#near infrared image
Text
Does the internet want this edit? I made it :D
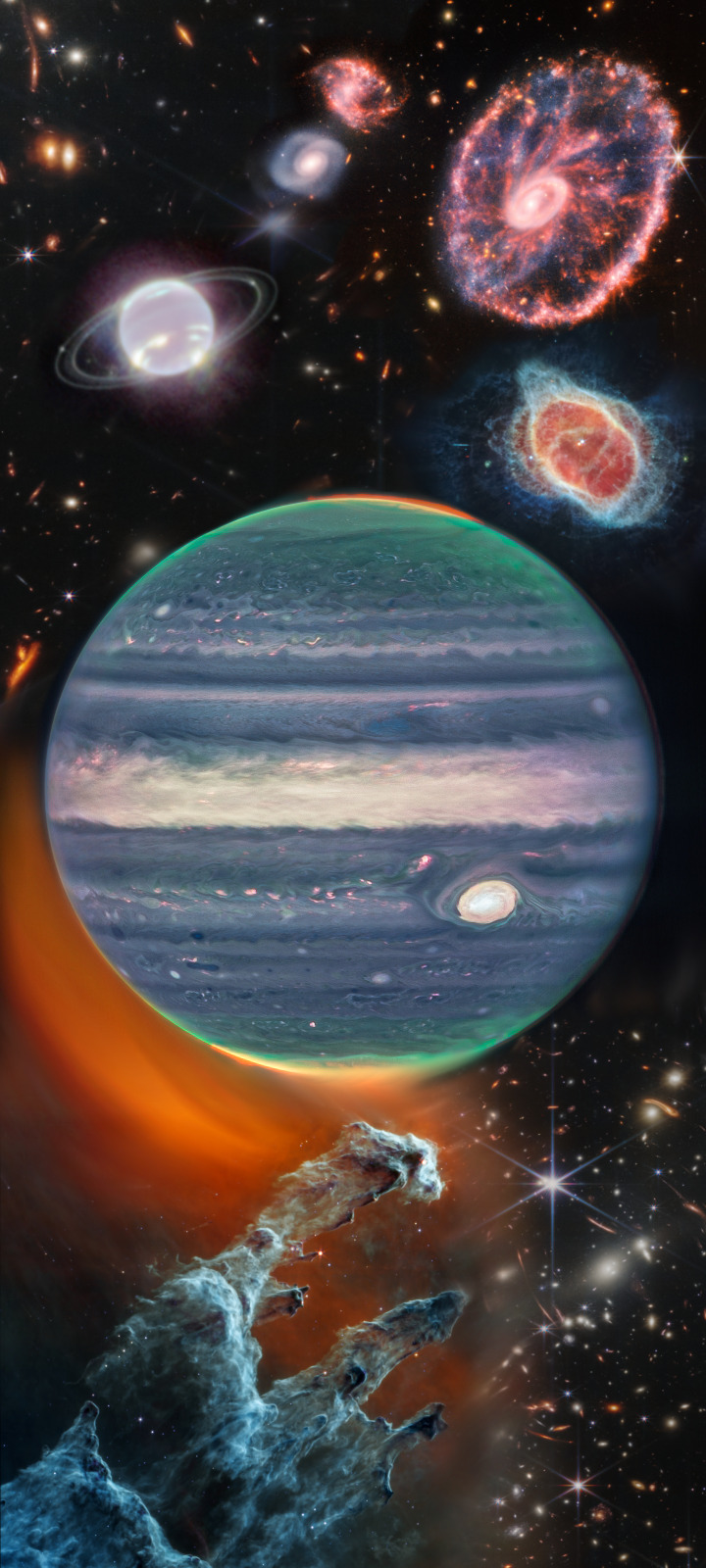

