#php check if array is empty
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Easy ways to check whether your PHP Array is empty or not by using simple syntaxes.
#php empty array#check if array is empty php#php if array is empty#php array empty#php check if array is empty
0 notes
Text
How to check Email and username availability live using jquery/ajax, PHP and PDO

In this tutorial, We will learn how to How to check Email and username availability live using jQuery/ajax and PHP-PDO.
Click : https://phpgurukul.com/how-to-check-email-and-username-availability-live-using-jquery-ajax-php-and-pdo/
File Structure for this tutorials
index.php (Main File)
config.php (Database Connection file)
check_availability.php (Used to check the Email and User availability)
Create a database with name demos. In demos database, create a table with name email_availabilty Sample structure of table email_availabilty
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `email_availabilty` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`username` varchar(255) NOT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
2. Create a database connection file
config.php
<?php
//DB Connection
define(‘DB_HOST’,’localhost’);
define(‘DB_USER’,’root’);
define(‘DB_PASS’,’’);
define(‘DB_NAME’,’demos’);
// Establish database connection.
try
{
$dbh = new PDO(“mysql:host=”.DB_HOST.”;dbname=”.DB_NAME,DB_USER, DB_PASS,array(PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_INIT_COMMAND => “SET NAMES ‘utf8’”));
}
catch (PDOException $e)
{
exit(“Error: “ . $e->getMessage());
}
3. Now Create an HTML form index.php
<?php
include_once(“config.php”);
?>
<table>
<tr>
<th width=”24%” height=”46" scope=”row”>Email Id :</th>
<td width=”71%” ><input type=”email” name=”email” id=”emailid” onBlur=”checkemailAvailability()” value=”” class=”form-control” required /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th width=”24%” scope=”row”></th>
<td > <span id=”email-availability-status”></span> </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th height=”42" scope=”row”>User Name</th>
<td><input type=”text” name=”username” id=”username” value=”” onBlur=”checkusernameAvailability()” class=”form-control” required /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th width=”24%” scope=”row”></th>
<td > <span id=”username-availability-status”></span> </td>
</tr>
</table>
4. Jquery/ajax script where you pass variable to check_availability.php page. put this in index.php inside head.
<script>
function checkemailAvailability() {
$(“#loaderIcon”).show();
jQuery.ajax({
url: “check_availability.php”,
data:’emailid=’+$(“#emailid”).val(),
type: “POST”,
success:function(data){
$(“#email-availability-status”).html(data);
$(“#loaderIcon”).hide();
},
error:function (){}
});
}
function checkusernameAvailability() {
$(“#loaderIcon”).show();
jQuery.ajax({
url: “check_availability.php”,
data:’username=’+$(“#username”).val(),
type: “POST”,
success:function(data){
$(“#username-availability-status”).html(data);
$(“#loaderIcon”).hide();
},
error:function (){}
});
}
</script>
5.check_availability.php page in this page you will check the availability of email or email.
<?php
require_once(“config.php”);
//code check email
if(!empty($_POST[“emailid”])) {
$uemail=$_POST[“emailid”];
$sql =”SELECT email FROM email_availabilty WHERE email=:email”;
$query= $dbh -> prepare($sql);
$query-> bindParam(‘:email’, $uemail, PDO::PARAM_STR);
$query-> execute();
$results = $query -> fetchAll(PDO::FETCH_OBJ);
if($query -> rowCount() > 0)
echo “<span style=’color:red’> Email Already Exit .</span>”;
else
echo “<span style=’color:green’> Email Available.</span>”;
}
// End code check email
//Code check user name
if(!empty($_POST[“username”])) {
$username=$_POST[“username”];
$sql =”SELECT username FROM email_availabilty WHERE username=:username”;
$query= $dbh -> prepare($sql);
$query-> bindParam(‘:username’, $username, PDO::PARAM_STR);
$query-> execute();
$results = $query -> fetchAll(PDO::FETCH_OBJ);
if($query -> rowCount() > 0)
echo “<span style=’color:red’> Username already exit .</span>”;
else
echo “<span style=’color:green’> Username Available.</span>”;
}
// End code check username
?>
PHP Gurukul
Welcome to PHPGurukul. We are a web development team striving our best to provide you with an unusual experience with PHP. Some technologies never fade, and PHP is one of them. From the time it has been introduced, the demand for PHP Projects and PHP developers is growing since 1994. We are here to make your PHP journey more exciting and useful.
Website : https://phpgurukul.com
1 note
·
View note
Text
Reading a CSV File using PHP
When working with CSV (Comma-Separated Values) files in PHP, you may need to read and process data from them. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to read a CSV file using PHP.
First step: Link the filepath of your CSV file. It can be from the Internet like Github Raw Usercontent
$filename = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jclosure/us-500-graph/master/data/us-500.csv';
Second step: Define the mode
$mode = 'r';
Read Mode ('r'): reading only Write Mode ('w'): Opens the file for writing. If the file already exists, it will be truncated (emptied). If the file doesn't exist, a new file will be created. Append Mode ('a'): Opens the file for writing, but it appends new data to the end of the file Read and Write Mode ('r+'): Opens the file for both reading and writing. Write and Read Mode ('w+'): Opens the file for both writing and reading. If the file already exists, it will be truncated; if not, a new file will be created. Append and Read Mode ('a+'): Opens the file for both appending and reading. It will place the pointer at the end of the file.
Third step: Open the file using fopen(). It returns a file pointer that can be used for reading. Store it in a variable for easier access later.
$file = fopen($filename, $mode);
To read a row from the CSV file:
The fgetcsv() reads and parses a line from the file and returns it as an array of values. We can store this array in a variable like $row, which will now contain the values of the row. We can now access the row values like a normal array, example, $row[0] and store it inside an HTML tag like <td>.
To read all rows from the CSV file:
Fgetscv() returns an array of values from a specific row. A $row variable stores this array. We can just do a loop that checks if $row is empty or false. If it's empty, it means fgetscv wasn't able to read a row anymore from the file.
Remember to fclose();
Remember to do an if-else that checks if the file was successfully opened or not.
0 notes
Text
Filling a PHP array dynamically means that instead of hardcoding the values, you're adding values to the array based on some logic, external input, or data sources. Here's a basic overview and some examples:
1. Create an Empty Array
You can create an empty array using the 'array()' function or the '[]' shorthand.
$dynamicArray = array(); // OR $dynamicArray = [];
2. Add Elements to the Array
You can add elements to an array in various ways:
Append to the array:
$dynamicArray[] = 'value1'; $dynamicArray[] = 'value2';
Add with a specific key:
$dynamicArray['key1'] = 'value1'; $dynamicArray['key2'] = 'value2';
3. Dynamically Filling the Array
Here's how you can fill an array based on various scenarios:
From a database (using PDO for this example)
$stmt = $pdo->query("SELECT value FROM some_table"); while ($row = $stmt->fetch()) { $dynamicArray[] = $row['value']; }
From a form (using POST method as an example):
if (isset($_POST['inputName'])) { $dynamicArray[] = $_POST['inputName']; }
Based on some logic:
for ($i = 0; $i < 10; $i++) { if ($i % 2 == 0) { $dynamicArray[] = $i; } }
This would fill $dynamicArray with even numbers between 0 and 9.
4. Tips and Best Practices
Sanitize external input: Always sanitize and validate data, especially when it's coming from external sources like user input, to ensure security.
Use associative arrays wisely: If you're using string keys, ensure they're unique to avoid overwriting values.
Check existing values: When adding to an array, you may want to check if a value already exists to avoid duplicates.
if (!in_array($value, $dynamicArray)) { $dynamicArray[] = $value; }
Using these methods and principles, you can effectively and dynamically fill a PHP array based on any set of conditions or data sources.
#PHPDevelopment#DynamicArrays#WebDevelopment#ProgrammingTips#DataHandling#PHPArrays#BackEndDevelopment#CodingBestPractices#WebProgramming#DatabaseIntegration#vinhjacker#mageplaza
0 notes
Text
Json decode

#JSON DECODE HOW TO#
#JSON DECODE CODE#
#JSON DECODE FREE#
With the help of the Online JSON Parser Tool, we can easily format our minify JSON Data and easily find key and value pairs and identify changes quickly.
JSON Data mainly used when we need to transfer data with different platforms and it’s easy to synchronize and used in any system.
All Data are available in Key and value pair. Decode a JSON document from s (a str beginning with a JSON document) and return a 2-tuple of the.
Here, In the above sample JSON data Name, Country, and Age are known as key and Jone, USA, and 39 known as a Value.
In Treeview, You can Search and highlight, and Sorting Data.
jsondecode converts JSON data types to the MATLAB data types in this table.
Minify or Compact JSON Data to resave and reduct its Size. JSON supports fewer data types than MATLAB.
JSON Validator for your Online Changes and your other JSON Data.
Redo and Undo facility when you edit your JSON online.
#JSON DECODE HOW TO#
How to Parse Large JSON Data with Isolates in Dart 2.The JSON Parser Tools have Below the main functionality:.
#JSON DECODE CODE#
How to Parse JSON in Dart/Flutter with Code Generation using FreezedĪnd if you need to parse large JSON data, you should do so in a separate isolate for best performance.In such cases, code generation is a much better option and this article explains how to use it: If you have a lot of different model classes, or each class has a lot of properties, writing all the parsing code by hand becomes time-consuming and error-prone. Restaurant Ratings example - JSON Serialization code.While the example JSON we used as reference wasn't too complex, we still ended up with a considerable amount of code: consider using the deep_pick package to parse JSON in a type-safe way.for nested JSON data (lists of maps), apply the fromJson() and toJson() methods.add explicit casts, validation, and null checks inside fromJson() to make the parsing code more robust.create model classes with fromJson() and toJson() for all domain-specific JSON objects in your app.When null, JSON objects will be returned as. When true, JSON objects will be returned as associative array s when false, JSON objects will be returned as object s. PHP implements a superset of JSON as specified in the original RFC 7159. use jsonEncode() and jsonDecode() from 'dart:convert' to serialize JSON data This function only works with UTF-8 encoded strings.But if we want our apps to work correctly, it's very important that we do it right and pay attention to details: JSON serialization is a very mundane task. You can build anything with Appwrite! Click here to learn more. Appwrite is a secure, self-hosted solution that provides developers with a set of easy-to-use REST APIs to manage their core backend needs. Open-Source Backend Server for Flutter Developers. Help me keep it that way by checking out this sponsor:
#JSON DECODE FREE#
Serializing Nested ModelsĪs a last step, here's the toJson() method to convert a Restaurant (and all its reviews) back into a Map:Ĭode with Andrea is free for everyone. You need to write the parsing code that is most appropriate for your use case. This specific implementation makes some assumptions about what may or may not be null, what fallback values to use etc.
if the reviews are missing, we use an empty list ( ) as a fallback.
map() operator to convert each dynamic value to a Review object using omJson()
the values in the list could have any type, so we use List.
the reviews may be missing, hence we cast to a nullable List.

1 note
·
View note
Text
Five Common PHP Problems and Solutions
PHP is a vast subject that needs lots of study to get done. It is a most-used open fount general-purpose scripting language that is particularly satisfied for web development and can be inserted into HTML. Today we are giving answers of top Php related question which will help you to done the process. Here solutions are provided by the top PHP Development Company, AResourcePool.
How to store image in core Php using input type file?
Are you looking for the ways to upload or store an image in core Php using input type file? If yes, so here we are.
Php script is very popular as it is using with a HTML form to let the users to upload files to the different server. At first the files are uploaded into a transitory directory as well as, it moved to a target by a PHP script.
Here are some procedures of uploading a file. So, here you go:
· Open a page which contains a HTML where you can feature an image, text files, and browser button as well as submit button.
· Now, click on the browser button and select the desired file to upload from your computer or laptop.
· You will now see the entire file of the selected path. So, choose where you wanna store it and press submit button.
· The file will send to the directory which is only temporary on the server.
· Php script was particular as the outline handler in the form’s action attribute. Now check is the file exist and then copy to the directory.
· You can make sure your success by using PHP script.
Meanwhile, it is really important to seek permission when writing files for permanent location or for temporary location. Whatever file you are uploading can be the image file or it can be the text file or whatever document you are uploading.
How to create an upload form?
To create an upload form you will need HTM coding because it has certain attribute of post as well as enctype attribute which is set to multipart.
<?php
if(isset($_FILES[‘image’])){
$errors= array();
$file_name = $_FILES['image’]['name’];
$file_size =$_FILES['image’]['size’];
$file_tmp =$_FILES['image’]['tmp_name’];
$file_type=$_FILES['image’]['type’];
$file_ext=strtolower(end(explode(’.’,$_FILES['image’]['name’])));
$extensions= array(“jpeg”,“jpg”,“png”);
if(in_array($file_ext,$extensions)=== false){
$errors[]=“extension not allowed, please choose a JPEG or PNG file.”;
}
if($file_size > 2097152){
$errors[]='File size must be excately 2 MB’;
}
if(empty($errors)==true){
move_uploaded_file($file_tmp,“images/”.$file_name);
echo “Success”;
}else{
print_r($errors);
}
}
?>
<html>
<body>
<form action=“” method=“POST” enctype=“multipart/form-data”>
<input type=“file” name=“image” />
<input type=“submit”/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
How can I test to see if value is 0 or null in PHP?
