#oral glucose tolerance test
Text
Understanding Different Types of Diabetes and Their Impact on the Body

Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It disrupts the body's ability to regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels, leading to serious health complications if not managed properly. There are several types of diabetes, each with unique characteristics and impacts on the body. This article will explore the different types of diabetes, how they affect the body, and the tests provided by RML Pathology to diagnose and manage this condition.
1. Type 1 Diabetes
Description:
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This results in little to no insulin production, which is essential for regulating blood sugar levels.
Impact on the Body:
Requires lifelong insulin therapy.
Increases the risk of complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a potentially life-threatening condition.
Long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, kidney damage (nephropathy), nerve damage (neuropathy), and vision problems (retinopathy).
Can cause frequent urination, excessive thirst, extreme hunger, weight loss, fatigue, and irritability.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Description:
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin. Lifestyle factors such as obesity, poor diet, and lack of exercise significantly contribute to its development.
Impact on the Body:
Often managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin.
Can lead to complications like heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye problems, and nerve damage.
Symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, increased hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, slow-healing sores, and frequent infections.
3. Gestational Diabetes
Description:
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased needs. It usually resolves after childbirth but increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Impact on the Body:
Can cause high blood pressure during pregnancy (preeclampsia).
Increases the risk of having a large baby, leading to complications during delivery.
May result in low blood sugar levels in the newborn and a higher risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes in the child later in life.
4. Prediabetes
Description:
Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes. It is a critical stage for intervention to prevent the progression to type 2 diabetes.
Impact on the Body:
Often reversible with lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise.
Increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
Symptoms are often absent or mild, making regular screening important.
Tests Provided by RML Pathology
RML Pathology offers a comprehensive range of tests to diagnose and manage diabetes effectively. These include:
Fasting Blood Glucose Test:
Measures blood sugar levels after fasting for at least 8 hours.
Helps diagnose diabetes and prediabetes.
HbA1c Test:
Provides an average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months.
Used to diagnose diabetes and monitor long-term glucose control.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT):
Measures the body's response to a glucose solution.
Commonly used to diagnose gestational diabetes.
Random Blood Sugar Test:
Measures blood sugar levels at any time of the day.
Useful for diagnosing diabetes when symptoms are present.
Gestational Diabetes Test:
Specifically designed for pregnant women to detect gestational diabetes.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of diabetes and their impact on the body is crucial for effective management and prevention. Regular testing and early detection play a vital role in managing diabetes and preventing complications. RML Pathology provides a wide range of diagnostic tests to help you monitor and manage your diabetes effectively. If you have any symptoms or risk factors for diabetes, consider visiting RML Pathology for a comprehensive evaluation.
Contact RML Pathology Today:
📞 7991602001, 7991602002 📞 0522-4034100 🌐 www.rmlpathology.com
Experience the best in diagnostics with RML Pathology – where your health is our priority.
#diabetes#type 1 diabetes#type 2 diabetes#gestational diabetes#prediabetes#diabetes management#blood sugar#glucose levels#RML Pathology#diabetes tests#HbA1c#fasting blood glucose#oral glucose tolerance test#random blood sugar test#health#healthcare#diabetes diagnosis
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Know Everything About Oral Glucose Tolerance (Ogtt) Test at Livlong
Discover the complete details of the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) to diagnose diabetes. Visit Livlong for more information on OGTT test at Livlong
0 notes
Text
Everything You Need to Know About Diabetes Tests - A Journey of Uncertainty and Surprises!
Prepare yourself for a roller-coaster ride through the perplexing world of diabetes tests! Embark on this whirlwind tour of different tests, diabetes types, interpreting results, and managing the enigmatic condition. Gain insights to take control of your health in this exhilarating adventure!
Introduction to Diabetes Tests – The Enigmatic Puzzle Unveiled!
Diabetes, a mysterious metabolic…

View On WordPress
#benefits of diabetes testing#conclusion#continuous glucose monitoring#diabetes educators#diabetes tests#diagnostic criteria for diabetes#fasting plasma glucose test#frequently asked questions#HbA1c test#insulin level test#interpreting test results#Lifestyle Changes#limitations of diabetes testing#managing diabetes#medication adjustments#oral glucose tolerance test#preparing for diabetes tests#random plasma glucose test#understanding diabetes
0 notes
Text

This infographic explains the different types of blood sugar tests used to diagnose and manage diabetes and other conditions. Learn more about fasting blood sugar tests, random blood sugar tests, and oral glucose tolerance tests, and their respective uses. The Physicians Clinic is a leading healthcare provider that offers blood sugar testing and other medical services to patients.
#Blood sugar#Glucose#Diabetes#Health screening#Medical tests#Fasting#Oral glucose tolerance test#Gestational diabetes#Insulin resistance#Prediabetes#Monitoring#Lifestyle changes#Nutrition#Healthcare#Patient education
0 notes
Text
I've been trying to figure out what the deal is with prediabetes so I can write a meaningful response to an ask I got about it, and I just keep going wait--okay--here's one paper--but here's another one--here's a Cochrane review--but here's a different meta-analysis--and here's newer data from an RCT...
It's nuts! It's bananas. And anybody who says we have good, crisp, clear guidelines around what prediabetes even IS, much less what to do about it, is FULL OF SHIT.
