#solution smart building
Text
okay love the idea of rayllum sharing a bed at the inn bc one was broken but may I present to you: them deciding to just build a fort and sleep in that instead of sharing a bed
#rayllum#they argued back and forth about who got the unbroken bed until they were like “a fort!!#fanfic authors PLSSSS#they finished building it and we’re like we’re so smart. this was the only solution to our problem#tdp#okay that is all I am done#tdp season 5#they try and stay up but they pass out at 9 pm like the peepaws they are
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
How IoT Solutions Enhance Efficiency and Sustainability in Smart Buildings
In the era of smart technology, the Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a game-changer for various industries, including the real estate sector. IoT solutions for buildings are transforming traditional infrastructures into intelligent, efficient, and sustainable environments. This blog explores how IoT solutions enhance efficiency and sustainability in smart buildings, highlighting the key benefits of IoT platforms and IoT utilities.
Enhancing Efficiency with IoT Solutions
IoT solutions for buildings provide a comprehensive approach to managing and optimizing various building systems. These solutions leverage interconnected devices and sensors to monitor and control building operations in real-time. Here are some ways IoT enhances efficiency in smart buildings:
Automated Building Management
An IoT platform for smart buildings can integrate various systems, such as HVAC, lighting, security, and elevators, into a single, unified network. This integration enables automated control and monitoring, ensuring that all systems work harmoniously. For instance, IoT sensors can adjust lighting and temperature based on occupancy, reducing energy waste and enhancing occupant comfort.
Predictive Maintenance
IoT utilities can predict potential equipment failures by continuously monitoring the performance of critical building systems. Predictive maintenance reduces downtime and extends the lifespan of equipment by addressing issues before they become major problems. This proactive approach not only improves efficiency but also lowers maintenance costs.
Energy Management
Energy management is a critical aspect of building efficiency. IoT solutions for buildings provide detailed insights into energy consumption patterns, helping facility managers identify areas for improvement. By optimizing energy use, buildings can significantly reduce their operational costs. Smart meters and sensors can track real-time energy usage, enabling precise control and minimizing waste.
Promoting Sustainability with IoT
Sustainability is a growing priority in the real estate sector. IoT solutions play a crucial role in promoting sustainable practices in smart buildings. Here’s how:
Reduced Energy Consumption
IoT utilities enable smart buildings to achieve optimal energy efficiency by using data-driven insights to reduce unnecessary energy consumption. For example, IoT sensors can turn off lights in unoccupied rooms or adjust HVAC settings based on real-time weather conditions. These adjustments lead to substantial energy savings and lower carbon footprints.
Waste Management
IoT solutions for buildings can also improve waste management practices. Smart bins equipped with sensors can monitor waste levels and optimize collection routes, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Additionally, IoT-enabled recycling systems can sort and manage waste more efficiently, promoting sustainable disposal practices.
Water Conservation
Water conservation is another critical area where IoT solutions make a significant impact. Smart irrigation systems can adjust watering schedules based on soil moisture levels and weather forecasts, preventing overwatering and conserving water resources. Similarly, IoT-enabled leak detection systems can identify and address leaks promptly, reducing water waste.
Conclusion
In conclusion, IoT solutions for buildings are revolutionizing the way we manage and operate smart buildings. By enhancing efficiency and promoting sustainability, IoT platforms, and utilities are creating smarter, greener, and more cost-effective environments. As technology continues to advance, the adoption of IoT in building management will be essential for achieving long-term efficiency and sustainability goals. Smart buildings equipped with IoT solutions are not just the future; they are the present, leading the way toward a more sustainable world.
0 notes
Text
Elevator Designing Company in Dombivli
Elevate your building's elegance with our top-rated elevator designing company in Dombivali.Rohit elevator customized solutions to seamlessly integrate style and functionality in your vertical transportation needs.
#elevators lifts escalators in Dombivli#elevators lifts escalators companies in Dombivli#Capsule Elevator Cabin#Glass Automatic Elevator Doors#Elevator Gate Lock#Elevator Junction Box#Elevator Car Top Box#Elevators & Escalators#Elevator design Dombivli#Custom elevator design Dombivli#Residential elevator design Dombivli#Commercial elevator design Dombivli#Luxury elevator design Dombivli#Modern elevator design Dombivli#Elevator aesthetics Dombivli#Elevator cab design Dombivli#Bespoke elevator design Dombivli#Elevator interior design Dombivli#High-rise elevator design Dombivli#Elevator architecture Dombivli#Innovative elevator design Dombivli#Sustainable elevator design Dombivli#Elevator engineering Dombivli#Smart elevator design Dombivli#Accessible elevator design Dombivli#Elevator planning Dombivli#Building elevator solutions Dombivli#Dombivli elevator specialists#Dombivli elevator architects#Dombivli elevator planning
0 notes
Text

Advantages of Smart Building Automation Service
There are numerous benefits of smart building automation solutions. Let's explore it all.
Energy Efficiency
Installing Smart devices such as HVAC systems, Lighting, and other systems can lower overall energy consumption. The smart system ensures that all lights and devices are turned off when unused, saving energy and reducing utility bills. So, call us if you seek the best and most effective smart building automation solution We provide the best and most reliable sustainable solutions.

Lower Operating Costs
Another reason you should go ahead with smart building solutions is that smart buildings have several modern technologies that lower operation costs for building owners and managers. It also saves energy by turning off when the devices are not in use. Plus, there are additional benefits to equipping buildings with smart technologies. If you are looking for the best company for sustainable smart building automation solutions, please feel free to contact us.
Improved Comfort and Productivity
The smart building provides a more comfortable space. Smart technology evaluates the space's temperature and balances it to determine whether it needs to be cooler, warmer, or neutral. The building's smart technology controls everything from temperature to Lighting and makes everything easier. It also saves time and effort and promotes better productivity.

So, please feel free to contact us whenever you think of transforming your building into a smart one. We are a reputed company providing the best smart building automation solutions.
Enhanced Maintenance and Uptime
Another benefit of smart buildings is that smart technology detects all issues early and eliminates expensive repair and maintenance costs. It reduces downtime and disruptions for occupants. However, automated systems support easy and better maintenance by detecting issues and alerting building owners and managers about maintenance.