Php is a vast subject that contains many elements and one of the major elements of Php is to check 0, null or empty and isset status. It has various functions to check whether it is good or not or to test the value of the variables. There are three important functions of Php such as isset(), empty() and is_null(). This factors help to return a Boolean value. Boolean value is the used to determine the value of these functions. The result would be unexpected if it is not used in a right ways. There are two functions which functions opposite isset() and empty(). Well, it is not always true there is certain difference between all. So, here have a look at these functions:
1. isset()From PHP manual – isset():
Isset is used to decide that if a variable is set and is not NULL. If we say in other words then, it is used to determine the return is true only when not null is the variable.
2. empty()From PHP Manual – empty():
Empty is used to decide that if a variable is empty.If we talk in other terms then, it will return true if the variable is empty. It will show false, array(), NULL, “0?, 0, and an unset variable.
3. is_null()From PHP Manual – is_null():
Null is used to find if a variable is Null or not. In other words if we say then the returns true then, only when the variable shows null result. is_null() is opposite of isset(), except for one difference that isset() can be applied to unknown variables, but is_null() only to declared variables.
How to delete row from table using PHP pdo?
You can utilize the assignments table in the example database for the showing. Before going ahead with this instructional exercise, you ought to pursue the PHP MySQL make table instructional exercise to make the errands table and addition test information for rehearsing.
PHP MySQL Delete: Tasks Table:To erase information in a table, you utilize the accompanying advances: Associate with the MySQL database by making another case of the PDO object.
First of all, build a DELETE explanation to erase a column, numerous lines, or all lines in a table. On the off chance that you need to erase all columns in a major table rapidly and all the more proficiently, you utilize the TRUNCATE TABLE proclamation. Execute the DELETE articulation by calling the executive() strategy for the PDO object or the execute() technique for the PDOStatement object.
· PHP MySQL Delete information models
· PHP MySQL: erase a solitary column model
· To erase a solitary column in a table, you utilize the DELETE articulation with a WHERE condition that determines which line to erase.
· The accompanying content erases a column with id 2 in the assignments table.
How it functions?
When we talk about__construct() technique for the DeleteDataDemo class, we interface with the MySQL database by starting a case of the PDO class, and in the __destruct() strategy, we close the database association. The erase() technique acknowledges the id as the contention. In the first place, we call the get ready() technique for the PDO item to set up the DELETE explanation for execution, and after that we pass an exhibit that contains values comparing to the named placeholders in the DELETE proclamation to the execute() strategy for the PDOStatement object.
To erase the undertaking with id 2, we make an example of the DeleteDataDemo class and call the erase() strategy.
PHP MySQL: erase all columns in a table precedents
There are two different ways to erase all columns in a table:
· Issue a DELETE explanation without a WHERE statement.
· Issue a TRUNCATE TABLE explanation.
Getting Data from Multiple Databases:
There can be different issues which can face while fetching data from multiple databases but, issue you will have is consolidating the information. In a solitary database you keep up information honesty by characterizing outside keys. Different tables may have things identified with clients, so they may have a user_id field.
In a solitary database you would characterize a remote key connection between that user_id field and the id field on the client table, which means just existing id esteems from the client table, could be embedded in the othertable::user_id field. You can’t do outside key connections between tables in various databases, so I don’t have the foggiest idea how you’re going to interface the two arrangements of information into a solitary dataset.
Notwithstanding, expect you have a pseudo remote key, as above, however itwon’t be utilized by the databases to look after honesty. At that point need to do some sort of for/for each circle more than one dataset, remove the key which joins it to the next dataset, at that point glance through the second dataset for the coordinating key.
So, there are certain steps which involved in it so, have a look:
· make first association config ($conn1 = mysqli_connect($server1, $username, $password, $dbname)
· make second association config ($conn2 = mysqli_connect($server2, $username, $password, $dbname2);)
· select information with $conn config and store into $result variable (exhibit)
· for each $result, embed it into second database utilizing $conn2
How to display data record in database from vertical to horizontal:
There are many different ways to arrange data in a vertical to the horizontal database in Php. You will get two favourable circumstances and weaknesses to these strategies for social database information association. I completely depend on the requirements of the business as well it also depends on the need for the development.
The traditional way of any data in a table is a horizontal layout. Whatever data is recorded is go in a row and columns format runs horizontally. On the other hand, the second way is vertical. This way is very specific as well as it stores data that only have a column for real data. Here have a look at the example of data record in database from vertical to horizontal.
Table for Horizontal:
ID
First_Name
Last_Name
Dept
Sex
123
Vlad
Kofman
IT
M
234
Jim
Cramer
Marketing
M
456
Olimpia
Dukakis
Accounting
F
Table for Vertical
ID
Key
Value
123
First_Name
Vlad
234
First_Name
Jim
456
First_Name
Olimpia
123
Last_Name
Kofman
234
Last_Name
Cramer
456
Last_Name
Dukakis
123
Dept
IT
234
Dept
Marketing
456
Dept
Accounting
123
Sex
M
234
Sex
M
456
Sex
F
How enable in php long query strings:
Selecting Encrypted Username from DB:
There is very common question always hit the mind of the users that how Selecting Encrypted Username from DB? So, to encrypt the process does the data in the database unreadable from data in word processors. There can be no one decipher of its data when the database is encrypted.
Any database can be encrypted by utilizing the standard access menus. In both, the cases database that you are encrypting cannot be opened.
Follow this step to Encrypted Username from DB:
· Step 1: Select the tool by going to the setting. You will get options like Encrypt/Decrypt Database in the menu options.
· Step 2: You will see the encrypt/decrypt database dialogue from which choose the file which you want to encrypt. Press Okay.
· Step 3: If a user chooses the name which already exists in the files then, access will remove the original file after it concludes the process of encryption is successful. One of the best things that you can do in this situation is to take back up of the original database.
Encrypting with Code:
If you have used runtime version of Access to distribute your application and wants to give all the Php users the capability to encrypt the database you have to enter database course such as ADO. The following code will look like this:
Sub Encrypt(strDBNotEncrypted As String, _
strDBEncrypted As String)
Dim je As Nwe JRO.JetEngine
Je.CompactDatabase SourceConnection:=“Data Source=” _
& strDBNotEncrypted & “;”, _
DestConnection:=“Data Source=” & strDBEncrypted & _
"; Jet OLEDB:Encrypt Database=True"
End Sub
That’s all the folk about Php. If you are looking for such services you can contact Aresourcepool. The company has the best solution for all the above mentioned concept.
0 notes
Text
PHP empty() function use with MySQL NULL
PHP provides a handy function, empty(), that is used to determine whether a variable is empty. Perhaps that is a bit confusing to someone unfamiliar with the empty() function and I can see how. In this blog post, I will cover: what empty() means in PHP, what the empty() function does, and a use case pairing up empty() with the PHP ternary operator conditional construct. Both used in combination with the MySQL NULL value. Continue reading and see examples of empty()… Photo by Debby Hudson on Unsplash Self-Promotion: If you enjoy the content written here, by all means, share this blog and your favorite post(s) with others who may benefit from or like it as well. Since coffee is my favorite drink, you can even buy me one if you would like! I’ll use these various variables for examples throughout the post: $name = 'Josh'; $another_name = NULL; $some_name = ''; $an_age = 0; $another_age = '0'; $different_age = 12; Before we see what values are returned when the above variables are passed to empty(), let’s visit the PHP documentation on empty() for additional information, that way we know what to expect. Here is the description: “Determine whether a variable is considered to be empty. A variable is considered empty if it does not exist or if its value equals FALSE. empty() does not generate a warning if the variable does not exist.” empty() returns a value – either TRUE or FALSE – depending on if the variable that is passed to empty() as an argument exists and is either non-empty or non-zero. So what exactly is non-empty and non-zero? Let’s find out… Echo PHP empty() function in the browser For more context, I’ll echo out the return values of each of the below calls to empty(), passing in the previously defined variables above as arguments in each call: echo '$name variable empty value is: '.empty($name).' '; echo '$another_name variable empty value is: '.empty($another_name).' '; echo '$some_name variable empty value is: '.empty($some_name).' '; echo '$an_age variable empty value is: '.empty($an_age).' '; echo '$another_age variable empty value is: '.empty($another_age).' '; echo '$different_age variable empty value is: '.empty($different_age).' '; Return results from empty echo’ed in the browser Understanding PHP empty() function What does empty consider to be empty? empty() considers any of these values to be empty: The empty string – “” The integer 0 (zero) The float 0.0 The string “0” The NULL value. The FALSE boolean An empty array(). Based on the above list, the first variable, ‘$name’, and the last variable ‘$different_age’, are not considered empty, as they both have actual values (none of which are those included on the empty list). When passed to empty() as arguments, both variables return FALSE whereas all of the other variables return TRUE. In PHP, a FALSE can be considered 0 (zero) where a TRUE value can be considered 1. For more information on PHP booleans, visit the online PHP Booleans documentation. In order to see the actual boolean result, we can use the var_dump() function, passing the empty() function call with the variable parameter as var_dump()‘s own parameter: echo var_dump(empty($name)).' '; echo var_dump(empty($another_name)).' '; echo var_dump(empty($some_name)).' '; echo var_dump(empty($an_age)).' '; echo var_dump(empty($another_age)).' '; echo var_dump(empty($different_age)).' '; Using var_dump to echo out boolean values. What can we use the PHP empty() function for? Now that we have an idea of what empty() does, we can use it in a simple example and see the benefits of such a handy function. I have recently used an empty() trick in a LAMP stack application I have been working on and just had to share it here on my blog (although it is by no stretch of the imagination, sacred knowledge). Suppose we have this MySQL table, structure, and data: Current data in the project_pdf table The requirement is, provide a simple button for each project name in the table. However, each rows’ button should only be clickable if there is a pdf document file for that projects’ table row. We can use empty() to test the ‘pdf_doc’ column variable and determine if the value is NULL or not and set the button accordingly. Recall NULL is considered empty and if passed to the empty() function will return TRUE. We first need a connection to the database along with a SELECT query, retrieving all rows from the ‘project_pdf’ table: include __DIR__.'/includes/DatabaseConnection.php'; $query = "SELECT `id`, `project_name`, `pdf_doc` FROM `project_pdf` ORDER BY `project_name` ASC;"; $results = $pdo->query($query); foreach ($results as $row) { $rows[] = ['id' => $row['id'], 'project_name' => $row['project_name'], 'pdf_doc' => $row['pdf_doc']]; } The next part of the script contains the dynamic PHP, which provides a list of Bootstrap buttons; one for each of the returned records from the MySQL database: PHP foreach loop using empty() function to set button attributes Notice the call to empty() in the button class attribute. Using the PHP ternary operator, each button’s ‘$row[‘pdf_doc’]’ value is checked. The ternary operator uses this syntax: conditional_test ? truth_result_code : false_result_code If the ‘$row[‘pdf_doc’]’ value is NULL, then empty() returns TRUE. That buttons’ class attribute is set to btn btn-secondary disabled along with the disabled attribute itself. Should the ‘$row[‘pdf_doc’]’ value not be empty() (returns false), then the class attribute is set to btn btn-primary (with no disabled attribute) and stays active. The following screenshots show the active and inactive buttons for each MySQL table row: Button list of all current projects Button in active state. Mouse cursor on Bootstrap inactive button. Notice the ‘Project 3’ button is inactive since its row in the database has a NULL value for the ‘pdf_doc’ column. Be sure and check out these 2 posts on storing and retrieving a .pdf file with PHP and the MySQL BLOB datatype: Use MySQL BLOB column with PHP to store .pdf file PHP MySQL BLOB PDF: Display in Browser I hope through this post, you can find ways to use empty() for similar types of functionality where you see fit. I think it’s pretty neat myself. What creative ways have you used empty()? Tell me about them in the comments below. I’d love to know and learn more uses myself. Like always, if you see anything in the code I can improve on or correct, please let me know via the comments below. Like what you have read? See anything incorrect? Please comment below and thanks for reading!!! A Call To Action! Thank you for taking the time to read this post. I truly hope you discovered something interesting and enlightening. Please share your findings here, with someone else you know who would get the same value out of it as well. Visit the Portfolio-Projects page to see blog post/technical writing I have completed for clients. To receive email notifications (Never Spam) from this blog (“Digital Owl’s Prose”) for the latest blog posts as they are published, please subscribe (of your own volition) by clicking the ‘Click To Subscribe!’ button in the sidebar on the homepage! (Feel free at any time to review the Digital Owl’s Prose Privacy Policy Page for any questions you may have about: email updates, opt-in, opt-out, contact forms, etc…) Be sure and visit the “Best Of” page for a collection of my best blog posts. Josh Otwell has a passion to study and grow as a SQL Developer and blogger. Other favorite activities find him with his nose buried in a good book, article, or the Linux command line. Among those, he shares a love of tabletop RPG games, reading fantasy novels, and spending time with his wife and two daughters. Disclaimer: The examples presented in this post are hypothetical ideas of how to achieve similar types of results. They are not the utmost best solution(s). The majority, if not all, of the examples provided, is performed on a personal development/learning workstation-environment and should not be considered production quality or ready. Your particular goals and needs may vary. Use those practices that best benefit your needs and goals. Opinions are my own. The post PHP empty() function use with MySQL NULL appeared first on Digital Owl's Prose. https://joshuaotwell.com/php-empty-function-use-with-mysql-null/
0 notes
Text
WordPress Knowledge Base & Wiki Plugin for WordPress with Frontend Submission
New Post has been published on https://intramate.com/wordpress-plugins/wordpress-knowledge-base-wiki-plugin-for-wordpress-with-frontend-submission/
WordPress Knowledge Base & Wiki Plugin for WordPress with Frontend Submission

LIVE PREVIEWGet it now for only $20

Pixel Knowledge Base is a Powerful WordPress Knowledge Base & Wiki Plugin for WordPress that comes with a huge host of well thought out essential options and possibilities.
