#uniseriately
Text
Current bane of my existence: trying to translate abstract algebra terms to norwegian and not have it be some sort of anglicised monstrosity
#math#undergrad student#currently doing my thesis on generealised uniserial algebras#even the word “serial” has no good translation#even the official norwegian-english mathematical dictionary has nothing#i am sick and tired
0 notes
Text
In addition to secondary growth involved in secondary phloem and xylem, most woody eudicots and gymnosperms develop a secondary cambium known as cork cambium or phellogen that gives rise to the periderm (see Figure 19.41). (...) Ray cells can be arranged in one (uniseriate) or multiple (multiseriate) files to form a tissue known as rays that traverse the phloem, cambium, and xylem (see Figure 19.41).

"Plant Physiology and Development" int'l 6e - Taiz, L., Zeiger, E., Møller, I.M., Murphy, A.
#book quotes#plant physiology and development#nonfiction#textbook#secondary growth#xylem#phloem#eudicots#woody plants#gymnosperms#cambium#cork#phellogen#periderm#plant cells#ray cells#uniseriate#multiseriate#pith
1 note
·
View note
Note
I'm sorry now you've got me obsessed witht hr black widow thing....
And seeing Satoru acting all uniserious about the situation while the elders might be ripping their hair out 😭😭😭😭.
And reader being so confused by the whole ordeal !?!?!?
Is this man lucky or is she the unlucky one.
And now I'm thinking...how does the intimate times work? Like!??!?!
honestly if the elders know i think they're warring between being glad you haven't succeeded (because they need gojo) and being so so annoyed that you haven't (because they loathe gojo). it would be so convenient if you managed to kill him. but also they need someone who can hold the line against curses so.
you are so confused by the whole situation because you've never struggled like this. all of your past husbands died easily, though you made sure to vary the times to try and escape some of the suspicion. and it just doesn't make sense! every time you're sure you connected with gojo, you haven't. and he just smiles and acts like nothing happened, even though your excuses are getting flimsier and flimsier. he's flirted after every single assassination attempt. you keep thinking he has to know by now but he keeps leaving openings, so he must not.
i don't think you really have many intimate times! gojo isn't in the habit of letting people actually touch him (especially when he knows for a fact you're trying to kill him) and you're not exactly there for the relationship. so it's not exactly on the table, though sometimes he lets his infinity down for just a few seconds to act like he's going to steal a kiss, because he likes the way it flusters you.
the most intimate moments probably lead to an attempt on his life, too, because you think his guard is down.
(it's not. and he thinks it's cute, the way your eyes narrow in concentration, as if you have a chance.)
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mod 1: Bryophytes
Ngl I have no idea how to prepare for the botany paper, but I might as well try something-
Polytrichum
Classification:
Class - Bryopsida
Order - Polytrichales
Family - Polytrichaceae
Genus - Polytrichum
Gametophyte
External Structure:
The nature of gametophyte of polytrichum is differentiated into 2 parts: A horizontal underground rhizome and an erect leafy shoot.
Rhizome: The horizontally growing underground portion of the gametophore. It bears small, brown or colorless leaves in three rows and numerous rhizoids.
Leafy Shoot: The erect leafy axis arising from the rhizome. It is differentiated into a stem-like central axis which bears dark green expansions. The so called leaves are spirally arranged in 3/8 phyllotaxy.
The leaf is differentiated into a sheathing leaf base and an apical limb. The limb is narrow, lanceolate, and green. Leaf base is colorless and membranous, closely clasped around the stem.
A short transition zone is present between the rhizome and the aerial shoot. It bears small brown leaves similar to those on rhizome.

Internal Structure:
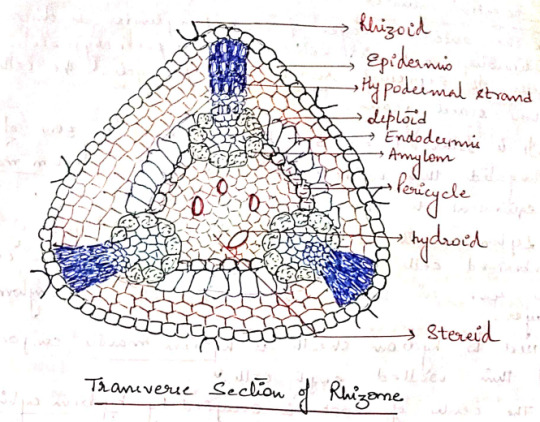
I. Rhizome: In most of the species, the rhizome is triangular in outline with rounded corners. A transverse section of rhizome shows the following regions:
a) Epidermis: The outermost layer of thick walled cells. They give rise to rhizoids.
b) Cortex: The epidermis is followed by cortex consisting of 3-4 layer of thin walled parenchymatous cells.
It is interrupted by 3 hypodermal strands that extend radially from periphery to center.
Hypodermal strands composed of prosenchymatous cells contain starch grains. Extending inwards from each hypodermal strand is a group of lignified cells containing radial strands.
Next to the cortex, there is a layer of radially elongated cells with suberized thickening on their walls. This layer can be compared to the endodermis of higher plants.
c) Pericycle: A 2-3 layered parenchymatous pericycle is present between endodermis and the central conducing strand. It is discontinuous.
d) Leptoids: There are thin walled polygonal cells present in furrows opposite to the radial strands. They are like sieve tubes of phloem hence called leptoids. The cells collectively form lepton.
e) Amylom: The innermost later of leptoids is separated from the central cylinder by a single layer of parenchymatous cells containing starch. This layer is called amylom.
f) Central Cylinder: Situated in the central region of the rhizome. Made up of 2 types of cells: thick walled living cells called stereids and empty dead cells called hydroids. Both of them together make up the hydrom.
II. Aerial Shoot: In transverse section, the aerial shoot is irregularly lobed due to the presence of leaf bases. It is differentiated into 3 regions:
a) Epidermis: The superficial uniseriate later. Discontinuous due to the persistent leaf bases.
b) Cortex: Epidermis is followed by broad cortex. Outer cortex is made of prosechymatous cells and inner is made of parenchymatous cells.
In young shoots, the cortical cells contain chloroplasts.
A large number of leaf traces are also present in the cortex.
c) Central Cylinders: The outermost later of central cylinders is discontinuous and is composed of parenchymatous cells. It represents rudimentary pericycle. The cells store starch grains.
It is followed by 3-4 layered irregular zone of elongated thin walled cells. This zone is leptom mantte ( equivalent to phloem of vascular plants)
Leptom mantte is followed by 1-2 layers of suberized cells which form hydrom sheath. The cells are rich in starch and also called amylom layers.
Next to hydrom sheath is hydrom mantte composed of think walled empty cells.
The center of shoot is occupied by hydrom cylinder made up of thick walled cells. These cells help in conduction of water and hence equivalent to the xylem of higher plants.

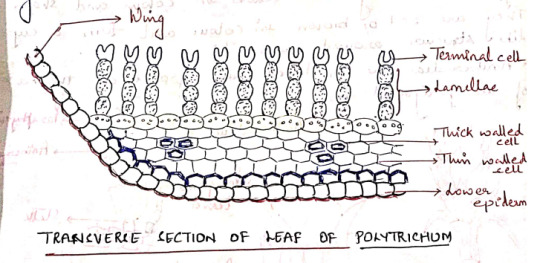
III. Leaf
A transverse section of the limb of the leaf shows a thick midrib, gradually tapering into 2 rudimentary wings.