Whenever you think of transforming your building into a smart one, please feel free to contact us. We are providing the best and most reliable sustainable smart building automation solutions, so our company is the right choice for you. We are providing the best service to all. Also, if you would like the best carbon footprint accounting service, please contact us again for the best assistance. We offer the best service.
#smart building automation solutions#carbon footprint accounting#Decarbonization Maritime Industry#Marine Environmental Impact Assessment#Fisheries and Aquaculture#Life Cycle Assessment Services#Environmental Product Declaration
1 note
·
View note
Text
How can companies ensure their technology tools are secure?
Companies need security for various reasons, and It's very important for different aspects of their operations. So maintaining business security companies ensure their technology tools.
#anti counterfeit solution#smart packaging#vcqru#build loyalty#smart labels#e warranty#cash transfer
0 notes
Text
Revolutionize Your Space with Smart Building Solutions
Unlock the future of building management with Pratiti Tech’s Smart Building Solutions. Harness the power of Digital Twins to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and comfort in your commercial or residential space. Our cutting-edge technology offers real-time insights and intelligent automation, ensuring optimal performance, energy savings, and a superior environment for occupants. Explore innovative solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of your building, transforming it into a smarter, more responsive, and sustainable asset.
0 notes
Text
Top 5 Eco-Friendly Technologies You Need to Know About
Introduction
Eco-friendly technologies are designed not to disturb nature and its processes. The domains of such technologies include energy, transportation, construction, waste management, and many more. This blog outlines 5 of the best eco-friendly technologies that create a visible difference as we walk towards becoming a sustainable world. Read to continue link
#Eco-Tech#Tagsadvanced recycling technology#composting innovations#eco-friendly living#eco-friendly technologies#eco-friendly transportation#electric vehicles#energy-efficient designs#EV advancements#green building materials#green tech#renewable energy#smart irrigation systems#smart wind farms#solar power innovations#sustainable building practices#sustainable future#sustainable technology#waste management solutions#water conservation technology#wind energy developments#Technology#Science#business tech#Adobe cloud#Trends#Nvidia Drive#Analysis#Tech news#Science updates
1 note
·
View note
Text
A Step-by-Step Guide to Smart Building Solutions by Everest Industries
Discover more about Everest Industries, a leading provider of high-quality smart building and construction solutions for residential, commercial, and industrial projects. https://www.everestind.com/
0 notes
Text
BLIIoT | BACnet gateway BA113 for Building Automation BACnet and Modbus Devices to Cloud
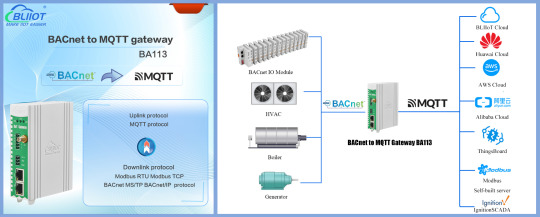
Introduction
With the development of communication technology and control technology, in order to achieve efficient and intelligent management of buildings, centralised monitoring and management has become an inevitable trend in the development of intelligent management of buildings. In this context, high-performance building HVAC data transmission solutions - protocol conversion gateway came into being, widely used in building automation and HVAC system applications.
BLIIoT always insists on the core of the user's needs, and constantly expands its applications in a variety of industrial fields. Recently, we have developed a new series of BLIIoT Building Automation HVAC gateways, This series of products not only have excellent stability and anti-interference capabilities, but also have deep industry applications, aiming to bring users a new building automation data collection and conversion experience.
Product Description
BACnet to MQTT gateway BA113 supports Modbus RTU, Modbus TCP, PLC, BACnet MS/TP, BACnet IP, and MQTT protocols.
BACnet to MQTT gateway BA113 hardware interface includes 2 or 6 RS485/RS232 serial ports, 2 network ports and 1 WiFi wireless transmission interface.
It not only supports mainstream cloud platforms (Alibaba Cloud, Huawei Cloud, Amazon AWS), but also integrates IoT platforms such as ThingsBoard, Ignition, and Zabbix to achieve seamless communication between devices and platforms.
The BACnet to MQTT gateway BA113 adopts an industrial-grade design to ensure reliability in harsh environments. Suitable for industrial automation systems, PLC remote monitoring and IoT applications, BA113 connects the future of industry and provides users with reliable BACnet device networking solutions.

By using BLIIoT patented guide rail buckle technology, the installation process is simplified and the practicality of the gateway is ensured.
Product features
Supported protocols:
Downlink protocol: Modbus RTU, Modbus TCP, BACnet MS/TP, BACnet IP.
Uplink protocols: MQTT.
Hardware interface:
6*RS485/RS232 serial ports: The serial ports are independent of each other. Each serial port parameter can be set to collect different protocols. The serial port can also set the master-slave relationship independently. It can be configured as either a master station or a slave station.
2*network ports: used for data collection and forwarding. The LAN port has a routing function and provides a channel for other devices to connect to the external network.
4G or WiFi wireless transmission interface: Provides diverse communication options to adapt to different industrial environment need.
Data security:
Support data TSL/SSL, X.509 certificate, SNMP V1/V2, key encryption and other security gateway functions.
Remote Configuration Support:
Support remote configuration, providing users with convenient management and monitoring methods, no longer need to visit engineers, saving maintenance costs.
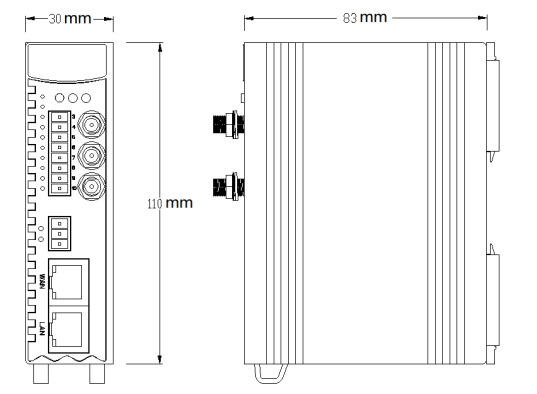
Product Size: L x W x H: 30 x 83 x 110mm

Safety and Stability:
Industrial-grade design: Durable shell material meets industrial environment requirements.