What I really need to know in order to feel more confident about my handle on whether to medicate pre-diabetes is the population incidence. Not prevalence. Because if I take the most optimistic studies about medication as an intervention, specifically, I could be looking at about a 30-40% reduction in risk of progression to diabetes. But! How many people is that, actually? Because medication is not without its harms! We need to compare number needed to treat with number needed to harm, we need to have high-quality evidence that says yes, if we give this medication to everyone who meets X level of criteria for pre-diabetes (it's different in different sources AND it's changed repeatedly over our lifetime!), we will see a level of benefit sufficient to justify making these other people who would not have progressed to diabetes without it endure the hassle and side effects of taking a medication for the rest of their lives.
AND HERE'S THE REAL FUN PART: we don't really know where tissue damage begins! We thought we did! 6.5-7ish A1c. But it turns out there is a marked risk of retinopathy beginning at 5.5! Which is considered normal. AND ALSO we should probably be thinking of it as at least three separate disease based on our current ability to measure--A1c is a broad marker that collapses multiple forms of dysregulated blood sugar, and when we use more fine-grained tests, we see meaningful distinctions that probably affect preferred treatments between people who have impaired fasting glucose, people who have abnormal values on an oral glucose tolerance test, and people who have both. We should treat these groups differently because they reflect different underlying pathways: elevated fasting glucose means your liver is breaking down too much glycogen while you sleep, which is one issue, while elevated post-prandial glucose means your skeletal muscles (OR SOMETHING ELSE they're not totally sure) are behaving abnormally in response to insulin. IT'S NOT THE SAME THING and people with both impaired fasting glucose and abnormal post-prandial glucose are at higher risk of progression to diabetes/tissue damage than people with just one of those. AND WHILE WE'RE AT IT, what is diabetes? What's the best cutoff? What's the best measure? How many underlying pathophysiologies are getting collapsed into the same group????
THE MORE I LEARN ABOUT THIS THE MORE QUESTIONS I HAVE and experts are all being serenely confident while contradicting each other so I have to actually dig in the data a lot harder than I usually do. I've been meaning to do this for months, but one of the presenters this morning made a comment about the benefits of putting prediabetics on metformin that made me go "hm, do I need to start doing that?" and I've gone from my kneejerk answer being "no, we studied this and it doesn't help" to "I don't fucking know and neither does anyone else."
...as always, Cochrane is probably right.
412 notes
·
View notes
Text
PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS OF INCREASED PHYSICAL AND MALE IMPOTENCE DURING DIABETES
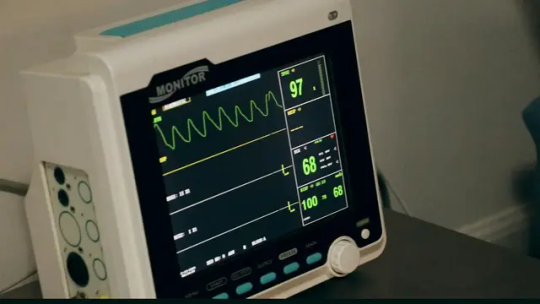
High blood sugar levels are a hallmark of diabetes, a chronic metabolic illness that is highly dangerous to one’s general health and well being. Male impotence, often known as erectile dysfunction, is one of the many issues linked to diabetes that many people face. For management and preventative initiatives to be effective, it is imperative to comprehend the complex interaction between male impotence and diabetes.
Overview of Diabetes
Diabetes can take many forms, the most common being Type 1 and Type 2, each with unique risk factors and underlying processes. Insulin resistance or inadequate insulin production causes Type 2 diabetes, while the body’s incapacity to create insulin causes Type 1 diabetes. Both kinds can cause blood sugar levels to rise, which can have devastating effects on different organ systems.
Understanding Male Impotence
The inability to obtain or sustain an erection strong enough for sexual activity is referred to as male impotence, sometimes known as erectile dysfunction. Numerous causes, including psychological and physical ones, might contribute to this illness. Physical reasons include vascular, neurogenic, or hormonal disorders; psychological aspects include stress, anxiety, or depression.
Every patient use this supplement to maintain your physical and Masculine Power during this disease click here

Link Between Diabetes and Male Impotence
There is a well-established link between diabetes and male impotence, with diabetes substantially raising the risk of erectile dysfunction. Male impotence is a result of the complex interactions between neuropathy, diabetes-induced vascular damage, and hormone abnormalities. Statistics show that compared to the general population, diabetics have a higher prevalence of erectile dysfunction.
Recognizing Symptoms
It is critical to identify the signs of male impotence and diabetes in order to begin treatment and early detection. Diabetes can cause weariness, increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. However, reduced sexual desire, nervousness during performance, and difficulties getting or keeping an erection are all signs of male impotence.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
In order to diagnose diabetes, blood sugar levels must be measured using a variety of diagnostic procedures, such as glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) testing, oral glucose tolerance testing, and fasting blood glucose assays. Similarly, physical examinations, blood testing, and psychological assessments may be used to diagnose male impotence. Treatment options include dietary adjustments and regular exercise, as well as pharmaceuticals such oral phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, hormone treatment, and surgical procedures like penile implants.
Prevention Strategies
Proactive diabetes management, including glucose control, medication adherence, and routine monitoring, is necessary to prevent diabetes-related male impotence. A balanced diet, frequent exercise, abstinence from tobacco and excessive alcohol use, and other healthy lifestyle choices can reduce the chance of developing diabetes and erectile dysfunction. Regular erectile dysfunction and diabetes screening lowers the risk of complications by enabling early detection and prompt treatments.
