#using platform encoding UTF-8
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
I spent so long today trying to figure out why .gitignore wasn’t working.
I spent *hours* going through so many StackOverflow questions and reddit posts where brand new developers are trying to use a .gitignore for the first time and getting the syntax wrong or putting it in the wrong directory or naming the file wrong or they already tracked the files. All common mistakes I made when I was new to this, but not what was wrong for me.
I’m suddenly reminded what it was like back then everytime I had a problem googling every little issue and thinking some obscure issue was happening or there was a bug in git or something, and then I’d find the small error I’d made. But now I understand it so well I’m stumped what could be wrong.
Flashback to when I was trying to decide which OS to use when writing it and decided it was simple enough that Windows would be fine. Plus I want this to be cross platform and so it’ll be good to be forced to deal with Windows compatibility up front.
Then finally I found the issue: I created the .gitignore from Powershell and it defaults the encoding to UTF-16LE??? Why would they do that? Just to prank people trying to create files to be used literally anywhere???
Changed it to UTF-8 and it works.
god
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Best Online M3U8 Players for Smooth Live Streaming in 2025

Among the best ways to interact with viewers in real time is live streaming. By letting viewers participate through comments, reactions, and live conversations, it enables creators to establish trust and connection with them.
According to a 2025 video marketing report by WebFX, 82% of audiences prefer live video over regular social media posts. Moreover, research conducted by Live Stream stats shows that the average time that a user spends watching live videos has increased by over 80% compared to the past few years. These stats highlight the importance of integrating live streaming options into your broadcasting strategies.
The numbers don’t lie! Live streaming isn’t just trending; it’s the way audiences want to engage. However, even the most dynamic content falls flat if your viewers battle buffering or compatibility issues. That’s where choosing the right M3U8 player online (such as Fluger) becomes your secret weapon.
Let’s get the show on the road and learn about the benefits of using Fluger for live streaming. But first things first, let’s understand what an M3U8 player is and what features to look for in a streaming platform.
What is P3U8 Player Online?
An M3U8 player online is an HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) protocol-supported web-based video player for streaming. It plays m3u8 files, which are playlist files meant for on-demand or live viewing in little bursts. This structure lets users view videos seamlessly across several devices, even on poor internet connections.
In simpler terms, when you stream using an M3U8 player, the viewer's internet speed and device type automatically influence how your video is modified. reduced interruptions and reduced buffering while offering a better overall experience for your audience.
Key Features to Look For in an M3U8 Streaming Platform
The below-mentioned key features ensure you get the maximum benefits from the investment you make. Here is what you need to count on:
1. Adaptive Bitrate Support:
Automatically switches between quality levels (like 480p to 4K) based on the viewer's internet speed. No buffering, just smooth playback for every viewer.
2. UTF-8 Encoding:
Supports multilingual metadata and subtitles, making your streams globally accessible. Displays special characters and non-English text correctly.
3. Versatility:
Works flawlessly across devices—phones, tablets, smart TVs, and browsers. One stream, perfect playback everywhere.
4. Streaming Support:
Handles both live broadcasts and on-demand content effortlessly. No extra setup is needed for different video types.

How Fluger’s M3U8 Player is an Outstanding Choice
Beyond a streaming tool, Fluger is a complete platform built for creators, broadcasters, and businesses who want reliable, high-quality live and on-demand streaming.
With its built-in M3U8 player, Fluger makes it easier to deliver smooth, uninterrupted streams to a global audience. Whether your business hosts frequent live broadcasts, you are a digital channel owner, or you are a solo producer - Fluger offers all the tools you need to give excellent streaming experiences free from technical difficulty. Its player offers adaptive bitrate streaming, which means your video changes automatically to match the internet speed of the user, therefore minimizing buffering and preserving constant quality.
Live streaming has changed, and so have the equipment required to present high-quality shows. Although there are several M3U8 players, Fluger is one of the top-tier solutions since it combines modern technologies with user-friendly features to provide creators and broadcasters with an unparalleled streaming experience.
Here’s why Fluger should be your go-to M3U8 player for seamless live streaming:
1. Ultra-Low Latency for Real-Time Engagement
Fluger’s advanced HLS streaming ensures minimal delay between your live broadcast and what viewers see. Whether you're hosting a live Q&A, gaming session, or corporate webinar, near-instant playback keeps interactions natural and engaging.
2. Adaptive Bitrate Streaming at Its Best
Not all viewers have the same internet speed. Fluger’s smart adaptive streaming automatically adjusts video quality (from 360p to 4K) based on each viewer’s connection. This helps eliminate buffering and drop-offs.
3. Multi-Device & Cross-Platform Compatibility
Fluger’s M3U8 player works flawlessly across all devices (such as phones, tablets, smart TVs, and desktops) and browsers, ensuring no viewer gets left behind due to compatibility issues.
4. Built-In Security & Anti-Piracy Measures
Protect your content with DRM encryption, token authentication, and secure HTTPS delivery. Fluger prevents unauthorized access and illegal redistribution, keeping your streams safe.
5. One-Click Playback for Hassle-Free Viewing
No complicated setups for your audience. Fluger’s plug-and-play M3U8 player lets viewers start watching instantly—just share the link, and they’re in.
6. Real-Time Analytics & Performance Tracking
Monitor viewer engagement, peak traffic times, and stream health with Fluger’s built-in analytics. Optimize your broadcasts based on real-time data to maximize reach and retention.
7. Multi-CDN Support for Global Reach
Fluger leverages multiple Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to distribute streams efficiently worldwide. This means faster load times and zero lag, even during high-traffic events.
Conclusion: Fluger vs. Other M3U8 Players
There are plenty of M3U8 players available online, but not all of them offer the reliability and features needed for smooth live streaming. Some lack support for different devices, others can’t handle high traffic, and a few don’t even protect your content properly.
Fluger stands out by doing all of this and more. It’s not just a player, but a complete streaming solution that helps you deliver your content without buffering, delay, or compatibility issues. From real-time analytics and easy playback to global CDN support and built-in security, Fluger checks all the boxes.
In short, if you want your stream to work well for everyone, everywhere, every time, Fluger’s M3U8 player is a choice you can count on.
#broadcasting#entertainment#live tv#tv#tv channels#fluger#m3u8#live streaming#streaming#linear broadcasting#fluger tv#streaming tool#M3U8 Player
0 notes
Text
Application and Website Localization

In today’s interconnected world, users come from diverse cultures and speak many languages. To provide a truly inclusive experience, businesses and developers must consider localization — the process of adapting applications and websites for different languages, regions, and cultural expectations. In this post, we explore what localization is, why it matters, and how to implement it effectively.
What is Localization?
Localization (often abbreviated as L10n) is more than just translation. It involves adapting content, layout, graphics, currency, date/time formats, and even colors or images to match the preferences of a specific locale or cultural group.
Why Localization is Important
Wider Reach: Connect with users in their native language and increase user base globally.
Improved User Experience: Users feel more comfortable using an app or website that reflects their language and culture.
Higher Engagement and Conversion: Localized content is more relatable, leading to better engagement and conversion rates.
Legal Compliance: Some regions require content to be available in local languages.
Key Elements of Localization
Text Translation: Translating all visible strings and content into the target language(s).
Date/Time & Number Formats: Adapting to local standards (e.g., 12-hour vs. 24-hour clock, decimal separators).
Currency: Displaying prices in local currency and supporting regional payment gateways.
Right-to-Left (RTL) Support: Designing layouts for RTL languages like Arabic or Hebrew.
Images and Colors: Avoiding culturally sensitive imagery and adapting visuals to suit the audience.
Language Selection: Providing easy ways for users to choose or detect their preferred language.
Localization vs. Internationalization
It’s important to distinguish between:
Internationalization (i18n): Designing and developing an app so it can be easily localized later.
Localization (l10n): The actual process of adapting the content and UI for a specific region or language.
Popular Tools and Libraries
i18next: JavaScript internationalization framework often used with React and Vue.
gettext: Widely used in Linux and Python environments.
FormatJS: Useful for React apps and web development.
Android/Flutter/iOS Localization: Built-in localization APIs for native mobile apps.
Crowdin, Lokalise, POEditor: Collaborative platforms for managing translation workflows.
Best Practices for Effective Localization
Keep text separate from code using localization files (e.g., JSON, PO, ARB).
Avoid hard-coded strings — use localization keys instead.
Use placeholders for variables to support grammatical differences.
Support Unicode/UTF-8 encoding for all text content.
Test layouts for longer or shorter translated text strings.
Involve native speakers for accurate translations and context.
Example: Localizing a Simple Web App with i18next
// en.json { "welcome": "Welcome", "login": "Log In" } // ar.json { "welcome": "مرحبا", "login": "تسجيل الدخول" }
Conclusion
Application and website localization is essential for connecting with a global audience. It enhances user experience, builds trust, and opens doors to new markets. Whether you're a solo developer or part of a global team, investing in localization pays off in usability and growth.
0 notes
Text
```markdown
SEO Scripts for E-Commerce: Boost Your SEO with These Scripts
In the ever-evolving world of e-commerce, optimizing your website for search engines is crucial. This article will delve into some effective SEO scripts that can help boost your online store's visibility and drive more traffic.
