#selenium junit
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Must-Know Core Java Concepts for Every Programmer
(A Guide for Full Stack Software Testing Enthusiasts in KPHB)
Java remains the backbone of enterprise applications, and a strong grasp of its core concepts is essential for every programmer. Whether you are an aspiring software tester, a backend developer, or a full-stack engineer, understanding Java fundamentals is non-negotiable. Let’s break down the most crucial Java concepts that you must master.

1. Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
Java is inherently object-oriented, which means everything revolves around objects and classes. The four key pillars of OOP in Java are:
✔ Encapsulation – Bundling data and methods together to protect data integrity. ✔ Abstraction – Hiding implementation details and exposing only what’s necessary. ✔ Inheritance – Allowing one class to derive properties from another. ✔ Polymorphism – Enabling multiple implementations of a method.
Why It Matters?
For software testers, understanding OOP principles helps in creating reusable and scalable test automation frameworks.
2. Java Memory Management
Memory management is a crucial aspect that determines the performance of Java applications. It consists of:
✔ Heap & Stack Memory – Heap stores objects, while Stack holds method calls and local variables. ✔ Garbage Collection (GC) – Java has an automatic garbage collector that frees up memory by removing unused objects.
Why It Matters?
Full Stack Testers must understand memory leaks and performance bottlenecks in Java-based applications.
3. Exception Handling
Exception handling ensures that runtime errors don’t crash the application. Java provides:
✔ try-catch-finally – Handles exceptions and ensures resource cleanup. ✔ throws & throw – Used for explicitly handling custom exceptions. ✔ Checked vs. Unchecked Exceptions – Checked exceptions (like IOException) must be handled, while unchecked exceptions (like NullPointerException) occur at runtime.
Why It Matters?
Testers need to handle exceptions effectively in automation scripts to avoid script failures.
4. Multithreading & Concurrency
Multithreading allows multiple parts of a program to run simultaneously. Important concepts include:
✔ Thread Lifecycle – From creation to termination. ✔ Runnable & Callable Interfaces – Implementing threads in Java. ✔ Synchronization & Locks – Avoiding race conditions and ensuring thread safety.
Why It Matters?
In performance testing, understanding multithreading helps simulate real-world user load.
5. Collections Framework
Java provides a robust Collections Framework for handling groups of objects efficiently. The key interfaces are:
✔ List (ArrayList, LinkedList) – Ordered and allows duplicates. ✔ Set (HashSet, TreeSet) – Unordered and doesn’t allow duplicates. ✔ Map (HashMap, TreeMap) – Stores key-value pairs.
Why It Matters?
Test automation frameworks use collections extensively for data handling and assertions.
6. File Handling & I/O Operations
File handling is critical for reading, writing, and manipulating files in Java.
✔ BufferedReader & BufferedWriter – Efficient file reading and writing. ✔ FileInputStream & FileOutputStream – Handling binary data. ✔ Serialization – Converting objects into byte streams.
Why It Matters?
For automation testers, handling logs, reports, and configuration files is a routine task.
7. JDBC & Database Connectivity
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) allows applications to interact with databases.
✔ DriverManager – Manages database connections. ✔ PreparedStatement – Prevents SQL injection. ✔ ResultSet – Retrieves query results.
Why It Matters?
Full Stack Testers should understand JDBC for validating database operations in automation scripts.
8. Java Frameworks
Mastering Java alone isn’t enough; knowing key frameworks is essential.
✔ Spring Boot – Microservices and dependency injection. ✔ Selenium with Java – Web automation testing. ✔ TestNG & JUnit – Test automation frameworks.
Why It Matters?
These frameworks power large-scale software applications and automation testing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the best way to practice Core Java concepts? A: Work on small projects, participate in coding challenges, and contribute to open-source repositories.
Q2: How is Java used in Full Stack Software Testing? A: Java is used for writing test automation scripts, interacting with databases, and integrating test frameworks.
Q3: What is the difference between Checked and Unchecked Exceptions? A: Checked exceptions must be handled (e.g., IOException), whereas unchecked exceptions occur at runtime (e.g., NullPointerException).
Q4: Why is Java preferred for automation testing? A: Java offers robust libraries like Selenium, TestNG, and JUnit, making automation testing efficient and scalable.
Q5: What are the key Java concepts needed for API Testing? A: Understanding HTTP methods, JSON parsing, and REST API calls using libraries like RestAssured and Jackson is crucial.
Final Thoughts
Mastering Java fundamentals is the key to excelling in software development and automation testing. Whether you are preparing for a Full Stack Software Testing role in KPHB or looking to enhance your coding skills, these core Java concepts will set you apart.
#Java#CoreJava#FullStackTesting#SoftwareTesting#AutomationTesting#JavaProgramming#Selenium#TestAutomation#OOP#Coding#JavaDeveloper#JUnit#TestNG#FullStackDevelopment#KPHB#TechLearning
0 notes
Text
Exploring Essential Tools for Continuous Integration in DevOps

In the realm of DevOps, continuous integration (CI) plays a pivotal role in streamlining software development processes. Discover the essential tools that empower teams to automate builds, run tests efficiently, and integrate code seamlessly. From popular CI/CD platforms like Jenkins and GitLab CI to robust testing frameworks like Selenium and JUnit, this comprehensive guide dives deep into the tools that drive continuous integration in DevOps workflows.
Are you navigating the complexities of DevOps testing? Dive into our comprehensive guide on testing in DevOps, where we explore the critical role of continuous integration in ensuring software quality and reliability. Discover the latest tools and best practices that empower teams to automate testing, streamline workflows, and achieve faster, more reliable releases.
#devops#continuousintegration#ci#cd#softwaredevelopment#automation#testing#jenkins#gitlabci#selenium#junit#devopstesting#softwarequality#workflowautomation#releasemanagement#development#technology#innovation
0 notes
Text
How-To IT
Topic: Core areas of IT
1. Hardware
• Computers (Desktops, Laptops, Workstations)
• Servers and Data Centers
• Networking Devices (Routers, Switches, Modems)
• Storage Devices (HDDs, SSDs, NAS)
• Peripheral Devices (Printers, Scanners, Monitors)
2. Software
• Operating Systems (Windows, Linux, macOS)
• Application Software (Office Suites, ERP, CRM)
• Development Software (IDEs, Code Libraries, APIs)
• Middleware (Integration Tools)
• Security Software (Antivirus, Firewalls, SIEM)
3. Networking and Telecommunications
• LAN/WAN Infrastructure
• Wireless Networking (Wi-Fi, 5G)
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)
• Communication Systems (VoIP, Email Servers)
• Internet Services
4. Data Management
• Databases (SQL, NoSQL)
• Data Warehousing
• Big Data Technologies (Hadoop, Spark)
• Backup and Recovery Systems
• Data Integration Tools
5. Cybersecurity
• Network Security
• Endpoint Protection
• Identity and Access Management (IAM)
• Threat Detection and Incident Response
• Encryption and Data Privacy
6. Software Development
• Front-End Development (UI/UX Design)
• Back-End Development
• DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
• Mobile App Development
• Cloud-Native Development
7. Cloud Computing
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
• Platform as a Service (PaaS)
• Software as a Service (SaaS)
• Serverless Computing
• Cloud Storage and Management
8. IT Support and Services
• Help Desk Support
• IT Service Management (ITSM)
• System Administration
• Hardware and Software Troubleshooting
• End-User Training
9. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
• AI Algorithms and Frameworks
• Natural Language Processing (NLP)
• Computer Vision
• Robotics
• Predictive Analytics
10. Business Intelligence and Analytics
• Reporting Tools (Tableau, Power BI)
• Data Visualization
• Business Analytics Platforms
• Predictive Modeling
11. Internet of Things (IoT)
• IoT Devices and Sensors
• IoT Platforms
• Edge Computing
• Smart Systems (Homes, Cities, Vehicles)
12. Enterprise Systems
• Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
• Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
• Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS)
• Supply Chain Management Systems
13. IT Governance and Compliance
• ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
• COBIT (Control Objectives for Information Technologies)
• ISO/IEC Standards
• Regulatory Compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, SOX)
14. Emerging Technologies
• Blockchain
• Quantum Computing
• Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
• 3D Printing
• Digital Twins
15. IT Project Management
• Agile, Scrum, and Kanban
• Waterfall Methodology
• Resource Allocation
• Risk Management
16. IT Infrastructure
• Data Centers
• Virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V)
• Disaster Recovery Planning
• Load Balancing
17. IT Education and Certifications
• Vendor Certifications (Microsoft, Cisco, AWS)
• Training and Development Programs
• Online Learning Platforms
18. IT Operations and Monitoring
• Performance Monitoring (APM, Network Monitoring)
• IT Asset Management
• Event and Incident Management
19. Software Testing
• Manual Testing: Human testers evaluate software by executing test cases without using automation tools.