Psychological Impact
Male impotence associated with diabetes has psychological effects in addition to medical ones. These effects frequently include mental discomfort, low self-esteem, and strained interpersonal connections. In order to manage the combined burden of erectile dysfunction and diabetes, psychological stressors must be addressed through couples therapy, support groups, or counselling. Navigating the obstacles posed by sexual dysfunction requires partners to have open lines of communication and mutual understanding.
maintain your physical and Masculine Power during this disease click here

Seeking Support
Consulting with medical specialists, such as primary care physicians, endocrinologists, urologists, or mental health specialists, can be very helpful in controlling male impotence caused by diabetes. Additionally, connecting with others going through similar struggles through support groups or online forums promotes a feeling of community and solidarity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, men with diabetes who experience male impotence face serious medical and psychological difficulties. People can effectively manage diabetes and erectile dysfunction and enhance their overall quality of life by comprehending the complex relationship between the two disorders, putting preventive strategies into practice, and seeking timely intervention and assistance. To attain the best results and foster wellbeing, holistic techniques that treat psychological as well as physical issues must be prioritised.
#Sugar patient#muscular#Muscular pain#Male impotence#Week muscular#Muscular medicine#Blood sugar#gut health#fitness tips#vitamins
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Diabetes
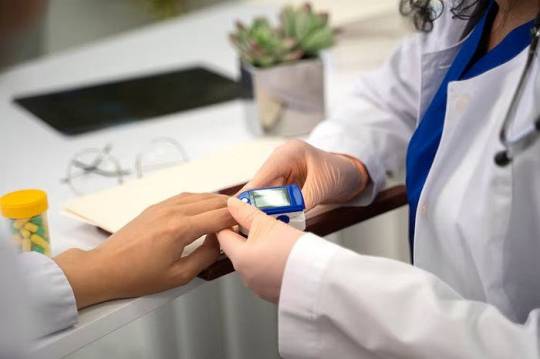
Introduction to Diabetes
Diabetes, a metabolic disorder characterized by chronic hyperglycemia, arises from abnormalities in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The condition’s prevalence has reached epidemic proportions globally, with significant health, economic, and social implications.
Types of Diabetes
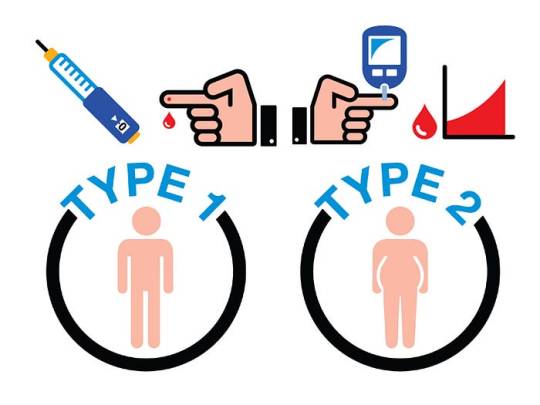
Type 1 Diabetes: This autoimmune disease results from the destruction of pancreatic beta cells, leading to absolute insulin deficiency. Genetics and environmental triggers play pivotal roles in its pathogenesis. Despite being less common than Type 2 diabetes, its onset during childhood or adolescence significantly impacts individuals’ lives.
Type 2 Diabetes: Predominantly a disorder of insulin resistance, Type 2 diabetes accounts for the majority of diabetes cases worldwide. Lifestyle factors, genetic predisposition, and obesity contribute to its development. Its insidious onset often leads to delayed diagnosis and increased risk of complications.
Gestational Diabetes: Occurring during pregnancy, gestational diabetes poses risks to both maternal and fetal health. Hormonal changes and insulin resistance characterize its pathophysiology. Effective screening and management are crucial to prevent adverse outcomes.
Other Types of Diabetes: Variants like MODY, LADA, and secondary diabetes present unique challenges in diagnosis and management, requiring tailored approaches to care.
Epidemiology and Prevalence
Diabetes prevalence varies across demographics, with disparities observed in age, gender, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. The escalating burden of diabetes underscores the urgent need for targeted prevention and management strategies.
Symptoms and Causes
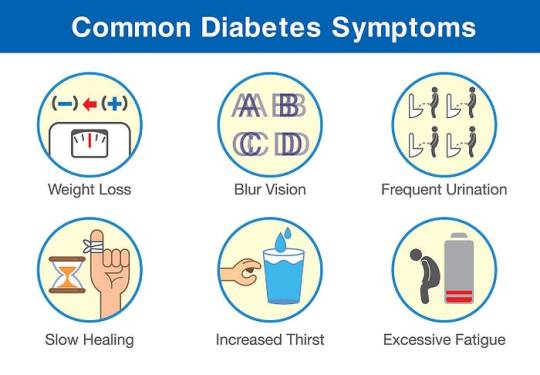
Hyperglycemia-induced symptoms like polyuria, polydipsia, and unexplained weight loss serve as clinical indicators for diabetes diagnosis. Understanding the complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors elucidates the condition’s etiology.
Complications
Diabetes complications encompass a spectrum of microvascular and macrovascular disorders, significantly impacting quality of life and life expectancy. From diabetic retinopathy to cardiovascular disease, nephropathy, neuropathy, and diabetic foot complications, the ripple effects of uncontrolled diabetes are profound.