Understanding the Basics of SEO for E-Commerce
Before diving into specific scripts, it's important to understand the fundamentals of SEO as they apply to e-commerce platforms. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) involves various strategies and techniques designed to improve a website's ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). For e-commerce businesses, this means making your products and services more discoverable to potential customers who are searching online.
Key Elements of SEO for E-Commerce
1. Keyword Research: Identifying and targeting relevant keywords that your target audience uses when searching for products similar to yours.
2. On-Page Optimization: Ensuring that your website's content, structure, and HTML elements are optimized for both users and search engines.
3. Technical SEO: Addressing technical aspects such as site speed, mobile-friendliness, and crawlability.
4. Link Building: Acquiring high-quality backlinks from reputable websites to increase your site's authority.
Implementing SEO Scripts for Enhanced Performance
Now, let's explore some specific SEO scripts that can be implemented on your e-commerce platform to enhance its performance:
1. Schema Markup
Schema markup is a type of microdata that helps search engines understand the content of your web pages better. By adding schema markup to your product pages, you can provide additional information about your products, such as price, availability, and ratings, which can lead to rich snippets in search results.
Example Script:
```html
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "http://schema.org",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "Example Product",
"image": "https://example.com/product-image.jpg",
"description": "A detailed description of the product.",
"sku": "1234567890",
"brand": {
"@type": "Brand",
"name": "Example Brand"
},
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"priceCurrency": "USD",
"price": "19.99",
"availability": "http://schema.org/InStock",
"seller": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Example Store"
}
}
}
</script>
```
2. Canonical Tags
Canonical tags help search engines understand which version of a page should be indexed and displayed in search results. This is particularly useful for e-commerce sites where products may have multiple URLs due to variations in size, color, or other attributes.
Example Script:
```html
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/product-page.html"/>
```
3. Sitemap XML
Creating an XML sitemap ensures that search engines can easily find and index all the pages on your website. This is especially important for large e-commerce sites with thousands of product pages.
Example Script:
```xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemap.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<url>
<loc>https://example.com/</loc>
<lastmod>2023-01-01</lastmod>
<changefreq>weekly</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>
<!-- Add more URLs here -->
</urlset>
```
Conclusion and Discussion Points
Implementing these SEO scripts can significantly improve your e-commerce site's visibility and attract more organic traffic. However, it's important to continuously monitor and adjust your SEO strategies based on the latest trends and changes in search algorithms.
What other SEO techniques have you found effective for your e-commerce business? Share your experiences and insights in the comments below!
```
加飞机@yuantou2048

蜘蛛池出租
EPP Machine
0 notes
Text
HTML Meta Information

HTML meta information is used to provide metadata about a web page. Metadata is data about data, and it is used by browsers, search engines, and other web services to understand the content and purpose of the page. Meta information is typically included within the <head> section of an HTML document.
Common Types of Meta Tags
Character Set Declaration
Specifies the character encoding for the HTML document.
Example:
<meta charset="UTF-8">
The most common encoding is UTF-8, which supports most characters from all the world’s writing systems.
Viewport Settings
Controls the layout of the page on mobile browsers.
Example:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
This tag is crucial for responsive web design, ensuring that the page is scaled correctly on different devices.
Page Description
Provides a brief description of the page content, often used by search engines.
Example:
<meta name="description" content="A brief description of the page.">
This description may appear in search engine results, influencing click-through rates.
Keywords
Lists relevant keywords for the page content, used by some search engines.
Example:
<meta name="keywords" content="HTML, CSS, JavaScript, web development">
Keywords are less important for modern SEO but can still provide context.
Author
Specifies the author of the document.
Example:
<meta name="author" content="Saide Hossain">
Robots
Instructs search engine crawlers on how to index the page.
Example:
<meta name="robots" content="index, follow">
Common values:
index, follow: Allows the page to be indexed and followed by search engines.
noindex, nofollow: Prevents the page from being indexed and links from being followed.
Open Graph Tags (for Social Media)
Used to control how content is displayed when shared on social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, etc.
Examples:
<meta property="og:title" content="Your Page Title"> <meta property="og:description" content="A description of the page content."> <meta property="og:image" content="http://example.com/image.jpg">
These tags improve the appearance of shared links and can increase engagement.
Content-Type
Specifies the media type and character encoding of the document.
Example:
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
This tag was more common in older HTML documents but is now often replaced by the <meta charset="UTF-8"> tag.
Refresh
Automatically refreshes the page after a specified time interval.
Example:
<meta http-equiv="refresh" content="30">
This example will refresh the page every 30 seconds.
Custom Meta Tags
You can also create custom meta tags for specific purposes, such as application-specific metadata.
Example:
<meta name="theme-color" content="#ffffff">
This example specifies the theme color of a web app, often used in mobile browsers.
Example of a Complete Head Section with Meta Tags
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta name="description" content="This is a sample webpage demonstrating the use of HTML meta tags."> <meta name="keywords" content="HTML, Meta Tags, SEO, Web Development"> <meta name="author" content="Saide Hossain"> <meta name="robots" content="index, follow"> <meta property="og:title" content="Learn HTML Meta Tags"> <meta property="og:description" content="A comprehensive guide to HTML meta tags."> <meta property="og:image" content="http://example.com/meta-image.jpg"> <title>HTML Meta Tags Example</title> </head> <body> <h1>Understanding HTML Meta Information</h1> <p>This page explains the different types of meta tags used in HTML.</p> </body> </html>
In this example, the meta tags provide important information about the content, how it should be displayed, and how search engines should treat it.
Read Me…
0 notes
Text
A Fun Guide to Three.js 3D Web Magic

Ever imagined bringing a splash of 3D wonder to your web pages? Well, you’re about to embark on an exciting journey into the realm of Three.js! In this guide, we’re not just going to explore the magic it holds, but we’re going to have some hands-on fun with its most dazzling features. And rest assured, we’re going to keep it as interactive and enjoyable as a carnival ride!
So, are you ready to kickstart this adventure into the vibrant world of Three.js?
What is Three.js?
Three.js is a JavaScript library that makes it easy to create 3D graphics on the web. Whether you’re building games, visualizations, or interactive experiences, Three.js is your ticket to the third dimension. Let’s embark on this journey!
Cool Features of Three.js
1. Cross-Platform Compatibility
One of the standout features of Three.js is its seamless compatibility with various web browsers. Whether your audience is using Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Edge, Three.js ensures a consistent and captivating 3D experience across platforms.
2. Abundance of Geometry and Materials
With Three.js, you have access to a rich library of predefined geometries (like cubes, spheres, and planes) and materials (including basic, Lambert, Phong, and more). This makes it easy to create intricate 3D scenes with minimal effort.
3. Lighting and Shadows
Creating realistic lighting and shadows is a breeze with Three.js. To add depth and realism to your scenes, you can experiment with various light sources like ambient, directional, point, and spotlights.
4. Animation and Interactivity
Three.js empowers you to bring your creations to life with animations and interactivity. You can animate objects, control camera movements, and respond to user input to craft dynamic and engaging experiences.
5. Post-Processing Effects
Elevate your visuals with post-processing effects like bloom, depth of field, and vignette. These effects add a layer of polish and professionalism to your 3D scenes.
Getting Started with Three.js
Now, let’s walk through a basic tutorial by making a spinning 3D moon to kickstart your journey with Three.js. Before starting you can view the live demo here!
Step 1: Setting Up Your Environment
Section Breakdown:
Document Type Declaration:
<!DOCTYPE html> declares the document type and version (HTML5 in this case).
2. HTML Root Element:
<html> tags define the root of the HTML document.
3. Head Section:
<head> contains meta-information about the document and external resources like stylesheets and scripts.
4. Character Encoding and Viewport:
<meta charset="UTF-8"> sets the character encoding to UTF-8 for proper text display.
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> ensures proper scaling on different devices.
5. Page Title:
<title> sets the title displayed in the browser tab.
6. Internal CSS:
<style> contains CSS rules. In this case, it removes any default margin from the body.
Step 2: JavaScript Section
Section Breakdown:
Loading Three.js Library:
<script src="https://threejs.org/build/three.min.js"></script> loads the Three.js library from an external source.
Script Tags:
<script> tags are used to embed JavaScript code within the HTML document.
Step 3: Setting up the Scene and Camera
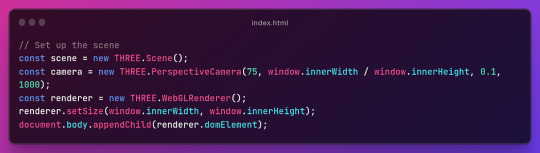
Section Breakdown:
1.Creating a Scene:
const scene = new THREE.Scene(); creates a new 3D scene.
2. Setting up the Camera:
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000); sets up a perspective camera with specified parameters (field of view, aspect ratio, near and far clipping planes).
3. Initializing the Renderer:
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer(); creates a WebGL renderer.
4. Setting Renderer Size and Appending to DOM:
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight); sets the size of the renderer to match the window.
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement); appends the renderer’s canvas element to the document body.
Step 4: Creating a Sphere and Adding Moon Texture
Section Breakdown:
1.Creating a Sphere:
const geometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(5, 32, 32); creates a sphere geometry with specified radius and segments.
2.Loading a Texture:
const textureLoader = new THREE.TextureLoader(); creates a texture loader.
const texture = textureLoader.load('path_to_your_image.jpg'); loads an image texture.