Stability: Efficient communication protocol conversion ensures stable operation of the system.
Environmental adaptation:
Operating temperature range: -40~80℃, adapting to various industrial environments. Protection grade: IP30, ensuring the reliability of the equipment in harsh environments.
Model List

Application scenarios

BA113 is widely used in building automation-related Modbus and BACnet devices to provide stable and reliable solutions to the cloud.
More information about BACnet to MQTT Gateway BA113: https://www.bliiot.com/industrial-iot-gateway-p00424p1.html
#IoT#IoT Solution#Smart Building#BMS#BAS#HVAC#MQTT#BACnet MS/TP#BACnet/IP#Ignition#SCADA#Thingsboard#AWS#Huawei cloud#Ali Cloud#BLIIoT
0 notes
Text
Smart Box Cabin Projects: Showcasing Sustainable Prefab in India
Explore our portfolio of Smart Box Cabin projects, showcasing sustainable prefab constructions in India. Witness innovative designs and green building initiatives for modern living.
#Smart Box Cabin projects India#Prefab construction showcase#Modular homes portfolio#Sustainable building projects#Prefabricated structures India#Eco-friendly housing designs#Innovative prefab constructions#Smart living spaces India#Green building initiatives#Prefab architecture showcase#best modular home manufacturers#best peb companies in india#best prefab companies#best prefab home builders in india#best prefab home companies#build innovative prefab#cheap prefab cabins#build innovative solution#commercial shed construction#industrial shed manufacturers
0 notes
Text
As we bid farewell to 2023, the facility management industry stands as a testament to transformation and growth amid evolving consumer and business preferences.
This year marked a pivotal shift towards a holistic approach, where tangible business spaces are integrated seamlessly with cutting-edge technology to enhance user experiences and operational efficiencies.
0 notes
Text
The smart building solutions market is projected to experience consistent growth with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12.5% from 2023 to 2033. By 2033, it is anticipated to capture a market share of US$ 15.6 billion, while in 2023, the market is forecasted to be worth US$ 1.35 billion.
0 notes
Text
Smart Buildings by Zenatix
"Smart Buildings by Zenatix" refers to innovative building management solutions offered by Zenatix, a company specializing in smart technology. These solutions leverage advanced sensors, data analytics, and automation to enhance energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and operational performance in commercial and residential buildings.

#energy analytics#building automation system#building management system#energy management system#energy savings#energy management#iot companies in india#remote asset management#energy management solutions#iot bms#smart building
0 notes
Text
BLIIoT BACnet/IP Distributed IO Module BL207 Used in Smart Buildings

1. Introduction
Smart building technologies are rapidly emerging, bringing unprecedented changes to building management, efficiency and comfort. In enabling this change, BACnet/IP distributed IO modules play a key role. This article will introduce the basic concepts of BLIIoT BACnet/IP Distributed Ethernet IO Module BL207 and their key applications in smart buildings.
2. BACnet/IP distributed IO module
What is BACnet/IP?

BACnet (Building Automation and Control Networks) is a communication protocol standard for smart building automation. It allows devices of different brands and types to communicate with each other, enabling device interoperability. BACnet/IP is the implementation of the BACnet protocol on the IP network, allowing devices to communicate through standard Ethernet, making it more flexible and convenient.
How the BLIIoT BACnet/IP Distributed Ethernet IO module BL207 works?
BLIIoT BACnet/IP Distributed Ethernet IO Module BL207 with other devices via the BACnet protocol. They can receive sensor data such as temperature, humidity, light, etc., and can also control actuators such as air conditioning systems, lighting systems, etc. These modules upload data to a central control system to enable real-time monitoring and control of all aspects of the building.
3. Smart building needs
Energy Management
In today's context of increasing environmental awareness, energy management has become particularly critical. BACnet/IP IO Module BL207 can monitor energy usage and optimize HVAC systems, lighting and power distribution to reduce energy costs and reduce carbon footprint.
Safety
Safety has always been one of the top priorities of building management. BACnet/IP IO Module BL207 can integrate intrusion detection, fire alarm and surveillance systems to ensure building security.
Environmental Control
Providing a good indoor environment is essential for user comfort. These modules can monitor parameters such as temperature, humidity, air quality and adjust HVAC and lighting systems accordingly to provide a comfortable indoor environment.
User Comfort
Smart building technology can enhance user experience, such as providing personalized lighting solutions through smart lighting systems or convenient access control through smart security systems.
Data Collection and Analysis
Smart building systems generate large amounts of data that can be used for decision making and performance analysis. BACnet/IP IO Module BL207 make data collection and analysis easier by transmitting data to a central system.
4. Advantages of BACnet/IP distributed IO modules
Flexibility and Scalability
BACnet/IP IO Module BL207 can be flexibly laid out and expanded as needed without heavy rewiring. This makes management of the building easier.
Data Interoperability
BACnet/IP IO Module BL207 communicate seamlessly with other BACnet devices, making it easy to share data between various systems, thereby increasing overall system efficiency.
High Efficiency
These modules are highly efficient and capable of processing and transmitting large amounts of data in real time, ensuring fast response and accuracy of the system.
Integration
BACnet/IP IO Module BL207 can be integrated with other smart devices and systems for comprehensive building automation and management.
5. Application examples of BLIIoT BACnet/IP Distributed Ethernet IO Module BL207

Energy Management System
BACnet/IP IO Module BL207 can be used to monitor energy usage and automatically adjust lighting and air conditioning systems to minimize energy waste and reduce energy costs.
Security System
These modules can be integrated with security systems to monitor intrusion and fire alarm conditions and automatically take action to protect the building and the people and property within it.
Air Conditioning and Lighting Control
BACnet/IP IO Module BL207 can adjust according to indoor environmental parameters, providing a comfortable indoor atmosphere and reducing energy consumption when no one is around. For example, during the day, they can automatically adjust curtains and lighting to take full advantage of natural light and reduce lighting energy use.
Building Automation
The core of smart buildings is building automation, and BBACnet/IP IO Module BL207 are a key component in achieving this goal. They can control various systems within a building, such as heating, ventilation, air conditioning, power and lighting, to improve operational efficiency and user experience.