Diagnosis and Tests
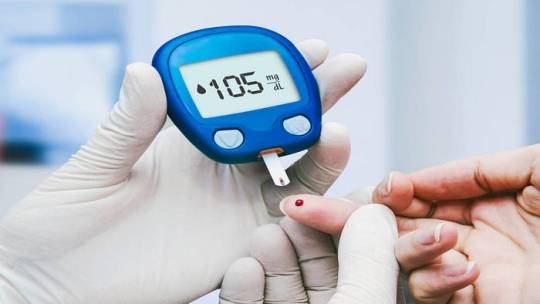
Accurate diagnosis relies on comprehensive evaluation, including fasting glucose, oral glucose tolerance tests, and hemoglobin A1c measurements. Screening recommendations aim to identify at-risk individuals early, facilitating timely intervention and risk reduction.
Management and Treatment
Diabetes management strategies encompass pharmacotherapy, lifestyle modifications, patient education, and multidisciplinary care. Individualized treatment plans address glycemic control, blood pressure management, lipid optimization, and prevention of complications.
Prevention
Prevention initiatives target modifiable risk factors through health promotion, public health interventions, and community engagement. Emphasizing the role of nutrition, physical activity, and behavioral changes empowers individuals to mitigate their diabetes risk.
Outlook and Prognosis
Prognostic factors such as glycemic control, adherence to therapy, comorbidity burden, and psychosocial support influence long-term outcomes. Enhanced collaboration among healthcare providers, policymakers, and stakeholders is essential to improve diabetes prognosis globally.
Living With Diabetes

Coping with diabetes requires resilience, self-management skills, and social support networks. Empowering individuals through education, self-monitoring tools, and peer support enhances their capacity to navigate the challenges of daily diabetes management.
Impact on Individuals and Society
Diabetes exerts a profound socioeconomic burden, encompassing healthcare costs, productivity losses, and reduced quality of life. Addressing the psychosocial dimensions of diabetes care is integral to fostering holistic well-being and societal resilience.
Future Directions and Research

Advancements in diabetes research, including precision medicine, digital health technologies, and novel therapeutics, offer promising avenues for disease management and prevention. Collaborative research endeavors aim to translate scientific discoveries into tangible clinical benefits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetes represents public health challenge necessitating a comprehensive, patient-centered approach. By fostering awareness, promoting early detection, and advancing evidence-based interventions, we can mitigate the impact of diabetes on individuals, families, and communities worldwide.
Medical students encounter significant academic challenges during their studies, balancing coursework, clinical rotations, research, and personal commitments. Expert Academic Assignment Help offers tailored assistance to meet their needs, providing study materials, tutoring, assignment help, and exam preparation. Beyond academics, it fosters a supportive environment for mentorship and guidance. In essence, Expert Academic Assignment Help is a valuable resource for medical students, empowering them to excel academically and develop into competent healthcare professionals. Contact at [email protected] for assistance.
#assignment help#healthcare#medical students#nursing student#nursing school#medical school#medical student#medicine#health tips#health and wellness#health#health & fitness#diabetes#diabetic#medical help#medical assistance#pharmacy student#pharmacy technician#homework help#academic assignments#expert assignment writers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
anyway i have to do an oral glucose tolerance test because im 0.1 over the normal blood sugar range (and still 1.0 below the diabetes cutoff) as well as a coeliac test because i have low iron. if i have coeliac though its fine because izzy already has it so we can have gluten free kisses between us even if not with anyone else
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Helpful template for transgender care:
Pt presents today to discuss HRT for transition
Preferred name/pronouns:
Pt has or is establishing w/ counseling/therapy
Reviewed support systems in place such as family, friends, therapy
Hx of SI/HI/anx/dep:
Sexual activity:
STI screening:
Pt is attracted to:
Feminizing effects: decreased libido, erections, breast growth (max at 2-3 yrs), decreased testes volume, decreased sperm counts, redistribution of fat, decreased muscle mass, softening of skin, decreased terminal hair
Estrogen therapy risks: VTE risk, CV disease/event risk, weight gain, hypertriglyceridemia, HTN, decreased glucose tolerance, biliary disease, benign prolactinoma, mental health effects, infertility
Nonreversible changes: breast enlargement
Reversible changes: fertility (though sperm counts may drop), variations in libido, voice changes
Other considerations: risks of tucking, management of residual facial/body hair
Reviewed to please not acquire hormone tx from non-clinical/pharmacy sources
Reviewed recs regarding risks associated w/ tucking and testicular entrapment
Considered speech referral to help manage voice changes
Lab work intervals:
Hgb/Hct at baseline and then annually
Lipids, LFT's, A1c as indicated
Estradiol at 3, 6, 13 mo and then routinely every 6-12 months
Testosterone at 6 and 12 months and then annually
Electrolytes and Bun/Cr at baseline and then routinely every 6-12 months
Goals:
Androgen blocker therapy goal: uptitrated until testosterone is suppressed to below 55ng/dL
Estradiol level: 100-200 pg/mL
Spironolactone: 50-300 mg daily (oral)
Spironolactone SE's: increased urination, hypotension, hyperkalemia, dehydration
Finasteride: 1-5mg daily (stops hair loss) (oral)
Lupron: GnRH agonist (injectable)
Casodex: androgen receptor inhibitor (injectable)
Cyproterone acetate: synthetic progestagen (transdermal)
Prometrium/provera/depo-provera (progestins) - risks include CV disease increase, breast CA, weight gain, depression. Benefits: weight gain, increased energy/libedo
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Had my oral glucose tolerance test today. That drink has made me super hyper and I literally want to come out of my skin. Hoping for good results. 😆 My baby definitely enjoyed it, so much movement...