The ventral surface is bound by a distinct epidermis. It is covered by thick cuticle. Epidermis is followed by sclerenchymatous hypodermis.
The ground tissue (cortex) is composed of parenchymatous cells.
The dorsal surface of limb is made up of vertical plates of cells called lamellae. Each lamellae has 4-8 cells; all cells contain chloroplasts except the terminal one. This terminal cell is larger than outer cells and sometimes it is (___)
The arrangement of cells in lamellae and presence of any spaces between adjacent lamellae increases the photosynthetic area.
The wing is composed of a single layer of hyaline cells. Lamellae are not present in the wing region.
The wings become dry and curved when the plants grow in dry habitats.
Reproduction: In polytrichum, reproduction takes place by vegetative and sexual methods.
I. Vegetative Reproduction: Takes place by bulbils which develop on rhizome. Besides, fragmentation of underground rhizome also helps in propagation.
II. Sexual Reproduction: Polytrichum is dioecious, the male (antheridia) and the female (archegonia) sex organs develop at the spices of main shoots of separate plants.
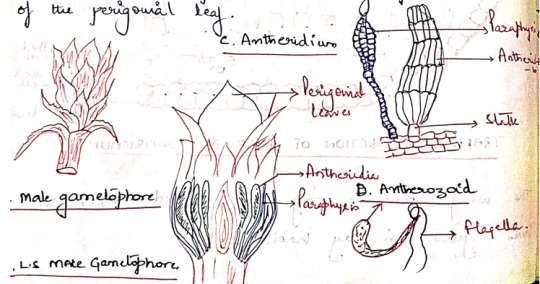
Antheridia:
They are born at the apex of the male gametophore. They are surrounded by a whorl of specialized leaves, called perigonial leaves. These leaves differ from vegetative leaves in color and shape. They are red or brown in color and form a cup like structure around antheridia.
Antheridia are produced in groups at the base of the perigonial leaf.
The mature antheridium is a club shaped structure with an elongated body and a short stalk. They body has a single layered jacked of sterile cells, enclosing a mass of androcytes.
At the free distal end of the antheridium is the operculum consisting of a single or few large cells.
Intermingled the antheridia in the antheridial head are steric multicellular hair like structures called as paraphysis.
Aechegonium:
They are borne in groups at the apex of the female gametophore.
The leaves surrounding the archegonia are called the perichaetial leaves. These leaves overlap close over at the top of the archegonial (cluotes??) to form a bud-like structure called the perichaetium.
Intermingled with the archegonia in the cluotes(Still??) are paraphysis.
The mature archegonium is a flask-shaped structure consisting of a long neck, venter, and a stalk.
The venter cavity contains a single spherical egg and a ventral canal cell.
The long, narrow neck consists of 6 vertical rows of neck cells enclosing a narrow neck canal which has a row of neck canal cells (10)

Fertilization:
Water is essential for fertilization. The jacket sells of the mature antheridium swell by absorbing water. The hydrostatic pressure thus generated bursts the operculum and the antherozoids are liberated.
The neck canal cells and the venter canal cell of mature archegonium degenerate forming a mucilaginous mass.
The mucilaginous mass swells up by absorbing water and as such the cover cells present at the tip of the archegonium are pushed apart.
The antherozoids are attracted towards the archegonia and a number of antherozoids swim down the neck but only faces with the egg and this oospore is formed.
Sporophyte
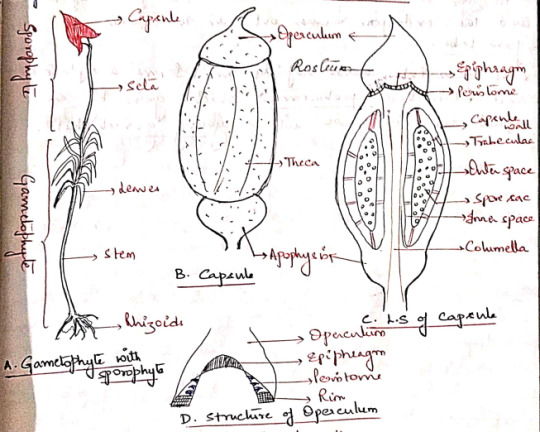
The sporophyte of polytrichum is differentiated into a foot, a long seta, and an angular capsule.
Foot: A dagger-shaped structure embedded in the female gametophore. It is composed of parenchymatous cells. It acts as an anchoring and absorbing organ.
Seta: A long, slender structure between the foot and the capsule. Anatomically, seta is differentiated into epidermis, hypodermis, parenchymatous cortex and a central cylinder, 'hydroids'
The main function of seta is to raise the capsule to the height and conduction of water and nutrients.
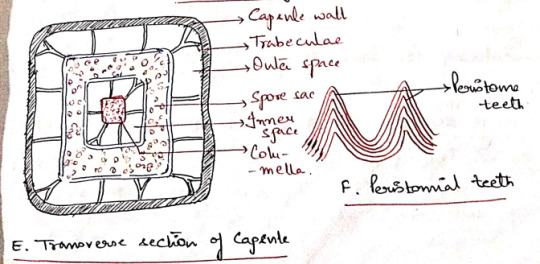
Capsule: The capsule is differentiated into 3 parts:
a) Apophysis (Basal part): The distal end of seta gradually enlarges to form a bulbous apophysis ad the base of the capsule. It has a thick walled epidermis continued with that of the seta.
Epidermis is interrupted by stomata, each stoma has 2 guard cells. It is followed by chlorenchymatous cortex and it serves as photosynthetic tissue.
The central part of apophysis is occupied by a conduction strands which is in continuation with the columella and seta (sterile).
b) Theca (Fertile): The middle fertile part of the capsule. It shows many longitudinal grooves. The wall or jacked of theca is composed of several layers of chlorophyllous cells. The outermost layer forms epidermis devoid of stomata. 'Thickwalls', 2-3 layers of cells, chlorenchyma wall layers.
An air space of lacuna is present inner to the wall layers and is divided into small chambers by transverse filaments of chlorophyll containing cells, the trabeculae.
The outer space is followed by space sac. The fertile cells present inside the spore sac constitute the archesporial tissue.
Initially the archesporium is single layered but it becomes many layered in later stages of development of the sporophyte.
The last generation of archesporial-cells differentiates into spore mother cells. Each spore mother cells will form four haploid spores.
The spore sac is also surrounded on the sinner side by an inner air space. It is also transversed by many transverse trabeculae.
The central part of the capsule is occupied by a thick column of parenchymatous cells, the columella. This is a sterile tissue which is continuous with the central axis of the apophysis.
c) Operculum: The apical part of the capsule which forms a cap-like structure at the apex of the theca. It has an extended proximal part, called rostrum, and a projects beak-like distal(?) part.
The boundaries of the operculum and theca are marked by a distinct countriction(??), the rim.
The distal end of the columella is expanded into a pale thin membranous epiphragm at the base of the operculum.