• Automated Testing: Use of testing tools (e.g., Selenium, JUnit) to run automated scripts and check software behavior.
• Functional Testing: Validating that the software performs its intended functions.
• Non-Functional Testing: Assessing non-functional aspects such as performance, usability, and security.
• Unit Testing: Testing individual components or units of code for correctness.
• Integration Testing: Ensuring that different modules or systems work together as expected.
• System Testing: Verifying the complete software system’s behavior against requirements.
• Acceptance Testing: Conducting tests to confirm that the software meets business requirements (including UAT - User Acceptance Testing).
• Regression Testing: Ensuring that new changes or features do not negatively affect existing functionalities.
• Performance Testing: Testing software performance under various conditions (load, stress, scalability).
• Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities and assessing the software’s ability to protect data.
• Compatibility Testing: Ensuring the software works on different operating systems, browsers, or devices.
• Continuous Testing: Integrating testing into the development lifecycle to provide quick feedback and minimize bugs.
• Test Automation Frameworks: Tools and structures used to automate testing processes (e.g., TestNG, Appium).
19. VoIP (Voice over IP)
VoIP Protocols & Standards
• SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
• H.323
• RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol)
• MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol)
VoIP Hardware
• IP Phones (Desk Phones, Mobile Clients)
• VoIP Gateways
• Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs)
• VoIP Servers
• Network Switches/ Routers for VoIP
VoIP Software
• Softphones (e.g., Zoiper, X-Lite)
• PBX (Private Branch Exchange) Systems
• VoIP Management Software
• Call Center Solutions (e.g., Asterisk, 3CX)
VoIP Network Infrastructure
• Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) for VoIP
• VoIP Traffic Shaping & Bandwidth Management
• Firewall and Security Configurations for VoIP
• Network Monitoring & Optimization Tools
VoIP Security
• Encryption (SRTP, TLS)
• Authentication and Authorization
• Firewall & Intrusion Detection Systems
• VoIP Fraud DetectionVoIP Providers
• Hosted VoIP Services (e.g., RingCentral, Vonage)
• SIP Trunking Providers
• PBX Hosting & Managed Services
VoIP Quality and Testing
• Call Quality Monitoring
• Latency, Jitter, and Packet Loss Testing
• VoIP Performance Metrics and Reporting Tools
• User Acceptance Testing (UAT) for VoIP Systems
Integration with Other Systems
• CRM Integration (e.g., Salesforce with VoIP)
• Unified Communications (UC) Solutions
• Contact Center Integration
• Email, Chat, and Video Communication Integration
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Integrate Testing Automation Tools into Your CI/CD Pipeline
Integrating testing automation tools into your Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline is crucial for enhancing software quality and accelerating delivery cycles. The first step is to select the right automation tool that aligns with your technology stack and project requirements. Popular choices include Selenium for web applications, Appium for mobile apps, and JUnit for Java-based projects.
Once the tool is chosen, configure your CI/CD pipeline to include automated testing at various stages. Begin with unit tests during the build phase to catch issues early. Tools like Jenkins, CircleCI, or GitLab CI can be configured to trigger these tests automatically with each code commit. Ensure that the testing environment mirrors the production setup to achieve accurate results.
Next, integrate automated functional and regression tests in the pre-deployment phase. These tests should validate end-to-end functionalities and ensure that new changes do not break existing features. Using frameworks like TestNG or Cucumber can help manage these tests effectively.
Additionally, incorporate performance and load testing tools like JMeter or Gatling to assess the application's behavior under stress. These tests can be scheduled to run during off-peak hours to avoid interference with regular development activities.
Finally, maintain a robust reporting mechanism to track test results and generate insights. Tools like Allure or TestRail can provide detailed reports and dashboards, facilitating quick identification and resolution of issues.
By strategically integrating testing automation tools into your CI/CD pipeline, you ensure a reliable, efficient, and scalable approach to software delivery, ultimately leading to higher quality products and faster release cycles.
#codeless test automation#codeless testing platform#test automation software#automated qa testing#no code test automation tools
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Revolutionizing Web Testing: A Deep Dive into Selenium's Automation Dynamics
In the rapidly evolving digital arena, the assurance of flawless functionality, optimal performance, and responsiveness of web applications is a non-negotiable aspect of software development. Selenium, an open-source automation framework, emerges as a formidable force in achieving these objectives. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the intricacies of Selenium, unraveling its role in automation, dissecting the components comprising its toolkit, and understanding its profound impact on modern web testing practices.

1. Decoding Selenium: A Core Element of Automation Mastery
At its essence, Selenium represents a suite of tools meticulously crafted to automate web browsers. This automation plays a pivotal role in the testing domain, where the simulation of user interactions is imperative for validating the functionality and performance of web applications. Beyond testing, Selenium significantly contributes to the efficiency and reliability of the software development lifecycle.
2. The Toolbox Essentials: Navigating Selenium's Arsenal
Selenium's toolkit comprises three indispensable components, each serving a distinct purpose in the automation journey.
Selenium IDE:
Selenium IDE, a browser extension, simplifies the recording, editing, and debugging of tests. With a user-friendly interface, testers can effortlessly create and modify test cases.
Selenium WebDriver:
The crux of Selenium lies in WebDriver, a tool facilitating interaction with web browsers through diverse programming languages. This component is instrumental in crafting dynamic and programmable test scripts.
Selenium Grid:
Selenium Grid acts as a scalable solution enabling parallel test execution across multiple machines and browsers. This feature expedites the testing process by distributing test cases effectively.
3. Language Flexibility: Adaptable Automation at its Finest
A standout feature of Selenium is its support for multiple programming languages, including Java, Python, C#, and Ruby. This flexibility empowers testers and developers to harness Selenium's capabilities within their preferred programming language, fostering seamless integration into existing workflows.
4. Cross-Browser Compatibility: Ensuring Uniformity in Diversity
Selenium's prowess shines in its ability to conduct cross-browser testing with efficiency. In the era where web applications must perform consistently across various browsers, Selenium ensures uniformity in testing scenarios across Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and more. This cross-browser compatibility is paramount for delivering a consistent user experience.
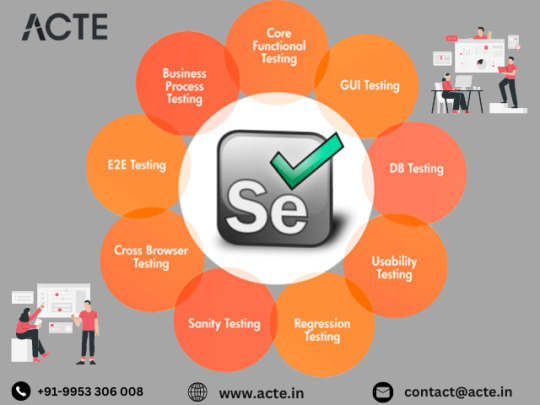
5. Dynamic Web Element Handling: Mastering Change
In the dynamic landscape of web development, the adept handling of dynamic web elements stands as a critical testing aspect. Selenium excels in providing robust mechanisms to identify and interact with elements that undergo changes based on user interactions. This adaptability guarantees accurate testing even in scenarios where web elements are subject to modification.
6. Integration with Testing Frameworks: Orchestrating Efficient Test Management
Selenium seamlessly integrates with renowned testing frameworks like JUnit and TestNG. This integration enhances the efficiency of test management, execution, and reporting. Testing frameworks offer a structured approach to test development, simplifying the management, execution, and analysis of test results.
7. Parallel Test Execution: Turbocharging Processes
Selenium Grid emerges as a powerhouse solution for accelerating test execution. By facilitating parallel execution of tests across multiple machines and browsers, Selenium Grid substantially reduces test execution time. This parallelization proves invaluable, especially when dealing with extensive test suites that require swift execution.