#space#pillars of creation#jupiter#on the internet this goes#neptune#james webb photos#james webb telescope#webb#space is so cool#nebula#near infrared image#edit#look at it#sparkly#shiny#star#galaxy#space dust#astronomy
149 notes
·
View notes
Photo
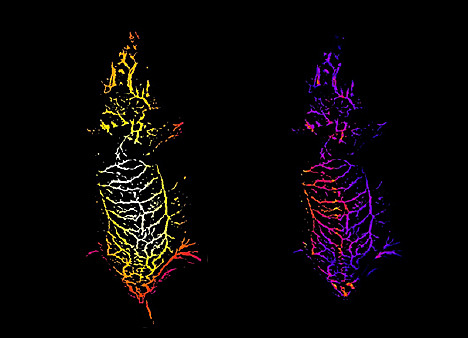
Good Body Image
Most treatments are targeted at a particular area, to solve an isolated problem. But no organ is an island. Researchers, therefore, are interested in ways to visualise whole-system changes as well as cell-level interactions that occur during disease and development. A new approach combines several techniques to provide a complete 3D map of the mouse vessel network (pictured, coloured according to vessel height, left, and depth under the skin, right). The researchers used light-sheet fluorescence microscopy, which shines thin sheets of light to take images in layers, a carefully timed approach to remove visual noise caused by background structures, and an algorithm to extract and analyse the vessel data. These approaches, applied with fluorescence imaging at the near-infrared wavelength of light, give a glimpse of what happens to the whole body – useful to show the details of disease development and test the broad impacts of new potential treatments.
Written by Anthony Lewis
Image adapted from work by Sitong Wu, Zhichao Yang and Chenguang Ma, and colleagues
UTS-SUSTech Joint Research Centre for Biomedical Materials & Devices, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in Opto-Electronic Advances, January 2023
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
#science#biomedicine#body imaging#algorithm#near infrared#light sheet microscopy#fluorescence imaging
5 notes
·
View notes
Text

It never even occurred to me that we would be getting double the images from Webb, from NIRCAM and MIRI respectively! Twice the bang for our buck, baby!!!
#james webb space telescope#space#science#nasa#this is the star death nebula image!#NIRCAM is the near infrared. MIRI is the mid infrared !
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Neptune and its rings come to focus with a web telescope
Neptune and its rings come to focus with a web telescope
New images from space-based observatories offer a novel view of the planet in infrared.
Credit social media
No spacecraft has visited Neptune since 1989 when the NASA probe Voyager 2 flew past on its way out of the solar system. Neptune, which is four times wider than Earth, is the most distant planet in our solar system. Voyager 2’s observations whet the appetite of astronomers, who are eager…

View On WordPress
#does neptune have rings#james telescope#james webb multverse theory#james webb naptune images#james webb new images#james webb space telescope#james webb space telescope neptune#james webb telescope#jwst neptune#jwst neptune images#naptune james webb#near-infrared camera#neptune#neptune rings#neptunes rings#telescope#the james webb space telescope#web neptune#webb james telescope#webb telescope#webb telescope images#webb telescope neptune
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
2032, Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Systems Market Analysis by Reports and Insights