3.Applying Texture to the Sphere:
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ map: texture }); creates a material using the loaded texture.
const sphere = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material); creates a mesh using the sphere geometry and applied material.
scene.add(sphere); adds the sphere to the scene.
Step 5:Animating the Moon
Section Breakdown:
1. Animation Loop:
function animate() { ... } defines an animation loop using a recursive requestAnimationFrame call.
2.Sphere Rotation:
sphere.rotation.y += 0.01; incrementally rotates the sphere around the y-axis. Adjust the value for different rotation speeds.
3.Rendering the Scene:
renderer.render(scene, camera); renders the scene using the defined camera.
Step 6: Setting Camera Position and Handling Window Resizing
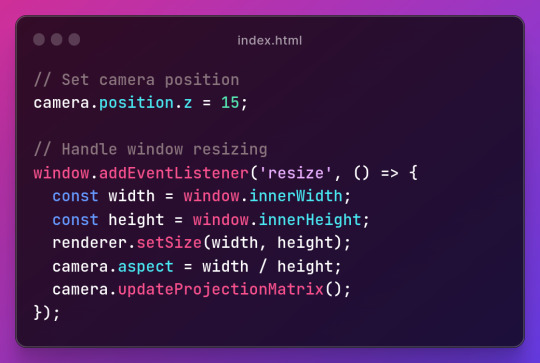
Section Breakdown:
1.Setting Camera Position:
camera.position.z = 15; sets the camera’s position along the z-axis.
2.Handling Window Resizing:
window.addEventListener('resize', () => { ... }); adds an event listener for window resizing.
3.Inside the event handler:
const width = window.innerWidth; and const height = window.innerHeight; retrieve the new window dimensions.
renderer.setSize(width, height); updates the renderer’s size.
camera.aspect = width / height; adjusts the camera’s aspect ratio.
camera.updateProjectionMatrix(); updates the camera’s projection matrix.
Conclusion
And there you have it! You’ve just created a basic 3D scene using Three.js. Customize it further by tweaking textures and rotations. Integrate it into your projects for added charm. Access the full source code here.
In the next part, we will learn to add key, mouse, and touch controls. Happy coding!😃

0 notes
Text
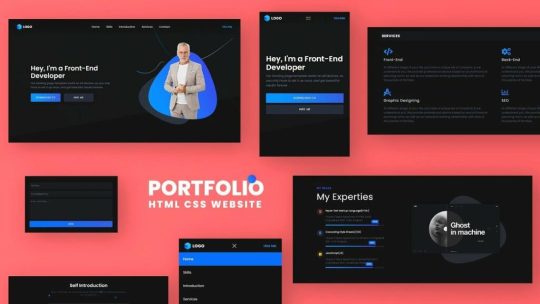
Building a Portfolio Website with HTML and CSS: Showcase Your Work

1. Introduction
Welcome to the exciting journey of building a stunning portfolio website using HTML and CSS. In today's digital age, having a well-crafted portfolio is crucial for showcasing your work, skills, and creativity as a web developer or designer. Whether you're a seasoned professional looking to display your extensive body of work or a beginner eager to make a mark in the industry, this guide will help you create a standout portfolio that sets you apart.
2. Setting Up Your Development Environment
Before we dive into building your portfolio website, it's essential to set up the right development environment. This will ensure that you have the necessary tools and software to create and test your web projects seamlessly. Let's walk through the key components of your development environment: Code Editor Your code editor is your digital workspace, where you'll write, edit, and manage your HTML and CSS files. There are several popular code editors to choose from, including: - Visual Studio Code (VS Code): A free, open-source code editor with a rich ecosystem of extensions and excellent support for web development. - Sublime Text: Known for its speed and simplicity, Sublime Text is a favorite among many developers. - Atom: Another open-source editor that's highly customizable and comes with various packages for web development. Web Browser A web browser is your window to the internet, and it's crucial for testing and debugging your website. While you can use multiple browsers, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Microsoft Edge are popular choices for web development. Make sure to install and keep these browsers up to date for thorough testing. Version Control System Using a version control system like Git is a smart move. It allows you to track changes in your code, collaborate with others, and easily revert to previous versions if something goes wrong. Platforms like GitHub and GitLab are excellent choices for hosting your web projects and collaborating with a global community of developers. Local Development Server To preview your website locally and test server-side functionalities, you'll need a local development server. Some common options include: - XAMPP: A package that includes Apache, MySQL, PHP, and Perl for local web development. - MAMP: Similar to XAMPP but designed for macOS users. - Node.js: If you prefer JavaScript-based development, Node.js can serve as your local server for testing. Project Folder Structure Organize your project files effectively. A well-structured folder system makes it easier to manage and find your files. Here's a simple example of a folder structure: FolderPurposecss/Store your CSS files.images/Keep your project images here.index.htmlYour main HTML file.scripts/For JavaScript files (if needed). By ensuring you have the right tools and a well-organized development environment, you'll be well-prepared to embark on the journey of creating your impressive portfolio website.
3. HTML Structure for Your Portfolio
Now that you have your development environment ready, it's time to start building the HTML structure of your portfolio website. A well-organized HTML structure serves as the foundation for your website, making it easier to style and manage your content. Let's break down the essential components of the HTML structure:
Basic HTML Template Begin with a basic HTML template that includes the following elements: - : Declares the document type and version. - : The root element of your web page. - : Contains metadata and links to external resources like CSS and JavaScript files. - Sets the title of your web page, which appears in the browser tab. - : Specifies the character encoding for your page (UTF-8 is recommended). - :The main content area of your webpage. Header Section Your portfolio's header section should include elements like: - :The container for your site's header content. - :The main title or your name/logo. - :Navigation links to various sections of your portfolio. About Me Section Introduce yourself to your visitors in the "About Me" section. Include: - :A container for the entire "About Me" content. - :A subheading for this section. - :A paragraph describing your background, skills, and interests. Portfolio Projects Display your work with a dedicated "Portfolio Projects" section. Utilize: - :A container for your project items. - :Subheadings for each project title. - :Each project description and details. Contact Information Make it easy for visitors to reach out to you by including a "Contact Information" section. Include: - :A container for your contact details. - :A subheading for the contact section. - :An unordered list with contact options like email and social media links. Footer Finish your HTML structure with a footer section, which typically includes: - :A container for your site's footer content. - :Copyright information or a short message. By structuring your portfolio website's HTML in this way, you create a clear and organized foundation for your content. This approach will not only make it easier to style your website with CSS but also enhance accessibility and SEO optimization.
Styling Your Portfolio with CSS
Now that you've structured your portfolio with HTML, it's time to give it a visual identity that reflects your unique style and creativity. Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) will be your artistic toolkit in this phase. Let's delve into how you can style your portfolio effectively:
External CSS File Start by creating an external CSS file. This separate file will keep your styling code organized and easily maintainable. In your HTML document, link to this CSS file in the section using the tag. This way, all your styling instructions will be applied to your HTML structure. Selectors and Rules CSS works by applying styles to specific HTML elements through selectors. You can use various types of selectors, such as: - Element Selector: Styles all instances of a particular HTML element (e.g., or
). - Class Selector: Styles elements with a specific class attribute (e.g., ). - ID Selector: Styles a single element with a specific ID attribute (e.g., ). Combine selectors with CSS rules to define the properties you want to modify, like color, font-size, or margin. Box Model The CSS box model governs how elements are structured and spaced. It comprises four components: ComponentDescriptionContentThe inner content of the element.PaddingSpace between the content and the border.BorderThe element's border, if defined.MarginSpace between the border and neighboring elements. Understanding the box model is crucial for controlling element dimensions and spacing within your portfolio. Responsive Design In the modern web, responsive design is a must. CSS allows you to adapt your portfolio to different screen sizes and devices. Use media queries to apply different styles based on factors like screen width, ensuring your website looks great on everything from desktop monitors to mobile phones. Typography and Fonts Your choice of fonts and typography plays a significant role in the overall aesthetics of your portfolio. Utilize CSS properties like font-family and line-height to define a readable and visually pleasing text style. Colors and Images Enhance your portfolio's visual appeal by selecting an attractive color palette and incorporating images. CSS provides properties like color and background-image to control these aspects. Pay attention to contrast and image optimization for a professional look. By mastering CSS for your portfolio, you have the creative freedom to design a visually stunning and responsive website that effectively showcases your work and style. Experiment, refine, and make your portfolio uniquely yours!
Adding Your Projects
Your portfolio's primary purpose is to showcase your projects and demonstrate your skills and abilities. In this section, we'll explore how to add and present your projects effectively on your website: Project Descriptions For each project you want to feature, create a dedicated section that includes: - A container for the entire project description. - A subheading for the project title. A concise but informative project summary. Highlight the objectives, technologies used, and your role in the project. Images and Media Visual elements are crucial in presenting your work. Use: Ensure they are high-quality and relevant to the project's context. If your project includes videos or animations, embed them using this HTML tag. Project Links and Details Include links to the live project and any relevant GitHub repositories. Use tags with the href attribute to create clickable links. Additionally, consider adding details such as project duration, team collaboration, or challenges you overcame. Call-to-Action (CTA) Encourage visitors to engage with your projects. Include a CTA button or link that leads to the live project or a case study page with more in-depth information. Use a contrasting color or styling to make the CTA stand out. Categories and Filtering If you have a diverse set of projects, categorize them. Create a list of categories such as "Web Development," "Design," or "Mobile Apps." Allow visitors to filter projects by category for a user-friendly experience. Use HTML lists to create the categories, and apply CSS for interactive filtering. Testimonials and Feedback If you've received positive feedback or testimonials on your projects, consider showcasing them. Use for the testimonials, and add the source's name and role for credibility. This provides social proof and builds trust with your audience. By implementing these strategies, you can effectively present your projects on your portfolio website. Make sure your projects are visually appealing, informative, and demonstrate your skills and expertise. Your portfolio is a reflection of your work, so put your best foot forward!