8. Community Support and Continuous Advancement: Sustaining an Ecosystem
Selenium thrives on the strength of its community. With a dynamic community of developers, testers, and automation enthusiasts, Selenium undergoes continuous refinement and enhancement. Regular updates, bug fixes, and the introduction of new features ensure that Selenium aligns seamlessly with the ever-evolving web technology landscape.
Conclusion: Selenium as the Cornerstone of Automated Precision
In conclusion, Selenium stands tall as a cornerstone in the realm of automation, particularly in web testing. Its adaptability, cross-browser testing capabilities, integration with testing frameworks, and support for parallel test execution position it as an indispensable tool for ensuring the quality and reliability of web applications.
Whether you're a seasoned tester or a developer navigating the intricacies of web testing, Selenium equips you to streamline your testing processes. Its impact resonates in the delivery of high-quality software, contributing to the seamless user experience expected in the dynamic digital landscape.
As we delve into the myriad facets of Selenium, we uncover its transformative power in reshaping testing practices and fortifying the foundations of robust and reliable web applications. Embrace the influence of Selenium, and let it be your guiding force in the captivating journey of web automation.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unraveling Selenium's Testing Odyssey: Pros and Cons Unveiled
In the ever-evolving realm of software testing, Selenium stands as a stalwart, renowned for its versatility and capabilities. As testing teams explore this dynamic tool, it's essential to navigate through its strengths and challenges. This exploration takes a deep dive into the advantages and disadvantages of Selenium, offering insights into what makes it a formidable ally and where it presents potential hurdles.

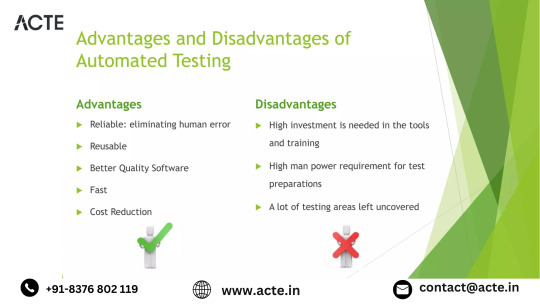
Pros of Leveraging Selenium:
Seamless Cross-Browser Compatibility: Selenium's prowess lies in its ability to seamlessly support an array of browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. This ensures that web applications undergo thorough and consistent testing across diverse user environments.
Flexibility in Programming Language Support: A distinguishing feature of Selenium is its support for various programming languages – Java, Python, C#, and Ruby. This adaptability empowers testing teams to choose languages that align with their expertise or project requirements, fostering a dynamic and adaptable testing environment.
Efficient Parallel Execution: Selenium's capability to execute test scripts in parallel enhances efficiency, especially when dealing with extensive test suites. This feature significantly reduces the time required for test runs, a crucial aspect in meeting tight development timelines.
Robust Community and Abundant Resources: Beyond its features, Selenium thrives on the strength of its community. A vibrant and vast user community, coupled with an abundance of online resources, ensures quick problem-solving, continuous updates, and a wealth of knowledge accessible to testers at all skill levels.
Seamless Integration with Test Frameworks: Selenium effortlessly integrates with popular test frameworks like TestNG and JUnit. This integration elevates test management capabilities, streamlining reporting and supporting the implementation of advanced testing scenarios. The synergy between Selenium and these frameworks enhances overall testing efficiency.
Cons of Navigating Selenium's Landscape:
Limitations in Non-Web Application Support: Selenium excels in web application testing but presents limitations in handling non-web applications. This can be a challenge for projects involving diverse application types, necessitating additional tools for comprehensive testing.
Steep Learning Curve: Selenium's feature-rich nature comes with a learning curve, particularly for newcomers. The tool's intricacies may require time and dedication to master. While this curve poses a challenge, the investment in learning pays off in enhanced testing capabilities.
Reporting Dependencies on Third-Party Tools: Selenium lacks comprehensive reporting features, leading testers to rely on third-party tools or integrate additional reporting plugins. While this adds a layer of complexity, it is a common practice to ensure thorough and insightful test reports.
Challenges in Dynamic Element Identification: Dynamic web pages with frequently changing elements can pose challenges for Selenium. Ensuring stable and reliable identification of dynamic elements may require advanced strategies, influencing the resilience of test scripts. Employing dynamic element identification techniques becomes crucial.
Limited Support for Image-based Testing: Selenium's primary focus on interacting with HTML elements results in limited support for image-based testing. For projects heavily reliant on visual validation, additional tools may be necessary to complement Selenium's capabilities.
Conclusion:
Selenium stands as a robust ally in the testing arena, offering a spectrum of advantages for web application testing. However, understanding its limitations, especially in handling non-web applications and dynamic elements, is crucial. Testers must weigh these pros and cons, considering the learning curve and potential challenges, to make informed decisions about integrating Selenium into their testing toolkit.
In essence, Selenium empowers testing teams with flexibility and efficiency, serving as a reliable companion in ensuring the quality and reliability of software applications. As the testing landscape continues to evolve, Selenium remains a cornerstone, contributing to the ever-advancing field of software testing.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
GQAT Tech’s QA Arsenal: Powerful Tools That Make Quality Assurance Smarter
In this technology-driven age, delivering high-quality software is not an optional function but a necessity. Clients now expect us to produce digital products— apps, websites, etc.-- that are made quickly and error-free. The best way to achieve this is with a quality assurance (QA) process and effective tools to adapt to their needs.
The GQAT Tech QA team calls their QA efficient and effective tools combined, and their QA arsenal productive platforms, automation, tools, and proven processes. These testing tools and approaches can help a QA team find bugs more quickly, decrease hands-on effort, and allow more test coverage depending on the software project.
Now, let's look at what a QA Arsenal is, why it is important, and how QA will help your business produce better software.
What is the QA Arsenal?
The "QA Arsenal" refers to the collection of tools, frameworks, and strategies at GQAT Tech that the QA team employs to provide quality testing to clients. The QA Arsenal is like a toolbox, where everything a tester needs to complete the project is in the toolbox.
It includes:
Automation testing tools
Manual testing techniques
Defect tracking systems
Performance testing platforms
Mobile and web testing tools
CI/CD integrations
Reporting and analytics dashboards
What Makes GQAT’s QA Arsenal Unique?
We do not use tools haphazardly. We use the most appropriate tools based on the client's type of project, technology stack, service timeline, and quality. The QA Arsenal is designed to offer flexibility and therefore considers:
Web apps
Mobile apps
Embedded systems
IoT devices
Enterprise software
Whether functional test, compatibility test, API test, performance test, GQAT Tech utilizes a custom mixture of tools to ensure that it is reliable, secure, and ready for launch.
Tools Included in the QA Arsenal
Here are some common tools and platforms GQAT Tech uses:
🔹 Automation Tools
Selenium – For web application automation
Appium – For mobile app automation
TestNG / JUnit – For running and managing test cases
Robot Framework – For keyword-driven testing
Postman – For API testing
JMeter – For performance and load testing
🔹 Defect & Test Management
JIRA – To log, track, and manage bugs
TestRail / Zephyr – For test case management
Git & Jenkins – For CI/CD and version control
BrowserStack / Sauce Labs – For cross-browser and device testing
How It Helps Clients
Using the QA Arsenal allows GQAT Tech to:
Detect Bugs Early – Catch issues before they reach end-users
Save Time – Automation reduces time spent on repetitive tasks
Test on Real Devices – Ensures compatibility across systems
Generate Reports – Easy-to-read results and test status
Integrate with DevOps – Faster release cycles and fewer rollbacks
Improve Product Quality – Fewer bugs mean a better user experience
Real Results for Real Projects
GQAT Tech’s QA Arsenal has been successfully used across different domains like:
FinTech
Healthcare
E-commerce
Travel & Transport
EdTech
AI and IoT Platforms
With their domain expertise and knowledge of tools, they help businesses go faster, mitigate risks, and build customer diligence.
Conclusion
Building a great QA team is essential, but having them equipped with the right tools makes all the difference. GQAT Tech’s QA Arsenal provides their testers with everything they need to test faster, smarter, and more comprehensively.
If you are building a digital product and want to ensure it is released in the real world, you need a testing partner who does not leave things to chance. You need a testing partner with a battle-tested QA arsenal.
