#php foreach syntax
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Complete PHP Tutorial: Learn PHP from Scratch in 7 Days
Are you looking to learn backend web development and build dynamic websites with real functionality? You’re in the right place. Welcome to the Complete PHP Tutorial: Learn PHP from Scratch in 7 Days — a practical, beginner-friendly guide designed to help you master the fundamentals of PHP in just one week.
PHP, or Hypertext Preprocessor, is one of the most widely used server-side scripting languages on the web. It powers everything from small blogs to large-scale websites like Facebook and WordPress. Learning PHP opens up the door to back-end development, content management systems, and full-stack programming. Whether you're a complete beginner or have some experience with HTML/CSS, this tutorial is structured to help you learn PHP step by step with real-world examples.
Why Learn PHP?
Before diving into the tutorial, let’s understand why PHP is still relevant and worth learning in 2025:
Beginner-friendly: Easy syntax and wide support.
Open-source: Free to use with strong community support.
Cross-platform: Runs on Windows, macOS, Linux, and integrates with most servers.
Database integration: Works seamlessly with MySQL and other databases.
In-demand: Still heavily used in CMS platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal.
If you want to build contact forms, login systems, e-commerce platforms, or data-driven applications, PHP is a great place to start.
Day-by-Day Breakdown: Learn PHP from Scratch in 7 Days
Day 1: Introduction to PHP & Setup
Start by setting up your environment:
Install XAMPP or MAMP to create a local server.
Create your first .php file.
Learn how to embed PHP inside HTML.
Example:
<?php echo "Hello, PHP!"; ?>
What you’ll learn:
How PHP works on the server
Running PHP in your browser
Basic syntax and echo statement
Day 2: Variables, Data Types & Constants
Dive into PHP variables and data types:
$name = "John"; $age = 25; $is_student = true;
Key concepts:
Variable declaration and naming
Data types: String, Integer, Float, Boolean, Array
Constants and predefined variables ($_SERVER, $_GET, $_POST)
Day 3: Operators, Conditions & Control Flow
Learn how to make decisions in PHP:
if ($age > 18) { echo "You are an adult."; } else { echo "You are underage."; }
Topics covered:
Arithmetic, comparison, and logical operators
If-else, switch-case
Nesting conditions and best practices
Day 4: Loops and Arrays
Understand loops to perform repetitive tasks:
$fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"]; foreach ($fruits as $fruit) { echo $fruit. "<br>"; }
Learn about:
for, while, do...while, and foreach loops
Arrays: indexed, associative, and multidimensional
Array functions (count(), array_push(), etc.)
Day 5: Functions & Form Handling
Start writing reusable code and learn how to process user input from forms:
function greet($name) { return "Hello, $name!"; }
Skills you gain:
Defining and calling functions
Passing parameters and returning values
Handling HTML form data with $_POST and $_GET
Form validation and basic security tips
Day 6: Working with Files & Sessions
Build applications that remember users and work with files:
session_start(); $_SESSION["username"] = "admin";
Topics included:
File handling (fopen, fwrite, fread, etc.)
Reading and writing text files
Sessions and cookies
Login system basics using session variables
Day 7: PHP & MySQL – Database Connectivity
On the final day, you’ll connect PHP to a database and build a mini CRUD app:
$conn = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "", "mydatabase");
Learn how to:
Connect PHP to a MySQL database
Create and execute SQL queries
Insert, read, update, and delete (CRUD operations)
Display database data in HTML tables
Bonus Tips for Mastering PHP
Practice by building mini-projects (login form, guest book, blog)
Read official documentation at php.net
Use tools like phpMyAdmin to manage databases visually
Try MVC frameworks like Laravel or CodeIgniter once you're confident with core PHP
What You’ll Be Able to Build After This PHP Tutorial
After following this 7-day PHP tutorial, you’ll be able to:
Create dynamic web pages
Handle form submissions
Work with databases
Manage sessions and users
Understand the logic behind content management systems (CMS)
This gives you the foundation to become a full-stack developer, or even specialize in backend development using PHP and MySQL.
Final Thoughts
Learning PHP doesn’t have to be difficult or time-consuming. With the Complete PHP Tutorial: Learn PHP from Scratch in 7 Days, you’re taking a focused, structured path toward web development success. You’ll learn all the core concepts through clear explanations and hands-on examples that prepare you for real-world projects.
Whether you’re a student, freelancer, or aspiring developer, PHP remains a powerful and valuable skill to add to your web development toolkit.
So open up your code editor, start typing your first <?php ... ?> block, and begin your journey to building dynamic, powerful web applications — one day at a time.

0 notes
Video
youtube
Tech talk with Arcoiris Logics #mobileappdevelopment #webinsights #codin...
Hidden Laravel Tips to Boost Your Development Workflow
Laravel is a popular choice among developers for web application development due to its elegant syntax and powerful toolkit. However, some lesser-known tips can take your Laravel development to the next level. In this article, we’ll share hidden Laravel tips that can streamline your workflow and enhance application performance.
1. Use Eloquent's $with Property to Reduce Queries
In Laravel, eager loading is essential for performance optimization. Setting $with in your Eloquent model avoids repetitive calls to the database and reduces N+1 issues.
phpCopy codeprotected $with = ['relation1', 'relation2'];
By including relations directly in your models, you’ll cut down on the database queries, improving the speed of your applications significantly.
2. Speed Up Route Caching for Production
When deploying your Laravel application, optimize your routes for production by using Laravel's route caching. It’s one of the fastest ways to make your routes more efficient.
bashCopy codephp artisan route:cache
This command compiles all of your application’s routes into a single file for faster execution, which is beneficial for high-traffic applications.
3. Utilize @once Directive for Blade Templates
If you need a piece of code to execute only once within a loop, Laravel’s @once directive can be a game-changer.
phpCopy code@once <script> // JavaScript or any other code that should only run once </script> @endonce
Using @once is a clever way to prevent redundant code execution, especially when working with loops in Blade templates.
4. Customize Your Exception Handler
Laravel provides a flexible exception handler. For example, custom logic can help differentiate between user errors and system errors, directing the user experience smoothly.
phpCopy codepublic function render($request, Exception $exception) { if ($exception instanceof CustomException) { return response()->view('errors.custom', [], 500); } return parent::render($request, $exception); }
Customized error handling can improve the overall user experience and ensure smoother application performance.
5. Optimize Database Performance with Query Chunking
Large datasets can often overwhelm your memory. Laravel’s chunk function helps in processing data in smaller parts, preventing memory exhaustion.
phpCopy codeDB::table('users')->chunk(100, function ($users) { foreach ($users as $user) { // Process user } });
Using chunking is essential when dealing with extensive datasets, as it allows your application to manage memory efficiently.
Boost Your Laravel Expertise Today
These hidden Laravel tips can significantly boost your productivity and app performance. Whether you're optimizing database queries or refining Blade templates, implementing these tips will help you build faster, more reliable Laravel applications.