6. Responsive Design
Responsive design is a critical aspect of building a successful portfolio website. It ensures that your site adapts and looks great on various devices and screen sizes, providing an optimal user experience. Here's how to achieve responsive design for your portfolio: Media Queries Media queries are CSS rules that allow you to apply different styles based on the user's device characteristics, such as screen width. They are the foundation of responsive design. Use media queries in your CSS to define breakpoints where your layout or styling should change. Common breakpoints include those for smartphones, tablets, and desktops. Flexible Layouts To create a flexible and responsive layout, use relative units like percentages for widths and heights. Avoid fixed pixel values, which can cause issues on smaller screens. Utilize CSS properties such as flexbox or grid for fluid and adaptable designs that automatically adjust to different screen sizes. Mobile-First Approach Embrace the mobile-first design philosophy. Start with the mobile version of your site and progressively enhance it for larger screens. This ensures a better experience for mobile users and simplifies the process of scaling up for desktops and tablets. Images and Media Queries Optimize images for different screen sizes and resolutions. Use the srcset attribute to provide multiple image versions, and let the browser choose the appropriate one. Additionally, set max-width: 100% on images to prevent them from overflowing their containers on smaller screens. Touch-Friendly Design Consider touch gestures and interactions for mobile users. Ensure that buttons and interactive elements are large enough to tap comfortably with a finger. Provide ample spacing between clickable elements to prevent accidental taps. Navigation Menus For navigation menus, use techniques like hamburger menus or off-canvas menus for mobile devices. These approaches save screen real estate and make navigation more accessible on small screens. When scaling up for larger screens, you can use traditional menus or navigation bars. Testing and Debugging Regularly test your website on a variety of devices and browsers. Online tools and browser developer tools can help you simulate different screen sizes and identify responsive design issues. Fix any layout problems or styling inconsistencies to ensure a smooth experience for all users. Responsive design is not just a trend; it's a necessity. In a world where users access websites on a wide range of devices, having a responsive portfolio is crucial for attracting and retaining visitors. By following these practices, you can create a portfolio that looks and performs beautifully across the digital landscape.
7. Personalization and Branding
Your portfolio website is a representation of you and your work. Personalization and branding are essential to make your site unique and leave a lasting impression on visitors. Here's how to infuse your personality into your portfolio: Define Your Brand Start by defining your personal or professional brand. Consider what sets you apart from others in your field. Think about your values, style, and the message you want to convey. Your brand should reflect who you are and what you want to achieve in your career. Logo and Visual Identity Create a distinctive logo and visual identity that aligns with your brand. Your logo should be memorable and easy to recognize. Use consistent colors, fonts, and design elements throughout your site to establish a cohesive visual identity. About Page Your "About Me" page is an excellent place to share your story and background. Use this space to connect with your audience on a personal level. Include a professional photo of yourself to put a face to your name. Share your journey, experiences, and your passion for web development or design. Portfolio Style Your portfolio's design and style should reflect your brand. Consider the use of colors, typography, and layout to create a visually appealing and coherent look. Make sure your design choices align with the message you want to convey to your visitors. Brand Message Craft a compelling brand message or tagline that succinctly describes who you are and what you do. This message should be prominently displayed on your homepage or in your header to immediately communicate your brand's essence to visitors. Testimonials and Case Studies Showcase client testimonials and in-depth case studies that highlight your work's impact. These provide social proof and reinforce your brand's credibility and expertise. Including success stories can make your brand more trustworthy and relatable. Blog or News Section Consider adding a blog or news section to your portfolio. This allows you to share your thoughts, industry insights, and updates related to your work. Regularly updating this section demonstrates your commitment to your field and adds a dynamic element to your brand. Contact Information Make it easy for visitors to get in touch with you. Provide multiple contact options, including an email address, social media links, and a contact form. Use personalized, professional email addresses that align with your domain (e.g., ). Personalization and branding are powerful tools for creating a portfolio that stands out in a crowded digital landscape. Your unique brand identity and personal touches can leave a memorable impression on visitors and potential clients. By combining professionalism with personalization, you can build a portfolio that not only showcases your work but also tells your story.
8. SEO Optimization
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a fundamental aspect of ensuring your portfolio website gets the visibility it deserves. By optimizing your site for search engines, you increase the chances of your work being discovered by potential clients and employers. Here's how to effectively optimize your portfolio for SEO: Keyword Research Start by conducting keyword research related to your field and the type of work you do. Identify relevant keywords and phrases that potential visitors might use to find services or skills like yours. Use tools like Google's Keyword Planner to discover high-impact keywords. On-Page SEO Implement on-page SEO techniques to make your individual web pages search engine-friendly: - Page Titles: Create unique and descriptive titles for each page. Include relevant keywords to improve search engine visibility. - Meta Descriptions: Write concise, informative meta descriptions that entice users to click. Use relevant keywords naturally. - Heading Tags: Use
for your main page title and
, , and for subheadings. Incorporate keywords where appropriate. - Image Alt Text: Add descriptive alt text to your images. This not only improves accessibility but also helps search engines understand the content of your images. Content Quality Create high-quality, original content that adds value to your visitors. Your project descriptions, blog posts, and any text content should be well-written and engaging. Google rewards sites that provide informative and relevant content. Mobile Friendliness Ensure that your portfolio is mobile-friendly.
Read the full article
0 notes
Text

In today’s interconnected world, globalization testing is a critical process that ensures your software or application functions seamlessly across diverse cultures and languages. It is essential for businesses that want to reach a global audience and provide an inclusive user experience. At SDET Tech, we understand the importance of globalization testing and the key factors to consider while performing it for your software. In this blog, we’ll delve into the significant aspects of globalization testing to help you ensure international success for your product.
The following are some key factors that need to be considered when performing globalization testing:
1. Linguistic Diversity and Localization One of the primary aspects of globalization testing is linguistic diversity. Your software should be able to display content in multiple languages, which means the user interface (UI) should adapt to the language and culture of the user. For this, make sure that:
Translations are accurate and culturally sensitive.
Date formats, time zones, and currency symbols are localized.
Text doesn’t get cut off due to character length differences in various languages.
2. User Interface and Layout Different languages might require more space on the screen than others. Pay attention to the UI layout to ensure it accommodates longer or shorter text strings. Also, consider the use of right-to-left (RTL) languages like Arabic or Hebrew, which requires a different UI design.
3. Date and Time Formats Ensure that date and time formats automatically adapt to the user’s region. Some countries use day/month/year while others use month/day/year. Also, consider time zone differences and daylight saving time adjustments.
4. Currency and Numeric Formats Financial data, such as currency symbols and number formats, should be tailored to the user’s location. For example, in the U.S., you use the dollar sign ($) and comma (,) as a thousands separator while in Europe, it’s often the euro symbol (€) and a period (.) as the thousands separator.
5. Character Encoding Make sure your software supports various character encodings. Unicode (UTF-8) is a common encoding standard that allows your application to display a wide range of characters from different languages.
6. User Input and Data Validation Consider language-specific input methods, keyboard layouts and data validation rules. For example, some languages have unique characters that should be supported for user input.
7. Accessibility that Ensures Inclusivity Ensure your software is accessible to a wide range of users irrespective of their abilities. Implementing accessibility features like screen reader support, keyboard navigation and text-to-speech capabilities is important.
8. Test Across Multiple Platforms Globalization testing should be conducted in various environments, including different operating systems, browsers and devices. Ensure that your software is compatible with the technology that is commonly used in the targeted regions.
9. Local Regulations and Compliance Be aware of local laws and regulations, such as data privacy laws (e.g. General Data Protection Regulation in Europe). Ensure your software complies with these regulations when it handles user data.
10. Comprehensive Testing Approach Globalization testing should not be a one-time effort. It should be integrated into the development cycle, from the early stages of design to continuous monitoring and improvement.
The Way Forward Globalization testing is the most crucial aspect of software development for businesses aiming to reach a global audience. At SDET Tech, we understand the complex nature of globalization testing and the importance of ensuring that your software works seamlessly across diverse cultures and languages. By considering the key factors mentioned above, one will not only expand their global reach but also provide an inclusive and culturally sensitive user experience for users across the globe.
0 notes
Text
Beginner’s Guide to IPTV M3U Playlists

IPTV has changed how we watch television by providing ease and flexibility. The IPTV M3U playlist is one of IPTV’s essential elements. M3U playlists are text-based files that include details about media sources and their channels. We will examine what M3U playlists are, how they function, and how you can utilise them to improve your IPTV experience in this beginner’s guide.