WordPress Knowledge Base Features:
Templating system baked into the core just like WooCommerce
Restrict Knowledge Base Categories by any role
Smart Ajax Live Search
Sort by date, title, views or number or votes without refreshing the page
Unique Voting System
Localization / I8ln support
Seamless plug and play installation – no coding experience required
Custom Templates Support
Knowledge Base Categories with 1/2/3 or 4 columns Per Row and drag and drop re-order
Change the knowledge base and associated category slug in a few simple steps
Lots of public template actions for developers to create unique layouts.
Gracefully degrades so compatible with all modern browsers
Lightweight Progressive CSS that inherits your themes styles by default – just 5KB when minified!
Found a bug? World Class support included.
What Can Pixel Knowledge Base for WordPress Do?
Restrict Knowledge Base Content Based on User Roles
Are you running a membership service and only want to show certain knowledge base categories to certain users? easy!
With a few clicks of a button you can easily restrict what your members get to see by role.
Set Knowledge Base Category Colors
Admin can now set unique colors for each of your knowledge base categories!
Submit Posts from The Frontend
In version 1.2, we added the ability for knowledge base posts to be submitted from the frontend of your website.
Allow your users to submit new posts to the backend of the site while retaining the ability to control which roles can and cannot submit posts and even if they are published or set as drafts.
Ajax Powered Search
Lightening quick ajax search returns the result your user wants fast with slick CSS3 animations to wow your users.
Sort Results by Date, Views, Title and Votes Instantly!
Instantly order and sort any results with a click of the button…no page refresh needed!
Interactive Voting Experience
Our smart voting system allows the user to help your community by voting for what was helpful and what was not.
Let users rank your questions for you.
Easily Categorize Your Knowledge Base
Pixel Knowledge Base comes with categories already registered, all you need to do it activate the plugin and your set to go.
Change Log
Version 1.0.0
Pixel Knowledge Base Release
Version 1.0.1
Fixed a bug with permalinks
Version 1.1.0
Added User Role Restrictions to Categories, Children and Posts
Hidden empty categories with no posts from the sidebar widget
Added custom template actions allowing dynamic templates to be created
* BUG FIX * Fixed wrong display in breadcrumbs when knowledge base was empty
Version 1.2.0
Added user submissions from the frontnend
User can set draft or publish default post status
can restrict submissions by user role
Single shortcode to check if user can submit and output form on any page
Version 1.3.3
Admins can now assign colours to individual knowledge base categories.
Version 1.3.4
Comments have been enabled for knowledge base answers
Added Localization / Translation Support
Added Restricted Category to the Demo Website
Added a new options to allow users to display restricted categories in the sidebar regardless of wether they have the permissions to view or not.
Fixed some PHP errors where array index was not defined
Fixed CSS bug with sidebar widget borders
Version 1.3.5
New Shortcode: Users can now show items anywhere on their website
Version 1.3.6
New Widget: Show Knowledge Base Search Form in Any Widget Area
New Widget: Show Latest Items in Any Widget Area
New Widget: Show Items by Category in Any Widget Area
IMPROVEMENT New UI Changes
Version 1.4.1
Fixed a being appended to titles
Added translation file
Added new function to enable translations
New Widget: Show Latest posts or posts from a knowledge base category in any widget area
Version 1.4.2
changed Self:: selectors to lowercase
changed Parent:: selectors to lowercase
updated spelling error in core files.
Version 1.4.3
Add cleaner styles for sidebar widgets
New Widget: Show all posts in a categorised form
LIVE PREVIEWGet it now for only $20
0 notes
Text
Web Scraping Using PHP – Parse IMDB.com Movies HTML
youtube
Upgrade your Clever Techie learning experience:
UPDATE! (9/13/19) New features and improvements for Clever Techie Patreons:
1. Download full source code with detailed comments – easy to learn and understand code 2. Weekly source code file updates by Clever Techie – every time I learn new things about a topic I will add it to the source file and let you know about the update – keep up with the latest coding technologies 3. Library of custom Clever Techie functions with descriptive, easy to understand comments – skyrocket coding productivity, code more efficiently by using Clever library of custom re-usable functions 4. Syntax code summary – memorize and review previously learned code faster 4. Organized file structure – access all Clever Techie lessons, source code, graphics, diagrams and cheat sheet from a single workspace – no more searching around for previously covered material and source code – save enormous amount of time and effort 5. Outline of topics the source file covers – fast review of all previously learned coding lessons 6. Access to all full HD 1080p videos with no ads 7. Console input examples – interactive examples that make it easier to understand and learn coding 8. Access to updated PHP Programming Book by Clever Techie 9. Early access to Clever Techie videos
Subscribe to Clever Techie patreon:
““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““`
Using PHP and regular expressions, we’re going to parse the movie content of IMDB.com and save all the data in one single array. Web scraping using regex can be very powerful and this video proves it. We account for empty elements by matching groups of HTML blocks, looping through the blocks of matched content and then matching single elements, if they’re found from the block. This technique of matching content and web scraping can be used on just about any web site to parse out it’s content.
““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““` Hey guys, I’m now using Patreon to share improved and updated video lesson material. For a small fee you can access all the downloadable files from this lesson (source code, icons & graphics, cheat sheets) and everything else included in the video from the Patreon page. Additionally, you will get access to ALL Clever Techie videos in HD format with no ads. Thank you so much for supporting Clever Techie

Download this video’s files here:
This download (Patreon unlock) includes: (PHP regex function source code, PHP regex screen shots, PHP regex cheat sheet) + ( You also get access to ALL source code and any downloadable content of ALL Clever Techie videos, as well as access to ALL videos in HD 1080p quality format with all video ads removed! )
““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““` In this web scraping tutorial we’re going to be using regular expressions to parse HTML. This is a more advanced tutorial so you can check out my video on regular expressions before going through this. We’re going to be parsing out the IMDb website, which is an Internet movie database, and I’m going to be using a website called www.regex101.com to test regular expressions against strings to make sure we’re matching them correctly. Because this is an advanced tutorial, I’ll be posting each portion of code and explaining how it works as we walk through it. Directly below is the full source code, but skip down further and I’ll walk through each portion of the code.
““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““` ( Website ) – PHP, JavaScript, WordPress, CSS, and HTML tutorials in video and text format with cool looking graphics and diagrams.
( YouTube Channel )
( Google Plus ) – clever techie video tutorials.
( Facebook )
( Twitter ) Nguồn:https://phprealestatescript.com/ Xem Thêm Bài Viết Khác:https://phprealestatescript.com/lap-trinh-php
Share Tweet Share
The post Web Scraping Using PHP – Parse IMDB.com Movies HTML appeared first on PHP Realestate Script.
from PHP Realestate Script https://ift.tt/2RQe8hr via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
Web Scraping Using PHP – Parse IMDB.com Movies HTML
youtube
Upgrade your Clever Techie learning experience:
UPDATE! (9/13/19) New features and improvements for Clever Techie Patreons:
1. Download full source code with detailed comments – easy to learn and understand code 2. Weekly source code file updates by Clever Techie – every time I learn new things about a topic I will add it to the source file and let you know about the update – keep up with the latest coding technologies 3. Library of custom Clever Techie functions with descriptive, easy to understand comments – skyrocket coding productivity, code more efficiently by using Clever library of custom re-usable functions 4. Syntax code summary – memorize and review previously learned code faster 4. Organized file structure – access all Clever Techie lessons, source code, graphics, diagrams and cheat sheet from a single workspace – no more searching around for previously covered material and source code – save enormous amount of time and effort 5. Outline of topics the source file covers – fast review of all previously learned coding lessons 6. Access to all full HD 1080p videos with no ads 7. Console input examples – interactive examples that make it easier to understand and learn coding 8. Access to updated PHP Programming Book by Clever Techie 9. Early access to Clever Techie videos
Subscribe to Clever Techie patreon:
““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““`
Using PHP and regular expressions, we’re going to parse the movie content of IMDB.com and save all the data in one single array. Web scraping using regex can be very powerful and this video proves it. We account for empty elements by matching groups of HTML blocks, looping through the blocks of matched content and then matching single elements, if they’re found from the block. This technique of matching content and web scraping can be used on just about any web site to parse out it’s content.
““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““` Hey guys, I’m now using Patreon to share improved and updated video lesson material. For a small fee you can access all the downloadable files from this lesson (source code, icons & graphics, cheat sheets) and everything else included in the video from the Patreon page. Additionally, you will get access to ALL Clever Techie videos in HD format with no ads. Thank you so much for supporting Clever Techie

Download this video’s files here:
This download (Patreon unlock) includes: (PHP regex function source code, PHP regex screen shots, PHP regex cheat sheet) + ( You also get access to ALL source code and any downloadable content of ALL Clever Techie videos, as well as access to ALL videos in HD 1080p quality format with all video ads removed! )
““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““` In this web scraping tutorial we’re going to be using regular expressions to parse HTML. This is a more advanced tutorial so you can check out my video on regular expressions before going through this. We’re going to be parsing out the IMDb website, which is an Internet movie database, and I’m going to be using a website called www.regex101.com to test regular expressions against strings to make sure we’re matching them correctly. Because this is an advanced tutorial, I’ll be posting each portion of code and explaining how it works as we walk through it. Directly below is the full source code, but skip down further and I’ll walk through each portion of the code.
““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““““` ( Website ) – PHP, JavaScript, WordPress, CSS, and HTML tutorials in video and text format with cool looking graphics and diagrams.
( YouTube Channel )
( Google Plus ) – clever techie video tutorials.
( Facebook )
( Twitter ) Nguồn:https://phprealestatescript.com/ Xem Thêm Bài Viết Khác:https://phprealestatescript.com/lap-trinh-php
Share Tweet Share
The post Web Scraping Using PHP – Parse IMDB.com Movies HTML appeared first on PHP Realestate Script.
from PHP Realestate Script https://ift.tt/2RQe8hr via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
“Notice: Undefined variable”, “Notice: Undefined index”, and “Notice: Undefined offset” using PHP
I’m running a PHP script and continue to receive errors like:
Notice: Undefined variable: my_variable_name in C:wampwwwmypathindex.php on line 10
Notice: Undefined index: my_index C:wampwwwmypathindex.php on line 11
Line 10 and 11 looks like this:
echo "My variable value is: " . $my_variable_name; echo "My index value is: " . $my_array["my_index"];
What is the meaning of these error messages?
Why do they appear all of a sudden? I used to use this script for years and I’ve never had any problem.
How do I fix them?
This is a General Reference question for people to link to as duplicate, instead of having to explain the issue over and over again. I feel this is necessary because most real-world answers on this issue are very specific.
Related Meta discussion:
What can be done about repetitive questions?
Do “reference questions” make sense?
28 Answers
Notice: Undefined variable
From the vast wisdom of the PHP Manual:
Relying on the default value of an uninitialized variable is problematic in the case of including one file into another which uses the same variable name. It is also a major security risk with register_globals turned on. E_NOTICE level error is issued in case of working with uninitialized variables, however not in the case of appending elements to the uninitialized array. isset() language construct can be used to detect if a variable has been already initialized. Additionally and more ideal is the solution of empty() since it does not generate a warning or error message if the variable is not initialized.
From PHP documentation:
No warning is generated if the variable does not exist. That means empty() is essentially the concise equivalent to !isset($var) || $var == false.
This means that you could use only empty() to determine if the variable is set, and in addition it checks the variable against the following, 0, 0.0, "", "0", null, false or [].
Example:
$o = []; @$var = ["",0,null,1,2,3,$foo,$o['myIndex']]; array_walk($var, function($v) { echo (!isset($v) || $v == false) ? 'true ' : 'false'; echo ' ' . (empty($v) ? 'true' : 'false'); echo "n"; });
Test the above snippet in the 3v4l.org online PHP editor
Although PHP does not require a variable declaration, it does recommend it in order to avoid some security vulnerabilities or bugs where one would forget to give a value to a variable that will be used later in the script. What PHP does in the case of undeclared variables is issue a very low level error, E_NOTICE, one that is not even reported by default, but the Manual advises to allow during development.
Ways to deal with the issue:
Recommended: Declare your variables, for example when you try to append a string to an undefined variable. Or use isset() / !empty() to check if they are declared before referencing them, as in:
//Initializing variable $value = ""; //Initialization value; Examples //"" When you want to append stuff later //0 When you want to add numbers later //isset() $value = isset($_POST['value']) ? $_POST['value'] : ''; //empty() $value = !empty($_POST['value']) ? $_POST['value'] : '';
This has become much cleaner as of PHP 7.0, now you can use the null coalesce operator:
// Null coalesce operator - No need to explicitly initialize the variable. $value = $_POST['value'] ?? '';
Set a custom error handler for E_NOTICE and redirect the messages away from the standard output (maybe to a log file):
set_error_handler('myHandlerForMinorErrors', E_NOTICE | E_STRICT)
Disable E_NOTICE from reporting. A quick way to exclude just E_NOTICE is:
error_reporting( error_reporting() & ~E_NOTICE )
Suppress the error with the @ operator.