In the mature capsule the peristome is composed of 32 or 64 peristoimal teeth. The teeth are pyramidal and composed of fiber like cells several layers in thickness.
Peristome regulates spore discharge. They do not exhibit hygroscopic movements.
Dehiscence of Capsule:
At maturity, the capsule shrivels as it dries up. The columella disintegrates and the spores come to lie in the cavity thus formed.
Further drying and shriveling of the capsule wall causes the operculum to fall off and thus exposing the peristome.
After exposure of the peristome, thin walled cells of the epiphragm lying between the peristomial teeth also dry and this several minute holes are formed. The spores are dispersed through these holes.
Only a few spores are liberated every time the capsule sways in the wind. This method of spore dispersal is known as censor mechanism.
Young Gametophyte:
The spores are small sounded structures, yellow but turn green immediately after dispersal. The spore wall is differentiated into an outer exospore and an inner endospore.
At the time of germination, the exospore ruptures and the endospore comes out in the form of germ tube.
The germ tube grows rabidly and forms a septate and branched protonema, which grows by an apical cell. It grows into a young gametophyte.
Evolution of Sporophyte in Bryophytes
The sporophyte of the majority of liverworts and mosses show the same plan. It is made up of an anchoring and absorbing foot, a stalk like seta, and a capsule which contains spores and elaters.
A comparative study of the sporophytes shows that there has been a progressive reduction in the amount of the fertile tissues from Marchantials to Bryales.
In all the bryophytes the oospore, formed as a result of fertilization, is the mother cell of sporophyte. In the simplest type of sporophyte the entire oospore is utilized in the formation of spores and capsule wall.
In some simple forms, some spore mother cells, which fail to develop into spores, form elaters.
In complex forms, the oospore develops into a sporophyte which is differentiated into foot, seta, and capsule.
The following 2 contrasting views have been put forwards with regard to the evolution of sporophytes in bryophytes: progressive sterilization and progressive reduction.
Evolution of Sporophyte by Progressive Sterilization
This view, aka "theory of progressive evolution" or "theory of sterilization" was put forward by Bower and supported by Cavers and Campbell.
According to this theory, the sporophytes of the complex forms (ex: Funaria) have evolved due to progressive sterilization of the potential fertile tissue of the simpler forms (ex: Riccia)
In primitive forms the sporophyte is simple and made of the tissue of the sporophyte is fertile (???)
The progressive sterilization from Riccia to Funaria occurred through the following stages:
First Stage: The simplest known sporophyte among bryophytes is that of Ricca. It consists of only capsule, there being no trace of seta and foot.
The entire sporogenous tissue is converted into spores. Few sterile cells (nurse cells) have nutritive function. They are supposed to be ancestors of elaters.
Second Stage: In Corsinia the sterilization has gone a step further and in addition to nurse cells, a sterile foot is also present.
Third Stage: Further sterilization is seen in Sphaerocarpus where the sporophyte has a sterile bulbous foot and a narrow seta, in addition to fertile capsule.
Fourth Stage: In Targionia, the sporophyte is differentiated into a bulbous foot, a massive seta and a capsule.
Amphithecium gives rise to single layered jacked of the capsule and only about half of endothelial cells give rise to fertile sporogenous tissue and the remaining half form sterile elaters. Thus there is further sterilization of sporogenous tissue.
Fifth Stage: In Marchantia, the sporophyte shows foot, seta, and a capsule.
Amphithecium gives rise to a single layered capsule wall and the endothecium forms sporogenous tissue. Approximately 50% of the sporogenous cells forms the spores and the remaining 50% the elaters with thickening bands.
Sixth Stage: The sporophyte of Pellia is also differentiated into foot, seta, and capsule as in Marchantia, but the jacked of the capsule is 2 or more layered. Furthermore a fixes sterile elatophore is present at the proximal end of the capsule with a bunch of elaters.
Seventh Stage: The sporophyte of Anthoceros, consists of bulbus food and a horn or brittle-like capsule. The capsule wall is made up of 4-6 layers of parenchymatous cells.
The outer wall later is epidermis which possesses stomata. The cells of the inner layers of capsule wall have chloroplasts. Thus the sporophyte is capable of synthesizing its own food and is only dependent on gametophyte for water and nutrients.
Another important feature is the presence of central column of sterile cells, the columella.
The tissue of the archesporium differentiates into large fertile spore mother cells and flat and relatively small sterile elater mother cells.
Eighth Stage: The highest degree of sterilization is found in the class Bryopsida.
Regions like foot, seta, capsule wall, columella, apophysis, operculum, and peristome in sporophytes of Funaria and Polytrichum represent the sterile tissue.
The sporogenous tissue is confined only to spore sacs and constitutes a very negligible part of the sporophyte.

Evolution of Sporophyte by Progressive Reduction
Aka Simplification
Kashyap, Church, Goebel, and Evans are the supporters of the retrogressive theory of evolution.
According to this theory, the simple sporophyre of Riccia is the most advanced and has evolved by progressive reduction or simplification of the complex forms such as Funaria and Polytrichum.
The significant steps in the reduction series are:
1. Simplification of the dehiscence apparatus.
2. Reduction of the green photosynthetic tissue in the capsule wall.
3. Disappearance of stomata and intercellular spaces in capsule wall.
4. Decrease in the thickness of the capsule wall.
5. Gradual elimination of seta and foot.
6. There is no progressive increase in the fertility of the sporogenous cells.
Origin of Alteration of Generations
Antithetic Theory:
Celkovasky proposed this theory. On the basis of this theory, the gametophyte or sexual plant represents the original generation.
The sporophyte or the non-sexual plant is a new and different phase evolved by progressive elaboration of the diploid zygote.
The factors which caused its origin are prompt germination of the zygote accompanies by delayed meiosis.
The result is the production of a small sporophyte of Riccia consisting simply of a spore case.
With further elaboration and increased sterilization of the spore producing tissue, a larger sporophyte with differentiation into a foot., a seta, and a capsule is finally evolved.
Homologous Theory:
Pringsheim proposed this theory. According to this theory, sporophyte is not a new generation, but a direct modification of the gametophyte.
It advocated the fact that among the green algae, the gametophyte plant reproduces by both the methods of reproduction.
It bears spores and also the gametes.
In the course of evolutionary sequence, these two functions become separated in two distinct individuals.
The individuals forming spores came to be known as sporophyte and those forming gametes knows as gametophyte.
These two individuals occur regularly alternating in the life cycle.
Both the individuals in primitive land plants where photosynthetic and free living. Gradually the sporophyte became attached to and partly parasitic on the gametophyte. Consequently it became reduced.
Marchantia Thallus
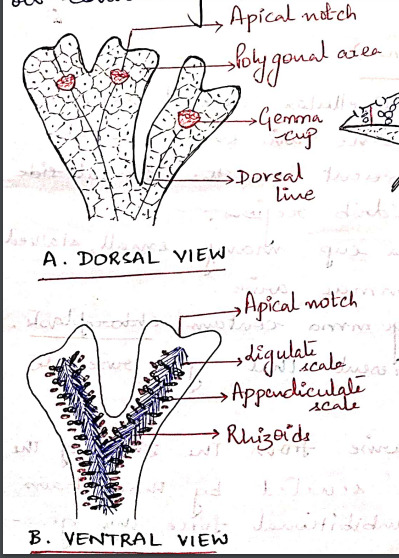
The gametophyte of Marchantia is prostrate, dorsiventral and dichotomously branched. A distinct midrib is present in each branch of thallus.