Data Collection and Analysis
BACnet/IP IO Module BL207 upload real-time data to a central system where it can be used for trend analysis, troubleshooting and performance optimization. Through data analysis, building managers can make more informed decisions and improve system maintainability and sustainability.
6. In Conclusion
BACnet/IP IO Module BL207 are a key component in enabling smart building technologies, and they bring significant benefits to the management and operation of buildings. As technology continues to develop and innovate, smart buildings will continue to have a positive impact on our society and environment. Building owners and managers should actively explore and adopt these advanced technologies to improve building efficiency, sustainability and user experience.
More information about BLIIoT BACnet/IP Distributed IO Module BL207 : https://www.bliiot.com/bacnet-ip-io-module-p00397p1.html
0 notes
Text
Smart Home Building Systems in Florida: Creating Modern Luxury Custom Homes with Affordable Panelized Solutions!

Are you ready to transform your dream of owning a modern luxury custom home in Florida into a reality? Look no further than the cutting-edge smart home building systems that are revolutionizing the construction industry. With a focus on innovation, efficiency, and sustainability, these systems are taking the concept of home building to a whole new level.
Smart Homes for the Future
Smart home technology has rapidly gained popularity across the USA, and Florida is no exception. With the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, homeowners are seeking integrated solutions that make their lives more convenient and efficient. Imagine controlling your lighting, thermostat, security cameras, and entertainment systems with a simple voice command or a few taps on your smartphone. Smart home building systems are designed to seamlessly incorporate these technologies, providing you with unparalleled convenience and control.
Florida’s Modern Luxury Custom Homes
Florida’s unique blend of natural beauty, vibrant culture, and desirable weather has made it a hotspot for luxury living. Modern luxury custom homes are in high demand, and the incorporation of smart home technology has become a defining feature of these residences. From state-of-the-art kitchens equipped with touchless faucets and smart appliances to energy-efficient HVAC systems that adapt to your preferences, these homes are designed to enhance your lifestyle while reducing your environmental footprint.
Affordable Panelized Home Building Solutions
One common misconception about luxury custom homes is that they come with a hefty price tag. However, thanks to affordable panelized home building solutions, you can achieve your dream home without breaking the bank. Panelized construction involves prefabricating sections of the home in a controlled factory environment. These panels are then assembled on-site, significantly reducing construction time and labor costs. This approach not only makes the process more efficient but also ensures a higher level of precision and quality in the final product.
Creating Your Smart Luxury Home in Florida
Building a smart luxury home in Florida is an exciting journey that starts with finding the right design and construction team. Look for builders experienced in implementing smart home building systems and panelized construction techniques. They will work closely with you to understand your vision, preferences, and budget, ensuring that your dream home comes to life exactly as you imagined.
As you embark on this exciting venture, remember that your smart luxury home is not just a residence; it’s a reflection of your lifestyle, values, and aspirations. With the power of smart home technology and innovative building solutions, you can create a haven that blends modernity, luxury, and sustainability in the heart of Florida.
In conclusion, the synergy between smart home building systems and modern luxury custom homes is reshaping the way we perceive and experience home ownership. The integration of technology and design is not only enhancing our daily lives but also contributing to a more sustainable future. If you’re ready to turn your dream into a reality, explore the possibilities offered by smart home building systems and affordable panelized solutions in the beautiful state of Florida.
Ready to work with the best-panelized home kit builders in New York, New Jersey, and Connecticut?
Talk to an expert!
#Smart Home Building Systems in Florida#Modern Luxury Custom Homes#Affordable Panelized Solutions#affordable panelized home building solutions
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Pursuit of Zero Hunger: Unlocking a World Without Hunger

Introduction
Hunger is a persistent global issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a fundamental human right to have access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food, yet achieving this goal remains a challenge. The United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) include Goal 2: Zero Hunger, which aims to end hunger, achieve food security, improve nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture by 2030. This article explores the significance of Goal 2, the current state of global hunger, and the steps being taken to eradicate hunger and ensure food security for all.
The Scope of Global Hunger
Hunger is a multifaceted issue that extends far beyond the simple absence of food on one's plate. It encompasses a range of factors that contribute to individuals, communities, and entire nations being deprived of regular access to sufficient and nutritious food. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the alarming statistic of more than 690 million people, approximately 8.9% of the global population, suffering from chronic hunger serves as a stark reminder of the challenges we face in achieving zero hunger.
Poverty is undoubtedly one of the primary drivers of hunger. Insufficient income and resources leave individuals and families unable to afford an adequate quantity and quality of food. Poverty often leads to a cycle of hunger and malnutrition, as individuals struggle to break free from the grip of poverty, which further perpetuates food insecurity. Breaking this cycle requires comprehensive poverty alleviation strategies that address the root causes of poverty and provide opportunities for economic empowerment.
Inadequate access to nutritious food is another critical aspect of the hunger problem. Even when food is available, it may lack the necessary nutrients for individuals to lead healthy and active lives. Malnutrition, both undernutrition and overnutrition, poses significant health risks and hinders proper physical and cognitive development. Access to a diverse range of nutritious food, including fruits, vegetables, proteins, and essential vitamins and minerals, is essential for combating malnutrition and achieving food security.
Climate change poses a formidable threat to global food security. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events disrupt agricultural systems, leading to reduced crop yields and food shortages. Small-scale farmers, who are often the most vulnerable, bear the brunt of these climate impacts. Droughts, floods, and unpredictable growing seasons further exacerbate the challenges they face in producing enough food to sustain themselves and their communities. Addressing climate change and implementing climate-resilient agricultural practices are critical components of the zero hunger agenda.
Conflict and political instability also contribute to hunger and food insecurity. In regions affected by armed conflicts or political crises, food production and distribution systems are disrupted, and access to food becomes limited. Civil unrest, displacement, and the destruction of infrastructure further compound the problem, leaving populations in desperate need of assistance. Resolving conflicts, promoting peace, and ensuring humanitarian access to affected areas are essential steps towards achieving zero hunger.