Note: It’s strongly recommended to implement just point 1.
Notice: Undefined index / Undefined offset
This notice appears when you (or PHP) try to access an undefined index of an array.
Ways to deal with the issue:
Check if the index exists before you access it. For this you can use isset() or array_key_exists():
//isset() $value = isset($array['my_index']) ? $array['my_index'] : ''; //array_key_exists() $value = array_key_exists('my_index', $array) ? $array['my_index'] : '';
The language construct list() may generate this when it attempts to access an array index that does not exist:
list($a, $b) = array(0 => 'a'); //or list($one, $two) = explode(',', 'test string');
Two variables are used to access two array elements, however there is only one array element, index 0, so this will generate:
Notice: Undefined offset: 1
$_POST / $_GET / $_SESSION variable
The notices above appear often when working with $_POST, $_GET or $_SESSION. For $_POST and $_GET you just have to check if the index exists or not before you use them. For $_SESSION you have to make sure you have the session started with session_start() and that the index also exists.
Also note that all 3 variables are superglobals and are uppercase.
Related:
Notice: Undefined variable
Notice: Undefined Index
Try these
Q1: this notice means $varname is not defined at current scope of the script.
Q2: Use of isset(), empty() conditions before using any suspicious variable works well.
// recommended solution for recent PHP versions $user_name = $_SESSION['user_name'] ?? ''; // pre-7 PHP versions $user_name = ''; if (!empty($_SESSION['user_name'])) { $user_name = $_SESSION['user_name']; }
Or, as a quick and dirty solution:
// not the best solution, but works // in your php setting use, it helps hiding site wide notices error_reporting(E_ALL ^ E_NOTICE);
Note about sessions:
When using sessions, session_start(); is required to be placed inside all files using sessions.
http://php.net/manual/en/features.sessions.php
Error display @ operator
For undesired and redundant notices, one could use the dedicated @ operator to »hide« undefined variable/index messages.
$var = @($_GET["optional_param"]);
This is usually discouraged. Newcomers tend to way overuse it.
It’s very inappropriate for code deep within the application logic (ignoring undeclared variables where you shouldn’t), e.g. for function parameters, or in loops.
There’s one upside over the isset?: or ?? super-supression however. Notices still can get logged. And one may resurrect @-hidden notices with: set_error_handler("var_dump");
Additonally you shouldn’t habitually use/recommend if (isset($_POST["shubmit"])) in your initial code.
Newcomers won’t spot such typos. It just deprives you of PHPs Notices for those very cases. Add @ or isset only after verifying functionality.
Fix the cause first. Not the notices.
@ is mainly acceptable for $_GET/$_POST input parameters, specifically if they’re optional.
And since this covers the majority of such questions, let’s expand on the most common causes:
$_GET / $_POST / $_REQUEST undefined input
First thing you do when encountering an undefined index/offset, is check for typos: $count = $_GET["whatnow?"];
Is this an expected key name and present on each page request?
Variable names and array indicies are case-sensitive in PHP.
Secondly, if the notice doesn’t have an obvious cause, use var_dump or print_r to verify all input arrays for their curent content:
var_dump($_GET); var_dump($_POST); //print_r($_REQUEST);
Both will reveal if your script was invoked with the right or any parameters at all.
Alternativey or additionally use your browser devtools (F12) and inspect the network tab for requests and parameters:
POST parameters and GET input will be be shown separately.
For $_GET parameters you can also peek at the QUERY_STRING in
print_r($_SERVER);
PHP has some rules to coalesce non-standard parameter names into the superglobals. Apache might do some rewriting as well. You can also look at supplied raw $_COOKIES and other HTTP request headers that way.
More obviously look at your browser address bar for GET parameters:
http://example.org/script.php?id=5&sort=desc
The name=value pairs after the ? question mark are your query (GET) parameters. Thus this URL could only possibly yield $_GET["id"] and $_GET["sort"].
Finally check your <form> and <input> declarations, if you expect a parameter but receive none.
Ensure each required input has an <input name=FOO>
The id= or title= attribute does not suffice.
A method=POST form ought to populate $_POST.
Whereas a method=GET (or leaving it out) would yield $_GET variables.
It’s also possible for a form to supply action=script.php?get=param via $_GET and the remaining method=POST fields in $_POST alongside.
With modern PHP configurations (≥ 5.6) it has become feasible (not fashionable) to use $_REQUEST['vars'] again, which mashes GET and POST params.
If you are employing mod_rewrite, then you should check both the access.log as well as enable the RewriteLog to figure out absent parameters.
$_FILES
The same sanity checks apply to file uploads and $_FILES["formname"].
Moreover check for enctype=multipart/form-data
As well as method=POST in your <form> declaration.
See also: PHP Undefined index error $_FILES?
$_COOKIE
The $_COOKIE array is never populated right after setcookie(), but only on any followup HTTP request.
Additionally their validity times out, they could be constraint to subdomains or individual paths, and user and browser can just reject or delete them.
Generally because of “bad programming”, and a possibility for mistakes now or later.
If it’s a mistake, make a proper assignment to the variable first: $varname=0;
If it really is only defined sometimes, test for it: if (isset($varname)), before using it
If it’s because you spelled it wrong, just correct that
Maybe even turn of the warnings in you PHP-settings
It means you are testing, evaluating, or printing a variable that you have not yet assigned anything to. It means you either have a typo, or you need to check that the variable was initialized to something first. Check your logic paths, it may be set in one path but not in another.
I didn’t want to disable notice because it’s helpful, but wanted to avoid too much typing.
My solution was this function:
function ifexists($varname) { return(isset($$varname)?$varname:null); }
So if I want to reference to $name and echo if exists, I simply write:
<?=ifexists('name')?>
For array elements:
function ifexistsidx($var,$index) { return(isset($var[$index])?$var[$index]:null); }
In page if I want to refer to $_REQUEST[‘name’]:
<?=ifexistsidx($_REQUEST,'name')?>
The best way for getting input string is:
$value = filter_input(INPUT_POST, 'value');
This one-liner is almost equivalent to:
if (!isset($_POST['value'])) { $value = null; } elseif (is_array($_POST['value'])) { $value = false; } else { $value = $_POST['value']; }
If you absolutely want string value, just like:
$value = (string)filter_input(INPUT_POST, 'value');
Its because the variable ‘$user_location’ is not getting defined. If you are using any if loop inside which you are declaring the ‘$user_location’ variable then you must also have an else loop and define the same. For example:
$a=10; if($a==5) { $user_location='Paris';} else { } echo $user_location;
The above code will create error as The if loop is not satisfied and in the else loop ‘$user_location’ was not defined. Still PHP was asked to echo out the variable. So to modify the code you must do the following:
$a=10; if($a==5) { $user_location='Paris';} else { $user_location='SOMETHING OR BLANK'; } echo $user_location;
In reply to “”Why do they appear all of a sudden? I used to use this script for years and I’ve never had any problem.”
It is very common for most sites to operate under the “default” error reporting of “Show all errors, but not ‘notices’ and ‘deprecated'”. This will be set in php.ini and apply to all sites on the server. This means that those “notices” used in the examples will be suppressed (hidden) while other errors, considered more critical, will be shown/recorded.
The other critical setting is the errors can be hidden (i.e. display_errors set to “off” or “syslog”).
What will have happened in this case is that either the error_reporting was changed to also show notices (as per examples) and/or that the settings were changed to display_errors on screen (as opposed to suppressing them/logging them).
Why have they changed?
The obvious/simplest answer is that someone adjusted either of these settings in php.ini, or an upgraded version of PHP is now using a different php.ini from before. That’s the first place to look.
However it is also possible to override these settings in
.htconf (webserver configuration, including vhosts and sub-configurations)*
.htaccess
in php code itself
and any of these could also have been changed.
There is also the added complication that the web server configuration can enable/disable .htaccess directives, so if you have directives in .htaccess that suddenly start/stop working then you need to check for that.
(.htconf / .htaccess assume you’re running as apache. If running command line this won’t apply; if running IIS or other webserver then you’ll need to check those configs accordingly)
Summary
Check error_reporting and display_errors php directives in php.ini has not changed, or that you’re not using a different php.ini from before.
Check error_reporting and display_errors php directives in .htconf (or vhosts etc) have not changed
Check error_reporting and display_errors php directives in .htaccess have not changed
If you have directive in .htaccess, check if they are still permitted in the .htconf file
Finally check your code; possibly an unrelated library; to see if error_reporting and display_errors php directives have been set there.
the quick fix is to assign your variable to null at the top of your code
$user_location = null;
I used to curse this error, but it can be helpful to remind you to escape user input.
For instance, if you thought this was clever, shorthand code:
// Echo whatever the hell this is <?=$_POST['something']?>
…Think again! A better solution is:
// If this is set, echo a filtered version <?=isset($_POST['something']) ? html($_POST['something']) : ''?>
(I use a custom html() function to escape characters, your mileage may vary)
In PHP 7.0 it’s now possible to use Null coalescing operator:
echo "My index value is: " . ($my_array["my_index"] ?? '');
Equals to:
echo "My index value is: " . (isset($my_array["my_index"]) ? $my_array["my_index"] : '');
PHP manual PHP 7.0
I use all time own useful function exst() which automatically declare variables.
Your code will be –
$greeting = "Hello, ".exst($user_name, 'Visitor')." from ".exst($user_location); /** * Function exst() - Checks if the variable has been set * (copy/paste it in any place of your code) * * If the variable is set and not empty returns the variable (no transformation) * If the variable is not set or empty, returns the $default value * * @param mixed $var * @param mixed $default * * @return mixed */ function exst( & $var, $default = "") { $t = ""; if ( !isset($var) || !$var ) { if (isset($default) && $default != "") $t = $default; } else { $t = $var; } if (is_string($t)) $t = trim($t); return $t; }
In a very Simple Language. The mistake is you are using a variable $user_location which is not defined by you earlier and it doesn’t have any value So I recommend you to please declare this variable before using it, For Example:
$user_location = ''; Or $user_location = 'Los Angles';
This is a very common error you can face.So don’t worry just declare the variable and Enjoy Coding.
why not keep things simple?
<?php error_reporting(E_ALL); // making sure all notices are on function idxVal(&$var, $default = null) { return empty($var) ? $var = $default : $var; } echo idxVal($arr['test']); // returns null without any notice echo idxVal($arr['hey ho'], 'yo'); // returns yo and assigns it to array index, nice ?>
WHY IS THIS HAPPENING?
Over time, PHP has become a more security-focused language. Settings which used to be turned off by default are now turned on by default. A perfect example of this is E_STRICT, which became turned on by default as of PHP 5.4.0.
Furthermore, according to PHP documentation, by default, E_NOTICE is disabled in php.ini. PHP docs recommend turning it on for debugging purposes. However, when I download PHP from the Ubuntu repository–and from BitNami’s Windows stack–I see something else.
; Common Values: ; E_ALL (Show all errors, warnings and notices including coding standards.) ; E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE (Show all errors, except for notices) ; E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT (Show all errors, except for notices and coding standards warnings.) ; E_COMPILE_ERROR|E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR|E_ERROR|E_CORE_ERROR (Show only errors) ; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED ; Development Value: E_ALL ; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT ; http://php.net/error-reporting error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
Notice that error_reporting is actually set to the production value by default, not to the “default” value by default. This is somewhat confusing and is not documented outside of php.ini, so I have not validated this on other distributions.
To answer your question, however, this error pops up now when it did not pop up before because:
You installed PHP and the new default settings are somewhat poorly documented but do not exclude E_NOTICE.
E_NOTICE warnings like undefined variables and undefined indexes actually help to make your code cleaner and safer. I can tell you that, years ago, keeping E_NOTICE enabled forced me to declare my variables. It made it a LOT easier to learn C, were not declaring variables is much bigger of a nuisance.
WHAT CAN I DO ABOUT IT?
Turn off E_NOTICE by copying the “Default value” E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED and replacing it with what is currently uncommented after the equals sign in error_reporting =. Restart Apache, or PHP if using CGI or FPM. Make sure you are editing the “right” php.ini. The correct one will be Apache if you are running PHP with Apache, fpm or php-fpm if running PHP-FPM, cgi if running PHP-CGI, etc. This is not the recommended method, but if you have legacy code that’s going to be exceedingly difficult to edit, then it might be your best bet.
Turn off E_NOTICE on the file or folder level. This might be preferable if you have some legacy code but want to do things the “right” way otherwise. To do this, you should consult Apache2, Nginx, or whatever your server of choice is. In Apache, you would use php_value inside of <Directory>.
Rewrite your code to be cleaner. If you need to do this while moving to a production environment or don’t want someone to see your errors, make sure you are disabling any display of errors, and only logging your errors (see display_errors and log_errors in php.ini and your server settings).
