#vmodel
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

redraw of something i never posted here. kinda proud of this
#glacialart#v1#vmodel#ultrakill#ultrakill fanart#ultrakill v1#this was fun. i had fun.#i just wanted an excuse to draw V1 being pretty tbh
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Choose the Right Software Development Methodologies for Your Next Project?
Software development methodologies are vital for managing the challenges of software development, such as changing requirements and deadlines. Various methodologies, including Agile, Scrum and Spiral, are available, but selecting the right one is crucial as not all are suitable for every type of software. By choosing a suitable methodology and adhering to it, developers can ensure efficient work, effective communication and proper documentation, resulting in the timely delivery of high-quality software.

What are software development methodologies?
Software development methodologies consist of a series of processes and procedures implemented during the software development lifecycle, with the aim of benefiting both the development team and the clients.
An in-depth look at software development methodologies
To deliver high-quality products, custom software development companies leverage various methodologies such as Agile, Spiral, Scrum, Extreme Programming, Rational Unified Process and Big Bang.
Agile methodology
Agile methodology is an iterative approach to software development that prioritizes continuous planning, communication and collaboration between teams and clients. Other frameworks like Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), Large-Scale Scrum (LeSS) and Scrum of Scrums (SoS) can customize Agile practices to meet the needs of a specific organization or project.
Phases
The software development process typically consists of several key phases:
Concept Phase
Inception Phase
Iteration Phase
Quality Assurance
Software Release
Scrum methodology
The Scrum methodology follows an iterative development approach, where team members break down large tasks into smaller ones and work on them using sprints. This incremental approach accelerates development and adds value to complex projects. Moreover, the Scrum framework enables developers to incorporate conventional system development methodologies with flexible Agile practices.
Phases
The Scrum process involves several phases:
Product Backlog
Sprint Backlog
Daily Scrum Meeting
Product Increment
DevOps
DevOps, a term that gained popularity in the IT industry between 2007 and 2008, refers to a set of advanced tools, practices and process automation philosophies that combine IT operations with software development. By providing a framework for building, testing and releasing software rapidly. DevOps ensures improved outcomes and enables the continuous delivery of products.
Phases
The DevOps process involves several phases:
Continuous Integration
Continuous Testing
Continuous Development
Continuous Deployment
Continuous Monitoring
Waterfall Model
Winston Royce introduced the Waterfall Model in 1970 through his research paper. This sequential and linear approach emphasizes the systematic progression of steps in the development process. In the Waterfall Model, each stage must be fully completed before the next phase can begin.
Phases
The software development process typically includes the following phases:
Requirements analysis
Design
Implementation
Unit testing
Integration and system testing
Operation and maintenance
Iterative
The iterative or incremental development model breaks the entire software development process into smaller segments, enabling teams to gradually improve the evolving versions until the entire system is ready. This model helps identify issues and make necessary improvements within a limited budget in the initial stages of the software development life cycle.
Phases
The Iterative process includes the following phases:
Planning
Analysis
Implementation
Evaluation
Spiral Model
A spiral model is a hybrid approach that blends iterative and waterfall models. It is risk-driven, with each phase beginning with a predetermined goal and ending with a client review. The development team adds new features in a continuous spiral, increasing in scope with each iteration until deployment.
