplify His work, the creation of the universe … I was simultaneously discussing similar matters with [Valery] Rubakov [by telephone] … I was sitting in my bathroom, since all my children and my wife were already sleeping at the time … After the whole picture had crystallized, I was very excited. I came to my wife and I woke her up and I said: “It seems that I know how the universe originated.”
I visited Linde recently at his home in Stanford, California, to get an update on his theory and its place in our view of the world. Linde and his wife live in a lush neighborhood of winding streets, tropical gardens, and houses set up on hills. He was casually dressed in a black fleece sweater over a black T-shirt, black pants, and sandals with black socks—all in dramatic contrast with his snow-white hair. His English is good but retains a thick Russian accent. We sat at his kitchen table.
First, I asked Linde if he believes that spatial infinity truly exists. (Theoretical physicists and mathematicians are infamous for building hypothetical universes of 17 dimensions and other such surrealities.) “Do you think dinosaurs truly existed?” he replied, and paused. “Everything works as if spatial infinity exists.” Linde is careful with language. He distinguishes between reality, which we can never know, and our models and inferences about reality. He has always had a strong interest in philosophy. He remembers having debates with high-school classmates about science versus art.
I asked him how he thought about infinity, whether he attempted to visualize it. “No matter how far you go, you can go farther,” he said. Then he made an analogy to a garden: “But there’s no fence.”
Anaximander’s conception of infinity was abstract and could not reasonably be associated with physical space. In fact, the early Greek philosophers pictured the cosmos as limited in size, with an outer boundary, although they did not claim to know the actual distances.
The first person to postulate in concrete terms a spatially infinite universe seems to have been a 16th-century English mathematician and astronomer named Thomas Digges. In 1576, Digges published a new edition of his late father’s almanac, A Prognostication Everlasting. In an appendix, Digges abolished the outer sphere of the stars. At the center of his diagram is the face of the sun, with spiky rays issuing forth. Then the “orbes” of the planets. And beyond this region and extending to the edge of the page are the stars, scattered here and there through infinite space.
Digges agreed with Copernicus and Aristotle about one thing: The cosmos on the whole was at rest—a magnificent and immortal cathedral. It had existed forever and would exist forever, from the infinite past to the infinite future. This conception sat quietly for another 300 years. Even Albert Einstein’s 1917 cosmological model, based on his new theory of gravity, proposed a static and eternal universe.
Then came the Big Bang. In 1927, a Belgian priest and physicist named Georges Lemaître suggested that the previously observed outward motion of galaxies meant the universe was expanding. The cosmos was not, in fact, static. Einstein pronounced the idea “abominable.” However, two years later, Lemaître’s suggestion was confirmed by the American astronomer Edwin Hubble, who found that the speed at which other galaxies are flying away from us is proportional to their distance, as if all the galaxies were dots painted on an expanding balloon. From the viewpoint of any dot, it appears that all the other dots are moving away. No dot is the center.
Read: Why Earth’s history appears so miraculous
If you let the air out of the balloon—going backward in time—all the dots rush toward each other until you reach a moment in the past when all the dots are on top of each other. That moment is the “beginning” of the universe, the so-called Big Bang, t = 0. By measuring the rate at which the universe is expanding today, we can estimate when the universe “began”—about 14 billion years ago. Since that moment, the universe has been expanding, thinning out, and cooling. It is important to note that the balloon analogy is only an analogy. In particular, unlike a balloon, the universe could be infinite in extent. What astronomers mean when they say the universe is expanding is that the distance between any two galaxies is increasing with time.
The Big Bang model is more than an idea. It is a detailed set of equations describing how the universe has evolved since t = 0, specifying in quantitative detail such things as the average density and temperature of the universe at each point in time. The model has been supported by several pieces of evidence. For one, the age of the universe as calculated by its rate of expansion approximately agrees with the age of the oldest stars, calculated by our understanding of stellar astrophysics. For another, the Big Bang model predicts that there should be a flood of radio waves coming from all directions in outer space and produced when the universe was about 300,000 years old. That predicted flood of radio waves, called “cosmic background radiation,” was discovered in 1965. There are other confirmed predictions as well, such as the observed proportions of the lightest chemical elements. The Big Bang theory does not say whether space and time existed before the cosmic balloon began expanding. That profound question would be left to Linde and others.
Linde would have heard about the Big Bang model as a physics university student in Moscow in the late 1960s, if not earlier. However, he was trained not as a cosmologist but as a particle physicist, as was Alan Guth. Particle physicists study nature at the smallest sizes, while cosmologists study it at the largest. The two branches of physics seemingly had little to do with each other. But in the early 1970s, Linde became interested in certain phenomena that occur at extremely high temperatures, far beyond what can be created in the laboratory, temperatures that could have existed only in the fantastically hot conditions of the infant universe. Describing one of his theories at the time, a prelude to his work on inflation, Linde said, “At the first glance, this theory seemed to be too exotic. We developed it in 1972, but for two years nobody believed us. People were laughing.” But in 1974, some American physicists confirmed the main conclusions.
This response to Linde’s early work—first doubts, and then often acceptance—seems to have been a pattern in his career. In our conversation, we talked about the manner in which scientific theories, and especially maverick theories, are confronted by the scientific community. Linde described what he calls a strong “sociological” effect: the biases and prejudices of scientists, their institutional stature, and the inherent caution of the scientific enterprise. Linde himself is not a cautious person. His colleagues describe him as someone who shoots from the hip with lots of ideas, some right and some wrong. He is a person of extreme self-confidence, a showman in his popular lectures and articles.
By the early 1970s, some physicists were worrying about problems with the Big Bang model, despite its successes. One lasting concern, for example, was that the cosmic radio waves are highly uniform in temperature, no matter what direction we’re looking in.
There are two possible explanations for this: Either the universe began in an extremely uniform condition, with all parts at the same temperature, or any initial non-uniformities were smoothed out in time, much as hot and cold water in a bathtub will come to the same temperature by exchanging heat. However, heat exchange takes time. According to the Big Bang model, the different parts of the universe we see today would not have had enough time to exchange heat during the first 300,000 years of the universe, when the cosmic radio waves were created. Thus, the second explanation doesn’t work. On the other hand, physicists consider the first explanation unpalatable because it sweeps the problem under the rug: “It is what it is because it was what it was.” In general, physicists detest such arguments.
The Guth-Linde inflation theory solves the puzzle of the cosmic radio waves, as well as other problems with the Big Bang model. During the period when the infant universe was expanding at blinding speed, a very tiny patch of space, tiny enough that all its parts could have homogenized, would have quickly inflated to encompass today’s entire observable universe. No matter what the initial conditions, inflation would have produced a universe of uniform temperature.
Most important, the inflation theory explains why such inflation would occur and includes equations for the various energies and forces involved. The key ingredient of the theory, and the cause of the extremely rapid expansion of the infant cosmos, is a kind of energy called a “scalar field.” Most energy fields, like gravity, are invisible, yet they can exert forces. Some scalar fields produce a repulsive gravitational force: They push things apart rather than pull things together.
The Guth-Linde theory was developed over a period of several years, from 1979 to 1986, beginning with work by Alexei Starobinsky in Moscow. During that period, problems arose and were fixed, and physicists proposed various versions of the theory.
One of Linde’s ideas is that in the early universe, scalar field energy should be constantly created at various magnitudes due to quantum effects. A strange aspect of quantum physics is that energy and matter can suddenly appear out of nothing for short periods of time. If you could examine space with a strong enough microscope, you would find that it is constantly fluctuating, seething with ghost-like particles and energies that randomly appear and disappear. Quantum phenomena are normally apparent only in the tiny world of the atom, but near t = 0 the entire observable universe was smaller than an atom. If at a certain point in the infant universe sufficient scalar field energy had materialized, its repulsive gravitational effect would have caused space to expand so rapidly that an entire universe would have been created. Since such quantum fluctuations would have been going on at random places and times—this is the “chaos” in Linde’s eternal chaotic inflation theory—new universes would have been constantly forming.
Indeed, Linde’s theory requires that we redefine what we mean by universe.
Some physicists now take the word to mean a region of space that will be quarantined into the infinite future, that may have been in contact with other parts of the cosmos in the past but can never communicate with the rest of the cosmos again. Because of the mind-bending way in which gravity alters the geometry of space in Einstein’s theory, there could conceivably be multiple universes, each infinite in extent. Physicists predict that the new universes created by quantum fluctuations have a wide range of properties: Some might be infinite in extent, others finite; some might have the right conditions to make stars and planets and life; others might be lifeless and unformed deserts of subatomic particles and energy; some might even have different dimensions than our own universe. In this vision, universes endlessly spawn new universes, each with its own Big Bang beginning. Our t = 0 would not be the beginning of space and time in the larger cosmos, only in our particular universe.
Read: How to measure all the starlight in the universe
In some of his papers, Linde represents his eternal chaotic inflation model as a thick hedge of branching bulbs, each bulb a separate universe, connected to ancestor bulbs and descendant bulbs by thin tubes. The entire hedge might be called the “cosmos.” Sometimes, it’s called the “multiverse.” It is startling to look at Linde’s picture and realize that each bulb represents an entire universe, some containing stars and planets, cities, office buildings, trees, ants or ant-like creatures, sunsets. Unfathomable—yet a human mind has fathomed this thick hedge of the imagination. “It can’t be, but it is,” says the Bible peddler in “The Book of Sand.”
One cannot resist comparing Linde’s “map of the universes” to the Babylonian “Map of the World,” one of the oldest-known maps drawn by human beings, found on a clay tablet in present-day Iraq and now housed in the British Museum. In this ancient map of the known world (ca. 600 B.C.), the city of Babylon is perched on the Euphrates River. Pictured and named (in Akkadian) are a few other cities, including Urartu, Susa, Assyria, and Habban; a mountain; and a circular ocean (labeled “bitter river”) enveloping the inhabited cities.* Finally, spikes radiating out from the circular ocean represent some unnamed and unknown outer regions. Could one compare these unnamed spikes to the unnamed bulbs in Linde’s map? Both lie far beyond the realm of physical exploration. Both require leaps of the imagination. Yet Linde’s bulbs follow as logical consequences of certain mathematical equations. As Linde would acknowledge, those equations are also works of the human imagination, models of reality instead of reality itself. Linde’s ideas are at once visionary and grounded in logical thinking. Although mathematically proficient in the manner of all theoretical physicists, Linde described himself to me as more intuitive than technical, a Steve Jobs more than a Steve Wozniak.
The Babylonian Map of the World is a static picture. By contrast, Linde’s map of the universes suggests evolution and change, movement. The various universes spawn each other in time.
I do not feel unlimited looking at Linde’s map. Instead, I feel small and insignificant, like the Bible peddler, who says that if space is infinite, we are nowhere in space, nowhere in time. How can anything we do be of consequence when we are nowhere in space, nowhere in time, when our brief lives are lived out on one small planet, itself one of zillions of planets in a universe that might be infinite in size, and our entire universe simply one bulb in Linde’s thick hedge of universes? On the other hand, there might be something majestic in being a part, even a tiny part, of this unfathomable chain of being, this infinitude of existence. We pass away, our sun will burn out, our universe might become a dark and lifeless void a hundred billion years from now—but, according to Linde, other universes are constantly being born, some surely with life, renewing something precious that cannot be named.
It is unlikely that we will ever know if Linde’s infinity of universes exists. But the rest of the Guth-Linde inflation theory is being actively tested today. One of the most important tests, Linde explained to me, is a search for something called “B-mode polarization,” a slight twisting pattern in the vibrations of the cosmic radio waves predicted by the inflation theory.
Refined measurements of the B-mode polarization are now being conducted by the POLARBEAR experiment in the Atacama Desert in northern Chile and by the BICEP experiment at the South Pole, among others. These experiments are international collaborations, including more than a dozen institutions in the United States, England, Wales, France, Japan, and Canada. Thousands of scientists worldwide, both theorists and experimentalists, are actively working to test the inflation theory and to probe its consequences. Almost all cosmologists today accept it as the best working hypothesis we have to describe the first moments of our universe. The theory must be considered a triumph of the human mind.