To expand on option 3: This is the ideal. If you can go this route, you should. If you are not going this route initially, consider moving this route eventually by testing your code in a development environment. While you’re at it, get rid of ~E_STRICT and ~E_DEPRECATED to see what might go wrong in the future. You’re going to see a LOT of unfamiliar errors, but it’s going to stop you from having any unpleasant problems when you need to upgrade PHP in the future.
WHAT DO THE ERRORS MEAN?
Undefined variable: my_variable_name – This occurs when a variable has not been defined before use. When the PHP script is executed, it internally just assumes a null value. However, in which scenario would you need to check a variable before it was defined? Ultimately, this is an argument for “sloppy code”. As a developer, I can tell you that I love it when I see an open source project where variables are defined as high up in their scopes as they can be defined. It makes it easier to tell what variables are going to pop up in the future and makes it easier to read/learn the code.
function foo() { $my_variable_name = ''; //.... if ($my_variable_name) { // perform some logic } }
Undefined index: my_index – This occurs when you try to access a value in an array and it does not exist. To prevent this error, perform a conditional check.
// verbose way - generally better if (isset($my_array['my_index'])) { echo "My index value is: " . $my_array['my_index']; } // non-verbose ternary example - I use this sometimes for small rules. $my_index_val = isset($my_array['my_index'])?$my_array['my_index']:'(undefined)'; echo "My index value is: " . $my_index_val;
Another option is to declare an empty array at the top of your function. This is not always possible.
$my_array = array( 'my_index' => '' ); //... $my_array['my_index'] = 'new string';
(additional tip)
When I was encountering these and other issues, I used NetBeans IDE (free) and it gave me a host of warnings and notices. Some of them offer very helpful tips. This is not a requirement, and I don’t use IDEs anymore except for large projects. I’m more of a vim person these days :).
undefined index means in an array you requested for unavailable array index for example
<?php $newArray[] = {1,2,3,4,5}; print_r($newArray[5]); ?>
undefined variable means you have used completely not existing variable or which is not defined or initialized by that name for example
<?php print_r($myvar); ?>
undefined offset means in array you have asked for non existing key. And the solution for this is to check before use
php> echo array_key_exists(1, $myarray);
Regarding this part of the question:
Why do they appear all of a sudden? I used to use this script for years and I’ve never had any problem.
No definite answers but here are a some possible explanations of why settings can ‘suddenly’ change:
You have upgraded PHP to a newer version which can have other defaults for error_reporting, display_errors or other relevant settings.
You have removed or introduced some code (possibly in a dependency) that sets relevant settings at runtime using ini_set() or error_reporting() (search for these in the code)
You changed the webserver configuration (assuming apache here): .htaccess files and vhost configurations can also manipulate php settings.
Usually notices don’t get displayed / reported (see PHP manual) so it is possible that when setting up the server, the php.ini file could not be loaded for some reason (file permissions??) and you were on the default settings. Later on, the ‘bug’ has been solved (by accident) and now it CAN load the correct php.ini file with the error_reporting set to show notices.
If working with classes you need to make sure you reference member variables using $this:
class Person { protected $firstName; protected $lastName; public function setFullName($first, $last) { // Correct $this->firstName = $first; // Incorrect $lastName = $last; // Incorrect $this->$lastName = $last; } }
Another reason why an undefined index notice will be thrown, would be that a column was omitted from a database query.
I.e.:
$query = "SELECT col1 FROM table WHERE col_x = ?";
Then trying to access more columns/rows inside a loop.
I.e.:
print_r($row['col1']); print_r($row['col2']); // undefined index thrown
or in a while loop:
while( $row = fetching_function($query) ) { echo $row['col1']; echo "<br>"; echo $row['col2']; // undefined index thrown echo "<br>"; echo $row['col3']; // undefined index thrown }
Something else that needs to be noted is that on a *NIX OS and Mac OS X, things are case-sensitive.
Consult the followning Q&A’s on Stack:
Are table names in MySQL case sensitive?
mysql case sensitive table names in queries
MySql – Case Sensitive issue of tables in different server
Using a ternary is simple, readable, and clean:
Pre PHP 7 Assign a variable to the value of another variable if it’s set, else assign null (or whatever default value you need):
$newVariable = isset($thePotentialData) ? $thePotentialData : null;
PHP 7+ The same except using Null Coalescing Operator. There’s no longer a need to call isset() as this is built in, and no need to provide the variable to return as it’s assumed to return the value of the variable being checked:
$newVariable = $thePotentialData ?? null;
Both will stop the Notices from the OP question, and both are the exact equivalent of:
if (isset($thePotentialData)) { $newVariable = $thePotentialData; } else { $newVariable = null; }
If you don’t require setting a new variable then you can directly use the ternary’s returned value, such as with echo, function arguments, etc:
Echo:
echo 'Your name is: ' . isset($name) ? $name : 'You did not provide one';
Function:
$foreName = getForeName(isset($userId) ? $userId : null); function getForeName($userId) { if ($userId === null) { // Etc } }
The above will work just the same with arrays, including sessions etc, replacing the variable being checked with e.g.: $_SESSION['checkMe'] or however many levels deep you need, e.g.: $clients['personal']['address']['postcode']
Suppression:
It is possible to suppress the PHP Notices with @ or reduce your error reporting level, but it does not fix the problem, it simply stops it being reported in the error log. This means that your code still tried to use a variable that was not set, which may or may not mean something doesn’t work as intended – depending on how crucial the missing value is.
You should really be checking for this issue and handling it appropriately, either serving a different message, or even just returning a null value for everything else to identify the precise state.
If you just care about the Notice not being in the error log, then as an option you could simply ignore the error log.
One common cause of a variable not existing after an HTML form has been submitted is the form element is not contained within a <form> tag:
Example: Element not contained within the <form>
<form action="example.php" method="post"> <p> <input type="text" name="name" /> <input type="submit" value="Submit" /> </p> </form> <select name="choice"> <option value="choice1">choice 1</option> <option value="choice2">choice 2</option> <option value="choice3">choice 3</option> <option value="choice4">choice 4</option> </select>
Example: Element now contained within the <form>
<form action="example.php" method="post"> <select name="choice"> <option value="choice1">choice 1</option> <option value="choice2">choice 2</option> <option value="choice3">choice 3</option> <option value="choice4">choice 4</option> </select> <p> <input type="text" name="name" /> <input type="submit" value="Submit" /> </p> </form>
Probably you were using old PHP version until and now upgraded PHP thats the reason it was working without any error till now from years. until PHP4 there was no error if you are using variable without defining it but as of PHP5 onwards it throws errors for codes like mentioned in question.
When dealing with files, a proper enctype and a POST method are required, which will trigger an undefined index notice if either are not included in the form.
The manual states the following basic syntax:
HTML
<!-- The data encoding type, enctype, MUST be specified as below --> <form enctype="multipart/form-data" action="__URL__" method="POST"> <!-- MAX_FILE_SIZE must precede the file input field --> <input type="hidden" name="MAX_FILE_SIZE" value="30000" /> <!-- Name of input element determines name in $_FILES array --> Send this file: <input name="userfile" type="file" /> <input type="submit" value="Send File" /> </form>
PHP
<?php // In PHP versions earlier than 4.1.0, $HTTP_POST_FILES should be used instead // of $_FILES. $uploaddir = '/var/www/uploads/'; $uploadfile = $uploaddir . basename($_FILES['userfile']['name']); echo '<pre>'; if (move_uploaded_file($_FILES['userfile']['tmp_name'], $uploadfile)) { echo "File is valid, and was successfully uploaded.n"; } else { echo "Possible file upload attack!n"; } echo 'Here is some more debugging info:'; print_r($_FILES); print "</pre>"; ?>
Reference:
http://php.net/manual/en/features.file-upload.post-method.php
I asked a question about this and I was referred to this post with the message:
This question already has an answer here:
“Notice: Undefined variable”, “Notice: Undefined index”, and “Notice: Undefined offset” using PHP
I am sharing my question and solution here:
This is the error:
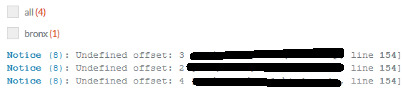
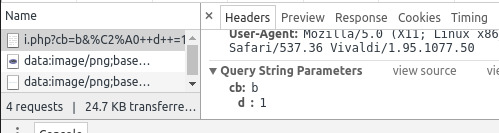
Line 154 is the problem. This is what I have in line 154:
153 foreach($cities as $key => $city){ 154 if(($city != 'London') && ($city != 'Madrid') && ($citiesCounterArray[$key] >= 1)){
I think the problem is that I am writing if conditions for the variable $city, which is not the key but the value in $key => $city. First, could you confirm if that is the cause of the warning? Second, if that is the problem, why is it that I cannot write a condition based on the value? Does it have to be with the key that I need to write the condition?
UPDATE 1: The problem is that when executing $citiesCounterArray[$key], sometimes the $key corresponds to a key that does not exist in the $citiesCounterArray array, but that is not always the case based on the data of my loop. What I need is to set a condition so that if $key exists in the array, then run the code, otherwise, skip it.
UPDATE 2: This is how I fixed it by using array_key_exists():
foreach($cities as $key => $city){ if(array_key_exists($key, $citiesCounterArray)){ if(($city != 'London') && ($city != 'Madrid') && ($citiesCounterArray[$key] >= 1)){
These errors occur whenever we are using a variable that is not set.
The best way to deal with these is set error reporting on while development.
To set error reporting on:
ini_set('error_reporting', 'on'); ini_set('display_errors', 'on'); error_reporting(E_ALL);
On production servers, error reporting is off, therefore, we do not get these errors.
On the development server, however, we can set error reporting on.
To get rid of this error, we see the following example:
if ($my == 9) { $test = 'yes'; // Will produce error as $my is not 9. } echo $test;
We can initialize the variables to NULL before assigning their values or using them.
So, we can modify the code as:
$test = NULL; if ($my == 9) { $test = 'yes'; // Will produce error as $my is not 9. } echo $test;
This will not disturb any program logic and will not produce Notice even if $test does not have value.
So, basically, its always better to set error reporting ON for development.
And fix all the errors.
And on production, error reporting should be set to off.
Those notices are because you don’t have the used variable defined and my_index key was not present into $my_array variable.
Those notices were triggered every time, because your code is not correct, but probably you didn’t have the reporting of notices on.
Solve the bugs:
$my_variable_name = "Variable name"; // defining variable echo "My variable value is: " . $my_variable_name; if(isset($my_array["my_index"])){ echo "My index value is: " . $my_array["my_index"]; // check if my_index is set }
Another way to get this out:
ini_set("error_reporting", false)
In PHP you need fist to define the variable after that you can use it. We can check variable is defined or not in very efficient way!.
//If you only want to check variable has value and value has true and false value. //But variable must be defined first. if($my_variable_name){ } //If you want to check variable is define or undefine //Isset() does not check that variable has true or false value //But it check null value of variable if(isset($my_variable_name)){ }
Simple Explanation
//It will work with :- true,false,NULL $defineVarialbe = false; if($defineVarialbe){ echo "true"; }else{ echo "false"; } //It will check variable is define or not and variable has null value. if(isset($unDefineVarialbe)){ echo "true"; }else{ echo "false"; }
Archive from: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/59057108/php-send-information-links
from https://knowledgewiki.org/notice-undefined-variable-notice-undefined-index-and-notice-undefined-offset-using-php/
0 notes
Text
Display data in the table, JSON or CSV format with WP CLI Formatter
From the last few articles, we are familiar with the WP CLI command.
In this article let’s learn about how to display custom data in the table, JSON or CSV format.
Note: If you read some recent articles then you can skip some below steps that are related to plugin creation.
Create Empty Plugin #Create Empty Plugin
Create a new folder wordpress-examples into plugins directory /wp-content/plugins/
Create a file wordpress-examples.php and add the below code into it.
<?php /** Plugin Name: WordPress Examples */
Note: If you want to add some additional information then you can get it from gist snippet – WordPress Complete Plugin Readme File.
Now you can see our WordPress Examples plugin exists into the plugins list.
Now, Activate the WordPress Examples plugin.
Register WP CLI Command #Register WP CLI Command
Register PHP class WordPress_Examples_WP_CLI e.g.
if ( ! class_exists( 'WordPress_Examples_WP_CLI' ) && class_exists( 'WP_CLI_Command' ) ) : class WordPress_Examples_WP_CLI extends WP_CLI_Command { } endif;
Here,
We have registered a new class WordPress_Examples_WP_CLI and extend it with WP_CLI_Command.
Add Examples Command #Add Examples Command
Now let’s register the examples. E.g.
WP_CLI::add_command( 'examples', 'WordPress_Examples_WP_CLI' );
Here,
We have used the function WP_CLI::add_command() to register our examples command.
The function WP_CLI::add_command() accepts 2 parameters. The first parameter is the command name. Which is examples in our case.
And second is a callback class which is WordPress_Examples_WP_CLI.
Add list sub command #Add list sub command
public function list( $args, $assoc_args ) { WP_CLI::line( 'Hello' ); }
Here,
We have added a function list() with two parameters.
$args contain the arguments.
$assoc_args contain the associate arguments.
Testing the Command #Testing the Command
Open command prompt/terminal. Go to your WordPress setup. I have set up WordPress in D:\xampp\htdocs\dev.test
So, Execute the below commands:
cd D:\xampp\htdocs\dev.test
wp examples list
You can see the output something like below:
λ wp examples list Hello
This command just shows the string Hello.