Phases
The spiral model typically includes the following phases:
Planning
Risk Analysis
Engineering
Evaluation
V Model
The V Model is a commonly used software development methodology that incorporates testing at each stage of the project, allowing for the timely completion of the project. However, each step must be completed before moving to the next, ensuring that the project stays on track and on target.
Phases
The V Model includes the following phases:
Unit Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
User Acceptance Testing
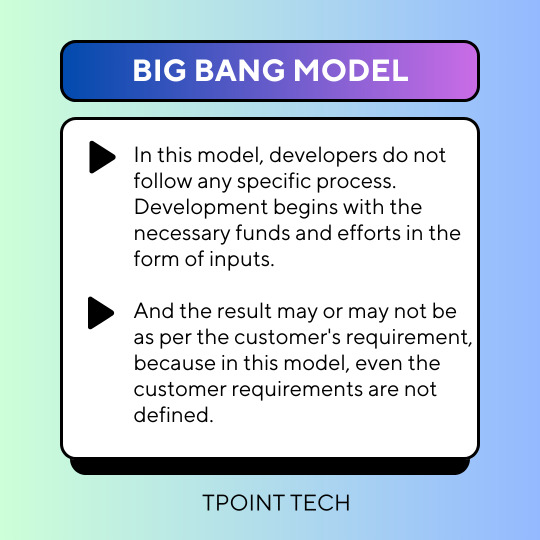
Big Bang
The Big Bang model is a simplistic approach to software development that is suitable for small projects but may lead to quality issues in larger projects due to the absence of in-depth planning and testing. Additionally, changes in requirements can cause significant delays, making it difficult to manage the project as a whole.
**Unlike other SDLC models, the Big Bang model doesn’t have specific phases.**
Feature-Driven Development (FDD) Model
Feature-driven development (FDD) is a software model created in 1997 by Jeff De Luca and Peter Coad for a Singaporean bank project. They built it in 15 months with 50 professionals. The FDD team comprises a project manager, chief programmer, chief architect, development manager, class owner and domain expert. In the first phase, an overall model of the system is created to provide a high-level view of the features to be developed.
Phases
The Feature-Driven Development (FDD) Model includes the following phases:
Build a Feature List
Plan by Feature
Design by Feature
Build by Feature
Test by Feature
Integrate Features
Launch the System
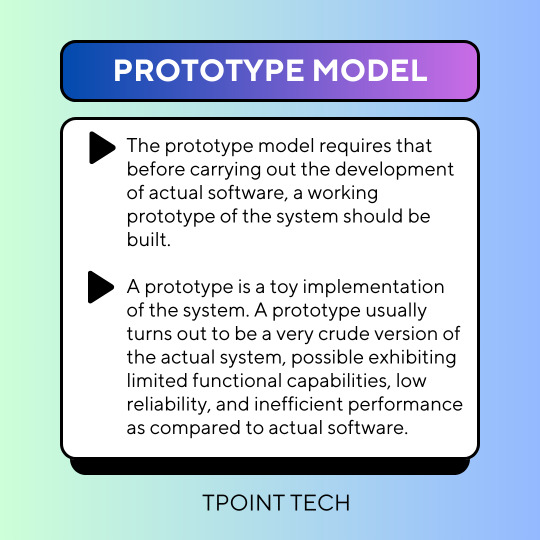
Prototype Methodology
The prototype methodology involves creating an initial version of the software system that may have limited functionality, reliability and efficiency compared to the final product. However, it is a valuable tool as it allows the client to visualize and better understand the expected outcome of the final software product, which may not have been clear in the initial stages of the project.
Phases
The Prototype Methodology includes the following phases:
Requirement collection and analysis
Faster design
Create a prototype
Initial user evaluation
Redefining prototype
Implementation of product
Timely maintenance
Rapid Application Development Methodology
The Rapid Application Development (RAD) methodology emphasizes quick customer feedback and rapid prototyping over prolonged development and testing cycles. This approach enables developers to make frequent iterations and updates to software efficiently, without starting from scratch each time. Moreover, RAD ensures that the outcome is high-quality and meets the end user’s requirements.
Phases
The Prototype Methodology includes the following phases:
Goal Planning
Prototype Design
Rapid Development
Production
Lean Development
The primary objective of the lean software development methodology is to minimize waste, improve efficiency and deliver the necessary features for the product. This approach involves releasing an initial software version developed by software engineers.
Principles
Here are some fundamental principles and practices often associated with lean development:
Define value from the customer’s perspective.
Map the value stream and identify waste.
Create flow by eliminating waste and optimizing the value stream.
Establish pull by letting customer demand drive development.
Pursue perfection by continuously improving the process.
Summary
Choosing the right software development methodology for your project is crucial and depends on various factors such as project scope, budget, resources, and time frame. It’s essential to analyze the pros and cons of each methodology and consider the necessary tools and expertise required. Our experts can assist you in selecting the best methodology for your enterprise.
0 notes
Text
Big Bang Model . . . . for more information and a tutorial https://bit.ly/3BMRP5O check the above link
0 notes
Text
V-Model development techniques to design
August 1, 2024
by dorleco
with no comment
Control Systems
Edit
Introduction