Unequal distribution of resources exacerbates hunger within and between countries. Concentration of wealth, land ownership, and access to markets and resources in the hands of a few can perpetuate a vicious cycle of food insecurity. Reducing inequality and promoting equitable distribution of resources and opportunities are crucial for creating a fair and just food system that leaves no one behind.
Addressing the complexity of hunger requires a multi-dimensional and holistic approach. It involves not only increasing food production but also improving access to nutritious food, addressing poverty, mitigating climate change, promoting peace and stability, and advocating for equitable resource distribution. Governments, international organizations, civil society, and the private sector must collaborate and work together to implement comprehensive strategies and policies that tackle the root causes of hunger.
Efforts to combat hunger must also prioritize the empowerment of marginalized and vulnerable groups, including women, indigenous communities, and rural populations. These groups often face additional barriers to accessing food and resources, and their voices and needs must be central to any hunger eradication initiatives. By empowering these groups and ensuring their active participation in decision-making processes, we can foster more inclusive and sustainable solutions.
Hunger is a complex issue intertwined with poverty, inadequate access to nutritious food, climate change, conflict, and unequal distribution of resources. Achieving zero hunger requires addressing these interconnected challenges through comprehensive strategies that encompass poverty alleviation, sustainable agriculture, nutrition education, climate resilience, peacebuilding, and equitable resource distribution. By recognizing the multifaceted nature of hunger and taking collective action, we can pave the way towards a world where every individual has access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food, and where hunger is no longer a harsh reality.
Understanding Food Insecurity
Food insecurity is a complex and multifaceted issue that extends beyond the simple concept of hunger. While hunger specifically refers to the sensation of not having enough food to eat, food insecurity encompasses a broader set of circumstances that prevent individuals, communities, and entire nations from accessing a consistent supply of nutritious food necessary for a healthy and active lifestyle.
At its core, food insecurity is characterized by a lack of regular access to sufficient and nutritious food. It encompasses both the quantity and quality of food available to individuals and communities. It means not having enough food to meet basic dietary needs and not having access to a variety of foods that are essential for a balanced and nutritious diet. Without adequate access to nutritious food, individuals and communities face numerous challenges that can have detrimental effects on their health, well-being, and overall development.
Food insecurity affects individuals, communities, and entire nations. On an individual level, it can lead to undernutrition or malnutrition, compromising physical and cognitive development, and increasing the risk of disease and mortality. Communities and nations grappling with food insecurity face significant socio-economic challenges, hindering their progress and development.
Several factors contribute to food insecurity, including income inequality, limited agricultural productivity, and unstable food systems. Income inequality is a critical driver of food insecurity, as it affects individuals' purchasing power to access food. In societies with wide income disparities, those with lower incomes often struggle to afford an adequate and nutritious diet, leading to food insecurity. Addressing income inequality is essential to reduce food insecurity and ensure equal access to food for all.
Limited agricultural productivity is another key factor contributing to food insecurity. Insufficient agricultural production, whether due to environmental factors, inadequate access to resources, or outdated farming practices, can result in insufficient food supply. This directly affects food availability and affordability, particularly in regions heavily dependent on agriculture for sustenance. Enhancing agricultural productivity through sustainable farming practices, technology adoption, and investments in rural infrastructure is crucial to achieving food security.
Unstable food systems, including volatile food prices, inadequate storage facilities, and unreliable supply chains, also contribute to food insecurity. Fluctuations in food prices can make nutritious food unaffordable for vulnerable populations, pushing them further into food insecurity. Weak supply chains and insufficient infrastructure can lead to food losses and wastage, exacerbating the problem. Strengthening food systems and improving their resilience is vital for reducing food insecurity.
Achieving zero hunger requires addressing these underlying issues comprehensively. It necessitates a multi-faceted approach that encompasses not only increasing food production but also improving access to nutritious food, promoting income equality, and building sustainable and resilient food systems.
To address income inequality and improve access to food, efforts should focus on creating employment opportunities, implementing social protection programs, and promoting inclusive economic growth. Policies and initiatives that aim to reduce poverty, increase access to education, and empower marginalized communities can significantly contribute to reducing food insecurity.
Investments in agricultural research and development, modern farming techniques, and sustainable farming practices can enhance agricultural productivity and ensure a stable food supply. Support for small-scale farmers, including access to credit, technology, and markets, is crucial for their productivity and income generation, ultimately contributing to food security.
Strengthening food systems involves improving infrastructure, storage facilities, and transportation networks to reduce post-harvest losses and ensure efficient distribution of food. It also requires promoting market transparency, fair trade practices, and reducing food waste along the supply chain. International cooperation and partnerships are vital to sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices to build resilient and sustainable food systems globally.
Education and awareness play a critical role in addressing food insecurity. Nutrition education programs can empower individuals and communities to make informed choices about their diets, promote healthy eating habits, and maximize the nutritional value of available resources. Education on sustainable agricultural practices can also promote environmentally friendly farming methods, improve resource management, and enhance long-term food security.
Achieving zero hunger requires collaborative efforts and strong governance at various levels. Governments, civil society organizations, international institutions, and the private sector must work together to develop and implement comprehensive policies, programs, and initiatives that address the underlying causes of food insecurity. International cooperation and partnerships are vital for sharing knowledge, expertise, and resources to build a sustainable and inclusive global food system.
Food insecurity is a complex issue that encompasses more than just hunger. It refers to the lack of regular access to sufficient, nutritious food necessary for a healthy and active life. Factors such as income inequality, limited agricultural productivity, and unstable food systems contribute to food insecurity. Achieving zero hunger requires addressing these underlying issues through a comprehensive approach that includes promoting income equality, improving agricultural productivity, strengthening food systems, and raising awareness through education and collaboration. Only through concerted efforts can we create a world where everyone has access to adequate and nutritious food, thereby achieving the goal of zero hunger.
Tackling Hunger through Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture serves as a critical pillar in the global effort to combat hunger and achieve food security. It focuses on promoting farming practices that not only increase food production but also ensure the long-term preservation of natural resources and the environment. By adopting sustainable agricultural techniques, we can address the challenges of food security while mitigating the negative impacts of agriculture on ecosystems and climate change.