For testing, let’s create a static array which have some dummy data.
public function list( $args, $assoc_args ) { $list = array( array( 'id' => '1', 'first' => 'Mahesh', 'last' => 'Waghmare', ), array( 'id' => '2', 'first' => 'Swapnil', 'last' => 'Dhanrale', ), array( 'id' => '3', 'first' => 'Madhav', 'last' => 'Shikhare', ), ); WP_CLI::line( print_r( $list ) ); }
Let’s execute the command wp examples list.
λ wp examples list Array ( [0] => Array ( [id] => 1 [first] => Mahesh [last] => Waghmare ) [1] => Array ( [id] => 2 [first] => Swapnil [last] => Dhanrale ) [2] => Array ( [id] => 3 [first] => Madhav [last] => Shikhare ) ) 1
Here, we have just print the array with WP_CLI::line( print_r( $list ) );.
Now, Let’s display this array data in a well-formatted order.
Using \WP_CLI\Formatter() #Using \WP_CLI\Formatter()
We are using the in-build WP CLI helper class \WP_CLI\Formatter() to format our array in table format.
Let’s use the Formatter class into our code:
public function list( $args, $assoc_args ) { $list = array( array( 'id' => '1', 'first' => 'Mahesh', 'last' => 'Waghmare', ), array( 'id' => '2', 'first' => 'Swapnil', 'last' => 'Dhanrale', ), array( 'id' => '3', 'first' => 'Madhav', 'last' => 'Shikhare', ), ); $formatter = new \WP_CLI\Formatter( $assoc_args, array( 'id', 'first', 'last', )); $formatter->display_items( $list ); }
Here,
$formatter We have created a variable which stores the instance of the class new \WP_CLI\Formatter().
new \WP_CLI\Formatter class initialized bypassing 2 values.
$assoc_args – which contain the associated arguments.
array( 'id', 'first', 'last') – It contains the keys of our array. We will check some examples below to understand why it was passed.
$formatter->display_items( $list ); – We have called the display_items() method of Formatter class and pass the $list into it.
Let’s try some commands to see how it works.
wp examples list
After executing above command we see the output like:
λ wp examples list +----+---------+----------+ | id | first | last | +----+---------+----------+ | 1 | Mahesh | Waghmare | | 2 | Swapnil | Dhanrale | | 3 | Madhav | Shikhare | +----+---------+----------+
Hurray! Our array is displayed in the table format. Because of by default class \WP_CLI\Formatter() display items in Table format.
If we want to see the same data in another format then we need to set associate argument --format
Using –format #Using –format
Let’s try another example with --format associate argument.
Example 1
wp examples list --format=json
After executing above command we can see the result something like below:
λ wp examples list --format=json [{"id":"1","first":"Mahesh","last":"Waghmare"},{"id":"2","first":"Swapnil","last":"Dhanrale"},{"id":"3","first":"Madhav","last":"Shikhare"}]
Here, We have passed the --format=json for that, the data is display as JSON.
Example 2
wp examples list --format=csv
After executing above command we can see the result something like below:
λ wp examples list --format=csv id,first,last 1,Mahesh,Waghmare 2,Swapnil,Dhanrale 3,Madhav,Shikhare
In the --format associate argument we can pass values ‘table‘, ‘json‘, ‘csv‘, ‘yaml‘, ‘ids‘ and ‘count‘.
Try some other format yourself and understand how it displays it.
Using –field #Using –field
In our example, we have 3 keys those are id, first and last.
Let’s assume that we have 15+ keys. So, when we execute our list command then all the data will be display.
Maybe we just want to display a single column.
With the --field the associate argument we can display only specific column data.
Example 1
wp examples list --field=id
After executing above command we can see the result something like below:
λ wp examples list --field=id 1 2 3 D:\xampp\htdocs\dev.test
Here, Only Id’s column is visible for us.
Example 2
wp examples list --field=id --format=json
We have used --field=id and --format=json. Let’s see what it display.
λ wp examples list --field=id --format=json ["1","2","3"]
Example 3
wp examples list --field=ID
The output of the above command is below:
D:\xampp\htdocs\dev.test λ wp examples list --field=ID Error: Invalid field: ID.
Aah! Why it display the error? Because the value of the field is case sensitive. So all the below values considered as different:
--field=ID
--field=Id
--field=iD
--field=id
Using –fields #Using –fields
Same as --field the argument we can use --fields.
The only difference is that we can pass multiple arguments into it.
Let’s try some examples.
Example 1
wp examples list --fields=id,first
λ wp examples list --fields=id,first +----+---------+ | id | first | +----+---------+ | 1 | Mahesh | | 2 | Swapnil | | 3 | Madhav | +----+---------+
Here, We can see only the id and the first column.
Example 2
wp examples list --fields=first,id
Let’s try to change the sequence of the keys by passing values first and then id.
λ wp examples list --fields=first,id +---------+----+ | first | id | +---------+----+ | Mahesh | 1 | | Swapnil | 2 | | Madhav | 3 | +---------+----+
Interesting right! Let’s get the first and last column in JSON format.
Example 3
wp examples list --fields=first,last --format=json
Here, we have passed the --fields=first,last and --format=json.
The output is as below:
λ wp examples list --fields=first,last --format=json [{"first":"Mahesh","last":"Waghmare"},{"first":"Swapnil","last":"Dhanrale"},{"first":"Madhav","last":"Shikhare"}]
Showing data in the table, JSON or CSV format in WP CLI program!
Tweet
from WordPress http://bit.ly/2qRu6NC via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
Creating A Shopping Cart With HTML5 Web Storage
Creating A Shopping Cart With HTML5 Web Storage
Matt Zand
2019-08-26T14:30:59+02:002019-08-26T13:06:56+00:00
With the advent of HTML5, many sites were able to replace JavaScript plugin and codes with simple more efficient HTML codes such as audio, video, geolocation, etc. HTML5 tags made the job of developers much easier while enhancing page load time and site performance. In particular, HTML5 web storage was a game changer as they allow users’ browsers to store user data without using a server. So the creation of web storage, allowed front-end developers to accomplish more on their website without knowing or using server-side coding or database.
Online e-commerce websites predominantly use server-side languages such as PHP to store users’ data and pass them from one page to another. Using JavaScript back-end frameworks such as Node.js, we can achieve the same goal. However, in this tutorial, we’ll show you step by step how to build a shopping cart with HTML5 and some minor JavaScript code. Other uses of the techniques in this tutorial would be to store user preferences, the user’s favorite content, wish lists, and user settings like name and password on websites and native mobile apps without using a database.
Many high-traffic websites rely on complex techniques such as server clustering, DNS load balancers, client-side and server-side caching, distributed databases, and microservices to optimize performance and availability. Indeed, the major challenge for dynamic websites is to fetch data from a database and use a server-side language such as PHP to process them. However, remote database storage should be used only for essential website content, such as articles and user credentials. Features such as user preferences can be stored in the user’s browser, similar to cookies. Likewise, when you build a native mobile app, you can use HTML5 web storage in conjunction with a local database to increase the speed of your app. Thus, as front-end developers, we need to explore ways in which we can exploit the power of HTML5 web storage in our applications in the early stages of development.
I have been a part of a team developing a large-scale social website, and we used HTML5 web storage heavily. For instance, when a user logs in, we store the hashed user ID in an HTML5 session and use it to authenticate the user on protected pages. We also use this feature to store all new push notifications — such as new chat messages, website messages, and new feeds — and pass them from one page to another. When a social website gets high traffic, total reliance on the server for load balancing might not work, so you have to identify tasks and data that can be handled by the user’s browser instead of your servers.
Project Background
A shopping cart allows a website’s visitor to view product pages and add items to their basket. The visitor can review all of their items and update their basket (such as to add or remove items). To achieve this, the website needs to store the visitor’s data and pass them from one page to another, until the visitor goes to the checkout page and makes a purchase. Storing data can be done via a server-side language or a client-side one. With a server-side language, the server bears the weight of the data storage, whereas with a client-side language, the visitor’s computer (desktop, tablet or smartphone) stores and processes the data. Each approach has its pros and cons. In this tutorial, we’ll focus on a simple client-side approach, based on HTML5 and JavaScript.
Note: In order to be able to follow this tutorial, basic knowledge of HTML5, CSS and JavaScript is required.
Project Files
Click here to download the project’s source files. You can see a live demo, too.
Overview Of HTML5 Web Storage
HTML5 web storage allows web applications to store values locally in the browser that can survive the browser session, just like cookies. Unlike cookies that need to be sent with every HTTP request, web storage data is never transferred to the server; thus, web storage outperforms cookies in web performance. Furthermore, cookies allow you to store only 4 KB of data per domain, whereas web storage allows at least 5 MB per domain. Web storage works like a simple array, mapping keys to values, and they have two types:
Session storage This stores data in one browser session, where it becomes available until the browser or browser tab is closed. Popup windows opened from the same window can see session storage, and so can iframes inside the same window. However, multiple windows from the same origin (URL) cannot see each other’s session storage.
Local storage This stores data in the web browser with no expiration date. The data is available to all windows with the same origin (domain), even when the browser or browser tabs are reopened or closed.
Both storage types are currently supported in all major web browsers. Keep in mind that you cannot pass storage data from one browser to another, even if both browsers are visiting the same domain.
Build A Basic Shopping Cart
To build our shopping cart, we first create an HTML page with a simple cart to show items, and a simple form to add or edit the basket. Then, we add HTML web storage to it, followed by JavaScript coding. Although we are using HTML5 local storage tags, all steps are identical to those of HTML5 session storage and can be applied to HTML5 session storage tags. Lastly, we’ll go over some jQuery code, as an alternative to JavaScript code, for those interested in using jQuery.
Add HTML5 Local Storage To Shopping Cart
Our HTML page is a basic page, with tags for external JavaScript and CSS referenced in the head.
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html lang="en-US"> <head> <title>HTML5 Local Storage Project</title> <META charset="UTF-8"> <META name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no"> <META NAME='rating' CONTENT='General' /> <META NAME='expires' CONTENT='never' /> <META NAME='language' CONTENT='English, EN' /> <META name="description" content="shopping cart project with HTML5 and JavaScript"> <META name="keywords" content="HTML5,CSS,JavaScript, html5 session storage, html5 local storage"> <META name="author" content="dcwebmakers.com"> <script src="Storage.js"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" href="StorageStyle.css"> </head>
Below is the HTML content for the page’s body:
<form name=ShoppingList> <div id="main"> <table> <tr> <td><b>Item:</b><input type=text name=name></td> <td><b>Quantity:</b><input type=text name=data></td> </tr> <tr> <td> <input type=button value="Save" onclick="SaveItem()"> <input type=button value="Update" onclick="ModifyItem()"> <input type=button value="Delete" onclick="RemoveItem()"> </td> </tr> </table> </div> <div id="items_table"> <h3>Shopping List</h3> <table id=list></table> <p> <label><input type=button value="Clear" onclick="ClearAll()"> <i>* Delete all items</i></label> </p> </div> </form>
Adding JavaScript To The Shopping Cart
We’ll create and call the JavaScript function doShowAll() in the onload() event to check for browser support and to dynamically create the table that shows the storage name-value pair.
<body onload="doShowAll()">
Alternatively, you can use the JavaScript onload event by adding this to the JavaScript code:
window.load=doShowAll();
Or use this for jQuery:
$( window ).load(function() { doShowAll(); });
In the CheckBrowser() function, we would like to check whether the browser supports HTML5 storage. Note that this step might not be required because most modern web browsers support it.
/* =====> Checking browser support. //This step might not be required because most modern browsers do support HTML5. */ //Function below might be redundant. function CheckBrowser() { if ('localStorage' in window && window['localStorage'] !== null) { // We can use localStorage object to store data. return true; } else { return false; } }
Inside the doShowAll(), if the CheckBrowser() function evaluates first for browser support, then it will dynamically create the table for the shopping list during page load. You can iterate the keys (property names) of the key-value pairs stored in local storage inside a JavaScript loop, as shown below. Based on the storage value, this method populates the table dynamically to show the key-value pair stored in local storage.
// Dynamically populate the table with shopping list items. //Step below can be done via PHP and AJAX, too. function doShowAll() { if (CheckBrowser()) { var key = ""; var list = "<tr><th>Item</th><th>Value</th></tr>\n"; var i = 0; //For a more advanced feature, you can set a cap on max items in the cart. for (i = 0; i <= localStorage.length-1; i++) { key = localStorage.key(i); list += "<tr><td>" + key + "</td>\n<td>" + localStorage.getItem(key) + "</td></tr>\n"; } //If no item exists in the cart. if (list == "<tr><th>Item</th><th>Value</th></tr>\n") { list += "<tr><td><i>empty</i></td>\n<td><i>empty</i></td></tr>\n"; } //Bind the data to HTML table. //You can use jQuery, too. document.getElementById('list').innerHTML = list; } else { alert('Cannot save shopping list as your browser does not support HTML 5'); } }
Note: Either you or your framework will have a preferred method of creating new DOM nodes. To keep things clear and focused, our example uses .innerHTML even though we’d normally avoid that in production code.