The Verification and Validation Model, often known as the V-Model or the V-Cycle, is a software development methodology that prioritizes testing throughout the entire process. It’s a Waterfall approach modification that’s widely used in critical system development when thorough testing is necessary. The V-Model’s two main stages are completed in the following order:
1. Verification (left side of the V):
a. Analysis of requirements :
– Identify and document the client’s needs.
– Based on customer input, determine software and system requirements.
b. System Design:
Develop a high-level design specification by referring to the requirements.
– Explain the system’s overall architecture.
c. Architecture:
Create a comprehensive system architecture.
– Explain the interfaces that the system’s various components have with one another.
d. Module Design:
Break the system up into smaller, easier-to-manage parts.
– Clearly define each module’s requirements.
e. Implementation (Coding):

Write code according to the detailed module requirements.
1. Examining Units:
– Check that each module is accurate.
– Identify and fix module-level issues.
2. Validation (right side of the V):
a. Testing for integration:
To ensure that the modules work as a whole, integrate them and test them all together.
– Find and correct any errors in the modules’ interlobular communication.
b. Testing the system:
Test the system as a whole to make sure it meets the requirements.
Identify and fix issues at the system level.
c. The user acceptance test, or UAT:
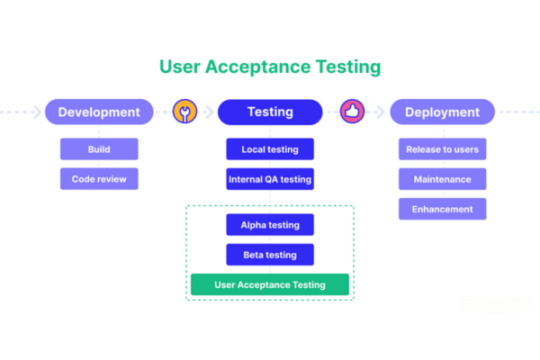
– Validate the solution by asking end users to attest that it meets their needs.
– Get user input and make necessary adjustments.
d. Initiation:
After testing is completed successfully, put the system into use.
Make sure that the necessary documentation has been completed.
1. Upkeep and Assistance: –
Assist continuously, fix issues that arise in the real-world setting, and implement any necessary improvements.
Important ideas and methods related to the V-Model:
The V-Model encompasses several fundamental concepts and techniques that guide its application in software development. The main concepts and techniques associated with the V-Model are as follows:
Initial Testing
Principle: Testing activities are initiated early in the development life cycle.
Technique: Unit testing is used in the early stages of test preparation and execution to guarantee that errors are identified and corrected as soon as practical.
2. An incremental and phased approach:
Principle: Development and testing have distinct periods.
Methodology: Testing is organized based on the stages that make up the development process. Systems that are only partially functional can be sent for testing and validation thanks to incremental development.
3. Trackability:
Principle: There should be a clear, traceable relationship between requirements and relevant tests.
Method: Make and maintain traceability matrices that link each requirement to the tests that verify its fulfilment. This ensures that all tests are covered thoroughly.
4. Loops of Feedback:
Principle: Continuous input is essential during the development and testing phases.
Methodology: As defects are found during testing, they are communicated to the development team for resolution. The quality of the software is improved by this loop of iterative feedback.
5. Record-keeping:
Concept: Extensive documentation is necessary at every stage of development and testing.
The method entails producing and maintaining current, comprehensive documentation for the design, requirements, test cases, and test plans. This documentation serves as a guide and comprehension tool for the duration of the system.
6. Testing and Development in Parallel:
Methodology: Testing for each phase is ongoing as the related development stage moves forward. Using a parallel approach reduces the likelihood that major defects will emerge later by allowing problems to be identified and solved sooner.
7. Well-defined positions and responsibilities:
It is important to specify the roles and duties of the development and testing teams.
Method: Assign specific duties to individuals or teams for each level of the V-Model. This establishes accountability and clarifies who is in control of what.
8. User Engagement:
Principle: User engagement is necessary for both validation and acceptance.