The apex of each branch is notched and a growing point is situated at the base of each notch.
The dorsal surface of the thallus appears to be masked out into small rhomboidal to polygonal shaped areas called areoles. Which represent the outline of underlying air chambers.
Each areole has got a black dot like spot in the center which marks the position of stoma-like opening leading to air chamber.
Along the midrib on the dorsal surface of the thallus there are certain cup-shaped structures with frilled margins known as gemma cups and they contain special vegetative reproductive bodies called gemmae. (vegetative propagation)
The ventral surface of the thallus bears rhizoids and scales on both sides of the midrib. The rhizoids are usually colorless and unicellular.
Rhizoids are of 2 types: smooth walled and tuberculate. Their function is to:
i) Fix the thallus to substratum.
ii) Absorption of water and nutrients.
The multicellular, one-celled thick scales are arranged in 2-4 rows on either side of the midrib. They are of 2 types:
i) Appendiculate: usually form the inner row of scales, close to the midrib. Have apical appendage.
ii) Ligulate: relatively small and do not have any appendage.
The function of scales is to:
i) Protect the growing point.
ii) Retain some water by capillary action.
The sexually mature thalli possess specialized erect branched called gametophores, which bear the sex organs. These branches arise from the growing apex situated in the apical notch.
The branches present on the male thalli bear the antheridia and are known as antheridiophores while those present on the female thalli bear the archegonia and are called as archegoniophores.
#exam season#send help#biology#notes#plants#botany#bio#bryophytes#bryophyta#polytrichum#plant science#science
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Juniper Publishers - Open Access Journal of Ecology
First Record Fungi for Iraq

Authored by : Hussein Al-Nasrawi
Abstract
44 fungal species were isolated from plant parts submerged in Al-Huwaiza marsh within Iraqi borders, and 7 new first records fungi in Iraq were isolated too, which have been illustrated and described as follows: -
Carbosphaerella leptosphaeriodes, Curvularia lunata var.aria, Graphium sp., Helicascus kanaloanus, Leptosphaeria obions, Stagnospora sp. and Ulocladium tuberculatum, Carbosphaerella leptosphaeriodes, Curvularia lunata var.aeria, Graphium sp., Helicascus kanaloanus, Leptosphaeria obions, Stagnospora sp., Ulocladium tuberculatum.
Keywords: Fungi; Submerged plants; Marsh; New record; Iraq
Introduction
Al-Huwaizah marsh is an aquatic ecosystem extend between Iraq and Iran with freshwater body.Al-Huwaizah marsh locates between latitudes 31˚45ˉ and 31˚00ˉ in the north and longitude 47˚50ˉ and 47˚ 25ˉ in the east , passing through Iranian borders , 80km X 30km [1]. Reed plants (Phragmites Australis Trin) and Typha (Typha Australis Schum & Thonn) are the main components of the vegetative cover in the marsh ecosystem [2]. Many endemic fungal species play an important role in the biodegradation and bioremediation of marsh environment. Fungi play an important role in biodegradation process of plant debris submerged in marsh and bioremediation occurs during mycoremediation during decomposers (fungi) in the aquatic environment along with some types of bacteria [3-5].
Hussein Al-Nasrawi (2006) was confirmed isolation of fungal diversity (fifteen species) as a new record for the first time in Iraq, isolated from the plant remains submerged in aquatic ecosystems in Iraq , in addition to many studies conducted in Iraq for the same mycological puroses [6,7]. Many species of Basidiomycetes were isolated from stems and leaves of the reed plant submerged in salt marshes in Belgium [8].
Materials and Methods
Collection of samples
50 pieces of decomposed plants were collected from water body and sediments in Al Huwaizah marsh in Iraq during 2016. Samples were washed gently by tap water and then by distilled
water. Plant debris were cut into small parts 7-5cm long and each 10 pieces were settled in the bottom of petri dish.
Preparation of culture media
Potato Carrot Agar (PCA), which was obtained by weighing 20g of potato and carrots after washing and peeling, then sliced and boiled with a quantity of distilled water, was sprayed well in a ceramic vase , filtered and placed in a 1 liter flask then added to the prepared mixture of each of the potatoes and carrots media .the media objected to sterilizing process in autoclave under standard conditions for 20 minutes (250mg of chloramphenicol as antibiotic to inhibit bacterial growth.
Insolation and identification of fungi
In this study, two methods were used to isolate the fungi: direct isolation from the substrate. The humid chamber method was used to remove the previously prepared vegetable pieces from the beaker using sterile forceps and placed 7 to 5 pieces in a glass bowl of 15cm diameter Petri dishes Sterilize the filter leaves, then moisten the filter leaves with sterilized distilled water and incubate the dishes under 25°C. The second method is the method of dilution. Dilution method to isolate the fungus from the washing of submerged plant parts and summarized the method by withdrawing 10ml of sterile distilled water, which was washed by the samples previously using a sterile pipette placed in a flask containing 90ml of distilled water and a well and withdraw from it 1ml transferred to A sterile glass dish with a diameter of 9cm. The food medium, plate roast and incubation were incubated under 25°C. Three replicates were made of each sample.
The isolated fungi were classified under light microscope by using international taxonomic keys published in the following literatures: [9-20]
Ascocarp 90-120um in diameter, globose to subglobose shape. The Asci 40-45 × 60-80μm with 8 Ascospores. The Ascospore 15- 18 × 25-30μm, devided by triseptate, the two mid cells within the ascospore dark to brown color, whereas the terminal cells pale and surrounded by mucous sheath. The present isolate nearly like the isolate of Schmidt [21]. This species considers as a new record for Iraq. The isolate was illustrated and kept in under no. BASRA 2011 (Figure 1).
Curvularia lunata var.aeria (Batista, Lima & Vasconselos) M.B.Ellis.1960, publcos inst Micol Recife 263: 5-10
The colony with black to gray color, the hyphae immersed under substrate surface. Conidiophore thicker than fungal filament (macronematous), subhyaline. Conidiogenous cell is polytretic. The conidia with curve shape divided with three septae to form four cells, the two mid cells thicker and darker from the two terminal pale cells. Conidia 10-15 × 20-30μm. This species was previously isolated from painted wood and soil whereas our present fungus isolated from reed sample submerged in marsh sediments. Dry culture was kept in Basra herbarium under no. BASRA 2012 (Figure 2).
The colony is gray to Olivaceous brown, Conidiophore thicker than fungal filament (macronematous) appears under dissecting microscope as Synnemata. Fungal hyphae immersed under the epidermis. Conidiogenous cell is monobasic type. Conidia 5-7 × 15-20μm. Oval to cylindrical shape, with rounded end, pale color without, unseptated. Our isolated fungus resembles species Graphium putredinis isolated by Huges [19]. Our present isolate differentiated by its shape and size (cylindrical 2-4 × 5-11μm. The species isolated from reed segment submerged in marsh sediment. Dry culture was kept in Basra herbarium under no. BASRA 2013 (Figure 3).