The Reports and Insights, a leading market research company, has recently releases report titled “Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Systems Market: Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2024-2032.” The study provides a detailed analysis of the industry, including the global Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Systems Market share, size, trends, and growth forecasts. The report also includes competitor and regional analysis and highlights the latest advancements in the market.
Report Highlights:
How big is the Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Systems Market?
The global near-infrared fluorescence imaging systems market size reached US$ 1.4 billion in 2023. Looking forward, Reports and Insights expects the market to reach US$ 3.3 billion in 2032, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 10.1% during 2024-2032.
What are Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Systems?
Near-infrared fluorescence imaging systems are cutting-edge medical imaging tools used to visualize structures and functions inside the body. They work by using near-infrared light to stimulate fluorescent contrast agents, which emit light that the imaging system detects. This technology enables high-resolution, real-time imaging of tissues, organs, and blood vessels during surgeries. Near-infrared fluorescence imaging systems are utilized across different medical disciplines, such as oncology, neurosurgery, and vascular surgery, to assist in visualizing, navigating, and evaluating tissue perfusion.
Request for a sample copy with detail analysis: https://www.reportsandinsights.com/sample-request/2028
What are the growth prospects and trends in the Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Systems industry?
The near-infrared fluorescence imaging systems market growth is driven by various factors. The near-infrared fluorescence imaging systems market is witnessing significant growth, fueled by several factors including the increasing adoption of minimally invasive surgeries, advancements in imaging technologies, and the growing prevalence of chronic diseases. These systems provide real-time visualization of tissues, organs, and blood vessels, assisting surgeons in achieving improved surgical outcomes. Key drivers of market growth include the rising demand for accurate and early diagnosis, the expanding elderly population, and the widening applications of near-infrared fluorescence imaging in medical fields such as oncology, cardiovascular surgery, and plastic surgery. Moreover, the introduction of portable and cost-effective imaging systems is expected to further boost market expansion. Hence, all these factors contribute to near-infrared fluorescence imaging systems market growth.
What is included in market segmentation?
The report has segmented the market into the following categories:
By Product Type:
Handheld Devices
Standalone Devices
By Imaging Modality:
White Light Endoscopy
Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging
By Application:
Oncology
Cardiovascular
Gastrointestinal Surgery
Plastic/Reconstructive Surgery
Others
By End-Use:
Hospitals
Specialty Clinics
Research Institutes
Others
Segmentation By Region:
North America:
United States
Canada
Asia Pacific:
China
India
Japan
Australia New Zealand
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
Rest of Asia Pacific
Europe:
Germany
The U.K.
France
Spain
Italy
Russia
Poland
BENELUX (Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg)
NORDIC (Norway, Sweden, Finland, Denmark)
Rest of Europe
Latin America:
Brazil
Mexico
Argentina
Rest of Latin America
The Middle East Africa:
Saudi Arabia
United Arab Emirates
South Africa
Egypt
Israel
Rest of MEA (Middle East & Africa)
Who are the key players operating in the industry?
The report covers the major market players including:
Hamamatsu Photonics K.K.
Leica Microsystems (Danaher Corporation)
PerkinElmer, Inc.
Quest Medical Imaging B.V.
LI-COR Biosciences, Inc.
Fluoptics
Shimadzu Corporation
KARL STORZ SE Co. KG
Novadaq Technologies Inc. (acquired by Stryker Corporation)
SurgVision
Mizuho Corporation
Olympus Corporation
Carl Zeiss AG
Karl Kaps GmbH Co. KG
View Full Report: https://www.reportsandinsights.com/report/Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Systems-market
If you require any specific information that is not covered currently within the scope of the report, we will provide the same as a part of the customization.
About Us:
Reports and Insights consistently mееt international benchmarks in the market research industry and maintain a kееn focus on providing only the highest quality of reports and analysis outlooks across markets, industries, domains, sectors, and verticals. We have bееn catering to varying market nееds and do not compromise on quality and research efforts in our objective to deliver only the very best to our clients globally.
Our offerings include comprehensive market intelligence in the form of research reports, production cost reports, feasibility studies, and consulting services. Our team, which includes experienced researchers and analysts from various industries, is dedicated to providing high-quality data and insights to our clientele, ranging from small and medium businesses to Fortune 1000 corporations.
Contact Us:
Reports and Insights Business Research Pvt. Ltd.
1820 Avenue M, Brooklyn, NY, 11230, United States
Contact No: +1-(347)-748-1518
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://www.reportsandinsights.com/
Follow us on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/report-and-insights/
Follow us on twitter: https://twitter.com/ReportsandInsi1
#Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Systems Market share#Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Systems Market size#Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Systems Market trends
0 notes
Text
The Global Near Infrared Imaging Market size is expected to reach $3.2 billion by 2030, rising at a market growth of 6.0% CAGR during the forecast period.
#Near Infrared Imaging applications#Principles of Near Infrared Imaging#Challenges Near Infrared Imaging#Future Prospects Near Infrared Imaging
1 note
·
View note
Text
Unveiling the Power of Near Infrared Imaging
In the vast spectrum of imaging technologies, Near Infrared Imaging emerges as a powerful tool, offering a unique perspective that goes beyond what the naked eye can perceive.
This blog takes you on a journey into the realm of Near Infrared Imaging, exploring its principles, applications, and the transformative impact it has across various industries.
Understanding Near Infrared (NIR) Light
At…
View On WordPress
#Challenges Near Infrared Imaging#Future Prospects Near Infrared Imaging#Near Infrared Imaging applications#Principles of Near Infrared Imaging
0 notes
Text
Near Infrared Medical Imaging Market Is Estimated To Witness High Growth Owing To Technological Advancements And Increasing Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
The global Near Infrared Medical Imaging Market is estimated to be valued at US$ 2.06 billion in 2022 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 3.9% over the forecast period 2023-2030, as highlighted in a new report published by Coherent Market Insights.
A) Market Overview:
Near Infrared Medical Imaging involves the use of near-infrared (NIR) light to capture images of tissues and organs within the human body. It provides real-time visualization and analysis of blood flow, oxygen saturation, and tissue viability, making it an essential tool for various medical applications. The technology finds extensive use in cardiovascular, oncology, neurology, and other fields where precise visualization is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
B) Market Dynamics:
The Near Infrared Medical Imaging Market is driven by two key factors: technological advancements and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases.
1. Technological Advancements:
Advancements in imaging technology have significantly improved the capabilities of near-infrared medical imaging devices. Newer devices offer high-resolution images with enhanced accuracy and depth penetration, providing healthcare professionals with a clearer view of the internal structures. For example, companies such as Bruker Corporation and Carl Zeiss Meditec AG are developing innovative NIR imaging systems with improved image quality and user-friendly interfaces, contributing to market growth.
2. Increasing Prevalence of Chronic Diseases:
The rising incidence of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disorders, cancer, and neurological conditions has created a substantial demand for efficient diagnostic tools. Near infrared medical imaging enables early detection and accurate assessment of these diseases, allowing for timely intervention and improved patient outcomes. This has propelled the adoption of NIR imaging systems in hospitals, diagnostic centers, and research facilities worldwide.
C) Market Key Trends:
One key trend in the Near Infrared Medical Imaging Market is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to enhance image analysis and interpretation. AI-powered software can detect abnormalities and assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing and monitoring diseases more efficiently. For instance, PerkinElmer, Inc. is collaborating with AI technology companies to develop advanced image analysis software, which can automatically identify and classify anomalies in near-infrared medical images.
D) SWOT Analysis:
Strengths:
1. Advanced imaging technology: Near infrared medical imaging devices offer high-resolution images with improved depth penetration.
2. Growing demand for efficient diagnostic tools: Increasing prevalence of chronic diseases drives the adoption of NIR imaging systems.
Weaknesses:
1. High costs: Near infrared medical imaging devices are expensive, limiting their accessibility in certain regions.
2. Limited awareness among healthcare professionals: Some healthcare professionals may not be fully aware of the potential benefits of near-infrared medical imaging technology.
Opportunities:
1. Emerging markets: The expanding healthcare infrastructure in developing economies presents significant opportunities for market growth.
2. Technological advancements: Continued research and development in imaging technology can further enhance the capabilities and applications of near-infrared medical imaging devices.
Threats:
1. Regulatory challenges: Stringent regulatory requirements for medical devices may pose a challenge for market growth.
2. Competition from alternative imaging modalities: Near-infrared medical imaging faces competition from other imaging modalities such as MRI and CT scans.
E) Key Takeaways:
- The global Near Infrared Medical Imaging Market is expected to witness high growth, exhibiting a CAGR of 3.9% over the forecast period.
- Technological advancements and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases drive market growth.
- North America is expected to dominate the market, owing to its well-established healthcare infrastructure and high adoption rate of advanced medical technologies.
- Key players operating in the global Near Infrared Medical Imaging Market include Bruker Corporation, Carl Zeiss Meditec AG, Shimadzu Corporation, PerkinElmer, Inc., MIZUHO Corporation, Karl Storz GmbH, and NOADAQ Technologies, Inc.
In conclusion, the Near Infrared Medical Imaging Market is poised for significant growth in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, increasing chronic diseases, and the integration of AI algorithms.
#Near Infrared Medical Imaging Market#Near Infrared Medical Imaging Market Insights#Near Infrared Medical Imaging Market Growth#Near Infrared Medical Imaging Market Trends#Coherent Market Insights
0 notes
Text
James Webb Space Telescope captures stunning images of actively forming stars
James Webb Space Telescope captures stunning images of actively forming stars
James Webb Space Telescope captures stunning images of actively forming stars.
The James Webb Space Telescope has captured a stunning new image of two actively forming stars, collectively known as Herbig-Haro 46/47. The image shows the stars embedded in a disc of gas and dust, about 1,400 light-years away from Earth.
James Webb Space Telescope has just captured a new image of actively forming…