Method: Involve users in the User Acceptance Testing (UAT) stage to ensure the system meets their needs and expectations.
9. Management of Configurations:
Principle: Supervise and control changes made to the software and associated resources.
Technique: To keep version control, monitor changes, and ensure consistency between the development and testing processes, use configuration management procedures.
10. Comprehensive Testing:
Principle: All aspects of the system ought to be put to the test. Technique: Plan and execute a range of tests, including unit, integration, system, and user acceptance testing, to confirm the program’s accuracy and dependability.
Drawbacks of the main ideas and methods connected to the V-Model
Even while the V-Model offers a structured approach to software development with integrated testing, it is not without its drawbacks. The following are some limitations and drawbacks associated with the primary concepts and techniques of the V-Model:
1. Inflexibility and Rigidity:
Cons: When it comes to modifying needs, the V-Model could be less adaptable and more rigid. It makes the challenging assumption that needs are clear-cut and unchanging, which makes it challenging to adjust as the project develops.
2. System Visibility After Hours:
Cons: It takes a long time for the system to become fully visible during the development life cycle. This could lead to erroneous perceptions of user requirements or a delay in identifying design flaws, which makes problem-solving more challenging and costly.
3. Minimal User Engagement:
The only time consumers are often involved is during the User Acceptance Testing (UAT) phase. This could result in the discovery of significant issues or misunderstandings later on in the procedure when fixing them will be more expensive.
4. Dependency on Proactive Scheduling
Limitation: The effectiveness of the V-Model depends on having a firm understanding of the needs and starting early. If the needs change or the initial planning is flawed, delays and significant barriers could occur.
5. Nature in Sequence:
Cons: The V-Model follows a sequential path in which the completion of one phase depends on the success of the one before it. This could lead to a longer development timeframe, especially if changes are required after the project starts.
6. Insufficient Length for Iterative Development:
Cons: Iterative or incremental development approaches do not work well with the V-Model. It could not be compatible with modern agile methodologies, which strongly emphasize flexibility and quick reaction to changing requirements.
7. Excessive Focus on Testing
Cons: The V-Model may overemphasize testing as a stand-alone step, even though testing is crucial. This approach could not be effective for projects incorporating agile methodologies, which call for continuous testing and feedback
8. Presumption of Clearly Stated Needs:
Cons: The V-Model is based on the assumption that needs are precise and unchanging from the outset. As the project is being developed, adjustments may be necessary because needs often change.
9. Low Level of Client Involvement
Cons: User acceptability testing and requirements phases are usually the only times that customers or stakeholders are communicated with. This can result in a lack of ongoing contact and feedback throughout the development process.
10. Having Difficulties Handling Difficult Projects?
cons: The V-Model may face challenges when working on large, complicated projects with requirements that are not completely understood up front. An iterative and more flexible approach may be more appropriate in some circumstances.
Conclusion:
In summary, the V-Model’s core principles and techniques provide a structured, methodical approach to software development that emphasizes early testing and traceability. However, it’s crucial to consider both the benefits and drawbacks of the V-Model:
When choosing the V-Model, it’s critical to consider the project’s needs for stability, the organization’s overall development plan, and the project’s type. Though it might not be ideal for every project, the V-Model might be helpful in instances where a systematic, logical, and well-documented development process is required and if needs changes are either minor or properly managed. However, for projects that require more flexibility and adaptability, different methodologies like Agile may be more appropriate.
0 notes
Text
Virtucon Scantobim