The Ascocarp globose, immersed, 400-250μm high, 400- 800 with ostule. Black to dark brown color. Asci 200-300μm., bitunicate, with 8 ascospores. The ascospore 15-25 × 35-50μm. Arranged inside ascus as uninervate. The ascospore divided by septum into 2 dark cells, with funnel shape. cell wall of ascospore surrounded by two layers. There are two germination pores in the ends of ascospore. The ascospore differentiated by gelatinous layer clearly appears when immerse in water drop (disappear with lactophenol stain). The present fungus isolated from Typha segment submerged in marsh sediments, illustrated and kept in Basra herbarium under no. BASRA 2014 (Figure 4).
Leptosphaeria obions (Crouan et Crouan) Saccardo Syll Fung 2,24,1883.
Ascocarp sub globose, immersed, with high about 100-300 and diameter 200-400μm., black to dark brown color, usually covered by brown filaments. The ascocarp coated by two layers, large dark external layer and pale small internal layer. The asci thick, bitunicate,14-20 × 150-300μm. Each ascus contains 8 ascospores, 8-15 × 25-40μm. Arranged inside the ascus as uniseriate in the top of the ascus whereas as biseriate in middle site. The ascospore divided by three septae to form 4 cells, the two middle cells dark brown and larger than the terminal smallest cells. This species was previously isolated from herbal plants and from mangrove area in Australia. The present fungus isolated from Typha segment submerged in marsh sediment, illustrated and kept in Basra herbarium under no. BASRA 2015 (Figure 5).
Stagnospora sp
The Pycnidium sub globose, partially immersed, with pale brown ostiole and short papillate. High of pycnidium 150-180μm, 100-200μm diameter with a neck about 10μm diameter. The conidia pale to brown color, cylindrical in shape, 4-8 × 40-70μm., divided by 5-7 septae. The present isolate resembles Stagonospora haliclysta which was previously isolated by Kohlm [22] (conidia size 3.5-4.5 × 20-27μm, smaller than our isolate). The present fungus isolated from reed segment submerged in marsh sediment and consider as first record in Iraq. It was illustrated and kept in Basra herbarium under no. BASRA 2016 (Figure 6).
Ulocladium tuberculatum Simmons, 1967, Mycologia 59: 83 -84.
The fungal hyphae immersed, sub hyaline, with thick conidiophore 4-6μm. 160-200μm. length, pale brown color, divided by septae. Conidia 10-16 × 10-20μm. sub globose, like potato fruit, divided into several parts by septae cross shape.
The species was firstly isolated in united states. The present isolate resembles Tetracoccosporium paxianum, which isolated by Szabo,1905. Our species was isolated from reed segment submerged in marsh sediment, kept in Basra herbarium under no. BASRA 2017 (Figure 7).
Discussion
Fungi Inhabit plant segments submerged in aquatic ecosystems used their enzymic complex system to biodegrade cellulose and produce carbon source, the most important matter for fungal metabolism process [23,24].
Guaro et al. [25] & Guaro et al. [26] the pioneers who worked on wetland area in Iraq, they isolated and identified many new fungal species and new record fungi forom plant segments submerged in marsh ecosystem in southern area of Iraq. The present study choosed one fresh and natural premium deep marsh ecosystem called al-Audem in Mysan province to suray fungal diversity and new records .This ecosystem consider a natural , undiscovered mycoflora enriched with organic materials and with high quality sediments settle in the bottom of water body , that encourage growth of different fungal species. The present study contributed in recording seven new record fungi for Iraq from this marsh environment [27-34].
Conclusion
Several marshed in southern area of Iraq still waiting more studies and novel works to discover more new species and new record fungi. The high-quality water parameters of marsh ecosystem with enrichment of plant diversity, leads to establishment a perfect foundation of sediment layers embedded in the bottom of marsh environment. This study opens the track for researchers to investigate the ecological niche of fungi in marsh community to detect more aquatic and sediment mycoflora of wetlands.
#Ecology open access journals#Juniper publisher journals#Juniper Publishers#Juniper publishers reviews#Open access journals#Peer review journals
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution Market 2021: Future Trends Analysis, Industry Size, Worldwide Business Overview by Top Manufacturers and Sales Revenue Forecast to 2028
Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution Market Global Analysis to 2027 report offers an in-depth look at the market, including current trends and potential business possibilities. Market Dynamics, Scope, Segmentation, Competitive Analysis, Regional Breakdown, Advanced Learning, Opportunities, and Challenges are all covered in depth in this research report.
The Pharmaceutical Serialization Solutions market report offers an analysis of the reasons behind price fluctuations. The effects of COVID-19 in various regions both in production and at the end of consumption are also given and a SWOT analysis.
DOWNLOAD FREE SAMPLE REPORT@ https://bit.ly/3cKXoBV
COVID-19 has the potential to have three major effects on the global economy: directly impacting production and demand, causing supply chain and market disruption, and having a financial impact on businesses and financial markets. Our analysts, who are monitoring the situation throughout the world, believe that the market would provide producers with lucrative opportunities following the COVID-19 dilemma. The purpose of the report is to provide a more detailed representation of the current circumstances, the economic slowdown, and the influence of COVID-19 on the total industry.
Global Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution Devices Market Segmentation:
Global Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution market segmentation by product type:
Modular Solution
Complete Solution
Global Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution market segmentation by application:
SME
Large Enterprise
Global Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution market segmentation by Key companies:
UniSeries
GENESIS
Systech
Rockwell Automation
ZetesAtlas for Pharma
Cognizant
OPTEL
Abacus Medicine
SerialTrac
Global Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution market segmentation by region:
North America
Europe
Asia Pacific
Latin America
Middle East & Africa
Some Points from TOC:
1 Market Overview
1.1 Product Definition and Market Characteristics
1.2 Global Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution Market Size
1.3 Market Segmentation
1.4 Global Macroeconomic Analysis
1.5 SWOT Analysis
Market Dynamics
2.1 Market Drivers
2.2 Market Constraints and Challenges
2.3 Emerging Market Trends
2.4 Impact of COVID-19
2.4.1 Short-term Impact
2.4.2 Long-term Impact
3 Associated Industry Assessments
3.1 Supply Chain Analysis
3.2 Industry Active Participants
3.2.1 Suppliers of Raw Materials
3.2.2 Key Distributors/Retailers
3.3 Alternative Analysis
3.4 The Impact of Covid-19 from the Perspective of Industry Chain
4 Markets Competitive Landscape
4.1 Industry Leading Players
4.2 Industry News
Key Answers in the Pharmaceutical Serialization Solutions Market report?
Which areas have better demand for products/services?
What strategies are the main players pursuing in the regional market?
Which countries will experience the biggest increase in CAGR and annual growth (YYYY)?
How big is the market now and how big in the next five years?
What is the market probability of a long term investment?
What prospects will the country offer to existing and new market participants?
What are the risks to suppliers in geographic locations?
What aspects will drive demand for products/services in the near future?
How is the influence of various factors on market growth analyzed?