They also took my iron which is great 👍 last time I was low so I want to be on top of that.
Lastly, an interesting job was posted whose office is literally the next street over. 🤞 Going to try for it and see... I don't want to juggle both job and household stuff (husband works 50/60 hour weeks) but atm the cost of living is just so ridiculously high.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Managing Complications of Diabetes with Dr. Sanchayan Roy’s Expertise

Managing diabetes is a complex and lifelong commitment that demands professional care, lifestyle changes, and ongoing support. Dr. Sanchayan Roy, a leading Diabetes Specialist based in Delhi, is known for his expertise in helping patients effectively manage this condition. With his vast knowledge and dedication to personalized patient care, Dr. Roy ensures that individuals living with diabetes can lead a fulfilling and healthy life. This article delves into his approach, expertise, and why he is one of the best choices for managing diabetes.
Understanding Diabetes: Types and Challenges
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body converts food into energy. The pancreas either doesn’t produce enough insulin or the body cannot effectively use the insulin it makes. Dr. Sanchayan Roy specializes in treating all types of diabetes, particularly Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes: This is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells. Patients require lifelong insulin therapy.
Type 2 Diabetes: The most common type of diabetes, usually linked to lifestyle factors such as poor diet and lack of exercise, causing insulin resistance.
Gestational Diabetes: This develops during pregnancy and poses risks for both mother and baby, but with proper management, it can be controlled.
Dr. Roy focuses on educating his patients about the nature of their condition and customizes treatment plans to meet their specific needs.
Symptoms and Early Detection
Many people with Type 2 diabetes don’t exhibit any symptoms until the disease has progressed. Symptoms such as increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision are often overlooked. Dr. Sanchayan Roy emphasizes the importance of early detection through routine blood tests and regular check-ups. He advocates for HbA1c tests, fasting glucose levels, and oral glucose tolerance tests to identify prediabetes or undiagnosed cases of diabetes.
By focusing on preventive care, Dr. Roy helps patients understand the warning signs of Sugar Specialist Doctor and encourages early intervention, which can significantly reduce long-term complications.
Personalized Diabetes Management Plans
Every individual’s diabetes specialist management plan is unique, and Dr. Sanchayan Roy adopts a comprehensive approach that considers medical history, lifestyle, and personal goals. His plans typically include:
Medication Management: From oral hypoglycemics to insulin therapy, Dr. Roy ensures that medications are carefully tailored to each patient. Adjustments are made based on blood sugar levels, lifestyle changes, and progress.
Dietary Counseling: Proper nutrition plays a critical role in controlling blood sugar levels. Dr. Roy works closely with dietitians to develop balanced meal plans that help patients maintain a healthy weight and stable blood glucose.
Exercise Guidance: Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps lower blood sugar levels. Dr. Roy provides customized exercise plans that are safe and effective, taking into account each patient’s physical condition and abilities.
Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, cholesterol, and blood pressure is essential. Dr. Sanchayan Roy stresses the importance of frequent follow-ups to adjust treatment plans and ensure optimal health outcomes.
Advanced Technology for Diabetes Care
In the modern era of healthcare, technology plays a pivotal role in managing chronic conditions like diabetes. Dr. Sanchayan Roy is at the forefront of integrating advanced diabetes management tools into his practice, ensuring that his patients have access to the latest innovations. Some of the technologies he employs include:
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): These devices allow patients to track their blood glucose levels in real-time, helping them make informed decisions about diet, medication, and physical activity.
Insulin Pumps: For patients requiring insulin therapy, Dr. Roy recommends insulin pumps, which provide continuous insulin delivery and help maintain stable glucose levels throughout the day.
Telemedicine Services: To ensure convenience and continuous care, Dr. Roy offers telemedicine consultations, allowing patients to receive expert guidance without leaving their homes.
Complications of Diabetes and Preventive Care
Untreated or poorly managed Sugar Doctor Near Me can lead to severe complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision loss. Dr. Sanchayan Roy is an expert in diabetes complications management, and his proactive approach focuses on preventing these issues through early detection and intervention.
Cardiovascular Health: Diabetic patients are at high risk for heart disease. Dr. Roy emphasizes regular cardiovascular screenings and recommends lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Kidney Health: The kidneys are particularly vulnerable to damage from high blood sugar levels. Dr. Roy ensures regular kidney function tests and advises on dietary changes that can prevent or delay diabetic nephropathy.
Nerve Damage and Foot Care: Neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes, leading to a loss of sensation in the limbs, particularly the feet. Dr. Sanchayan Roy stresses the importance of foot care, regular check-ups, and maintaining healthy blood flow to prevent infections and ulcers.
Eye Health: Diabetes can lead to diabetic retinopathy, which damages the blood vessels in the retina. Dr. Roy ensures that patients undergo regular eye exams and works closely with ophthalmologists to prevent vision loss.
Why Choose Dr. Sanchayan Roy?
Dr. Sanchayan Roy is more than just a diabetes specialist; he is a compassionate and committed physician who genuinely cares about the well-being of his patients. His holistic approach to diabetes care goes beyond just prescribing medications. He focuses on:
Patient Education: Dr. Roy believes that empowering patients with knowledge is key to managing diabetes specialist. He takes the time to explain the condition, treatment options, and lifestyle changes in a way that is easy to understand.