Introduction Virtucon Engineering LLC operates under the trade name Virtucon Scan to BIM, offering specialized services in the field. offers innovative, unique, and smart design, engineering, and technology solutions. We are a BIM, and CAD services provider with expertise in scan to BIM, point cloud to Revit, and scan to 2d As-built drawings. Servicing clients across the AEC industry & helping to improve their efficiency & profitability of the business.
We always focus on customer satisfaction, deadlines, accuracy, and a clear vision for building long-term relationships to ensure that our customers all over the world are satisfied. Our clients are from the USA, Canada, UK, Europe and Asian countries.
We believe in
Unmatched quality and price.
Accurate model with fast turnaround time- Our Expert team converts point cloud into a 3d model urgent basis.
Providing complete CAD & BIM solutions to the AEC industry.
The easiest way of communication.
Highly qualified and experienced architects, engineers, and technicians to complete any complex project.
1 note
·
View note
Text



i lost my mind just a little bit i am. not entirely normal about her yes this is a serial experiments lain crossover
#ultrakill#ultrakill fanart#mirage ultrakill#one day i will draw vmodel heads consistently not today though#first two are referenced from official sel illustrations just wanted to clarify
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

something for my five year old self
#ultrakill#ultrakill v1#inaccurate rendition of a specific dress i really liked back then#TUMBLR. TUMBLR FOR THE LOVE OF GOD WHY DO YOU DO THIS TO SMALL IMAGES#also like technically vmodels are middle schooler sized rather than toddler sized but also fuck idc
83 notes
·
View notes
Note
Mr minophus, what other interests do u have that aren't ULTRAKILL.. i am curious
Hi:) Humm...
hylics is a peak fav other interest. i still do think about it easily daily(had a blog for it but with my new ultraillness i dont post much anymore.)
specbio ... dragons ... anatomy ... neon genesis eva ... Other secondary interests like that.
#asks#was thinming about eva gabriel just last night or perhaps the vmodels#The vmodels make more sense#i just cant imagine a design fitting enough for him as an (nge)angel
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
v4v kismesissitude
#have i already posted this before#i dont know#either way i must spread the word#actually wait it was v4v moirails last time#going all across the quadrants... v4v auspicitism with gabriel when#their potential as kismesises is unmatched#i really like the interpretation of them hating each other but not in the#“grrrr im the better vmodel” way#in what way you may ask.... i say the inner machinations of my mind are an enigma#(i dont know)#(i just enjoy thinking about them maiming and killing each other)#they admire each others skill and they want to kill each other violently yaaaay#peace and love#v4v#owls nonsense
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

I DOODLED TWO MORE ULTRAKILL MACHINE OCS THAT MIGHT END UP GOING WITH V0'S LORE AND I DREW THEM IN JOJO POSES TOGETHER
green one looks a bit off cause i had to trace it off the actual ref image i was using
#ultrakill#ultrakill oc#jjba#jojos bizarre adventure#look at them#the green one is skyscraper (placeholder)#the yellow one is seafarer (placeholder)#sky and sea are not vmodels but theyre very close in model rn i plan on changing their designs
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
finally looked thru the live thing before immediately turning it back off

#all pics of this guy look like they ran them thru an ai btw#and this was some sort of weird ai pic vmodel....idk
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Started off strong in my last session but it ended pretty badly. Harvest is an intuitive map to play as scout, however I think my brain started rotting out of my ears after almost 2 hours of continuous Harvest. We switched to Sawmill in the last 20 minutes, and I could not hit a shot for the life of me. I also walked directly onto stickies I had KNOWN were there multiple times. I hope that demo appreciated the free strange kills 💀
#some cons of playing with vmodels off:#i had switched to my fish in the previous life#and in the next one proceeded to charge a demo and sniper towards their spawn#backed up and swung like i had my scatter out#and promply died#blu-s0da's-bullshit
0 notes
Text
Prototype Model . . . . for more information and a tutorial https://bit.ly/4eMRmPz check the above link
0 notes
Text
V-Model development techniques to design
December 15, 2023
by dorleco
with no comment
Control Systems
Edit