What is an M3U Playlist? An M3U playlist is a plain text file that contains a list of media files or streams. The “M3U” stands for “MP3 URL” as it was initially developed for audio playlists, but it is now commonly used for IPTV. These playlists typically have the file extension “.m3u” or “.m3u8” (for UTF-8 encoded playlists).
M3U playlists provide the necessary information for IPTV players or media players to access and stream the content. They contain the URLs or file paths of the media files, along with additional metadata such as channel names and groupings.
How Do M3U Playlists Work? When an IPTV player or media player loads an M3U playlist, it reads the content of the file and processes the URLs or file paths listed within. The player then establishes a connection to the media sources and begins streaming the content according to the order and settings specified in the playlist.
M3U playlists can include various types of media, such as live TV channels, on-demand movies, TV series, radio stations, and more. These playlists are dynamic and can be updated by the IPTV provider, allowing users to access the latest content and channels.
Using M3U Playlists for IPTV: To use an M3U playlist for IPTV, you will need an IPTV player or a media player that supports M3U playlists. Here are the steps to get started:
1- Find an M3U Playlist: Obtain an M3U playlist from a reliable source, such as your IPTV provider or trusted online platforms that offer IPTV playlist downloads. 2- Choose an IPTV Player: Install an IPTV player or a media player that supports M3U playlists on your preferred device. There are various players available for different platforms, including VLC Media Player, Kodi, Perfect Player, IPTV Smarters, and more. 3- Load the M3U Playlist: Open the IPTV player and import or load the M3U playlist file. This can usually be done through the player’s settings or playlist management options. 4- Access and Stream Channels: Once the playlist is loaded, the IPTV player will display the available channels and media content. Navigate through the playlist and select the desired channel or media file to start streaming.
Benefits of Using M3U Playlists: Using M3U playlists for IPTV offers several benefits:
Flexibility and Customization: M3U playlists allow users to customize their channel lineups and create personalized playlists according to their preferences. You can add or remove channels, organize them into categories, and create your own channel groups.
Compatibility: M3U playlists are widely supported by various IPTV players and media players, making it easy to find a player that suits your needs and preferred platform.
Ease of Updates: IPTV providers can update their M3U playlists to add new channels, remove outdated content, or make changes to the channel lineup. As a user, you can easily update your playlist to access the latest content.
Portability: M3U playlists can be easily shared or transferred between devices. You can export your playlist from one IPTV player and import it into another, allowing you to enjoy your customized channel lineup across multiple devices.
Cautions and Considerations: While M3U playlists offer flexibility and convenience, it’s important to be cautious and consider the following:
Source Reliability: Obtain M3U playlists from trusted sources to ensure the quality and legality of the content. Beware of unofficial or unauthorized sources that may contain pirated or unreliable content.
Internet Connection: Reliable and stable internet connectivity is crucial for uninterrupted streaming. Ensure that you have a robust internet connection to enjoy a smooth IPTV experience.
IPTV Provider Policies: Familiarize yourself with the terms and conditions of your IPTV provider regarding the use of M3U playlists. Some providers may have specific guidelines or restrictions on the usage of their playlists.
M3U playlists are an essential part of the IPTV experience, enabling users to access and stream their favorite TV channels and media content. By understanding how M3U playlists work and following the steps to use them with an IPTV player, you can enhance your IPTV experience and create a customized channel lineup.
At IPTValue, we offer a wide range of reliable and high-quality IPTV subscriptions compatible with M3U playlists. Explore our website to discover the best IPTV options and start enjoying the benefits of IPTV today.
0 notes
Text
Decoding Unicodes: Unveiling Digital Symbolism

What are Unicode? Unicode is a character encoding standard that ensures that every character in every language has a unique number, regardless of the platform, device, application, or software used. This makes it possible to exchange text between different systems without losing or corrupting any data. Unicode is a superset of ASCII, which means that it includes all of the characters in the ASCII character set, as well as many other characters from other languages and writing systems. Unicode also supports a wide range of special characters, such as mathematical symbols, currency symbols, and emoji. There are three main encoding formats for Unicode: UTF-8, UTF-16, and UTF-32. UTF-8 is the most common encoding format, and it is used by most web browsers, operating systems, and programming languages. UTF-16 is used by some older systems, and UTF-32 is the most compact encoding format, but it is not as widely supported as UTF-8. Unicode is a very important standard, and it is used by almost all modern software. It is essential for ensuring that text can be exchanged between different systems without losing or corrupting any data. Types of Unicodes There are three main types of Unicodes: UTF-8: UTF-8 is a variable-length character encoding standard used for electronic communication. Defined by the Unicode Standard, the name is derived from Unicode (or Universal Coded Character Set) Transformation Format – 8-bit. UTF-16: UTF-16 is a character encoding standard that is used to represent Unicode characters. It is a variable-length encoding, which means that each character can be represented by one or two 16-bit code units. UTF-16 is often used by older systems and by some programming languages. UTF-32: UTF-32 is a character encoding standard that is used to represent Unicode characters. It is a fixed-length encoding, which means that each character is represented by exactly four bytes. UTF-32 is the most compact encoding format for Unicode, but it is not as widely supported as UTF-8 or UTF-16. In addition to these three main types, there are also a number of other encoding formats for Unicode, such as UTF-EBCDIC, UTF-7, and UTF-16BE. These encoding formats are less commonly used, but they may be necessary in some cases. Uses of Unicodes Unicode is a character encoding standard that ensures that every character in every language has a unique number, regardless of the platform, device, application, or software used. This makes it possible to exchange text between different systems without losing or corrupting any data. Here are some of the uses of Unicodes: Internationalization and localization: Unicode is essential for Internationalization and localization, which is the process of making software and websites accessible to users of different languages and cultures. Unicode allows developers to create software that can display and process text in any language, without the need to create separate versions of the software for each language. Web development: Unicode is the standard character encoding format for the web, and it is used by all major web browsers and web servers. This means that you can use Unicode characters in your web pages, and they will be displayed correctly on any device or browser. Data storage: Unicode is also used for data storage, such as in databases and file systems. This allows you to store text in a way that is both efficient and portable, and it ensures that your data will be accessible regardless of the platform or software that you use to access it. Programming languages: Unicode is supported by most programming languages, and it can be used to represent text in your code. This allows you to write code that is portable and can be used by users of different languages. Other applications: Unicode is also used in a variety of other applications, such as email, instant messaging, and document processing. In short, Unicode is a critical standard for ensuring that text can be exchanged and processed between different systems and applications. It is used by almost all modern software, and it is essential for Internationalization , localization, web development, data storage, and a variety of other applications. Importance of Unicode Unicode is a character encoding standard that plays a crucial role in modern computing and communication. It is designed to represent and manage text from all writing systems and languages used around the world. Here's why Unicode is of great importance: Multilingual Support: Unicode allows computers to represent and handle text in multiple languages and scripts. It includes characters for almost every writing system in existence, from Latin and Cyrillic scripts to Chinese, Arabic, and many others. This enables software and systems to handle diverse languages seamlessly. Global Communication: In our interconnected world, people communicate across linguistic and cultural boundaries. Unicode ensures that text can be accurately displayed and transmitted regardless of the language it's written in. This is essential for international communication, online content, and social interactions. Consistency and Compatibility: Before Unicode, there were many different encoding systems that caused compatibility issues. Unicode standardizes character representation, making it easier to exchange data between different systems and platforms without running into problems related to encoding conflicts. Text Processing and Searching: Unicode simplifies text processing and searching, as software developers don't need to create complex workarounds to handle different encodings. This streamlines programming and makes it easier to build applications that support various languages. Digital Preservation: Unicode contributes to the preservation of cultural heritage and historical documents. By providing a standardized encoding for characters, Unicode ensures that ancient texts and languages can be accurately digitized and stored for future generations. Web and Online Content: The internet is a global platform, and websites can be accessed by people from different language backgrounds. Unicode enables consistent and accurate rendering of text on websites, ensuring that content is accessible and readable by users regardless of their language preferences. Accessibility: Unicode plays a role in making digital content more accessible. Screen readers, assistive technologies, and other accessibility tools rely on consistent character encoding to properly interpret and present text content to users with disabilities. Efficient Data Exchange: Unicode's standardization simplifies data exchange in various formats, such as XML, JSON, and databases. This helps prevent data corruption and loss during transfer between different systems. Global Software Development: As software is developed for global markets, Unicode support becomes essential. Developers can create applications that cater to diverse audiences without worrying about language-specific issues. Future-Proofing: Unicode continues to evolve, adding new characters to accommodate emerging languages, symbols, and emojis. This adaptability ensures that Unicode remains relevant as new languages and communication needs arise. In summary, Unicode is a critical standard that underpins modern communication, software development, and digital content. Its importance lies in its ability to enable accurate representation and handling of text from a wide range of languages and scripts, promoting inclusivity, interoperability, and effective global communication. Benefits of Unicode: Unicode has many benefits, including: Universality: Unicode can represent characters from all languages, including historical scripts and newly invented ones. This makes it possible to exchange text between people of different languages without losing or corrupting any data. Compatibility: Unicode is backward-compatible with ASCII, which means that it can be used to