Personalized Care: No two diabetes patients are the same, and Dr. Sanchayan Roy ensures that each patient receives individualized attention and care plans tailored to their unique needs.
Experience and Expertise: With years of experience in treating diabetes and its complications, Dr. Roy has established himself as a trusted name in the medical community. He stays updated with the latest research and advancements in Best Sugar Specialist Doctor Near Me, ensuring that his patients receive the best possible treatment.
Commitment to Long-Term Health: Diabetes is a lifelong condition, and Dr. Roy is committed to helping his patients achieve long-term health goals. He builds lasting relationships with his patients, guiding them through every step of their diabetes specialist.
Conclusion
Dr. Sanchayan Roy is undoubtedly one of the most trusted and experienced diabetes specialist in Delhi. His patient-centered approach, use of advanced technologies, and dedication to preventing complications make him a top choice for individuals seeking comprehensive diabetes care. By addressing the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of diabetes, Dr. Roy ensures that his patients can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. Also check about Best Pulmonologist in Delhi.
Get for more information:
Name: Dr. Sanchayan Roy
Phone No.: 7838384440
Address: B — 404, Lower Ground Floor, Market No 1, Bipin Chandra Pal Marg, next to Bangiya Samaj close to, Block B, Chittaranjan Park, New Delhi — 110019
Website: https://healthfirstcenter.in/
Direction: https://maps.app.goo.gl/VW7PqGovVpt8yRJEA
0 notes
Text
Diagnosing Diabetes in Children: Key Considerations
Diagnosing Diabetes in Children: Key Considerations
https://ift.tt/gwRrbJQ
Diabetes, a disease where the body’s ability to produce or respond to insulin is impaired, is a serious and increasingly common condition affecting children worldwide. Insulin, a hormone, is critical for the body to correctly manage sugar. While it may seem daunting to consider the possibility of your child having diabetes, early diagnosis, and management are crucial for their health and well-being. Understanding the critical considerations in diagnosing diabetes in children can help parents and caregivers navigate this process with confidence and clarity.
Recognizing Symptoms: One of the first steps in diagnosing diabetes in children is recognizing the signs and symptoms. These include increased thirst and urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, irritability, and blurred vision. If you notice any of these symptoms in your child, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly.
Family History: A family history of diabetes can increase a child’s risk of developing the condition. If there is a family history of diabetes, it’s essential to monitor your child’s health and discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider.
Routine Screening: Children who are overweight or obese, as well as those with other risk factors, such as a family history of diabetes or specific ethnic backgrounds, may be screened for diabetes during routine medical appointments. Screening typically involves blood tests to measure blood glucose levels, including fasting blood sugar, random blood sugar, and oral glucose tolerance tests.
HbA1c Testing: Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) testing is another essential tool for diagnosing diabetes in children. This blood test provides an average of a person’s blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. Elevated HbA1c levels may indicate diabetes or pre-diabetes and can help healthcare providers assess a child’s risk and manage their condition accordingly.
Type 1 vs. Type 2 Diabetes: It’s essential to distinguish between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes when diagnosing children. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. In Type 2 diabetes, the cells of the body don’t respond normally to insulin. Type 2 diabetes is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity and physical inactivity. While Type 1 diabetes is more common in children, the prevalence of Type 2 diabetes in youth is increasing.
Comprehensive Evaluation: Diagnosing diabetes in children requires a thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider, including a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. This evaluation helps determine the type of diabetes, assesses the child’s overall health, and guides treatment decisions.
Multidisciplinary Approach: Managing diabetes in children often requires an interdisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals such as pediatricians, endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators. Together, these professionals can provide comprehensive care, including medical management, nutritional counseling, and support for the child and their family.
Resources: There are many resources online as well as special, in-person programs such as camps for children with diabetes.
The post Diagnosing Diabetes in Children: Key Considerations first appeared on Dr. Colin Knight | Pediatrics | Miami, Florida.
via Dr. Colin Knight | Pediatrics | Miami, Florida https://ift.tt/wyrjpkG
September 18, 2024 at 10:14AM
0 notes
Text
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes
Diabetes, a chronic medical condition as common as sand in the desert, casts a wide net, affecting millions of people globally. Understanding this persistent foe is no small task, given its complexity and variety. Two primary types—type 1 and type 2 diabetes—emerge from the shadows, each with its unique characteristics, causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies. By unlocking…

View On WordPress
#A1C test#Blood sugar tests#diabetes diagnosis#Diabetes screening#Fasting blood sugar test#glucose testing#Hemoglobin A1C test#Oral glucose tolerance test#Random blood sugar test#Urine tests for diabetes
0 notes
Text
Where can I get tested for diabetes?
Why Get Tested
Early Detection: Identifying diabetes early can help you manage it better and reduce the risk of complications.
Prevention: If you’re at risk, testing can help catch prediabetes, allowing you to make lifestyle changes to prevent full-blown diabetes.
Management: If you’re already diagnosed, regular testing helps track your blood sugar levels and adjust treatment as needed.

When to Get Tested
Routine Screening:
Adults: If you’re over 45, it’s a good idea to get tested every 3 years, especially if you’re overweight or have other risk factors.