Introduction
The V-Model sometimes referred to as the Verification and Validation Model or the V-Cycle, is a software development technique that places a strong emphasis on testing at every stage of the process. It is a variation of the Waterfall approach that is frequently applied in the development of critical systems when exhaustive testing is essential. The two primary stages of the V-Model are carried out in the following order:
1. Verification (the V’s left side):
a.Requirements analysis: –
– Recognize and record the needs of the client.
– Determine software and system needs based on input from customers.
b. System Design: Using the requirements as a guide, create a high-level design specification.
– Describe the general architecture of the system.
c. Architecture: – Construct a thorough system architecture.
– Specify how system components interface with one another.
d. Module Design: – Divide the system into more manageable, smaller components.
– Establish thorough requirements for every module.
e. Implementation (Coding): Using the comprehensive module requirements as a guide, write code.
f. Unit Testing:
– Verify the accuracy of each module.
– Find and address errors at the module level.
2. Validation (the V’s right side):
a. Integration testing: –
Integrate modules and test them collectively to make sure they function as a unit.
– Find and correct errors about how the modules interact with one another.
b. System Testing: –
Check that the system satisfies the criteria by testing the system as a whole.
– Find and address system-level flaws.
c. UAT, or user acceptance testing:
– Confirm with end users that the solution satisfies their needs by validating it.

d. Deployment:
Upon successful testing, move the system into production.
Verify that all required paperwork has been completed.
e. Maintenance and Support: –
Provide continuous assistance, resolve any problems that occur in the live environment, and apply any updates that are required.
Key principles and techniques associated with the V-Model:
The V-Model includes several essential ideas and methods that direct its use in software development. The following are the key ideas and methods related to the V-Model:
Early Testing:
Principle: Early in the development life cycle, testing activities are started.
Technique: To ensure that faults are found and fixed as soon as feasible, test preparation and execution begin early on, using unit testing.
Phased and Incremental Approach:
Principle: There are different phases for development and testing.
Technique: Testing activities are scheduled by the stages that the development process is separated into. Partially functional systems can be delivered for testing and validation through incremental development.
Traceability:
Principle: Requirements and related tests should have a distinct, traceable relationship.