Yet Andrei Linde does not appear to be a man completely at peace with his place in the world. Something eludes him. When he talks about the history of the inflation theory, he seems still to be defending his ideas against naysayers and rival theorists, still competing with Guth and others for priority of discovery, still infused with a powerful desire for vindication. In my conversations with him and in his review articles and autobiographical statements, he portrays himself as someone who heroically developed a new view of the cosmos, struggled against doubters, corrected other people’s mistakes and misunderstandings, and was often misunderstood himself. One story he enjoys telling is about a lecture that Stephen Hawking gave at the Sternberg Astronomical Institute in Moscow in October 1981. Linde was asked to translate for the Russian audience. At that time, various physicists, including Hawking, were trying to patch up a serious problem (too much inhomogeneity) in Guth’s original inflation theory. Linde had devised his own inflation theory, a revision of Guth’s, but it was not yet published. During the lecture, Hawking would mumble a few seemingly incoherent words, one of his graduate students familiar with his speech would translate into understandable English, and then Linde would translate into Russian. With this painfully slow process under way, Hawking announced that Linde had a good idea, but it was wrong. For the next half hour, he proceeded to explain why it was wrong. All the while, Linde had to translate. At the end of the lecture, Linde told the audience, “I have translated, but I disagree.” He then went with Hawking to another room of the building, closed the door, and explained to him more details of his new theory. According to Linde, Hawking had to admit that he was right after all. Linde recalled that Hawking “was sitting there about one hour and a half and saying to me the same words: ‘But you did not tell this before. But you did not tell this before.’”
Perhaps Linde’s ego and bravado were essential for the conception of his phantasmagoric cosmology. Other scientists with equal brainpower but more cautious dispositions have not ventured nearly so far in their theories of the world. The equations are the equations, but they must be imagined and interpreted in the human mind, a particular human mind, a complex universe itself, endlessly variable in its quirks and possibilities. Then again, any scientist who works on the origin of our universe—and hundreds do worldwide—must possess a certain amount of chutzpah.
“At the beginning, I was like a young kid, making discoveries,” Linde told me.
Now I feel a deep responsibility. There are hundreds of people working on the theory of inflation and lots [of expensive] experiments to test it. You feel yourself a bit heavy with responsibility … I would hate to die just being a physicist. I enjoy photography. That allows me to feel another part of my brain. There is something beyond physics that is not measurable … Photography is my art. You need to have a first priority and then a second priority. When I was 60, someone gave me a camera. With a camera, you can produce beauty. I can produce things that are better than what I see in museums. You see, I am now talking like an arrogant American. I am producing images that make my heart sing—both my photographs and the computer graphics illustrating inflation. I am among the first to see the beauty in it. Without the part of my mind beyond physics, I would be unable to create the computer graphics of cosmology.
Linde went to his computer and eagerly showed me his Flickr website, where he has posted hundreds of his photographs. “Sit down,” he said, and offered me a seat near the screen. One of his photographs, titled “Alcazar Dreams,” depicts a subterranean pool beneath the Patio del Crucero in Seville, Spain. A series of stone arches, glowing in eerie orange light, bend over the elongated pool, one after another after another out to a distant vanishing point. Another image, titled “Hide Thy Face,” is an extreme close-up of the interior of an orchid. Around the outside edges unfolds a diaphanous blue halo. At the middle of the flower is a two-chambered yellow heart covered with red speckles, with white-and-red-striped arms emerging from it, and further out pale green and yellow petals. Altogether, an intricate jewel, a tiny splash in infinity.
This article was excerpted from Lightman’s forthcoming book, Probable Impossibilities.
* This article previously misstated the language in which the Babylonian "Map of the World" was written and the material from which it was made.
👇 📚 👇
https://www.theatlantic.com/science/archive/2021/02/to-infinity-and-beyond/617965/?utm_source=pocket-newtab
0 notes
Text
Finish the Job
A Message Of Concern
The Merciful Benefactor, The Merciful Redeemer
Out of Respect for Man’s Creator
A Message of Concern
By Imam W. Deen Mohammed 1982,
What would happen if people would sit in churches throughout the world for centuries with the image of an African American man as savior of the world before them?
What would this do to the mind of the world’s children?
What would happen to the world’s children put under a figure of a particular race presented, pitiable, and in pain “the Savior of all men”?
Qur’an, Surah 3, verse 64:
“Say, Oh people of the Book! Come to common terms as between us and you: that we worship none but G-d, that we associate no partner with Him, that we erect not from among ourselves lords and patrons other than G-d. If then they turn back, say ye ‘bear witness that we (at least) are Muslims (bowing to G-d’s Will).’”
Civilized nations should want that their religions be also civilized.
False worship is the worst form of oppression. We are no gods. We are only men, “mortals from the mortals, He (Allah) created.” (Qur’an)Happy Fathers Day weekend brother !
God bless all you do as a father! Send to all the great fathers you know !THE RED SEA
It's Parting
It is reported that God assigned Aaron as a helper to Moses because Moses felt that he could not express himself clearly. Before Moses went to Pharaoh, the Qur'an says, he and Aaron felt a sense of fear. "They (Moses and Aaron) said: Our Lord! We fear lest He hastens with insolence against us or lest he transgresses all bounds." In response, ALLAH not only told them not to fear Pharaoh and his hosts, but He instructed them on how to speak to Pharaoh. ALLAH said, "Fear not for I am with you: I hear and see (everything) ... But speak to him mildly, perchance he may take warning or fear ALLAH" (H.Q. 20:44-46).
Let us understand that Moses was going to debate with the ruler of the greatest nation of that time. He along with Aaron was assigned to debate with the wisest people around. Moses had no army, he had no weapons. Pharaoh had an army, educational institutions, highly skilled and astute doctors of law; mathematicians, philosophers. Moses had to go up against a man who thought he was God. Moses had to confront the very people who built the great pyramids of Gizah, Masters of the physical and human sciences. Moses knew how Pharaoh and his people were; he was raised in Egypt, in the house of Pharaoh. Reflect! Think! Can you imagine what Moses must have felt? Imam W. Deen Muhammad stated in Dallas, Texas (1982)
" .... They (Egyptians) had one of the most elaborate religious orders that history has recorded. We are not talking about savage man. We are not talking about barbaric man. We are talking about an ancient kingdom that knew science, knew medicine, knew chemistry, knew physics. We are talking about the ancient kingdom that made the first dust pan, that made the first broom, that made the first modern furniture. Some of the modern furniture today does not look any more modern than the furniture that they have in the museum of Cairo, Egypt, (furniture) that those people made three and four thousand years ago .... So we are not talking about a shabby society, a shabby nation. We are talking about an advanced, well established nation; a nation that boasted in its material accomplishments, in its industry. A nation that boasted in its sciences, a nation from which we trace our own science which we call psychology."
According to the story, Moses went to Pharaoh and delivered the message. Pharaoh in turn became'very arrogant and said, "Who is the Lord, that I should obey his voice to let Israel go? I knew not the Lord, neither will I let Israel go." (Exodus 5: 2).
It is reported that Pharaoh made his slaves make bricks from straw and mud, which means that they had to develop or arrive at solid, biological, concrete truth, from hollow, unbalanced and unstabled concepts. The Qur'an says that Pharaoh became so arrogant and conceited until he told his builders to erect him a tower because he wanted to go up into the heaven and find the mystery God. "And Pharaoh said: 0 Chiefs! I know not that ye have a God other than me, so kindle for me (a fire) 0 Haman, to bake the mud; and set up for me a lofty tower in order that I may survey the God of Moses; and Lo! I deem him of the liars" (28:38). Pharaoh thought he was God in the flesh. He thought he was the owner, the maker, the cream of the planet earth, God of the universe. Pharaoh said to Moses, " .. .I consider thee, indeed to have been worked upon by sorcery!" "Then he (Pharaoh) collected his men and made a proclamation, saying "I am your Lord, Most High ." (H.Q.79: 23,24).
After Moses showed Pharaoh some of the knowledge he had received from God, Pharaoh claimed that Moses was well versed in magic and he said, "If indeed thou hast come with a sign, show it forth--if thou tellest the truth." Then (Moses) threw his rod, and behold! it was serpent plain (for all to see)! And he drew out his hand, and behold! It was white to all beholders! Said the Chiefs of the people of Pharaoh: "This is indeed a sorcerer well-versed." (H.Q.7:106-109).
It is further reported that Pharaoh sought advise and consultation (that is a sign of a wise man, not a fool). He said, "His (Moses') plan is to get you out of your land: then what is it ye counsel?" They said: "Keep him and his brother in suspense (for a while); and send to the cities men to collect--and bring up to thee all (our) sorcerers well-versed." (H.Q.7:110-112).
The story goes on to say that Moses and Aaron met in the court of Pharaoh's Kingdom. It is reported that Pharaoh had promised his Magicians, socerers, philosophers, wizards, etc. a better and closer place to him in the kingdom if they defeated him. In other words, instead of being in the fields they would be allowed in the house. Before the debate began the question was asked, "who shall go first?" Moses said: "ye be the first to go." So when Pharaoh's men threw their rods down, they began to move like serpents, too. When Aaron threw Moses' rod down it consumed Pharaoh's men's rods. The point here is that there was a strategy used by Moses: he allowed them to show off their knowledge first, and then he showed that the knowledge that he got from the Creator was superior. It has often been asked, "what was the debate concerning, knowledge of what?" An analysis of this event will reveal that they threw the rods down on the earth, which implies that it had to do with the material sciences, or the human sciences, as opposed to the spiritual sciences. A serpent moves on the earth. The Bible tells us that later he raised the rod to the sky or heaven; but in this particular event they cast it on the earth.
The Bible relays the event in these words: "And Moses and Aaron went in unto Pharaoh, and they did so as the lord had commanded: And Aaron cast down his rod before Pharaoh, and before his servants, and it became a serpent. Then Pharaoh also called the wise men, and the sorcerers: now the magicians of Egypt, they also did in like manner with their enchantments. For thy cast down every man his rod, and they become serpents,: but Aaron's rod swallowed up their rods." (Exodus 7: 10-12).
The Holy Qur'an explains: "So the sorcerers were got together for the appointment of a day well-known, and the people were told: "Are ye (now) assembled? - That we may follow the sorcerers (in religion) if they win?" So when the sorcerers arrived, they said to Pharaoh: "Of course - shall we have a (suitable) reward if we win? He said: "Yea, (and more), --for ye shall in that case be (raised to posts) nearest (to my person)." Moses said to them: "Throw ye - that which ye are about the throw!" So they threw their ropes and their rods, and said: "By the might of Pharaoh, it is we who will certainly win!" Then Moses threw his rod, when, behold it straightway swallows up all the falsehoods which they fake! Then did the sorcerers fall down prostrate in adoration, saying: "We believe in the Lord of the Worlds. The Lord of Moses and Aaron." (26:38-48).
According to the Scriptures Moses and his people eventually left Egypt and wandered in the wilderness in search of the promised land. Pharaoh and his army with chariots and horses had pursued them up to the Red Sea, where Moses raised his rod to the heaven and then pointed down to the water causing it to part for Moses and his people.
SYMBOLIC MEANING OF PARTING OF THE RED SEA
The Scripture says Pharaoh's army drowned in the red sea.
Symbolically the chariot represents a principle or method of controlling human drives and behavior (horses). The horses represent human drives, human motivations and human behavior that are blind. Blinders are put over horses' eyes. Pharaoh was pursuing Moses and his people with human science, he was trying to control their behavior, their human drives and aspirations. Moses' raising the rod to heaven and stretching his hand over the red sea, refers to the great blessing that he received from on high. Raising the rod means that he was using the higher knowledge that he received from ALLAH (God) near the burning bush. Stretching out his hand over the red sea means he passed that knowledge on, he didn't keep it secret. He appealed to the people with higher knowledge of God.
According to Scripture Pharaoh had a small concept of the Creator. He thought he was God. Moses appealed to the red sea(the masses). Red symbolizes anger, activity and life. Blood is red and it is the life of the body. The sea or water alludes to morality and communication. Therefore, red sea symbolizes active, expressive moral life. Moses communicated to these morally active people and they allowed Moses and his people to walk across on dry ground, solid foundation. It is further reported that Pharaoh's army, because they did not have the higher knowledge, were drawn or overtaken by the people. Pharaoh's concept of God and human behavior could not be universally applied. It was too narrow. It was good for Egypt and some surrounding cities, but it was not accepted universally. It was part truth, not whole truth. Modern man should take a lesson from this great event. As long as the leaders of this world try to appeal to the world of man with narrow, extreme nationalist ideas they stand to be toppled. The universal appeal, respect for the Creator, high principles, and human worth can be accepted by all men.
Imam Mustafa El AminA BLACK & WHITE SKIN COLOR WAR
Seeing Black and White skin " knocks you out ."
A lecture with a lesson many need to heed, in 2020. Why ? There is a major attempt to manipulate African Americans into a Black, White skin color war !
Imam WD Mohammed Ramadan Session 2007 ( Just Seeing Black and White Skin Hurts Your Vision ) " Many of them did not even enjoy them because their mind was too small. Their brain was too much like a black-eyed pea. If you get a black eye it means some damage has come here. The blow came to close to the eye or came to the eye. Right? It is not Mohammad Ali. He did not throw that punch. You hit yourself with your ignorant controls. You blackened your own eye. Mr. Fard said don't eat black-eyed peas. I'm eating black-eyed peas. I love them. They taste good.Someone may say, "He's bragging that he does not follow the Nation of Islam's teacher." Yes, I do follow the Nation of Islam's teacher. It is to lead me beyond a black-eyed pea that you buy in a grocery store and see the black-eyed pea in the mind of the black man where his brain has turned out to be nothing but a little black-eyed pea. All his mind is black and white, the black man and the white man. He is nothing but a black-eyed pea in the brain and it hurts his vision. He has had a terrible blow. Now Mr. Fard did not tell you the extent of that black-eye we have. It is so bad it is like we got hit first by Sonny Listen, then by Joe Frazier, then by Muhammad Ali, and the members of the Nation of Islam.