Younger Adults: If you’re under 45 but have risk factors like obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, or a family history of diabetes, you might need testing earlier.
Pregnant Women:
Early Screening: If you’re at high risk for gestational diabetes (e.g., you’re overweight, have a family history, or had it in a previous pregnancy), you might be tested earlier.
Routine Screening: Typically, gestational diabetes screening is done between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Symptoms:
If you have symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, extreme fatigue, or blurred vision, get tested right away.
Types of Tests
Fasting Blood Sugar Test:
What It Is: Measures blood sugar after an overnight fast.
Normal Level: Less than 100 mg/dL.
Prediabetes: 100-125 mg/dL.
Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT):
What It Is: Measures blood sugar before and 2 hours after drinking a sugary solution.
Normal Level: Less than 140 mg/dL after 2 hours.
Prediabetes: 140-199 mg/dL after 2 hours
Diabetes is indicated by a blood sugar of 200 mg/dL or more two hours after a glucose test.
Hemoglobin A1c Test:
What It Is: Reflects average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
Normal Level: Less than 5.7%.
Prediabetes: 5.7% to 6.4%.
Diabetes: 6.5% or higher.
Random Blood Sugar Test:
What It Is: Measures blood sugar at any time, regardless of when you last ate.
Diabetes: 200 mg/dL or higher, along with symptoms.
Tests for Gestational Diabetes
Initial Screening:
Glucose Challenge Test: A preliminary test where you drink a sugary liquid, and your blood is tested after 1 hour. If the result is high, further testing is needed.
Confirmatory Testing:
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): If the initial screening is abnormal, this test measures blood sugar at fasting and then at intervals after consuming a sugary drink
After a Diagnosis
Follow-Up:
Regular Monitoring: Depending on your diagnosis, you’ll need regular tests to monitor your blood sugar levels.
Lifestyle Changes: Adjustments in diet, exercise, and sometimes medication will be recommended.
Education and Support:
Diabetes Management: You’ll get advice on managing diabetes, including monitoring blood sugar, understanding your medication, and making lifestyle changes

NEW SCIENTIFIC BREAKTHROUGH OFFERS HOPE FOR BETTER DIABETES CONTROL
Where to Get Tested for Diabetes
Primary Care Physician:
Your doctor can order tests and interpret the results.
Specialty Clinics:
Endocrinologists or diabetes clinics specialize in diabetes care.
Laboratories:
Many independent labs offer diabetes testing.
Hospitals:
Hospitals may conduct tests and provide diagnostic services.
Pregnancy Care Clinics:
If you’re pregnant, your obstetrician or midwife will arrange gestational diabetes testing.
0 notes
Text
Everything You Need to Know About the Diabetic Profile Test: A Comprehensive Guide

When it comes to managing diabetes, regular testing is crucial. One of the most important tests for individuals at risk or those managing diabetes is the diabetic profile test. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about this essential test, including its purpose, what to expect, and how it can help in diabetes management.
What is a Diabetic Profile Test?
A diabetic profile test is a comprehensive series of blood tests that evaluates your body's ability to manage glucose levels effectively. This test is crucial for understanding your glucose metabolism and plays a significant role in diagnosing diabetes. It is also used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment in individuals already diagnosed with diabetes, helping to ensure optimal management of the condition.
Why is the Diabetic Profile Test Important?
Early Detection: The diabetic profile test is essential for identifying prediabetes or diabetes before symptoms become evident. Early detection allows for timely intervention, which can prevent the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of complications.
Monitoring: For individuals with an existing diabetes diagnosis, this test is vital for tracking blood sugar levels over time. Regular monitoring helps healthcare providers adjust treatment plans as needed to maintain optimal glucose control and prevent potential health issues.
Risk Assessment: This test also evaluates various risk factors associated with diabetes-related complications. By assessing these risks, the diabetic profile test helps in identifying potential issues such as heart disease or kidney problems, allowing for proactive management and preventive measures.
Key Components of the Diabetic Profile Test
Fasting Blood Glucose Test: This test measures your blood sugar levels after fasting overnight. Elevated levels in this test may indicate diabetes or prediabetes, making it a crucial diagnostic tool.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): The OGTT involves fasting overnight, then drinking a glucose-rich solution. Your blood sugar levels are tested at specific intervals to assess how effectively your body processes glucose. This test helps diagnose diabetes and evaluate glucose metabolism.
Hemoglobin A1c Test: This test provides an average of your blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It offers a broader view of your long-term glucose control, helping to assess how well diabetes is being managed over time.
Random Blood Glucose Test: Unlike other tests, the random blood glucose test measures your blood sugar at any time of the day, regardless of when you last ate. It is useful for assessing blood sugar levels outside of fasting conditions.
Preparing for the Test
Fasting: Many components of the diabetic profile test require an 8-12 hour fast. Follow your healthcare provider’s specific instructions regarding fasting and medication to ensure accurate results.
Hydration: Staying hydrated is important before the test. Drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration, which can affect test outcomes.
Medication: Inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking. Some medications can impact blood sugar levels or interfere with test results, so it’s important to disclose this information.
What to Expect During the Test
Blood Sample Collection: During the diabetic profile test, a healthcare professional will draw a small sample of blood, typically from your arm. The process is quick and generally causes minimal discomfort.
Duration: The duration of the test can vary. While most tests are completed swiftly, the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) may take several hours due to the need for multiple blood samples at different intervals.