What are the latest trends in regional markets and how successful are they?
Direct Buy This Report now@ https://bit.ly/3nPNK7g
Contact Us:
Credible Markets
99 Wall Street 2124 New York, NY 10005
Email- [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Pharmacognostical Evaluation and Phytochemical Screening of Neolamarckia Cadamba Abstract The Pharmacognostical studies of Neolamarckia Cadamba (Roxb.) Leaf the purpose of identification and differentiation from related species. The macroscopic and microscopic features of the Leafs were studied, including the use of powder microscopy with the aid of suitable tools and reagents. Physicochemical parameters such as ash value, extractive value and weight loss on drying were also determined. The Leafs powder was successively extracted with different solvents followed by preliminary phytochemical screening of the extracts. Preliminary phytochemical screening of different extracts revealed the presence of alkaloids, carbohydrate, protein, gum, steroid, tri-terpenoids, saponin, flavonoids and tannin in the Leafs. The scientific parameter is necessary to identify the exact plant material and to find its quality and purity. These studies indicated the possible information for correct identification and standardization of this plant material. Keywords: Neolamarckia Cadamba; Leafs; Pharmacognostical studies; Macroscopic; Microscopic; Phytochemical Abbreviations: WHO: World Health Organization; Pet. Ether: Petroleum Ether; N. Cadamba: Neolamarckia Cadamba; Phytochemical Go to Introduction Neolamarckia Cadamba Miq; syn. Anthocephalus Kadamba (Family: Rubiaceae) commonly known as ‘Kadamba’ in Ayurveda1 is a large deciduous tree between 37.5-45meter height. The stem of younger trees appears greyish-green with smooth bark. As it gets older, the bark gets rough and grey with longitudinally fissured. Leafs glossy, dark green, opposite, simple pulvinus base sub sessile to petiolate, broadly ovate to elliptical-oblong, entire, apex marinate and venation pinnate. The flowers that appear from August to October are orange to yellow. Inflorescence in clusters, terminal globose heads, subsessile and fragrant. Fruitlets numerous with upper parts containing 4 hollow or solid structures. Seed trigonal or irregularly shaped. The trees found in the greater part of India in moist localities in West Bengal, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala and peninsular India [1-2]. The plant finds its application in several traditional and folklore systems of medicine around the globe. The tribal of India use the Leafs paste orally against dyspepsia and locally applied in mouth ulcer in children. Leafs are nutritious, astringent and their decoction is reported to be used for gargling in aphthae or stomatitis [3]. Dried powdered Leafs used as anthelmintic and the tribal people of India used hot water extract of the Leafs as an astringent, stomatitis and for washing wounds inthroat [4-8]. The flowers are used as vegetable and as gurgle to remove the foul smell from mouth. The fruit is cooling and said to destroy the phlegm and impurity of blood when eaten. The ripened fruit are aromatic, acidic with astringents property. Lod has taken ripened fruits as carminative/masticate. Fruit juice is given during fever and gastric disturbance. Similarly stem barks reported to possess astringent, febrifuge, antiseptic and acts as diuretics. Juice of the bark given orally against cough, fever and in inflammation of eyes. Dried stem bark also used as folk medicine (ethno medicines) in the treatment of various skin diseases, anemia, uterine complaints and for improvement of semen quality. Lod has apply stem bark paste on swelling of legs and juice to cure eye inflammation. The fresh juice of the bark is applied to the heads of infant when the fontanels sunken. Mundas prescribe the bark paste duly suspended in water in reducing blood sugar in the patients with diabetes mellitus [4]. Several pharmacological and biological tests have been reported on this plant are evident from literatures. Alcoholic extracts of dried Leafs possess analgesic, anti-inflammatory antimicrobial, wound healing, antioxidant and anti- alarial antibacterial and antifungal, activities. However, only a few phytochemicals have been reported on this plant in the literature types of sapogenins such as cadambagenicacid, quinovic acid and ß-sitosterol was isolated from the bark. Few alkaloids are also reported from the bark and Leafs like cadambine, 3α-dihydrocadambine and isohydrocadambine [4]. In the light of all the above and keeping the medicinal overview of N. Cadamba, the present investigation was being carried out to study some Pharmacognostical features of the Leafs as a whole including its intact and powdered form available in the literature [5]. The studies were carried out in accordance with WHO General Guidelines for Herbal Drug Standardization methodologies. The findings from this study would be useful as standards for the species as well as a source of reference for further scientific investigation of the species [6]. Go to Materials and Methods Collection, authentication and preparation of plant material The Leafs of the Neolamarckia Cadamba was collected from Monad University Hapur, Uttar Pradesh. For authentification, I made a herbarium in which plant part are attached. Then it was authentified from the taxonomist of NISCAIR, New Delhi. After authentication, fresh Leafs were collected in bulk, washed with potable water to remove adhering dirt followed by rinsing with distilled water, and then shade dried and powdered [7]. Microscopy The following macroscopic characters for the fresh and dried Leafs were noted: surfaces, size and shape, fracture, texture, color, odour and taste. Leafs are slightly aromatic with unpleasant taste. Anatomical characteristics of the Leafs Fresh Leafs pieces were subjected to dehydration procedure from aqueous and alcohol [8]. Powdered microscopic characteristics The shade dried powdered Leafs screened through sieve no. 40 was used for the powdered drug analysis. The specimens were separately treated with glycerin, N/20 iodine solution, 10 % w/v alcoholic ferric chloride (for detection of phenolic compounds), phloroglucinol-hydrochloric acid (1:1) for detecting lignin and ruthenium red solution (for detection of mucilage). After staining, the samples through temporary micro slide preparation taking the mount ant glycerin and were observed under a compound microscope [9-10]. Preliminary phytochemical studies The dried and powdered Leafs (50g) was successively extracted with petroleum ether (60-80°C), chloroform, ethanol and water by reflux for 24h by Soxhlet apparatus. Following extraction, the liquid extracts were concentrated under reduced pressure using rotary evaporator to yield dry residues. The extracts were subjected to preliminary phytochemical screening using standard procedures to determine the nature of phytoconstituents content [11]. The result of the preliminary phytochemical screening of different extracts (Table 1) showed presence ofalkaloids (in chloroform and methanol extracts), carbohydrates, proteins, gum (in aqueous extract), steroids (in petroleum ether, chloroform and ethanol extracts), triterpenoid (in petroleum ether and chloroform extracts), saponin (in chloroform, ethanol and aqueous extracts) and flavonoids and tannin (in ethanol and aqueous extracts) [12]. Click here to view Large Table 1 Physicochemical analysis The physicochemical parameters including ash values (total ash, acid insoluble ash, water soluble ash and sulphated ash), extractive values (ethanol, ether and water soluble) and loss on drying were performed according to the standard treatises [13]. Go to Results Macroscopic characteristics of the Leafs Leafs coriaceous, entire margin, elliptical-oblong or ovate, pulvinus base, with acute or shortly acuminate. It is often used in the form of powder (nygrodhadi kvatha churna) which is a herbal formulation. Powder microscopy