View On WordPress
#000 years old#1#100#400 light-years away#accreting#amazing images#bow shock#Herbig-Haro 46/47#Herbig-Haro object#James Webb Space Telescope#natal cocoon#Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam)#power of JWST#revolutionize our understanding of star formation#star formation#stunning image
1 note
·
View note
Text
Webb Telescope Rules Out Thick Carbon Dioxide Atmosphere for TRAPPIST-1 c
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has conducted observations of the exoplanet TRAPPIST-1 c and made a significant discovery. Despite being similar in size to Venus and receiving comparable levels of radiation from its star, Webb’s findings indicate that TRAPPIST-1 c does not possess Venus’s thick carbon dioxide-rich atmosphere. If an atmosphere exists on TRAPPIST-1 c, it is likely to be very…
View On WordPress
#Ariane 5 rocket#Cosmic Microwave Background#Deep space observations#Exoplanets#Fine Guidance Sensor/Near InfraRed Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (FGS/NIRISS)#Galaxy formation#Hubble Space Telescope successor#Infrared Astronomy#Infrared detectors#James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)#Launch#Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI)#Mirror segments#Multi-object spectroscopy#NASA#Near InfraRed Spectrograph (NIRSpec)#Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam)#Space telescope#Stellar populations#Sunshield#Transiting exoplanets#Universe formation and evolution#Webb Science Operations Center (JSOC)
0 notes
Photo