Post-Test: After the test, you might experience minor discomfort at the site where blood was drawn. However, most people can return to their regular activities immediately without any significant issues.
Interpreting Your Results
Normal Range: Each component of the diabetic profile test has its own normal range. Understanding these ranges helps you interpret your results accurately and assess your glucose management.
Follow-Up: Once your results are available, discuss them with your healthcare provider. They can explain what the results mean in the context of your health and recommend any necessary follow-up actions or adjustments to your treatment plan.
Managing Your Health Post-Test
After undergoing a diabetic profile test, it’s essential to focus on managing your health based on the results. Here’s how you can take proactive steps to improve and maintain your well-being:
Diet and Lifestyle Adjustments
Dietary Changes: Your test results may indicate the need for dietary modifications. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels. Your healthcare provider might suggest reducing your intake of sugary foods and refined carbohydrates, which can cause spikes in blood glucose levels. They may also recommend specific dietary plans tailored to your needs, such as the Mediterranean or low-carb diet.
Physical Activity: Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine is crucial for blood sugar management. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and aids in glucose control. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, like brisk walking or cycling, each week. Your healthcare provider can guide you on suitable activities and exercise routines that align with your health goals.
Weight Management: If your test results show elevated blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight can significantly impact your glucose control. Weight loss, if needed, can improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Working with a nutritionist or dietitian can provide you with a structured plan to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Regular Monitoring
Follow-Up Testing: Regular testing is essential for effective diabetes management. Based on your initial results, your healthcare provider will determine the frequency of follow-up tests. Routine checks, including fasting blood glucose, HbA1c levels, and other relevant tests, help monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Self-Monitoring: In addition to professional tests, self-monitoring your blood glucose levels at home can provide immediate feedback on how well your management strategies are working. Using a glucose meter as advised by your healthcare provider allows you to track daily fluctuations and make informed decisions about diet and medication.
Medication Adherence: If your results indicate the need for medication, it’s crucial to adhere to your prescribed regimen. Consistently taking your medication as directed helps maintain stable blood glucose levels and prevents complications. Regular consultations with your healthcare provider ensure that your medication is effective and adjusted as necessary.
Conclusion
The diabetic profile test is a crucial component in the early detection and management of diabetes. By understanding the test’s purpose and preparing adequately, you can take significant steps towards better health. The test results provide valuable insights into your glucose metabolism, enabling you and your healthcare provider to make informed decisions about your diet, lifestyle, and treatment plan.
Effective diabetes management involves making necessary lifestyle adjustments, adhering to prescribed treatments, and engaging in regular monitoring. With these proactive measures, you can manage your health more effectively and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
For personalized advice and a comprehensive interpretation of your test results, always consult with your healthcare provider. They can offer tailored recommendations and support to help you achieve optimal health.
0 notes
Text
An Information About Blood Tests For Diabetes In Modesto CA
In recent years, diabetes has become a big issue for many Modesto, CA residents, as millions of individuals across the United States are affected by it. One significant aspect of managing and diagnosing diabetes is regular blood tests. These tests provide vital information about blood sugar levels and overall metabolic health. Here’s a closer examination of the types of blood tests available and what you need to know about them. All we need to say is that it is information about blood tests for diabetes in Modesto CA.

Some common blood tests
Several blood tests are used in diagnosing and monitoring diabetes, including:
Fasting blood sugar test: It involves the measurement of the level of blood glucose after a person has fasted overnight. It is one of the standard tests for diagnosing diabetes. It's a simple test that many of the local clinics and hospitals in Modesto, CA, can do to see if your blood sugar levels are high.
Hemoglobin A1c test: This test provides an idea about the average blood sugar over the past 2-3 months. The A1c is considered a fundamental tool for the diagnosis of this disease and also for monitoring the results of treatment, reflecting long-term glucose control. In Modesto, most healthcare providers do this test in order to gain a better understanding regarding a patient's blood sugar management.
OGTT (Oral glucose tolerance test): The test involves fasting overnight prior to the test. Following this, the patient is required to consume a glucose solution. Blood sugar levels are tested afterward at certain intervals to detect how well your body is able to process glucose. It's specifically useful in diagnosing type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes. In Modesto, specialized labs and endocrinology clinics frequently conduct this test. Even the best health care in Riverbank CA conducts this test.
From where can you get blood tests for diabetes in Modesto CA?
Modesto serves a wide range of facilities where one can easily do blood tests for diabetes:
Urgent care centers and local clinics: Many local clinics and urgent care centers in Modesto provide blood tests for diabetes. The labs in these locations tend to be fast and may give you results right away.
Specialty diabetes clinics: In order to guarantee optimal care for everyone who has diabetes, there are numerous diabetes centers and endocrinologist’s offices located within Modesto town that offer specialized blood tests as well as follow-up consultations. These facilities are committed to diabetes management and provide various diagnostic services to clients.
Modesto’s hospital labs: Blood tests for diabetes typically take place in Modesto’s hospital labs. Diagnostic services are often extensive at such hospitals and staff qualified to interpret results are readily available. The best blood tests also take place in the blood cholesterol treatment in Riverbank CA.
Conclusion
Therefore, normal blood tests are necessary for diagnosing and managing diabetes effectively. In Modesto, CA, there are different test options available for local clinics or specialized diabetes centers. If you are worried about diabetes or need routine tests, one of these establishments can help you with information and support in maintaining your health.
0 notes