Tip: If you’d like to use jQuery to bind data, you can just replace document.getElementById('list').innerHTML = list; with $(‘#list’).html()=list;.
Run And Test The Shopping Cart
In the previous two sections, we added code to the HTML head, and we added HTML to the shopping cart form and basket. We also created a JavaScript function to check for browser support and to populate the basket with the items in the cart. In populating the basket items, the JavaScript fetches values from HTML web storage, instead of a database. In this part, we’ll show you how the data are inserted into the HTML5 storage engine. That is, we’ll use HTML5 local storage in conjunction with JavaScript to insert new items to the shopping cart, as well as edit an existing item in the cart.
Note: I’ve added tips sections below to show jQuery code, as an alternative to the JavaScript ones.
We’ll create a separate HTML div element to capture user input and submission. We’ll attach the corresponding JavaScript function in the onClick event for the buttons.
<input type="button" value="Save" onclick="SaveItem()"> <input type="button" value="Update" onclick="ModifyItem()"> <input type="button" value="Delete" onclick="RemoveItem()">
You can set properties on the localStorage object similar to a normal JavaScript object. Here is an example of how we can set the local storage property myProperty to the value myValue:
localStorage.myProperty="myValue";
You can delete local storage property like this:
delete localStorage.myProperty;
Alternately, you can use the following methods to access local storage:
localStorage.setItem('propertyName','value'); localStorage.getItem('propertyName'); localStorage.removeItem('propertyName');
To save the key-value pair, get the value of the corresponding JavaScript object and call the setItem method:
function SaveItem() { var name = document.forms.ShoppingList.name.value; var data = document.forms.ShoppingList.data.value; localStorage.setItem(name, data); doShowAll(); }
Below is the jQuery alternative for the SaveItem function. First, add an ID to the form inputs:
<td><b>Item:</b><input type=text name="name" id="name"></td> <td><b>Quantity:</b><input type=text name="data" id="data"></td>
Then, select the form inputs by ID, and get their values. As you can see below, it is much simpler than JavaScript:
function SaveItem() { var name = $("#name").val(); var data = $("#data").val(); localStorage.setItem(name, data); doShowAll(); }
To update an item in the shopping cart, you have to first check whether that item’s key already exists in local storage, and then update its value, as shown below:
//Change an existing key-value in HTML5 storage. function ModifyItem() { var name1 = document.forms.ShoppingList.name.value; var data1 = document.forms.ShoppingList.data.value; //check if name1 is already exists //Check if key exists. if (localStorage.getItem(name1) !=null) { //update localStorage.setItem(name1,data1); document.forms.ShoppingList.data.value = localStorage.getItem(name1); } doShowAll(); }
Below shows the jQuery alternative.
function ModifyItem() { var name1 = $("#name").val(); var data1 = $("#data").val(); //Check if name already exists. //Check if key exists. if (localStorage.getItem(name1) !=null) { //update localStorage.setItem(name1,data1); var new_info=localStorage.getItem(name1); $("#data").val(new_info); } doShowAll(); }
We will use the removeItem method to delete an item from storage.
function RemoveItem() { var name=document.forms.ShoppingList.name.value; document.forms.ShoppingList.data.value=localStorage.removeItem(name); doShowAll(); }
Tip: Similar to the previous two functions, you can use jQuery selectors in the RemoveItem function.
There is another method for local storage that allows you to clear the entire local storage. We call the ClearAll() function in the onClick event of the “Clear” button:
<input type="button" value="Clear" onclick="ClearAll()">
We use the clear method to clear the local storage, as shown below:
function ClearAll() { localStorage.clear(); doShowAll(); }
Session Storage
The sessionStorage object works in the same way as localStorage. You can replace the above example with the sessionStorage object to expire the data after one session. Once the user closes the browser window, the storage will be cleared. In short, the APIs for localStorage and sessionStorage are identical, allowing you to use the following methods:
setItem(key, value)
getItem(key)
removeItem(key)
clear()
key(index)
length
Shopping Carts With Arrays And Objects
Because HTML5 web storage only supports single name-value storage, you have to use JSON or another method to convert your arrays or objects into a single string. You might need an array or object if you have a category and subcategories of items, or if you have a shopping cart with multiple data, like customer info, item info, etc. You just need to implode your array or object items into a string to store them in web storage, and then explode (or split) them back to an array to show them on another page. Let’s go through a basic example of a shopping cart that has three sets of info: customer info, item info and custom mailing address. First, we use JSON.stringify to convert the object into a string. Then, we use JSON.parse to reverse it back.
Hint: Keep in mind that the key-name should be unique for each domain.
//Customer info //You can use array in addition to object. var obj1 = { firstname: "John", lastname: "thomson" }; var cust = JSON.stringify(obj1); //Mailing info var obj2 = { state: "VA", city: "Arlington" }; var mail = JSON.stringify(obj2); //Item info var obj3 = { item: "milk", quantity: 2 }; var basket = JSON.stringify(obj3); //Next, push three strings into key-value of HTML5 storage. //Use JSON parse function below to convert string back into object or array. var New_cust=JSON.parse(cust);
Summary
In this tutorial, we have learned how to build a shopping cart step by step using HTML5 web storage and JavaScript. We’ve seen how to use jQuery as an alternative to JavaScript. We’ve also discussed JSON functions like stringify and parse to handle arrays and objects in a shopping cart. You can build on this tutorial by adding more features, like adding product categories and subcategories while storing data in a JavaScript multi-dimensional array. Moreover, you can replace the whole JavaScript code with jQuery.
We’ve seen what other things developers can accomplish with HTML5 web storage and what other features they can add to their websites. For example, you can use this tutorial to store user preferences, favorited content, wish lists, and user settings like names and passwords on websites and native mobile apps, without using a database.
To conclude, here are a few issues to consider when implementing HTML5 web storage:
Some users might have privacy settings that prevent the browser from storing data.
Some users might use their browser in incognito mode.
Be aware of a few security issues, like DNS spoofing attacks, cross-directory attacks, and sensitive data compromise.
Related Reading
“Browser Storage Limits And Eviction Criteria,” MDN web docs, Mozilla
“Web Storage,” HTML Living Standard,
“This Week In HTML 5,” The WHATWG Blog

(dm, il)
0 notes
Text
How To Use Advanced Custom Fields (ACF) in WordPress
Out of the box, WordPress is a really easy to use, simple blogging platform. What gives you the ability to turn WordPress into a full-on CMS (content management system) and run just about any type of website is its powerful and flexible plugin system. One of the best plugins to help you do that is Advanced Custom Fields (ACF).
ACF is without a doubt our most used plugin for WordPress sites. (If you’re interested in some other plugins we use all the time, check out our post about our top 10 WordPress plugins). I don’t think there’s a project I have worked on where Advanced Custom Fields isn’t installed. In case you hadn’t guessed from the name, ACF allows you to add custom data fields to just about any object in your WordPress install. This is great when you are building or customising a theme and need finer control over the data attached to each object (post, page etc) than simply the title and content.
We’re going to go through some of the field types here in a little detail. If you just want to see how to use ACF, you can skip to here.
Types of ACF Fields
Before we get started, let’s take a quick look at the types of field you can add to posts using ACF. There are a huge number of types of field you can add using ACF, and even more available through add-ons and extensions. The ACF documentation is a great resource for info on how to use it, and what fields are available. We’ll quickly look into some of the more commonly use field types.
Text
The text field is the most basic field you can add to a post with Advanced Custom Fields. It will accept a string of text or HTML, and can be configured to limit the length of the content, append or prepend text to the output and a few other features. You’ll use this field really often, so it’s worth being familiar with. The text field returns simply the text entered (with any modifications you have specified) and can be printed out to the screen.
Image
The image field is really easy to use and uses the built in WordPress media library functions and image selector. The image field can either return an array of image data, or the chosen image ID. The array of image data contains pretty much all the information that exists about the image, so it is really useful. Check the documentation for details on how to use it.
Gallery
The gallery field works in much the same way as the image field, but it lets you select multiple images to make up a gallery. You can change the order of the images to suit by dragging them into the order you like. My only complaint about the gallery field type is that it would be really helpful if you could add a caption to images that is not the same as the caption that is stored against the image in the media library. This would be useful if, for example, you wanted to use the same image in two galleries with a differing caption.
Link & Page Link
The link and page link field types are ways of linking to some other content. The link field is exactly the same as the link editor you use in the normal WordPress content editor and allows you to specify a URL, title and target. The page link field is slightly more restrictive and only allows you to select a page or post (or custom post type) from within your site and will return the URL for that.
Post Object
The post object field type allows you to select one or multiple posts and returns an array of all the post data. This is really useful in conjunction with a repeater field to do things like show some related posts.
Repeater
The repeater is one of a couple of field types that are reserved for users of the pro version of the plugin. It is one of the field types that I use most commonly, however, and is one of the reasons I think ACF pro is worth the purchase! The repeater basically allows you to have a group of fields that can be repeated multiple times. Let’s take my complaint about the gallery field type from above, where we’d like to have a gallery with a caption for each image. We could use a repeater which has an image field and a text field inside it. Then we can add rows to the repeater for each image and it’s caption in our gallery. This type of functionality is really great when you need to allow for repeatable content but you don’t necessarily know how much content there will be. If the concept is still a little unclear, read on to our example below.
Flexible Content
The flexible content field is another field, like the repeater, that is reserved to the pro version. I’m not going to go into too much detail here on the flexible content field, but it is really really powerful. It works a lot like the repeater field, except instead of each row being the same (e.g. image, text to use the example above) you can specify different presets that can be applied. For example I might have a row that is image & text, but the next row is a post object. It’s really useful, and can be great for building more complicated layouts like home or landing pages.
Get Started
Ok, that’s enough about the field types, let’s get straight into some examples of how to use them!
Install ACF
If you haven’t done so already, install the Advanced Custom Fields plugin. You can find it by heading into your WordPress admin, plugins, add plugin and search for ACF. Alternatively you can download it from https://ift.tt/1xnQFBZ however I highly recommend heading over to the ACF site and purchasing the pro version. Pricing is AU$25 for a single site or AU$100 for unlimited sites and it’s well worth it.
1. Getting Started + Basic: Text
We’ll start off with a really simple example to get going: adding a text field to a post. There are three parts to any ACF setup; 1) Configure your custom fields and settings in the admin panel, 2) set up your template (front end) to use your newly configured custom fields and 3) put some data in your custom fields. So we’ll start off at the beginning and configure some custom fields.
Start by logging in to your WordPress admin, then in the menu find Custom Fields and hit Add New in Field Groups. Custom fields are organised by group, and the rules for what post types etc to show the fields on are set per group. Once you’ve hit Add New you should see something like this.
Although not necessary, we’re going to start by setting a title.
Next, we’re going to add a field. Click Add Field, and set a the Field Label. In this case we’re going to create an Alternative Title for the page so that’s what we’ve called the field. Each field needs to have a unique slug, just like a post. ACF will create the slug for you from the label if it’s empty, so in this case ACF has given us “alternative_title” and we’re going to leave it that way. Finally we need to choose the Field Type. In this case we’re using a text field so go ahead and choose that (text should be the default option anyway).
There are quite a few other settings that we could set, such as some instructions that are shown to authors when setting the content, setting the field to required, setting a default value and so-on. For now we’re going to leave these as default, but feel free to have a look through and change any that you want.
Scroll down to the Location meta box. This is where we can set the rules that determine what post types, pages, etc that this field group will show up for. We want this field group to show up on normal posts, so we’re going to set Post Type equal to Post.
There is a final Settings meta box below that controls a few general settings for the field group, however for most cases the defaults will do. Leave the default settings here and hit Publish.
Next we need to set a value for our custom field so we can test. Find a post you can edit, and jump in to the editor. You should find a meta-box with the title of the field group you created in the previous step. We named ours “Test”. (We’re using WP5/Gutenberg so our meta-box is below the gutenberg editor area).
Enter a value for your Alternative Title and save your post. We’re done in WordPress for now, so fire up your favourite editor so we can edit theme files (or edit them via the WordPress appearance editor if you’re a savage like that…)
Which file to edit will depend on your theme. We want to edit the file that shows the single post title. In our case our theme uses single.php which then loads template-parts/content.php. The line we’re looking for is the_title which is the wordpress function that prints the post title. In our case our code looks like this;
<?php //template-parts/content.php ?> <article <?php post_class(); ?> id="post-<?php the_ID(); ?>"> <header class="entry-header"> <?php the_title( sprintf( '<h1 class="entry-title"><a href="%s" rel="bookmark">', esc_url( get_permalink() ) ), '</a></h1>' ); ?> </header><!-- .entry-header --> ... </article>
Let’s start very simply by refactoring this bit of code to make it accept our alternative title. We’re going to take the h1 and a tags and wrap them around the the_title call.
<article <?php post_class(); ?> id="post-<?php the_ID(); ?>"> <header class="entry-header"> <?php //Print the opening H1 and anchor echo sprintf( '<h1 class="entry-title"><a href="%s" rel="bookmark">', esc_url( get_permalink() )); //Print the title the_title( ); //CLose the anchor and H1 echo '</a></h1>' ?> </header><!-- .entry-header --> ... </article>
Ok, with that done, quickly view your post; it should all look the same. Check the source to make sure.