Explore more tech tips and services at Arcoiris Logics!
#LaravelTips #WebDevelopment #PHP #Eloquent #BladeTemplates #WebAppOptimization #TechTips #DevelopersLife #CodeOptimization #ArcoirisLogics #LaravelCommunity
0 notes
Text

Understanding Laravel Blade: Templates and Directives - Sohojware
Laravel Blade, a templating engine for the Laravel PHP framework, simplifies the process of creating dynamic and visually appealing web applications. It offers a clean syntax that integrates seamlessly with Laravel’s features, allowing developers to focus on building exceptional user experiences. This article from Sohojware, a leading web development company, dives deep into the world of Laravel Blade, exploring its core functionalities — templates and directives.
Templates: The Foundation of Laravel Blade
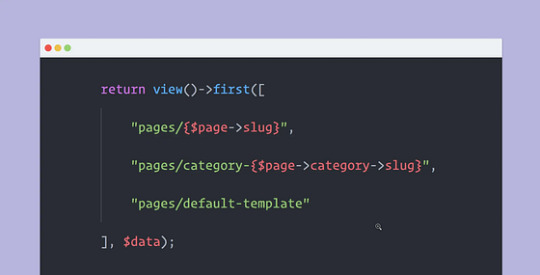
Here’s a breakdown of how Blade templates work:
Content Sections: Blade templates are divided into sections using directives like @section and @endsection. These sections allow you to create reusable components, promoting code maintainability and reducing redundancy.
Layouts: Imagine a master page that serves as the foundation for all your application’s views. This is precisely what Layouts are in Laravel Blade. You can define a layout template and extend it within other Blade templates, inheriting the common layout elements while customizing specific content sections.
Inheritance: Building upon layouts, Blade allows inheritance between templates. This enables you to create a base layout template with shared elements like headers, footers, and navigation bars. Individual views can then extend this layout, focusing solely on the content unique to each page.
Sohojware’s experienced Laravel developers can help you leverage Blade templates effectively to craft well-organized and maintainable applications.
Directives: The Powerhouse of Blade Templates
Directives are special instructions embedded within Blade templates that extend their capabilities beyond basic HTML. These directives, identified by the @ symbol, interact with Laravel’s functionalities to generate dynamic content.
Let’s explore some commonly used Laravel Blade directives:
@yield: This directive is used within layouts to insert content from sections defined in views that extend the layout. It ensures that the appropriate content is displayed in the designated areas of your application’s interface.
@section: As mentioned earlier, this directive marks the beginning of a reusable content section within a Blade template.
@endsection: This directive signifies the end of a content section defined using @section.
@include: This directive allows you to include another Blade template within the current template. This promotes code reusability and simplifies complex layouts.
@if, @else, @endif: These directives provide conditional logic within Blade templates. You can use them to display content based on specific conditions within your application.
@foreach, @endforeach: Laravel Blade offers powerful looping capabilities through these directives. You can iterate through collections of data and dynamically generate content for each item.
Sohojware’s team of Laravel experts can guide you in mastering these directives and unlocking the full potential of Blade templating.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Blade Techniques
While the core concepts of templates and directives form the foundation of Laravel Blade, there’s a treasure trove of advanced techniques to further enhance your development experience. Here are a few noteworthy examples:
Slots: Slots provide an alternative approach to content sections, offering more granular control over where content is placed within a layout.
Components: Blade allows you to define reusable components that encapsulate both HTML structure and logic, promoting a more modular development approach.
Mixins: Mixins are reusable code blocks that can be included in multiple Blade templates, reducing code duplication and improving maintainability.
Sohojware’s Laravel development services can empower you to leverage these advanced Blade techniques to build scalable and efficient web applications.
FAQs on Laravel Blade (Sohojware)
What are the benefits of using Laravel Blade?
Laravel Blade offers several advantages, including:
Clean and expressive syntax: Blade’s syntax integrates seamlessly with PHP, making it easy to learn and use.
Separation of concerns: Blade templates separate presentation logic from business logic, promoting code maintainability.
Reusable components: Sections, layouts, and other features encourage code reusability, reducing development time and effort.
Dynamic content generation: Laravel Blade empowers you to create dynamic and interactive web applications.
Is Laravel Blade difficult to learn?
The core concepts of Laravel Blade are relatively easy to grasp, especially for developers with experience in PHP and templating engines. Sohojware’s team can provide comprehensive guidance and support to help you master Blade effectively.
What are some real-world applications of Laravel Blade?
Laravel Blade is widely used to build various web applications, including:
E-commerce platforms: Blade’s templating capabilities facilitate the creation of dynamic product catalogs, shopping carts, and checkout pages.
Content management systems (CMS): Blade simplifies the development of CMS interfaces, allowing content editors to easily manage website content.
Social media platforms: Blade can be used to build user profiles, news feeds, and other interactive features of social media applications.
Enterprise applications: Blade’s flexibility and scalability make it suitable for developing complex enterprise-level web applications.
Can I use Laravel Blade with other PHP frameworks?
While Laravel Blade is primarily designed for Laravel, it’s possible to integrate it into other PHP frameworks with some modifications. However, it’s generally recommended to stick with Laravel for a seamless development experience.
How can Sohojware help me with Laravel Blade development?
Sohojware’s team of experienced Laravel developers can provide comprehensive services related to Laravel Blade, including:
Custom template design: Our designers can create visually appealing and user-friendly templates tailored to your specific requirements.
Template optimization: We can optimize your Blade templates for performance and SEO.
Component development: We can build reusable components to streamline your development process.
Integration with other Laravel features: We can seamlessly integrate Blade with other Laravel functionalities like routing, authentication, and database interactions.
By partnering with Sohojware, you can leverage the power of Laravel Blade to create exceptional web applications that meet your business goals.
Conclusion
Laravel Blade is a powerful and versatile templating engine that simplifies the development of web applications. Its clean syntax, reusable components, and integration with Laravel’s features make it a popular choice among developers. By understanding the core concepts of templates and directives, and exploring advanced techniques, you can unlock the full potential of Laravel Blade and build exceptional web applications.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Loops in php with syntax and examples
Loops in php with syntax and examples Loops are used to execute a block of code repeatedly for a specified number of times or until a certain condition is met. PHP supports several types of loops: For Loop: Syntax: for (init; condition; increment) { code } Example: for ($i = 0; $i < 5; $i++) { echo $i; } Foreach Loop: Syntax: foreach (array as value) { code } Example: $fruits =…
0 notes
Text
Mastering PHP: The Ultimate Guide for Aspiring Expert PHP Developers

Introduction
Welcome to CompleteGurus, your go-to resource for all things tech! Today, we’re diving into the world of PHP development. Whether you’re a novice just starting out or an experienced coder looking to level up, becoming an expert PHP developer requires dedication, continuous learning, and practical experience. Let’s explore the roadmap to mastering PHP and the essential skills every expert PHP developer should have. #expertPHPdeveloper
Understanding the Basics
What is PHP?
PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) is a widely-used, open-source scripting language designed for web development. It’s embedded in HTML and is known for its efficiency in handling dynamic content, databases, and session tracking.
Why PHP?
Ease of Use: PHP’s syntax is easy to understand and learn, making it a favorite among beginners.
Community Support: A large, active community provides extensive resources, frameworks, and libraries.
Compatibility: PHP is compatible with various servers and databases, including Apache, Nginx, MySQL, and PostgreSQL.
Performance: PHP is fast and efficient, especially when it comes to handling server-side scripting.
Building a Strong Foundation
Learning the Language
To become an expert, you must have a thorough understanding of PHP’s syntax, functions, and features. Here are some key areas to focus on:
Variables and Data Types: Understand how to declare and use different data types.
Control Structures: Master if-else statements, switch cases, loops (for, while, foreach).
Functions: Learn to create and use functions, including variable scope and anonymous functions.
Arrays and Strings: Work extensively with arrays (indexed, associative, multidimensional) and string manipulation functions.
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
OOP is a critical aspect of advanced PHP development. Ensure you understand the following concepts:
Classes and Objects: Learn how to define and instantiate classes.
Inheritance: Understand how child classes inherit properties and methods from parent classes.
Encapsulation: Learn to protect the state of an object using access modifiers.
Polymorphism: Understand how objects can take on many forms through interfaces and abstract classes.
Advanced PHP Development
Frameworks
To streamline development and maintain code quality, familiarize yourself with popular PHP frameworks:
Laravel: Known for its elegant syntax and powerful features, Laravel is a favorite among developers.
Symfony: Offers a robust set of reusable PHP components and a modular architecture.
CodeIgniter: Lightweight and straightforward, ideal for small to medium projects.
Working with Databases
An expert PHP developer must be proficient in database management:
SQL: Master SQL queries to interact with databases.
PDO and MySQLi: Learn to use PHP Data Objects (PDO) and MySQLi for secure and efficient database operations.
ORM: Understand Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) with tools like Eloquent in Laravel.
Security Practices
Security is paramount in web development. Ensure you follow best practices:
Data Sanitization and Validation: Always sanitize and validate user inputs.
Prepared Statements: Use prepared statements to prevent SQL injection.
Password Hashing: Securely store passwords using hashing algorithms like bcrypt.
HTTPS: Ensure secure data transmission by implementing HTTPS.
Testing and Debugging
Quality assurance is essential. Learn to:
Unit Testing: Write unit tests to ensure code reliability using PHPUnit.
Debugging: Use debugging tools and techniques to identify and fix issues.
Version Control: Use Git for version control and collaboration.
Continuous Learning and Community Engagement
Stay Updated
The tech world evolves rapidly. Stay ahead by:
Reading Blogs: Follow blogs and forums like CompleteGurus, PHP.net, and Stack Overflow.
Attending Conferences: Participate in PHP conferences and meetups.
Taking Courses: Enroll in advanced PHP courses on platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and LinkedIn Learning.
Contribute to the Community
Open Source Projects: Contribute to open-source projects to gain real-world experience.
Writing and Speaking: Share your knowledge through blogging, speaking at events, or creating tutorials.
Networking: Connect with other developers, join PHP groups, and participate in discussions.
Conclusion
Becoming an expert PHP developer is a journey that involves mastering the language, understanding advanced concepts, and continuously learning. By following this roadmap and engaging with the community, you'll hone your skills and stay at the forefront of PHP development. Ready to take the next step? Dive into the resources available here at CompleteGurus and embark on your path to becoming an #expertPHPdeveloper!
0 notes
Text
Mastering PHP: A Complete Guide to PHP Certification Course
In the fast-evolving world of web development, PHP remains a cornerstone technology powering millions of websites across the globe. Despite the rise of newer programming languages and frameworks, PHP holds its ground thanks to its simplicity, flexibility, and wide adoption. If you’re looking to build a strong foundation in backend development, enrolling in a PHP Certification Course is a smart step toward a rewarding career. This article explores everything you need to know about PHP, the benefits of getting certified, course content, career prospects, and tips for choosing the right program.
What is PHP?
PHP, or Hypertext Preprocessor, is a widely-used open-source server-side scripting language. Designed specifically for web development, it can be embedded within HTML and used to manage dynamic content, session tracking, databases, and even build entire e-commerce websites.
Created by Rasmus Lerdorf in 1994, PHP has undergone numerous improvements and currently powers platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Magento. It's also integrated seamlessly with databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle, making it a go-to language for developers.
Why Get PHP Certified?
A PHP Certification is more than just a document – it validates your knowledge and skills, offering tangible proof of your ability to potential employers or clients. Here's why pursuing a PHP certification course can be a game-changer:
1. Structured Learning
A certification course provides a structured learning path from basics to advanced topics. This approach ensures that you understand core concepts such as syntax, loops, and functions before moving on to complex subjects like object-oriented programming (OOP), database integration, and security.
2. Industry Recognition
A certification from a reputable institution adds value to your resume and signals to employers that you have formal training and a serious attitude toward your professional development.
3. Hands-On Experience
Most PHP certification programs include practical assignments and projects. These real-world applications strengthen your understanding and prepare you for actual development work.
4. Career Advancement
Whether you're a fresher or an experienced developer looking to upskill, a PHP certification can open doors to better job opportunities, freelance gigs, and even entrepreneurial ventures.
Who Should Take a PHP Certification Course?
A PHP certification course is ideal for:
Students in computer science or IT who want to enhance their web development skills.
Aspiring web developers looking to specialize in backend development.
Freelancers who want to offer dynamic website creation as a service.
Software professionals seeking to diversify their skill set.
Entrepreneurs or business owners who want to build or manage their websites without depending entirely on developers.
No prior programming experience is strictly necessary, though familiarity with HTML and basic coding concepts is helpful.
What Does a PHP Certification Course Cover?
While the syllabus may vary depending on the institution or online platform, most certification courses include the following key modules:
1. Introduction to PHP
History and evolution of PHP
Server vs. client-side scripting
Installing and configuring PHP
2. PHP Basics
Syntax and variables
Data types
Operators and expressions
Conditional statements (if, else, switch)
Loops (for, while, foreach)
3. Functions and Arrays
Creating and invoking functions
Built-in functions
Recursive functions
Indexed, associative, and multidimensional arrays
4. Forms and User Input
Handling GET and POST requests
Validating form data
Sanitization and security
5. Working with Databases
Introduction to MySQL
Connecting PHP to MySQL
Executing queries (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE)
Prepared statements and data sanitization
6. Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in PHP
Classes and objects
Constructors and destructors
Inheritance, encapsulation, and polymorphism
7. File Handling and Session Management
Reading and writing files
Cookies and sessions
Authentication and authorization
8. Advanced Topics
MVC architecture
Using PHP with AJAX and JavaScript
Error handling and debugging
Web services and APIs
9. Capstone Project
Most courses include a final project, such as building a blog, e-commerce website, or content management system, which allows learners to apply everything they’ve learned.