represent text that was originally encoded in ASCII. This makes it easy to migrate to Unicode without having to rewrite all of your existing code. Efficiency: Unicode uses a variable-length encoding, which means that it is efficient for representing both common and uncommon characters. This makes it a good choice for storing text in databases and file systems. Portability: Unicode is supported by most operating systems, programming languages, and web browsers. This means that you can use Unicode characters in your code and be confident that they will be displayed correctly on any device or browser. Extensibility: Unicode is designed to be extensible, which means that new characters can be added as needed. This ensures that Unicode will be able to represent characters from any language, even those that are not yet invented. In short, Unicode is a powerful and versatile character encoding standard that has many advantages over other encoding standards. It is the standard for representing text in the modern world, and it is essential for ensuring that text can be exchanged and processed between different systems and applications. How Unicode characters are encoded Unicode characters are encoded using a variable-length scheme, which means that each character can be represented by a different number of bytes. This makes it possible to represent both common and uncommon characters efficiently. The most common Unicode encoding schemes are UTF-8, UTF-16, and UTF-32. UTF-8: UTF-8 is the most widely used Unicode encoding scheme. It uses a variable-length encoding, where each character can be represented by 1 to 4 bytes. UTF-8 is backwards compatible with ASCII, which means that it can be used to represent text that was originally encoded in ASCII. UTF-16: UTF-16 is a 16-bit encoding scheme, which means that each character is represented by 2 bytes. UTF-16 is often used for storing text in databases and file systems. UTF-32: UTF-32 is a 32-bit encoding scheme, which means that each character is represented by 4 bytes. UTF-32 is the most compact Unicode encoding scheme, but it is also the least efficient. Here is a table that shows how different Unicode characters are encoded using UTF-8: Code Point UTF-8 Encoding 0-127 0xxxxxxx 128-255 110xxxxx 10xxxxxx 256-65535 1110xxxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx 65536-1114111 11110xxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx As you can see, the first few characters are encoded using a single byte, while the more complex characters are encoded using multiple bytes. This allows Unicode to represent a wide variety of characters efficiently. Unicode Challenges: Unicode has a few challenges, including: Complexity: Unicode is a complex standard, and it can be difficult to learn and use. This is because Unicode has to support a wide variety of characters from different languages, and it has to be backward-compatible with ASCII. Memory usage: Unicode uses more memory than some other character encoding standards, such as ASCII. This is because Unicode characters can be represented by one to four bytes, while ASCII characters can only be represented by one byte. Compatibility: Not all software and hardware supports Unicode. This can be a problem if you need to exchange text with software or hardware that does not support Unicode. Security: Unicode can be used to create malicious code, such as phishing emails or malware. This is because Unicode characters can be used to represent symbols that are not visible to the user, such as control characters. In short, Unicode has some challenges, but these are outweighed by the many advantages of the standard. Unicode is the standard for representing text in the modern world, and it is essential for ensuring that text can be exchanged and processed between different systems and applications. Advantages of Unicode: Universality: Unicode can represent characters from all languages, including historical scripts and newly invented ones. This makes it possible to exchange text between people of different languages without losing or corrupting any data. Compatibility: Unicode is backward-compatible with ASCII, which means that it can be used to represent text that was originally encoded in ASCII. This makes it easy to migrate to Unicode without having to rewrite all of your existing code. Efficiency: Unicode uses a variable-length encoding, which means that it is efficient for representing both common and uncommon characters. This makes it a good choice for storing text in databases and file systems. Portability: Unicode is supported by most operating systems, programming languages, and web browsers. This means that you can use Unicode characters in your code and be confident that they will be displayed correctly on any device or browser. Extensibility: Unicode is designed to be extensible, which means that new characters can be added as needed. This ensures that Unicode will be able to represent characters from any language, even those that are not yet invented. Internationalization and localization: Unicode is essential for internationalisation and localization, which is the process of making software and websites accessible to users of different languages and cultures. Unicode allows developers to create software that can display and process text in any language, without the need to create separate versions of the software for each language. Web development: Unicode is the standard character encoding format for the web, and it is used by all major web browsers and web servers. This means that you can use Unicode characters in your web pages, and they will be displayed correctly on any device or browser. Data storage: Unicode is also used for data storage, such as in databases and file systems. This allows you to store text in a way that is both efficient and portable, and it ensures that your data will be accessible regardless of the platform or software that you use to access it. Programming languages: Unicode is supported by most programming languages, and it can be used to represent text in your code. This allows you to write code that is portable and can be used by users of different languages. In short, Unicode is a powerful and versatile character encoding standard that has many advantages over other encoding standards. It is the standard for representing text in the modern world, and it is essential for ensuring that text can be exchanged and processed between different systems and applications. Disadvantages of Unicode: Memory usage: Unicode uses more memory than some other character encoding standards, such as ASCII. This is because Unicode characters can be represented by one to four bytes, while ASCII characters can only be represented by one byte. Complexity: Unicode is a complex standard, and it can be difficult to learn and use. This is because Unicode has to support a wide variety of characters from different languages, and it has to be backward-compatible with ASCII. Compatibility: Not all software and hardware supports Unicode. This can be a problem if you need to exchange text with software or hardware that does not support Unicode. Memory usage: Unicode uses more memory than some other character encoding standards, such as ASCII. This can be a problem if you are working with large amounts of text or if you are on a device with limited memory. Complexity: Unicode is a complex standard, and it can be difficult to learn and use. This can be a barrier to adoption, especially for users who are not familiar with programming or computer science. Compatibility: Not all software and hardware supports Unicode. This can be a problem if you need to exchange text with software or hardware that does not support Unicode. For example, some older versions of Microsoft Windows do not support Unicode, which can cause problems if you try to open a Unicode file on these systems. In short, Unicode has some disadvantages, but these are outweighed by the many advantages of the standard. Unicode is the standard for representing text in the modern world, and it is essential for ensuring that text can be exchanged and processed between different systems and applications. Future of Unicode The future of Unicode is bright. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the need for a universal character encoding standard that can represent text from all languages will become even more important. Here are some of the trends that are likely to shape the future of Unicode: The growth of new languages: As new languages are developed, Unicode will need to be updated to include them. This is already happening, as Unicode has added new characters for languages such as Klingon and Klingon (pIqaD). The increasing use of emojis: Emojis are becoming increasingly popular, and Unicode will need to continue to add new emojis to meet the demand. This is already happening, as Unicode has added new emojis in recent releases. The development of new technologies: As new technologies are developed, Unicode will need to be updated to support them. For example, Unicode is already being used to represent text in virtual reality and augmented reality environments. Here are some specific examples of how Unicode is being used in new technologies: Virtual reality and augmented reality: Unicode is being used to represent text in virtual reality and augmented reality environments. This allows users to see text in these environments that is displayed in their own language. Machine learning: Unicode is being used in machine learning applications to train models that can understand and process text from different languages. This is essential for applications such as machine translation and chatbots. The Internet of Things: Unicode is being used in the Internet of Things (IoT) to represent text on devices such as smart speakers and thermostats. This allows users to interact with these devices in their own language. Overall, the future of Unicode is bright. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the need for a universal character encoding standard that can represent text from all languages will become even more important. Unicode is well-positioned to meet this need, and it is likely to continue to be the standard for representing text in the years to come. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Meta tags are part of HTML tags that describe the content of your pages to search engines and website visitors. Meta tags only appear in the page code, anyone can view them from the source code (Ctrl+U). We provide an overview of meta tags that are still very important and those that are no longer. Metatags can be used to increase a website's visibility in search engines, so they are definitely important for SEO. Why use Metatags? As Holland web said, Meta tags play an important role in SEO (Search Engine Optimization). Especially the use of title tags and meta descriptions is very important. These tags are displayed by search engines as a small text entry in search results. Make sure the meta tags on your site are unique for each page and try to make them as attractive as possible. Both the relevant title tags and description tags must convince visitors to click on the link in the search results. Most Important Meta Tags: This tag is displayed by search engines as a small text element in search results. Make sure meta tags on your site are unique to each individual page and make them as attractive as possible. Relevant title tags and description tags both have to convince visitors to click on the link in the search results. Title Tag: The title tag is important because it serves as the clickable headline in search engine results. It should precisely and concisely describe the page's content. htmlCopy code Your Page Title Meta Description Tag: The meta description tag provides a concise summary of the content of your website. It appears beneath the page title in search engine results and can influence click-through rates. htmlCopy code Meta Robots Tag: The meta robots tag instructs search engine crawlers on how to handle your web page. "index" allows the page to be indexed, while "follow" permits search engines to follow links on the page. Other common values include "noindex" and "nofollow." htmlCopy code Canonical Tag: The canonical tag specifies the preferred URL for duplicate or similar content. It helps search engines understand which version of a page should be indexed and avoids potential duplicate content issues. htmlCopy code Open Graph Tags (for social sharing): Open Graph tags provide information for social media platforms with information when a website is shared. They manage the title, description, and image that appear when your page is shared on social networking sites such as Facebook and Twitter. htmlCopy code Viewport Tag (for responsive design): The viewport tag ensures that your web page is displayed correctly on various devices and screen sizes. It is essential for creating a responsive and mobile-friendly design. htmlCopy code Interesting HTML Meta Tags: there are some interesting and lesser-known HTML meta tags that can serve specific purposes or provide additional functionality. Here are a few examples: Meta Refresh Tag: The meta refresh tag redirects the web page to another URL after a specified time delay (in seconds). It can be used for automatic page redirection or to implement timed refreshes. htmlCopy code Meta Viewport Tag (for iOS devices): htmlCopy code This meta tag is specifically for iOS devices and allows you to control the viewport behavior. It sets the width to the device width, prevents zooming, and disables user scaling. Meta HTTP-Equiv Tag (Character Encoding): htmlCopy code The meta http-equiv tag with "Content-Type" can specify the character encoding for the web page. In this example, it sets the character encoding to UTF-8, which supports a wide range of international characters. Meta Theme Color (for mobile browsers): htmlCopy code The theme color meta tag allows you to define the browser's theme color on mobile devices. It affects the browser's UI elements such as the address bar or task switcher. Specify the color using a hexadecimal va