Investing in research and innovation is essential for advancing sustainable agriculture. By developing and disseminating improved crop varieties and farming methods, we can enhance productivity and resilience in agricultural systems. This includes investing in agricultural research to create crops that are more resistant to pests, diseases, and adverse weather conditions. Furthermore, innovation in farming techniques, such as precision agriculture and vertical farming, can optimize resource use and maximize yields.
Crop diversity is a fundamental aspect of sustainable agriculture. By promoting a variety of crops, farmers can reduce the risks associated with relying on a single crop. Diversification enhances resilience to pests, diseases, and climate variability. It also contributes to a more balanced and nutritious diet, as diverse crops provide a broader range of essential nutrients. Encouraging farmers to grow a variety of crops through training, access to seeds, and market incentives can enhance both their livelihoods and the overall food security of a region.
Efficient irrigation techniques are crucial in sustainable agriculture, particularly in regions facing water scarcity. Practices such as drip irrigation and precision water management minimize water waste and ensure that water resources are used optimally. By improving irrigation infrastructure and promoting water-saving practices, we can maximize agricultural productivity while conserving water for other essential needs.
Empowering small-scale farmers is vital for achieving sustainable agriculture and food security. Smallholder farmers constitute a significant portion of the world's food producers, particularly in developing countries. Enhancing their access to resources, including land, credit, seeds, and technology, can significantly improve their productivity and livelihoods. Supporting farmers' cooperatives, providing training on sustainable practices, and facilitating access to markets can help small-scale farmers overcome barriers and strengthen their position in the agricultural value chain.
Improving access to markets and financial resources is crucial for small-scale farmers. Limited market access often hinders their ability to sell their produce at fair prices and take advantage of economic opportunities. By improving infrastructure, connecting farmers to markets, and promoting fair trade practices, we can ensure that farmers receive equitable returns for their products. Additionally, providing financial services tailored to the needs of farmers, such as microcredit and crop insurance, can enhance their resilience and enable investment in sustainable agricultural practices.
Sustainable agriculture also embraces practices that minimize the use of harmful agrochemicals and promote organic farming methods. By reducing reliance on synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, sustainable agriculture protects soil health, biodiversity, and water quality. Organic farming practices prioritize natural inputs, such as compost, crop rotation, and biological pest control, to maintain soil fertility and minimize environmental impacts. Encouraging the adoption of organic farming practices through training, certification programs, and market incentives can contribute to sustainable agricultural systems.
Sustainable agriculture plays a crucial role in combating hunger and achieving food security. By promoting environmentally friendly farming practices, investing in research and innovation, encouraging crop diversity, adopting efficient irrigation techniques, empowering small-scale farmers, and improving market access, we can increase food production while preserving natural resources for future generations. Sustainable agriculture not only addresses the immediate challenge of hunger but also contributes to building resilient and sustainable food systems that can sustainably nourish the world's population.
Nutrition: Beyond Calorie Intake
Ensuring access to nutritious food is a fundamental component of achieving the goal of zero hunger. While addressing calorie intake is important, it is equally crucial to emphasize the quality and diversity of food consumed. Malnutrition, which encompasses both undernutrition and overnutrition, remains a significant global concern. To tackle this issue effectively, efforts must focus on promoting balanced diets, improving access to essential nutrients, and educating communities about healthy eating habits.
One of the key aspects of addressing malnutrition is promoting balanced diets. A balanced diet includes a variety of foods from different food groups, providing essential nutrients such as proteins, carbohydrates, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals. It is essential to ensure that individuals have access to a diverse range of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products. Promoting dietary diversity can help prevent nutrient deficiencies and promote overall health and well-being.
Improving access to essential nutrients is another critical element of addressing malnutrition. This includes enhancing the availability and affordability of nutrient-rich foods, particularly for vulnerable populations. It involves strategies such as promoting local food production, supporting small-scale farmers, and strengthening food supply chains. By ensuring that nutritious foods are accessible and affordable, individuals and communities can have a greater opportunity to meet their nutritional needs.
Education and awareness play a vital role in promoting healthy eating habits and preventing malnutrition. Nutrition education programs can provide information on the importance of balanced diets, the benefits of consuming different food groups, and the risks associated with poor nutrition. These programs can also teach practical skills, such as meal planning, food preparation, and cooking techniques, to empower individuals to make healthier food choices. By promoting nutrition education at schools, healthcare facilities, and community centers, we can foster a culture of healthy eating and long-term behavior change.
Collaboration among governments, NGOs, and the private sector is crucial for implementing effective interventions and policies to address malnutrition. Governments should prioritize nutrition in their national agendas and develop comprehensive strategies that encompass food security, health, and education. They can implement policies that support sustainable agriculture, regulate food labeling and advertising, and provide incentives for the production and consumption of nutritious foods. NGOs and the private sector can contribute by partnering with communities, implementing nutrition programs, and promoting corporate social responsibility initiatives that address malnutrition.
Efforts should also focus on addressing specific nutritional needs in different population groups. For instance, targeting maternal and child nutrition is essential for breaking the intergenerational cycle of malnutrition. Providing adequate nutrition during pregnancy and early childhood is crucial for healthy growth and development. Additionally, addressing micronutrient deficiencies, such as iron, vitamin A, and iodine, is vital in reducing the prevalence of nutrient-related disorders and improving overall health.
Furthermore, innovative approaches can be utilized to improve access to nutritious food. For example, initiatives such as school feeding programs, community gardens, and urban farming can increase the availability of fresh and locally sourced produce. These approaches not only provide nutritious food but also promote community engagement, sustainability, and economic empowerment.
Ensuring access to nutritious food is a key aspect of achieving zero hunger. Efforts should go beyond addressing calorie intake alone and focus on the quality and diversity of food consumed. By promoting balanced diets, improving access to essential nutrients, and educating communities about healthy eating habits, we can effectively address malnutrition. Collaboration among governments, NGOs, and the private sector is crucial for implementing effective interventions and policies. By prioritizing nutrition and implementing comprehensive strategies, we can pave the way for a healthier and more food-secure future for all.