Choosing the Right PHP Certification Course
With countless options available, selecting the right course can be overwhelming. Here are a few tips to guide your decision:
1. Accreditation and Recognition
Choose a course offered by a recognized institution or reputed online platform like Coursera, Udemy, LinkedIn Learning, or a local university or training center.
2. Comprehensive Curriculum
Ensure the course covers both basic and advanced concepts, as well as real-world projects.
3. Qualified Instructors
Check the background of the instructors. Look for experienced developers or educators with practical industry knowledge.
4. Hands-on Learning
The best courses offer practical coding exercises, quizzes, and projects, not just theoretical lessons.
5. Support and Community
Access to mentors, forums, and peer groups can enhance your learning experience, especially when you run into coding challenges.
Top Online Platforms Offering PHP Certification
Here are a few popular online learning platforms that offer high-quality PHP certification courses:
Udemy – Offers beginner to advanced courses with lifetime access.
Coursera – Includes PHP courses from universities like the University of Michigan.
edX – Offers structured programs, often in collaboration with institutions.
LinkedIn Learning – Ideal for professionals looking to upskill quickly.
W3Schools – Offers beginner-friendly content and an exam for certification.
Career Opportunities After PHP Certification
A PHP certification can qualify you for a wide range of roles in web development. Some of the most common job titles include:
PHP Developer
Backend Developer
Full Stack Developer
Web Developer
Software Engineer
WordPress Developer
Freelance Web Developer
According to industry data, PHP developers can earn between $50,000 to $100,000 annually, depending on location, experience, and specialization.
Additionally, PHP skills are in demand for freelance work, remote development positions, and building personal projects or startups.
Final Thoughts
The digital economy is booming, and web development remains at the core of this growth. PHP continues to play a crucial role in web applications, and having formal training in this technology can give you a significant edge in the job market.
A PHP Certification Course not only equips you with practical skills but also enhances your credibility as a developer. Whether you're just starting your tech career or seeking to advance in it, this certification can be a stepping stone to many professional opportunities.
Take the leap today—invest in learning PHP and unlock your potential in the world of web development.
#php certification course#PHP Training in Chandigarh#Python Training in Chandigarh#CCNA Training in Chandigarh
0 notes
Link
Java program to generate the Fibonacci series is a program design employed in the codings. where the past two components combine to frame the new component. Initialise the opening and the following number to 0 and 1.
0 notes
Text
How To Create Custom Blade Directive in Laravel 10 Tutorial
Inside this article we will see the concept of How To Create Custom Blade Directive in Laravel 10 Tutorial. Article contains classified information about How to register custom blade directive in Laravel Application.
Laravel Blade is a templating engine that compiles its special syntax back into PHP and HTML. Its special syntax includes directives. Directives are sugar-added functions hiding complex or ugly code behind them.
Few laravel directives are @if, @foreach, @csrf ,etc
https://bit.ly/40XPaNk
0 notes
Text
How to use foreach in php - A Complete Guide
Foreach is a very useful construct in PHP that allows you to loop through arrays and other iterable data structures. Here is a complete guide on how to use foreach in PHP: Basic syntax The basic syntax of foreach in PHP is as follows: php foreach ($array as $value) { // code to execute } In the above code, $array is the array you want to loop through, and $value is a variable that represents the…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
【 PHP 】PHP8に入門してみた 93日目 PHPの基本 ( 制御構文 Alternate syntax! )
【 PHP 】PHP8に入門してみた 93日目 PHPの基本 ( 制御構文 Alternate syntax! )
PHP8技術者認定初級試験 が始まるようなので 試験に向けて (できるだけ)勉強しようと思います! 使用する書籍は独習PHP 第4版(山田 祥寛)|翔泳社の本 (shoeisha.co.jp) となります。 制御構文 別の世界 if,switch,while,for,foreachの命令は中カッコを記述して処理を記述することで処理を制御しました。 実はPHPではこれらの命令において、中カッコ以外の表現方法があるというのです😮 PHPでは、中カッコの{の代わりに:(コロン)をしようし、中カッコの}にendxx;で制御構文を表現できます。 xxの部分は命令によって異なります。例えばif命令ならendif;という具合です。 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="ja"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
JetBrains PhpStorm 3.1.2021 Free License [LATEST]

JetBrains PhpStorm Crack supplies an editor application for PHP, HTML, SQL, and JavaScript with on-the-fly code evaluation, error avoidance, and automatic refactorings feature such as PHP and JavaScript code. Using this PhpStorm you can easily create your own website or apps for android devices or pc.
JetBrains PhpStorm Crack With License Key
JetBrains PhpStorm Crack is a code conclusion that supports PHP 5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6 & 7.0 (contemporary and heritage projects), such as generators, coroutines, the last keyword, listing in foreach, namespaces, closures, characteristics, and brief array syntaxes. It features a full-size SQL editor using editable question success.JetBrains PhpStorm License Key is developed on IntelliJ IDEA, which can be written in JavaScript. Users may expand the Smart PHP IDE by installing plugins made to your IntelliJ Platform or compose their plugins On their sites.
All features offered in WebStorm are contained in PhpStorm, which provides support for PHP and databases. WebStorm ships using pre-installed JavaScript plugins and many more that can be supplied for JetBrains PhpStorm Free Download without any cost. Additionally, it includes giving the advice, code for users automated complete code quality exert evaluation troubleshooting code mistakes that occur during the cade, and many more.JetBrains PhpStorm Free Download PhpStorm 2021 is a remarkable application for PHP development language that is predicated on the JetBrains IntelliJ IDEA platform.
It’s packed with the attributes that are contained in the JetBrains WebStorm Download. This app has that innovative navigation that’s contained in another JetBrains IDEs.You can easily boost up your efficiency and productivity for both programmers. It’s a sophisticated PHP editor also supports various languages of HTML, JavaScript, and CSS. The conclusion of code for programming of different DOM-based programming languages.It’s graphical and visual debugging capabilities and contains instantaneous and offline editing of code in Browser.
You do not need to reload every single time to the editing of code. It offers tools and facilities for working with many different databases.Webstorm Crack Reddit contemporary (IDE). It is an editor to the PHP, code, and all of the languages which are front-end. It gives code decisions, goals, syntax highlighting & refactoring, reviews, and code quality evaluation.The application also contains code partitioning & zero-configuration debugging, unit analysis profiling, fashions, and several other capabilities. JetBrains PhpStorm License Key provides the code conclusion that’s refactorings, on-the-fly error avoidance,m better, and much more.