First Posted By Mohammed HassanALL FROM FATHER ADAM
Allah says, in the Quran, that you all are descendants from Adam, and Adam was made from dust. What is Allah telling us this for? To let us know that no man, no race, no ethnic group has any grounds for boasting of a superiority over another. Maybe I could trace my history back to the great history or to the great life of Sinmutsin, the great architect, the great builder who built pyramids for Hatshepsut, the Egyptian queen in ancient Egypt, Maybe I can trace my history — my ancestry back to Mina, the great Pharaoh that started the pyramid building.
The first Bilalian (one of African descent) mentioned in American history is in the late centuries of the Egyptian dynasty. But, the Egyptians themselves say that Mina, the father of pyramid building, was a Bilalian. Why shouldn't he be? Isn't that the continent of Bilalian people? Why shouldn't he have been a Bilalian?
Dear beloved people, the Holy Quran lets us know that we're foolish trying to trace some superiority back in time. You might run into some greatness and superiority, but keep tracing and you're going to run into your inferiority, God shows us, He doesn't tell us. God never gives us the whole history of our existence to let us know how human beings came into existence. He shows us every time a child is born. That baby is born from a thick water—again, the teachings of the Quran— and from the matter that is in the ovaries of the mother. They come together and the baby begins to gradually evolve into human form. He takes on the physical human form in the womb of his mother. But he doesn't become a thinking, growing intelligent being until he's delivered out of his mother into the world of physical messages from God's physical environment and comes under the guidance of his mother and his father, and sisters and brothers of his community.
So, you want to know how you came about? God is showing you every time a baby is born. You want to see your origin? Look at the sperm, and if you can, look at the ovum. You'll find out where you came from.
How should we deal with the question of racism? Deal with it the same way we have to deal with the Bible—with a rational mind. Approach it rationally and scientifically. Treat it with knowledge, not with emotionalism, and explain it so that a child could understand his blackness if he's black or his whiteness if he's white. That's how we have to deal with it.
COLOR: SUPERIOR/INFERIOR?
In our textbooks now, we're trying to get rid of the racist feelings, or prevent racist feelings from coming into the children, by showing Bilalian and Caucasian children living together in peace, working in peace, and playing in peace. Will that do the job? No. Why? Because that's a picture of some people living together. If the racism is in the public that child is going to grow up to see that the book is a contradiction and not the reality. They go to school and the nice pictures are there. The child goes back home and hears the mother saying: "I hate them, honkeys, I hate them white pigs," and the little Caucasian child perhaps hears his old bigoted mother saying: "What they should do is send those niggers back to Africa; or enslave them all again." What effect can the book have when the real world is full of racism? No effect. And you can't change people by simply creating a picture of what you want.
The way to change it is to teach the people to follow truth, to obey truth, to respect truth and follow it. Teach them to interpret and understand problems of racism as a doctor of anthropology would understand it. The facts that speak to racism from anthropology, from our sciences, are not above the heads of the elementary child, or the high school student. We have to design textbooks that deal with racism in a scientific way. We have to tell children at a very early age the truth about the origin of their color, the texture of their hair, their features and everything. You might say, well, do we know anything about that? Yes, we do. Get a good book on anthropology. Study physiology, and you'll see that a lot of these explanations are given in the books that we have presently.
We know that the sun is the painter that paints the color of creation. The sun gives color to the flowers, to the plants, to the animals, even to stones, and the sun has given us our color. Your whole make-up-how you look, your colors, your features, the texture of your hair, and your skin, everything—is determined by your physical environment. What you eat, what you drink, the climate where you live, the temperature; the dryness of the air or the humidity in the air; the cold and the heat, the intensity of the sun—all of these things form color and shape, plus language.
Even your language gives shape or gives features to your face. If you speak a language that's greatly different, then you're going to look different even though you have the same climate. Everything else can be the same, but if the language is greatly different, then the people in time would have different features because the habit of using your mouth in a certain way is going to make your mouth grow in a certain way.
If you live in a hot climate that is humid, the volume of air, the unit of air has less oxygen in it than the same unit of air in a cold climate that is not as humid. The humidity takes up the space in the air, and the heat expands the molecules of air, and makes the volume have less oxygen in it. In a cold climate the air is condensed, and if it's dry too there is much more oxygen in the same volume of air.
So, the people who come from the tropics— from the humid and hot parts of what we call Africa and the whole tropical belt going around the earth —find those people in that zone and study their features. I've done it. I find that they have broad noses. The Filipinos, many of the Asiatics, Aborigines, and the Africans—broad noses. Occasionally, you will find a Caucasian with a broad nose.
But you'll find many of those people living in the hot and humid climates—the tropical belt—with broad noses. Why? They need a big opening to get enough air. You're hot, you need more air. The air is expanded so you need more volume. The humidity is in it, you'll need more volume. So, your nose, in time...don't think it will happen in one lifetime, but over a period of about a half-million years it can turn a razor sharp Caucasian nose into an Isaac Hayes nose.
All of this talk—"I'm a black man, he's a white man." What are you talking about? What kind of mind do you have? You might be a black man with a boy's mind, or a Caucasian, with a boy's mind, right? Or a dog's mind. That's nothing to brag about. And if I would take a sharp razor and hit your black skin real fast and hard with it, you'll see that you're a white nigger. That's right. If I hit you real hard and fast with a sharp razor and lay that meat open, you'll see white. Is that right? I've seen it happen. Not a razor, but I've seen a black person—more than one, I saw one get a bad wound, a quick wound, and the skin was—the meat was—white. So, he's a white man under that skin.
Imam W.D. Mohammed (raa)Wakiyl "TRUSTED FRIEND"( وَكِيۡلًا )
رَبُّ الۡمَشۡرِقِ وَالۡمَغۡرِبِ لَاۤ اِلٰهَ اِلَّا هُوَ فَاتَّخِذۡهُ وَكِيۡلًا
(73:9) He is the Lord of the East and the West; there is no god but He. So take Him alone for your Guardian.
Wakil is a person in whom one has complete faith; so much so that one can entrust all his affairs to him with full satisfaction of the heart. Thus, the verse means: Do not feel distressed at the hardships that you are experiencing at the storm of opposition that has been provoked by your invitation to the faith.
Your Lord is He Who is the Owner of the East and the West, (of the whole universe) besides Whom no one else possesses the powers of Godhead. Entrust your affair to Him and be satisfied that He will fight your case, He will deal with your opponents, and He will look after all your interests well.
رَّبُّ
(The) Lord
ٱلْمَشْرِقِ
(of) the east
وَٱلْمَغْرِبِ
and the west;
لَآ
(there is) no
إِلَـٰهَ
god
إِلَّا
except
هُوَ
Him,
فَٱتَّخِذْهُ
so take Him
وَكِيلاً
(as) Disposer of Affairs.THE MEANING OF AR-RAHMAN
By Imam W. Deen Mohammed
(Editor's note: The following is excerpted from a Ta'lim lecture delivered December 15 in Chicago by Imam Muhammad.
Now we come to the names that are given in Qur'an that belong to Allah. The Qur'an says, "La-illaha-illalah, there is no God except Allah." and the Qur'an gives us names that belong to Allah. And the first one Ar-Rahman is given. Ar-Rahmanu means the Gracious. It's translated in different ways in English. Some translations say 'the Gracious,' some say, 'the kind.' If you look up 'kind' in the dictionary it doesn't only mean nice, it also means generous. So, 'kind' and 'generous.' the combination, means niceness and generosity, goodness and generosity.
Some translations have given it as 'beneficent,' which means 'befitting' out of His kindness and grace. That's correct, too. All of these English terms are correct. But understand that the term 'Rahman' means to show mercy. So whatever God does that's good to us is a help to us, is kindness to us, out of His graces. It comes from His mercy.
He's a merciful God. He doesn't like to see His Creatures suffer. He doesn't like to see His creatures experience bad times, and misery, so it is His way to extend mercy to them. He is Ar-Rahman.
THE NEXT NAME THAT is given is Ar-Raheem. These are the two most often repeated names in the Holy Qur'an. In fact; every chapter except the 9th Chapter begins like that.
Bismillah, With the Name of God. Ar-Rahman. Ar-Raheem. the Gracious, the Compassionate, or the Gracious, the Merciful, the Beneficent, the Merciful.
As I have explained, there are different English words and they all can be suitable for the names Ar-Rahman and Ar-Raheem. Ar-Raheem is translated as the Merciful, but some Arabs have translated it to mercy-giving. I hope with a few comments on this name I will be able to make clear to you why some of them feel that to say "the Merciful," is not good enough.
'Ra-hi-mah.' means to show mercy, or give mercy. And this word, 'ar-Rah-ma-nu.' means the one who gives out of His gracious gift, from His bounty, from His great and unlimited resources to His creatures, and He does it out of mercy.
AR-RAHEEM too, has a connection with this word: both have connection with this word.
THIS CONCEPT of God comes from the understanding that before the creature became conscious of its needs. God had already been merciful and kind to that creature.
The baby is in the womb of his or her mother for nine months. We don't believe that it's conscious of its needs. But look at the nice situation that God has put that baby in. It slept on a waterbed before we did. That's a nice situation for that baby. It's shockproof, so if anybody punched the mother's stomach, the water bag cushions it, right? Yes. So we believe that God, before we are even aware that we need something, has already been generous and kind to us.
We come into this world, and we say, 'oh, I'm poor. But it is you who's poor. The world is not poor, the world is rich.
Why are you poor? Either because you are not yet-aware, or you're not yet ready to change your situation and go after the riches, or there are overwhelming forces that are keeping you away from it.
BUT THE world is not poor, God is generous! He has filled the world with all that is rich, more than we can see, more than we consume.
God has already put it here. So He is Gracious. He is Gracious. Ar-Rahmanu, out of His mercy. He is Gracious. Then, Ar-Raheemu. The condition comes now, and God has provided, but His creatures can't see it. Then He comes and makes a way for His creatures to get it against those barriers, odds or obstructions. He comes and opens the way so he can get it. That's the ar-Rahman, ar-Raheem.THE ROBE
Lost Knowledge
Now, let’s continue here. What is the robe symbolic of? Do you recall? Symbolic of the way you use the knowledge, the dress, symbolic of the way you use the knowledge. The sheet is the knowledge, the pages, the script.Remember now, when Jesus was crucified, he lost his robe and they gambled to see who would possess his robe. Now if you understand the meaning of robe, then you should understand that this world doesn’t have the true knowledge, the true use of the knowledge that Jesus gave them.
The knowledge was lost from Jesus’ body and it fell in the hands of crooked sinners. They gambled for it. Not only that, the silver cup, the special cup, it was lost too. Which tells us not only the proper use of the knowledge was lost, but also the moral cleanliness was lost from the religion.Silver chalice I think they call it. Is that what they call it? I think it is called Silver chalice. It was lost from Christianity. So how would they explain this? Ask the preacher next Sunday morning at 11 o’clock. Ask him. Say preacher; please tell me what it means in Christianity when they say that they lost the Silver chalice, the silver cup. Ask the preacher, how they can have the shroud of Jesus, in this city that is called Turin.
When the Bible says that his robe fell into the hands of sinners and they gambled to see who would possess it. So how can they have his robe there? If they have it, sinners gave it to them and if the sinners gave it up, it wasn’t fit to wear. That’s right. That robe wasn’t fit to wear. After it fell into the hands of sinners, who would want to wear it?
What is sweeter than honey?
Let’s continue now, it says he gave them another riddle. And this riddle is: “What is sweeter than honey?” And “What is stronger than a lion?”So he gave two riddles. In fact four parts to it.Second one is, “What is sweeter than honey?What is stronger than a lion?” All right. You know honey means the beauty of pure scripture. How do we know this? We know it because in the Qur’an this word is used. Honey is a good word for scripture. The honey is the essence of the flower and flowers are symbolic of beautiful culture.What is sweeter than the beauty that G-d offers you? What is sweeter than the sweetness that you find in G-d’s pure scripture? That’s what he’s telling them. And what is stronger than a lion? What he’s telling them is that, the east has honey.