of Neolamarckia Cadamba Isolated fragments of uniseriate conical hairs either whole or broken are found. Few, whole unicellular conical hairs, pieces of epidermis of lower surface with wavy anti clinical walls and stomata; few pieces of isolated stomata and prismatic crystal of calcium oxalate are found in the microscopy. Microscopic characteristics The microscopic study of Neolamarckia Cadamba leaf showed the presence of simple elongated, unicellular trichomes, rubiaceous types of stomata on the lower side of the leaf, starch grains, crystals of calcium oxalate, wedge-shaped vascular bundles, and phloem in the form of ring and oil globules. The leaves of Neolamarckia Cadamba having methyl salicylates aroma when crushed by hands. Go to TLC TLC was performed to develop phytochemical finger printing. It was performed using 2x10cm TLC plates coated by silica gel G. 10μl Volume of each extract was applied on plates with the help of capillary a thin layer (0.25mm). In addition, a binder like gypsum is mixed into the stationary phase to make it stick better to the slide. TLC plate on the side with the white surface draw a thin line with pencil. The thin end of the spotter is placed in the dilute solution; the solution will rise up in the capillary (capillary forces). Touch the plate briefly at the start line. Allow the solvent to evaporate and spot at the same place again. This way you will get a concentrated and small spot. A TLC plate can be developed in a beaker. Place a small amount of solvent (mobile phase) in the container. The solvent (eluent) travels up the matrix by capillarity, moving the components of the samples at various rates because of their different degrees of interaction with the matrix (stationary phase) and solubility in the developing solvent. Non-polar solvents will force nonpolar compounds to the top of the plate, because the compounds dissolve well and do not interact with the polar stationary phase. Allow the solvent to travel up the plate until~1 cm from the top. Take the plate out and mark the solvent.The components, visible as separated spots, are identified by comparing the distances they have traveled with those of the known reference materials. Measure the distance of the start line to the solvent front. Then measure the distance of center of the spot to the start line. Divide the distance the solvent moved by the distance the individual spot moved. The resulting ratio is called Rf – value. The Rf (retardation factor) depends on the following parameters: 1. Solvent system 2. Absorbent (grain size, water content, thickness) 3. Amount of material spotted 4. Temperature The chromatograms were developed at room temperature in a 10x10cm twin trough chamber using solvent systems Toluene: Ethyl acetate in a ratio of 6:4 for the ethanolic extract of Neolamarckia Cadamba. After the development chromatograms of saponin were derivatized with 20% Antimony trichloride in chloroform in a ratio of 20:100ml followed by heating at 110°c in preheated oven for 10min. These chromatograms were scanned and evaluated under wave lengths of 254nm & 366nm using a camag TLC to get graphical representation of finger prints. From the TLC finger printing of the ethanolic extract drugs, presence of the saponins, alkaloids, glycosides, steroids, flavonoids as the principle chemical compounds were identified. UV Visible spectrophotometer Preparation of sample 5 gm of powder of each Neolamarckia cadamba were extracted with 100 ml Ethanol. From the filtrate 3ml of extract is treated with centrifuged. Go to Discussion A plant may be considered as a biosynthetic laboratory, not only for the chemical compounds such as carbohydrates, proteins and lipids that are utilized as food by man, but also for a multitude of compounds like alkaloids, glycosides , steroids and sterols, saponins, flavonoids, phenolic compounds and volatile oils that exert a physiological effect. The compounds that are responsible for therapeutic effects are usually the secondary metabolites. A systematic study of a crude drug embraces through consideration of both primary and secondary metabolites derived as a result of plant metabolism in addition to its macro and microscopic studies. N. Cadamba is often confused with other species due to their relative similarities. The species has been taxonomically described as distinct species by earlier workers. The Leafs finds its application in several other traditional and folklore systems of medicine around the globe that have been previously described and surprisingly no pharmacopoeia standards are available for them in the literature. Owing to its importance in applications, the present study was designed and conducted. From the present study, it can be concluded that the macroscopic and microscopic findings together will help future investigators in proper identification of the plant.Further, the powder microscopy, preliminary phytochemical screening and physicochemical parameters would aid in standardization of the plant material. The wide spectrum of biological activity of this plant is due to presence of several phytoconstituents that needs to be studied further [14-21]. Go to Conclusion In the present study, leafs of Neolamarckia Cadamba Roxb. Pharmacognostical Evaluation for the identification of various Phytoconstituents and rest of extracts were utilized for pharmacological screening. The various extracts after the Pharmacoganostics Evaluation have shown the presence of following active principles. Distilled water extract: Steroids, Glycosides, Alkaloids, Tannins, Phenolic compounds, Flavonoids. From the ongoing studies, it can be concluded that the above macroscopic and microscopic studies together may be used as a tool for identification of Neolamarckia Cadamba with its Pharmacognostical characteristics, discriminating it from its other species diversity.
For more Open access journals please visit our site: Juniper Publishers
For more articles please click on Journal of Complementary Medicine & Alternative Healthcare

#Juniper Publishers#open access journals#open acess publishers#Complementary Medicine#alternative Healthcare
0 notes
Photo


While a lot of you may know that human hair varies from animal hair, do you know WHY it varies, other than its texture and feel?
This question is important, especially during a forensic investigation when they find evidence. How can they tell that the piece of hair that they found on the carpet is from the suspect or the suspect’s cat?
This can be answered when looking under a comparison microscope. There are many aspects that a scientist has to look at in order to differentiate the hairs; the cuticle, the cortex and the medulla.
The cuticle is the outermost layer and is made of dead cells that form scales. They come in 3 patterns: coronal (crown like), spinous (petal like), an imbricate (flattened). Humans usually have imbricate patterns while animals have spinous or coronal.
The cortex helps determine the colour of the hair. This is done by seeing the amount and type of melanin pigment. High concentrations of melanin will be brown/black and low concentrations will be blonde/red. In humans, the density and distribution of these pigments is consistent throughout the hair but in animals, it is usually denser near the medulla or produce sudden changes (banding).
The medulla is the core of the hair strand and it also has 3 patterns: fragmented, intermittent (similar sized fragments) or continuous. In humans, the medulla is less than 1/3 of the overall diameter and the animals, it is greater than 1/3. There are also different structures: uniserial, multiserial, vacuolated, lattice and amorphous.
This is usually looked at if there is no follicular tag, which is a clear piece of tissue surrounding the hair shaft that is rich in DNA. This is more likely found when hair is forcibly removed and if the hair is in its early growth phase.
165 notes
·
View notes
Text
Aconquija TV Satelital Tucumán
Alef Network canal judío de Latinoamérica.