DOWNLOAD NOW
0 notes
Photo

PHP Control Structures and Loops: if, else, for, foreach, while, and More
Today, we're going to discuss control structures and loops in PHP. I'll show you how to use all the main control structures that are supported in PHP, like if, else, for, foreach, while, and more.
What Is a Control Structure?
In simple terms, a control structure allows you to control the flow of code execution in your application. Generally, a program is executed sequentially, line by line, and a control structure allows you to alter that flow, usually depending on certain conditions.
Control structures are core features of the PHP language that allow your script to respond differently to different inputs or situations. This could allow your script to give different responses based on user input, file contents, or some other data.
The following flowchart explains how a control structure works in PHP.
As you can see in the above diagram, first a condition is checked. If the condition is true, the conditional code will be executed. The important thing to note here is that code execution continues normally after conditional code execution.
Let's consider the following example.
In the above example, the program checks whether or not the user is logged in. Based on the user's login status, they will be redirected to either the Login page or the My Account page. In this case, a control structure ends code execution by redirecting users to a different page. This is a crucial ability of the PHP language.
PHP supports a number of different control structures:
if
else
elseif
switch
while
do-while
for
foreach
and more
Let's take a look at a few of these control structures with examples.
Learning PHP Control Structures
In the previous section, we learned the basics of control structures in PHP and their usefulness in application development. In this section, we'll go through a couple of important control structures that you'll end up using frequently in your day-to-day application development.
PHP If Statement
The if construct allows you to execute a piece of code if the expression provided along with it evaluates to true.
Let's have a look at the following example to understand how it actually works.
<?php $age = 50; if ($age > 30) { echo "Your age is greater than 30!"; } ?>
The above example should output the Your age is greater than 30! message since the expression evaluates to true. In fact, if you want to execute only a single statement, the above example can be rewritten as shown in the following snippet without brackets.
<?php $age = 50; if ($age > 30) echo "Your age is greater than 30!"; ?>
On the other hand, if you have more than one statements to execute, you must use brackets, as shown in the following snippet.
<?php if (is_array($user)) { $user_id = isset($user['user_id']) ? $user['user_id'] : ''; $username = isset($user['username']) ? $user['username'] : ''; // and more statements... } ?>
PHP Else Statement
In the previous section, we discussed the if construct, which allows you to execute a piece of code if the expression evaluates to true. On the other hand, if the expression evaluates to false, it won't do anything. More often than not, you also want to execute a different code snippet if the expression evaluates to false. That's where the else statement comes into the picture.
You always use the else statement in conjunction with an if statement. Basically, you can define it as shown in the following pseudo code.
if (expression) { // code is executed if the expression evaluates to TRUE } else { // code is executed if the expression evaluates to FALSE }
Let's revise the previous example to understand how it works.
<?php $age = 50; if ($age < 30) { echo "Your age is less than 30!"; } else { echo "Your age is greater than or equal 30!"; } ?>
So when you have two choices, and one of them must be executed, you can use the if-else construct.
PHP Else If Statement
We can consider the elseif statement as an extension to the if-else construct. If you've got more than two choices to choose from, you can use the elseif statement.
Let's study the basic structure of the elseif statement, as shown in the following pseudo code.
if (expression1) { // code is executed if the expression1 evaluates to TRUE } elseif (expression2) { // code is executed if the expression2 evaluates to TRUE } elseif (expression3) { // code is executed if the expression3 evaluates to TRUE } else { // code is executed if the expression1, expression2 and expression3 evaluates to FALSE, a default choice }
Again, let's try to understand it using a real-world example.
<?php $age = 50; if ($age < 30) { echo "Your age is less than 30!"; } elseif ($age > 30 && $age < 40) { echo "Your age is between 30 and 40!"; } elseif ($age > 40 && $age < 50) { echo "Your age is between 40 and 50!"; } else { echo "Your age is greater than 50!"; } ?>
As you can see in the above example, we have multiple conditions, so we've used a series of elseif statements. In the event that all if conditions evaluate to false, it executes the code provided in the last else statement.
PHP Switch Statement
The switch statement is somewhat similar to the elseif statement which we've just discussed in the previous section. The only difference is the expression which is being checked.
In the case of the elseif statement, you have a set of different conditions, and an appropriate action will be executed based on a condition. On the other hand, if you want to compare a variable with different values, you can use the switch statement.
As usual, an example is the best way to understand the switch statement.
<?php $favourite_site = 'Code'; switch ($favourite_site) { case 'Business': echo "My favourite site is business.tutsplus.com!"; break; case 'Code': echo "My favourite site is code.tutsplus.com!"; break; case 'Web Design': echo "My favourite site is webdesign.tutsplus.com!"; break; case 'Music': echo "My favourite site is music.tutsplus.com!"; break; case 'Photography': echo "My favourite site is photography.tutsplus.com!"; break; default: echo "I like everything at tutsplus.com!"; } ?>
As you can see in the above example, we want to check the value of the $favourite_site variable, and based on the value of the $favourite_site variable we want to print a message.
For each value you want to check with the $favourite_site variable, you have to define the case block. If the value is matched with a case, the code associated with that case block will be executed. After that, you need to use the break statement to end code execution. If you don't use the break statement, script execution will be continued up to the last block in the switch statement.
Finally, if you want to execute a piece of code if the variable's value doesn't match any case, you can define it under the default block. Of course, it's not mandatory—it's just a way to provide a default case.
So that's the story of conditional control structures. We'll discuss loops in PHP in the next section.
Loops in PHP
Loops in PHP are useful when you want to execute a piece of code repeatedly until a condition evaluates to false. So code is executed repeatedly as long as a condition evaluates to true, and as soon as the condition evaluates to false, the script continues executing the code after the loop.
The following flowchart explains how loops work in PHP.
As you can see in the above screenshot, a loop contains a condition. If the condition evaluates to true, the conditional code is executed. After execution of the conditional code, control goes back to the loop condition, and the flow continues until the condition evaluates to false.
In this section, we'll go through the different types of loops supported in PHP.
While Loop in PHP
The while loop is used when you want to execute a piece of code repeatedly until the while condition evaluates to false.
You can define it as shown in the following pseudo code.
while (expression) { // code to execute as long as expression evaluates to TRUE }
Let's have a look at a real-world example to understand how the while loop works in PHP.
<?php $max = 0; echo $i = 0; echo ","; echo $j = 1; echo ","; $result=0; while ($max < 10 ) { $result = $i + $j; $i = $j; $j = $result; $max = $max + 1; echo $result; echo ","; } ?>
If you're familiar with the Fibonacci series, you might recognize what the above program does—it outputs the Fibonacci series for the first ten numbers. The while loop is generally used when you don't know the number of iterations that are going to take place in a loop.
Do-While Loop in PHP
The do-while loop is very similar to the while loop, with the only difference being that the while condition is checked at the end of the first iteration. Thus, we can guarantee that the loop code is executed at least once, irrespective of the result of the while expression.