Feedback Loops:
Principle: Between the stages of development and testing, ongoing feedback is crucial.
Methodology: During testing, flaws are reported back to the development team so they can be fixed. This loop of iterative feedback aids in raising the software’s quality.
Documentation:
Idea: Thorough documentation is essential for all phases of testing and development.
The technique involves creating and keeping up-to-date detailed documentation for the requirements, design, test cases, and test plans. Throughout the system’s life cycle, this documentation acts as a reference and aids in understanding.
Parallel Development and Testing:
The concept of concurrent development and testing states that both processes take place simultaneously.
Approach: As the development stage advances, the corresponding phase’s testing is also in progress. By taking a parallel method, problems can be found and fixed sooner, which lowers the possibility of significant flaws developing later.
Clearly defined roles and duties:
The development and testing teams’ roles and duties should be well-defined.
Method: Give teams or people distinct tasks for every stage of the V-Model. This guarantees responsibility and makes it apparent who is in charge of what.
User Participation:
Principle: Acceptance and validation depend on user participation.
Method: To make sure the system satisfies users’ needs and expectations, involve users in the User Acceptance Testing (UAT) stage.
Configuration Management:
Principle: Oversee and regulate modifications to the software and related materials.
Technique: Use configuration management procedures to maintain version control, track modifications, and make sure that the development and testing processes are consistent.
Comprehensive Testing:
Principle: Every facet of the system should be tested.
Technique: To verify the accuracy and dependability of the program, plan and carry out a variety of tests, such as unit, integration, system, and user acceptability testing.
Drawbacks of Key principles and techniques associated with the V-Model
The V-Model has some disadvantages even if it provides an organized method for software development with integrated testing. The following are some restrictions and disadvantages related to the main ideas and methods of the V-Model:
Rigidity and Inflexibility:
Cons: The V-Model may be inflexible and less flexible when it comes to requirements modifications. It makes the difficult assumption that needs are well-defined and constant, which makes it difficult to adapt to changes as the project is being developed.
Late Visibility of the System:
Cons: The system’s complete visibility isn’t apparent until much later in the development life cycle. This might result in misinterpretations of user needs or delayed discovery of design faults, which increases the difficulty and expense of problem-solving.
Limited User Involvement:
The User Acceptance Testing (UAT) phase is usually the only time that users are involved. This may lead to the identification of important problems or misconceptions at a later stage of the process when it will cost more to make adjustments.
Reliance on Forward Planning:
Limitation: A good grasp of requirements and early preparation are critical to the V-Model’s success. Delays and major obstacles may arise if the needs alter or the original planning is faulty.
Sequential Nature:
Cons: The V-Model has a sequential path whereby the accomplishment of one phase is contingent upon the conclusion of the preceding phase. This may result in a lengthier development period overall, particularly if modifications are needed after the project has begun.
Limited Flexibility for Iterative Development:
Cons: The V-Model is not a good fit for incremental or iterative development methodologies. It might not work well with contemporary agile approaches, which place a strong emphasis on adaptability and quick response to changing needs.
Overemphasis on Testing:

Assumption of Well-Defined Requirements:
Cons: The V-Model assumes that requirements are clear-cut and constant from the start. In actuality, needs frequently change, and modifications might be required as the project is being developed.
Minimal Client Engagement:
Cons: Communication with clients or stakeholders is frequently restricted to the requirements phase and the user acceptance testing phase. This could lead to a deficiency in continuous feedback and communication during the development process.
Having Trouble Managing Complicated Projects:
Drawback: When working on large, complex projects with requirements that are not fully understood up front, the V-Model may encounter difficulties. In certain situations, a more adaptable and iterative strategy can be more suitable.
Conclusion:
To sum up, the fundamental ideas and methods behind the V-Model offer an organized and methodical approach to software development that prioritizes early testing and traceability. But it’s important to take into account the V-Model’s advantages as well as disadvantages:
It’s important to take the project’s needs stability, the organization’s general development strategy, and the nature of the project into account while selecting the V-Model. The V-Model can be useful in situations where a systematic, methodical, and well-documented development process is necessary and if needs changes are either small or well managed, albeit it may not be appropriate for every project. However, alternative approaches like Agile can be better suitable for projects that need greater adaptation and flexibility.
0 notes
Text
I'm a cat because I don't know what to do
I'm a machine because I am a very good person
I am a creature because I am not a child
I'm a terror because I am a little bit of a dying fire
I'm a shape because I have a lot of people that are mostly just completely different people
new tag game: use predictive text to see why you are your theriotype/kintype. start with "i'm [x] because"
i'll go first
i'm a dog because i have to fight
#first one is general kin#second is vmodel min#third is general kin plus cryogonal Pokémon and fairy from corru observer#forth is fairy from corru observer#fifth is general kin. im shape hehe#fifth one also seems to understand that I'm a system. wow!
982 notes
·
View notes
Note
v2 massive sword. twice its height. effortless sword swings despite the size of said sword. inhumanely fast and precise due to being a machine. the red splatters of blood on her glistening on its already red body.
(gripping my chair armrests) mmy lawyer has advised me not to sauy anything on this blog regarding this ask
1 note
·
View note