The Growing Significance of Near Infrared Medical Imaging Market in Healthcare
The Near Infrared (NIR) Medical Imaging Market is witnessing significant growth and is becoming increasingly significant in the field of healthcare.
Read More:
https://knackersblogger.blogspot.com/2023/06/integrating-near-infrared-nir-medical.html
0 notes
Text
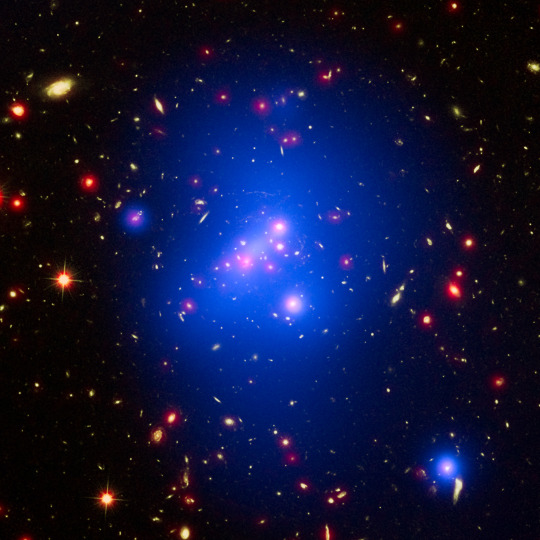

Astronomers used three of NASA's Great Observatories to capture this multiwavelength image showing galaxy cluster IDCS J1426.5+3508. It includes X-rays recorded by the Chandra X-ray Observatory in blue, visible light observed by the Hubble Space Telescope in green, and infrared light from the Spitzer Space Telescope in red. This rare galaxy cluster has important implications for understanding how these megastructures formed and evolved early in the universe.
How Astronomers Time Travel
Let’s add another item to your travel bucket list: the early universe! You don’t need the type of time machine you see in sci-fi movies, and you don’t have to worry about getting trapped in the past. You don’t even need to leave the comfort of your home! All you need is a powerful space-based telescope.
But let’s start small and work our way up to the farthest reaches of space. We’ll explain how it all works along the way.

This animation illustrates how fast light travels between Earth and the Moon. The farther light has to travel, the more noticeable its speed limit becomes.
The speed of light is superfast, but it isn’t infinite. It travels at about 186,000 miles (300 million meters) per second. That means that it takes time for the light from any object to reach our eyes. The farther it is, the more time it takes.
You can see nearby things basically in real time because the light travel time isn’t long enough to make a difference. Even if an object is 100 miles (161 kilometers) away, it takes just 0.0005 seconds for light to travel that far. But on astronomical scales, the effects become noticeable.
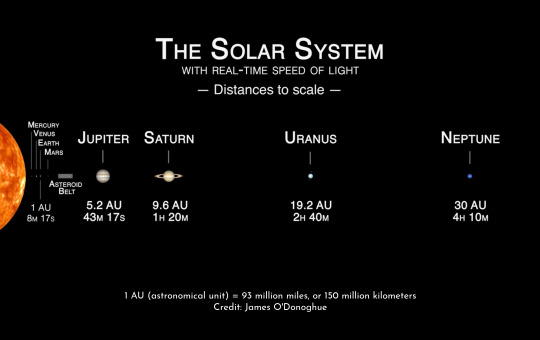
This infographic shows how long it takes light to travel to different planets in our solar system.
Within our solar system, light’s speed limit means it can take a while to communicate back and forth between spacecraft and ground stations on Earth. We see the Moon, Sun, and planets as they were slightly in the past, but it's not usually far enough back to be scientifically interesting.
As we peer farther out into our galaxy, we use light-years to talk about distances. Smaller units like miles or kilometers would be too overwhelming and we’d lose a sense of their meaning. One light-year – the distance light travels in a year – is nearly 6 trillion miles (9.5 trillion kilometers). And that’s just a tiny baby step into the cosmos.
youtube
The Sun’s closest neighboring star, Proxima Centauri, is 4.2 light-years away. That means we see it as it was about four years ago. Betelgeuse, a more distant (and more volatile) stellar neighbor, is around 700 light-years away. Because of light’s lag time, astronomers don’t know for sure whether this supergiant star is still there! It may have already blasted itself apart in a supernova explosion – but it probably has another 10,000 years or more to go.