They have the beauty of G-d’s revelation. And you have the strength of a lion. I’ve got something that makes you stronger, and I’ve got something to give you to make your doctrine sweeter than their honey.You see this thing? Yes, it’s plain. So he gave them, the Gentile world, the doctrine of love, the love of Christ that was sweeter than the moral and spiritual teachings to weak people, than the pure teachings of the Prophet. It’s sweeter to them … that G-d loves you sinners so much, that he gave his only begotten son, that he should be scorned, mocked, spat on, tortured, crucified, and die and be buried for your sins. Oh that’s sweet to ignorant weak people, sweeter than the truth of G-d’s scripture. So he said what is sweeter than honey? This lie I am going to give you is sweeter than the pure honey of Scripture that the east has.
Cheated Samson out of his heifer
And what is stronger than a lion? This subtle psychology…. (indiscernible) and he himself was going to destroy the Philistines. They have cheated him out of his heifer; I am talking about right now!The Christian Church that he thought would be his heifer betrayed him. Say oh, you can have business, you can have media, you can have this, but you are not going to run our churches. The Gentile doesn’t want any Jews over their churches. If you want to have something, you can have Peter. Go and tutor the Pope in secrecy. He’ll accept it. But these ordinary Gentiles are not going to accept that no Jew rule over them.So you mean to tell me you are not going to give me my heifer? So why don’t you, can’t you all do it through me, can’t you all carry out my orders?No we can’t do it. They are not going to listen to it. Well very good. Well then can I tell you what kind of doctrine you should give to the masses that won’t follow Peter?Yes it’s okay. All right. I’m going to make bread again. I’m going to get on a wheel. I’m going to make Marxism. I’m going to make Communism.I’m going to make the Age of Reason. I’m going to exalt logic. I’ll give them some new flour, is that okay? Well that’s okay. As long as you don’t take over the church. No, I won’t bother the church. Okay. Go on to the wheel again. It’s okay.
Bring society down on me and them
Now listen. After all that he still was not satisfied. Is that right? Yeah look at the story now, remember, he still is not satisfied. So he said, “I am blind, but I got something that they don’t know I’ve got. I got special power, in my arms.” “All I want to do is just have somebody show me to the pillars of the foundation of their society. And if I just can get to the two pillars that hold up the structure of their society, I’m going to bring it down on me and them.”So Samson goes and stands between the two pillars with the help of a little boy. He couldn’t see but he used the help of a little boy. What is the help of that little boy? Psychology. Psychology.
Don’t think it’s another person; he’s not even a person. Persons carry it out, but he’s a knowledge body. Then he goes and he used a little boy, psychology. Don’t human beings use psychology before they use intelligence?That’s why in psychology in this particular context it’s called a little boy. Your little children, before they are able to compete with you on an intelligence plane, they already using psychology on you. So psychology is an early development in the human being. That’s why the Jahcubite’s cousin, Fard Muhammad said Yakub conceived his idea at the age 6, as a little boy, a psychology. He’ll be surprised to know that I know that. I hope he gets this. I understand that he’s back home now. So he’ll get this message, Insha ‘Allah. Now, let me continue. With the help of psychology, he finds his way to the foundations of the new society. And when he gets to the foundation, what does he do? He forms a cross of himself and he begins pressing with all his might. That’s what the Scripture says. Said he pressed with all his might, with all his strength on the pillars, forming of himself a cross. What does this mean? This is more than Trinitarianism, this is the psychology of the mentality that Trinitarianism has produced.
Weaknesses in the mentality that trinitarianism has produced
He has now learned that there are certain weaknesses in the mentality that Trinitarianism has produced. And he knows that he can appeal to their emotions, and he can push in two directions at the same time.He didn’t pull the pillars, he pushed. He can push in opposite directions at the same time. Make one people give in to emotions, and the other people give in to logic. Push them. So that some will become highly emotional and some will become highly logical.And in doing this the logic will act against the emotions, and emotions will act against the logic. The emotional makeup will kill the logic, the logic will offend the emotions, the society will be divided against itself and the pillars will fall. Don’t you know that’s a strategy that is used in this Society? Whenever the hidden evil in the structure is about to be exposed they began firing the society with emotion, sentiment, flower children, love for everybody, crazy kind of sentimentality and emotionalism. They fire it up and build up strong emotions, this is depressing. Now when he does it it’s going to drop the whole thing. If he can be successful and bring in the sentimental and emotional elements against the logic, it’s going to destroy the whole thing.But look, he will certainly, he will be killed, as a knowledge body. He was already blind wasn’t he? What the hell has he lost? Nothing. Once he brings it down, he would start up all over again. Do, ra, mi, fa, sol, la, ti.
By the Grace of G-d, through IWDM, America was not destroyedJust in a few years that have passed us dear people, that scheme has tried to destroy America. But by the grace of G-d, through me, America was not destroyed. Why do I say through me? Because I was the only one that came out when the trend was to go in the form of the cross. When the trend was to become emotional, highly emotional and give one side to dry logic, I came up in the middle of that action and said there is a scheme going on, there is a trick going on.This whole thing is designed to fire up your sentiments, your emotions and topple the society. Somebody must have heard me and believed others who had been talking before I started, and all of it came together to save America. Yes.
See they didn’t believe others who were saying, there is a scheme, there is a hidden scheme. But when I began to speak, they say look, now we know this boy, we’ve been watching this boy since his father raised him up. We know that this boy is not a tool of outside influence. So if he says these things that ring a bell, where did he get it from? We believe maybe G-d is inspiring Wallace D. Mohammed. So they went back to the desk. And they begin to pull out things from the old file and they studied history all over again. And they said that Wallace D. Mohammed is an inspired man, he sees something. And what he is saying is what we’ve heard before. It might be something to it. How else could he get it?
Simple Simon met a pie man on the way to the square
Say oh no, let’s check this thing. Let’s check this thing. Said I’m sorry, you can’t get sixpence today, only one. Sorry, we aren’t buying pies today. We’re buying cakes. You heard that old story of Simple Simon … Simple Simon met a pie man on the way to the square. I think it goes,” … said Simple Simon to the pie man, would you have a sixpence to spare?” And I think he said, “If I was selling sixpence, I wouldn’t be selling pies!” Well, that’s another one of the conspirators’ riddles. And I will tell you what it means. Sixpence means the knowledge behind the scheme. It’s said the man was made on the 6th day. The sixpence is the knowledge behind the scheme. Simon was given seven (7), not six (6). He couldn’t see 6, six (6) was ruling seven (7). But he wanted the six (6).What is the secret in this? Will you tell me please, Mr. Pie man? You know what Pi is? 3.1416, I think it is. It’s a formula for finding the circumference of the earth. It’s a formula for world dominance. Now I’m not saying anything that I didn’t want to say, I know it’s a formula for finding the circumference of a circle. It’s a formula for world dominance.
If I was selling my own secrets you think I’d be selling pies And Peter, the Catholic Church wanted it. But the conspirator wouldn’t give it to them. Said if I was selling my own secrets you think I’d be selling pies? You think I’d be telling you how to get the world, if I was selling the secret to how to get it.I’ll just tell you how to get it; I’m not going to tell you my secret. You get it from me. Yes. All Peter got was some magic beans; he did manage to get those didn’t he? You remember that riddle? Nursery rhyme, whatever you want to call it. Jack and the beanstalk. Yeah. He had Jack, which is nothing again but Peter, or the Western society. Pardon me, I shouldn’t say Peter, not Peter, Jack is not the Catholic Church, it’s the Western society, Protestant society. Catholic Church headquarters is in Rome. This is typical American. Jack is talking about typical America. That’s why we call each other Jack. You know, hey jack, what’s happening Jack?
Yes, so, it was Peter, the Pope who asked them for his sixpence. But Jack, the American Christian society, they asked for magic beans. Well really they didn’t know what to ask for. All they wanted was really to be rescued, because their cow had got so lean, it was about to die.Everything was going bad. And they wanted to know how to bring back life. How can my cows get fat again? How can the society thrive again?So, while they were (wandering) wondering, this funny looking thing jumped out in the road. And he made himself visible and he said, “Magic beans want to buy some magic beans, like to buy some magic beans?” And Jack agreed to give his cow up for the magic beans. I’m showing you that this is not only in Scripture. If it is only in Scripture that means that what I’m talking about may not be existing in the world today. Or maybe it was just a story that was only in Scripture, maybe it was just fiction. But if it’s in the world too, we should listen.
What do the magic beans represent?
Now. Says this little funny thing, man, jumped out, and he talked Jack into giving up his cow for these magic beans. Right. Some of you remember it. He went away with his cow. What do the magic beans represent? A way to, again, to the secret knowledge in Christian religion. A way to the secret knowledge in Christian religion.And dumb Protestant society gave up their lean cow for this heavenly knowledge. What is the lean cow? The lean cow represents what they had before. What did they have before? They had rational growth. The Protestant movement began with an interest in rational growth. Is that right? Yes.
Our knowledge is weak, our cow is lean
They wanted to pursue knowledge. The Catholic Church had suppressed enlightenment, had suppressed education. The people weren’t allowed to learn. The masses couldn’t learn and educate themselves. So a thirst for knowledge came with Martin Luther. Right. And they began to want knowledge to develop their minds.Here comes Jake, Jack pardon me, feeling himself desperately in need of help. We have the interest in rational development of our society, but our knowledge is weak, our cow is lean. We haven’t yet produced anything. We need help. Who would help us?Oh Lord Jesus, help us. We got this logic. But Rome is powerful. We got this logic and Rome is powerful. G-d help us please! Ding, ding. Jahcubite conspirator. I will help you! Would you like to have some magic beans? If I give you my magic beans you’ll have to give me your lean cow. In effect he was saying the same thing that Samson said. I’m going to give you a new world, but you’re going to have to give me the one that you got now. And if you give him the one you got now, when it becomes fat, who does it belong to? Belong to him. He got it. He got it in exchange for the magic beans.
Over the heavenly kingdom was a mean old giant
So he (Jack) went home and planted. Went home and he didn’t know the value of them right? But I think accidentally one fell into the ground right? The thing grew up and it went up, up, up. He saw it going up past his window, he ran out and jumped on it, and the thing took him up into heaven. (It) took him up on the plane of clouds, into a castle that was in the clouds. Right. Yes.There he found a nice old woman that befriended him. But over that heavenly kingdom was a mean old giant. That right? Yes. He said fee, fi, fo, fom, I smell the blood of an Englishman, be he live or be he dead; I’ll grind his bones with my bread. With my bread. Remember bread is of two kinds. Leaven and unleavened. I’ll grind his bones with my bread.So, he managed to escape with the help of this woman up there, old woman who was nice. He managed to escape. Who is the old woman who was nice? Means people in the religious knowledge of the secrets of religion that weren’t corrupt. Didn’t have no evil designs on the world like the conspirators. They shared with him after he got up there. They shared with him some knowledge. Helped him to get the golden knowledge down from heaven.
The Golden knowledge it came from the hen right? The hen who laid golden eggs. But the hen couldn’t lay any golden eggs without music playing. When music played the hen would lay the eggs. The music stopped, the hen stop laying the golden eggs. Which means that the wisdom is tied to music? Do, re, mi, fa, sol, la, ti, do. Do, ra, mi, fa, sol, la, ti, do. Now when he got the musical scheme, he came back down with the hen and the music harp plus the knowledge, and he tied them together, then he had wisdom.He had wisdom to bring back down with the hen, and the music harp right, according to the story. From heaven, he brought back with him, they don’t say heaven, but it is the heaven of religious symbolism — Biblical symbolism. He came back down with the music maker and with the egg layer. You needed both in order to get the wisdom. The golden egg means wisdom. All right.
Giant’s fall from heaven left a big hole in the earth
The giant fell from heaven. Is that right? He was so big and heavy that when he fell he knocked a big hole in the earth, left there a big hole in the earth. The giant was finished. Who was finished? Who is the big giant that was finished? The people in the secret religion. The Pope.The Pope and certain others that I don’t care to name right now, that hoard the secrets of religion. When the Protestant was given the secret way to get it, and when Protestant leadership got it, got their share. Don’t think they got all, they got their share. Catholic got his share yes. Protestant got their share. The conspirators got the whole share.When they got it, the position of superiority of them over American Christian leadership fell. When it fell, it knocked a big hole in the ground. What is that symbolic of? Actually they were not spiritual people, they were material people.And when they fell a big part of the material that they had before was taken out. So much of the material wealth that was under Catholicism, and under other secret conspirators in religion, fell to Jack, to the American Christian Society. Is that right? Yes.Then they began to rise. But they only had magic beans. Magic beans is not knowledge. Magic. The only way you can get it is through magic. You have to have the knowledge of the magic to know how to work them. And, they were secret, so only a few of the Jack people can have them.
Jack: the American Christian society
Let me quickly tell you what Jack represents in the American Christian Society. It represents the intelligent leadership, Jack represents the intelligent leadership. Now Jack is not as long as Jacob. So their knowledge is shorter than Jacob, you see?Jack is a derivative of the word Jacob. Jacob is the origin, Jack is a derivative, derived from Jacob. So Jack is just a short …. they don’t have Jacob that’s long. But they do have enough to enable them to keep this same rhythm going.Rotating events, with a seven note scale, or is it eight. Yes, an eight note scale that goes to seven, and comes back to where it started. Right? Do, ra, mi, fa, sol, la, ti, do, come back to where it started. So they were given knowledge of how to keep society going through these changes, psychological changes.