💬 Ready to experience smarter quality assurance?
👉 Explore GQAT Tech’s QA Arsenal and get in touch with their expert team today!
#QA Arsenal#Software Testing Tools#Quality Assurance Strategies#Automation Testing#Manual Testing#Selenium#Appium#Test Management Tools#CI/CD Integration#Performance Testing#Defect Tracking#Cross-Browser Testing#GQAT Tech QA Services#Agile Testing Tools#End-to-End Testing
0 notes
Text
Top Tools and Technologies Every Full Stack Java Developer Should Know
In today's fast-paced software development landscape, Full Stack Java Developers are in high demand. Companies seek professionals who can work across both the frontend and backend, manage databases, and understand deployment processes. Whether you're just starting your career or planning to upskill, mastering the right set of tools and technologies is key.
If you're considering a full stack java training in KPHB, this guide will help you understand the essential technologies and tools you should focus on to become industry-ready.

1. Java and Spring Framework
The foundation of full stack Java development starts with a deep understanding of Core Java and object-oriented programming concepts. Once you’ve nailed the basics, move to:
Spring Core
Spring Boot – simplifies microservices development.
Spring MVC – for building web applications.
Spring Security – for handling authentication and authorization.
Spring Data JPA – for database operations.
Spring Boot is the most widely adopted framework for backend development in enterprise applications.
2. Frontend Technologies
A full stack Java developer must be proficient in creating responsive and interactive UIs. Core frontend technologies include:
HTML5 / CSS3 / JavaScript
Bootstrap – for responsive designs.
React.js or Angular – for building dynamic SPAs (Single Page Applications).
TypeScript – especially useful when working with Angular.
3. Database Management
You’ll need to work with both relational and non-relational databases:
MySQL / PostgreSQL – popular SQL databases.
MongoDB – a widely used NoSQL database.
Hibernate ORM – simplifies database interaction in Java.
4. Version Control and Collaboration
Version control systems are crucial for working in teams and managing code history:
Git – the most essential tool for source control.
GitHub / GitLab / Bitbucket – platforms for repository hosting and collaboration.
5. DevOps and Deployment Tools
Understanding basic DevOps is vital for modern full stack roles:
Docker – for containerizing applications.
Jenkins – for continuous integration and delivery.
Maven / Gradle – for project build and dependency management.
AWS / Azure – cloud platforms for hosting full stack applications.
6. API Development and Testing
Full stack developers should know how to develop and consume APIs:
RESTful API – commonly used for client-server communication.
Postman – for testing APIs.
Swagger – for API documentation.
7. Unit Testing Frameworks
Testing is crucial for bug-free code. Key testing tools include:
JUnit – for unit testing Java code.
Mockito – for mocking dependencies in tests.
Selenium / Playwright – for automated UI testing.
8. Project Management and Communication
Agile and collaboration tools help manage tasks and teamwork:
JIRA / Trello – for task and sprint management.
Slack / Microsoft Teams – for communication.
Final Thoughts
Learning these tools and technologies can position you as a highly capable Full Stack Java Developer. If you're serious about a career in this field, structured learning can make all the difference.
Looking for expert-led Full Stack Java Training in KPHB? ✅ Get industry-ready with hands-on projects. ✅ Learn from experienced instructors. ✅ Job assistance and certification included.
👉 Visit our website to explore course details, check out FAQs, and kickstart your journey today!
0 notes
Text
What is a QA Software Testing Course, and Why is it Important in Today’s Tech Industry?
Introduction
Imagine launching a new app, only to find users abandoning it due to bugs and glitches. In the fast-paced tech world, such failures can cost companies millions. That’s where QA (Quality Assurance) software testing comes in. A QA software testing course teaches learners how to ensure digital products function smoothly, meet customer expectations, and maintain brand credibility. Today, businesses can't afford to release faulty products. The demand for skilled QA professionals is growing across sectors. Quality assurance testing courses are designed to equip learners with practical skills to meet this demand. Whether you're new to tech or switching careers, enrolling in a QA Testing Online Training Course can open doors to a stable and high-paying job in the IT industry.
What is a QA Software Testing Course?
A QA software testing course is a structured program that trains individuals to test software applications to ensure they are bug-free, functional, and meet user requirements. It typically includes both manual and automated testing techniques.
Key Concepts Covered
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC)
Manual Testing Basics
Automation Testing (using tools like Selenium, QTP)
Defect Tracking and Reporting
Agile and DevOps Methodologies
Test Planning and Documentation
Why is QA Testing Important in the Tech Industry?
1. Quality Control Saves Money
According to the Consortium for IT Software Quality, poor software quality costs the U.S. economy over $2 trillion annually. QA testers prevent such losses by identifying issues early.
2. User Experience Matters
A broken app leads to bad reviews and customer loss. QA testing ensures a seamless user experience.
3. Security Compliance
Many industries like healthcare and finance require thorough testing to comply with regulatory standards. QA testers are crucial in ensuring this.
4. Faster Time-to-Market
Automated QA processes allow developers to release updates quickly without sacrificing quality.
What You Will Learn in a QA Testing Online Training Course
1. Manual Testing Techniques
Learn to write and execute test cases, report bugs, and perform usability testing.
2. Automation Testing Tools
Master tools like Selenium, JUnit, TestNG, and Jenkins. Real-world use cases include writing test scripts and running automated regression tests.
3. Test Management Tools
Explore tools like JIRA, Bugzilla, and TestRail for project and defect tracking.
4. Agile and Scrum Frameworks
Work in sprints, participate in stand-ups, and collaborate in cross-functional teams.
5. Live Projects
Get hands-on experience with real-world scenarios, helping you build a solid portfolio.
Real-World Applications of QA Testing Skills
Software Development Companies
Tech firms rely heavily on QA testers to maintain software integrity.
Banking and Finance
Ensuring the security of financial transactions is non-negotiable. QA testers are responsible for safeguarding sensitive data.
E-Commerce
Testing ensures that checkout flows, payment gateways, and inventory systems work flawlessly.
Healthcare
Medical software must be error-free to avoid risks to patient safety. QA professionals ensure compliance with HIPAA and other standards.
Industry Demand for QA Testers
According to Glassdoor, QA Analysts earn an average salary of $75,000 annually in the U.S. A LinkedIn 2024 report listed "QA Testing" as one of the top 10 in-demand tech skills. With the increasing relevance of QA testing courses, more professionals are gaining the skills needed to meet industry standards. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts a 25% job growth for QA roles from 2023 to 2030, making it a promising and future-proof career path.
Course Structure: Step-by-Step Learning
Week 1-2: Fundamentals of Testing
Introduction to SDLC & STLC
Writing test cases
Week 3-4: Manual Testing Deep Dive
Exploratory Testing
Regression Testing
Week 5-6: Automation Basics
Introduction to Selenium
Writing basic scripts
Week 7-8: Advanced Automation
Framework Development
Integration with Jenkins and Git
Week 9-10: Tools and Frameworks
JIRA and Test Management
Real-time project simulation
Week 11-12: Capstone Project
Apply all skills to a live project
Get feedback from mentors
Who Should Take This Course?
Beginners in IT looking to start a tech career.
Non-tech professionals wanting to transition into QA.
Students aiming to build a strong portfolio.
Manual testers planning to upskill with automation.
Benefits of QA Testing Online Training Course
Flexibility
Learn at your pace, from anywhere, without compromising on your schedule.
Affordable
Online courses are often more cost-effective than bootcamps or college programs.
Certification
Get a shareable certificate that can boost your resume and LinkedIn profile.
Placement Assistance
Many platforms offer career support, including resume building, mock interviews, and job referrals.
Common Tools Taught in QA Testing Courses
Tool
Use Case
Selenium
Automated web testing
JIRA
Bug tracking and project management
TestNG
Test framework for Java
Postman
API testing
Jenkins
Continuous integration
Student Testimonials
"After completing my QA Testing Online Training Course, I landed a job within three months. The hands-on projects made all the difference." - Priya K., Software Tester
"I had zero coding experience. This course taught me everything step by step, from manual testing to automation." - Alex R., QA Analyst
Tips for Succeeding in QA Testing Courses
Practice writing test cases daily
Join QA forums and communities for peer support
Complete all assignments and capstone projects
Regularly update your resume with new skills
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Do I need a tech background to join this course?