Let's have a look at the syntax of the do-while loop.
do { // code to execute } while (expression);
Let's go through a real-world to understand possible use-cases where you can use the do-while loop.
<?php $handle = fopen("file.txt", "r"); if ($handle) { do { $line = fgets($handle); // process the line content } while($line !== false); } fclose($handle); ?>
In the above example, we're trying to read a file line by line. Firstly, we've opened a file for reading. In our case, we're not sure if the file contains any content at all. Thus, we need to execute the fgets function at least once to check if a file contains any content. So we can use the do-while loop here. do-while evaluates the condition after the first iteration of the loop.
For Loop in PHP
Generally, the for loop is used to execute a piece of code for a specific number of times. In other words, if you already know the number of times you want to execute a block of code, it's the for loop which is the best choice.
Let's have a look at the syntax of the for loop.
for (expr1; expr2; expr3) { // code to execute }
The expr1 expression is used to initialize variables, and it's always executed. The expr2 expression is also executed in the beginning of a loop, and if it evaluates to true, the loop code is executed. After execution of the loop code, the expr3 is executed. Generally, the expr3 is used to alter the value of a variable which is used in the expr2 expression.
Let's go through the following example to see how it works.
<?php for ($i=1; $i<=10; ++$i) { echo sprintf("The square of %d is %d.</br>", $i, $i*$i); } ?>
The above program outputs the square of the first ten numbers. It initializes $i to 1, repeats as long as $i is less than or equal to 10, and adds 1 to $i at each iteration.
For Each in PHP
The foreach loop is used to iterate over array variables. If you have an array variable, and you want to go through each element of that array, the foreach loop is the best choice.
Let's have a look at a couple of examples.
<?php $fruits = array('apple', 'banana', 'orange', 'grapes'); foreach ($fruits as $fruit) { echo $fruit; echo "<br/>"; } $employee = array('name' => 'John Smith', 'age' => 30, 'profession' => 'Software Engineer'); foreach ($employee as $key => $value) { echo sprintf("%s: %s</br>", $key, $value); echo "<br/>"; } ?>
If you want to access array values, you can use the first version of the foreach loop as shown in the above example. On the other hand, if you want to access both a key and a value, you can do it as shown in the $employee example above.
Breaking Out of the Loop
There are times when you might want to break out of a loop before it runs it course. This can be achieved easily using the break keyword. It will get you out of the current for, foreach, while, do-while or switch structure.
You can also use break to get out of multiple nested loops by supplying a numeric argument. For example, using break 3 will break you out of 3 nested loops. However, you cannot pass a variable as the numeric argument if you are using a PHP version greater than or equal to 5.4.
<?php echo 'Simple Break'; for($i = 1; $i <= 2; $i++) { echo "\n".'$i = '.$i.' '; for($j = 1; $j <= 5; $j++) { if($j == 2) { break; } echo '$j = '.$j.' '; } } /* Simple Break i = 1 j = 1 i = 2 j = 1 */ echo 'Multi-level Break'; for($i = 1; $i <= 2; $i++) { echo "\n".'$i = '.$i.' '; for($j = 1; $j <= 5; $j++) { if($j == 2) { break 2; } echo '$j = '.$j.' '; } } /* Multi-level Break i = 1 j = 1 */ ?>
Another keyword that can interrupt loops in PHP is continue. However this only skips the rest of the current loop iteration instead of breaking out of the loop altogether. Just like break, you can also use a numerical value with continue to specify how many nested loops should it skip for current iteration.
<?php echo 'Simple Continue'; for($i = 1; $i <= 2; $i++) { echo "\n".'$i = '.$i.' '; for($j = 1; $j <= 5; $j++) { if($j == 2) { continue; } echo '$j = '.$j.' '; } } /* Simple Continue i = 1 j = 1 j = 3 j = 4 j = 5 i = 2 j = 1 j = 3 j = 4 j = 5 */ echo 'Multi-level Continue'; for($i = 1; $i <= 2; $i++) { echo "\n".'$i = '.$i.' '; for($j = 1; $j <= 5; $j++) { if($j == 2) { continue 2; } echo '$j = '.$j.' '; } } /* Multi-level Continue i = 1 j = 1 i = 2 j = 1 */ ?>
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed different control structures and loops in PHP. They are an essential part of PHP—or any programming language for that matter.
Learn PHP With a Free Online Course
If you want to learn PHP, check out our free online course on PHP fundamentals!
In this course, you'll learn the fundamentals of PHP programming. You'll start with the basics, learning how PHP works and writing simple PHP loops and functions. Then you'll build up to coding classes for simple object-oriented programming (OOP). Along the way, you'll learn all the most important skills for writing apps for the web: you'll get a chance to practice responding to GET and POST requests, parsing JSON, authenticating users, and using a MySQL database.
FREE
PHP
PHP Fundamentals
Jeremy McPeak
by Sajal Soni via Envato Tuts+ Code https://ift.tt/31EUx8s
0 notes
Text
PHP empty() function use with MySQL NULL
PHP provides a handy function, empty(), that is used to determine whether a variable is empty. Perhaps that is a bit confusing to someone unfamiliar with the empty() function and I can see how. In this blog post, I will cover: what empty() means in PHP, what the empty() function does, and a use case pairing up empty() with the PHP ternary operator conditional construct. Both used in combination with the MySQL NULL value. Continue reading and see examples of empty()… Photo by Debby Hudson on Unsplash Self-Promotion: If you enjoy the content written here, by all means, share this blog and your favorite post(s) with others who may benefit from or like it as well. Since coffee is my favorite drink, you can even buy me one if you would like! I’ll use these various variables for examples throughout the post: $name = 'Josh'; $another_name = NULL; $some_name = ''; $an_age = 0; $another_age = '0'; $different_age = 12; Before we see what values are returned when the above variables are passed to empty(), let’s visit the PHP documentation on empty() for additional information, that way we know what to expect. Here is the description: “Determine whether a variable is considered to be empty. A variable is considered empty if it does not exist or if its value equals FALSE. empty() does not generate a warning if the variable does not exist.” empty() returns a value – either TRUE or FALSE – depending on if the variable that is passed to empty() as an argument exists and is either non-empty or non-zero. So what exactly is non-empty and non-zero? Let’s find out… Echo PHP empty() function in the browser For more context, I’ll echo out the return values of each of the below calls to empty(), passing in the previously defined variables above as arguments in each call: echo '$name variable empty value is: '.empty($name).' '; echo '$another_name variable empty value is: '.empty($another_name).' '; echo '$some_name variable empty value is: '.empty($some_name).' '; echo '$an_age variable empty value is: '.empty($an_age).' '; echo '$another_age variable empty value is: '.empty($another_age).' '; echo '$different_age variable empty value is: '.empty($different_age).' '; Return results from empty echo’ed in the browser Understanding PHP empty() function What does empty consider to be empty? empty() considers any of these values to be empty: The empty string – “” The integer 0 (zero) The float 0.0 The string “0” The NULL value. The FALSE boolean An empty array(). Based on the above list, the first variable, ‘$name’, and the last variable ‘$different_age’, are not considered empty, as they both have actual values (none of which