So America unknowingly, has been going through these changes. Look at the trends, one fad behind another. Pretty soon you are wearing what you wore 20 years ago. Right. Pretty soon you’re dancing the way you danced 20 years ago. You are talking the way you talked 20 years ago. You are thinking the way you thought 20 years ago.So they keep rotating. They have the Jahcubite scheme, but they have only that pie that Jahcubite wanted them to have. Jahcubite sell pies all over the world Jahcubite sell pies all over the world. Sold the Pope a pie. Sold Protestant America a pie. Sold Communists East a pie, called it the red pie. Yes, the red pie. I’m getting ready to let you go now.
What does the red represent? What do they mean red? You say passions? That’s to trick you. Yes,Red means passions in the other octave. It has been played. It’s another octave. It takes on another color, it takes on another dress. It don’t keep the same dress, it says I will sell you changes. You see?Yes, it meant passions in one place, but not passions in Communist Russia, although passions are involved. It means the social life. Red means the social life. What ties me together with my brother? Blood. Blood is red. See. So people, as a social group are tied together first by blood. And they call each other brother, you see. So that’s blood.Red stands for blood. What blood? Human blood. Human blood, according to the Bible, New Testament in particular, should combine with water, which is human spirit, symbolic of human spirit.
Bring the social life too
So people should be spiritual, as well as social, according to the New Testament teaching. You shouldn’t just be blood. Christ Jesus says, “I come not of water only, but of blood also.”What does this mean? It means that before him, the people were all spiritual, but were neglecting the social development of society, the development of the relationship of person-to-person, people to people, communities to communities.He came to bring the blood, means to bring the social life up too, with the spiritual life. This is in the Scripture.So now, if the East has become red, it means that they now have gone to another … see the world was spiritual, and then it became religious.Now they are trying to get it to become all red. No spirituality, take the spirituality out of it. Make it all red, that we are social group and we are born out of materialism, so material concepts should govern us. We shouldn’t have spiritualism in our life. Give up; give out the water, only the red.
Imam W.D. Mohammed (raa)SEVEN LOCKS
The Jahcubite Conspiracy
Seven locks. L-O-C-K-S. You need a key to open a lock. His (Samson) strength was in this, that his knowledge was locked up. Seven locks of hair. His knowledge wasn’t exposed to other people. And the moment he exposed it to Delilah whom he trusted, he lost his strength. Is that right. Yes.All right let’s continue now. Seven locks. Yes. So the locks you understand is a secret knowledge, secret knowledge that runs the course, it’s a knowledge that runs the course and it’s to be repeated (. Do Re Mi Fa So La Ti Do...) Because once it runs a course, it can’t be…. can’t keep going, you have to start it back over again. You start with doe, re, mi, fa, sol, la, ti. When you get to ti, that’s the cross, now you can’t keep going with the cross, you have to bring in doe again. So you bring in Communism, or something else and you start the world all over again — do, re, mi, fa, sol, la, ti and you bring them to worship the Jahcubite again. And when they caught him, when they catch up with him, can’t keep the tee going, got to stop the worship of the Jahcubite. But start the world all over again with a new knowledge, do, re, and all the way up to ti again. So you keep going from one knowledge that is invented by the Jahcubite conspirators that lead you to the worship of the Jahcubite. Once you catch onto them that you’re worshiping them, they create another knowledge that brings you right to the same place again. So this is the seven locks of Samson that was his strength.
Samson fell in love with the hell he created and got weak But he fell in love so much with Delilah, Delilah is sin and darkness. Samson got weak. He fell in love with the hell he had created for the Gentiles. Delilah wasn’t meant for him to fall in love with. He wasn’t supposed to love Delilah; he was supposed to marry a different girl.So he ends up falling in love with Delilah that he didn’t really want. He didn’t want Delilah. But Delilah kept putting herself in his way. Why because he was raising a whole lot of hell in the world, and hell got so thick in the world, that even Samson couldn’t escape it.So sin and corruption came even against Samson … and the Jewish boys starts getting in the filth and the Jewish girls start going astray, and pretty soon the Jewish community gets disordered. Oh yeah.In love with the corruption that they created for other people.So what they got to do now? Well. Too late. Once the Jewish conspirators get weak for the sins of the wicked environment that they themselves formed, then they began to let out secrets to the people in the sinful environment.
They become drunk with the corruption that they created. And they lose mental fortitude or composure, they lose the composure, they lose the ability to hold in, what they shouldn’t let out. And they began to let out, not by word all the time, by their actions, by the mannerisms. The dark society began to peep their hold card. Ooooh, I see something. Yes, you get too intimate; somebody is going to see something. You see? So the people see. When the people see, then they expose the Jahcubite scheme. When the Jahcubite scheme is exposed, they have no strength. They become like ordinary people. Have no supernatural strength anymore. And their knowledge then is just on a level with our knowledge. So they are in the dark with us. They see no more than we see. So he becomes blind. Samson became blind. He had no superior eyesight. It was no more than the blindness of the society, because they had gotten his special knowledge. You understand? All right.
Samson can produce more fine flour of enlightenment
He’s blind now, and the world begins to use him. Not because they forced it on him. It looks like Samson was forced to do this. That’s all tricks. No, he has no other recourse; he has no other way, no other alternative. They know my secret now. My secret wisdom is of no power to me. Now what I’ll do is show them that I am stronger than an ox. I can grind more corn than their ox.I am going to get at the wheels of their economy. I’m going to get at the wheels of their academic knowledge, schools of thought. I am going to show them,I can produce more fine flour of academic knowledge. I can produce more fine flour of enlightenment. I will show them that I can produce what they want, and they won’t kill me, they will keep me as their workhorse, their ox, to grind the fine flour.So he goes from one conspiracy to another one.He goes underground like the Mafia and the Ku Klux Klan sometimes. And you say, “Oh I don’t see him anymore, they must be gone”. He’s not gone. He’s just grinding flour; he’s going to make bread all over again. And when he makes his bread, he will start again with do and he will go to re, mi, fa, sol, la, ti.
So he can’t see any more than you, but he knows how to grind the flour and he has the strength of the ox. So he grinds the flour of knowledge and he works with you in your blind world, in the darkness, right with you. But in time, he rises to the superior position. He has made him some flour that is special. Oh yes. And he is going to make him some dough that is special. And pretty soon he’s going to have all the bread. And when he gets the bread, he’s going to have the power. And then he will bring in re. And then after he brings in re, the world will come back to him, he would have mi again, and he will bring it on back up to fa, sol, la, ti, and when he gets to ti, he’ll have the world worshiping the Jahcubite again. And this thing continues over and over again, an endless circle. This is the true knowledge of the secret Jahcubite conspiracy. Not from the protocols of Zion. This is straight from the horse’s mouth. And you will find four horses in the Bible.
Imam W.D. Mohammed (raa)THE MEANING OF AR-RAHMAN
By Imam W. Deen Mohammed
(Editor's note: The following is excerpted from a Ta'lim lecture delivered December 15 in Chicago by Imam Muhammad.
Now we come to the names that are given in Qur'an that belong to Allah. The Qur'an says, "La-illaha-illalah, there is no God except Allah." and the Qur'an gives us names that belong to Allah. And the first one Ar-Rahman is given. Ar-Rahmanu means the Gracious. It's translated in different ways in English. Some translations say 'the Gracious,' some say, 'the kind.' If you look up 'kind' in the dictionary it doesn't only mean nice, it also means generous. So, 'kind' and 'generous.' the combination, means niceness and generosity, goodness and generosity.
Some translations have given it as 'beneficent,' which means 'befitting' out of His kindness and grace. That's correct, too. All of these English terms are correct. But understand that the term 'Rahman' means to show mercy. So whatever God does that's good to us is a help to us, is kindness to us, out of His graces. It comes from His mercy.
He's a merciful God. He doesn't like to see His Creatures suffer. He doesn't like to see His creatures experience bad times, and misery, so it is His way to extend mercy to them. He is Ar-Rahman.
THE NEXT NAME THAT is given is Ar-Raheem. These are the two most often repeated names in the Holy Qur'an. In fact; every chapter except the 9th Chapter begins like that.
Bismillah, With the Name of God. Ar-Rahman. Ar-Raheem. the Gracious, the Compassionate, or the Gracious, the Merciful, the Beneficent, the Merciful.
As I have explained, there are different English words and they all can be suitable for the names Ar-Rahman and Ar-Raheem. Ar-Raheem is translated as the Merciful, but some Arabs have translated it to mercy-giving. I hope with a few comments on this name I will be able to make clear to you why some of them feel that to say "the Merciful," is not good enough.
0 notes
Text
Inside the Government’s ‘Quantum Computing Summer School’
The internet was down at Los Alamos National Laboratory. Two thousand forested feet above Albuquerque, the relatively remote spot was once a hidey-hole for the Manhattan Project. Today, it is tasked with keeping the many resulting nuclear warheads stable. But it has also, and not unrelatedly, become a hub of quantum-computing research—and a bad place for the internet to fritz out.
It was June 17, and quantum thermodynamicist Zoe Holmes was in town during the outage, participating in LANL’s Quantum Computing Summer School, a 10-week boot-camp for students. “Everybody was really frustrated,” she says. But then, instead of Googling and Githubbing and StackExchanging, she and her peers went analog.
“We spent all day by the whiteboard doing calculations,” she said. “I’ve not done that before.” It was… nice.
Since getting plugged in once again, Holmes and 14 other students have been humming away on projects, going to lectures, and generally steeping themselves in the quantum-computing universe. It’s a subject that, for the most part, doesn’t exist in universities. Only a few schools offer courses and even fewer offer specializations.
Since the schools of the present weren’t preparing the quantum workforce of the future, LANL started the summer school last year to do so for them. In 2018, LANL had 90 applicants for 10 spots; this year, the program had 230 applicants for 15 spots.
“It’s sort of a buyers’ market for us,” said Patrick Coles, a quantum physicist and the summer school’s organizer. And indeed, the lab does kind of buy its students, paying them a stipend to spend 10 weeks in the high altitudes of New Mexico, learning about the strange machines of the future.
But why would the Department of Energy care about bringing students like Holmes here to collaborate in the first place? Why has the agency invested hundreds of millions of dollars in quantum computing, just in the past year?
For one, classical computers—while great at scrolling Twitter or even modeling how matter spread out after the Big Bang—suck at simulating quantum systems, ones subject to the physical laws of the super small. But quantum computers can simulate complicated systems that involve lots of individual objects, mimicking atoms or optimizing shipping logistics. If you want to model a chemical reaction, or understand how material behaves in a superconductor, you call D-Wave, not Dell.
“If you have a classical supercomputer that can simulate a molecule with at most 10 atoms, then you would have to double the size of that supercomputer just to simulate 11 atoms,” said Coles. You kind of hit a wall because your computer has to grow exponentially just to add atoms.
If quantum computers can successfully simulate atoms and particles, scientists can understand how the nuclear material inside existing bombs is behaving, what will happen as it sits inert, and what would happen if someone pressed the big red button
Quantum computers, though, only have to grow linearly when you add atoms, giving them more flex for their size. Chemical research of that sort could accelerate pharmaceutical development, whipping up digital chemical reactions you couldn’t digitally replicate before. It could reveal how best to route cargo carriers, or any other system with a ton of moving parts.
And yeah, LANL delves into those topics. But the hot core of LANL’s mission is nuclear security. And if quantum computers can successfully simulate atoms and particles, scientists can understand how the nuclear material inside existing bombs is behaving, what will happen as it sits inert, and what would happen if someone pressed the big red button. Since we’re not supposed to just blow up bombs in the desert anymore to understand them, scientists could simulate nuclear blasts (and the sitting-still bombs) on quantum computers.
While we have a good sense of what they can do, if you ask a quantum computer person how the computers work, you likely won’t get a satisfying answer. That’s partly because it’s complicated. But it’s also because quantum mechanics has no practical bearing on our interactions with the world. Our brains did not evolve while observing Schrodinger’s Cat, and we did not spend our formative years watching entangled electrons. As physicist Richard Feynman famously put it, “I think I can safely say that nobody understands quantum mechanics.”
Nevertheless, here’s an attempt to explain: Classical computers encode information in bits, each either a 0 or a 1. Quantum computers use qubits, entangled quantum systems where each bit represents both 0 and 1 at the same time. That superposition makes certain calculations—like simulating what atoms are up to—faster with less computing power.