Building Resilience and Adaptation
Climate change presents a formidable challenge to global food security. As temperatures rise, extreme weather events become more frequent, and precipitation patterns shift, the agricultural sector faces disruptions that exacerbate hunger and threaten the livelihoods of millions of people. To address these challenges, it is crucial to build resilience and implement adaptation strategies that can mitigate the impact of climate change on food systems.
One of the key approaches to combat the effects of climate change on food security is through the development and implementation of climate-smart agriculture practices. Climate-smart agriculture encompasses a range of techniques and methods that aim to increase agricultural productivity while reducing greenhouse gas emissions, enhancing the resilience of farming systems, and promoting sustainable land and water management. These practices include conservation agriculture, agroforestry, precision farming, and integrated pest management. By adopting climate-smart agriculture, farmers can better cope with the changing climatic conditions and maintain or increase their agricultural productivity.
Investing in the development and dissemination of climate-resistant crop varieties is another essential strategy. Plant breeding programs can focus on developing crop varieties that are more tolerant to heat, drought, flooding, and pests. These climate-resistant varieties have the potential to withstand extreme weather events and produce higher yields under challenging conditions. Additionally, promoting crop diversity and utilizing traditional and local crop varieties that are adapted to specific climate conditions can contribute to enhancing the resilience of agricultural systems.
Implementing early warning systems is crucial for anticipating and responding to weather-related risks. Timely and accurate information about weather patterns, such as rainfall, temperature, and extreme events, allows farmers to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions to protect their crops and livelihoods. Early warning systems enable farmers to adjust their planting and harvesting schedules, implement protective measures, and access support and resources in advance of potential disasters. These systems can be enhanced through the use of technology, including weather monitoring tools, satellite data, and mobile communication networks.
In addition to on-farm strategies, addressing climate change and food security requires collaborative efforts at regional, national, and international levels. Governments, international organizations, research institutions, and civil society must work together to develop and implement policies and initiatives that promote climate resilience in the agricultural sector. This includes investing in climate-smart infrastructure, improving access to climate information and resources for farmers, and supporting sustainable land and water management practices.
Promoting climate-smart agriculture also involves integrating climate change considerations into broader development strategies. This includes incorporating climate resilience and adaptation measures into national agricultural policies, land-use planning, and disaster risk reduction frameworks. It also requires supporting small-scale farmers, particularly in vulnerable regions, by providing access to financial services, agricultural inputs, and capacity-building programs that equip them with the knowledge and tools to adapt to changing climate conditions.
Furthermore, international cooperation and financial support are essential to help developing countries build resilience and adapt to climate change. Industrialized nations, as major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, should fulfill their commitments to provide financial resources and technology transfer to support climate change adaptation and mitigation efforts in developing countries. This includes funding for research and development, capacity-building programs, and infrastructure improvements that enhance climate resilience in agriculture.
Climate change poses significant challenges to food security by disrupting agricultural production and exacerbating hunger. Building resilience and implementing adaptation strategies are crucial to mitigate the impact of climate change on food systems. This involves developing and promoting climate-smart agriculture practices, investing in climate-resistant crop varieties, implementing early warning systems, and integrating climate considerations into broader development strategies. Through collaborative efforts at all levels, we can work towards ensuring a sustainable and secure food supply in the face of a changing climate.
Promoting Gender Equality
Achieving zero hunger is intricately linked to addressing gender inequality, as women play a pivotal role in agriculture and food production worldwide. However, they often face significant barriers that limit their access to resources, land, credit, and decision-making power. Empowering women and promoting gender equality in agriculture and food systems is crucial for enhancing agricultural productivity, improving food security, and ultimately achieving the goal of zero hunger.
Women make up a substantial portion of the agricultural labor force, particularly in developing countries. They are involved in various stages of food production, from planting and harvesting to processing and marketing. Despite their significant contributions, women face systemic challenges that hinder their productivity and restrict their ability to access resources. Gender norms and discriminatory practices often result in unequal access to land ownership, credit facilities, agricultural inputs, and extension services. This inequality not only undermines women's economic empowerment but also hampers overall agricultural productivity and food production.
Empowering women in agriculture involves dismantling the barriers that hinder their full participation and addressing gender-based inequalities. Providing women with secure land rights and access to productive resources is a crucial step towards ensuring their equal participation. This can be achieved through legal reforms, awareness campaigns, and support for women's land rights organizations. By enabling women to have control over land and other productive assets, they gain the autonomy and resources necessary to make decisions about agricultural practices and investments.
Access to credit is another critical factor in empowering women in agriculture. Financial institutions and development programs should prioritize providing women with access to affordable credit and financial services. By ensuring equal access to credit facilities, women can invest in agricultural inputs, machinery, and technology, thereby enhancing their productivity and contributing to food security. Moreover, targeted financial literacy programs can equip women with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively manage their finances and make informed decisions regarding agricultural investments.
Gender-responsive extension services and training programs play a vital role in empowering women farmers. These programs should address the specific needs and priorities of women, providing them with the necessary knowledge and skills to adopt sustainable farming practices, improve crop productivity, and manage post-harvest activities. Furthermore, mentorship programs and networking opportunities can facilitate the exchange of experiences and knowledge-sharing among women farmers, enabling them to learn from each other and strengthen their capacities.
Promoting women's participation in decision-making processes is essential for achieving gender equality in agriculture and food systems. Women's voices and perspectives need to be heard and considered in the development and implementation of policies, programs, and initiatives related to agriculture and food security. This requires creating inclusive spaces for women to engage in decision-making at all levels, from local communities to national and international platforms. Strengthening women's leadership and representation in farmer organizations, cooperatives, and agricultural institutions can contribute to more equitable and effective decision-making processes.
Recognizing and valuing the unpaid care and domestic work performed by women is also crucial for achieving gender equality in agriculture. The burden of household chores and caregiving responsibilities often falls disproportionately on women, limiting their time and energy for productive activities. Investing in infrastructure, such as water and sanitation facilities, energy sources, and transportation, can alleviate the burden of unpaid care work, reduce drudgery, and create opportunities for women to engage in income-generating activities.