No, many courses are beginner-friendly and start with the basics.
2. What if I miss a class?
Most QA Testing Online Training Courses offer recorded sessions.
3. Are there any prerequisites?
Basic computer skills and logical thinking are enough to get started.
4. Will I get a certificate?
Yes, most platforms offer a verifiable certificate of completion.
Key Takeaways
QA software testing is essential for delivering high-quality, reliable software.
A QA Testing Online Training Course can equip you with in-demand skills for a growing industry.
Real-world applications span healthcare, finance, retail, and beyond.
Learn tools like Selenium, JIRA, and Jenkins with step-by-step guidance.
Online training is affordable, flexible, and career-focused.
Conclusion
Mastering QA testing skills is one of the smartest career moves in today’s tech-driven job market. Whether you're just starting or aiming to switch careers, a QA Testing Online Training Course offers the tools, support, and flexibility you need to succeed. With comprehensive QA software testing courses, learners gain hands-on experience in identifying bugs, improving software quality, and understanding testing methodologies that are essential in the IT industry. These skills are not only in high demand but also open doors to a wide range of roles in software development and quality assurance.
Ready to test your future? Enroll in a QA Testing Online Training Course today and start building your dream tech career!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Is Online QA Training Enough to Start a Career in Software Testing?
In today’s fast-paced tech landscape, software quality is non-negotiable. Every app, tool, and platform must meet user expectations for performance, reliability, and security. Behind this invisible guarantee lies the work of skilled Quality Assurance (QA) professionals. If you're eyeing a career in software testing, you may be asking: "Is online QA training enough to get started?" The short answer? Yes, if you choose the right training and apply yourself effectively.
Let’s dive into how Quality assurance courses online can serve as a solid launchpad for a successful career in software testing, what to look for in a quality course, and the steps you should take beyond training to truly stand out.
What Is QA in Software Testing?
Quality Assurance (QA) is the process of ensuring that software meets certain quality standards before it goes live. QA professionals test software to identify bugs, usability issues, and performance gaps. They are essential in delivering a seamless, error-free experience to users.
QA testing typically involves:
Writing and executing test cases
Using tools like Selenium, JIRA, and TestNG
Performing manual and automated testing
Documenting bugs and verifying fixes
Collaborating with developers and business analysts
Why Online QA Training Has Gained Popularity
With the rise of remote learning and global demand for skilled testers, Quality assurance tester course programs have become increasingly popular. The reasons include:
Flexibility: Learn at your own pace, from anywhere.
Affordability: Often less expensive than traditional classroom training.
Access to Tools: Many courses offer hands-on labs, simulations, and tool access.
Certification Prep: Tailored content to help you pass industry-recognized exams.
But is it enough to make you job-ready?
Core Skills You Can Learn in Online QA Training
High-quality online QA training covers both theoretical knowledge and practical skills that recruiters look for. Here are the essential competencies you can expect to gain:
1. Foundations of Software Testing
SDLC and STLC (Software Development and Testing Life Cycle)
Types of testing: Unit, Integration, System, Regression, UAT
Testing methodologies: Agile, Waterfall
2. Manual Testing Techniques
Writing test cases and test plans
Bug tracking and defect reporting
Testing across browsers, devices, and platforms
3. Automation Testing Tools
Selenium WebDriver for UI automation
TestNG or JUnit frameworks
Scripting languages like Java or Python
4. Bug Tracking and Management Tools
JIRA
Bugzilla
Quality Center
5. Soft Skills
Communication and documentation
Analytical thinking
Attention to detail and problem-solving
Real-World Applications: Can You Perform on the Job?
Online QA training that includes real-time projects, mock interviews, and tool-based simulations can help bridge the gap between theory and practice.
Example:
An online course that teaches Selenium might give you a capstone project to:
Automate login/logout for a demo application
Validate UI elements using locators
Generate test reports using TestNG
Such hands-on experience mirrors real QA job tasks and is highly valuable in interviews.
What Employers Expect from Entry-Level QA Testers
Many QA jobs welcome entry-level applicants who have completed a comprehensive training program. Here's what hiring managers generally look for:
Basic understanding of testing concepts
Hands-on experience with testing tools
Portfolio of projects or GitHub test scripts
Certification (optional but advantageous)
Willingness to learn and adapt
With the right online QA training, you can check all these boxes especially if the program includes career support such as resume building, mock interviews, and job placement assistance.
Limitations of Online QA Training (and How to Overcome Them)
While online training is an excellent foundation, it does come with potential downsides if not approached correctly:
1. Lack of Interaction
Solution: Join online forums, Slack groups, or Discord communities where you can interact with peers and mentors.
2. Self-Discipline Required
Solution: Create a learning schedule. Treat your course like a job.
3. No On-the-Job Experience
Solution: Volunteer for open-source projects, internships, or freelance gigs to gain real-world exposure.
4. Outdated Curriculum
Solution: Choose training platforms that update their content regularly and focus on current tools like Selenium 4, API testing, or DevOps integration.
The Role of Certifications in Boosting Your QA Career
Certifications aren’t mandatory to land your first QA role, but they do increase credibility, especially if you’re new to tech.
Popular certifications include:
ISTQB Foundation Level
Certified Software Tester (CSTE)
Certified Agile Tester (CAT)
Automation Testing with Selenium certification
Many online QA training programs prepare you for these certifications, making them an excellent investment.
Career Paths After Online QA Training
Once you complete your online training and start your QA career, a world of opportunities opens up. Some roles you can explore include:
Entry-Level Roles:
QA Analyst
Software Tester
Manual Tester
Test Engineer
Growth Opportunities:
Automation Test Engineer
QA Lead
Performance Tester
QA Manager
Software Development Engineer in Test (SDET)
With added skills in scripting, DevOps, or API testing, you can transition into even more specialized roles.
Tips to Maximize Your Online QA Training
Here’s how to make your training more effective and career-focused:
Choose Hands-On Courses
Go beyond lectures—look for interactive labs and assignments.
Build a Portfolio
Upload your test scripts and projects to GitHub or GitLab.
Practice Bug Reporting
Use real websites to find issues and practice logging them.
Stay Updated
Follow blogs, attend webinars, and stay tuned to QA trends.
Connect with the QA Community
Engage on LinkedIn, Reddit, and QA-specific forums.
Get Mock Interview Practice
Many online QA training programs offer interview preparation. Use it.
Real Success Stories from QA Professionals
Let’s take a look at real-world inspiration:
Case Study 1: Sarah, Manual Tester Turned Automation Engineer
Sarah enrolled in a 12-week online QA training program while working a retail job. She practiced daily, completed capstone projects, and posted her work online. Three months later, she landed her first QA Analyst role. A year later, after upskilling in Selenium, she moved into automation and now earns 2x her initial salary.
Case Study 2: Ajay, Non-IT to QA Engineer
With a background in finance, Ajay switched careers by taking an online QA training course. Though he had no coding experience, the structured path and mentorship helped him become job-ready. He’s now a full-time tester in a healthcare software firm.
Final Verdict:
Yes, QA certification online is enough to start a career in software testing, provided it is practical, up-to-date, and career-focused. It works best when combined with self-motivation, hands-on learning, and proactive career building.
If you’re serious about breaking into QA, an online course can equip you with the skills, tools, and confidence needed to start strong. But don’t stop there, apply what you learn, keep practicing, and never stop exploring the world of software testing.
Key Takeaways
Online QA training offers the flexibility and depth needed to launch a testing career.
A strong course covers manual testing, automation, tools, and practical projects.
Employers look for hands-on skills, real-world exposure, and willingness to learn.
Success depends not just on the training itself but on how you apply and extend your learning.
Certifications, portfolios, and internships can greatly boost your chances.
Ready to start your QA journey? With the right online QA training, dedication, and smart strategies, you’re already well on your way to a promising career in software testing.
0 notes
Text
Beginner’s Guide to Software Testing – Save This for Later!
Software testing plays a vital role in the software development lifecycle. It ensures that applications function as intended, are free from critical bugs, and meet user expectations. If you're new to this field, this beginner's guide to software testing will help you understand the fundamentals, types of testing, and how to get started effectively.

What Is Software Testing?