are those included on the empty list). When passed to empty() as arguments, both variables return FALSE whereas all of the other variables return TRUE. In PHP, a FALSE can be considered 0 (zero) where a TRUE value can be considered 1. For more information on PHP booleans, visit the online PHP Booleans documentation. In order to see the actual boolean result, we can use the var_dump() function, passing the empty() function call with the variable parameter as var_dump()‘s own parameter: echo var_dump(empty($name)).' '; echo var_dump(empty($another_name)).' '; echo var_dump(empty($some_name)).' '; echo var_dump(empty($an_age)).' '; echo var_dump(empty($another_age)).' '; echo var_dump(empty($different_age)).' '; Using var_dump to echo out boolean values. What can we use the PHP empty() function for? Now that we have an idea of what empty() does, we can use it in a simple example and see the benefits of such a handy function. I have recently used an empty() trick in a LAMP stack application I have been working on and just had to share it here on my blog (although it is by no stretch of the imagination, sacred knowledge). Suppose we have this MySQL table, structure, and data: Current data in the project_pdf table The requirement is, provide a simple button for each project name in the table. However, each rows’ button should only be clickable if there is a pdf document file for that projects’ table row. We can use empty() to test the ‘pdf_doc’ column variable and determine if the value is NULL or not and set the button accordingly. Recall NULL is considered empty and if passed to the empty() function will return TRUE. We first need a connection to the database along with a SELECT query, retrieving all rows from the ‘project_pdf’ table: include __DIR__.'/includes/DatabaseConnection.php'; $query = "SELECT `id`, `project_name`, `pdf_doc` FROM `project_pdf` ORDER BY `project_name` ASC;"; $results = $pdo->query($query); foreach ($results as $row) { $rows[] = ['id' => $row['id'], 'project_name' => $row['project_name'], 'pdf_doc' => $row['pdf_doc']]; } The next part of the script contains the dynamic PHP, which provides a list of Bootstrap buttons; one for each of the returned records from the MySQL database: PHP foreach loop using empty() function to set button attributes Notice the call to empty() in the button class attribute. Using the PHP ternary operator, each button’s ‘$row[‘pdf_doc’]’ value is checked. The ternary operator uses this syntax: conditional_test ? truth_result_code : false_result_code If the ‘$row[‘pdf_doc’]’ value is NULL, then empty() returns TRUE. That buttons’ class attribute is set to btn btn-secondary disabled along with the disabled attribute itself. Should the ‘$row[‘pdf_doc’]’ value not be empty() (returns false), then the class attribute is set to btn btn-primary (with no disabled attribute) and stays active. The following screenshots show the active and inactive buttons for each MySQL table row: Button list of all current projects Button in active state. Mouse cursor on Bootstrap inactive button. Notice the ‘Project 3’ button is inactive since its row in the database has a NULL value for the ‘pdf_doc’ column. Be sure and check out these 2 posts on storing and retrieving a .pdf file with PHP and the MySQL BLOB datatype: Use MySQL BLOB column with PHP to store .pdf file PHP MySQL BLOB PDF: Display in Browser I hope through this post, you can find ways to use empty() for similar types of functionality where you see fit. I think it’s pretty neat myself. What creative ways have you used empty()? Tell me about them in the comments below. I’d love to know and learn more uses myself. Like always, if you see anything in the code I can improve on or correct, please let me know via the comments below. Like what you have read? See anything incorrect? Please comment below and thanks for reading!!! A Call To Action! Thank you for taking the time to read this post. I truly hope you discovered something interesting and enlightening. Please share your findings here, with someone else you know who would get the same value out of it as well. Visit the Portfolio-Projects page to see blog post/technical writing I have completed for clients. To receive email notifications (Never Spam) from this blog (“Digital Owl’s Prose”) for the latest blog posts as they are published, please subscribe (of your own volition) by clicking the ‘Click To Subscribe!’ button in the sidebar on the homepage! (Feel free at any time to review the Digital Owl’s Prose Privacy Policy Page for any questions you may have about: email updates, opt-in, opt-out, contact forms, etc…) Be sure and visit the “Best Of” page for a collection of my best blog posts. Josh Otwell has a passion to study and grow as a SQL Developer and blogger. Other favorite activities find him with his nose buried in a good book, article, or the Linux command line. Among those, he shares a love of tabletop RPG games, reading fantasy novels, and spending time with his wife and two daughters. Disclaimer: The examples presented in this post are hypothetical ideas of how to achieve similar types of results. They are not the utmost best solution(s). The majority, if not all, of the examples provided, is performed on a personal development/learning workstation-environment and should not be considered production quality or ready. Your particular goals and needs may vary. Use those practices that best benefit your needs and goals. Opinions are my own. The post PHP empty() function use with MySQL NULL appeared first on Digital Owl's Prose. https://joshuaotwell.com/php-empty-function-use-with-mysql-null/
0 notes
Text
Mastering PHP: The Ultimate Guide to PHP Online Courses
In today's fast-evolving digital era, web development continues to play a vital role in shaping online experiences. One of the most trusted and widely-used server-side scripting languages in this domain is PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor). Whether you are a beginner aiming to break into web development or a seasoned programmer looking to expand your skills, enrolling in a PHP online course is a smart and strategic move.
What is PHP?
PHP is a powerful scripting language specifically designed for web development. It is open-source, easy to learn, and integrates seamlessly with HTML, databases like MySQL, and content management systems such as WordPress. PHP runs on almost all operating systems including Linux, Windows, and macOS, making it incredibly versatile.
Since its creation in 1994 by Rasmus Lerdorf, PHP has evolved dramatically. Today, it powers over 75% of websites on the internet, including big names like Facebook, Wikipedia, and WordPress. Its simplicity and wide applicability make it a must-know language for aspiring web developers.
Why Learn PHP Online?
1. Flexibility and Convenience
One of the biggest advantages of choosing an online PHP course is the flexibility it offers. Whether you're a college student, a working professional, or a freelance developer, you can learn PHP at your own pace, anytime and anywhere.
2. Cost-Effective Learning
Online courses are typically more affordable than in-person classes. Many platforms even offer free PHP tutorials or low-cost courses that deliver high-quality content.
3. Access to Quality Resources
Most online PHP courses provide a wealth of resources, including video lectures, downloadable content, quizzes, code editors, and forums. These materials make it easier to grasp complex concepts and practice coding in real-time.
4. Certification and Career Growth
Many PHP online courses offer certificates upon completion. These certificates can enhance your resume and make you stand out in the job market. With PHP skills, you can pursue roles such as Web Developer, Full-Stack Developer, Backend Developer, or Software Engineer.