While quantum computers are in an embryonic stage of development, scientists have already written algorithms that do certain simple things, like factor numbers. You can look those up and then string them together and plug them into an existing system, like the ones IBM, Rigetti, and D-Wave run in the cloud. These real-world instruments aren’t ready for primetime: They’re more proofs of concept than productive problem-solvers. The biggest universal quantum processor—the traditional sort—comes courtesy of Google and has just 72 qubits.
Right now, for almost every task, a classical computer will beat out its experimental quantum counterpart, so the systems mostly exist so that researchers can figure out how these computers could work in the future. The summer school, says Holmes, focuses not on the distant blue-sky future but what might come for the field in the next 5-10 years.
Also, the idea that other countries will get good at quantum computing spooks the US government: Quantum computers could theoretically break certain kinds of encryption, the security of which relies on the fact that a classical computer could take centuries to brute-force decode it. “This kind of encryption is based on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into primes,” Elizabeth Crosson, a professor in the Center for Quantum Information and Control at the University of New Mexico and a lecturer for the summer school, said. “This is something that a quantum computer can do efficiently but a classical computer can’t.”
A quantum computer can also itself encrypt information, entangling subatomic particles to do so rather than relying on eighth-grade math. That’s why the US wants to build its own functional computers first: because it’s the best, obviously, and because it could decode others’ secrets and more safely store its own. The National Institute of Standards and Technology is currently pouring resources into “post-quantum cryptography,” classical encryption that can work even if a computer has 15 times the qubits of Google’s current superlative system.
For any of that, though, you need human power, not just computing power. And if schools aren’t spitting out such humans, you send them to summer school—a laid-back way, complete with barbecues, to try to save information security.
This is part of what drew Holmes, who started out as a philosophy major and added physics as a double major, to the topic and the LANL program. “I liked it when physics got philosophical,” she said. “And when philosophy was asking questions about the real world.” Quantum mechanics seemed like a place where the two entangled themselves most tightly. Today, she’s doing a PhD focusing on quantum thermodynamics at Imperial College London. She came to the summer school to broaden her subatomic knowledge, and for the collaboration that isn’t always part of theoretical physics.
Even the bigwigs chill out at LANL’s program: Last summer, Coles invited MIT mathematician Peter Shor—the guy who developed the quantum algorithm that does the kind of factoring that could unscramble our secret scrambled bits. “He’s arguably the biggest name in our field,” said Coles. Coles has a picture of him casually eating sourdough bread out of a paper bag. Students and faculty sip beer in the background, taking a break from the future to enjoy the present. Or, perhaps, like a qubit, they’re superimposing those states of being.
Inside the Government’s ‘Quantum Computing Summer School’ syndicated from https://triviaqaweb.wordpress.com/feed/
0 notes
Photo

Catholic Physics - Reflections of a Catholic Scientist - Part 74
Are We Special? New Thoughts about the Anthropic Principle
Story with images:
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/catholic-physics-reflections-scientist-part-74-harold-baines/?published=t
William Blake, Europe--A Prophecy from Wikimedia Commons (Caption for linked image)
“Scientists are slowly waking up to an inconvenient truth - the universe looks suspiciously like a fix. The issue concerns the very laws of nature themselves. For 40 years, physicists and cosmologists have been quietly collecting examples of all too convenient "coincidences" and special features in the underlying laws of the universe that seem to be necessary in order for life, and hence conscious beings, to exist. Change any one of them and the consequences would be lethal. Paul Davies, winner of the 1995 Templeton Prize
"It is a strange fact, incidentally, that religious apologists love the anthropic principle. For some reason that makes no sense at all, they think it supports their case. Precisely the opposite is true. The anthropic principle, like natural selection, is an alternative to the design hypothesis. It provides a rational, design-free explanation for the fact that we find ourselves in a situation propitious to our existence.” Richard Dawkins, The God Delusion
INTRODUCTION
You see in the quotes above two different views of the Anthropic Principle, that our universe is finely tuned to support carbon-based life; it's known in several versions ranging in acronym form from Weak Anthropic Principle (WAP), to Strong Anthropic Principle (SAP), to Christian Anthropic Principle (CAP), to Completely Ridiculous Anthropic Principle (you do the acronym).
My interest has been awakened again by conversations (via email) with an author who believes that the Anthropic Principle, as exemplified in a series of physical events and values for constants -- the anthropic coincidences -- strongly and quantitatively (via probability arguments) supports the proposition of a creating God.
I also believe that these anthropic coincidences help us to believe in God, but I do not believe that probability arguments, as they have been used heretofore, are valid. Rather, I take the point of view of the psalmist in Psalm 19:
"The heavens declare the glory of God; and the firmament sheweth his handywork. Day unto day uttereth speech, and night unto night sheweth knowledge. There is no speech nor language, where their voice is not heard." KJV
THE ANTHROPIC COINCIDENCES AND FINE-TUNING
These anthropic coincidences have been discussed in two other posts on this blog: Philosophic Issues in Cosmology 6, The Theology of Water. I'll summarize the arguments presented in these posts; if you, the reader, are not familiar with the ins and outs of the anthropic principle, I urge you to read these posts and the references contained therein.
I'll not go through an exhaustive list -- that's done in references given in the linked posts; rather they can be categorized as follows:
Features of the universe -- e.g. space dimensionality 3; the mass/energy content of the initial universe that enabled expansion but not immediate collapse; uniformity in very early universe; size;
Finely tuned values for fundamental physical parameters -- e.g. the mass difference between proton and neutrons that enables stability for nuclear processes; the carbon-12 excited state energy that by resonance enhances the probability of carbon-12 nucleus formation from a rare collision of three He nuclei;
Nature of physical laws -- e.g ratio of electromagnetic force to gravitational force; inverse cube force law for gravity; quantum mechanical laws that enable chemical bonding and (see below) the special properties of water;
"Accidental" geo-astronomical features -- e.g. tilt of the earth's axis enabling life-friendly climate, unusually large moon shielding earth from asteroid and meteor collision.
It must be emphasized that there are many more instances of such fine tuning -- parameters for which the values have to lie between narrow limits to enable a life-supporting universe, and many more examples of geo-astronomical and chemical features. Ellis, in the reference linked above, specifies general conditions that must obtain for a universe to contain life as we know it.
IS THERE A PROBABILITY FOR THE UNIVERSE?
Some Christian apologists use the anthropic coincidences as an argument for the existence of God by citing the very low probability for their occurrence; all these happening would not occur by chance. A major objection to this procedure, which Ellis points out, is that the universe is a single datum -- probability arguments are generally applied to samples from larger collections for which we have information about variability.
For example, if you've examined 20,000 crates of oranges and found 100 crates containing bad oranges, you'd be justified in putting a probability of 100/20,000 or .005 in finding a bad orange in the next crate. But if you've only come across one crate of oranges, then it's speculation to put a probability on finding a bad orange. (But see below.)
Another error one finds is that some apologists list a string of fine tuning examples (call them a,b,c,d...x), and then use the argument that P(a,b,c,d...x) = P(a) P(b) P(c)P(d)...P(x). They say that the probability of the total set is the product of the probabilities for each member of the set.
This would be true if the events were independent, in other words if what happened for one event did not depend on what happened for another.* Such independence will not necessarily hold. Consider, for example, the properties of water that are life-friendly:
Model of Ice Structure, red: oxygen; white, hydrogen Dashed lines represent hydrogen bonds - From Wikimedia Commons (Caption for linked image)
thermodynamic -- high freezing and boiling points, high specific heat, etc.;
physical -- surface tension, low specific gravity of ice, maximum density of liquid water at 4 deg C.
These properties all depend on the very unusual capacity of protons in a H2O molecule to form strong hydrogen bonds to oxygen atoms in other H2O molecules. And that hydrogen bonding capability arises from quantum mechanics and the physical nature of electrostatic attraction. So it is one feature, not many, for which a probability should entered. . And how do you assess the probability of quantum mechanics giving rise to hydrogen-bonding?
PROBABILITY AS A MEASURE OF BELIEF
"But is it probable that probability brings certainty?" Blaise Pascal, Pensees 496
I'm going to try a different approach, using probability as a measure of belief. (I apologize to those professional statisticians and mathematicians who will certainly be offended by my presumption.) The approach is my take on Richard Jeffrey's Subjective Probability.
Let's start with a different definition of probability, based on strength of belief. Consider the following examples for betting on a horse race. You overhear a trainer telling a pal that "the next race is fixed for Trump's Nag to win, with odds of 9/1". You bet $10, expecting to win $90. The defined probability, working from the odds ratio, is 1/(9+1) = 0.10. The probability of losing your bet is then 1- 0.10 = 0.90. The expectation value is 0 = 0.10 x 90 + 0.90 x(-10).
The next step is to consider conditional probability, that is how the probability of an event depends on a linked event. Let A represent the event that the stock price rises to $100. Let B represent the event that information about the possible rise of the stock is given. Then the conditional probability is denoted as p(A|B), the probability of event A given that event B occurs. Note that there is no causal relation implied here--it's only a matter of evidence.
Now to the meat of the matter. Let F represent the event of fine-tuning for the universe; G, that God exists; N, that God does not exist (or that "Naturalism= materialism" accounts for everything). Then
p(G| F ) is a probability, a degree of belief, that F --> G, i.e. fine-tuning is evidence for the existence of God;
p(N | F) is a probability that fine-tuning implies that God does not exist;
p(F | G) is the probability that if God exists then He can fine-tune the universe;
p(F | N) is the probability that a fine-tuned universe would occur in the absence of God;
p(G) is the probability--the degree of belief--that God exists;
p(N) is the probability--the degree of belief--that God does not exist.
Then straightforward manipulation gives (see note **) yields
P(G | F)) = [ P(G) ] [ P(F | G) ]
P(N | F) [ P(N) ] [ P(F | N)]
1 2 3
Term 1 is a likelihood ratio for belief that fine-tuning implies the existence of God to belief that fine-tuning implies no God; term 2 is a likelihood ratio for belief in God to belief in no God (naturalism); term 3 is a likelihood ratio for belief that God, if He exists, would create a fine-tuned universe to support life to belief that naturalism/materialism would yield a fine-tuned universe.
Now certainly term 3 is a number much greater than 1, even if the exact value is indeterminate. The value for term 2 will depend on the individual -- for a Christian martyr, it would be a huge number; for Richard Dawkins or Lawrence Kraus it would be a very small number.
Here's the point: the value you impute to term 1, the likelihood ratio for belief that a fine-tuned universe is evidence for the existence of God, will be greater than 1 if you are not a hard core atheist. If you're agnostic -- it's a 50/50 proposition that God exists -- then certainly fine tuning should convince you that God exists. If you're an extreme atheist, then term 2 could become small enough to swamp term 3, even if the latter is very large.
So the upshot is that if you do believe in God or if you're an agnostic, fine tuning can be evidence for God's creating hand. If you're an atheist -- this will not be sufficient evidence. And we come again to Grace given by the Holy Spirit as the mechanism for faith.
NOTES
* Further, if you do this with a large number of events, it will certainly not lead to useful information. Consider a series of 50 independent events, each of which has a probability of 0.9. Then the probability for all the events happening together is 0.9 ^ 50 = .0052. which is small, even though the probability for the events individually is large.
**Consider p(A and B), the probability that both A and B occur (or that both A and B are true propositions). Then a form of Bayes' theorem is that
p(A and B) = p(A | B) p(B) = p (B | A) p(A);
whence p(A | B) = [p(A)/p(B)] [ p( B | A) ]
From a series of articles written by: Bob Kurland - a Catholic Scientist
0 notes
Text
Refrigerator for quantum computer systems located
New Post has been published on https://pagedesignhub.com/refrigerator-for-quantum-computer-systems-located/
Refrigerator for quantum computer systems located
The international race closer to a functioning quantum laptop is on. With destiny quantum computer systems, we will be able to clear up previously not possible issues and increase, for example, complicated drug treatments, fertilizers, or synthetic intelligence.
The studies results posted nowadays inside the medical journal, Nature Communications, advocate how dangerous errors in quantum computing may be removed. This is a brand new twist toward a functioning quantum laptop.
Even a quantum computer needs cooling fins
How quantum computer systems differ from the computer systems that we use nowadays is that instead of ordinary bits, they compute with quantum bits or qubits. The bits being crunched to your PC are either zeros or ones, while a qubit can exist simultaneously in both states. This versatility of qubits is wanted for complicated computing, but it also makes them touchy to external perturbations.
Just like ordinary processors, a quantum laptop also wishes a cooling mechanism. In the future, hundreds or maybe thousands and thousands of logical qubits may be simultaneously utilized in computation, and with a view to gain the suitable end result, every qubit must be reset at the beginning of the computation. If the qubits are too hot, they can not be initialized because they’re switching between different states an excessive amount of. This is the hassle Möttönen and his institution has evolved a strategy to.
A refrigerator makes quantum gadgets more reliable
The nanoscale refrigerator evolved by means of the research organization at Aalto University solves a massive project: with its assist, most electric quantum gadgets can be initialized quickly. The gadgets for that reason come to be extra effective and dependable.