Software testing is the method used to check whether a software application works as intended. It involves examining the functionality of the system to ensure it meets the defined requirements. Testing helps identify flaws, inconsistencies, or errors in the software. The primary aim is not just to detect bugs but also to confirm that the software performs reliably, securely, and efficiently in real-world conditions.
Why Is Software Testing Essential?
Testing is a fundamental part of software development that helps deliver dependable and efficient applications. It serves multiple purposes, such as verifying core functionality and catching errors before a product reaches users. Here are some key benefits:
Maintains consistency and reliability in the final product
Uncovers defects early in the development cycle
Enhances the overall user experience
Saves time and money by preventing costly fixes later
Supports smooth and optimized system performance
In today’s fast-paced tech world, providing software that runs smoothly and meets user expectations is vital for staying ahead of the competition.
Key Software Testing Terms for Beginners
If you're new to software testing, there are a few basic terms you should know before getting into testing methods. These concepts will help you understand how testing works:
Bug or Defect: A mistake or flaw in the application that causes it to behave differently from what is expected.
Test Case: A detailed set of actions and conditions used to check whether a specific part of the software works correctly.
Test Plan: A document that outlines the overall approach to testing, including tools, timelines, and goals.
Test Environment: The setup of systems, devices, and tools where the testing process is carried out.
Learning these terms is the first step toward becoming confident in the world of quality assurance and software testing.
Types of Software Testing Explained
Software testing can be grouped into two primary approaches based on how the testing is carried out:
1. Manual Testing
In manual testing, testers perform the checks themselves without using automated scripts or tools. Each function is tested step by step to ensure it works as expected. This approach is particularly useful for checking user experience, appearance, and overall usability.
Common manual testing types include:
Functional Testing – Verifies that each feature behaves according to the requirements.
Smoke Testing – Basic checks to confirm the core functions work before deeper testing.
Regression Testing – Ensures that updates or bug fixes haven't broken existing features.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) – Final testing done by real users to validate the product.
2. Automated Testing
Automated testing is a process where testing activities are carried out using software tools instead of manual execution. This method is especially useful when tests need to be repeated frequently, such as in large-scale applications with ongoing updates. By using automation, teams can validate functionality quickly, consistently, and with minimal human effort.
Examples of widely adopted automation tools include:
Selenium – Used for simulating user behavior in web environments across different browsers.
JUnit – A tool tailored for testing small blocks of Java code, typically individual methods or classes.
TestNG – An advanced testing framework that offers powerful features like grouping and parallel execution.
Cypress – Optimized for modern web applications, it enables real-time testing directly in the browser.
Appium – A versatile tool that automates user interactions in mobile applications across platforms like Android and iOS.
Using both automated and manual testing together enables software teams to increase test efficiency, minimize human errors, and deliver robust applications faster and with greater confidence.
Steps to Start Your Software Testing Journey
Starting as a software tester doesn’t require a computer science degree. Follow these steps to begin your career:
1. Learn the Basics
Study the SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) and STLC (Software Testing Life Cycle). Familiarize yourself with testing types, bug lifecycle, and testing methodologies.
2. Practice Writing Test Cases
Understand the logic behind test case creation. Start with simple applications and write functional test cases.
3. Get Familiar with Bug Tracking Platforms
Learning how to use issue-tracking systems is crucial for any aspiring tester. Tools such as JIRA, Bugzilla, and Mantis are widely used in the industry to document and manage bugs throughout the development cycle. By practicing how to report, prioritize, and follow up on bugs, you’ll develop skills essential for real-world QA environments.
4. Explore the Basics of Automation Tools
Even if you’re starting with manual testing, gaining an understanding of automation can give you a competitive edge. Begin with beginner-friendly tools like Selenium for web testing or Postman for testing APIs. Knowing how automated tests are written and executed will expand your capabilities and open the door to advanced testing roles.
5. Build Connections Through QA Communities
Becoming part of online groups focused on software testing can greatly support your learning process. These communities—found on platforms like LinkedIn, Reddit, and niche QA forums—are filled with discussions, tips, and shared experiences from testers at all levels. By taking part in these conversations, you’ll gain insights into industry practices, new tools, and problem-solving strategies. Additionally, staying active in such networks can introduce you to job openings, training resources, and professionals who may help guide your testing career.
Career Opportunities in Software Testing
Software testing offers diverse roles and steady career growth. As demand rises for high-quality software, skilled testers are highly valued across industries.
Common roles include:
QA Tester – Checks software for bugs and reports issues.
Test Engineer – Designs and runs test cases.
Automation Tester – Uses scripts and tools to speed up testing.
Performance Tester – Evaluates how software performs under stress.
QA Lead – Manages testing teams and strategies.
With experience, testers can move into advanced roles in DevOps, test automation architecture, or quality assurance leadership.
Software testing is an essential and rewarding career path. Whether you’re aiming to be a manual tester or an automation expert, learning the basics of Software testing is the first step. With dedication and consistent practice, you can master the skills required to succeed in this field.
0 notes
Text
Driving Innovation Through Expert Consultation: Java, Python, and Automation Testing Services
In today’s highly competitive software-driven marketplace, businesses need more than just code to thrive—they need strategic technology guidance. Whether it’s building scalable back-end systems with Java, deploying rapid prototypes with Python, or ensuring software quality through automation testing, the right consultation can make a transformative difference. That’s where MentorForHire steps in, offering tailored solutions in Java Consultation, Python Consultation, and Automation Testing Consultation.
Java Consultation: Engineering Excellence from the Ground Up
Java has long been a trusted language for developing robust, secure, and scalable enterprise applications. However, building Java solutions that truly deliver value requires architectural vision and deep platform expertise.
MentorForHire’s Java Consultation services are designed to bridge the gap between business goals and technical execution. With decades of combined experience in enterprise Java ecosystems, our consultants bring insights that extend far beyond the syntax.
Our Java consulting offerings include:
Application Architecture Design: We help clients architect resilient, modular systems using best practices from frameworks like Spring Boot, Hibernate, and MicroProfile.
Performance Optimization: Our team audits your existing Java codebase to identify memory leaks, threading issues, or bottlenecks—and proposes fixes grounded in real-world experience.
Code Reviews & Refactoring: Improve code maintainability and readability through clean, efficient refactoring guided by proven design patterns.
Migration & Upgrades: Stay current with the latest Java releases, frameworks, and build tools without disrupting your production systems.
Whether you're scaling a startup SaaS product or re architecting legacy enterprise software, MentorForHire’s Java consultants ensure your backend is secure, efficient, and future-proof.
Python Consultation: Accelerating Business with Agile Solutions
Python’s meteoric rise is no accident. Its simplicity, flexibility, and massive ecosystem make it ideal for applications ranging from machine learning and automation to web development and API integration. Yet the true power of Python is unlocked only when combined with domain knowledge and strategic planning.
MentorForHire’s Python Consultation services focus on leveraging Python’s strengths to deliver business outcomes quickly and effectively.
We specialize in:
Rapid Prototyping and MVPs: Get your product off the ground fast with well-structured prototypes and Minimum Viable Products developed in Django, Flask, or FastAPI.
Data Engineering & Analysis: From data cleaning to advanced analytics and visualizations, we build solutions that extract real insights from your data using libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib.
Machine Learning Integration: Incorporate AI/ML models using scikit-learn, TensorFlow, or PyTorch, with a focus on real-world deployment.
Python Automation: Streamline your workflows by automating repetitive tasks, file operations, and third-party integrations via well-crafted Python scripts.
We also provide mentorship and code reviews to improve team skills, ensuring your developers grow alongside your applications.
Automation Testing Consultation: Boosting Quality and Speed
Modern software demands faster releases without sacrificing quality. Automation testing is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. But without the right strategy, tools, and implementation, automation can become a costly, underutilized resource.
MentorForHire’s Automation Testing Consultation empowers teams to test smarter, faster, and more efficiently.
Key areas of expertise include:
Test Strategy Development: We help design end-to-end test automation strategies aligned with Agile and DevOps principles.
Tool Selection and Integration: From Selenium and Cypress for UI testing, to Postman for API tests and JUnit/TestNG for backend testing, we help select the right tools for your tech stack.
CI/CD Integration: Ensure that your automated tests run seamlessly as part of your build and deployment pipelines with tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab CI.
Test Framework Development: Create reusable and scalable frameworks with best practices in test structure, reporting, and data management.