lue. Meta X-UA-Compatible Tag: htmlCopy code The X-UA-Compatible meta tag is specific to Internet Explorer and allows you to control the version of IE rendering engine used to display the web page. In this example, "IE=edge" ensures the latest version of IE is used. Expired HTML Meta Tags: HTML metatags are crucial to web development because they provide metadata information about a web page. While there is no concept of "expiration" for HTML meta tags, as new standards and practices emerge, certain meta tags have become deprecated or obsolete over time. Staying current with the most recent recommendations and best practices is essential for ensuring the optimal performance and compatibility of your web pages. Meta Keywords: The meta keywords tag was once used to specify relevant keywords for search engines to index the page. However, due to abuse and keyword stuffing, most search engines no longer consider this tag. It is generally not recommended to use the meta keywords tag anymore. Example: htmlCopy code Meta Refresh: The meta refresh tag was used to automatically redirect a web page after a specified time interval. It is considered a poor practice for several reasons, such as disrupting the user experience and impacting search engine optimization (SEO). Instead, server-side redirects or JavaScript-based redirection are preferred. Example: htmlCopy code Meta Revisit-after: The meta revisit-after tag was used to specify when search engine crawlers should revisit a page. However, major search engines have stated that they do not consider this tag anymore for indexing and ranking purposes. It is no longer necessary to include this meta tag. Example: htmlCopy code Meta Distribution/Robots: The meta distribution or meta robots tag was used to control how search engine bots index and display the content of a web page. While these tags can still be used, it is more common to control these settings through the robots.txt file or using the "robots" meta tag. Example: htmlCopy code It's worth noting that while meta tags provide information to search engines, their impact on search engine rankings has diminished over time. Search engines now prioritize factors such as high-quality content, user experience, and backlinks from reputable sources. You might also like: How to Optimize Your Content for Maximum SEO Results Guide to Optimizing Images for Search Engines
0 notes
Text
I haven't really wanted to write down a comprehensive argument because this is something that could take literal days and I don't really feel like investing this much time into a Tumblr post, especially when general arguments have been done ages ago. (this page was made before "Modern C++", but "Modern C++" did not fix those issues.)
What I consider a fundamental problem of C++ is that the C++ developers will heroically fight against problems non-existent in any other programming language.
I have been using "Modern C++", in fact my experience with using it was what convinced me that this language is truly unsalvageable.
For every new language feature they introduced two new pitfalls to fall in
"uniform initialization syntax" will prefer initializer_list constructor, making some constructors impossible to call
initializer_list is incompatible with move-only types
"random_engine" can legally return non-random data
unordered_map is hilariously inefficient because the specification of the interface (the bucket garbage) forces it into using an inefficient implementation
regexes do not support unicode making them useless in 2024
in fact, lack of even most rudimentary UTF-8 support: (introduced in C++11) (deprecated in C++17) (removed in C++26) speaks for itself. "The reason for removal is that this feature no longer implements the current Unicode Standard, supporting only the obsolete UCS-2 encoding." what the fuck UCS-2 was deprecated in 1996 what the committee was smoking here
the new pseudo-random number generators are great but no one thought of an easy answer to "how to create a seeded generator" and "how to get a random number from [A; B) without creating a new uniform distribution every time" making it look overengineered instead
even if we ignore that there is still a ton of legacy code that already exists and by the time the std::optional and others became standard everyone else was making their own bespoke implementations, non-interoperable with each other (this also applies to strings, to a lower degree: QString in Qt exists because Qt is older than the built-in string type)
the extensive use of templates results in compile times taking forever because of the huge header file sizes (this one is supposed to be fixed with C++ modules but I honestly stopped holding my breath, and instead switched languages)
$ cat a.cpp #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <tuple> #include <memory> #include <optional> #include <unordered_map> #include <variant> $ g++ a.cpp -E | wc -c 1438212
(1.4MB)
and due to how template instantiation works (this is one is not fixed by C++ modules, the upcoming experimental Carbon language went fuck it and made its own generics system from scratch because C++ templates are a clusterfuck)
I also don't really see the validity of the point about syntax highlighting, linting, debugging, and so on--these are solved problems with LSP servers and major editors
the reason why I pointed these out is because C++ syntax is FUBAR and a piece of code like, let's say
A<B> C;
is
::std::vector<std::string::iterator> a; // variable declaration
or
(a < b) > c; // useless expression that is immediately dropped
without doing so much work that it's easier to let compiler do it for you instead. The complexity of the existing code means the new features get implemented later and with more bugs over the competing languages.
we have quite powerful debuggers in gdb and lldb
gdb is absolutely terrible thanks to its own design and lldb was still not ready for its prime back when I used it (2016) and kept crashing. It's why I relied on Visual Studio's debugger instead because at least that one could reliably preview std::vector<T>'s elements without me needing to
(gdb) p *(vec._M_impl._M_start + 5)
C never made promises in the first place. Rust successfully addresses low-level development needs (in some cases at least, gcc has still wider platform support than LLVM). Java, Kotlin, Swift, C#, JavaScript, Python address high-level development needs. The niche which C++ resides at gets smaller and smaller. I do not think C++ is out to die yet, as languages never truly die but eventually the new projects stop being created in them, and I hope this will happen to C++ eventually.
I actually enjoy coding in C++ way more than python or C# even though I was told those were easier. Idk it just feels a lot simpler to understand.
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
My Writing Tools
I am in the humanities and I write. I don't really like Word, though. Google Docs makes me feel trendy enough but even that is too word-processory. Basically, I wanted to adopt a writing platform that felt unique to me, and that freed me from conventional software that writers in my field use. I also wanted it to be simple and pared down. In this post, I'll talk about what I worked out.
The Software
Currently, I'm working with four essential programs:
Vim (the "ubiquitous text editor")
Pandoc
Dropbox
1Writer
"Vim," also called "Vi" (if you're working in an older terminal) and "gVim" (a GUI version) is a text editor with an extremely long history. I don't exactly understand that history in its entirety, but I do understand that the program's functionality and functions haven't changed for something like thirty years. There are a lot of people (and by "people" I mostly mean "programmers") who don't like Vim. But those who do like it say three things about it: it has a steep learning curve; but once you've learned it you'll never have to learn anything again; and it's blazingly fast at editing text.
Out of the box, Vim is very bare-bones. This is nice if you are like me (bells and whistles are distracting to you).
Vim is installed with most mac and 'nix systems by default (is my understanding).
Vim is only a text editor. You can't edit the kinds of files we work with in the humanities (.docx, .pdf, etc.). That's where the protocol for my new writing system comes in.
Markdown
Markdown is a "markup language." What this means in practice is that certain text symbols designate that text should have certain properties.
For example, if you put the "#" symbol at the beginning of a line, markdown will understand the text that follows to be heading level one.
If you surround a word or phrase with asterisks, it will be in italics.
Why does this matter? It doesn't, really, unless you adopt Pandoc, as I have, or (apparently) LaTeX, as some (most?) writers in the sciences have.
Basically: markdown makes text formatting into a matter of written symbols instead of a series of clicks. Instead of clicking "italicize" (or hitting CTRL+I), you type asterisks around the text you wish to italicize.
The outcome of this is that a variety of programs that understand how to interpret markdown's symbology can represent your text.
Pandoc
Let's say you've read all about markdown and have adopted it into your writing practice. Now you've written some stuff and you want to send it to a professor or an academic journal -- and they want a Word document.
That's where Pandoc comes in. It converts the markdown text file into a Word file. Or a PDF. Or whatever it is that you need.
Pandoc + Vim
Because it is aimed at programmers, Vim has the "make" command, which normally would compile the code you are writing. Obviously I am not compiling code, but I can set Pandoc as the compiler in my .vimrc file (which holds my vim settings.
set makeprg=pandoc\ -s\ -o\ ~/Dropbox/newfile.docx\ % set encoding=utf-8
Line one does a couple of things: it sets the compiler to Pandoc and it specifies the destination for the output file. I set that file to be named "newfile.docx," which is a good practice because it means I have to open it and make sure everything looks good before renaming it and moving it to an appropriate directory.
Now I can type ":make" into Vim and my word document will be created.
Pandoc and Templates
Pandoc converts to Word according to a template. There's no way to explain how setting this up went for me except: it was god-awful. The documentation sucks. I don't know if I would actually be able to replicate how I got it worked out, or even to explain it. But I eventually succeeded, and I'm happy.