“I even have labored in this system for 5 years and it sooner or later works!” rejoices Kuan Yen Tan, who works as a postdoctoral researcher in Möttönen’s institution.
Tan cooled down a qubit-like superconducting resonator utilizing the tunneling of single electrons through a two-nanometer-thick insulator. He gave the electrons slightly too little power from an external voltage supply than what is needed for direct tunneling. Therefore, the electron captures the missing energy required for tunneling from the close by the quantum device, and for this reason, the device loses energy and cools down. The cooling can be switched off by adjusting the external voltage to 0. Then, even the energy to be had from the quantum tool isn’t always sufficient to push the electron thru the insulator.
Quantum Computing Imagine a computer whose memory is exponentially larger than its apparent physical size; a laptop which can control an exponential set of inputs concurrently; a laptop that computes in the twilight sector of space. You might be considering a quantum computer. Relatively few and simple concepts from quantum mechanics are had to make quantum computer systems a possibility. The subtlety has been in getting to know to manipulate these principles. Is this kind of PC an inevitability or will it be too tough to build?
By the unusual legal guidelines of quantum mechanics, Folger, a senior editor at Discover, notes that; an electron, proton, or different subatomic particle is “in multiple vicinities at a time,” because person particles behave like waves, those unique locations are distinctive states that an atom can exist in concurrently.
What’s the big deal about quantum computing? Imagine you had been in a huge workplace building and also you had to retrieve a briefcase left on a desk picked at random in considered one of masses of places to work. In the identical way that you would ought to stroll through the building, starting doorways one after the other to find the briefcase, an everyday pc has to make it manner via long strings of 1’s and zero’s until it arrives at the solution. But what if as a substitute of getting to search with the aid of yourself, you could instantly create as many copies of your self as there had been rooms within the building all the copies could simultaneously peek in all of the offices, and the one that finds the briefcase becomes the real you, the relaxation simply disappear. – (David Freeman, discover )
David Deutsch, a physicist at Oxford University, argued that it can be viable to construct a very effective pc primarily based in this ordinary reality. In 1994, Peter Shor, a mathematician at AT&T Bell Laboratories in New Jersey, proved that, in theory at the least, a full-blown quantum pc could aspect even the largest numbers in seconds; an accomplishment impossible for even the quickest traditional pc. An outbreak of theories and discussions of the opportunity of building a quantum laptop now permeates itself although out the quantum fields of technology and studies.
It’s roots may be traced returned to 1981, whilst Richard Feynman noted that physicists constantly seem to run into computational problems when they are attempting to simulate a device wherein quantum mechanics might take region. The calculations related to the conduct of atoms, electrons, or photons, require a massive amount of time on modern computer systems. In 1985 in Oxford England the primary description of ways a quantum laptop might work surfaced with David Deutsch’s theories. The new tool might now not most effective be capable of surpass brand new computers in pace, however additionally could carry out a few logical operations that conventional ones could not.
This studies began searching into absolutely constructing a tool and with the pass beforehand and further investment of AT&T Bell Laboratories in Murray Hill, New Jersey a brand new member of the crew was introduced. Peter Shor made the discovery that quantum computation can significantly velocity factoring of complete numbers. It’s more than only a step in micro-computing generation, it could provide insights into actual world packages which include cryptography.
“There is a hope on the quit of the tunnel that quantum computer systems may also one day come to be a reality,” says Gilles Brassard of University of Montreal. Quantum Mechanics supply an unexpected readability within the description of the conduct of atoms, electrons, and photons at the microscopic tiers. Although this statistics isn’t relevant in ordinary family makes use of it does without a doubt practice to each interaction of matter that we will see, the actual advantages of this knowledge are simply starting to reveal themselves.
In our computers, circuit boards are designed so that a 1 or a 0 is represented by means of differing quantities of strength, the outcome of 1 possibility has no impact on the alternative. However, a trouble arises whilst quantum theories are introduced, the results come from a single piece of hardware existing in two separate realities and those realties overlap one another affecting both outcomes without delay. These troubles can turn out to be one of the greatest strengths of the brand new pc but, if it is viable to software the effects in any such way so that undesirable results cancel themselves out at the same time as the advantageous ones make stronger every other.
0 notes
Text
Throwback to this baller design for a 1995 steam engine: using two periodic vectors (all torque and stuff set by altering the green vector) and their pivot to generate a binary system of movement from a differentiable ‘function.’ When not being moved by the vectors, the connecting piece becomes a, ‘pendulum,�� (not control by gravity but by property/frequency/etc differences between the green and yellow vectors) so the bottom vector moves (like the bottom of a pendulum) but the pivot doesn’t.
Exacts: if green vector is stronger than yellow vector and is behind on its arc, pendulum effect until it exits its arc or yellow vector grows stronger, then standard movement.
#physics#math#mathematics#mathblr#american history#rotation#mathematician does physics with 0 knowledge of any physics at all
0 notes
Text
New Post has been published on Globeinfrom
New Post has been published on https://globeinform.com/super-computer-simulates-45-qubit-quantum-computer/
Super computer simulates 45 qubit quantum computer
Near-term quantum computer systems will quickly reach sizes which might be hard to directly simulate, even when employing the maximum effective supercomputers. Yet, the capacity to simulate those early gadgets the use of classical computer systems is essential for calibration, validation, and benchmarking. If you want to employ the total capacity modern-day systems proposing multi- and plenty of middle processors, we use automatic code generation and optimization latest computes kernels, which also enables performance portability. We practice a scheduling algorithm to quantum supremacy circuits If you want to reduce the desired conversation and simulate a 45-qubit circuit at the Cori II supercomputer the use of 8,192 nodes and 0.five petabytes trendy memory. To our expertise, this constitutes the biggest quantum circuit simulation to this date. Our incredibly-tuned kernels in aggregate with the decreased conversation necessities permit and development in time-to-answer over simulators via more than an order contemporary magnitude at each scale.
They demonstrated simulations modern up to 45 qubits the usage of up to 8,192 nodes. With the same amount latest computer sources, the simulation cutting-edge 46 qubits are possible while the usage of single-precision floating factor numbers to represent the complex amplitudes. The offered optimizations are fashionable and our code generator improves performance portability across a wide range state-of-the-art processors. Extending the range cutting-edge the code generator to the area today’s GPUs is an ongoing task.
Additional optimizations at the quantum circuit description permit to reduce the required verbal exchange via an order brand new value. As an end result, the simulation contemporary a forty nine-qubit quantum supremacy circuit could require most effective two global-to-local change operations. At the same time as the memory requirements to simulate any such large circuit are beyond what’s feasible today, the low quantity trendy communication may also allow the use of, e.G., strong-state drives. The simulation effects may also then be used for verification and calibration brand new Near-time period quantum gadgets.
Quantum Computing Consider a PC whose memory is exponentially large than its apparent physical size; a laptop which could manipulate an exponential set modern inputs concurrently; a laptop that competes in the twilight area state-of-the-art space. You would be state-of-the-art a quantum computer. Quite a few and easy principles from quantum mechanics are needed to make quantum computers an opportunity. The subtlety has been in brand new to control these standards. Is such a pc an inevitability or will it be too difficult to build?
by way of the unusual laws latest quantum mechanics, Folger, a senior editor at Discover, notes that; an electron, proton, or other subatomic particle is “in a couple of location at a time,” due to the fact character debris behave like waves, those specific places are unique states that an atom can exist in simultaneously.
What’s the large deal about quantum computing? Consider you were in a huge office building and you had to retrieve a briefcase left on a desk picked at random in one in every of hundreds present day contemporary. in the same manner, which you could stroll thru the building, opening doors separately to locate the briefcase, an everyday PC has to make it manner through long strings of one’s and 0’s until it arrives at the answer. However what if alternatively modern-day to go looking by means of your self, you can right away create as many copies contemporary yourself as there have been rooms inside the constructing all of the copies could concurrently peek in all of the today’s, and the only that reveals the briefcase turns into the real you, the relaxation simply disappear. – (David Freeman, Discover )
David Deutsch, a physicist at Oxford College, argued that it may be viable to construct an extremely effective computer based totally in this extraordinary truth. In 1994, Peter Shor, a mathematician at AT&T Bell Laboratories in New Jersey, proved that in principle at least, a full-blown quantum PC could factor even the most important numbers in seconds; an accomplishment not possible for even the fastest traditional computer. A plague ultra-modern theories and discussions state-of-the-art the possibility cutting-edge constructing a quantum PC now permeates itself though out the quantum fields contemporary generation and studies.
It is rooted can be traced again to 1981, when Richard Feynman referred to that physicists always appear to run into computational issues when they are trying to simulate a gadget in which quantum mechanics would take location. The calculations related to the conduct latest atoms, electrons, or photons, require a massive quantity ultra-modern time on modern-day computers. In 1985 in Oxford England the primary description of the way a quantum computer would possibly work surfaced with David Deutsch’s theories. The brand new device might not only be capable of surpassing contemporary computers in speed, However also ought to perform some logical operations that conventional ones couldn’t.
This studies started looking into genuinely building a device and with the cross ahead and extra investment trendy AT&T Bell Laboratories in Murray Hill, New Jersey a brand new member latest the crew was added. Peter Shor made the invention that quantum computation can substantially pace factoring brand new complete numbers. It is more than only a step in the microcomputing era, it could offer insights into real global programs inclusive of cryptography.
“There’s a hope on the stop present day the tunnel that quantum computers may also in the future turn out to be a truth,” says Gilles Brassard today’s College cutting-edge Montreal. Quantum Mechanics deliver a sudden readability within the description cutting-edge the conduct cutting-edge atoms, electrons, and photons on the microscopic levels. Despite the fact that this information isn’t applicable in normal household trendy it does certainly practice to each interplay modern day rely on that we will see, the actual benefits brand new this knowledge is simply beginning to expose themselves.
In our computers, circuit forums are designed in order that a 1 or a zero is represented with the aid of differing quantities latest strength, the outcome of 1 opportunity has no effect on the opposite. However, a problem arises while quantum theories are added, the outcomes come from an unmarried piece latest hardware current in separate realities and these realities overlap each other affecting both results right away. these problems can end up one of the best strengths cutting-edge The brand new computer But, if it’s miles possible to program the outcomes in this kind of way in order that undesirable effects cancel themselves out While the advantageous ones give a boost to each different.
This quantum machine ought to be capable of application the equation into it, confirm It is a computation, and extract the effects. Numerous viable structures have been checked out by means of researchers, one among which entails using electrons, atoms, or ions trapped inside state-of-the-art magnetic fields, intersecting lasers could then be used to excite the confined debris to the right wavelength and a 2nd time to repair the particles to their ground country. A series ultra-modern pulses may be used to array the particles into a sample usable in our gadget cutting-edge equations.
0 notes
Text
Latest Quantum Computing
New Post has been published on https://myupdatesystems.com/2017/04/09/latest-quantum-computing/
Latest Quantum Computing
Quantum Computing
Imagine a computer whose memory is exponentially larger than its apparent physical size; a computer that can manipulate an exponential set of inputs simultaneously; a computer that computes in the twilight zone of space. You would be thinking of a quantum computer. Relatively few and simple concepts from quantum mechanics are needed to make quantum computers a possibility. The subtlety has been in learning to manipulate these concepts. Is such a computer an inevitability or will it be too difficult to build?
By the strange laws of quantum mechanics, Folger, a senior editor at Discover, notes that; an electron, proton, or other subatomic particle is “in more than one place at a time,” because individual particles behave like waves, these different places are different states that an atom can exist in simultaneously.
What’s the big deal about quantum computing? Imagine you were in a large office building and you had to retrieve a briefcase left on a desk picked at random in one of the hundreds of offices. In the same way that you would have to walk through the building, opening doors one at a time to find the briefcase, an ordinary computer has to make it way through long strings of 1’s and 0’s until it arrives at the answer. But what if instead of having to search by yourself, you could instantly create as many copies of yourself as there were rooms in the building all the copies could simultaneously peek in all the offices, and the one that finds the briefcase becomes the real you, the rest just disappear. – (David Freeman, discover )
David Deutsch, a physicist at Oxford University, argued that it may be possible to build an extremely powerful computer based on this peculiar reality. In 1994, Peter Shor, a mathematician at AT&T Bell Laboratories in New Jersey, proved that in theory at least, a full-blown quantum computer could factor even the largest numbers in seconds; an accomplishment impossible for even the fastest conventional computer. An outbreak of theories and discussions of the possibility of building a quantum computer now permeates itself though out the quantum fields of technology and research.
Its roots can be traced back to 1981 when Richard Feynman noted that physicists always seem to run into computational problems when they try to simulate a system in which quantum mechanics would take place. The calculations involving the behavior of atoms, electrons, or photons, require an immense amount of time on today’s computers. In 1985 in Oxford England the first description of how a quantum computer might work surfaced with David Deutsch’s theories. The new device would not only be able to surpass today’s computers in speed, but also could perform some logical operations that conventional ones couldn’t.