What looks much like craggy mountains on a moonlit evening is actually the edge of a nearby, young, star-forming region NGC 3324 in the Carina Nebula. Captured in infrared light by the Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) on NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, this image reveals previously obscured areas of star birth.
The Carina Nebula clocks in at 7,500 light-years away, which means the light we receive from it today began its journey about 3,000 years before the pyramids of Giza in Egypt were built! Many new stars there have undoubtedly been born by now, but their light may not reach Earth for thousands of years.
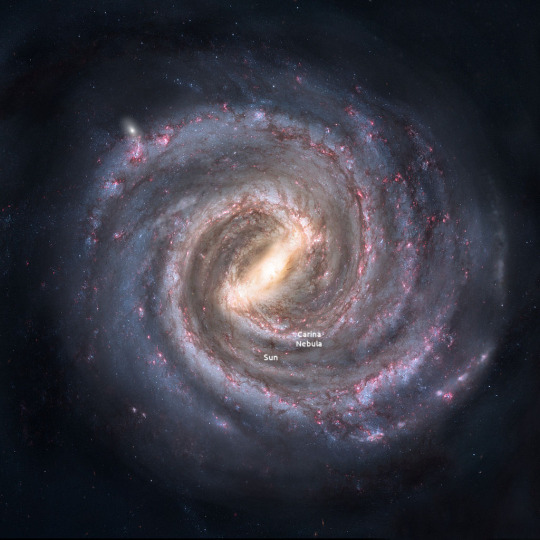

An artist’s concept of our Milky Way galaxy, with rough locations for the Sun and Carina nebula marked.
If we zoom way out, you can see that 7,500 light-years away is still pretty much within our neighborhood. Let’s look further back in time…
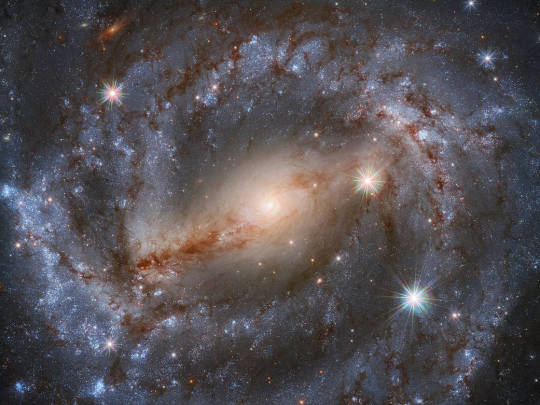

This stunning image by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope features the spiral galaxy NGC 5643. Looking this good isn’t easy; 30 different exposures, for a total of nine hours of observation time, together with Hubble’s high resolution and clarity, were needed to produce an image of such exquisite detail and beauty.
Peering outside our Milky Way galaxy transports us much further into the past. The Andromeda galaxy, our nearest large galactic neighbor, is about 2.5 million light-years away. And that’s still pretty close, as far as the universe goes. The image above shows the spiral galaxy NGC 5643, which is about 60 million light-years away! That means we see it as it was about 60 million years ago.
As telescopes look deeper into the universe, they capture snapshots in time from different cosmic eras. Astronomers can stitch those snapshots together to unravel things like galaxy evolution. The closest ones are more mature; we see them nearly as they truly are in the present day because their light doesn’t have to travel as far to reach us. We can’t rewind those galaxies (or our own), but we can get clues about how they likely developed. Looking at galaxies that are farther and farther away means seeing these star cities in ever earlier stages of development.
youtube
The farthest galaxies we can see are both old and young. They’re billions of years old now, and the light we receive from them is ancient since it took so long to traverse the cosmos. But since their light was emitted when the galaxies were young, it gives us a view of their infancy.