By choosing MentorForHire, organizations move from manual QA bottlenecks to a proactive testing culture where code quality is a shared responsibility.
Why MentorForHire?
There’s no shortage of consultants, but few offer the deep mentorship and personalized service that MentorForHire provides. Our consultants don’t just deliver solutions—they empower your team to build, learn, and grow.
What sets us apart:
Experience Meets Mentorship: Our experts have not only built scalable systems, but also trained and mentored teams at all levels.
Customized Consultation: Every project is different. We tailor our services to your unique challenges and organizational context.
Transparent Communication: Expect clear documentation, regular updates, and collaborative decision-making throughout the engagement.
Results-Oriented Approach: Whether your goal is faster time-to-market, lower technical debt, or improved system reliability, we focus on delivering measurable results.
Getting Started
The consultation process at MentorForHire is collaborative and efficient:
Discovery Call: Share your project goals, current challenges, and desired outcomes.
Assessment: We analyze your existing infrastructure, codebase, or workflows to identify gaps and opportunities.
Strategy Proposal: Based on our findings, we present a strategic roadmap, complete with timelines, tool recommendations, and execution plans.
Implementation & Support: Our consultants guide or implement the solution, followed by continuous support and mentoring.
Conclusion
In a world driven by technology, success hinges on making the right choices—quickly and confidently. Whether you need enterprise-grade Java systems, rapid Python development, or automation testing that scales with your growth, MentorForHire is your trusted partner in transformation. Our consultation services combine deep technical skill with business acumen to deliver not just solutions, but lasting value.
0 notes
Text
🚀 Master Selenium WebDriver with Java: From Basics to Advanced Frameworks

Whether you're just beginning your journey in automation testing or looking to level up your testing framework with real-world applications, Selenium WebDriver with Java is your gateway to becoming a test automation pro. This powerful duo not only helps you automate web applications efficiently but also empowers you to build scalable and reusable testing frameworks trusted by top tech companies.
In this blog, we’ll take a complete walkthrough of Selenium WebDriver – from Java basics to building an advanced Selenium framework – so you’re not just learning tools, but mastering them in a real-world context.
Oh, and if you're serious about hands-on mastery, here’s a practical Selenium WebDriver Web-Based Automation Testing Udemy course that covers everything in depth – highly recommended! ✅
👨💻 What is Selenium WebDriver?
Selenium WebDriver is a browser automation framework that allows testers and developers to create robust, browser-based regression automation tests and suites. Unlike its predecessor Selenium RC, WebDriver directly communicates with the browser using native compatibility.
The major benefit? It gives you control over the browser just like a real user would, making it an incredibly powerful tool for web automation testing.
🧱 Why Use Java with Selenium?
Java is one of the most widely used programming languages in the automation testing space. Here’s why it’s a perfect match for Selenium:
Open-source and versatile
Large community support
Easy integration with testing tools like TestNG, Maven, JUnit
Fast execution compared to other scripting languages
Java and Selenium together offer great flexibility and cross-platform support, making them an ideal pair for both beginners and experts.
🧪 Selenium WebDriver Java Basics – Get Started Fast
Before diving into frameworks and real-world scenarios, you need to understand the basics. Let’s go over the foundational blocks.
🛠 Setting up Your First Selenium Project
Install Java JDK and set the environment variables.
Download and set up Eclipse IDE (or IntelliJ).
Add Selenium WebDriver JAR files to your project.
Choose your preferred browser (Chrome/Firefox/Edge) and download the driver accordingly.
📄 Writing Your First Script
Here’s a sample Java + Selenium code snippet to open Google and search:
javaCopy
Edit
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver; import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver; import org.openqa.selenium.By; public class GoogleSearch { public static void main(String[] args) { System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "path_to_chromedriver"); WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(); driver.get("https://www.google.com"); driver.findElement(By.name("q")).sendKeys("Selenium WebDriver"); driver.findElement(By.name("btnK")).submit(); driver.quit(); } }
Pretty simple, right?
🧠 Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) + Java in Testing
Once you’ve got the basics, you’ll notice that Java’s OOP concepts can help you create more reusable and maintainable code. This becomes essential when your test suite grows.
Key Java Concepts for Selenium:
Classes and Objects
Inheritance and Polymorphism
Abstraction and Encapsulation
In your test automation code, using these principles will help you reduce duplication and manage tests effectively.
⚙️ Page Object Model (POM): Structuring Your Code the Smart Way
As projects scale, maintaining thousands of test cases can become a nightmare. Enter Page Object Model – a design pattern that separates the test logic from the UI elements.
javaCopy
Edit
public class LoginPage { WebDriver driver; @FindBy(id="username") WebElement username; @FindBy(id="password") WebElement password; @FindBy(id="login") WebElement loginButton; public void login(String user, String pass) { username.sendKeys(user); password.sendKeys(pass); loginButton.click(); } }
POM allows you to reuse classes and methods, making test scripts more modular and readable.
🔄 TestNG: Managing Test Execution with Ease
TestNG is a testing framework inspired by JUnit but packed with extra features like:
Annotations
Grouping
Parallel testing
Data-driven testing
Why use it with Selenium?
Because it lets you define test flow, configure setup/teardown, and generate reports with minimal effort.
javaCopy
Edit
@Test public void loginTest() { LoginPage login = new LoginPage(driver); login.login("admin", "password123"); }
With TestNG, you can also create test suites and execute test cases in parallel, speeding up the overall testing cycle.
🚀 Advance Concepts: Building a Complete Selenium Framework
Once you’re familiar with Java basics, TestNG, and POM, it’s time to build an actual Selenium Framework.
🧱 Key Components of an Advanced Selenium Framework:
Base Class – Driver initialization and teardown.
Utility Classes – For reusable functions like waits, screenshots, etc.
Configuration Files – Store URL, credentials, browser type.
Reporting – Generate custom HTML reports using tools like ExtentReports or Allure.
Data-Driven Testing – Use Excel, JSON, or XML to feed test data.
Continuous Integration (CI) – Tools like Jenkins can be integrated for automated test runs.
A complete automation framework not only supports testing but makes your workflow faster, collaborative, and easily maintainable.
🧪 Selenium Grid: Test on Multiple Environments
Selenium Grid allows you to run tests across multiple machines and browsers in parallel, which is crucial for real-world web applications.
Hub: The central controller
Node: The machines where browsers are running
This setup is ideal for teams that need cross-browser and cross-platform testing.
🤖 Real-Time Scenarios You’ll Learn in This Udemy Course
The Selenium WebDriver Web-Based Automation Testing Udemy course is a must if you're ready to step into actual industry-level projects.
What You’ll Learn:
Building frameworks from scratch
Automating dynamic elements
Handling popups, alerts, frames
Capturing screenshots, logs, and reports
Integration with GitHub and Jenkins
Working with REST APIs through Selenium + Java
This course is hands-on, filled with real-time projects, and is designed to take you from "just learning" to actually applying.
💼 Career Benefits of Learning Selenium WebDriver with Java
Still wondering why you should master this stack? Here’s what you gain:
🚀 In-demand skillset – Automation testing is one of the top IT skills.
💼 Higher salaries – QA automation engineers with Selenium + Java earn 30–50% more than manual testers.
🌍 Global opportunities – Selenium is accepted across industries from fintech to healthcare to e-commerce.
🔧 Developer-friendly – Being in Java means you can collaborate better with development teams and understand systems inside-out.
🧩 Common Mistakes Beginners Should Avoid
Hardcoding test data – Always externalize your data.
Ignoring waits – Use WebDriverWait or FluentWait to stabilize your tests.
Not using POM or frameworks – Will make your code messy and unmanageable.
Skipping exception handling – Catch those edge cases!
Neglecting logs and screenshots – Crucial for debugging failures.
Mastering Selenium WebDriver means writing smart code, not just functional code.
🚀 Ready to Build Real Frameworks?
If you're aiming to break into automation testing or scale your existing skills, there’s no better time to learn Selenium WebDriver with Java.
The Selenium WebDriver Web-Based Automation Testing Udemy course not only teaches theory but also immerses you in real-life projects – from building frameworks to integrating with CI/CD pipelines.
You’ll come out of it job-ready. 👩💻👨💻
Final Thoughts
Selenium WebDriver + Java isn’t just a tool combo – it’s your career launchpad. With the increasing demand for automation testers who can code, understand frameworks, and integrate with DevOps tools, now is the time to act.