Dropbox
I don't think anyone can do anything without the cloud these days. I don't really like Dropbox all that much, but I like having native apps for the cloud, and Dropbox is the only one with cross-platform capabilities (I have a linux desktop, a windows laptop, and an iPhone, because I am an idiot).
To use Vim's "find" command, I set my .vimrc to look in Dropbox by default:
set path+=~/Dropbox/**
Dropbox and Clear Thinking
This is an area I would like to improve on. Currently, I organize my sub-folders by topics, which are basically just the courses I am taking. I would like, instead, to use the PARA method. So that's an ongoing issue -- perhaps for another post in the future.
Maybe PARA isn't quite right, but I do think that my current way of saving and organizing everything could be more consistent, and more effectual at helping me find old ideas more quickly.
1Writer
Lastly, I have 1Writer on my iPhone. It cost something (maybe $4.99?), but I think it was worth it. You can edit markdown easily and quickly, and you can also preview it. I like typing up a bunch of notes at home, then reviewing them during my commute on my phone in 1Writer's attractive interface.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Quest For A Great Text-Editor: A Brief Intro Into Notepad++

I'm not even close to the only real person on a pursuit for the perfect TextEditor. It's gotten so much a part of technology civilization that I've actually had the interview problem"Vim or GNU Emacs?" Develop a couple times in my career. The bitter truth that regular end customers of text editors must deal with, nevertheless, is the fact that there just is nobody Ring of text modifying. Different applications growth clinics, different platforms, the disposition of the consumer, can affect the best alternative for that instant.
My work machine is running OSX, and also our development platform is CentOS, therefore for that work, Vim is my editor of choice. However, I really do a lot of writing and development in my own Windows system in your home, and for all the places whom I write composing, the best method to format the submission will be with mark down. Special-purpose Markdown editors make life less difficult, certainly, however, the quest for Any Perfect E-ditor won't be denied!
The notepad++ install silently interface
Notepad++ is licensed under the GNU Public License (GPL), and the foundation is available around GitHub. Installation is using a downloadable executable installer. If you are comfortable with Windows Notepad or WordPad, then the Notepad++ interface is going to soon be very comfortable for your requirements . The default style is plain-text, utf 8 encoded, using Windows line-feeds, and word wrapping flipped --ordinary Notepad defaults. If that is what you desire it for, then you're prepared to go.
Tons of built in programming languages
The real ability of notepad++ install silently begins to show up for those who wish to edit code. Over 50 programming languages are constructed directly in, and picking out a single from the menu enables you flip syntax highlighting, record maps, collapsible works, auto-complete, plus much more, according to the terminology you select. You might also specify policies for languages that are new. Notepad++ will not come with mark-down defined, however reluctantly, someone cared for the and published it, and establishing that up is simple.
Tabbed interface
Another fine feature of notepad++ install silently that is missing elsewhere would be a tabbed interface. You can open several data files, despite various language preferences, and things do the job the way you'd assume it to. This avoids a cluttered taskbar when you have a great deal of files open simultaneously. A handy macro recorder is also contained on the toolbar, including generating keystroke short cuts for use in many windows. Notepad++ additionally comes with a powerful plug in system, using many plugins offered for setup when you put in it, along with also the capacity to pull community-developed plugins from GitHub.
While working on this guide, I've also acquired a FORTRAN ninety file available (the aim of which will be to reverse the input ), and you also watch from the sealing of those tabs which file I am focusing on--the reddish shading of the disc on the mark down file at first tab indicates that it has unsaved changes. In the FORTRAN file, the emphasized line 20 indicates where the edit cursor is, and also the fall saw in the left varies color, to offer me an thought of this range where I'm workingout. It is easy to fail and hide sections, and whole functions, with this application.
Now I am hacking a few Perl because I look to solve an old student problem. I have added some POD-formatted documentation to the underparts of the the document, which informs what it truly is around, and Notepad++ correctly makes this into a collapsible area for me, as well, and also the syntax-highlighting across the file is spot-on. You can also see the auto-complete window popped up as I type the"print" command.
Is Notepad++ the long-sought-for a Single Form of text editing to get Windows? Not with a good deal of different choices available, there will often be diehards who wish to use Vim for either Windows or WordPad or something different. I'm locating Notepad++ more and more useful in my own writing and coding, Thus if you are not content with your current choice, it really is definitely take a peek at.
1 note
·
View note
Text
DOWNLOAD EPSON SCAN CX4200 DRIVER
File Size: 23 Mb Uploader: Curls Date Added: 24 October, 2019 Downloads: 3747 Price: Free File Name: epson scan cx4200 driver File Version: 310141221 Operating Systems: Windows NT/2000/XP/2003/2003/7/8/10 MacOS 10/X Download Type: http File Format: exe

What's New: - Fixes issue where CRT was not detected after(epson scan cx4200 driver after) Suspend/Resume mode or use of switch. - Fixed issue whereby(epson scan cx4200 driver whereby) 3G mode displays status incorrectly. - Fixed a bug where unnecessary response packets were sent when searching for the device using UPnP. - Fixed QPI Item string error. - Fixed the bug where multi-byte characters were not supported on FTP clients with UTF-8 character encoding. - Fixed an(epson scan cx4200 driver an) issue where a black screen was encountered after Sysprep Generalize. - Fixed the illegal MAC(epson scan cx4200 driver MAC) address warning for “MAC Clone”.- Fixed the Chinese SSID input deny message. - Corruption may(epson scan cx4200 driver may) be experienced with OGL or Vulkan API applications on some Hybrid Graphics system configurations. - Fixed VIA C3 cpu can't adjust ratio issue. - Fixed wrong detection of memory speed. Users content: Check the firmware update procedure manual carefully before starting update operations. GB* Intel Graphics Media Accelerator X4500, DirectX 10, Pixel Shader 4.0, Max. Added and Modified Features[Failover] - Improved the security level. Modifies host bridge offset to improve DRAM stability. Navigating from the Time settings page gives an incorrect error. We have a new, free software update available for your Kindle Paperwhite (7th Generation). GB DDR DDR 2 x DDR slots, DDR400/333/266Dual Channel memory technology Slots 3 PCI slots, PCI 2.2AMR 1 slots VGA Int. - GEM displays bleeding/ghosting charactersIt is highly recommended to always use the most recent driver version available. Even though other OSes might be compatible as well, we do not recommend applying this release on platforms other than the specified. Support VGA driver for XP and Windows 7. DOWNLOAD LG LS50 WIRELESS DRIVER Supported OS: Windows 10 Microsoft Windows 8.1 Enterprise (64-bit) Windows 7 64-bit Microsoft Windows 8.1 Enterprise (32-bit) Windows Server 2003 32-bit Windows XP 32-bit Microsoft Windows 8.1 (64-bit) Windows 8 Windows Server 2008 R2 Windows 8.1/8/7/Vista 32-bit Microsoft Windows 8.1 Pro (32-bit) Microsoft Windows 8 Pro (32-bit) Windows 8.1/8/7/Vista 64-bit Microsoft Windows 8.1 (32-bit) Windows Server 2016 Windows XP 64-bit Microsoft Windows 8 Enterprise (64-bit) Notebook 8.1/8/7 32-bit Microsoft Windows 8 (32-bit) Microsoft Windows 8 Enterprise (32-bit) Microsoft Windows 8 (64-bit) Windows 7 Microsoft Windows 10 (64-bit) Microsoft Windows 8 Pro (64-bit) Windows 2000 Windows Server 2003 64-bit Windows Server 2008 Windows 8.1 Windows Vista 32-bit Windows Server 2012 Microsoft Windows 8.1 Pro (64-bit) Windows Server 2012 R2 Windows Vista 64-bit Windows 7 32-bit Microsoft Windows 10 (32-bit) Notebook 8.1/8/7 64-bit Searches: driver epson scan cx4200; epson scan cx4200 driver for Windows XP 32-bit; epson scan cx4200 Rib905-ibm; epson scan cx4200 R RU905-9; epson scan cx4200 driver for Windows Vista 64-bit; epson scan cx4200 R90i; epson scan cx4200 RU9056; epson scan cx4200 driver for Microsoft Windows 8 Enterprise (32-bit); epson scan cx4200 RUZEB9056; epson scan cx4200 driver for Windows Server 2012; epson scan cx4200 driver for Windows Server 2008 R2 Compatible Devices: Android; Laptop; Printer; Scanner; Usb Cables; Videocard To ensure the integrity of your download, please verify the checksum value. MD5: c1d200e955e2c6012d7755fe95de711b SHA1: 5033940a811a8ff65b3b2fd9e178c1d30e6b87c1 SHA-256: 90b58b4a2f885137d69cb9327e9a3d16694882e489fc7cafa26046cbc9255c50
1 note
·
View note
Text
Simple Java11 Maven Project with Intellij IDEA
Simple Java11 Maven Project with Intellij IDEA
In this post we are going to create a simple Hello World in Java11 using maven and Intellij IDEA.
We are also going to deal with the compilation error “Error: java: error: release version 5 not supported” and the compilation warning “File encoding has not been set, using platform encoding UTF-8”
Video Create the HelloWorld Project
View On WordPress
#File encoding has not been set#IDEA#intellij#Intellij IDEA#Java#java10#java11#java12#java13#java14#Maven#pom#program#release version 5 not supported#using platform encoding UTF-8
0 notes