This research began looking into actually constructing a device and with the go ahead and additional funding of AT&T Bell Laboratories in Murray Hill, New Jersey a new member of the team was added. Peter Shor made the discovery that quantum computation can greatly speed factoring of whole numbers. It’s more than just a step in micro-computing technology, it could offer insights into real world applications such as cryptography.
“There is a hope at the end of the tunnel that quantum computers may one day become a reality,” says Gilles Brassard of the University of Montreal. Quantum Mechanics give an unexpected clarity in the description of the behavior of atoms, electrons, and photons on the microscopic levels. Although this information isn’t applicable in the everyday household uses it does certainly apply to every interaction of matter that we can see, the real benefits of this knowledge are just beginning to show themselves.
In our computers, circuit boards are designed so that a 1 or a 0 is represented by differing amounts of electricity, the outcome of one possibility has no effect on the other. However, a problem arises when quantum theories are introduced, the outcomes come from a single piece of hardware existing in two separate realities and these realities overlap one another affecting both outcomes at once. These problems can become one of the greatest strengths of the new computer, however, if it is possible to program the outcomes in such a way so that undesirable effects cancel themselves out while the positive ones reinforce each other.
This quantum system must be able to program the equation into it, verify it’s computation, and extract the results. Several possible systems have been looked at by researchers, one of which involves using electrons, atoms, or ions trapped inside of magnetic fields, intersecting lasers would then be used to excite the confined particles to the right wavelength and a second time to restore the particles to their ground state. A sequence of pulses could be used to array the particles into a pattern usable in our system of equations.
Another possibility by Seth Lloyd of MIT proposed using organic-metallic polymers ( the one-dimensional molecule made of repeating atoms). The energy states of a given atom would be determined by its interaction with neighboring atoms in the chain. Laser pulses could be used to send signals down the polymer chain and the two ends would create two unique energy states.
A third proposal was to replace the organic molecules with crystals in which information would be stored in the crystals in specific frequencies that could be processed with additional pulses. The atomic nuclei, spinning in either of two states (clockwise or counterclockwise) could be programmed with a tip of an atomic microscope, either “reading” it’s surface or altering it, which of course would be “writing” part of information storage. “Repetitive motions of the tip, you could eventually write out any desired logic circuit, ” DiVincenzo said.
This power comes at a price, however, in that these states would have to remain completely isolated from everything, including a stray photon. These outside influences would accumulate, causing the system to wander off track and it could even turn around and end up going backward causing frequent mistakes. To keep this from forming new theories have arisen to overcome this. One way is to keep the computations relatively short to reduce chances of error, another would be to restore redundant copies of the info on separate machines and take the average (mode) of the answers.
This would undoubtedly give up any advantages to the quantum computer, and so AT&T Bell Laboratories have invented an error correction method in which the quantum bit of data would be encoded in one of nine quantum bits. If one of the nine were lost it would then be possible to recover the data from what information did get through. This would be the protected position that the quantum state would enter before being transmitted. Also since the states of the atoms exist in two states, if one were to be corrupted the state of the atom could be determined simply by observing the opposite end of the atom since each side contains the exact opposite polarity.
The gates that would transmit the information is what is mainly focused on by researchers today, this single quantum logic gate and its arrangement of components to perform a particular operation. One such gate could control the switch from a 1 to a 0 and back, while another could take two bits and make the result 0 if both are the same, 1 if different.
These gates would be rows of ions held in a magnetic trap or single atoms passing through microwave cavities. This single gate could be constructed within the next year or two yet a logical computer must have the millions of gates to become practical. Tycho Sleator of NYU and Harald Weinfurter of UIA look at the quantum logic gates as simple steps towards making a quantum logic network.
These networks would be but rows of gates interacting with each other. Laser beams shining onions cause a transition from one quantum state to another which can alter the type of collective motion possible in the array and so a specific frequency of light could be used to control the interactions between the ions. One name given to these arrays has been named “quantum-dot arrays” in that the individual electrons would be confined to the quantum-dot structures, encoding information to perform mathematical operations from simple addition to the factoring of those whole numbers.
The “quantum-dot” structures would be built upon advances in the making of microscopic semiconductor boxes, whose walls keep the electrons confined to the small region of material, another way to control the way information is processed. Craig Lent, the main researcher of the project, base this on a unit consisting of five quantum dots, one in the center and four and at the ends of a square, electrons would be tunneled between any of the two sites.
Stringing these together would create the logic circuits that the new quantum computer would require. The distance would be sufficient to create “binary wires” made of rows of these units, flipping the state at one end causing a chain reaction to flip all the units states down along the wire, much like today’s dominoes transmit inertia. Speculation on the impact of such technology has been debated and dreamed about for years.
In the arguing points, the point that its potential harm could be that the computational speed would be able to thwart any attempts at security, especially the now NSA’s data encryption standard would be useless as the algorithm would be a trivial problem to such a machine. On the latter part, this dreamed reality first appeared in the TV show Quantum Leap, where this technology becomes readily apparent when Ziggy –the parallel hybrid computer that he has designed and programmed– is mentioned, the capabilities of a quantum computer mirror that of the show’s hybrid computer.
0 notes
Text
Quantum laptop learns to ‘see’ trees
New Post has been published on https://pressography.org/quantum-laptop-learns-to-see-trees/
Quantum laptop learns to ‘see’ trees
Scientists have trained a quantum computer to recognize trees. That may not seem like a huge deal, however, the resulting manner that researchers are a step towards the usage of such computers for complex device learning issues like sample reputation and PC vision.
The team used a D-Wave 2X laptop, an advanced version from the Burnaby, Canada–based totally agency that created the arena’s first quantum laptop in 2007. Traditional computers can already use sophisticated algorithms to apprehend styles in snapshots, but it takes plenty of reminiscence and processor power. That is due to the fact classical computers save data in binary bits–both a zero or a 1. Quantum computers, in assessment, run on a subatomic level the use of quantum bits (or qubits) which could constitute a zero and a 1 at the same time. A processor the usage of qubits could theoretically solve issues exponentially more quickly than a traditional computer for a small set of specialized issues. The character of quantum computing and the constraints of programming qubits has intended that complicated troubles like PC imaginative and prescient have been off-limits until now.
Within the new look at, physicist Edward Boyda of St. the Mary’s University of California in Moraga and colleagues fed masses of NASA satellite pix of California into the D-Wave 2X processor, which incorporates 1152 qubits. The researchers asked the computer to don’t forget dozens of features—hue, saturation, even mild reflectance—to decide whether clumps of pixels have been bushes in preference to roads, homes, or rivers. They then told the PC whether or not its classifications had been right or incorrect in order that the computer ought to research from its mistakes, tweaking the formulation it uses to determine whether or not something is a tree.
After it turned into educated, the D-Wave became ninety% accurate in spotting trees in aerial photographs of Mill Valley, California, the team reviews in PLOS ONE. It became handiest slightly greater accurate than a Traditional PC could have been on the equal trouble. but the results exhibit how scientists can program quantum computers to “appearance” at and analyze snapshots and opens up the opportunity of using them to remedy other complicated problems that require heavy records crunching.
As an instance, Nemani says the study lays the basis for better weather forecasting. Via poring over NASA’s satellite tv for PC imagery, quantum processors could take a system gaining knowledge of the approach to uncover new styles in how weather movements internationally over the direction of weeks, months, or maybe years, he says. “Say you’re living in India—you may get an improve word of a cyclone 6 months in advance of time because we see a sample of climate in northern Canada.”
but it’s going to take an awesome deal of work earlier than quantum computing is the norm in fixing complex computational problems. “There’s a famous belief that quantum computers do matters that classical computers cannot, but the only difference is velocity,” says Itay Chook, a PC scientist at the University of Southern California in Marina del Rey, who become now not worried with the research. “This specific painting hasn’t shown that the D-Wave device can beat preferred computers in that.” Chicken points out that during researchers’ look for methods to harness the power of quantum computing, a few applications might be useless ends. “A system gaining knowledge of the application, like the one In the paper, is one course” for quantum computers, Fowl says. “but it’s uncertain whether or not or not there’s desire there.”
Quantum Computing
Imagine a laptop whose memory is exponentially large than its obvious physical length; a laptop that may manage an exponential set of inputs concurrently; a PC that computer Within the twilight zone of space. You will be taking into consideration a quantum computer. Especially few and easy standards from quantum mechanics are needed to make quantum computers an opportunity. The subtlety has been in mastering to control these standards. Is this type of computer an inevitability or will it be too tough to build?
With the aid of the extraordinary legal guidelines of quantum mechanics, Folger, a senior editor at Find out, notes that; an electron, proton, or different subatomic particle is “in more than one place at a time,” because man or woman debris behave like waves, these different locations are specific states that an atom can exist in concurrently.
What is the huge deal about quantum computing? Consider you were in a big office constructing and you had to retrieve a briefcase left on a desk picked at random in one in every of masses of places to work. In the equal manner that you would walk thru the constructing, starting doors one after the other to find the briefcase, an ordinary laptop has to make it manner through long strings of one’s and zero’s till it arrives at the answer. however what if alternatively of having to go looking With the aid of your self, you may immediately create as many copies of yourself as there were rooms In the constructing all of the copies ought to simultaneously peek in all the offices, and the one that unearths the briefcase turns into the real you, the relaxation simply disappear. – (David Freeman, Find out )
David Deutsch, a physicist at Oxford College, argued that it is able to be viable to build an exceedingly effective laptop based in this atypical fact. In 1994, Peter Shor, a mathematician at AT&T Bell Laboratories in New Jersey, proved that in theory at the least, a complete-blown quantum computer ought to the element even the biggest numbers in seconds; an accomplishment impossible for even the fastest Conventional PC. A pandemic of theories and discussions of the possibility of building a quantum laptop now permeates itself though out the quantum fields of generation and research.
Its roots may be traced returned to 1981, when Richard Feynman stated that physicists usually seem to run into computational troubles while they are trying to simulate a system in which quantum mechanics might take location. The calculations involving the conduct of atoms, electrons, or photons, require an immense amount of time on present day computers. In 1985 in Oxford England the first description of the way a quantum laptop would possibly work surfaced with David Deutsch’s theories. The brand new tool could now not most effective be able to surpass modern day computers in speed, however also should perform a few logical operations that Traditional ones could not.
This research started searching into simply constructing a device and with the go ahead and further funding of AT&T Bell Laboratories in Murray Hill, New Jersey a brand new member of the group become delivered. Peter Shor made the discovery that quantum computation can substantially speed factoring of whole numbers. It is extra than only a step in a micro-computing generation, it is able to offer insights into actual world applications such as cryptography.
“There may be a hope at the end of the tunnel that quantum computers may additionally sooner or later come to be a reality,” says Gilles Brassard of College of Montreal. Quantum Mechanics give a sudden readability Inside the description of the conduct of atoms, electrons, and photons on the microscopic levels. Despite the fact that this information is not relevant in the ordinary family uses it does really practice to every interaction of depending that we will see, the real benefits of this expertise are simply starting to reveal themselves.
In our computers, circuit boards are designed in order that a 1 or a 0 is represented Through differing quantities of strength, the outcome of one possibility has no impact on the other. However, a trouble arises when quantum theories are delivered, the outcomes come from an unmarried piece of hardware current in separate realities and those realities overlap one another affecting both consequences straight away. these problems can emerge as one of the best strengths of The brand new computer But, if it’s far viable to program the effects in the sort of way in order that unwanted results cancel themselves out while the nice ones improve every other.
This quantum machine should be able to the application the equation into it, verify It’s computation, and extract the consequences. Several feasible structures have been checked out By using researchers, one of which involves using electrons, atoms, or ions trapped inner of magnetic fields, intersecting lasers would then be used to excite the limited debris to the proper wavelength and a 2nd time to restore the debris to their floor kingdom. A chain of pulses might be used to array the particles right into a pattern usable in our gadget of equations.
Another opportunity By Seth Lloyd of MIT proposed the use of natural metallic polymers (one-dimensional molecule manufactured from repeating atoms). The energy states of a given atom would be determined Through its interaction with neighboring atoms Inside the chain. Laser pulses might be used to send alerts down the polymer chain and the two ends would create two unique electricity states.
A 3rd concept became to update the organic molecules with crystals in which records might be saved Inside the crystals in precise frequencies that might be processed with extra pulses. The atomic nuclei, spinning in either of two states (clockwise or counterclockwise) may be programmed with a tip of an atomic microscope, either “reading” It is surface or changing it, which of the route would be “writing” a part of facts garage. “Repetitive motions of the end, you can finally write out any preferred good judgment circuit, ” DiVincenzo stated.
0 notes