Key Topics Covered in a PHP Online Course
A comprehensive PHP course typically includes the following modules:
1. Introduction to PHP
What is PHP?
Installation and setup (XAMPP, WAMP)
Syntax and basic structure
Embedding PHP in HTML
2. PHP Variables and Data Types
Strings, integers, floats, booleans
Arrays (indexed and associative)
Constants
Type casting
3. Control Structures
Conditional statements (if, else, switch)
Looping structures (for, while, do-while, foreach)
4. Functions and Scope
Creating and calling functions
Function parameters and return values
Variable scope (local, global, static)
5. Forms and User Input
Handling GET and POST methods
Form validation
Superglobals like $_GET, $_POST, $_REQUEST, $_SERVER
6. Working with Databases
Connecting PHP with MySQL
CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete)
Using PDO and MySQLi
Prepared statements for security
7. Error Handling
Types of errors (syntax, runtime, logical)
Try-catch blocks
Custom error handlers
8. Sessions and Cookies
Creating and managing sessions
Setting and reading cookies
Session security best practices
9. File Handling in PHP
Reading and writing files
Uploading files via forms
File permissions
10. Object-Oriented Programming in PHP
Classes and objects
Constructors and destructors
Inheritance, encapsulation, polymorphism
Interfaces and traits
11. PHP and Web Security
Input validation and sanitization
Preventing SQL injection and XSS
HTTPS and secure sessions
12. Advanced PHP Topics
PHP with AJAX
REST APIs in PHP
MVC Frameworks like Laravel and CodeIgniter
Composer and dependency management
Popular Platforms Offering PHP Online Courses
Here are some of the best platforms where you can learn PHP online:
1. Udemy
Udemy offers a wide range of PHP courses for all levels. Courses like “PHP for Beginners” and “Object-Oriented PHP & MVC” are among the top-rated, featuring lifetime access and a certificate upon completion.
2. Coursera
Partnering with universities and colleges, Coursera offers structured PHP programs. You can audit most courses for free or pay to receive a certification. A good example is the Web Applications for Everybody course from the University of Michigan.
3. edX
edX features PHP-related content through universities like Harvard and MIT. Though primarily focused on computer science and web development, several PHP courses are included under broader programming paths.
4. LinkedIn Learning
LinkedIn Learning provides bite-sized PHP lessons with project-based learning. A subscription gives access to multiple courses, helpful if you're pursuing more than just PHP.
5. FreeCodeCamp and W3Schools
Both platforms are excellent for beginners who want to explore PHP basics for free. W3Schools, in particular, is well-known for its hands-on “Try It Yourself” editor.
Who Should Take a PHP Online Course?
1. Beginners in Web Development
If you're new to coding and want to start with a language that's widely used and beginner-friendly, PHP is a great option.
2. Students and Computer Science Graduates
Learning PHP alongside HTML, CSS, and JavaScript can give you a competitive edge when applying for internships or junior developer roles.
3. Freelancers and Entrepreneurs
If you're planning to build your own website or work on client projects, PHP enables you to create dynamic, database-driven websites quickly.
4. Working Professionals
Developers who want to expand their backend skills or transition into full-stack development will benefit significantly from PHP expertise.
Career Opportunities After Learning PHP
Once you complete a PHP online course, several doors open for your professional growth:
Web Developer: Design and build dynamic websites.
Backend Developer: Manage server-side logic and database interactions.
Full-Stack Developer: Handle both frontend and backend tasks.
WordPress Developer: Customize and develop plugins/themes using PHP.
Freelance Developer: Build and manage websites for clients.
According to recent job market statistics, PHP developers earn an average salary of $60,000–$90,000 annually, depending on experience, location, and industry.
Tips for Success in an Online PHP Course
Set Clear Goals: Decide whether you’re learning for a job, freelance projects, or personal growth.
Practice Regularly: The best way to learn coding is by doing it. Practice through exercises and mini-projects.
Join Online Communities: Platforms like Stack Overflow, Reddit, and GitHub can help you learn collaboratively.
Work on Real Projects: Apply what you learn by building real-world applications—this boosts your confidence and portfolio.
Keep Up With Updates: PHP continues to evolve (e.g., PHP 8.x versions), so staying updated ensures your skills remain relevant.
Conclusion
PHP remains a cornerstone of modern web development, and mastering it through an online course is an effective, convenient, and affordable way to jumpstart or advance your programming journey. With comprehensive learning resources, expert instructors, and real-world projects, PHP online courses provide everything you need to build robust, scalable, and dynamic websites.
Whether you're starting from scratch or adding PHP to your skillset, now is the perfect time to enroll and harness the power of this essential language.
#php online course#PHP Training in Chandigarh#Python Training in Chandigarh#CCNA Training in Chandigarh#MERN Stack Training in Chandigarh
0 notes
Link
The PHP foreach as loop works just on arrays and is employed to loop through each key/value pair in an array. The foreach build gives the least demanding approach to indicate the array segments. It goes on at array and objects both.
0 notes
Text
PHP Internship in Udaipur
PHP is a scripting language that is used to create dynamic websites and web applications that can be integrated within your HTML code. Yug Technology’s PHP Internship is comprehensive and practical so you can go back to work and apply the knowledge you gained during your PHP course straight away.
All the PHP trainers of the Yug Technology are experts in their field and passionate about delivering inspiring PHP courses, so you know you’re in safe hands. So whether you’re new to PHP and want an introductory course or have some experience is trying to find a more advanced PHP course we’ve got the course for you. Yug Technology is the best digital marketing company that provides the best PHP Internship in Udaipur.
Course Details: PHP Basic Course Content
Unit 1: Introduction To PHP
What is PHP?
History of PHP
Usage of PHP
Advantage of using PHP
Unit 2: Server Management
Configure PHP Installation
Some Basic settings
More about the directory structure
Details about different types of a server
Unit 3: PHP Basics
The PHP Character Set
Constants / Variables
Keywords & Data Type
PHP Structure and Syntax
Passing Variable between Pages
Unit 4: Expressions and Their Types
Using if-else & Foreach statement
Operators
Date function format
File Include
Use of Functions
Array – Associated and Numeric Array
Sorting Arrays
Alternates to the echo command
way to use Javascript and CSS.
Unit 5: Form Elements
Working with Text box
Password, Select Box
Check box
Radio button
Multiple List Box
Text Area
File Upload, Page Redirect
Form Validations
Unit 6: File Operations
Opening and Shutting Files
FileModes
PHP Functions for FILE handling
Reading a file
Dynamically create and Read a file
Unit 7: CSS Management
CSS Basics
Application of CSS with HTML
Types of CSS with examples
Unit 8: Javascript Management
Variables
Array Declaration
Loop, Statements, InnerHTML,Math functions, Events, Javascript validations,
Using PHP with Javascript

0 notes