Now for the fun part, this is where we are actually going to use ACF. The primary function provided by ACF is get_field. Get field is a powerful and flexible function that takes one required parameter: the field slug. Using our example, we will call get_field(‘alternative_title’). We’re going to store the value returned from get_field in a variable called $alternative_title. Lastly we’ll check whether an alternative title has been set, and if so, print it. Otherwise we’ll print the original title.
<article <?php post_class(); ?> id="post-<?php the_ID(); ?>"> <header class="entry-header"> <?php //Get the alternative title $alternative_title = get_field('alternative_title'); //Print the opening H1 and anchor echo sprintf( '<h1 class="entry-title"><a href="%s" rel="bookmark">', esc_url( get_permalink() )); //Print the title if($alternative_title && !empty($alternative_title)) { //If the alternative title has been set, use that echo $alternative_title; } else { the_title( ); } //CLose the anchor and H1 echo '</a></h1>' ?> </header><!-- .entry-header --> ... </article>
And that’s it! Save your file, upload to your webserver (if running remotely), and refresh your post in the browser. You should see your alternative title in place of the post title.
2. Basic Image
Next we’re going to look at adding an image to a post. Note that realistically this is probably a waste of time as we could use the built in featured image, but just like the title, maybe we want an override for some reason.
Let’s start by configuring our custom field. Edit your field group and add a new field. We’re going to call it Alternative Image and set the slug to alternative_image. The important extra step here is to select Image for the field type.
There is one other configuration field of interest here, the Return Value. The text field type can only return text, so that’s easy. The image field can return an array, the original URL of the image, or the image ID. We’re going to use the array as that gives us the most flexibility. We could use the URL, however we lose the ability to use WordPress’ image sizes and can’t necessarily serve the best image to the user.
Click Update and save the field group. Next we need to set a value for the field so we can test. Jump back to your post editor (refresh it to see the new field if you already had it open).
Select an image to use by clicking Add Image and either uploading or selecting one from your media library. Once you’ve done that, save your post and jump back in to your editor. We need to again look for the file that outputs a single post. We’re going to print out the alternative image below the heading, but this time we’re going to ignore whether a featured image has been set. Start looking in single.php. Again, in my case, single.php loads template-parts/content.php so that’s where we’ll be working.
... </header><!-- .entry-header --> <a class="post-thumbnail" href="<?php the_permalink(); ?>" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"> <?php the_post_thumbnail( 'post-thumbnail', array( 'alt' => the_title_attribute( array( 'echo' => false, ) ), ) ); ?> </a> <div class="entry-content"> ...
In our template, we’ve got an anchor that is wrapping the post thumbnail function. What we’re going to do is add our alternative image after this.
The simplest way to print out the image HTML (and use responsive images!) is to use WordPress’ built int wp_get_attachment_image. Fortunately ACF works really well with this.
... </header><!-- .entry-header --> <a class="post-thumbnail" href="<?php the_permalink(); ?>" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"> <?php the_post_thumbnail( 'post-thumbnail', array( 'alt' => the_title_attribute( array( 'echo' => false, ) ), ) ); ?> </a> <?php //Get the image field $image = get_field('alternative_image'); $size = 'full'; // (thumbnail, medium, large, full or custom size) if( $image ) { //Print the image HTML (responsive) echo wp_get_attachment_image( $image['ID'], $size ); } ?> <div class="entry-content"> ...
Save your code, upload and refresh your post. You should see your alternative image! Easy as.
Summary
ACF can completely change the way WordPress can be used to manage website content. Hopefully this guide on how to use Advanced Custom Fields has helped you learn! The ACF website has some great examples on how to use the various field types, as well as a list of code examples, so don’t forget to check that out as well.
The post How To Use Advanced Custom Fields (ACF) in WordPress appeared first on The Coding Bus.
from WordPress https://ift.tt/32RRx8I via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
isset() and unset() Function In PHP – Examples
isset() and unset() Function In PHP – Examples
PHP isset () and unset () Function. In this tutorial, we would lo
Also, this tutorial teaches you, how to use isset () in PHP Forms and how to check unset function arrays in PHP.
You should also read this php post: PHP empty () – Check Variable is Empty in PHP
isset and unset Function in PHP
H
PHP isset () Function
isset () function in PHP is used to check whether a variable is set or not. This…
View On WordPress
#difference between isset and unset#difference between isset and unset in php#isset and unset#isset and unset function in php#isset and unset in php#isset unset empty php#isset unset session
0 notes
Text
Use MySQL BLOB column with PHP to store .pdf file
Like always I am sharing new things I learn here on my blog. I was recently working on a requirement for a LAMP stack web application reporting dashboard in which I needed to store – and eventually – retrieve a .pdf file. I have read in several places (this fantastic book is a great resource) that a viable option is storing images or documents (.pdf in this case) in the actual database table as opposed to on the server file system. MySQL has the BLOB datatype that can be used to store files such as .pdf, .jpg, .txt, and the like. In this blog post, I cover how I accomplished uploading and storing the actual .pdf file in a BLOB column in MySQL using PHP. Any corrections, tips, pointers, and recommendations for best practices are always welcome. We all learn as we go!!! Photo by Laika Notebooks on Unsplash Self-Promotion: If you enjoy the content written here, by all means, share this blog and your favorite post(s) with others who may benefit from or like it as well. Since coffee is my favorite drink, you can even buy me one if you would like! I am using a table named ‘project_pdf’ with 3 columns (see accompanying screenshot) to store the data: ‘id’: type INTEGER ‘project_name’: type TEXT ‘pdf_doc’: type BLOB Table structure for the project_pdf table. With the below simple HTML web form, we can collect the ‘project_name’ and enable the .pdf file attachment upload: Simple web form to upload a pdf to the database. Below is the HTML source code for the above web form:
Upload PDF
Upload A PDF To The Database
Project Name
Submit To Database
Looking at the code… We will use this PHP code stored in a script submit.php – which is the form action – along with some best practices utilizing if/else conditional blocks and wrapping all of the database operations in a try/catch block to complete the .pdf INSERT in the MySQL BLOB column: <!?phpif (isset($_POST['submit']) && !empty($_FILES['pdf_file']['name'])) { //a $_FILES 'error' value of zero means success. Anything else and something wrong with attached file. if ($_FILES['pdf_file']['error'] != 0) { echo 'Something wrong with the file.'; } else { //pdf file uploaded okay. //project_name supplied from the form field $project_name = htmlspecialchars($_POST['project_name']); //attached pdf file information $file_name = $_FILES['pdf_file']['name']; $file_tmp = $_FILES['pdf_file']['tmp_name']; if ($pdf_blob = fopen($file_tmp, "rb")) { try { include __DIR__."/includes/DatabaseConnection.php"; $insert_sql = "INSERT INTO `project_pdf` (`project_name`, `pdf_doc`) VALUES(:project_name, :pdf_doc);"; $stmt = $pdo->prepare($insert_sql); $stmt->bindParam(':project_name', $project_name); $stmt->bindParam(':pdf_doc', $pdf_blob, PDO::PARAM_LOB); if ($stmt->execute() === FALSE) { echo 'Could not save information to the database'; } else { echo 'Information saved'; } } catch (PDOException $e) { echo 'Database Error '. $e->getMessage(). ' in '. $e->getFile(). ': '. $e->getLine(); } } else { //fopen() was not successful in opening the .pdf file for reading. echo 'Could not open the attached pdf file'; } }} else { //submit button was not clicked. No direct script navigation. header('Location: choose_file.php');} Verify the button is clicked and a file is attached The first if/else block verifies that the ‘submit’ button from the form has been clicked and that the ‘pdf_file’ field has an attachment using the PHP functions isset() and empty() (the converse of truth by negating with the not ! operator for the empty() function): 1 isset($_POST['submit']) && !empty($_FILES['pdf_file']['name'])) Tip: More validation can be implemented here to verify the file type is an actual .pdf since that file type is what we are expecting to store in the database. Informational: Visit the official PHP online documentation for more information on isset() and empty(). Check PHP $_FILES array for errors The $_FILES array provides several related error codes for file attachments. A value of 0 (zero) means everything is okay with the file and it is successfully uploaded. In this particular if/else, block if that value is not 0 (zero), then we echo in the browser that something is wrong with the file upload: 1 $_FILES['pdf_file']['error'] != 0 Related: See the official PHP online documentation for more information on file upload errors. PHP $_POST and $_FILES Data The $_POST associative array has the value for the ‘project_name’ input field captured in the form and sent through the HTTP POST method. Likewise, the $_FILES associative array has several values for a file or attachment. I am assigning 2 of them to variables, but using only one – ['tmp_name'] – in the subsequent code: ['name'] – The actual file name from the client. (Could be used in a file name column if needed ['tmp_name'] – Temporary file name of the uploaded file as stored on the server. 123 $project_name = htmlspecialchars($_POST['project_name']);$file_name = $_FILES['pdf_file']['name'];$file_tmp = $_FILES['pdf_file']['tmp_name']; Related: Read more about POST upload methods in the official online PHP documentation. Read in .pdf binary data and prepare to store in MySQL BLOB column with PHP The call to fopen() reads in the file in binary format ("rb") into a ‘$pdf_blob’ variable. If fopen() cannot open the file, this if/else block echo‘s the message in the else block to the browser: 1 $pdf_blob = fopen($file_tmp, "rb") MySQL database connection and prepared statements Finally, we look at the entire try/catch block. I have all database connection information stored in a separate file named DatabaseConnection.php and include it in the script at this point using the include directive. Since we are introducing user-supplied input from the web form into the database, we use prepared statements leveraging the PHP PDO methods: prepare() bindParam() execute() INSERT .pdf file into MySQL BLOB column with PHP If the call to execute() is not successful, we echo a message to the browser that the information could not be saved. Otherwise, the data is successfully inserted and we echo ‘Information saved’: 12345678910111213141516171819 try { include __DIR__."/includes/DatabaseConnection.php"; $insert_sql = "INSERT INTO `project_pdf` (`project_name`, `pdf_doc`) VALUES(:project_name, :pdf_doc);"; $stmt = $pdo->prepare($insert_sql); $stmt->bindParam(':project_name', $project_name); $stmt->bindParam(':pdf_doc', $pdf_blob, PDO::PARAM_LOB); if ($stmt->execute() === FALSE) { echo 'Could not save information to the database'; } else { echo 'Information saved'; }} catch (PDOException $e) { echo 'Database Error '. $e->getMessage(). ' in '. $e->getFile(). ': '. $e->getLine(); } Note: It is generally not a good practice to echo any sort of database error information to the browser. Errors should be written to a log file instead. However, for the purpose of this blog post as a learning experience, I echo out any exceptions that may arise in the catch block. Using the form to store .pdf in MySQL BLOB column with PHP Let’s try out the form and PHP code to verify the upload works. Here is a simple sample .pdf file I created for a demo run: Contents of SamplePDF.pdf document to upload with form. See this screenshot in which I fill in the ‘project name’ field with a generic ‘First Project’ name and attach the SimplePDF.pdf file: Filled out web form with pdf attachment for upload. Upon clicking the ‘Submit’ button, the information is successfully stored in the database and the success message is displayed in the browser: Message displayed in the browser after successful pdf upload. Here is the data saved in the MySQL database table from the successful upload via our web form and the PHP code: The project_pdf table with inserted pdf and project name. It works!!! In the next blog post, I will cover how to retrieve the .pdf file from the database and display it in the browser. If you see anything in the code that I can improve on or any mistake, please let me know via the comments section below. Additional PHP/MySQL Reading Be sure and visit these other blog posts I have written on PHP and MySQL: PHP PDO lastInsertId() method with examples in MySQL Beginning Perspective on PHP Arrays Sorting associative arrays in PHP with array_multisort() – New learning Dynamic HTML drop-down with PHP and MySQL Like what you have read? See anything incorrect? Please comment below and thanks for reading!!! A Call To Action! Thank you for taking the time to read this post. I truly hope you discovered something interesting and enlightening. Please share your findings here, with someone else you know who would get the same value out of it as well. Visit the Portfolio-Projects page to see blog post/technical writing I have completed for clients. To receive email notifications (Never Spam) from this blog (“Digital Owl’s Prose”) for the latest blog posts as they are published, please subscribe (of your own volition) by clicking the ‘Click To Subscribe!’ button in the sidebar on the homepage! (Feel free at any time to review the Digital Owl’s Prose Privacy Policy Page for any questions you may have about: email updates, opt-in, opt-out, contact forms, etc…) Be sure and visit the “Best Of” page for a collection of my best blog posts. Josh Otwell has a passion to study and grow as a SQL Developer and blogger. Other favorite activities find him with his nose buried in a good book, article, or the Linux command line. Among those, he shares a love of tabletop RPG games, reading fantasy novels, and spending time with his wife and two daughters. Disclaimer: The examples presented in this post are hypothetical ideas of how to achieve similar types of results. They are not the utmost best solution(s). The majority, if not all, of the examples provided, is performed on a personal development/learning workstation-environment and should not be considered production quality or ready. Your particular goals and needs may vary. Use those practices that best benefit your needs and goals. Opinions are my own. The post Use MySQL BLOB column with PHP to store .pdf file appeared first on Digital Owl's Prose. https://joshuaotwell.com/use-mysql-blob-column-with-php-to-store-pdf-file/
0 notes