Promoting gender equality in agriculture and food systems is not only a matter of social justice but also a strategic imperative. Studies have shown that closing the gender gap in agriculture could increase agricultural productivity and contribute to global food security. When women have equal access to resources and decision-making power, they are more likely to invest in the well-being of their families, improve farming practices, and adopt sustainable agricultural technologies. Moreover, empowering women in agriculture can have a multiplier effect, as they tend to invest a significant portion of their income in education, health, and nutrition, benefiting their households and communities.
Achieving zero hunger requires addressing gender inequality in agriculture and food systems. Empowering women, ensuring their equal access to resources, land, credit, and decision-making, is essential for enhancing agricultural productivity, improving food security, and promoting sustainable development. By promoting gender equality, we unlock the full potential of women as agents of change in the fight against hunger. Investing in women farmers and recognizing their invaluable contributions can pave the way for a more equitable and food-secure future for all.
Collaboration and Partnerships
The journey towards achieving zero hunger is a complex and multifaceted task that requires collaboration and partnerships among various stakeholders. No single entity can tackle this challenge alone. Governments, international organizations, civil society, and the private sector must come together, pooling their resources, sharing knowledge, and coordinating efforts to implement effective policies, programs, and initiatives that address the underlying causes of hunger and achieve sustainable development.
Governments play a central role in driving the efforts to eradicate hunger. They have the responsibility to establish and implement national policies and strategies that prioritize food security and nutrition. This includes allocating sufficient resources, developing sustainable agricultural practices, investing in rural infrastructure, and ensuring access to social protection programs for vulnerable populations. Governments should also create an enabling environment that encourages private sector investments in agriculture and promotes the engagement of civil society organizations in hunger alleviation initiatives.
International organizations, such as the United Nations agencies, the World Bank, and regional development banks, have a crucial role in coordinating global efforts to combat hunger. These organizations provide technical expertise, policy guidance, and financial support to countries in their efforts to achieve food security and nutrition goals. They facilitate knowledge exchange, promote best practices, and coordinate international partnerships for sustainable development. Additionally, they monitor progress, assess the impact of interventions, and advocate for policy changes at the global level to address systemic issues related to hunger.
Civil society organizations, including non-governmental organizations (NGOs), community-based organizations, and grassroots movements, are instrumental in mobilizing communities, raising awareness, and implementing on-the-ground interventions to address hunger. They work closely with local communities, advocating for their rights and empowering them to actively participate in decision-making processes related to food security and nutrition. Civil society organizations also play a crucial role in monitoring and holding governments accountable for their commitments to achieving zero hunger.
The private sector has a significant role to play in advancing the goal of zero hunger. Companies involved in agriculture, food processing, and distribution can contribute through sustainable business practices, innovation, and investment in agricultural value chains. Public-private partnerships can be formed to leverage the expertise, technology, and resources of the private sector in addressing the challenges of food security and nutrition. Engaging the private sector can lead to increased productivity, improved market access for smallholder farmers, and the development of innovative solutions to reduce post-harvest losses and improve food distribution systems.
Collaboration and partnerships among these stakeholders are crucial for maximizing the impact of interventions and addressing the root causes of hunger. By pooling resources and expertise, stakeholders can achieve greater efficiency, avoid duplication of efforts, and scale up successful initiatives. Collaboration also allows for the sharing of knowledge and best practices, facilitating innovation and learning from each other's experiences. Through coordinated efforts, stakeholders can identify gaps, develop comprehensive strategies, and implement integrated approaches that address the complex and interconnected challenges of hunger.
Multi-stakeholder partnerships should be based on principles of inclusivity, transparency, and accountability. All stakeholders, including marginalized groups, small-scale farmers, women, and youth, should have a seat at the table and actively participate in decision-making processes. Partnerships should prioritize the needs and priorities of those most affected by hunger and ensure that interventions are context-specific and culturally appropriate.
Achieving zero hunger requires collaboration and partnerships among governments, international organizations, civil society, and the private sector. By working together, stakeholders can pool their resources, share knowledge, and coordinate efforts to implement effective policies, programs, and initiatives that address the underlying causes of hunger and achieve sustainable development. With collective action and a shared commitment, we can create a world where everyone has access to sufficient, nutritious food and no one goes to bed hungry.
Conclusion
Goal 2: Zero Hunger stands as a testament to our collective commitment to eradicating hunger and achieving food security for all. While the challenges are immense, significant progress has been made in recent years. However, there is still a long way to go. By addressing the root causes of hunger, promoting sustainable agriculture, improving nutrition, building resilience, empowering women, and fostering collaboration, we can unlock a future where hunger is nothing but a distant memory. The pursuit of zero hunger is not just a noble aspiration; it is a moral imperative that demands our unwavering dedication and concerted action. Together, we can create a world where no one goes to bed hungry, where food becomes a basic right rather than a luxury, and where the potential of every individual is unleashed.
#How to achieve zero hunger through sustainable agriculture#Addressing food insecurity: a comprehensive approach to zero hunger#Empowering women in agriculture for zero hunger#Climate change and its impact on food security#The role of partnerships in achieving zero hunger#Achieving zero hunger through collaborative efforts#Promoting gender equality for sustainable food systems#Climate-smart agriculture: a solution for food security#Strategies to combat hunger and promote sustainable development#The importance of access to nutritious food in achieving zero hunger#Tackling food insecurity: a global priority for sustainable development#Addressing the root causes of hunger for long-term solutions#The role of governments in achieving zero hunger#Building resilience in agriculture to mitigate the impact of climate change on food security#Harnessing the potential of small-scale farmers for zero hunger#Innovative approaches to promote food security and nutrition#Ensuring equal access to resources for sustainable food production#Strengthening agricultural value chains for zero hunger#The role of education in promoting sustainable food systems and zero hunger#Integrating gender equality into agricultural policies for food security#Sustainable farming practices for achieving zero hunger#Leveraging technology to enhance food production and reduce hunger#Overcoming barriers to food access and nutrition for vulnerable populations#Promoting sustainable land and water management for food security#The impact of income inequality on hunger and food insecurity#Investing in agricultural research and innovation for zero hunger#Advocating for policy changes to address hunger and promote sustainable agriculture#Strategies to improve market access for smallholder farmers and reduce hunger#Strengthening early warning systems for climate-related risks and food security#Creating a roadmap for achieving zero hunger: lessons learned and best practices
0 notes