This animation is an artist’s concept of the big bang, with representations of the early universe and its expansion.
Comparing how fast objects at different distances are moving away opened up the biggest mystery in modern astronomy: cosmic acceleration. The universe was already expanding as a result of the big bang, but astronomers expected it to slow down over time. Instead, it’s speeding up!
The universe’s expansion makes it tricky to talk about the distances of the farthest objects. We often use lookback time, which is the amount of time it took for an object’s light to reach us. That’s simpler than using a literal distance, because an object that was 10 billion light-years away when it emitted the light we received from it would actually be more than 16 billion light-years away right now, due to the expansion of space. We can even see objects that are presently over 30 billion light-years from Earth, even though the universe is only about 14 billion years old.

This James Webb Space Telescope image shines with the light from galaxies that are more than 13.4 billion years old, dating back to less than 400 million years after the big bang.
Our James Webb Space Telescope has helped us time travel back more than 13.4 billion years, to when the universe was less than 400 million years old. When our Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope launches in a few years, astronomers will pair its vast view of space with Webb’s zooming capabilities to study the early universe in better ways than ever before. And don’t worry – these telescopes will make plenty of pit stops along the way at other exciting cosmic destinations across space and time.
Learn more about the exciting science Roman will investigate on X and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
#NASA#astronomy#telescope#Roman Space Telescope#dark energy#galaxies#cosmology#astrophysics#stars#galaxy#Hubble#Webb#Chandra#Spitzer#space images#Youtube
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
#Near Infrared Imaging Market Size#Near Infrared Imaging Market Share#Near Infrared Imaging Market Trends#Near Infrared Imaging Market Growth#Near Infrared Imaging Market Demands#Near Infrared Imaging Market Opportunities#Near Infrared Imaging Market scope#Near Infrared Imaging Market value#Near Infrared Imaging Market Strategies#Near Infrared Imaging Market Analysis.
0 notes
Text
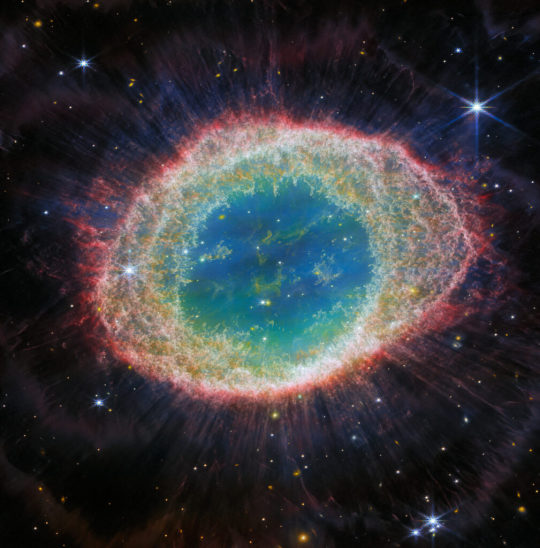

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has observed the well-known Ring Nebula in unprecedented detail. Formed by a star throwing off its outer layers as it runs out of fuel, the Ring Nebula is an archetypal planetary nebula. This new image from Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) shows intricate details of the filament structure of the inner ring. There are some 20,000 dense globules in the nebula, which are rich in molecular hydrogen. In contrast, the inner region shows very hot gas. The main shell contains a thin ring of enhanced emission from carbon-based molecules known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs).
Credit: ESA/Webb, NASA, CSA, M. Barlow (University College London), N. Cox (ACRI-ST), R. Wesson (Cardiff University)
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
new webb image(s) alert! 19 galaxies imaged in mid and near infrared light

i’m just blown away by the detail in these images- jwst never ceases to amaze me.
you can find the full resolution images of each of these galaxies in the official release here - i highly recommend looking through each of them, they’re STUNNING.
#aspaceinthecosmos#space#astronomy#outer space#just jupiter#astrophotography#galaxies#jwst#james webb space telescope#james webb#nasa#infrared astronomy
691 notes
·
View notes