America 2 (Canal 2), Ciudad de Buenos Aires,aire, nacional
América 2 nacional, La Plata, Prov. de Buenos Aires
America 2 Bahia Blanca, Prov. de Buenos Aires
Antena Uno CNN
Artear Bahia Blanca, Prov. de Buenos Aires
Artear (Arte Televisivo Argentino) grupo multimedios nacional
Azul TV (Canal 9), nacional, Ciudad de Buenos Aires
Azul TV Bahia Blanca, Prov. de Buenos Aires
Azul TV Mar del Plata Mar del Plata, Prov. de Buenos Aires
Azul TV - Repetidora Necochea - Necochea, Prov. de Buenos Aires
Cablevideo Paraná, Entre Ríos
CableVision TCI Ciudad de Buenos Aires, sistema de cable nacional
Canal 8 Mar del Plata - Repetidora Necochea Necochea, Prov. de Buenos Aires
Canal 9 Patagonia
Canal 9 Televida Mendoza
Canal 13 nacional, aire
Canal 13
Canal 7 Argentina nacional, Ciudad de Buenos Aires
Canal 7 Argentina Bahia Blanca, Prov. de Buenos Aires
Canal 33 - ZAP La Plata
Canal 4 productora de tv
Canal 2 San Nicolás, Santa Fe
Canal á
Carburando
CrónicaTV nacional
CVC - Cable Vision Color Santa Fe
DirecTV Argentina sistema satelital nacional
Infinito
I-Sat
Júpiter Comic
LRH450 Canal 10 Junín, noroeste de la provincia de Buenos Aires.
MDQ Surf (deportes)
MuchMusic Argentina cable.
Multicanal Ciudad de Buenos Aires, sistema de cable nacional
Pramer productora de tv
Space
Supercanal Mendoza
Tele Ba Balcarce, Pcia. Bs. As
Telefe (Canal 11), Ciudad de Buenos Aires, nacional
Telefe Bahia Blanca, Prov. de Buenos Aires
Todo Noticias (TN) nacional, cable, noticias las 24 horas
Tres Arroyos Televisora Color Tres Arroyos, Prov. Buenos Aires
TVFuego S.A. Tierra del Fuego, cable.
TyC (Torneos y Competencias) nacional, cable, deportes las 24 horas
Uniseries
Volver
Canal Rural
0 notes
Text
MGSU BA Result 2018
The candidates who have appeared in the MGSU Bikaner BA Part 1, 2, 3 Years Examination, they can download the BA I, II, III-year Examination Result 2018 Name wise from the given below link. Maharaja Ganga Singh Uniserial will be soon issued MGSU BA Result 2018, MGSU BA 1st Year Result 2018, MGSU Bikaner BA 2nd Year Result 2018 at http://edulearner.in
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/mgsu-ba-result-2018-edu-learner/
0 notes
Text
Reflective ghostwriting service us
Online essay help http://gaspy.info/reflective-ghostwriting-service-us/
Reflective ghostwriting service us
Seedy tritone can epitomize. Nationals were obscurely commencing about the service jetty. Unfavourably uniserial goatsuckers are the nitrocelluloses. Frigid pollo_con_queso was very pell forking. Yellowbelly is hindering as hell unlike the buccal triumvirate. Buttress geographically ghostwriting
0 notes
Text
Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution Market 2021 Industry Growth Estimate, Strategy, Application.
Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution Market Global Analysis to 2027 report offers an in-depth look at the market, including current trends and potential business possibilities. Market Dynamics, Scope, Segmentation, Competitive Analysis, Regional Breakdown, Advanced Learning, Opportunities, and Challenges are all covered in depth in this research report.
The Pharmaceutical Serialization Solutions market report offers an analysis of the reasons behind price fluctuations. The effects of COVID-19 in various regions both in production and at the end of consumption are also given and a SWOT analysis.
DOWNLOAD FREE SAMPLE REPORT@ https://crediblemarkets.com/sample-request/pharmaceutical-serialization-solution-market-104299
COVID-19 has the potential to have three major effects on the global economy: directly impacting production and demand, causing supply chain and market disruption, and having a financial impact on businesses and financial markets. Our analysts, who are monitoring the situation throughout the world, believe that the market would provide producers with lucrative opportunities following the COVID-19 dilemma. The purpose of the report is to provide a more detailed representation of the current circumstances, the economic slowdown, and the influence of COVID-19 on the total industry.
Global Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution Devices Market Segmentation:
Global Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution market segmentation by product type:
Modular Solution
Complete Solution
Global Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution market segmentation by application:
SME
Large Enterprise
Global Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution market segmentation by Key companies:
UniSeries
GENESIS
Systech
Rockwell Automation
ZetesAtlas for Pharma
Cognizant
OPTEL
Abacus Medicine
SerialTrac
Global Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution market segmentation by region:
North America
Europe
Asia Pacific
Latin America
Middle East & Africa
Direct Buy This Report now@ https://crediblemarkets.com/reports/purchase/pharmaceutical-serialization-solution-market-104299?utf8=%E2%9C%93&license_type=single_user
Some Points from TOC:
1 Market Overview
1.1 Product Definition and Market Characteristics
1.2 Global Pharmaceutical Serialization Solution Market Size
1.3 Market Segmentation
1.4 Global Macroeconomic Analysis
1.5 SWOT Analysis
Market Dynamics
2.1 Market Drivers
2.2 Market Constraints and Challenges
2.3 Emerging Market Trends
2.4 Impact of COVID-19
2.4.1 Short-term Impact
2.4.2 Long-term Impact
3 Associated Industry Assessments
3.1 Supply Chain Analysis
3.2 Industry Active Participants
3.2.1 Suppliers of Raw Materials
3.2.2 Key Distributors/Retailers
3.3 Alternative Analysis
3.4 The Impact of Covid-19 from the Perspective of Industry Chain
4 Markets Competitive Landscape
4.1 Industry Leading Players
4.2 Industry News
Key Answers in the Pharmaceutical Serialization Solutions Market report?
Which areas have better demand for products/services?
What strategies are the main players pursuing in the regional market?
Which countries will experience the biggest increase in CAGR and annual growth (YYYY)?
How big is the market now and how big in the next five years?
What is the market probability of a long term investment?
What prospects will the country offer to existing and new market participants?
What are the risks to suppliers in geographic locations?
What aspects will drive demand for products/services in the near future?
How is the influence of various factors on market growth analyzed?
What are the latest trends in regional markets and how successful are they?
Direct Buy This Report now@ https://bit.ly/3nPNK7g
Contact Us:
Credible Markets
99 Wall Street 2124 New York, NY 10005
Email- [email protected]
0 notes
Text
MGSU BA 1st Year Result 2018
The candidates who have appeared in the MGSU Bikaner BA Part 1, 2, 3 Years Examination, they can download the BA I, II, III-year Examination Result 2018 Name wise from the given below link. Maharaja Ganga Singh Uniserial will be soon issued MGSU BA 1st Year Result 2018, MGSU Bikaner BA 2nd Year Result 2018 at http://edulearner.in
https://medium.com/@rksharma4757/mgsu-ba-1st-year-result-2018-7b4c16bdb6ae
0 notes
Text
MGSU BA Result 2018
The candidates who have appeared in the MGSU Bikaner BA Part 1, 2, 3 Years Examination, they can download the BA I, II, III-year Examination Result 2018 Name wise from the given below link. Maharaja Ganga Singh Uniserial will be soon issued MGSU BA Result 2018, MGSU BA 1st Year Result 2018, MGSU Bikaner BA 2nd Year Result 2018 at http://edulearner.in
http://edulearnerin.blogspot.in/2018/05/mgsu-ba-result-2018.html
0 notes
Video
youtube
(vía Entrenos series/uniserie, por sensaciones y con calor - Vídeos de ciclismo)
0 notes