Don’t just learn Selenium. Master it. Apply it. Own it.
Take the next step with the Selenium WebDriver Web-Based Automation Testing Udemy course and accelerate your testing career today.
0 notes
Video
youtube
Can You Really Get a Six Figure QA Job in 6 Months?
🚀 How to Earn a $100K+ Salary in 6 Months with QA Automation | SQA Career Roadmap 💼💻 Want to break into tech fast and potentially earn over $100,000/year? In this video, we break down a proven, strategic path to land high-paying Software QA Automation Engineer roles—even if you're starting from scratch. ✅ Here's what you'll learn: 🔹 Top Skills You Need: Programming languages (Python, Java) Automation tools (Selenium, Appium) API testing (Postman, RestAssured) Frameworks (JUnit, TestNG, pytest, Cucumber) CI/CD tools (Jenkins, GitLab CI) 🔹 Step-by-Step Learning Plan (0-6 Months): Best bootcamps & courses (Udemy, Careerist, TripleTen) How to build real automation projects Open-source contributions for experience Fast-tracking with internships & entry-level roles 🔹 Job Search Strategy for Fast Results: Resume & LinkedIn tips Networking that gets results Interview prep for automation roles Targeting remote jobs & high-paying markets like Charlotte, NC 💸 Real Salary Data: Average QA Automation Engineer salary: $86K–$104K Senior roles: $114K+ 75th percentile can reach $120K+ 📈 Whether you're switching careers or looking for a lucrative new path in tech, QA automation is one of the fastest ways to break in and level up.
0 notes
Text
Deciding Between Selenium with Python and Selenium with Java: An In-Depth Comparison
In the domain of automated testing, Selenium emerges as a pivotal tool for ensuring the reliability and quality of web applications. When it comes to selecting the programming language to harness Selenium's capabilities, two prominent contenders often come into play: Python and Java. Both languages offer distinct advantages and considerations, making the decision between them crucial for any automation project.

In this blog post, we'll conduct a thorough comparison of Selenium with Python and Selenium with Java, exploring their unique strengths, use cases, and factors to consider. By the end, readers will have a clearer understanding of which option aligns best with their project requirements, team proficiencies, and organizational objectives.
Python with Selenium:
Python, celebrated for its simplicity and readability, has garnered significant traction within the automation testing community. Let's delve into some key benefits of leveraging Python with Selenium:
Simplicity and Readability: Python's hallmark characteristics include simplicity and readability. Its concise syntax enables developers to express ideas in fewer lines of code, resulting in scripts that are easier to comprehend and maintain. For testers, this translates to expedited development cycles and reduced overhead in managing test suites.
Extensive Ecosystem: Python boasts a vast ecosystem of libraries and frameworks that complement Selenium, augmenting its capabilities for test automation. Whether handling data manipulation, conducting API testing, or generating test reports, Python's rich library support caters to diverse automation needs. Furthermore, the active Python community ensures an abundance of resources, tutorials, and documentation to aid testers throughout the automation journey.
Rapid Prototyping: Python's dynamic nature lends itself well to rapid prototyping and iterative development. Testers can swiftly experiment with different approaches, adapt scripts on-the-go, and respond promptly to evolving requirements. This flexibility seamlessly aligns with agile development methodologies, empowering teams to deliver high-quality software with agility.
Integration Compatibility: Python's interoperability with other tools and technologies makes it an appealing choice for Selenium automation. Whether integrating with continuous integration (CI) pipelines, test reporting frameworks, or version control systems, Python's versatility ensures smooth interoperability, streamlining the testing workflow and bolstering overall efficiency.

Java with Selenium:
Java, renowned for its robustness and performance, has long been a cornerstone in enterprise software development. Here are some compelling reasons to consider Java for Selenium automation:
Robustness and Performance: Java's static typing and strong object-oriented principles contribute to the robustness and performance of Selenium test suites. Its compile-time error checking aids in identifying potential issues early in the development phase, resulting in more stable and reliable automation scripts. For large-scale enterprise projects with stringent quality requirements, Java's reliability is a significant asset.
Widespread Adoption: Java enjoys widespread adoption within the enterprise landscape, making it a natural choice for organizations with existing Java codebases or a Java-centric development environment. The abundance of Java expertise in the workforce, coupled with extensive community support and industry recognition, solidifies its status as a preferred language for Selenium automation in many corporate settings.
Mature Tooling: Java's mature ecosystem of testing tools and frameworks, including JUnit and TestNG, seamlessly integrate with Selenium to offer comprehensive test automation solutions. These frameworks furnish advanced features such as parameterized testing, parallel execution, and built-in reporting capabilities, empowering testers to design and execute sophisticated test suites effortlessly.
Enterprise Support: Java's popularity in enterprise environments translates to robust support from vendors, extensive documentation, and a plethora of third-party integrations. For organizations seeking enterprise-grade features, reliability, and scalability in their Selenium automation endeavors, Java's ecosystem and support infrastructure present a compelling value proposition.
Conclusion:
In summary, both Selenium with Python and Selenium with Java present compelling options for test automation, each with its unique strengths and considerations. Python excels in simplicity, rapid development, and a vast ecosystem, making it an ideal choice for agile teams and projects with evolving requirements. Conversely, Java offers robustness, performance, and widespread enterprise support, rendering it well-suited for large-scale enterprise applications with stringent quality standards.
Ultimately, the decision between Python and Java for Selenium automation hinges on various factors such as project prerequisites, team proficiencies, and organizational preferences. By meticulously evaluating these factors and weighing the pros and cons of each option, stakeholders can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and aspirations. Whether opting for the simplicity of Python or the robustness of Java, Selenium remains an indispensable tool for driving quality and efficiency in web application testing.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Disclosing Selenium Expertise: Handling the Web Automation Landscape
Introduction: Unraveling Selenium's Potential
Selenium, a versatile open-source framework, takes center stage in the realm of automating web applications. Tailored for testers and developers, it arms them with essential tools and libraries, streamlining web testing across diverse platforms. Delving into Selenium's capabilities is made even more impactful through Selenium Training in Pune. This training empowers individuals with the skills and knowledge to unlock the full potential of Selenium, enabling them to adeptly tackle web automation challenges and contribute significantly to their fields.
Understanding the Dynamics of Selenium Automation Testing: A Swift Overview
1. Purpose of Selenium: Elevating the Landscape of Web Application Testing
At its essence, Selenium stands as an automation powerhouse for testing web applications. Testers leverage its capabilities to script interactions in languages like Java or Python, replicating user actions and engagements with web elements.
2. Key Features: Navigating the Strengths of Selenium
Cross-Browser Compatibility: Seamlessly supporting browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge, ensuring consistent behavior across diverse platforms.
Programming Language Support: Accommodating Java, Python, C#, Ruby, providing versatility for testers and developers.
Parallel Execution: Unlocking the potential for concurrent test runs, amplifying overall testing efficiency.
Integration with Frameworks: Seamlessly integrating with renowned frameworks like TestNG and JUnit, delivering advanced test management capabilities.

3. Components of Selenium: Unveiling the Toolkit's Arsenal
Selenium IDE: A browser extension facilitating the recording and playback of interactions, ideal for beginners. To grasp the full potential of Selenium and master the art of web automation, consider enrolling in the Top Selenium Online Training.
Selenium WebDriver: Empowering direct interaction with browsers using various programming languages.
Selenium Grid: Facilitating parallel test execution across machines and browsers, optimizing testing resources.
4. How Selenium Operates: Behind the Scenes Mastery
Selenium operates through commands, interacting with web elements. Test scripts, crafted in a programming language, execute actions like button clicks and text entries. The WebDriver acts as a vital bridge, connecting these scripts with the browser, breathing life into automation.
In the domain of web application testing, Selenium emerges as a game-changer, offering a user-friendly framework to craft robust automated tests. Whether you don the hat of a tester or a developer, Selenium extends the flexibility and cross-browser compatibility necessary to elevate your web application testing endeavors.
In essence, Selenium simplifies the testing landscape, guaranteeing the functionality and quality of web applications through the potent force of automation. As you embark on your Selenium journey, embrace the efficiency and effectiveness it brings to the dynamic world of web application testing.
2 notes
·
View notes